Page 1

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 1/55
LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide
Contents
1 Introduction
1.1 About This Manual
1.2 About The Reader
1.3 About CalAmp
1.4 About the CalAmp Location Messaging Unit-LMU-5000™
2 System Overview
2.1 Overview
2.2 Component Descriptions
2.2.1 Wireless Data Network
2.2.2 LMU-5000™
2.2.3 LM Direct™ Server
2.2.4 Backend Software
2.2.5 PULS™
2.2.6 LMU Manager™
3 Hardware Overview
3.1 Location Messaging Unit-LMU-5000™
3.1.1 LMU-5000™ Handling Precautions
3.1.2 Battery Back-up devices
3.1.3 Environmental Specifications
3.2 LMU-5000™Connectors
3.2.1 Power Connector
3.2.2 I/O Connector
3.2.3 Serial Interface Connectors
3.2.4 Serial Interface Cables & Accessories
3.2.5 Accessories
3.3 GPS Receiver
3.4 RF Connector
3.5 I/O Descriptions
3.5.1 Ignition and Inputs
3.5.2 Open Collector Outputs
3.5.3 LED Outputs
3.5.4 Status LEDs
4 Configuration and Activation
4.1 Quick Start - General Config
4.2 Auto provisioning of GSM or HSPA LMUs
4.3 Activating GSM or HSPA LMU using AT Commands
4.4 Accessing the SIM
4.5 Activating a CDMA LMU-5000™
4.5.1 Activating a CDMA LMU-5000™ – Verizon
4.5.2 Activating a CDMA LMU-5000™ – Sprint
4.5.3 Activating a CDMA LMU-5000™ – Bell Mobility
5 Installing the LMU
5.1 Preparing for Installation
Page 2

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 2/55
5.2 Plan The Installation
5.2.1 Size and Placement of LMU Unit
5.2.2 Placement of Antennas
5.2.3 Access to the SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) Card
5.2.4 Protection from Heat
5.2.5 Visibility of Diagnostic LEDs
5.2.6 Cable Length
5.2.7 Moisture and Weather Protection
5.2.8 Preventing Accidental or Unauthorized Modification
5.3 Installing the LMU in a Vehicle
5.3.1 Place the LMU unit in the vehicle.
5.3.2 Connect power, ignition, and ground.
5.3.3 Place the GPS antenna.
5.3.4 Mount the Comm. Antenna.
5.3.5 Typical Connection Sequence
5.4 Installation Verification
5.4.1 Comm Verification
5.4.2 GPS Verification
5.4.3 Inbound Verification
5.4.4 Verification via SMS
6 LMU-5000 Router Configuration & Management
6.1 Home Page Parameters
6.2 Provisioning Information: EV-DO “WAN Cellular” Page
6.3 Provisioning Information: HSPxA “WAN Cellular” Page
6.4 Provisioning Information On “WAN Cellular” Page
6.5 Activation (EV-DO)
6.6 Activation (HSxPA) Page
6.7 Dial Settings (EV-DO Version)
6.8 Dial Settings (HSxPA Version)
6.9 LAN Settings Page
6.9.1 Remote Administration
6.9.2 Disabling DHCP
6.10 Port Forwarding
6.11 GPS Status
6.12 GPS Reporting
6.13 Virtual Private Network (VPN)
6.14 System Upgrade
7 License Agreement
8 Limited Warranty
9 Regulatory Information
LMU-5000™
Hardware and Installation Guide
Page 3

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 3/55
IMPORTANT: DO NOT INSTALL OR USE THE SOFTWARE OR DOCUMENTATION UNTIL YOU
HAVE READ AND AGREED TO THE LICENSE AGREEMENT AND REVIEWED THE LIMITED
WARRANTY AND REGULATORY INFORMATION.
1 Introduction
Welcome to the LMU-5000™ Hardware and Installation Guide. This manual is intended to give you information on
the basic setup and installation of the CalAmp LMU-5000™ product(s) including hardware descriptions,
environmental specifications, wireless network overviews and device installation.
1.1 About This Manual
The LMU-5000™ is one of the most flexible economy mobile tracking hardware products available. In order
to accurately describe the functionality of these units we have broken this manual into the following sections:
System Overview – A basic description of a CalAmp LMU-5000™ based tracking system.
This includes a description of roles and responsibilities of each of the CalAmp components as
well as a brief overview of the wireless data technologies used by the LMU-5000™.
Hardware Overview – Describes the physical characteristics and interfaces of the LMU5000™.
Installation and Verification – Provides guidance for the installation of the LMU-5000™ in a
vehicle and instructions on how to verify the installation is performing adequately.
1.2 About The Reader
In order to limit the size and scope of this manual, the following assumptions have been made about the
reader.
You are familiar with GPS concepts and terminology
You have some experience with installing equipment in vehicles
You are familiar with the use of AT Commands
You are familiar with the use of terminal programs such as HyperTerminal or PuTTY
1.3 About CalAmp
CalAmp is a leading provider of wireless communications products that enable anytime/anywhere access to
critical information, data and entertainment content. With comprehensive capabilities ranging from product
design and development through volume production, CalAmp delivers cost-effective high quality solutions to a
broad array of customers and end markets. CalAmp is the leading supplier of Direct Broadcast Satellite
Page 4

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 4/55
(DBS) outdoor customer premise equipment to the U.S. satellite television market. The Company also
provides wireless data communication solutions for the telemetry and asset tracking markets, private wireless
networks, public safety communications and critical infrastructure and process control applications. For
additional information, please visit the Company’s website at www.calamp.com (http://www.calamp.com/) .
1.4 About the CalAmp Location Messaging Unit-LMU-5000™
The CalAmp Location and Messaging Unit-LMU-5000™ (LMU-5000™) is a mobile device that resides in
private, commercial or government vehicles. The LMU-5000™ is a single box enclosure incorporating a
processor, a GPS receiver, a wireless data modem, and a vehicle-rated power supply. The LMU-5000™
also supports inputs and outputs to monitor and react to the vehicular environment and/or driver actions.
Flexibility
The LMU-5000™ features CalAmp's industry leading advanced on-board alert engine that monitors vehicle
conditions giving you the most flexible tracking device in its class. The PEG™ (Programmable Event
Generator) application supports hundreds of customized exception-based rules to help meet customers'
dynamic requirements. Customers can modify the behavior of the device to meet with a range of applications
preprogrammed before shipment or in the field. Combining affordability and device intelligence with your
unique application can give you distinct advantages over your competition.
Over-the-Air Serviceability
The LMU-5000™ also incorporates CalAmp's industry leading over-the-air device management and
maintenance system software, PULS™ (Programming, Updates, and Logistics System). Configuration
parameters, PEG rules, and firmware can all be updated over the air. Our web-based maintenance server,
PULS™ scripts, and firmware, can all be updated over-the-air. PULS™ offers out-of-the-box hands free
configuration and automatic post-installation upgrades. You can also monitor unit health status across your
customers' fleets to quickly identify issues before they become expensive problems.
2 System Overview
2.1 Overview
The entire purpose behind a fleet management system is to be able to remotely contact a vehicle, determine its
location or status, and do something meaningful with that information. This could include displaying the vehicle
location on a map, performing an address look-up, providing real-time driving directions, updating the vehicles
ETA, monitoring vehicle and driver status or dispatching the vehicle to its next pick up.
These functions, of course, are completely dependent on the capabilities of the vehicle management
application. The role of the CalAmp LMU-5000™ is to deliver the location information when and where it is
needed.
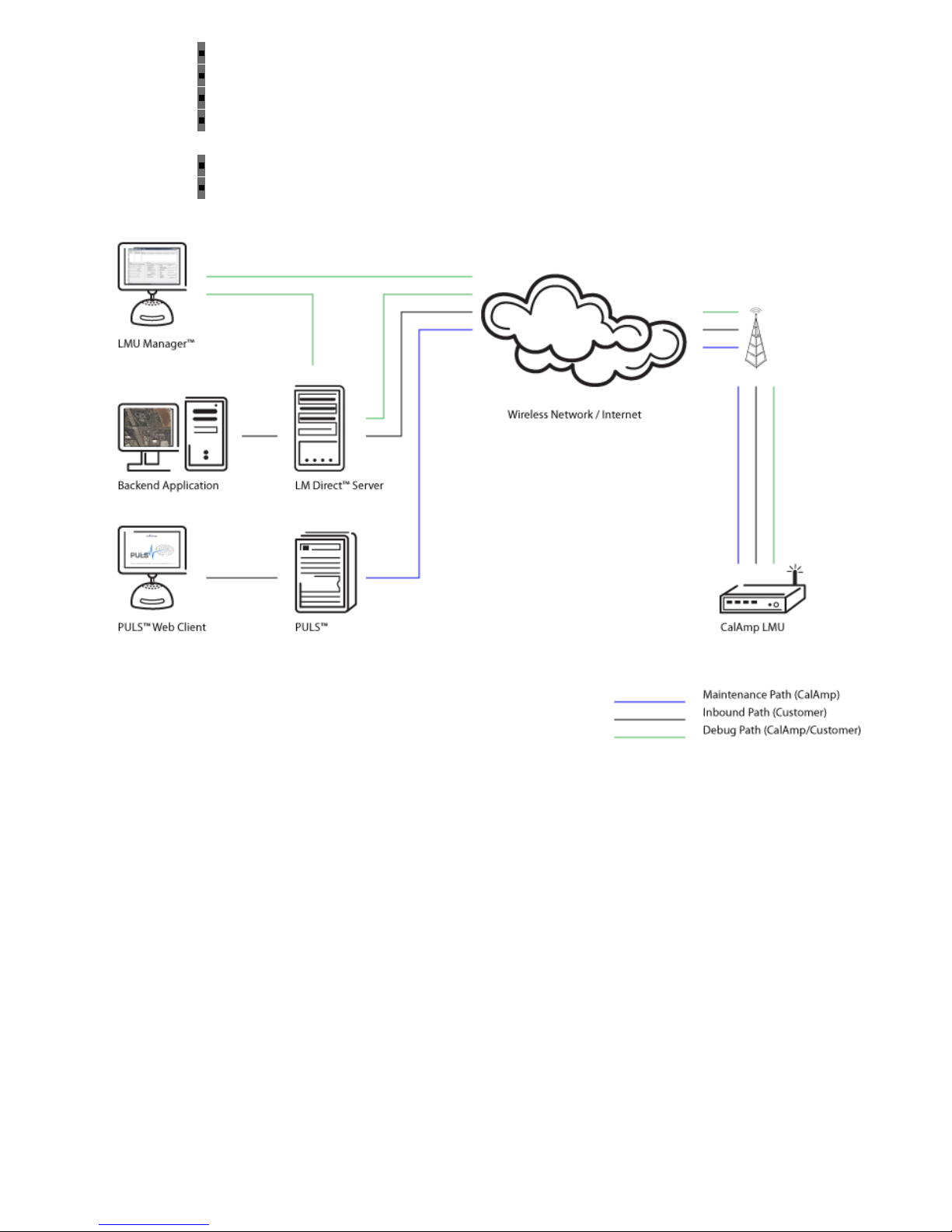
A typical fleet management system based on a CalAmp device includes the following components:
A wireless data network
Page 5
10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 5/55
An LMU-5000™
Host Device (GPS NMEA only)
An LM Direct™ communications server
Backend mapping and reporting software which typically includes mapping and fleet reporting
functions
PULS™
LMU Manager™
Basic System Architecture
2.2 Component Descriptions
2.2.1 Wireless Data Network
The Wireless Data Network provides the information bridge between the LM Direct™ server and the LMU5000™. Wireless data networks can take a variety of forms, such as cellular networks, satellite systems or
local area networks. Contact the CalAmp sales team for the networks available to the LMU-5000™.
2.2.2 LMU-5000™
The LMU-5000™ is responsible for delivering the location and status information when and where it is
Page 6

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 6/55
needed. Data requests mainly come from the following sources:
PEG™ script within the LMU-5000™
A location or status request from the LM Direct™ server
A location or status request from LMU Manager
An SMS request made from a mobile device such as a customer’s cell-phone
In some cases, it is necessary to run an application in the vehicle while it is being tracked by the backend
software. Such examples could include instant messaging between vehicles or a central office, in-vehicle
mapping or driving directions, email or database access. In most of these cases you will be using the LMU5000™ as a wireless modem as well as a vehicle-location device.
2.2.3 LM Direct™ Server
LM Direct™ is a CalAmp proprietary message interface specification detailing the various messages and their
contents the LMU-5000™ is capable of sending and receiving. This interface allows System Integrators to
communicate directly with LMU-5000's™. Please refer to the LM Direct Reference Guide for details.
2.2.4 Backend Software
Backend software is a customer provided software application. Regardless of its purpose, one of its primary
functions is to parse and present data obtained from the LM Direct™ server. This allows the application to do
any of the following:
Display location database on reports received from the LMU-5000™ in a variety of formats
Present historic information received from the LMU-5000™, typically in a report/chart style
format
Request location updates from one or more LMU-5000s™
Update and change the configuration of one or more LMU-5000s™
2.2.5 PULS™
PULS™ (Programming, Update and Logistics System) is CalAmp’s web-based maintenance server offering
out-of-the-box hands free configuration and automatic post-installation upgrades. PULS™ provides a means
for configuration parameters, PEG scripts, and firmware to be updated Over-The-Air (OTA) and allows
CalAmp customers to monitor unit health status across your customers’ fleets to quickly identify issues before
they become expensive problems.
2.2.6 LMU Manager™
LMU Manager is the primary configuration tool in the CalAmp system. It allows access to almost every
feature available to the LMU-5000™. Unlike the backend software, it has the option of talking directly to an
LMU-5000™ or making a request forwarded by the LM Direct™ server.
Page 7

