Page 1

IRM/LM
LOCAL MANAGEMENT
FOR THE CABLETRON SYSTEMS
IRM
USER’S MANUAL
CABLETRON SYSTEMS, P.O. BOX 5005, ROCHESTER, NH 03867-5005
Page 2

Page 3

NOTICE
Cabletron Systems reserves the right to make changes in specifications
and other information contained in this document without prior notice.
The reader should in all cases consult Cabletron Systems to determine
whether any such changes have been made.
The hardware, firmware, or software described in this manual is subject to
change without notice.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CABLETRON SYSTEMS BE LIABLE FOR
ANY INCIDENTAL, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES WHATSOEVER (INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
LOST PROFITS) ARISING OUT OF OR RELATED TO THIS
MANUAL OR THE INFORMATION CONTAINED IN IT, EVEN IF
CABLETRON SYSTEMS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF, KNOWN, OR
SHOULD HAVE KNOWN, THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
© Copyright August 1991 by:
Cabletron Systems Inc.
P.O. Box 5005, Rochester, NH 03867-5005
All Rights Reserved
Printed in the United States of America
Order Number: 9030152-03 August 91
DEC, LAN Bridge 100,
and
VT
are trademarks of Digital Equipment
Corporation.
Local Management/LM is a trademark of Cabletron Systems.
Prime
is a trademark of Prime Computer.
i
Page 4

NOTICE
ii
Page 5

CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 USING THIS MANUAL................................................................1-1
1.2 GETTING HELP..........................................................................1-2
1.3 LOCAL MANAGEMENT FOR THE CABLETRON SYSTEMS
IRM..............................................................................................1-3
1.4 RELATED MANUALS..................................................................1-4
CHAPTER 2 GETTING STARTED
2.1 TERMINAL CONFIGURATION...................................................2-1
2.1.1 VT100 Series Setup........................................................ 2-1
2.1.2 Prime 200 Series Setup..................................................2-2
2.2 CABLE CONFIGURATION..........................................................2-3
2.2.1 VT100 Series..................................................................2-3
2.2.2 Prime 200 Series ............................................................2-3
2.3 ACCESSING LOCAL MANAGEMENT........................................2-4
2.4 EXITING LOCAL MANAGEMENT...............................................2-6
CHAPTER 3 USING LOCAL MANAGEMENT FOR THE IRM
3.1 GENERAL TIPS ..........................................................................3-1
CHAPTER 4 MAIN MENU
4.1 THE MMAC MAIN SCREEN .......................................................4-1
4.1.1 MMAC Main Screen Fields.............................................4-2
CHAPTER 5 STATISTICS SCREENS
5.1 MMAC STATISTICS SCREEN....................................................5-1
5.1.1 MMAC Statistics Screen Fields ......................................5-2
5.2 BOARD STATISTICS SCREEN..................................................5-4
5.2.1 Ethernet Board Statistics Screen....................................5-4
5.2.1.1 Board Statistics Screen Fields (Ethernet) ......5-4
5.2.2 Token Ring Board Stats.................................................. 5-9
5.2.2.1 Token Ring Board Status Screen Fields......5-10
5.3 PORT STATISTICS SCREEN (ETHERNET)............................5-13
5.3.1 Port Statistics Screen Fields.........................................5-14
CHAPTER 6 SETTING SYSTEM PARAMETERS
6.1 RESET SYSTEM PARAMETERS SCREEN...............................6-1
6.1.1 Reset System Parameters Screen Fields.......................6-2
iii
Page 6

CONTENTS
6.1.2 Editing the Reset System Parameters Screen................6-3
6.1.2.1 Setting the Current Date.................................6-3
6.1.2.2 Setting the Current TIme.................................6-4
6.1.2.3 Setting the Audible Alarms Option..................6-4
6.1.2.4 Setting the Segmented Port Alarms Option....6-4
6.1.2.5 Setting the Management Auto Send Option ...6-5
6.1.2.6 Setting the Screen Refresh Time....................6-5
6.1.2.7 Setting the Minimum Alarm Duration Time.....6-5
6.1.2.8 Setting the MMAC IP Address........................6-6
6.1.2.9 Setting the Stats Polling Interval Time............6-6
6.1.2.10 Setting the Stats Polling Interval # of Packets6-6
6.1.3 Saving System Parameters.............................................6-7
CHAPTER 7 SETTING ALARM LIMITS
7.1 RESET SYSTEM PARAMETERS SCREEN ...............................7-1
7.2 SET BOARD ALARM LIMITS SCREEN ......................................7-3
7.2.1 Set Board Limits Screen Fields.......................................7-3
7.3 SET PORT ALARM LIMITS SCREEN.........................................7-6
7.3.1 Set Port ALarm Limits Screen Fields ..............................7-7
7.4 SETTING AN ALARM LIMIT........................................................7-8
CHAPTER 8 USING THE REDUNDANCY FUNCTION
8.1 CABLE REDUNDANCY SCREEN...............................................8-1
8.1.1 Cable Redundancy Screen Fields...................................8-2
8.1.2 Setting Up A Cable Redundancy.....................................8-3
CHAPTER 9 SETTING ALTERNATE MMAC BOARD NAMES
9.1 MMAC BOARD NAMES SCREEN ..............................................9-1
9.2 MMAC BOARD NAMES SCREEN FIELDS.................................9-2
9.3 ASSIGNING BOARD NAMES .....................................................9-2
CHAPTER 10 PORT STATUS SCREEN
10.1 PORT STATUS SCREEN..........................................................10-1
10.1.1 Port Status Screen Fields..............................................10-2
CHAPTER 11 PORT LINK STATUS OPTION
11.1 LINK STATUS SCREEN............................................................11-1
11.1.1 Link Status Screen Fields..............................................11-1
CHAPTER 12 USING THE PREVIOUS COUNTER SCREENS
12.1 PREVIOUS COUNTER SCREENS ...........................................12-1
12.2 PREVIOUS COUNTER X SCREEN FIELDS.............................12-2
iv
Page 7

CONTENTS
CHAPTER 13 USING OTHER AVAILABLE FUNCTIONS
13.1 RESTARTING THE IRM............................................................13-1
13.2 RESETTING IRM COUNTERS.................................................13-1
13.3 RESETTING AUTO MODE (TOKEN RING) .............................13-2
13.4 ENABLING AND DISABLING ALL ETHERNET OR
TOKEN RING PORTS...............................................................13-2
13.4.1 Enabling and Disabling All Ethernet Ports....................13-2
13.4.2 Enabling and Disabling All Token Ring Ports ...............13-3
13.4.3 Enabling and Disabling All Ports on Individual
Ethernet Boards............................................................13-3
13.4.4 Enabling and Disabling All Ports on Individual
Token Ring Boards.......................................................13-3
13.4.5 Enabling and Disabling Individual Ethernet and
Token Ring Ports..........................................................13-4
13.5 ATTACHING AND DETACHING TOKEN RING BOARDS .......13-4
13.6 CHANGING THE PASSWORD.................................................13-4
v
Page 8

CONTENTS
vi
Page 9

CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
Welcome to Cabletron Systems'
Management for Cabletron Systems' IRM User's Manual
designed this manual to serve as a simple reference guide for using
IRM/LMIM™. Local Management is accessed through the Console Port
on the IRM.
IRM/LM - Local Network
. We have
1.1 USING THIS MANUAL
Chapter 1,
Local Management for the IRM The chapter also includes a list of related
user manuals.
Chapter 2,
Management for the IRM. This chapter includes procedures for entering
the password as well as a list of the necessary terminal and cable
configurations for communicating IRM/LM.
Chapter 3,
provides general screen information and instructions for getting around
IRM/LM.
Introduction
Getting Started
Using Local Management for the Cabletron Systems IRM
, discusses the capabilities of Cabletron Systems'
, lists procedures for accessing Local
,
Chapter 4,
Chapter 5,
both the Ethernet and Token Ring boards installed in your MMAC. There
is also a description of each field on the screens.
Chapter 6,
Reset System Parameter Screen as well as instructions on how to modify
these fields.
Chapter 7,
MMAC, e.g. the MMAC Alarm Limits on the Reset System Parameter
Screen, the Board Alarm Limits on the Board Limits Screen, and the Port
Alarm Limits on the Port Limits On Board X Screen.
Main Menu
Statistics Screens
Resetting System Parameters
Setting Alarm Limits
, describes each field on the MMAC Main Screen.
, discusses the type of statistics available for
, describes each field on the
, details how to set alarm limits on the
1-1
Page 10

INTRODUCTION
Chapter 8,
Using the Redundancy Feature
, describes each field on the
Cable Redundancy Screen-. Instructions are also included for setting up
redundant links.
Chapter 9,
Setting Alternate MMAC Board Names
, describes each field
on the MMAC Board Names Screen. Instructions are also included for
changing these field names to names of your own choice.
Chapter 10,
Using the Port Status Function
, describes the fields on the
Port Status Screen for both Ethernet and Token Ring boards.
Chapter 11,
Using the Link Status Function
, describes the Link Status
Screen and its applications to Ethernet and Token Ring boards.
Chapter 12,
Using the Previous Counter Scr eens
, provides a description
of the Previous Counters Screen.
Chapter 13,
Using Other Available Functions
, provides instructions on
restarting and resetting the IRM counters, and enabling and disabling
ports and boards.
We assume that you have a general working knowledge of Ethernet or
IEEE 802.3 type data communications networks and their physical layer
components.
1.2 GETTING HELP
If you need additional support related to Cabletron Systems' Local
Management Network Control Management for the Cabletron Systems
IRM, or if you have any questions, comments or suggestions related to
this manual or any of our Ethernet products, feel free to contact Cabletron
Systems' Technical Support at:
Cabletron Systems
P.O. Box 5005
Rochester, N.H. 03867-5005.
Phone: (603) 332-9400
1-2
Page 11

INTRODUCTION
1.3 LOCAL MANAGEMENT FOR THE CABLETRON
SYSTEMS IRM
Cabletron Systems Local Management for the Cabletron Systems IRM
provides unique network management and control capabilities for a
Cabletron Systems Multi Media Access Center (MMAC) with an IRM
installed. With Local Management, you have full control of your network.
Local Management provides the network manager with many tools to
control and manage the MMAC and its attached segments. By setting
various threshold v alues (Alarm Limits), you can be advised that a certain
condition has been reached. When an alarm limit has been reached, an
MMAC can be set to advise you that the condition has been reached or set
to automatically reroute network traffic.
For example, if you want to know if the MMAC processes a specific
number of good packets or collisions over a set period of time (e.g., 2000
packets in 1 second), an MMAC Limit can be set to notify you that this
condition has been reached. Limits can also be set for each individual
board (Board Limits) and for each individual port (Port Limits). These
limits can be set to disable the MMAC, board, or port when the limit is
reached.
If these limits are set to turn off the MMAC, board, or port, Local
Management allows you to reroute network traffic automatically. This
feature is called call redundancy. Redundancy keeps your network up and
running at all times. For example, if a limit set for a port is reached and
the port is set to turn off automatically, a backup port can be set to pick up
network traffic automatically from the disabled port.
Local Management also gives you the ability to gather a vast amount of
statistical information about the MMAC at three increasingly detailed
levels: for the MMAC as a whole, for each board, and for each port.
Statistical information on the MMAC is broken down into three
categories: packets, collisions and alarms. Totals for each of these
categories are recorded at the MMA C, board, and port le vel. This data can
be sampled at two user-defined interv als—a time-based interval calibrated
to the second, and a total packet count interval calibrated to one packet.
These statistics illustrate how packets, collisions, and alarms correlate
over time.
1-3
Page 12

INTRODUCTION
1.4 RELATED MANUALS
The manuals listed below should be used to supplement the procedures
and other technical data provided in this manual. Their procedures are
referenced where appropriate, but are not repeated in this manual.
Cabletron Systems'
Installation Guide
Cabletron Systems'
Feature
Instruction Sheet
Intelligent Repeater Module (IRM/IRM-1)
Local Management for the IRM Change Password
1-4
Page 13

CHAPTER 2
GETTING STARTED
This chapter lists procedures for entering the password so you can access
Local Management for the IRM. It also provides the terminal and cable
configurations for setting up a terminal for accessing Local Management.
Instructions are included for exiting Local Management.
2.1 TERMINAL CONFIGURATION
Local Management for the IRM is accessed through a VT™ 100 Series
terminal, a Prime™ 200 Series terminal, or a compatible system running
an emulation program. The terminal is attached to the port labeled
CONSOLE on the IRM by an RS-232 cable. For instructions to set up
your terminal, refer to the applicable node user's manual.
The terminal configurations must be set as follows so the terminal can
communicate with Local Management.
2.1.1 VT100 Series Setup
If you have a VT100 series terminal, press F3 to access the Setup
Directory.
Display Set-up Menu
Columns 80 Columns
Controls Interpret Controls
Auto Wrap No Auto Wrap
Text Cursor No Cursor
General Set-up Menu
Mode (VT220) VT200, 7 Bit Control
(VT320) VT300, 7 Bit Control
Cursor Keys Normal Cursor Keys
2-1
Page 14

GETTING STARTED
Communications Set-up Menu
Transmit Transmit=9600
Receive Receive=Transmit
XOFF any option
Bits Parity 8 bits, No Parity
Stop Bit 1 Stop Bit
Local Echo No Local Echo
Port (VT220) EIA Port, Data Leads Only
(VT320) DEC-423 Data Leads Only
Transmit any option
Keyboard Set-up Menu
Keys Typewriter Keys
Auto Repeat any option
Keyclick any option
Margin Bell No Margin Bell
Warning Bell Warning Bell
Auto Answerback No Auto Answerback
2.1.2 Prime 200 Series Setup
If you have a PRIME 200 series terminal, press SETUP to access the
Setup Directory.
Cursor Type any option
Brightness any option
Screen Size 80 x 24
Screen V ideo Normal
Control Representation OFF
Line Feed Mode ON
Line Truncate OFF
Transmission CHAR
Keyboard Repeat Rate any option
N-key Rollover any option
Margin Bell Volume OFF
Key Click Volume any option
Scroll any option (hard is preferred)
Speed any option
Kybd U.S.
Char U.S.
Menu English
2-2
Page 15

