Page 1

IRM3
INTELLIGENT REPEATER
MODULE
USER’S GUIDE
IRM3
SN
RESET
PWR BOK
MGMT
CLN
PWRON
ON LNK
T
X
R
X
RCV
POK
A
U
I
F
O
I
R
L
ETHERNET
U
P
S
C
O
N
S
O
L
E
Page 2
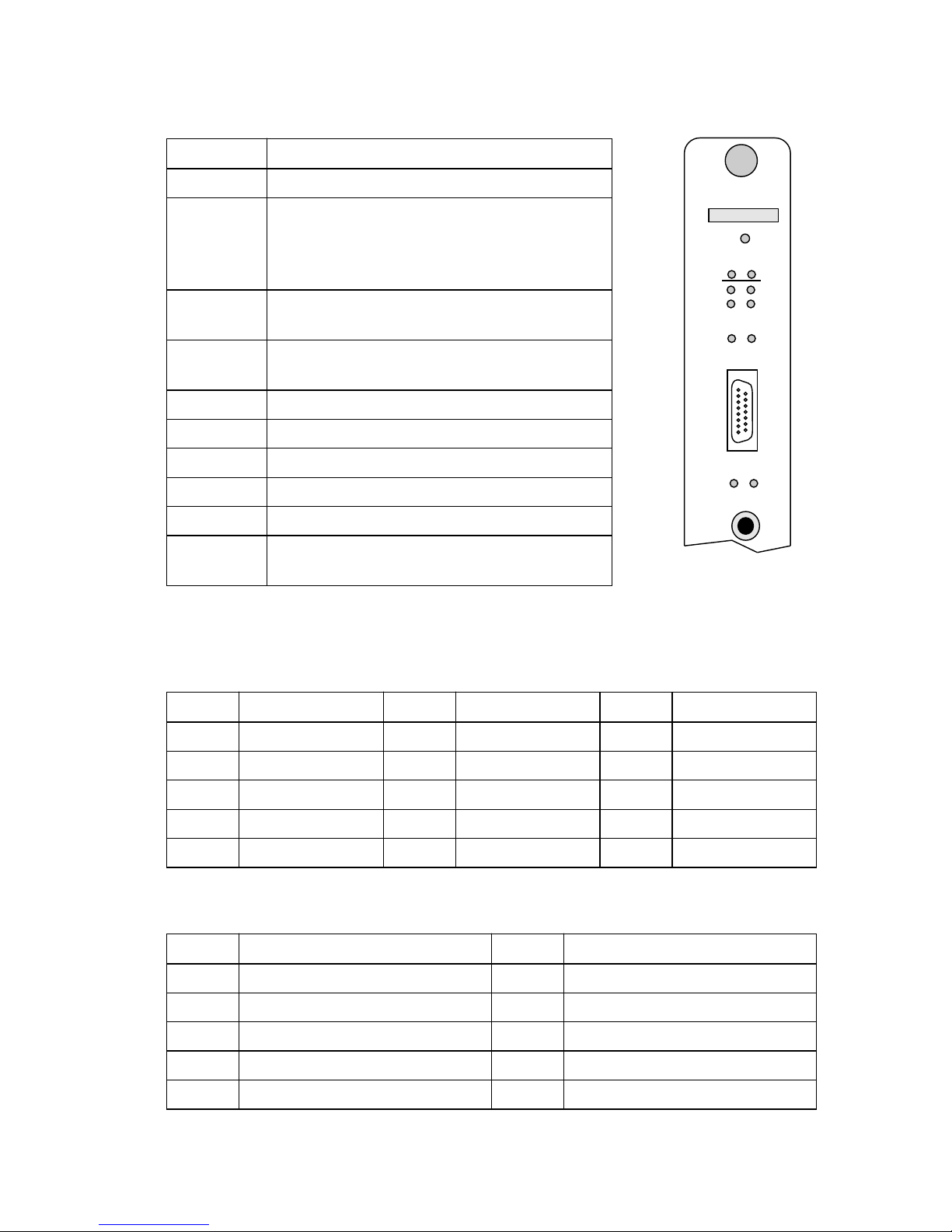
IRM3 QUICK REFERENCE CARD
LED INDICATORS
LED Description
PWR IRM3 is receiving power from MMAC.
BOK LED lit-Board is operating properly.
LED not lit-Initialization problem. Press
Reset switch.
RCV IRM3 is repeating packet received from a
connected segment.
MGMT IRM3 is receiving/transmitting management
packets.
CLN Collision detected on a segment.
POK Internal repeater port is OK.
ON (AUI) AUI port is active repeater port.
PWR (AUI) AUI port is receiving power.
ON (FO) Fiber Optic port is active repeater port.
LNK (FO) Link is established between port and Fiber
Optic device.
CONNECTIONS
IRM3
SN
RESET
PWR BOK
MGMT RCV
CLN POK
ON PWR
A
U
ON LNK
T
X
F
O
I
AUI Port: 15-pin D type receptacle
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 Logic Ref 6 Power Return 11 Logic Ref
2 Collision+ 7 No Connection 12 Receive3 Transmit+ 8 Logic Ref 13 Power (+12Vdc)
4 Logic Ref 9 Collision- 14 Logic Ref
5 Receive+ 10 Transmit- 15 No Connection
Console/Modem Port: Standard 9-pin RS232 port
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 Carrier Detect (CD) 6 Receive Clock (RXCL)
2 Transmit (TXD) 7 Request to Send (RTS)
3 Receive (RXD) 8 Clear to Send (CTS)
4 Data Terminal Ready (DTR) 9 Ring Indicator (RI)
5 Logic Ref
IRM3 User’s Guide Part of 9030494 -01
Page 3
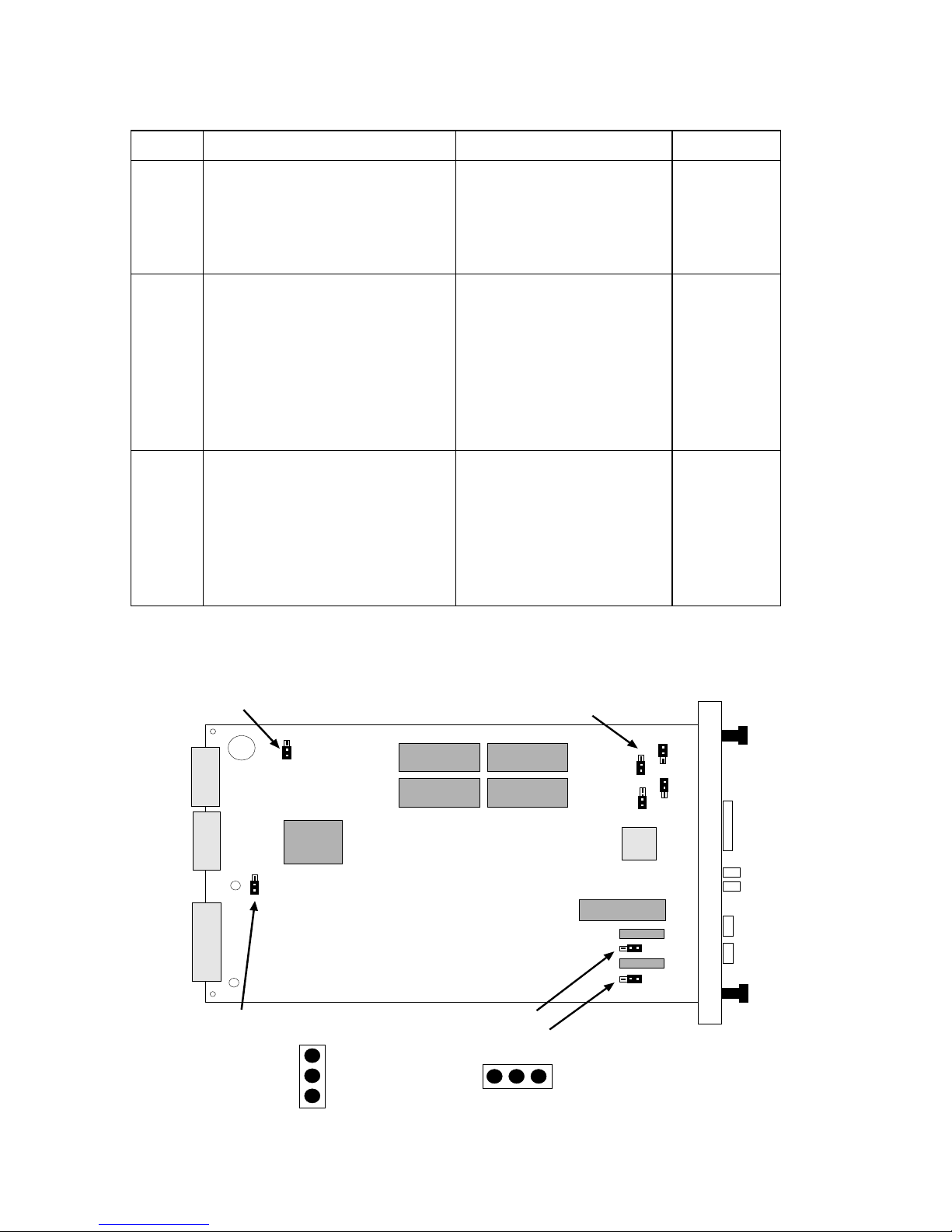
IRM3 QUICK REFERENCE CARD
JUMPER SETTINGS
Jumper Function Setting Default
H1 Enables/Disables Battery.
When enabled, user-entered
parameters are saved if power
to the IRM3 fails. When
disabled, parameters are lost.
JP1 Makes IRM3 compatible with
any THN-MIMs being used in
the MMAC. This jumper is set
for THN-MIMs with part
numbers 9000043-06 and
above and for THN-MIMs with
part numbers below
9000043-06.
H6
and H8
Sets IRM3 console and modem
ports for either internal (signal
generated by IRM3) or external
(signal generated by attached
device) Request to Send (RTS)
and Clear to Send (CTS)
signals.
Enable: Jumper over pins
1 and 2
Disable: Jumper over pins
2 and 3
9000043-06 and up:
Jumper over pins 2 and 3
Below 9000043-06:
Jumper over pins 1 and 2
If using both, set over 1
and 2
Internal: Jumper over pins
1 and 2
External: Jumper over
pins 2 and 3
Disable
Jumper
over pins 2
and 3
External
Battery
Enable/Disable
THN-MIM Jumper
H1/JP1
Pin Numbers
JP1
H1
For Cabletron Use Only
H4
H5
CTS-Modem Port
CTS-Console Port
1
2
3
H6/H8
Pin Numbers
1 2 3
H2
H3
H8
H6
0494104
Part of 9030494-01 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 4

NOTICE
Cabletron Systems reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information
contained in this document without prior notice. The reader should in all cases consult Cabletron
Systems to determine whether any such changes have been made.
The hardware, firmware, or software described in this manual is subject to change without notice.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CABLETRON SYSTEMS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INCIDENTAL,
INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES WHATSOEVER (INCLUDING BUT
NOT LIMITED TO LOST PROFITS) ARISING OUT OF OR RELATED TO THIS MANUAL OR
THE INFORMATION CONTAINED IN IT, EVEN IF CABLETRON SYSTEMS HAS BEEN
ADVISED OF, KNOWN, OR SHOULD HAVE KNOWN, THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGES.
Copyright 1996 by Cabletron Systems, Inc., P.O. Box 5005, Rochester, NH 03866-5005
All Rights Reserved
Printed in the United States of America
Order Number: 9030494-01 January 1996
SPECTRUM, LANVIEW, MicroMMAC
Manager, EPIM, EPIM-A, EPIM-F1, EPIM-F2, EPIM-F3, EPIM-T, EPIM-X, FOT-F, FOT-F3
HubSTACK, IRM3, SEH, SEHI
All other product names mentioned in this manual may be trademarks or registered trademarks of
their respective companies.
, and
, and
TMS-3
BRIM
are trademarks of Cabletron Systems, Inc.
are registered trademarks and
Element
,
IRM3 User’s Guide i
Printed on Recycled Paper
Page 5

Notice
FCC NOTICE
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any
interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
NOTE:
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment.
This equipment uses, generates, and can radiate radio frequency energy and if not installed in
accordance with the operator’s manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause interference in which case the user
will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
WARNING:
party responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital
Changes or modifications made to this device which are not expressly approved by the
DOC NOTICE
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class A limits for radio noise emissions from digital
apparatus set out in the Radio Interference Regulations of the Canadian Department of
Communications.
Le présent appareil numérique n’émet pas de bruits radioélectriques dépassant les limites applicables
aux appareils numériques de la class A prescrites dans le Règlement sur le brouillage radioélectrique
édicté par le ministère des Communications du Canada.
VCCI NOTICE
This equipment is in the 1st Class Category (information equipment to be used in commercial and/or
industrial areas) and conforms to the standards set by the Voluntary Control Council for Interference
by Information Technology Equipment (VCCI) aimed at preventing radio interference in commercial
and/or industrial areas.
Consequently , when used in a residential area or in an adjacent area thereto, radio interference may be
caused to radios and TV receivers, etc.
Read the instructions for correct handling.
ii IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 6

