Page 1

SmartSwitch 9000
9M426-02
Local Management Appendix
9032253-01
Page 2

Page 3

Appendix
9M426-02 Module Specific
Information
Introduction
This appendix contains Local Management information that is speciÞc to the
9M426-02 Dual HSIM Switch Module.
This module has two slots for two High Speed Interface Module (HSIM)
interfaces (not included and may be purchased separately). These HSIMs operate
in various modes (ATM, FDDI, WAN, etc.), depending on the HSIM installed in
the module.
HSIM UserÕs Guides, in Portable Document Format, are available from the
NOTE
World Wide Web at the following site: http://www.cabletron.com/
Modifying Fields and User Privileges
To modify Þelds on this module, you must have read-write or super-user
privileges. If you have read-only privileges, you can view information; however,
you cannot modify any Þelds. For more information about user privileges and
community names, refer to the
Guide.
SmartSwitch 9000 Module Local Management UserÕs
1
Page 4
9M426-02 Module Specific Information
Module Interfaces
The 9M426-02 Module can have as few as 8, and as many as 112, interfaces.
Table 1 lists the identifying number, name, and description of each interface.
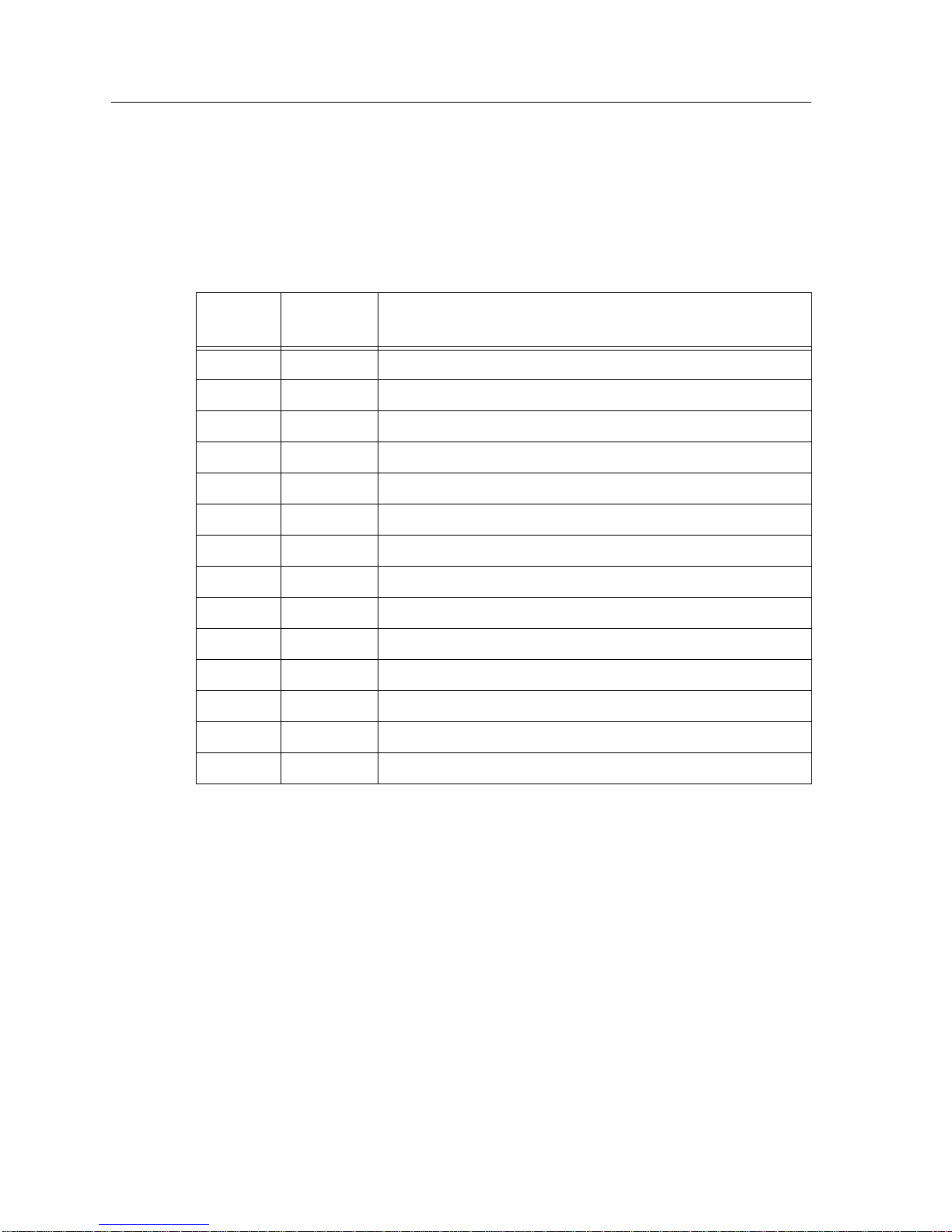
Table 1. 9M426-02 Module Interfaces
Interface