GETTING STARTED
Online/Local ON LINE
Host Stop Bits 1
Aux Stop Bits any option
Host Baud Rate 9600
Host Parity 8-bit none, 7-bit space
Aux Baud Rate any option
Aux Parity any option
2.2 CABLE CONFIGURATION
Local Management is accessed by a modified RS-232 cable, available
from Cabletron Systems. This cable connects the terminal to the IRM's
Console port.
The pin out for a cable with a 25 pin connector at the terminal end of the
cable, and a 9 pin connector at the MMAC end of the cable, should be
configured as follows:
2.2.1 VT100 Series
9 Pin Male Connector to 25 Pin Female Connector
(MMAC End) (Terminal End)
Pin 1 (Receive) to Pin 2 (Transmit)
Pin 4 (Transmit) to Pin 3 (Receive)
Pin 5 (Ground) to Pin 7 (Ground)
Pin 6 (Request to Send) to Pin 5 (Clear to Send)
Pin 9 (Clear to Send) to Pin 4 (Request to Send)
2.2.2 Prime 200 Series
9 Pin Male Connector to 25 Pin Female Connector
(MMAC End) (Terminal End)
Pin 1 (Receive) to Pin 2 (Transmit)
Pin 4 (Transmit) to Pin 3 (Receive)
Pin 5 (Logic Ground) to Pin 7 (Logic Ground)
Pin 9 (Clear to Send) to Pin 4 (Request to Send)
to Pin 5 (Clear to Send)
Pins 6, 8, and 20 on the 25 pin connector are jumpered.
2-
3
Page 16
GETTING STARTED
2.3 ACCESSING LOCAL MANAGEMENT
This section contains instructions for attaching the terminal to the IRM,
and for accessing Local Management through the IRM's Console port.
This procedure assumes that the special 9 to 25 pin RS-232 cable,
provided by Cabletron Systems, is being used to connect the terminal to
the IRM.
1. Plug the 9 pin end of the RS-232 cable into the RS232 port labeled
CONSOLE on the IRM.
2. Plug the 25 pin end of the RS-232 cable into the COMM port on the
terminal.
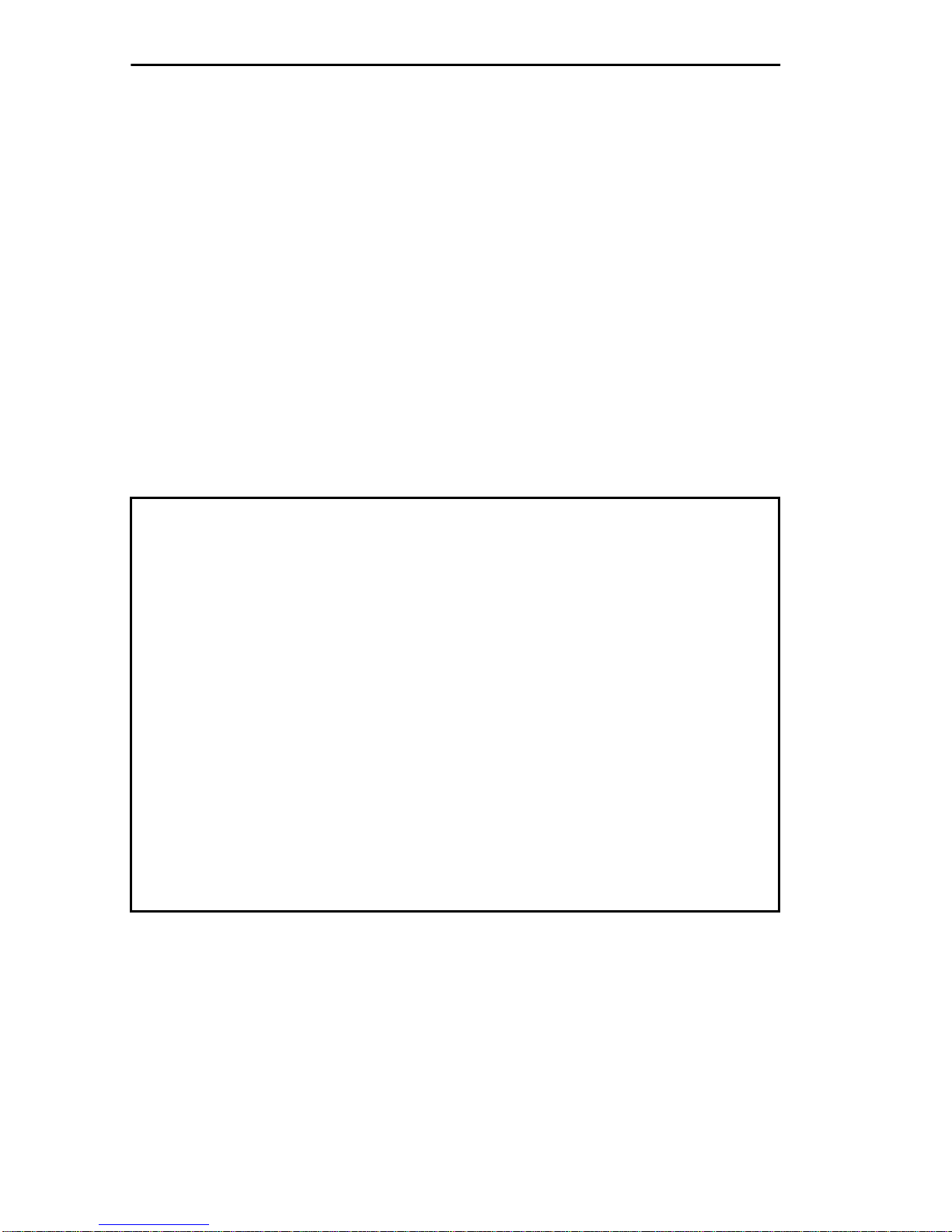
3. Turn the terminal on. The Terminal Type Menu Screen, Figure 2-1,
will appear, prompting you to select the terminal type.
TERMINAL TYPE MENU
1. VT 100 Series
2. PRIME 200 Series
Select Terminal Type-->
Figure 2-1 Terminal Type Menu Screen
4. Type 1 or 2, depending upon your terminal type. The MMAC
Password Screen, Figure 2-2, will appear on the screen.
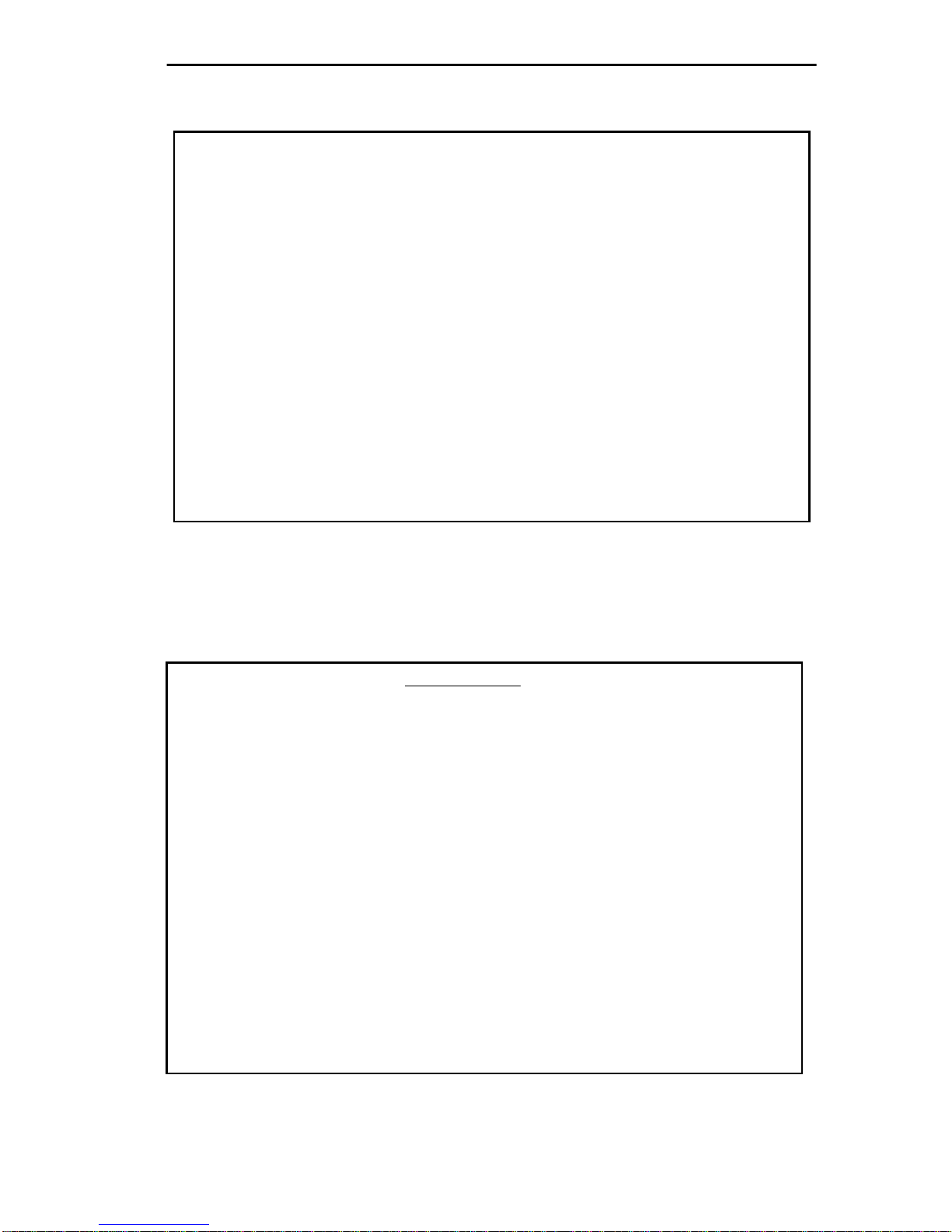
5. Type your password into the
Enter Password
field.
6. Press
Return
. The MMAC Main Screen, Figure 2-3, will appear on
the terminal. Local Management is now ready for operation.
2-4
Page 17
GETTING STARTED
MULTIMEDIA ACCESS CENTER
Cabletron Systems Incorporated
P.O. Box 6257 Rochester, NH 03867 U.S.A.
(C) Copyright Cabletron Systems Inc. 1989, 1990
(603)-332-9400
Enter Password:
Figure 2-2 MMAC Password Screen
02/16/90 14:26:43 MMAC MAIN SCREEN Last Reset: 02/16/90 08:10:11
Values displayed reflect previous system configuration
MMAC Name: Tech Writing MMAC Address: 00-00-1D-00-36-06
Total MMAC Packets: 2532
Total MMAC Collisions: 0
Total Alarms: 0
Packets/ Auto Ports
Colls. Within Shut-off ON OFF
MMAC Limit: 1000 -C 00:00:10 DISABLED NO 16 0
Audible Alarms: YES
Segmented Port Alarms: NO
Management Auto Send: NO
Screen Refresh Time: 6 seconds
Minimum Alarm Duration: 10 seconds
MMAC IP Address: 0.0.0.0
Stats. Polling Interval - Time: 00:00:20 # of Packets: 10000
MMAC STATISTICS RESET SYSTEM PARAMETERS PORT STATUS LINK STATUS
PREVIOUS COUNTERS 0 EXIT
Figure 2-3 MMAC Main Screen
2-
5
Page 18

GETTING STARTED
2.4 EXITING LOCAL MANAGEMENT
To exit Local Management:
1. Return to the MMAC Main Screen. If you are presently at the MMAC
Main Screen, move to step #3. If you are at any other screen, highlight
the
MAIN
option at the bottom of the screen using the arrow keys.
2. Press
3. Highlight the
4. Press
Return
Return
. The MMAC Main Screen will appear.
EXIT
option at the bottom of MMAC Main Screen.
. The MMAC Password Screen will appear.
5. Turn off the terminal.
WARNING
: DO NOT disconnect the power cable fr om the MMAC. If you
disconnect the power cable, you will disable communication on all
network segments linked directly to the MMAC.
2-6
Page 19

CHAPTER 3
USING LOCAL MANAGEMENT FOR THE IRM
Local Management's screens can be easily accessed by manipulating the
arrow keys on your terminal. This chapter explains how to move around
Local Management for the MMAC (HUB).
3.1 GENERAL TIPS
• You have the option to return to the MMA C Main Screen by selecting
MAIN
• Use the arrow keys on the mid bank of keys to move the cursor up,
down, left, or right on the screen to select fields or options.
• The Tab key performs the same function as the right arrow key.
• To select a board or port at a command field, use the shift and plus to
toggle the board or port number forward or the minus key to toggle the
board or port number backward. For example, if you want to view
STATS-BOARD 3 and the command field currently displays
STATS-BOARD 1, press the
times until the command field reads ST ATS- BOARD 3. If you want to
view Board 0, press the minus ke y once. The command field will no w
read STATS-BOARD 0.
at the bottom of the screen.
shift
and
plus
keys simultaneously two
3-1
Page 20

