Page 1

VANGUARD
MULTICARRIER 3G/4G CELLULAR BROADBAND
ROUTER
User Manual
Vanguard Series Fixed and Mobile models
Revised October 2014
Page 2

REVISION HISTORY
REV
DATE
REVISION DETAILS
0
April 2012
Initial release. Part number 001-7300-100.
1
December 2012
Updated for Vanguard router fixed location and mobile, and added UL information.
A
September 2013
Updated for firmware version 5.1.2A with DeviceOutlook™.
B
September 2013
Updated Cable number on Page 5. Changed 150-7001-004 to 150-7500-004.
C
November 2014
Added regulatory statements. Miscellaneous copy editing.
Page 3

Copyright Notice
© 2011-2013 CalAmp. All rights reserved.
CalAmp reserves the right to modify the equipment, its specification or this manual without prior notice, in the interest
of improving performance, reliability, or servicing. At the time of publication all data is correct for the operation of the
equipment at the voltage and/or temperature referred to. Performance data indicates typical values related to the
particular product. Product updates may result in differences between the information provided in this manual and the
product shipped. For access to the most current product documentation and application notes, visit www.calamp.com.
No part of this documentation or information supplied may be divulged to any third party without the express written
consent of CalAmp. Products offered may contain software which is proprietary to CalAmp. The offer or supply of these
products and services does not include or infer any transfer of ownership.
Modem Use
The Vanguard Series modems are designed and intended for use in fixed and mobile applications. “Fixed” assumes the
device is physically secured at one location and not easily moved to another location. Please keep the cellular antenna
at a safe distance from your head and body while the modem is in use.
Regulatory Statements
Note: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to part
15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a
residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is
no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is
encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures: i) Reorient or relocate the
receiving antenna. II) Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver. III) Connect the equipment into an
outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected. Iv) Consult the dealer or an experienced
radio/TV technician for help.
This device complies with Industry Canada licence-exempt RSS standard(s). Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) this device may not cause interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference, including
interference that may cause undesired operation of the device.
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d'Industrie Canada applicables aux appareils radio exempts de licence.
L'exploitation est autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes : (1) l'appareil nedoit pas produire de brouillage, et (2)
l'appareil doit accepter tout brouillage radioélectrique subi, même si le brouillage est susceptible d'en compromettre le
fonctionnement.
Under Industry Canada regulations, this radio transmitter may only operate using an antenna ofa type and maximum
(or lesser) gain approved for the transmitter by Industry Canada. To reduce potential radio interference to other users,
the antenna type and its gain should be so chosen that the equivalent isotropically radiated power (e.i.r.p.) is not more
than that necessary for successful communication.
Conformément à la réglementation d'Industrie Canada, le présent émetteur radio peut fonctionner avec une antenne
d'un type et d'un gain maximal (ou inférieur) approuvé pour l'émetteur par Industrie Canada. Dans le but de réduire les
risques de brouillage radioélectrique à l'intention des autres utilisateurs, il faut choisir le type d'antenne et son gain de
sorte que la puissance isotrope rayonnée équivalente (p.i.r.e.) ne dépasse pas l'intensité nécessaire à l'établissement
d'une communication satisfaisante.
IC ICES-003 standard compliance notice:
CAN ICES-3 (B)/NMB-3(B)
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page i
Page 4

Important
When operating at elevated temperature extremes, the surface may exceed +70 Celsius. For user safety, the
Vanguard should be installed in a restricted access location.
WARNING — EXPLOSION HAZARD, do not connect while circuit is live unless area is known to be nonhazardous.
Maintain a distance of at least 20 cm (8 inches) between the transmitter antenna and any person while in use. This
modem is designed for use in applications that observe the 20 cm separation distance.
Interference Issues
Avoid possible radio frequency (RF) interference by following these guidelines:
The use of cellular telephones or devices in aircraft is illegal. Use in aircraft may endanger operation and disrupt the
cellular network. Failure to observe this restriction may result in suspension or denial of cellular services to the
offender, legal action, or both.
Do not operate in the vicinity of gasoline or diesel fuel pumps unless use has been approved or authorized.
Do not operate in locations where medical equipment that the device could interfere with may be in use.
Do not operate in fuel depots, chemical plants, or blasting areas unless use has been approved and authorized.
Use care if operating in the vicinity of protected personal medical devices, i.e., hearing aids and pacemakers.
Operation in the presence of other electronic equipment may cause interference if equipment is incorrectly
protected. Follow recommendations for installation from equipment manufacturers.
Mobile Application Safety
Do not change parameters or perform other maintenance of the Vanguard while driving.
Road safety is crucial. Observe National Regulations for cellular telephones and devices in vehicles.
Avoid potential interference with vehicle electronics by correctly installing the Vanguard modem. CalAmp
recommends installation by a professional.
UL Listed models only
For more information see APPENDIX C — UL Installation Instructions and Non-Incendive Field Wiring.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page ii
Page 5

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Product Overview ........................................................................................................................... 1
1.1 Module Identification ............................................................................................................................................ 1
1.2 Features and Benefits of the Vanguard Multicarrier Cellular Router .................................................................... 2
1.3 General Specifications ............................................................................................................................................ 2
1.4 Mechanical Specifications ...................................................................................................................................... 3
1.5 Order Information .................................................................................................................................................. 4
1.5.1 Mounting Brackets ........................................................................................................................................ 4
1.5.2 Accessories ................................................................................................................................................... 5
1.6 External Connectors ............................................................................................................................................... 6
1.7 Antenna .................................................................................................................................................................. 8
1.8 Power Cable Pinout ................................................................................................................................................ 8
1.9 RS-232 Serial Port Integration Parameters ............................................................................................................ 9
1.9.1 ODP (Open Developers Platform) Over RS-232 ............................................................................................ 9
2 Getting Started .............................................................................................................................. 10
2.1 Package Contents ................................................................................................................................................. 10
2.2 Device Connections .............................................................................................................................................. 10
2.3 LAN Configuration ................................................................................................................................................ 11
2.4 Cellular Connections ............................................................................................................................................ 11
2.4.1 GSM Users................................................................................................................................................... 12
2.4.2 CDMA Users ................................................................................................................................................ 12
3 Vanguard Web Interface ............................................................................................................... 13
3.1 Unit Status ............................................................................................................................................................ 14
3.1.1 Status .......................................................................................................................................................... 15
3.1.2 Identity ........................................................................................................................................................ 20
3.1.3 Basic Settings .............................................................................................................................................. 20
3.2 Cell Connection .................................................................................................................................................... 21
3.2.1 Carrier ......................................................................................................................................................... 22
3.2.2 GSM Settings ............................................................................................................................................... 25
3.2.3 CDMA Settings ............................................................................................................................................ 27
3.2.4 System Monitor .......................................................................................................................................... 31
3.2.5 Dynamic DNS .............................................................................................................................................. 33
3.3 LAN Settings ......................................................................................................................................................... 34
3.3.1 MAC Filtering .............................................................................................................................................. 39
3.3.2 IP Filtering ................................................................................................................................................... 40
3.4 WLAN Settings ...................................................................................................................................................... 43
3.4.1 Main ............................................................................................................................................................ 44
3.4.2 Client ........................................................................................................................................................... 45
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. B| Page iii
Page 6

3.4.3 Access Point ................................................................................................................................................ 47
3.4.4 Stats ............................................................................................................................................................ 49
3.4.5 Site Survey .................................................................................................................................................. 50
3.5 Router .................................................................................................................................................................. 50
3.5.1 Port Forwarding .......................................................................................................................................... 50
3.5.2 Static Routes ............................................................................................................................................... 52
3.6 Security ................................................................................................................................................................ 54
3.6.1 Status .......................................................................................................................................................... 54
3.6.2 PPTP ............................................................................................................................................................ 55
3.6.3 IPsec ............................................................................................................................................................ 56
3.6.4 GRE.............................................................................................................................................................. 60
3.7 Serial .................................................................................................................................................................... 61
3.7.1 External Serial ............................................................................................................................................. 61
3.7.2 Internal Serial .............................................................................................................................................. 67
3.8 GPS ....................................................................................................................................................................... 68
3.8.1 Settings ....................................................................................................................................................... 69
3.8.2 Status .......................................................................................................................................................... 72
3.9 Diagnostics ........................................................................................................................................................... 74
3.9.1 SNMP .......................................................................................................................................................... 74
3.9.2 SMS ............................................................................................................................................................. 76
3.9.3 DeviceOutlook™ .......................................................................................................................................... 78
3.9.4 Logging ........................................................................................................................................................ 79
3.10 I/O Settings .......................................................................................................................................................... 81
3.10.1 Status .......................................................................................................................................................... 81
3.10.2 Settings ....................................................................................................................................................... 82
3.10.3 Labels .......................................................................................................................................................... 85
3.11 Firmware Update ................................................................................................................................................. 85
4 IP Addressing ................................................................................................................................. 87
4.1 Overview .............................................................................................................................................................. 87
4.2 IP Addressing Tutorial .......................................................................................................................................... 88
4.3 Private Versus Public IP Addresses ...................................................................................................................... 88
4.4 Port Forwarding ................................................................................................................................................... 89
4.5 DMZ ...................................................................................................................................................................... 90
4.6 Friendly IP Address ............................................................................................................................................... 90
5 IPsec and VPN Pass-Through Deployment Guide ......................................................................... 90
5.1 Benefits of IPsec ................................................................................................................................................... 90
5.2 Configuration Summary ....................................................................................................................................... 91
5.2.1 Case #1: Vanguard Configured IPsec Client ................................................................................................ 91
5.2.2 Case #2 Vanguard Configured to use a DMZ for VPN Pass-Through .......................................................... 96
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page iv
Page 7

6 User I/O Port ................................................................................................................................. 97
6.1 Input Circuit for Analog Inputs ............................................................................................................................. 99
6.2 Simplified Circuit for Digital Input ........................................................................................................................ 99
6.3 Simplified Circuit for Mechanical Relays .............................................................................................................. 99
6.4 Inserting Wires Into User Port Connector .......................................................................................................... 100
APPENDIX A — Abbreviations and Definitions ................................................................................. 101
APPENDIX B — Mechanical Specifications ........................................................................................ 103
APPENDIX C — UL Installation Instructions and Non-Incendive Field Wiring .................................. 108
APPENDIX D — SMS Interface ........................................................................................................... 110
SMS Message Routing ................................................................................................................................................... 110
Client Interface ............................................................................................................................................................. 111
SMS Message Text Format ............................................................................................................................................ 114
APPENDIX E — NMEA I/O Agent ....................................................................................................... 115
Specifications ................................................................................................................................................................ 115
PDU Types ..................................................................................................................................................................... 118
APPENDIX F — Firmware Upgrade Instructions ............................................................................... 122
To Perform Firmware Upgrades ................................................................................................................................... 123
To Perform a Full Firmware Install ................................................................................................................................ 126
To Upgrade Using a Two-Part Upgrade File .................................................................................................................. 129
APPENDIX G — Service and Support And Warranty Statement ....................................................... 130
Warranty Statement ..................................................................................................................................................... 131
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page v
Page 8
1 PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Figure 1 Example VG identification label
The Vanguard ™ Series from CalAmp — simple, reliable wireless connectivity without limitations – GSM and CDMA
connectivity in a single device.
Uniquely designed for operation on both GSM and CDMA networks, Vanguard router offers more choice and
redundancy in carrier networks. This single, flexible platform addresses a variety of wireless communications needs
with serial to IP conversion, over-the-air configuration and system monitoring for optimal connectivity. This ready to
deploy broadband router enables wireless data connectivity for up to two LAN and one serial device over public cellular
networks at 3G/4Gspeeds.
Equipped for a broad range of fixed applications, Vanguard router provides reliable connectivity for Programmable
Logic Controllers (PLCs), Remote Terminal Units (RTUs), Ethernet web cameras or any other Ethernet or serial device.
For mobile applications, this intelligent broadband router incorporates an optional highly sensitive 16-channel GPS
receiver and an intelligent algorithm that offers outstanding receive sensitivity and improved accuracy, integrity and
availability of GPS signals – even when the vehicle is off. An optional, built-in WiFi access point also allows your
tethered devices to remain connected even when you leave the vehicle.
This widely deployed wireless solution delivers countless software capabilities. OEMs may tailor the Vanguard router
by loading their application on the Open Developer Platform (ODP) which allows a Linux application to run on a
partition of the embedded Linux operating system.
1.1 MODULE IDE NTIFICATION
The module identification label can be found on the bottom of your Vanguard router. This label contains the product
part number, the serial number, FCC and IC IDs as well as carrier-specific information that will be required when
activating your data account.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 1
Page 9

