Cabletron Systems ELS10-26TX User Manual

SmartSTACK 10
ELS10-26 USER GUIDE
ELS10-26TX
RESET
PORT STATUS MODE
TX ACT FDX MON
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
341
785
2
RX COL 100 USR
STATUS
PWR
CPU
COM
6
2X 4X 6X 8X 10X 12X 14X 16X 18X 20X 22X 24X MONX 26X
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
131415
11129
16
10
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
21
19
17
22
20
18
LINK
STATUS
23
25
26
24
MON
27
10BASE-T/
100BASE-TX
FEPIM
27
9032243-01


Only qualified personnel should perform installation
procedures.
NOTICE
Cabletron Systems reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information
contained in this document without prior notice. The reader should in all cases consult Cabletron
Systems to determine whether any such changes have been made.
The hardware, firmware, or software described in this manual is subject to change without notice.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CABLETRON SYSTEMS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INCIDENTAL,
INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES WHATSOEVER (INCLUDING BUT
NOT LIMITED TO LOST PROFITS) ARISING OUT OF OR RELATED TO THIS MANUAL OR
THE INFORMATION CONTAINED IN IT, EVEN IF CABLETRON SYSTEMS HAS BEEN
ADVISED OF, KNOWN, OR SHOULD HAVE KNOWN, THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGES.
Copyright 1997 by Cabletron Systems, Inc., P.O. Box 5005, Rochester, NH 03866-5005
All Rights Reserved
Printed in the United States of America
Order Number: 9032243-01 September 1997
Cabletron Systems, SPECTRUM,
SmartSTACK, ELS10-26TX, FEPIM, FEPIM-TX and FEPIM-FX
Cabletron Systems, Inc.
All other product names mentioned in this manual may be trademarks or registered trademarks of
their respective companies.
and
LANVIEW
are registered trademarks and
are trademarks of
FCC NOTICE
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any
interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
NOTE:
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment.
This equipment uses, generates, and can radiate radio frequency energy and if not installed in
accordance with the operator’s manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause interference in which case the user
will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
WARNING:
party responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Changes or modifications made to this device which are not e xpressly appro v ed by the
Printed on Recycled Paper
i

Notice
DOC NOTICE
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class A limits for radio noise emissions from digital
apparatus set out in the Radio Interference Regulations of the Canadian Department of
Communications.
Le présent appareil numérique n’émet pas de bruits radioélectriques dépassant les limites applicables
aux appareils numériques de la class A prescrites dans le Règlement sur le brouillage radioélectrique
édicté par le ministère des Communications du Canada.
VCCI NOTICE
This is a Class A product based on the standard of the Voluntary Control Council for Interference by
Information Technology Equipment (VCCI). If this equipment is used in a domestic environment,
radio disturbance may arise. When such trouble occurs, the user may be required to take corrective
actions.
CABLETRON SYSTEMS, INC. PROGRAM LICENSE AGREEMENT
IMPORTANT:
This document is an agreement between you, the end user, and Cabletron Systems, Inc. (“Cabletron”)
that sets forth your rights and obligations with respect to the Cabletron software program (the
“Program”) contained in this package. The Program may be contained in firmware, chips or other
media. BY UTILIZING THE ENCLOSED PRODUCT, YOU ARE AGREEING TO BECOME
BOUND BY THE TERMS OF THIS AGREEMENT, WHICH INCLUDES THE LICENSE AND
THE LIMITATION OF WARRANTY AND DISCLAIMER OF LIABILITY. IF YOU DO NOT
AGREE TO THE TERMS OF THIS AGREEMENT, PROMPTLY RETURN THE UNUSED
PRODUCT TO THE PLACE OF PURCHASE FOR A FULL REFUND.
Before utilizing this product, carefully read this License Agreement.
ii