Number
1 SMB1 1 Mbps System Management Bus
2 SMB10 10 Mbps System Management Bus
3 HOST
4 INB Internal Network Bus
5 HSIM1 Physical Port (if HSIM installed; otherwise, a Reserved Port)
6 HSIM1 Reserved Port
7 HSIM2 Physical Port (if HSIM installed; otherwise, a Reserved Port)
8 HSIM2 Reserved Port
9 ATM Virtual Ports (if HSIM-A6DP installed)
10 ATM Virtual Port (if 1 or more HSIM-A6DPs are installed)
.. .
.. .
.. .
Interface
Name
Interface
Description
112 ATM Virtual Port (if 1 or more HSIM-A6DPs are installed)
If the HSIMs installed are ATM, ports 9Ð112 are ATM virtual ports.
The default interface is limited to SMB10 (Interface 2) or the HOST (Interface 3) on
the General ConÞguration Screen.
2
Page 5
9M426-02 Module Specific Information
Local Management Screens Hierarchy
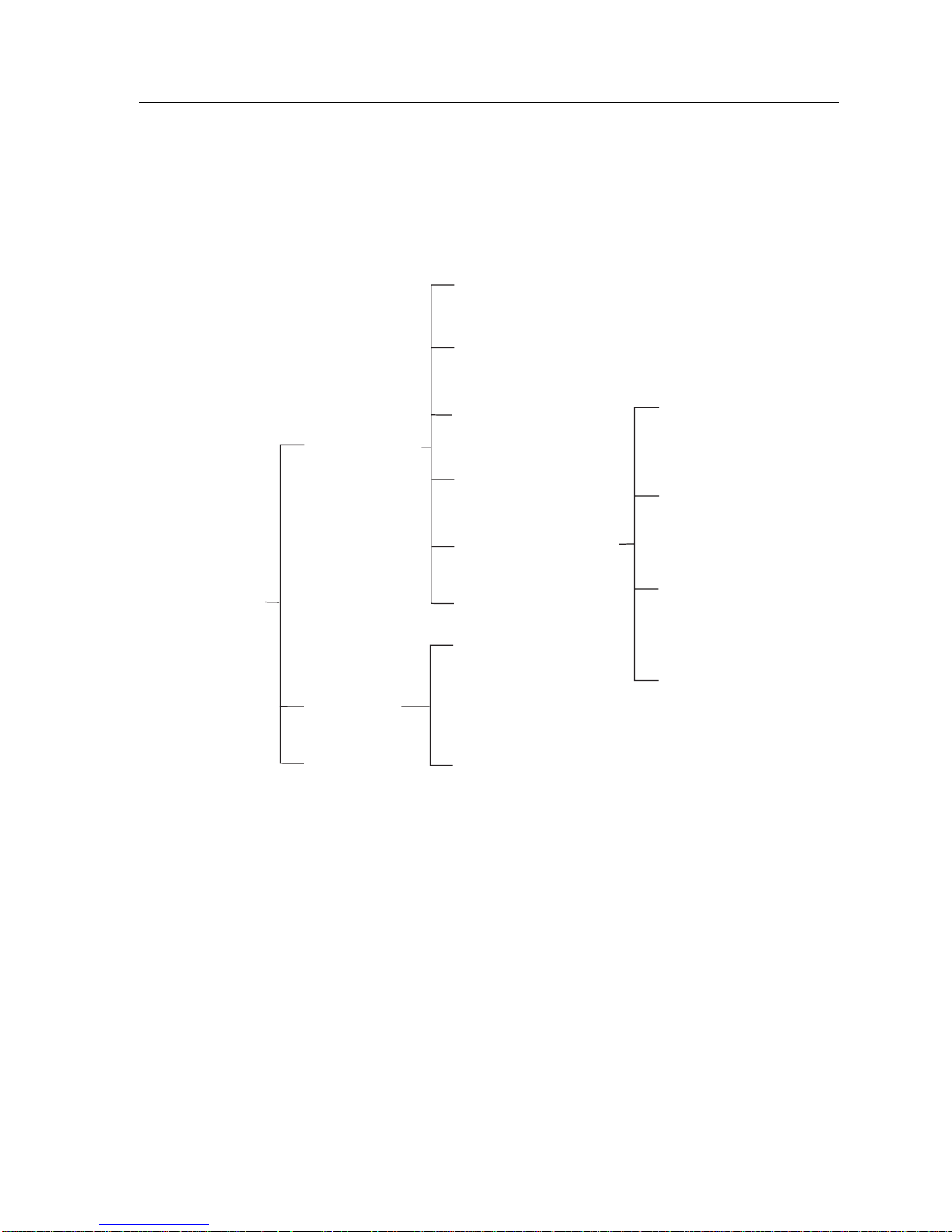
Figure 1 shows the hierarchy for the 9M426-02 Module Local Management
Screens.
General Configuration
SNMP Community Names
Module Menu Screen
Module Configuration
Module Statistics
Network Tools
Figure 1. 9M426-02 LM Screen Hierarchy
SNMP Traps
Switch Configuration
Module Specific Configuration
Smart Trunk Configuration
Switch Statistics
Interface Statistics
System Resources
HSIM Configuration Screens
Flash Download
Broadcast Suppression
3
Page 6