1.2 FEATURES AND BENEF I TS OF THE VANGUARD MUL T I C A R R I E R CELLULAR R O U T ER
Interface Connectors
RS-232 DE-9S Connector (DCE female)
10/100 Base-T Full Duplex (Dual)
10 Pin I/O Port
Mini USB Service port — provided for convenience when upgrading cell module only.
Power Connector
Molex 43045-4000 MicroFit 3.0, 4 pin header with Ignition Sense input
LED Indicators
RSSI, SVC, NET, GPS, AUX
Antenna Interface
Primary Antenna 50-ohm SMA Female
Diversity Antenna 50-ohm SMA Female
GPS Antenna (Mobile only) 50-ohm, 3.3V SMA Female
WiFi Antenna (Mobile only) 50-ohm RP-SMA Female
Size
4.5 (L) x 6.0 (W) x 1.9(H) inches (11.4 x 15.2 x 4.8 cm)
Weight
1.94lb (0.88 kg)
Power Input
9-32 VDC
Maximum TX Power
CDMA 25 dBm
GSM/EDGE 33 dBm
UMTS 24 dBm
Rx Sensitivity
CDMA >-107 dBm
GSM/EDGE >-105 dBm
UMTS >-109 dBm
Frequencies
Cellular: TX: 824-849 MHz; Rx: 869-894 MHz
PCS: TX: 1850-1910 MHz; Rx: 1930-1990 MHz
Temperature
Operating: -30°C to +70°C 100% duty cycle. Note: Cellular TX power may be reduced
outside this range; Storage: -40° to +85°C (-40° to +185°F)
Emissions
FCC Part 15b
Transport Protocols
UDP/TCP
Command Protocol
Web Interface
Multiple carriers in a single device
Supports dynamic or static IP
Inbound and outbound Ethernet routing
DHCP server and Inbound port mapping/translation (Port Forwarding)
Firewall configuration for increased network security
Diversity antenna port/auxiliary port for increased receive sensitivity
Local or remote configuration using HTML web server
TCP/IP packet assembler and disassembler for serial connected devices
Inbound IP termination with static IP
Modem domain names with dynamic DNS
Embedded Linux on ARM9 processor
Internet access and web browsing via Ethernet connector
VPN support
On board 1.8/3V SIM socket (Active only when GSM carrier is selected)
1.3 GENERAL SPECIFICAT IONS
Product specifications are subject to change without notice.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 2
Page 10
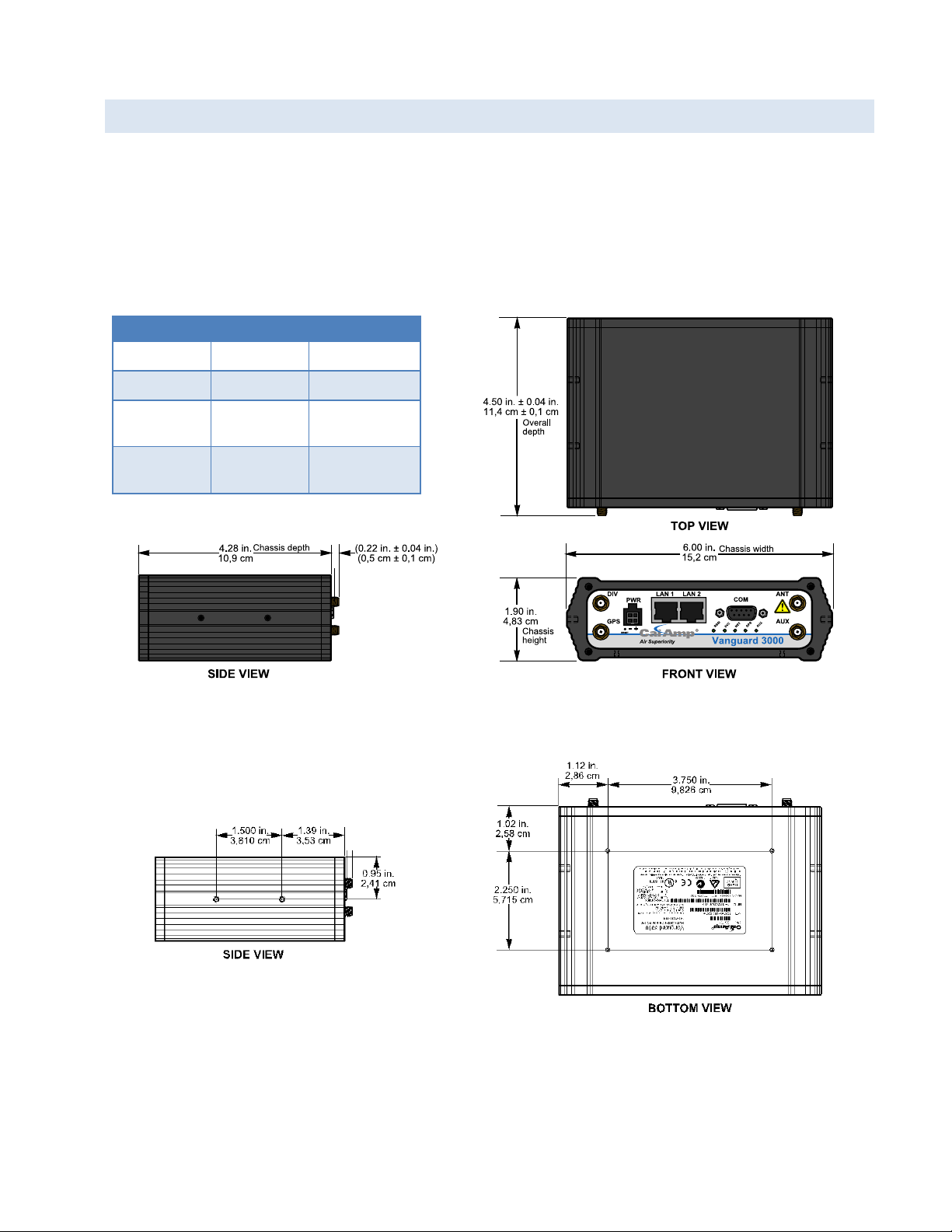
1.4 MECHANICAL SPE C IFICATIONS
Table 1 Vanguard router chassis overall dimensions
Dimension
Inches
Centimeters
Height
1.90
4,83
Width
6.00
15,2
Depth
(Overall)
4.50 ± 0.04
11,4 ± 0,1
Depth
(Chassis only)
4.28
10,9
Figure 3 Vanguard router chassis overall dimensions
Figure 4 Side tapped mounting hole location detail — typical
both sides.
#8-32 UNC – 2B thread × 0.30 in. (0,76 cm) depth
2 holes for mounting both sides (4 holes total).
Figure 5 Base tapped mounting hole location detail — bottom of chassis only.
#6-32 UNC – 2B thread × 0.12 in. (0,30 cm) depth
4 holes for base mounting (bottom surface only).
The following table and figure show overall dimensions of the Vanguard router for fixed and mobile models. (Both
models have the same dimensions and differ only slightly in appearance: the fixed model has only two antenna
connectors in the front of the unit, where the mobile model has four.) Dimensioned drawings of units with mounting
brackets are provided in APPENDIX B. The drawings and associated data may be used for layout reference, but it is
advised that a physical comparison be made to the modem and bracket before laying out and drilling mounting holes.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 3
Page 11
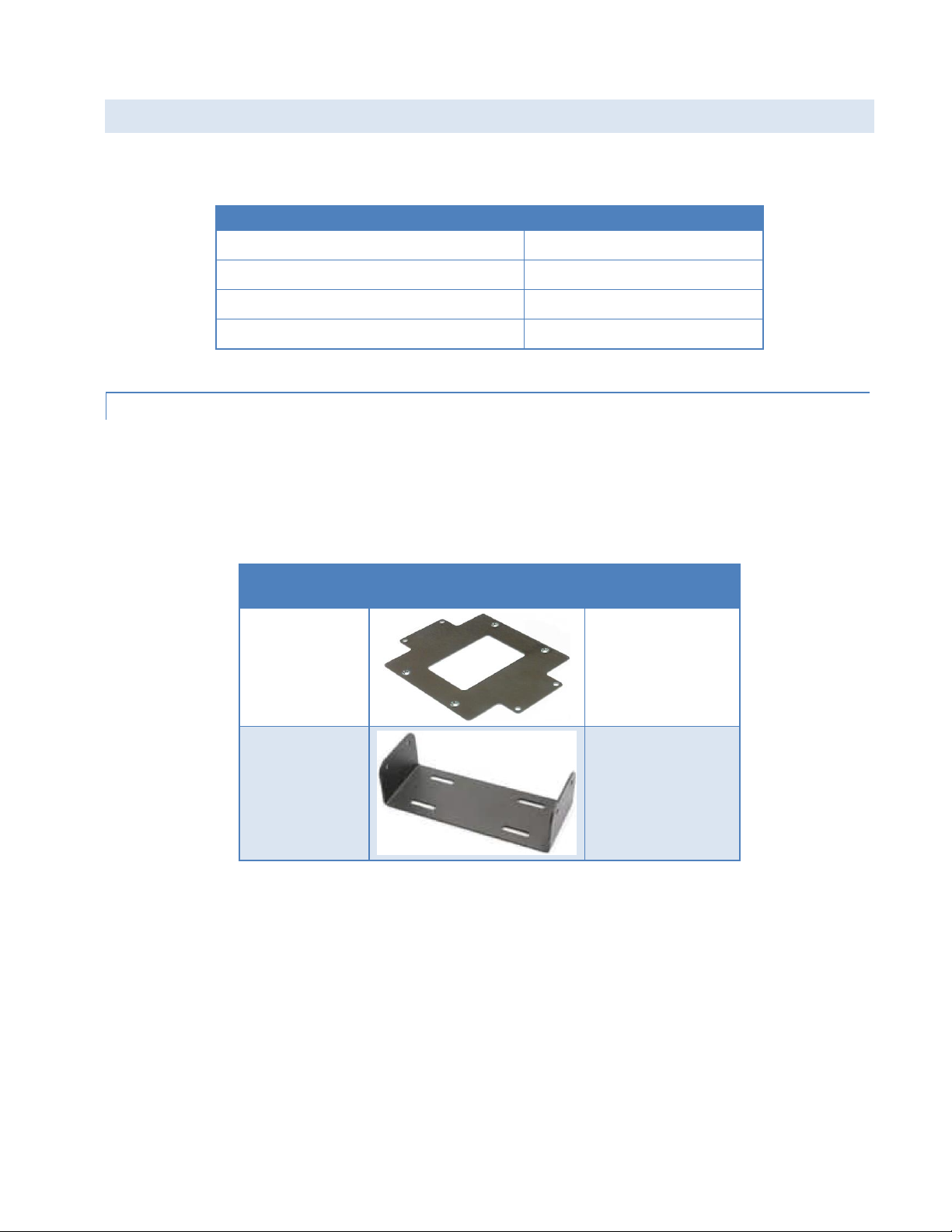
1.5 ORDER INFORMATION
Router
Model Part Number
Vanguard TM Fixed
VG-PXS-F-GEN
Vanguard
TM
Mobile
VG-PXS-M-GEN
Vanguard 5530
TM
Fixed
VG5530-PXS-F –GEN
Vanguard 5530
TM
Mobile
VG5530-PXS-M-GEN
Application
Bracket
Part Number /
Description
Fixed (standard)
817-7010-500
Flat plate
(fastens to the
bottom of the
Vanguard chassis)
Mobile
817-2225-900
U-bracket
(fastens to the sides
of Vanguard chassis
for top or bottom
mounting)
The following table shows the available order options and part numbers required for ordering Vanguard routers.
Table 2 Vanguard Router Order Information
1.5.1 MO U NTING BRACKETS
A mounting bracket is provided with each Vanguard. The type of bracket provided is determined by the typical
mounting method for each application.
For fixed-location applications, a flat-plate bracket provides for low-profile, space-saving bottom mounting.
For mobile applications, a U-shaped bracket is provided to allow for top- or bottom-mounting flexibility.
Table 3 Vanguard Mounting Brackets
Four screws are provided with each bracket to fasten the bracket to the body of the Vanguard router.
Fixed — Four #6-32 × ¼ (3/16-inch thread length) clear-zinc plated stainless steel Philips undercut flat head (82°
Mobile — Four #8-32 × ½ (3/8-inch thread length) black plated stainless steel slotted hex flange head cap screws
countersink) screws are provided to fasten the flat-plate mounting bracket to the bottom of the Vanguard chassis.
are provided to fasten the U-bracket at the sides of the Vanguard chassis for top- or bottom-mounting.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 4
Page 12
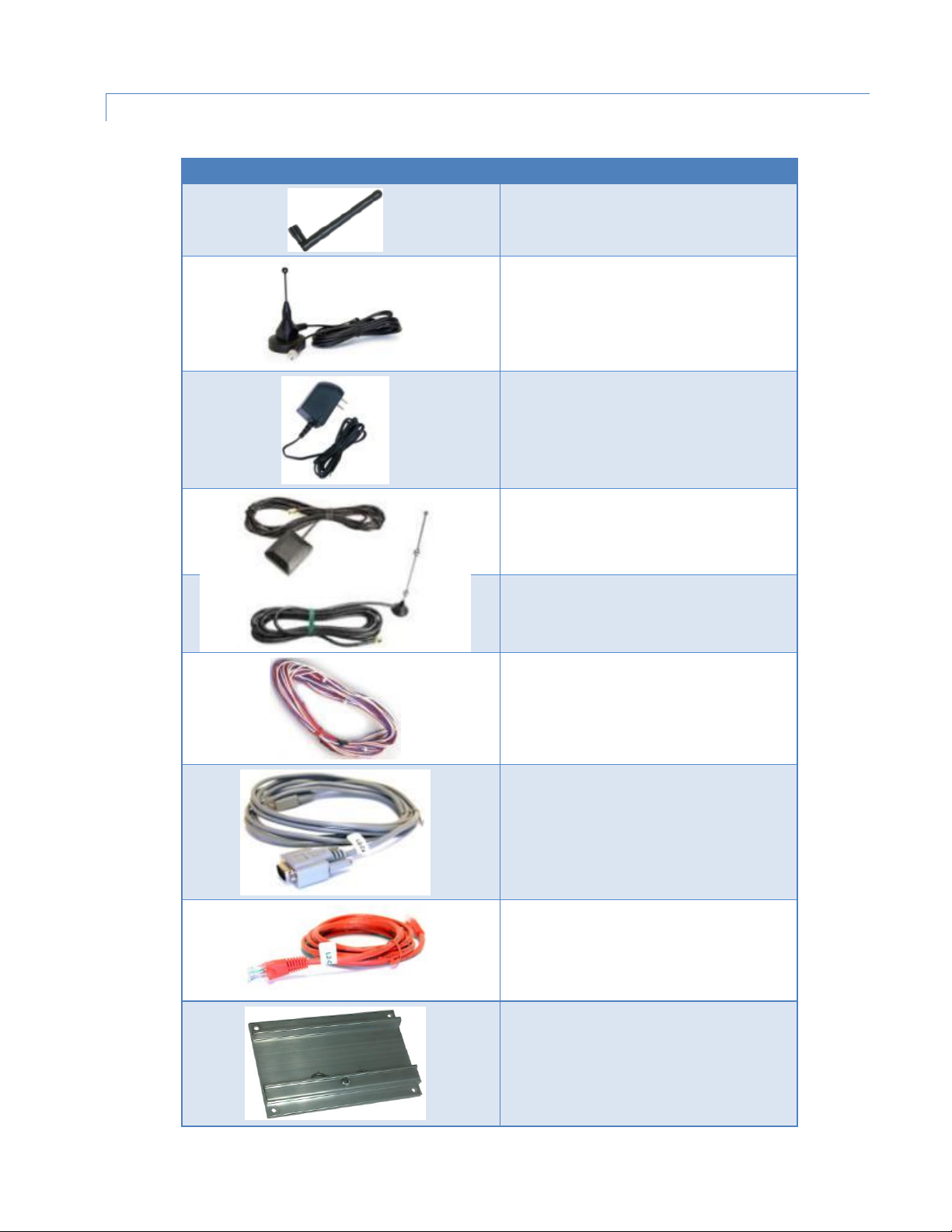
1.5.2 ACC E S S O R IES
Accessory
Part Number / Description
401-7500-001
4" plastic “Rubber Duck” style Antenna
L2ANT0003
3" Mag Mount Antenna
150-7001-005
110 VAC Input Power
401-7100-003
GPS SMA Mag-Mount Antenna
401-7100-004
WiFi Mag-Mount Antenna
150-7001-002
22' DC Power Cable (Mobile models)
150-7500-004
6' DC 3-wire Power Cable (Fixed models)
L2CAB0002
DE-9 Serial Cable
L2CAB0006
7' Ethernet Cable
250-5800-410
DIN Rail Mount — kit includes DIN
mounting plate assembly (with retainer
spring and screw), four #6-32 × ¼-inch
length cap screws and four #6 lock washers
for fastening to bottom of Vanguard chassis.
Table 4 Vanguard router Accessories
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 5
Page 13
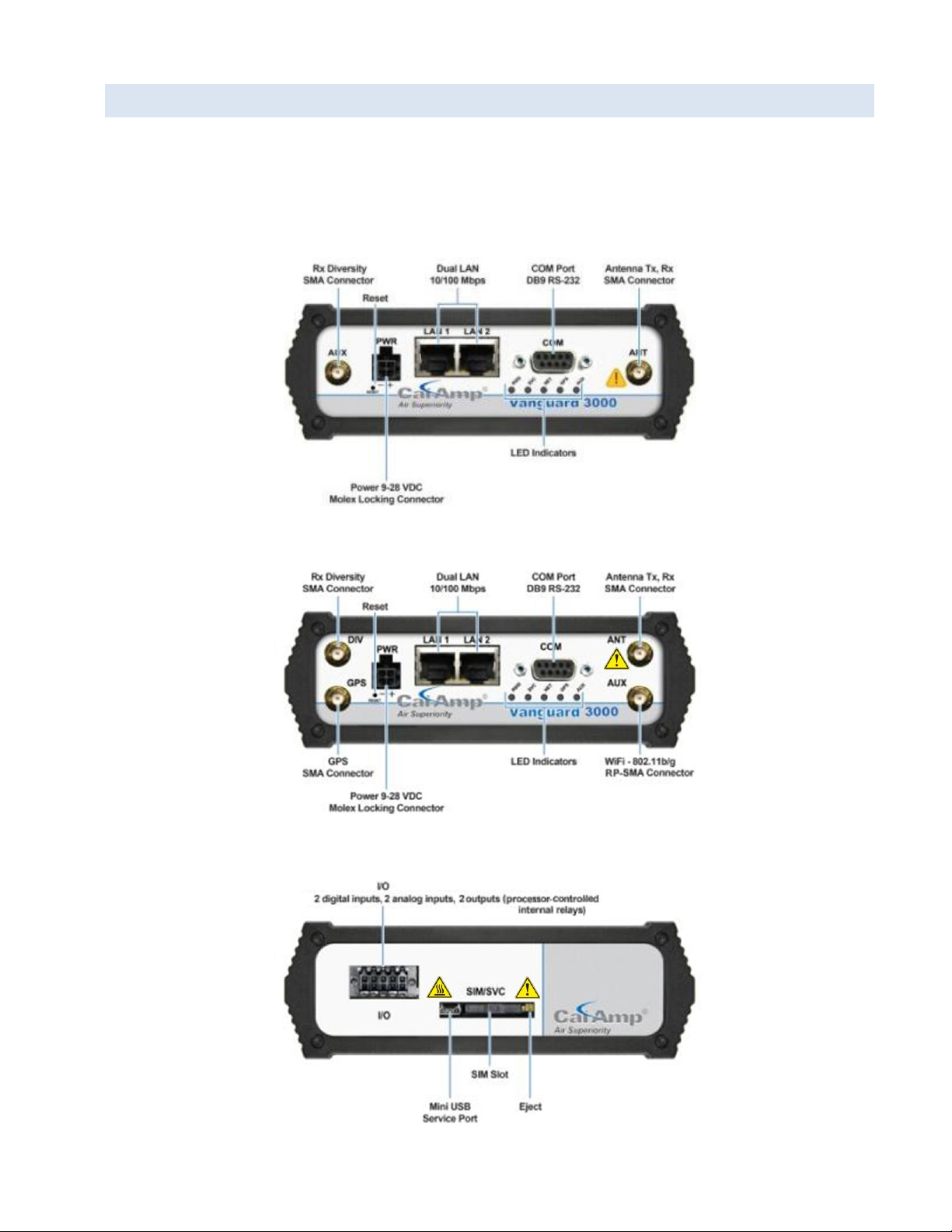
1.6 EXTERNAL CONNECTOR S
This section describes the external connectors for the Vanguard router.
Figure 6 shows the front panel connections for standard fixed models.
Figure 7 shows the front panel connections for Mobile models with GPS and WiFi.
Figure 8 shows the rear panel for all models.
Figure 6 Front panel — Standard Fixed models
Figure 7 Front panel — Mobile models with GPS and WiFi
Figure 8 Rear panel connections
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 6
Page 14
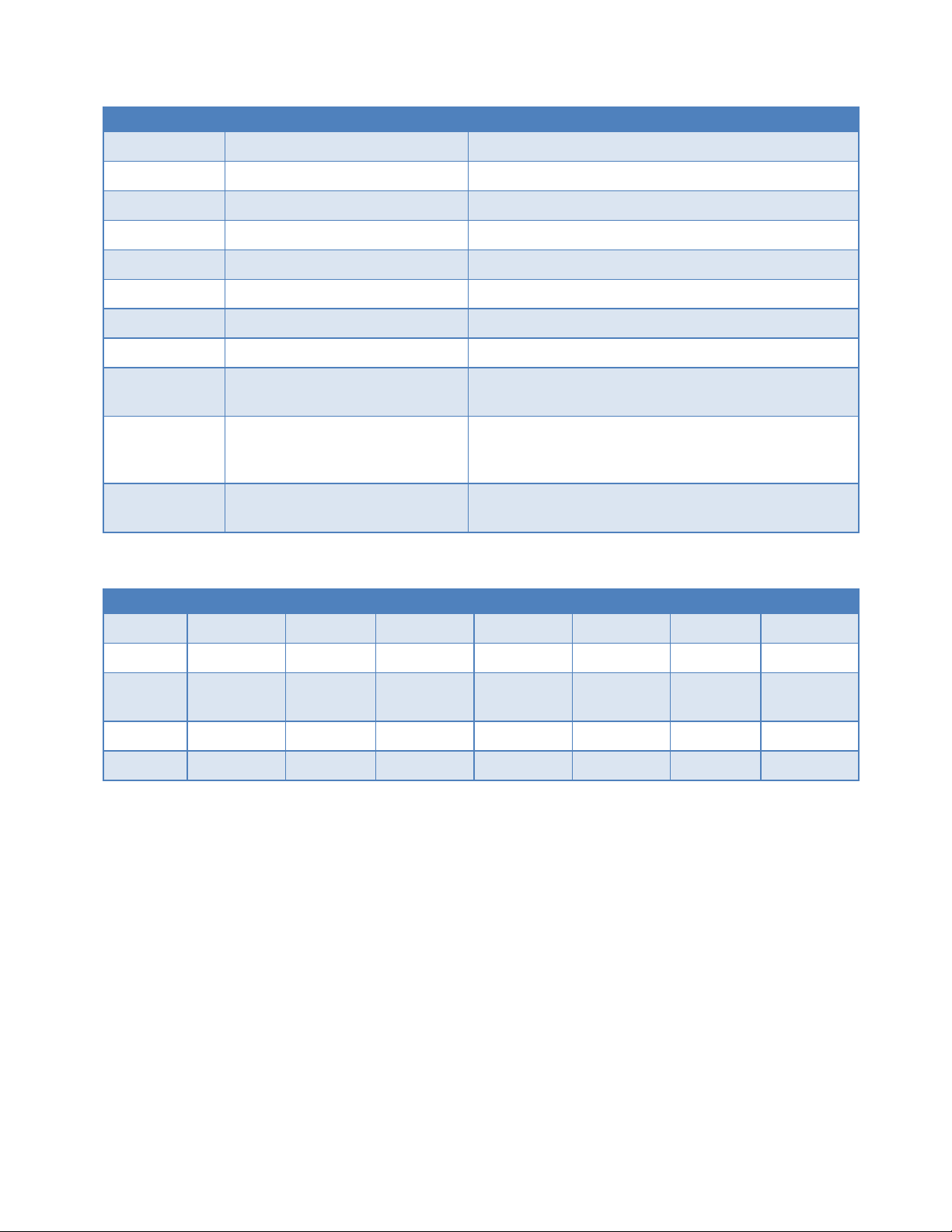
Table 5 External connectors
Panel Indicators
Connection
Description
COM
RS-232
Serial to IP conversion use
ANT
SMA
Primary RF Antenna
AUX (Figure 6)
SMA
Cellular Diversity antenna
AUX (Figure 7)
RP-SMA
WiFi antenna
GPS
SMA
GPS Antenna
DIV
SMA
Cellular Diversity Antenna
LAN 1, LAN 2
RJ-45
Interface for Ethernet connection to devices
SIM/SVC
USB Mini
Available for CalAmp Support Use Only
RESET
Hold for one second to reset unit. If held for at least 4 sec,
unit will reconfigure to factory default settings.
PWR Jack
Molex 43025-0400 receptacle for
four-pin power plug with optional
ignition sense
Bottom pins: +9-30VDC power (pin 1) and ground (pin 2)
Top pins: optional ignition-sense (3) and not connected (4).
See diagram for compatible cable on the following page.
SIM/SVC
SIM Card socket
Interface for SIM card. Your wireless service provider will
supply the SIM card with your wireless service contract.
Function
Off
Green
Flash Green
Red
Flash Red
Amber
Flash Amber
RSSI
Strong
Weak/None
Medium
SVC 3G/4G
3G/4G/NC
NC
2G
2G/NC
NET
No
connectivity
Rx data
Tx data
Rx/Tx
GPS
Disabled
Fix
Search
No fix
AUX
Disabled
Good
Failed
Table 6 Status LEDs
If SVC is solid, then the modem is connected to the Internet. If it is flashing, the modem is trying to connect to the
network.
AUX refers to WiFi in mobile models.
The LEDs behavior is different than the table at boot. The boot sequence is: all red, all amber, all green, all flash green
three times, and then the boot sequence is complete.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 7
Page 15
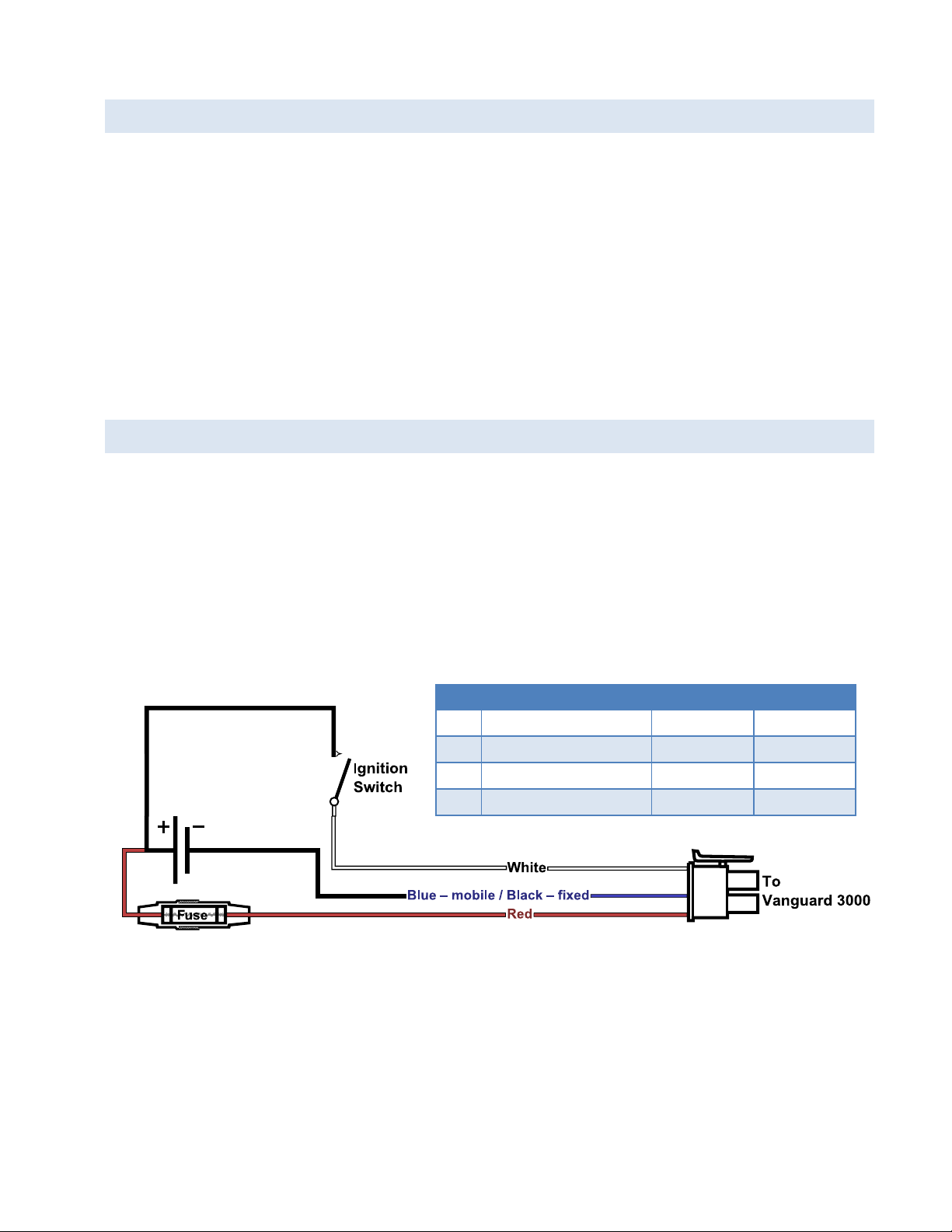
1.7 ANTENNA
Figure 9 Wiring for ignition sense
Table 7 Power Cable pin-out, signal, and wire colors
Pin
Signal
Color Mobile
Color Fixed
1
V
IN
/ V
Batt
= 9 to 28 VDC
Red
Red 2 Ground
Blue
Black
3
Ignition Sense
White
White
4
No Connect
NA
NA
Primary cellular antenna connections are SMA female connectors and must be used with antenna with SMA male
connectors. When using a direct mount or rubber duck antenna, choose the antenna specific to your band
requirements. Mounting options and cable lengths are user’s choice and application specific.
The diversity antenna connector, labeled AUX on fixed location models and DIV on mobile models, can be used for a
Diversity antenna. The diversity port supports Cellular (850 MHz) and PCS (1900 MHz) bands. Connect a dual band
cellular antenna to this port to implement RX diversity on the unit and increase receive sensitivity on the cellular
network.
For mobile models equipped with 802.11, the antenna connector labeled AUX is an RP-SMA female connector for 2.4
GHz WiFi that facilitates 802.11 b and 802.11 g wireless networks.
1.8 POWER CABLE P I NO U T
Depending on the version (fixed or mobile) of Vanguard router ordered, different power cables are provided. The
mobile version ships with a 22-foot power cable that requires a fuse (included). The fixed version ships with a 6 foot DC
three-wire power cable that does not contain a fuse. An AC power adapter is available as an optional accessory.
Regardless of the cable length, the pinout is the same and only the color of the ground wire differs (blue in the mobile
wire harness, and black in the fixed).
When installed for a fixed application or if the Ignition-sense line is not required in a mobile application, the ignition
sense line (white wire) should be shorted to VIN / V
(red wire).
Battery
The fuse provided inside the fuse-holder that is part of the wiring for mobile applications is a 2 Amp fast-acting fuse
(EF2AL250VP).
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 8
Page 16
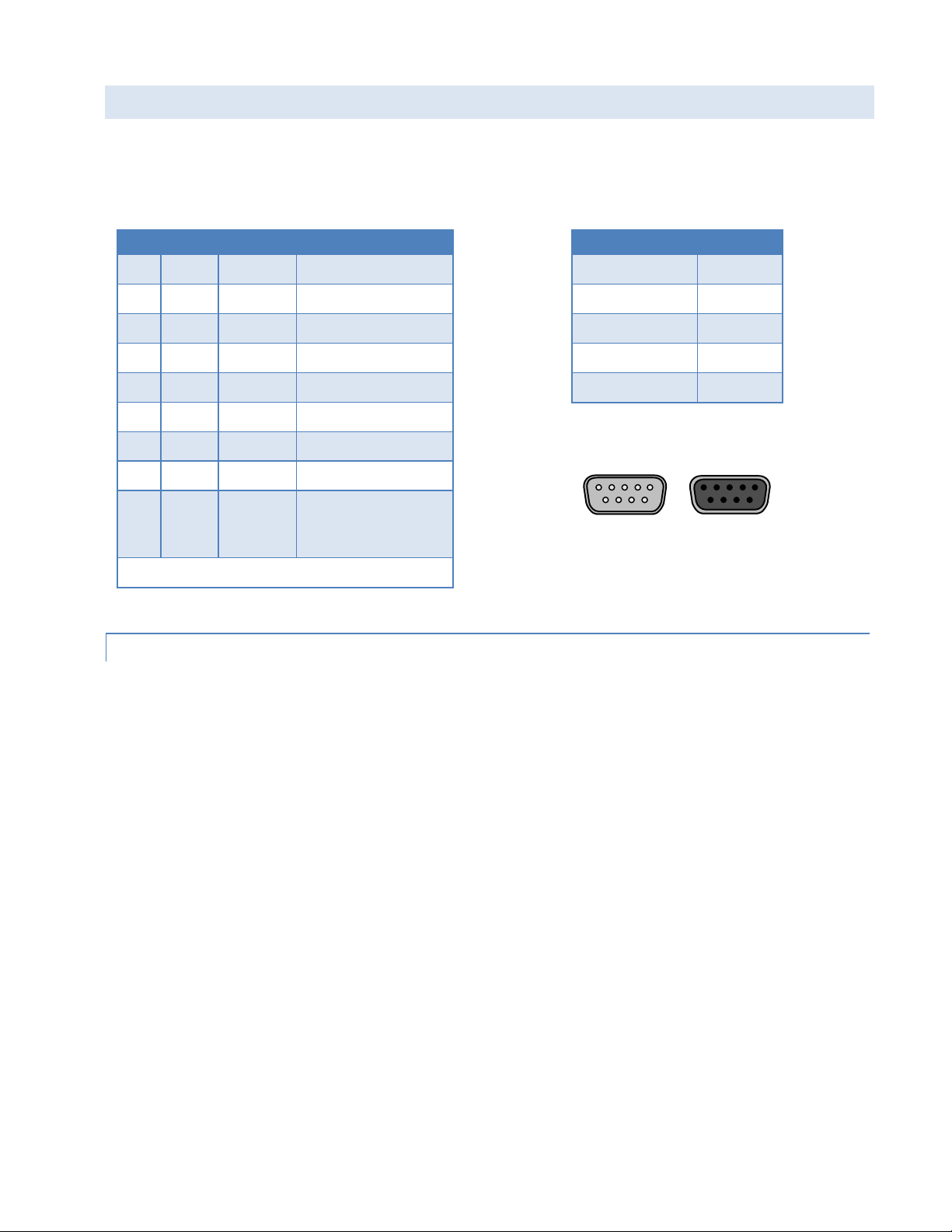
1.9 RS-232 SERIAL PO R T INTEGRATION P AR AM E T ERS
Table 8 Standard RS-232 DE-9 Pinout
Pin
Name
Direction
Description
1
CD ← Carrier Detect
2
RX ← Receive Data
3
TX → Transmit Data
4
DTR → Data Terminal Ready
5
GND
System Ground
6
DSR ← Data Set Ready
7
RTS → Request to Send
8
CTS ← Clear to Send
9
RI ← Ring Indicator
(tied to + 5 V DC in
the Vanguard )
Note: Direction is DTE relative DCE
Table 9 Default RS-232 Communications Parameters
Parameter
Value
Bits Per Second
115,200
Data Bits
8
Parity
None
Stop Bits
1
Flow Control
None
Figure 10 DE-9 Connectors
1 15 5
6 9 9 6
Male Female
Table 8 provides the serial cable design information to integrate the Vanguard modem into your system. Table 9 gives
the default RS-232 communication parameters.
1.9.1 OD P (OPEN DEVELOPERS PLATFORM) OVER RS -232
This device includes the Open Developers Platform (ODP), which permits customers to develop their own Linux based
applications which run on the modem’s ARM9 processor. The customer’s application can utilize the external RS-232
port, the external I/O port, and/or an internal 3 pin (GND, RXD, TXD) RS-232 port and is able to transfer data over the
cellular WAN using the Linux socket libraries. The Vanguard firmware also supports an API that allows the customer’s
application to access diagnostic data from the cell module such as connection status and RSSI. More information and
support is provided by CalAmp’s Applications Engineering organization.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 9
Page 17