Notice
CABLETRON SOFTWARE PROGRAM LICENSE
1. LICENSE
package subject to the terms and conditions of this License Agreement.
You may not copy, reproduce or transmit any part of the Program except as permitted by the
Copyright Act of the United States or as authorized in writing by Cabletron.
2. OTHER RESTRICTIONS. You may not reverse engineer, decompile, or disassemble the
Program.
3. APPLICABLE LA W. This License Agreement shall be interpreted and governed under the laws
and in the state and federal courts of New Hampshire. You accept the personal jurisdiction and
venue of the New Hampshire courts.
. You have the right to use only the one (1) copy of the Program provided in this
EXCLUSION OF WARRANTY AND DISCLAIMER OF LIABILITY
1. EXCLUSION OF
writing, Cabletron makes no warranty, expressed or implied, concerning the Program (including
its documentation and media).
CABLETRON DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, OTHER THAN THOSE SUPPLIED TO
YOU BY CABLETRON IN WRITING, EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING
BUT NOT LIMITED TO IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, WITH RESPECT TO THE PROGRAM, THE
ACCOMP ANYING WRITTEN MA TERIALS, AND ANY A CCOMP ANYING HARDWARE.
2. NO LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES. IN NO EVENT SHALL
CABLETRON OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES WHATSOEVER
(INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF BUSINESS,
PROFITS, BUSINESS INTERRUPTION, LOSS OF BUSINESS INFORMATION, SPECIAL,
INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR RELIANCE DAMAGES, OR OTHER LOSS)
ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS CABLETRON PRODUCT,
EVEN IF CABLETRON HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGES. BECAUSE SOME STATES DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, OR
ON THE DURATION OR LIMITATION OF IMPLIED WARRANTIES, IN SOME
INSTANCES THE ABOVE LIMITATIONS AND EXCLUSIONS MAY NOT APPLY TO
YOU.
WARRANTY. Except as may be specifically provided by Cabletron in
UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT RESTRICTED RIGHTS
The enclosed product (a) was developed solely at private expense; (b) contains “restricted computer
software” submitted with restricted rights in accordance with Section 52227-19 (a) through (d) of the
Commercial Computer Software - Restricted Rights Clause and its successors, and (c) in all respects
is proprietary data belonging to Cabletron and/or its suppliers.
For Department of Defense units, the product is licensed with “Restricted Rights” as defined in the
DoD Supplement to the Federal Acquisition Regulations, Section 52.227-7013 (c) (1) (ii) and its
successors, and use, duplication, disclosure by the Government is subject to restrictions as set forth in
subparagraph (c) (1) (ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software clause at
252.227-7013. Cabletron Systems, Inc., 35 Industrial Way, Rochester, New Hampshire 03867-0505.
iii

Notice
DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
Application of Council Directive(s):
Manufacturer’s Name:
Manufacturer’s Address:
European Representative Name:
European Representative Address:
Conformance to Directive(s)/Product Standards:
Equipment T ype/Environment:
W e the undersigned, hereby declare, under our sole responsibility, that the equipment packaged
with this notice conforms to the above directives.
Manufacturer Legal Representative in Europe
89/336/EEC
73/23/EEC
Cabletron Systems, Inc.
35 Industrial Way
PO Box 5005
Rochester, NH 03867
Mr. J. Solari
Cabletron Systems Limited
Nexus House, Newbury Business Park
London Road, Newbury
Berkshire RG13 2PZ, England
EC Directive 89/336/EEC
EC Directive 73/23/EEC
EN 55022
EN 50082-1
EN 60950
Networking Equipment, for use in a
Commercial or Light
Environment.
Industrial
Mr. Ronald Fotino Mr. J. Solari
___________________________________ ___________________________________
Full Name Full Name
Principal Compliance Engineer Managing Director - E.M.E.A.
___________________________________ ___________________________________
Title Title
Rochester, NH, USA Newbury, Berkshire, England
___________________________________ ___________________________________
Location Location
iv

CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 ABOUT THIS MANUAL ........................................................................1-1
1.2 GETTING HELP.......................................................................................1-2
1.4 RELATED DOCUMENTATION ...........................................................1-4
1.5 OVERVIEW...............................................................................................1-4
1.5.1 SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 Architecture.....................................1-6
1.5.2 SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 Bridge Address Table.....................1-9
1.5.3 SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 Port Monitoring ............................1-10
1.5.4 SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 Sample Applications ....................1-11
1.6 LOCAL CONSOLE MANAGER..........................................................1-18
1.6.1 Command Syntax Conventions.................................................1-18
1.6.2 Basic LCM Commands................................................................1-20
CHAPTER 2 UNPACKING AND INSTALLING
YOUR ELS10-26
2.1 ELS10-26 FRONT PANEL.......................................................................2-1
2.2 INSTALLING AN FEPIM.......................................................................2-4
2.3 INSTALLING THE ELS10-26.................................................................2-5
2.4 CHECKING THE POWER-UP DIAGNOSTICS SEQUENCE...........2-8
2.5 CONNECTING THE LOCAL CONSOLE MANAGER .....................2-9
2.6 CONNECTING TO THE NETWORK...................................................2-9
2.6.1 Connecting UTP Cables ..............................................................2-10
2.6.2 Connecting a UTP Segment to the FE-100TX ..........................2-11
2.6.3 Connecting a Multimode Segment to the FE-100FX...............2-13
CHAPTER 3 CONFIGURING YOUR ELS10-26
3.1 ASSIGNING IP ADDRESSES.................................................................3-2
3.1.1 Displaying IP Addresses...............................................................3-3
3.1.2 Deleting an IP Address .................................................................3-3
3.1.3 Changing a Subnet Mask..............................................................3-4
3.2 ENABLING BRIDGING..........................................................................3-4
3.3 DISABLING BRIDGING.........................................................................3-5
3.4 DISPLAYING BRIDGING FUNCTIONS .............................................3-5
3.5 ENABLING TRUNKING........................................................................3-6
3.6 DISABLING TRUNKING.......................................................................3-9
3.7 DISPLAYING TRUNKING STATUS....................................................3-9
3.8 ENABLING PORT MONITORING.....................................................3-11
3.9 DISABLING MONITORING................................................................3-12
v

