Page 1

Title Page
®
Portable Management Application
for the
EMM-E6
User’s Guide
Page 2

Page 3

Notice
Cabletron Systems reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information
contained in this document without prior notice. The reader should in all cases consult Cabletron
Systems to determine whether any such changes have been made.
The hardware, firmware, or software described in this manual is subject to change without notice.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CABLETRON SYSTEMS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INCIDENTAL, INDIRECT,
SPECIAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES WHATSOEVER (INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED
TO LOST PROFITS) ARISING OUT OF OR RELATED TO THIS MANUAL OR THE INFORMATION
CONTAINED IN IT, EVEN IF CABLETRON SYSTEMS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF, KNOWN, OR
SHOULD HAVE KNOWN, THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Virus Disclaimer
Cabletron has tested its software with current virus checking technologies. However, because no
anti-virus system is 100% reliable, we strongly caution you to write protect and then verify that the
Licensed Software, prior to installing it, is virus-free with an anti-virus system in which you have
confidence.
Cabletron Systems makes no representations or warranties to the effect that the Licensed Software is
virus-free.
Copyright © 1998 by Cabletron Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Printed in the United States of America.
Order Number: 9030964-E7 April 1998
Cabletron Systems, Inc.
35 Industrial Way, P.O. Box 5005
Rochester, NH 03867-0505
SPECTRUM , MiniMMAC , FNB , Multi Media Access Center , and DNI are registered trademarks,
and Portable Management Application , IRM , IRM2 , IRM3 , IRBM , ETSMIM , EFDMIM , EMME ,
ETWMIM , FDMMIM , FDCMIM , MRXI , MRXI-24 , NB20E , NB25E , NB30 , NB35E , SEHI , TRBMIM ,
TRMM , TRMMIM , TRXI , Media Interface Module , MIM , and Flexible Network Bus are
trademarks of Cabletron Systems, Inc.
UNIX and OPENLOOK is a trademark of Unix System Laboratories, Inc. OSF/Motif and Motif are
trademarks of the Open Software Foundation, Inc. X Window System is a trademark of Massachusetts
Institute of Technology. Ethernet and XNS are trademarks of Xerox Corporation. Apple and
AppleTalk are registered trademarks of Apple Computer, Inc. Banyan is a registered trademark of
Banyan Systems, Inc. DEC net is a registered trademark of Digital Equipment Corporation. Novell is a
registered trademark of Novell, Inc. CompuServe is a registered trademark of CompuServe. Sun
Microsystems is a registered trademark, and Sun , SunNet , and OpenWindows are trademarks of Sun
Microsystems, Inc.
i
Page 4

Restricted Rights Notice
(Applicable to licenses to the United States Government only.)
1. Use, duplication, or disclosure by the Government is subject to restrictions as set forth in
subparagraph (c) (1) (ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software clause at DFARS
252.227-7013.
Cabletron Systems, Inc., 35 Industrial Way, Rochester, New Hampshire 03867-0505.
2. (a) This computer software is submitted with restricted rights. It may not be used, reproduced, or
disclosed by the Government except as provided in paragraph (b) of this Notice or as otherwise
expressly stated in the contract.
(b) This computer software may be:
(1) Used or copied for use in or with the computer or computers for which it was acquired,
including use at any Government installation to which such computer or computers may
be transferred;
(2) Used or copied for use in a backup computer if any computer for which it was acquired
is inoperative;
(3) Reproduced for safekeeping (archives) or backup purposes;
(4) Modified, adapted, or combined with other computer software, provided that the
modified, combined, or adapted portions of the derivative software incorporating
restricted computer software are made subject to the same restricted rights;
(5) Disclosed to and reproduced for use by support service contractors in accordance with
subparagraphs (b) (1) through (4) of this clause, provided the Government makes such
disclosure or reproduction subject to these restricted rights; and
(6) Used or copied for use in or transferred to a replacement computer.
(c) Notwithstanding the foregoing, if this computer software is published copyrighted computer
software, it is licensed to the Government, without disclosure prohibitions, with the minimum
rights set forth in paragraph (b) of this clause.
(d) Any other rights or limitations regarding the use, duplication, or disclosure of this computer
software are to be expressly stated in, or incorporated in, the contract.
(e) This Notice shall be marked on any reproduction of this computer software, in whole or in part.
ii
Page 5

Chapter 1 Introduction
Using the EMM-E6 User’s Guide ...............................................................................1-1
What’s NOT in the EMM-E6 User’s Guide. . .................................................... 1-3
Conventions................................................................................................................... 1-4
Screen Displays ......................................................................................................1-5
Using the Mouse ....................................................................................................1-6
Getting Help .................................................................................................................. 1-7
EMM-E6 Firmware ....................................................................................................... 1-8
Year 2000 Compliance...........................................................................................1-8
Contents
Chapter 2 Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
Using the Hub View.....................................................................................................2-1
Navigating Through the Hub View ....................................................................2-2
Hub View Front Panel........................................................................................... 2-2
EMM-E6 Ports Display.......................................................................................... 2-5
Using the Mouse in a Hub View Module........................................................... 2-6
Hub View Port Color Codes.................................................................................2-7
Monitoring Hub Performance..................................................................................... 2-8
Port Display Form..................................................................................................2-9
Checking Device Status and Updating Front Panel Info...............................2-13
Checking Network Status...................................................................................2-14
Checking Module Status.....................................................................................2-16
Checking Port Status...........................................................................................2-17
Viewing the IP Address Table ............................................................................ 2-19
Launching the Global Find MAC Address Tool.............................................. 2-20
Checking Statistics............................................................................................... 2-20
General/Error Statistics............................................................................... 2-22
The EMM-E6 Error Priority Scheme..........................................................2-24
Protocols/Frames Statistics......................................................................... 2-25
Viewing the Port Source Address List..............................................................2-25
Managing the Hub...................................................................................................... 2-27
Setting the Polling Intervals...............................................................................2-27
Configuring FNB Connections........................................................................... 2-29
Configuring RIC MIM Connections........................................................... 2-30
Configuring TPXMIM Connections........................................................... 2-30
Setting a Port’s Trunk Type ................................................................................2-32
Enabling/Disabling MIM Ports......................................................................... 2-34
iii
Page 6

Contents
Chapter 3 Alarm Configuration
Using Alarm Configuration.........................................................................................3-2
Configuring Alarms...............................................................................................3-3
Setting Repeater Alarms...............................................................................................3-4
Setting and Changing Alarms..............................................................................3-5
Setting Module and Port Alarms................................................................................3-6
Setting Module Alarms.........................................................................................3-6
Setting Port Alarms................................................................................................3-8
Chapter 4 Link/Seg Traps
What is a Segmentation Trap?.....................................................................................4-1
What is a Link Trap?.....................................................................................................4-2
Enabling and Disabling Link/Seg Traps ...................................................................4-2
Configuring Link/Seg Traps for the Repeater...................................................4-4
Viewing and Configuring Link/Seg Traps for Hub Modules.........................4-4
Viewing and Configuring Link/Seg Traps for Ports ........................................4-6
Chapter 5 Repeater Redundancy
Setting Network Circuit Redundancy........................................................................5-1
Configuring a Redundant Circuit........................................................................5-2
Monitoring Redundancy..............................................................................................5-6
Chapter 6 Source Addressing
Displaying the Source Address List............................................................................6-1
Setting the Aging Time..........................................................................................6-4
Setting the Hash Type................................................................................................... 6-4
Locking Source Addresses...........................................................................................6-5
Source Address Locking on Older Devices........................................................6-6
Configuring Source Address Traps.............................................................................6-7
Repeater-level Traps..............................................................................................6-8
Module- and Port-level Traps...............................................................................6-9
Finding a Source Address ..........................................................................................6-11
Chapter 7 Security
What is LANVIEWsecure?...........................................................................................7-2
The Newest LANVIEWsecure Features..............................................................7-4
Security on Non-LANVIEWsecure MIMs..........................................................7-5
Configuring Security.....................................................................................................7-6
Boards with Multiple Caches.............................................................................7-10
Resetting Learned Addresses............................................................................. 7-11
Tips for Successfully Implementing Eavesdropper Protection.....................7-11
iv
Page 7

Enabling Security and Traps......................................................................................7-12
Repeater-level Security and Traps.....................................................................7-14
Module-level Security and Traps....................................................................... 7-15
Port-level Security and Traps............................................................................. 7-17
Chapter 8 Front Panel Redundancy
Setting Front Panel Redundancy................................................................................8-1
Configuring a Redundant Circuit........................................................................8-2
Appendix A EMM-E6 MIB Structure
IETF MIB Support........................................................................................................A-1
EMM-E6 MIB Structure............................................................................................... A-1
MIB Components.................................................................................................. A-2
A Brief Word About MIB Components and Community Names.................. A-5
Contents
v
Page 8

Contents
vi
Page 9

Chapter 1
Introduction
How to use the EMM-E6 User’s Guide; manual conventions; contacting the Cabletron Systems Global
Call Center; EMM-E6 firmware versions supported by SPMA
The EMM-E6 (Ethernet Management Module for Ethernet with six ports)
provides intelligence for Cabletron Systems’ Multi-Media Access Center (MMAC)
hubs. The EMM-E6 is designed to work with the repeater MIM family of media
interface modules (FORMIM, CXRMIM, TPRMIM, and TPXMIM) to take full
advantage of the MMAC Flexible Network Bus (FNB). The EMM-E6 uses the
dedicated Ethernet channel (channel A) on the MMAC backplane and creates two
more Ethernet channels (B and C) using the FNB, then bridges among these three
interfaces, as well as a fourth channel (D) provided by a set of redundant EPIM
ports located on its front panel. Fifth and sixth channels are provided by optional
BRIM modules, also installed on the front panel, which support cross-platform
bridging and routing. The EMM-E6 also provides management and serves as a
repeater for older MIMs that are not part of the repeater MIM family.
Although the Hub View window displays the presence and general status (on or off) of
NOTE
any installed BRIM modules, you cannot perform any management of BRIM ports from
the Hub View application. The functions associated with any BRIM modules installed in
your EMM-E6 can be configured and managed via the SPMA BRIM Launcher
application; the BRIM Launcher is described in the SPMA BRIM User’s Guide .
Using the EMM-E6 User’s Guide
Your SPECTRUM Portable Management Application (SPMA) for the EMM-E6
consists of a number of different applications, each of which provides a portion of
the overall management functionality. Each of these applications can be accessed
from the icon menu (if you are using a management platform) and from the
1-1
Page 10

Introduction
Stand-alone Launcher or the command line (if you are running in stand-alone
mode); in addition, several applications can also be accessed from within the Hub
View, a graphical display of the EMM-E6 and the hub it is managing.
The EMM-E6 User’s Guide describes how to use many of the applications
included with the module; note that the instructions provided in this guide apply
to the EMM-E6 module regardless of the operating system or management
platform you are using. Instructions for launching each individual function from
the command line (stand-alone mode) are also included in each chapter.
Following is a description of the applications covered in this guide; while we
provide as much background information as we can, we do assume that you’re
familiar with Ethernet networks and general network management concepts:
• Chapter 1, Introduction , provides a list of related documentation, describes
certain software conventions, and shows you how to contact the Cabletron
Systems Global Call Center.
• Chapter 2, Using the EMM-E6 Hub View , describes the visual display of the
Hub and explains how to use the mouse within the Hub View; the operation
of some basic functions (changing the Hub View display, opening menus and
windows, enabling and disabling ports, checking device and module status,
and so on) available only from within the Hub V iew is also described. You can
access the Hub View application from the icon menu or the command line.
• Chapter 3, Alarm Configuration , describes how to set thresholds and enable
or disable alarms at the network (channel), module, and port levels. You can
access the Alarm Configuration application from the icon menu, the Hub V iew ,
or the command line.
• Chapter 4, Link/Seg Traps , describes how to configure link and segmentation
traps to suit your management needs. You can access the Link/Seg Traps
application from the icon menu, the Hub View, or the command line.
• Chapter 5, Redundancy , describes how to configure redundant circuits to keep
your network connections up and running in the event of a single port’s
failure. You can access the Redundancy application from the icon menu, the
Hub View, or the command line.
• Chapter 6, Source Addressing , describes how to display the Source Address
List, how to set the ageing time, and how to configure source address traps; it
also discusses the effects of source address locking. You can access the Source
Address application from the icon menu, the Hub View, or the command line.
• Chapter 7, Security , describes how to configure intruder protection for all
MIMs installed in the EMM-E6-controlled hub, and how to configure
eavesdropper protection for any installed
LANVIEW
SECURE
MIMs. You can
access the Security application from the icon menu, the Hub View, or the
command line.
1-2 Using the EMM-E6 User’s Guide
Page 11

• Chapter 8, Front Panel Redundancy , describes how to configure redundancy
for the two Channel D EPIM ports on the EMM-E6’s front panel. You can
access the Front Panel Redundancy application from the icon menu, the Hub
View, or the command line.
• Appendix A, EMM-E6 MIB Components , lists the IETF MIBs supported by
the EMM-E6, and describes their arrangement in a series of MIB components.
A description of the objects controlled by each component is also included.
What’s NOT in the EMM-E6 User’s Guide. . .
The following standard SPMA tools are available through the EMM-E6 module
and are explained in the SPECTRUM Portable Management Application Tools
Guide :
• Bridge View
Introduction
• Charts, Graphs, and Meters
• Community Names
• Distributed LAN Monitor (DLM)
• MIB I, II
• MIBTree
• Path
• Telnet
• TFTP Download
• Trap Table
• UPS
• Utilities (Global Community Names, Find MAC Address and TFTP)
Charts, Graphs, and Meters are accessible from the Hub View and the command
line; the Utilities, MIBTree, and RMON Configuration applications are accessible
from the platform console window Tools menu, the Stand-alone Launcher
applications menu, or the command line; and the rest of the tool applications
(except Telnet) are available from the icon menu, the Hub View, or the command
line. (The T elnet application is available only fr om the icon menu or the command
line.)
An additional application may also appear on the platform console window T ools
menu or the Stand-alone Launcher applications menu:
• RMON Configuration
Note that this application must be purchased separately, and is documented in its
own User’s Guide .
Using the EMM-E6 User’s Guide 1-3
Page 12

Introduction
NOTE
If you are using SPMA in a stand-alone mode or in conjunction with the SunNet
Manager or Solstice Enterprise Manager platforms, the RMON option will be available
for all appropriate devices whether or not you have purchased the RMON application
module. If you are using SPMA in conjunction with HP Network Node Manager or IBM
NetView, however, the RMON option will only appear when the module has been
purchased and installed.
Instructions on discovering Cabletron devices, creating icons, and accessing the
icon menus within your management platform are included in your Installing
and Using SPECTRUM for... guide. If you are using SPMA for the EMM-E6 in
stand-alone mode — that is, without benefit of a specific network management
system — instructions for starting each application from the command line are
included in each chapter of this guide and the
SPMA Tools Guide .
NOTE
NOTE
Graphing capabilities are provided by an application that is included in HP Network
Node Manager and IBM NetView; therefore, graphs are only available when SPMA is
run in conjunction with one of these network management platforms. If you are running
SPMA in a stand-alone mode or in conjunction with SunNet Manager or Solstice
Enterprise Manager, no graphing capabilities are available and no graph-related options
will be displayed on buttons or menus. Note that the screens displayed in this guide will
include the graph-related options where they are available; please disregard these
references if they do not apply.
Also available from the icon menu or the command line is the option which
provides access to BRIM-related applications and two options which provide
access to router-related applications: the BRIM option is described in the SPMA
BRIM Applications User’s Guide ; the Basic Router Config , and Advanced
Router Config , options are described in documentation shipped with your order
of routing applications, which must be purchased separately.
Please note that the routing functionality for your EMM-E6, as well as the SPMA
management modules that allow you to configure and manage that functionality, must be
purchased separately. Contact the Cabletron Systems Global Call Center or your local
sales representative for more information.
Conventions
SPECTRUM Portable Management Applications — including the EMM-E6
module — can work with a number of different network management systems
running on several different operating systems and graphical user interfaces. This
versatility presents two documentation problems: first, there is no standard
terminology; and second, the appearance of the windows will differ based on the
1-4 Conventions
Page 13
graphical interface in use. For the sake of consistency, the following conventions
will be followed throughout this and other SPMA guides.
Screen Displays
SPMA runs under a variety of different operating systems and graphical user
interfaces. To maintain a consistent presentation, screen displays in this and other
SPMA guides show an OSF/Motif envir onment. If you’r e used to a dif fer ent GUI,
don’t worry; the differences are minor. Buttons, boxes, borders, and menus
displayed on your screen may look a bit different fr om what you see in the guide,
but they’re organized and labelled the same, located in the same places, and
perform the same functions in all screen environments.
Some windows within SPMA applications can be re-sized; those windows will
display the standard window resizing handles employed by your windowing
system. Re-sizing a window doesn’t re-size the information in the window; it just
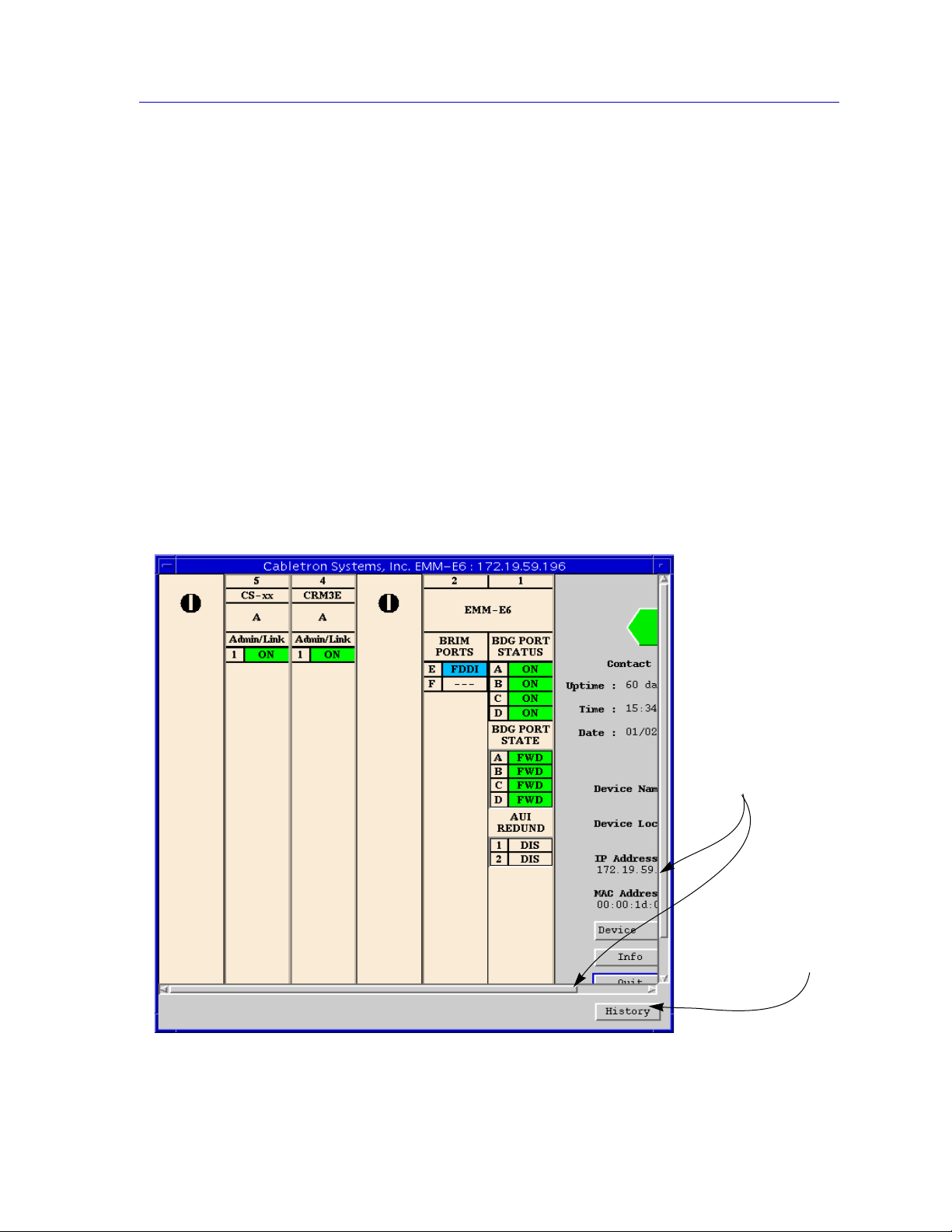
changes the amount of information that can be displayed (see Figure 1-1). When
you shrink a window, scroll bars will appear as necessary so that you can scroll to
view all the information that is available.
Introduction
Use the scroll bars
provided to choose
what to display in a
window that’s been
resized
Click here to
display footer
message history
Figure 1-1. Window Conventions
Conventions 1-5
Page 14
Introduction
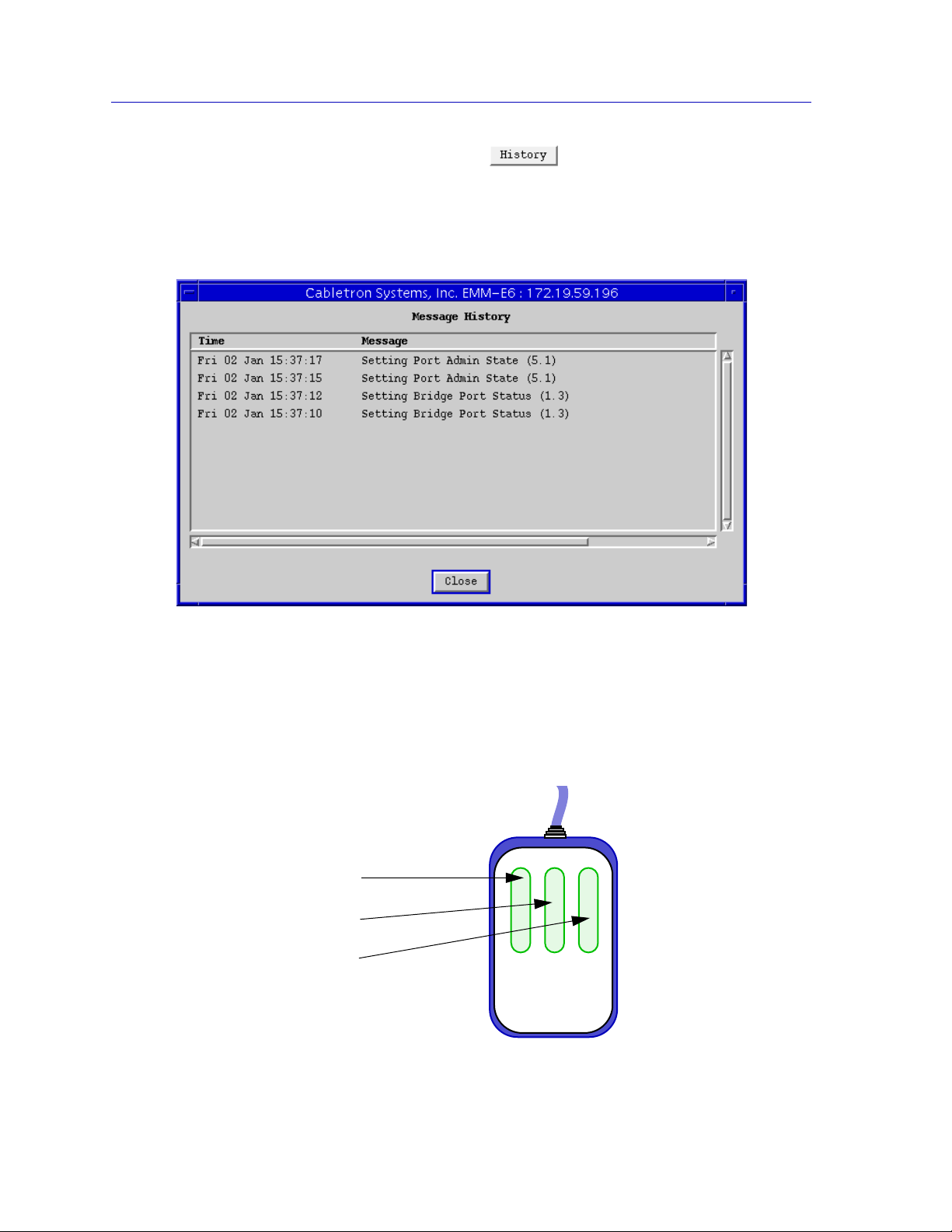
Some windows will also contain a button; selecting this button
launches a History window (Figure 1-2) which lists all footer messages that have
been displayed since the window was first invoked. This window can help you
keep track of management actions you have taken since launching a management
application.
Using the Mouse
The UNIX mouse has three buttons. Procedures within the SPMA document set
refer to these buttons as follows:
Figure 1-2. The History Window
Button 1
Button 2
Button 3
Figure 1-3. Mouse Buttons
1-6 Conventions
Page 15

