Page 1

USER’S
GUIDE
M
EASURE
M
ASTER
C
LASSIC
™
M
ODEL
4015
Page 2
I
NTRODUCINGMEASUREMASTERCLASSIC
. . . . . 3
KEY DEFINITIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
O
PERATING BASICS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Power On and Off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Basic Math Operations . . . . . . . . . . 10
Memory Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Fractional Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
“Paperless Tape” Feature . . . . . . . . 17
USING THE MEASURE MASTER CLASSIC . . . . 20
Entering Dimensions and Units . . . . 20
Linear Conversions . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Square and Cubic Dimensions . . . . . 21
Square Conversions . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Cubic Conversions . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Estimating Materials . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Area Calculations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Volume Calculations . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Volume/Weight Calculations . . . . . . 32
Squaring Up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Common Rafter Length . . . . . . . . . . 36
Circular Solutions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Scale Modeling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
Graphic Arts – Column Width . . . . . .39
FORMULAS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Area Formulas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Surface Area and Volume Formulas . 41
APPENDIX . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Calculator Information . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Product Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Warranty Repair . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page 3
Designed for anyone who works with
dimensions, the
Measure Master Classic
is so simple to use, even first-time users
will find it easy to solve all kinds of dimension-related problems.
◆ Solves dimensional math
◆ Works in and converts between all
common dimensional units
◆ Finds square and rectangular areas,
cubic volumes, circular areas and
circumferences
◆ Weight per volume function
◆ Material estimations
◆ Paperless tape function
◆ And much, much more!
It also works as a standard math calculator with memory and percent functions
plus battery-saving auto shut-off.
INTRODUCING
MEASURE MASTER CLASSIC
™
User’s Guide – 3
Page 4
[+] [–] [x] [÷] [=]
Arithmetic operation keys.
[%]
Four-function percent key.
0 – 9 and [ • ]
Digits used for entering numbers.
[Off] — Off Key
Turns power off.
[On/C] — On/Clear Key
Turns power on. If on, pressing once
clears the last entry and the display.
Pressing twice clears all temporary registers (stored values).
[Conv]
Used with the dimensional keys to convert between dimensions. Dimensions
can only be converted within the same
convention (i.e., linear , square or cubic).
Can also access special functions when
used with other keys.
[ ] — Square Root
Used to find the square root of a number .
The calculator will display the word
“
ERROR” if you try to find the square root of
a linear or volume value.
KEY DEFINITIONS
4 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 5
[Conv] [ ] — x2Function
Finds the square of the displayed number. The calculator will display “
ERROR
” if
you try to find the square of an area or
volume value.
[M+] — Memory Plus
Stores or adds the displayed number to
memory.
[Conv] [M+] — Memory Minus
Subtracts the displayed value from memory.
[Rcl] — Recall Key
Recalls values stored in any register (i.e.,
[Rcl] [M+]
displays the value stored in
memory).
[Conv] [Rcl] — Memory Clear
Clears the value in memory without
changing the display.
Dimension Keys
[Yds] — Yards Key
This is an entry and conversion key. You
can enter whole or decimal numbers. To
convert a displayed value to yards, press
[Conv] [Yds]
.
User’s Guide – 5
Page 6
[Feet] — Feet Key
This is an entry and conversion key. You
can enter whole or decimal numbers. You
can also use this key to enter values in
feet-inch-fraction format:
(2 [Feet] 1 [Inch]
1 [/] 2)
. To convert a displayed value to
feet, press
[Conv] [Feet]
. Repeated
presses toggle between feet-inches and
decimal feet formats.
[Inch] — Inch Key
This is an entry and conversion key
(when used with the
[Conv]
key). You can
enter whole or decimal numbers. You can
also use this key with the
[/]
key to enter
fractional inch values. For example to
enter 3-3/4 inches, press
3 [Inch] 3 [/] 4
.
To convert a displayed value to inches,
press
[Conv] [Inch]
. Repeated presses
toggle between fractional inch and decimal inch formats.
[/] — Fraction Key
E
nters a fraction. To enter a fraction,
enter the numerator, the fraction key [/]
and then the denominator: 1 [/] 2.
Fractions can be entered as proper
(1 or less – 1/2, 1/8, 1/16) or improper
(greater than 1 – 3/2, 65/64). If the
denominator (the bottom number) is
not entered, then the currently selected
fractional denominator is used. [Rcl] [/]
6 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 7
displays the current fractional denominator and accesses the fractional setting
mode. See the “
Fractional Setting
” sec-
tion on page 15 for more information.
[Cu] — Cubic Key
Used with a dimension key (feet, inches,
yards, meters, etc.) to identify a volume
dimension. Example:
5 [Cu] [Yds]
.
[Sq] — Square Key
Used with a dimension key (feet, inches,
yards, meters, etc.) to identify an area
dimension. Example:
10 [Sq] [Feet]
.
[m] — Meters Key
This is an entry and conversion key
(when used with the
[Conv]
key). You can
enter decimal meters or convert a displayed dimension to decimal meters.
[cm] — Centimeters Key
This is an entry and conversion key
(when used with the [Conv] key). You
can enter decimal centimeters or convert a displayed dimension to decimal
centimeters.
[mm] — Millimeters Key
This is an entry and conversion key
(when used with the [Conv] key). You
can enter decimal millimeters or convert a displayed dimension to decimal
millimeters.
User’s Guide – 7
Page 8
[Weight] — Weight Key
Enters or converts (a volume value) to
tons, pounds, metric tons or kilograms.
Repeated presses will cycle through
these units.
[Conv] [%] — Weight per Volume
Enters or converts the Weight per volume
setting as Tons/Yard
3
, Lbs/Yd3, Lb/Ft3,
Metric Ton/m
3
or kg/m3. Repeated press-
es will cycle through these settings.
[Circ] — Circle Key
Used to enter a circular diameter and
find the area and circumference.
Pressing this key displays values in the
following order: 1) diameter, 2) area 3)
circumference.
[Conv] [Circ] — Arc Length
Used to find the arc length based on an
entered diameter and angle.
Special Functions
[Conv] [÷]
Reciprocal, or 1/x function.
[Conv] [x] — All Clear
Clears all values including memory.
Resets to default settings.
8 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 9
[Conv] [+] — Pi (π)
Internal constant = 3.141593.
[Conv] [–] — Change Sign Function
Toggles the sign of a value between positive and negative values.
[Rcl] [=] — Paperless Tape Feature
Accesses the paperless tape mode. See
the “
Paperless Tape
” section on page 17
for more information.
[Rcl] [x] — Metric Mode Toggle
Toggles between Imperial and Metric
defaults for the weight per volume factor
and the weight key. When you are in
Metric Mode, any value in meters will be
limited to three decimal places to the
right. To verify which mode you are in, do
an all clear (
[Conv] [x]
), then press
[Rcl]
[Weight]
. If the displayed unit of measurement is kilograms, you are in Metric
Mode. If the displayed unit is tons, you
are in Imperial Mode.
[Conv] [•] — Per Unit Function
Used to calculate total material cost, if
you multiply the total amount of material
by the per unit cost of the item. For example, to find the cost of 39.7 square yards
of carpet at $11.75 per square yard, enter
39.7
[Sq] [Yds] [x] 11.75 [Conv] [•]
which will give you $466.48.
User’s Guide – 9
Page 10
Power On and Off
Turn the calculator on by pressing
the [
On/C
] key. To turn it off, press the
[
Off
] key.
Auto Shut-Off
The calculator will turn itself off if it is not
used within 8-12 minutes.
Basic Math Operations
Your calculator uses standard chaining
logic which simply means that you enter
your first value, the operator (+, –, x, ÷),
the second value and then the equals
sign (=).
3 [+] 2 [=] 5
3 [–] 2 [=] 1
3 [x] 2 [=] 6
3 [÷] 2 [=] 1.5
This feature also makes the calculator
simple to use for dimensional math, as
shown in the following examples:
OPERATING BASICS
10 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 11
Adding Dimensions
Add 7 feet 3-1/2 inches to 11 feet 4 inches:
7 [Feet] 3 [Inch] 1[/] 2 [+]
11 [Feet] 4 [Inch] [=] 18 FT 7-1/2 IN
Add 11 inches to 2 feet 1 inch:
11 [Inch] [+] 2 [Feet] 1 [Inch] [=] 36 IN
Add 2 feet 1 inch to 11 inches:
2 [Feet] 1 [Inch] [+]
11 [Inch] [=] 3 FT 0 IN
Note: The format of the first value you enter
determines the format of the answer.
However, with the [Conv] key you can
change to any format you want, provided
that you maintain convention.
Subtracting Dimensions
Subtract 3 feet from 11 feet 7-1/2 inches:
11 [Feet] 7 [Inch] 1 [/] 2
[–] 3 [Feet] [=] 8 FT 7-1/2 IN
Subtract 32 inches from 81 inches:
81 [Inch] [–] 32 [Inch] [=] 49 IN
Multiplying Dimensions
Multiply 5 feet 3 inches by 11 feet 6-1/2 inches:
5 [Feet] 3 [Inch] [x]
11 [Feet] 6 [Inch] 1 [/] 2 [=] 60.59375 SQ FT
User’s Guide – 11
Page 12