USING REMOTE LANVIEW
3-2
Page 21
CHAPTER 4
MAIN MENU
The Main Menu of Local Management for the IRM displays various
parameters to which Local Management is set. A summary of network
activity that has been detected by the MMAC is also displayed.
4.1 THE MMAC MAIN SCREEN
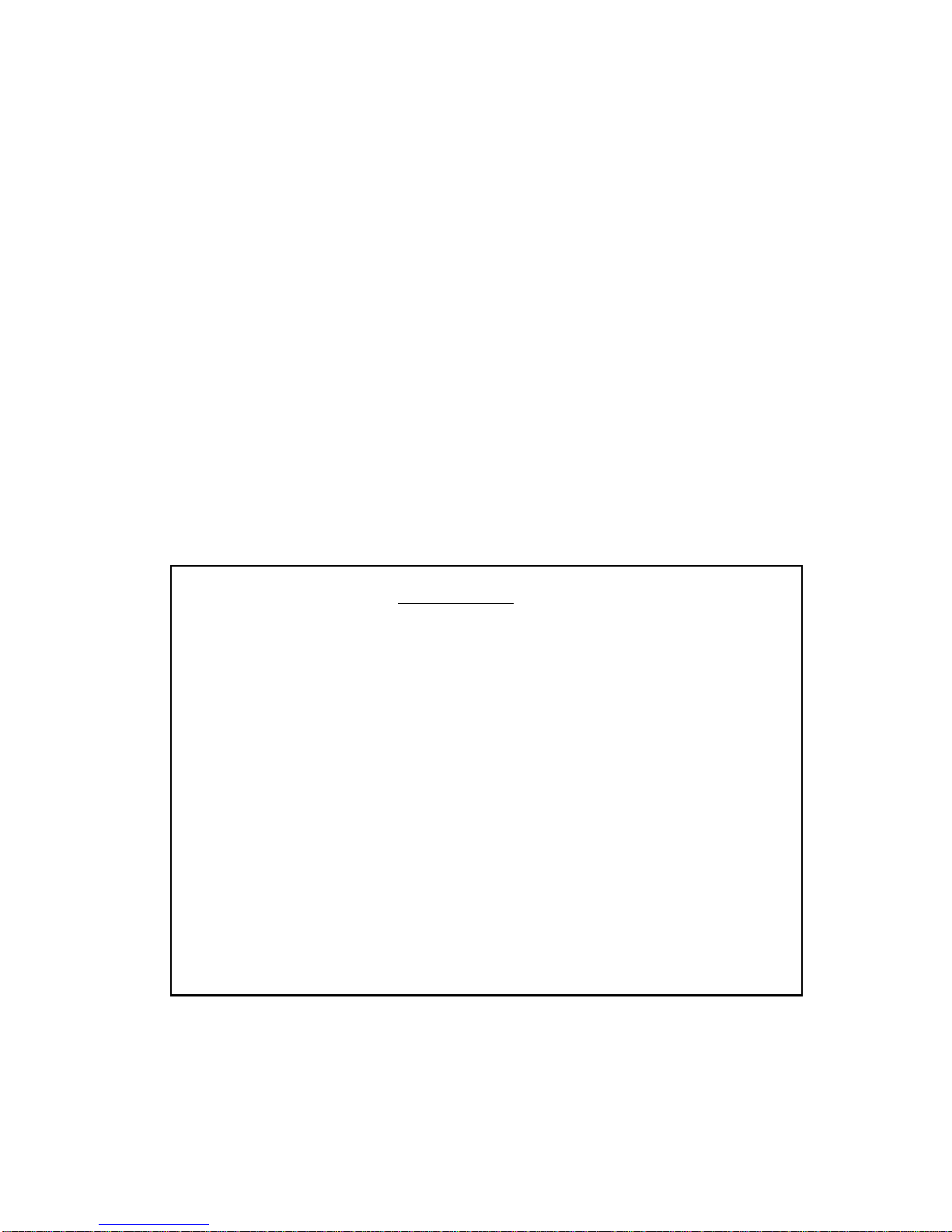
The MMAC Main Screen, Figure 4-1, is the first screen to appear after the
correct password is entered. This screen displays general configuration
information as well as current tallies of good packets that the MMA C has
processed and collisions that the MMAC has detected. It also displays the
number of times the MMAC has exceeded MMAC, Board, or Port Alarm
Limits set for the MMAC. No fields can be edited at this screen.
02/16/90 14:26:43 MMAC MAIN SCREEN Last Reset: 02/16/90 08:10:11
Values displayed reflect previous system configuration
MMAC Name: Tech Writing MMAC Address: 00-00-1D-00-36-06
Total MMAC Packets: 2532
Total MMAC Collisions: 0
Total Alarms: 0
Packets/ Auto Ports
Colls. Within Shut-off ON OFF
MMAC Limit: 1000 -C 00:00:10 DISABLED NO 16 0
Audible Alarms: YES
Segmented Port Alarms: NO
Management Auto Send: NO
Screen Refresh Time: 6 seconds
Minimum Alarm Duration: 10 seconds
MMAC IP Address: 0.0.0.0
Stats. Polling Interval - Time: 00:00:20 # of Packets: 10000
MMAC STATISTICS RESET SYSTEM PARAMETERS PORT STATUS LINK STATUS
PREVIOUS COUNTERS 0 EXIT
Figure 4-1 MMAC Main Screen MAIN MENU
4-1
Page 22

MAIN MENU
4.1.1 MMAC Main Screen Fields
(Date/Time)
Displays the current date and time of the MMAC.
Last Reset:
Displays the date and time that the IRM counters of the MMAC were last
reset to 0.
MMAC Name:
Displays the user-defined name given to the MMAC. The MMAC Name
is the same name given to Board 0 (the IRM) at the MMAC Board Names
Screen.
MMA C Address:
Displays the Ethernet address of the MMAC.
Total MMAC Packets:
Displays the total number of good packets the MMAC has processed.
Total MMAC Collisions:
Displays the total number of collisions the MMAC has detected.
T otal Alarms:
Displays the total number of times the MMAC reached a user-defined
MMAC, Board, or Port Alarm Limit.
MMAC Limit:
Displays the MMAC Alarm Limit set for the MMA C. The MMAC Alarm
Limit is the number of good packets or collisions that can pass through
the MMAC within a given time period before the limit is reached. For
example, the MMA C Alarm Limit will be e xceeded when more than 1000
collisions (Packets/Colls.) are detected by the MMAC in less than 10
seconds (Within).
The following indicates what the MMAC Alarm Limit is set to.
Packets/Colls. Displays the number of packet or collisions that must
pass through the MMAC before the MMAC Alarm Limit
is checked. To the right of the field is a -P or a -C. A -P
indicates the entry is a certain number of good packets.
A -C indicates that the entry is a certain number of
collisions. If O -P or O -C is displayed in this field, the
MMAC Alarm
4-2
Page 23

MAIN MENU
Limit will not be checked. The default entry in this
field is 1000 -C.
Within Displays the time period in which the number of
packets or collisions, listed in the Packets/Colls.
display, may occur before the MMAC Alarm Limit is
reached. -TIME to the right of the entry indicates the
entry is a time period. If 00:00:00 or DISABLED! is
displayed in this field, the MMAC Alarm Limit will not
be checked. The default entry in this field is 00:00: 10
-DISABLED.
Auto Shut-off Indicates whether or not the MMAC will automatically
shut off all of its ports when the MMA C Alarm Limit is
reached. YES indicates that the MMAC will shut off
automatically when the limit is reached. NO indicates
that the MMAC will not shut off when the limit is
reached. The default value for this field is NO.
Ports ON/OFF Displays the number of ports on each MMAC that are
ON (enabled or segmented) and the number of ports
that are OFF (disabled).
A udible Alarms:
Indicates whether a beep will sound when an error, alarm, or status
message appears on the terminal connected to the IRM's Console port.
YES indicates that a beep will be generated by the terminal connected to
the IRM's Console port when a message appears. NO indicates that no
sound will be generated. The default value for this field is YES.
Segmented Port Alarms:
Indicates whether an alarm message will appear if a port is segmented
from the MMAC. YES indicates that a message will appear at the top of
the screen, listing which board and port was segmented. NO indicates that
no alarm message will appear. The default value for this field is NO.
Management A uto Send:
Indicates whether an MMAC Management P acket will be generated when
Local Management gathers statistics. YES indicates that a management
packet will be generated when the MMAC has gathered statistics. NO
indicates that a management packet will not be generated when the
MMAC has gathered statistics. The default value for this field is NO.
4-3
Page 24

MAIN MENU
Screen Refresh Time:
Display, in seconds, how often each screen on the terminal connected to
the IRM’s Console port is updated. The default value for this field is 10
seconds.
Minimum Alarm Duration:
Display, in seconds, how long an error, alarm, or status message will
appear on the second line of the terminal’s screen before being erased.
The default value for this field is 10 seconds.
MMAC IP Address:
Displays the MMAC’s IP (Internet Protocol) address.
Stats Polling Interval:
Displays the intervals at which MMAC statistics are being gathered.
Statistics are gathered by time (i.e., every minute) and by the number of
good packets (i.e., after every 1,000th good packet passes through the
MMAC).
Time Displays the time interval in which Timer Statistics are
being gathered. If 00:00:00 is displayed, no time related
statistics will be gathered. The default value for this field
is 00:00:20 (20 seconds).
# of Packets Displays the number of good packets that must pass
through the MMAC before Counter Statistics are
gathered. If 0 is displayed, no count related statistics will
be gathered. The default value for this field is 10000
packets.
4-4
Page 25
CHAPTER 5
STATISTICS SCREENS
The Statistic Function of Local Management gives you the ability to
gather a vast amount of statistical information about your MMAC.
Statistics are gathered at three increasingly detailed levels: for the MMA C
as a whole, for each board, and for each port.
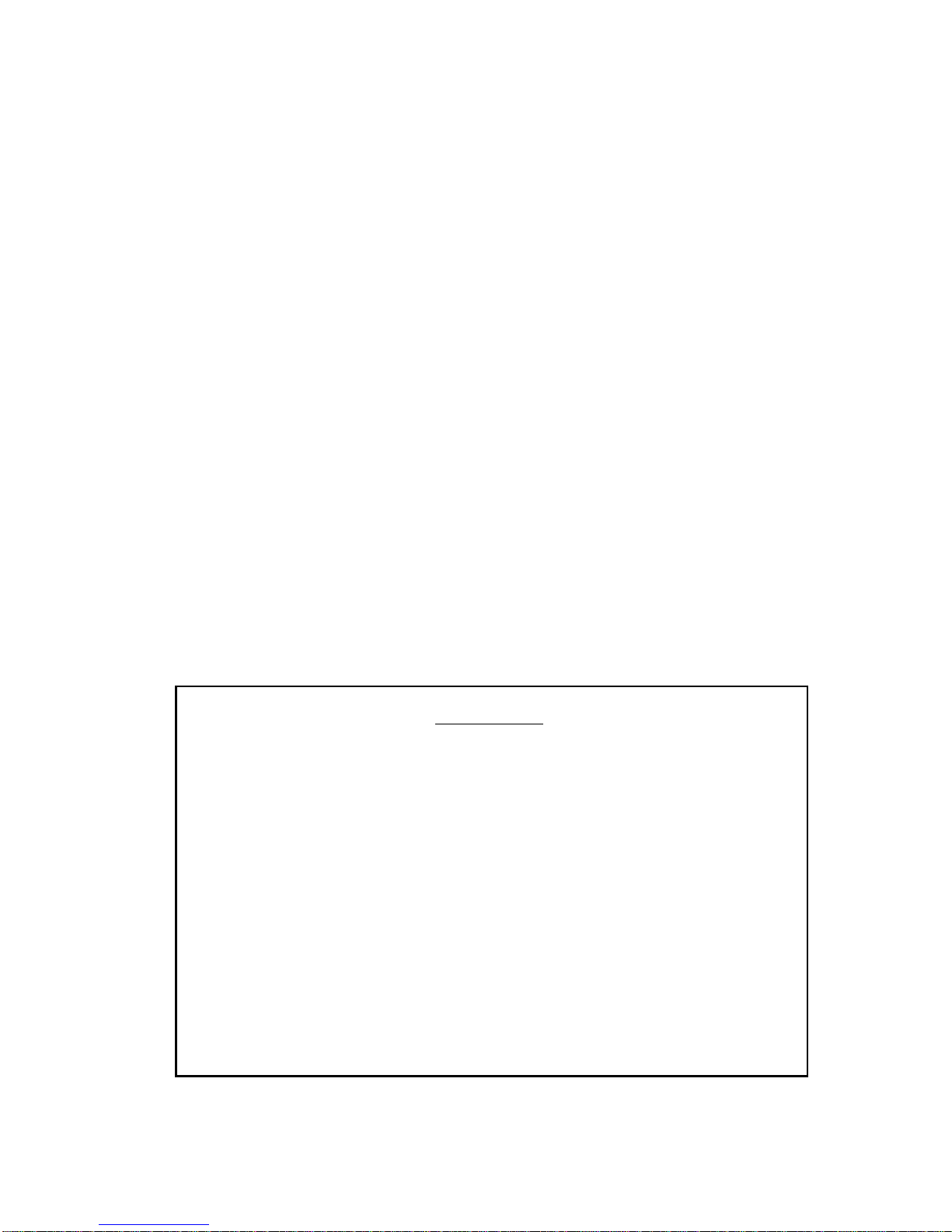
5.1 MMAC STATISTICS SCREEN
The MMAC Statistics screen displays general statistical information for
the MMAC as a whole, such as the number of good packets or collisions
that have passed through the MMAC. No fields can be modified at this
screen.
To access this screen:
1. Highlight the MMAC STATISTICS option at the bottom of the
MMAC Main Screen.
2. Press Return. The MMAC Statistics screen, Figure 5-1, will appear.
02/16/90 14:38:03 MMAC STATISTICS Last Reset: 02/16/90 08:10:11
MMAC Name: IRM Board MMAC Address: 00-00-1D-00-03-F0
MMAC Port Status - ON: 16 OFF: 0
MMAC : Timer Statistics Configured Interval: 00:00:20
Total : Elapsed Average Peak
Packets: 2661114 : 143 49 143
Colls.: 0 : 0 0 0
Alarms: 0 : 0 0 0
Delta Time: : 20 20 20
Last Sample Time: 14:37:55
Slot Name Board/MMAC | Slot Name Board/MMAC
0 IRM Board 100 | 1 Board 1 99
2 Board 2 0 | 3
4 | 5
6 | 7
MAIN STATS-BOARD 0 ENABLE ETHERNET ENABLE TOKEN RING
DISABLE ETHERNET DISABLE TOKEN RING
Figure 5-1 MMAC Statistics Screen
5-1
Page 26