Introduction
If you’re using a two-button mouse, don’t worry. SPMA doesn’t make use of
mouse button 2. Just click the left button for button 1 and the right mouse button
when instructed to use mouse button 3.
Whenever possible, we will instruct you on which mouse button to employ;
however, menu buttons within SPMA applications will operate according to the
convention employed by the active windowing system. By convention, menu
buttons under the Motif windowing environment are activated by clicking the left
mouse button (referred to as mouse button 1 in SPMA documentation), and there
is no response to clicking the right button (mouse button 3). Under
OpenWindows, menu buttons can be activated by clicking the right button, and
convention dictates that the left button activates a default menu option; within
SPMA, that default option will also display the entire menu. Because of this
difference, references to activating a menu button will not include instructions
about which mouse button to use. All other panels from which menus can be
accessed, and all buttons which do not provide access to menus, will operate
according to SPMA convention, as documented.
Getting Help
If you need technical support related to SPMA, or if you have any questions,
comments, or suggestions related to this manual or any of our products, please
feel free to contact the Cabletron Systems Global Call Center. Before calling,
please have the following information ready:
• The product name and part number.
• The version number of the program that you need help with. SPMA is
Y ou can contact the Cabletr on Systems Global Call Center via any of the following
methods:
By phone: Monday through Friday between 8 AM and 8 PM
By mail: Cabletron Systems, Inc.
By Internet mail: support@ctron.com
modular, which means each application will have a specific revision number.
Where applicable, an INFO button provides the version number; you can also
view the version number for any application by typing the command to start
the application followed by a -v.
Eastern Standard Time at (603) 332-9400.
PO Box 5005
Rochester, NH 03866-5005
FTP: ftp.ctron.com (134.141.197.25)
Login anonymous
Password your email address
By BBS: (603) 335-3358
Getting Help 1-7
Page 16

Modem Setting 8N1: 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, No parity
For additional information about Cabletron Systems products, visit our
World Wide Web site: http://www.cabletron.com/. For technical support,
select Service and Support.
EMM-E6 Firmware
SPMA for the EMM-E6 has been tested against firmware versions 3.22.01; if you
have an earlier version of firmware and experience problems running SPMA
contact the Cabletron Systems Global Call Center for upgrade information.
As a general rule, firmware versions for new products are liable to change rapidly; contact
NOTE
the Cabletron Systems Global Call Center for upgrade information for the latest customer
release of firmware.
Introduction
Year 2000 Compliance
Previous users of SPMA will note a few display changes related to Year 2000
compliance. All SPMA applications now have the ability to display a four-digit
year value where this information is available. For example, the Stand-alone
Launcher window — which uses your workstation’s system time value to display
the time and date of the last contact change — will now display these date values
with eight digits (05/31/1998) instead of six (05/31/98).
Please keep in mind, however, that SPMA’s ability to display a four-digit year
value in device-specific windows — such as the Device Status window available
from the Hub View or the Bridge View — is dependent on the firmware’s ability
to provide a four -digit value. Not all firmware versions support this ability; contact
Cabletron Systems’ Global Call Center for information specific to your device
firmware.
EMM-E6 Firmware 1-8
Page 17

Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
Navigating through the Hub View; monitoring hub performance; managing the hub
The heart of the SPECTRUM Portable Management Application (SPMA) for the
EMM-E6 is the Hub View, a graphical interface that gives you access to many of
the functions that provide control over the EMM-E6-managed hub.
Using the Hub View
There are two ways to open the Hub View: if you are working within a network
management system, you can select the Hub View option from the icon menu;
specific directions for creating a EMM-E6 icon and accessing the icon menu can be
found in the appropriate Installing and Using SPECTRUM for ... guide. If you are
running the EMM-E6 module in a stand-alone mode, type the following at the
command line:
Chapter 2
NOTES
spmarun emme <IP address> <community name>
The community name you use to start the module must have at least Read access;
for full management functionality, you should use a community name that
provides Read/Write or Superuser access. For more information on community
names, consult the appropriate Installing and Using SPECTRUM for... guide,
and/or the Community Names chapter in the SPMA Tools Guide.
The spmarun script invoked first in the above command temporarily sets the environment
variables SPMA needs to operate; be sure to use this command any time you launch an
application from the command line. This script is automatically invoked when you launch
an application from the icon menu or from within the Hub View.
If there is a hostname mapped to your EMM-E6’s IP address, you can use <hostname>
in place of <IP addr ess> to launch the Hub View . Please note, however, that the hostname
is not the same as the device name which can be assigned via Local Management and/or
SPMA; you cannot use the device name in place of the IP address.
2-1
Page 18
Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
Navigating Through the Hub View
Within the Hub View, you can click mouse buttons in different areas of the
window to access various menus and initiate certain management tasks. The
following diagrams describe the information displayed in the Hub View and
show you how to use the mouse to display the Device, Network, Module, and
Port menus.
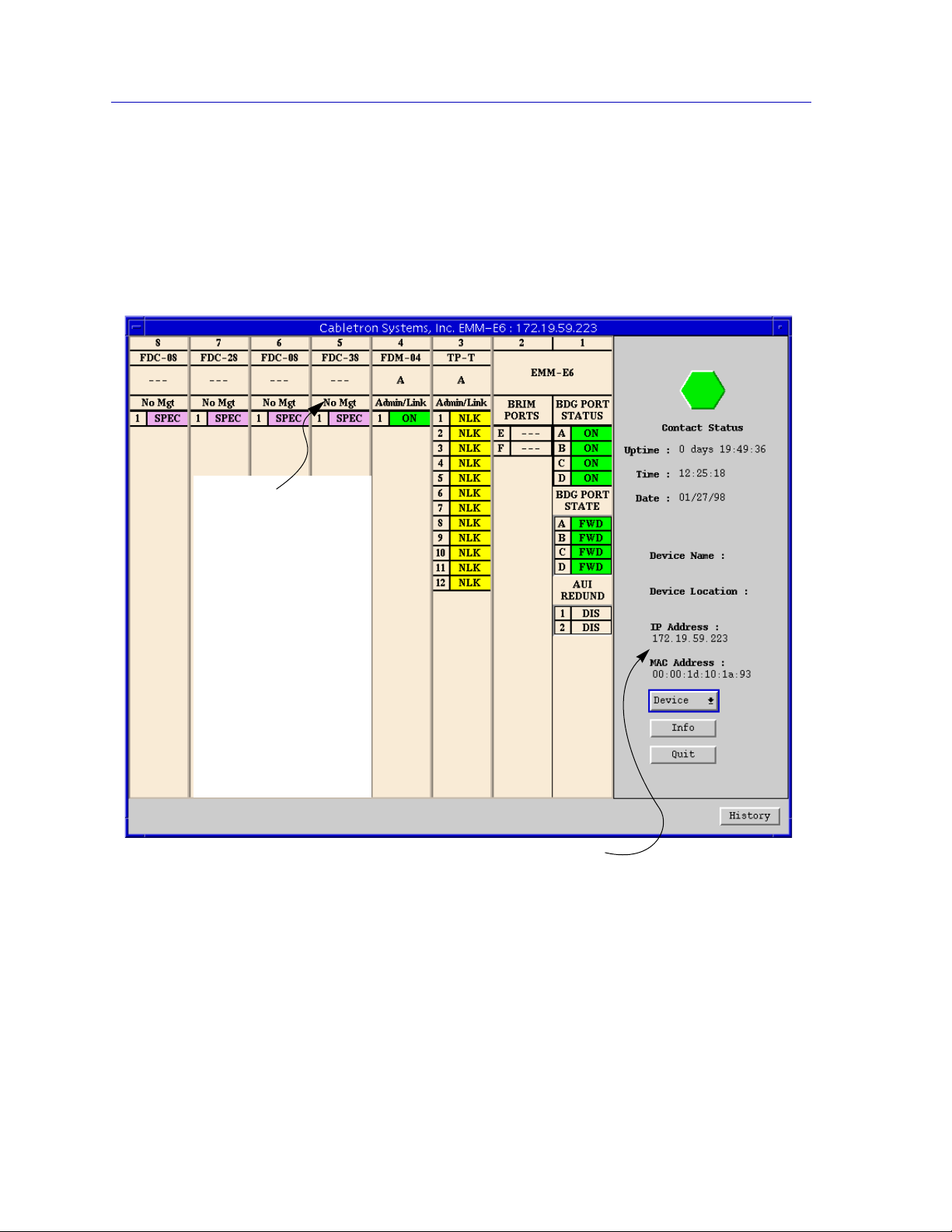
No Mgmt
Depending on the
version of firmware
installed in your
EMM-E6, certain MIMs
either may not display
at all, or may display
with the message “No
Mgt” in the Port Display
Form box. For more
information about the
specific capabilities of
different versions of
EMM-E6 firmware,
contact the Cabletron
Systems Global Call
Center.
Front Panel
Device summary information
Figure 2-1. EMM-E6 Hub View
Hub View Front Panel
In addition to the graphical display of the modules, the Hub View gives you
device level summary information. The following Front Panel information
appears to the right of the module display in the Hub View:
2-2 Using the Hub View
Page 19

Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
Contact Status is a color code that shows the status of the connection between
SPMA and the device:
• Green means a valid connection.
• Blue means that SPMA is trying to reach the device but doesn’t yet know if the
connection will be successful.
• Red means that SPMA is unable to contact or has lost contact with the device.
Uptime
The time that the device has been running without interruption. The counter
resets to 0 days 00:00:00 (days HH:MM:SS) when one of the following occurs:
• Power to the device is cycled.
• The device is reset manually.
Date and Time
The date and time are taken from the device’s internal clock.
Device Name
A text field that you can use to help identify the device; you can edit the device
name via the Device Status window, described on page 2-13.
Device Location
A text field that you can use to help identify the device; you can edit the device
location via the Device Status window, described on page 2-13.
IP Address
The device’s Internet Protocol address; this field will display the IP address you
have used to create the EMM-E6 icon (if you are running the Hub View from a
management platform) or the IP address you used to launch the Hub View
program (if you are running in stand-alone mode). You cannot change the
EMM-E6’s IP address from SPMA; however, you can view the MAC addresses of
all installed interfaces (up to six), along with any associated IP addresses that
have been assigned, by using the IP Address Table function described on
page 2-19.
MAC Address
The device’s factory-set hardware address; this field will display the MAC
address associated with the IP address used to define the icon (if you are running
the Hub View fr om a management platform) or the IP addr ess you used to launch
the Hub View program (if you are running in stand-alone mode). The MAC
addresses cannot be changed.
Clicking the Device button displays the Device menu, Figure 2-2.
Using the Hub View 2-3
Page 20

Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
Figure 2-2. EMM-E6 Hub View Device Menu
The Device menu lets you perform the following:
• Open the Device Status window
• Access the IP Address Table
• Open the Polling Intervals window
• Change the Port Display Form
• Launch the Global Find MAC Address Tool
• Start the Alarm Configuration application
• Start the Link/Seg Traps application
• Start the Repeater Redundancy application
• View the Source Address List
• Access the Security application
• Start the Front Panel Redundancy application
Note that the Device menu does not provide access to every application available
to the EMM-E6. Some information is only available from the Network, Module,
and/or Port menus, and several applications can only be accessed either from the
icon menu (if you are running under a network management platform) or from
the command line (if you are running in stand-alone mode). See Chapter 1,
Introduction, for a complete list of applications available to the EMM-E6 and how
to access each one.
2-4 Using the Hub View
Page 21

Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
If you need to call the Cabletron Systems Global Call Center about a problem with
the Hub View application, you’ll need the information provided in the Info
window:
SPMA for the EMM-E6
application version
EMM-E6 firmware revision,
firmware boot prom version, and
hardware version
Figure 2-3. Hub Information Window
Clicking mouse button 1 on the Quit button closes all Hub View application
windows; any open applications which can also be accessed from the command
line or from the icon menu will remain open.
EMM-E6 Ports Display
The EMM-E6 module display in the Hub View shows the device’s first four
channels in two different modes: their Bridge Port Status (ON or OFF), and their
Bridge Port State (Listening, Learning, Forwarding, Blocking, or Disabled). Status
displays are color coded green for ON, blue for OFF; state displays are color
coded yellow for Listening and Learning, green for Forwarding, red for Blocking,
and blue for Disabled. The current redundancy status (Active or Inactive) of the
Channel D EPIM ports is also displayed. BRIM ports E and F will display status
colors (green for ON, blue for OFF) for any installed BRIM modules, along with
the BRIM type (FDDI, WAN, TR, ATM, or ENET).
Although the Hub View displays the presence and general status (ON or OFF) of any
NOTE
installed BRIM modules, you cannot enable or disable these ports from the Hub View. To
manage any installed BRIMs, launch the Bridge application from the Device menu, or
launch any other application available for your BRIM from the BRIM Launcher
application; see Chapter 1 for more information on how to access BRIM-specific
management.
Using the Hub View 2-5
Page 22
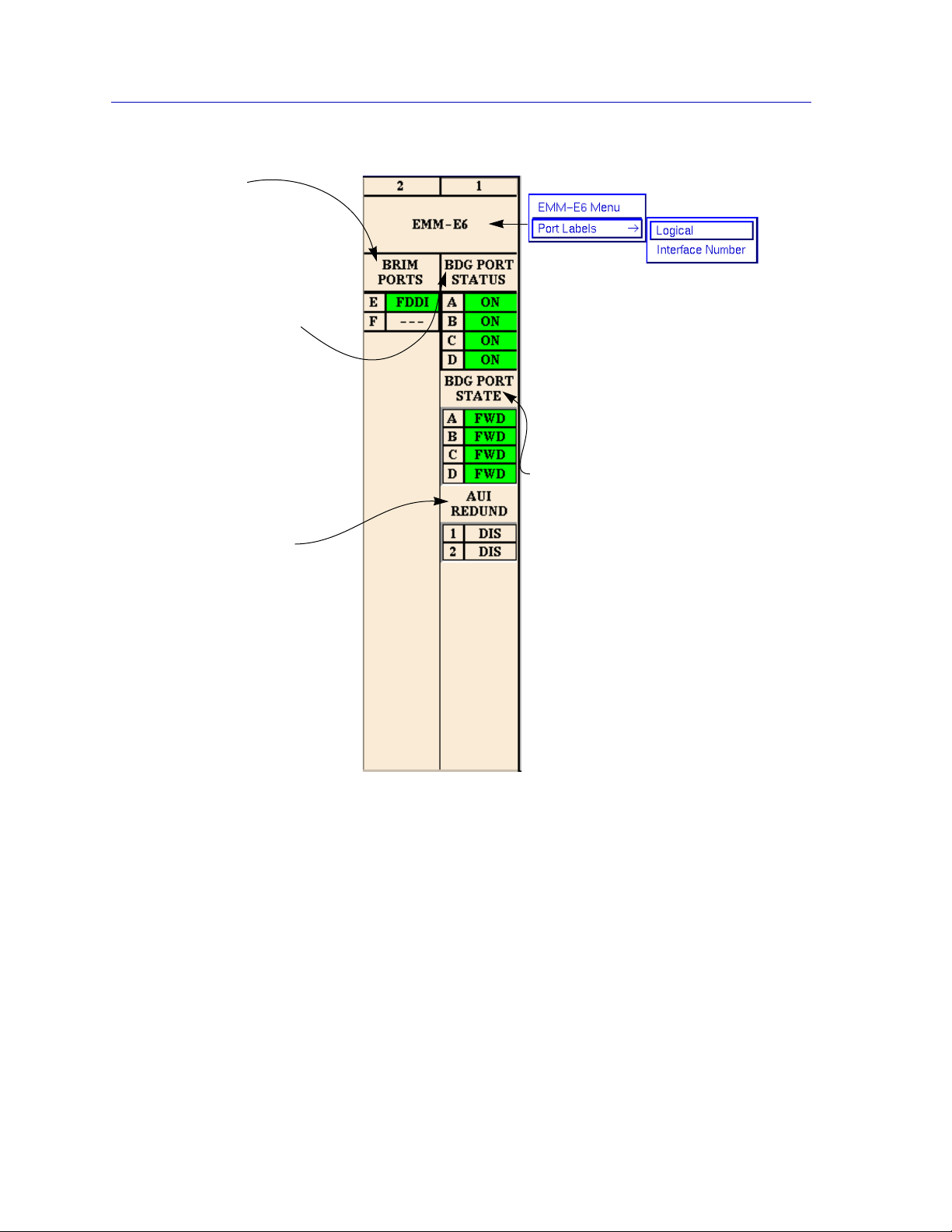
Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
BRIM Ports
BRIM ports E and F will
display status colors (green
for ON, blue for OFF) for any
installed BRIM modules,
along with the BRIM type
(FDDI, WAN, etc.).
Bridge Port Status
Displays the current
administrative status of
bridge ports A, B, C, and D:
ON (green) or OFF (blue).
This display will always be
the same regardless of the
Port Display Form selected
for MIM ports. Click mouse
button 1 to toggle the ports
ON or OFF.
AUI Redundancy
If you have configured and
enabled a redundant circuit
for the front panel Channel D
ports, their current
redundancy status — Active
or Inactive — will be
displayed. If no redundant
circuit has been enabled for
these ports, the boxes will
remain uncolored and DIS
(disabled) will be displayed.
Note that these boxes only
display the ports’
redundancy status, not their
link or admin status.
EMM-E6 Menu
Click mouse button 3 on the
Module Type box to access the
EMM-E6 menu; drag right to select
Logical, which displays the
EMM-E6 bridge ports with their
logical names (A, B, C, D, E, and
F); or Interface Number, which
displays the port names
numerically (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6).
Bridge Port State
Displays the current bridging state
for channels A, B, C, and D:
Learning (yellow; the port is
monitoring network traffic, learning
network addresses); Listening
(yellow; the port is monitoring
BPDU traffic on the network while
preparing to move to the
Forwarding state); Forwarding
(green); Blocking (red); or DIS
(blue; port status is OFF).
Figure 2-4. EMM-E6 Ports
Using the Mouse in a Hub View Module
Each media interface module, or MIM, installed in the EMM-E6-controlled hub
will be displayed in the hub view; use the mouse as indicated in the illustration
below to access Network, Module, and Port menus and functions.
2-6 Using the Hub View
Page 23
Depending on the version of firmware installed in your EMM-E6, certain MIMs either
NOTE
may not display at all, or may display with the message “No Mgt” in the Port Display
Form box. For more information about the specific capabilities of different versions of
EMM-E6 firmware, contact the Cabletron Systems Global Call Center.
Module Type
Click button 1 to open the Module
Status window.
Click button 3 to displa y the Module
menu.
Port Display Form
Using the Module, Network, or
Device menus, you can change the
port display form shown in the
Module Status boxes to any one of
the following:
- Load (% of theoretical maximum)
- Traffic (Pkts/sec)
- Collisions (Colls/sec)
- Errors (Errors/sec, total or by type)
- Protocols (% of total packets)
- Frame Sizes (% of total packets)
- Admin/Link Status
- Admin Status
- Active Ports
-Topology (station or trunk)
- FNB Channel
Port Index
Click button 1 to toggle the port
between enabled and disabled.
Click button 3 to display the Port
menu.
Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
Module Index
Indicates the module’s slot number
within the MMAC. (Slots are
numbered from right to left; the
management module slot is slot
#1.) Click button 3 to display the
Module menu.
Network Connection
A module managed by an EMM-E6
shows its network connection: A, B ,
C, or ---- (stand-alone). RIC MIMs
can be set to network B, C, or
stand-alone; non-repeater MIMs
will always be on network A. Click
mouse button 3 to display the
Network menu; click mouse button
1 to display the Network Status
window.
Port Status
The Port Status display changes
with the type of port display format
selected. Statistical selections
display values in a statistic/second
format. Load displays traffic as a
percentage of theoretical
maximum capacity. Port Type
displays port status (ON, OFF,
SEG, NLK, etc.). Click button 1 to
toggle the port between enabled
and disabled. Click button 3 to
display the Port menu.
Figure 2-5. Mousing Around a Module Display
Hub View Port Color Codes
The Port Status boxes in the Hub View are color coded to indicate the port’s
connection status. The colors are consistent for all Port Display Forms except
Admin Status and FNB Channel; the exceptions are noted below.
Using the Hub View 2-7
Page 24

Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
• Green indicates that the port is active; that is, the port has been enabled by
management, has a valid Link signal (if applicable), and is able to
communicate with the station at the other end of the port’s cable segment.
Note that an AUI or transceiver port will display as active as long as it has been
enabled by management, even if no cable is connected.
• Blue indicates that the port has been disabled through management.
• Yellow indicates that the port is enabled but does not currently have a valid
connection. This usually indicates that the device at the other end of the
segment is turned off, or that there is no cable attached.
• Red indicates that the port is enabled, but is not able to pass packets. This
generally means that the port has been segmented by management after
experiencing an excessive number of collisions; for a BNC (thin coax) port,
however, this may only mean that no cable or terminator has been connected.
• Magenta indicates that the EMM-E6 can’t manage the device.
When the Admin Status port display option is active, only two colors apply: a
port will be displayed in green if it is enabled by management, regardless of
whether or not there is a cable attached or a valid link signal detected; a port
disabled by management will display as blue.
When the FNB Channel option is active, an entirely different color scheme is
employed: salmon = Channel A; light blue = Channel B; orange = Channel C, and
grey = stand-alone.
Monitoring Hub Performance
The information displayed in the Hub View can give you a quick summary of
device activity, status, and configuration. SPMA can also provide further details
about hub performance via its four-level menu structure. The Device, Network,
Module, and Port menus (Figure 2-6, below) give you control over the hub at four
levels and give you access to the tools, menus, and windows that let you monitor
specific aspects of hub performance, change hub display options, and set
EMM-E6 operating and notification parameters. Remember, though many
functions will operate the same at each level, those accessed via the Device menu
control or provide information about all modules in the hub; those accessed via
the Network menu control or provide information about all modules in a
particular network, or channel; those accessed via the Module menu control or
provide information about a single module; and those accessed via the Port menu
control or provide information about a single port.
2-8 Monitoring Hub Performance
Page 25

Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
Figure 2-6. The EMM-E6’s Device, Network, Module, and Port Menus
Hub performance data available through these menus includes:
• Device, Network, Module, and Port status descriptions.
• Network, Module, and Port statistics, which provide a complete br eakdown of
packet activity.
• Network-, Module-, and Port-level pie charts, graphs, and meters, for a
graphic representation of the types and levels of traffic passing through the
hub. (For more information about pie charts, graphs, and meters, see the
Charts, Graphs, and Meters chapter in the SPMA Tools Guide.)
Graphing capabilities are provided by an application that is included in HP Network
NOTE
Node Manager and IBM NetView; therefore, graphs are only available when SPMA is
run in conjunction with one of these network management platforms. If you are running
SPMA in a stand-alone mode or in conjunction with SunNet Manager or Solstice
Enterprise Manager, no graphing capabilities are available and no graph-related options
will be displayed on buttons or menus. Note that the screens displayed in this guide will
include the graph-related options where they are available; please disregard these
references if they do not apply.
Port Display Form
You can change the type of information displayed for each port in the hub by
using the Port Display Form option on the Device, Network, and Module menus.
Monitoring Hub Performance 2-9
Page 26

Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
Changing the port display form via the Device menu will affect all manageable
ports in the hub; using the Network menu will affect all ports on a specific
channel, or network; and using the Module menu will affect all ports on the
appropriate module.
If there is a TPXMIM in multi-channel mode installed in your EMM-E6-managed hub,
NOTE
the Port Display Form option will not be available from that MIM’s Network menu; in
addition, a TPXMIM in multi-channel mode will not respond to changes in Port Display
Form made via any other MIM’s Network menu. However, the TPXMIM will always
respond to changes in port display form initiated via the Module or Device menus.
For more information about the TPXMIM and its multi-channel capabilities, see
Configuring TPXMIM Connections, page 2-30.
To change the port display form:
1. Click in the appropriate area to display the Device, Network, or Module menu
(refer to Figure 2-5, page 2-7).
2. Drag down to Port Display Form , then right as necessary to select one of the
port display options. The current selection will be displa y ed in the Port Display
Form text box(es) on the module displays.
Port display form options are:
Load
Shows a percentage for each active port that represents that port’s portion of the
theoretical maximum traffic level — for Ethernet networks, 10 megabits per
second.
Traffic
Displays port traffic data in a packets/second format.
Collisions
Displays port traffic data in a collisions/second format. The EMM-E6 counts both
receive collisions — those collisions it detects while receiving a transmission —
and transmit collisions —those it detects while transmitting (i.e., the EMM-E6
transmitted one of the colliding packets); however, those counts are combined
and a single total value is displayed.
Errors
Shows port traffic errors in an errors/second format. You can display any one of
the following types of errors:
• Total errors
• Alignment errors
• CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) errors
• Runts
• Giants
2-10 Monitoring Hub Performance
Page 27

Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
• OOW (Out-of-Window) Collisions
For error type descriptions, see Checking Statistics on page 2-20.
Protocols
Displays a percentage for each active port that represents what portion of that
port’s traffic is of a particular protocol type. You can display any one of the
following protocol types:
•IP
• OSI
• XNS
• DECNet
• Novell
• Appletalk
• Banyan
• Cabletron
• Other
Frame Sizes
Displays a percentage for each active port that represents what portion of that
port’s traffic is of a specific size, measured in bytes. You can display any one of the
following frame sizes:
NOTE
• Runts (packets with fewer than 64 bytes)
• 64-127
• 128-255
• 256-511
• 512-1023
• 1024-1518
• Giants (packets with more than 1518 bytes)
For the statistical port display form options listed above, three dashes (---) will display for
all inactive ports; any active (green) port will display a numeric value, even if it’ s 0.0000.
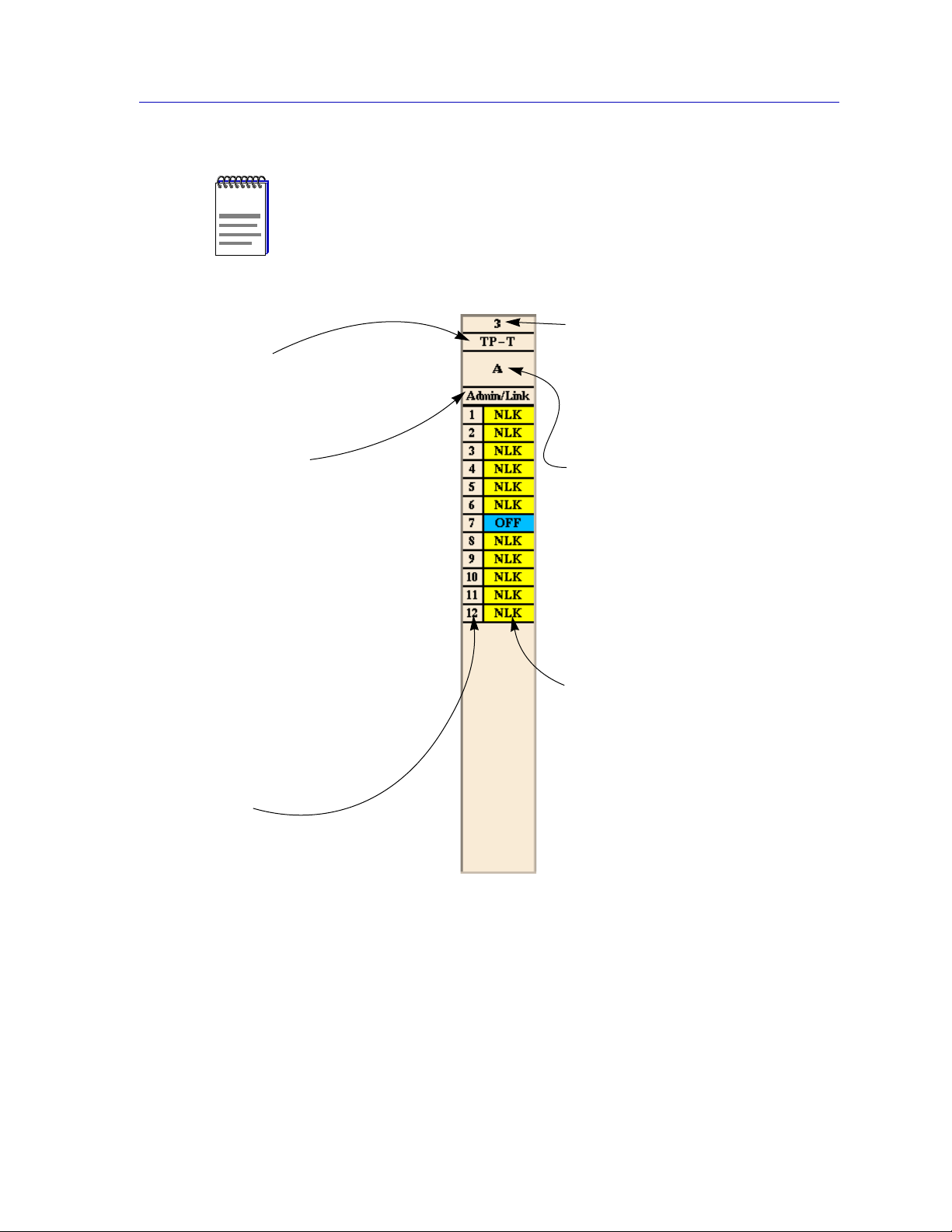
Port T ype
Provides the following administrative information about the port:
• Admin/Link Status indicates the connection status of the port:
- ON indicates that the port has a valid link signal or does not support a link
signal.
- OFF indicates that the port has been turned off through management
action.
- NLK (No Link) indicates that the port does not have a link to a device at
the other end of the cable, or that there is no cable attached.
Monitoring Hub Performance 2-11
Page 28

Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
- SEG (Segmented) indicates that the port has been segmented by the
Because BNC thin coax, AUI, and transceiver ports do not support the link feature, the
NOTE
displayed Admin/Link status for those ports may be misleading: for example, a BNC port
will display as segmented when, in fact, there is no cable or terminator attached or the
cable has been disconnected; and AUI or transceiver port will display as on (with a valid
link signal) even when no cable is attached. Be sure to keep these anomalies in mind when
troubleshooting a hub so equipped.
• Admin Status displays either ON or OFF, an indication of whether
management has the port enabled or disabled. A port can be ON but not
operational; for example, under the Admin display, ports that are segmented
or not linked are shown as ON.
• Active Ports displays either YES or NO for any active (gr een) port, indicating
whether or not that port has seen any traffic at all since the device was last
initialized; this port display form can tell you whether any port whose
statistics are not currently incrementing has seen some activity in the past.
Non-green (presumably inactive) ports will display three dashes (---),
regardless of their past statistical activity.
repeater due to an excessive collision level.
NOTE
• Topology displays either TRUNK or STN (station), a status which is defined
by how many source addresses are communicating through that port at any
given moment: if zero, one, or two addresses are communicating, the port is
considered to be a station port; if more than two addresses ar e communicating,
the port is considered to be a trunk port. See Setting a Port’s Trunk Type,
page 2-32, for more information.
If you use the Trunk Type option on the Port menu to manually change a port’s topology
status from Force Trunk to Not Forced, any status change from trunk to station will not
be reflected in the port display until the current cycle of the Source Address timer is
complete. See Chapter 6, Source Addressing, for more information on the timer.
Older versions of EMM-E6 firmware (previous to revision level 2.00.16) use slightly
different definitions of station and trunk status: station ports are defined as those which
are detecting no source addresses or only a single source address; trunk ports are those
detecting two or more. If you have any questions about which definition your version of
firmware employs, or if you would like information about upgrading your EMM-E6
firmware, contact the Cabletron Systems Global Call Center. Also, see Chapter 6, Source
Addressing, and Chapter 7, Security, for more information about station and trunk
status.
• FNB Channel displays a letter which indicates each port’s current channel
assignment: A, B, C, or SA (stand-alone).
2-12 Monitoring Hub Performance
Page 29

Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
Checking Device Status and Updating Front Panel Info
The Device Status window is where you change the information displayed on the
Hub View Front Panel and where you can see summary information about the
current state of the hub.
To open the Device Status window:
1. Click on to display the Device menu.
2. Drag down to Status and release.
Figure 2-7. EMM-E6 Device Status Window
Name and Location
These text fields help identify this EMM-E6. The information you enter in the
Name and Location boxes is written to the EMM-E6’s MIB and appears on the
Hub View front panel.
Contact
Use the Contact box to record the name and phone number of the person
responsible for the device. Note that the information entered here is not displayed
on the Hub View front panel.
Date and Time
Displays the current date and time from the EMM-E6’s internal clock. Although
the fields are static in the window, the front panel display is a real-time
presentation.
Monitoring Hub Performance 2-13
Page 30

Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
If your device firmware can accept four-digit year values, the Date field will allow you to
NOTE
enter the year portion in one-, two-, or four-digit format. If you choose to enter one or two
digits for the year, any value greater than or equal to 88 will be presumed to be in the
1900s; a value of 87 or less is presumed to be in the 2000s. No matter which entry format
you choose, the year will still be displayed and set as a four-digit value.
If your device firmware cannot accept four-digit year values, the Date field will allow you
to enter the year portion in one- or two-digit format (with leading zeros supplied
automatically for single-digit entries). No presumption is made about the century, and
any two-digit year value (from 00 to 99) will be accepted.
Attempts to set the date may result in one of three different error messages. Two of these
messages will indicate that the wrong number of digits has been used for the year value,
and will indicate the appropriate number of digits to use for the selected device; the third
message will indicate that the entered date is invalid because it is not an actual calendar
date (such as 02/29 in a non-leap year , any month value gr eater than 12, or any day value
greater than 31).
Chassis Type
Indicates the type of hub that houses this EMM-E6 — MMAC-M3FNB,
MMAC-M5FNB, and so forth — and whether or not the hub contains a shunting
backplane.
To change the name, location, contact, date, or time:
1. Highlight the appropriate field and type the new values.
2. Press Enter or Return on the keyboard to save each change before moving
on to another; each change will appear on the front panel as soon as Enter or
Return is pressed.
The Device Status window also allows you to enable or disable the audible
chassis alarm for your chassis. When the chassis alarm is enabled, an alarm will
sound when high temperature or low voltage conditions occur in the chassis. To
enable or disable the chassis alarm:
1. In the Audible Alarm State field, click on the Enab led or Disabled option, as
desired. The chassis alarm will be enabled or disabled, as selected.
Checking Network Status
The Network Status window provides information about each active repeating
network, or channel, on the EMM-E6.
To access the Network Status window:
1. Click mouse button 1 in the appropriate Network Connection box (one
displaying the letter that identifies the network you are interested in:
A, B, or C).
2-14 Monitoring Hub Performance
Page 31
Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
or
Click mouse button 3 on the appropriate Network Connection box to open the
Network menu.
2. Drag down to Status and release.
Figure 2-8. EMM-E6 Network Status window
Note that the information in the Network Status window applies to all MIMs
connected to the selected channel, regardless of which MIM display was used to
access the window. The name of the selected channel (A, B, or C) is displayed in
the window title. Note that no Network Status window is available for channels
D, E, and F, as those channels do not serve as repeaters. Note also that no
Network Status window is available for RIC MIMs operating in stand-alone, or
isolated mode — that is, those which are not connected to any EMM-E6 channel.
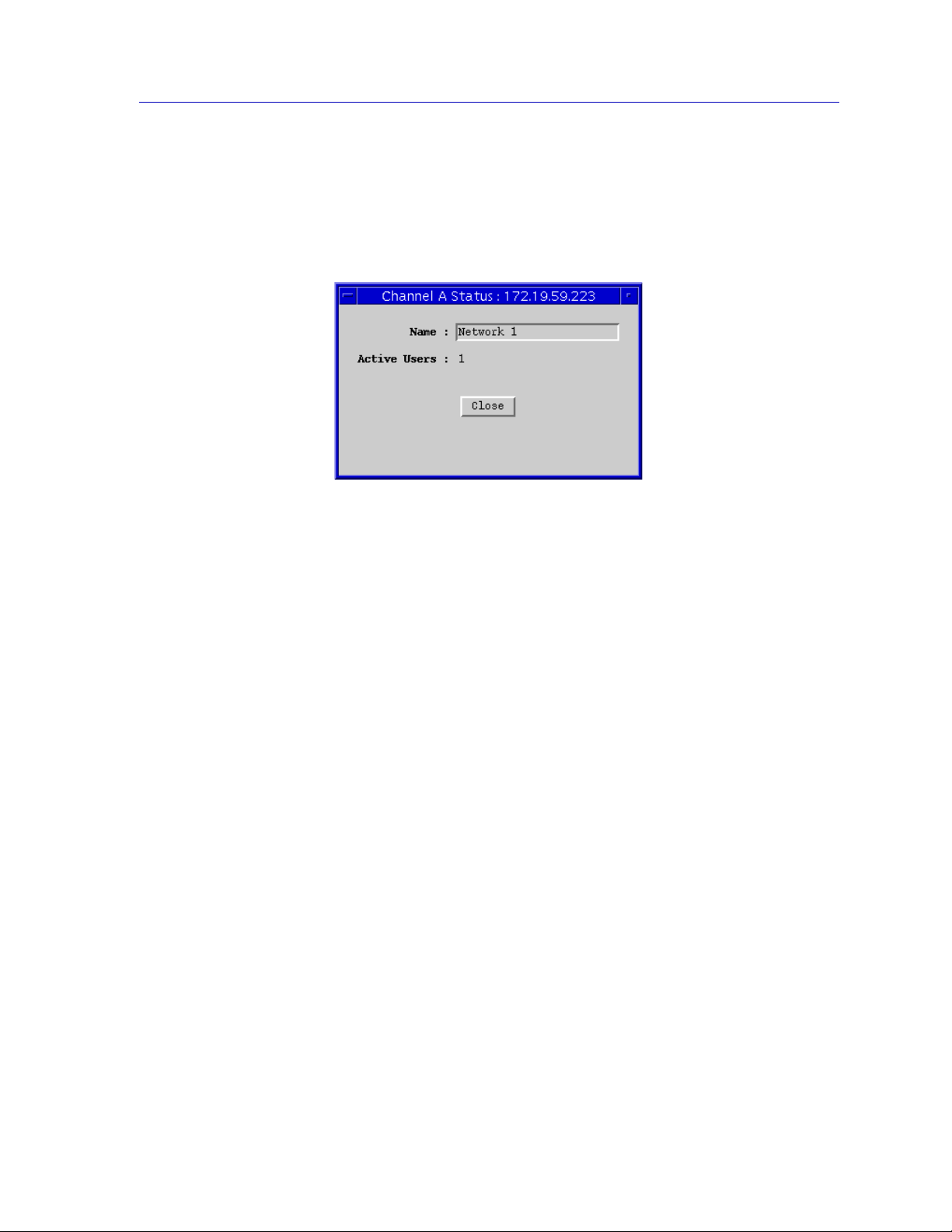
The Network Status window contains the following fields:
Name
This is a text field you can use to help identify this network. For example, if the
selected channel connects users in one department, or users on one floor or one
area of a building, you can use this field to name the network or channel,
accordingly: Accounting, or 3r d Floor Bldg. C. The information entered her e is not
displayed anywhere else in the Hub View.
To change the network name:
1. Highlight the existing text (if necessary) and type the new name.
2. Press Enter or Return on the keyboard to save your change.
Active Users
Displays the number of active source addresses that are communicating on this
network, or channel.
Monitoring Hub Performance 2-15
Page 32

Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
Checking Module Status
You can open a Module Status window for any manageable module in the
EMM-E6-controlled hub. To open the Module Status window:
1. Click button 1 in the Module Type box.
or
Click button 3 in the Module Index, Module Type, or Port Display Form box to
display the Module menu.
2. Drag down to Status and release.
Figure 2-9. EMM-E6 Module Status Window
Note that the window title includes the module number in parentheses; the rest of
the window contains the following fields:
Name
This text field can help identify this module; the information entered here does
not appear anywhere else in the Hub View.
To edit the Module Name:
1. Highlight the text in the Name box and type in a new name.
2. Press Enter or Return on the keyboard to save your change.
Active Users
Displays the number of active source addresses communicating through this
module.
Module Type
The type of MIM installed in the selected slot — THN, TP-T, CXR, etc. This is the
same information as that displayed in the Module Type box on the MIM display.
2-16 Monitoring Hub Performance
Page 33

Checking Port Status
You can open a Port Status window for any port on any manageable module
installed in the hub. To open the Port Status window:
1. Click button 3 in the Port Index or Port Status box to display the Port menu.
2. Drag down to Status and release.
Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
Figure 2-10. EMM-E6 Port Status Window
Note that the window title includes the module and port number in parentheses;
the rest of the window contains the following fields:
Name
This text field can help identify the port; the information entered here is not
displayed anywhere else in the Hub View.
To edit the Name:
1. Highlight the text in the Name box and type in a new name.
2. Press Enter or Return on the keyboard to save your change.
Link Status
The port’s Link Status tells you whether or not the port has a valid connection to
the node at the other end of the cable segment. The possible Link conditions are:
• Active — The port has a valid connection with the device at the other end of
the port’s cable.
• Inactive — The device at the other end of the cable is turned off, there is a
break in the cable, or there is no device or cable connected.
Monitoring Hub Performance 2-17
Page 34

Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
• Not Supported — The selected port does not support the Link feature, so the
EMM-E6 cannot determine link status; this value will show only for thin coax
(BNC), AUI, or transceiver ports.
The fact that thin coax (BNC), AUI, and transceiver ports do not support the link feature
NOTE
can cause some misleading port status indicators: for example, a BNC port may show as
segmented when, in fact, the cable has been disconnected; or an AUI or transceiver port
may appear to have an active link when no cable has been attached. You should keep these
anomalies in mind when troubleshooting a hub so equipped.
• Unknown — The EMM-E6 can’t determine a link status.
Status
The port’s Status can be one of three states:
• Segmented—A port becomes segmented (that is, disabled by the repeater
module) when the port experiences 32 consecutive collisions, or when the
port’s collision detector is on for longer than approximately 2 to 3
milliseconds.
NOTE
Because they do not support the link feature, thin coax (BNC) ports will display as
segmented when there is no cable or terminator attached or the cable or terminator has
been disconnected (i.e., a “no link” condition).
• Active —The port is operating normally.
• Unknown — The EMM-E6 cannot determine port status.
Active Users
Each active source address communicating through the port is counted as an
active user. If Active Users is greater than two (or one for firmware versions
previous to 2.00.16), it indicates that the port is supporting a trunk connection.
Media Type
Indicates the type of cable segment connected to the port. MIMs generally
support a single media type. The supported media types are:
• BNC (thin coax)
• AUI
• Transceiver Port AUI
• Twisted Pair: RJ45 conn(ector)
• Twisted Pair: DB9 conn
• Twisted Pair: RJ71 conn
• Multi-Mode Fiber: SMA conn
• Multi-Mode Fiber: ST conn
• BNC EPIM
2-18 Monitoring Hub Performance
Page 35

NOTE
Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
• AUI EPIM
• Transceiver Port AUI EPIM
• Twisted Pair: RJ45 EPIM
• Multi-Mode Fiber: SMA EPIM
• Multi-Mode Fiber: ST EPIM
• Single-Mode Fiber: ST EPIM
• Hardwir ed AUI EPIM
• Unknown (for boards that don’t support media type)
T opology Type
Indicates how the port is being used. The available types are:
• Station—The port is receiving packets from no devices, from a single device,
or from two devices. Note that a port in station status may actually be
connected to multiple devices; station status simply indicates that no more
than two devices are currently active.
• Trunk—The port is receiving packets from three or more devices; it may be
connected to a coax cable with multiple taps, or to a repeater or another MIM.
If you use the Trunk Type option on the Port menu to manually change a port’s topology
status from Force Trunk to Not Forced, any status change from trunk to station will not
be reflected in the port display until the current cycle of the Source Address timer is
complete. See Chapter 6, Source Addressing, for more information on the timer.
Older versions of EMM-E6 firmware (previous to revision level 2.00.16) use slightly
different definitions of station and trunk status: station ports are defined as those which
are detecting no source addresses or only a single source address; trunk ports are those
detecting two or mor e. If you have any questions about which definitions ar e employed by
your version of firmware, or if you would like information about upgrading your
EMM-E6 firmware, contact the Cabletron Systems Global Call Center. Also, see Chapter
6, Source Addressing, and Chapter 7, Security, for more information about station and
trunk status.
Viewing the IP Address Table
You can use the IP Address Table option on the Device menu to view the MAC
(hardware) addresses of all installed interfaces, along with their associated
interface numbers, interface types, interface descriptions, and any assigned IP
addresses. The interface numbers 1-4 correspond to channel, or network,
designations A, B, C, and D; interfaces available via BRIM port E will be indexed
starting at 5, and those available via BRIM port F will follow.
You cannot change or assign an IP address from this window or from any other SPMA
NOTE
application.
Monitoring Hub Performance 2-19
Page 36

Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
To view the IP Address Table:
1. Click on to access the Device menu.
2. Drag down to IP Address Table and release.
Figure 2-11. EMM-E6 IP Address Table
Note that the I/F Description for the highlighted interface is repeated in the text
box at the bottom of the window; this allows for the complete display of the
description, which may be truncated in the main window.
Launching the Global Find MAC Address Tool
You can launch the Global Find MAC Address Tool directly from the Hub View.
With this tool you can perform a chassis-wide search for any bridge ports,
repeater ports, or token ring ports through which a particular MAC address is
communicating.
1. Click on to access the Device menu.
2. Drag down to Find MAC Address and release. The Global Find MAC
Address Tool will launch. For more information on the Global Find MAC
Address Tool, see the Utilities chapter in your
Checking Statistics
The Hub View can provide a summary of Ethernet statistics at the Network,
Module, and Port levels. The windows that display the statistics contain the same
statistical categories at each level.
SPMA T ools Guide
.
2-20 Monitoring Hub Performance
Page 37

Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
To view hub statistics at the Network, Module, or Port levels:
1. Display the Network, Module, or Port menu by clicking mouse button 3 in the
appropriate area (refer to Figure 2-5, page 2-7).
2. Drag down to Statistics and then right to either General/Errors or
Protocols/Frames, and release.
Figure 2-12. EMM-E6 Statistics Windows (Network Level)
Note that the network level statistics windows include the channel name in the
window title; the module statistics windows include the module number in the
title; and the port statistics windows includes the module and port number in the
window title.
All statistical counters begin to increment when the windows are opened; to reset
counters to zero, click mouse button 1 on . Statistical counts are
cumulative.
Monitoring Hub Performance 2-21
Page 38

Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
Unless you close, then re-open, a window or use the Reset button, statistical counters
NOTE
will continue to increment until a value of 232-1 (approximately 4 billion) is reached, at
which point they will roll over and restart at 0.
General/Error Statistics
The General/Errors statistics windows display the following fields:
Received Bytes
The total number of bytes of data received by this network (channel), module, or
port since the statistics window was opened or the Reset button was pressed.
Total Packets
The total number of packets of all types received by this network (channel),
module, or port since the statistics window was opened or the Reset button was
pressed.
Avg Packet Size
The average number of bytes per packet received by this network (channel),
module, or port since the statistics window was opened or the Reset button was
pressed. The average packet size is calculated after each polling interval by
dividing the cumulative number of bytes received by the cumulative number of
packets received.
Broadcast Packets
The total number of broadcast packets received by this network (channel),
module, or port since the statistics window was opened or the Reset button was
pressed. Broadcast packets have a single address recognized by each station on
the net: this address is designated in IP form as 255.255.255.255, or in MAC
hexadecimal form as FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF. The ARP and RARP requests sent by
bridges and routers are broadcast packets.
Multicast Packets
The total number of multicast packets received by this network (channel),
module, or port since the statistics window was opened or the Reset button was
pressed. Multicast packets are simultaneously addressed to more than one
address, but fewer than all addresses.
Collisions
The total number of collisions recorded by this network (channel), module, or
port since statistics window was opened or the Reset button was pressed. The
EMM-E6 counts both receive collisions — those detected while a port is receiving
data — and transmit collisions — those detected while a port is transmitting data
(i.e., the port has transmitted one of the colliding packets); however, these counts
are combined and a single total value is displayed. Collisions of this type (called
2-22 Monitoring Hub Performance
Page 39

Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
“legal” collisions, as opposed to the OOW collisions described below) are a
natural by-product of a busy network; if you are experiencing high numbers of
collisions, it may be time to redirect network traffic by using bridges or routers.
Extremely high collision rates can also indicate a data loop (redundant
connections) or a hardware problem (some station transmitting without listening
first).
Total Errors
The total number of errors of all types recorded by this network (channel),
module, or port since the statistics window was opened or the Reset button was
pressed.
Alignment Errors
The total number of misaligned packets recorded since the statistics window was
opened or the Reset button was pressed. Misaligned packets are those which
contain any unit of bits which is less than a byte — in other words, any group of
bits fewer than 8. Misaligned packets can result from a packet formation problem,
or from some cabling problem that is corrupting or losing data; they can also
result from packets passing through more than two cascaded multi-port
transceivers (a network design which does not meet accepted Ethernet spec).
CRC Errors
CRC, or Cyclic Redundancy Check, errors occur when packets are somehow
damaged in transit. When each packet is transmitted, the transmitting device
computes a frame check sequence (FCS) value based on the contents of the packet,
and appends that value to the packet. The receiving station performs the same
computation; if the FCS values differ, the packet is assumed to have been
corrupted and is counted as a CRC error. CRC errors can result from a hardware
problem causing an inaccurate computation of the FCS value, or from some other
transmission problem that has garbled the original data. The CRC error counter
shows the total number of CRC errors that were recorded since the statistics
window was opened or the Reset button was pressed.
OOW Collisions
The total number of out-of-window collisions recorded since the statistics
window was opened or the Reset button was pressed. OOW collisions occur
when a station receives a collision signal while still transmitting, but more than
51.2 µsec (the maximum Ethernet propagation delay) after the transmission
began. There are two conditions which can cause this type of error: either the
network’s physical length exceeds IEEE 802.3 specifications, or a node on the net
is transmitting without first listening for carrier sense (and beginning its illegal
transmission more than 51.2 µs after the first station began transmitting). Note
that in both cases, the occurrence of the errors can be intermittent: in the case of
excessive network length, OOW collisions will only occur when the farthest
stations transmit at the same time; in the case of the node which is transmitting
without listening, the malfunctioning node may only fail to listen occasionally,
and not all of its failures to listen will result in OOW collisions — some may
simply result in collisions (if the 51.2 µs window has not yet closed), and some
will get through fine (if no one else happens to be transmitting).
Monitoring Hub Performance 2-23
Page 40

Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
Runt Frames
The total number of received packets smaller than the minimum Ethernet frame
size of 64 bytes (excluding preamble). This minimum size is tied to the maximum
propagation time of an Ethernet network segment — the maximum propagation
time is 51.2 µs, and it takes approximately 51.2 µs to transmit 64 bytes of data;
therefore, every node on the segment should be aware that another node is
transmitting before the transmission is complete, providing for more accurate
collision detection. Runts can sometimes result from collisions, and, as such, may
be the natural by-product of a busy network; however, they can also indicate a
hardware (packet formation), transmission (corrupted data), or network design
(more than four cascaded repeaters) problem.
Giant Frames
The total number of received packets that are longer than the maximum Ethernet
size of 1518 bytes (excluding preamble). Giant packets typically occur when you
have a jabbering node on your network — one that is continuously transmitting,
or transmitting improperly for short bursts — probably due to a bad transmitter
on the network interface card. Giant packets can also result from packets being
corrupted as they are transmitted, either by the addition of garbage signal, or by
the corruption of the bits that indicate frame size.
The EMM-E6 Error Priority Scheme
Each Cabletron device employs an error priority scheme which determines how
packets with multiple errors will be counted, and ensures that no error packet is
counted more than once. The priority scheme for the EMM-E6 counts errors in the
following order:
1. OOW Collisions
2. Runts
3. Giants
4. Alignment Errors
5. CRC Errors
Knowing the priority scheme employed by the EMM-E6 can tell you a lot about
the error counts you are seeing. For example, you know that the number of
packets counted as CRC errors had only CRC errors — they were of legal size (not
runts or giants) and had no truncated bytes. You also know that any packet less
than 64 bytes long has been counted as a runt, even if it also had alignment
and/or CRC problems (which is likely if the runt is the result of a collision or
other transmission problem).
2-24 Monitoring Hub Performance
Page 41

For more detailed information about error statistics and the possible network conditions
NOTE
Protocols/Frames Statistics
they represent, consult the Cabletron Systems Network Troubleshooting Guide,
included with this package.
The Protocols/Frames statistics windows display the following fields:
Protocols
• OSI Frames
• Novell Frames
• Banyan Frames
• DECNet Frames
• XNS (Xerox Network Systems) Frames
• IP Frames
• Ctron Frames
• AppleTalk Frames
• Other Frames
Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
Frame Sizes
• Runt Frames (packets smaller than 64 bytes)
• 64-124 (byte) Frames
• 128-255 Frames
• 256-511 Frames
• 512-1023 Frames
• 1024-1518 Frames
• Giant Frames (packets larger than 1518 bytes)
Viewing the Port Source Address List
The Port Source Address List accessible via the port-level menus displays the
MAC address and its associated vendor name for each device communicating
through a specific port in the EMM-E6-managed hub.
To view a port’s Source Address List:
1. Click mouse button 3 in the appropriate Port Status or Port Index box to
display the Port menu.
2. Drag down to Source Address List, and release.
Monitoring Hub Performance 2-25
Page 42
Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
Figure 2-13. Port Source Address List
The Source Address List window displays the MAC addresses of all devices that
have transmitted packets through the selected port within a time period less than
the SAT’s defined aging time (addresses that have not transmitted a packet
during one complete cycle of the aging timer will be purged). The Aging Time is
user-configurable; see Setting the Aging T ime in Chapter 6 for mor e information.
The list window can display about ten addresses at once; use the scroll bar to the
right of the list window to view additional addresses, if necessary.
Since the SAT is constantly changing as old entries are aged out and new entries
are added, you should occasionally update the displayed list by using the
button. Once displayed, the list is static and will not reflect recent
changes. Also static is the displayed number of Active Users; this field will also
update when you click on .
2-26 Monitoring Hub Performance
Page 43

The snapshots of the Source Address List that you can obtain via this feature do not r eflect
NOTE
the current port security status of the SAT — that is, when Source Address Locking is
enabled, you can still observe addresses being aged out of the table and new addresses
being added as you refresh the Source Address List displayed in this window. However,
the EMM-E6 remembers the addresses that were in the table when locking was enabled,
and will continue to protect all locked ports from access by unauthorized sources. For
more information, see Locking Source Addresses in Chapter 6; see also Chapter 7,
Security.
Also, keep in mind that the port-level source address list provides information about a
single port only; for a complete list of source addresses communicating through the device
as a whole, use the Source Addressing option on the Device menu. Again, see Chapter 6
for more information.
Managing the Hub
In addition to the performance information described in the preceding sections,
the Hub View also provides you with the tools you need to configure your hub
and keep it operating properly. Hub management functions include setting
polling intervals, changing a RIC MIM’s channel assignment, setting a port’s
trunk type, and enabling and disabling ports at the module level and
individually.
Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
Setting the Polling Intervals
To set the polling intervals used by SPMA and the EMM-E6:
1. Click on to display the Device menu.
2. Drag down to Polling Intervals, and release.
Managing the Hub 2-27
Page 44

Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
Figure 2-14. EMM-E6 Polling Intervals
3. To activate the desired polling, click mouse button 1 on the selection box to
the right of each polling type field.
4. To change a polling interval, highlight the v alue y ou w ould like to change, and
enter a new value in seconds. Note that the Use Defaults option must
selected, or values will revert back to default levels when you click on
, and your changes will be ignored.
5. If you wish to use your new polling interval settings as the default values that
SPMA will use for each EMM-E6 you are managing, use mouse button 1 to
select the Save As Defaults option.
6. If you wish to replace existing v alues with the current set of default v alues, use
mouse button 1 to select the Use Defaults option.
7. Click mouse button 1 on once your changes are complete.
Changes take effect after the current polling cycle is complete.
You can set the update intervals for the following:
Contact Status
This polling interval controls how often the EMM-E6 is “pinged” to check SPMA ’s
ability to maintain a connection with the device.
Device General Status
This polling interval controls how often the Hub V iew Fr ont Panel Information —
such as Uptime, Device Name, and so forth — and some network, module, and
port status information is updated.
not
be
2-28 Managing the Hub
Page 45

NOTE
Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
Device Configuration
This polling interval controls how often a survey is conducted of the type of
equipment installed in the EMM-E6-managed hub; information from this poll
would change the Hub View to reflect the addition and/or removal of a MIM or
MIMs.
Port Operational State
This polling interval controls the update of the information displayed in the Port
Status boxes for each port in the hub. Port state information includes link state
(the color code) and admin state (on or off).
Statistics
This polling interval controls how often the information displayed in the Port
Status boxes is updated when the Port Display Form is set to a rate or percentage,
and how often the Network, Module, and Port statistics counts are updated.
SPMA generates network traffic when it retrieves the above-described information; keep
in mind that shorter intervals mean increased network traffic. Range limits for these
polling times are 0-999,999 seconds; however, an entry of 0 will be treated as a 1.
Configuring FNB Connections
Cabletron Systems’ MultiChannel technology allows you to configure multiple,
separately-repeated channels in the same MMAC. Hubs which incorporate the
Flexible Network Bus (FNB) design have three internal channels: the original
power and management channel (designated as Channel A), and two additional
Ethernet channels (designated as Channel B and Channel C) that are repeated
separately.
Cabletron’s original Media Interface Modules (MIMs) are automatically
configured to operate on the original backplane channel, Channel A. However,
Cabletron Systems’ latest family of MIMs — Repeater, or RIC, MIMs (the
FORMIM, CXRMIM, TPRMIM, and TPXMIM) — can be selectively configured to
operate on the B or C channel, or, since they provide their own repeater
functionality, in a stand-alone mode.
In addition, the newest member of the RIC MIM family — the TPXMIM —
provides the ability to assign the entire board to a channel (bank switching), or to
assign each individual port to a channel (port assignment). Also unique to the
TPXMIM is the ability to assign each of its ports or the board as a whole to
Channel A. The following sections describe how to configure the FNB connections
for these MIMs.
Managing the Hub 2-29
Page 46

Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
Configuring RIC MIM Connections
Because each RIC MIM repeats packets independently, you can insert it into the
network via backplane channels B or C, or isolate it to act as a self-contained
network.
To change a RIC MIM’s channel assignment:
1. Click mouse button 3 in the appropriate area to display the Network menu
(refer to Figure 2-5, page 2-7). Be sure to display the Network menu from the
RIC MIM you wish to change, as this menu option applies
from which it was accessed.
2. Drag down to Change Channel, and right to select Channel B, Channel C,
or Standalone. The new channel assignment will be displayed in the
appropriate Network Connection box on the MIM display.
Change Channel is the only option on the Network menu which does not apply to all
NOTE
MIMs operating on the same channel! If you wish to change a RIC MIM’s channel
assignment, you must do so by accessing the Network menu from each RIC MIM you
wish to re-configure.
only
to the RIC MIM
Note that a RIC MIM in stand-alone mode becomes an “orphan MIM” and is no
longer in full communication with the EMM-E6, and most network, module, and
port menu options are disabled for that MIM. In addition, unless there is a direct
cable connection, the packets it repeats are not being repeated to the other MIMs
in the hub. However, you can still use the Network menu to put the RIC MIM
back onto Channel B or C to re-enable all menu options and re-establish
connection with the hub.
If your SPMA workstation is connected to a RIC MIM and you configure that RIC MIM
!
CAUTION
NOTE
Configuring TPXMIM Connections
to stand-alone mode, you will cut your station’s contact with the network. If this happens,
you will not be able to access the network again until you physically reconnect your
station to a port that is active on the network.
If the FNB backplane in a non-shunting MMAC is broken by an empty slot between the
RIC MIM and the EMM-E6, all MIMs to the left of the break which are operating on
channels B and C will revert to the orphan, or stand-alone, state described above. This
state change will be reflected in the Hub View display.
The TPXMIM provides two levels of FNB connectivity: you can assign the board
as a whole or each individual port to one of the three internal FNB channels: A, B,
or C; in addition, you can configure the whole board to operate in a stand-alone
2-30 Managing the Hub
Page 47

Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
mode. When configured to operate on channels B or C, the TPXMIM provides its
own repeating; when operating on Channel A, its ports depend on the EMM-E6
for repeater functionality. All TPXMIM ports default to channel B when first
installed.
To configure FNB connectivity for the board as a whole:
1. Click mouse button 3 in the appropriate area to display the Network menu
(refer to Figure 2-5, page 2-7). Be sure to display the Network menu from the
TPXMIM you wish to change, as this menu option applies
only
to the TPXMIM
from which it was accessed.
2. Drag down to Change Channel, and right to select Channel A, Channel B,
Channel C, Standalone, or Restore B/C State, as appropriate:
a. Use the Channel A, Channel B, or Channel C options to switch the
TPXMIM’s channel to A, B, or C, as desired; keep in mind that each of
these board-level settings will override any individual port-level settings.
b. Use the Standalone option to switch all ports currently configured to use
channels B or C to a stand-alone mode; this stand-alone mode is identical
to the stand-alone mode for the other RIC MIMs, and has similar
implications. However, note that any ports which are configured to
operate on Channel A will remain connected to Channel A, and will not
switch to stand-alone.
NOTE
Be sure to refer to the Release Notes that were shipped with your EMM-E6 firmware for
more information about the implications of operating your TPXMIM in a stand-alone
mode.
c. Use the Restore B/C State option to switch stand-alone ports back to the
configuration status they had before they were switched to stand-alone:
ports that were on Channel B will return to Channel B; ports that were on
Channel C will return to Channel C. Again, this option does not affect any
ports that were configured for Channel A; those will remain connected to
Channel A. This option should only be used when the board is in a
stand-alone state; if y ou select it when the board is assigned to a channel,
the set will fail and an error message will be displayed.
To configure FNB connectivity for an individual port:
1. Click mouse button 3 on the appropriate P ort Status or Port Index bo x to open
the Port menu.
2. Drag down to Change Channel, then right to select Channel A, Channel B,
or Channel C, as desired. Note that individual ports cannot be placed in
stand-alone mode via this menu.
Managing the Hub 2-31
Page 48

Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
To place only selected ports in stand-alone mode, you must configure all other ports so
NOTE
that they are connected to Channel A; those ports will remain connected to Channel A
when stand-alone mode is implemented, and only those ports connected to channels B or
C will be put in stand-alone.
If you have configured the ports on the TPXMIM so that they are connected to
different channels, the board’s Network Connection box will display a letter
representing each channel to which a TPXMIM port is connected. If the entire
board is in stand-alone mode, three dashes (---) will display; if some ports are still
connected to Channel A, two dashes and an A (-A-) will display.
In addition, keep in mind that most Network and Module menu selections can
only provide information about a single network channel. When your TPXMIM is
in multi-channel mode, making a selection from one of those menus will first
bring up a channel selection window (Figure 2-15, below); click to select the
appropriate channel, and the desired information will be displayed as usual.
Figure 2-15. TPXMIM Channel Selection Window
Setting a Port’s Trunk Type
Station ports and trunk ports are defined by how many source addresses are
communicating through that port at any given moment: if zero, one, or two
addresses are communicating, the port is considered to be a station port; if three
or more are communicating, the port is considered to be a trunk port.
Note that the window
title indicates the
menu option you hav e
selected
2-32 Managing the Hub
Page 49

TIP
Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
Older versions of EMM-E6 firmware (revision levels previous to 2.00.16) use slightly
different definitions of station and trunk status: station ports are defined as those which
are detecting no source addresses or only a single source address; trunk ports are those
detecting two or more.
If you are running an older version of firmware, and all of the ports in your
EMM-E6-controlled hub happen to be serving as station ports at the time you enable
Source Address Locking — either because they are connected to a single node, or because
users connected to that port happen not to be on the network at the time Source Address
Locking is enabled — you may end up locking out devices or nodes that should have
access. To avoid this, you may want to force key ports to trunk status, since trunk ports
are unaffected by Source Address Locking.
If you are running a newer version of firmware, you can protect ports fr om being locked by
forcing them to an Unsecurable status; see Chapter 7, Security, for details. Note, too, that
any port with more than 35 source addresses in its source address table is automatically
considered to be unsecurable.
If you have any questions about which definitions your version of firmware employs, or if
you would like information about upgrading your EMM-E6 firmware, contact the
Cabletron Systems Global Call Center. Also, see Chapter 6, Source Addressing, and
Chapter 7, Security, for more information about station and trunk status.
NOTE
To change a port’s topology status:
1. Click mouse button 3 on the appropriate Port Status box to open the Port
menu.
2. Drag down to Trunk T ype, then right to Force T runk or Not Forced, and
release.
There are three ways to view a port’s current topology status befor e making changes to its
trunk type: check the Port Status window, which provides both the current number of
active users and the current topology status; check the port’s Source Address List, which
lists the MAC address of each active user; or use the Topology port display form.
Once Source Addr ess Locking is enabled, a port’s topology state (trunk or station)
cannot be changed, even by using the option described above. Once Source
Address Locking is disabled, a port will respond to a change in topology status
(either one forced by the Trunk Type option above, or one that occurs naturally
due to a change in the number of active source addresses) at the beginning of the
next Source Address Aging Time cycle.
Managing the Hub 2-33
Page 50

Using the EMM-E6 Hub View
If you use the Trunk Type option on the Port menu to manually change a port’s topology
NOTE
status from Force Trunk to Not Forced, any status change from trunk to station will not
be reflected in the port display until the current cycle of the Source Address timer is
complete. See Chapter 6, Source Addressing, for more information on the timer.
Enabling/Disabling MIM Ports
You can enable and disable ports on any manageable MIM from both the Module
menu, which affects all ports on a single module, and the Port menu, which
affects individual ports.
To enable or disable all ports in a module:
1. Click button 3 on the Module Index or Module Type box to open the Module
menu.
2. Drag down to Enable All Ports or Disable All Ports, as appropriate, and
release. Disabled ports are blue.
!
CAUTION
When disabling all ports on a module, make sure you don’t disable the port thr ough which
your management station is communicating with the hub, or you will lose contact with
the device.
To enable or disable an individual port:
1. Click button 1 on the Port Status box to toggle the port On or Off.
or
1. Click button 3 on the Port Index or Port Status box to display the Port menu.
2. Drag down to Enable or Disable, as appropriate, and release. The selected
port changes color when its state changes. A disabled port is blue.
2-34 Managing the Hub
Page 51

Chapter 3
Alarm Configuration
Using Alarm Configuration; setting repeater alarm configuration; setting port and module alarm
configuration
Alarms work in conjunction with your network management system to let you
know when defined thresholds have been reached. You define the conditions that
will trigger an alarm using the Alarm Configuration application. The EMM-E6
monitors activity and reports to your network management station, in the form of
a trap, when a defined threshold is reached. You can set alarms at three levels:
• Repeater alarms monitor the combined activity of all ports within a single hub
network.
NOTE
• Module alarms monitor the combined activity of all ports within a single
module.
• Port alarms monitor the activity of a single port.
The effect of an alarm depends on the parameters you have set via your
management station.
SPMA does not accept trap messages; that task is left to your network management
system. (See the appropriate network management system documentation for details
about viewing trap messages.) When this application is used in stand-alone mode, traps
will either be ignored when they return to the workstation from which you are running
SPMA for the EMM-E6, or they will turn up at another management workstation which
has been configured to accept traps. Note also that, regardless of the configuration
performed using this application, NO traps will be sent by the device unless its trap table
has been properly configured; see the EMM-E6 hardware manual and/or the Trap Table
chapter in the SPMA Tools Guide for more information.
3-1
Page 52

Alarm Configuration
Using Alarm Configuration
To open the Alarms window
from the icon:
1. Click on the appropriate EMM-E6 icon to display the icon menu.
2. Drag down to Alarm Configuration and release.
from the Hub View:
1. In the Hub View, click on to display the Device menu.
2. Drag down to Alarm Configuration and release to open the Repeater Alarms
window .
from the command line (stand-alone mode):
1. From the appropriate directory type:
spmarun r4al <IP Address> <community name>
NOTES
The spmarun script invoked first in the above command temporarily sets the environment
variables SPMA needs to operate; be sure to use this command any time you launch an
application from the command line. The script is automatically invoked when you launch
the application from the icon menu or from within the Hub View.
If you wish to change any Alarm Configurations, be sure to use a community name with
at least Read/Write access. If you only wish to view current settings, a community name
with Read access will be sufficient.
If there is a hostname mapped to your EMM-E6’s IP address, you can use <hostname>
in place of <IP address> to launch this application. Please note, however, that the
hostname is not the same as the device name which can be assigned via Local
Management and/or SPMA; you cannot use the device name in place of the IP address.
Figure 3-1. Repeater Alarms Window
3-2 Using Alarm Configuration
Page 53

Configuring Alarms
While configuring alarms for your EMM-E6 you must set the threshold and
timebase that will factor in triggering the alarm. From the repeater alarms
window you set an alarm timebase that applies to all enabled alarms at the
repeater, module and port level; this timebase is the interval (in seconds) over
which the selected variable(s) will be counted for comparison to the threshold
values. The thresholds are configured separately for each alarm type and at each
alarm level (repeater, module, and port). For example, if the Broadcasts alarm is
enabled, the repeater-level threshold is set at 1000, and the timebase is set to 10
seconds, the EMM-E6 will generate an alarm if 1000 broadcast packets are
processed within a 10-second time period; if the module-level threshold is set to
100, the EMM-E6 will also generate an alarm if 100 broadcast packets are
processed by that module within the 10-second time period.
Since alarm condition samples are taken at the end of the defined timebase interval, alarm
NOTE
conditions which occur over the span of two timebase intervals will not be detected even if
the threshold is crossed within the defined timebase. For example, if the timebase is set to
10 seconds and the broadcast alarm threshold is set to 20, 20 or more broadcast packets
may be detected in the last 5 seconds of one time interval and the first five seconds of the
subsequent interval (for a total time interval of 10 seconds), but no alarm will be triggered
because the broadcasts occurred within two different timebase intervals. The shorter the
timebase, the more likely this condition is to occur.
Alarm Configuration
You can set alarm thresholds for the following variables:
Traffic
The traffic threshold determines the total number of packets that can be processed
by the repeater, module, or port within the user-defined timebase before an alarm
is triggered. Allowable values are 1 to ≈ 4 billion.
Collisions
The collisions threshold sets the number of collisions per good packet that will be
allowed on the repeater, module, or port in the user-defined timebase before an
alarm is generated. Allowable values are 1 to 15 collisions per good packet.
Errors
The errors threshold determines what percentage of total packets received by the
repeater, module, or port within the specified timebase can be errors of the
selected type or types before an alarm is triggered. Allowable values are one to
100; percentages will be calculated based on the number of error packets of all
types selected. You can select any combination of the following error types:
CRC If this check box is selected, all packets with Cyclical
Redundancy Check (CRC) errors will be included in
calculating the overall percentage of errors.
Using Alarm Configuration 3-3
Page 54

Alarm Configuration
Alignment If this check box is selected, all misaligned packets will
be included in calculating the overall percentage of
errors. A misaligned packet is one with an non-integral
number of bytes; these are also sometimes referred to as
framing errors.
Runts If this check box is selected, the number of runt packets
will be included in calculating the overall percentage of
errors. A runt packet is one that is less than the minimum
Ethernet frame size of 64 bytes.
Giants If this check box is selected, the number of giant packets
will be included in calculating the overall percentage of
errors. A giant packet exceeds the maximum Ethernet
frame size of 1518 bytes (excluding the preamble).
OOW Collisions If this check box is selected, all collisions out of the
standard collision window (51.2µs) will be included in
calculating the overall percentage of errors. Out-ofwindow collisions are typically caused by faulty network
design.
The CARGO description displayed in the alarm type list is an acronym
representing the available error types: C = CRC, A = Alignment, R = Runts,
G = Giants, O = OOW Collisions.This mask will only display the letters
corresponding to the error types you have chosen to include in the overall
percentage of errors.
Broadcast
The broadcasts threshold determines the number of broadcast packets that must
be processed by the repeater, module, or port within the user-defined timebase
before an alarm is reached. Allowable values are 1 to ≈ 4 billion.
Setting Repeater Alarms
A repeater alarm is based on the combined conditions of a hub network. You can
set alarms for error levels (for all errors or just specific types of errors), broadcast
packet traffic, data traffic, and collisions.
If an alarm type is not supported by your device the alarm configuration options of this
NOTE
type will be grayed out.
3-4 Setting Repeater Alarms
Page 55

Setting and Changing Alarms
1. In the Alarms window, click mouse button 1 on a repeater selection in the
scroll list.
2. Click mouse button 1 on to open the Set Repeater Alarms
window.
Alarm Configuration
Figure 3-2. Set Repeater Alarms Window
3. In the Set Repeater Alarms window, select one of the alarm types:
Collisions, Errors, Traffic, or Broadcast. If you select Errors, the Mask
check boxes become active and you can select all or just some of the five
different error types. The mask CARGO, displayed in the alarm type list, is an
acronym for the error types: C = CRC, A = Alignment, R = Runts, G = Giants,
O = OOW Collisions.
4. Highlight and edit the Alarm Threshold, which is the number that, if reached
within the Timebase, triggers the alarm.
5. If necessary , highlight and edit the Timebase, which is the number of seconds
you are allowing for an alarm condition to take place. For example, if the
Timebase is set to 10, the Broadcast Alarm Type is enabled, and the Alarm
Threshold is set to 25, the EMM-E6 generates an alarm if it observes 25
Broadcast packets within 10 seconds. A collision alarm is based on the
number of collisions per good packet within the Timebase. Error alarms are
based on the percentage of errors per total packets within the Timebase.
6. Click mouse button 1 on the Enable or Disable button to set the highlighted
alarm’s status, then click .
Setting Repeater Alarms 3-5
Page 56

Alarm Configuration
The Timebase applies to all enabled alarms, port-level and module-level alarms as well as
NOTE
repeater-level alarms. The Timebase appears in each alarms window — repeater, module,
and port — but you can only edit it in the Repeater Alarms window.
Since alarm condition samples are taken at the end of the defined timebase interval, alarm
conditions which occur over the span of two timebase intervals will not be detected even if
the threshold is crossed within the defined timebase. For example, if the timebase is set to
10 seconds and the broadcast alarm threshold is set to 20, 20 or more broadcast packets
may be detected in the last 5 seconds of one time interval and the first five seconds of the
subsequent interval (for a total time interval of 10 seconds), but no alarm will be triggered
because the broadcasts occurred within two different timebase intervals. The shorter the
timebase, the more likely this condition is to occur.
Setting Module and Port Alarms
The following sections describe procedures for setting module and port alarm
limits. Module-level alarms are based on the combined traffic within a particular
module, while port-level alarms are based on an individual port.
Setting Module Alarms
1. In the Alarms window, click mouse button 1 on a repeater selection in the
scroll list.
2. Click mouse button 1 on to open the Set Module Alarms
window.
3-6 Setting Module and Port Alarms
Page 57

Alarm Configuration
Figure 3-3. Set Module Alarms Window
3. Select one or more modules in the scroll list. To apply one set of conditions to
all modules, you can either select each module in the list or use the Set
Alarm For box at the bottom of the window to choose either Selected
Modules, which applies the conditions to the modules you selected in the
module list, or All Modules, which applies the conditions to all modules in the
hub network.
4. Click mouse button 1 on one of the four Alarm Types: Collisions, Errors,
Traffic, or Broadcast. (Alarm Types not available for this device are grayed.)
If you select Errors, the Mask check boxes become activ e and you can select
all or just some of the five error types. The Error Mask CARGO, displayed in
the module list, is an acronym for the error types: C = CRC, A = Alignment,
R = Runts, G = Giants, O = OOW Collisions.
5. Set the Status to Enabled.
6. Highlight and edit the Alarm Threshold, which is the percentage of
errors/total packets, or the number of traffic packets, broadcast packets, or
collisions/good packet within the Timebase that will activate the alarm.
Setting Module and Port Alarms 3-7
Page 58

Alarm Configuration
7. If you select Yes for Disable Module on Alarm, the defined condition will
cause the device to disable the module.
If a module is disabled by an alarm, you must manually re-enable the module before it can
NOTE
again pass traffic. Resetting the device does not re-enable the module.
8. Click mouse button 1 on .
Setting Port Alarms
1. In the Alarms window, click mouse button 1 on a repeater selection in the
scroll list.
2. Click mouse button 1 on to open the Set Port Alarms window.
Figure 3-4. Set Port Alarms Window
3-8 Setting Module and Port Alarms
Page 59

Alarm Configuration
3. Select one or more ports in the scroll list. To apply one set of conditions to all
ports, you can either select each port in the list or use the Set Alarm For box
at the bottom of the window to choose either Selected Ports, which applies
the conditions to the ports you selected in the port list, or All Ports on
Repeater, which applies the conditions to all the ports on the repeater, or All
Ports on Module, which applies the conditions to all the ports on the module.
4. Click mouse button 1 on one of the four Alarm Types: Collisions, Errors,
Traffic, or Broadcast. (Alarm Types not available for this device are grayed.)
If you select Errors, the Mask check boxes become activ e and you can select
all or just some of the five error types. The Error Mask CARGO, displayed in
the module list, is an acronym for the error types: C = CRC, A = Alignment,
R = Runts, G = Giants, O = OOW Collisions.
5. Set the Status to Enabled.
6. Highlight and edit the Alarm Threshold, which is the percentage of
errors/total packets, or the number of traffic packets, broadcast packets, or
collisions/good packet within the Timebase that will activate the alarm.
7. If you select Yes for Disable Port on Alarm, the defined condition will cause
the device to disable the port.
NOTE
NOTE
If a port is disabled by an alarm, you must manually re-enable the port before it can again
pass traffic. Resetting the device does not re-enable the port.
8. Click mouse button 1 on .
The Timebase applies to all enabled alarms, Port-level and module-level alarms as well as
repeater-level alarms. The T imebase appears in each alarms window , repeater, module, and
port, but you can only edit it in the Repeater Alarms window.
Setting Module and Port Alarms 3-9
Page 60

Alarm Configuration
3-10 Setting Module and Port Alarms
Page 61

Chapter 4
Link/Seg T raps
What are Link and Segmentation traps; enabling and disabling these traps at the device, module,
and port levels
Among the traps which Cabletron devices are designed to generate are traps that
indicate when a repeater port gains or loses a link signal, when the repeater
segments (disconnects) a port due to collision activity, and when a segmented
port becomes active again. In some networks, these Link and Segmentation traps
may be more information than a network manager wants to see. So SPMA
provides you with a means to selectively enable and disable Link and
Segmentation traps: you can turn traps on and off for all ports on the device, all
ports on a selected module or modules, or for individual ports.
SPMA does not accept the trap messages; that task is left to your network management
NOTE
system. (See the appropriate network management system documentation for details
about viewing trap messages.) When this utility is used in stand-alone mode, traps will
either be ignored when they return to the workstation from which you ar e running SPMA
for the EMM-E6, or they will turn up at another management workstation which has
been configured to accept traps. Note also that, regardless of the configuration performed
using this utility, NO traps will be sent by the device unless its trap table has been
properly configured; see the EMM-E6 hardware manual and/or the Trap T able chapter in
the SPMA Tools Guide for more information.
What is a Segmentation Trap?
Cabletron’s Ethernet repeaters count collisions at each port. If a port experiences
32 consecutive collisions, the repeater segments the port to isolate the source of
the collisions from the rest of the network. When the repeater segments a port, it
generates a portSegmenting trap. As soon as a segmented port receives a good
packet, the repeater reconnects the port to the network and generates a
portUnsegmenting trap.
4-1
Page 62