Multiply 2 feet 7 inches by 10 :
2 [Feet] 7 [Inch] [x] 10 [=] 25 FT 10 IN
Dividing Dimensions
Divide 30 feet 4 inches by 7 inches:
30 [Feet] 4 [Inch] [÷] 7 [Inch] [=] 52
Divide 20 feet 3 inches by 9:
20 [Feet] 3 [Inch] [÷] 9 [=] 2 FT 3 IN
Percentage Calculations
The Percent [%] key is used to find a
percent of a number or for working addon, discount or division percentages. It
can be used with any type of number,
any dimension (feet, inch, millimeter,
etc) and convention (non-dimensioned,
linear , square or cubic).
Find 18% of 500 feet:
500 [Feet] [x] 18 [%] 90 FT 0 IN
Add 10% for waste to 137 square feet:
137 [Sq] [Feet] [+] 10 [%] 150.7 SQ FT
Take 20% away from 552 feet 6 inches:
552 [Feet] 6 [Inch] [–] 20 [%] 442 FT 0 IN
Divide 350 cubic yards by 80%:
350 [Cu] [Yds] [÷] 80 [%] 437.5 CU YD
12 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 13
Memory Functions
Whenever the
[M+]
key is pressed, the
displayed value will be added to memory .
Other memory functions:
Function Keystrokes
Recall total in memory [Rcl] [M+]
Display and clear memory [Rcl] [Rcl]
Clear memory, no display [Conv] [Rcl]
Subtract from memory [Conv] [M+]
Replace memory with
displayed value [Conv] [Rcl] [M+]
The memory is semi-permanent; it will
only be cleared when you:
1) turn off the calculator;
2) press [Rcl] [Rcl];
3) press [Conv] [Rcl];
4) press [Conv] [x] (all clear).
User’s Guide – 13
Page 14
How to use memory functions:
Steps Keystrokes Display
Add to memory 355 [M+] 355.
Add to memory 255 [M+] 255.
Recall total mem. [Rcl] [M+] 610.
Subt. from mem. 745 [Conv] [M+] 745.
Recall total mem. [Rcl] [M+] – 135.
Replace memory 50 [Conv]
[Rcl] [M+] 50.
Recall and clear [Rcl] [Rcl] 50.
The memory function can also be used
with dimensional units, as long as they
are of the same convention (all linear,
square or cubic). The calculator will
display the word “
ERROR” if you try to enter
numbers of different conventions.
14 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 15
Fractional Settings
When you first receive your calculator it is
set to its default state. When in this state,
fractional values are rounded to the nearest
1/16 of an inch. However , you may program
your preference for six different accuracy
levels and two different modes ( Normal and
Fixed), all of which remain in permanent
memory until revised or reset.
The fractional level can be revised by
using the keystrokes below:
Keystroke Fraction Setting
[Conv] 1 1⁄ 16
[Conv] 2 1⁄ 2
[Conv] 3 1⁄ 32
[Conv] 4 1⁄ 4
[Conv] 6 1⁄ 64
[Conv] 8 1⁄ 8
Note: Whenever the calculator is set to
anything other than 1⁄16 normal mode, a
star (★) will appear in the bottom left of the
display during power up to indicate a special fractional setting has been stored within. The fractional setting can be displayed
at any time by pressing [Rcl] [/].
User’s Guide – 15
Page 16
Normal Fractional Mode
The default,
Normal Mode
([Conv] 7),
reduces a fraction to its lowest common
denominator (for example, 8/16 reduces
to 1/2). If a fraction is entered having a
higher fractional accuracy than the current setting, the setting will be temporarily revised to the level of accuracy of the
entered value.
Fixed Fractional Mode
In the
Fixed Mode
(
[Conv] 9
), fractional
results are displayed in the set fractional
value, not reduced. Entries of higher
accuracy values will be rounded to the
nearest fraction of the accuracy setting
(for example, for a fraction level setting of
1/16, an entry of 5 [/] 32 [=] will result in
a display of 3/16).
Flashing Denominator
Your calculator can be set to flash the
denominator (bottom) when entering
fractions by pressing
[Conv] [/]
. In this
way, you can see what fractional accuracy level is set. Pressing
[Conv] [/]
again
will turn the flashing denominator off. This
is a permanent setting that will remain
until revised or reset.
16 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 17
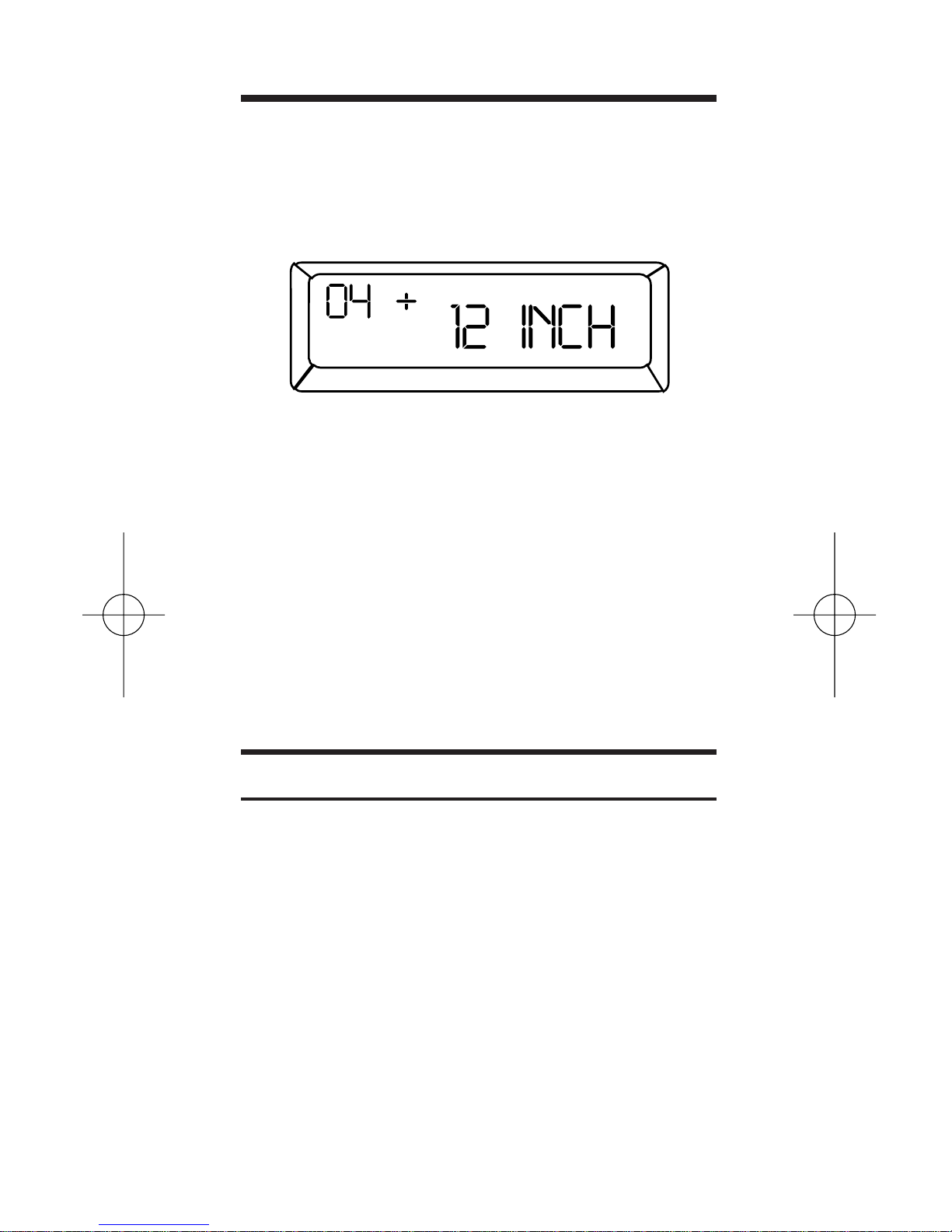
“Paperless Tape” Feature
The “Paperless Tape” feature allows the
user to display the last 20 entries. While
in the Paperless Tape mode, your display
will look similar to this:
The display shows the entered or calculated value (12 Inch), sequence number
(04), and the math operator (in this case
it is “+”) for each entry. As you scroll
through the entries, you will see the designators
TTL
and
SUB
. “
SUB
” indicates a
subtotal. “
TTL
” indicates the final total (all
subtotals combined).
How to Use the Tape
Steps/Keystrokes Display
1. Clear calculator and enter a string of
numbers:
[On/C] [On/C] 0.
4 [Feet] [+] 4 FEET 0 INCH
5 [Feet] [+] 9 FEET 0 INCH
6 [Feet] [+] 15 FEET 0 INCH
7 [Feet] [=] 22 FEET 0 INCH
(Cont’d)
User’s Guide – 17
Page 18
(Cont’d)
2. Access the Tape function
[Rcl] [=] TTL= 22
FEET 0 INCH
3. Scroll forward from first value to total:
[+] 01 4
FEET 0 INCH
[+] 02+ 5 FEET 0 INCH
[+] 03+ 6 FEET 0 INCH
[+] 04+ 7 FEET 0 INCH
[+] TTL= 22 FEET 0 INCH
4. Scroll back to last 2 values:
[–] 04+ 7
FEET 0 INCH
[–] 03+ 6 FEET 0 INCH
5. † Display total and add more values:
[=] TTL= 22
FEET 0 INCH
[+] 22 FEET 0 INCH
2 [Feet] [=] 24 FEET 0 INCH
† Note: At this point, you can press any
key twice (except
[Off]
, [+] or [–]) to exit
the tape feature.
When you press a key to exit the tape,
the total value displays. The next key
press begins a new tape function.
18 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 19
Clearing the Paperless Tape
The paperless tape is cleared:
1) when you press [On/C] [On/C] (clear);
2) when you press [Conv] [x] (all clear);
3) when you turn the unit off.
User’s Guide – 19
Page 20
USING THE MEASURE
MASTER CLASSIC
Entering Dimensions and Units
When entering feet-inch dimensional values, you must enter the largest dimension first — feet before inches, inches