STATISTICS SCREENS
5.1.1 MMAC Statistics Screen Fields
MMAC Name
Displays the user-defined name assigned to the IRM at the MMA C Board
Names Screen.
MMA C Address
Displays the Ethernet address of the MMAC.
MMAC Port Status - ON:xx OFF:xx
Displays the number of ports in the MMAC that are ON (enabled or
segmented) and the number of ports that are OFF (disabled). This number
includes Token Ring Station and Ring-in/Ring-out ports. (Each ring port
is counted separately.) For a port to be considered ON, it must be enabled
by management.
MMA C Total
The MMAC Total displays the number of good packets or collisions the
MMAC has processed, and also displays the number of times the MMAC
reached any alarm limit.
Packets Displays the total number of good packets the MMAC has
processed.
Colls. Displays the total number of collisions the MMAC has
processed.
Alarms Displays the total number of times that the MMAC reached
an MMAC, board, or port alarm limit.
Timer Statistics
Timer Statistics allo w you to sample activity on the MMAC for a set time
period. You can set this time period at the Stats Polling Intervals display
on the System Parameter Screen. For example, if you set Time to 10
seconds, the figure under Elapsed - Packets will be the number of packets
that the MMAC processes during that 10 second interval.
5-2
Page 27

STATISTICS SCREENS
The T imer Statistics portion of the screen displays the f ollowing timer
statistics for the MMAC as a whole:
Elapsed Displays the number of good packets, collisions, or alarms
the MMAC processed during the last sample checked.
Average Displays the average number of good packets, collisions or
alarms which occurred since the IRM counters were last
reset.
Peak Displays the peak number of good packets, collisions, or
alarms since the IRM counters were last reset.
The elements that are monitored by the Timer Statistics portion of
the screen are:
Packets Displays statistics based on the number of good packets.
Colls. Displays statistics based on the number of collisions.
Alarms Displays statistics based on the number of alarms.
Delta Time Displays the actual time between the gathering of Timer
Statistics.
Configured Interval
Displays how often the MMAC is being polled or sampled. This value is
set at the System Parameter Screen in the Stats Time Sampling Rate field.
For example, if Time is set to 10 seconds, the figure under Elapsed Packets will be the number of packets that the MMAC processes during
that 10 second interval.
Last Sample Time: XX:XX:XX
Displays the last time that Timer Statistics were gathered.
Slot
Displays the slot number that the board occupies in the MMAC. Available
board slot numbers are O through 2 for an MMAC-3, or O through 7 for
an MMAC-8.
5-3
Page 28

STATISTICS SCREENS
Name
Displays the user-defined name assigned to the board at the Board Names
Screen.
Board/MMA C
Displays the percentage of activity for which each board is responsible,
based on total MMAC activity.
5.2 BOARD STATISTICS SCREEN
The Board X Statistics Screen displays board level statistics for the
MMAC. The Ethernet board statistics are broken do wn to T imer Statistics
(statistics based on a time period) and counter statistics (statistics
gathered based on a count of good MMAC packets).
For Token Ring boards, you can view the status of the ports on the board,
including the number of ports enabled or wrapped. You can also see
which ports are being used as Ring-in/Ring-out ports.
5.2.1 Ethernet Board Statistics Screen
To access this screen:
1. Highlight the STATS - BOARD X option at the bottom of the MMAC
Statistics Screen.
2. Select the board you intend to access at this command field by pressing
the shift and + keys or the - key until the appropriate board number
appears.
3. Press Return. The Board X Statistics Screen (Ethernet), Figure 5-2,
will appear.
5.2.1.1 Board Statistics Screen Fields (Ethernet)
MMAC Name
Displays the user-defined name assigned to the IRM at the Board Names
Screen.
5-4
Page 29

STATISTICS SCREENS
02/16/90 14:26:43 Board 0 Statistics Last Reset: 02/16/90 08:10:11
MMAC Name: IRM Board Board Name: IRM Board
MMAC Total Board Total % Board/MMAC Port Status
Packets: 266003 1388 1 ON OFF
Colls.: 0 0 0 MMAC: 16 0
Alarms: 0 0 0 Board 0: 4 0
Timer Statistics Configured Interval: 00:00:20 Port %Port/Board Status
Elapsed Average Peak 1 0 SEG
Packets: 6 6 6 2 0 SEG
Colls. 0 0 0 3 0 SEG
Alarms: 0 0 0 4 100 ON
Delta Time: 20 20 20
Counter Statistics Configured Level: 10000
Elapsed Average Peak
Packets: 53 15 1067
Colls. 0 0 40
Alarms: 0 0 0
Delta Time: 2627 4038 18142
MAIN STATE-MMAC STATS-BOARD 0 STATS-PORT 1 ENABLE BOARD 0 DISABLE BOARD 0
Figure 5-2 Board X Statistics Screen (Ethernet)
Board Name
Displays the user-defined name assigned to the board at the Board Names
Screen.
MMA C Total
The MMAC Total displays the number of good packets or collisions the
MMAC has processed, and also the number of times the MMAC has
reached any alarm limit.
Packets Displays the total number of good packets the MMAC has
processed.
Colls. Displays the total number of collisions the MMAC has
processed.
Alarms Displays the total number of times the MMAC reached an
MMAC, board, or port alarm limit.
Board Total
The Board Total displays the number of good packets or collisions the
board has processed, and also the number of times the board has reached a
Board Alarm Limit.
5-5
Page 30

STATISTICS SCREENS
Packets Displays the total number of good packets the board has
processed.
Colls. Displays the total number of collisions the board has
processed.
Alarms Displays the total number of times the board reached a board
alarm limit.
% Board/MMAC
The % Board/MMAC indicates the percentage of activity for which the
board is responsible, based on total MMAC activity.
Packets Displays the percentage of good packets for which the board
is responsible, based on total MMAC activity.
Colls. Displays the percentage of collisions for which the board is
responsible, based on total MMAC activity.
Alarms Displays the percentage of alarm limits for which the board
has been responsible in the MMAC.
Port Status
MMAC Displays the number of ports in the MMAC that are enabled
or segmented (ON), and the number of ports that are disabled
(OFF).
Board Displays the number of ports on the board that are enabled or
segmented (ON), and the number of ports that are disabled
(OFF).
Timer Statistics
Timer Statistics allow you to sample activity on the board by a set time
period. This time period is set at the Stats Polling Intervals display on the
System Parameter Screen. For example, if Time is set to 10 seconds, the
figure under Elapsed - Packets will be the number of packets the board
processes during that 10 second interval.
5-6
Page 31

STATISTICS SCREENS
The T imer Statistics portion of the screen displays the f ollowing timer
statistics for the board:
Elapsed Displays the number of good packets, collisions, or alarms
the board processed during the last sample checked.
Average Displays the average number of good packets, collisions, or
alarms processed since the IRM counters were last reset.
Peak Displays the peak number of good packets, collisions, or
alarms processed since the IRM counters were last reset.
The elements that are monitored by the Timer Statistics portion of
the screen are:
Packets Displays statistics based on the number of good packets.
Colls. Displays statistics based on the number of collisions.
Alarms Displays statistics based on the number of alarms.
Delta Time Displays the actual time between the gathering of Timer
Statistics.
Configured Interval
Displays how often the board is being polled or sampled. This value is set
at the System Parameter Screen in the Stats Time Sampling Rate field.
For example, if Time is set to 10 seconds, the figure under Elapsed Packets will be the number of packets that the board processes during that
10 second interval.
% Port/Board
The % Port/Board displays the percentage of activity for which each port
on a board is responsible, based on total board activity.
5-7
Page 32

STATISTICS SCREENS
Port Displays the Port number on the Board. Available port
numbers are 1 through 12 for each board except the
IRM, FOT-MIM-16, FOT-MIM-26 and the MT8-MIM.
The port numbers for a FOT-MIM-16 and a
FOT-MIM-26 are 1 through 6. The port numbers on an
MT8-MIM are 1 through 8. The port numbers on an
IRM are 1 through 4.
% Port/Board Displays the percentage of activity for which each port
is responsible, based on total board activity.
Status Displays port status: enabled (ON), segmented (SEG),
or disabled (OFF).
Counter Statistics
Counter Statistics allow you to sample acti vity on the board after a certain
number of good packets have passed through the MMAC. This number is
set at the Stats Polling Intervals display on the System Parameter Screen.
For example, if # of Packets is set to 1000 packets, the figure under
Elapsed - Packets will be the number of packets the board has processed
during that 1000 MMAC packet interval.
This portion of the screen displays the following Counter Statistics
for the board:
Elapsed Displays the number of good packets, collisions, or
alarms that occurred during the last sample checked.
Average Displays the average number of good packets,
collisions, or alarms that have occurred since the IRM
counters were last reset.
Peak Displays the peak number of good packets, collisions,
or alarms that have occurred since the IRM counters
were last reset.
The elements that are monitored by the part of the screen are:
Packets Displays statistics based on the number of good
packets.
5-8
Page 33

STATISTICS SCREENS
Colls. Displays statistics based on the number of collisions.
Alarms Displays statistics based on the number of alarms.
Delta Time Displays the actual time between the gathering of
Counter Statistics.
5.2.2 Token Ring Board Stats
To access the Token Ring Board Status screen:
1. Highlight the STATS-BOARD X option at the bottom of the MMAC
Statistics Screen.
2. Select the board you intend to access at this command field by pressing
the shift and + keys (or the - key) until the appropriate board number
appears.
3. Press Return. The Token Ring Board X Status Screen, Figure 5-3,
will appear. (If the board you have selected is not a Token Ring board,
Figure 5-2, Board X Statistics Screen, will appear.)
02/16/90 14:26:43 Token Ring Board 0 Status Last Reset: 02/16/90 08:10:11
MMAC Name: IRM Board Board Name: Board 1
TR Port Status
ON OFF
Speed: 16 Mhz MMAC: 28 0
AUTO MODE BOARD 1: 12 0
Board Connection Status Port Linked Enabled Status
Left-Slot 2: Right-IRM 1 NO YES ENABLED
FAULTED NOT A TR-MIM 2 NO YES ENABLED
***BOARD IS BYPASSED*** 3 NO YES ENABLED
4 NO YES ENABLED
5 NO YES ENABLED
6 NO YES ENABLED
7 NO YES ENABLED
8 NO YES ENABLED
9 NO YES ENABLED
10 NO YES ENABLED
11 NO YES ENABLED
12 NO YES ENABLED
MAIN STATS-MMAC ENABLE PORT 1 ENABLE BOARD SET SPEED 4Mhz
STATS-BOARD 1 DISABLE PORT 1 DISABLE BOARD DETACH BOARDS 1&2
Figure 5-3 Token Ring Board X Status Screen
5-9
Page 34

STATISTICS SCREENS
5.2.2.1 Token Ring Board Status Screen Fields
TR Port Status
MMAC ON/OFF Indicates the number of ports that are ON (enabled)
or OFF (disabled) on all the boards on the MMAC.
This number includes Token Ring station and
ring-/ring-out ports. (Each ring port is counted
separately.) For a port to be considered ON, it must
be enabled by management.
BOARD ON/OFF Indicates the number of ports that are ON (enabled)
or OFF (bypassed) on the user-defined board.
Speed
Indicates the speed to which the board has been set. The default speed is
dependent on the setting of the jumpers on the board. Consult the IRM
Installation Guide for more information on the proper jumper settings.
Auto Mode
Indicates that the board will set up using the power-up defaults. The
defaults are listed below:
• Speed is selected by jumper placement on the board
• All ports are enabled
• Any ring-in/ring-out ports are enabled
• The board is connected to all adjacent Token Ring boards running at
the same speed
The board will remain in AUTO MODE until you use one of the Token
Ring command options at the bottom of selected IRM screens (such as
ENABLE or DISABLE TOKEN RING). After the first use of a command,
the board will enter the MANAGEMENT MODE and will remain that
way until AUTO MODE is restored at the RESET SYSTEM
PARAMETERS screen or the firmware on the board is changed.
Board Connection Status
Displays the status of the boards in the slots to the immediate left and
right of the Token Ring board in the MMAC. If the Token Ring board is
the last board in the MMAC, no status is given for the board to the left.
5-10
Page 35

STATISTICS SCREENS
There are five possible board connection status messages:
NO BOARD The slot is empty.
NOT A TR-MIM The board in the slot is not a Token Ring board.
DETACHED Management has set this board so that it will not
communicate with the Token Ring board in the
associated slot. This message will only occur on boards
in the MANAGEMENT MODE.
ATTACHED Management has set this board to communicate with
the Token Ring board in the associated slot and
communication was successfully achieved.
FAULTED Management has set this board to communicate with
the Token Ring board in the associated slot, but
communication was not achieved.
Board is Bypassed
Indicates that data is passing between the board on the left and the board
on the right (if both are present), but the bypassed board is not seeing the
data. This status will appear only if the condition is present.
Ring Speed Fault
Indicates that the board is operating at a different speed from the
management configured speed.
Port
Indicates the number of the port on the board.
Linked
Indicates the Link status of both station and ring-in/ring-out ports.
Station Indicates whether there is a station attached to this port.
YES indicates that there is a station attached to this
port. NO indicates that no station is attached to the
port.
Ring /Ring-out Displays the port type. The two port types are ring-in or
ring-out.
5-11
Page 36