9M426-02 Module Specific Information
Switch Configuration Screen
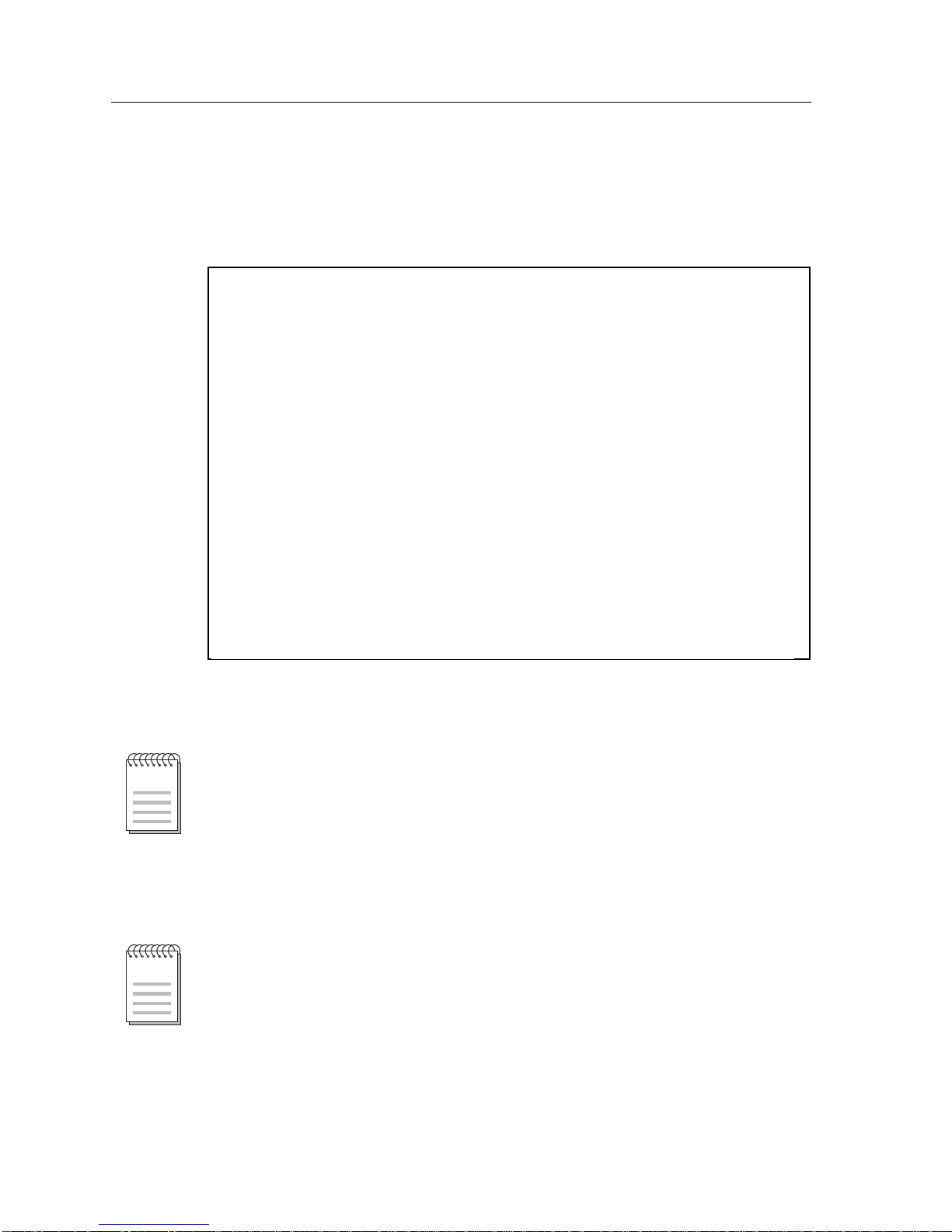
The Switch ConÞguration Screen (Figure 2) provides the basic setup options to
make a switch operational in your network.
MMAC-Plus Local Management
Switch Configuration
Module Name: 9M426-02 Firmware Revision: 01.00.03
Slot Number: 2 BOOTPROM Revision: 01.01.00
Switch Address: 00-00-1D-BA-DB-AE Type of STA: [IEEE]
Numbers of Ports: 109
Port # MAC Address State Status
NOTE
1 00-00-1D-BA-DB-AE forwarding [ENABLED]
2 disabled [ENABLED]
3 disabled [ENABLED]
4 00-00-1D-BA-DB-B0 forwarding [ENABLED]
5 disabled [ENABLED]
6 disabled [ENABLED]
7 disabled [ENABLED]
8 disabled [ENABLED]
SAVE [ 9-16 ] EXIT RETURN
Figure 2. Switch Configuration Screen
The port numbering for Table 1 is MIB II interface numbering.
The port numbering for this screen is 802.1D Bridge Port numbering.
- Port 1 corresponds to the INB.
- Ports 2 & 3 correspond to HSIM1.
- Ports 4 & 5 correspond to HSIM2.
Information for up to 8 ports can appear on the screen. If additional ports exist, a
NOTE
command containing the range of ports, such as [ 9-16 ], appears on the command
line at the bottom of the screen. To view any additional ports, highlight the range
of ports command, and then press the Return key.
4
Page 7

