Page 1

SmartSwitch 9000
9T125-08
Local Management Appendix
9032052-02
Page 2

Page 3

Appendix
9T125-08 Module Specific
Information
Introduction
This appendix contains local management information that is specific to the
9T125-08 Token Ring MicroLAN Switch Module.
Module Interfaces
The 9T125-08 Token Ring MicroLAN Switch Module has five interfaces. Table 1
lists the identifying number, name, and description of each interface.
System
Interface
Number
1 SMB-1 1 Mbps System Management Bus
2 SMB-10 10 Mbps System Management Bus
3 1 FNB Flexible Network Bus (FDDI)
4 2 TOKEN RING 1 Token Ring 1 Front Panel Interface
5 3 TOKEN RING 2 Token Ring 2 Front Panel Interface
Bridge
Interface
Number
Table 1. 9T125-08 Module Interfaces
Interface
Name
Interface
Description
1
Page 4
9T125-08 Module Specific Information
FNB Resource Configuration Codes
The 9T125-08 Module provides connectivity between one of three interfaces: the
front panel Token Ring interface(s) and the FDDI rings on the backplane (FNB-1
or FNB-2).
The FNB Resource Configuration Screen allows you to connect the module’s front
panel Token Ring interface to one of the chassis’ two FDDI networks (FNB-1 or
FNB-2) via a bridge/switch.
The FNB Resource Configuration Screen lists all the possible connections that the
specified module can support on the FNB, displays the current connection, and
allows you to change the connection. Table 2 lists and describes the FDDI
Connections from which you can select.
Table 2. 9T125-08 Module FNB Resource Configuration Codes
Configuration
ID
1 NORING <-> TRNG
2 FNB1 <-> TRNG
3 FNB2 <-> TRNG
Connections
FDDI
Description
Neither the FNB-1 nor the FNB-2 on
the chassis’ backplane is connected to
the module’s bridge/switch.
The FNB-1 on the chassis’ backplane
and the module’s front panel Token
Ring interfaces are connected to the
same bridge/switch.
The FNB-2 on the chassis’ backplane
and the module’s front panel Token
Ring interfaces are connected to the
same bridge/switch.
2
Page 5
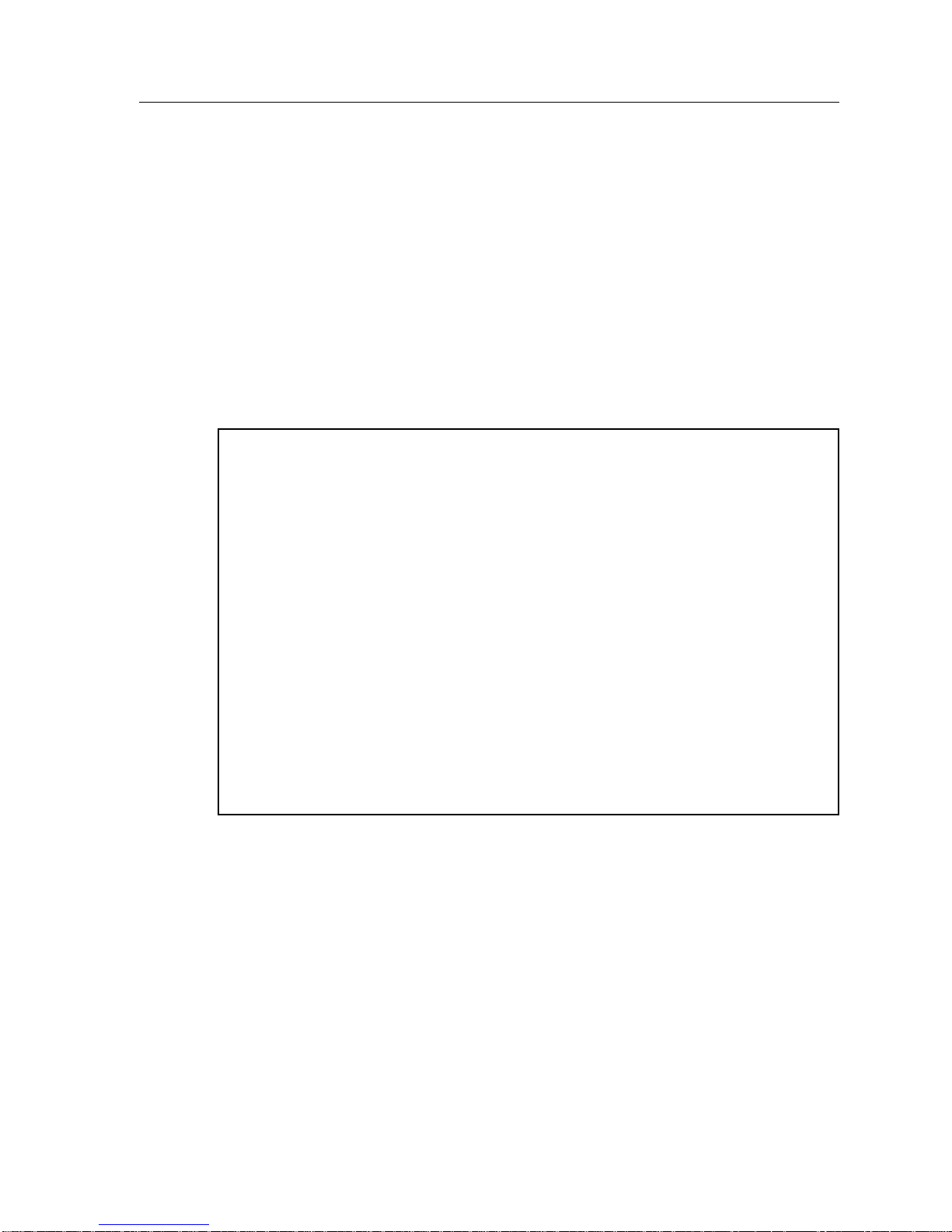
General Configuration Screen
The General Configuration Screen (Figure 1), displays various information about
the selected module and allows you to set the following general parameters:
• Date and Time
• Screen Update Time
• Screen Lockout Time
• Host IP Address
• Subnet Mask
• Default Gateway
• Default Interface
• TFTP Gateway IP Address
SmartSwitch 9000 Local Management
9T125-08 Module Specific Information
General Configuration
Module Name: 9T125-08 Firmware Revision: 01_00_00
Slot Number: 10 BOOTPROM Revision: 01.00.05
Module Serial #: Module Date: 04/15/1997
Module Board Revision: Module Time: 14:02:11
Screen Refresh Time: 03 sec
Screen Lockout Time: 15 min
FLASH Memory: 0 MB
Host IP Address: 134.141.144.117
Subnet Mask: 255.255.0.0
Default Gateway: NONE DEFINED
Default Interface: NONE DEFINED
Base MAC Address: 00-00-1D-2E-02-5C
TFTP Gateway IP: 0.0.0.0
SAVE EXIT RETURN
Figure 1. General Configuration Screen
3
Page 6