STATISTICS SCREENS
Enabled
Indicates that the port has been enabled by management.
Station YES indicates the port has been enabled by
management. NO indicates that the port has not
been enabled by management.
Ring-in/Ring-out YES indicates the port has been enabled by
management. NO indicates that the port is
wrapped.
Status
Indicates the current state of the station and the ring-in/ring-out ports on
the board.
Station Ports
The four possible status messages for station ports are:
ENABLED The ports has been enabled by management, and there
is a station linked to the port.
BYPASSED The port has been disabled by management, and there
is no station linked to the port.
LINKED The port has been disabled by management, and there
is a station linked to the port.
INSERTED The port is enabled by management, and there is a
station linked to the port.
There are four possible station port status message combinations:
Link
ed Enabled Status
NO NO BYPASSED
NO YES ENABLED
YES NO LINKED
YES YES INSERTED
Ring-in/Ring-out Ports
The three possible status messages for ring-in/ring-out ports are:
WRAPPED There has been a termination of data communication at
the port, and data has been re- routed into the ring.
5-12
Page 37

STATISTICS SCREENS
USING BA CKUP The port is active and the backup path of the port is
being used.
ACTIVE The port has been activated by management.
The four possible combinations of status messages for each ring-in/
ring-out pair are:
Link
ed Enabled Status
RING-IN NO WRAPPED
RING-OUT NO WRAPPED
RING-IN YES USING BACKUP
RING-OUT NO WRAPPED
RING-IN NO WRAPPED
RING-OUT YES USING BACKUP
RING-IN YES ACTIVE
RING-OUT YES ACTIVE
5.3 PORT STATISTICS SCREEN (ETHERNET)
The Port X Statistics Screen displays port level statistics for the MMAC.
These port statistics are broken down to Timer Statistics (statistics based
on a time period) and counter statistics (statistics gathered based on a
count of good MMAC packets).
To access this screen:
1. Highlight the STATS - PORT X option at the bottom of the Board X
Statistics Screen.
2. Select the port you wish to access by pressing the shift and + keys or
the - key until the appropriate port appears.
3. Press Return. The Port X Statistics Screen, Figure 5-4, will appear.
5-13
Page 38

STATISTICS SCREENS
02/16/90 14:44:13 Port 4 Statistics Last Reset: 02/16/90 08:10:11
MMAC Name: IRM Board Board 0: IRM Board
MMAC Total Board Total Port Total % Board/MMAC % Port/Board % Port/MMAC
Packets: 266712 1448 1448 1 100 1
Colls.: 0 0 0 0 0 0
Alarms: 0 0 0 0 0 0
Timer Statistics Configured Interval: 00:00:20
Elapsed Average Peak Port Status
Packets: 6 0 12 ON OFF
Colls.: 0 0 0 MMAC: 16 0
Alarms: 0 0 0 Board 0: 4 0
Delta Time: 20 20 20 Port: SEG
Counter Statistics Configured Interval: 10000
Elapsed Average Peak
Packets: 54 45 1067
Colls.: 0 0 0
Alarms: 0 0 0
Delta Time: 2627 4038 18142
MAIN STATS-MMAC STATS-BOARD 0 ENABLE PORT 1 DISABLE PORT 1
Figure 5-4 Port X Statistics Screen
5.3.1 Port Statistics Screen Fields
MMAC Name
Displays the user-defined name assigned to the IRM at the Board Names
Screen.
Board
Displays the slot number that the board occupies in the MMAC. Available
board slot numbers are O through 2 for an MMAC-3, or O through 7 for
an MMAC-8.
Board Name
Displays the user-defined name assigned to the board at the Board Names
Screen.
5-14
Page 39

STATISTICS SCREENS
MMA C Total
The MMAC Total displays the number of good packets or collisions the
MMAC has processed, and also the number of times the MMAC has
reached an alarm limit.
Packets Displays the total number of good packets the MMAC has
processed.
Colls. Displays the total number of collisions the MMAC has
processed.
Alarms Displays the total number of times the MMAC reached an
MMAC, board, or port alarm limit.
Board Total
The Board Total displays the number of good packets or collisions the
board has processed, and also the number of times the board has reached a
board alarm limit.
Packets Displays the total number of good packets the board has
processed.
Colls. Displays the total number of collisions the board has processed.
Alarms Displays the total number of times the board has reached a
board alarm limit.
Port Total
The Port Total displays the number of good packets or collisions the port
has processed, and also the number of times the port has reached a port
alarm limit.
Packets Displays the total number of good packets the port has
processed.
Colls. Displays the total number of collisions the port has processed.
Alarms Displays the total number of times that the port has reached a
port alarm limit.
5-15
Page 40

STATISTICS SCREENS
% Board/MMAC
% Board/MMAC indicates the percentage of activity for which the board
is responsible, based on total MMAC activity.
Packets Displays the percentage of good packets for which the
board is responsible, based on total MMAC activity.
Colls. Displays the percentage of collisions for which the board is
responsible, based on total MMAC activity.
Alarms Displays the percentage of alarm limits for which the board
has been responsible in the MMAC.
% Port/Board
% Port/Board indicates the percentage of activity for which the port is
responsible, based on total board activity.
Packets Displays the percentage of good packets for which the port
is responsible, based on total board activity.
Colls. Displays the percentage of collisions for which the port is
responsible, based on total board activity.
Alarms Displays the percentage of alarm limits for which the port
has been responsible, based on total board activity.
% Port/MMAC
% Port/MMAC indicates the percentage of activity for which the port is
responsible, based on total MMAC activity.
Packets Displays the percentage of good packets for which the port
is responsible, based on total MMAC activity.
Colls. Displays the percentage of collisions for which the port is
responsible, based on total MMAC activity.
Alarms Displays the percentage of alarm limits for which the port
has been responsible on the MMAC.
5-16
Page 41

STATISTICS SCREENS
Timer Statistics
Timer Statistics allow you to sample activity on the port by a set time
period. You can set this time period at the Stats Polling Intervals display
on the System Parameter Screen. For example, if Time is set to 10
seconds, the figure under Elapsed - Packets will be the number of packets
that the port processes during that 10 second interval.
The T imer Statistics portion of the screen displays the f ollowing timer
statistics for the port:
Elapsed Displays the number of good packets, collisions, or alarms
that occurred during the last sample checked.
A v erage Displays the average number of good packets, collisions, or
alarms that have occurred since the IRM counters were last
reset.
Peak Displays the peak number of good packets, collisions, or
alarms since the IRM counters were last reset.
The elements that are monitored by the Timer Statistics portion of
the screen are:
Packets Displays statistics based on the number of good packets.
Colls. Displays statistics based on the number of collisions.
Alarms Displays statistics based on the number of alarms.
Delta Time Displays the actual time between the gathering of Timer
Statistics.
Counter Statistics
Counter Statistics allow you to sample activity on the port after a certain
number of good packets have passed through the MMAC. This number is
set at the Stats Polling Intervals display on the System Parameter Screen.
For example, if # of Packets is set to 1000 packets, the figure under
Elapsed - Packets will be the number of packets that the port processes
during that 1000 packet interval.
5-17
Page 42

STATISTICS SCREENS
This portion of the screen displays the following Counter Statistics
for the board.
Elapsed Displays the number of good packets, collisions, or alarms
that occurred during the last sample checked.
A v erage Displays the average number of good packets, collisions, or
alarms that have occurred since the IRM counters were last
reset.
Peak Displays the peak number of good packets, collisions or
alarms since the IRM counters were last reset.
The elements that are monitored by this part of the screen are:
Packets Displays statistics based on the number of good packets.
Colls. Displays statistics based on the number of collisions.
Alarms Displays statistics based on the number of alarms.
Delta Time Displays the actual time between the gathering of Counter
Statistics.
Port Status
Port Status displays the number of ports on the MMAC and the Board that
are ON (enabled or segmented) and the number of ports that are OFF
(disabled). The status of the selected port is also displayed.
MMAC Displays the number of ports in the MMAC that are ON
(enabled or segmented) and the number of ports that are
OFF (disabled).
Board Displays the number of ports on the board that are ON
(enabled or segmented) and the number of ports that are
OFF (disabled).
Port Displays if the port is enabled (ON), segmented (SEG), or
disabled (OFF).
5-18
Page 43

CHAPTER 6
SETTING SYSTEM PARAMETERS
From the Reset System Parameter Screen, you can set or change various
parameters for the terminal connected to the IRM's Console port.
6.1 RESET SYSTEM PARAMETERS SCREEN
The Reset System Parameters Screen allows you to alter Local
Management's system parameters that appear on the MMAC Main
Screen.
To access this screen:
1. Highlight the RESET SYSTEM PARAMETERS option at the
bottom of the MMAC Main Screen.
2. Press Return. The Reset System Parameters Screen, Figure 6-1, will
appear.
02/16/90 14:26:43 RESET SYSTEM PARAMETERS Last Reset: 02/16/90 08:10:11
Unit Name: Tech Writing MMAC Address: 00-00-1D-00-36-06
Current Date: 07/15/89
Current Time: 14:28:20
Packets/ Auto Parts
Colls. Within Shut-off ON OFF
MMAC Limit: 1000 -C 00:00:10 DISABLED! NO 16 0
Audible Alarms: YES
Segmented Port Alarms: NO
Management Auto Send: NO
Screen Refresh Time: 10 seconds
Minimum Alarm Duration: 10 seconds
MMAC IP Address: 0.0.0.0
Stats. Polling Intervals - Time: 00:00:20 # of Packets: 10000
MAIN SAVE BOARD NAMES BOARD LIMITS CHANGE PASSWORD CABLE REDUNDANCY
RESET AUTO MODE BOARD 1 RESET IRM COUNTERS CLEAR REDUNDANCY RESTART IRM
Figure 6-1 Reset System Parameters Screen
6-1
Page 44

SETTING SYSTEM PARAMETERS
6.1.1 Reset System Parameters Screen Fields
Unit Name:
Displays the user-defined name given to the MMAC. The MMAC Name
is the same name given to Board 0, the IRM, and the MMAC Board
Names Screen for the MMAC.
MMA C Address:
Displays the Ethernet address of the MMAC.
Current Date:
Displays the date to which the MMAC is set.
Current Time:
Displays the time entered at this field.
MMAC Limit:
Allows you to set the MMAC Alarm Limit on the MMAC. Refer to
Chapter 6, Setting Alarm Limits, for a description on setting the MMAC
Alarm Limit.
A udible Alarms:
Indicates whether a beep will sound when an error, alarm, or status
message appears on the screen of the terminal connected to the IRM's
Console port. YES indicates that a beep will be generated by the terminal
connected to the IRM's Console port when a message appears. NO
indicates that no sound will be generated. The default value for this field
is YES.
Segmented Port Alarms:
Indicates whether alarms for segmented ports will be generated and
recorded at the MMAC Main Screen. YES indicates that a message will
appear at the top of the MMAC Main Screen, listing which board and port
was segmented. NO indicates that no message will be generated. The
default for this field is NO.
Management A uto Send:
Indicates whether an MMAC' Management Packet will be generated
when Local Management gathers statistics. YES indicates that a
management packet will be generated when the MMAC has gathered
statistics. NO indicates that a management packet will not be generated
when the MMAC has gathered statistics. The def ault v alue for this field is
NO.
6-2
Page 45

SETTING SYSTEM PARAMETERS
Screen Refresh Time:
Displays, in seconds, how often each screen on a terminal connected to
the IRM's Console port will be updated. The default value for this field is
10 seconds.
Minimum Alarm Duration:
Displays, in seconds, how long an error, alarm, or status message will
appear on the second line of the terminal's screen. The default value for
this field is 10 seconds.
MMAC IP Address:
Displays the MMAC IP (Internet Protocol) Address. The IP routing
function is disabled when the value is 0.0.0.0.
Stats. Polling Intervals:
Displays the interval by which statistics are being gathered. Statistics are
gathered by time (i.e. every minute) and by the number of good packets
(i.e. after every 1,000th good packet passes through the MMAC).
Time Displays the time interval by which Timer Statistics are
being gathered. If 00:00:00 is displayed, no time related
statistics will be gathered. The default v alue for this field is
00:00:20 (20 seconds).
# of Packets Displays the number of good packets that must pass
through the MMAC before Counter Statistics are gathered.
If 0 is displayed, no count-related statistics will be
gathered. The default value for this field is 10000 packets.
6.1.2 Editing the Reset System Parameters Screen
6.1.2.1 Setting the Current Date
To set the current date:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the Current Date field.
2. Enter the new data in one of these formats: MM/DD/YY or
MMDDYY. For example: 08/01/88 or 080188.
6-3
Page 46

SETTING SYSTEM PARAMETERS
3. Press Return. If an invalid date is entered, the error message,
ILLEGAL DATE ENTERED, will appear at the top left corner of the
screen.
6.1.2.2 Setting the Current Time
To set the current time:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the Current Time field.
2. Enter the new time into the field as follows: HH:MM:SS or
HHMMSS. For example 16:29 or 111629.
3. Press Return. If an invalid time is entered, the error message,
ILLEGAL TIME ENTERED, will appear at the top left corner of the
screen.
6.1.2.3 Setting the Audible Alarms Option
To set the Audible Alarms option:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the Audible Alarm field.
2. Press Return to toggle the field to Yes or No. YES indicates that a
beep will sound if a message appears on the terminal. NO indicates
that no sound will be generated.
6.1.2.4 Setting the Segmented Port Alarms Option
To set the Segmented Port Alarms option:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the Segmented Port Alarms field.
2. Press Return to toggle the field to Yes or No. YES indicates that a
message will appear alerting the user if a port becomes segmented. NO
indicates that no message will be generated.
6-4
Page 47