Switch Configuration Screen Fields
The following information brießy explains each Switch ConÞguration Screen
Þeld.
Switch Address (Read-Only)
Displays the MAC address of the switch.
Number of Ports (Read-Only)
Displays the total number of switched ports on the module.
Type of STA (Selectable)
Allows you to set the method that switches use to decide which switch is the
controlling (Root) switch when two or more switches exist in parallel (Spanning
Tree Algorithm). Valid entries include IEEE, DEC, and NONE.
9M426-02 Module Specific Information
NOTE
Port # (Read-Only)
Lists each switch port on the module.
The port numbering for Table 1 is MIB II interface numbering.
The port numbering for the Switch ConÞguration Screen is 802.1D Bridge Port
numbering.
- Port 1 corresponds to the INB.
- Ports 2 & 3 correspond to HSIM1.
- Ports 4 & 5 correspond to HSIM2.
MAC Address (Read-Only)
Displays the hardware address assigned to each listed port.
State (Read-Only)
Displays the current state of each listed interface. The possible interface states
include:
Blocking In the Blocking state, an interface is not forwarding trafÞc.
TrafÞc that is received is discarded.
Station location information is not added to the Filtering Database.
The Blocking state can be entered from the Listening, Learning, or
Forwarding states.
5
Page 8

9M426-02 Module Specific Information
The Blocking state is entered in either of two ways:
¥ Following initialization of the switch.
¥ From the Disabled state when management enables the
interface.
The Blocking state is exited in any of three ways:
¥ When a protocol timer expires.
¥ When a ConÞguration BPDU is received on this port or another
port.
¥ Through management action.
Listening In the Listening state, an interface is preparing to forward trafÞc.
TrafÞc that is received is discarded.
Station location information is not added to the Filtering Database.
The Listening state is entered from the Blocking state, when the
Spanning Tree Algorithm and Protocol determines that the
interface should participate in forwarding trafÞc.
The Listening state is exited in any of three ways:
¥ When a protocol timer expires (the Learning state is then
entered).
¥ When a BPDU is received on this port or another port (the
Blocking state is then entered).
¥ Through management action (either the Blocking or the
Disabled state is then entered).
Learning In the Learning state, an interface is preparing to forward trafÞc,
and is learning network addresses to minimize the forwarding of
unnecessary trafÞc.
TrafÞc that is received is discarded.
Station location information is added to the Filtering Database.
The Learning state is entered from the Listening state when a
protocol timer expires.
6
Page 9