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 7/55
For further details on using LMU Manager, please refer to the LMU Manager Users Guide.
3 Hardware Overview
3.1 Location Messaging Unit-LMU-5000™
3.1.1 LMU-5000™ Handling Precautions
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is the sudden and momentary electric current that flows between two objects at
different electrical potentials caused by direct contact or induced by an electrostatic field. The term is usually
used in the electronics and other industries to describe momentary unwanted currents that may cause damage
to electronic equipment.
ESD Handling Precautions
ESD prevention is based on establishing an Electrostatic Protective Area (EPA). The EPA can be a small
working station or a large manufacturing area. The main principle of an EPA is that there are no highly
charging materials in the vicinity of ESD sensitive electronics, all conductive materials are grounded, workers
are grounded, and charge build-up on ESD sensitive electronics is prevented. International standards are used
to define typical EPA and can be obtained for example from International Electro-technical Commission
(IEC) or American National Standards Institute (ANSI).
This ESD classification of the sub assembly will be defined for the most sensitive component, therefore the
following classifications apply:
Class 1B – Human Model (< 1 kV)
Class M1 – Machine Model (< 100V)
When handling the LMU-5000’s™ main-board (i.e. sub assembly) by itself or in a partial housing proper
ESD precautions should be taken. The handler should be in an ESD safe area and be properly grounded.
GPS Ceramic Patch Handling
When handling the sub assembly it may be natural to pick it up by sides and make contact with the antenna
boards. In an uncontrolled ESD environment contact with the center pin of ceramic patch antenna can create
a path for electrostatic discharge directly to the GPS Module. The GPS Module is very sensitive to ESD and
can be damaged and rendered non-functional at low levels of ESD.
One should avoid contact with the center pin of the patch during handling. The Factory will be placing a
protective layer of Kapton® tape over the patch element to eliminate this ESD path.
Packaging
Anytime the sub assembly is shipped and it is not fully packaged in its final housing it must be sealed in an
ESD safe bag.
Page 8

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 8/55
Electrical Over-Stress (EOS)
The GPS receiver can be damaged if exposed to an RF level that exceeds its maximum input rating. Such
exposure can happen if a nearby source transmits an RF signal at sufficiently high level to cause damage.
Storage and Shipping
One potential source of EOS is proximity of one LMU-5000™ GPS Antenna to another LMU-5000™
GSM Antenna. Should one of the units be in a transmit mode the potential exists for the other unit to become
damaged. Therefore any LMU-5000™ GPS Antenna should be kept at least four inches apart from any
active LMU-5000™ GSM Antenna or any other active high power RF transmitter with power greater than 1
Watt.
3.1.2 Battery Back-up devices
Please properly dispose of the battery in any of the CalAmp products that utilize one, do not just throw used
batteries, replaced batteries, or units containing a back-up battery into the trash. Consult your local waste
management facility for proper disposal instructions.
3.1.3 Environmental Specifications
The LMU-5000™ is designed to operate in environments typically encountered by fleet vehicles, including
wide temperature extremes, voltage transients, and potential interference from other vehicle equipment.
To ensure proper operation in such an environment, the LMU-5000™ was subjected to standard tests
defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE). The specific tests included temperature, shock,
vibration, and EMI/EMC. These tests were performed by independent labs and documented in a detailed test
report. In accordance with Appendix A of SAE J1113 Part 1, the Unit is considered a “Functional Status
Class B, Performance Region II” system that requires Threat Level 3 Testing.
The following shows the environmental conditions the LMU is designed to operate in and the relevant SAE
tests that were performed. No formal altitude tests were conducted.
Dimensions
5.2 (L) x 2.7 (W) x 1.2” (H), (131 x 67 x 29mm)
Weight
5.4 oz (153 g)
Temperature
-30° C to 70° C (Operating), -40° C to 85° C (Storage)
Humidity
Page 9

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 9/55
95% RH @ 50° C non-condensing
Shock and Vibration
U.S. Military Standard202G and 810G, SAE J1455
EMC/EMI
SAE J1113
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
EMC compliant for a ground vehicle environment
SAE Test: SAE J1113 Parts 2, 12, 21 and 41
Operating Voltage Range
The LMU-5000™ supports vehicles with 12 or 24 VDC systems including transients and electrical
system noise; this includes ranges from 6 to 32 VDC.
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)
No damage or performance degradation after the ESD disturbance.
SAE Test: SAE J1113 Part 13
Power Consumption
Operating Voltage
7 to 32 Volts (running), 9-30 (starting)
Power consumption
< 10 mW (Deep Sleep)
< 1 W (Sleep on GPRS Network)
< 2.4 W (Active Tracking)
3.2 LMU-5000™Connectors
The LMU-5000™ offers 5 connectors to access power, I/O, serial communications and other expansion
capabilities. These connectors are:
SIM AccessSlot access
CellularSMA main, SMA diversity
External GPSSMA (with tamper monitoring, 3.0v)
Ethernet10/100 Base-T RJ45
USBHost standard-SUB, Device-Mini-USB
SerialDB-9 (RS232), 5 Pin Molex (switch power TTL Levels)
4-Pin Molex Power, Ignition, I/O
22-Pin MolexI/O connections
Page 10

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 10/55
LMU-5000™ Connectors
3.2.1 Power Connector
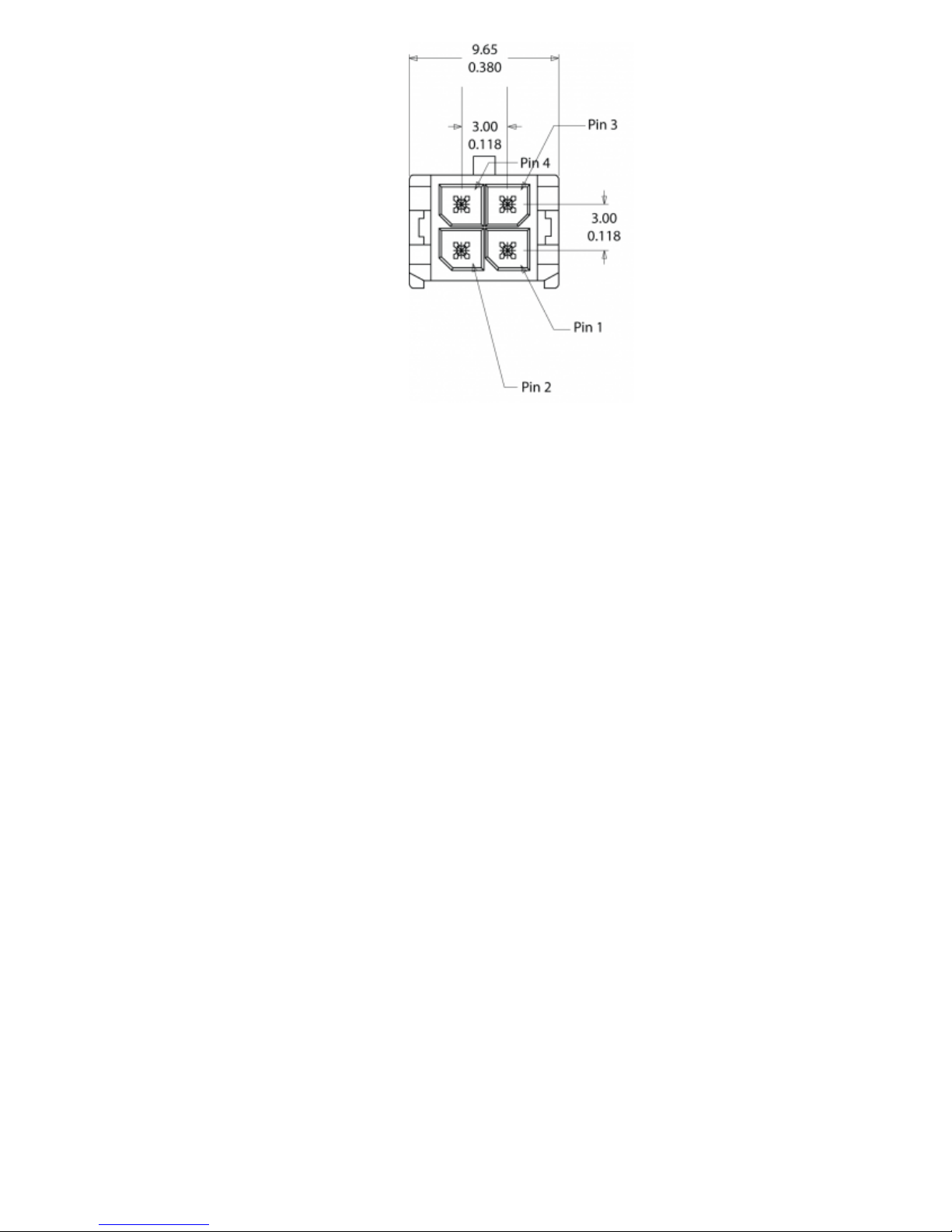
The LMU-5000™ uses a 4 pin Molex 43045-0402 connector as its power connection. The pin out is as
follows:
Pin
Signal
Name
Description
5C888
Color
Input or
Output
1 VIN Power Red Power / Input
2 GND Ground Black Ground
3 ADC1 Analog to Digital Input 1 Green Input
4 INPUT 0
Input 0 / Ignition Sense – Digital
Input
White Input
Page 11
10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 11/55
LMU-5000™ Header (looking into LMU)
3.2.2 I/O Connector
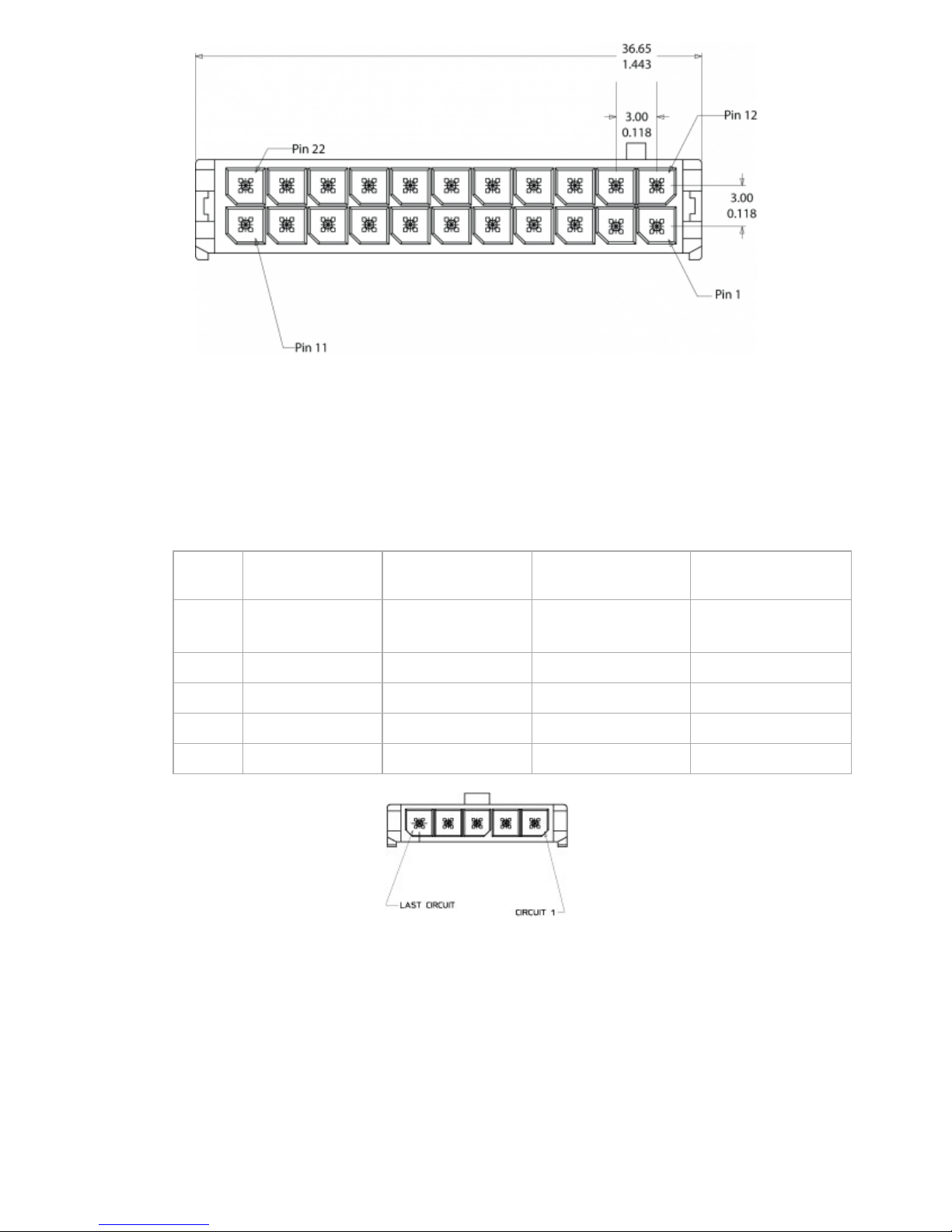
The LMU-5000™’s features expanded I/O capabilities via its 22-Pin Molex 43045-2202 connector. Its pinout is as follows:
Page 12