2 GETTING STARTED
2.1 PACKAGE CONTENTS
Vanguard Router
Power Cable
Mounting bracket
Quick-Start Guide
Installation Guide
Information Card
2.2 DEVICE CONNECTIONS
1. (GSM users) Place the SIM card in the tray and insert it into the SIM/SVC slot as shown.
Figure 11 Place SIM card in SIM/SVC tray and insert tray in slot
2. Connect a cellular antenna (for Tx/Rx) to the female SMA connector labeled ANT on the front of the Vanguard
modem. Optionally, a second cellular antenna may be connected to the female SMA connector on the front panel
of the Vanguard modem for Rx diversity. The Rx diversity SMA connector is labeled AUX on fixed-location model
and labeled DIV on mobile models.
Note: Use of dual band cellular antennas is preferred.
3. Connect an Ethernet cable into the LAN 1 port and plug the other end into the network port of your PC.
4. Connect the DC power cable (or optional AC power adapter) to an applicable power source and plug the connector
into the modem power (PWR) connector. If using the fused power cable to connect to a DC supply (car battery),
use the diagram in Figure 9 Wiring for ignition sense and accompanying pin-out information in Table 7 to connect
the unit.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 10
Page 18
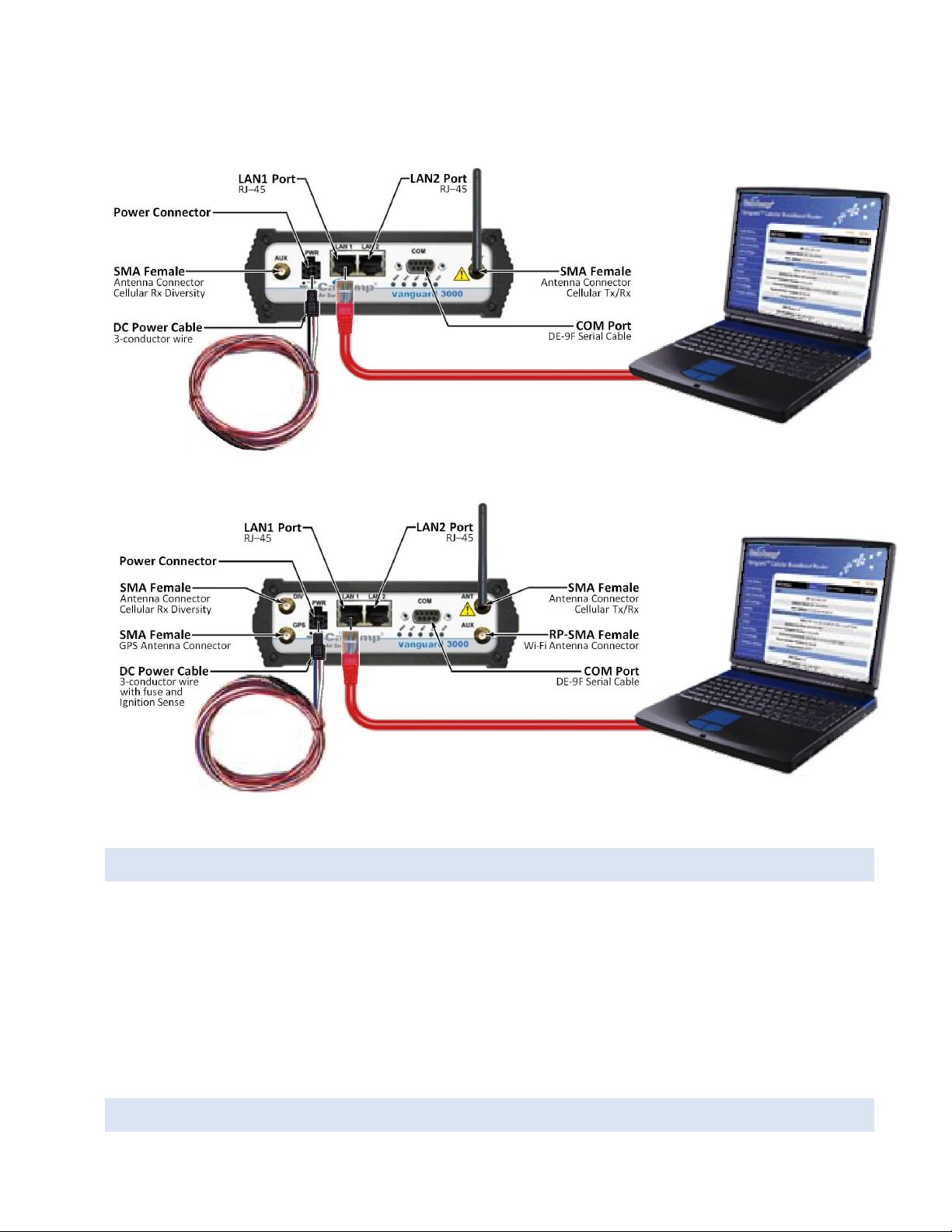
Figure 12 Connect antenna to ANT connector, connect Ethernet cable to LAN 1, and connect power cable
Fixed model
Mobile model
2.3 LAN CONFIGURATION
The Vanguard router is configured via a Web-browser interface and contains a DHCP server which will automatically
assign an IP address to your computer, however in some cases it may be necessary to change the network settings on
your computer to accept the IP address assigned by the Vanguard. Refer to your operating system documentation for
detailed network setup instructions.
Figure 13 LAN Configuration Windows
2.4 CELLULAR CONNECTIO N S
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 11
Page 19
Before you begin, you will need an active Cellular account with the carrier of your choice.
2.4.1 GS M USERS
Insert the SIM card with the gold side up into the SIM/SVC slot in the rear of the device. Push the card completely into
the slot until it clicks in place. If you have already powered your device, you will need to cycle power to register the SIM
for proper operation.
2.4.2 CD M A USERS
Refer to Section 3.2.3 to provision your modem for proper operation.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 12
Page 20
3 VA NGUARD WEB INTERFA CE
Figure 14 CalAmp Vanguard Cellular Broadband Router Web Interface banner
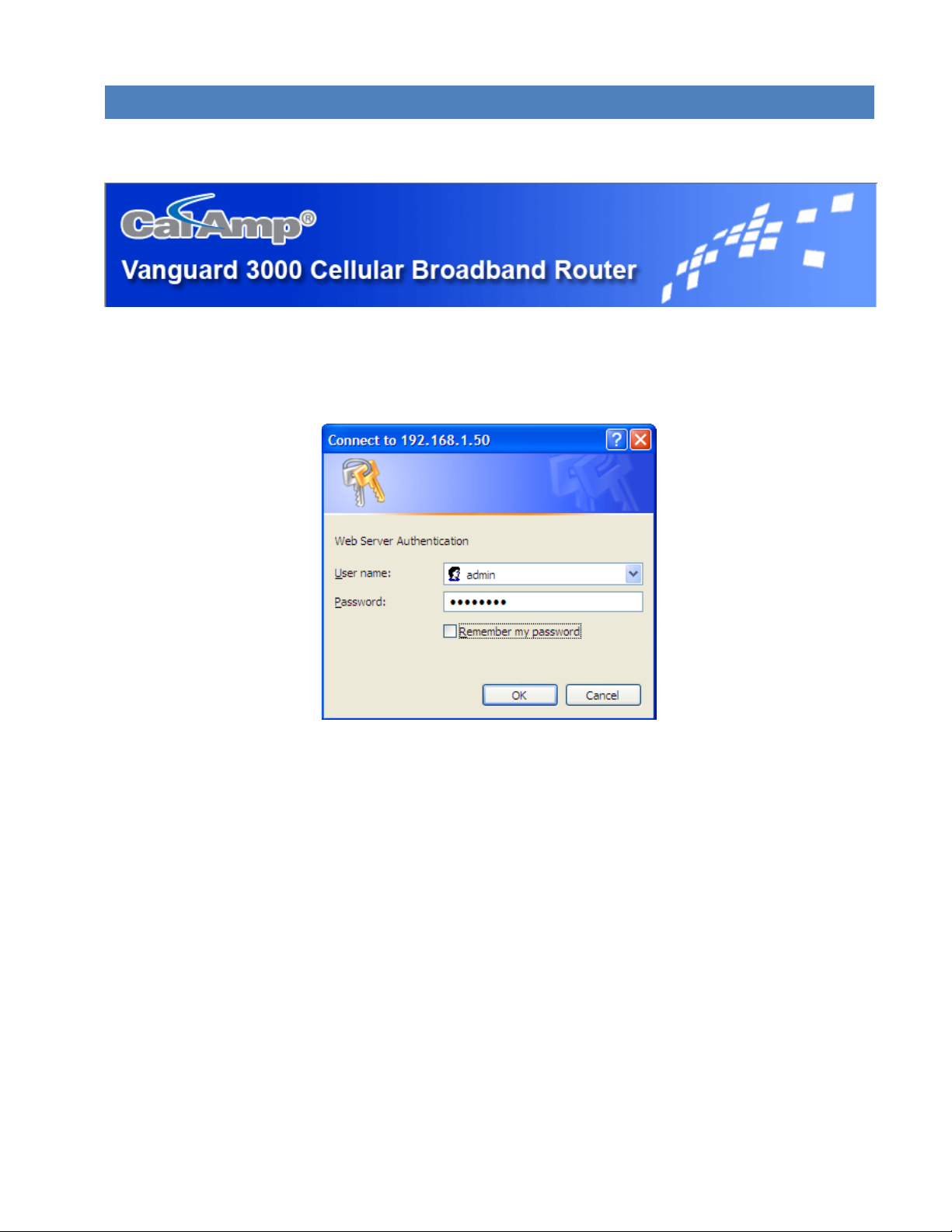
Start your Web browser and enter 192.168.1.50 in the address bar. A Web Server Authentication window appears.
Figure 15 Web Server Authentication window
Enter the User Name: admin and the Password: password and click OK to log into the modem’s Home Page. Vanguard
Web interface is divided into two sections. On the left is the main navigation pane (shown in the following figure). On
the right is the content area for the desired page (shown on the following pages).
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 13
Page 21