Notice
CABLETRON SYSTEMS, INC. PROGRAM LICENSE AGREEMENT
IMPORTANT:
This document is an agreement between you, the end user, and Cabletron Systems, Inc. (“Cabletron”)
that sets forth your rights and obligations with respect to the Cabletron software program (the
“Program”) contained in this package. The Program may be contained in firmware, chips or other
media. BY UTILIZING THE ENCLOSED PRODUCT, YOU ARE AGREEING TO BECOME
BOUND BY THE TERMS OF THIS AGREEMENT, WHICH INCLUDES THE LICENSE AND
THE LIMITATION OF WARRANTY AND DISCLAIMER OF LIABILITY. IF YOU DO NOT
AGREE TO THE TERMS OF THIS AGREEMENT , PR OMPTLY RETURN THE UNUSED
PRODUCT TO THE PLACE OF PURCHASE FOR A FULL REFUND.
Before utilizing this product, carefully read this License Agreement.
CABLETRON SOFTWARE PROGRAM LICENSE
1. LICENSE
package subject to the terms and conditions of this License Agreement.
You may not copy, reproduce or transmit any part of the Program except as permitted by the
Copyright Act of the United States or as authorized in writing by Cabletron.
2. OTHER RESTRICTIONS. You may not reverse engineer, decompile, or disassemble the
Program.
3. APPLICABLE LA W. This License Agreement shall be interpreted and governed under the laws
and in the state and federal courts of New Hampshire. You accept the personal jurisdiction and
venue of the New Hampshire courts.
. You have the right to use only the one (1) copy of the Program provided in this
EXCLUSION OF WARRANTY AND DISCLAIMER OF LIABILITY
1. EXCLUSION OF
writing, Cabletron makes no warranty, expressed or implied, concerning the Program (including
its documentation and media).
CABLETRON DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, OTHER THAN THOSE SUPPLIED TO
YOU BY CABLETRON IN WRITING, EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING
BUT NOT LIMITED TO IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, WITH RESPECT TO THE PROGRAM, THE
ACCOMPANYING WRITTEN MATERIALS, AND ANY A CCOMPANYING HARDWARE.
2. NO LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES. IN NO EVENT SHALL
CABLETRON OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES WHATSOEVER
(INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF BUSINESS,
PROFITS, BUSINESS INTERRUPTION, LOSS OF BUSINESS INFORMATION, SPECIAL,
INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR RELIANCE DAMAGES, OR OTHER LOSS)
ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS CABLETRON PRODUCT,
EVEN IF CABLETRON HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGES. BECAUSE SOME STATES DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, OR
ON THE DURATION OR LIMITATION OF IMPLIED WARRANTIES, IN SOME
INSTANCES THE ABOVE LIMITATIONS AND EXCLUSIONS MAY NOT APPLY TO
YOU.
WARRANTY. Except as may be specifically provided by Cabletron in
IRM3 User’s Guide iii
Page 7

Notice
UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT RESTRICTED RIGHTS
The enclosed product (a) was developed solely at private expense; (b) contains “restricted computer
software” submitted with restricted rights in accordance with Section 52227-19 (a) through (d) of the
Commercial Computer Software - Restricted Rights Clause and its successors, and (c) in all respects
is proprietary data belonging to Cabletron and/or its suppliers.
For Department of Defense units, the product is licensed with “Restricted Rights” as defined in the
DoD Supplement to the Federal Acquisition Regulations, Section 52.227-7013 (c) (1) (ii) and its
successors, and use, duplication, disclosure by the Government is subject to restrictions as set forth in
subparagraph (c) (1) (ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software clause at 252.227-
7013. Cabletron Systems, Inc., 35 Industrial Way, Rochester, New Hampshire 03867-0505.
iv IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 8

CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Using This Manual.......................................................................1-1
1.2 The Intelligent Repeater Module (IRM3) .....................................1-2
1.3 IRM3 Front Panel ........................................................................1-4
1.3.1 IRM3 Features................................................................1-5
1.4 Repeater Functionality.................................................................1-5
1.5 Network Management Capabilities..............................................1-6
1.6 Getting Help.................................................................................1-7
1.7 Document Conventions............................................................... 1-8
1.8 Related Manuals..........................................................................1-9
CHAPTER 2 NETWORK PLANNING AND CONFIGURATION
2.1 Network Requirements................................................................2-1
2.1.1 802.3 Repeater Requirements........................................ 2-1
2.1.2 AUI Port Requirements................................................... 2-1
2.1.3 Fiber Optic Port Requirements .......................................2-2
2.2 The IRM3 in the Multi Media Access Center...............................2-3
2.2.1 Media Interface Modules ................................................2-4
2.3 Sample Network Configuration....................................................2-5
CHAPTER 3 INSTALLING THE IRM3
3.1 Unpacking the IRM3....................................................................3-1
3.2 Setting the IRM3 Jumpers...........................................................3-2
3.2.1 Setting the Battery Enable/Disable Jumper (H1)............3-2
3.2.2 Setting the CTS External/Internal Jumper (H6, H8)........ 3-3
3.2.3 Setting the THN-MIM Jumper (JP1)................................3-4
3.3 Installing the IRM3 into an MMAC Chassis.................................3-4
3.4 Pre-installation Test.....................................................................3-7
3.5 Connecting the IRM3 to the Network...........................................3-8
3.5.1 Connecting to the Network Through the AUI Port ..........3-9
3.5.2 Connecting to the Network Through the
Fiber Optic Port3-10
3.6 Installation Checkout................................................................. 3-12
3.7 Connecting to the UPS Through the Console Port....................3-13
IRM3 User’s Guide v
Page 9

Contents
CHAPTER 4 LOCAL MANAGEMENT
4.1 Accessing Local Management Using a Terminal.........................4-3
4.1.1 Configuring a Local Management Terminal ....................4-3
4.1.2 Terminal Attachment Cable Configuration ......................4-4
4.1.3 Connecting the Terminal and Accessing Local
Management4-5
4.2 Accessing Local Management Using a Modem...........................4-7
4.2.1 Modem Configurations....................................................4-7
4.2.2 Modem Attachment Cable Configuration ........................4-7
4.2.3 Connecting the Modem and Accessing Management.....4-8
4.3 The Password Screen..................................................................4-9
4.4 The Device/Board/Port Counters Screen...................................4-10
4.4.1 Configuring the Device/Board/Port Counters Screen....4-11
4.4.2 Device/Board/Port/Counters Screen Fields...................4-12
4.4.3 Resetting the Device/Board/Port Counters ...................4-13
4.4.4 Using the Enable Board/Disable Board Options ...........4-14
4.4.5 Using the Enable Port/Disable Port Option...................4-14
4.4.6 Available Options from the Device/Board/Port Counters
Screen4-14
4.5 Community Names Screen........................................................4-15
4.5.1 Accessing the Community Names Screen....................4-16
4.5.2 Community Names Screen Fields.................................4-16
4.5.3 Editing the Community Names Screen .........................4-17
4.6 The Setup Screen......................................................................4-18
4.6.1 Accessing the Setup Screen.........................................4-19
4.6.2 Setup Screen Fields......................................................4-19
4.6.3 Setting the Set IP Address Option.................................4-20
4.6.4 Setting the Set Current Date Option..............................4-21
4.6.5 Setting the Set Current Time Option.............................4-21
4.6.6 Setting the Device Lock Option.....................................4-21
4.6.7 Setting the Set Refresh Time Option.............................4-22
4.7 Port Association Screen.............................................................4-22
4.7.1 Accessing the Port Association Option .........................4-22
4.7.2 Port Association Screen Fields .....................................4-23
4.7.3 Changing the Port Association......................................4-24
4.8 The Token Ring Board Status Screen.......................................4-24
4.8.1 Accessing the Token Ring Board Status Screen ..........4-25
4.8.2 Token Ring Board Status Screen Fields.......................4-26
4.8.3 Editing the Token Ring Board Status Screen................4-29
vi IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 10

Contents
CHAPTER 5 TROUBLESHOOTING
5.1 Using LANVIEW..........................................................................5-1
5.2 Troubleshooting Checklist...........................................................5-4
5.3 Using the Reset Switch ...............................................................5-5
5.4 Before Calling Technical Support................................................5-5
APPENDIX A SPECIFICATIONS
A.1 Repeater Functionality.................................................................A-1
A.2 AUI Port.......................................................................................A-2
A.3 Fiber Optic Interface....................................................................A-2
A.4 Console Port................................................................................A-3
A.5 Microprocessors and Memory.....................................................A-3
A.6 Environmental Requirements......................................................A-3
A.7 Agency Approvals........................................................................A-4
A.8 Service.........................................................................................A-4
A.9 Physical Properties......................................................................A-4
INDEX
IRM3 User’s Guide vii
Page 11

CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
Welcome to the Cabletron Systems
(IRM3) User’s Guide
management, and reference guide for the IRM3, and includes a
description of the IRM3 capabilities and special features. The IRM3
provides a high performance IEEE 802.3 repeater with sophisticated
network management capabilities for use in a Cabletron Systems Multi
Media Access Center (MMAC).
. This manual serves as an installation,
Intelligent Repeater Module
1.1 USING THIS MANUAL
Before installing and operating the IRM3, read through this guide to gain
a full understanding of its capabilities.
It is assumed that you have a general working knowledge of Ethernet or
IEEE 802.3 type data communications networks and their physical layer
components.
This guide is organized as follows:
Chapter 1,
including an explanation of the IRM3 repeater functionality and its
management capabilities. This chapter concludes with instructions on
how to get help if needed and a list of related manuals.
Chapter 2,
configuration requirements to consider before installing the IRM3. This
chapter also includes a sample configuration for the IRM3.
Chapter 3,
IRM3 into an MMAC. This chapter also includes instructions for
connecting the IRM3 to the network.
Introduction
Network Planning and Configuration
Installing the IRM3
, describes the capabilities of the IRM3,
, contains instructions for installing the
, provides
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 1-1
Page 12

Chapter 1:
Introduction
Chapter 4,
Local Management
, describes Local Management (LM) and
control capabilities for the IRM3. Local Management provides the tools
to manage the IRM3 and its attached segments.
Chapter 5,
Troubleshooting,
details the LANVIEW LEDs incorporated
into the IRM3, which enable you to quickly diagnose any problems that
may occur with the IRM3. This chapter also includes a troubleshooting
checklist, procedures for using the reset switch and instructions for
calling technical support.
Appendix A,
Specifications
, contains location requirements and
operating specifications for the IRM3.
1.2 THE INTELLIGENT REPEATER MODULE (IRM3)
The Intelligent Repeater Module (IRM3) (Figure 1-1) is the heart of the
Cabletron Systems Multi Media Access Center (MMAC). The IRM3
incorporates a high performance IEEE 802.3 repeater to allow maximum
data paths between devices connected to the MMAC.
The IRM3 is Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) compliant,
and can be controlled and monitored by a variety of SNMP Network
Management packages. These include Cabletron Systems SPECTRUM
Element Manager for Windows, Cabletron Systems SPECTRUM, and
third party SNMP network management packages. Additionally, the
IRM3 can be controlled and monitored by IRM3/LM - Local
Management for the IRM3 through a terminal connected locally or
through a Hayes compatible modem.
Page 1-2 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 13
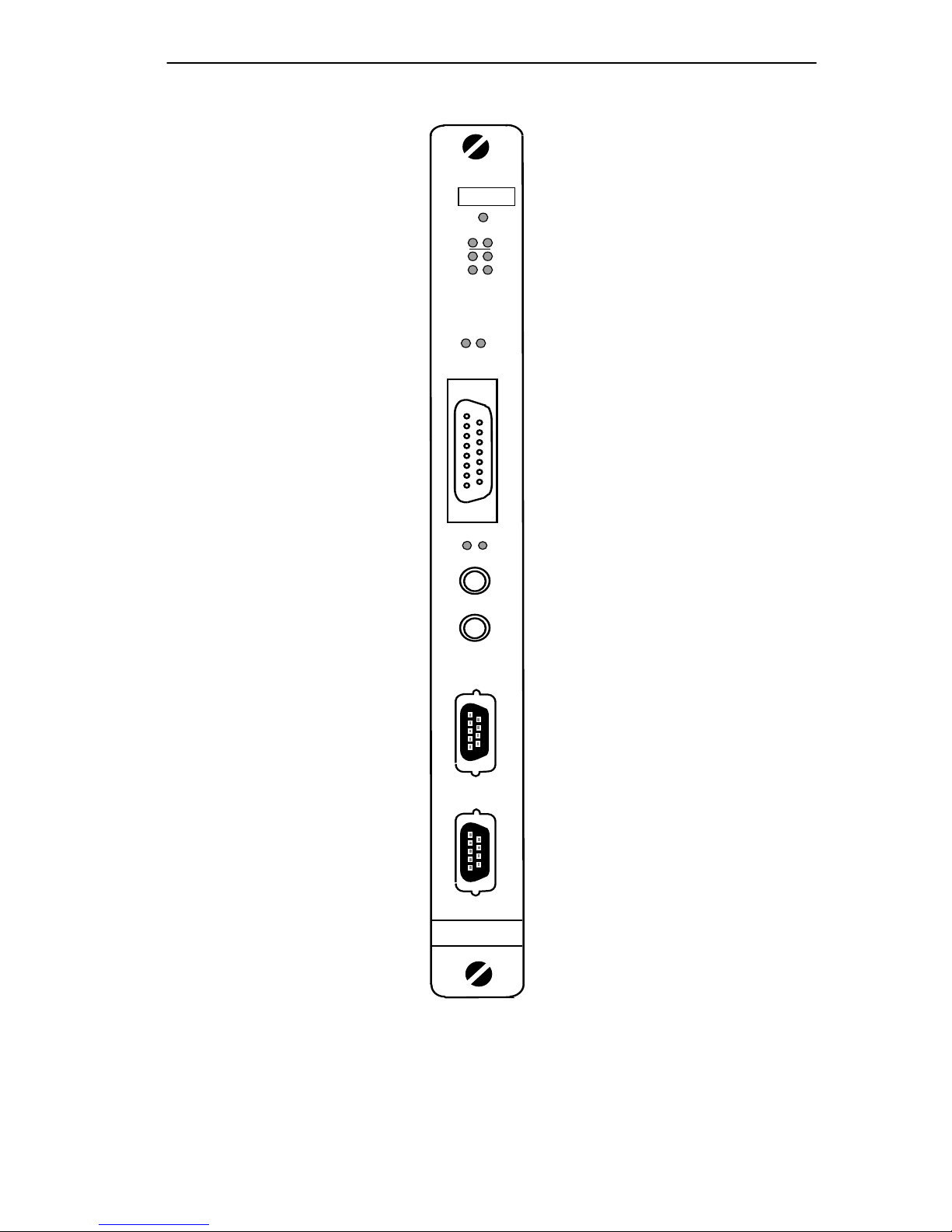
The Intelligent Repeater Module (IRM3)
.
IRM3
SN
RESET
PWR BOK
MGMT
CLN
RCV
POK
PWRON
A
U
I
ON LNK
T
X
R
O
R
X
ETHERNET
F
I
L
U
P
S
C
O
N
S
O
L
E
Figure 1-1 Intelligent Repeater Module (IRM3)
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 1-3
0494101
Page 14