9T125-08 Module Specific Information
General Configuration Screen Fields
The following information briefly explains each General Configuration Screen
field.
Module Serial #
Displays the serial number of the selected module.
Module Board Revision
Displays the version number of the selected module.
FLASH Memory
Displays the amount (megabytes) of flash memory in the selected module.
Module Date
Contains a value that the module recognizes as the current date. To enter a new
date, highlight the field and enter the date in MM/DD/YYYY format. The month
and day portion of the date must include two digits. Therefore, enter a leading
zero for months January through September, and for dates less than 10. For
example, for June 4, 1996, enter 06/04/1996 (slashes are optional). If you do not
enter slashes to separate the month, day, and year values, the first eight digits you
enter in this field represent an entry (i.e., 06041996).
NOTE
Module Time
Contains a value that the module recognizes as the current time. To enter a new
time, highlight the field and enter the time in HH:MM:SS format. Notice that
there is no AM/PM indicator. Time should be entered based upon a 24 hour clock.
For 4:07 p.m., enter 16:07:00 (colons are optional). If you do not enter colons to
separate the hours, minutes, and seconds values, the first six digits you enter in
this field represent an entry (i.e., 160700). For 6:12 a.m., enter 6:12:00 or 061200.
The module’s default date and time settings are indeterminate. The internal
calendar and clock begin running as soon as you install the module.
Screen Refresh Time
Contains the rate at which the module’s screens are updated. This setting
determines how frequently (in seconds) information is updated on the screen. To
enter a new refresh rate, highlight the field and enter a number. The default
refresh rate is 3 seconds. The range is 3 - 99 seconds.
4
Page 7