SETTING SYSTEM PARAMETERS
6.1.2.5 Setting the Management Auto Send Option
To set the Management Auto Send option:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the Management Auto Send field.
2. Press Return to toggle the field to Yes or No. YES indicates that a
management packet will be generated when the MMAC has gathered
statistics. NO indicates that a management packet will not be
generated when the MMAC has gathered statistics.
6.1.2.6 Setting the Screen Refresh Time
To set the Screen Refresh Time:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the Screen Refresh Time field.
2. Enter the new time into the field. A time of 2 to 99 seconds may be
entered.
3. Press Return. If the MMAC Screen Refresh is set to 1 second, the
error message, NUMERIC ENTRY MUST BE GREATER THAN
OR EQUAL TO 2, will appear on the second line of the screen.
6.1.2.7 Setting the Minimum Alarm Duration Time
To set the Minimum Alarm Duration Time:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the Minimum Alarm Duration field.
2. Enter the new time into the field. This time can be set anywhere from
0 to 99 seconds.
3. Press Return.
6-5
Page 48

SETTING SYSTEM PARAMETERS
6.1.2.8 Setting the MMAC IP Address
To set the MMAC IP Address:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the MMAC IP Address field.
2. Enter the address into the field. The format for this entry is
XXX.XXX.XXX, with values from 0-9.
3. Press Return.
6.1.2.9 Setting the Stats Polling Interval Time
To set the Stats Polling Interval Time:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the Stats Polling Interval Time field.
2. Enter the new time in one of these formats: HH:MM:SS or HHMMSS.
For example: 00:00:10 or 000010.
3. Press Return. If an invalid time is entered, the error message,
ILLEGAL TIME ENTERED, will appear in the upper left hand corner
of the screen.
6.1.2.10 Setting the Stats Polling Interval # of Packets
To set the Stats Polling Interval # of Packets:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the Stats Polling Interval # of
Packets field.
2. Enter the new value into the field.
3. Press Return. The number can be set anywhere from 0 to 999999999
packets.
6-6
Page 49

SETTING SYSTEM PARAMETERS
6.1.3 Saving System Parameters
When you have finished changing the system parameters, you must save
all changes before going to another screen.
To save the new system parameters:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the SAVE command field.
2. Press Return. The message, MMAC SYSTEM PARAMETERS
HAVE BEEN SAVED! BY IRM OPERATOR, will appear in the
upper left hand corner of the screen.
The new system parameters are now saved.
6-7
Page 50

SETTING SYSTEM PARAMETERS
6-8
Page 51

CHAPTER 7
SETTING ALARM LIMITS
The alarm limit function of Local Management allows you to set alarm
limits for the MMAC as a whole, for each individual board or for each
individual port. Alarm limits can be set to notify you that a limit has been
reached, or to disable an MMAC, board, or port when a limit is reached.
7.1 RESET SYSTEM PARAMETERS SCREEN
The MMAC Alarm Limit can be set to advise you that a certain number of
good packets or collisions have passed through the MMAC within a given
time period. For example, an MMAC Alarm Limit can be set to indicate
that more than 1,000 collisions have passed through the MMAC in 10
seconds. This limit can be set to turn off the MMAC when the limit is
reached.
The MMAC Alarm Limit is set at the Reset System Parameters Screen
(See Figure 7-1). You can also configure your MMAC at this screen by
setting parameters that will affect various functions and screens of Local
Management. In this section, however, we deal only with setting alarm
limits. Refer to Chapter 5 for details regarding System Parameters of the
MMAC.
MMAC Limit:
Displays the MMAC Alarm Limit set for the MMA C. The MMAC Alarm
Limit is the number of good packets or collisions that can pass through
the MMAC within a given time period before the limit is reached. For
example, the MMAC Alarm Limit will be exceeded when more than
1,000 collisions (Packets/Colls.) are detected at the MMAC in less than
10 seconds (Within).
7-1
Page 52

SETTING ALARM LIMITS
02/16/90 14:28:20 RESET SYSTEM PARAMETERS Last Reset: 02/16/90 14:29:40
Unit Name: TECH WRITING MMAC Address: 00-00-1D-00-36-06
Current Date: 07/15/89
Current Time: 14:28:20
Packets/ Auto Parts
Colls. Within Shut-off ON OFF
MMAC Limit: 1000 -C 00:00:10 DISABLED! NO 16 0
Audible Alarms: YES
Segmented Port Alarms: NO
Management Auto Send: NO
Screen Refresh Time: 10 seconds
Minimum Alarm Duration: 10 seconds
MMAC IP Address: 0.0.0.0
Stats. Polling Intervals - Time: 00:00:20 # of Packets: 10000
MAIN SAVE BOARD NAMES BOARD LIMITS CHANGE PASSWORD CABLE REDUNDANCY
RESET IRM COUNTERS CLEAR REDUNDANCY RESTART IRM
Figure 7-1 Reset System Parameters Screen
The following indicates the MMAC Alarm Limit settings:
Packets/Colls. Displays the number of packets that must pass through
the attached MMAC before the MMAC Alarm Limit is
checked. To the right of the field is a -P or a -C. A -P to
the right of the entry indicates the entry is a certain
number of good packets. A-C indicates that the entry is
a certain number of collisions. If O -P or O -C is
displayed in this field, the MMAC Alarm Limit will not
be checked. The default entry in this field is 1000 -C.
Within Displays the time period in which the number of
packets, listed in the Packets/Colls. display, may occur
before the MMAC Alarm Limit is reached. -TIME to
the right of the entry indicates the entry is a time
period. If 00:00:00 or DISABLED! is displayed in this
field, the MMAC Alarm Limit will not be checked. The
default entry in this field is 00:00:10 - DISABLED.
7-2
Page 53

SETTING ALARM LIMITS
Auto Shut-off Indicates whether or not the MMAC will shut off
automatically when the MMAC Alarm Limit is
reached. YES indicates that the MMAC will shut off
automatically when the limit is reached. NO indicates
that the MMAC will not shut off when the limit is
reached. The default value for this field is NO.
For instructions on setting the MMAC Alarm Limit, refer to Section 7.4,
Setting An Alarm Limit.
7.2 SET BOARD ALARM LIMITS SCREEN
Board Alarm Limits allow you to set alarm limits for each board in the
MMAC. They can be configured to advise you that a certain number of
good packets or collisions have passed through the board within a certain
time period, or that a specified number of good packets or collisions have
passed through the board based on a certain number of packets the
MMAC has processed. For example, a Board Alarm Limit can be set to
advise you when more than 1,000 good packets have passed through the
board in 10 seconds. This limit can be set to disable the board when the
limit is reached.
Board Alarm Limits are set at the Set Board Limits Screen. To access this
screen:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the BOARD LIMITS option at the
bottom of the Reset System Parameter Screen.
2. Press Return. The Set Board Limits Screen, Figure 7-2, will appear.
7.2.1 Set Board Limits Screen Fields
MMAC Name
Displays the user-defined name giv en to the MMA C. The MMA C name is
the same name given to the IRM at the MMAC Board Names Screen.
7-3
Page 54

SETTING ALARM LIMITS
02/16/90 14:30:47 Set Board Alarm Limits Last Reset: 02/16/90 14:29:40
MMAC Name: TECH WRITING
Packets/ Auto Parts
Colls. Within Shut-off ON OFF
MMAC Limit: 1000 -C 00:00:10 DISABLED! NO 16 0
Packets/ Auto Parts
Slot Name Media Colls. Within Shut-off ON OFF
0 TECH WRITING IRM 1000 -C 00:00:10 DISABLED! NO 4 0
1 Board 1 THINMIM 1000 -C 00:00:10 DISABLED! NO 12 0
MAIN SAVE PORT LIMITS-BOARD 0 SYSTEM PARAMETER SCREEN
Figure 7-2 Set Board Alarm Limits Screen
MMAC Limit
Displays the MMAC Alarm Limit. The MMAC Alarm Limit is the
number of good packets or collisions that can pass through the MMAC
within a given time period before the MMAC Alarm Limit is reached.
Refer to Section 7.1, Reset System Parameters Screen, for a description
of each individual field under the MMAC Alarm Limit.
Slot
Displays the number of the slot the MIM occupies in the MMAC.
Available board slot numbers are O through 2 for an MMAC-3, or O
through 7 for an MMAC-8.
Name
Displays the user-defined name assigned to the board at the MMAC
Board Names Screen.
Media
Indicates the media type of the board.
7-4
Page 55

SETTING ALARM LIMITS
The following fields relate to setting the Board Alarm Limit. For
instructions on setting a Board Alarm Limit, refer to Section 7.4, Setting
An Alarm Limit.
Packets/Colls.
Allows you to indicate the number of packets that must pass through the
board before the Board Alarm Limit is checked. To the right of this field is
a -P or -C. A -P indicates that the entry is a certain number of good
packets. -C indicates that the entry is a certain number of collisions. If 0
-P or 0 -C is displayed in the field, the Board Alarm Limit will not be
checked. The default value for this field is 1000 -C.
Within
Displays time or count parameters in which the number of packets
entered in the Packets/Colls. display may occur before the Board Alarm
Limit is reached. When -TIME is to the right of the field, Within can be
within a time period. When -M-PACKET is to the right of the field,
Within can be within a certain number of MMA C pack ets. For e xample, if
Within is a certain time period, an alarm will be triggered when more than
1000 packets (Packets/Colls. 1000 -P) pass through the board in 10
seconds (Within 00:00:10 -TIME).
If Within is a certain number of MMAC packets, an alarm will be
triggered if the board processes more than 1000 good packets
(Packets/Colls. 1000 -P) for every 2000 MMAC packets (Within 2000 M-PACKET). If 00:00:00 -TIME, 0 -M-PACKET or DISABLED! is
selected, the Board Alarm Limit will not be checked. The default value
for this field is 00:00:10 DISABLED!.
Auto Shut-off
Allows you to choose whether or not the board will shut of f automatically
when a Board Alarm Limit is reached. YES indicates that the board will
shut off automatically when the limit is reached. NO indicates that the
board will not shut off automatically when the limit is reached. The
default value for this field is NO.
Ports ON OFF
Displays the number of ports on each board that are enabled or segmented
(ON), and the number of ports that are disabled (OFF).
7-5
Page 56

SETTING ALARM LIMITS
7.3 SET PORT ALARM LIMITS SCREEN
Port Alarm Limits allow you to set an alarm limit for each port on a board.
These alarm limits can be configured to advise you that a certain number
of good packets or collisions have passed through the port within a given
time period, within a specified count of good packets or collisions
processed by the MMAC, or by a specified count of good packets or
collisions processed by a board. For example, a Port Alarm Limit can be
set to advise you when more than 1,000 good packets have passed through
the port in 10 seconds. This limit can be set to disable the port when the
limit is reached.
Port Alarm Limits are set at the Set Port Alarm Limits Screen. To access
this screen:
1. Highlight the PORT LIMITS - BOARD X option at the bottom of the
Board Limits Screen.
2. Press Return. The Set Port Alarm Limits Screen, Figure 7-3, will
appear.
02/16/90 14:32:01 Set Port Alarm Limits Last Reset: 02/16/90 14:29:40
MMAC Name: TECH WRITING Board 0 Name: TECH WRITING
Packets/ Auto Parts
Colls. Within Shut-off ON OFF
MMAC Limit: 1000 -C 00:00:10 DISABLED! NO 16 0
Board 0 Limit: 1000 -C 00:00:10 DISABLED! NO 4 0
Port Packets/Colls. Within Auto Shut-off Status
1 100 -C 00:00:10 DISABLED! NO SEG
2 100 -C 00:00:10 DISABLED! NO SEG
3 100 -C 00:00:10 DISABLED! NO SEG
4 100 -C 00:00:10 DISABLED! NO ON
MAIN SAVE BOARD LIMITS SCREEN SYSTEM PARAMETER SCREEN
Figure 7-3 Set Port Alarm Limits Screen
7-6
Page 57

SETTING ALARM LIMITS
7.3.1 Set Port Alarm Limits Screen Fields
MMAC Name
Displays the user-defined name giv en to the MMA C. The MMA C name is
the same name given to the IRM at the MMAC Board Names Screen.
Board X Name
Displays the user-defined name assigned to the board at the MMAC
Board Names Screen.
MMAC Limit
Displays the MMAC Alarm Limit. The MMAC Alarm Limit is the
number of good packets or collisions that can pass through the MMAC
within a given time period before the MMAC Alarm Limit is reached.
(Refer to Section 7.2, Reset System Parameters Screen for a description
of each individual field under the MMAC Alarm Limit.)
Board X Limit
Displays the Board Alarm Limit for the selected board. The Board Alarm
Limit is the number of good packets or collisions that can pass through
the board, in a set time period or by a count of good packets or collisions
processed by the MMAC before the Board Alarm Limit is reached. (Refer
to Section 7.1, Set Board Limits Screen, for a description of each
individual field under the Board Alarm Limit.)
Port
Displays the number of the port on the board.
Packets/Colls.
Allows you to indicate the number of packets that must pass through the
port before the Port Alarm Limit is checked. To the right of this field is a
-P or -C. A -P indicates that the entry is a certain number of good packets.
A -C indicates that the entry is a certain number of collisions. The default
value for this entry is 100 -C.
7-7
Page 58