Chapter 1:
Introduction
1.3 IRM3 FRONT PANEL
The IRM3 incorporates two ports that connect to external network
segments:
• One pair of IEEE 802.3 FOIRL fiber optic ports. The fiber optic ST
port accommodates a wide variety of multimode fiber optic cable,
µ
including 50/125
up to 2 km in length.
• An IEEE 802.3 compliant AUI port. The AUI port allows you to
connect the module to a variety of Ethernet transmission media
including twisted pair, fiber optic, and/or thick or thin Ethernet coaxial
cable by way of an external transceiver.
Either one of these ports can act as the repeater port to the external
network. When the IRM3 is first powered up, the AUI port acts as the
repeater port and the fiber ports are off. Using the IRM3 network
management capabilities (see Chapter 4,
reverse this configuration to ha ve the fiber port act as the repeater port and
have the AUI port off. This configuration allows you to connect the IRM3
to a fiber optic link segment directly without having to use an external
fiber optic transceiver.
m, 62.5/125 µm, and 100/140 µm fiber optic cable,
Local Management
), you can
The IRM3 also provides the option, through remote management, to set
one port as the active repeater port and the other port as a redundant
repeater port.
Built into the front panel of the IRM3 are two standard 9-pin RS232
console ports labeled CONSOLE and UPS. The CONSOLE port enables
you to access the IRM3/LM locally or remotely using a Hayes compatible
modem. If you are using a CS-600R/CS-1250R series Uninterruptible
Power Source (UPS), the UPS port enables you to monitor and control the
UPS through the IRM3 using SPECTRUM Element Manager for
Windows or SPECTRUM. The front panel also has a reset switch to
initialize the IRM3 processor.
The IRM3 incorporates the Cabletron Systems LANVIEW Status
Monitoring and Diagnostic System. If a problem arises, such as a power
failure or a cable fault, the LANVIEW LEDs (see Section 5.1,
LANVIEW
) help you to diagnose it.
Using
Page 1-4 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 15

Repeater Functionality
The LANVIEW LEDs on the IRM3 indicate the following conditions:
• The IRM3 is receiving power
• An error has been detected with the IRM3
• The IRM3 is receiving packets from any segment connected to the
MMAC
• The IRM3 is detecting a collision from the network
1.3.1 IRM3 Features
There are a number of features that provide for efficient use and
maintenance of the IRM3. These features include the following:
• Flash EPROM. This feature enables you to upgrade the IRM3 without
replacing firmware. Flash EPROMs can be updated remotely by
downloading the new software by way of Cabletron Systems
SPECTRUM Element Manager for Windows.
• Thermal Sensors. These sensors warn the management station if the
IRM3 begins to overheat.
• Ethernet SNMP Proxy. With SNMP proxy , you can use IRM3 remote
management to control power settings for the American Power
Conversion’s uninterruptible power source (UPS).
• Connect the UPS to the IRM3 UPS port to control the power supply
through an SNMP compliant network management tool, such as
Cabletron Systems SPECTRUM Element Manager for Windows and
SPECTRUM.
1.4 REPEATER FUNCTIONALITY
The IEEE 802.3 compliant repeater on the IRM3 provides the MMAC
with the ability to achieve maximum data paths on all Ethernet
transmission media, including 10BASE-T, fiber optic, and thick or thin
Ethernet type cabling. To attain maximum data paths, the IRM3 retimes
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 1-5
Page 16

Chapter 1:
Introduction
data packets and regenerates the preamble of each data packet that enters
the MMAC.
In addition, IRM3 repeater functionality assures that problem segments
connected to any port on the MMAC do not affect any other segments
connected to the MMAC. If 32 consecutive collisions are detected on any
segment, or if a collision detector is on for more than 2.4 ms, the IRM3
automatically partitions that segment. The segment automatically
reconnects to the MMAC after a packet is transmitted onto the segment
without causing a collision.
1.5 NETWORK MANAGEMENT CAPABILITIES
The Cabletron Systems IRM3 can be controlled and managed by a variety
of network management packages which include the following:
• Cabletron Systems SPECTRUM
• Cabletron Systems SPECTRUM Element Manager for Windows
• Cabletron Systems IRM3/LM (Local Management)
• Third Party SNMP compliant Network Management Packages
The IRM3 network management capabilities provide the necessary
management tools for the IRM3 to operate at its full capacity . Your ability
to set up parameters within the network management capabilities ensures
optimal performance of the IRM3, and, hence, the network.
For example, a great deal of statistical information on the port, board, and
MMAC device level is gathered by the IRM3, including each of the
following:
• Packets • Bytes Received
• Collisions • Giant Packets
• Runt Packets • Misaligned Packets
• Frame Size • Out of Window Collisions
• Breakdowns • CRC Errors
Page 1-6 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 17

Getting Help
To help you see how your network is being used, and to help you plan for
future network use, the IRM3 also provides Ethernet protocol counters on
the port and board level for the following protocols:
• AppleTalk
• Banyan
• Cabletron
• DECnet
• ISO/OSI
• Novell
• TCP/IP
• XNS
• Other
For further specific information on in-band management of the IRM3,
refer to the applicable Network Management Package User’s Manual.
1.6 GETTING HELP
If you need additional support related to the IRM3, or if you have any
questions, comments, or suggestions related to this manual, contact
Cabletron Systems Technical Support:
By phone (603) 332-9400
8 P.M. Eastern time
Monday–Friday, 8
By CompuServe GO CTRON from any ! prompt
By Internet mail: support@ctron.com
By FTP ctron.com (134.141.197.25)
Login:
Password:
anonymous
your email address
A.M –
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 1-7
Page 18
Chapter 1:
Introduction
Before calling Cabletron Systems Technical Support, be prepared to
provide the following information:
• A detailed description of the failure.
• A description of any action already taken to resolve the problem
(swapping the bad unit with a unit known to work properly, etc.)
• A description of your network (environment, layout, cable type and
length, etc.)
• Serial numbers of all Cabletron Systems products used in the network.
• Revision level of all Cabletron Systems products in the network
• Revision level of firmware installed on all Cabletron Systems products
• The network load and frame size at the time of the failure, if known
• Product history (had the product been returned previously, did it have
the same problem, etc.)
• The RMA number generated, if any
1.7 DOCUMENT CONVENTIONS
The following conventions are used throughout this document:
NOTE
TIP
NOTE
information that may be of special importance.
TIP
actions.
symbol. Calls the reader’s attention to any item of
symbol. Conveys helpful hints concerning procedures or
CAUTION
!
CAUTION
WARNING
Page 1-8 IRM3 User’s Guide
damage to the equipment.
WARNING
equipment damage, personal injury or death.
symbol. Contains information essential to avoid
symbol. Warns against an action that could result in
Page 19

Related Manuals
1.8 RELATED MANUALS
The manuals listed below should be used to supplement the procedures
and other technical data provided in this manual. The procedures will be
referenced where appropriate, but will not be repeated.
Cabletron Systems
Guide.
Multi Media Access Center Overview and Setup
Cabletron Systems
Windows.
IRM3 Management Module Guide for Microsoft
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 1-9
Page 20

CHAPTER 2
NETWORK PLANNING AND CONFIGURATION
This chapter addresses some of the configuration issues that you should
consider when installing the IRM3, including 802.3 standards related to
repeaters, transceivers, and cables. This chapter also gives an overview of
Cabletron Systems Multi Media Access Center (MMAC) and the Media
Interface Modules (MIM) that can be managed by the IRM3. Finally, an
example of a network configuration using the IRM3 is provided.
2.1 NETWORK REQUIREMENTS
When connecting network segments to the IRM3, you must follow the
network guidelines listed below.
2.1.1 802.3 Repeater Requirements
Depending on the size of your network, you may need to use multiple
repeaters. When planning your network, keep in mind that 802.3
standards allow for no more than four repeaters in one data path. If your
network requires more than four repeaters, use a bridge to create a new
data path.
2.1.2 AUI Port Requirements
The IRM3 provides the flexibility of connecting to a network with
different types of media through the AUI port. Using an AUI cable along
with the proper Cabletron Systems transceiver, you can connect to the
network with AUI cable, coaxial cable, twisted pair cable, or fiber optic
cable.
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 2-1
Page 21

Chapter 2: Network Planning and Configuration
When connecting a network segment to the IRM3 through a transceiver
and an AUI cable, the following requirements must be met:
• The transceiver to which the IRM3 will be connected must meet
Ethernet Version 1, Version 2 or IEEE 802.3 standards.
• The A UI cables connecting the IRM3 to the transceiver on the netw ork
must be IEEE 802.3 type cables and must not exceed 50 meters in
length.
• The Signal Quality Error (SQE) function on the transceiver must be
disabled.
The SQE function is used to confirm that the collision signaling
NOTE
of the transceiver is working properly. However, when
connecting a transceiver to the IRM3, or any other repeater,
you must disable the SQE test function. If SQE is not disabled,
the repeater regards each SQE signal as a collision and
resends the JAM packet, causing a considerable slowdown of
network operations.
2.1.3 Fiber Optic Port Requirements
When connecting a Fiber Optic Link Segment to the IRM3 fiber optic ST
ports, the following requirements must be met:
• Cable Type - The fiber optic link segment should consist of one of the
following:
- 50/125 µm fiber optic cabling
- 62.5/125 µm fiber optic cabling
- 100/140 µm fiber optic cabling
• Attenuation - The fiber optic cable must be tested with a fiber optic
attenuation test set that is adjusted for an 850 nm wavelength. This test
verifies that the signal loss in a cable is within an acceptable level:
- 13.0 dB or less for 50/125 µm fiber cable segment
- 16.0 dB or less for 62.5/125 µm fiber cable segment
- 19.0 dB or less for 100/140 µm fiber cable segment
Page 2-2 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 22
The IRM3 in the Multi Media Access Center
• Budget and Propagation Delay - When determining the maximum
fiber optic cable length, the fiber optic budget delay and total network
propagation should be calculated and taken into consideration before
fiber runs are incorporated in any network design. Fiber optic budget
is the combination of the optical loss due to the fiber optic cable,
in-line splices, and fiber optic connectors. Propagation delay is the
amount of time it takes a packet to travel from the sending device to
the receiving device.
• Length - IEEE 802.3 specifications for fiber optic cable allow for a
maximum of 1 km. Howe ver , distances of at least 2 km can usually be
achieved.
2.2 THE IRM3 IN THE MULTI MEDIA ACCESS CENTER
The IRM3 is designed to be installed in a Cabletron Systems Multi Media
Access Center (MMAC) network hub with the Flexible Network Bus
(FNB) - See Figure 2-1. The MMAC is fully protocol independent and is
available in an eight slot (MMAC-M8FNB), five slot (MMAC-M5FNB)
and three slot (MMAC-M3FNB) model.
When installed in an MMAC, the IRM3 supports 10 Mbps Ethernet
(IEEE 802.3), as well as 4 and 16 Mbps Token Ring (IEEE 802.5) Media
Interface Modules (MIMs) using shielded twisted pair (STP) or
unshielded twisted pair (UTP), fiber optic, thin or thick coaxial and
standard AUI transceiver cabling. The IRM3 retimes and regenerates
packets for each port of each Ethernet MIM installed in the MMAC, and
allows users to access management information for all Token Ring and
Ethernet MIMs in the MMAC.
Power & Management Bus
Ethernet A Bus
Flexible Network Bus
Ethernet B Bus
Ethernet C Bus
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 2-3
0494102
Figure 2-1 MMAC with FNB
Page 23