Contents
3.10 DISPLAYING MONITORING STATUS...........................................3-12
3.11 DEFINING AND DELETING WORKGROUPS ..............................3-14
3.12 ASSIGNING A COMMUNITY NAME.............................................3-16
3.13 CONFIGURING BROADCAST/MULTICAST STORM
PROTECTION ......................................................................................3-17
3.14 MODIFYING MIB VARIABLES.........................................................3-18
3.15 SYSTEM CONTACT............................................................................3-18
3.16 SYSTEM NAME ...................................................................................3-18
3.16.1 System Location .......................................................................3-19
3.16.2 Community Names..................................................................3-19
3.16.3 Aging Parameter ......................................................................3-19
CHAPTER 4 MONITORING AND MANAGING
YOUR ELS10-26
4.1 ELS10-26 MANAGEMENT TOOLS ......................................................4-1
4.2 ELS10-26 STATISTICS.............................................................................4-1
4.2.1 Gathering Statistics ........................................................................4-2
4.2.2 System Statistics .............................................................................4-2
4.2.3 Ethernet Port Statistics ..................................................................4-3
4.3 USING LCM TO CHECK ELS10-26 STATUS ......................................4-4
4.3.1 Displaying Status ...........................................................................4-4
4.3.2 Displaying MAC Addresses.........................................................4-6
4.3.3 Displaying Manufacturing Information .....................................4-8
4.4 MANAGING THE ELS10-26..................................................................4-9
4.5 USING LCM TO MANAGE THE ELS10-26.........................................4-9
4.5.1 Disabling a Port..............................................................................4-9
4.5.2 Enabling a Port .............................................................................4-10
4.5.3 Changing a Subnet Mask ............................................................4-11
4.5.4 Changing a Community Name..................................................4-12
4.5.5 Setting the Baud Rate ..................................................................4-13
4.5.6 Setting a Reboot Time..................................................................4-14
vi

Contents
CHAPTER 5 ELS10-26 DIAGNOSTICS AND
TROUBLESHOOTING
5.1 POWER-UP DIAGNOSTICS..................................................................5-1
5.1.1 Power-up LED Sequence ..............................................................5-1
5.1.2 Specific Power-up Tests................................................................5-2
5.1.3 Software Checksum Comparison................................................5-2
5.1.4 Power-up Diagnostics Results .....................................................5-3
5.2 RESPONSES TO FAILURES AT POWER-UP......................................5-3
5.3 STATUS AND ACTIVITY INDICATORS ............................................5-3
5.4 TROUBLESHOOTING............................................................................5-6
5.5 ELS10-26 DOES NOT POWER UP ........................................................5-6
5.5.1 Connectivity Problems..................................................................5-6
5.5.2 ELS10-26 Has Rebooted ................................................................5-6
5.5.3 ELS10-26 Does Not Respond to NMS.........................................5-7
APPENDIX A TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
A.1 ELS10-26 SPECIFICATIONS ...............................................................A-1
A.2 Serial Cable Pin Assignments .............................................................A-3
A.3 10BASE-T Pin Assignments .................................................................A-4
A.4 Straight-through Wiring ......................................................................A-5
A.5 Crossover Wiring.................................................................................. A-6
A.6 The 5 - 4 - 3 Rule ....................................................................................A-6
A.7 FEPIM Specifications ............................................................................A-7
APPENDIX B GLOSSARY
vii

Contents
viii

CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
1.1 ABOUT THIS MANUAL
This manual is for system administrators responsible for
configuring, monitoring, and maintaining the SmartSTACK 10
ELS10-26TX. You should have a familiarity with networking
concepts and principles. In addition, a basic understanding of
SNMP is helpful.
Some SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 configurations can only be done
using an SNMP-based Network Management System (NMS).
Where applicable, this manual provides instructions for using the
Local Console Manager (LCM) to perform basic configuration.
Where it is not possible to use LCM, general instructions and
guidelines applicable to most NMSs are provided.
The contents of each chapter are described below.
• Chapter 1,
and provides an overview of the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26’s
switching functions, applications, and the Local Console
Manager (LCM).
• Chapter 2,
the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 front and rear panels, how to
install the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26, how to connect the Local
Console Manager (LCM), and how to connect the ELS10-26 to
the network.
• Chapter 3,
for configuring the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 using the Local
Console Manager (LCM). It also provides some common
Management Information Base (MIB) variables you may want to
change.
• Chapter 4,
how to monitor SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 status and statistics.
It also describes how to manage the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26
Ethernet ports using the Local Console Manager (LCM).
Introduction
Unpacking and Installing Your ELS10-26
Configuring Your ELS10-26
Monitoring and Managing Your ELS10-26
, outlines the contents of this manual
, provides instructions
, describes
, describes
1-1

Introduction
• Chapter 5,
ELS10-26 Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
,
describes the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 diagnostics and
provides information on troubleshooting common problems.
• Appendix A,
Technical Specifications
, provides the
SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 specifications and basic cabling pin
assignments.
• Appendix B,
Glossary
, provides a glossary of terms both specific
to the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 and common to the networking
field.
1.2 GETTING HELP
If you need additional support related to the SmartSTACK 10
ELS10-26, or if you have any questions, comments, or suggestions
concerning this manual, contact Cabletron Systems Global Call
Center:
Phone: (603) 332-9400
Internet mail: support@ctron.com
FTP: ctron.com (134.141.197.25)
Login: anonymous
Password: your email address
BBS: (603) 335-3358
Modem setting: 8N1: 8 data bits, No parity, 1 stop bit
1-2