Figure 16 Main Navigation Pane — Fixed (standard)
Figure 17 Main Navigation Pane — Mobile (with GPS and WiFi)
Note: If the computer you are using has previously been used to set up a CalAmp router, you may need to delete
browser history (specifically, temporary Internet files) for some pages of the web interface to display correctly.
If you have a Fixed (standard) model, you will not see options in the navigation pane for WLAN Settings or GPS that
appear for the Mobile model.
3.1 UNIT STATUS
The Unit Status is the first page displayed when navigating to the Vanguard modem Web interface and is the home
page of the modem Web interface. Select Unit Status from the left navigation pane (or select Home) to return to this
page. From this page you can view Status or Identity information or access Basic Settings of the modem.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 14
Page 22
3.1.1 ST A T U S
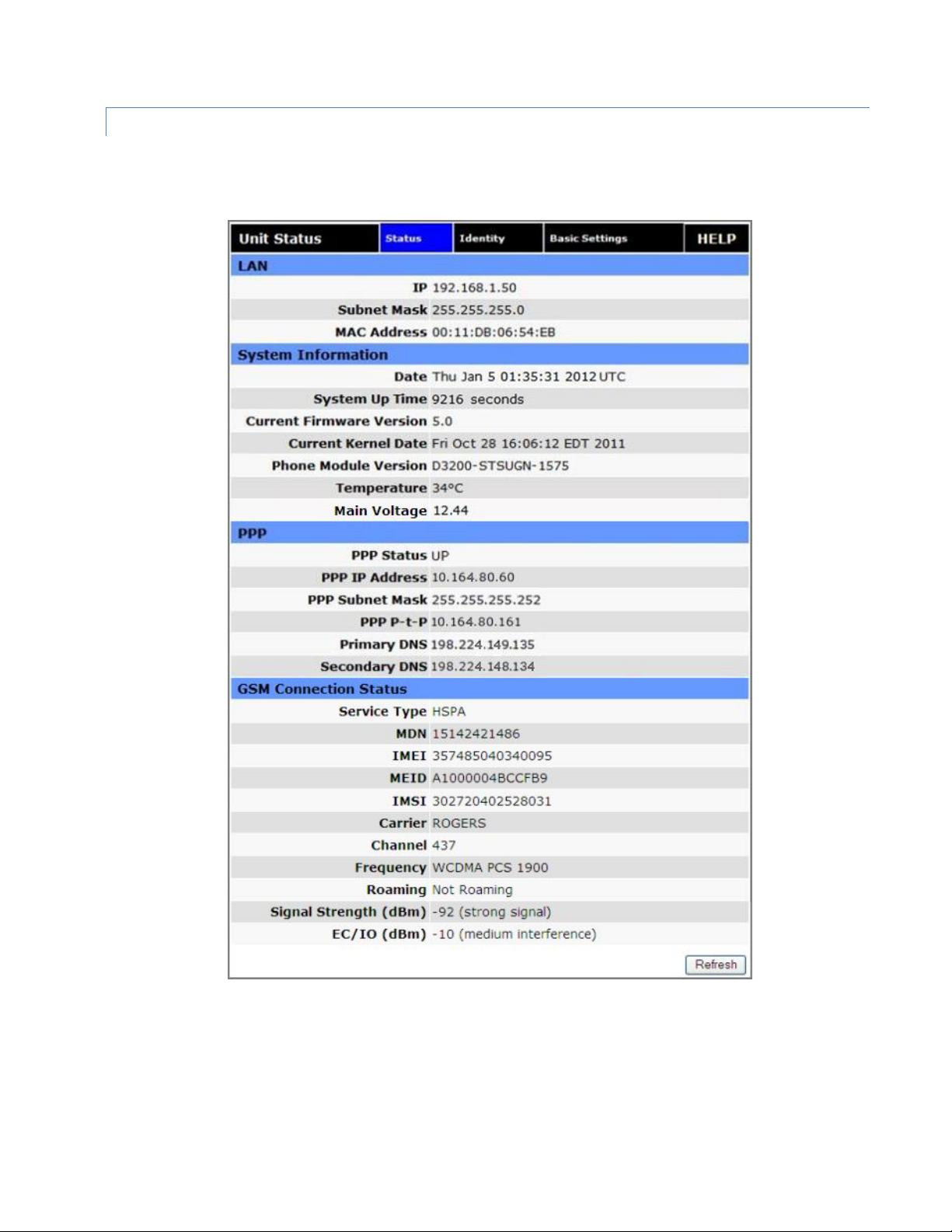
The Status tab for GSM or CDMA (3G Only) is displayed, depending on your configuration.
Figure 18 Vanguard Unit Status (GSM) Status tab
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 15
Page 23
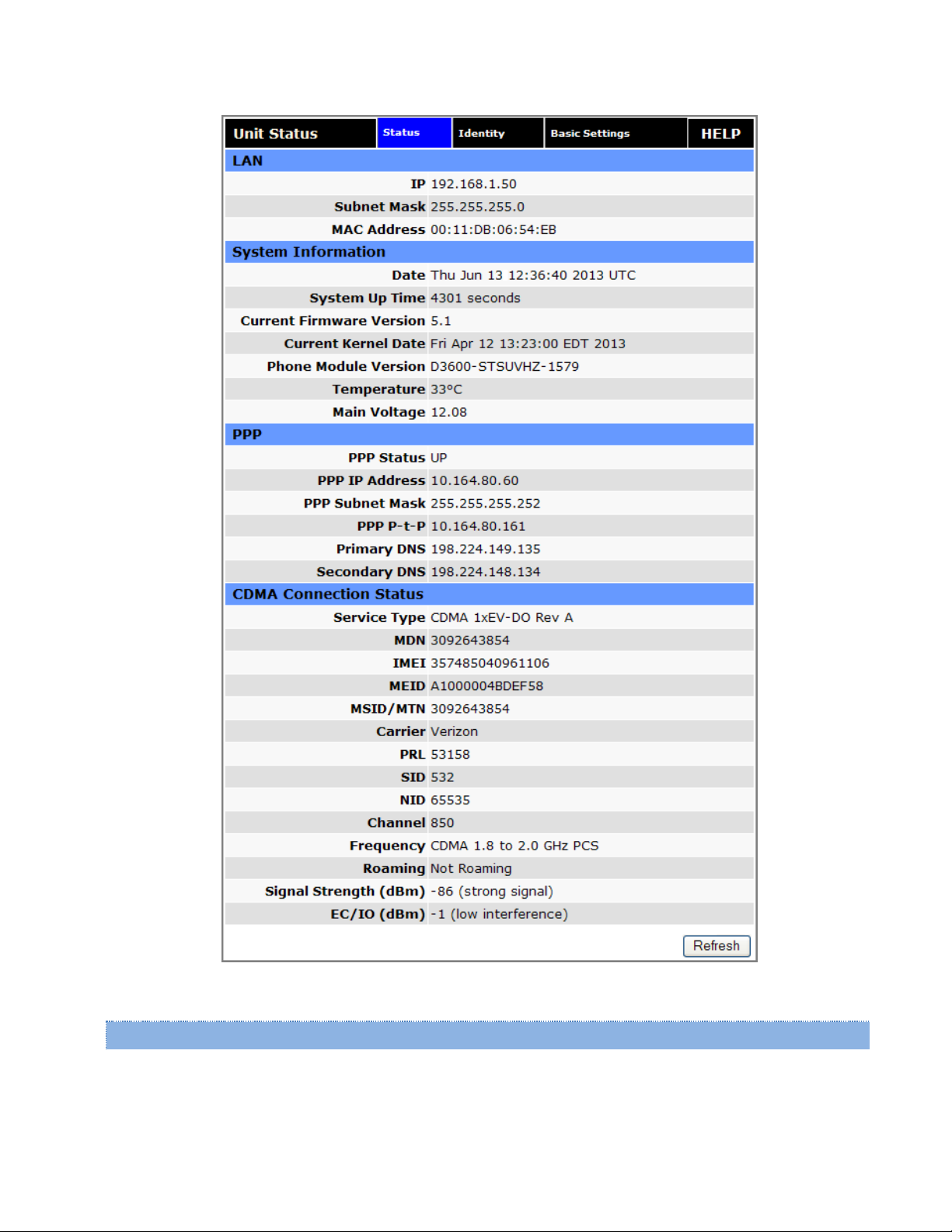
Figure 19 Vanguard Unit Status (CDMA) Status tab
LAN
IP
LAN IP address of this device (the modem).
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 16
Page 24
Subnet Mask
LAN subnet mask for the modem.
MAC Address
Media Access Control Address. Every Ethernet device (i.e. LAN cards) has a unique hardware serial number or MAC
address to identify each Network Device from all others.
System Information
Date
Current date and time (UTC) as received from the GPS receiver (mobile models) or from a time server (see Basic
Settings » Network Time).
System Up time
Uptime in seconds.
― 1 minute = 60 seconds.
― 1 hour = 3600 seconds.
― 1 day =86,400 seconds.
― 1 (365-day) year = 31,536,000 seconds.
Current Firmware Version
Firmware version currently loaded. Please visit www.calamp.com for the latest updates.
Kernel Date
Date of the operating system kernel the unit is running.
Phone Module Version
Varies depending on the active carrier. See the Carrier tab of the Cell Connection page.
Temperature
Current internal temperature of the Vanguard .
Main Voltage
System input voltage sensed by the nmode.
PPP
PPP Status
Status of the cellular connection, usually UP when connected properly. May display additional status information in
parenthesis when Automatic Carrier Switching Is enabled.
PPP IP Address
IP address of the Vanguard on the cellular network.
PPP Subnet Mask
Subnet Mask of the Vanguard on the cellular network.
PPP P-t-P
The “point-to-point” address of the gateway on the cellular network, It may be possible to ping this address to
determine if a PPP IP Address assigned is routable from the Internet.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 17
Page 25

Primary DNS
The Primary DNS server, as assigned by the cellular carrier, when PPP is UP.
Secondary DNS
The Secondary DNS server, as assigned by the cellular carrier, when PPP is UP.
CDMA Connection Status
Service Type
Determines the type of network your device is connected to; GPRS, EDGE, UMTS, HSDPA, CDMA 1xRTT, EVDO Rev0
or RevA.
ESN
The Electronic Serial Number is only applicable for the CDMA product line, and is carrier specific (Verizon, Sprint,
etc).
MDN/MTN
The actual phone number of the device as supplied by the carrier. When the unit is successfully provisioned, the
phone number for the user account will be displayed.
MIN/IMSI
This number is used by the Mobile Telephone Network and will be different if ported from another carrier (not used
by end user of device).
PRL
Preferred Roaming List, only applicable for the CDMA product line, carrier specific (Verizon, Sprint, etc).
SID
System ID (Identity), provided by the Carrier.
NID
Network Identifier, as reported by the network.
Channel
Cell Site channel number at which the modem is connected. This may be used by the carrier for troubleshooting.
Frequency
Cellular frequency band the modem is using. All U.S. carriers use 800MHz and/or 1900MHz; carriers in other
countries may use 850MHz or 450MHz.
Roaming
Options are either Roaming or Not Roaming and may defer from the PRL in the case of CDMA.
Signal Strength (dBm)
Measured in dBm, this is the Received Signal Strength Indication (RSSI).
EC/IO
Measured in dBm, EC/IO is a measure of interference. Values closer to 0 indicate weaker interference.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 18
Page 26

GSM Connection Status
Service Type
Determines the type of network your device has connected to; GPRS, EDGE, HSDPA, HSUPA, or HSPA. "Check SIM"
will be displayed if the SIM is invalid, missing, or if the PIN needs to be entered.
MDN
The Mobile Directory Number is the phone number assigned to the SIM card supplied by the carrier. The MDN may
display “NOT AVAILABLE” if the PIN status is disabled or the MDN is unknown.
IMEI
The International Mobile Equipment Identity is a unique 15-digit number that serves as the serial number of the
GSM module in the modem.
IMSI
The International Mobile Subscriber Identity is a unique number which designates the subscriber. This number is
used for provisioning in network elements. The IMSI may display “NOT AVAILABLE” if a SIM card is not detected.
Country
Country name or code associated with the GSM network.
Carrier
Cellular provider name or code.
Cell ID
Network Identifier, this is supplied automatically from the network.
Channel
Cell Site channel number at which the modem is connected and is useful for the carrier in the event of
troubleshooting.
Frequency
Cellular frequency band the modem is using. All U.S. carriers use 850MHz and/or 1900MHz; carriers in other
countries may use 900MHz or 1800MHz.
Roaming
Options are either Roaming or Not Roaming.
Signal Strength (dBm)
Measured in dBm, this is the Received Signal Strength Indication (RSSI).
EC/IO
Measured in dBm, EC/IO is a measure of interference. Values closer to 0 indicate weaker interference.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 19
Page 27
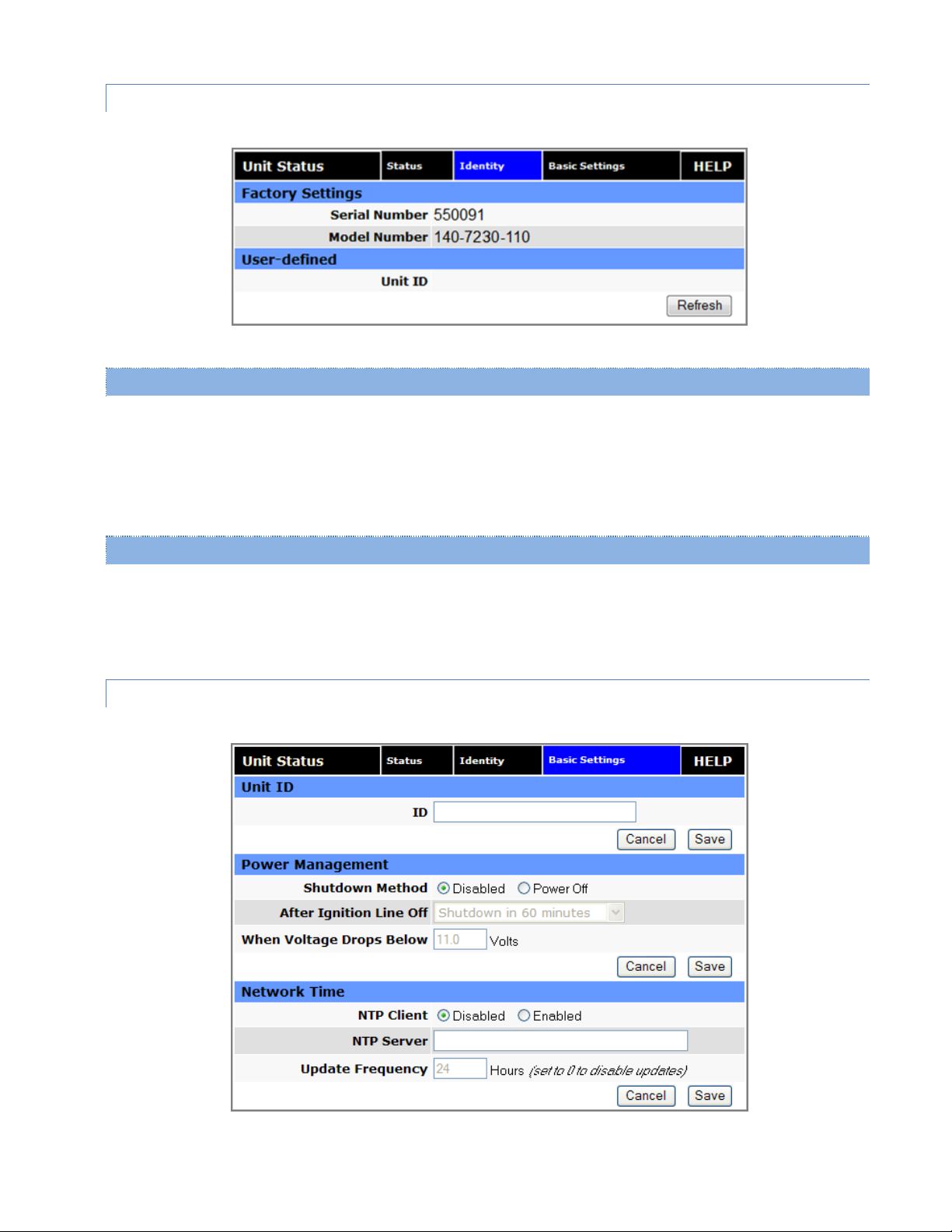
3.1.2 ID E N T I T Y
Figure 20 Unit Status — Identity
Factory Settings
Serial Number
Unique serial number for this unit.
Model Number
Unit model number defining its capacity and features.
User-defined
Unit ID
The User-defined ID set in Basic Settings (see below). Used by SNMP and other services to identify the modem.
3.1.3 BASIC SETTINGS
Figure 21 Unit Status — Basic Settings
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 20
Page 28
Unit ID
ID
Identification number that distinguishes this unit from other units in the network. Unit ID also serves as the TAIP
identification used for GPS reporting, and serves as the 'syslocation' for SNMP..
Power Management
The Vanguard staysON regardless of whether the vehicle ignition is on. The unit can be configured to automatically
shut down 1, 5, 30, 60 or 240 minutes after ignition has been turned off or when the supply voltage drops to a certain
level. Leaving the unit live allows the driver to use the modem without idling the vehicle; defining a shut-off time limit
prevents the modem from draining the battery when the vehicle is unoccupied.
Shutdown Method
Disabled by default. Select "Power off" to enable power management.
After Ignition Line Off
Select a time limit: 1, 5, 30, 60 or 240 minutes.
When Voltage Drops Below
Enter desired voltage. Enter "0" to disable (and give precedence to the “After Ignition Line Off” time limit).
Network Time
The Vanguard is capable of maintaining the current time (UTC) by synchronizing itself with a Network Time Protocol
(NTP) Server. The user may specify a server URL and how frequently the router should synchronize with the server. The
router must have an internet connection to synchronize with the server. The router does not save or track time while
powered off, so time will be inaccurate until the router can connect with the server, which it does on startup (in
addition to synchronizing according the Update Frequency specified).
NTP Client
Disabled by default. Select Enabled to activate the router’s NTP client to synchronize with the specified server.
NTP Server
Enter the URL of the desired NTP Server. Most NTP Servers have a posted usage policy. A review of usage policies
and the choice of an appropriate server is recommended.
Update Frequency
Set to 24 hours by default. Specify the frequency to synchronize the router time with the specified NTP Server.
3.2 CELL CONNECTION
Select Cell Connection from the left navigation pane to access the carrier, GSM, CDMA, System Monitor, and Dynamic
DNS settings tabs.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 21
Page 29
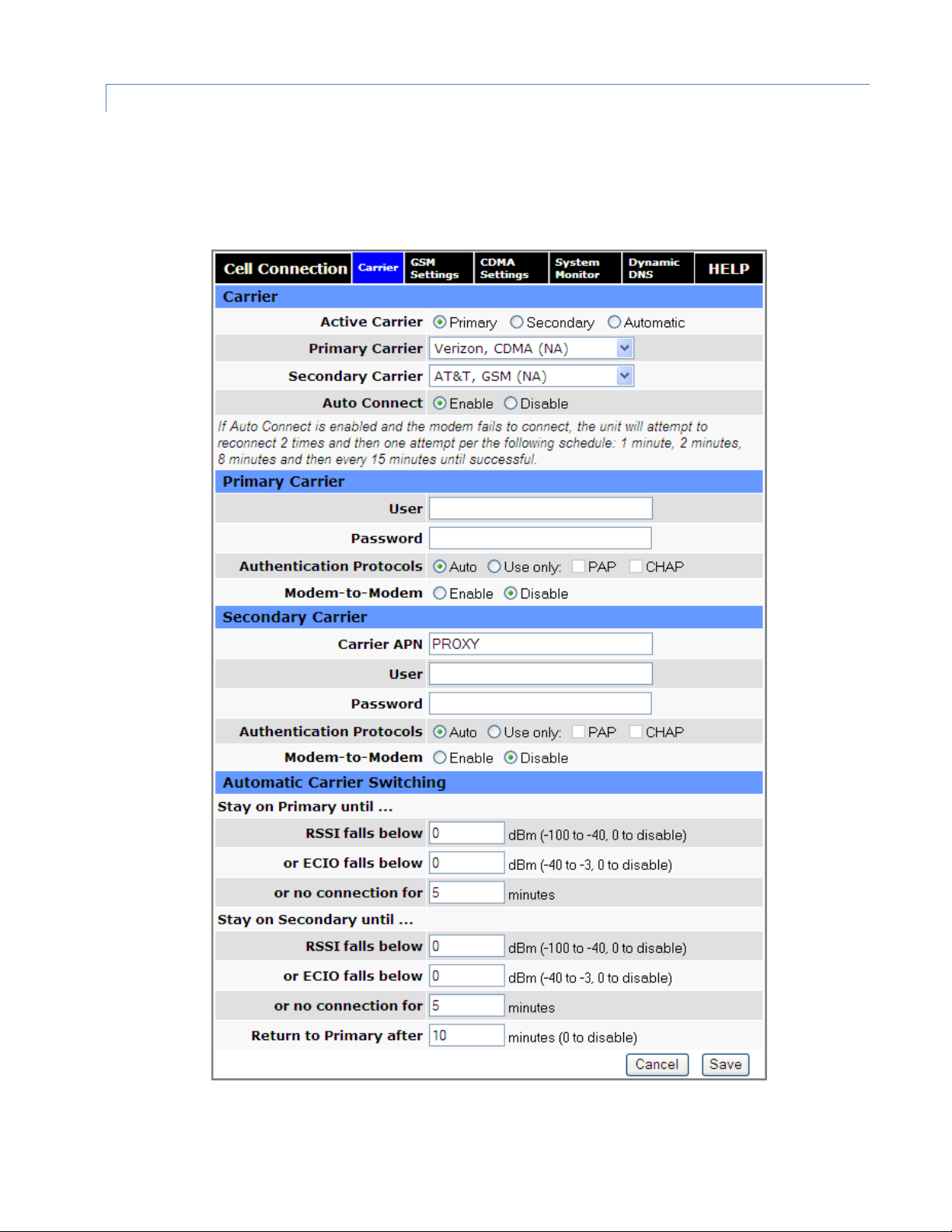
3.2.1 CAR R I E R
Use the carrier tab to configure the carrier (cellular provider) and credentials to be use for data calls. Two carriers can
be configured and either of them chosen to be the active carrier, or you can set parameters for automatic carrier
switching. Depending on the carrier(s) selected, more settings and actions are available in the GSM Settings or CDMA
settings tabs.
Figure 22 Cell Connection — Carrier
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 22
Page 30