9M426-02 Module Specific Information
The Learning state is exited in any of three ways:
¥ When a protocol timer expires (the Learning state is then
entered).
¥ When a BPDU is received on this port or another port (the
Blocking state is then entered).
¥ Through management action (either the Blocking or the
Disabled state is then entered).
Forwarding In the Forwarding state, an interface is forwarding trafÞc.
Station location information is added to the Filtering Database.
The Forwarding state is entered from the Learning state.
The Forwarding state is exited in either of two ways:
¥ When a BPDU is received on this port or another port (the
Blocking state is then entered).
¥ Through management action (either the Blocking or the
Disabled state is then entered).
Disabled In the Disabled state, an interface is not forwarding trafÞc.
TrafÞc that is received is discarded.
Station location information is not added to the Filtering Database.
The Disabled state is entered from any other state through
management action.
The Disabled state is exited when the port is enabled by
management action (the Blocking state is entered).
Status (Toggle)
Allows you to enable or disable a port by setting the status of the listed interface
to either ENABLED or DISABLED.
7
Page 10

9M426-02 Module Specific Information
System Resources Screen
The System Resources Screen (Figure 3) displays information about the amount of
FLASH memory, DRAM, and NVRAM that is installed and how much of that
memory is available.
MMAC-Plus Local Management
System Resources
Module Name: 9M426-02 Firmware Revision: 01.00.03
Slot Number: 2 BOOTPROM Revision: 01.01.00
CPU Type : i960 HT 75MHz
Flash Memory Installed: 4 MB Available: 0 Bytes
DRAM Installed: 20 MB Available: 7716772 Bytes
NVRAM Installed: 127 KB Available: 122185 Bytes
Current Switch Utilization: 0 %
Peak Switch Utilization: 2 %
Reset Peak Switch Utilization: [NO]
SAVE EXIT RETURN
Figure 3. System Resources Screen
8
Page 11

System Resources Screen Fields
The following information brießy explains each System Resources Screen Þeld.
CPU Type (Read-only)
Indicates the microprocessor, and the speed (in MHz) at which it is operating.
Flash Memory Installed/Available (Read-only)
Indicates the amount of FLASH memory installed in the module and how much
is currently available.
DRAM Installed/Available (Read-only)
Indicates the amount of DRAM installed in the module and how much of it is
currently available.
NVRAM Installed/Available (Read-only)
Indicates the amount of NVRAM installed in the module and how much of it is
currently available.
9M426-02 Module Specific Information
Current Switch Utilization (Read-only)
Shows how much (percentage) of the switch capacity of the module is currently
being used.
Peak Switch Utilization (Read-only)
Shows the peak percentage of maximum switching capacity since the last reset.
Reset Peak Switch Utilization (Toggle)
Allows you to reset the Peak Switch Utilization Þeld. The switch may be set to
either YES or NO. YES resets the Peak Switch Utilization Þeld to zero.
9
Page 12

9M426-02 Module Specific Information
HSIM Configuration Screens
For complete information about HSIMs, refer to the HSIM UserÕs Guides,
available (in Portable Document Format) from the World Wide Web, at the
following site: http://www.cabletron.com/
10
Page 13

Flash Download Screen
The Flash Download Screen (Figure 4) allows you to choose the method of
downloading ßash, and whether or not the module will reboot after the
download.
MMAC-Plus Local Management
Flash Download
Module Name: 9M426-02 Firmware Revision: 01.00.03
Slot Number: 2 BOOTPROM Revision: 01.01.00
Download Method: [BOOTP]
Reboot After Download: [YES]
9M426-02 Module Specific Information
TFTP Gateway IP Addr: 0.0.0.0
Last Image Server IP: XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX
Last Image File Name: /usr/tftpboot/r10003.fls
EXECUTE EXIT RETURN
Figure 4. Flash Download Screen
11
Page 14

9M426-02 Module Specific Information
Flash Download Screen Fields
The following information brießy explains each Flash Download Screen Þeld.
Download Method (Selectable)
Toggles between TFTP, RUNTIME and BOOTP.
¥ If set for BOOTP, the module sends out a BootP request to determine the IP
address of the TFTP server and the Þle name of the image to be downloaded.
¥ If set for TFTP or RUNTIME, the module attempts a TFTP download based on
the IP address and Þle name entered in the Þelds at the bottom of the Flash
Download Screen. See the download procedures at the end of this section.
Reboot After Download (Modifiable only when RUNTIME is chosen)
NotiÞes you that the module will reboot after the download is complete. If a
RUNTIME Download is performed this Þeld toggles between YES and NO.
¥ If YES is selected, the module reboots after the download is completed. The
module stores the new Þrmware image in FLASH memory. When the module
is reset, the module will boot from FLASH memory using the new image.
¥ If NO is selected, the module will continue using the existing Þrmware image.
TFTP Gateway IP Addr (Selectable)
Displays the IP address of the TFTP gateway deÞned in the General
ConÞguration Screen.
Last Image Server IP (Read-only)
Displays the IP address of the server used for the previous FLASH Download.
Last Image File Name (Read-only)
Displays the complete path and Þle name of the last image downloaded to
FLASH.
Download Server IP (Displayed only with RUNTIME or TFTP)
The IP address of the TFTP server that will download the image to the module.
Download File Name (Displayed only with RUNTIME or TFTP)
The desired directory path and Þle name to be downloaded from the TFTP server.
12
Page 15