before fractions. To enter fractions of an
inch, enter the numerator (value above
the line), press [/] (fraction bar key) and
then enter the denominator (value below
the line).
numerator 3
fraction bar —
denominator 16
For all other units of measurement, you
can only enter whole numbers or decimal
numbers. You cannot enter combinations
of units (for example, you cannot enter 12
meters 6 centimeters 4 millimeters).
20 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 21
Linear Conversions
Convert 14 feet to other linear values:
Steps Keystrokes Display
Enter 14 ft. 14 [Feet] 14
FEET
Conv. to yds [Conv] [Yds] 4.666667
YD
Conv. to feet-inch [Conv] [Feet] 14
FEET0 INCH
Conv. to inches [Conv] [Inch] 168
INCH
Conv. to mm [Conv] [mm] 4267.2
MM
Conv. to cm [Conv] [cm] 426.72
CM
Conv. to meters [Conv] [m] 4.2672
M
Square and Cubic Dimensions
Square and cubic dimensions are
entered in the following order:
1) Numerical Value
2) Convention — Square or Cubic
3) Unit — Meters, Yards, Feet, Inches
Below are examples of how square and
cubic dimensions are entered:
Steps Keystrokes Display
5 Cubic Yards 5 [Cu] [Yds] 5
CU YD
130 Square Feet 130 [Sq] [Feet] 130
SQ FEET
33 Square Meters 33 [Sq] [m] 33
SQ M
User’s Guide – 21
Page 22
Square Conversions
Convert 14 square feet to other square
dimensions:
Steps Keystrokes Display
Enter 14 sq ft. 14 [Sq] [Feet] 14
SQ FEET
Conv. to inch [Conv] [Inch] 2016
SQ INCH
Conv. to yds [Yds] 1.555556
SQ YD
Conv. to meters [m] 1.300643
SQ M
Conv. to mm [mm] 1300643
SQ MM
Conv. to cm [cm] 13006.43
SQ CM
Cubic Conversions
Convert 14 cubic feet to other cubic
dimensions:
Steps Keystrokes Display
Enter 14 cu ft 14 [Cu] [Feet] 14
CU FEET
Conv. to yds [Conv] [Yds] 0.518519
CU YD
Conv. to meters [m] 0.396436
CU M
Conv. to cm [cm] 396435.9
CU CM
Conv. to mm [mm] 0.396436
CU M
*
*If a calculation results in an answer that exceeds
the standard 7-digit range of the display, the
answer will be automatically displayed in a larger
unit of measurement (instead of showing “
ERROR
”).
For example, “10,000,000 mm” cannot be displayed because it is out of the range of the 7-digit
display, so “10,000 m” will be displayed instead.
This auto-ranging also applies to other dimensional units, such as inches to feet, feet to yards, etc.
22 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 23
Estimating Materials
Calculating Lumber
How many 2 feet 2 inch pieces can be
made from fifteen 10 foot boards?
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
Enter board length 10 [Feet] 10
FEET
Divide by [÷] 2 [Feet] 2 [Inch]
smaller cuts [=] 4.615385
(or 4 whole boards)
Multiply by total number of
10 foot boards 4 [x] 15 [=] 60
(2 feet 2 inch pieces)
Estimating Bricks
How many standard bricks (3.75 inch
by 8 inch) are required for a 36.5 foot by
8 foot wall?
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
Find brick area 3.75 [Inch] [x]
8 [Inch] [=] 30
SQ INCH
Store in memory [M+]
M
30
SQ INCH
Find wall area 36.5 [Feet] [x]
8 [Feet] [=] 292
SQ FEET
Divide by brick area to find
number of bricks
[÷] [Rcl] [M+] [=] 1401.6 (Bricks)
Add 5% spoilage [+] 5 [%]
1471.68 (1472 Bricks)
Clear memory
[Rcl] [Rcl] [On/C] or [Set] [x]
0.
User’s Guide – 23
Page 24
24 – Measure Master Classic
™
Calculating the Number of Studs
Find the number of 16 inch on-center studs
needed for an 18 inch 7-1/2 inch wall.
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
Enter wall length 18 [Feet] 7 [Inch] 1 [/] 2
Divide by on- [÷] 16 [Inch]
center spacing [=]
13.96875 (studs)
Add first stud [+] 1 [=]
14.96875 (round to 15)
Roof Covering — Shingles
You’re going to use 12 inch wide by 36
inch long asphalt (strip) shingles with 5
inch weather exposure. How many shingles are required for a 1745 sq. ft. roof?
(Shingle exposure area = exposure x
length, and number of shingles = roof
area ÷ shingle exposure area)
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
Find shingle 5 [Inch] [x]
exposure area 36 [Inch] [=] 180
SQ INCH
Store in memory [M+]
M
180
SQ INCH
Enter surface area 1745 [Sq] [Feet] 1745
SQ FEET
Divide by [÷] [Rcl] [Rcl] [=]
shingle area 1396 (shingles)
Add 10% waste [+] 10 [%]
1535.6 (1536 shingles)
Page 25
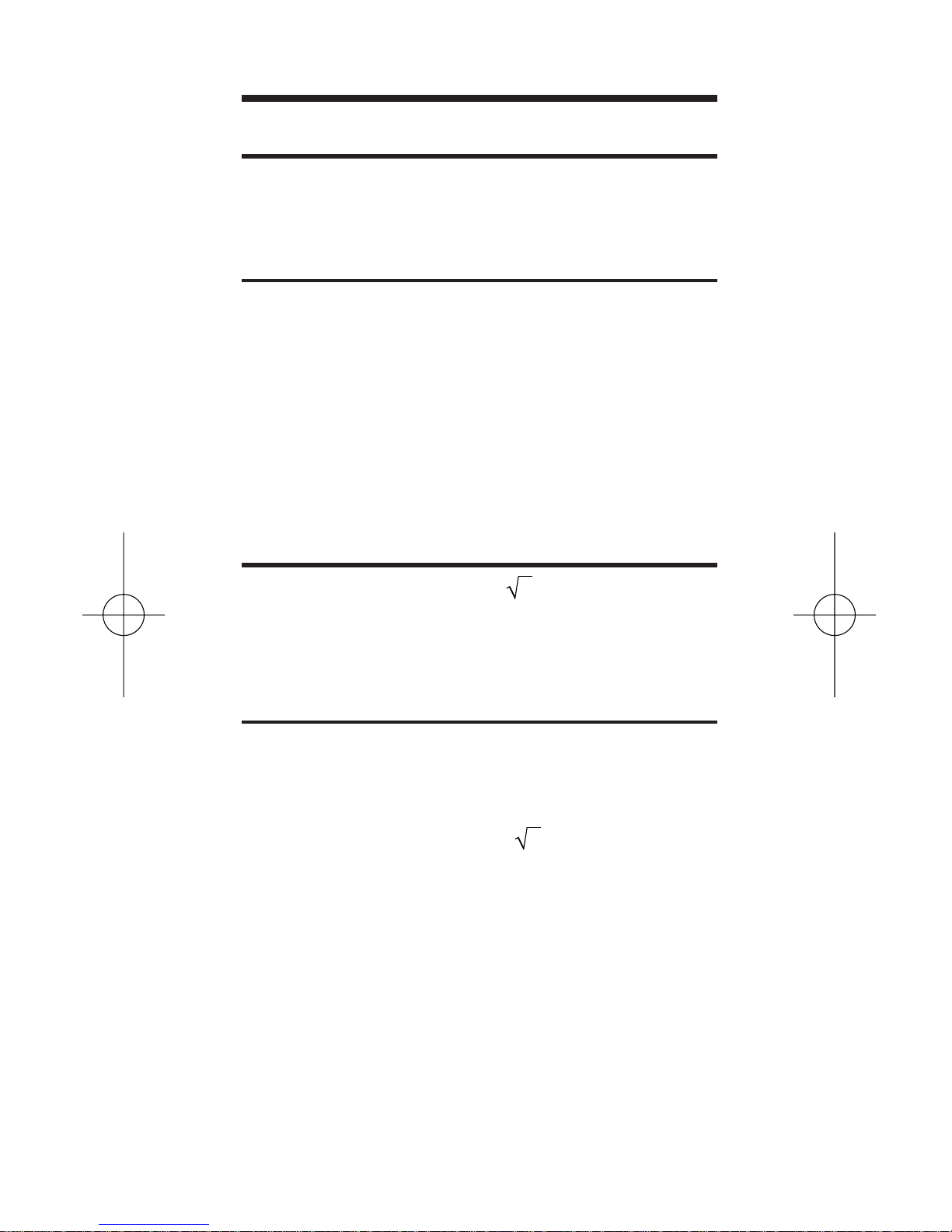
Area Calculations
Area of a Rectangle
What is the area of a room measuring
12 feet 6 inches by 15 feet 8 inches?
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
Enter room length 12 [Feet]
6 [Inch] 12
FEET6 INCH
Multiply by width [x] 15 [Feet] 8 [Inch] [=]
195.8333
SQ FEET
Area of a Square
Using the x2 (
[Conv]
[ ]) function, find
the area of a square with sides of
4 feet 7 inches.
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
Enter length 4 [Feet] 7 [Inch] 4
FEET7 INCH
Find square area [Conv ][ ]
21.00694
SQ FEET
User’s Guide – 25
Page 26
Area — Floor Covering
You have an apartment with two rooms that
need to have the carpet replaced. The room
dimensions are as follows: 12 feet 4 inches by
10 feet and 14 feet 8 inches by 16 feet. How
many square yards of carpet are needed and
what is the total cost at $11.75 per sq. yd.?
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
1 – Find Area of Room 1
Enter length 12 [Feet] 4 [Inch]
of room 1 12- 4
FEET INCH
Multiply by width [x] 10 [Feet] [=]
123.3333
SQ FEET
Store in memory [M+]
M
123.3333
SQ FEET
2 – Find Area of Room 2
Enter length 14 [Feet] 8 [Inch]
of room 2
M
14
FEET8 INCH
Multiply by width [x] 16 [Feet] [=]
M
234.6667
SQ FEET
Add to memory [M+]
M
234.6667
SQ FEET
3 – Find Total Area
Recall total [Rcl] [Rcl] 358
SQ FEET
Conv to sq yds [Conv] [Yds] 39.77778
SQ YD
Enter per unit price/
estimate $ cost [x] 11.75 [Conv] [•] $467.39
26 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 27