Carrier
Active Carrier
Select which carrier, Primary or Secondary (3G Only), and credentials to use for carrier connection. The Secondary
Carrier cannot be selected if None is selected from the list. Changing carrier selections may take up to a minute to
complete and refresh the page after you click Save. Select Automatic to have the modem choose a carrier based on
conditions defined in the Automatic Carrier Switching section at the bottom of the page.
Primary Carrier
Select the appropriate carrier with cellular protocol (GSM/CDMA) from this list that will serve as the primary carrier.
The Primary Carrier selected cannot be the same as the Secondary Carrier. GSM carriers require that a proper SIM
be installed.
Secondary Carrier (3G Only)
Select the appropriate carrier with cellular protocol (GSM/CDMA) from this list that will serve as the secondary
carrier. This selection cannot be the same as the Primary Carrier. If there is no secondary carrier, select None. GSM
carriers require that a valid SIM be installed.
Auto Connect
Select Enable (the default and recommended setting), and the modem will automatically dial the connection upon
startup, and to attempt reconnection if the connection is lost. Select Disable to prevent the modem from
automatically connecting upon startup.
If Auto Connect is enabled and the modem fails to connect, the unit will attempt to reconnect two times and then
make an attempt at one minute, at two minutes, at eight minutes, and then every fifteen minutes until successful.
Primary Carrier / Secondary Carrier (details)
Carrier APN
This field is visible only when the corresponding carrier supports GSM. Enter the APN provided by the carrier.
User
If your cellular provider requires a user name, enter it here. Leave blank if not required.
CAUTION: If used in combination with this modem’s VPN server, this user name and password (below) will also be
valid on this modem’s VPN server.
Password
If your cellular provider requires a password, enter it here. Leave blank if not required. See the Caution message
associated with the User field above.
Authentication Protocols
Select the authentication protocol used. If Auto is selected (the default and recommended setting for most
applications), the Vanguard will try to negotiate a protocol with the cell tower if the cellular carrier allows
negotiation. If Use Only is chosen, then the Vanguard will only offer to connect using the specified protocol(s),
where PAP is Password Authentication Protocol and CHAP is Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol.
Note: Normally the cell provider does not require a username or password, in which case leave the User and
Password fields blank. An issue has been identified with SIMs from two carriers (AT&T and Bell Mobility) for special
applications where a username and password are required (which is uncommon but possible). In this case, it is
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 23
Page 31

necessary to select either PAP or CHAP authentication establish a PPP session. (Selecting Auto will not connect.)
Selecting either PAP or CHAP will allow connection.
Modem-to-Modem
In applications that require modems to communicate directly with each other, as compared to communicating only
with Hosts or having a Host relaying communications between two modems, carriers might assign “nearby” IP
addresses to the other modems which overlap with the network defined by Unit Status » PPP » PPP IP Address and
PPP Subnet Mask. Set this to Enable to force the PPP Subnet Mask to 255.255.255.255 to work around this.
Important: This setting may not resolve this issue in all cases. It may be necessary to request that the carrier
reassign IP addresses of some modems.
Automatic Carrier Switching
Stay on Primary until
Settings in this section allow you to set parameters so that if the modem is unable to connect to the primary carrier,
sees a low received signal strength or ECIO, or loses connection with the primary carrier for the number of minutes you
specify, the modem will switch to the secondary carrier. The switchover from primary to secondary, or vice versa, will
take 30-60 seconds, during which the device will not have network connectivity.
RSSI falls below
If the received signal strength for the primary carrier falls below this number, the modem will switch to the
secondary carrier. Enter the RSSI level threshold for which if the primary carrier connection drops below, the system
will attempt to switch to the secondary carrier. (To disable automatic switching to the secondary carrier determined
by RSSI, enter 0.)
or ECIO falls below
If the ECIO for the primary carrier falls below this number, the modem will switch to the secondary carrier. (To
disable automatic switching to the secondary carrier determined by ECIO, enter 0.)
or no connection for
Enter the number of minutes for which to wait before attempting to switch to the secondary carrier if the primary
carrier connection is dropped.
Stay on Secondary until
Settings in this section allow you to set parameters so that once the modem has switched service to the secondary
carrier, it will attempt to maintain connection with the secondary carrier unless it is unable to connect, sees a low
received signal strength or ECIO, or loses connection with the secondary carrier for the number of minutes you specify.
RSSI falls below
If the received signal strength for the secondary carrier falls below this number, the modem will switch to the
primary carrier. (To disable automatic switching to the primary carrier determined by RSSI, enter 0.)
or ECIO falls below
If the ECIO for the secondary carrier falls below this number, the modem will switch to the primary carrier. (To
disable automatic switching to the primary carrier determined by ECIO, enter 0.)
or no connection for
Enter the number of minutes for which to wait before attempting to switch to the primary carrier if the secondary
carrier connection is dropped.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 24
Page 32

Return to Primary after
Enter the number of minutes the modem can stay on the secondary carrier before attempting reconnection to the
primary carrier. (To disable this setting, enter zero for the number of minutes.)
Note: Connectivity will be lost for 30-60 seconds while attempting to reconnect to the primary carrier.
3.2.2 GSM S E T TINGS
When the Active Carrier supports GSM (UTMS), fields on this page are enabled. A specific band of operation can be
chosen, status of the SIM is displayed, and PIN settings associated with the SIM can be cleared or set.
One of the key features of GSM is the Subscriber Identity Module (SIM), commonly known as SIM card. The SIM is a
detachable smart card containing the user’s subscription information. This allows the user to retain his or her
information when switching handsets or wireless devices, independent of which handset or wireless device they are
using. The SIM has a security feature which, when enabled, requires the user to enter a valid PIN before the modem
will connect to the cellular network.
Figure 23 Cell Connection — GSM Settings
Band Selection
Band
A list of frequency bands appropriate for the Active Carrier. Select a specific band or (recommended) select All Bands.
Current Status
The Current Status section displays the current status of the SIM (whether a SIM card is present, and if so whether it is
valid) and PIN (whether a PIN has been entered and PIN security enabled).
SIM Status (status text)
“SIM ACCEPTED” displays when a valid SIM card is inserted properly in the modem.
“NO SIM, Insert Valid SIM and Press Reset” displays if the SIM card is invalid, missing, or installed incorrectly.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 25
Page 33

PIN Status (status text)
“PIN DISABLED” displays when PIN security is not enabled.
“PIN ENABLED” displays when PIN security is enabled.
“PIN ACCEPTED” displays when PIN security is enabled and a valid PIN is entered.
“NO SIM, Insert Valid SIM and Press Reset” displays if the SIM card is invalid, missing, or installed incorrectly.
Change PIN Status
The Change PIN Status section allows you to enter a PIN and enable PIN security or disable it. Instructions for the
available actions and associated options displayed in this section of the Web page change depending on the SIM status,
whether a PIN has been entered, and whether PIN security is enabled or disabled.
The default setting for PIN security is disabled and you will see the status message “Action: PIN is disabled. To change
it, it must be enabled first.”
Note: Before enabling PIN security, make sure you have the PIN provided by your wireless carrier.
To enter the PIN provided by your wireless carrier (for a new modem)
Change Disable PIN from Yes to No, enter your carrier-provided PIN into the Current PIN field, and click Save to access
the PIN security settings.
To change your PIN or change PIN security settings
(enable or disable PIN security, change whether PIN is remembered, or change your PIN)
Change Disable PIN from Yes to No, enter your PIN into the Current PIN field, and click Save to access the PIN security
settings.
Figure 24 PIN Accepted; Change PIN Status options
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 26
Page 34

To Change the PIN Status
Once the PIN has been entered successfully, the status message displays “Action: You may change only one of the
following 3 options at a time,” and three options are presented.
Remember PIN (Enter Current PIN) Yes / No
- To have your PIN remembered (not need to be entered each time to establish connection), select Yes.
- To not enable this feature (not have your PIN remembered), select No.
Enter your PIN in the Current PIN field and click Save to make your selection take effect.
Disable PIN (Enter Current PIN) Yes / No
- To disable PIN security, select Yes.
- To enable PIN security, select No.
Enter your PIN in the Current PIN field and click Save to make your selection take effect.
Change PIN (Enter Current PIN, New PIN and Confirm PIN) Yes / No
- To change your PIN, select Yes. Enter your PIN in the Current PIN field, enter your new PIN in the New PIN field,
and enter your new PIN again in the Confirm New PIN field. (The PIN you enter in the New PIN and Confirm New
PIN fields must match exactly.)
Note: If you enter too many or too few characters, or characters that are not allowed in a PIN, rules for valid PIN
length and character selection are displayed.
- To not change your PIN, select No.
Click Save to make your selection take effect.
When you have made and saved your change successfully, the PIN Status text changes accordingly, reflecting the
change you made.
3.2.3 CD M A SETTINGS – 3G R OUTER ONLY
When the Active Carrier supports CDMA, fields on this page are enabled. A specific band of operation can be chosen
and various settings associated with provisioning the modem can be set.
When a new modem is powered up for the first time, most of the provisioning information is blank or has information
that needs to be changed. The modem is usually shipped with the radio ready to be provisioned on a cellular carrier’s
network. Features called Over-The-Air Service Provisioning (OATSP) and Open Mobile Alliance Device Management
(OMA-DM) are supported, which allow the cellular providers to program the modem with specific information to
activate the account.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 27
Page 35

Figure 25 Cell Connection — CDMA Settings
Band Selection
Band
A list of frequency bands appropriate for the Active Carrier. Select a specific band or (recommended) select All
Bands.
Current Status
MEID
The Mobile Equipment Identifier is used by the cellular carrier as the means to identify the cellular module. This is
the identifier is used to set up the user account with the cellular provider.
MDN/MTN
The actual phone number of the device as supplied by the carrier. When the unit is successfully provisioned, the
phone number for the user account will be displayed.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 28
Page 36

MIN/IMSI
This number is used by the Mobile Telephone Network and will be different if ported from another carrier (not used
by end user of device).
PRL
Preferred Roaming List, only applicable for the CDMA product line, carrier specific (Alltel, Verizon, Sprint, etc).
SID
System ID (Identity), provided by the Carrier.
NID
Network Identifier, this is supplied automatically from the network.
Channel
Cell Site channel number to which the modem is connected. This number can be useful to the cellular provider for
troubleshooting purposes.
Frequency
Cellular frequency band the modem is using, 800MHz and 1900MHz are mainly in the US and outlying areas. In
some cases 900 and 1800 will be seen for European or Foreign carriers.
Roaming
Will be either Roaming or Not Roaming. Roaming indicates service is being provided by an alternate carrier who has
a roaming agreement with your contracted carrier. While Roaming, additional charges may apply. For provisioning,
the unit must be Not Roaming.
Signal Strength (dBm)
Measured in dBm, this is the Received Signal Strength Indication (RSSI). For provisioning, the signal strength should
be greater than -95 dBm.
Enable/Disable OMA-DM Activation
This section will only be displayed for units which are capable of automatic (OMA-DM) provisioning. Sprint supports
OMA-DM. You may choose to enable or disable the automatic provisioning and save your desired setting. If enabled,
and the unit is not provisioned (activated), each time at power-on (only) the unit will attempt an auto-activation. This
capability is dependent on whether or not it is offered by your cellular carrier.
Auto-Activation
Choose Enable to direct an unprovisioned unit to attempt OMA-DM activation once per power-up.
Click Save to save your desired setting after making a change.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 29
Page 37

Manual Initiation of OMA-DM Provisioning
This section will only be displayed for units which are capable of automatic (OMA-DM) provisioning. The activation
status is displayed, and a button is provided to direct the unit to begin an OMA-DM provisioning attempt. Depending
on changes to your carrier's network, it may be necessary to re-provision a unit that has already been activated. The
OMA-DM capability is dependent on whether or not it is offered by your cellular carrier.
Activation Status
Displays the activation status as Activated or Not Activated.
Click OMA-DM to trigger an OMA-DM provisioning attempt.
Carrier-assisted Activation
This section is displayed for units that use automatic OTASP provisioning instead of OMA-DM. Availability of OTASP or
OMA-DM is carrier dependent. For carriers that support OTASP, the provisioning process is started by entering a
carrier-specific command (such as *22899 for Verizon) and clicking the OTASP button.
Command (OTASP Only)
The dial command used for provisioning the modem. For Verizon the number is *22899.
Click OTASP to start the provisioning process for units using Verizon.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 30
Page 38

3.2.4 SY S T E M MONITOR
Select Cell Connection from the left navigation pane. The System Monitor tab allows user access to the configuration
of additional self-monitoring for the modem to determine when service provider connections may have been
terminated.
Figure 26 Cell Connection — System Monitor
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 31
Page 39

Cell Connection – System Monitor
Reset on Signal Loss
Fixed-point connections expect to have consistent access to the cellular network, compared to mobile connections
that may temporarily lose access depending on coverage. This option causes the modem to reset if the cell
connection is lost for longer than the duration that you specify in the Signal Loss Timeout.
Signal Loss Timeout
If a reset on Signal loss (above) is enabled; specify the amount of time in seconds for which a loss of connection will
trigger a reset of the modem.
Periodic Reset Timer
Periodic Reset Type
Sets the Periodic Modem Reset timer to a time Interval or a scheduled time, or disables it.
Interval Length
Sets the Periodic Modem Reset time from 15 to 65,535 minutes. The Periodic Reset is disabled when set to 0.
Default is set to 4320 min. (approximately 3 days)
Scheduled Time
Sets the Periodic Modem Reset to occur at the specified time. Select the days of week desired or 'All' for everyday.
Time is specified in UTC, not Local Time where the modem is located. The modem's current time is shown on the
"home" page.
Periodic Ping Settings
Destination Address
User may enter an accessible IP address or URL that will respond to a ping command.
Secondary Address
User may enter an accessible IP address or URL that will respond to a ping command. This address will be used if the
entered number of consecutive ping failures using the first address is reached.
Periodic Ping Timer
User may enter an interval in increments of 10 seconds. The modem will ping the destination at that interval. Enter
0 to disable this feature.
Fail Count
The modem will reset if the number of consecutive ping failures is equal to or greater than this entry and the
secondary address is being used. Otherwise the modem will switch from the first address to the secondary address
for the ping test.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 32
Page 40

WAN Data Usage Estimates
This section tracks the data received from and transmitted to the cellular network. This is a tool that may be used to
estimate network usage. These totals are tracked by the router. Your carrier maintains separate statistics from which
your billing is determined. One way to use this tool is to track usage over a fairly short period of typical usage. The total
then can be extrapolated to estimate longer time periods. This router updates these statistics once approximately
every 30 seconds. Press the Clear button to reset the totals to 0.
Rx Bytes
The total number of bytes received by the modem from the cell network. All statistics will be cleared automatically
if this count exceeds 1 billion (1,000,000,000).
Rx Packets
The total number of TCP and UDP packets received by the modem from the cell network.
Rx Errors
The number of corrupted TCP and UDP packets received by the modem from the cell network.
Rx Packets Dropped
The number of TCP and UDP packets received by the modem from the cell network that were not accepted. This
may occur due to memory or throughput problems.
Tx Bytes
The total number of bytes transmitted by the modem to the cell network. All statistics will be cleared automatically
if this count exceeds 1 billion (1,000,000,000).
Tx Packets
The total number of TCP and UDP packets transmitted by the modem to the cell network.
Tx Errors
The number of corrupted TCP and UDP packets received by the modem that were meant to be transmitted on the
cell network.
Tx Packets Dropped
The number of TCP and UDP packets received by the modem for transmit to the cell network that were not
accepted. This may occur due to memory or throughput problems.
Click Clear to reset the totals to 0. These totals are NOT cleared by a modem reboot.
3.2.5 DY NAMIC DNS
Select Cell Connection from the left navigation pane. Select the Dynamic DNS tab to open the Dynamic DNS
configuration page. Dynamic DNS is a system which allows the domain name data of a computer with a varying
(dynamic) IP addresses held in a name server to be updated in real time in order to make it possible to establish
connections to that machine without the need to track the actual IP address themselves at all times. A number of
providers offer Dynamic DNS services ("DDNS"), free or for a charge. For example, a free service provided by NO-IP
allows users to setup between one and five host names on a domain name provided by NO-IP. No-IP is the default DNS
service.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 33
Page 41

Figure 27 Cell Connection — Dynamic DNS
Dynamic DNS
Dynamic DNS
Selecting Enable will allow the modem to provide the selected service dynamic IP address information. Selecting
Disable will stop any IP information from being sent to the selected service.
Dynamic DNS Address
The internet address to communicate the Dynamic DNS information to. Default is dynupdate.no-ip.com.
Port Number
The port number for the internet address give above. Default is 8245.
User Account
The username used when setting up the account. Used to login to the Dynamic DNS service.
User Password
The password associated with the username account.
Hostname
The hostname identified to the Dynamic DNS service. For example http:/test.myserver.com.
Update Interval
Sets the interval, in minutes (0 to 65,535), the modem will update the Dynamic DNS server of its carrier assigned IP
address. It is recommended to set this interval as long as necessary. Each update is considered a data call by the
cellular provider and could deplete low usage data plan minutes.
You must click Save for changes to take effect.
3.3 LAN SETTINGS
Select LAN Settings from the main navigation pane for access to the LAN Settings, MAC Filtering, and IP Filtering tabs.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 34
Page 42

Figure 28 LAN — LAN Settings
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 35
Page 43

LAN Settings
Ethernet IP Address
This sets the IP address of this device and is the address used to access the configuration pages. If the IP address
changes you will have to re-enter the new IP address in your browser to access the configuration pages. The default
IP is 192.168.1.50 and should be changed for security purposes.
Ethernet Subnet Mask
Sets the subnet mask for the LAN side of the modem to the device.
Important: The LAN subnet must not overlap with the WLAN subnet defined in the Access Point tab of the WLAN page.
LAN Masquerade
When enabled, the Vanguard masquerades all Ethernet traffic to the LAN, making all WAN traffic appear as if it
originated from the Vanguard . This can be useful in applications where less-capable equipment on the local LAN
cannot cope with connections from multiple Host IP addresses.
Bind Services to Eth IP
UDP datagrams or TCP sockets from services inside the Vanguard (Serial, IO, GPS) normally appear to come from the
interface (LAN or WAN) closest to the destination. Enable this option to force the source address to be the LAN
Ethernet IP address. This can be useful if packets are being sent through a VPN tunnel. Note that outside of a
tunnel, NAT may still force the source address to be rewritten to the WAN address.
DNS Resolving
DNS Auto
Selecting Enable will allow the servers set as DNS Server 1 or 2 to automatically resolve domain names to IP
addresses. These servers communicate with name servers by sending DNS queries and heeding DNS responses.
Selecting Disable will not allow DNS Sever 1 or 2 to resolve domain names.
DNS Server 1 IP Address
The Ethernet IP address of the preferred DNS server. The default address is 192.168.1.50, the same as the LAN
Ethernet IP Address for the modem. If the LAN Ethernet ID Address changes, the DNS Server 1 address will
automatically change to the same.
DNS Server 2 IP Address
Ethernet address of the alternate DNS server. The default is set to 0.0.0.0.
DHCP Configuration
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol; a protocol used by client devices that are connected to the LAN port of this
device to automatically obtain an IP address assigned by this device. Selecting Enable will configure this device to
assign IP addresses to client devices taken from a pool specified by the values entered in DHCP start range and
DHCP end range. Selecting Disable will turn off this DHCP server functionality.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 36
Page 44

DHCP start range
DHCP server starting IP address. The default is set as 192.168.1.100.
DHCP end range
DHCP server ending IP address. The maximum usable number is 253.
DHCP Lease Time
Sets the duration, in seconds, the connected device is allowed to keep the assigned IP address. In many cases it is
possible for the device to receive the same IP address after the lease time expires.
Remote Administration
Web Server Port
Enter the port number to be used by the web server.
Remote Configure
Selecting Enable will allow remote access to the modem’s configuration interface through the cellular network
connection. Selecting Disable will shut off the ability to remotely access the modem’s configuration interface.
Incoming Port
Sets the port number used to remotely configure the modem. (Note: Remote Configuration will be unavailable if the
Incoming Port number also appears in an entry in Router » Port Forwarding » IP Mapping Table.)
Admin Password
Sets the password required for remote configuration.
Confirm Password
Re-type the Admin Password to confirm the correct spelling.
Friendly IP Address
Specifies the IP address from which remote administration is permitted. Entering 0.0.0.0 will allow any IP address.
Leave the fifth box blank (after the /) if specifying a specific IP, or 0.0.0.0. A subnet mask may be entered in the fifth
box. The mask indicates how many bits of the IP address to match. This can be a value from 1 to 32.
Apply Friendly IP Address
Check the box next to a service to allow remote access to the service only from the friendly IP address. Uncheck this
box to allow any IP address access.
SSH, Telnet, and SNMP Ports
Enter the port number that will be used for remote access to the service. Entering zero for the port number will
block remote access to the service. Once a service is blocked (0 entered) or moved to another port, the default port
number (such as 23 for Telnet) can be used in a Port Forwarding rule to provide access to a user device located
behind the modem. Port Forwarding has precedence so if the SSH, Telnet or SNMP port also appears as an Incoming
Port in an entry in Router » Port Forwarding » IP Mapping Table then that service will be unavailable.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 37
Page 45

RADIUS Settings
RADIUS Authentication
Enable or disable RADIUS authentication for webpage access.
Server IP Address
The IP address of the RADIUS server.
Server Port
The port of the server.
Server Secret
Sets the secret to use with the server.
Confim Secret
Re-type the Server Secret to confirm the correct spelling.
Timeout
Specify how many seconds to wait before a retry.
Retries
Specify how many times to retry authenticating with the server before giving up.
Click Save to keep the currently displayed value for each parameter. Once you have clicked Save, Cancel cannot be
used to return to previous settings. Press Cancel to abort changes and redisplay the last saved parameters for this
page.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 38
Page 46

3.3.1 MA C F I L TERING
Select LAN Settings from the left navigation pane. The MAC Filtering tab opens the MAC filtering configuration page.
MAC filtering allows up to five unique device MAC addresses access to the network.
Figure 29 LAN — MAC Filtering
MAC Filtering
MAC Filtering
Select Enable or Disable to enable or disable MAC filtering.
Allowed MAC Address
Enter the MAC address for a device to be allowed on the network.
Comment
Enter an optional comment that describes the device at the allowed MAC address.
Clear
To clear a MAC address from the list of allowed addresses, click Clear on the Comment line under the MAC Address.
Click Save or Cancel to implement or cancel changes.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 39
Page 47

3.3.2 IP FILTERING
Figure 30 LAN — IP Filtering
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 40
Page 48

The "IP Filtering" page is used to configure IP filters.
The user can enter up to 20 IP filters. Each IP filter is identified by a unique number (from 1 to 20). An IP packet goes
through the filtering logic when IP filtering is enabled and:
1) An IP packet is received on one of the interfaces and is destined to the Vanguard unit
OR
2) An IP packet is sent by the Vanguard unit
OR
3) An IP packet is forwarded by the Vanguard unit.
The filtering logic is the following:
if exists(filter[1]) AND match(packet, filter[1]) then apply(action[1])
else if exists(filter[2]) AND match(packet, filter[2]) then apply(action[2])
else if exists(filter[3]) AND match(packet, filter[3]) then apply(action[3])
else if exists(filter[20]) AND match(packet, filter[20]) then apply(action[20])
else process packet normally.
Where:
exists(filter[n]) -> The user as defined filter number n.
match(packet, filter[n]) -> The IP packet matches filter number n.
apply(action[n]) -> The action identified in filter number n.
IP Filters
IP Filtering
Enable: IP filtering is enabled. Any custom IP filters entered by the user will be taken into account when processing
IP packets. The predefined IP filters will also be taken into account.
Disable: IP filtering is disabled.
Add Custom IP Filters
Filter Number
Each IP filter is identified by a unique number from 1 to 20. Note that if you enter a filter number that is already in
use, the new filter will overwrite the old filter with no warning or confirmation.
Source IP Address
Any: Any source IP Address will satisfy this criteria.
Specific: A specific Host IP address.
Range: A range of IP addresses.
If the Exclude field is checked, it means that in order for the packet to match with this criteria, it must NOT have this
source IP address (or NOT be in the given source IP address range).
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 41
Page 49