Chapter 2: Network Planning and Configuration
2.2.1 Media Interface Modules
The following is a description of the types of Cabletron Systems MIMs
that can be installed in the MMAC and managed by the IRM3.
THN-MIM Thin Coaxial Module
The THN-MIM has 12 Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 compliant attachments to
either thin or thick coaxial cable through a thick-to-thin adapter. The thin
coaxial segment, which may be up to 185 meters in length, can
accommodate up to 29 connections per segment. The thick coaxial
segment may extend to 500 meters in length and provide up to 99
connections.
MT8-MIM Multiport Transceiver Interface Module
The MT8-MIM provides eight separate transceivers in one unit that can
be inserted into the MMAC. The MT8-MIM provides eight IEEE
802.3-compatible medium attachment unit (MAU) ports, which allows a
direct connection to any type of media.
TPMIM 10BASE-T Modules
Cabletron Systems TPMIM 10BASE-T modules are available with 12 or
24 ports equipped with DB9, RJ45, or RJ71 connectors for
shielded/unshielded twisted pair connections of up to 125 meters in
length.
FOMIM Fiber Optic Modules
Cabletron Systems FOMIM fiber optic modules are available with 6, 12
or 18 ports equipped with either ST (straight tip) or SMA (subminiature
type A) connectors, with models that support either single mode or
multimode cable. The FOMIMs provide Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 Fiber Optic
Inter Repeater Link (FOIRL) compatible attachments over 50, 62.5 or 100
µm core multimode fiber cabling, or 8/125 - 12/125 µm core single mode
cabling. Each port of the multimode modules can drive fiber optic link
segments up to 2 km in length. Each port on the single mode modules can
drive fiber segments up to 10 km, provided that system budgets are met.
Page 2-4 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 24
Sample Network Configuration
TRMIM Token Ring Modules
Cabletron Systems TRMIM Token Ring modules are available with 12 or
24 ports equipped with either RJ45 or DB9 connectors. Token Ring
modules that support unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable provide for
segments of up to 100 meters. With modules that support shielded twisted
pair (STP) cable, you can attach segments of up to 200 meters.
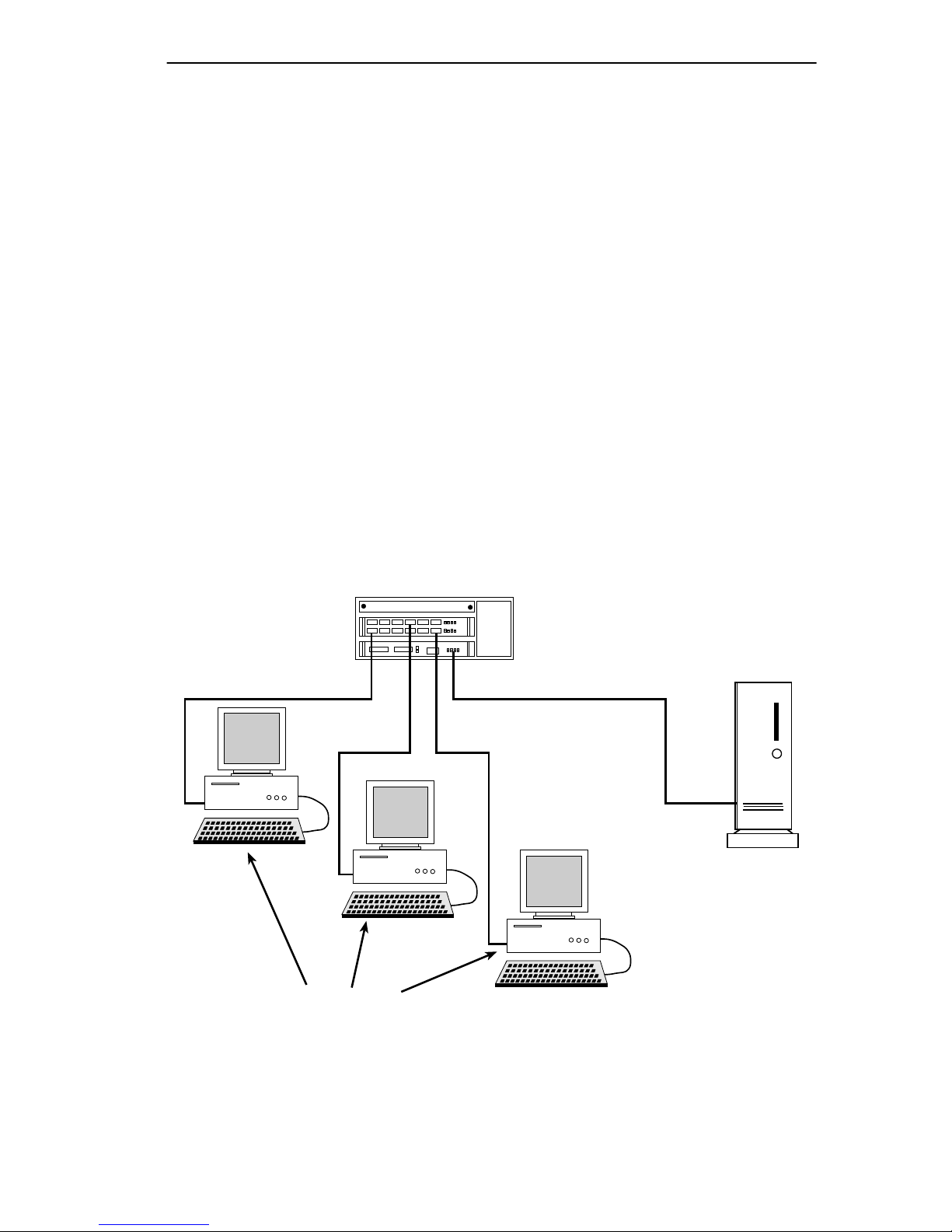
2.3 SAMPLE NETWORK CONFIGURATION
The following illustrates a simple network configuration that provides a
general idea of how the IRM3 can be used in a network. Each workstation
will have access to each other and the server through the TPMIM and the
IRM3. The IRM3 manages the backplane and repeating functions
between the users on the network. The TPMIM provides access to the
backplane for the workstations while the IRM3 repeats the incoming
traffic to the other stations on the network. Control of the boards and ports
is accessed through the IRM3 Local Management.
Workstations
MMAC3 with IRM3
Server
0494103
Figure 2-2 Example of a Small Network Configuration
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 2-5
Page 25

CHAPTER 3
INSTALLING THE IRM3
This chapter provides the instructions needed to install and verify the
proper operation of the IRM3 into a network. The information in this
chapter pre-supposes that the previous sections have been completed
properly.
To install and test the IRM3 perform the following:
• Unpack the IRM3
• Set and verify the IRM3 jumper settings
• Install the IRM3 into an MMAC chassis
• Perform pre-installation checkout
• Connect to the network through either of the following:
- AUI port
- Fiber Optic port
• Perform installation checkout
• Connect UPS (if required)
3.1 UNPACKING THE IRM3
Before installing the IRM3, visually inspect the module. To unpack the
module, proceed as follows:
1. Remove the shipping material covering the IRM3 in the shipping box.
2. Carefully remove the module from the shipping box. Leave the
module in its conductive bag until you are ready to install it. Save the
shipping box and materials in the event the unit has to be reshipped.
3. Visually inspect the module. If you see any damage, contact Cabletron
Systems Technical Support immediately.
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 3-1
Page 26

Chapter 3: Installing the IRM3
3.2 SETTING THE IRM3 JUMPERS
There are eight jumpers on the IRM3 as shown in Figure 3-1. Four of the
jumpers, H1, H6, H8, and JP1 can be changed. The remaining jumpers are
for Cabletron Systems use only and should not be changed from their
default positions.
3.2.1 Setting the Battery Enable/Disable Jumper (H1)
The Battery Enable/Disable Jumper (H1, Figure 3-1) allows you to enable
or disable the Battery Back-up for RAM on the IRM3. When set to the
enabled position, all parameters that you enter into the IRM3 will be
saved if power to the MMAC should fail, or if the IRM3 is remo ved from
the MMAC. When set to the disabled position, all parameters entered into
the IRM3 will be lost if power is removed from the IRM3.
To set the Battery Enable/Disable Jumper perform the following:
• To enable the battery back-up , place the jumper over Pins 1 and 2.
• To disable the battery back-up, place the jumper over Pins 2 and 3.
This is the position in which the IRM3 is shipped.
Page 3-2 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 27

Battery
Enable/Disable
Setting the IRM3 Jumpers
For Cabletron Use Only
THN-MIM Jumper
H1/JP1
Pin Numbers
JP1
H1
CTS-Modem Port
CTS-Console Port
1
2
3
H6/H8
Pin Numbers
1 2 3
Figure 3-1 IRM3 Jumper Locations
H4
H5
H2
H3
H8
H6
0494104
3.2.2 Setting the CTS External/Internal Jumper (H6, H8)
The IRM3 UPS port and CONSOLE port are RS232 interfaces that use
Request to Send (RTS), Clear to Send (CTS), and Data Terminal Ready
(DTR) to control data flow. If the device connected to either the UPS port
or CONSOLE port does not provide RTS or DTR, the IRM3 must be
configured to compensate (internally) for the lack of these signals. In
those situations, the CTS External/Internal jumpers (H6 for the UPS port
and H8 for the CONSOLE port) allow the IRM3 to generate the CTS
signal internally . Refer to the Users Manual of the de vice to determine the
requirements for this jumper setting.
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 3-3
Page 28

Chapter 3: Installing the IRM3
Set the CTS External/Internal Jumper as follows:
• If RTS or DTR is generated by your device to the IRM3, place the
jumper over pins 2 and 3. This is the position in which the IRM3 is
shipped.
• If RTS or DTR must be generated internally by the IRM3, place the
jumper over pins 1 and 2.
3.2.3 Setting the THN-MIM Jumper (JP1)
The THN-MIM Jumper (JP1, Figure 3-1) may need to be set depending
on the revision level of the THN-MIMs installed in your MMAC. To
check the revision level of the THN-MIM, refer to the part number
located in the lower left corner of the module (same side as the backplane
connector). Set the THN-MIM Jumper as follows:
• If you are using THN-MIM part numbers 9000043-06 and above in
your MMAC, place the jumper over pin 2 and pin 3. This is the
position in which the IRM3 is shipped.
• If you are using THN-MIM part numbers 9000043-05 and below in
your MMAC, place the jumper over pin 1 and pin 2.
If THN-MIM part numbers 9000043-05 and below and
!
CAUTION
9000043-06 and above are both installed in your MMAC, the
THN-MIM Jumper must be placed over pin 1 and pin 2.
3.3 INSTALLING THE IRM3 INTO AN MMAC CHASSIS
The IRM3 is designed to be installed into slot 1 of any MMAC. No
special skills or tools are required to install the IRM3. To install the IRM3
into an MMAC, continue as follows:
1. Power off the MMAC.
2. Slide the IRM3 (Figure 3-2) into Slot 1 of the MMAC card cage. Be
sure that the card is in the top and bottom slot guides.
Page 3-4 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 29

MMAC-8
Installing the IRM3 into an MMAC Chassis
IRM-3
KNURLED
KNOBS
BOARD SLOT 1
Figure 3-2 IRM3 Installation
0494105
3. Secure the module to the MMAC by turning the knurled knobs. Be
sure that the module is firmly attached to the MMAC. Failure to do so
may result in improper operation.
Fill all open slots in the MMAC hub with blank plates. If the
WARNING
plates are not installed, the MMAC may fail to comply with
allowed limits of conducted and radiated emissions.
4. Power on the MMAC.
5. Observe the status of the LANVIEW LEDs on the IRM3. See
Figure 3-3. After approximately 2 seconds, the LEDs should be in the
following conditions:
• PWR lit, indicating that the IRM3 is receiving power.
• POK lit, indicating that the network interface chip associated with
the IRM3 internal repeater ports have passed the internal loopback
test and are now ready for transmission.
• BOK lit, indicating the IRM3 is operating properly.
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 3-5
Page 30

Chapter 3: Installing the IRM3
IRM3
SN
RESET
PWR BOK
MGMT RCV
CLN POK
ON PWR
ON LNK
RESET SWITCH
LANVIEW LEDS
A
U
I
NOTES
T
X
F
O
0494106
Figure 3-3 LANVIEW LEDs
When the IRM3 is first powered up, the AUI port acts as the
repeater port and the Fiber ports are off. This configuration can
be altered using IRM3 Local Management or network
management tools so that the Fiber ports act as the repeater
port and the AUI port is off.
Powering off the IRM3 or using the Reset switch will not alter
the Repeater port settings if the battery back-up is enabled. F or
further information, refer to the discussion of Port Association
in Chapter 4.
Page 3-6 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 31

Pre-installation T est
3.4 PRE-INSTALLATION TEST
Before installing the IRM3 in a live network, test the module in a
controlled situation to ensure that it is repeating packets. With the IRM3
installed in an MMAC hub with a Media Interface Module (MIM), this
test can be performed with two workstations (Figure 3-1) by completing
the following steps:
1. Install a Media Interface Module (TPMIM, FOMIM, THN-MIM, etc.)
into the same MMAC chassis as the IRM3.
2. Connect the first workstation to either the MIM, using the appropriate
cable and transceiver; or to the IRM3 using either the AUI port, using
a transceiver and an AUI cable; or to the fiber optic port, using fiber
optic cable; depending on which is the active repeater port.
The AUI port is the default active repeater port. If you want to
NOTE
test the IRM3 using the fiber port, it must be selected through
Local Management. Please refer to Chapter 4 for more
information on selecting the active repeater port.
3. Connect the second workstation to the MIM, using the appropriate
transceivers and cable.
4. Set the first workstation as the file server and the second as the client
(refer to the workstation documentation for setting up the workstations
as file server and client). When the workstations are properly set up,
proceed to send packets between the workstations and verify that the
IRM3 is operating properly.
A “ping” test will verify that the IRM3 is operating properly.
NOTE
However, both server and client workstations must have their
own unique IP Adresses.
If failures occur, refer to the Troubleshooting section in Chapter 5.
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 3-7
Page 32

Chapter 3: Installing the IRM3
MMAC 3/FNB with IRM3 and TPMIM
TPT
File Server Workstation
Client Workstation
0494109
Figure 3-4 Pre-installation Test
3.5 CONNECTING THE IRM3 TO THE NETWORK
This section provides procedures for connecting the IRM3 to the network
using the AUI port or the Fiber Optic ports.
Page 3-8 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 33

Connecting the IRM3 to the Network
3.5.1 Connecting to the Network Through the AUI Port
Connect to the network through the AUI port by performing the following
steps:
Be sure to disable the SQE test function on the transceiv er y ou
!
CAUTION
1. Attach an external transceiver to the segment to which the AUI port
will be attached. Refer to the applicable transceiver manual.
2. Attach the female end of an AUI cable, no more than 50 meters in
length, to the transceiver.
3. Attach the male connector on the AUI cable (Figure 3-5) to the AUI
port on the IRM3.
connect to the IRM3 AUI port. Failure to do so will result in
improper operation of the IRM3. Refer to the applicable
transceiver manual.
4. Move the slide latchon the AUI port to secure it to the lock post on the
AUI connector.
.
SLIDE LATCH
SLIDE LATCH
AUI PORT
AUI PORT
AUI CONNECTOR
AUI CONNECTOR
0494107
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 3-9
Figure 3-5 Connecting to the AUI Port
Page 34

Chapter 3: Installing the IRM3
3.5.2 Connecting to the Network Through the
Fiber Optic Port
When connecting a fiber optic link segment to the IRM3 Fiber Optic
ports, you must keep the following in mind:
• ST connectors attach to ST ports much like BNC connectors attach to
BNC ports. The connector is inserted into the port with the alignment
slot on the connector inserted into the alignment key on the port. The
connector is then turned clockwise to lock it down.
• The physical communication link consists of two strands of fiber optic
cabling: the T ransmit (TX) and the Receive (RX). The T ransmit strand
from the fiber optic port on the module will be connected to the
Receive port of a fiber optic Ethernet device at the other end of the
segment. The Recei ve strand of the fiber optic port on the module will
be connected to the Transmit port of the fiber optic Ethernet device.
• Label the fiber optic cable to indicate which fiber is Receive and which
is T ransmit. When you buy fiber optic cable from Cabletron Systems,
it is labeled so that at one end of the cable, one fiber is labeled 1, and
the other fiber is labeled 2. This pattern is repeated at the other end of
the cable. If you did not purchase your cable from Cabletron Systems,
be sure to label your cable in this manner.
Do not touch the ends of the fiber optic strands, and do not let
!
CAUTION
the ends come in contact with dust, dirt, or other contaminants.
Contamination of the ends can cause problems in data
transmissions. If the ends become contaminated, clean them
with denatured alcohol using a soft, clean, lint free cloth.
Connect a fiber optic link segment to an IRM3 FOIRL Fiber Optic port by
performing the following steps:
1. Remove the protective plastic covers from the fiber optic ports and
from the ends of the connectors on each fiber strand.
2. Attach the fiber labeled 1 (Figure 3-6) to the receive port, labeled RX,
on the module.
3. Attach the fiber labeled 2 to the transmit port, labeled TX, on the
module.
Page 3-10 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 35