User’s Guide – 27
Work Area — Spacing/Partitions
You are setting up partitioned cubicles
along a wall that is 22 feet 6 inches. If you
need three (3) office/work areas, how
wide will each be?
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
Enter wall length 22 [Feet] 6 [Inch]
22
FEET6INCH
Divide by number
of work areas [÷] 3 [=] 7
FEET6 INCH
Spacing Shelves Evenly
You want to horizontally place four (4)
shelves that measure 3 feet 5 inches each
on a 20 foot wide wall. How far should you
space the shelves for even spacing?
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
Calculate 3 [Feet] 5 [Inch]
shelf space [x] 4 [=] 13
FEET8 INCH
Store in memory [M+]
M
13
FEET8 INCH
Enter wall length 20 [Feet]
M
20
FEET
Subtract shelf [–] [Rcl] [Rcl]
space [M+] [=] 6
FEET4 INCH
Divide by number of
spaces between shelves
to find spacing [÷] 3 [=] 2
FEET1 INCH
5/16
Page 28

Cabinets — Drawers
You are building a 32 inch high cabinet
and want four (4) evenly spaced drawers
with 1 inch in between them (3 inch total).
Find the height of each drawer, allowing
for 1 inch at the top and bottom.
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
Enter cabinet height
32 [Inch] 32
INCH
Subtract spacing [-] 5 [Inch] [=] 27
INCH
Divide by 4 to
find drawer height [÷] 4 [=] 6-3/4
INCH
28 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 29

User’s Guide – 29
Volume Calculations
Rectangular Containers
What is the volume of a container 3 feet
by 1 foot 9-5/8 inches by 2 feet 4 inches?
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
Enter length 3 [Feet] 3
FEET
Multiply by width [x] 1 [Feet] 9 [Inch]
5 [/] 8 1
FEET
9-5/8
INCH
Multiply by height [x] 2 [Feet]
4 [Inch] [=] 12.61458
CU FEET
Shipping Containers
You have a dry freight container that is 20
feet x 8 inches x 8 feet 6 inches. How many
3 foot x 2 foot x 1 foot boxes will fit in it?
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
Find box volume 3 [Feet] [x] 2 [Feet]
[x] 1 [Feet] [=] 6.
CU FEET
Store into Memory [M+]
M
6.
CU FEET
Find container 20 [Feet] [x] 8 [Feet]
volume [x] 8 [Feet] 6 [Inch] [=]
1360.
CU FEET
Divide by box
volume to find
number of boxes
[÷] [Rcl] [M+] [=]M226.6667
Page 30

Concrete Volume
You’re going to form up and pour your
own driveway and you need to accurately calculate the cubic yards of concrete
required for the job. The measurements
are 36 feet 3 inches by 11 feet 6 inches
by 4 inches deep. What’s the volume of
your driveway, and if concrete costs $55
per cubic yard, how much will the concrete driveway cost?
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
1 — Find Volume
Enter length 36 [Feet]
3 [Inch] 36
FEET
- 3
INCH
Multiply by width [x] 11 [Feet]
6 [Inch] 11
FEET
- 6
INCH
Multiply by depth [x] 4 [Inch][=]
138.9583
CU FEET
Convert to cu yds [Conv] [Yds] 5.146605
CU YD
2 — Multiply by Cost
Multiply by price per cubic yard
to find total cost [x] 55 [Conv] [•] $ 283.06
30 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 31

Concrete Columns
You’re going to pour five columns, each
of which has a diameter of 3 feet 4-1/2
inches and a height of 11 feet 6 inches.
How many cubic yards of concrete will
you need for all five columns?
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
1 — Find Surface Area of Column
Enter diameter 3 [Feet] 4 [Inch]
1 [/] 2 [Circ]
DIA
3- 4 1/2
FEET INCH
Find surface area [Circ] 8.946176
SQ FEET
2 — Find Volume
Multiply by [x] 11 [Feet]
height 6 [Inch] [=] 102.881
CU FEET
Convert to yards [Conv] [Yds] 3.810408
CU YD
Multiply by 5 columns to find total cubic yards
of concrete
[x] 5 [=] 19.05204
CU YD
Volume of a Cylinder
You want to calculate the volume of a
cylinder with a diameter of 2 feet 4
inches and a height of 4 feet 6 inches.
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
Enter diameter 2 [Feet] 4 [Inch] 2
FEET4 INCH
Find circle area [Circ] [Circ] 4.276057
SQ FEET
Multiply by height [x] 4 [Feet]
6 [Inch] [=] 19.24225
CU FEET
User’s Guide – 31
Page 32

Volume/Weight Calculations
Concrete Footing
Find the total volume of concrete
required to pour five 24 inch by 12 inch
footings, each 2 feet deep. Then find the
weight of the concrete (use the default
weight factor of 1.5 tons per cubic yard).
Steps Keystrokes Display
All Clear [Conv] [x] 0.
Recall weight
per cubic yard [Rcl] [%] 1.5
TON PER CU YD
1 — Find Volume
Enter depth 2 [Feet] 2
FEET
Multiply by length [x] 24 [Inch] 24
INCH
Multiply by width [x] 12 [Inch] [=] 4
CU FEET
Convert to yards [Conv] [Yds] 0.148148
CU YD
Multiply by
5 footings [x] 5 [=] 0.740741
CU YD
2 — Find the Weight of Concrete
Find tons [Conv] [Weight] 1.111111
TON
Find pounds [Weight] 2222.222
LB
Find metric tons [Weight]
MET
1.007983
TON
Find kilograms [Weight] 1007.983 KG
32 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 33

Tank Volume — Rectangular
What is the volume of a rectangular tank
with a length of 5 feet 6 inches, width of
7 feet and depth of 4 feet?
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
Enter length 5 [Feet] 6 [Inch] 5
FEET6 INCH
Multiply by width [x] 7 [Feet] 7
FEET
Multiply by depth
to find volume [x] 4 [Feet] [=] 154.
CU FEET
Multiply by conversion factor to find
number of gallons [x] 7.48 [=] 1151.92
CU FEET
*
(1151.92
GALLONS
)
*ignore CU feet on display
Tank Volume — Round
What is the volume of a round tank with
a diameter of 10 inches and side water
depth of 15 feet?
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
Enter diameter
10 [Feet][Circ]
DIA
10
FEET0 INCH
Find circle area [Circ]
AREA
78.53982
SQ FEET
Multiply by depth
to find volume [x] 15 [Feet] [=]
1178.097
CU FEET
Multiply by conversion factor to find
number of gallons [x] 7.48 [=]
8812.167
CU FEET
*
(8812.167
GALLONS
)
*ignore CU feet on display
User’s Guide – 33
Page 34

34 – Measure Master Classic
™
Squaring Up
Assume you want to “square-up” forms
for a concrete foundation measuring 45
feet 6 inches by 24 feet 4 inches. In order
for the forms to be square, what should
both of the diagonal measurements be?
(You can use the Pythagorean theorem to
solve the next problems. See the diagram
after "Common Rafter" on page 36.)
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
1 — Find 1st side (a)
Find a
2
45 [Feet] 6 [Inch]
[Conv] [ ] 2070.25
SQ FEET
Put in memory [M+]
M
2070.25
SQ FEET
2 — Find 2nd side (b)
Find b
2
24 [Feet] 4 [Inch]
[Conv][ ]
M
592.1111
SQ FEET
Put in memory [M+]
M
592.1111
SQ FEET
3 — Solve for 3rd Side (c)
Recall a2+ b
2
[Rcl] [M+] M2662.361
SQ FEET
Find c [ ]
M
51 7-3/16
FEET INCH
Clear memory
[Rcl] [Rcl] [On/C] or [Set] [x]
0.
Page 35

User’s Guide – 35
Pipefitting — Right Triangles
Aright triangle has a rise of 6 feet 3 inches and a run of 7 feet 6 inches. Find the
travel or hypotenuse.
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
Enter and 6 [Feet] 3 [Inch] 6
FEET3 INCH
square rise [Conv] [ ] 39.0625
SQ FEET
Store in memory [M+]
M
39.0625
SQ FEET
Enter and 7 [Feet] 6 [Inch] 7
FEET6 INCH
square run [Conv] [ ]
M
56.25
SQ FEET
Store in memory [M+]
M
56.25
SQ FEET
Recall total
in memory [Rcl] [M+]
M
95.3125
SQ FEET
Find the square root,
or the “travel” [ ]
M9 FEET
9-1/8
INCH
Clear memory
[Rcl] [Rcl] [On/C] or [Set] [x]
0.
Page 36

36 – Measure Master Classic
™
Common Rafter
You have a rise of 6 feet 11 inches and a
run of 14 feet 6 inches. Find the common
rafter length.
Steps Keystrokes Display
Reset calculator [Conv] [x] 0.
1 — Find 1st side (a)
Enter rise 6 [Feet] 11 [Inch]
[Conv] [ ] 47.84028
SQ FEET
Put in memory [M+]
M
47.84028
SQ FEET
2 — Find 2nd side (b)
Enter run 14 [Feet] 6 [Inch]
[Conv] [ ]
M
210.25
SQ FEET
Put in memory [M+]
M
210.25
SQ FEET
Recall total [Rcl] [M+]
memory
M
258.0903
SQ FEET
3 — Solve for 3rd Side (c)
Find common rafter length
[ ]
M
16 0-13/16
FEET INCH
Clear memory
[Rcl] [Rcl] [On/C] or [Set] [x]
0.
Page 37

User’s Guide – 37
Circular Solutions
Sewing—Yardage of Material
You want to sew a round tablecloth and
need to order material. If the table measures 48 inches in diameter and you want it
to hang over the table by 12 inches (24 inches on both sides), what is the total square
yardage of material you’ll need? What is the
cost of material, at $11 per square yard?
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
Enter circle 48 [Inch] [+]
diameter 24 [Inch] [=] 72
INCH
Find circle area [Circ] [Circ]
AREA
4071.504
SQ INCH
Convert to sq yds [Conv] [Yds] 3.141593
SQ YD
Find total cost [x] 11 [Conv] [•] $
PER
34.56
Arc Lengths
Find the arc length of an 85° portion of a
circle with a 5 foot diameter.
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
Enter diameter 5 [Feet] [Circ]
DIA
5-0
FEET INCH
Enter arc angle,
find arc length 85 [Conv] [Circ]
ARC
3- 8-1/2
FEET INCH
Convert to decimal feet
[Conv] [Feet] 3.708825
FEET
Page 38