Using TFTP to Download Image File
To download an image Þle using TFTP:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Download Method Þeld.
2. Press the Space Bar to select TFTP.
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the TFTP Gateway IP Addr Þeld.
4. Set the IP address of the TFTP gateway server (this defaults to the same IP
address as that set in the TFTP Gateway IP Addr Þeld on the General
ConÞguration Screen).
5. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Download Server IP Þeld.
6. Enter the IP address of the TFTP server using the standard quad dotted octet
format.
9M426-02 Module Specific Information
7. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Download File Name Þeld.
8. Enter the complete path and Þle name of the image stored on the download
server.
9. Use the arrow keys to highlight EXECUTE at the bottom of the screen and
press the Enter key. The message ÒTFTP DOWNLOAD. WILL COMMIT TO
FLASH. REBOOT IN PROGRESS...Ó displays in the event message line at the
top of the screen and the new image is downloaded into FLASH memory.
Using RUNTIME to Download Image File
To download an image Þle using RUNTIME:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Download Method Þeld.
2. Press the Space Bar to select RUNTIME.
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Reboot After Download Þeld.
4. Press the Space Bar to select either YES or NO. Select YES if you want the
module to reboot after the download is completed. Select NO if you want the
module to store the new image in FLASH memory until the module is
manually reset.
5. Use the arrow keys to highlight the TFTP Gateway IP Addr Þeld.
6. Set the IP address of the TFTP gateway server (this defaults to the same IP
address as that set in the TFTP Gateway IP Addr Þeld on the General
ConÞguration Screen).
13
Page 16

9M426-02 Module Specific Information
7. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Download Server IP Þeld.
8. Enter the IP address of the TFTP server using the standard quad dotted octet
format.
9. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Download File Name Þeld.
10. Enter the complete path and Þle name of the image stored on the download
server.
11. Use the arrow keys to highlight EXECUTE at the bottom of the screen and
press the Enter key. The message ÒRUNTIME DOWNLOAD. WILL COMMIT
TO FLASH.Ó displays in the event message line at the top of the screen and
the new image is downloaded into FLASH memory.
Using BOOTP to Download Image File
To download an image Þle using BOOTP:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Download Method Þeld.
2. Press the Space Bar to select BOOTP.
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the TFTP Gateway IP Addr Þeld.
4. Set the IP address of the TFTP gateway server (this defaults to the same IP
address set in the TFTP Gateway IP Addr Þeld in the General ConÞguration
Screen).
5. Use the arrow keys to highlight EXECUTE at the bottom of the screen and
press the Enter key. The message ÒBOOTP DOWNLOAD. WILL COMMIT TO
FLASH. REBOOT IN PROGRESS...Ó displays in the event message line at the
top of the screen and the new image is downloaded into FLASH memory.
14
Page 17

Broadcast Suppression Screen
The Broadcast Suppression Screen (Figure 5) allows you to throttle the forwarding
of broadcast packets. You can set limits.
MMAC-Plus Local Management
Broadcast Suppression
Module Name: 9M426-02 Firmware Revision: 01.00.03
Slot Number: 2 BOOTPROM Revision: 01.01.00
Port# Total RX Peak Rate Time Since Peak Threshold Reset Peak
7 0 0 0:00:00 612740 [NO]
9M426-02 Module Specific Information
SAVE EXIT RETURN
Figure 5. Broadcast Suppression Screen
15
Page 18

9M426-02 Module Specific Information
Broadcast Suppression Screen Fields
The following information brießy explains each Broadcast Suppression Screen
Þeld.
Port# (Read-only)
The number of the port receiving and forwarding the Broadcast packets.
Total RX (Read-only)
The total number of broadcast packets received on this port.
Peak Rate (Read-only)
The maximum number of broadcast packets received on this port.
Time Since Peak (Read-only)
The time (in hours, minutes, and seconds) since the peak occurred.
Threshold (Read-only)
The upper limit set for the rate broadcast packets are forwarded out the port.
Reset Peak (Command)
Use this command to reset the Peak Rate.
Resetting the Peak Rate
Use the following procedure to reset the Peak Rate:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Peak Rate Þeld.
2. Press the Space Bar until you see YES, and then press the Enter key.
16
Page 19