Link/Seg Traps
Unterminated BNC (thin coax) ports appear in the Hub View as segmented ports. When
NOTE
you attach a thin coax cable or a 50 Ω terminator to a port, the repeater generates a
portUnsegmenting trap; when you remove the cable or terminator, the repeater
generates a portSegmenting trap. Note also that devices at both ends of the cable will
generate the portUnsegmenting and portSegmenting traps, even if only one end of the
cable has been disconnected.
What is a Link Trap?
Some Cabletron Ethernet repeater ports — including RJ45 twisted pair and fiber
optic ports — generate a link signal to monitor the status of their connection with
the device at the other end of the cable segment. If the cable is removed or broken,
the port’s link status goes to “No Link” and the repeater generates a
portLinkDown trap. When a port in a “No Link” condition receives a link signal,
the port goes to a “Link” condition and the repeater generates a portLinkUp trap.
Note that devices at both ends of the disconnected or broken cable will generate
the portLinkDown and portLinkUp traps, even when only one end of the cable
has been removed.
BNC (thin coax), AUI, and transceiver ports do not support a link signal. As described
NOTE
above, BNC ports respond to changes in link status by generating portSegmenting and
portUnsegmenting traps; AUI and transceiver ports do not respond at all to changes in
link status (unless the port has been segmented due to excessive collisions), and will
always display as on, even if no cable is connected.
Enabling and Disabling Link/Seg Traps
Although each Cabletron device comes with a number of traps built in to the
firmware, no device will generate these traps unless it is configured to do so. This
can be accomplished via Local Management (by enabling traps and entering your
workstation’s IP address in the Community Names screen), or via the SPMA Trap
Table utility, accessible from the icon menu or from the command line. Once traps
as a whole have been enabled, you can use the Link/Seg Traps feature to
selectively enable and disable link and segmentation traps as required by your
network management needs.
To open the Repeater Link/Seg Traps window
from the icon:
1. Click on the appropriate EMM-E6 icon to display the icon menu.
2. Drag down to Link/Seg T raps and release.
4-2 What is a Link Trap?
Page 63
NOTES
Link/Seg Traps
from the Hub View:
1. Click on to display the Device menu.
2. Drag down to Link/Seg T raps and release.
from the command line (stand-alone mode):
1. From the appropriate directory, type
spmarun r4hwtr <IP address> <community name>
The spmarun script invoked first in the above command temporarily sets the environment
variables SPMA needs to operate; be sure to use this command any time you launch an
application from the command line. This script is automatically invoked when you launch
an application from the icon menu or from within the Hub View.
If you wish to change any Link/Seg Trap settings, be sure to use a community name with
at least Read/Write access. If you only wish to view current settings, a community name
with Read access will be sufficient.
If there is a hostname mapped to your EMM-E6’s IP address, you can use <hostname>
in place of <IP address> to launch this application. Please note, however, that the
hostname is not the same as the device name which can be assigned via Local
Management and/or SPMA; you cannot use the device name in place of the IP address.
The main Repeater Link/Seg Traps window, Figure 4-1, will appear.
Figure 4-1. Repeater Link/Seg Traps Window
Enabling and Disabling Link/Seg Traps 4-3
Page 64

Link/Seg Traps
Configuring Link/Seg Traps for the Repeater
To enable or disable Link and Segmentation traps for all ports on a repeater:
1. In the Repeater Link/Seg Traps window , click mouse button 1 on the repeater
interface for which you would like to configure link and segmentation traps.
2. Click mouse button 1 on ; the Channel X Link/Seg Traps
window, Figure 4-2, will appear.
Figure 4-2. Channel X Link/Seg Traps Window
3. In the Link T raps field, click mouse button 1 on the appropriate selection to
Enable or Disable link traps for the repeater.
4. In the Segmenting T raps field, click mouse button 1 on the appropriate
selection to Enable or Disable segmenting traps for the repeater.
5. Click mouse button 1 on to save your changes; the current status
will be displayed in each field to the right of the field name. Click on
to exit the window.
Viewing and Configuring Link/Seg Traps for Hub Modules
To enable or disable Link and Segmentation traps for all ports on the selected hub
module or modules:
1. In the Repeater Link/Seg Traps window, select a repeater interface in the
scroll list.
2. Click mouse button 1 on ; the module tr aps window, Figure 4-3,
will appear.
4-4 Enabling and Disabling Link/Seg Traps
Page 65

Link/Seg Traps
Figure 4-3. The Module Traps Window
3. In the Module Traps window, click mouse button 1 to select the module for
which you wish to configure link and segmentation traps. If the Set T rap
Status For field displays
to select any modules; to de-select an y highlighted module , click on it again. If
the selection
available modules will be automatically selected; if you de-select any module,
the Set Trap Status For field will automatically rev ert to the
setting. To change the setting in the Set Trap Status For field, click mouse
button 1 on the currently displayed setting, and drag down to select a new
setting.
4. Click on the appropriate selection in the Link T raps field to Enable or Disable
link traps for the selected modules, as desired.
5. Click on the appropriate selection in the Segmenting T raps field to Enable or
Disable segmenting traps, as desired.
6. Click on to save your changes; click on to exit the
window.
All Modules
Selected Modules
is displayed in the Set Trap Status For field, all
(the default setting), you can clic k
Selected Modules
Enabling and Disabling Link/Seg Traps 4-5
Page 66

Link/Seg Traps
Viewing and Configuring Link/Seg Traps for Ports
To enable or disable Link and Segmentation traps for individual ports:
1. In the Repeater Link/Seg Traps window, select a repeater in the scroll list.
2. Click mouse button 1 on ; the port traps window, Figure 4-4, will
appear.
Figure 4-4. The Port Traps Window
3. In the port traps window, click mouse button 1 to select the port or ports for
which you wish to configure traps. If the Set Trap Status For field displays
Selected Ports
select any highlighted port, click on it again. If the selection
Module
port at a time; trap status will be set for all ports on the same module as the
selected port. If the selection
Trap Status For field, all available ports will be automatically selected; if you
de-select any port, the Set Trap Status For field will automatically revert to
the
field, click on the currently displayed setting, and drag down to select a new
setting.
4. Click on the appropriate selection in the Link T raps field to Enable or Disable
link traps for the selected modules, as desired.
is displayed in the Set Trap Status For field, you can select only one
Selected Ports
(the default setting), you can click to select any ports; to de-
All Ports on
All Ports on Repeater
setting. To change the setting in the Set Trap Status For
is displayed in the Set
4-6 Enabling and Disabling Link/Seg Traps
Page 67

Link/Seg Traps
5. Click on the appropriate selection in the Segmenting T raps field to Enable or
Disable segmenting traps, as desired.
6. Click on to save your changes; click on to exit the
window.
Enabling and Disabling Link/Seg Traps 4-7
Page 68

Link/Seg Traps
4-8 Enabling and Disabling Link/Seg Traps
Page 69

Repeater Redundancy
This chapter describes how to configure and enable redundant circuits
Setting Network Circuit Redundancy
The redundancy application gives you the ability to define redundant circuits for
your EMM-E6 to ensure that critical network connections remain operational.
Each circuit has a designated primary port and one or more backup ports. The
EMM-E6 monitors the link status of the primary port’s connection to one or more
network IP addresses; if the link fails, the EMM-E6 automatically switches traffic
to a backup port.
Chapter 5
NOTE
Before you configure redundancy, make sure that only the primary physical link is
connected to the network. If a backup port is connected before you configure and enable
redundancy, you create a data loop.
To open the main Repeater Redundancy window
from the icon:
1. Click on the appropriate EMM-E6 icon to display the icon menu.
2. Drag down to Redundancy and release.
from the Hub View:
1. Click on to display the Device menu.
2. Drag down to Redundancy and release.
5-1
Page 70

Repeater Redundancy
from the command line (stand-alone mode)
1. From the appropriate directory, type:
The spmarun script invoked first in the above command temporarily sets the environment
NOTES
variables SPMA needs to operate; be sure to use this command any time you launch an
application from the command line. The script is automatically invoked when you launch
the application from the icon menu or from within the Hub View.
If you wish to change any redundancy settings, be sure to use a community name with
at least Read/Write access. If you only wish to view current settings, a community name
with Read access will be sufficient.
If there is a hostname mapped to your EMM-E6’s IP address, you can use <hostname>
in place of <IP address> to launch this application. Please note, however, that the
hostname is not the same as the device name which can be assigned via Local
Management and/or SPMA; you cannot use the device name in place of the IP address.
The main Repeater Redundancy window, Figure 5-1, will appear.
spmarun r4red <IP address> <community name>
Figure 5-1. The Repeater Redundancy Window
Configuring a Redundant Circuit
To establish or edit a redundant circuit:
1. In the Repeater Redundancy window, click mouse button 1 on the repeater
interface for which you would like to edit or establish a redundant circuit, then
click . The Channel X Redundancy window, Figure 5-2, will appear.
5-2 Setting Network Circuit Redundancy
Page 71

Repeater Redundancy
Figure 5-2. The Channel X Redundancy Window
2. If you want to change a circuit’s name or the number of retries, highlight the
appropriate circuit and click . The Change Circuit
window, Figure 5-3, will appear.
Figure 5-3. The Change Circuit Window
Setting Network Circuit Redundancy 5-3
Page 72

Repeater Redundancy
3. With the appropriate Circuit Name highlighted, click to access the
In the appropriate boxes, enter a new circuit name (up to 16 alphanumeric
characters) and/or number of retries; Retries is the number of times the
EMM-E6 tests the connection to the first IP address listed in the Circuit
Addresses window before it gives up and moves on to the next address. The
valid range of retries you can enter into this field is 0-16. Be sure to click on
before exiting the window to save your changes.
Add Circuit Address window, Figure 5-4.
Figure 5-4. The Add Circuit Address Window
NOTE
In this window you can define IP addresses of up to 8 devices on the netw ork.
These addresses identify the destination nodes that the EMM-E6 looks for to
determine the status of the active link. If the device determines that it has lost
the link with the first address in the Circuit Addresses list, it checks the link
status with the next address. If it can’t establish a link with any address in the
list, the device switches traffic to a backup port.
a. To add a circuit address, enter a valid network IP address and then click
. Repeat as necessary to add additional addresses. Click
to exit the window.
The EMM-E6 will poll the circuit addresses in the order they were entered.
b. To delete a circuit address, highlight the address in the Circuit Addresses
list in the Channel X Redundancy window, and click .
4. The bottom half of the Channel X Redundancy window is where you define
the primary port and backup ports for the highlighted Circuit Name. Using the
Module and Port boxes and the Add button, enter up to 8 ports to define the
circuit.
5-4 Setting Network Circuit Redundancy
Page 73

NOTE
Repeater Redundancy
5. By default, all ports are created as Inactive Backup ports. Y ou should set one
port to be the Primary port and one port to be the Active port. Typically, the
same port is both Primary and Active but this is not required. To select primary
and active ports, click button 1 on a port to highlight it then click ;
select the same or another port and click . Only one port can be
the Primary port and only one port can be Active at any one time; if you set a
different port to be Primary or Active, the original Primary or Active port
automatically resets to Backup/Inactive.
The Status of the Circuit Name must be set to Disabled when you configure the port list.
All backup ports will be disabled as soon as you enable the redundant circuit; the ports
remain disabled until they become active due to primary port failure. Ports cannot be
manually re-enabled until you have disabled and reset the circuit of which they were a
part. Backup ports which are part of a disabled circuit cannot be manually re-enabled.
6. Once you have configured all the ports that compose the redundant circuit,
enable the circuit by clicking .
NOTE
NOTE
Be sure to make all physical connections to the backup ports once the redundant circuit
has been configured and enabled.
To clear the settings in one circuit, highlight the Circuit Name that you want to
clear, and click on .
To clear all redundancy configurations, click on in the All Circuits
portion of the window. Reset does the following:
• Deletes all entries in the Circuit Addresses box
• Changes the status of every Circuit to Disabled
• Reverts to previous Circuit Name(s)
• Clears all module and port entries
After clearing redundancy settings by either method, backup ports remain disabled until
you manually reenable them so that data loops do not occur. Before you enable the ports,
disconnect their physical connections.
Setting Network Circuit Redundancy 5-5
Page 74

Repeater Redundancy
Monitoring Redundancy
Once you have configured your redundant circuits, you can use the fields in the
All Circuits box to set the parameters that the EMM-E6 uses to periodically test
each of the circuits. The EMM-E6 automatically polls all enabled circuits through
the Primary port and all Backup ports at the time specified in the Test T ime box. If
the first poll fails (results in a no link condition with all of the circuit IP addr esses),
the EMM-E6 checks the circuit’s Retries field. If Retries is greater than 0, the
EMM-E6 waits the number of seconds specified in the Poll Interval field, and
then polls the circuit again.
To set the Poll Interval:
1. In the All Circuits box, type in a new value in the Poll Interval field and click
. Poll Interval is the time in seconds between retries (if the first
attempt is unsuccessful).
To set the Test Time:
1. In the All Circuits box, type a new test time in the Test Time field in a 24-hour
HH:MM:SS format and click . The Test Time is the time of day when
the EMM-E6 polls the addresses listed in each of the enabled circuits.
To immediately test all enabled circuits:
1. Click in the All Circuits box.
5-6 Monitoring Redundancy
Page 75

Chapter 6
Source Addressing
Displaying the Source Address list; setting the Aging Time; selecting the Hash Type; effects of Source
Address Locking; configuring Source Address traps; finding a Source Address
Displaying the Source Address List
The Source Address List, or Table (SAT), contains the MAC address and its
associated vendor name for each device communicating through a port in the
EMM-E6-controlled hub. Each detected source address is also identified by the
module and port through which it is communicating with the EMM-E6.
To view a EMM-E6’s Source Address List:
from the icon:
1. Click on the appropriate EMM-E6 icon to display the icon menu.
2. Drag down to Source Address and release.
from the Hub View:
1. Click on to display the Device menu.
2. Drag down to Source Address and release.
from the command line (stand-alone mode):
1. From the appropriate directory, type
spmarun r4sa <IP address> <community name>
6-1
Page 76

Source Addressing
NOTES
The spmarun script invoked first in the above command temporarily sets the environment
variables SPMA needs to operate; be sure to use this command any time you launch an
application from the command line. This script is automatically invoked when you launch
an application from the icon menu or from within the Hub View.
If you wish to change any Source Address settings, be sure to use a community name
with at least Read/Write access. If you only wish to view current settings, a community
name with Read access will be sufficient. If you wish to lock or unlock ports, you must use
a community name with SuperUser access.
If there is a hostname mapped to your EMM-E6’s IP address, you can use <hostname>
in place of <IP address> to launch this application. Please note, however, that the
hostname is not the same as the device name which can be assigned via Local
Management and/or SPMA; you cannot use the device name in place of the IP address.
The Repeater Source Address window, Figure 6-1, will appear.
Figure 6-1. The Repeater Source Address Window
The Repeater Source Address window provides a list of the repeater interfaces
available on the EMM-E6, as well as command buttons that allow you to display
the Source Address List and enable and disable module and port source
addressing traps.
The ability to enable or disable source addressing traps at the module and port level is not
NOTE
available in all versions of repeater device firmware; if the Module Trap and Port Trap
buttons are grayed out, these features are not available on your device. Contact the
Cabletron Systems Global Call Center for more information on upgrading your device
firmware.
6-2 Displaying the Source Address List
Page 77
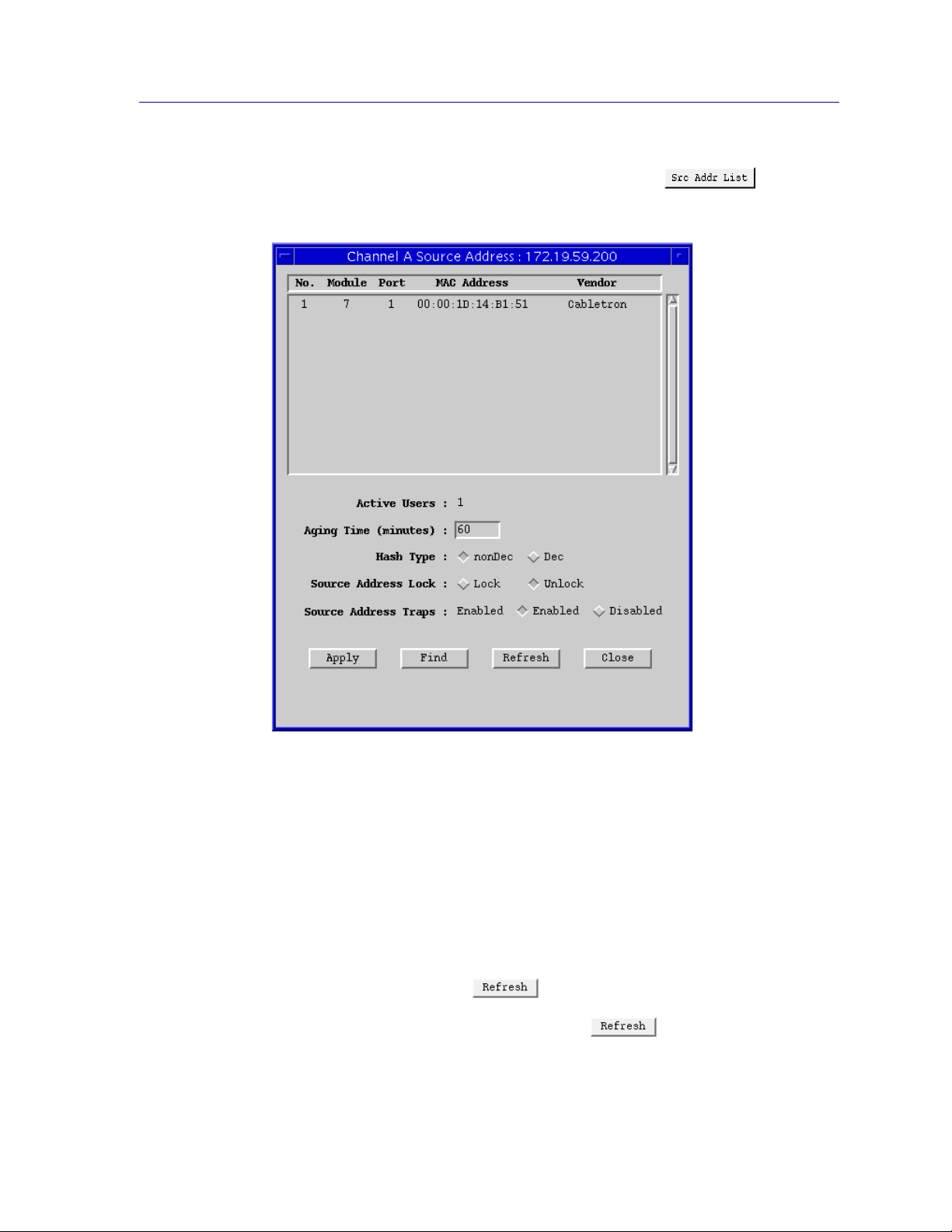
Source Addressing
To view the source address list for the device, highlight the interface for which
you wish to view the SAT, then click mouse button 1 on ; the Source
Address List window, Figure 6-2, will appear.
Figure 6-2. The Source Address List Window
The Source Address List window displays addresses of all devices that have
transmitted packets through the EMM-E6 within a time period less than the SA T’s
defined aging time (addresses that have not transmitted a packet during one
complete cycle of the aging timer will be purged). The Aging Time is userconfigurable; see Setting the Aging Time, page 6-4. The list window can display
about ten addresses at once; use the scroll bar to the right of the list window to
view additional addresses, if necessary.
Since the SAT is constantly changing as old entries are aged out and new ones
learned from the network, you should occasionally update the displayed list by
clicking mouse button 1 on . Once displayed, the list is static and will
not reflect recent changes. Also static is the displayed number of Active Users;
this field will also update when you click on .
Displaying the Source Address List 6-3
Page 78

Source Addressing
The snapshots of the Source Address List that you can obtain via this feature do not r eflect
NOTE
the current port security status of the SAT — that is, when Source Address Locking is
enabled, you can still observe addresses being aged out of the table and new addresses
being added as you refresh the Source Address List displayed in this window. However,
the EMM-E6 remembers the addresses that were in the table when locking was enabled,
and will continue to protect locked ports from access by unauthorized sources. For more
information, see Locking Source Addresses, page 6-5.
Setting the Aging Time
The source address list Aging Time determines the minimum amount of time an
inactive source address will remain in the Source Address Table before it is
purged. The source address timer runs continuously beginning at the time the
device is turned on; source addresses that are added to the SAT during one timer
cycle will remain in the table for the rest of the current cycle and at least through
the next complete cycle. If no packets have been received from that address
during one complete cycle, the address will be purged.
The Aging Time is user-configurable, and can be set using the Aging Time text
box in the Source Address list window.
To change the Aging Time:
1. In the Source Address List window (Figure 6-2, page 6-3), highlight the
displayed aging time.
2. Enter your desired aging time in minutes; allowable range is 0 to 4320 (three
days).
3. Click mouse button 1 on to save your change.
The new Aging Time takes effect immediately.
Setting the Hash Type
You can increase the efficiency with which your EMM-E6 handles the Source
Address Table by selecting the appropriate hashing algorithm. If you are
operating in a DECnet environment, or one which incorporates some DECnet
elements, select the DEC hashing algorithm; if your network contains no DECnet
elements (or at least none operating on the same network segment as your
EMM-E6), select the non-DEC hashing algorithm. Making the wrong selection
won’t do any damage, but making the correct selection will optimize
performance.
To set the Hash Type for a repeater interface, or channel:
1. In the Repeater Source Address window , click mouse b utton 1 on the repeater
interface for which you would like to set the hash type.
6-4 Setting the Hash Type
Page 79