SETTING ALARM LIMITS
Within
Allows you to set time or count parameters in which the number of
packets entered in the Packets/Colls_ display may occur before the Port
Alarm Limit is reached. When -TIME is to the right of the field, Within
can be within a time period. When -M-PACKET is to the right of the field,
Within can be within a certain number of MMAC packets. If -B-PA CKET
is to the right of the field, Within can be a certain number of board
packets.
For example, if Within is a time period, an alarm will be triggered when
more than 1000 packets (Packets/Colls. 1000 -P) pass through the port in
10 seconds (Within 00:00:10 -TIME). If Within is a certain number of
MMAC packets, an alarm will be triggered when the port has processed
100 packets (Packets/Colls. 100 -P) for every 2000 MMAC packets
(Within 2000 -M-PACKET). If Within is a certain number of board
packets, an alarm will be triggered when the port processes more than 100
packets (Packets/Colls. 100 -P) for every 1000 board packets (Within
1000 -B-PACKET). If 00:00:00 -TIME, 0 - M-PACKET, 0 -B-PACKET,
or DISABLED! is selected, the Port Alarm Limit will not be checked. The
default value for this field is 00:00:10 DISABLED!.
Auto Shut-off
Allows you to choose whether or not the port will shut off automatically
when a Port Alarm Limit is reached. YES indicates that the port will shut
off automatically when the limit is reached. NO indicates that the port
will not shut off automatically when the limit is reached. This field can be
changed by pressing Return. The default value for this field is NO.
Status
Displays whether the port is enabled (ON), segmented (SEG), or disabled
(OFF).
For instructions on setting a Port Alarm Limit, refer to Section 7.4,
Setting An Alarm Limit.
7.4 SETTING AN ALARM LIMIT
To set an Alarm Limit:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Packets/Colls. field.
2. Enter the desired number of packets or collisions.
7-8
Page 59

SETTING ALARM LIMITS
3. Press Return.
4. Highlight the next field, -P or -C.
5. Press Return to toggle the field from -P to -C. The field should be set
to -P if the entry made in step 2 is packets. If the entry was collisions,
the field should be -C.
6. Highlight the Within field.
7. If you are setting a MMAC Alarm Limit, enter a time into the field in
one of the following formats: 00:00:10, 000010. If you are setting a
Board or Port Alarm Limit and the limit is going to be set based on a
timeperiod, enter a time into the field in 00:00:10 or 000010 format. If
the limit is going to be set based on a count of packets, enter the count
of packets.
8. Press Return. If an invalid time is entered, the error message,
ILLEGAL TIME ENTERED), will appear on the second line of the
screen.
9. Highlight the next field, -B-PACKET (Port Alarm Only), -M-
PACKET (Board and Port Alarm Only), -TIME, or DISABLED!.
10. Press Return to toggle the field from -B-PACKET, -M- PACKET,
-TIME, or DISABLED!. If you are setting a MMAC Alarm Limit, the
field should be set to -TIME. If you are setting a Board Alarm Limit,
the field should be set to -M-PACKET if the Board Alarm Limit will
be based on the count of packets that the MMAC processes, or -TIME
if the limit will be based on a period of time. If you are setting a Port
Alarm Limit, the field should be set to -B-PACKET if the Port Alarm
Limit will be based on the count of packets that the Board processes,
-M-PACKET if the Port Alarm Limit will be based on the count of
packets the MMAC processes, or -TIME if the Limit will be based on
a period of time. If DISABLED! is selected, the Alarm Limit will not
be checked.
11. Highlight the Auto Shut-off field.
7-9
Page 60

SETTING ALARM LIMITS
WARNING: Setting an MMAC limit with Auto Shut-off selected to YES
can be very dangerous. When the MMAC alarm limit is reached, all ports
on the MMAC will be disabled.
12. Press Return to toggle the field from YES or NO.
13. Highlight the SAVE option at the bottom of the screen.
14. Press Return. The Alarm Limit is now saved and active.
7-10
Page 61

CHAPTER 8
USING THE REDUNDANCY FUNCTION
Cabletron Systems' Local Management Redundancy feature is designed
to keep your network up and running in the event that a critical data path
fails. Local Management allows you to set up alternate data paths
(redundant segments) for critical data paths on the network. This is called
cable redundancy.
Cable redundancy allows you to avoid failures that can occur over your
network, such as cable shorts, software failures, and power failures. This
redundancy scheme is based on the ability of an MMAC to communicate
directly with one or more user defined MMACs o ver a primary port. If the
MMAC loses its ability to communicate over this port, a user defined
backup port is enabled to reestablish communications with the selected
MMAC(s).
A cable redundancy is set up by connecting several cables either to a
backbone cable or directly to other devices. If the current cable being
used is faulted, then the MMAC switches communications to another
cable that is not faulted. (A segment is considered faulted if it cannot
support communications.)
8.1 CABLE REDUNDANCY SCREEN
The Cable Redundancy Screen allows you to create a cable redundancy
scheme that will insure continued communication flow across your
network in the event of a network failure.
To access this screen.
1. Highlight the CABLE REDUNDANCY option at the bottom of the
Reset System Parameters Screen.
2. Press Return. The ('able Redundancy Screen, Figure 8-1, will appear.
8-1
Page 62

USING THE REDUNDANCY FUNCTION
02/16/90 14:34:16 CABLE REDUNDANCY Last Reset: 02/16/90 14:29:40
|
|
|
Redundant Circuits | Polling Addresses
|
ADD NEW CIRCUIT | Board
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Poll Interval: 3 |
Cable Test: 01:00:00 |
MAIN SAVE CANCEL PERFORM CABLE TEST RESET SYSTEM PARAMETERS
Port Status
Figure 8-1 Cable Redundancy Screen
8.1.1 Cable Redundancy Screen Fields
Redundant Circuits
Displays the user defined names of the point-to-point cable connections.
Board
Displays the board where the primary or backup port can be found.
Port
Displays the Primary, Active, or Inactive port that provides the physical
link to the distant MMAC.
Status
Displays the status of the port. The port will be designated as P for
Primary, A for Active, or I for Inactive. A Primary port is the board and
port functioning as the main communications link in your redundancy
scheme. You may name only one port as the Primary. An Activ e port is the
port that is currently supporting communications. You may name only one
port as the Active. An Inactive port is a port that is currently not
supporting communications but will function as a backup. You may name
more than one port as the Inactive port.
8-2
Page 63

USING THE REDUNDANCY FUNCTION
Polling Addresses
Displays a list of MMAC Ethernet addresses associated with the selected
circuit.
Polling Interval
Displays the time in seconds that the primary sends out an individual
management packet to the addresses listed in the Polling Address field.
This field is common to all redundant circuits created.
Cable Test
Displays the test time interval in which the primary MMAC polls all the
elements in the circuit configuration to test which redundant circuits have
a good link or a bad link. A good link is one that can support
communication. A bad link is one that cannot support communications.
This test will run once every 24 hours (default time is 1:00 A.M.) at a
preset user-defined time. This test can also run automatically if it is
determined that a cable check needs to be done at a time other than the
user-defined one.
8.1.2 Setting Up A Cable Redundancy
To set up a cable redundancy:
1. Using the up arrow key, highlight the Cable Test text box.
2. Enter a new Cable Test time interval using the format HH:MM:SS.
(Press the up arrow key to accept the current time interval.)
3. Press the up arrow key. The Poll Interval text box will be highlighted.
4. Enter a new Polling Interval. (Press the up arrow key to accept the
current Polling Interval.)
5. Press the up arrow key. The ADD NEW CIRCUIT option will be
highlighted.
6. Press Return. The Name option will appear with a highlighted text
box.
7. Enter the name of the Redundancy circuit.
8-3
Page 64

USING THE REDUNDANCY FUNCTION
8. Press Return. The Retry Count text box will be highlighted.
9. Enter the new Retry Count. (Press the down arrow key to accept the
current Retry Count.)
10. Press Return. The ADD NEW POLL ADDR option will be
highlighted.
11. Press Return. The ADD NEW POLL ADDR text box will appear.
12. Enter the address of the MMAC you want to poll to establish the
redundant communication circuit.
13. Press Return. If you wish to add an additional MMAC address, press
Return again, and repeat steps 11 and 12.
14. Press the down arrow key. The text box under Board will be
highlighted.
15. Enter the Board number of the Primary port.
16. Press Return. (If you wish to delete a number you have entered, use
the appropriate arrow key.)
17. Enter the number of the Primary port.
18. Press Return. The text box under Status will be highlighted.
19. Press the down arrow key to accept the designation as the Primary
port. (If you wish to designate this Board/Port as Inactive (I) or Active
(A), enter the appropriate letter and Press Return. Remember that you
must have one Board/Port designated as the Primary.) The text block
under Board will be highlighted.
20. Enter the Board number of the Inactive port.
21. Press Return. The text box under Port will be highlighted.
22. Enter the number of the Inactive Port.
23. Press Return. The text box under Status will be highlighted.
8-4
Page 65

USING THE REDUNDANCY FUNCTION
24. Press the down arrow to accept the designation as the Inactive port.
(If you wish to designate this Board/Port Primary (P) or Active (A),
enter the appropriate letter and Press Return. Remember that you
must have at least one Board/Port designated as the Inactive.) The
ADD NEW BOARD PORT option will be highlighted.
25. Press Return to continue to add additional Board/Ports to the circuit,
or press the down arrow key to accept the cable redundancy you have
entered. The Main command button at the bottom of the screen will be
highlighted.
26. Press the right arrow key once. The SAVE command button will be
highlighted.
27. Press Return. The message, REDUNDANCY HAS BEEN SAVED
BY IRM OPERATOR, will appear in the upper left hand corner of the
screen.
8-5
Page 66

USING THE REDUNDANCY FUNCTION
8-6
Page 67

CHAPTER 9
SETTING ALTERNATE MMAC BOARD NAMES
With the Alternate Board Name function of Local Management, userdefined names can be assigned to the various boards in the MMAC.
9.1 MMAC BOARD NAMES SCREEN
At the MMAC Board Name Screen, you can assign your own names to
the boards in the MMAC. F or example, if one board is used to connect the
computers in your sales department to the network, you can rename that
board Sales Department.
To name or rename a board in your MMAC:
1. Highlight the BOARD NAMES option at the bottom of the System
Parameters Screen.
2. Press Return. The MMAC Board Names Screen, Figure 9-1, will
appear.
07/15/89 14:35:44 MMAC Board Names Last Reset: 07/15/89 08:10:11
Ports
Name Media Type ON OFF
Slot 0: TECH WRITING IRM 4 0
Slot 1: Board 1 THINMIM 12 0
Slot 2:
Slot 3:
Slot 4:
Slot 5:
Slot 6:
Slot 7:
Total: 16 0
MAIN SAVE SYSTEM PARAMETER SCREEN
Figure 9-1 MMAC Board Names Screen
9-1
Page 68

SETTING ALTERNATE MMAC BOARD NAMES
9.2 MMAC BOARD NAMES SCREEN FIELDS
Slot X
Displays the number of the slot the board occupies in the MMAC.
Available board slot numbers are O through 7.
Name
Displays the name assigned to the board. The name giv en to Board O will
also be the MMAC Name. If you change the name for Board 0, the
MMAC name automatically changes as well.
Media T ype
Displays the media type of the board, e.g., TR_12, THINMIM.
Ports ON OFF
Displays the number of ports on each board that are ON (enabled or
segmented) and the number of ports that are OFF (disabled).
Total
Displays the total number of ports in the MMAC that are ON (enabled or
segmented) or OFF (disabled).
9.3 ASSIGNING BOARD NAMES
To name or rename a board:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the Name field for the board to be
renamed.
2. Enter the new name, up to 20 characters in length, in the field.
3. Press Return.
4. Highlight the SAVE option at the bottom of the screen.
5. Press Return. The new name will be saved.
9-2
Page 69

CHAPTER 10
PORT STATUS SCREEN
The Port Status option allows you to see the state of all the ports on the
boards in your MMAC. You can find which Ethernet ports are on or off,
and which Token Ring ports are enabled or wrapped. In addition, you can
quickly view a summary of total ports enabled.
10.1 PORT STATUS SCREEN
At the Port Status screen, you can discover which ports on the Ethernet
boards in your MMAC are on, of f, or se gmented. You can see the status of
each port on the Token Ring boards. (For any Token Ring board that is in
a Ring Speed fault state, the total number of activ e ports will be displayed
in reverse video.)
To access the Port Status Screen:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the PORT STATUS option at the
bottom of the MMAC Main Screen.
2. Press Return.
The Port Status Screen, Figure 10-1, will appear.
07/15/89 14:35:44 Port Status Last Reset: 07/15/89 08:10:11
Slot 0 Slot 1 Slot 2 Slot 3 Slot 4 Slot 5 Slot 6 Slot 7
Port IRM TR_12 TR_12
1 SEG ENB INS
2 SEG ENB INS
3 SEG ENB INS
4 ON ENB INS
5 ENB INS
6 SEG ENB INS
7 SEG ENB INS
8 SEG ENB INS
9 SEG ENB INS
10 SEG ENB INS
11 SEG ENB INS
12 SEG ENB INS
Total
ON: 4 12 12
MAIN ENABLE BOARD 0 ENABLE ETHERNET ENABLE TOKEN RING
DISABLE BOARD 0 DISABLE ETHERNET DISABLE TOKEN RING
Figure 10-1 Port Status Screen
10-1
Page 70