Connecting the IRM3 to the Network
4. At the other end of the fiber optic cable, attach the fiber labeled 1 to
the transmit port of the device.
5. Attach the fiber labeled 2 to the receive port.
ST Fiber Optic
Ports
T
X
R
X
ST Connectors
Fiber 1
Figure 3-6 Connecting to the Fiber Optic Ports
0494108
Fiber 2
6. Check that the LNK LED for the fiber port on the IRM3 is lit
(Figure 3-3). If the LED is not lit, perform each of the following steps
until it is:
a. Check that the po wer is turned on for the device at the other end of
the link.
b. Verify that the fiber strands are properly crossed over between the
IRM3 and the fiber optic device at the other end of the fiber optic
link segment.
c. Verify that the fiber cable meets the dB loss specifications
outlined in Fiber Optic Port Requirements in Chapter 2,
Section 2.1.3.
If a link still has not been established, contact Cabletron Systems
Technical Support.
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 3-11
Page 36

Chapter 3: Installing the IRM3
3.6 INSTALLATION CHECKOUT
After the IRM3 is connected to the network, verify that packets can be
passed between the two Ethernet network segments through the IRM3. As
in the pre-installation checkout, use two workstations set up as file server
and client. Keep the server workstation stationary in the wiring closet
with the IRM3, and use the client workstation to move around to each
node that is connected to the IRM3 (Figure 3-7).
You can verify the installation checkout by performing the following
steps:
1. Connect the server workstation to either a MIM, using the appropriate
cable and transceiver, or to the IRM3 through either the AUI port,
using a transceiver and an AUI cable, or to the Fiber Optic port,
using fiber optic cable.
2. Going to each node connected to the MMAC, connect the client
workstation and proceed to test the segment.
A “ping” test will verify that the IRM3 is operating properly.
NOTE
If a failure occurrs, refer to Chapter 5, Troubleshooting, for further
assistance.
Page 3-12 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 37

Office Locations
Connecting to the UPS Through the Console Port
MMAC 3/FNB with IRM3 and TPMIM
TPT
File Server Workstation
Client Workstation
Figure 3-7 Installation Checkout
0494110
3.7 CONNECTING TO THE UPS THROUGH THE
CONSOLE PORT
If you are using an American Power Conversion CS-600R/CS-1250R
series Uninterruptible Power Source (UPS), you can monitor and control
the UPS through the IRM3, using SPECTRUM Element Manager for
Windows. To access UPS management from the IRM3, use a serial cable
to connect the console port on the IRM3 to the 9-pin RS232 connector on
the UPS.
Refer to the Cabletron Systems IRM3 Management Module Guide for
Microsoft Windows for information on managing the UPS.
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 3-13
Page 38

CHAPTER 4
LOCAL MANAGEMENT
The Cabletron Systems IRM3/LM provides unique management and
control capabilities for the IRM3. With Local Management for the IRM3,
you have the tools to manage the IRM3 and its attached segments. For
example, you can enable and disable ports and set parameters such as the
IP Address of your IRM3 or its current date and time. You can also use
Local Management to view a full array of statistics to the port le vel. Since
the IRM3 is an SNMP compliant device, you can also set community
names for the network management stations that will have access to the
IRM3.
Local Management is accessed either through a VT200 or VT300 series
terminal (or terminals running an emulation program), or through a Hayes
compatible modem. To set up your terminal or Hayes compatible modem,
see Sections 4.1 or 4.2 respectively.
This chapter
• Explains how to access Local Management for the IRM3 through
the CONSOLE port by using either a terminal or Hayes
compatible modem.
• Discusses the statistical information available concerning your
IRM3, and its boards and ports.
• Describes the Community Names Option, which allows you to
control access to the IRM3 and designate which workstations will
receive alarms from the device.
• Describes using the IRM3 Setup Option to set the IP Address,
current date, and current time for your IRM3.
• Explains the Port Association screen, which allows you to set
either the AUI port or Fiber Optic Link port on the IRM3 to act as
the repeater port.
• Describes the T oken Ring Board Status screen, which enables you
to monitor and manage any Token Ring boards installed in the
MMAC.
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 4-1
Page 39

Chapter 4: Local Management
Figure 4-1 shows the IRM3/LM screen flow.
Enter Password:
IRM3 SNMP LOCAL
MANAGEMENT
INTRODUCTORY SCREEN
DEVICE/BOARD
PORT/COUNTERS
SETUP
COMMUNITY NAMES
PORT ASSOCIATION TOKEN RING BOARD
Figure 4-1 IRM3 Local Management Screen Flow
Page 4-2 IRM3 User’s Guide
0494111
Page 40

Accessing Local Management Using a Terminal
4.1 ACCESSING LOCAL MANAGEMENT USING A
TERMINAL
This section describes how to access local management using a terminal.
Local Management for the IRM3 is accessed through a VT200 or VT300
series terminal, or terminals running emulation programs for these series
terminals. The terminal or emulating terminal is attached to the 9-pin port
labeled CONSOLE on the IRM3.
4.1.1 Configuring a Local Management Terminal
The following section explains how to configure your terminal (console)
to communicate with Local Management. Refer to your specific terminal
manual for more instructions if necessary.
Table 4-1 lists the setup parameters necessary to configure your terminal
(console) to communicate with Local Management. If the terminal is a
Digital Equipment Corporation VT320 terminal, press F3 to access the
Setup Directory. If the local management terminal uses terminal
emulation of the VT320, refer to the equipment user manual for setup
procedures.
Table 4-1 Terminal Setup Parameters
Menu Function Selection
Display Setup
General Setup
Columns 80 Columns
Controls Interpret Controls
Auto Wrap No Auto Wrap
Test Cursor Cursor
Mode 7 Bit Control
Cursor Keys Normal Cursor Keys
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 4-3
Page 41

Chapter 4: Local Management
Table 4-1 Terminal Setup Parameters (Continued)
Menu Function Selection
Communications
Setup
Keyboard Setup
Transmit Transmit = 9600
Receive Receive = Transmit
XOFF any option
Bits, Parity 8 Bits, No Parity
Stop Bit 1 Stop Bit
Local Echo No Local Echo
Port
Transmit any option
Auto Answerback No Auto Answerback
Auto Repeat any option
Keyclick any option
Margin Bell Margin Bell
Warning Bell Warning Bell
Auto Answerback No Auto Answerback
DEC-423, Data Leads
Only
4.1.2 Terminal Attachment Cable Configuration
Local Management is accessed by an RS232 cable available from
Cabletron Systems. This cable connects the terminal to the IRM3 Console
port.
The pin-out for a cable with a 25-pin or a 9-pin connector at the terminal
end of the cable, and a 9-pin connector at the IRM3 end of the cable,
should be configured as shown in the table below:
Table 4-2 9-pin to 25-pin Pinouts
9-Pin Male Connector
(IRM3 End)
Pin 3 (Receive) to Pin 2 (Transmit)
Pin 2 (Transmit) to Pin 3 (Receive)
Pin 5 (Ground) to Pin 7 (Ground)
Pin 7 (Request to Send) to Pin 5 (Clear to Send)
Pin 8 (Clear to Send) to Pin 20 (Data Terminal Ready)
to
25-Pin Female Connector
(Terminal End)
Page 4-4 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 42

Accessing Local Management Using a Terminal
Table 4-3 9-pin to 9-pin Pinouts
9-Pin Male Connector
(IRM3 End)
Pin 3 (Receive) to Pin 3 (Transmit)
Pin 2 (Transmit) to Pin 2 (Receive)
Pin 5 (Ground) to Pin 5 (Ground)
Pin 7 (Request to Send) to Pin 8 (Clear to Send)
Pin 8 (Clear to Send) to Pin 7 (Request to Send)
to
9-Pin Female Connector
(Terminal End)
4.1.3 Connecting the Terminal and Accessing Local
Management
This procedure assumes that the 9- to 25-pin RS232 cable, available from
Cabletron Systems, is being used to connect the terminal to the IRM3.
If the terminal you are using does not generate a Clear to Send
NOTE
(CTS) signal, Request to Send (RTS) signal, or a Data Terminal
Ready (DTR) signal, the CTS jumpers on the IRM3 must be set
to compensate for these signals. Refer to Chapter 3 for
information on setting the CTS jumper.
To access Local Management, proceed as follows:
1. Plug the 9-pin end of the RS232 cable into the RS232 port labeled
CONSOLE on the IRM3.
2. Plug the 25-pin end of the RS232 cable into the COMM port on the
terminal.
3. Turn the terminal on. The IRM3 Password screen, shown in Figure 4-3
appears. Refer to Section 4.3 for more information regarding this
screen.
4. Enter your password. (The default password is the RETURN key.)
If you have entered a Superuser name at the Community
NOTE
Names screen (refer to Section 4.5), the password will be the
Superuser name. If you have entered more than one
Superuser name, any of those names may be used as the
password.
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 4-5
Page 43

Chapter 4: Local Management
5. Press RETURN. The IRM3 SNMP Local Management introductory
screen, shown in Figure 4-2, appears on the terminal.
IRM3 SNMP LOCAL MANAGEMENT
Cabletron Systems Incorporated
P.O. Box 5005 Rochester NH, 03867-5005 U.S.A.
(603) 332-9400
IRM3 SNMP Version 0.00.xx
(C) Copyright Cabletron Systems Inc. 1992
MAIN
0494112
Figure 4-2 IRM3 SNMP Local Management Introductory Screen
6. Press RETURN. The Device/Board/Port Counters screen (Main),
shown in Figure 4-4, appears. Refer to Section 4.4 for more
information regarding this screen.
Local Management for the IRM3 is now ready for operation.
Page 4-6 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 44

Accessing Local Management Using a Modem
4.2 ACCESSING LOCAL MANAGEMENT USING A
MODEM
Local Management for the IRM3 is accessed through a Hayes, or Hayes
Compatible Modem meeting the AT Command Set. The modem is
attached to the 9-pin port labeled CONSOLE on the IRM3.
4.2.1 Modem Configurations
The modem configuration must be set as follows so that the modem can
communicate with the IRM3 Local Management. Refer to your modem
manual for instructions on setting the modem.
Modem Dialing Out from a PC
Data Bits 8
Parity None
Flow Control None
Stop Bits 1
Modem Connected to the IRM3
Auto Answer On
4.2.2 Modem Attachment Cable Configuration
Local Management is accessed by an RS232 cable available from
Cabletron Systems. This cable connects the modem to the IRM3
CONSOLE port.
The pin-out for a cable with a 25-pin connector at the modem end of the
cable, and a 9-pin connector at the IRM3 end of the cable, should be
configured as follows:
Table 4-4 9-pin to 25-pin Pinouts
9-Pin Male Connector
(IRM3 End)
Pin 2 (Transmit) to Pin 3 (Receive)
Pin 3 (Receive) to Pin 2 (Transmit)
Pin 5 (Ground) to Pin 7 (Ground)
to
25-Pin Female Connector
(Modem End)
Pin 7 (Request to Send) to Pin 20 (Data Terminal Ready)
Pin 8 (Clear to Send) to Pin 8 (Data Carrier Detect)
Pin 9 (Ring Indicator) to Pin 22 (Ring Indicator)
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 4-7
Page 45

Chapter 4: Local Management
4.2.3 Connecting the Modem and Accessing
Management
If the modem you are using does not generate a Clear to Send
NOTE
To access Local Management, proceed as follows:
1. Plug the 9-pin end of the RS232 cable into the RS232 port labeled
CONSOLE on the IRM3.
2. Plug the 25-pin end of the cable into the 25-pin MODEM port on the
modem.
(CTS) signal, Request to Send (RTS) signal, or a Data Terminal
Ready (DTR) signal, the CTS jumpers on the IRM3 must be set
to compensate for these signals. Refer to Chapter 3 for
information on setting the CTS jumper.
3. Turn the modem on and dial into the modem connected to the IRM3.
The IRM3 Password screen, shown in Figure 4-3, appears once your
connection is established. Refer to Section 4.3 for more information on
this screen.
4. Enter your password. (The factory default password is the RETURN
key.)
If you have entered a Superuser name at the Community
NOTE
Names screen (refer to Section 4.5), the password will be the
Superuser name. If you have entered more than one
Superuser name, any of those names may be used as the
password.
5. Press RETURN. The IRM3 SNMP Local Management introductory
screen, shown in Figure 4-2, appears on the terminal.
6. Press RETURN. The Device/Board/Port Counters screen (Main),
shown in Figure 4-4, appears. Refer to Section 4.4 for more
information on this screen.
Local Management for the IRM3 is now ready for operation.
Page 4-8 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 46

The Password Screen
4.3 THE PASSWORD SCREEN
When either the terminal or modem are properly connected to the IRM3,
the Password screen shown in Figure 4-3 will appear. The Password
screen is the first step in accessing the local management screens of the
IRM3.
Enter Password:
0494113
Figure 4-3 IRM3 Password Screen
To access local management continue as follows:
1. Enter your password. (The default password is the RETURN key.)
If you have entered a Superuser name at the Community
NOTE
Names screen (See Figure 4-5), the password will be the
Superuser name. If you have entered more than one
Superuser name, any of those names may be used as the
password.
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 4-9
Page 47