Introduction
Before calling Cabletron Systems Global Call Center, have the
following information ready:
• Your Cabletron Systems contract number
• A description of the failure
• A description of any action(s) already taken to resolve the
problem (e.g., changing mode switches, rebooting the unit, etc.)
• The serial and revision numbers of all Cabletron Systems
products in the network
• A description of your network environment (layout, cable type,
etc.)
• Network load and frame size at the time of trouble (if known)
• The device history (i.e., have you returned the device before, is
this a recurring problem, etc.)
• Any previous Return Material Authorization (RMA) numbers
For additional information about Cabletron Systems products,
visit our World Wide Web site: http://www.cabletron.com
1.3 DOCUMENT CONVENTIONS
The following conventions are used throughout this document:
LCM commands, prompts, and information displayed by the
computer appear in Courier typeface, for example:
Current Number of Learned Addresses: 133
Information that you enter appears in Courier bold typeface, for
example:
ELS10-26 >
Information that you need to enter with a command is enclosed in
angle brackets < >. For example, you must enter a port number
status
1-3

Introduction
and an IP address to execute the
ipaddr <port #> <IP address>
command:
ELS10-26 >
ipaddr 6 192.138.217.40
Field value options appear in bold typeface.
The following conventions are also used in this document:
Note:
Calls the reader’s attention to any item of information that may be
of special importance.
Tip:
Caution:
Conveys helpful hints concerning procedures or actions.
Contains information essential to avoid damage to the
equipment.
Warning:
Warns against an action that could result in equipment
damage, personal injury or death.
1.4 RELATED DOCUMENTATION
The following documentation may assist the user in using this
product:
•
Getting Started with the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26
- contains the
basic information for using the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26.
•
SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 MIB Reference Guide
– contains
enterprise MIB information.
•
Interconnections, Bridges and Routers,
Radia Perlman, Addison
Wesley © 1992.
•
Internetworking with TCP/IP: Principles, Protocols, and Architecture
(2nd edition), Volumes I and II, Douglas Comer, Prentice Hall ©
1991.
•
The Simple Book, An Introduction to Management of TCP/IP-based
internets
1-4
, Marshall T. Rose, Prentice Hall © Second Edition, 1994.

Introduction
1.5 OVERVIEW
The SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26TX is an intelligent Ethernet-toEthernet switch that is configured with 25 IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T
Full Duplex Ethernet ports, one fixed 100BASE-TX copper
connection, one port supporting either a copper or fiber 100 Mbps
FEPIM (Fast Ethernet Port Interface Module), and one fixed RJ45
for port monitoring of the 10 Mbps ports.
It also includes an RS232C port for out-of-band management.
Figure 1-1 shows the front panel for the SmartSTACK 10
ELS10-26TX.
.
ELS10-26TX Front Panel
ELS10-26TX
PORT STATUS MODE
TX ACT FDX MON
RX COL 100 USR
STATUS
PWR
CPU
RESET
COM
LINK
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
3412785611129
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
10
LINK
STATUS
2X 4X 6X 8X 10X 12X 14X 16X 18X 20X 22X 24X MONX 26X
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
131415
17
16
18
LINK
STATUS
21
19
23
25
26
22
20
24
MON
27
FEPIM
10BASE-T/
100BASE-TX
27
Figure 1-1. SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 Front Panel
The SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26
• Provides dedicated bandwidth for each network connected to
its ports.
• Provides full store and forward bridging functionality.
• Provides complete error checking functionality.
• Provides port trunking to increase bandwidth.
• Provides a dedicated monitor port for enhanced
troubleshooting.
• Supports Auto-negotiation.
1-5