9T125-08 Module Specific Information
Screen Lockout Time
Contains the maximum number of minutes that the Local Management
application will display a module’s screen while pending input or action from a
user. For example, if you enter 5 in this field, users will have up to five minutes to
respond in some fashion to each of the specified module’s Local Management
screens. In our example, after five minutes of “idleness” (no input or action), the
Local Management application terminates the session on the selected module and
the Slot Selection Screen reappears. To enter a new lockout time, highlight the
field and enter a number. The default lockout time is 15 minutes. The range is 1 30 minutes.
Host IP Address
Contains the Internet Protocol address currently assigned to the selected module.
Set this field according to your network requirements. Highlight the Host IP
Address field and enter the desired IP address using dotted decimal notation (4
decimal values between 1 and 255 separated by periods) as follows:
255.255.255.255
(255 is the maximum number that you can enter in any of the four segments.
Default = 0.0.0.0 .) This address can be used by any of the system interfaces on
the module.
Subnet Mask
Contains the subnet mask for the selected module. A subnet mask “masks out”
the network bits of the IP address by setting the bits in the mask to 1 when the
network treats the corresponding bits in the IP address as part of the network or
subnetwork address, or to 0 if the corresponding bit identifies the host. The
default subnet mask uses the first two portions of the IP address to identify the
network id, leaving the rest of the IP address to identify specific nodes. To enter a
new subnet mask, highlight the field and enter a new value using dotted decimal
notation (4 decimal values between 1 and 255 separated by periods) as follows:
255.255.255.255
(The Subnet Mask field defaults to the natural mask value, based on the IP
Address that you entered for the device.)
Default Gateway
Contains the IP Address of the device to which all packets addressed to an
unknown network or host are sent. If you do not configure a Default Gateway,
any packets that are addressed to an unknown network or host will be dropped.
This field is not defined until you enter an appropriate value using dotted
decimal notation (4 decimal values between 1 and 255 separated by periods).
5
Page 8
9T125-08 Module Specific Information
Default Interface (Toggle)
Contains the number that represents the interface that is connected to the
module’s Default Gateway. In some instances, dissimilar modules have different
corresponding interface numbers. For example, if you are assigning a default
interface to a 9E133-36 module and you enter a 3, then the default interface is the
Flexible Network Bus. However, if you are assigning a default interface to a
9F310-02 module and you enter a 3, then the default interface is the Internal
Network Bus. See Table 1 for module-specific interface information. The default
is NONE, meaning no default interface selected.
The Default Interface field becomes active after you enter an IP address in the
NOTE
Default Gateway field.
Base MAC Address
Displays the MAC Address of the selected module. This is the MAC Address of
the SMB-10 interface.
TFTP Gateway IP
The IP address of the router that connects to or is closest to the module. Configure
this address when you are performing TFTP downloads in a routed environment
(if proxy ARP is disabled on the router).
6
Page 9
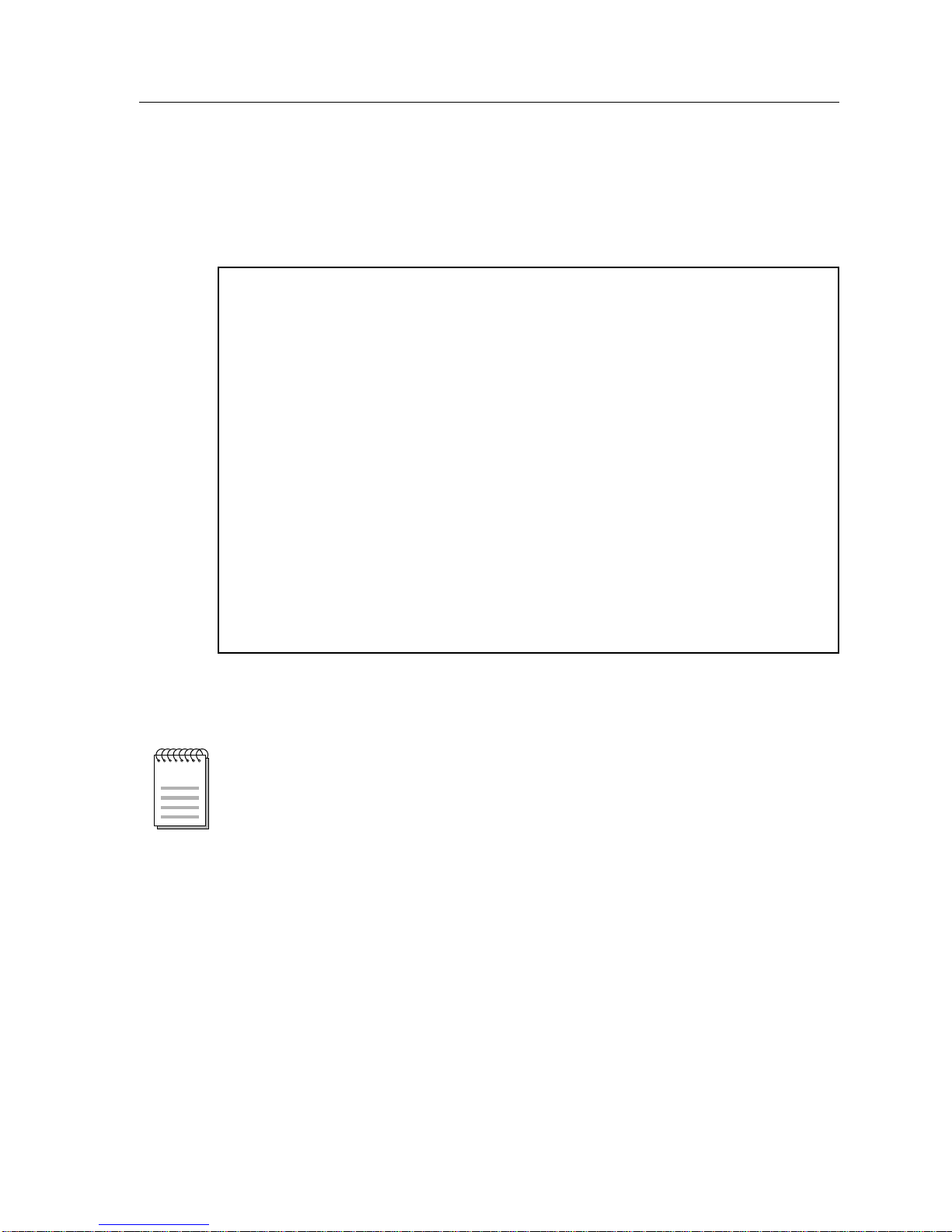
Switch Configuration Screen
The Switch Configuration Screen (Figure 2), provides basic setup options for
making a switch operational in your network.
SmartSwitch 9000 Local Management
Switch Configuration
Module Name: 9T125-08 Firmware Revision: 01_00_00
Slot Number: 10 BOOTPROM Revision: 01.00.05
Bridge Address: 00-00-1D-2E-02-5C Bridging Interfaces: 3
Bridge Priority Label (hex): 8000 Type of STA: [IEEE]
Bridge Path Cost (hex): 0000000A Novell Xlat: [NONE]
9T125-08 Module Specific Information
NOTE
Interface MAC/Local Address Ring Bridge Status
Speed State
1 (FNB) 00-00-B8-74-40-BA 100 forwarding [ENABLED]
2 (TR1) 00-00-B8-74-40-7A [16] forwarding [ENABLED]
3 (TR2) 00-00-B8-74-40-FA [16] forwarding [ENABLED]
SAVE SRT CONFIGURATION EXIT RETURN
Figure 2. Switch Configuration Screen
To modify a non-toggle field on this screen, use the arrow keys to highlight the
field, then press the Enter key. Now you can modify the field.
7
Page 10

9T125-08 Module Specific Information
Switch Configuration Screen Fields
The following information briefly explains each Switch Configuration Screen
field.
Bridge Address
Displays the MAC Address of the bridge.
Bridge Priority Label
Allows you to enter a hexadecimal number that identifies the write-able portion
of the Bridge ID, i.e., the first two octets of the Bridge ID. Valid bridge priority
labels range from 0000 to FFFF.
Bridge Path Cost
Allows you to enter (as a hexadecimal number) the cost of the path to the root as
seen from the specified bridge. Valid bridge path costs range from 00000001 to
0FFFFFFF.
!
CAUTION
Bridging Interfaces
Displays the total number of bridging interfaces on the selected module.
Type of STA (Toggle)
Allows you to set the method that bridges use to decide which bridge is the
controlling (Root) bridge when two or more bridges exist in parallel (Spanning
Tree Algorithm). Valid entries include IEEE and NONE. Press the Space Bar to
toggle to the desired value.
All bridges in a network must use the same Spanning Tree protocol. The IEEE
protocol has a unique format for its Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDU). Trying
to mix STA protocols results in an unstable network.
Novell Xlat (Toggle)
Specifies the type of address swapping for Novell translation. Novell Xlat is one
of the following:
• NONE - Address swapping is disabled
• DLC - Bit reversal of the datalink destination address and source address
• LLC - Bit reversal of Netware payload-based MAC addresses
Press the Space Bar to toggle to the desired value. You must SAVE your choice for
it to affect Novell translation.
Interface
Lists each bridge interface on the selected module: FNB, TR1, and TR2.
8
Page 11