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 12/55
Pin
Signal
Name
Description 5C889 Color
Input or
Output
1 Input 1 Input 1 – Digital Input Blue Input
2 Input 2 Input 2 – Digital Input Orange Input
3 Input 3 Input 3 – Digital Input Violet Input
4 Input 4 Input 4 – Digital Input Gray Input
5 Input 5 Input 5 – Digital Input Green & White Input
6 Input 6 Input 6 – Digital Input Blue & White Input
7 Input 7 Input 7 – Digital Input Black & White Input
8 1BB T Data 1 Bit Bus Data (T) Green & Black Input/Output
9 1BB GND 1 Bit Bus Ground Black Ground
10 1 BB R Data 1 Bit Bus Data (R) Orange & Black Input/Output
11 1 BB Gnd 1 Bit Bus Ground Black Ground
12 Output 0
Output 0 - Starter Disable
Relay Driver
Green Output
13 Output 1 Output 1 - Digital Output Brown Output
14 Output 2 Output 2 - Digital Output Yellow Output
15 Output 3 Output 3 - Digital Output
Blue & White &
Orange
Output
16 Output 4 Output 4 - Digital Output
Green & Black &
Orange
Output
17
Output 5 -
LED
Output 5 - LED 1 Driver Red & Green Output
18
Output 6 -
LED
Output 6 - LED 2 Driver Orange & Green Output
19 ADC 2 Analog to Digital Input 2 Black & Red Input
20 ADC 3 Analog to Digital Input 3 White & Red Input
21 ADC 4 Analog to Digital Input 4 Orange & Red Input
22 ADC 5 Analog to Digital Input 5 Blue & Red Input
Page 13
10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 13/55
LMU-5000™ Header (looking into LMU)
3.2.3 Serial Interface Connectors
The LMU-5000™ offers 2 serial interface connections (Host/Aux1 and DB-9 SerialAux 2) on its front face.
These are provided via 2 Molex 43650-0501 connectors using the following pin outs.
Pin
Signal
Name
Description
133337-5
Color
Input or
Output
1 VIN_FILT
Filtered LMU
Power
Red Power Supply
2 VCC3V3 3.3V Power Orange Power Supply
3 Ground Ground Black Ground
4 TX Transmit Data Blue Input to LMU
5 RX Receive Data Green Output From LMU
Serial Interface Connector
Users should only use CalAmp approved serial adapters with these connections. (Part Number 133337-5
and 133564-1)
3.2.4 Serial Interface Cables & Accessories
The Serial interfaces located on the front of the LMU-5000™ via 5-pin Molex and DB-9 Female connectors
are used to extend I/O functions and provide serial access to the LMU-5000™. It should only be used with
CalAmp expansion harnesses. The available accessories are:
Page 14

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 14/55
Serial Combo Adapter (Part Number 133337-5)
The Serial Combo Adapter is designed to allow laptops, and PDAs to communicate with the LMU-5000™
via a direct serial connection. While using this cable, the LMU-5000™ will accept AT Commands and act as
a modem. No setup of the LMU-5000™ is necessary to use this cable.
Serial Combo Adapter (Part Number 133564-1)
The Serial Combo Adapter is designed to allow laptops, MDTs, barcode readers and other devices to
communicate with the LMU-5000™ via a direct serial connection. While using this cable, the LMU-5000™
will accept AT Commands and act as a modem. No setup of the LMU-5000™ is necessary to use this cable.
The 133564-1 also has switched power capabilities which allow for power to the serial device to be
regulated.
This cable will allow ‘dumb’ serial devices to use the LMU-5000™ to pass data to/from a remote
application. In general, when in MDT mode, the LMU-5000™ will package any data received over the serial
port into a ‘User Message’ and send it to its inbound address. Any User Messages received from the remote
application that have an appropriate Message Type will be passed from the LMU-5000™ to the dumb serial
device. The setup of this mode is controlled by S130 - 139 and is described in detail later in this document.
3.2.5 Accessories
See the Harness Diagrams page for more information on LMU accessories, and supported products table.
3.3 GPS Receiver
Location Technology 50 channel GPS with SBAS, DGPS
Location Accuracy 2.0 meter CEP (with SBAS)
Tracking Sensitivity -160 dBm
Acquisition Sensitivity -147 dBm
Kick Start 3 sec @ -130 dBm
AGPS capable
3.4 RF Connector
LMU-5000’s™ uses an SMC connector with a 50 Ω impedance.
3.5 I/O Descriptions
The LMU-5000™ provides the following inputs and outputs (I/O):
Page 15

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 15/55
Digital Inputs
Input 0: Ignition Sense (Always biased low)
Input 1: Generic Digital Input (Biased high or low/ S-158 Bit 1)
Input 2: Generic Digital Input (Biased high or low/ S-158 Bit 2)
Input 3: Generic Digital Input (Biased high or low/ S-158 Bit 3)
Input 4: Generic Digital Input (Biased high or low/ S-158 Bit 4)
Input 5: Generic Digital Input (Biased high or low/ S-158 Bit 5)
Input 6: Generic Digital Input (Biased high or low/ S-158 Bit 6)
Input 7: Generic Digital Input (Biased high or low/ S-158 Bit 7)
Analog to Digital Inputs
A/D 0: External Power Supply Monitor
A/D 1: External A/D Input (From Power Connector)
A/D 2: External A/D Input (From 22 Pin I/O Conenctor)
A/D 3: External A/D Input (From 22 Pin I/O Conenctor)
A/D 4: External A/D Input (From 22 Pin I/O Conenctor)
A/D 5: External A/D Input (From 22 Pin I/O Conenctor)
A/D 6: GPS Antenna Sense
A/D 7: LMU-5000, Internal Temp Monitor
Outputs:
Output 0: Standard Open Collector Relay Output
Output 1: Standard Open Collector Relay Output
Output 2: Standard Open Collector Relay Output
Output 3: Standard Open Collector Relay Output
Output 4: Standard Open Collector Relay Output
Output 5: LED Driver Output 1
Output 6: LED Driver Output 2
iButton / 1 Bit Bus
iButton ID Support
1Wire bus with current boost for temperature sensors
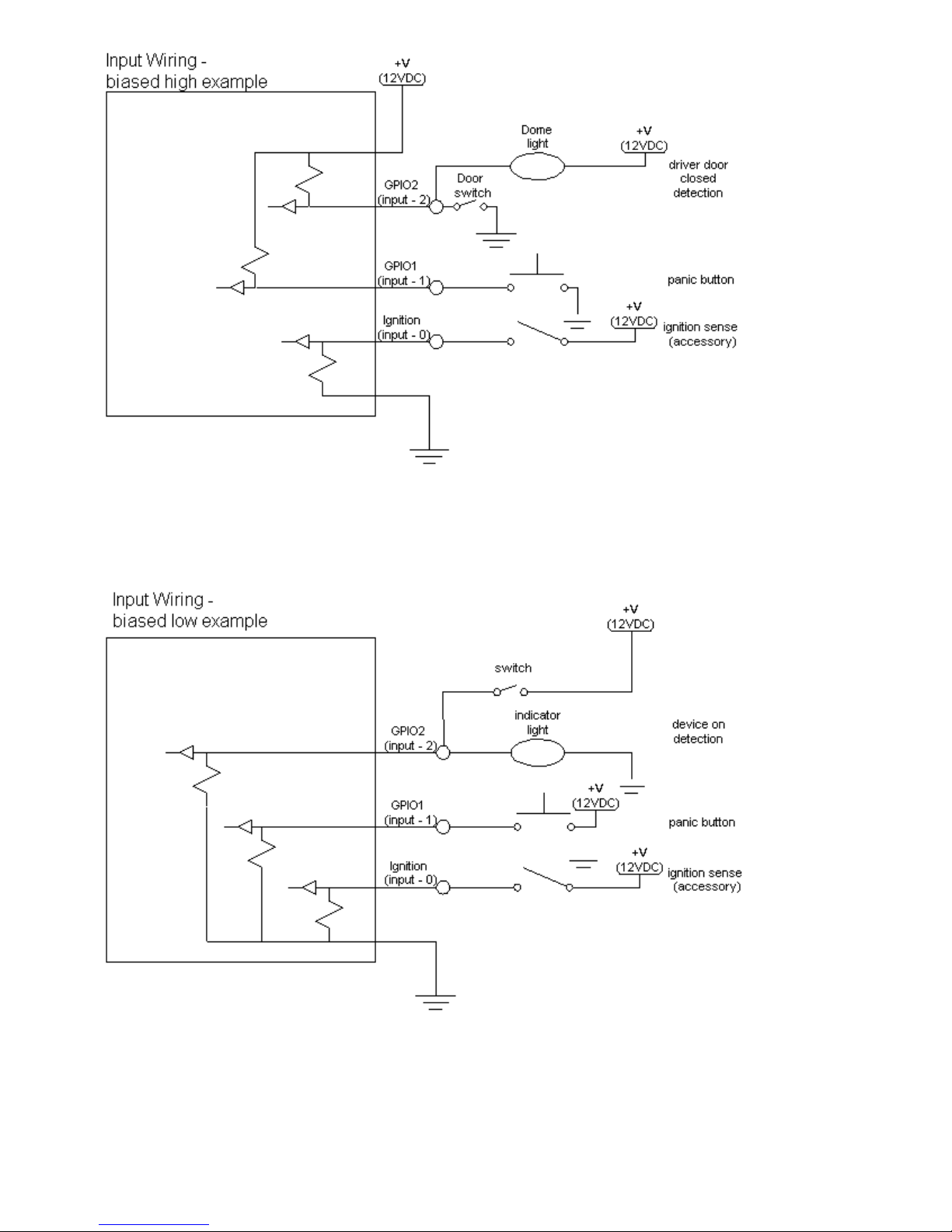
3.5.1 Ignition and Inputs
The LMU-5000™ provides up to 7 High/low selectable inputs and one Ignition Sense input.. These inputs
are protected from typical vehicle transients and can be directly connected to most vehicle level logical inputs
from 4 volts up to the vehicle power input level (typically 12 VDC). Their input impedance is approximately
10k. One of these inputs is dedicated to sensing the vehicle’s ignition status to provide for flexible power
management. The other seven inputs may be used to sense vehicle inputs such as cooling unit operation, a
hidden driver “Panic” switch, taxi on-duty/off-duty meter status or many others.
The ignition input is pulled to ground through the 10k resistance, where the other inputs can be configured to
be normally High (i.e. pulled to +12v through a 200K10k resistor) or Low (i.e. pulled to ground through a
100K10k resistor). The diagrams below show how to connect the inputs in both a high- and low-biased
configuration:
Page 16
10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 16/55
Sample Input Wiring
3.5.2 Open Collector Outputs
The LMU’s outputs are designed to drive external relays. These outputs provide a high-current, opencollector driver that can sink up to 200 mA each. These drivers may be used to drive external relays that can
Page 17
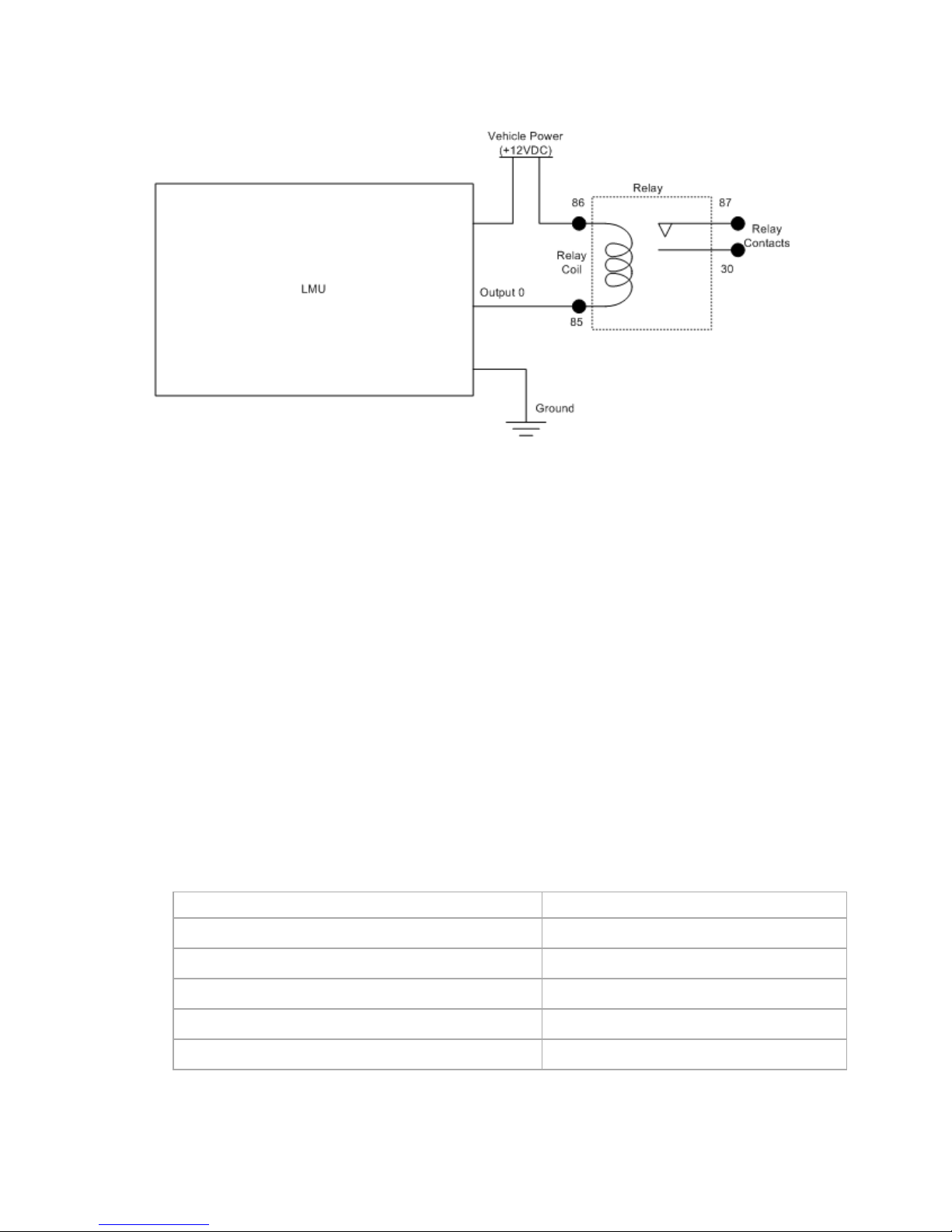
10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 17/55
then control vehicle functions such as door locks, fuel shut-off valves, sirens and lights. If additional current is
required to drive the relays, external circuitry can be added to source the current. This diagram is a typical use
of an output to drive a relay.
Sample Relay Wiring
3.5.3 LED Outputs
The LMUs 2 LED outputs are designed specifically to control external LEDs. The LED outputs have two
states. When on, they provide 3.3V to the external connector through a 100ohm series resistor. When off,
these outputs are high impedance
3.5.4 Status LEDs
The LMU-5000™ is equipped with two Status LEDs, one for GPS and one for COMM (wireless network
status). The LEDs use the following blink patterns to indicate service:
LED #1 (Comm LED - Orange) Definitions
Condition LED 1
Modem Off Off
Comm On - Searching Slow Blinking
Network Available Fast Blinking
Registered but no Inbound Acknowledgement Alternates from Solid to Fast Blink every 1s
Registered and Received Inbound Acknowledgement Solid
LED #2 (GPS LED - Green) Definitions
Page 18