Destination IP Address
Any: Any destination IP Address will match.
Specific: A specific Host IP address.
Range: A range of IP addresses.
If the Exclude field is checked, it means that for the packet to match this filter, it must NOT have this destination IP
address (or NOT be in the given destination IP address range).
Protocol
Any: Any protocol number.
ICMP: The ICMP protocol (1).
TCP: The TCP protocol (6).
UDP: The UDP protocol (17).
Other: Any other IP protocol.
If the Exclude field is checked, it means that for the packet to match this filter, it must NOT have this protocol
number.
Source Port
Any: Any source port number.
Specific: Select a specific source port number.
Range: Select a range of source port number.
If the Exclude field is checked, it means that for the packet to match this filter, it must NOT have this source port
number (or NOT be in the given source port number range).
Destination Port
Any: Any destination port number.
Specific: Select a specific destination port number.
Range: Select a range of destination port number.
If the Exclude field is checked, it means that for the packet to match this filter, it must NOT have this destination
port number (or NOT be in the given destination port number range).
Direction
The direction corresponds to the path taken by the IP packet inside the Vanguard unit.
An IP packet can TERMINATE inside the Vanguard unit.
WAN to Vanguard: The IP packet is received from the WAN (cellular) interface and is destined to the Vanguard
unit.
LAN to Vanguard: The IP packet is received from the LAN interface and is destined to the Vanguard unit.
WLAN to Vanguard: The IP packet is received from the WiFi interface and is destined to the Vanguard unit.
An IP packet can ORIGINATE from the Vanguard unit.
Vanguard to WAN: The IP packet is sent by the Vanguard unit to the WAN (cellular) interface.
Vanguard to LAN: The IP packet is sent by the Vanguard unit to the LAN interface.
Vanguard to WLAN: The IP packet is sent by the Vanguard unit to the WiFi interface.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 42
Page 50

An IP packet can be FORWARDED by the Vanguard unit.
AUX LED Color / State
Meaning
Off
The WLAN interface is not installed.
Red
The WLAN interface is disabled.
Amber
The WLAN interface is configured for Client mode and is searching for an Access Point.
Green
The WLAN interface is not configured for Client mode and is connected to an Access
Point, or is configured for Access Point mode and is ready to accept connections.
Flashing Green
There is data traffic on the WLAN channel.
WAN to LAN: The IP packet is received on the WAN(cellular) interface and forwarded to the LAN interface.
WAN to WLAN: The IP packet is received on the WAN(cellular) interface and forwarded to the WiFi interface.
LAN to WAN: The IP packet is received on the LAN interface and forwarded to the WAN (cellular) interface.
LAN to WLAN: The IP packet is received on the LAN interface and forwarded to the WiFi interface.
WLAN to LAN: The IP packet is received on the WiFi interface and forwarded to the LAN interface.
WLAN to WAN: The IP packet is received on the WiFi interface and forwarded to the WAN (cellular)
interface.
If the Exclude field is checked, it means that for the packet to match this filter, it must NOT be processed in the
given direction.
Action
Keep: If IP filtering is enabled and an IP packet matches all criteria in the IP filter, keep the IP packet (continue
normal processing of the IP packet).
Drop: If IP filtering is enabled and an IP packet matches all criteria in the IP filter, drop the IP packet.
Custom IP Filters
Del
Click Del to delete a filter.
3.4 WLAN SETTINGS
The Mobile model Vanguard Cellular Broadband Router contains a wireless LAN (WLAN) interface that can be set up as
a Client or Access Point.
The AUX LED displays the status of the WLAN interface.
Table 10 AUX LED color / state and status of the WLAN interface
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 43
Page 51

3.4.1 MA I N
Mode
Explanation
Disable
The WLAN interface is disabled.
Client
The WLAN interface operates in Client mode. Parameters can be set on the Client tab.
Access Point
The WLAN interface operates in Access Point mode. Parameters can be set on the Access Point tab.
Figure 31 WLAN — Main
Configuration
The following table gives explanations of the Wireless Mode options.
Table 11 Explanation of Wireless Mode options
Status
IP Address
IP Address assigned to the WLAN interface.
Subnet Mask
Subnet mask assigned to the WLAN interface.
SSID
Name of the wireless local area network.
Authentication
Authentication method currently used.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 44
Page 52

Encryption
Encryption method currently used.
Channel
Channel currently in use.
State
Current state of the WLAN interface. In Access Point mode, indicates how many clients are connected.
RSSI
Received Signal Strength indication.
3.4.2 CL I E N T
The user can configure up to 20 Access Points. The Vanguard Cellular Broadband Router will try to connect to the best
Access Point in the list that is reachable. When the Vanguard unit connects to an Access Point, it starts a DHCP client on
the interface. The Access Point must provide a DHCP server. The DHCP server must provide an IP address, network
mask and gateway to the Vanguard unit. When the Vanguard unit is connected to an Access Point, the default route is
set to point to the gateway address obtained from the DHCP server.
Note: The Access Point must broadcast the SSID in order for the Client to be able to connect to it.
Figure 32 WLAN — Client
The following table shows the types of authentication methods available and corresponding encryption methods.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 45
Page 53

Table 12 Authentication and encryption methods
Authentication
Encryption
Open
none, WEP
Shared
WEP
WPA none
TKIP, AES
WPA–PSK
TKIP, AES
WPA2–PSK
AES
WEP Key
64-bit
128-bit
ASCII (Text)
5 character string (alphanumeric)
Example: Hello
13-character string (alphanumeric)
Example: LongHello1234
Hex
10 Hexadecimal digits
Example: 1A2B3C4D5E
26 Hexadecimal digits
Example: 1A2B3C4D5E6F7788990A0B0C0D
TKIP Key
Description
Example
ASCII (Text)
A string of 8 to 63 characters (alphanumeric)
Hello123
AES Key
Description
Example
ASCII (Text)
A string of 8 to 63 character (alphanumeric)
Hello123
The following table describes WEP keys (ASCII and Hexadecimal; 64-bit and 128-bit) and gives examples.
Table 13 Descriptions of WEP keys and examples
The following table describes TKIP keys.
Table 14 TKIP key description and example
The following table describes AES keys.
Table 15 AES key description and example
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 46
Page 54

3.4.3 ACC E S S P OINT
Authentication
Encryption
Open
none, WEP
Shared
WEP
WPA none
TKIP, AES
Figure 33 WLAN — Access Point
Wireless Settings
Wireless Parameters for Access Point mode.
The following table shows the types of authentication methods available and corresponding encryption methods.
Table 16 Authentication and encryption methods
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 47
Page 55

The following table describes WEP keys (ASCII and Hexadecimal; 64-bit and 128-bit) and gives examples.
WEP Key
64-bit
128-bit
ASCII (Text)
5 character string (alphanumeric)
Example: Hello
13-character string (alphanumeric)
Example: LongHello1234
Hex
10 Hexadecimal digits
Example: 1A2B3C4D5E
26 Hexadecimal digits
Example: 1A2B3C4D5E6F7788990A0B0C0D
TKIP Key
Description
Example
ASCII (Text)
A string of 8 to 63 characters (alphanumeric)
Hello123
AES Key
Description
Example
ASCII (Text)
A string of 8 to 63 character (alphanumeric)
Hello123
Table 17 Descriptions of WEP keys and examples
The following table describes TKIP keys.
Table 18 TPIK key description and example
The following table describes AES keys.
Table 19 AES key description and example
IP Settings
IP Address
This sets the IP address for the WLAN side of the Vanguard.
Subnet Mask
Sets the subnet mask for the WLAN side of the Vanguard unit.
Important: The WLAN subnet must not overlap with the LAN subnet defined on the LAN Settings tab of the LAN page.
DNS Masquerade
DNS Auto
Selecting Enable will automatically set the preferred DNS Server to the WLAN IP address of the Vanguard unit.
Selecting Disable will allow the user to select the preferred and alternate DNS servers.
DHCP Server
DHCP Server
Selecting "Enable" will configure this device to assign IP addresses to client devices taken from a pool specified by
the values entered in "Start IP Address" and "End IP Address". Selecting "Disable" will turn off the DHCP server
functionality for the Ethernet interface.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 48
Page 56

The Vanguard helps to protect against addressing conflict by preventing the operator from saving the configuration
when the DHCP lease range conflicts with the interface IP address. If such a conflict exists, a message is displayed
upon clicking Save.
Start IP Address
The DHCP server’s IP address pool starting value.
End IP Address
The DHCP server's IP address pool ending value.
Lease Time
Sets the duration, in seconds, that the client is allowed to keep the assigned IP address.
Domain Name Suffix
The DNS suffix to be assigned by the DHCP server.
Preferred DNS Server
IP address of the preferred DNS server.
Alternate DNS Server
IP address of the alternate DNS server.
3.4.4 ST A T S
Figure 34 WLAN — Stats
Transmit
TX Packets
Indicates number of packets sent by the Vanguard over the WLAN interface.
TX Bytes
Indicates number of bytes sent by the Vanguard over the WLAN interface
Receive
TX Packets
Indicates number of packets received by the Vanguard from the WLAN interface.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 49
Page 57

TX Bytes
Indicates number of bytes received by the Vanguard over the WLAN interface.
3.4.5 SIT E S U R VEY
When the WLAN interface of the Vanguard unit is configured for Client mode, this page scans for and displays the
WLAN Access Points that it detects. (This operation can take some time to complete.)
Figure 35 WLAN — Site Survey
3.5 ROUTER
Select Router from the left navigation pane to access the Port Forwarding and Static Routing tabs.
3.5.1 PO RT FORWARDING
Port Forwarding is a technique for transmitting and receiving network traffic through a router that involves re-writing
the source and/or destination IP addresses and usually the TCP/UDP port numbers of IP packets as they pass through.
The various routing configurations will be displayed in the IP mapping table at the bottom of the Port Forwarding page.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 50
Page 58

Figure 36 Router — Port Forwarding
DMZ Support
DMZ is a host on the internal network that has all ports exposed, except those ports specified otherwise for forwarding.
DMZs
Select Enable to allow the modem to use DMZ routes using the address set in the Destination IP Address.
Select Disable to shut down the DMZ functionality.
Friendly IP Address
Optionally restricts DMZ access to only the specified IP address. If set to 0.0.0.0, the DMZ is open to all incoming IP
Addresses.
Destination IP Address
The IP address which has all ports exposed, except ports defined in the Port Forwarding configuration.
You must click Save for changes to take effect.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 51
Page 59

Port Forwarding Support
Port Forwarding
Select Enable to allow the modem to use the Port Forwarding routes described in the IP mapping table.
Select Disable to shut down the Port Forwarding functionality.
You must click Save for changes to take effect.
Port Forwarding Configuration
Map Name
Sets the Map Name for the IP mapping table at the bottom of the page. The Map Name can be up to ten characters
in length. Do not use spaces in the character string.
Protocol
Sets the data protocol as either TCP, UDP, or all.
Friendly IP Address
Specifies an IP address that is allowed to access the modem or a wildcard IP address of 0.0.0.0 that allows all IP
addresses to access the modem. Leave the fifth box blank (after the /) if specifying a specific IP, or 0.0.0.0. A subnet
mask may be entered in the fifth box. The mask indicates how many bits of the IP address to match. This can be a
value from 1 to 32.
Inbound Port
Sets the external port number for incoming requests. (Note: Port Forwarding rules take precedence over the
services specified in LAN Settings » Remote Administration » Incoming port, SSH Port, Telnet Port or SNMP Port.)
Destination IP Address
Sets the Local Area Network Address of the device connected to the modem's Ethernet jack. Inbound requests will
be forwarded to this IP address.
Destination Port
Sets the Local Area Network port number used when forwarding to the destination IP address.
Once you have completed the entry of the above fields, click ADD to save the new entry.
3.5.2 ST A T I C R OUTES
Select the Static Routes tab to open the routing configuration page. Static route tables may be created in this page and
appear at the bottom. Static Routing refers to a manual method used to set up routing between networks.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 52
Page 60

Figure 37 Router — Static Routes
Static Routes
Route Name
Sets the alphanumeric identifier of the static route in the Static Route table.
Destination IP Address
Sets the IP address of the destination network.
IP Subnet Mask
Sets the subnet mask of the destination network.
Gateway
Sets PPP (this router's wireless Internet connection), PPTP (VPN), GRE Tunnel, WLAN (if applicable), or the local
network IP address for the gateway to the destination network.
Gateway IP Address
This is only used if local IP address was selected for gateway. Enter the address of the local gateway.
Metric
Enter a number from 1 to 20. The lower the metric value the higher the route priority.
Click Add to add the configured route to the Static Route Table.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 53
Page 61

3.6 SECURITY
From the main navigation pane, select Security to access the PPTP, IPsec and GRE tabs.
3.6.1 ST A T U S
Figure 38 Security — Status
PPTP Client
PPTP Client Status
Indicates the status of the PPTP Client interface, usually UP when connected properly. PPTP is the Point-to-Point
Tunneling Protocol used to implement a Virtual Private Network (VPN).
PPTP Client IP Address
The current IP address assigned to the modem by the VPN server.
PPTP Client Subnet Mask
Usually set to 255.255.255.255, but may be different depending on VPN.
PPTP Client P-t-P
The PPTP P-t-P is the LAN address of your VPN server.
PPTP Server
PPTP Server Status
The PPTP Server is either ENABLED or DISABLED based on user's selection on Security page.
Connected Users
Number of users currently connected to the PPTP Server.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 54
Page 62

IPsec Tunnels
Status
The number of established IPsec tunnels based on the number of tunnels Enabled on the Security | IPsec page.
3.6.2 PP TP
The Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is a method for implementing virtual private networks (VPN).
Figure 39 Security — PPTP
PPTP Client Configuration
PPTP Client
Selecting Enable will allow the PPTP functionality. Selecting Disable will shut off PPTP functionality.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 55
Page 63

Set Default Route to PPTP
Selecting Enable will route all IP traffic through the PPTP network. Selecting Disable will route only PPTP traffic
through the PPTP network.
PPTP Server
The IP address of the virtual private network server on which to connect.
Username
The username required by the VPN server.
Password
The password, associated with the username, required by the VPN server.
PTPP Server Configuration
PPTP Server
Selecting Enable starts the VPN server, and selecting Disable stops it.
Server Local IP
The IP address that clients will use to communicate with the server after they connect.
Client IP Range
The pool of IP addresses assigned to clients.
Protocols Allowed
Selecting a protocol will instruct the VPN server to accept clients who use that protocol. The server will reject clients
using any of the un-selected protocols.
Encryption
Selecting Use MPPE will enable Microsoft Point-to-Point Encryption for communication between the server and
clients. This option requires the MS-CHAP or MS-CHAPv2 protocol.
PPTP Server User Configuration
Full Name
This name can be used as a more descriptive name for a client. It is not used by the server. No spaces are allowed in
the name.
Username
The name used by a client to log in to the server.
Password
The password, with associated username, used by a client to log in to the server.
3.6.3 IPSE C
IPsec serves to configure secured communication tunnels. The various tunnel configurations will be displayed in the
Tunnel Table at the bottom of the page. All tunnels are created using the ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) protocol.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 56
Page 64

Figure 40 Security — IPsec
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 57
Page 65

IPsec Support
IPsec
Selecting Enable will launch the IPsec process and start all enabled tunnels. Selecting Disable will stop all tunnels
and shutdown the IPsec process. Note that all enabled tunnels will be launched automatically when the unit
connects to the cellular carrier.
NAT Mode
Determines how packets are addressed. Selecting Bypass will allow packets coming from Local Subnet addresses
through the NAT firewall unchanged. This may be sufficient when traffic only travels from Local Subnet to Remote
Subnet. (LAN Settings » Bind to Eth IP may need to be enabled to make sure that packets generated by Vanguard
services appear to originate from a Local Subnet address.) NAT changes the source address to match the Status »
PPP IP Address. NAT-Traversal enables the NAT-T protocol which can support traffic beyond just the Local and
Remote Subnets.
Tunnel Monitor
To supplement/complement Dead Peer Detection, tunnels can be monitored by sending periodic pings, with the
tunnels being restarted if the pings repeatedly fail. Tunnel monitoring is controlled by the following parameters.
IP Address 1 & IP Address 2
Up to two addresses may be entered. Only those tunnels where the IP address matches the Remote IP Address or
belongs to the Local Subnet or Remote Subnet are monitored. A value of 0.0.0.0 disables monitoring.
Delay
How often, in seconds, to send pings over the tunnel.
Fail count threshold
The number of successive pings that need to fail to cause the tunnel to be restarted.
Success count threshold
The number of successive pings that need to succeed for the tunnel to be considered “up” and for the process of
counting failed pings to begin.
Tunnel Configuration
Tunnel Item
Tunnel number, starts from 1 and increments for each new tunnel. To update an existing tunnel, use its
corresponding number from the tunnel table. To add a new tunnel, add one to the item number of the tunnel listed
last in the Tunnel Table.
Label
This is a label to identify a tunnel and corresponds to the name specified for the remote endpoint.
Remote IP Address
The IP address of the remote endpoint of the tunnel.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 58
Page 66

Remote ID
If the IP address of the remote endpoint is behind a firewall, this is the IP address of the firewall.
Remote Subnet
Choose None if encrypted packets are only destined for the Remote IP Address. Use an IP address / mask if
encrypted packets are also destined for the specified network that is beyond the Remote IP Address.
IMPORTANT: The Remote Subnet and Local Subnet addresses must not overlap!
Local Subnet
Choose None if only packets generated by Vanguard services will be sent over the tunnel. Choose Ethernet if
packets from the local LAN will also be sent over the tunnel. (LAN Settings » Bind to Eth IP may need to be enabled
to make sure that packets generated by Vanguard services appear to originate from a Local Subnet address.) Use an
IP address / mask if a network beyond the local LAN will be sending packets over the tunnel.
IMPORTANT: The Remote Subnet and Local Subnet addresses must not overlap!
Phase 1 Encryption
Use AES-128, AES-256 or 3DES encryption.
Phase 1 Authentication
Use MD5 or SHA1 hashing.
Phase 1 DH Group
Negotiate (Auto) or use 768 (Group 1), 1024 (Group 2), 1536 (Group 5) or 2048 (Group 14) bit keys.
Phase 1 Key Lifetime
How long the keying channel of a connection should last before being renegotiated.
Phase 2 Encryption
Use AES-128, AES-256 or 3DES encryption.
Phase 2 Authentication
Use MD5 or SHA1 hashing.
Phase 2 Lifetime
How long a particular instance of a connection should last, from successful negotiation to expiry.
Pre-shared Key
Predetermined key known to both the local unit and the remote side prior to establishing the tunnel.
Negotiation Mode
Choose Normal to allow IPsec to negotiate some connection parameters. Choose Aggressive to require that only
those parameters selected above can be used to create the tunnel.
Perfect Forward Secrecy
Enable Perfect Forward Secrecy for the session keys.
Dead Peer Detection Delay
Tunnel keepalive time for R_U_THERE packets during idle periods.
Dead Peer Detection Timeout
Timeout time during tunnel idle periods where no R_U_THERE_ACK has been received.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 59
Page 67

Dead Peer Detection Action
Action to be taken when timeout value is reached.
Once you have completed the entry of the above fields, click Add/Update to save the new entry.
Tunnel Table
Enable
Check Enable to enable a tunnel. The tunnel’s state is saved across resets.
View
Click View to open a page showing the log of the tunnel’s negotiation activity.
Delete
Click Del to delete the tunnel.
3.6.4 GR E
The GRE page is used to add and delete GRE (Generic Route Encapsulation) tunnels. Current tunnels are listed below.
Up to two networks that lie beyond the tunnel may be specified and routes to those networks are automatically
created when the tunnel is established. Static local and remote IP addresses are necessary to allow for the tunnel
automatic (re)connection.
Figure 41 Security — GRE
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 60
Page 68