9T125-08 Module Specific Information
MAC/Local Address
Lists the hardware address of each listed bridge interface.
Ring Speed (Toggle)
Allows you to set each token ring interface’s operating speed (either 4 Mbps or 16
Mbps). Press the Space Bar to toggle to the desired value.
Bridge State
Displays the current state of each listed interface. The possible interface states
include:
Disabling: Management has disabled this interface. No traffic can be received
or forwarded while the interface is disabled.
Learning: The bridge is learning this interface’s network addresses. The
bridge enters the learning state when the Transparent Database is
created (during start-up or after being deleted), or when the
Spanning Tree Algorithm detects a network topology change.
Listening: The bridge is not adding information to the Transparent Database.
The bridge is monitoring BPDU traffic while preparing to move
from the learning to the forwarding state.
Forwarding: The bridge is on-line and this interface is forwarding traffic.
Blocking: This interface will not forward any traffic through the bridge.
Status (Toggle)
Allows you to set the bridge forwarding status of the listed interface (either
ENABLED or DISABLED). Press the Space Bar to toggle to the desired value.
Displaying the SRT Configuration Screen
To display the SRT Configuration Screen, use the arrow keys to highlight SRT
CONFIGURATION, then press the Return key.
9
Page 12

9T125-08 Module Specific Information
SRT Configuration Screen
The SRT Configuration Screen (Figure 3), provides basic setup options for making
a switch operational in your network.
SmartSwitch 9000 Local Management
SRT Configuration
Module Name: 9T125-08 Firmware Revision: 01_00_00
Slot Number: 10 BOOTPROM Revision: 01.00.05
Bridge Number (hex): 1
Interface Ring Hop Bridge Explorer |--SRT Protocol Transmission-----|
Number Count Method Type TCP/IP IPX SNA NetBios Other
1 (FNB) 001 TP TP
2 (TR1) 002 6 [SRT] [STE] [ SR ] [ SR ] [ SR ] [ SR ] [ SR ]
3 (TR2) 003 6 [SRT] [STE] [ SR ] [ SR ] [ SR ] [ SR ] [ SR ]
SAVE EXIT RETURN
Figure 3. SRT Configuration Screen
10
Page 13

SRT Configuration Screen Fields
The following information briefly explains each SRT Configuration Screen field.
Bridge Number
Allows you to enter a hexadecimal number that uniquely identifies a bridge when
more than one bridge is used to span the same two segments. Valid bridge
numbers range from 01 to 0F (15).
Interface
Lists each bridge interface on the selected module: FNB, TR1, and TR2.
Ring Number
Allows you to set the hexadecimal number that uniquely identifies the ring to
which the specified interface is connected. Valid ring numbers range from 001 to
FFF.
Hop Count
Allows you to set the maximum number (1 through 6) of routing descriptors
allowed in All Routes or Spanning Tree Explorer frames.
9T125-08 Module Specific Information
Bridge Method (Toggle)
Displays one of the following bridge methods:
• Source Route (SR) - All frames from the FNB are forwarded on the front panel
Token Rings with a source route RIF. There is no transparent frame support.
The Token Ring interface may only receive and transmit SR frames in this
mode. All TP frames are filtered when they are received by the Token Ring
interface.
• Source Route Transparent (SRT) - Performs source route bridging when
required, transparent bridging when required, and translational bridging. The
Token Ring interface can receive and transmit both SR and TP frames.
• Transparent (TP) - There is no source routing support. The bridge performs
transparent 802.1d bridging. All SR frames are filtered when they are received.
11
Page 14

9T125-08 Module Specific Information
Table 3. Bridge Methods and Explorer Type Choices
Bridge Method Explorer Type Choices
TP - Frames that are destined for an unknown destination
address (not in bridge database) or a broadcast destination
TP
address are forwarded on to the Token Ring(s) as TP frames.
No translation for source routing is performed.
ARE - Frames that are destined for an unknown destination
address (not in bridge database) or a broadcast destination
address are forwarded onto the Token Ring(s) as All Route
Explorer (ARE) frames. FDDI TP frames are translated to
this type of source routed frame.
NOTE
SR
SRT (default)
SRT Protocol Transmission (Toggle)
STE - Frames that are destined for an unknown destination
address (not in bridge database) or a broadcast destination
address are forwarded onto the Token Ring(s) as Spanning
Tree Explorer (STE) frames. FDDI TP frames are translated
to this type of source routed frame.
ARE (See ARE definition above)
STE (See STE definition above). This is the default.
When the destination address is unknown, SRT Protocol Transmission specifies
the method of transmission, per protocol, onto the Token Ring. Valid methods are:
• SR - Source Route packet
• TP - Transparent packet
• Auto - Transmits both an SR and a TP packet
These methods only appear when the Bridge Method is set to SRT.
12
Page 15