Introduction
• Operates in either Half Duplex or Full Duplex modes on all
ports.
• Implements the Spanning Tree protocol (802.1d).
• Configured with factory-set defaults for immediate plug-andplay capability (IP address is not configured at factory).
In addition, the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 offers the following
features that can help you manage and maintain your network:
• RMON support.
• Configuration and management using the Simple Network
Management Protocol (SNMP) with either an in-band or out-ofband connection.
• Protection against broadcast/multicast storms.
• Ability to define virtual workgroups for more efficient
bandwidth usage. The SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 ports can be
segmented into 8 separate broadcast domains.
• Compilation of statistics (by port) for traffic generated by each
user device connected to a SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 segment.
1.5.1 SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 Architecture
The SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 enables you to link two or more
Local Area Networks (LANs) together. To accomplish this, the
SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 regulates network traffic on the basis of
the source and destination addresses that are in each data packet it
receives.
The SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 is protocol-transparent, meaning it
can handle different types of network traffic regardless of the
network protocol, such as IP and IPX. As the SmartSTACK 10
ELS10-26 reads addresses from the packets it processes, it builds a
dynamic database of addresses called the
this way, the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 continuously learns the
addresses of all connected devices. Consequently, you can add
1-6
Bridge Address Table
. In
Introduction
new devices to the network, change device addresses, and remove
devices from the network without having to reconfigure the
SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26.
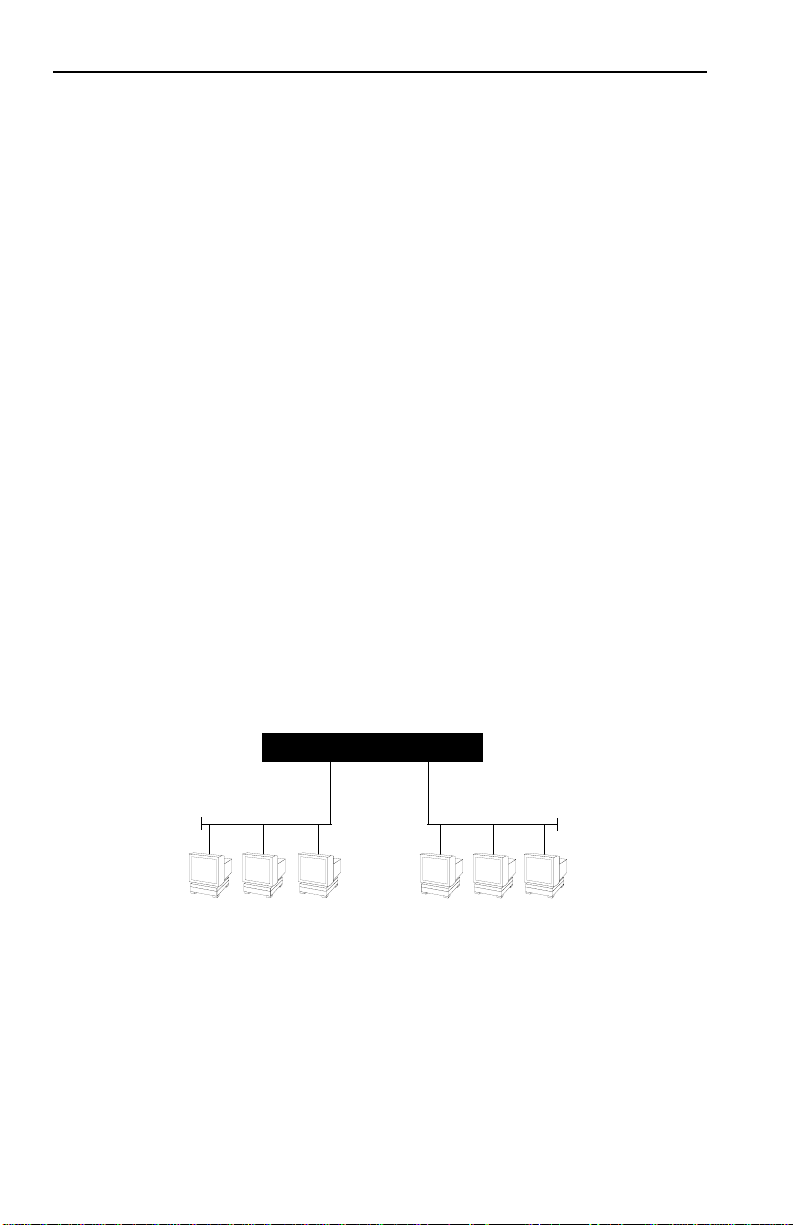
The Open System Interconnection (OSI) Reference Model,
developed by the International Standards Organization (ISO),
identifies the levels of functionality inherent in each of its seven
layers. The SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 operates at the Media Access
Control (MAC) sub-layer of the Data Link layer. Figure 1-2 shows
the OSI Reference Model.
7
Application
Presentation
6
5
Session
Transport
4
3
Network
2
Data Link
ELS10-26 operates at Layer 2
1
Physical
Figure 1-2. OSI Reference Model
Because the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 does not process any
Network Layer information, it provides a high level of
performance in terms of packet throughput. In addition, the
SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 does not need to learn network
topology, requiring less programming and configuration time.
Store and Forward Switching
As an intelligent Ethernet switch, the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26
uses store and forward switching. Store and forward switching
allows the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 to temporarily store packets
until network resources, typically an unused link, are available for
forwarding. This allows for complete error checking, and limits the
amount of time between when a device requests access to the
1-7
Introduction
network and when it is granted permission to transmit. In
addition, full store and forward switching ensures data integrity,
thus preventing network error conditions from being generated
throughout the network.
Discarding Local Traffic
The SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 checks all incoming packets for
their destination address against the Bridge Address Table. If a
packet’s destination address is not on the same network segment
as the originating packet, the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 forwards
the packet to the network segment associated with that destination
address, if known. However, if the packet’s source and destination
address are on the same network segment, known as
the packet is automatically discarded (i.e., ignored by the
SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26).
For example, a file transmitted from Workstation A to Workstation
C in Figure 1-3 does not need to leave LAN 1. The SmartSTACK 10
ELS10-26 connected to LANs 1 and 2 sees all traffic from LAN 1,
including LAN 1 local traffic.
local traffic
,
1-8
ELS10-26
FastNet 10
LAN 1
ABC
Figure 1-3. Typical Switching Application
LAN 2