Bolt Circle
Find the distance (in inches) between 6
bolts on a circle, if the radius is 5 inchs
(diameter 10 inches).
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
Enter diameter 10 [Inch] [Circ]
DIA
10
INCH
Find circumference
[Circ] [Circ]
CIRC
31-7/16
INCH
Divide by number of bolts
[÷] 6 [=] 5-1/4
INCH
Scale Modeling
You have a 1/24th scale model car and
you’d like to add a model person to
the layout next to the car . What is the correct scale size you should use, to be in
proportion to an actual man 6 feet 1-1/2
inches tall?
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
Find scale ratio 1 [÷] 24 [=] 0.041667
Multiply by [x] 6 [Feet]
actual height 1 [Inch] 1 [/] 2 [=]
0
FEET
3-1/16
INCH
Convert to decimal inch
to find scale size [Inch] [Inch] 3.0625
INCH
Clear calculator [Conv] [x] 0.
38 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 39

User’s Guide – 39
Graphic Arts — Column Width
You’re publishing a newsletter on standard 8-1/2 inches by 11 inches letter-size
paper . You wish to have a 3/8 inch border
on each side and 1/2 inch between
columns. If you want three equal width
columns, how wide will each column be?
Steps Keystrokes Display
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C] 0.
Enter total
border width 3 [/] 8 [x] 2 [=] 0-3/4
INCH
Add distance
between columns [+] 1 [Inch] [=] 1-3/4
INCH
Store in memory [M+]
M1 INCH
Enter paper width 8 [Inch] 1 [/] 2
M
8-1/2
INCH
Subtract borderand
column spacing
[-] [Rcl] [M+] [=]M6-3/4
INCH
Divide by number
of columns to find
column width [÷] 3 [=]
M
2-1/4
INCH
Clear memory
[Rcl] [Rcl] [On/C] or [Set] [x]
0.
Page 40

40 – Measure Master Classic
™
Formulas
Area Formulas
Page 41

User’s Guide – 41
Surface Area and Volume Formulas
Page 42

Calculator Information
A
CCURACY
/D
ISPLAY
— Your calculator has an
eleven digit display. This is made up of seven
digits (normal display) and four digits for the
fraction. In a standard calculation, each calculation is carried out internally to ten digits and
is rounded to a seven-digit standard display. A
5/4 rounding technique is used to add one to
the least significant digit in the display if the
next non-displayed digit is five or more. If this
digit is less than five, no rounding occurs.
A
UTO-RANGE
— If a calculation results in an
answer that exceeds the standard sevendigit range of the display , the answer will be
automatically displayed in a larger unit of
measurement (instead of showing “
ERROR
”).
For example, “10,000,000 mm” cannot be
displayed because it is out of the range of
the seven-digit display, so “10,000 m” will
be displayed instead. This auto-ranging
also applies to other dimensional units,
such as inches to feet, feet to yards, etc.
ERRORS — When you make an incorrect entry,
or the answer is beyond the range of the calculator, it will display the word “
ERROR.” To clear
an error condition you must hit the [On/C]
key
. You must then re-enter the problem. An
error will occur if you enter a mathematical
impossibility such as division by zero.
42 – Measure Master Classic
™
APPENDIX
Page 43

B
ATTERYINFORMATION
— The calculator is powered by a single 3-Volt Lithium CR-2032
battery. This should last upwards of 800
hours of actual use (one year plus for most
people). Should the display become very
dim or erratic, replace the battery.
WARNING: Please use caution when
disposing of your old batteries as they
contain hazardous chemicals.
The calculator is designed to shut itself off
after about 8-12 minutes of non-use. V alues in
memory or on the display will be cleared.
FULL RESET/ALL–CLEAR
— Your calculator is
equipped with a special two-key sequence
– [Conv] [x] – to clear all memory registers
to their initial default values.
Product Specifications
Dimensions
2.75 inches x 5.25 inches x 0.25 inches
(133mm x 70mm x 6.5mm)
Weight
4 oz. (114 g)
Accuracy
10 digits (internal)
User’s Guide – 43
Page 44

Calculated Industries, Inc. (“CI”) warrants this product against defects in
materials and workmanship for a period of one (1) year from the date of original consumer purchase in the U.S. If a
defect exists during the warranty period, CI at its option will either repair
(using new or remanufactured parts) or
replace (with a new or remanufactured
unit) the product at no charge.
THE WARRANTY WILL NOT APPLY TO THE
PRODUCT IF IT HAS BEEN DAMAGED BY MIS
-
USE, ABUSE, ALTERATION, ACCIDENT,
IMPROPER HANDLING OR OPERATION, OR IF
UNAUTHORIZED REPAIRS ARE ATTEMPTED
OR MADE
. SOME EXAMPLES OF DAMAGES
NOT COVERED BY WARRANTY INCLUDE
, BUT
ARE NOT LIMITED TO
, BATTERY LEAKAGE,
BENDING, OR VISIBLE CRACKING OF THE
LCD WHICH ARE PRESUMED TO BE DAM-
AGES RESULTING FROM MISUSE OR ABUSE.
To obtain warranty service in the
U.S., ship the product postage paid to
the CI Authorized Service Provider listed on the back page of the User’s
Guide. Please provide an explanation
of the service requirement, your name,
address, day phone number and dated
proof of purchase (typically a sales
receipt). If the product is over 90 days
old, include payment of $6.95 for return
shipping and handling within the con-
44 – Measure Master Classic
™
WARRANTY REPAIR
Page 45

User’s Guide – 45
tiguous 48 states. (Outside the contiguous 48 states, please call CI for
return shipping costs.)
A repaired or replacement product
assumes the remaining warranty of the
original product or 90 days, whichever
is longer.
NON-WARRANTY REPAIR SERVICE — U.S.A.
Non-warranty repair covers service
beyond the warranty period or service
requested due to damage resulting
from misuse or abuse.
Contact the CI Authorized Service
Provider listed on the back page of the
User ’s Guide to obtain current product
repair information and charges.
Repairs are guaranteed for 90 days.
REPAIR SERVICE — OUTSIDE THE U.S.A.
Not all countries have CI Authorized
Service Providers or the same warranty and service policies. To obtain warranty or non-warranty repair service for
goods purchased outside the U.S.,
contact the dealer through which you
initially purchased the product.
If you cannot reasonably have the
product repaired in your area, you may
contact CI to obtain current product
repair information and charges, including freight and duties.
Page 46

DISCLAIMER
CI makes no warranty or representation,
either express or implied, with respect to
the product’s quality, performance, merchantability, or fitness for a particular purpose. As a result, this product, including
but not limited to, keystroke procedures,
mathematical accuracy and preprogrammed material, is sold “as is,” and
you the purchaser assume the entire risk
as to its quality and performance.
In no event will CI be liable for direct,
indirect, special, incidental, or consequential damages resulting from any
defect in the product or its documentation.
The warranty, disclaimer, and remedies set forth above are exclusive and
replace all others, oral or written,
expressed or implied. No CI dealer,
agent, or employee is authorized to make
any modification, extension, or addition to
this warranty.
Some states do not allow the exclusion or limitation of implied warranties or
liability for incidental or consequential
damages, so the above limitation or
exclusion may not apply to you. This
warranty gives you specific rights, and
you may also have other rights which
vary from state to state.
46 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 47
User’s Guide – 47
FCC CLASS B
This equipment has been certified to
comply with the limits for a Class B computing device, pursuant to Subpart J of
Part 15 of FCC rules.
LEGAL NOTICES
Software copyrighted and licensed
to Calculated Industries by Construction
Master, LLC, 2002.
User ’s Guide copyrighted by Calculated
Industries, 2002.
Measure Master Classic™
and Calculated Industries®
are registered trademarks of
Calculated Industries, Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
LOOKING FOR NEW IDEAS
Calculated Industries, a leading manufacturer of special function calculators
and digital measuring instruments, is
always looking for new product ideas in
these areas.
If you have one, or if you have any
suggestions for improvements regarding
this product or its User’s Guide, please
call or write our Product Development
Department. Thank you.
Page 48

Mail
Calculated Industries, Inc.
4840 Hytech Drive
Carson City, NV 89706 U.S.A.
Phone
1–775–885–4900
Fax
1–775–885–4949
Email
techsup@calculated.com
World Wide Web
http://www.calculated.com
HOW TO REACH CI HEADQUARTERS
Page 49

M
EASURE
M
ASTER
C
LASSIC
™
Guide de l’utilisateur
Calculated Industries, Inc.
4840 Hytech Drive
Carson City, NV 89706 U.S.A.
Page 50

Conçue pour les professionnels de la
construction qui sont très occupés, la
nouvelle calculatrice Measure Master
Classic vous propose une solution rapide
et précise à des centaines de problèmes
de dimension exprimés en pieds et en
pouces ou en unités de mesure
métriques!
◆ Une solution rapide aux équations
arithmétiques dimensionnelles
◆ Conversion instantanée des unités de
mesure
◆ Conversion de toutes les unités de
mesure métriques et impériales
◆ Calcul de l’aire des rectangles et des
carrés
◆ Définition de volumes
◆ Conversion entre les unités de volume
et de masse
◆ Aire, circonférence et longueurs d’arc
d’un cercle
◆ Estimation des quantités de matériaux
◆ Fonction de ruban virtuel
◆ Et bien plus encore!
VOICI LA CALCULATRICE
MEASURE MASTER CLASSIC
™
2 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 51

Description des touches
et des fonctions
Fonctions de base
[+] [–] [x] [÷] [=]
Touches d’équations arithmétiques.
[%]
Touche de pourcentage à quatre fonctions.
0 – 9
Chiffres utilisés pour entrer des nombres.
[ • ]
Point décimal.
[Off]
Mise hors tension. Retour à l’affichage
de démarrage. Ferme tous les registres
temporaires.
[On/C]
Mise sous tension. Appuyer une fois sur
la touche pour effacer la dernière donnée
et revenir à l’affichage antérieur . Appuyer
deux fois de suite pour annuler tous les
registres temporaires.
[Conv]
Conversion entre différentes unités de
mesure. Les unités de mesure ne
Guide de l’utilisateur – 3
AVANT DE DÉBUTER
Page 52

peuvent être converties que si elles sont
affectées du même exposant (unités de
distance, d’aire ou de volume). Activation
de fonctions spéciales.
[ ]
Racine carrée d’un nombre.
[Conv] [ ] — x
2
Élévation au carré de la valeur à l’écran.
[M+] — Mémoire plus
Enregistre le nombre à l’écran dans la
mémoire semi-permanente. Additionne
également le nombre à l’écran à toute
valeur enregistrée antérieurement dans la
mémoire. Pour afficher la somme des
valeurs entrées dans la mémoire, appuyer
sur [
Rcl
] avant d’appuyer sur [
M+
].
[Conv] [M+] — Mémoire moins (M–)
Soustrait le nombre à l’écran de la valeur
emmagasinée dans la mémoire.
[Rcl] — Rappel
Rappelle les valeurs entrées dans n’importe quel registre (appuyer sur [
Rcl
] puis
sur la touche de la fonction dont on veut
obtenir la valeur). Appuyer sur [
Rcl
] [
M+
]
pour afficher le contenu de la mémoire.
*********************************************
4 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 53