Saving SRT Configuration Choices
To save your modifications of the values on the SRT Configuration Screen:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight SAVE at the bottom of the screen, then press
the Return key.
2. When the message “SAVED OK” appears, the edits you have made are saved.
If you exit without saving, the message “NOT SAVED -- PRESS SAVE TO
KEEP CHANGES” appears. If you exit without saving, your edits will be lost.
Exiting the SRT Configuration Screen
To exit the SRT Configuration Screen, use the arrow keys to highlight RETURN,
then press the Return key.
9T125-08 Module Specific Information
13
Page 16

9T125-08 Module Specific Information
Token Ring Port Configuration
The Token Ring Port Configuration Screen (Figure 4), allows you to view the
current operational and administrative status of the module’s ports. This screen
also allows you to change the administrative status of each port (turn each port on
or off).
SmartSwitch 9000 Local Management
Token Ring Port Configuration
Module Name: 9T125-08 Firmware Revision: 01_00_00
Slot Number: 10 BOOTPROM Revision: 01.00.05
RING #1 RING #2
RO WRP RO WRP ^
1 ENB 1 ENB |
2 ENB 2 ENB |
3 ENB 3 ENB |
4 ENB 4 ENB
RI WRP RI WRP Token Flow
|
|
|
|
|
[ OPERATIONAL ] EXIT RETURN
Figure 4. Token Ring Port Configuration Screen
The current configuration mode (either OPERATIONAL or ADMINISTRATIVE)
appears on the command line.
14
Page 17

Token Ring Port Configuration Screen Fields
The following information briefly explains each Token Ring Port Configuration
Screen field.
Ring #
Displays the current status/settings of the module ports that are attached to each
token ring. The information that appears, and whether that information is
modifiable, varies according to the configuration mode you select.
Token Flow
Graphically displays the direction in which the token travels. In other words:
RI 4 3 2 1 Bridge RO
Interface
9T125-08 Module Specific Information
Changing From Operational Mode to Administrative Mode
The configuration mode command allows you to toggle between two values:
ADMINISTRATIVE or OPERATIONAL. To change the mode:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight either ADMINISTRATIVE or OPERATIONAL
at the bottom of the screen.
2. Press the Space Bar to toggle to the desired mode.
3. Press the Return key. The selected mode becomes effective.
The ADMINISTRATIVE mode is detailed on page 16.
The OPERATIONAL mode is detailed on page 18.
15
Page 18

9T125-08 Module Specific Information
Token Ring Port Configuration Screen Administrative Mode
The Token Ring Port Configuration Screen (Administrative Mode) (Figure 5),
allows you to turn a module’s ports ON (administratively enable) or OFF
(administratively disable). You can turn ports ON/OFF individually or all on the
token ring.
SmartSwitch 9000 Local Management
Token Ring Port Configuration
Module Name: 9T125-08 Firmware Revision: 01_00_00
Slot Number: 10 BOOTPROM Revision: 01.00.05
RING #1 RING #2
RO [ON ] RO [ON ] ^
1 [ON ] 1 [ON ] |
2 [ON ] 2 [ON ] |
3 [ON ] 3 [ON ] |
4 [ON ] 4 [ON ]
RI [ON ] RI [ON ] Token Flow
|
|
|
|
|
[ ENABLE ALL ] [ADMINISTRATIVE] EXIT RETURN
Figure 5. Token Ring Port Configuration Screen (Administrative Mode)
16
Page 19

9T125-08 Module Specific Information
Configuring Administratively an Individual Port
To administratively configure an individual port:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the value in the field of the port that you want
to configure. Press the Space Bar until the desired value appears in the field
(either ON or OFF).
2. Press the Return key.
Configuring Administratively All Ports on a Token Ring
To administratively configure all ports on a Token Ring (Token Ring 1 or Token
Ring 2):
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the value in the ENABLE/DISABLE
command (lower left portion of the screen).
2. Press the Space Bar until the desired value appears in the field (ENABLE ALL
or DISABLE ALL, ENABLE TOKEN RING 1 or DISABLE TOKEN RING 1,
ENABLE TOKEN RING 2 or DISABLE TOKEN RING 2).
3. Press the Return key.
Exiting the Port Configuration Screen
To exit the Port Configuration Screen, use the arrow keys to highlight RETURN,
then press the Return key.
17
Page 20

9T125-08 Module Specific Information
Token Ring Port Configuration Screen Operational Mode
The Port Configuration Screen (Operational Mode) (Figure 6), displays the
current status of each port in the module’s token ring. The status value that
appears in a port’s field is determined by the type of port (Lobe or RI/RO), and its
administrative status (On/Off).
SmartSwitch 9000 Local Management
Token Ring Port Configuration
Module Name: 9T125-08 Firmware Revision: 01_00_00
Slot Number: 10 BOOTPROM Revision: 01.00.05
RING #1 RING #2
RO WRP RO WRP ^
1 ENB 1 ENB |
2 ENB 2 ENB |
3 ENB 3 ENB |
4 ENB 4 ENB
RI WRP RI WRP Token Flow
|
|
|
|
|
[ OPERATIONAL ] EXIT RETURN
Figure 6. Port Configuration Screen (Operational Mode)
18
Page 21

And if the port is
If the port is a...
Ring Port
RI (ring-in) or
RO (ring-out)
Lobe Port ON
administratively
9T125-08 Module Specific Information
Table 4. Token Ring Port Operational Codes
Then, the operational status is:
turned...
ACT (Active)
The port is on and is passing data to the ring.
ON
WRP (Wrapped)
The port is on, but it is autowrapped, either because of a
cable failure or because the cable is not connected.
OFF DIS (Disabled)
The port is off (wrapped by Management).
INS (Inserted - Phantom link is detected)
The lobe port is inserted into the ring.
ENB (Enabled - No phantom link is present)
The lobe port is not inserted into the ring.
LNK (Linked - Phantom link is detected)
The lobe port is trying to gain access to the ring, but it has
OFF
ON or OFF
been prevented.
BYP (Bypassed - No phantom link is present)
The lobe port is not attempting to gain access to the ring.
FLT (Speed Fault)
The ring speed of the port is in conflict with the ring speed
of the designated token ring. The port will remain
wrapped.
Exiting the Port Configuration Screen
To exit the Port Configuration Screen, use the arrow keys to highlight RETURN,
then press the Return key.
19
Page 22