Introduction
By forwarding only packets addressed to devices on other network
segments, the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 reduces unnecessary
traffic and thereby enhances the overall performance of the
network.
Note:
If the packet address is not found in the Bridge Address Table, it
will be forwarded (flooded) to all network segments.
Spanning T ree Algorithm
The SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 supports the IEEE 802.1d Spanning
Tree algorithm. The Spanning Tree algorithm converts multiple
LANs into a “spanning tree” of networks. It is used to prevent
bridging loops. This standard defines a logical (not physical)
network configuration consisting of one extended LAN without
active duplicate paths between spanning tree bridges.
The SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26, along with other IEEE 802.1d
Spanning Tree compliant bridges in the network, dynamically
configure the network topology into a single Spanning Tree by
exchanging Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs). Typically, each
LAN segment is sent one BPDU every two seconds (this is the
default setting).
When there are multiple SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26s connecting
LANs in a loop, the Spanning Tree algorithm determines which
SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 should forward packets to the LAN. If
there is a cable break or a port failure, the network topology is
automatically reconfigured by the Spanning Tree protocol to create
an alternate path to the LAN.
1.5.2 SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 Bridge Address Table
The SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 creates and maintains a dynamic
database of addresses called the Bridge Address Table. The
SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 examines every packet to determine its
source address and LAN segment origin. It then compares the
source address and segment information it finds to the entries in
the Bridge Address Table.
1-9

Introduction
If a packet’s address is not already stored in the Bridge Address
Table, the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 adds the learned address,
associated segment number, and a timer value indicating the age
of the observation. Consequently, the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26
knows the address and associated segment number the next time it
sees that address. By using the information stored in the Bridge
Address Table, the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 is able to quickly
forward each packet to the correct LAN segment.
The SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 learns addresses from all packets,
including data transmissions and “keep alive” packets (packets
sent by an idle station to let other stations know it is present and
functional). When devices are added to the network, removed
from it, or relocated, you do not have to reconfigure the
SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26. The unit automatically learns new
device addresses, recognizes when a previously used address is
missing, or when a device has been moved to a new LAN segment.
An address stored in the Bridge Address Table is discarded if there
is no subsequent activity from that address after a configured
length of time (five minutes by default). This aging process ensures
that the Bridge Address Table is continually updated.
Addresses are continually added to and deleted from the Bridge
Address Table, reflecting the dynamic nature of internetwork
traffic.
Each dynamic entry includes:
• An Ethernet MAC address
• A single port number of the LAN on which the address resides
• The age of the entry
The SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 stores 979 dynamic (learned) entries
in its Bridge Address Table.
1-10