GRE Tunnel Configuration
Local IP Address
The local (normally WAN interface) IP address associated with the tunnel.
Remote IP Address
The remote IP address associated with the tunnel.
Tunnel IP Address
The IP address assigned to the tunnel interface.
[ Example: 192.168.10.100 ]
Tunnel Subnet & Mask
The tunnel subnet and mask that must include the above Tunnel IP Address.
[ Example: 192.168.10.0/24 ]
Remote User Subnet 1 & Mask
The IP network representing that of the remote user subnet, accessible via the tunnel.
[ Example: 192.168.20.0/24 ]
Remote User Subnet 2 & Mask
A possible second IP network representing another remote user subnet.
[ Example: 192.168.15.0/24 ]
Note:
All subnets must differ from one another and must not overlap.
If more than two remote user subnets are necessary, additional routes can be setup manually via the Router » Static
Routes tab using the Tunnel IP Address as the gateway.
3.7 SERIAL
From the main navigation pane, select Serial for access to both external and internal serial port configuration pages.
3.7.1 EX T ERNAL SERIAL
Use the External Serial tab to define and configure the functioning of the RS-232 Serial Port, which can be set to output
GPS position reports or to function as a Packet Assembler and Disassembler (PAD), transferring all serial data to or from
a specified TCP/UDP port.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 61
Page 69

Figure 42 Serial — External Serial
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 62
Page 70

Serial Port Settings
Serial Port
When disabled, the external serial port is left free for use by an ODP application.
GPS Configuration
Select GPS to enable GPS reports through the serial port. Note that the report format is set in the GPS » Settings tab.
Set the appropriate TCP Server Format in the Local and/or Remote Delivery sections.
Report Trigger
On Loss of Cellular Signal: Select this if the GPS reports are output only when the cellular signal is lost. Note that
there can be a delay of around 30 seconds before the serial reports appear on the serial port after the cellular signal
is lost.
Always: GPS reports are always sent out the serial port.
Reports
Local (1/sec): Select this to have the Local report sent out the serial port each second.
Remote (AAVL): Select this to have the Remote report sent out the serial port. The report rate is based on the AAVL
settings.
Baud Rate
Select the serial port baud rate. The character format is fixed at 8 data bits, No parity, 1 stop bit.
External Serial Port Configuration
Show Version on Boot
When enabled, the router model number and firmware version are transmitted out the serial port at router boot.
Additionally, "OK" is transmitted when router is ready to receive data and when PPP connection is made. When
disabled, these indicators will not be transmitted out the serial port.
Baud Rate
Sets the baud rate of the serial port. Settings may range from 300 to 115,200 bits per second. The default baud rate
is 115,200 bps.
Data bits, Stop bits, and Parity
Sets these parameters, which must be specified for serial communication.
Inter Character Timeout
Sets the Inter Character Timeout from 1 to 65,535 ms.
DTR
Defines the Data Terminal Ready behavior. Refer to the following table for DTR descriptions.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 63
Page 71

Table 20 DTR Descriptions
DTR
Description
AT&D0
Ignore DTR.
AT&D1
If in the Online Data State, upon an on-to-off transition of DTR, the modem enters Online Command
State and issues an OK result code; the call remains connected. Otherwise, ignore DTR.
AT&D2
If in the Online Data State or Online Command State upon an on-to-off transition of DTR, the modem
performs an orderly clear-down of the call and returns to the command state. Automatic answer is
disabled while DTR remains off.
AT&D4
The modem auto-dials the default remote station upon an off-to-on transition of DTR and enters the
Online Data State. The modem ends the call and enters the command state upon an on-to-off
transition of DTR.
AT&D5
The modem auto-dials the default remote station upon an on-to-off transition of DTR and enters the
Online Data State. The modem ends the call and enters the command state upon an off-to-on
transition of DTR.
AT&D6
Upon an on-to-off transition of DTR, the modem performs an orderly clear-down of any session and
turns OFF the RF module. Upon an off-to-on transition of DTR, the modem turns ON the RF module and
reestablishes the radio session.
AT&D7
Upon an on-to-off transition of DTR, the modem performs an orderly clear-down of any session and
turns OFF the RF module. Upon an off-to-on transition of DTR, the modem turns ON the RF module and
reestablishes the radio session.
AT&D8
The modem auto-dials the default remote station upon determining DTR is OFF and enters the Online
Data State. The modem ends the call and enters the command state upon determining DTR is ON.
AT&D9
The modem auto-dials the default remote station upon determining DTR is ON and enters the Online
Data State. The modem ends the call and enters the command state upon determining DTR is OFF.
Flow Control
Sets the Flow Control to None or Hardware control.
DSR
Sets the Data Set Ready to Always On, On When Available, On When Connected or Always Off. The DSR parameter
determines how the modem controls the state of the Data Set Ready circuit. The default value is Always Off.
― Always On: DSR is always on.
― On When Available: DSR is on when the RF signal present and phone registered on network.
― On When Connected: DSR is on when connected to CDMA.
― Always Off: DSR is always off.
DCD
The DCD parameter determines how the modem controls the state of the Carrier Detect circuit and the amber DCD
LED on the front panel. The default value is Connect On.
― Always On: DCD is always on.
― Connect On: DCD is on when connected to a remote host.
― Always Off: DCD is always off.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 64
Page 72

External PAD Settings
PAD Mode
Select button to set the PAD mode of the modem as a Server or Client. In Client mode, the modem will initiate an
outbound connection to the Remote Host IP Address with the Outgoing Port based on the selected DTR setting. In
Server mode, the modem will accept one incoming connection on the specified Incoming Port. The modem will not
accept multiple incoming connections at the same time – additional connections are arbitrated based on the Server
Session Closed On and Timeout parameters. Note: It is possible to override Server mode and make an outgoing
client connection using the RS-232 command set.
atd*xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:yyyyy – When in server mode, and no connection is active, the atd* command (followed by an
IP address) can be issued to initiate an outbound client connection to the specified IP address and port as specified
after the colon. If no port is specified, the port number used is the Outgoing Port parameter. To hang-up such a
connection, 3 ‘+’ characters must be inserted into the outgoing stream (“+++”). The modem will return to command
mode once it has seen the “+++” and respond with OK. The connection can then be broken by entering “ath”. The
modem will return to server mode. Such a client connection can be repeated again as necessary, as long as each
connection is hung-up before a new one is made.
Additional note: The modem is capable of only 1 PAD connection at a time. When a manual client connection is in
progress (atd*xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx), a connection attempt by an incoming client may result in the disabling of the PAD
function until the next device reset.
Pad Protocol
Sets the data protocol of the PAD to TCP or UDP data. If you have set PAD Mode as server you can choose either to
support either type of client.
Incoming Friendly IP Address
Sets the IP address of the device using the PAD functionality.
Server Session Closed On
This is only available if PAD mode is Server. This option selects under which condition the server will terminate an
established connection.
New Client: If a different client attempts to connect, it will be successful and the current client will be forcibly
disconnected, without any warning. Otherwise, the current client remains connected indefinitely.
Timeout: A new client will be accepted only after a specified timeout. The duration of the timeout is specified by the
Inactivity timeout, or the Hard timeout, or a combination of both.
The default value is New Client.
Server Inactivity Timeout
Time after which the current connection with Client will be terminated without warning. This time starts over again
each time the Client sends data to the server. This parameter is ignored if the session closes on New Client. If PAD
protocol is tcp, the timeout is specified in minutes. If UDP, the timeout is specified in seconds. The valid range for
either is 1-65535. 0 will disable this timer.
If both Inactivity Timeout and Hard Timeout are enabled, (neither is 0), then a client session will be terminated
when either timeout is met. In this case, the value for Hard Timeout must exceed the value for Inactivity Timeout. If
the Inactivity Timeout is met, the client will be terminated. If the Hard Timeout is exceeded without meeting the
Inactivity Timeout, the client will be terminated by the Hard Timeout.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 65
Page 73

Server Hard Timeout
Time after which the current connection with Client will be terminated without warning. This is a fixed time from
the initial connection, no matter how much or how often the Client sends data to the server. This parameter is
ignored if the session closes on New Client. If PAD protocol is TCP, the timeout is specified in minutes. If UDP, the
timeout is specified in seconds. The valid range for either is 1-65535. 0 will disable this timer.
If both Inactivity Timeout and Hard Timeout are enabled, (neither is 0), then a client session will be terminated
when either timeout is met. In this case, the value for Hard Timeout must exceed the value for Inactivity Timeout. If
the Inactivity Timeout is met, the client will be terminated. If the Hard Timeout is exceeded without meeting the
Inactivity Timeout, the client will be terminated by the Hard Timeout.
Incoming Port
Sets the port number used to forward incoming requests to the serial port.
Outgoing Port
Sets the port number used to send outgoing requests from the serial port.
Remote Host IP Address
Sets the Server IP address to connect with when using the PAD in client mode.
TCP Client Keep Alive
When in client mode and enabled, TCP Keep Alive packets will be sent from the client to the server periodically in
order to detect a broken connection. The modem will automatically try to re-establish the connection if necessary.
Changing this setting will affect the use of TCP Keep Alive on the next client session. It will not affect an existing
session.
TCP Client Keep Alive Time
Time in seconds between keep alive cycles. A keep alive cycle will consist of one or more keep alive probes
separated by the keep alive interval.
TCP Client Keep Alive Probes
Number of keep alive packets that must fail before connection is considered closed.
TCP Client Keep Alive Intvl
Time in seconds after which a keep alive packet is considered to be failed (if not acknowledged). Another packet is
sent at this time if TCP Client Keep Alive Probes limit has not been reached.
PAD Log
When enabled, as data passes through the PAD, a copy is stored in a log file located on the modem at /tmp/pa dlog.
The log will stop saving data when full and data is lost at modem reset.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 66
Page 74

3.7.2 INTE R N AL SERIAL
The Internal Serial page is used to configure the internal RS232 Serial Port parameters and Packet Assembler and
Disassembler (PAD) functionality. The PAD feature forwards requests that come in on a specific port to the internal
serial port. For units with Dual Serial ports, the Internal Serial Page configures the second (back of the unit above the
SIM card) RS-232 port.
Figure 43 Serial — Internal Serial
Serial Port Configuration
Baud Rate
Sets the baud rate of the serial port. Settings may range from 300 to 115,200 bits per second. The default baud rate
is 115,200 bps.
PAD Settings
Remote IP Address
Sets the IP address of the device using the PAD functionality.
Remote Port
Sets the port number used by the remote device to accept requests from the Vanguard .
Local Port
Sets the port number used by the Vanguard to accept requests from the remote device.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 67
Page 75

PAD Mode
GPS LED Color / State
Meaning
Off
GPS is not installed or cell modem GPS is disabled.
Amber
Acquiring GPS position.
Green
Valid positions being reported.
Red
Position lost; reporting from last known position.
Flashing Red
Position lost for more than 2 minutes.
Select buttons to set the PAD mode of the Vanguard as a Server or Client.
PAD Protocol
Sets the data protocol of the PAD to TCP or UDP data.
TCP Client Keep Alive
When in client mode and enabled, TCP Keep Alive packets will be sent from the client to the server periodically in
order to detect a broken connection. The modem will automatically try to re-establish the connection if necessary.
Changing this setting will affect the use of TCP Keep Alive on the next client session. It will not affect an existing
session. When this option is enabled, the timing and number of Keep Alive attempts is controlled by parameters
defined on the External Serial page. It is not possible to have different timing settings for each serial port.
PAD Log
If enabled, a log of the data passed through the modem is saved at /tmp/intpadlog. The log will stop saving data
when full and data is lost at modem reset.
3.8 GPS
The Mobile model Vanguard Cellular Broadband Router contains a standalone, high-accuracy, high-report-rate (12
satellites with WAAS and Differential Correction, 1 report per second) GPS receiver.
The GPS LED on the front panel provides the status of the receiver.
Table 21 GPS LED Color State and GPS Status
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 68
Page 76

3.8.1 SE T T I N G S
Figure 44 GPS — Settings
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 69
Page 77

GPS Settings
Format
Definition
Example
TAIP, No ID
Trimble ASCII
Interface Protocol
(TAIP), No ID
>RPV73511+4549542-0736643100035822;*7F<
TAIP, With ID
Trimble ASCII
Interface Protocol
(TAIP), With ID
>RPV56655+4549542-073664300002;ID=ADAM12;*5E<
NMEA, GGA
NMEA GGA (Global
Positioning System Fix
Data)
$GPGGA,202742.0,4529.7240,N,7339.8585,W,2,9,0.9,28,M,,,,*3E
NMEA, GLL
NMEA GLL
(Geographic Latitude
& Longitude)
$GPGLL,4529.7241,N,7339.8584,W,202645.0,A,D*7C
NMEA, RMC
NMEA RMC
(Recommended
Minimum data)
$GPRMC,153716.00,A,4529.72428,N,07339.86082,W,0.007,,180108,,,A*69
NMEA, VTG
NMEA VTG (Vector
Track and speed over
Ground)
$GPVTG,,T,,M,0.004,N,0.008,K,A*2F
Differential Correction
Differential Correction allows WAAS correction information to be used to improve accuracy of the GPS position
reports.
Note: WAAS correction applies to North America only. The WAAS satellites currently in service are 48 (Galaxy 15)
and 51 (Anik F1R). The previous WAAS satellites 35 and 47 were taken out of service on 2007/07/30.
Report Rate
For applications that require it, GPS reports are normally received from the internal GPS receiver at a rate of once
per second. Local Delivery reports are sent at this rate. Remote Delivery reports are limited by the “But no less than
X seconds between reports” setting.
Autonomous Automatic Vehicle Location (AAVL) Settings
The Autonomous Automatic Vehicle Location (AAVL) feature adds the ability for GPS-equipped Vanguard Cellular
Broadband Routers to transmit position reports either to a host connected to the local Ethernet port or to a remote
host over the cellular network. AAVL allows the system designer to specify the maximum distance or the time interval
between remote position reports.
Position reports can be transmitted in a number of possible formats. When the format is disabled or the Address or
Port fields are blank, no report is sent.
Table 22 Position report format information
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 70
Page 78

GPS “sentences” are collected the from embedded GPS receiver in the Vanguard Cellular Broadband Router. These
sentences are converted into the above formats and are provided to both local and remote delivery services. Two TCP
ports are available for clients to connect to and receive reports at the local or remote reporting rate. Each report from
the TCP ports is terminated with carriage-return/linefeed characters (CRLF). Up to two local UDP Hosts and three
remote UDP Hosts may be specified. Reports are sent as a datagram with no terminating CRLF.
TAIP Vehicle ID
The TAIP, With ID format allows a report to contain a user-supplied field to identify the sending mobile. This readonly field, which may contain up to 8 letters or digits (special characters not allowed), is taken from the Unit ID that
can be set from Unit Status » Basic Settings » Unit ID » ID.
Local Delivery
The Vanguard Cellular Broadband Router will produce a report each second and send it to any connected TCP clients
and to the specified UDP hosts. IMPORTANT! Local reports should only be delivered to addresses reachable through
the local LAN or WLAN ports. Sending reports once per second or faster over the cellular network could result in a
congested cellular network and/or extremely large network usage charges.
TCP Server Format
Reports in the specified format (see the table above) are available to local clients that connect to TCP port 6257 of
the Vanguard Cellular Broadband Router.
UDP Host (1,2) Format
Reports in the specified format (see the table above) are sent to the specified IP address and port.
Note: Different reports can be directed to the same UDP Host address and port.
UDP Host (1,2) Address
IP address of the UDP Host in dotted decimal format.
UDP Host (1,2) Port
IP Port of the UDP Host (1024-65535).
Remote Delivery
The Vanguard Cellular Broadband Router can be configured to report after a certain time or distance.
Report every ( ) seconds
Triggers the sending of a new remote report if the time since the last remote report exceeds the specified number
of seconds.
Report every ( ) meters
Triggers the sending of a new remote report if the distance since the last remote report exceeds the specified
distance (in meters).
But no less than ( ) seconds between reports
To prevent a fast-moving vehicle from reporting too frequently, a lower limit on the time between reports can be
specified.
TCP Server Format
Reports in the specified format (see the table above) are available to remote clients that connect to TCP port 6258
of the Vanguard Cellular Broadband Router.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 71
Page 79

UDP Host (1,2,3) Format
Reports in the specified format (see the table above) are sent to the specified IP address & port.
NOTE: Different reports can be directed to the same UDP Host address and port.
UDP Host (1,2,3) Address
IP address of the UDP Host in dotted decimal format.
UDP Host (1,2,3) Port
IP Port of the UDP Host (1024-65535).
Store and Forward Settings
The Vanguard router can be configured to store reports generated by the Remote Delivery configuration when out of
coverage. Those reports will be forwarded to the specified host(s) when the router reestablishes its cellular connection.
Store and Forward
Enable or disable the Store and Forward feature of the Vanguard .
Deliver messages every ( ) seconds
This specifies the rate used to deliver the stored messages to the host(s) when the unit is again within coverage.
This MUST be configured faster than the reports being generated by the Remote Delivery configuration.
Max reports to store
This specifies the maximum number of reports to store. When filled, the oldest reports will be overwritten by new
reports. (This maximum is divided by the number of different formats that have to be stored and forwarded. For
example, if remote hosts only receive the GGA message, then up to 1800 reports can be stored; if remote hosts are
to receive GGA and RMC messages, then up to only 900 pairs can be stored.)
3.8.2 ST A T U S
This section displays the current status of the GPS receiver. Click Refresh to update the display.
Figure 45 GPS — Status
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 72
Page 80

Condition
Indicates the quality of received GPS reports.
Not Installed This unit does not have a GPS receiver installed.
Disabled The cell-module GPS receiver has be disabled.
No Fix / Invalid The GPS receiver has not yet acquired enough satellites to provide an accurate
position, or the previous Estimated Position is over 3 minutes old.
Standard GPS Fix GPS position is reported using no additional correction information.
Differential GPS Fix Differential GPS corrects various inaccuracies in the GPS system to yield
measurements accurate to a couple of meters when the mobile is moving and even
better when stationary.
Estimated / Satellite reception has degraded to the point where only an Estimated position or
Last Known Position the Last Known Position can be reported.
Number of Satellites
Indicates the number of satellite signals being received and used to calculate position.
UTC
The current time according to Universal Coordinated Time in hh:mm:ss, using a 24-hour clock format.
Position
The current position in Latitude (North-South) and Longitude (East-West). Positions are reported in degrees and
decimal minutes. For example, a Longitude of 73 degrees, 39 minutes, and 45 seconds West appears as: 73
39.75000 W.
Altitude
The current height above Mean Sea Level in meters.
True Course
Shows the current GPS-generated true course in degrees.
Ground Speed
Shows travel speed (in Km/h).
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 73
Page 81

3.9 DIAGNOSTICS
From the main navigation pane, select Diagnostics for access to the SNMP, DeviceOutlook™, and Logging configuration
pages.
3.9.1 SNM P
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is used in network management systems to monitor networkattached devices for conditions that warrant administrative attention. SNMP version v2c and v3 are supported with the
exception of INFORM.
Figure 46 Diagnostics — SNMP
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 74
Page 82

SNMP Configuration
SNMP
Selecting Enable will allow the SNMP functionality. Selecting Disable will shut off SNMP functionality.
Version
With SNMP Enabled, select the corresponding version that matches the SNMP Manager.
SNMP v2c
Read-only Community Name
The community string used for accessing the read-only Management Information Bases (MIBs).
Read-write Community Name
The community string used for accessing all Management Information Bases (MIBs) including writable objects.
SNMP v3
User Name
The user name for secure access to the Management Information Bases (MIBs) observing v3 standard.
Password
The corresponding user password for accessing the Management Information Bases (MIBs) including writable
objects.
Authentication
Selecting the authentication method for accessing the Management Information Bases (MIBs).
Traps
Traps
Selecting Enable will allow the active trap events to be reported to the defined server(s). Selecting Disable will
deactivate events reporting. Up to four destinations can be specified.
Server Address
IP address of server to which the trap events will be sent to.
Server Port
The corresponding server port to which the trap events will be sent to (default 162).
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 75
Page 83

3.9.2 SM S
The SMS CLI (Command-Line Interface) allows a small set of commands to be sent to the Vanguard using SMS.
More information about the Vanguard — SMS Interface is provided in APPENDIX D.
Figure 47 Diagnostics – SMS
All commands are prefixed with the slash “/” character. The supported commands are:
/status [pw=password]
Returns the following fields:
WAN= DOWN or the IP address of the cellular connection
RSSI= the signal strength of the cellular radio channel
ECIO= the interference on the cellular radio channel
PPTP= the state of the PPTP VPN: UP or DOWN
IPSEC= the number of active / enabled / defined tunnels
GPS= the latitude, longitude (in decimal degrees) of the modem
V= the main voltage of the modem
T= the temperature of the modem
D1=, D2= the state of the twor digital inputs: 0 (inactive) or 1 (active)
A1=, A2= the levels of the two analog inputs, in volts
R1=, R2= the state of the two relay outputs: O (open) or C (closed)
/pptpstart [pw=password]
Starts the PPTP VPN.
/pptpstop [pw=password]
Stops the PPTP VPN.
/ipsecstart [pw=password] tun=label
Starts the IPsec tunnel that has the specified label.
/ipsecstop [pw=password] tun=label
Stops the IPsec tunnel that has the specified label.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 76
Page 84