9T125-08 Module Specific Information
Token Ring Secured Station Configuration
The Token Ring Secured Station Configuration Screen (Figure 7), allows you to
control access to the module’s token ring network.
The Disabled mode (by default) allows all new stations to enter the ring.
When ring security is enabled in Alarm Only mode, the module stores the MAC
address of each station on the token ring network in a secure database or
“allowed list.” The module can store up to 250 station MAC addresses on the
allowed list. The module retains the allowed list in its battery-backed NonVolatile Random Access Memory (NVRAM). When the module is powered up or
reset, all MAC addresses are retained and ring security is reenabled automatically.
The Alarm Only mode allows new stations to enter the ring, but a “station added”
trap/alarm notifies the Network Management Station (NMS) of the event. The
trap/alarm includes the new station’s MAC address so that the network manager
can decide if the new station should be allowed on the ring.
!
CAUTION
Do not enter Remove/Alarm mode without first entering the Alarm Only mode
or adding nodes to the allowed list. All nodes not appearing in the list, currently
active on the ring, WILL BE REMOVED!
The Remove/Alarm mode sends a “Remove Station MAC Frame Command” to
new stations attempting to enter the ring, and a trap/alarm to the NMS informing
it of the action taken. If, after three attempts, the station (outside the hub) cannot
be removed from the ring, a trap/alarm is sent to the NMS informing it that “the
station could not be removed.” Also, the port is disabled for the station directly
connected to the hub and a trap/alarm is sent indicating port removal.
To access the Token Ring Secured Station Configuration Screen from the Module
Specific Configuration Menu:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Token Ring Security option.
2. Press the Enter key.
The Token Ring Secured Station Configuration Screen (Figure 7), appears.
20
Page 23

9T125-08 Module Specific Information
SmartSwitch 9000 Local Management
Token Ring Secured Station Configuration
Module Name: 9T125-08 Firmware Revision: 01_00_00
Slot Number: 10 BOOTPROM Revision: 01.00.05
Token Ring #1
Entry Station Address
001 00-00-B8-74-40-06
002 00-00-B8-74-40-7A
Stn Edit 00-00-00-00-00-00 [ ADD ] Security Mode [ Disabled ]
[TOKEN RING 1] [ 9-16 ]
EXIT RETURN
NOTE
Figure 7. Token Ring Secured Station Configuration Screen
Up to 8 station addresses appear on the screen. If additional station addresses
exist, a command containing the range of station addresses, such as [ 9-16 ],
appears on the command line (bottom of the screen). To view any additional
station addresses, highlight the range of station addresses command, then press
the Return key.
21
Page 24

9T125-08 Module Specific Information
Token Ring Secured Station Configuration Screen Fields
The following information briefly explains each Token Ring Secured Station
Configuration Screen field.
Station Address
Lists the MAC address of each station on the security “allowed” list. Up to 250
MAC addresses can appear in the list.
Stn Edit
Allows you to enter the MAC addresses of stations that you want to add or delete
from the security “allowed” list.
Token Ring Security Configuration Screen Commands
Add/Delete (Toggle)
Allows you to manually add or delete stations from the security “allowed” list.
TIP
Before you add stations manually, see the Alarm Only security mode information
on the following page.
To manually add a station to the allowed list:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Stn Edit field, then press the Return key.
2. Enter the MAC Address of the station you want to add to the allowed list,
then press the Return key.
You must enter the MAC Address in XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX format.
3. Highlight the ADD/DEL toggle command.
4. Press the Space Bar until the command toggles to display ADD.
5. Press the Return key.
The station appears in the Station Address list.
To manually delete a station from the allowed list:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Stn Edit field, then press the Return key.
2. Enter the MAC Address of the station you want to delete from the allowed
list, then press the Return key. You must enter the MAC Address in
XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX format.
3. Highlight the ADD/DEL toggle command.
22
Page 25

9T125-08 Module Specific Information
4. Press the Space Bar until the command toggles to display DEL.
5. Press the Return key.
The station appears in the Station Address list.
Security Mode (Toggle)
Allows you to set one of three security modes for the module’s token ring.
!
CAUTION
Make sure you understand the consequences of changing security modes.
Each mode offers more security than the previous mode. Select from the
following modes:
• Disabled (default) - Use this mode to temporarily disable ring security so that
new stations can enter the ring.
• Alarm Only - In this mode, new stations can enter the ring and are added to
the allowed list, but a “Station Added” trap/alarm is sent to the Network
Management Station. This trap message is only sent once, and it includes the
new station’s MAC address so that the network manager can decide if the new
station should be allowed on the ring.
When temporarily disabling ring security to allow new users to enter the ring,
use the Alarm Only mode to reenable ring security. In Alarm Only mode, the
management module stores the MAC address of each station on the ring in
the allowed list. This eliminates entering MAC addresses one at a time using
the Stn Edit field.
• Remove/Alarm - This is the highest level of ring security. In this security mode,
the ring is locked to new stations. The Remove/Alarm mode sends a “Remove
MAC Frame” command to a new station attempting to enter the ring, and a
trap/alarm to the NMS informing it of the action taken. If, after three attempts,
the station cannot be removed from the ring, remove alarm sends a trap/alarm
“Remove Failure” to the NMS, informing it that the station could not be
removed.
If you change directly from Disabled mode to Remove/Alarm mode, all stations
NOTE
that have not been added to the allowed list will be removed from the token ring.
23
Page 26