[Rcl] [x] — Système métrique ou impérial
Affichage et calcul en mesures métriques
ou impériales des données suivantes :
pente, hauteur de la contremarche des
escaliers, espacement des empannons
et des parois inclinées.
Remarque : Ce réglage est permanent.
Pour changer de système, enlever les piles
ou faire le réglage manuellement.
*********************************************
[Conv] [Rcl] — Efface le contenu
de la mémoire
Efface le contenu de la mémoire sans
modifier les valeurs affichées à l’écran.
Touches d’unités de mesure
[Yds] — Verges
Touche servant à entrer et à convertir des
valeurs (conjointement avec [
Conv
] pour
conversion).
[Feet] — Pieds
Touche servant à entrer et à convertir des
valeurs (conjointement avec [
Conv
] pour
conversion). Cette touche peut également être utilisée conjointement avec les
touches [
Inch
] (pouce) et [/] pour
exprimer des données en pieds, en
pouces et en fractions de pouce.
Guide de l’utilisateur – 5
Page 54

[Inch] — Pouces
Touche servant à entrer et à convertir des
valeurs (conjointement avec [
Conv
] pour
conversion). Cette touche peut également être utilisée conjointement avec la
touche [
/
] pour entrer des données
exprimées en fractions de pouce.
[/] — Barre des fractions
Cette touche sert à entrer des fractions.
Par exemple, pour entrer 1/2, il faut
appuyer sur les touches suivantes, dans
cet ordre :
1 [/] 2
.
[Cu] — Cubique
Cette touche est employée avec une touche
de mesure et indique que la valeur entrée
exprime un volume. Exemple :
5 [Cu] [Yds]
ou 5 verges cubes.
[Sq] — Au carré
Cette touche est employée avec une
touche de mesure et indique que la valeur
entrée exprime une aire. Exemple :
10 [Sq]
[Meters]
ou
10 m
2
.
[m] — Mètres
Touche servant à entrer et à convertir des
données, représentant des mètres,
exprimées en nombres décimaux.
[cm] — Centimètres
Touche servant à entrer et à convertir des
6 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 55

données représentant des centimètres.
S’utilise tel que décrit ci-dessus.
[mm] — Millimètres
Touche servant à entrer et à convertir des
données représentant des millimètres.
S’utilise tel que décrit ci-dessus.
[Weight] — Masse
Cette touche sert à convertir une donnée
exprimée en unités volumiques en unités
de masse à l’aide de la touche [
Conv
] et
du facteur de masse volumique (voir
ci-dessous). Chaque enfoncement de la
touche commute entre tonnes, livres et
kilogrammes.
[Conv] [%] — Masse volumique
Active le facteur masse volumique. Ce facteur peut être entré en kilogrammes par
mètre cube, en tonnes par verge cube ou
en livres par verge cube. Appuyer sur
[
Conv
] pour changer d’unité de mesure.
Exemple : 2 150 kg/m
3
: 2 150 [
Conv] [%].
[Circ] — Cercle
Valeur calculée d’après le diamètre
dimensionné entré. Appuyer plusieurs
fois de suite pour voir apparaître, dans
cet ordre : le diamètre (appuyer une fois),
l’aire du cercle (deux fois) et la
circonférence (trois fois).
Guide de l’utilisateur – 7
Page 56

[Conv] [Circ] — Longueur d’arc
Sert à calculer la longueur d’arc à partir
d’un angle et du diamètre du cercle. Par
exemple, après avoir appuyé sur 50 [mm]
[Circ] 180 [Conv] [Circ]
, l’écran affichera
une longueur d’arc de 78,53982 mm pour
un cercle dont le diamètre est de 50 mm
et dont l’angle mesure 180°.
Autres fonctions utilisées avec [Conv]
Lorsque utilisée conjointement avec les
touches suivantes, la touche [
Conv
]
permet d’utiliser ces fonctions :
[Conv] [÷]
Inverse ou fonction 1/x.
[Conv] [x] — Remise à zéro
Efface toutes les valeurs, y compris
celles enregistrées dans la mémoire.
Rétablit toutes les valeurs par défaut (les
réglages permanents sont effacés).
[Conv] [+] — Pi (π)
Constante dont la valeur est de 3,141593.
[Conv] [–] +/–
Change le signe de la valeur à l’écran.
[Conv] [=] — Bande
Active le mode « ruban virtuel ».
8 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 57

[Conv] [•] — Unitaire
Calcule le prix total des matériaux à partir
d’une mesure unitaire et d’un prix unitaire.
Réglage de l’arrondissement des fractions :
Lorsque votre calculatrice rétablit les
paramètres par défaut (après un changement de piles ou une réinitialisation des
paramètres par défaut), elle arrondit les
fractions au 1/16 de pouce. Toutefois, il
est possible de programmer vos
préférences et de créer six niveaux de
précision qui seront conservés dans la
mémoire jusqu’au prochain réglage. Pour
changer la précision de l’arrondissement
des fractions, appuyer sur :
[Conv] 1 Fraction arrondie au 1/16
[Conv] 2 Fraction arrondie au 1/2
[Conv] 3 Fraction arrondie au 1/32
[Conv] 4 Fraction arrondie au 1/4
[Conv] 6 Fraction arrondie au 1/64
[Conv] 8 Fraction arrondie au 1/8
Entrée des mesures
Tous les exemples ont été effectués en
utilisant des unités de mesure métriques.
Réglage du système métrique : Appuyer
sur
[Rcl] [x]
, et « METR » s’affichera à
l’écran.
Guide de l’utilisateur – 9
Page 58

Mesures linéaires
Les exemples qui suivent décrivent comment entrer les mesures.
Mesure Touches
17,5 mètres 17.5 [m]
5 pieds 5 [Feet]
1/2 pouce 1 [/] 2
5 pieds 1 pouce 5 [Feet] 1 [Inch]
5 pieds 1 1/2 pouce 5 [Feet] 1 [Inch] 1 [/] 2
10 verges 10 [Yds]
205 millimètres 205 [mm]
Aire et volume
Les valeurs exprimant une aire ou un
volume doivent être entrées dans l’ordre
suivant : 1) valeur numérique; 2)
exposant affectant l’unité de mesure (au
carré ou au cube); 3) unité de mesure
(mètre, verge, pied, pouce).
Les exemples qui suivent montrent la
façon d’entrer l’aire ou le volume d’un
corps :
Mesure Touches
33 millimètres carrés 33 [Sq] [mm]
5 verges cubes 5 [Cu] [Yds]
130 pieds carrés 130 [Sq] [Feet]
123 mètres cubes 123 [Cu] [m]
10 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 59

Conversion d’unités de mesure
Conversion d’unités de mesure
linéaires
Voici comment convertir 14 pieds en
d’autres unités de mesure linéaires :
Touches Résultat
14 [Feet] . . . 14. FEET
[Conv] [m] 4.267 M
[Conv] [cm] 426.72 CM
[Conv] [mm] 4267.2 MM
[Conv] [Yds] 4.666667 YD
[Conv] [Feet] 14 FEET 0 INCH
[Conv] [Feet] 14. FEET
[Conv] [Inch] 168. INCH
Conversion d’unités de mesure
d’aire
Voici comment convertir 14 pieds carrés
en d’autres unités de mesure d’aire :
Touches Résultat
14 [Sq] [Feet] . . . 14. FEET
[Conv] [m] 1.301 SQ M
[cm] 13006.43 SQ CM
[mm] 1300643. SQ MM
[Inch] 2016. SQ INCH
[Yds] 1.555556 SQ YD
Remarque : Pour faire une conversion,
n’appuyer qu’une seule fois sur la touche
[Conv].
Guide de l’utilisateur – 11
Page 60

Conversion d’unités de mesure
volumiques
Voici comment convertir 14 pieds cubes en
d’autres unités de mesure volumiques :
Touches Résultat
14 [Cu] [Feet] . . . 14. FEET
[Conv] [m] 0.396 CU M
[cm] 396435.9 CU CM
[mm] 0.396 CU M *
[Inch] 24192. CU INCH
[Yds] 0.518519 CU YD
* Remarquer que, lorsqu’une valeur est
convertie en millimètres, la solution est
automatiquement convertie en mètres. À
défaut de ce réglage, le nombre de chiffres
formant la solution dépasserait l’affichage
normal de la calculatrice, qui est de 7
chiffres.
Opérations mathématiques
Votre calculatrice utilise la logique de
chaînage standard. Autrement dit, il suf fit
d’entrer la première valeur suivie de
l’opérateur (+, -, x, ∏), la deuxième valeur
et, enfin, le signe d’égalité (=).
A. 3 [+] 2 [=] 5
B. 3 [–] 2 [=] 1
C. 3 [x] 2 [=] 6
D. 3 [÷] 2 [=] 1.5
Grâce à cette caractéristique, la
calculatrice demeure très facile à utiliser.
12 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 61

Les exemples qui suivent illustrent cette
facilité d’utilisation.
Addition et soustraction de mesures
1. Additionner 7 mètres à 11 pieds et 4
pouces :
7 [m] [+] 11 [Feet] 4 [Inch]
[=] 10.454
M
2. Soustraire 3 pieds à 11 pieds 7 1/2
pouces :
11 [Feet] 7 [Inch] 1 [/] 2 [–] 3 [Feet]
[=] 8
FEET
7-1/2
INCH
Remarque : L’unité de mesure de la
première valeur entrée dans la calculatrice
détermine l’unité de mesure de la solution.
Il est toutefois possible de transformer la
solution en n’importe quelle unité de
mesure grâce à la touche [Conv], à
condition que le protocole de conversion
soit respecté.
Multiplication et division de mesures
1. Multiplier 5 pieds 3 pouces par 11
pieds 6 1/2 pouces :
5 [Feet] 3 [Inch]
[x] 11 [Feet] 6 [Inch] 1[/] 2
[=] 60.59375
SQ
FEET
2. Diviser 30 mètres par 16 pouces :
30 [m] [÷] 16 [Inch]
[=] 73.8189
Guide de l’utilisateur – 13
Page 62