/output [pw=password] m=v …
Controls the relay outputs, where:
r is “r”, “rly”, or “relay”;
n is “1” or “2”;
v is “0”, “o”, or “open” to open; “1”, “c”, “close”, or “closed” to close.
r and v can be in any case, upper or lower. Both relays can be set from one command.
SMS Commands
SMS Commands
– Enable allows the Vanguard to respond to received SMS commands.
– Disable causes SMS messages (that start with a slash) to be accepted but quietly discarded.
Password
In nonblank, all commands require the password in the form pw=password as one of the arguments. The pw prefix
can occur in any case (“pw=”, “PW=”, “Pw=”, etc.) but the password must be in the exact case as entered on the
web page.
Allowed Senders
Sender 1 / Sender 2 / Sender 3
Commands can be restricted to be accepted only if they arrive from one of up to three “friendly” SMS Sender
addresses. Sender addresses are typically numeric digits only including the country code prefix. The check box in
front of each Sender address can be used to enable or disable the address entered in the adjacent field. If all three
addresses are disabled, then commands will be accepted from ALL senders.
Respond only to Senders
For security, command responses, including error messages, can be restricted to be returned only to the registered
Sender SMS addresses.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 77
Page 85

3.9.3 DE VICEOUTLOOK™
The DeviceOutlook™ tab allows configuration of the Vanguard to work with DeviceOutlook device and network
management system, which is built on the CalAmp Online Telemetry System (COLT) platform and CalAmp Enterprise
Services (CES).
Figure 48 Diagnostics — DeviceOutlook™
DeviceOutlook Client
DeviceOutlook
DeviceOutlook is enabled by default. Only disable this if not using Device Outlook or COLT services.
Version
Displays the version of the DeviceOutlook app currently running in the Vanguard .
Port
The UDP port number on which the DeviceOutlook client app listens. The default UDP port used for this is 20510.
DeviceOutlook Server Configuration
IP Address
The IP address of the DeviceOutlook server. The DeviceOutlook client will use this IP address to communicate with
the server if the Domain Name is not provided.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 78
Page 86

Domain Name
The domain name of the DeviceOutlook Server. The DeviceOutlook client app will use this domain name to
communicate with the server.
Port
The UDP port number of the DeviceOutlook server that the DeviceOutlook client app uses to send all messages.
ID Report
Enable this to have the DeviceOutlook client app generate periodic ID reports. Disable to not generate ID reports.
The default setting is to generate reports.
ID Report Frequency
If ID report generation is enabled, specify how often reports are to be generated by the DeviceOutlook client app.
DeviceOutlook Maintenance Server Configuration
IP Address
The IP address of the DeviceOutlook Maintenance server. The DeviceOutlook client app will use this IP address to
communicate with the server if the domain name is not provided.
Domain Name
The domain name of the DeviceOutlook Maintenance server. The DeviceOutlook client app will use this domain
name to communicate with the DeviceOutlook Maintenance server.
Port
The UDP port number of the DeviceOutlook Maintenance server that the DeviceOutlook client app uses to send all
messages.
3.9.4 LO G GING
The Logging page provides a way to capture the current status log of the modem. Log information is useful when
contacting CalAmp Technical Support to resolve operational problems.
Figure 49 Diagnostics — Logging
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 79
Page 87

Current Firmware Information
Version
Displays the modem firmware version currently loaded in the unit.
Kernel Date
Displays the date of the operating system kernel the unit is running.
Logging Settings
Auto-Logging
Selecting Enable and clicking Save will enable the logging capability which saves periodic and event driven logs to
permanent memory. Technical Services personnel may find such logs useful in analyzing field issues. Selecting
Disable and clicking Save will disable the logging capability. This is the default setting. To make best use of available
memory it is recommended to only enable the logging capability if it is necessary to help diagnose an issue.
Log File Actions
Log Action
― Store in modem: Selecting Store in Modem and pressing Go will create a current status log, and overwrite any
previously saved log. This action will save a log even if auto-logging is disabled. It is best to save the log
immediately following the adverse event, and before any reboot. This log will contain only information
collected since the most recent reboot of the device.
― Display: Selecting Display and pressing Go will display a previously stored log directly to the web browser. You
can use your mouse to select the text, copy it, and paste it into a text editor to save the log on your computer.
― TFTP to Server: Selecting TFTP to Server and pressing Go will initiate a transfer of a previously saved log file to a
specified IP address using the TFTP protocol. In order for the transfer to be successful, a reachable IP address
must be entered under TFTP Server IP and the computer at that IP address must be running a TFTP Server
program. Many free TFTP Servers are available for download over the internet. Note that TFTP is different than
FTP.
TFTP Server IP
When selecting TFTP to Server and pressing Go a valid and reachable IP address must be entered here in order to
complete the transfer of the saved log file using the TFTP protocol. In order for the transfer to be successful, a
reachable IP address must be entered under TFTP Server IP and the computer at that IP address must be running a
TFTP Server program. Many free TFTP Servers are available for download over the internet. Note that TFTP is
different than FTP.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 80
Page 88

3.10 I/O SETTINGS
3.10.1 STATUS
Figure 50 I/O Settings — Status
Device Input Status
Main Voltage
Displays current voltage applied to the unit, in Volts.
Modem Temperature
Displays temperature of the Wireless Modem, in Celsius.
Analog Input Status
Analog Input 1, Analog Input 2
Displays voltage of the specified analog input, in Volts.
Digital Input Status
Digital Input 1, Digital Input 2
Displays the status of the specified input: Active (high state) or Normal (low state).
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 81
Page 89

Digital Output Status
Digital Output 1, Digital Output 2
Currently Not Available.
Relay Output Status
Relay Output 1, Relay Output 2
Displays the status of the specified output as open or closed.
3.10.2 SETTINGS
Status Monitoring is provided via NMEA-based protocol. The Vanguard I/O subsystem operates according to a
manager/agent model. The PC-hosted manager sends requests to the Vanguard I/O agent, which performs the
required actions. The Vanguard agent reports alarms to the PC-hosted manager.
More information about the Vanguard — NMEA I/O Agent is provided in APPENDIX E.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 82
Page 90

Figure 51 I/O Settings — Settings
NMEA Connection
Manager IP address/port
The IP address and service port of the NMEA server (manager).
Manager connection type
The connection protocol to communicate with the NMEA server (manager).
NMEA Identification
Unit ID
The Unit Name to be included in the NMEA message payload.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 83
Page 91

Source Identification
The Unit's IP address that will be included in the NMEA message payload.
SMS Notification
Destination 1 / Destination 2 / Destination 3
Alarms and notifications can be sent to up to three SMS destination addresses. Destination addresses are typically
numeric digits only including the country code prefix. The check box in front of each destination address can be
used to enable or disable each address entered in the adjacent field. The report will consist of the Unit ID and colon
(:) if the Unit ID is not blank, and the appropriate label from the I/O Settings » Labels tab.
More information about the Vanguard — SMS Interface is provided in APPENDIX D.
Triggers – Device
Cell Temperature and thresholds
Enable or disable NMEA alarm and notification when temperature goes out of range.
Triggers – Analog Input
Analog Input and thresholds (1 or 2)
Enable or disable NMEA alarm and notification when an analog input goes out of range.
Triggers – Digital Input
Digital Input 1, Digital Input 2
Enable or disable NMEA alarm and notification when the input state changes.
NMEA Message Format
Messages generated by the Vanguard I/O Agent subsystem for alarms and indications conform to NMEA 0180.
Explanation of the Protocol Data Unit (PDU) format that is used and example messages are provided in APPENDIX E.
These messages will be sent to the manager at the NMEA manager IP address and port specified in the above field.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 84
Page 92

3.10.3 LABELS
Each diagnostic value can be user-defined messages indicating its normal and abnormal conditions.
Figure 52 I/O Settings — Labels
3.11 FIRMWARE UPDATE
When newer versions of the modem firmware become available, the user can download the proper file from the
CalAmp web site and manually update the unit by uploading the new firmware. Time required for uploading new
firmware, depending on the unit, may range from four to fifteen minutes. The estimated amount of time required is
indicated in the note in red under the progress indicator.
Firmware update files are typically given file names of the form upgrade_v{old}_to_v{new}.tar.gz. Make sure
{old} corresponds to the firmware version currently installed on the unit. Upgrading with the incorrect file may prevent
correct operation after the upgrade.
Caution: It is important to have a stable power source and ensure that power to the Vanguard is not interrupted
during a firmware upgrade.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 85
Page 93

Figure 53 Firmware Update
Current Firmware Information
Version
Displays the modem firmware version currently loaded in the unit.
Kernel Date
Displays the date of the operating system kernel the unit is running.
Upload New Firmware
The Upload New Firmware section allows you to upgrade to new firmware as new firmware versions become available,
as explained above. Updates can be done over the local Ethernet connection or over the cellular network if Remote
Administration is enabled, allowing remote access to the Vanguard Web Interface and the Firmware Update page.
CAUTION: At the time of this writing, use of Internet Explorer 7, Internet Explorer 9, and Internet Explorer 10 browsers
are not recommended for performing firmware upgrades.
File
Enter the update file name or you may use the browse button to locate the file from your hard drive.
Progress
Displays the update progress after Upload has been clicked.
Upload Button
After selecting the firmware upgrade filename above, press the Upload button to begin the firmware upgrade
process.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 86
Page 94

Configuration File
The Configuration File section allows you to create backups of how your Vanguard is configured and to restore all
configuration settings from a backup file if one has been created.
CAUTION: At the time of this writing, use of Internet Explorer 7, Internet Explorer 9, and Internet Explorer 10 browsers
are not recommended for backing up or restoring the configuration file.
File
Field to input the uploaded configuration file. The Browse button can be used to locate the file in a specific folder.
The configuration file to be uploaded must be named config.xml. If multiple files need to be maintained, it is
recommended that separate directories be used. The configuration backup or restore can be done over the local
Ethernet connection, or over the cellular network if Remote Administration is enabled, allowing remote access to
the Vanguard Web interface and the Firmware Update page. If restoring a configuration that specifies connection
on a different IP address for remote administration, you will need to know this IP address and enter it in your
browser address bar to navigate to the Vanguard Web interface after the Vanguard resets.
Upload Button
After selecting the firmware configuration filename above, press the Upload button to begin the configuration
loading process.
Save
Returns a link to the configuration file on the unit. Right-click the link and select “Save Target As…” to save the file.
The link page refreshes after 15 seconds. It is recommended to use the specified filename to save the file. If multiple
files need to be maintained, it is recommended to use directory paths to separate the files.
4 IP ADDRESSING
4.1 OVERVIEW
When Vanguard cellular router is connected to a cellular carrier, it will always have at least two IP addresses. The first is
the local area network (LAN) address. The Vanguard can be accessed through either the LAN 1 or LAN 2 Ethernet
connectors on the front panel using this IP address. This IP address is user configurable and is saved locally in the
Vanguard. The factory default IP address is 192.168.1.50 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
The second Vanguard IP address is assigned by the cellular carrier each time the Vanguard connects to the cellular
network. Often, this IP address is publicly accessible from the Internet, however in some instances the cellular carrier
may assign an IP address that is protected by firewalls. When a publicly accessible IP address is assigned, data flows can
be initiated from either the Vanguard or from the Internet. When an IP address is protected by cellular firewalls, data
flows can only be initiated from the Vanguard. In either case, after a data flow has been established, data is free to
move in both directions.
For mobile models equipped with WiFi, the Vanguard will be assigned a third IP address on the WiFi wireless network.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 87
Page 95

4.2 IP ADDRESSING TUTOR I AL
The default LAN subnet of the Vanguard consists of addresses from 192.168.1.0 to 192.168.1.255. The first and last IP
addresses of a subnet are always reserved, no matter what the subnet size is. The first IP address in the subnet is the
Network ID. The last IP address in the subnet is the Broadcast Address.
The example below illustrates a sample Vanguard network. The subnet consists of IP addresses ranging from
192.168.1.0 to 192.168.1.255. The subnet mask is 255.255.255.0. This is sometimes written in shorthand notation as:
192.168.1.50/24 since the subnet mask 255.255.255.0 contains 24 ones then 8 zeros when it is converted to binary.
The first address 192.168.1.0 is reserved for the Network ID. The last address 192.168.1.255 is reserved for the
broadcast address. There are 254 valid IP addresses that may be assigned to hosts on the LAN network.
Ethernet Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
Network ID 192.168.1.0 (reserved – first IP address in subnet)
Broadcast Address 192.168.1.255 (reserved – last IP address in subnet)
Vanguard 192.168.1.50/24
PLC/RTU #1 192.168.1.10/24
Computer #1 192.168.1.125/24
By changing the subnet mask, the network can be made to include as many or as few IP addresses as desired. Ethernet
devices can only talk directly to other devices that have IP addresses within the same IP subnet. For example,
Computer #1 from the example above can only talk with locally connected devices that have IP addresses between
192.168.1.1 and 192.168.1.254. When Computer #1 wants to talk to another server on the Internet, it will send its data
packet to the local gateway. In this case the local gateway is the Vanguard router. Since the Vanguard has two IP
addresses (each IP address is on a separate subnet), it can forward the packet from the LAN network (192.168.1.0/24)
to the cellular network. The packet will continue to be forwarded in a similar fashion, from subnet to subnet, until it
reaches its final destination.
4.3 PRIVATE VERSUS P U B L IC IP ADDR E S S E S
Certain address ranges in the in IPv4 address space have been reserved as private IP address. Private IP addresses can
be used by anyone, without the need to register for an IP address assignment from the IANA (Internet Assigned
Numbers Authority). However, private IP addresses are not routable on the Internet. Routers on the Internet will
typically drop any packets that are destined for a private IP address. These addresses are reserved for local use only.
Common Private IP Address Ranges
10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
Devices using Private IP addresses must have a router with NAT (network address translation) capability to access the
Internet. By default, the Vanguard will perform the NAT function on all outgoing traffic. The Vanguard router will
change the source IP address from the private IP of the local host to the Vanguard’s public IP address which was
assigned by the cellular carrier. Since the outgoing packet has been modified, a remote server or website on the
Internet will think the packet came directly from the Vanguard radio. It will reply back to the cellular IP address of the
Vanguard. The Vanguard radio remembers which traffic flows have been established and routes the incoming return
traffic back to the desired host device on the local area network.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 88
Page 96

4.4 PORT FORWARDING
NAT functionality is only useful for traffic flows that are initiated by the Vanguard or by a device that is physically
connected to the Vanguard. Port forwarding can be enabled to allow remote devices connecting through the Internet
to initiate traffic flows with a local device connected to a Vanguard router.
In the example configuration shown below, a host from the Internet can create either a TCP or UDP connection with
the local host at 192.168.1.250 on port 7000 by sending a packet to the cellular IP address of the Vanguard at port
8010. When the Vanguard receives a packet destined for port 8010 it will look through the Port Forwarding table to see
if a matching rule exists. It finds the rule that instructs it to forward this packet to port 7000 of IP address
192.168.1.250. The Vanguard then modifies the destination IP address and port number before forwarding the packet
onto the local area network.
Figure 54 Port Forwarding Example
Port forwarding is useful for field applications that use polling that is initiated by a polling master. The port forwarding
function allows the polling master to establish a data connection through the Internet. The incoming polling message is
forwarded by the Vanguard to the appropriate PLC or RTU on the Vanguard’s local area network.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 89
Page 97

4.5 DMZ
Alternately, DMZ can be enabled on the Vanguard router. When DMZ is enabled, all traffic destined to the Vanguard’s
cellular IP address that is received from the Internet is forwarded to the DMZ host. The IP address of the DMZ host is
specified by the user. Using DMZ can eliminate the need to specify many individual port forwarding rules. However, by
exposing all the ports on the local device, the local device may become more susceptible to attacks.
If specific Port Forwarding rules exist in the IP Mapping Table, they will take precedence over the DMZ host.
4.6 FRIENDLY IP ADD R E S S
Friendly IP addresses can be used with either port forwarding or DMZ to provide an additional layer of security. When
Friendly IP addresses are used, the Vanguard will only forward packets to the LAN if the source IP address of the
received packet matches either the specific IP address or range of IP addresses specified in the Friendly IP address field.
This feature can be disabled by entering 0.0.0.0 in the friendly IP address field. In this case, packets from any host on
the Internet can be forwarded to the LAN when either DMZ or Port Forwarding is enabled.
5 IPSEC AND VPN PASS-T HROUGH DEPLOYMENT G UIDE
This chapter will help anyone who wants to build a secure IP network using IPsec and the Calamp Vanguard Cellular
Modem. Case #1: Vanguard Configured IPsec Client will demonstrate the Vanguard when used as an IPsec client. Case
#2 Vanguard Configured to use a DMZ for VPN Pass-Throughwill show the Vanguard passing an IPsec connection from
WAN to LAN. (VPN Pass-through).
5.1 BENEFITS OF I P S E C
IPsec (Internet Protocol Security Standard) is an industry driven standard that ensures confidentiality, integrity, and
authenticity of an IP network. IPsec is a key component of this standard-based, flexible solution for deploying a
network-wide policy.
There are two significant benefits to IPsec compliance for our customers: enhanced security features and
interoperability.
― Enhanced security features provide the most secure and comprehensive standard available today for encryption
and authentication.
The Vanguard IPsec encryption support: AES-128, AES-256 and 3DES.
The Vanguard IPsec authentication support: MD5 and SHA1.
All tunnels are created using the ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) protocol.
― Protocol interoperability means that an IPsec compliant device, such as the Vanguard , will be able to exchange
keys and encrypted communications with another IPsec compliant product such as a CISCO router. IPSEC
compliance ensures that these two different products can negotiate and maintain a secure communication with
each other.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 90
Page 98

5.2 CONFIGURATION SUM M A R Y
The first case demonstrates configuring IPsec tunnels on the Vanguard . The second example demonstrates configuring
the Vanguard to use a DMZ for VPN pass-through between IPsec clients and a remote host over a router acting as a
VPN server.
Detailed configuration examples are provided for each scenario.
5.2.1 CASE # 1 : VANGUARD CONFIGURE D IPSEC CLIE N T
Overview
IPsec is a security protocol that provides secured communication tunnels over IP. As you create IPsec tunnels through
the Vanguard Web interface in the Security » IPsec tab, they will be displayed in the Tunnel Table at the bottom of the
IPsec tab. All tunnels are created using the ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) Protocol.
The following figure depicts an IPsec tunnel between a Remote Telemetry Unit (RTU) and Application Server.
Figure 55 Vanguard configured as an IPsec client
Prerequisite Information
In order to implement IPsec with the Vanguard and to successfully connect to a VPN server and secure data between
two endpoints, you will need to know the following information.
Tunnel Label
Vanguard local subnet
Vanguard PPP IP Address
Firewall IP Address (remote IP Address)
VPN Server IP Address (Remote ID optional—not usually required if firewall and VPN server are the same unit)
Remote Subnet
Phase1 Encryption details
Phase 2 Encryption details
Pre-Shared Key (PSK)
Perfect Forward Security (PFS) Enabled or Disabled
Dead Peer Detection (DPD) delay (seconds), timeout (seconds) and action
If you do not have this information, contact your network integrator.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 91
Page 99

Vanguard IPsec Client Connection
This example will use the following values to define two IPsec tunnels.
Tunnel 1 Example Tunnel 2 Example
Tunnel Label Ttunnel1 Ttunnel2
Vanguard local subnet 10.192.10.192/29 (LAN) 10.192.10.192/29 (LAN)
Vanguard PPP IP Address (Requires a Static IP) 162.123.98.68 162.123.98.68
Firewall IP Address (remote IP Address) 68.28.128.192 68.28.128.192
VPN Server IP Address (Remote ID) 10.168.86.192 10.168.86.192
Remote Subnet 192.32.8.254/32 10.0.198.198/32
Phase1 Encryption details 3DES/MD5/Group2 3DES/MD5/Group2
Phase 2 Encryption details 3DES/MD5 3DES/MD5
Pre-Shared Key (PSK) Password1! Secret2!
Perfect Forward Security (PFS) Enabled or Disabled Disabled Disabled
Dead Peer Detection (DPD) delay/timeout/action 120 /2 /Restart by Peer 120 /2 /Restart by Peer
The objective in this example is to create two IPsec tunnels with the above parameters. These tunnels and the
parameters used to define them will appear the Tunnel Table at the bottom of the Security » IPsec tab as shown in the
figure below. Once these IPsec tunnels have been defined and added to the table, they must be enabled to be
functional.
Figure 56 Tunnel Table using example values
Vanguard IPsec Client Configuration
Step 1 From the laptop connected to the LAN port of the Vanguard , ping the remote IP Address. The pings should
receive replies.
Step 2 Open a Web browser on the connected laptop and navigate to the Vanguard Web interface.
Step 3 From the main navigation pane, select Security, and from the Security page, select the IPsec tab.
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 92
Page 100

Step 4 In the IPsec Support section of the tab, click Enable. Set NAT Mode to Bypass if it is not already selected. Click
Save.
Figure 57 Enable IPsec, set NAT mode to Bypass, and Save
Step 5 In the Tunnel Configuration section of the same tab, enter IPsec tunnel configuration information for the first
tunnel, as shown in the following figure. When you have finished entering information for all the fields, click
Add/Update to save the tunnel configuration.
Figure 58 Security — IPsec tab Tunnel Configuration settings completed for first example
Vanguard Series Multicarrier Cellular Data Modem & IP Router PN 001-7300-100 Rev. C | Page 93
 Loading...
Loading...