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 18/55
Condition LED 2
GPS Off Off
GPS On Slow Blinking
GPS Time SyncFast Blinking
GPS Fix Solid
LED #3 (GPIO LED- RED) Definitions
Condition LED 3
GPIO Off Off
GPIO On On
GPIO Status #1 TBD
GPIO Status #2 TBD
4 Configuration and Activation
This section details how to quickly get an LMU-5000™ provisioned and configured to point at a specific server. It
is assumed that a PEG script has already been created and is being managed through LMU Manager or PULS™,
the CalAmp Maintenance System.
We are making three assumptions to simplify the setup process:
You have created, installed and configured an LM Direct™ Server to receive messages from the
LMU-5000™. (See LM Direct™ Reference Guide for details)
You are using the standard wiring harness from CalAmp and the serial port expansion harness.
You have created a HyperTerminal or Putty session.
You have contacted the CalAmp sales team regarding the network availability of the LMU5000™. This device may not be supported for all the carriers or networks listed in this section
(CDMA-Verizon, CDMA-Sprint, HSPA, GSM), for product availability consult the CalAmp sales
team.
4.1 Quick Start - General Config
All LMU-5000s™ must go through a common step during the configuration and provisioning process.
Specifically, this is pointing the LMU to your LM Direct™ server, either via IP or a URL.
This configuration process is accomplished via a series of AT Commands:
1. Power up the LMU-5000™ and connect a serial cable from the LMU to your laptop
2. Open a terminal session to the LMU-5000™
3. Enter the address of the LM Direct™ server:
AT$APP PARAM 2319,0,ddd.ddd.ddd.ddd
AT$APP PARAM 768,0,ddd.ddd.ddd.ddd (32-bit products only)
Page 19

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 19/55
AT$APP PARAM 769,0,ppppp
Where ddd.ddd.ddd.ddd is the publicly addressable IPV4 address of your LM Direct™ server
and ppppp is the UDP port number.
4. Alternatively if a URL has been set up for your LM Direct™ server, the LMU may be programmed
with:
AT$APP PARAM 2319,0,myURL.MyCompany.Com
Where myURL.MyCompany.com is the URL assigned to the server.
5. Enter ATIC to verify the correct settings are displayed for your Inbound Server.
This configuration process is accomplished via a series of SMS Commands:
1. Power up the LMU-5000™ and your handset
2. From the handset, send an SMS message to the LMU-5000™ phone number:
!RP,2319,0,ddd.ddd.ddd.ddd
!RP,768,0,ddd.ddd.ddd.ddd (32-bit products only)
!RP,769,ppppp
Where ddd.ddd.ddd.ddd is the publicly addressable IPV4 address of your LM Direct™ server
and ppppp is the UDP port number
3. Alternatively if a URL has been set up for your LM Direct™ server, the LMU may be programmed
with:
!RP,2319,0,myURL.MyCompany.Com
Where myURL.MyCompany.com is the URL assigned to the server
4. Verify your settings by sending the commands:
!RP?2319,0
!RP?769,0.
4.2 Auto provisioning of GSM or HSPA LMUs
For certain operators, the LMU can auto-populate the APN, username and password settings based on the
Page 20

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 20/55
Mobile Country Code (MCC) and the Mobile Network Code (MNC) of the SIM. Upon inserting a new
SIM the APN, username and password will switch to the new SIM card's defaults if the MCC and MNC
values change. The current list of supported MCC and MNC combinations are:
AT&T – formerly AT&T Wireless or Cingular Blue (MCC 310, MNC 38)
o APN 0: PROXY
o APN 1: PUBLIC
AT&T – formerly Cingular Wireless (MCC 310, MNC 17, 18, 41)
o APN 0 & 1: ISP.CINGULAR
o Username: ISP@CINGULARGPRS.COM
o Password: CINGULAR1
Manxpronto (MCC 234, MCN 058)
o APN web.manxpronto.net
o Username: gprs
o Password: gprs
O2 UK (MCC 234, MNC 02, 10, 11)
o APN 0 & 1: mobile.o2.co.uk
o Username: mobileweb
o Password: password
O2 Ireland (MCC 272, MNC 02)
o APN 0 & 1: open.internet
o Username: gprs
o Password: gprs
Orange UK (MCC 234, MNC 33, 34)
o APN 0 & 1: orangeinternet
o Username: user
o Password: pass
T-Mobile (MCC 310, MNC 16, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 31, 58, 66, 80)
o APN 0: INTERNET2.VOICESTREAM.COM
o APN 1: INTERNET3.VOICESTREAM.COM
T-Mobile UK (MCC 234, MNC 30,31,32)
o APN 0 & 1: general.t-mobile.uk
o Username: user
o Password: wap
TelCel Mexico (MCC 334 MNC 02)
o APN 0 & 1: INTERNET.ITELCEL.COM
o Username: webgprs
Page 21

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 21/55
o Password: webgprs2002
Telstra Australia (MCC 505, MNC 01, 11, 71, 72)
o APN 0 & 1: telstra.internet
Vodafone Ireland (MCC 272, MNC 01)
o APN 0 & 1: isp.vodafone.ie
o Username: vodafone
o Password: vodafone
Vodafone New Zealand (MCC 530, MNC 01)
o APN 0 & 1: internet
o Username: guest
o Password: guest
Vodafone UK (MCC 234, MNC 15)
o APN 0 & 1: internet
o Username: web
o Password: web
Unless otherwise stated, the username and password will be set to “dummy”.
This feature can be disabled by setting Bit 0 of S-Register 155.
AT$APP PARAM 1024,35,1,1
To re-enable auto-provisioning, use:
AT$APP PARAM 1024,35,1,0
Auto-provisioning occurs when the LMU detects a SIM with a new operator ID (i.e. the first 6 digits of the
IMSI) or when Bit 0 of S155 is cleared and the GPRS context is blank (i.e. Parameter 2306,0).
4.3 Activating GSM or HSPA LMU using AT Commands
Check with the CalAmp Sales team for availability of the LMU-5000™ with GSM or HSPA
modems. For a GSM/GPRS operator you will get the LMU in one of two varieties, one with a SIM and one
without.
If you get an LMU without a SIM (which is the typical case) the operator will simply ask for the IMEI of the
LMU. The IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identifier) is printed on the bottom of the LMU under the
LMU’s ESN. Again, DO NOT give the operator the ESN of the LMU.
Page 22

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 22/55
The operator will provide you with a SIM for each account activated. If they are especially nice (or you are
especially persistent) they will also give you a list tying the IMSI (International Subscriber Identifier) of the
SIM to the phone number assigned to it. Please note that the operator will likely tie the IMSI (i.e. the SIM) to
a specific IMEI. Making sure the specific SIM matches to the right IMEI isn’t strictly necessary, but it will
keep everyone’s book-keeping a little cleaner. You may also obtain this information by running a CSV report
in PULS (after the devices have connected to the network and sent in their first ID Report). See the PULS
Users Guide for more information.
If you do happen to have a SIM, the operator will ask for the IMSI and ICC-ID (Integrated Circuit Card
Identifier) along with the IMEI of the LMU. Again, in return you should get a list of IMSIs and Phone
Numbers.
The IMEI, IMSI and ICC-ID are all available through the ATI1 command. The IMEI should also be printed
on the bottom of the LMU.
You should also get an APN (Access Point Name) value. The APN is the device on the network that allows
a GPRS device (i.e. the LMU) to get to the internet. They tend to look like a URL, for example:
myAPN.myOperator.com
Operators can offer more than one type of APN and can even set up a custom APN just for your devices.
The rates they charge will vary depending on the APN service you want. Operators may also request you use
a blank APN. With the APN, you should also receive a username and password combination.
The last item an operator may provide is a SIM PIN. The PIN is effectively a password to the device. The
main difference here is that the PIN will restrict all the capabilities of the GSM device, where the SPC is used
just for configuration.
The activation sequence for a GSM LMU would therefore look as follows:
AT$APP PARAM 2306,0,“myAPN.myOperator.com”
AT$APP PARAM 2306,1,“myAPN.myOperator.com”
AT$APP PARAM 2314,0,“myUSername”
AT$APP PARAM 2315,0,“myPassword”
For a blank APN the following command can be used:
AT$APP PARAM 2306,0,“” (for a blank APN)
Only enter this next command if you have been given a non-zero PIN as any errors may lock you out of the
modem.
AT$APP PIN <SIM pin>
You can confirm activation by watching the Comm LED to see if it goes solid. You may also confirm
activation using
Page 23

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 23/55
AT$APP COMM STATUS?
A good response should look similar to the following:
GSM Registered: Yes
GPRS Registered: Yes
Connection: Yes
RSSI: -70 dBm
BER: 0
Channel: 0
Cell ID: 0
Base Station ID: 0
Local Area Code: 0
Network Code: 38
Country Code: 310
IMEI (Modem S/N): 500167110060440
IMSI (SIM S/N): 310380100521849
Phone Number:
GPRS APN: IP:Public
Quality of Srvc: 1,0,0,3,0,0
GSM Class: B
4.4 Accessing the SIM
4.5 Activating a CDMA LMU-5000™
Check with the CalAmp Sales team for availability of the LMU-5000™ with CDMA modems. For
CDMA devices, the activation sequence you will use varies from carrier to carrier. Each of the supported
carriers is documented below.
To obtain an account, a CDMA carrier will generally ask for three things, the Manufacturer, the Product Type
and the ESN. Obviously the first two items are answered by “CalAmp LMU”. The last one is a little
misleading. The ESN on the LMU is the CalAmp serial number. The one the operator is interested in is the
MSN-D (which they call the decimal ESN). DO NOT give them the CalAmp ESN (i.e. the top one on the
label). It will only lead to the carrier telling you that the product doesn’t exist and they can’t activate it for you.
What you should get back will vary from operator to operator; however at very least it will be the MDN
(Mobile Directory Number) and MIN (Mobile Information Number). You should also ask for the SPC
(Service Programming Code) in case it is not 000000. The SPC is effectively a password to the modem
which allows you to program some of the more sensitive items (ex: the MDN and MIN). Please note that the
MIN and MSID can be the same value.
4.5.1 Activating a CDMA LMU-5000™ – Verizon
Verizon supports a system that allows CDMA devices to be provisioned Over-The-Air. A CalAmp LMU5000™ will automatically use this system to attempt to self provision. This procedure assumes that the LMU5000™ has never been provisioned or activated before.
1. Power on the LMU-5000™, making sure you can observe the behavior of the Comm LED.
Page 24