Mémoire
Chaque fois que la touche [
M+
] est
activée, la valeur à l’écran est ajoutée à
la mémoire. Pour effacer cette valeur de
la mémoire, appuyer sur
[Conv] [M+]
.
La fonction
[Rcl] [M+]
cherche la valeur
totale de la mémoire et l’affiche à l’écran.
La fonction
[Rcl] [Rcl]
affiche la valeur
totale de la mémoire et efface ensuite le
contenu de la mémoire. Mettre la
calculatrice hors tension procure aussi le
même résultat.
Touches Résultat
1. 355 [M+] 355.
[Rcl] [Rcl] 355.
2. 355 [M+] 355.
255 [M+] 255.
745 [Conv] [M+] 745.
[Rcl] [Rcl] – 135.
Ruban virtuel
Le ruban virtuel est une fonction qui
permet à l’utilisateur d’afficher et de
réviser les vingt dernières données d’un
calcul. Pour activer le ruban virtuel,
appuyer sur
[Rcl] [=]
.
Pour faire défiler les dernières don-
nées, appuyer sur
[Rcl] [=]
afin d’activer la
fonction de ruban virtuel puis appuyer sur
[+] pour voir les données suivantes ou sur
[-] pour voir les données précédentes. Le
14 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 63

ruban virtuel se vide de sa mémoire
chaque fois que la touche
[On/C]
est
enfoncée deux fois ou que la calculatrice
est mise hors tension.
Fonctionnement du ruban virtuel
1. Entrer une série de nombres :
Touches Résultat
4 [cm] [+] 4.
CM
5 [cm] [+] 9. CM
6 [cm] [=] 15. CM
2. Activer la fonction de ruban virtuel :
Touches Résultat
[Rcl] [=] TTL= 15
CM
3. Faire défiler le ruban de la première
donnée jusqu’au total :
Touches Résultat
[+] 01 4.
CM
[+] 02+ 5. CM
[+] 03+ 6. CM
[+] TTL= 15. CM
4. Faire défiler les deux dernières
données :
Touches Résultat
[–] 03+ 6.
CM
[–] 02+ 5. CM
5. Pour quitter la fonction de ruban virtuel
touche
[On/C] [On/C]
.
Guide de l’utilisateur – 15
Page 64

P
ILE ET MISE HORS TENSION AUTOMATIQUE
—
La calculatrice fonctionne grâce à une pile au
lithium de 3 V de modèle CR-2032. Cette pile
devrait fonctionner pendant plus de 1 800
heures d’utilisation, ce qui équivaut à un peu
plus d’une année dans la plupart des cas.
Remplacer la pile si l’affichage à l’écran devient
très pâle ou intermittent.
La calculatrice est dotée d’un mécanisme
qui la met hors tension après de 8 à 12 minutes
d’inactivité.
PRECISION DE L’AFFICHAGE — L ’écran de la cal-
culatrice permet l’affichage de 11 chiffres, soit
7 chiffres entiers et 4 décimales. Les calculs
internes sont effectués avec 10 chiffres puis
arrondis au 5/4 afin de se conformer à
l’affichage standard à 7 chiffres.
« ERROR » — Lorsqu’une donnée incorrecte est
entrée ou que l’opération ne peut être exécutée
par la calculatrice, le code «
Error
» apparaît à
l’écran, indiquant qu’une erreur s’est produite.
Appuyer deux fois sur
[On/C]
pour annuler l’erreur . Une erreur peut également se produire
lorsqu’une opération mathématique est impossible, la division par zéro par exemple.
SÉLECTION AUTOMATIQUE DES UNITÉS — Si un
« bouchon » est causé par une entrée ou un
calcul de petites unités excédant 7 chiffres
(ordre de grandeur standard), la solution sera
automatiquement exprimée par les unités
supérieures les plus près.
Calculated Industries
®
© 2002, Calculated Industries
4840 Hytech Drive
Carson City, NV 89706 U.S.A.
16 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 65

M
EASURE
M
ASTER
C
LASSIC
™
Guía del Usuario
Calculated Industries, Inc.
4840 Hytech Drive
Carson City, NV 89706 U.S.A.
Page 66

¡Diseñada para servir a los atareados
profesionales de la construcción, la
Measure Master Classic le permite
resolver rápidamente y con precisión
cientos de problemas relacionados con
medidas en los formatos métrico o de
pies-pulgadas!
◆ Resuelva con facilidad matemáticas
dimensionales
◆ Conversiones instantáneas de medi-
das
◆ Conversiones completas entre los sis-
temas métrico e imperial (inglés)
◆ Calcule áreas de cuadrados y rectán-
gulos
◆ Encuentre volúmenes
◆ Haga conversiones entre volumen y
peso
◆ Encuentre áreas de círculos, circun-
ferencias y arcos
◆ Haga estimaciones de materiales
◆ Función de cinta de control “sin papel”
◆ ¡Y mucho, pero mucho más!
2 – Measure Master Classic
™
PRESENTANDO:
MEASURE MASTER CLASSIC™
Page 67

Guía del Usuario – 3
Definiciones /Funciones básicas
Funciones básicas
[+] [–] [x] [÷] [=]
Teclas de operaciones aritméticas.
[%]
Tecla de porcentaje de cuatro funciones.
0 – 9
Dígitos usados para entrar los números.
[ • ]
Punto decimal.
[Off]
Apaga la calculadora. Reinicializa la
pantalla y todos los registros no
permanentes.
[On/C]
Enciende la calculadora. Si se pulsa una
vez, borra la última entrada y la pantalla.
Si se pulsa dos veces sucesivas, se
borran todos los registros temporales.
[Conv]
Se utiliza para realizar conversiones
entre medidas. Las medidas sólo se
pueden convertir dentro de la misma
convención (por ejemplo, lineal, área o
PARA EMPEZAR
Page 68

volumen). También se utiliza para
acceder a funciones especiales.
[ ]
Se utiliza para encontrar la raíz cuadrada
de un número.
[Conv] [ ] — x
2
Encuentra el cuadrado del valor
visualizado.
[M+] — Memoria Más
Almacena el valor visualizado en pantalla
en la memoria semipermanente. Tam-bién
suma el valor en pantalla a cualquier valor
que se haya almacenado previamente en
la memoria. Para traer a la pantalla el total
almacenado en la memoria, pulse
[Rcl]
antes de
[M+]
.
[Conv] [M+] — Memoria Menos (M–)
Resta de la memoria el valor visualizado
en la pantalla.
[Rcl] — Recuperar
Recupera los valores almacenados en
cualquier registro (por ejemplo, pulse
[Rcl]
y luego la tecla de la que desee
visualizar su valor).
[Rcl] [M+]
visualiza el
contenido de la memoria.
*********************************************
4 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 69

Guía del Usuario – 5
[Rcl] [x] — Modo Imperial/Métrico
Selecciona los modos predeterminados
Imperial o Métrico para los siguientes
parámetros: paso, altura del
contraescalón de escalera y el espaciado
en el centro de cabios cortos y paredes
inclinadas.
Nota: Éste es un parámetro permanente
que sólo se puede eliminar quitando las
pilas o reinicializando manualmente.
*********************************************
[Conv] [Rcl] — Despeje de memoria
Despeja la memoria sin cambiar la
visualización actual.
Teclas de medidas
[Yds] — Yardas
Ésta es una tecla de entrada y conversión (cuando se usa con [
Conv
]).
[Feet] — Pies
Ésta es una tecla de entrada y
conversión (cuando se usa con [
Conv
]).
También se puede usar esta tecla junto
con las teclas [
Inch
] y [/] para entrar
fracciones de pies-pulgadas.
[Inch] — Pulgadas
Ésta es una tecla de entrada y
conversión (cuando se usa con [
Conv
]).
Page 70

También se puede usar esta tecla junto
con la tecla [
/
] para entrar valores en el
formato de fracciones de pulgadas.
[/] — Barra de fracción
Se usa esta tecla para entrar fracciones.
Por ejemplo, para entrar 1/2, la
secuencia sería:
1 [/] 2.
[Cu] — Volumen
Esta tecla se usa con una tecla de
medida para identificar un valor como un
volumen. Por ejemplo:
5 [Cu] [Yds]
.
[Sq] — Área
Esta tecla se usa con una tecla de
medida para identificar un valor como un
área. Por ejemplo:
10 [Sq] [Meters]
.
[m] — Metros
Ésta es una tecla de entrada y conversión
que se usa para entrar metros decimales
o para convertir metros decimales.
[cm] — Centímetros
Tecla de entrada y conversión para
centímetros, que se usa de la manera
descrita en el párrafo anterior.
[mm] — Milímetros
Tecla de entrada y conversión para
milímetros, usada de la manera descrita
en el párrafo anterior.
6 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 71

Guía del Usuario – 7
[Weight] — Peso
Esta tecla se usa para convertir volumen
a peso usando la tecla [
Conv
] y el factor
almacenado de Peso por volumen (ver a
continuación). Al pulsar repetidamente se
cambia entre toneladas, libras y
kilogramos.
[Conv] [%] — Peso por volumen
Se usa para definir el valor de Peso por
volumen. El factor se puede entrar en
kilogramos por metro cúbico, toneladas
por yarda cúbica, o libras por yarda
cúbica. Para establecer un peso por
volumen diferente, por ejemplo, 2150
kilogramos por metro cúbico, pulse 2150
[Conv] [%]
.
[Circ] — Círculo
Dependiendo de la entrada de un
diámetro dimensionado, las pulsadas
repetidas visualizarán los siguientes
valores circulares: 1) diámetro, 2) área
de la superficie y 3) circunferencia.
[Conv] [Circ] — Longitud de arco
Se usa para encontrar la longitud del
arco en función de la entrada de un
diámetro y un ángulo. Por ejemplo:
50
[mm] [Circ] 180 [Conv] [Circ]
visualizaría
una longitud de arco de 78.53982
milímetros para una entrada de diámetro
de 50 milímetros y un ángulo de 180°.
Page 72