Chapter 4: Local Management
2. Press RETURN. The IRM3 SNMP Local Management introductory
screen, shown in Figure 4-2, appears on the terminal.
3. Press RETURN. The Device/Board/Port Counters screen (Main),
shown in Figure 4-4, appears. Refer to Section 4.4 for more
information regarding this screen.
Local Management for the IRM3 is now ready for operation.
4.4 THE DEVICE/BOARD/PORT COUNTERS SCREEN
The Device/Board/Port Counters screen shown in Figure 4-4 of Local
Management for the IRM3 allows you to quickly scan statistical
information concerning the network traffic passing through the MMAC,
boards, and ports. You can see the number of bytes received, the total
number of packets, the total number of receive and transmit collisions,
and the number of errors.
11/15/91 14:26:43
Device Name: IRM3 00-00-1d-00-39-14
Bytes Received:
Packets:
Errors:
Receive Collisions:
Transmit Collisions:
Out of Window Collisions:
Runt Packets:
No Resources Available:
Frame Alignment Errors:
CRC Errors:
Giant Packets
Port Admin. Status: ON
SETUP ENABLE BOARD ENABLE PORT DISABLE PORT
BOARD 1 PORT 1 RESET COUNTERS
PORT ASSOCIA TION
DEVICE/BOARD/PORT COUNTERS
Ethernet Address:
IP Address:
Device
42586292
141995
Port Seg. Status: ON
DISABLE BOARD
Board 1
42598357
142314
14
1
0
0
0
1
0
2
2
TOKEN RING BOARD 3
134.141.52.48
14
1
0
0
0
1
0
2
2
COMMUNITY NAMESEXIT
Port 1
42598794
142336
0494114
14
1
0
0
0
1
0
2
2
Figure 4-4 IRM3 Device/Board/Port Counters Screen
Page 4-10 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 48

The Device/Board/Port Counters Screen
The errors are further broken down into the following categories:
• Out of Window Collisions
• Runt Packets
• No Resources Available
• Frame Alignment Errors
• CRC Errors
• Giant Packets
You can also perform the following functions:
• Reset all counter information associated with the MMAC back to zero.
• Enable and disable an individual board.
• Enable and disable an individual port.
Additionally, you can view Port Administrative and Segmentation Status
at this screen.
All other management options available for the IRM3 are also accessed
from the Device/Board/Port Counters screen.
4.4.1 Configuring the Device/Board/Port Counters
Screen
When the Device/Board/Port Counters screen (Figure 4-4) first appears,
information is displayed for the device (IRM3), Board 1, and Port 1. If
you wish to view counter information for another board or port, follow
these steps:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the appropriate option, BOARD X or
PORT X, at the bottom of the Device/Board/Port Counters screen.
2. Press the + key (press SHIFT and + key) to increment the board or port
number, or the - key to decrement the board or port number.
3. Press RETURN. Counter information associated with the selected
board and port will appear.
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 4-11
Page 49

Chapter 4: Local Management
4.4.2 Device/Board/Port/Counters Screen Fields
This section briefly describes the Device/Board/Port Counters screen
fields. Counter information is displayed separately on the screen for the
whole device (IRM3), the selected board, and the selected port.
Bytes Received
Displays the number of bytes received.
Packets
Displays the total number of packets received or transmitted.
Errors
Displays the number of errors detected.
Receive Collisions
Displays the number of receive mode collisions experienced by the
device, board, or port.
Transmit Collisions
Displays the number of transmit mode collisions experienced by the
device, board, or port.
Out of Window Collisions
Displays the number of collisions out of the standard collisions window
(51.2 µs) due to a network problem, such as the network being too long,
cable failure during transmission, or carrier sense violation by a node
(node transmitting at will).
Runt Packets
Displays the number of runt packets the device (IRM3), board, and port
have received from the network. A runt packet is one that is less than the
minimum Ethernet frame of 64 bytes not including preamble. The
originating station is the source of runts, which are caused by the packet
being cut off by additional traffic or not sensing the carrier, or by a
malfunctioning transceiver.
No Resources Available
Displays the number of times the IRM3 ran out of buffer space and was
not able to provide management statistics on each packet. The pack ets are
not lost, but some packet statistics may not be available.
Page 4-12 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 50

The Device/Board/Port Counters Screen
Frame Alignment Errors
Displays the number of errors due to misaligned packets.
CRC Errors
Displays the number of packets with bad Cyclical Redundancy Checks
(CRC) that have been recei ved from the netw ork. This error is caused by a
network device interfering with the original size of the packet when it is
transmitted or received.
Giant Packets
Displays the number of packets received whose size exceeded 1518 data
bytes, not including preamble. The originating station or transceiver is
responsible for creating giant packets.
Port Admin. Status
Displays the administrative status of the port. The two possible status
messages are ON or OFF. Status is affected by the Enable/Disable
Board/Port options and by the Port Association option.
Port Seg. Status
Displays the segmentation status of the port. The two possible status
messages are ON or SEG (Segmented). The port is normally ON, but is
segmented if 32 consecutive collisions occur.
4.4.3 Resetting the Device/Board/Port Counters
The Reset Counters option allows you to reset all counter information the
IRM3 has gathered to zero.
Reset the Device, Board, and Port counters as follows:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the RESET COUNTERS option at
the bottom of the Device/Board/Port Counters screen.
2. Press RETURN.
All counters will be reset to zero.
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 4-13
Page 51

Chapter 4: Local Management
4.4.4 Using the Enable Board/Disable Board Options
The Enable and Disable Board options allow you to enable or disable the
board that is displaying statistics at the Device/Board/Port Counters
screen.
Enable or disable the Board as follows:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the ENABLE BOARD or DISABLE
BOARD option at the bottom of the Device/Board/Port Counters
screen.
2. Press RETURN.
The Board is now Enabled or Disabled as selected.
4.4.5 Using the Enable Port/Disable Port Option
The Enable and Disable Port options allow you to enable or disable the
port that is displaying statistics at the Device/Board/Port Counters screen.
Enable or disable a port as follows:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the ENABLE PORT or DISABLE
PORT option at the bottom of the Device/Board/Port Counters screen.
2. Press RETURN.
The port will now be Enabled or Disabled as desired.
4.4.6 Available Options from the Device/Board/Port
Counters Screen
The Device/Board/Port Counters screen is the screen from which you
access all other screens or options available to manage your IRM3. Select
these options using the arrow keys to highlight the appropriate option at
the bottom of the screen and pressing RETURN. (The Board X, Port X,
and Reset Counters options were discussed in the previous sections.)
EXIT
If you select this option, you will exit out of Local Management for the
IRM3 to the Password screen.
Page 4-14 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 52

Community Names Screen
COMMUNITY NAMES
Select this option to designate community names for the devices attached
to your IRM3. With these names, you can set the SNMP compliant
network management workstations that will receive alarms from the
IRM3. Community names authenticate an SNMP request, since the IRM3
only responds to a community name contained in the Community Name
table.
Additionally, the Community Names screen acts as a password screen.
Any community name assigned Superuser access also acts as a password
to Local Management. Refer to Section 4.5 for more information.
SETUP
Select this option to set up parameters relating to the entire IRM3. Using
this option you can enter the IRM3 IP address, current date, and current
time. Refer to Section 4.6 for more information.
PORT ASSOCIATION
This option allows you to set the function of the IRM3 to either the AUI
port or the Fiber Optic Link port. Either port can be set as the repeater
port. Refer to Section 4.7 for more information.
TOKEN RING BOARD
This option enables you to select and monitor parameters for token ring
boards that are installed in the MMAC. Refer to Section 4.8 for more
information.
4.5 COMMUNITY NAMES SCREEN
Select the Community Names Option at the bottom of the
Device/Board/Port Counters screen (see Figure 4-4) to access the
Community Names screen shown in Figure 4-5. From this screen, you
decide the type of access SNMP workstations will have to the IRM3, and
whether those workstations will receive alarms from the device. You also
control read/write and Superuser access to your device. In addition, you
can change the password by entering new Superuser names or altering the
existing Superuser name.
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 4-15
Page 53

Chapter 4: Local Management
4.5.1 Accessing the Community Names Screen
To access the Community Names screen:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight COMMUNITY NAMES at the
bottom of the Device/Board/Port Counters screen (see Figure 4-4).
2. Press RETURN. The Community Names screen, Figure 4-5, appears.
The following describes the Community Names screen. Each field is
described, and instructions are given to set a Community Name.
COMMUNITY NAMES
Please note: SU names are local passwords
Community Name
public
ctron
SAVE RETURN
Access
RO
RW
SU
NA
NA
NA
NA
NA
Traps
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
Figure 4-5 Community Names Screen
4.5.2 Community Names Screen Fields
Trap IP Addr
0.0.0.0
0.0.0.0
0.0.0.0
0.0.0.0
0.0.0.0
0.0.0.0
0.0.0.0
0.0.0.0
0494115
The following briefly describes each field on the Community Names
screen.
Community Name
Displays the user defined name of the SNMP compliant network
management workstations that are allowed to control the IRM3 and
receive alarms.
Page 4-16 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 54

Community Names Screen
Access
Indicates the access status of the workstations. The possible conditions
are as follows:
• RO (Read Only)
These workstations have read only access to the IRM3.
• RW (Read/Write)
These workstations have read/write access. They can read and write to
the IRM3, but they cannot change the IP address or the Community
Names.
• SU (Superuser)
This is the Superuser workstation. It has read/write access to the IRM3
and can change all parameters including IP Address and Community
Names. Multiple Superusers can be assigned to have access to the
IRM3. In addition, any Community Name given Superuser Access
will act as a password to Local Management.
• NA (No Access)
These workstations have no access (read/write) to the IRM3.
Trap IP Address
Indicates the IP address of the management workstations that will receiv e
alarms from the IRM3.
4.5.3 Editing the Community Names Screen
Changing the factory default Superuser name, the RETURN
!
CAUTION
Make changes to the Community Names screen as follows:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the appropriate Community Name
field.
key, will change the password to Local Management. Any
Community name assigned Superuser access will be your
password to Local Management. Be sure to remember it.
2. Enter the user defined name of the workstation, up to 32 characters in
length, into the field.
3. Press RETURN. The Access field will be highlighted.
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 4-17
Page 55

Chapter 4: Local Management
4. Press RETURN until the appropriate selection appears. The Access
field is a toggle field that alternately displays RO, RW, SU, and NA
when you press RETURN.
5. Using the arrow keys highlight the TRAPS field.
6. Press RETURN until the appropriate selection appears. The TRAPS
field is a toggle field that alternately displays YES and NO when you
press RETURN. YES indicates alarms from the IRM3 will be sent to
the workstation. NO indicates alarms will not be sent from the IRM3
to the workstation.
7. Using the arrow keys, highlight the appropriate Trap IP address field.
8. Enter the IP address of the Network Management Station into the field
in dotted quad notation (XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX, where XXX is a
value between 0 and 255). The valid range is from 0.0.0.1 to
255.255.255.255. Press RETURN.
9. Using the arrow keys, highlight the SAVE command at the bottom of
the screen.
10. Press RETURN. You return to the IRM3 Main screen and the message
“Modified screen Information Has Been Saved!” appears on the
screen.
Alarms are now sent to the designated management workstations from the
IRM3, and the access modes will be implemented.
If a Community Name is given Superuser Access to the IRM3, the
Community Name also acts as a password to Local Management.
4.6 THE SETUP SCREEN
Using the IRM3 Setup option, you can set the IP address of the IRM3. In
addition, you can set the current date and time for your IRM3. The
following sections describe the Setup screen. Each field is described, and
instructions are given to alter applicable fields.
Once they are set, these options are saved in the battery backup memory
when you shut down your IRM3.
Page 4-18 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 56

The Setup Screen
4.6.1 Accessing the Setup Screen
To access the IRM3 Setup option:
1. Using the right arrow key, highlight the SETUP option at the bottom
of the Device/Board/Port Counters screen (see Figure 4-4).
2. Press RETURN. The Setup screen, Figure 4-6, appears.
11/15/91 14:28:49
Device Name: IRM3
SETUP
Ethernet Address:
IP Address:
Set IP Address:
Set Current Date:
Set Current Time:
Set Device Lock:
Set Refresh Time:
RETURN SAVE SETUP
134.141.52.48
11/15/91
14:28:49
UNLOCKED
10
Figure 4-6 Setup Screen
00-00-1d-00-39-14
134.141.52.48
0494116
4.6.2 Setup Screen Fields
The following briefly explains each field on the Setup screen.
Date
Displays the date to which the internal clock of the IRM3 is set.
Time
Displays the time, in a 24 hour format, to which the internal clock of the
IRM3 is set.
Device Name
Displays the name assigned to the device. The default name is IRM3.
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 4-19
Page 57

Chapter 4: Local Management
Ethernet Address
Displays the Ethernet address of the IRM3 in a hexadecimal format
(XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX).
IP Address and Set IP Address
Displays the current IP address of the IRM3.
Set Current Date
Displays the current date setting at the IRM3.
Set Current Time
Displays the current time setting (in 24 hour format) at the IRM3.
Set Device Lock
Displays the lock status of device. This can be set as either LOCKED or
UNLOCKED. This option enables/disables the source address security
for the IRM3. When enabled (LOCKED), the option prevents any new
source address access to the IRM3 through the station port. If the address
is not already in the source address database for that port, then the port is
turned off.
Set Refresh Time
Displays refresh time for the local console in seconds. The valid range is
from 2 to 99.
4.6.3 Setting the Set IP Address Option
To set the Set IP Address Option, perform the following steps:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the Set IP Address field.
2. Enter the IP address into the field in dotted quad notation
(XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX, where XXX is a value between 0 and 255).
The valid range is from 0.0.0.1 to 255.255.255.255.
3. Press RETURN. If an illegal IP address was entered in step 2, the error
message “Illegal Information Entered” appears on the screen.
4. Using the arrow keys, highlight the SAVE SETUP option at the
bottom of the Setup screen.
5. Press RETURN. The message “Modified screen Information Has
Been Saved!” appears on the screen.
Page 4-20 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 58