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 24/55
2. Wait until the Comm LED turns solid. This could take up to 5 minutes.
3. If after 5 minutes you observe that the Comm LED transitions from a slow blink to a fast blink
several times (i.e. more than twice) you will need to contact Verizon Wireless for further support on
account activation.
Once configured, you may verify that the LMU-5000™’s modem has registered to the CDMA network.
Enter:
AT$APP COMM STATUS?
The response should be similar to:
CDMA Service: IS-2000
Connection: Yes
RSSI: -80 dBm
Channel: 0
Band:Side: 800:B
Base Station ID: 0
Network ID: 0
System ID: 4
ESN (Modem S/N: 2676319948 [9F8566CC]
Phone Number: 1234567890
IMSI: 310001234567890
CarrierConfig: 5
Note that the Phone Number should match the MDN value the carrier gave you. The last 10 digits of the
IMSI field should match the MIN/MSID value they gave you.
For devices that have had previous activations, an Over-The-Air activation process may be manually started
using a single AT Command:
AT$APP MODEM UPDATE
This command is also used to initiate an Over-The-Air PRL Update for devices that are already provisioned.
Users may also force a reactivation with the command:
AT$APP MODEM ACTIVATE
Keep in mind, however, this may cause the modem to lose its credentials and become unable to register to the
network.
4.5.2 Activating a CDMA LMU-5000™ – Sprint
Page 25

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 25/55
Activating an LMU-5000™ on the Sprint CDMA network is identical to activating on the Verizon network.
1. Power on the LMU-5000™, making sure you can observe the behavior of the Comm LED.
2. Wait until the Comm LED turns solid. This could take up to 5 minutes.
3. If after 5 minutes you observe that the Comm LED transitions from a slow blink to a fast blink
several times (i.e. more than twice) you will need to contact Sprint for further support on account
activation..
Once configured, you may verify that the LMU-5000’s™ modem has registered to the CDMA network.
Enter:
AT$APP COMM STATUS?
The response should be similar to:
CDMA Service: IS-2000
Connection: Yes
RSSI: -80 dBm
Channel: 0
Band:Side: 800:B
Base Station ID: 0
Network ID: 0
System ID: 4145
ESN (Modem S/N: 2676319948 [9F8566CC]
Phone Number: 1234567890
IMSI: 310001234567890
CarrierConfig: 1
The Phone Number field should match the <Phone Number> value you used in step 3 or 4. The last 10 digits
of the IMSI field should match the <MSID> value you used in step 3 or 4.
4.5.3 Activating a CDMA LMU-5000™ – Bell Mobility
While the Bell Mobility network does support Over-The-Air activation processes like those used by Sprint or
Verizon Wireless, it requires that the user enter several menu choices in order to complete activation.
Unfortunately, this is something the LMU-5000™ does not support, so the activation must be performed
manually. Bell Mobility will provide you with a password to gain access to the network (ex: 8889).
The activation procedure will be as follows:
1. Power on the LMU-5000™.
2. Connect to the LMU-5000™ using HyperTerminal or PuTTY
3. Issue the following AT Command:
ATPASSTHRU
ATE1
AT$SPSPC=000000
AT+MNAM=,0,<MIN>,<MDN>,,,0,1000000,1,1,1,
ctrl C
Page 26

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 26/55
4. Program in the network password using:
AT$APP PARAM 2315,0,”<Bell Password>”
5. Program in the network username using:
AT$APP PARAM 2314,0,”<Phone Number>@1x.bell.ca”
6. Verify the above settings with:
AT$APP PPP?
The LMU-5000™ should return the following:
PPP 0 USER <Phone Number>@1x.bell.ca *
PPP 0 PASSWORD <Bell Password> *
PPP 1 USER
PPP 1 PASSWORD
OK
Once configured, you may verify that the LMU-5000™’s modem has registered to the CDMA network.
Enter:
AT$APP COMM STATUS?
The response should be similar to:
CDMA Service : IS-2000
Connection: Yes
RSSI : -80 dBm
Channel: 0
Band:Side: 800:B
Base Station ID: 0
Network ID: 0
System ID: 16410
ESN (Modem S/N: 2676319948 [9F8566CC]
Phone Number : 1234567890
IMSI : 310001234567890
CarrierConfig: 13
Page 27

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 27/55
The Phone Number field should match the <Phone Number> value you used in step 3 or 4. The last 10 digits
of the IMSI field should match the <MSID> value you used in step 3 or 4.
5 Installing the LMU
The installation of the LMU and its antennas can have a major impact on the LMU’s performance. It is
recommended that installers be familiar with the installation of GPS and cellular devices and are comfortable in a
vehicle environment.
5.1 Preparing for Installation
Be sure you have received all the LMU components you need. This must include:
The LMU to be installed
A power harness
GPS Antenna (for external devices)
Comm Antenna (for external devices)
Optional Components:
Input and output cables
Relays
LMU peripherals (i.e. Serial adapter, jPOD, TetheredLocator)
Host serial devices (e.g. PDAs, laptops, other serial devices)
5.2 Plan The Installation
Verify Powe r, Ground and Ignition. Be sure to check each source (power, ground and ignition) to ensure
that the proper signaling exists. This is typically accomplished with a multi-meter.
Before drilling any holes or running any wires, decide where each hardware component will be located (LMU,
antennas, peripherals, etc.). Be sure that the cables to the LMU are not bent or constricted in any way. Also
make sure that the LMU is kept free from direct exposure to the elements (sun, heat, rain, moisture etc...).
Be advise d that an installation that violates the environmental specifications of the LMU will void
the warranty.
The best way to ensure a trouble-free installation is to consider your options and make some decisions before
you start. Take a look at the vehicle and determine how to best install the LMU for the following purposes:
Accurate data gathering and simulation of how customers actually use your solution
Ongoing monitoring and maintenance of LMU equipment
Accidental or intentional alteration of the equipment or cable connections
The following sections cover some of the issues to consider when planning your LMU installation.
Page 28

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 28/55
5.2.1 Size and Placement of LMU Unit
The dimensions of the LMU should be taken into account, particularly when installing in a vehicle:
Whether you intend to place the LMU under a seat or into a cavity behind the vehicle’s interior molded trim,
be sure the LMU will fit before drilling any holes or running cable
Be certain that the cables running to the LMU will not be bent or constricted. Damage to the
cables may impede the LMU’s performance.
Be certain that the installation point will not violate any of the LMU’s environmental specification
(temperature, moisture, etc…) as improper installation of the LMU may void the warranty.
See the LMU Environmental Specifications for the exact measurements and specifications of the LMU5000™.
Typical installations will place the LMU under the vehicle dash board, or in the trunk. Make sure you can get
access to the unit afterwards as under some circumstances it may be necessary to add additional wiring or
connections to the LMU.
5.2.2 Placement of Antennas
There are effectively three options for placements of an antenna:
Roof-mount (magnetic or thru-hole)
Glass-mount
Covert (e.g. under the seat, dash, etc…)
Comm Antenna Placement Guidelines
The Comm. Antenna must be located at least 20cm away from vehicle passengers, other personnel, or
bystanders in order to comply with FCC radio frequency exposure limits.
Typically, the Comm antenna used by the LMU for wireless service is a standard 3-dB gain whip. It mounts
with standard mounts (i.e. thru-hole, magnetic mount or peel and stick) and requires a ground plane to work
properly. If possible, it should be located at least 3 feet from the GPS antenna. Ensure that the cable does not
get crushed during installation.
Please note that the antennas provided by CalAmp combine both the GPS and Comm portions.
GPS Antenna Placement Guidelines
In order to maximize the performance of the LMU the GPS antenna should have a clear view of the sky.
When installing the GPS antenna on a vehicle, make sure that there are no obstructions close to the antenna
that might block the view 360° to the horizon. Things like air horns, lights, vents, etc… should not block the
antenna beyond 5° above the horizon. The best location is usually near the center of the roof; however it is
also desirable to locate the cellular antenna as far from the GPS antenna as is practical.
Page 29

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 29/55
Examples of good and poor GPS antenna placements
The received signal levels at the GPS antenna from the satellites are very low in power (approximately -136
dBm), so any blockage of the antenna can affect the quality of the location computed by the receiver. Kinks
or tight knots in the antenna cable can also prevent the GPS receiver from operating properly. When laying
out the antenna cable, care should be taken so that the cable is not subjected to crushing or strain.
Placement of Combination and Internal Antennas
When dealing with combination antennas, it is more important to considered GPS performance over Comm
performance. GPS signal strengths are much lower than those typically seen by cellular networks supported
by the LMU. In order to maximize the performance the LMU should have a clear view of the sky as possible.
When installing the GPS antenna in a vehicle, make sure that there are as few obstructions as possible close to
the LMU that might block the view 360° to the horizon. As with stand-alone GPS antennas, nothing should
not block the combination antenna beyond 5° above the horizon with the best location being near the center of
the roof. For more covert installs, directly under the front or rear-windshields are also acceptable.
Examples of Good (Green), OK(Yellow) and Poor(Red) combo antenna
placements
Page 30

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 30/55
Examples OK(Yellow) and Poor(Red) internal antenna placements
5.2.3 Access to the SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) Card
When used in a GSM or iDEN network, each LMU uses a Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) card, which
should be inserted before you install the LMU for the first time. The SIM card is attached to the main-board
inside the housing of the LMU unit.
At some future time, you might need or want to replace the SIM card with a different one, so try to install the
LMU in such a way that the cover can be removed to make the SIM card accessible.
5.2.4 Protection from Heat
It is best not to place the LMU unit in an unusually warm location such as directly near heater vents, near hot
engine components or in direct sunlight. The maximum temperature that can be tolerated by the LMU is
described in the LMU Environmental Specifications section.
5.2.5 Visibility of Diagnostic LEDs
Status LED lights on the front of the LMU unit can provide valuable information about the operation of the
LMU. When feasible, attempt to install the LMU in such a way that these lights can be seen with reasonable
ease.
You may find it useful to be able to view the LEDs periodically to make sure that the LMU is operating
properly. If at any time you should encounter a problem with the LMU, you may need to read the LEDs in
order to troubleshoot the problem. If you cannot fix the LMU yourself, you will need to provide the LED
information to CalAmp customer support.
For information about how to interpret the LEDs, see the Status LED Behavior section.
5.2.6 Cable Length
Page 31

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 31/55
The RF cables which are provided for connecting to the LMU antennas should be used at the length
provided. Do not cut cables. Instead, coil any excess cable length, making sure not to crimp or flatten the
antenna cable.
5.2.7 Moisture and Weather Protection
The LMU unit must be located where it will not be exposed to moisture or water. In a typical installation
inside a vehicle this is not commonly thought to be a concern; however, it might be best to avoid locating the
LMU below a car’s cup holders, or where rain might easily splash into the compartment when a door is
opened.
5.2.8 Preventing Accidental or Unauthorized Modification
If you anticipate that fleet drivers or others might interfere with the LMUs once they are installed, take steps to
be sure that it is not easy to disconnect the antenna wiring, remove the LMU from its power source, etc.
Two common methods are the use of Tamper Proof Sealant or creation of PEG Script to detect power loss
or GPS antenna disconnections.
5.3 Installing the LMU in a Vehicle
This section provides instructions for installing an LMU in a vehicle.
Be sure to consider the design decisions described in the previous sections. When you are ready to begin
installing the LMU, follow these steps:
5.3.1 Place the LMU unit in the vehicle.
Typically, the LMU should be placed under the passenger seat or dashboard of the vehicle. LMUs with
internal antennas should be placed to maximize their GPS performance. A typical location include under the
dash close to the front wind-shield.
Attach the LMU to the solid body of the vehicle, not to plastic panels. The LMU can be placed out of sight
by removing interior trim and molding to expose available space, then replacing the trim once the LMU is in
place.
5.3.2 Connect power, ignition, and ground.
The power input (red wire) must be connected to a constant (un-switched) +12 VDC or +24 VDC supply;
preferably, connected directly to the vehicle battery terminal or as close to it as possible. This connection
point should be fuse protected to not more than 5 Amps.
The ignition input (white wire) must be connected to the vehicle ignition or another appropriate key operated
line, such as ACCESSORY, ensuring that power to the ignition wire is available only when the vehicle ignition
Page 32