2. Click mouse button 1 on ; the Channel X Source Address List
window, Figure 6-2 (page 6-3), will appear.
3. In the Hash Type field, click mouse button 1 on the appropriate selection to
apply Dec or nonDec hashing to all ports on the selected repeater channel.
4. Click mouse button 1 on to save your changes; click on
to exit the window.
If your EMM-E6 firmware does not support the Hash Type feature, this field will be
NOTE
unavailable.
Locking Source Addresses
When Source Address Locking is enabled, it puts into place a number of security
measures designed to protect your hub from unauthorized access. Depending on
the revision of firmware installed on your EMM-E6 and the kinds of MIMs in the
hub, locking ports can provide a number of different pr otections, including secure
address assignment, trunk port locking, configurable violation response, both
eavesdrop and intruder protection, multi-level locking modes, and new
definitions for station and trunk ports: station ports are those detecting zero, one,
or two source addresses; trunk ports are those detecting three or more.
Source Addressing
NOTE
Enabling port locking from the Source Address List window activates all
applicable security protections, as configured via the Security application
(described in Chapter 7 of this guide).
Since the multi-level locking feature cannot be implemented from the Source Addr ess List
window, locking ports from this window will apply Full lock status by default to any
ports which are currently unlocked. Any ports which are already in Continuous lock
mode, however, will remain so. For more information on these lock modes and other
security features, see Chapter 7, Security.
To enable or disable Source Address Locking:
1. Click mouse button 1 on the appropriate option in the Source Address Lock
field.
2. Click mouse button 1 on to set your new lock status.
Locking Source Addresses 6-5
Page 80

Source Addressing
NOTE
Remember, you must have SuperUser (SU) access to the device in order to lock or unlock
ports.
In addition to activating the security measures as configured via the Security
application, locking source addresses has the following effects:
• On devices running older versions of firmware, unlinked ports will be
disabled immediately after locking has been enabled; these ports can be reenabled using their port menus, but they will immediately be disabled again
if a device is connected and begins transmitting (since the port’s source
address table was locked in an empty state). On devices with newer firmware,
unlinked ports are not automatically disabled in response to port locking, but
they , too, will be immediately disabled if a device is connected and attempts to
transmit packets.
• Although the Source Aging Interval does not apply to station ports when
Source Address Locking is enabled, the snapshot of the SAT provided by the
Source Address List window may show a learned source address aging out if
that address remains inactive, and the appropriate trap will be generated.
• Once Source Address Locking has been enabled, each port’s topology status
(station or trunk) remains fixed and will not change while locking remains
enabled, regardless of any changes in the number of source addresses
detected.
• If Source Addr ess Locking has been enabled, and one or more ports have been
shut down because a new source address attempted access, those ports will
remain disabled even after the EMM-E6 has been reset, and must be re-enabled
manually .
Source Address Locking on Older Devices
If your EMM-E6 is running a firmware version previous to 2.00.16, Source
Address Locking is implemented somewhat differently:
• Station ports are defined as those detecting zero or one source address; trunk
ports as those detecting two or more.
• If a locked station port experiences a violation, the port will be automatically
disabled and no traffic will be allowed through — not even traffic from the
known source address.
• Trunk ports are never locked.
• Unlinked ports are immediately disabled.
• The Source Aging Interval does not apply to locked station ports.
6-6 Locking Source Addresses
Page 81

• A port’s topology status (station or trunk) remains fixed while locking is in
effect, even if the number of detected addresses changes.
• Any ports disabled due to a violation (or because they were unlinked when
locking was enabled) must be manually re-enabled via their Port menus, and
• There are no additional Security features available.
If you are not sure which set of port locking features your device firmware
supports, contact the Cabletron Systems Global Call Center.
Configuring Source Address Traps
The EMM-E6 can issue several different traps in response to changes in the Sour ce
Address Table; you can enable and disable certain of these traps for the repeater
as a whole, and, if your device has very new firmware, they can also be enabled or
disabled for each individual module and port.
If the Module Traps and Port Traps buttons on the Repeater Source Address screen are
NOTE
grayed-out, your device firmware does NOT support the ability to enable and disable
source addressing traps at the module and port levels. Contact the Cabletron Systems
Global Call Center for information about upgrading your device firmware.
Source Addressing
SPMA does not accept the trap messages; that task is left to your network management
system. (See the appropriate network management system documentation for details
about viewing trap messages.) When this utility is used in stand-alone mode, traps will
either be ignored when they return to the workstation from which you ar e running SPMA
for the EMM-E6, or they will turn up at another management workstation which has
been configured to accept traps. Note also that, regardless of the configuration performed
using this utility, NO traps will be sent by the device unless its trap table has been
properly configured; see the EMM-E6 hardware manual and/or the Trap T able chapter in
the SPMA Tools Guide for more information.
You can enable and disable the following Source Address traps:
•A newSourceAddress trap is generated when a station port — one receiving
packets from zero, one, or two source addresses — receives a packet from a
source address that is not currently in its source address table. Information
included in this trap includes the board number, port number, and source
address associated with the trap. Trunk ports — those receiving packets from
three or more source addresses — will not issue newSourceAddress traps.
•A sourceAddressTimeout trap is issued anytime a sour ce addr ess is aged out
of the Source Address Table due to inactivity. The trap’s interesting
information includes the board and port index, and the source address that
timed out. (See Setting the Aging Time,page 6-4, for more information.)
Configuring Source Address Traps 6-7
Page 82

Source Addressing
Other traps that will be sent in response to changes in source addressing (even
when the above traps have been disabled) include:
• PortTypeChanged traps are issued when a port’s topology status changes
from station to trunk, or vice versa. The interesting information includes the
board and port index, and the port’s new topology status.
•A lockStatusChanged trap is generated when the ports in the hub are locked
or unlocked using the Source Addr ess Lock option in the Sour ce Address List
window or by using the lock options in the Security application; the interesting
information is the new lock status. (See Locking Source Addresses,page 6-5,
or Chapter 7, Security, for more information.)
• PortSecurityViolation and portViolationReset traps are sent in response to
changes related to port locking: if ports are locked, the portSecurityViolation
trap indicates that a new source address has attempted access on one of the
ports, and the configured security actions are being taken; the interesting
information is the board and port index, and the violating address.
PortViolationReset traps are sent when management intervention has reenabled a port or ports previously disabled in response to a port security
violation; the interesting information is board and port index. Again, see
Locking Source Addresses,page 6-5, for more information.
Repeater-level T raps
The current status of the repeater-level sour ce addressing traps is displayed in the
Source Address Traps field in the Source Address List window (Figure 6-2,
page 6-3).
A status of Enabled indicates that source address traps have been enabled for all
ports on all modules installed in the EMM-E6-controlled hub; a status of Disabled
indicates that source address traps have been disabled for all ports on all modules;
and a status of Other indicates that there is some combination of enabled and
disabled source address traps on the modules and/or ports in the hub or device.
To change the current status and enable or disable traps for all ports in the EMME6-controlled hub:
1. Click mouse button 1 on the appropriate option in the Source Address Traps
field.
2. Click button 1 on to set your new trap status; the new status will
be displayed to the left of the options in the Sour ce Address Traps field. Note
that enabling or disabling traps at the repeater le vel will eliminate an y status of
Other by setting all ports on all modules to the same status.
6-8 Configuring Source Address Traps
Page 83

Module- and Port-level Traps
To set module- and port-level source addressing traps, select the appropriate
channel in the Repeater Source Address window, then click on to
enable and disable module-level traps, or on to enable and disable
port-level traps.
It is not necessary to close the Source Address List before launching the module and port
NOTE
traps windows; just move the Source Address List window out of the way , if necessary, to
reach the main Repeater Source Address window.
As with repeater-level trap status, a status of Other for any module indicates that
there is some combination of enabled and disabled source address traps on the
ports in that module.
To configure trap status for all ports on a selected module or modules:
1. In the Module Source Address Traps window (Figure 6-3, next page), click
mouse button 1 to select the module for which you wish to enable or disable
traps. If the Set Trap Status For field displays
setting), you can click to select any modules; to de-select any highlighted
module, click on it again. If the selection
Trap Status For field, all available modules will be automatically selected; if
you de-select any module, the Set Trap Status For field will automatically
revert to the
Status For field, click mouse button 1 on the currently displayed setting, and
drag down to select a new setting.
Selected Modules
Source Addressing
Selected Modules
All Modules
setting. To change the setting in the Set Trap
is displayed in the Set
(the default
2. Click on the appropriate selection in the Trap Status field to enable or disable
traps for the selected modules, as desired.
3. Click on to save your changes. Note that enabling or disabling
traps at the module level will eliminate any module status of Other by setting
all ports on the selected module or modules to the same status.
Configuring Source Address Traps 6-9
Page 84

Source Addressing
Figure 6-3. The Module Source Address Traps Window
To enable or disable port-level traps:
1. In the Port Source Address Traps window (Figure 6-4, below), click mouse
button 1 to select the port or ports for which you wish to enable or disable
traps. If the Set Trap Status For field displays
setting), you can click to select any ports; to de-select any highlighted port,
click on it again. If the selection
Traps Status For field, you can select only one port at a time; trap status will
be set for all ports on the same module as the selected port. If the selection
All Ports on Repeater
available ports will be automatically selected; if you de-select any port, the
Set Trap Status For field will automatically revert to the
setting. To change the setting in the Set Trap Status For field, click mouse
button 1 on the currently displayed setting, and drag down to select a new
setting.
is displayed in the Set Trap Status For field, all
All Ports On Module
Selected Ports
is displayed in the Set
(the default
Selected Ports
6-10 Configuring Source Address Traps
Page 85

Source Addressing
Figure 6-4. The Port Source Address Traps Window
2. Click on the appropriate selection in the Trap Status field to enable or disable
traps for the selected port(s), as desired.
3. Click on to save your changes.
Finding a Source Address
You can use the button to locate a source address in the list by the
module and port through which it is communicating with the EMM-E6. This
feature is especially useful when your device is very busy and your source
address table is quite large.
Note that each repeater channel maintains its own Source Address Table, and they are
NOTE
completely independent of one another; therefore, if you search for a source address
communicating via Channel B from the Channel A Source Address List window, the
result will be a “not found,” even though the address is connected to a port in the EMME6-controlled hub.
To find a source address:
1. Click mouse button 1 on in the Source Address List window
(Figure 6-2, page 6-3); the Find Source Address window, Figure 6-5, will
appear.
Finding a Source Address 6-11
Page 86

Source Addressing
Figure 6-5. Find Source Address Window
2. In the MAC Address field, enter the source address you wish to locate in a
hexadecimal (XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX) format.
3. Click on . If the address is in the table at the time the search is
initiated, the remaining fields in the window will display the module and port
through which the address is communicating with the EMM-E6. If the address
is not in the table, the message MAC Address Not Found will display in the
window. See Figure 6-6, below.
Figure 6-6. Results of MAC Address Search
4. Click on to exit the window.
6-12 Finding a Source Address
Page 87

Security
Chapter 7
Launching the Security application; LANVIEW
SECURE
defined; configuring security; enabling security
and traps at the repeater, module, and port levels; security on non-LANVIEW
The Security application allows you to configure and manage the
NOTE
LANVIEW
repeater family of MIMs: the TPRMIM-xxS, FORMIM-xxS, CXRMIM-S, and
TPXMIM-xxS.
allowing you to secure two source MAC addresses per port, along with an
additional floating cache of up to 32 addresses among ports on a single board; in
addition,
portion of each packet to all ports except the destination port.
Some portions of
E6-managed chassis, including ports residing on older, nonthese will be noted throughout the text, and summarized in the section entitled Security
on Non-
To launch the Security application
from the icon:
SECURE feature incorporated into the new generation of Cabletron’s
LANVIEW
LANVIEW
LANVIEW
SECURE provides enhanced intruder protection by
SECURE provides eavesdrop protection by scrambling the data
SECURE
functionality will apply to all ports in the EMM-
LANVIEW
LANVIEW
SECURE
MIMs, on page 7-5.
SECURE
MIMs
SECURE
MIMs;
1. Click on the appropriate EMM-E6 icon to display the icon menu.
2. Drag down to Security and release.
from the Hub View:
1. Click on to display the Device menu.
2. Drag down to Security and release.
7-1
Page 88
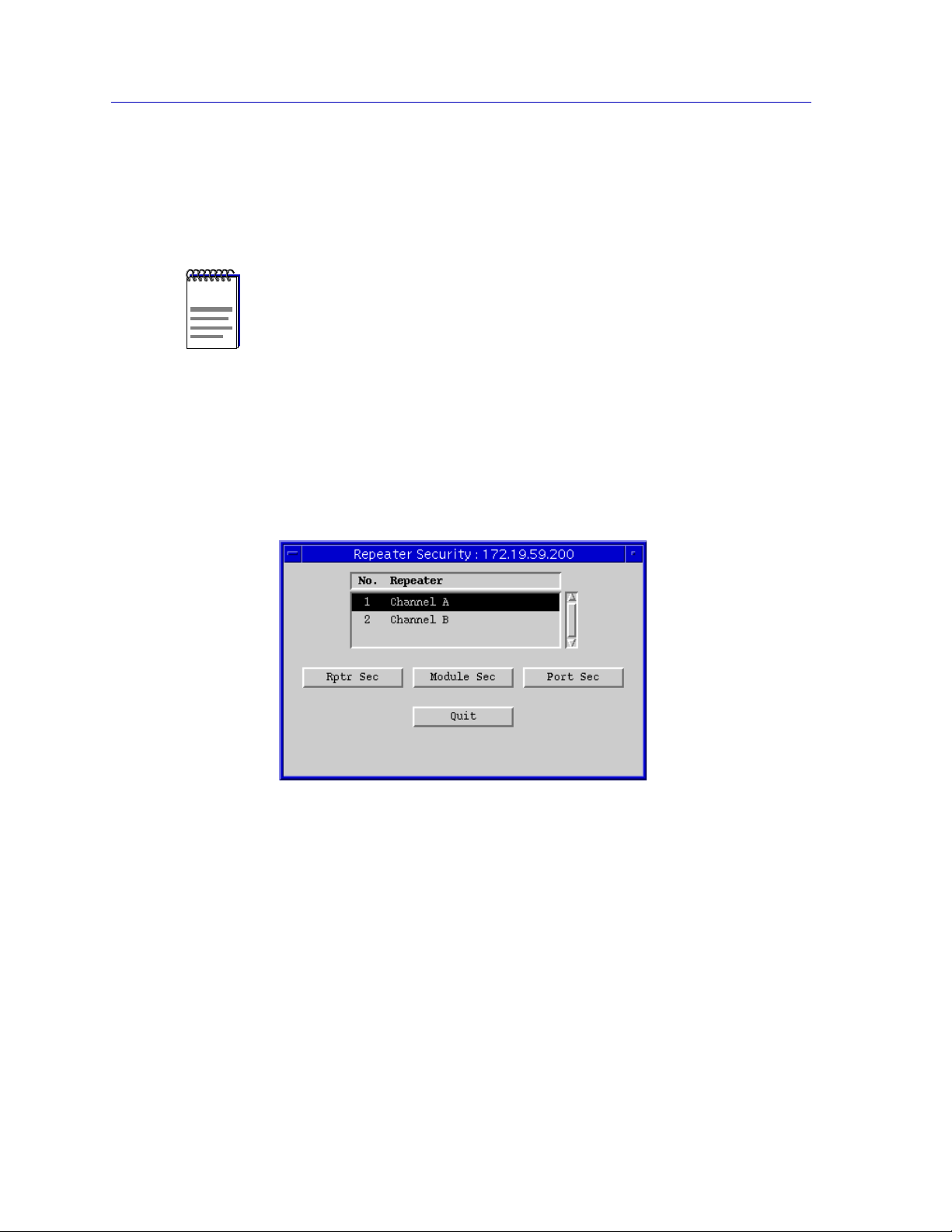
Security
NOTES
from the command line (stand-alone mode):
1. From the appropriate directory, type
spmarun r4sec <IP address> <SU community name>
The spmarun script invoked first in the above command temporarily sets the environment
variables SPMA needs to operate; be sure to use this command any time you launch an
application from the command line. This script is automatically invoked when you launch
an application from the icon menu or from within the Hub View.
You must use a community name with Superuser access to run the Security application.
If there is a hostname mapped to your EMM-E6’s IP address, you can use <hostname>
in place of <IP address> to launch this application. Please note, however, that the
hostname is not the same as the device name which can be assigned via Local
Management and/or SPMA; you cannot use the device name in place of the IP address.
The Repeater Security window, Figure 7-1, will appear.
Figure 7-1. The Repeater Security Window
The Repeater Security window provides a list of the repeater interfaces available
on the EMM-E6, as well as command buttons that allow you to configure security
at the repeater, module, and port levels.
What is
7-2 What is LANVIEWsecure?
LANVIEW
LANVIEW
implemented on the new generation of Cabletron’s repeater MIM family (as
designated by the letter “S” at the end of the module name); these features are
supported beginning with EMM-E6 firmware version 2.00.16, with the newest
enhancements supported by firmware versions 3.11.xx and later.
SECURE?
SECURE comprises a set of enhanced security features that have been
Page 89

Security
TIP
When the
LANVIEW
SECURE feature is enabled, it provides two kinds of
protection: intruder protection will prevent any unauthorized source addresses
from communicating with the network via a secure port, and can be configured to
secure both station and trunk ports; eavesdropper protection scrambles the data
portion of any packet transmitted via a secure port to all but the destination port,
and can be extended to broadcast and multicast packets as well as packets
destined for a single address. Security is activated by enabling port locking; you
can lock and unlock ports and enable or disable traps at the repeater-, module-,
and port-level Security windows, as well as via the Source Addr ess windows (see
Chapter 6, Source Address, for more information).
When you lock ports from a repeater-, module,-, or port-level Security window, you have
the option of setting two lock modes: Full or Continuous. When you lock ports via a
Source Address window, the lock setting will default to the Full lock mode. See the section
on Continuous Address Learning, below, or Enabling Security and Traps, page 7-12,
for more information on these two lock modes.
LANVIEW
SECURE includes the following features:
New definitions for station and trunk ports
Under
LANVIEW
SECURE, station ports are now defined as those detecting zero,
one, or two source addresses; trunk ports are defined as those detecting three or
more.
Secure address assignment
The first two source addresses detected on any port are automatically secured for
both station and trunk ports; you can accept these default addresses as your
secure addresses, or you can replace them. In addition, each board contains a
floating cache that allows you to assign an additional 32 secure addresses among
the ports of your choosing. Some boards even provide multiple caches; see
Boards with Multiple Caches, below.
Trunk port security
When locking is enabled, all ports will be secured — including natural trunk
ports. (Only ports which have been forced to trunk status will remain unlocked.)
Before implementing locking on trunk ports, however, be sure you have secured
the necessary source addresses; as with station ports, only the first two detected
source addresses are secured by default.
For devices with the newest security firmware (3.11.xx), a port’s topology status
— whether it is considered to be a station port or a trunk port — no longer
determines its securability; securability is only determined by the number of
source addresses in a port’s source address table: any port which detects fewer
than 35 source addresses will be locked. Ports which exceed those numbers are
designated “unsecurable,” and will be displayed as such in the port-level Security
window; in addition, a new feature allows you to force any port to an unsecurable
(that is, unlockable) state.
What is LANVIEWsecure? 7-3
Page 90

Security
TIP
If your EMM-E6 is running firmware more recent than 2.00.16 and previous to 3.11.xx,
you will not have the ability to force a port to unsecurable status; however, for firmware
versions in that range, ports which have been forced to trunk status will not be locked, so
you can use the force trunk feature — available from the Hub View port menus — to
render a port unsecurable if you wish.
Configurable violation response
Before
LANVIEW
down automatically; now, you can choose to allow ports to remain enabled even
after an unsecured address has attempted to access a locked port. If you choose
not to disable a port which has experienced a violation, however, the port’s only
response to an intruder will be to issue a trap after the first violation; all packets,
regardless of source address, will be allowed to pass. Ports in this state still have
active eavesdropper protection (see definition below), and all packets addressed
to any destination other than the secured address(es) will be scrambled.
Full or partial security against eavesdropping
In addition to the enhanced intruder protection features described above,
LANVIEW
data portion of each packet to all ports except the port on which the destination
address has been secured — in other words, the only port that will receive the
packet in an unscrambled (readable) format is the port to which the packet was
addressed. Two levels of eavesdropper protection are provided: full security
scrambles all packets not specifically destined to the secured port, including
broadcasts and multicasts; partial security scrambles only unicast packets.
SECURE provides protection against eavesdroppers by scrambling the
SECURE, any locked port which experienced a violation was shut
The Newest
LANVIEW
NOTE
SECURE Features
Additional
(3.11.xx) include:
Continuous learning mode
When configuring security on the newest
choose between two levels of lock status: Full lock status, which behaves as
locking has always done, and Continuous lock status, which essentially disables
intruder protection by allowing the port to continue to learn new source
addresses even when in a locked state. In this state, eavesdropper protection is
still active, and will adjust so that packets addressed to the current learned
address for a secured port are not scrambled.
Locking ports from a Source Address window automatically provides Full lock status;
however, locking ports from the repeater- or module-level Source Address window does
not override any existing Continuous lock status settings.
LANVIEW
SECURE features available on the newest firmware versions
LANVIEW
SECURE devices, you can now
7-4 What is LANVIEWsecure?
Page 91