The Setup Screen
4.6.4 Setting the Set Current Date Option
To use the Set Current Date option, perform the following steps:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the Set Current Date field.
2. Enter the date into the field in a mm/dd/yy format.
3. Press RETURN. If an illegal date was entered in step 2, the error
message “Illegal Information Entered” appears on the screen.
4. Using the arrow keys, highlight the SAVE SETUP option at the
bottom of the Setup screen.
5. Press RETURN. The message “Modified screen Information Has
Been Saved!” appears on the screen.
4.6.5 Setting the Set Current Time Option
To set the Set Current Time option, perform the following steps:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the Set Current Time field.
2. Enter the time into the field in an hh:mm:ss format. Note that the time
is recorded in 24 hour format.
3. Press RETURN. If an illegal time was entered in step 2, the error
message “Illegal Information Entered” appears on the screen.
4. Using the arrow keys, highlight the SAVE SETUP option at the
bottom of the Setup screen.
5. Press RETURN. The message “Modified screen Information Has
Been Saved!” appears on the screen.
4.6.6 Setting the Device Lock Option
When the Device Lock Option is enabled, new source addresses cannot
access the IRM3 through the station port (a point to point port).
To set the Device Lock option perform the following steps:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the Set Device Lock field.
2. Press the RETURN key to toggle between the LOCKED and
UNLOCKED options.
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 4-21
Page 59

Chapter 4: Local Management
3. Using the arrow keys, highlight the SAVE SETUP option at the
bottom of the Setup screen.
4. Press RETURN. The message “Modified screen Information Has
Been Saved!” appears on the screen.
If you have just unlocked the device, you must also reenable
NOTE
the boards. Refer to Section 4.4.4 for information on
enabling/disabling boards.
4.6.7 Setting the Set Refresh Time Option
To set the Set Refresh Time option perform the follosing steps:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the Set Refresh Time field.
2. Enter the refresh time. The valid range is from 2 to 99 seconds.
3. Press RETURN. If an illegal value was entered, the error message
“Illegal Information Entered” appears on the screen.
4. Using the arrow keys, highlight the SAVE SETUP option at the
bottom of the Setup screen.
5. Press RETURN. The message “Modified screen Information Has
Been Saved!” appears on the screen.
4.7 PORT ASSOCIATION SCREEN
The Port Association option allows you to set which of the IRM3 ports,
the AUI port or Fiber Optic Link port, acts as the repeater port. The
following sections describe the Port Association. Each field is described
in detail, and instructions are given on setting the repeater port.
4.7.1 Accessing the Port Association Option
To access the Port Association Option, perform the following steps:
1. Using the arrow ke ys, highlight the PORT ASSOCIATION option at
the bottom of the IRM3 Main screen.
2. Press RETURN. The Port Association screen, Figure 4-7, appears.
Page 4-22 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 60

Port Association Screen
11/15/91 14:26:43
Device Name: IRM3
Figure 4-7 Port Association Screen
PORT ASSOCIATION
Ethernet Address:
IP Address:
AUI Port FIBER Port
REPEATER, OFF
RETURN SAVE ASSOCIA TION
00-00-1d-00-39-14
134.141.52.48
0494117
4.7.2 Port Association Screen Fields
The following briefly explains each field on the Port Association screen.
Date
Displays the date to which the internal clock of the IRM3 is set.
Time
Displays the time, in a 24 hour format, to which the internal clock of the
IRM3 is set.
Device Name
Displays the name assigned to the IRM3 repeater functionality.
Ethernet Address
Displays the Ethernet address of the IRM3 repeater functionality in a
hexadecimal format (XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX).
IP Address
Displays the current IP address of the IRM3.
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 4-23
Page 61

Chapter 4: Local Management
AUI Port, FIBER Port
Displays the port association configuration the IRM3 is currently using.
The available configurations are as follows:
• REPEATER, OFF
Indicates that the AUI port is acting as the repeater and the Fiber port
is off.
• OFF, REPEATER
Indicates that the AUI port is off and the fiber port is acting as the
repeater.
4.7.3 Changing the Port Association
To change the Port Association, perform the following steps:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the AUI Port FIBER Port field.
2. Press the RETURN key until the appropriate selection appears. This is
a toggle field that alternately displays the available configuration
choices when you press RETURN.
3. Highlight the SAVE ASSOCIATION option at the bottom of the Port
Association screen.
4. Press RETURN. The message “Modified screen Information Has
Been Saved!” appears on the screen.
4.8 THE TOKEN RING BOARD STATUS SCREEN
The Token Ring Board Status option allows you to manage the Token
Ring modules installed in the MMAC. You can enable/disable ports, set
the ring speed, and set station port, ring port, and FNB status. The
following sections describe each Token Ring Board Status screen field,
and instructions are given to alter applicable fields. Once they are set,
these options are saved in the battery backup memory when you shut
down your IRM3.
Page 4-24 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 62

The Token Ring Board Status Screen
4.8.1 Accessing the Token Ring Board Status Screen
Access the IRM3 Token Ring Board Status Option as follows:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the Token Ring Board Status option
on the Device/Board/Port Counters screen.
If no Token Ring boards are installed, the option will be NO
NOTE
2. Press RETURN. The Token Ring Board Status screen, Figure 4-8,
appears.
TOKEN RING BO ARDS , and y ou will not be ab le to access the
Token Ring Board Status screen.
11/5/91 14:26:43
Device Name: IRM3 Slot Number: 3
Board Name: Board 3 Board Type: TRRMIM-4A
STATION PORT STATUS Board Mode: AUTO
PORT STATUS PORT STATUS | RING PORT STATUS
1 ENB
2 ENB
3 ENB
4 ENB
5 ENB
6 ENB
7 ENB
8 ENB
9 ENB
10 ENB
11 ENB
12 ENB
RETURN
STATION PORT 1
Enable Disable
Token Ring Board Status
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SET BOARD TO AUTOMODE
RING PORT Status
RI RO
status On On
phantom On On
Media STP FIB
FNB Status
Left ..... Detached
Right ..... Detached
Bypass ..... Bypassed
Board Settings
Speed ..... 16MBS
Figure 4-8 Token Ring Board Status Screen
SAVE
0494117
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 4-25
Page 63

Chapter 4: Local Management
4.8.2 Token Ring Board Status Screen Fields
The following explains each field on the Token Ring Board Status screen.
Date
Displays the date to which the internal clock of the IRM3 is set.
Time
Displays the time, in a 24 hour format, to which the internal clock of the
IRM3 is set.
Device Name
Displays the name assigned to the device. The default name is IRM3.
Board Name
Displays the name assigned to the Token Ring board. The default name is
Board # (# = slot number).
Slot Number
MMAC slot number where the Token Ring Board is located.
Board T ype
Displays the Cabletron Systems model name of the board.
Port Status
Displays the current status of each station port on the Token Ring board.
This field is blank if you have selected a Token Ring board without station
ports. The following are the possible status conditions for each station
port (also refer to Table 4-1 for status conditions displayed for each
station port configuration):
• ENB (Enable)
Indicates that the station port is enabled. There is not a station attached
to the port.
• BYP (Bypass)
Indicates that the station port is bypassed. The station port is disabled.
Disabling a port makes insertion impossible.
• LNK (Link)
Indicates that the station port is disabled and the attached station is
operational.
Page 4-26 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 64

The Token Ring Board Status Screen
• INS (Inserted)
Indicates that the station port is enabled and the attached station is
operational (inserted into the ring). The station port must be enabled in
order for the station to be inserted into the ring.
Table 4-5 Station Port Configurations
Station Attached
(physical connection)
No Station Attached
(no physical connection)
Station Port #
Port Status
ENABLE
INS BYP
ENB LNK
Port Status
DISABLE
This field displays only when boards with station ports are installed. This
field is used to select a station port. You can set the station port to
ENABLE or DISABLE.
Board Mode
Indicates the mode status of the board. There are two possible status
conditions:
• AUTO
Indicates that the board is in auto mode and will operate according to
hardware default settings. The board remains in auto mode until a
setting is changed (i.e., disable a port, change ring speed).
• MGMT
Indicates that you have changed one or more default settings of the
board. Board remains in management mode until you use the Set
Board to Automode
a description of how to use this option.
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 4-27
option on this screen. Refer to the next section for
Page 65

Chapter 4: Local Management
Ring Port Status
The Ring Port Status fields display only when you have a Token Ring
concentrator module with externally accessible ring ports installed in the
MMAC. These fields provide the Ring In (RI) and Ring Out (RO)
conditions for the following:
• STATUS
Indicates the On or Off condition for the Ring In and Ring Out ports.
• PHANTOM
This field appears only with boards that support a phantom current.
Indicates the status of the phantom current. An ON status indicates that
the signal is being generated and that the port is inserted in the ring.
An OFF status indicates that no signal is being generated.
• MEDIA
This field displays only with boards that support media selection for
ring ports. Indicates the media type setting for the Ring In and Ring
Out ports: Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) or Fiber Optic.
FNB Status
Token Ring boards incorporate a Flexible Network Bus (FNB)
multiplexer which controls the FNB right and FNB left paths. Each slot
supports a left and a right multiplexer connection. Six possible FNB
status conditions are listed below:
• LEFT...... ATT ACHED
Indicates the board is attached to the left FNB multiplexer. This
indicates that the adjoining board has an open right FNB multiplexer
(as long as both boards are set to the same ring speed, and are not in a
bypass state).
• LEFT...... DETACHED
Indicates that the board is disconnected from the left FNB multiplexer.
This means it is also disconnected from all boards to its left in the
MMAC.
• LEFT...... FAULTED
Indicates that the Token Ring board has attempted to attach Left, but
failed. Some reasons for a faulted condition include the following: no
board inserted to the left, a non-Token Ring board inserted to the left,
or a Token Ring board is installed but not properly configured for a
connection (i.e., different ring speed setting).
Page 4-28 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 66

The Token Ring Board Status Screen
• RIGHT...... ATT ACHED
Indicates the board is attached to the right FNB multiplexer. This
indicates that the adjoining board has an open left FNB multiplexer (as
long as both boards are set to the same ring speed, and are not in a
bypass state).
• RIGHT...... DETACHED
Indicates that the board is disconnected from the right FNB
multiplexer. This means it is also disconnected from all boards to its
right in the MMAC.
• RIGHT...... FAULTED
Indicates that the Token Ring board has attempted to attach Right but
failed. Some reasons for a faulted condition include the following: no
board inserted to the right, a non-Token Ring board inserted to the
right, or a Token Ring board is installed but not properly configured
for a connection (i.e., different ring speed setting).
The Bypass status of the board is also displayed here. There are two
possible status conditions for this field:
• BYPASS...... BYPASSED
Indicates that the board is bypassed and all ports on the board are
acting as a self-contained ring.
• BYPASS...... INSERTED
Indicates that the board is inserted and all ports on the board can be
connected to a ring network, depending on the status of surrounding
boards and FNB connections.
Board Settings
Displays the speed setting for the board. There are two possible speed
settings: 4 Mbps and 16 Mbps.
4.8.3 Editing the Token Ring Board Status Screen
The following procedures describe ho w to change the Station Port Status,
Board Mode, Ring Port Status, FNB Status, and Board Speed settings on
the Token Ring Board Status screen.
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 4-29
Page 67

Chapter 4: Local Management
Changing Station Port Status
For Token Ring boards equipped with station ports, use the following
option to change Station Port Status for any port on the board:
1. Using the arrow keys, highlight the STATION PORT X (X = port
number) option.
2. Press the + key (press SHIFT and + keys) to increment the port number
or the - key to decrement the port number.
3. When you have selected the port number, use the arrow keys to
highlight either the ENABLE or DISABLE option.
4. Press RETURN. The Port Status field will display the new status of the
port. If you enabled the port, the Port Status will be either ENB or INS.
If disabled, the status will be BYP or LNK. Refer to the Port Status
field description in the previous section for an explanation of these
status conditions.
5. Station port status settings will be saved when you exit the screen (it
is not necessary to use the SAVE command).
Changing Board Mode
The Board Mode field displays the current board mode setting. The
default board mode setting is AUTO, indicating that the board is using the
factory defaults. When you alter any board setting (i.e., port status, board
speed), the mode changes to MGMT, indicating that the default settings
are no longer being used.
To set the board back to AUTO mode:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SET BOARD TO AUTOMODE
option.
2. Press RETURN. The Board Mode field will display the AUTO status.
3. The board settings return to the factory defaults when you exit the
screen (it is not necessary to use the SAVE command).
Page 4-30 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 68

The Token Ring Board Status Screen
Changing Ring Port Status
The Ring Port Status option displays only when a Token Ring board with
externally accessible ring ports is installed in the MMAC. The Ring Port
Status option enables you to turn the Ring In and Ring Out ports on or off.
Depending on the type of board you have installed, the phantom current
and media type options may also display.
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the RI or RO options for the Status
field.
2. Press RETURN to toggle between turning the port On or Off.
3. If the board has a phantom current setting, use the arrow keys to
highlight the RI or RO options for the Phantom field.
4. Press RETURN to toggle between turning the signal On or Off.
5. If the board has a media type setting, use the arrow keys to highlight
the RI or RO options for the Media field.
6. Press RETURN to toggle between the STP and FIB settings.
7. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command and press
RETURN. The message “Modified screen Information Has Been
Saved!” appears on the screen.
Changing FNB Status/Bypass Status
To change the FNB Status or Bypass Status for a board, perform the
following steps:
1. From the Device/Board/Port Counters screen, select the Token Ring
board that you want to configure. Refer to Section 4.8.1 for
information on selecting a board.
2. From the Token Ring Board Status screen, use the arrow keys to
highlight the LEFT or RIGHT option if you want to configure the FNB
multiplexer.
3. To change the board’s bypass status, highlight the BYPASS option.
4. If you selected the LEFT or RIGHT option, press RETURN to toggle
between ATTACHED and DETACHED. If you selected the BYPASS
option, press RETURN to toggle between BYPASSED and
INSERTED.
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 4-31
Page 69

Chapter 4: Local Management
5. Refer to the previous section for a description of the FNB status
conditions.
6. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command and press
RETURN. The message “Modified screen Information Has Been
Saved!” appears on the screen.
Changing the Board Speed Setting
Token Ring boards can operate at 4 Mbps or 16 Mbps. To change the
board speed setting, perform the following:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SPEED option.
2. Press RETURN to toggle between the 4 Mbps and 16 Mbps speed
settings.
3. Use the arrow ke ys to highlight the SAVE command and press Return.
The message “Modified Screen Information Has Been Saved!”
appears on the screen.
Page 4-32 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 70