PORT STATUS SCREEN
10.1.1 Port Status Screen Fields
Slot X
Indicates the type of board installed in each slot of the MMAC, e.g.,
TR_12, THINMIM.
Port
Indicates the status of each port on the boards in the MMAC. There are
different status conditions for the Ethernet and Token Ring ports.
Ethernet Ports
There are three possible status conditions for Ethernet ports:
ON A port is considered ON only after the port has received
one good packet.
OFF A port is considered OFF if it has not been enabled.
SEG A port is considered SEG (Segmented) when it has been
turned on but has not received a good packet.
T
oken Ring Ports
Within Token Ring, there are different status conditions between the
station ports and the ring-in/ring-out ports:
Station Ports The status of the port is determined by its administrative
state (enabled or disabled) and its link state (linked or
bypassed).
There are four possible status conditions for Station ports:
BYP A port is considered BYP (Bypassed) if it has been
disabled by management and no station is linked to the
port.
LNK A port is considered LNK (Linked) if it is disabled by
management and there is a station linked to the port.
ENB A port is considered ENB (Enabled) if it has been enabled
by management and there is no station linked to the port.
10-2
Page 71

PORT STATUS SCREEN
INS A port is considered INS (Inserted) if it has been
enabled by management and there is a station
linked to the port.
Ring-in/Ring-out The status of Ring-in/Ring-out ports is determined
by the Ring-out administrative state of both of the
ports (wrapped or active).
There are four possible conditions for each pair of Ring-in/Ring-out
ports:
RI-WRP, RO-WRP Both the Ring-in and Ring-out ports are wrapped.
RI-WRP, RO-BAK The Ring-in port is wrapped, the Ring-out port is
active. The backup path of the ring-out port is
being used for the ring-in path.
RI-BAK, RO-WRP The Ring-in port is active and the Ring-out port is
wrapped. The backup path of the ring-in port is
being used for the ring-out path.
RI-ACT, RO-ACT Both the Ring-in and the Ring-out ports are active.
<—>, x—>, x—x, or <—x
Indicates that two adjacent, active Token Ring boards are connected
across a flexible network bus (FNB). If one or more of the arrow heads is
an 'x', the board on that side of the arrow is in the bypass mode. (This field
will appear only if the described condition exists.)
Total ON
Ethernet Displays the total number of enabled and segmented
ports on each board.
Token Ring Displays the total number of enabled station ports and
active ring-in/ring-out ports.
10-3
Page 72

PORT STATUS SCREEN
10-4
Page 73

CHAPTER 11
PORT LINK STATUS OPTION
With the Link Status option, you can quickly view the link status of each
port on the boards that generate a link status. These boards include the
Cabletron Systems' 10BASE-T Twisted Pair Media Interface Modules,
Fiber Optic Media Interface Boards, and Token Ring Media Interface
Boards. (For all Token Ring boards, the Port Status and Link Status
screens are functionally the same. The differences between administrati v e
and link statuses apply only to Ethernet boards.)
11.1 LINK STATUS SCREEN
At the Link Status Screen, you can view the link status of those boards
that broadcast a link status. You can also view the type of board installed
in each slot of the MMAC and the total number of ports that are ON and
SEG.
To access the Link Status Screen:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the LINK STATUS option at the
bottom of the MMAC Main Screen.
2. Press Return.
The Link Status Screen, Figure 11-1, will appear.
11.1.1 Link Status Screen Fields
Slot X
Indicates the type of board installed in each slot of the MMAC, e.g.,
TR_12, THINMIM.
Port
Indicates the link status of each port on the boards in the MMAC that
generate a link status.
11-1
Page 74

PORT LINK STATUS OPTION
08/31/90 13:44:45 Link Status Last Reset: 08/31/90 13:37:20
Slot 0 Slot 1 Slot 2 Slot 3 Slot 4 Slot 5 Slot 6 Slot 7
Port IRM TR_12 TR_12
1 N/A ENB INS
2 N/A ENB INS
3 N/A ENB INS
4 N/A ENB INS
5 ENB INS
6 ENB INS
7 ENB INS
8 ENB INS
9 ENB INS
10 ENB INS
11 ENB INS
12 ENB INS
Total
ON: 4 12 12
MAIN ENABLE BOARD 0 ENABLE ETHERNET ENABLE TOKEN RING
DISABLE BOARD 0 DISABLE ETHERNET DISABLE TOKEN RING
Figure 11-1 Link Status Screen
There are three possible Link Status messages for Ethernet boards:
LNK Link OK (LNK) indicates that a link is established between
that applicable port on the module and the device at the
other end of the 10BASE-T Twisted Pair or Fiber Optic
segment.
N/LNK No Link (NLNK) indicates that either a link has not been
established between the applicable port on the module and
the device at the other end of the 10BASE-T Twisted Pair
or Fiber Optic segment, or that a 10BASE-T Twisted Pair
or Fiber Optic segment is not connected to the port.
N/A Not Available (N/A) indicates that this port is not a
10BASE-T Twisted Pair or Fiber Optic Link port.
There are four possible Link Status messages for Token Ring boards:
ENB A port is considered Enabled (ENB) if it has been enabled by
management, and there is no station linked to the port.
11-2
Page 75

PORT LINK STATUS OPTION
BYP A port is considered Bypassed (BYP) if it has been
disabled by management, and there is no station linked to
the port.
LNK A port is considered Linked (LNK) if the port has been
disabled by management, and there is a station linked to the
port.
INS A port is considered Inserted (INS) if the port has been
enabled by management, and there is a station linked to the
port. This is the only state with a station inserted into the
ring successfully.
Total ON
Ethernet Displays the total number of enabled and segmented ports
on each Ethernet board.
Token Ring Displays the total number of enabled station ports and
active ring-in/ring-out ports.
11-3
Page 76

PORT LINK STATUS OPTION
11-4
Page 77

CHAPTER 12
USING THE PREVIOUS COUNTER SCREENS
Local Management also has the capability for storing statistical
information that the MMAC has gathered before the last two IRM resets.
This information can be accessed at a later time so that you can evaluate
and analyze the impact of network activity on the MMAC.
12.1 PREVIOUS COUNTER SCREENS
The Previous Counter X Screen, which displays counter statistics, is
labeled either O or 1(0 for the last IRM Counter Reset; 1 for the first IRM
Counter Reset). See Figure 12-1. No fields are modifiable at this screen.
02/15/90 14:50:44 Previous Counters 0 Last Reset: 02/15/90 08:10:11
Previous Rest: 07/15/89 08:10:11
MMAC Totals
Packets: 19752 Ports ON: 16
Collisions: 0 Ports OFF 0
Totals % B/MMAC ON Totals % B/MMAC ON
IRM Packets 530 3 4 Board 1 Packets 19222 97 12
Colls. 0 0 Colls. 0 0
MAIN
Figure 12-1 Previous Counter X screen
12-1
Page 78

USING THE PREVIOUS COUNTER SCREENS
To access this screen:
1. Highlight the PREVIOUS COUNTER X option at the bottom of the
MMAC Main Screen.
2. Press the shift and + keys or - key to move between screens 0 and 1.
3. Press Return. The Previous Counter X screen, Figure 12-1, will
appear.
The Previous Counter X screens work on a "first in, first out" basis. That
is, when the third IRM Counter Reset occurs, the first reset, stored as
number 1, will be deleted from the MMAC's memory.
12.2 PREVIOUS COUNTER X SCREEN FIELDS
Previous Reset
Displays the Date and Time that the reset associated with this screen
occurred.
MMA C Tools
The MMAC Totals list the following information:
Packets Displays the total number of packets the MMA C processed
before the reset occurred.
Colls. Displays the total number of collisions the MMAC
processed before the reset occurred.
Ports ON Displays the total number of ports in the MMAC that were
enabled or segmented when the reset occurred.
Ports OFF Displays the total number of ports in the MMAC that were
disabled when the reset occurred.
Board Total
Displays the number of good packets or collisions that each board has
processed.
12-2
Page 79

USING THE PREVIOUS COUNTER SCREENS
Name
Displays the user-defined name assigned to the board at the Board Names
Screen.
Packets/Totals
Displays the total number of good packets the board processed before the
last reset occurred.
Colls./Totals
Displays the total number of collisions the board processed before the last
reset occurred.
Packets/% B/MMAC
Displays the percentage of packets for which the board was responsible,
based on total MMAC activity before the last reset occurred.
Colls./% B/MMAC
Displays the percentage of collisions for which the board was responsible,
based on total MMAC activity before the last reset occurred.
ON
Displays the number of ports on the board that were enabled or segmented
when the last reset occurred.
12-3
Page 80

USING THE PREVIOUS COUNTER SCREENS
12-4
Page 81

CHAPTER 13
USING OTHER AVAILABLE FUNCTIONS
Other functions available with Local Management include Restarting the
IRM, Resetting IRM Counters, and Enabling and Disabling Ports and
Boards.
13.1 RESTARTING THE IRM
The Restart IRM function allows you to reset all configurable variables
(except Redundancy) to the default values resident on your Local
Management firmware. With this command, you can reset configurable
variables to their defaults, or you can reset variables at the System
Parameters Screen.
Restart IRM Counters from the Reset System Parameters Screen as
follows:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the RESTART IRM option at the
bottom of the screen.
2. Press Return. The message, MULTI MEDIA ACCESS CENTER
RESTARTED, will appear, indicating that the IRM has been restarted.
13.2 RESETTING IRM COUNTERS
The Reset IRM Counters function allows you to reset all statistics
gathered by Local Management back to zero. After you have reset IRM
counters, Local Management starts gathering statistics again.
Reset IRM Counters from the Reset System Parameter Screen by:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the RESET IRM COUNTERS
option at the bottom of the screen.
2. Press Return. The message, ALL MMAC COUNTERS HAVE
BEEN RESET BY IRM OPERATOR, will appear indicating that the
IRM counters have been reset. A summary of statistical information
will be saved and can be accessed at the Previous Counters X Screen.
13-1
Page 82

USING OTHER AVAILABLE FUNCTIONS
13.3 RESETTING AUTO MODE (TOKEN RING)
You can reset your Token Ring boards to Auto Mode at the Reset System
Parameters Screen. (For more information on Auto Mode and its
associated settings, please refer to Chapter 5.)
To reset your Token Ring boards to Auto Mode:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the RESET AUTO MODE
BOARD 1 option at the bottom of the screen.
2. Use the Shift I (or - ) key to toggle to the desired Board number.
3. Press Return. The message, TOKEN RING BOARD 1 AUTO
MODE RESET BY IRM OPERATOR, will appear indicating that the
designated Token Ring board has been reset to Auto Mode.
13.4 ENABLING AND DISABLING ALL ETHERNET OR
TOKEN RING PORTS
You can enable or disable all your Ethernet or Token Ring ports at the
following screens:
• MMAC Statistics
• Port Status
• Link Status
13.4.1 Enabling and Disabling All Ethernet Ports
To enable or disable the Ethernet boards at the Port Status or Link Status
Screens:
1. 1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the ENABLE ETHERNET or
DISABLE ETHERNET option at the bottom of the screen.
2. Press Return. The message ALL PORTS ENABLED (DISABLED)
BY IRM OPERATOR will appear.
13-2
Page 83

USING OTHER AVAILABLE FUNCTIONS
13.4.2 Enabling and Disabling All Token Ring Ports
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the ENABLE TOKEN RING or
DISABLE TOKEN RING option at the bottom of the screen.
2. Press Return. The message ALL PORTS ENABLED (DISABLED)
BY IRM OPERATOR will appear.
13.4.3 Enabling and Disabling All Ports on Individual
Ethernet Boards
You can turn all ports connected to an indi vidual board on or off from the
Board X Statistics Screen.
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the ENABLE BOARD X or
DISABLE BOARD X option at the bottom of the screen.
2. Press the shift and + key, or the - key, until the number of the board
you intend to enable or disable appears.
3. Press Return. The appropriate message, ALL PORTS ON BOARD X
(ENABLED, DISABLED) BY IRM OPERATOR, will appear on the
second line of the screen.
13.4.4 Enabling and Disabling All Ports on Individual
Token Ring Boards
You can turn all ports connected to an indi vidual board on or off from the
specific Token Ring Board X Status Screen.
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the ENABLE BOARD or DISABLE
BOARD option at the bottom of the screen. (You can only enable or
disable the ports on the Token Ring board listed at the top of the
screen. There is no toggle function similar to the one for Ethernet
boards.)
2. Press Return. The appropriate message, ALL PORTS ON BOARD X
(ENABLED, DISABLED) BY IRM OPERATOR, will appear on the
second line of the screen.
13-3
Page 84

USING OTHER AVAILABLE FUNCTIONS
13.4.5 Enabling and Disabling Individual Ethernet and
Token Ring Ports
You can turn individual ports connected to an individual board in the
MMAC on or off from the appropriate Port X Statistics Screen (Ethernet)
or the Token Ring Board X Status Screen.
To enable or disable an individual port from the Port X Statistics Screen
or the Token Ring Board X Status Screen:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the ENABLE PORT X or DISABLE
PORT X option at the bottom of the screen.
2. Press the shift and + key, or the - key, until the number of the board
you intend to enable or disable appears.
3. Press Return. The appropriate message, PORT X ON BOARD X
(ENABLED, DISABLED) BY IRM OPERATOR, will appear on the
second line of the screen.
13.5 ATTACHING AND DETACHING TOKEN RING
BOARDS
You can attach or detach the boards to the immediate left and right of the
board specified in the Token Ring Board X Status Screen. See Chapter 5
for more information on attaching and detaching boards.
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the DETACH (ATTACH) BOARDS
1 & 2 option at the bottom of the screen.
2. Press Return. The appropriate message, BOARDS 1 AND 2
DETACHED (ATTACHED) BY IRM OPERATOR, will appear.
13.6 CHANGING THE PASSWORD
Refer to Cabletron Systems' Local Management for the MMAC (HUB)
Change Password Feature Instruction Sheet.
13-4
 Loading...
Loading...