Funciones adicionales de la tecla
[Conv]:
Cuando se usa junto con las siguientes
teclas, la tecla
[Conv]
da acceso a estas
funciones adicionales:
[Conv] [÷]
Recíproco, o función 1/x.
[Conv] [x] — Despejar todo
Despeja todos los valores, incluyendo
la memoria. Reinicializa todos los
registros permanentes a sus valores
predeterminados.
[Conv] [+] — Constante Pi (π)
3.141593.
[Conv] [–] +/–
Cambia el signo del valor visualizado.
[Conv] [=] — Cinta
Da acceso al modo de cinta sin papel.
[Conv] [•] — Por unidad
Permite calcular un costo total de
materiales dados una medida unitaria y
una entrada de Costo por unidad.
Ajustes de redondeo fraccional:
Cuando su calculadora se encuentra en
una condición predeterminada (después
de un cambio de pila o reinicialización
8 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 73

Guía del Usuario – 9
total), el ajuste establecido es redondear
los valores fraccionales al 1/16 de pulgada más próximo. Sin embargo, usted
podrá programar su preferencia para 6
niveles de precisión diferentes, que permanecen en la memoria permanente
hasta que se revisen o reinicialicen. Para
cambiar el redondeo fraccional, pulse:
[Conv] 1 Fija la fracción a 1/16
[Conv] 2 Fija la fracción a 1/2
[Conv] 3 Fija la fracción a 1/32
[Conv] 4 Fija la fracción a 1/4
[Conv] 6 Fija la fracción a 1/64
[Conv] 8 Fija la fracción a 1/8
Entrada de medidas
Todos los ejemplos se realizan en el
Modo métrico (pulse
[Rcl] [x]
para ver
“METR” en la pantalla).
Medidas lineales
A continuación se dan algunos ejemplos
de cómo se entran las medidas lineales:
Medida Teclas
17.5 metros 17.5 [m]
5 pies 5 [Feet]
1/2 pulgada 1 [/] 2
5 pies 1 pulgada 5 [Feet] 1 [Inch]
5 pies1 1/2 pulgada 5 [Feet] 1 [Inch] 1 [/] 2
10 yardas 10 [Yds]
205 milímetros 205 [mm]
Page 74

Medidas de área y de volumen
Las medidas de área y de volumen se
entran en el orden siguiente: (1) Valor
numérico; (2) Convención—Área
[Sq]
o
Volumen [
Cu
]; (3) Unidades —Metros,
Yardas, Pies, Pulgadas.
A continuación se dan algunos ejemplos
de cómo se entran las medidas de área
y de volumen:
Medida Teclas
33 milímetros cuadrados 33 [Sq] [mm]
5 yardas cúbicas 5 [Cu] [Yds]
130 pies cuadrados 130 [Sq] [Feet]
123 metros cúbicos 123 [Cu] [m]
Conversión de medidas
Conversiones lineales
Convertir 14 pies a otras medidas
lineales:
Teclas La pantalla muestra
14 [Feet] . . . 14. FEET
[Conv] [m] 4.267 M
[Conv] [cm] 426.72 CM
[Conv] [mm] 4267.2 MM
[Conv] [Yds] 4.666667 YD
[Conv] [Feet] 14 FEET 0 INCH
[Conv] [Feet] 14. FEET
[Conv] [Inch] 168. INCH
10 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 75

Guía del Usuario – 11
Conversiones de área
Convertir 14 pies cuadrados a otras
medidas de área:
Teclas La pantalla muestra
14 [Sq] [Feet] . . . 14. FEET
[Conv] [m] 1.301 SQ M
[cm] 13006.43 SQ CM
[mm] 1300643. SQ MM
[Inch] 2016. SQ INCH
[Yds] 1.555556 SQ YD
Nota: Al realizar conversiones, sólo se
debe pulsar [Conv] una vez.
Conversiones de volumen
Convertir 14 pies cúbicos a otras medidas de volumen:
Teclas La pantalla muestra
14 [Cu] [Feet] . . . 14. FEET
[Conv] [m] 0.396 CU M
[cm] 396435.9 CU CM
[mm] 0.396 CU M *
[Inch] 24192. CU INCH
[Yds] 0.518519 CU YD
* Observe que en la conversión a
milímetros, la respuesta ha adoptado la
“Gama automática” y se visualiza en metros, ya que de lo contrario el número de
dígitos excedería la gama normal de
visualización de la calculadora, que es de
7 dígitos.
Page 76

Operaciones matemáticas
Su calculadora utiliza una lógica de encadenado estándar , que significa que usted
entra el primer valor, el operador (+, –, x,
÷), el segundo valor y luego el signo de
Igual (“=”).
A. 3 [+] 2 [=] 5
B. 3 [–] 2 [=] 1
C. 3 [x] 2 [=] 6
D. 3 [÷] 2 [=] 1.5
Esta propiedad facilita también el uso de
la calculadora para aplicaciones con
medidas, tal como se muestra en los
ejemplos siguientes:
Suma y resta de medidas
1. Sumar 7 metros a 11 pies 4 pulgadas:
7 [m] [+] 11 [Feet] 4 [Inch]
[=] 10.454 M
2. Restar 3 pies de 11 pies 7-1/2
pulgadas:
11 [Feet] 7 [Inch] 1 [/] 2 [–] 3 [Feet]
[=] 8
FEET
7-1/2
INCH
Nota: El formato de la respuesta queda
determinado por el formato del primer
valor que se entre. Sin embargo, usted
puede cambiar a cualquier formato que
desee usando la tecla
[Conv]
, siempre y
cuando mantenga la convención.
12 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 77

Guía del Usuario – 13
Multiplicación y división de medidas
1. Multiplicar 5 pies 3 pulgadas por
11 pies 6-1/2 pulgadas:
5 [Feet] 3 [Inch]
[x] 11 [Feet] 6 [Inch] 1[/] 2
[=] 60.59375
SQ
FEET
2. Dividir 30 metros por 16 pulgadas:
30 [m] [÷] 16 [Inch]
[=] 73.8189
Operaciones de la memoria
Siempre que se pulse la tecla
[M+]
, el
valor visualizado se añadirá a la
memoria. Se restará de la memoria el
valor visualizado pulsando
[Conv] [M+]
.
[Rcl] [M+]
recupera y visualiza el valor
total en la memoria.
[Rcl] [Rcl]
visualiza y
despeja el contenido de la memoria, de la
misma forma que se hace al apagar la
calculadora.
Teclas La pantalla muestra
1. 355 [M+] 355.
[Rcl] [Rcl] 355.
2. 355 [M+] 355.
255 [M+] 255.
745 [Conv] [M+] 745.
[Rcl] [Rcl] – 135.
Page 78

Cinta de control “sin papel”
La Cinta de control “sin papel” permite
visualizar y revisar las últimas 20
entradas de un cálculo. Se accede a esta
función pulsando
[Rcl] [=]
.
Para revisar los valores entrados,
pulse
[Rcl] [=]
a fin de acceder al modo
de cinta y luego pulse las teclas
[+] o [–]
para recorrer las entradas retrocediendo
o avanzando. La Cinta de control se
despeja cada vez que se pulsa dos veces
[On/C]
, o se apaga la unidad.
Revisar la Cinta de control “sin papel”
1. Entre una serie de números:
Teclas La pantalla muestra
4 [cm] [+] 4.
CM
5 [cm] [+] 9. CM
6 [cm] [=] 15. CM
2. Gane acceso a la función de Cinta:
Teclas La pantalla muestra
[Rcl] [=] TTL= 15
CM
3. Recorra desde el primer valor hasta el
total:
Teclas La pantalla muestra
[+] 01 4.
CM
[+] 02+ 5. CM
[+] 03+ 6. CM
[+] TTL= 15. CM
14 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 79

Guía del Usuario – 15
4. Recorra los últimos 2 valores:
Teclas La pantalla muestra
[–] 03+ 6.
CM
[–] 02+ 5. CM
5. Salga de la función de Cinta pulsando
[On/C] [On/C].
P
ILA Y APAGADO AUTOMÁTICO
— Su
calculadora funciona con una sola pila de
litio CR-2032 de 3 voltios. La pila deberá
durar aproximadamente 1,000 horas de
uso efectivo (más de 1 año para la
mayoría de los usuarios). En caso de que
la pantalla se vea muy tenue o funcione
erráticamente, cambie la pila.
Su calculadora ha sido diseñada para
que se apague automáticamente
después de permanecer sin uso durante
8 a 12 minutos.
P
RECISIÓN
/P
ANTALLA
— Su calculadora
tiene una pantalla de 11 dígitos (siete
dígitos normales y cuatro dígitos para las
fracciones). Los cálculos se realizan
internamente con una precisión de 10
dígitos y se redondean a la pantalla
normal de 7 dígitos usando una técnica
de redondeo de 5/4.
“E
RROR
” — Si realiza una entrada incor-
recta, o si la respuesta excede la gama
Page 80

de la calculadora, se visualizará la
palabra “
ERROR”. Para despejar una
condición de error, debe pulsar dos
veces el botón
[On/C]
. También ocurrirá
una condición de “
ERROR” si se entra una
imposibilidad matemática, tal como una
división entre cero.
G
AMA AUTOMÁTICA
— Si se produce un
“desbordamiento” debido a una entrada y
cálculos con unidades pequeñas que
excedan la gama estándar de 7 dígitos
de la pantalla, la respuesta se expresará
automáticamente en las unidades
próximas más grandes.
Calculated Industries
®
© 2002, Calculated Industries
4840 Hytech Drive
Carson City, NV 89706 U.S.A.
16 – Measure Master Classic
™
Page 81

Page 82

Page 83

Page 84

Printed in China
4015-UG-B
5/02
 Loading...
Loading...