9M426-02 Module Specific Information
SmartTrunk Configuration Screen
The SmartTrunk ConÞguration Screen (Figure 6) allows you to logically group
interfaces together between devices to achieve greater bandwidth between the
devices.
03/17/1998 14:58:34 MMAC-Plus Local Management
SmartTrunk Configuration Screen
Module Name: 9M426-02 Firmware Revision: 01.00.03
Slot Number: 2 BOOTPROM Revision: 01.01.00
Port # Port Name Connection SmartTrunk State Instance #STPorts
------ ------------- ---------- ---------------- -------- ------- 5 Atm [USER] NONE 0 0
6 Unknown [USER] NONE 0 0
7 Fddi [USER] NONE 0 0
8 Unknown [USER] NONE 0 0
9 Unknown [USER] NONE 0 0
ENABLE EXIT RETURN
Figure 6. SmartTrunk Configuration Screen
17
Page 20

9M426-02 Module Specific Information
SmartTrunk Configuration Screen Fields
The following information brießy explains each SmartTrunk ConÞguration Screen
Þeld.
Port # (Read-only)
Lists each MIB II interface number capable of SmartTrunking on the selected
module. If the number of listed ports is more than twelve, then additional ports
are listed on subsequent screens.
Port Name (Read-only)
Displays the names (assigned by Cabletron Systems) to each listed port.
Connection (Selectable)
Contains the connection type for each listed port (either USER or NETWORK).
USER connections do not participate in SmartTrunking. Only NETWORK
connections participate in SmartTrunking. At least two ports (redundantly
connected to the same remote device or network) must be designated as
NETWORK connections to participate in SmartTrunking. To change a portÕs
connection type, press the Space Bar once. The desired value appears in the Þeld.
SmartTrunk State (Read-only)
Displays the current operating state of each listed port. The possible states
include:
NONE The port is operating as a normal bridge port.
BLOCKING The port is load sharing, but in the blocked mode. A port
may be properly conÞgured for trunking but may be
blocked. If a path not involved with trunking between the
two chassis yields more bandwidth than the aggregate of
the trunking ports, the trunking ports will be placed in
blocking mode. The non-trunked, higher-bandwidth
connection will be used.
SMARTTRUNKING The port is load sharing with other Network designated
ports of the same instance.
Instance (Read-only)
Displays the ports associated with each redundant loop. A module can have
multiple instances.
#STPorts (Read-only)
Displays the total number of load sharing ports in the redundant loop.
18
Page 21

Switch Statistics Screen
The Switch Statistics Screen (Figure 7) displays information about frames
received, transmitted, Þltered, and forwarded.
MMAC-Plus Local Management
Switch Statistics
Module Name: 9M426-02 Firmware Revision: 01.00.03
Slot Number: 2 BOOTPROM Revision: 01.01.00
Port # Frames Rcvd Frames Txmtd Frames Fltrd Frames Frwded
1 0 0 0 0
4 0 0 0 0
9M426-02 Module Specific Information
CLEAR COUNTERS EXIT RETURN
Figure 7. Switch Statistics Screen
19
Page 22

9M426-02 Module Specific Information
Switch Statistics Screen Fields
The following information brießy explains each Switch Statistics Screen Þeld.
Port # (Read-Only)
IdentiÞes the 802.1D Bridge Port number.
Frames Rcvd (Read-Only)
Displays the number of frames received by this port.
Frames Txmtd (Read-Only)
Displays the number of frames transmitted by this port.
Frames Fltrd (Read-Only)
Displays the number of frames Þltered by this port.
Frames Frwded (Read-Only)
Displays the number of frames forwarded by this port.
CLEAR COUNTERS (Command)
Used to reset all statistic counters to zero.
Resetting Counters to Zero
To reset all the statistics counters to zero, use the arrow keys to highlight the
CLEAR COUNTERS Þeld, and then press the Enter key.
20
Page 23