9T125-08 Module Specific Information
Selecting a Security Mode
To select a Security Mode:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Security Mode field.
2. Press the Space Bar to toggle to the desired security mode (either Disabled,
Alarm Only, or Remove/Alarm).
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE/EXECUTE command.
4. Press the Return key. The selected mode of ring security becomes effective.
Viewing Previous/Next Page of Station Addresses
To view the previous/next page (if there is one) of station addresses, use the
arrow keys to highlight the appropriate range of station addresses command (for
example, [ 9-16 ]), then press the Return key.
Exiting the Token Ring Secured Station Configuration Screen
To exit the Token Ring Secured Station Configuration Screen, use the arrow keys
to highlight RETURN, then press the Return key.
24
Page 27

Switch Statistics Screen
The Switch Statistics (TOTAL) Screen (Figure 8), displays the module’s
transparent bridge and source route bridge statistics. The statistics are categorized
as follows:
• Transparent Unicast
• Transparent Broadcast
• Source Route Unicast (Not applicable on the FNB option)
• Source Route Broadcast (Not applicable on the FNB option)
SmartSwitch 9000 Local Management
Switch Statistics (TOTAL)
Module Name: 9T125-08 Firmware Revision: 01_00_00
Slot Number: 9 BOOTPROM Revision: 01.00.05
TOKEN RING Interface #1: System Up Time: 000 + 00:10:44
Transparent Transparent Source Rte Source Rte Totals
Unicast Broadcast Unicast Broadcast
9T125-08 Module Specific Information
Frames Transmitted: 0 0 0 0 0
Frames Received: 0 0 0 0 0
Kbytes Transmitted: 0 0 0 0 0
Kbytes Received: 0 0 0 0 0
Frames Filtered: 0 0 0 0 0
[ TOTAL ] [TOKEN RING 1] [REFRESH 3sec] EXIT RETURN
Figure 8. Switch Statistics (TOTAL) Screen
25
Page 28

9T125-08 Module Specific Information
Switch Statistics Screen Fields
The following information briefly explains each Switch Statistics Screen field.
FDDI Interface
Identifies the interface type as either FDDI Interface, TOKEN RING Interface #1,
or TOKEN RING Interface #2.
System Up Time
Indicates how long the module has been up and running.
000 + 00:00:00
Seconds
Minutes
Hours
Days
Frames T ransmitted
Displays the number of (transparent unicast, transparent broadcast, source route
unicast, and source route broadcast) frames transmitted by the interface, as well
as the total number of frames transmitted (sum of the four categories).
Frames Received
Displays the number of (transparent unicast, transparent broadcast, source route
unicast, and source route broadcast) frames received by the interface, as well as
the total number of frames received (sum of the four categories).
Kbytes T ransmitted
Displays the number of (transparent unicast, transparent broadcast, source route
unicast, and source route broadcast) kilobytes transmitted by the interface, as well
as the total number of kilobytes transmitted (sum of the four categories).
Kbytes Received
Displays the number of (transparent unicast, transparent broadcast, source route
unicast, and source route broadcast) kilobytes received by the interface, as well as
the total number of kilobytes received (sum of the four categories).
Frames Filtered
Displays the number of (transparent unicast, transparent broadcast, source route
unicast, and source route broadcast) frames filtered by the interface, as well as the
total number of frames filtered (sum of the four categories).
26
Page 29

Switch Statistics Screen Commands
TOTAL / ACCUMULATE / DELTA (Toggle)
Allows you to:
• Display a running TOTAL of statistics (statistics since the module was inserted
into the chassis).
• Reset the statistics to zero and then ACCUMULATE and display figures from
that point in time forward.
• Display statistics and then reset the statistics to zero each time the screen is
refreshed (DELTA).
Table 5 shows the various statistics after four screen refreshes:
Table 5. Statistics After Four Refreshes
9T125-08 Module Specific Information
After 1st
Screen Refresh
TOTAL 1623 1636 1685 1712
ACC0 136299
DELTA0 134927
After 2nd
Screen Refresh
After 3rd
Screen Refresh
After 4th
Screen Refresh
Press the Space Bar to toggle to the desired value, then press the Return key.
FNB / TOKEN RING 1/TOKEN RING 2 (Toggle)
Allows you to select the interface for which statistics are displayed.
• If you select FNB, statistics for the FDDI interface are displayed.
• If you select TOKEN RING 1, statistics for the module’s number one token ring
interface are displayed.
• If you select TOKEN RING 2, statistics for the module’s number two token ring
interface are displayed.
• Press the Space Bar to toggle to the desired value, then press the Return key.
REFRESH (Toggle)
Allows you to select the interval at which the screen will be updated (the range is
3 - 99 seconds). To increase the number of seconds, press the Space Bar while the
cursor is on the command. To decrease the number of seconds, press the Back
Space key while the cursor is on the command.
27
Page 30

9T125-08 Module Specific Information
CLEAR
A command that only appears when you select ACCUMULATE as a statistic
reporting method. The CLEAR command allows you to manually reset the
screen’s statistics to zero and then start to accumulate statistics from that point in
time. For example, you may have accumulated statistics for 45 minutes, but now
you want to see accumulated statistics for the current period. In this case, you
would position the cursor onto the CLEAR command and press the Space Bar.
The screen’s statistics will reset to zero and start to accumulate again.
RETURN
Allows you to exit the 9T125-08 Switch Statistics Screen.
28
Page 31