NOTE
Security
Forced non-secure status
With the original version of
LANVIEW
SECURE, all ports except those which had
been forced to trunk status could be locked, and would be locked automatically if
locking were enabled at the repeater or module level. With the enhanced version
of
LANVIEW
SECURE, this has changed in two ways: first, any port which has more
than 35 addresses in its source address table (or exactly 35 addr esses thr ough two
consecutive aging times) is automatically considered unsecurable and cannot be
locked while in this state; and second, you can force any port into this
unsecurable state (as long as it is not already locked).
Learned addresses reset
By selecting the Reset Learned Addresses option in the repeater-, board-, or portlevel Security window, you can clear all learned and secured addresses out of the
selected port(s) address table, and allow that port to begin learning (and securing)
new addresses. Note that you cannot reset learned addresses on a locked port or
on a port which is designated unsecurable.
You cannot reset learned addresses or force non-secure status on a port which is already
locked; in order to implement either of those features, you must first unlock the port.
Security on Non-
LANVIEW
MIMs designated as
and an “S” appended to the module name) and apply only to ports
communicating via FNB channels B or C. Some of the enhanced security features,
however, will apply to all MIMs installed in your EMM-E6-controlled hub,
regardless of their channel assignment or
New definitions for station and trunk ports
All ports in your EMM-E6-controlled hub will be defined as station or trunk ports
according to the new definitions: station ports are those detecting zero, one, or
two source addresses; trunk ports are those detecting three or more.
Secure address assignment
Up to two source addresses detected on any station port are still automatically
secured, and you can still accept or replace these default addresses. However, you
cannot assign more than two secure addresses to any port (as there is no floating
cache available), and neither natural nor forced trunk ports will ever be locked
while in a trunk state.
LANVIEW
SECURE features as described above apply in total only to repeater
SECURE MIMs
LANVIEW
SECURE (as indicated by a label on the front panel
LANVIEW
SECURE status:
What is LANVIEWsecure? 7-5
Page 92

Security
Configurable violation response
You can still choose to allow ports to remain enabled even after an unsecured
address has attempted to access a locked port. If you choose not to disable a port
which has experienced a violation, however, the port’s only response to an
intruder will be to issue a trap after the first violation; all packets, regardless of
source address, will be allowed to pass.
Forced non-secure status
With the enhanced version of
LANVIEW
SECURE MIMS can be forced to an unsecurable status (as long as they
LANVIEW
SECURE, even ports on non-
are currently unlocked).
Learned addresses reset
You can still use the Reset Learned Addresses option in the repeater-, board-, or
port-level Security window to clear all learned and secured addresses out of the
selected port(s) address table, and allow that port to begin learning (and securing)
new addresses. Note that you cannot reset learned addresses on a locked port or
on a port which is designated unsecurable.
Eavesdrop protection (scrambling), trunk port locking, continuous lock mode,
and the floating address cache are not available for non(A-channel MIMs and non-
LANVIEW
SECURE TPXMIM ports configured to operate on Channel A.
LANVIEW
SECURE RIC MIMs) or for any
LANVIEW
SECURE MIMs
Configuring Security
Most Security parameters are set via the port-level Security window; these will
apply to the configured port regardless of the level at which security is enabled.
To access the Port Security window:
1. In the Repeater Security window, click to select the interface for which you
would like to configure port-level security.
2. Click mouse button 1 on ; the Channel X P ort Security window,
Figure 7-2, will appear.
7-6 Configuring Security
Page 93
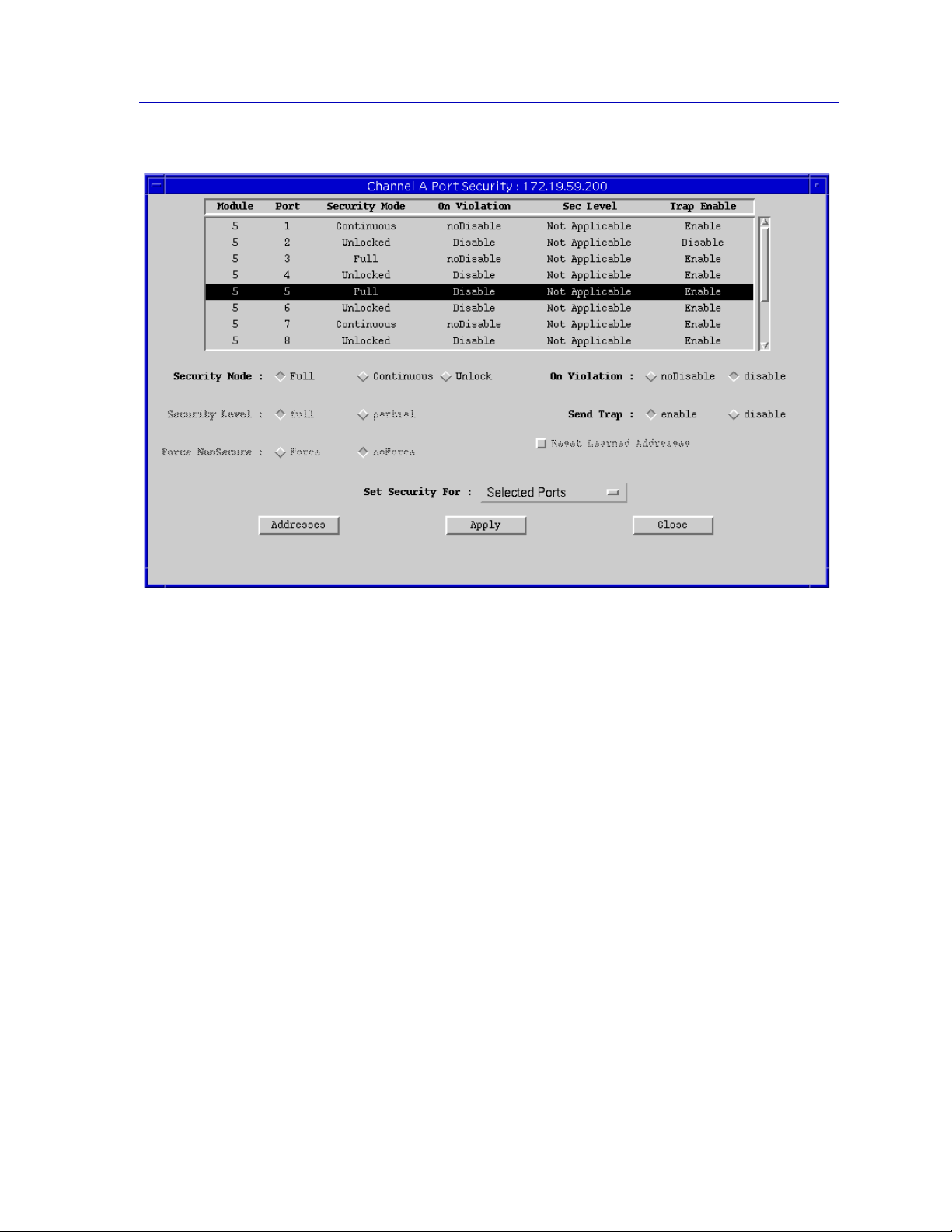
Security
Figure 7-2. Channel X Port Security Window
The top portion of the window contains a list box which displays each port
communicating on the selected channel, designated by module and port number.
Each port’s current Lock Status, violation response, Security Level, and Trap
status is also displayed. Note that any ports on a nonany
LANVIEW
SECURE TPXMIM ports configured to operate on Channel A will
LANVIEW
SECURE MIM or
display “not applicable” in the Security Level field; eavesdropper protection
(scrambling) and continuous lock mode cannot be implemented for these ports.
(See Security on Non-
LANVIEW
SECURE MIMs, page 7-5, for more information.)
The lower portion of the window provides the fields you need to configure
security for one or more of the listed ports. Note that if you select a group of ports
with different security capabilities, only those capabilities which apply to every
port in the selected group will be active; those which are not available for every
port in the selected group will be grayed out.
To configure security levels and violation response:
1. Use the Set Security For field or the mouse to select the port or ports for
which you wish to configure security (note that the settings in the Set
Security For field will change automatically as you click to select or de-select
ports).
Configuring Security 7-7
Page 94

Security
NOTE
2. In the On Violation field, click to select disable if you w ant the port or ports to
be disabled if any unauthorized source address is detected, or select
noDisable if you wish the port to remain operational after a violation. Note
that selecting the noDisable option effectively removes intruder protection
from the selected ports: a trap will be sent after the first violation, but all
packets, regardless of source address, will be allowed to pass. Ports in this
state still have active eavesdropper protection.
Any ports which are disabled in response to a violation will remain disabled even after the
EMM-E6 has been reset, and must be re-enabled manually. See Enabling /Disabling
MIM Ports in Chapter 2 for more information.
3. The Security Level field allows you to select which packets not addressed to
the selected ports will be scrambled: click to select partial if you wish to
scramble the data portion of all packets
except
broadcasts and multicasts;
select full if you wish to scr amble broadcasts and multicasts as w ell. Note that
scrambling can only be applied to
LANVIEW
SECURE MIMs operating on
channels B or C; this field will be grayed out if one or more non-
LANVIEW
SECURE MIM ports has been selected in the list box.
NOTE
4. Use the Force NonSecure field to designate which ports should be securable
(that is, lockable) and which should be unsecurable. By definition, any
LANVIEW
SECURE port with more than 35 addresses in its source address
table (or exactly 35 for two consecutive aging times) is unsecurable, as are
any non-
LANVIEW
SECURE ports with more than 3 addresses (or exactly 3 for
two consecutive aging times). Unsecurable ports — whether forced or natural
— cannot be locked, and will be designated in the list box as Unsecurable.
You cannot force a port to Unsecurable status if it is already locked.
5. Click on to save your changes; the new Security Level and
violation response settings will be displayed in the list box.
To assign secure addresses to a port:
1. Click to select a single port in the list box; the button will be
activated.
2. Click on ; the Addresses window, Figure 7-3, will appear.
7-8 Configuring Security
Page 95

Figure 7-3. The Addresses Window
Security
NOTE
3. On the left side of the window , the Learned Ad dresses list box will display all
source addresses detected by the selected port during the last aging interval
(see Chapter 6, Source Address, f or more information on the aging interval).
On the right side of the window, the Secure Addresses list box will display
the source addresses which have been secured for that port. Remember, as
long as the port is in a securable state, the first two addresses detected by the
port are automatically secured; you can add additional addresses, or delete
the default addresses and secure new ones, as follows:
a. To add a learned address, click to highlight the desired address in the
Learned Addresses list box, then click on . A confirmation
window will appear; click on Yes to secure the selected address.
If security has never been enabled, new addresses will replace any existing learned
addresses. If security has ever been enabled — even if it is not currently enabled — new
addresses will be stored in addition to any learned addresses.
b. To delete a secured address, click in the Secure Addresses list box to
highlight the address you wish to delete, then click on . A
confirmation window will appear; click on Yes to delete the address, or No
to leave the address secured.
c. To add an address not yet detected by the port, make sure no Learned
Addresses are highlighted, then click on ; the Add MA C Address
window , Figure 7-4, will appear.
Configuring Security 7-9
Page 96

Security
Figure 7-4. Add MAC Address Window
d. Enter the desired MAC address in an xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx format, then click
on . A confirmation window will appear; if you click on Yes to
secure the address, it will appear in the Secure Addresses list box.
4. To secure addresses f or additional ports, click to select the desired port in the
Channel X Port Security window; the Addresses window will automatically
display the Learned and Secure addresses for the new port.
If the maximum number of addresses has already been assigned to the floating
NOTE
cache on the selected board, or if you have already secured two addresses on a non-
LANVIEW
SECURE
MIM port, the Add button will be disabled.
You can clear both Learned and Secure addresses (and re-start the learning process) by
using the Reset Learned Addresses option in the repeater-, module-, or port-level Security
window; see Resetting Learned Addresses, page 7-11.
Boards with Multiple Caches
Because of the number of ports they contain, some boards provide two separate
floating address caches: one for each bank of ports. In effect, this circumstance
allows you to configure as many as 64 additional secure addresses, as long as no
more than 32 are configured for each set of ports. For example, the TPR-36S,
which has 26 ports, provides one 32-address cache for ports 1-13 and a second
cache for ports 14-26; the TPX-22S, which has 22 ports, provides one 32-address
cache for ports 1-10, and a second cache for ports 11-22.
NOTE
Note that
cache, as the floating cache feature is not supported for MIMs operating on Channel A.
Similarly, you will not be able to assign more than two secur e addr esses to any TPXMIM
port while it is configured to operate on Channel A.
LANVIEW
SECURE
TPXMIMs assigned wholly to Channel A contain no active
In any case, the Security application will keep track of how many caches are
present and how many addresses have been assigned to each, and will disable the
Add button as appropriate.
7-10 Configuring Security
Page 97

Resetting Learned Addresses
You can clear all learned and secured addresses out of a port’s address table, and
allow that port to begin learning (and securing) new addresses, as follows:
1. In the Repeater Security window, click mouse button 1 on the repeater
interface for which you would like to reset learned addresses.
2. Click mouse button 1 on , , or to
open the appropriate window.
3. In the Module or Port window , clic k to select the module(s) or port(s) for which
you wish to reset learned addresses.
You cannot reset learned addresses for any port which is already locked or in an
NOTE
unsecurable state (either natural or forced). If you select a group of ports which includes
one in a locked or unsecurable state, or if you select a module or a repeater which has a
port in one of these states, the Reset Learned Addresses option will be unavailable.
4. Click to select the Reset Learned Addresses option. A confirmation window
will appear; click on to reset addresses, or on to cancel.
The port’s address table will be cleared of all Learned and Secure addresses,
and the learning process will restart.
Security
Tips for Successfully Implementing Eavesdropper Protection
There are a couple of things to note about eavesdropper pr otection, or scrambling,
that must be taken into consideration as you are planning security for your
network.
• Security can only be implemented by locking a port, and can only be
completely disabled by unlocking the port. You cannot enable intruder
protection on a
protection. You can, however, effectively enable eavesdropper protection
alone by selecting the noDisable option for the violation response; selecting
noDisable basically eliminates intruder protection, as all packets will be
allowed to pass regardless of their source address. (Note, however, that the
port will issue a trap after the first violation.) Y ou can also enable eavesdropper
protection without intruder protection by selecting the Continuous lock mode;
see Enabling Security and Traps, page 7-12, for details.
• When locking has been enabled for a channel, packets travelling across the
inter-RIC bus on the FNB backplane between MIMs operating on that channel
will be scrambled to all but the destination port, and security operates as you
would expect it to. However, packets are always transmitted clean to the
EMM-E6’s bridge ports, so any packets transmitted to another channel will be
LANVIEW
SECURE MIM without also enabling eavesdropper
Configuring Security 7-11
Page 98

Security
transmitted clean to all ports on that channel unless security has been enabled
there, too. Packets bridged to Channel A will always be transmitted clean to all
ports, regardless of lock status; however, careful bridge configuration and
prudent use of each port’s forwarding and blocking abilities can provide some
measure of security in this case.
• Security must be disabled on any port which is connected to an external bridge,
or the bridge will discard all packets it receives as error packets (since the CRC
is not recalculated after a packet is scrambled).
• Security should also be disabled on any port which is supporting a trunk
connection, unless you are sure that no more than 34 source addresses will
attempt to use the port, and you have secured all necessary addresses. Note
that, with the newest versions of security, a
more than 35 addresses in its Source Addr ess table (or exactly 35 addresses for
two consecutive aging intervals) is considered unsecurable and cannot be
locked.
• Full security should not be implemented on any port which supports a name
server or a bootp server , as those devices would not r eceive the broadcast and
multicast messages they are designed to respond to (partial security — which
does not scramble broadcasts or multicasts — will not affect their operation).
Note that users who require responses to broadcast or multicast requests can
still operate successfully if their ports are fully secured, as the reply to a
broadcast has a single, specific destination address.
LANVIEW
SECURE port that sees
In general, scrambling is most effective when employed in a single chassis which
contains only
remember , nonnot support scrambling as part of their security functionality.
LANVIEW
LANVIEW
SECURE MIMs operating on channels B and/or C;
SECURE MIMs and any ports operating on Channel A do
Enabling Security and Traps
You can enable or disable all applicable protections by locking or unlocking ports
via the repeater, module, or port Security window, as described in the sections
below. There are two levels of lock status to choose from: if you select Full lock
status, the port will stop learning new source addresses, accept packets only from
secured source addresses, employ either full or partial eavesdrop protection (as
configured), and take the configured steps (send trap and/or disable port) if a
violation occurs; if you select Continuous lock status, the port will implement the
configured level of eavesdrop protection, but continue to learn source addresses
and allow all packets to pass, effectively disabling intruder protection.
Enabling and disabling traps from the Security windows has the same effect as
enabling and disabling them from the Source Address windows; you can enable
and disable the following traps:
7-12 Enabling Security and Traps
Page 99

Security
•A newSourceAddress trap is generated when a station port — one receiving
packets from zero, one, or two source addresses — receives a packet from a
source address that is not currently in its source address table. Information
included in this trap includes the board number, port number, and source
address associated with the trap. Trunk ports — those receiving packets from
three or more source addresses — will not issue newSourceAddress traps.
•A sourceAddressTimeout trap is issued anytime a sour ce addr ess is aged out
of the Source Address Table due to inactivity. The trap’s interesting
information includes the board and port index, and the source address that
timed out. (See Setting the Aging Time in Chapter 6, Source Addressing , for
more information.)
All other source address traps (portTypeChanged, lockStatusChanged,
portSecurityViolation, and portViolationReset, all defined in Chapter 6, Source
Addressing) will continue to be generated as appropriate, as will the securityspecific traps:
•A secureStateChange trap indicates that a port has changed from a securable
state to an unsecurable state, or vice versa; the interesting information includes
board and port index.
NOTE
•A learnStateChange trap indicates that a port has had its learned addresses
reset. Interesting information includes board and port index, and curr ent learn
state. Note that SPMA always maintains ports in a learn state, and just resets
that learn state to achieve a reset of existing learned and secure addresses.
•A learnModeChange trap is issued when a port is set to continuous lock
mode; interesting information includes board and port index, and current
learn mode.
When setting these parameters at the various levels, keep in mind that the most
recent setting will override the existing status: for example, if you lock one or
more ports at the port level, then unlock them at the module level, all ports on the
module will be unlocked. Similarly, if you enable traps at the module level, then
disable them at the repeater level, traps will be disabled for all ports on the
repeater.
Enabling and disabling locking from the Source Address application (described in
Chapter 6) will implement all applicable security features as they have been configured via
the port-level Security window. Note that locking ports from the Source Address window
implements Full lock status by default; however, this will not override the status of any
ports which have already been set to Continuous lock mode.
Enabling and disabling traps from the Source Address window also has the same effect as
enabling or disabling them from the Security application. Keep in mind, however, that
SPMA does not accept the trap messages; that task is left to your network management
system. (See the appropriate network management system documentation for details
about viewing trap messages.) Note, too, that no traps will be sent by the EMM-E6 unless
its trap table has been properly configured; see the EMM-E6 hardware manual and/or the
Trap Table chapter in the SPMA Tools Guide for more information.
Enabling Security and Traps 7-13
Page 100

Security
Repeater-level Security and Traps
Locking ports at the repeater, or channel, level applies all applicable security (as
configured via the Port Security window) to every port on the channel.
If you select a repeater whose ports have different security capabilities, you may still be
NOTE
able to select and apply security states which are not applicable to all ports. Applying
these kinds of settings will have no adverse affect on your network devices: those ports
which can accept the set will do so; those which cannot will either ignore the set or issue a
Set Failed.
To enable or disable security and traps for all ports on a repeater:
1. In the Repeater Security window, click mouse button 1 on the repeater
interface for which you would like to configure port locking and/or traps.
2. Click mouse button 1 on ; the Channel X Security window,
Figure 7-5, will appear. Note that the current repeater-level settings are
displayed immediately to the right of the field names; a repeater whose ports
have different Security Mode or Trap settings will display a status of
“Mismatch.”
Figure 7-5. Channel X Security Window
3. In the Security Mode field, click mouse button 1 on the appropriate selection
to apply Full or Continuous lock status to all ports on the selected repeater
channel, or to Unlock all ports on the channel. (Note that if your EMM-E6
does not support the newest security enhancements, the Continuous
selection will be unavailable.)
4. In the Send T rap field, click mouse button 1 on the appropriate selection to
Enable or Disable traps for the selected repeater channel.
7-14 Enabling Security and Traps
 Loading...
Loading...