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 32/55
is on.
The ground line (black wire) must be connected to chassis ground.
Failure to connect these lines in the manner described may result in discharge of the vehicle
battery.
For best results, it is strongly recommended that the LMU connection be on its own circuit. Connect the
power input directly to the vehicle battery if possible and protect the circuit with an inline fuse. If you must
connect through the fuse box, use standard commercial wiring practices to create a permanent installation
rather than using press-in fuse clips or other temporary measures.
DO NOT connect the power cable to the LMU at this time.
5.3.3 Place the GPS antenna.
The GPS antenna must have a clear view of the sky. Mount the GPS antenna on the vehicle’s highest point
(for example, the roof of a car). Make sure that there are no obstructions close to the antenna that might
block the view 360° to the horizon. Air horns lights, vents, etc.. should not block the antenna beyond 5°
above the horizon.
Kinks or knots in the antenna cable can prevent the GPS receiver from operating properly. When laying out
the antenna cable, take care that the cable is not subjected to crushing or strain.
The ideal location is typically near the center of the vehicle’s roof. However, it is also desirable to locate the
cellular antenna as far from the GPS antenna as possible.
GPS Antenna Location
5.3.4 Mount the Comm. Antenna.
When using separate Comm and GPS antennas, it is best to locate the Comm. Antenna at least 3 feet from
the GPS antenna. Ensure that the cable is not crushed during installation or normal vehicle operation.
Again, the Comm. Antenna must be located at least 20cm away from vehicle passengers, other personnel, or
bystanders in order to comply with FCC radio frequency exposure limits.
Page 33

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 33/55
Window Mount Antenna Location
5.3.5 Typical Connection Sequence
Attach the cable from the GPS antenna.
Connect the cable from the Comm.. antenna
Connect any peripherals to the LMU
Plug in the power harness.
The physical installation of the LMU hardware is now complete.
Completed Install – separate antennas
Completed Install - Internal antennas
Page 34

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 34/55
5.4 Installation Verification
In many cases it is desirable to verify that an installed LMU-5000™ is working properly. That is, installers
should verify that the GPS and communications functions of the LMU-5000™ are working properly before
departing the installation site. In more robust cases, some key configuration settings such as the Inbound
Address and URL should also be verified.
Note that these processes are all based on issuing AT Commands to the LMU-5000™. It is expected that
installers will have access to a serial port expansion cable and a laptop or PDA capable of a terminal
connection. Alternatively, an SMS message can be sent to an LMU-5000™ to obtain its current status.
5.4.1 Comm Verification
Installers should first verify that the LMU-5000™ has been acquired and has registered to the wireless
network. This may be verified in one of two ways. First, installers may look at the Comm LED (i.e., the one
closest to the SMC antenna connector). If this LED is solid, then the LMU has registered to the network and
established a data session.
If the LED is not visible, then Comm may be verified using an AT Command:
ATIC
Depending on the wireless network being used something similar to what is shown below will be displayed. It
is important to verify that 'Yes' values are displayed at the top for Data and Network registration and the
correct APN is displayed.
Radio Access : GSM
Network Reg. : Yes, Home
Data Reg. : Yes, Home
Connection : Yes
RSSI : -97 dBm
BER : 99
Channel : 737
Cell ID : 3441
Base Station ID : 40
Local Area Code : 31003
Network Code : 410
Country Code : 310
IMEI (Modem S/N): 351802055396182
IMSI (SIM ID) : 310410202524377
ICC-ID (SIM S/N): 89014102212025243778
Phone Number :
GPRS APN : ISP.CINGULAR
Maint. Server : maint.vehicle-location.com(216.177.93.246):20500
Inbound Server : (0.0.0.0):20500
Dual Comm : routing id=0, log cid=0, modem type=21, inbnd index=0
OK
If any of the responses return Not-Acquired or Not-Registered (and the APN is correct), the wireless
Page 35

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 35/55
network operator should be contacted for further troubleshooting.
Please note that it may take several seconds (or longer) for the LMU-5000™ to communicate with the
modem and acquire the wireless network.
5.4.2 GPS Verification
The next step is to verify that the GPS receiver is seeing enough satellites to obtain a valid GPS position.
Again, installers have two choices on how to perform this verification. First, like the Comm Verification, there
is a GPS status LED (i.e., the one closest to the SMA connector). If this LED is solid, then the LMU has
found GPS service.
If the LED is not visible then GPS service may be verified using an AT Command:
AT$APP GPS?
The response should be similar to:
Lat=3304713, Lon=-11727730, Alt=0
Hdg=113 Spd=0 3D-RTIME HDOP=130 nSats=7
Installers are looking for the 3D-RTIME setting along with a valid Lat, Long pair (i.e. something other than 0).
If the GPS receiver does not have a valid lock within 2-3 minutes, installers should check antenna placement
(see the Installation Notes section for placement suggestions), the antenna connector and that the antenna has
a clear view of the sky. For further troubleshooting, installers should contact CalAmp Support
(M2MSupport@CalAmp.com)
5.4.3 Inbound Verification
The last item to verify is that the LMU-5000™ is sending data to the correct server. In general, this is a twostep process that will need the aid of an observer on the back end. That is, a technician will have to be logged
in so they can monitor data coming into the backend mapping/vehicle management application.
First, verify that the LMU-5000™ is using the correct Inbound IP address by using:
AT$APP INBOUND?
The response should be similar to:
INBOUND LMD
INBOUND 0 ADDR ddd.ddd.ddd.ddd:ppppp *
INBOUND 0 URL myURL.myCompany.com
Page 36

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 36/55
INBOUND 1 ADDR 0.0.0.0:20500
INBOUND 1 URL
INBOUND 2 ADDR 0.0.0.0:20500
INBOUND 3 ADDR 0.0.0.0:20500
The installer will need to verify with a backend technician that the, URL (myURL.myCompany.com ), IP
address (ddd.ddd.ddd.ddd) and port (<ppppp>) are correct.
The second step is to verify that the LMU-5000™ is sending data. The best way to do this is to force the
LMU-5000™ to send in an unacknowledged Event Report (i.e., its current GPS location) with the following
command:
AT$APP PEG SUNRPT 255
The LMU-5000™ will respond with: OK
The backend monitor must then be contacted to confirm that they received an Event Report with Event Code
255.
Assuming that all three sections have passed, the installation can be considered to be complete.
5.4.4 Verification via SMS
The current Comm, GPS and Inbound status of a GSM LMU can be obtained via SMS provided you have
access to an SMS capable phone or PDA.
Using your handset, send the following SMS Message to the LMU:
!R0
Within a few minutes, the LMU should return a response in the following format:
APP: <App ID> <Firmware Version>
COM:<RSSI> [./d/D][./a/A][./L][IP address] [<APN>]
GPS:[Antenna <Short/Open/Off>] | [No Time Sync] | [<FixStatus> <Sat Count>]
INP:<inputs states> <vehicle voltage>
MID:<mobile ID> <mobile ID type>
INB:<inbound IP address>:<inbound port> <Inbound Protocol (LMD/LMX)>
APP:
o <App ID>:
The Application ID value of the LMU indicating the host platform and the wireless
networking technology of the LMU.
Page 37

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 37/55
o <Firmware Version>:
The current firmware version in use by the LMU
COM:
o <RSSI>:
This is the signal strength the wireless modem sees from the network. In general the LMU
is at least scanning for the network if the RSSI is not -113.
o [./d/D]:
If the character ‘D’ is present, it indicates the LMU had a data session established when it
responded to the status request. For the 8-Bit product line an upper case ‘D’ indicates
both the Inbound and Maintenance sockets are ready. The lower case ‘d’ indicates that
only the Maintenance socket is ready. A ‘.’ indicates no sockets are ready.
o [./a/A]:
This field indicates if the LMU has received an Acknowledgement from the Inbound
server. This field will be empty if the LMU has never received an ACK. The lower case
‘a’ will be present if it has received an ACK since the last cold boot (i.e. power cycle) but
not the last warm boot (App Restart or Sleep). The upper case ‘A’ will be present if the
LMU has received an ACK since the last warm boot. A ‘.’ Indicates no
acknowledgement has been received.
o [./L]:
This field indicates if the LMU’s log is currently active. An ‘L’ indicates that the log is
currently in use (i.e. one or more records have been stored) where a ‘.’ indicates the log is
inactive.
o [IP Address]:
This is an optional field if and is only present if the LMU has established a valid data
session. This field will contain the current IP address of the LMU as assigned by the
wireless network. Note that if you see a value of 192.168.0.0, this is an indication that the
LMU has not been able to establish a data session.
o [<APN>]
The current Access Point Name in use by a GSM LMU.
GPS:
o [Antenna <Short/Open/Off>]:
This field, if present, indicates a problem with the LMU’s GPS antenna. A value of Short
indicates that the antenna cable has likely been crushed. A value of Open indicates that
the antenna cable is either cut or disconnected. A value of Off indicates that the LMU’
GPS receiver is off.
o [No Time Sync]:
Page 38

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 38/55
If this field is present, it indicates that the LMU’s GPS receiver has not been able to find
even a single GPS satellite. This would likely been seen in conjunction with the above
antenna error, or if the LMU GPS antenna is otherwise blocked.
o [<FixStatus> <Sat Count>]:
If these fields are present it indicates that the LMU has, or had a valid GPS solution. The
<Sat Count> field indicates how many GPS satellites are currently in use by the LMU.
The <FixStatus> field indicates the type of fix. The Fix Status types are detailed in the LM
Direct Reference Guide.
INP:
o <input states>:
This field details the current state of each of the LMU’s discreet inputs. This field is
always 8 characters long. The left most character represents the state of input 7 where the
right most represents the state of input 0 (i.e. the ignition). A value of 1 indicates the input
is currently in the high state. A value of 0 indicates it is currently in the low state.
o <vehicle voltage>:
This field will contain the current reading of the LMU’s internal A/D. This will be the
supply voltage provided to the LMU in mV.
MID:
o <mobile ID>:
This will be the current mobile ID in use by the LMU.
o <mobile ID type>:
This will be the type of Mobile ID in use by the LMU. The available types are, Off, ESN,
IMEI, IMSI, USER, MIN and IP ADDRESS.
INB:
o <inbound IP address>:
This is the current IP address in use by the LMU. This value should match the IP address
of your LM Direct™ server.
o <inbound port>:
This is the current UDP port the LMU will use to deliver its LM Direct™ data. This value
should match UDP port you are using on your LM Direct™ server. It is typically 20500.
o <Inbound Protocol (LMD/LMX)>:
This is the current UDP/IP messaging protocol in use by the LMU. In general it should be
LMD.
Example GSM Response
Page 39

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 39/55
APP:081 8.3d
COM:0
GPS:No Time Sync
INP:11100111 13.7V
MID:4141000100 ESN
INB:207.7.101.227:20500 LMD
6 LMU-5000 Router Configuration & Management
The LMU-5000 has all the advanced routing features expected in a high-end 3G enterprise-grade device while
maintaining the simplicity and easy-of-use of many residential SOHO-class residential routers.
LMU-5000 Router Home Page
Page 40

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 40/55
6.1 Home Page Parameters
The home page is for status only, no configuration is available. Listed below are the most useful parameters
listed on the homepage:
IP: Lists the LAN IP address of the LMU5000. This IP becomes the gateway and DNS server
for all PCs and devices connected to the LAN. This value can be changed on the LAN Settings
Page.
System up Time: Counter that starts when the unit is powered on and resets when the unit is
powered down or reset. Note: This counter does NOT indicate how long the WAN connection
has been up.
PPP Status: UP or DOWN, indicates if the device has established connection to the WAN.
PPP IP Address: This is the WAN IP address of the LMU5000. Accessing the device
remotely requires entering this address into a browser. This address is assigned by the cellular
carrier and will be dynamic unless a static address is specifically requested
PPP P-t-P: WAN address of the network access point of the cellular carrier
Service Type: This indicates the type of service you are connected to. The LMU5000 will
always connect to the most advanced service available and will revert back to other networks if
3G is not available.
Roaming Status: Indicates ROAMING or NOT ROAMING
Signal Strength: Same as RSSI (Receive Signal Strength Indication), indicates the strength of the
network signal with both a numerical value and a good/medium/poor message.
6.2 Provisioning Information: EV-DO “WAN Cellular” Page
This page displays the current CDMA information related to the CDMA Carrier, Carrier connection,
Telephone number, Signal Strength, Etc.
WAN (Cellular)
Provisioning Information
Current Status (NOTE - please click refresh button on browser panel to refresh values)
ESN09604005309
MDN/MTN8057540654
MIN/MSI8057540654
Telephone Number8057540654
Wireless CarrierVerizon
PRL51918
SID26
NID1
Channel507
Frequency800 MHz Cellular
Signal Strength (dBm)-61 (strong)
EV-DO Wan Cellular Page
6.3 Provisioning Information: HSPxA “WAN Cellular” Page
Page 41