Token Ring LAN Statistics
The Token Ring LAN Statistics (TOTAL) Screen (Figure 9), displays the module’s
error statistics.
SmartSwitch 9000 Local Management
Token Ring LAN Statistics (TOTAL)
Module Name: 9T125-08 Firmware Revision: 01_00_00
Slot Number: 10 BOOTPROM Revision: 01.00.05
System Up Time: 000 + 00:33:36 Ring Number: 0x002
Frames Transmitted: 512 Ring Status: Normal
Frames Received: 508 Ring Speed (Mbps): 16
KBytes Transmitted: 25 Stations on Ring: 2
KBytes Received: 25 Ports Enabled: 6
Beacon States: 0 Active Monitor Changes: 0
Ring Purges: 2 Active Monitor Address: 00-00-B8-74-40-7A
ISOLATING ERRORS NON-ISOLATING ERRORS
Line Errors: 0 Lost Frame Errors: 0
Burst Errors: 2 Frame Copied Errors: 0
AC Errors: 0 Rcvr Congestion Errors: 0
Abort Transmit Errors: 0 Token Errors: 2
Internal Errors: 0 Frequency Errors: 0
9T125-08 Module Specific Information
[ TOTAL ] [TOKEN RING 1] [REFRESH 3sec] EXIT RETURN
Figure 9. Token Ring LAN Statistics (TOTAL) Screen
29
Page 32

9T125-08 Module Specific Information
Token Ring LAN Statistics Screen Fields
The following information briefly explains each Token Ring LAN Statistics Screen
field.
System Up Time
Indicates how long the module has been up and running.
000 + 00:00:00
Seconds
Minutes
Hours
Days
Frames T ransmitted
Displays the number of frames transmitted on the token ring.
Frames Received
Displays the number of frames received on the token ring.
Kbytes T ransmitted
Displays the number of kilobytes transmitted on the token ring.
Kbytes Received
Displays the number of kilobytes received on the token ring.
Beacon States
Displays the number of times that a beacon even occurred on the token ring.
Ring Purges
Displays the number of times that an Active Monitor on the token ring generated
a ring purge MAC frame to clear ring problems.
Ring Number
Identifies the source route ring number (a hexadecimal value) assigned to this
ring.
Ring Status
Displays the current condition of the token ring. Valid conditions include
Unknown, Closed, Normal, Purge, Contention, and Beaconing.
Ring Speed (Mbps)
Displays the token ring’s operating speed (either 4 Mbps or 16 Mbps).
30
Page 33

Stations on Ring
Displays the number of active stations on the token ring.
Ports Enabled
Displays the number of ports on the token ring that have an ENABLE status.
Active Monitor Changes
Displays the number of times that the Active Monitor has changed from one
station to another since the module was powered up.
Active Monitor Address
Displays the MAC Address of the station that currently is designated as the
Active Monitor.
ISOLATING ERRORS
Line Errors
Displays the number of corrupt frames that have been detected by a station on the
token ring.
9T125-08 Module Specific Information
Burst Errors
Displays the number of times a signal is not received by a station on the token
ring.
AC Errors
Displays the number of times that two successive AMP or SMP frames are
received with A and C bits set at zero.
Abort Transmit Errors
Displays the number of times that a station transmits an abort delimiter while
transmitting.
Internal Errors
Displays the number of times that a station encounters a recoverable internal
error. This information helps to detect a station in marginal operating condition.
NON-ISOLATING ERRORS
Lost Frame Errors
Displays the number of times that a station’s TRR timer expires before the station
receives the ending delimiter of the frame transmitted.
31
Page 34

9T125-08 Module Specific Information
Frame Copied Errors
Displays the number of times that a node receives a frame with its address as the
destination address, however the Address Recognized bit is already set to ‘1’.
Rcvr Congestion Errors
Displays the number of times that a station on the token ring recognizes its
address, but it cannot copy the frame because the buffer is full.
Token Errors
Displays the number of times that a token on the token ring has encountered a
problem along its path.
Frequency Errors
Displays the number of times that the frequency of an incoming signal differs by
more than 0.6% from the local oscillator.
Token Ring LAN Statistics Screen Commands
TOTAL / ACCUMULATE / DELTA (Toggle)
Allows you to:
• Display a running TOTAL of statistics (statistics since the module was inserted
into the chassis).
• Reset the statistics to zero and then ACCUMULATE and display figures from
that point in time forward.
• Display statistics and then reset the statistics to zero each time the screen is
refreshed (DELTA).
Table 6 shows the various statistics after four screen refreshes:
Table 6. Statistics After Four Refreshes
After 1st
Screen Refresh
TOTAL 1623 1636 1685 1712
ACC0 136299
DELTA0 134927
After 2nd
Screen Refresh
After 3rd
Screen Refresh
After 4th
Screen Refresh
Press the Space Bar to toggle to the desired value, then press the Return key.
32
Page 35

9T125-08 Module Specific Information
TOKEN RING 1/TOKEN RING 2 (Toggle)
Allows you to select the interface for which statistics are displayed.
• If you select TOKEN RING 1, token ring statistics for the module’s number one
interface are displayed.
• If you select TOKEN RING 2, token ring statistics for the module’s number two
interface are displayed.
Press the Space Bar to toggle to the desired value, then press the Return key.
REFRESH (Toggle)
Allows you to select the interval at which the screen will be updated (the range is
3 - 99 seconds). To increase the number of seconds, press the Space Bar while the
cursor is on the command. To decrease the number of seconds, press the Back
Space key while the cursor is on the command.
CLEAR
A command that only appears when you select ACCUMULATE as a statistic
reporting method. The CLEAR command allows you to manually reset the
screen’s statistics to zero and then start to accumulate statistics from that point in
time. For example, you may have accumulated statistics for 45 minutes, but now
you want to see accumulated statistics for the current period. In this case you
would position the cursor onto the CLEAR command and press the Space Bar.
The screen’s statistics will reset to zero and start to accumulate again.
RETURN
Allows you to exit the 9T125-08 Token Ring LAN Statistics Screen.
33
Page 36

9T125-08 Module Specific Information
34
 Loading...
Loading...