CHAPTER 5
TROUBLESHOOTING
This chapter includes information that will enable you to troubleshoot
your IRM3 if a problem should occur. This chapter describes the
LANVIEW LEDs on the IRM3, provides a troubleshooting checklist, and
outlines the information you should have on hand if you need to call
Cabletron Systems Technical Support.
5.1 USING LANVIEW
The IRM3 uses Cabletron Systems built-in visual diagnostic and status
monitoring system called LANVIEW. With LANVIEW, network
troubleshooting personnel can quickly scan LEDs to observe network
status, or diagnose network problems. Figure 5-1 shows the location of
the LANVIEW LEDs.
LANVIEW LEDs
IRM3
SN
RESET
PWR BOK
MGMT RCV
CLN POK
ON PWR
A
U
I
ON LNK
T
X
0494119
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 5-1
Figure 5-1 LANVIEW LEDS
Page 71

Chapter 5: Troubleshooting
Table 5-1 LANVIEW Troubleshooting
LED COLOR DESCRIPTION
ERROR
CONDITION/RECOMMENDED
ACTION
PWR
(Power)
BOK
(Board OK)
RCV
(Receive)
Green Indicates that the
IRM3 is receiving
power from the
MMAC.
Green Indicates that the
board is operating
properly.
Yellow When flashing the
IRM3 is repeating
data packets from
segments connected
to the MMAC.
If off, the IRM3 has lost power.
Check the MMAC Power
Supply.
Ensure that the IRM3 is firmly
installed and properly
connected to the MMAC
backplane.
If off, there is an initialization
problem with the board.
Press the reset switch on the
front panel to reinitialize the
board. If the board does not
reinitialize, it has probably
failed. Call Cabletron Systems
Technical Support.
If off, the IRM3 is not repeating
packets.
Check that each module is
firmly installed in the MMAC.
MGT
Yellow When flashing, the
(Management)
POK (Port
Green When on, the
OK)
Page 5-2 IRM3 User’s Guide
IRM3 is receiving
and transmitting
management
packets.
Network Interface
Chip associated with
the internal repeater
port has passed an
internal loopback
test and is ready for
transmission.
Also, ports may have been
turned off by network
management. Check that all
ports are enabled.
If off, the management station is
not polling the IRM3. Check that
the Management station is
enabled.
If off, the port has failed the
loopback test.
Reinitialize the board by
pressing the reset switch. If the
LED still does not light, call
Cabletron Systems Technical
Support.
Page 72

Table 5-1 LANVIEW Troubleshooting (Continued)
LED COLOR DESCRIPTION
Using LANVIEW
ERROR
CONDITION/RECOMMENDED
ACTION
CLN
(Collision
Present)
PWR (AUI
port power)
ON
(Fiber/AUI
ports)
Red When flashing, a
collision is being
detected on one or
more segments
connected to the
MMAC . You should
note that periodic
flashing is normal.
Green When on, the AUI
port is receiving
power.
Green This LED is on for
the port selected as
the active repeater
port, and off for the
port that is off.
Excessive flashing or on solid
indicates excessive collisions.
Ensure that the SQE test is
disabled for any transceiver
connected to the AUI port.
Check cabling for data loops.
If the AUI port is the selected
repeater port and this LED is
off, the port is not receiving
power.
Check the fuse associated with
the port.
If both LEDs are off, reinitialize
the board by pressing the reset
switch, If still not lit, call
Cabletron Systems Technical
Support
LNK
(Link/
Fiber
Port)
Green When on, a link is
established
between the IRM3
Fiber port and the
fiber device at the
other end of the
segment. LED is on
as long as the link is
maintained. The port
generates a 1 MHz
idle signal to
maintain the link
when no data is
being transmitted.
If off, the link between the port
and fiber device has been
broken.
Check the connectors at each
end of the segment to ensure
that they are free of dust. Clean
the connectors if necessary.
Reconnect the segment and
check the Link LED again.
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 5-3
Page 73

Chapter 5: Troubleshooting
5.2 TROUBLESHOOTING CHECKLIST
If your IRM3 is not operating properly, the following checklist describes
some of the problems that may occur with the IRM3 installed in an
MMAC, possible causes for the problem, and suggestions for resolving
the problem. Figure 5-1 shows the LED locations.
Table 5-2 Troubleshooting Checklist
Problem Possible Causes Recommended Action
No LEDs on. Loss of power to the
MMAC.
No Local
Management
Password screen.
Cannot contact
IRM3 from in-band
management.
A port on the IRM3
cannot access the
network, while other
ports on the same
IRM3 are able to.
Terminal Setup not
correct.
Improper console
cable pin-outs.
Improper Community
Names table.
IRM3 does not have an
IP address.
No link to device.
The port is off or
segmented.
Port cable is defective.
Check that the MMAC power supply
module is properly installed and plugged
into a live outlet.
Check the power supply LEDs to see if
they are green.
Refer to Chapter 4 for setup procedures.
Refer to Chapter 4 or Appendix A for
console pinouts.
Refer to Chapter 4 for Community
Names table setup.
Refer to Chapter 4 for IP address
procedures.
Check link to device.
Use Local or Remote Management to
enable the port.
Use a different cable.
User parameters are
lost when device is
powered down.
No power to an
external transceiver
connected to AUI
port.
High number of
collisions on AUI
port.
Battery jumper (H1) is
in the wrong position,
or battery is not
charged.
Fuse F1 is blown.
AUI cable is defective.
External transceiver
has SQE enabled.
Page 5-4 IRM3 User’s Guide
Refer to Chapter 3 for the proper H1
jumper setting. If battery is defective, call
Cabletron Systems Technical Support.
Replace fuse.
Replace AUI cable.
Disable SQE.
Page 74

Using the Reset Switch
5.3 USING THE RESET SWITCH
The IRM3 incorporates a recessed Reset switch, located above the LEDs.
See Figure 5-1. This Reset switch initializes the IRM3 processor. This
will not initialize the RAM where your network management parameters
are stored.
To use the Reset switch, use a small screw driver to press the switch in.
When this is done, the IRM3 will initialize itself.
5.4 BEFORE CALLING TECHNICAL SUPPORT
If you are not able to resolve a problem with your IRM3, call Cabletron
Systems Technical Support for assistance (see Chapter 1, Section 1.6,
Getting Help). Before calling, you should have as much information as
possible available in order to save time and to allow the support
representative to better serve you. When calling technical support, be
prepared to provide the following:
• A detailed description of the failure.
• A description of any action already taken to resolve the problem
(swapping the bad unit with a unit known to work properly, etc.)
• A description of your network (environment, layout, cable type and
length, etc.)
• Serial numbers of all Cabletron Systems products used in the network.
• Revision level of all Cabletron Systems products in the network
• Revision level of firmware installed on all Cabletron Systems products
• The network load and frame size at the time of the failure, if known
• Product history (had the product been returned previously, did it have
the same problem, etc.)
• The RMA number generated, if any
IRM3 User’s Guide Page 5-5
Page 75

APPENDIX A
SPECIFICATIONS
The operating specifications for Cabletron Systems IRM3 are included in
this Appendix. Cabletron Systems reserves the right to change these
specifications at any time without notice.
A.1 REPEATER FUNCTIONALITY
Delay Times (Port x In to Port x Out):
Start of Packet: 1450 ns maximum.
Collision to JAM: 1550 ns maximum.
Preamble:
Input: Minimum of 40 bits to a maximum
of 64 bits required.
Output: 64 bits minimum (last 2 bits are 1,
1).
JAM Output: If a collision occurs on one of the
segments, a pattern of 1, 0 is sent to
the other segments.
Minimum Packet Repeated: 96 bits including preamble (packet
fragments are extended using the
JAM [1, 0] data pattern).
FAULT Protection: Each segment disconnects itself
from the other segments if 32
consecutive collisions occur, or if
the segment’s collision detector is
on for longer than approximately
2.4 ms. This FAULT protection
resets automatically after a packet
is transmitted onto the FAULT
protected segment without causing
a collision.
IRM3 User’s Guide Page A-1
Page 76

Appendix A: Specifications
A.2 AUI PORT
Type: 15 position D type receptacle
Connector Shell: Protective Ground
Table A-1 AUI Port Connections
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 Logic Ref. 6 Power Return 11 Logic Ref.
2 Collision + 7 No Connection 12 Receive -
3 Transmit + 8 Logic Ref. 13
4 Logic Ref. 9 Collision - 14 Logic Ref.
5 Receive + 10 Transmit - 15 No Connection
Power
(+12Vdc)
A.3 FIBER OPTIC INTERFACE
Internal Transceiver: Cabletron Systems FOT-F Fiber
Optic Transcei v er
Type: ST Ports
Error Rate: Better than 10
The transmitter power levels and receive sensitivity levels
NOTE
given above are Peak Power Levels after optical overshoot. A
Peak Power Meter must be used to correctly compare the
values given abo v e to those measured on an y particular port. If
Power Levels are being measured with an Average Power
Meter, then 3 dBm must be added to the measurement to
correctly compare those measured values to the values listed
above (i.e., -30.5 dBm peak=-33.5 dBm average).
-10
Page A-2 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 77

Console Port
A.4 CONSOLE PORT
Type: Standard 9-pin RS232 Port
Table A-2 RS232 Port Pinouts
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 Carrier Detect (CD) 6 Receive Clock (RXCL)
2 Transmit (TXD) 7 Ready to Send (RTS)
3 Receive (RXD) 8 Clear to Send (CTS)
4 Data Terminal Ready (DTR) 9 Ring Indicator (RI)
5 Logic Reference
A.5 MICROPROCESSORS AND MEMORY
MICROPROCESSORS
Processor Type: Intel 80C186
LAN Controllers: National Semiconductor 8390
MEMORY
Dynamic RAM: 896 k
Static RAM: 128 k
ROM: 128 k
FLASH EPROM
Flash EPROM memory: 256 k bytes organized in
two 128 k x 8 chips
The Flash EPROM memory enables users to upgrade the IRM3 firmware
remotely. A special three page memory scheme allows for programming
the Flash EPROM as well as creating additional board functionality.
A.6 ENVIRONMENTAL REQUIREMENTS
Operating Temperature: +5°C to +40°C (+41°F to +104°F)
Storage Temperature: -30°C to +90°C (-22°F to +194°F)
Operating Humidity: 5% to 95% (non-condensing)
IRM3 User’s Guide Page A-3
Page 78

Appendix A: Specifications
A.7 AGENCY APPROVALS
SAFETY
Designed in accordance with UL1950, CSA C22.2, N0. 950, EN60950,
and IEC950.
Emissions
The IRM3 meets the emission requirements of FCC class A, EN55022
class A, and VCCI class I.
It is the responsibility of the person who sells the system of
NOTE
Immunity
The IRM3 complies with the requirements of EN 50082, which includes
IEC 801-2 Electrostatic Discharge, IEC 801-3 Radiated Susceptibility,
and IEC 801-4 Electric Fast Transient/Burst.
which the IRM3 will be a part to ensure that the total system
meets allowed limits of conducted and radiated emissions.
A.8 SERVICE
MTBF (MHBK-217): >175,202 hrs projected
MTTR <0.5 hr
A.9 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
Dimensions: 29.21H x 2.54W x 34.07D cm
(11.5H x 1.0W x 13.4D in)
Weight:
Unit: 0.85 kg (1.95 lbs)
Shipping: 1.34 kg (2.95 lbs)
Page A-4 IRM3 User’s Guide
Page 79

INDEX
A
Attenuation 2-2
AUI Port 4-24
AUI Port Requirements 2-1
AUTO 4-27
B
Battery Enable/Disable 3-2
Board Mode 4-27, 4-30
Board Settings 4-29
Board Speed 4-32
BYP 4-26
C
Cable length 2-3
Community Names 4-15
Community Names Screen
accessing 4-16
editing 4-17
fields 4-16
CRC Errors 4-13
D
Date 4-21
Device Name 4-19
Device/Board/Port Counters Screen
configuring 4-11
fields 4-12
options 4-14
resetting 4-13
E
ENB 4-26
Ethernet Address 4-20
FNB Status 4-28
FOMIM 2-4
H
Help 1-7
I
INS 4-27
IP Address 4-17, 4-20
IRM3
description 1-2
features 1-5
front panel 1-4
installation 3-1
installing into an MMAC 3-4
jumper locations 3-3
jumpers 3-2
locking 4-21
unpacking 3-1
J
Jumpers
CTS (H6,H8) 3-3
H1 3-2
setting 3-2
THN-MIM (JP1) 3-4
L
LANVIEW LEDs 3-6
location 5-1
LNK 4-26
Local Management
accessing 4-3
accessing with a modem 4-7
screen flow 4-2
F
Fiber Optic
cable 2-2
port 4-24
port requirements 2-2
IRM3 User’s Guide Index-1
M
Media 4-28
Media Interface Modules 2-4
MGMT 4-27
Page 80

Index
MMAC 2-3
Modem
configurations 4-7
connecting 4-8
MT8-MIM 2-4
N
Network
configurations 2-5
connecting to 3-8
management capabilities 1-6
requirements 2-1
O
Out of Window Collisions 4-12
P
Phantom 4-28
Port Admin. Status 4-13
Port Association 4-15
Port Association Screen
accessing 4-22
fields 4-23
Port Seg. Status 4-13
Ports
AUI 2-1, 3-8
console 3-13
description 1-4
fiber optic 2-2, 3-9
location 1-3
Propagation Delay 2-3
Setup 4-18
Token Ring Board Status 4-24
Setup Screen
accessing 4-19
fields 4-19
Signal Quality Error 2-2
Specifications A-1
Status 4-28
Superuser name 4-17
T
Terminal
cable pinouts 4-4
configuring 4-3
Testing
post-installation 3-12
pre-installation 3-7
THN-MIM 2-4
Time 4-21
Token Ring Board 4-15
Token Ring Board Status Screen
accessing 4-25
editing 4-29
fields 4-26
TPMIM 2-4
TRAPS field 4-18
TRMIM 2-5
Troubleshooting 5-1
U
Using LANVIEW 5-1
R
Reset Switch 5-5
Ring Port Status 4-28, 4-31
Runt Packets 4-12
S
Screens
Community Names 4-15
Device/Board/Port Counters 4-10
Password 4-9
Port Association 4-22
Index-2 IRM3 User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...