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 41/55
This page displays the Service Status, IMEI, Telephone number, Country, Roaming Status, Signal Strength,
Etc.
WAN (Cellular)
Provisioning Information
Current Status (NOTE - please click refresh button on browser panel to refresh values)
Service StatusService available
Service TypeHSPA (HSDPA+HSUPA)
IMEI352974025130857
MIN/MSI232590584
Telephone Number9529443434
CarrierATT
BandWCDMA 1900 MHz
CountryUSA
Cell ID30062
Roaming StatusNot Roaming
Signal Strength (dBm)-70 (strong)
Connection StatusLINK UP
HSxPA WAN Cellular Page
6.4 Provisioning Information On “WAN Cellular” Page
ESN: Electronic Serial Number, this number is assigned to the cellular module by WWAN Module
Manufacturer. This number must be provided to the carrier in order to activate the module.
MDN/MTN: Mobile Directory Number, this number is assigned by the carrier when the module is activated
MIN/MSI: Mobile Identification Number, Same as the MDN
Carrier Name: Name of the Service provider
Telephone #: Assigned by the carrier
PRL: Preferred Roaming List, A database that declares the priority of other carriers while roaming. This file
should be updated periodically to ensure proper connectivity while roaming
SID/NID/Channel: This data refers to the details of the established network connection.
Most users will not be concerned with this data.
Frequency: This indicates the band that the LMU5000 is connected to, it will either be the 800MHZ cellular
band or the 1900MHZ PCS Band
Signal Strength: Same as RSSI, indication of the signal strength of the incoming cellular signal.
IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity): A number that uniquely identifies a mobile device on
GSM/UMTS networks:
MIN/MSI (Mobile Identity Number/Mobile Subscriber International): Phone number for the account
Page 42

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 42/55
6.5 Activation (EV-DO)
Before activation of the cellular module, you must contact your service provider to activate a contract. The
carrier will need the ESN of the cellular module, which can be found on the LMU5000 home page or on a
label on the outside of the unit.
You must specify you need a “PACKET DATA” contract to your carrier. The Carrier will provide you a
“Mobile Directory Number” and possibly an Activation Code (for Sprint only).
EV-DO Activation Page
Command: This is a carrier specific command used when performing an OTASP. Its default is *22899 which
is the Verizon OTA command
Activation Type: Select the correct activation type depending on the carrier
OTASP: Over the Air Service Provisioning, used to activate a Verizon Contract
IOTA: Internet Over the Air, used to activate a Sprint contract
Once you have entered the command and selected the activation type, hit “Submit” to activate the device.
This will take a few minutes, if it does not work the first time, you may need to manually enter the
MDN and MIN numbers (these are the same numbers and are provided by the service carrier) in the
boxes above and retry.
6.6 Activation (HSxPA) Page
SIM Configuration
Old PIN code
Note: This is ONLY required for changing the PIN code. Field value will be cleared after settings.
PIN code (CHV1)
PIN unblock code
SIM unlock code (MEP)
SIM operation
HPxPA Activation Page
Use an activated SIM from the carrier
Page 43

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 43/55
MEP (Mobile Equipment Personalization) code:
-Stored on the modem
- To unlock a modem that has been factory-restricted to a specific carrier’s SIMs.
- Code must be obtained from the original carrier
CHV1 (Card Holder Verification) code:
Stored on the SIM
Restricts access to SIM
Used to lock/unlock SIM card
Correct CHV1 code must be input to the modem within 3 attempts
SIM gets locked after 3 failed CHV1 attempts. Must unlock the SIM by setting “PIN unblock
code”. Contact the carrier to obtain this code.
6.7 Dial Settings (EV-DO Version)
The Dial Setting page allows the user to Disable auto-connect. This is done if the user is concerned about the
amount of data transferred on their contract.
This page also contains information on the reconnect timers, these reconnect timers are defined by the Verizon
algorithm required to receive Carrier Certification. They cannot be modified by the user
Note: Most users will not need to enter a dial number, user or password. This is used for older
dial up cellular standards it is not used for 3G standards.
Dial Settings Page, EV-DO Version
6.8 Dial Settings (HSxPA Version)
The Dial Setting page allows the user to Disable auto-connect. This is done if the user is concerned about the
amount of data transferred on their contract.
Page 44

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 44/55
This page also contains information on the Frequency band in which the cell modem is currently configured.
The Band can be reconfigured by selecting one of the radio buttons.
The carrier APN and Dial number shall be configured to match the carrier requirements.
Note: Most users will not need to enter a dial number, user or password. This is used for older
dial up cellular standards it is not used for 3G standards.
Dial Settings HPxPA Version page
6.9 LAN Settings Page
This page contains the basic configuration setup needed to create a LAN with the LMU5000 as the network
connection point . Most of the configuration by the end user will occur on this page.
Page 45

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 45/55
LAN Settings Page
Ethernet IP address: LAN IP of the LMU5000. This address is entered into a browser if a LOCAL
PC wants to login to the LMU5000. Warning: Changing this value will cause the user to lose
connection to the LMU5000. They must enter the new address in a browser to reconnect. If the user
forgets or makes a type entering new the new value, it can be difficult to reconnect to the device.
DNS Server1 IP Address: Except in special cases, this should match the Ethernet IP address
DNS Server2 IP Address: This is used if a second DNS server is available.
DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, This function assigns IP addresses in a specified range
to all PCs connected to or joining the LAN.
DHCP Start/End Range: Sets the range of IP addresses assigned to the PCs. The user can limit the
# of devices allowed on the network by minimizing this range.
Warning: The addresses in this range should be the same as the Ethernet IP except for the last three
digits
Warning: The ethernet IP should not be in the DHCP range.
DHCP Lease Time: This timer dictates how long a device on the LAN can hold an IP address. In
almost all cases this should be set to the maximum (and default value) of 86400. Setting this value too
low will cause network connectivity problems.
Page 46

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 46/55
6.9.1 Remote Administration
Remote Configure: Default is “Enable” this can be disabled to add security.
Admin Password: Set the password for BOTH remote login and local login. The password must be
entered twice for the password to change.
Incoming Port: Change the port of incoming requests. This will not usually need to be changed unless
it conflicts with other devices on the network.
Note: Changing this remotely will cause the user to lose contact with the LMU5000. They will have to
login using the new port number to re-establish connection.
Warning: Users can be logged into a single unit both locally and remotely at the same time. Changes made on
one end will not be reflected on the other unless the webpage is refreshed.
Warning: There is no way to remotely reset the user name and password at this point. If a user changes the
user name or password and forgets them, the unit must be returned to the manufacturer to reset the password.
6.9.2 Disabling DHCP
When DHCP is enabled, anyone can plug a PC into the LMU5000 and use it to browse the internet. This can
cause security problems and add expense to the users data contract, to control what PCs can connect to the
LMU5000, perform the following steps.
Disable DHCP on the LAN settings page. Note: This will also disable DNS Masquerading.
WARNING: Disabling DHCP will wipe out all values in the DHCP and DNS sections. If
the user disables DHCP by accident or needs to re-implement DHCP and does not know
what the previous values were, they will have trouble getting the correct values.
To improve security, change the Ethernet IP of the LMU5000 to something other than the
default.
WARNING: If the DHCP is disabled, and the user forgets the ethernet IP of the device,
the user or support personal may not be able to login to the device. The device will have
to be returned to the mfg to have factory resets restored.
On the network setting page of each PC set the following
IP address: Set a unique address on the same subnet as the LMU5000
Subnet Mask: 255:255:255:0
Default Gateway: Ethernet IP of LMU5000
Preferred DNS: Ethernet IP of LMU5000
6.10 Port Forwarding
Port Forwarding is used to provide remote access to third party devices with an IP server such as Web
Cameras or printers.
Page 47

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 47/55
Port Forwarding Page
Enter Port Forwarding Configuration Information.
Port Fowarding Enable: Must enable to allow port forwarding. Default is disabled.
Mapping number: Generic number assigned by this user to this route.
Protocol: TCP or UDP, is driven by the protocol used by the third party device
Source IP address: Enter the IP address of the remote PC connecting to the device (this
should only be done if a single PC with a STATIC IP is accessing the device, or enter 0.0.0.0
(wildcard) to allow all external devices to access the device.
Incoming port: Set port of incoming request. This can be any non-conflicting port. It can be the
same as the Destination port.
Destination IP address: IP address of third party device.
Destination port: Port of the third party device. This will be assigned to the device by the third
party manufacturer and should be in the user manual of the device.
Warning: The password protection on the LMU5000 does not protect logging into a third party device.
Usually the device will require its own password protection, but this needs to be confirmed by the user if
password protection is required.
Hit “Add” when done configuring the route. The route will be displayed at the bottom of the page. You
can add other routes as long as they have a unique mapping number and port number. Once the route
is added you can enter the following on a remote PC to access the third party device.
Page 48

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 48/55
6.11 GPS Status
Reports the current position of the unit, # of Satellites visible, UTC time, Ground speed and Altitude.
GPS
GPS Status
ConditionStandard GPS Fix
Number of Satellites3
UTC (hh:mm:ss)17:28:37
Position (Lat, Long)44deg 50.33714min N, 93deg 35.90436min W
Altitude (meters)287.9
True Course103.2deg
Ground Speed (Km/h)1.8
GPS Status Page
6.12 GPS Reporting
Page 49

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 49/55
GPS Reporting Page
Periodic Location reports can be generated
Unit can be configured to generate Autonomous GPS reports over UDP/IP or TCP/IP
Reports can be delivered locally over LAN or Remotely over WWAN
6.13 Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A VPN is a mechanism for providing secure, reliable transport over Internet. The VPN uses authentication to
deny access to unauthorized users, and encryption to prevent unauthorized users from reading the private
network packets. The VPN can be used to send any kind of network traffic securely, including voice, video
or data.
VPN Configuration Page
VPN using SSLv2/TLSv1
Enable/Disable compression
Configurable VPN Server port
Configurable Client IP range
Page 50

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 50/55
6.14 System Upgrade
System Upgrade Page
Over-The-Air-SW upgrade
SW upgrade via Local LAN
OS and applications can be updated
SW Image encryption/decryption using 256 bit algorithm
SW can also be updated using a USB flash drive
7 License Agreement
FOR SOFTWARE, APPLICATION PROGRAMING INTERFACES (APIs) & DOCUMENTATION
IMPORTANT: DO NOT INSTALL OR USE THE SOFTWARE OR DOCUMENTATION UNTIL YOU
HAVE READ AND AGREED TO THIS LICENSE AGREEMENT.
This is a legal agreement between you, the Customer, and CalAmp DataCom Incorporated (“CalAmp”). By
installing and/or using the software or documentation, you are consenting to the terms of this License. If you
do not agree to the terms of this non-exclusive License Agreement, DO NOT INSTALL OR USE THE
SOFTWARE, APIs OR DOCUMENTATION. For a full refund, return the unused media package and all
accompanying materials within seven (7) days to CalAmp. Where there is no packaging or media, use of
the software and/or documentation constitutes acceptance.
Page 51

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 51/55
Definitions: As used in this License Agreement, “Software” means CalAmp’s LM Direct ™, LMU
Manager™, LapTop Locator™, LMU Application/Programmable Event Generator™, CDMA LMU
Provisioning Tool, GPRS LMU Provisioning Tool, iDEN™ Provisioning Tool, LMU Status, Clone Config,
Hex Dump, LM Exchange™ Traffic Monitor, Freewave Base Station Config, Remote Serial Port, App
Watcher Service and/or other software products licensed by CalAmp for use in computer applications
development or integration including the computer programs, libraries and related materials either contained
on the media provided to you by or from CalAmp, or which you have received or downloaded electronically.
“Application” means a compiled or executable software program created by Developer that uses some or all
of the functionality of the Software. “Software Copies” means the actual copies of all or any portion of the
Software including backups, updates, merged or partial copies permitted hereunder or subsequently licensed
to you. “Documentation” means the non-Software information contained on the media provided with this
package or downloaded and which is used with and describes the operation and use of the Software.
“Documentation Copies” means the actual copies of all or any portion of the Documentation including
backups, updates, merged or partial copies permitted hereunder or subsequently provided to you. “Related
Materials” means all other materials and whatever is provided by or from CalAmp, and the non-Software and
non-Documentation contained on the media supplied, downloaded, or otherwise supplied by or from CalAmp
for use with the Software and Documentation. “Server” means a single, networked computer that is accessible
to other client machines on the network. “User” means (i) a single person using an Application for his/her
internal, use or (ii) a single terminal or a single workstation of a computer used only by a person (and not
accessed otherwise) for accessing an Application. “Use License” means limited rights granted by CalAmp for
deployment of a single Application to a User. “Developer” means a single programmer developing an
Application. “Developer License” means the grant of certain limited rights to use and maintain the Software,
Software Copies, Documentation, Documentation Copies and Related Materials in development of
Applications.
Background: A Developer License is required for each Developer who uses the Software in building
Application(s). A Use License is required and must be purchased by Customer for each User to which
Customer provides access to an Application (unless a Server or Site license for unlimited or a specified
number of users has been purchased). Each Use License is specific to one client-side Application only and
may not be used for any other client-side Application. Each Server license is limited to Server-based
Applications deployed on that Server for which the license has been purchased as specified in a CalAmp
License Certificate. The Software is licensed on a per Developer, and on a per User, per Application basis. In
order to preserve and protect its rights under applicable law, CalAmp is not selling you ownership rights to
Software or Documentation (owned by or licensed to CalAmp). CalAmp specifically retains title to all
CalAmp Software, Documentation and Related Materials and CalAmp licensors retain title to items owned by
them.
Duration: This License Agreement is effective from the day you install or start using the Software, or receive
or download it electronically, and continues until terminated. If you fail to comply with any provision of the
License, termination is automatic, without notice from CalAmp and without the necessity for recourse to any
judicial authority. Upon termination, you must destroy the Related Materials, the Software, Documentation
and all Software and Documentation copies. CalAmp can also enforce its other legal and equitable rights.
Developer License Only—Uses Permitted: Software and Documentation may be used for the sole
Page 52