Interface Statistics Screen
The Interface Statistics Screen (Figure 8) displays MIB II interface statistics and
information.
MMAC-Plus Local Management
Interface Statistics
Module Name: 9M426-02 Firmware Revision: 01.00.03
Slot Number: 2 BOOTPROM Revision: 01.01.00
Interface: 4 Name: INB
InOctets: 0 Address: 00-00-1D-BA-DB-AE
InUnicast: 0 Last Change: 00 days 00:00:00
InNonUnicast: 0 Admin Status: UP
InDiscards: 0 Oper Status: UP
InErrors: 0
InUnknownProtos: 0 MTU: 8160
OutOctets: 677219 Speed: 2500000000
OutUnicast: 10733
OutNonUnicast: 0 Link Status: LINK
OutDiscards: 0 Duplex Mode: STANDARD
OutErrors: 0
OutQLen: 256
9M426-02 Module Specific Information
INTERFACE: [ 4] CLEAR COUNTERS EXIT RETURN
Figure 8. Interface Statistics Screen
21
Page 24

9M426-02 Module Specific Information
Interface Statistics Screen Fields
The following information brießy explains each Interface Statistics Screen Þeld.
Interface (Read-Only)
Displays the Interface number for which statistics are currently being displayed.
Figure 8 shows the Interface Þeld displaying 4. This represents Port 4 of the
device. To view statistics for another interface, refer to Viewing Statistics for
Another Interface at the end of this appendix.
Name (Read-Only)
Displays the type of interface for which statistics are being displayed.
InOctets (Read-Only)
Displays the total number of octets (bytes) that have been received on the
Interface. This includes bad frames and framing characters.
InUnicast (Read-Only)
Displays the total number of frames that have been received that were sent to a
single address.
InNonUnicast (Read-Only)
Displays the total number of frames that have been received that were delivered
to a broadcast or multicast address.
InDiscards (Read-Only)
Displays the total number of inbound frames that were discarded, even though
the frames contained no errors. This Þeld may increment because it was in an
initialization phase and not ready to forward frames, the switch needed to free up
buffer space, or the switch was being overutilized.
InErrors (Read-Only)
Displays the total number of inbound frames that have been discarded because
they contained errors. This Þeld represents the total number of errored frames,
regardless of the cause of the error.
InUnknownProtos (Read-Only)
Displays the total number of frames that were discarded because the frames were
in an unknown or unsupported format.
OutOctets (Read-Only)
Displays the total number of octets (bytes) that have been transmitted from the
interface.
22
Page 25

9M426-02 Module Specific Information
OutUnicast (Read-Only)
Displays the total number of frames transmitted that were sent to a single
address.
OutNonUnicast (Read-Only)
Displays the total number of frames transmitted to a broadcast or multicast
address.
OutDiscards (Read-Only)
Displays the total number of outbound frames that were discarded, even though
the frames contained no errors. This Þeld may increment, because the switch
needed to free up buffer space, or the switch was being overutilized.
OutErrors (Read-Only)
Displays the total number of outbound frames discarded because they contained
errors. This Þeld represents the total number of errored frames, regardless of the
cause of the error.
OutQLen (Read-Only)
Displays the length of the frames queue. The Þeld represents the total number of
frames that can be contained in queue.
Address (Read-Only)
Displays the MAC address of the interface that is currently being displayed.
Last Change (Read-Only)
Displays the last time that the interface was reset.
Admin Status (Read-Only)
Displays the current status of the interface. If this Þeld displays ÒTestingÓ, no
frames may be passed on this interface.
Oper Status (Read-Only)
Displays the current status of the interface. If this Þeld displays ÒTestingÓ, no
frames may be passed on this interface.
MTU (Read-Only)
Displays the maximum frame size (in octets) that a frame may contain to be
received or transmitted from this interface.
Speed (Read-Only)
Displays the theoretical maximum of the interfaceÕs bandwidth in bits per second.
Link Status (Read-Only)
Displays the current link status of the interface. This Þeld displays either ÒLinkÓ
or ÒNo LinkÓ.
23
Page 26

9M426-02 Module Specific Information
Duplex Mode (Read-Only)
Indicates whether the interface is operating in normal (standard) or full duplex
mode. This Þeld displays either ÒStandardÓ or ÒFull DuplexÓ.
INTERFACE [nn] (Command)
Use this command to enter an interface number for viewing statistics.
CLEAR COUNTERS (Command)
Use this command to reset all statistic counters to zero.
Viewing Statistics for Another Interface
Use the following procedure to view statistics for another interface.
1. Highlight the INTERFACE [nn] command.
2. Press the Space Bar until the desired interface is displayed, and then press the
Enter key.
Resetting Counters to Zero
To reset all the interface statistics counters to zero, use the arrow keys to highlight
the CLEAR COUNTERS command, and then press the Enter key.
24
 Loading...
Loading...