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 52/55
purpose of developing Applications and only by a licensed Developer. Software and Documentation may be
installed onto a hard disk drive or a Server, access to which is restricted to Developers for which a Developer
License has been purchased and may also be stored or installed on a storage device such as a network
server, used only to install or access the Software or Documentation on your other computers over an internal
network; however, you must have acquired a license for each separate computer on which the Software or
Documentation is installed or accessed from the storage device. A Developer License may not be shared or
used concurrently on different computers. One backup copy may be made for each legally obtained media
copy or electronic copy you have received, provided that all CalAmp and third party licensor information —
including copyright notices — are maintained and possession of the copy is retained in a secure location. In
addition, you agree to use reasonable efforts to protect the Software and Documentation from unauthorized
use, reproduction, distribution or publication. All rights not specifically granted in this License are reserved by
CalAmp.
Customer agrees to include the notice “Copyright © 1999 – 2009 CalAmp DataCom Inc., All Rights
Reserved” in Applications developed with the Software. Customer agrees to include the following CalAmp
Copyright and Government Restricted Use notice in all documentation and in any Application on-line help or
readme file.
“Portions of this computer program are owned by CalAmp DataCom Inc., Copyright © l999 – 2009,
CalAmp DataCom Inc., All Rights Reserved. Use, duplication or disclosure by the Government is subject to
restrictions as set forth in subparagraph ©(1)(ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software
clause at DFARS 252.227-7013 or subparagraphs ©(l) and (2) of the Commercial Computer SoftwareRestricted Rights at 48 CFR 52.227-19, as applicable. Manufacturer is CalAmp DataCom Inc., 1401 North
Rice Ave. Oxnard, CA 93030. Rights are reserved under copyright laws of the United States with respect to
unpublished portions of the Software.”
Developer(s) License—Uses Not Permitted: Unless Otherwise Agreed To In Writing with CalAmp, You
May Not (1) Make derivative works including but not limited to translations, adaptations, arrangements or
any other alteration (each of which would become the property of CalAmp or its licensors, as applicable) or
make copies of the Software or Documentation except as permitted above; (2) Make copies of the Related
Materials; (3) Use any CalAmp product to translate the product of another licensor unless you have the legal
right to do so; (4) Allow a greater number of Developers to access the Software at any one time than the total
number of Developer licenses for which you have paid; (5) Rent, lease, sublicense or lend the Software,
Software Copies, Documentation, Documentation Copies, Related Materials or your rights under this License
or allow access to the Software for unlicensed users; (6) Alter, decompile (except to the limited extent that
decompilation by the licensed Developer only is necessary as the only available way to achieve interoperability
with other programs and, in that situation, any resulting information cannot be used in developing, producing or
marketing any software substantially similar in expression to the Software), disassemble or reverse engineer
the Software; (7) Make any attempt to unlock or bypass any initialization system or encryption techniques
utilized by the Software or Documentation; (8) Alter, remove or obscure any proprietary legend, copyright or
trademark notice contained in or on Software, Documentation or Related Materials; or (9) use the Software
to create an Application intended solely to duplicate functionality of an existing CalAmp end user software
product.
Page 53

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 53/55
Use Licenses: For each Server or Site License purchased, CalAmp grants the Customer the right to
distribute Applications on a single Server or at a single Site, as the case may be, accessible to the number of
individual users (not concurrent users) for which the Server or Site License has been purchased as evidenced
by a CalAmp License Certificate. For each Use License purchased, as evidenced by a CalAmp License
Certificate, CalAmp grants the Customer the right to distribute a single Application to a single User. In no
circumstance may Customer distribute an Application under a site license or concurrent use license unless a
comparable license has been purchased for the Software as evidenced by a CalAmp License Certificate.
Customer agrees that distribution of an Application to a User will in all cases be accompanied by a license
agreement containing at a minimum terms and conditions substantially similar to and at least as restrictive as
the following:
The User may not (1) Make derivative works including but not limited to translations, adaptations,
arrangements or any other alteration of the Application or make copies of the Application, except one backup
copy may be made for each legally obtained copy of the Application, provided that all CalAmp and third
party licensor information — including copyright notices — are maintained and possession of the copy is
retained in a secure location; (2) Allow access to the Application for unlicensed users; (3) Rent, lease,
sublicense or lend the Application or its rights under the license; (4) Alter, decompile, disassemble or reverse
engineer the Application; (5) Make any attempt to unlock or bypass any initialization system or encryption
technique utilized by the Application; or (6) Alter, remove or obscure any proprietary legend, copyright or
trademark notice contained in or on the Application.
The User agrees to use reasonable efforts to protect the Application from unauthorized use, reproduction,
distribution or publication.
Audit: Customer shall keep records of all transactions involving Software for five (5) years after the
transaction. CalAmp shall have the right upon written notice to audit Customer’s records to verify compliance
with this License including the number of Use Licenses granted by Customer. Audit may take place at
Customer’s place or business during normal working hours. In the event that there is a discrepancy in excess
of five percent (5%) between the number of Use Licenses granted and the number paid for, Customer shall
pay all costs related to performing the audit in addition to remitting payment for those licenses granted in
excess of those paid for as evidenced by a CalAmp License Certificate.
General: This Agreement represents our entire understanding and agreement regarding the Software,
Software Copies, Documentation, Documentation Copies and Related Materials and supersedes any prior
purchase order, communication, advertising or representation and may only be modified in a written
amendment signed by an authorized CalAmp representative or by a specific prior or subsequent written
agreement between the parties. If any provision of this Agreement shall be unlawful, void or for any reason
unenforceable, that provision shall be deemed severable from, and shall in no way affect the validity or
enforceability of, the remaining provisions.
8 Limited Warranty
Page 54

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 54/55
Covering the Physical Media and Printed Materials: CalAmp warrants to you, the original licensee, that
the media on which the Software is recorded are free from defects in materials and workmanship under
normal use and service FOR A PERIOD OF NINETY (90) DAYS FROM THE DATE OF DEVELOPER
LICENSE PURCHASE. CalAmp’s entire liability and your exclusive remedy as to defective media,
Documentation or Related Material(s) shall be replacement of the media, Documentation or Related
Material(s) by CalAmp. Each defective item, along with proof of license purchase and date, must be sent in a
traceable manner to: CalAmp DataCom Inc., 1401 North Rice Ave. Oxnard, CA 93030.
Disclaime r Regarding the Software, Documentations and Related Materials: THE SOFTWARE,
DOCUMENTATION AND RELATED MATERIALS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS.” EXCEPT AS MAY
OTHERWISE BE EXPRESSLY SET FORTH HEREIN, CALAMP MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS
OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WITH RESPECT TO THE SOFTWARE,
DOCUMENTATION OR RELATED MATERIALS INCLUDING BY WAY OF EXAMPLE, AND
NOT LIMITATION, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. BY WAY OF FURTHER EXAMPLE AND NOT LIMITATION,
CALAMP MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WITH
RESPECT TO THE ACCURACY, RELIABILITY OR COMPLETENESS OF THE
DOCUMENTATION OR THE RELATED MATERIALS. THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO THE USE OF
THE SOFTWARE, DOCUMENTATION AND RELATED MATERIALS IS ASSUMED BY YOU. IN
NO EVENT SHALL CALAMP BE LIABLE TO YOU OR ANY OTHER PERSON, REGARDLESS OF
THE CAUSE, FOR THE EFFECTIVENESS OR ACCURACY OF THE SOFTWARE,
DOCUMENTATION OR RELATED MATERIALS OR FOR ANY SPECIAL, INDIRECT,
INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING FROM OR OCCASIONED BY YOUR
USE OF THE SOFTWARE, DOCUMENTATION OR RELATED MATERIALS, EVEN IF ADVISED
OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. IN THE EVENT THE FOREGOING IS FOUND BY A
COURT OF COMPETENT JURISDICTION TO BE INEFFECTIVE, YOU HEREBY AGREE THAT
CALAMP’S MAXIMUM LIABILITY FOR ANY CLAIM ARISING IN CONNECTION WITH THE
SOFTWARE, DOCUMENTATION AND/OR RELATED MATERIALS (WHETHER IN CONTRACT,
TORT, INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE, PRODUCT LIABILITY OR OTHERWISE) SHALL NOT
EXCEED THE LICENSE FEES PAID BY YOU WITH RESPECT TO THE SOFTWARE,
DOCUMENTATION AND/OR RELATED MATERIALS AT ISSUE. SOME STATES DO NOT
ALLOW THE LIMITATION OR EXCLUSION OF INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES, SO THE FOREGOING PROVISION, WITH RESPECT TO EXCLUDING OR LIMITING
SUCH DAMAGES, MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
Acknowledgement: You acknowledge that you have read this LIMITED WARRANTY, understand it and
agree to be bound by its terms and conditions. You also agree that: (1) No oral or written information or
advice given by CalAmp, its dealers, distributors, agents or employees shall in any way increase the scope of
this Limited Warranty and you may not rely on any such information or advice; (2) Unless a written governing
agreement signed by you and CalAmp exists, this License Agreement is the complete and exclusive statement
of agreement between CalAmp and you regarding the licensing of the Software, Documentation and Related
Materials and supersedes all proposals, oral or written, and any other communications you may have had
prior to purchasing your license; (3) Except for the price and delivery terms agreed upon by both parties, the
terms and conditions of this License Agreement shall supersede those set forth in any purchase order where
the purchase order conflicts or is inconsistent with or adds to the terms and conditions of this License and
those superseded purchase order terms and conditions shall be null and void; (4) You agree to assure that
copies of this License Agreement are distributed, read and agreed to by each Developer using the Software
Page 55

10/12/13 LMU-5000 Hardware & Installation Guide - PULS Wiki
https://puls.calamp.com/wiki/LMU-5000_Hardware_%26_Installation_Guide 55/55
and/or Documentation.
Governing Law: This Agreement shall be governed by the laws of the State of California, United States,
excluding its conflicts of law principles and excluding the United Nations Convention on Contracts for the
International Sale of Goods. You agree to exclusive jurisdiction of California State federal and state courts,
Ventura County, for resolution of any dispute related to this Agreement.
U.S. Government Protected Rights: The Software Documentation and Related Materials are provided
with RESTRICTED RIGHTS. Use, duplication or disclosure by the Government is subject to restrictions as
set forth in subparagraph ©(1)(ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software clause at DFARS
252.227-7013 or subparagraphs ©(1) and (2) of the Commercial Computer Software-Restricted Rights at
48 CFR 52.227-19, as applicable. Manufacturer is CalAmp DataCom Inc., 1401 North Rice Ave. Oxnard,
CA 93030. Rights are reserved under copyright laws of the United States with respect to unpublished
portions of the Software.
9 Regulatory Information
Human Exposure Compliance Statement
Pursuant to 47 CFR § 24.52 of the FCC Rules and Regulations, personal communications services (PCS)
equipment is subject to the radio frequency radiation exposure requirements specified in § 1.1307(b), §
2.1091 and § 2.1093, as appropriate.
CalAmp DataCom Inc. certifies that it has determined that the LMU-5000™ complies with the RF hazard
requirements applicable to broadband PCS equipment operating under the authority of 47 CFR Part 24,
Subpart E of the FCC Rules and Regulations. This determination is dependent upon installation, operation and
use of the equipment in accordance with all instructions provided.
The LMU-5000™ is designed for and intended to be used in fixed and mobile applications. “Fixed” means
that the device is physically secured at one location and is not able to be easily moved to another location.
“Mobile” means that the device is designed to be used in other than fixed locations and generally in such a
way that a separation distance of at least 20 cm is normally maintained between the transmitter’s antenna and
the body of the user or nearby persons. The LMU-5000™ is not designed for or intended to be used in
portable applications (within 20 cm of the body of the user) and such uses are strictly prohibited.
To ensure that the LMU-5000™ complies with current FCC regulations limiting both maximum RF output
power and human exposure to radio frequency radiation, a separation distance of at least 20 cm must be
maintained between the unit’s antenna and the body of the user and any nearby persons at all times and in all
applications and uses. Additionally, in mobile applications, maximum antenna gain must not exceed 3 dBi.
 Loading...
Loading...