Introduction
1.5.3 SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 Port Monitoring
Port monitoring allows the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 to redirect
network traffic (including MAC layer errors) from one port to the
port monitoring port (MONX port), in effect “mirroring” all
network traffic to this port. This feature allows users who have
existing investments in external analyzers, external RMON probes,
TM
or devices like Network General's Distributed Sniffer System
to
continue to receive expert analysis and packet decode functions in
a switched environment -- simply use the port mirroring function
to mirror switched traffic to the designated “diagnostic” port to
which the analyzer is attached.
The SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 supports local port mirroring.
Local port mirroring is when the diagnostic port is on the same
SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 as the mirrored port. The mirrored port
has to be local to the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26.
Packet Capturing and Monitoring
Only the 10BASE-T ports on the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 (and
not the 100BASE ports) can be mirrored. The monitoring of
network traffic is performed by the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26
hardware.
1.5.4 SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 Sample Applications
Just as a six lane highway allows you to travel much faster than a
single lane highway, a network backbone creates high-speed
connections for your network. In general, a network backbone
allows you to distribute access to important network resources
such as file or print servers. Additional SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26
features, such as trunking, Fast Ethernet, and virtual workgroups
allow you to optimize bandwidth and design a more efficient flow
for your network traffic.
1-11
Introduction
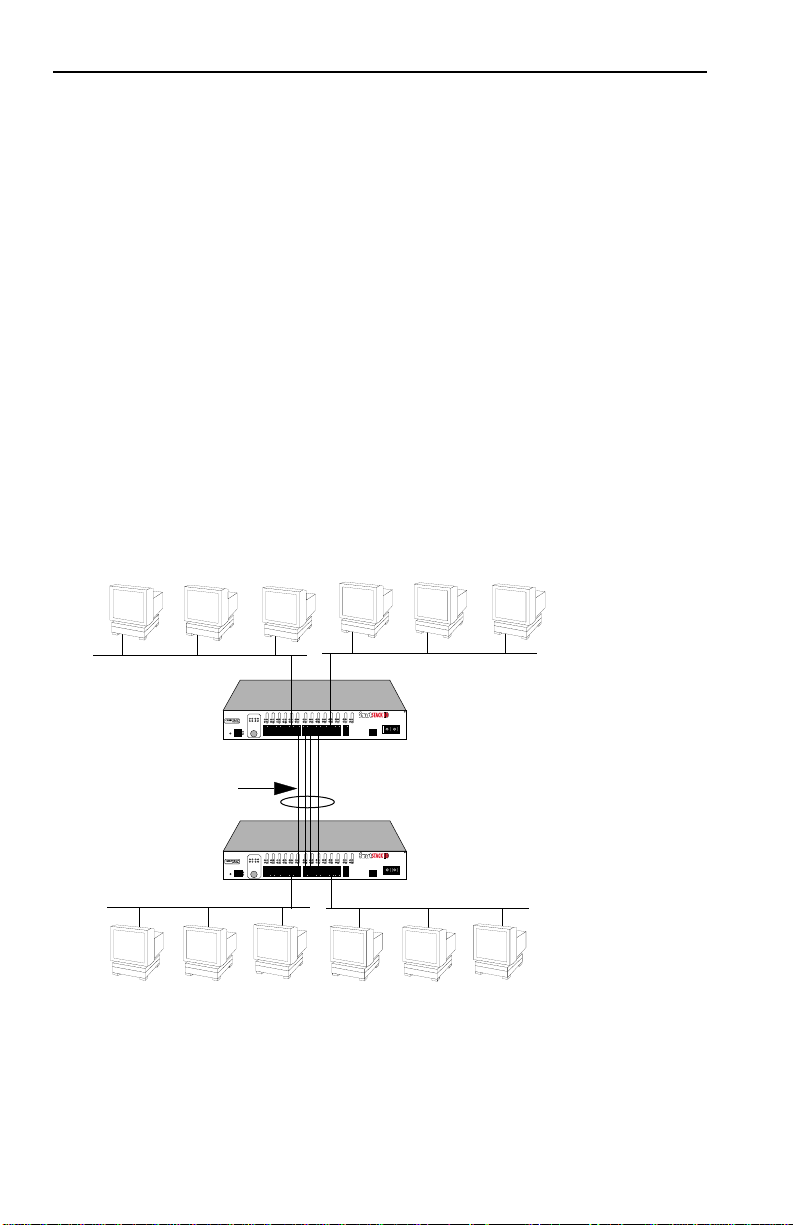
SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 Trunking
The SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 allows two trunk groups with up to
eight ports each to be connected between the SmartSTACK 10
ELS10-26 and other devices in the FastNetwork and SmartSTACK
families. This capability provides a scalable dedicated bandwidth
of up to 160 Mbps for 10 Mbps ports and 400 Mbps for 100 Mbps
ports.
For example, local traffic, such as the Manufacturing Department’s
internal traffic, can be easily handled by a single, 10 Mbps
connection. However, when the Manufacturing Department needs
access to the corporate database, the traffic could travel over a
trunk line, thereby increasing the speed of transmission.
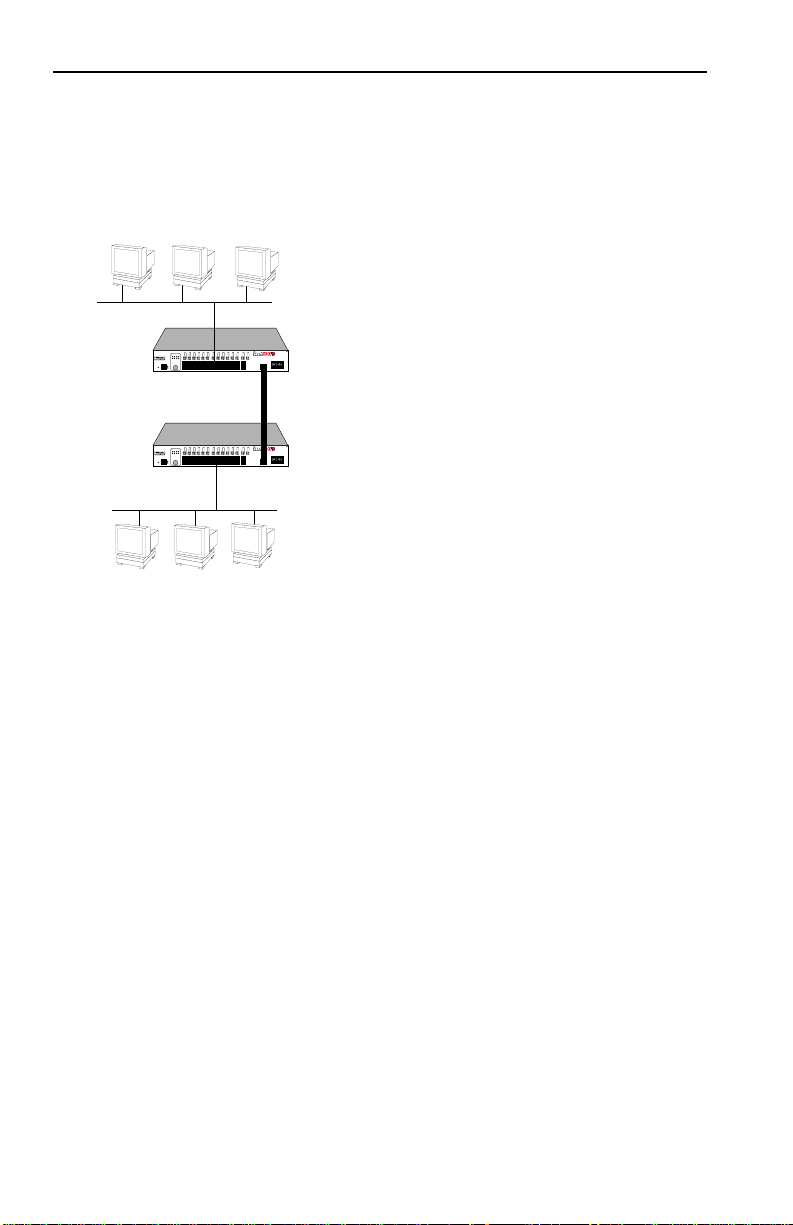
Figure 1-4 illustrates the trunking of multiple SmartSTACK 10
ELS10-26 ports to increase the bandwidth.
10 Mbps
ELS10-26TX
PORT STATUS MODE
TXACT FDXMON
RXCOL 100 USR
STATUS
PWR
CPU
RESET
COM
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
3412785611129
2X 4X 6X 8X 10X 12X 14X 16X 18X 20X 22X 24X MONX 26X
10 Mbps
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
21
19
1314151623
17
25
26
22
20
24
18
MON
27
10
FEPIM
10BASE-T/
100BASE-TX
27
ELS10-26
Up to 80 Mbps
Bandwidth
ELS10-26TX
PORT STATUS MODE
TXACT FDXMON
RXCOL 100 USR
STATUS
PWR
CPU
RESET
COM
10 Mbps
LINK
STATUS
LINK
3412785611129
2X 4X 6X 8X 10X 12X 14X 16X 18X 20X 22X 24X MONX 26X
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
LINK
STATUS
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
10
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
1314151623
17
18
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
21
19
22
20
24
Trunk Lines
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
25
26
MON
27
FEPIM
10BASE-T/
100BASE-TX
27
10 Mbps
ELS10-26
Figure 1-4. SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 Trunking with 10 Mbps Ports
1-12
LAN segments
LAN segments
Introduction
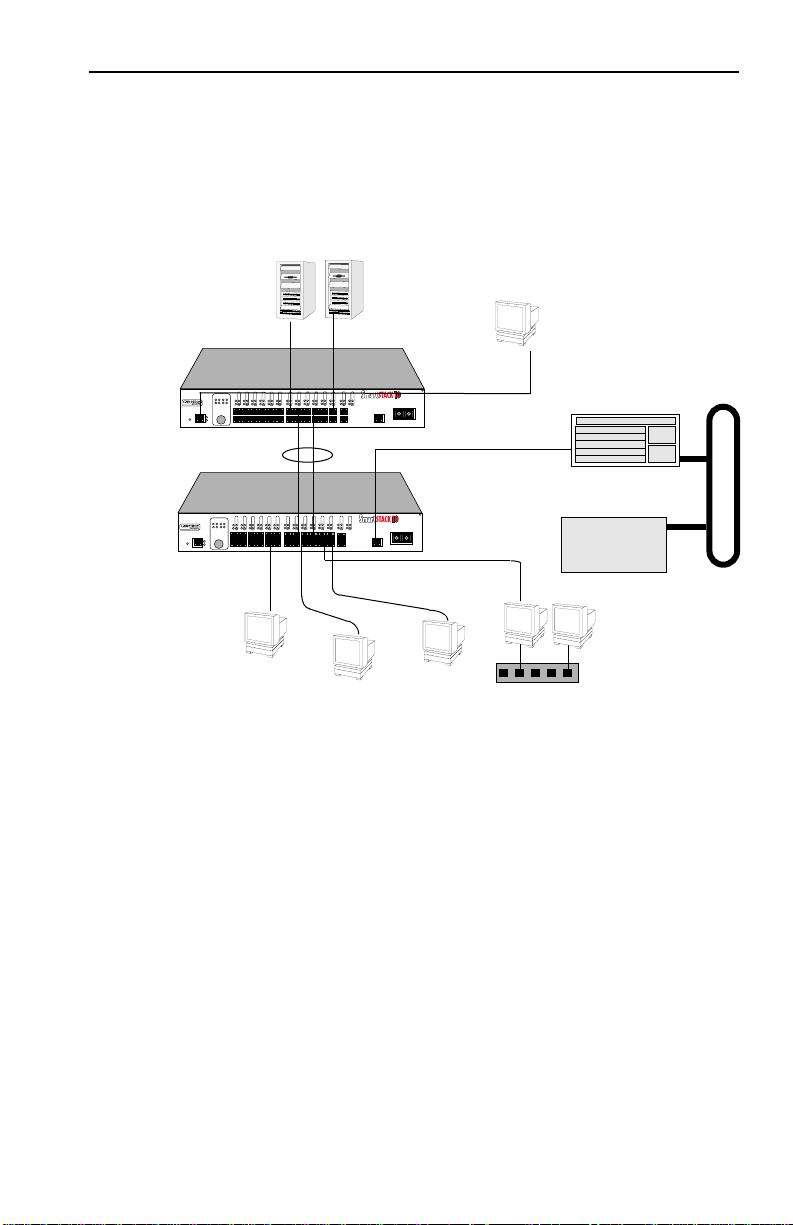
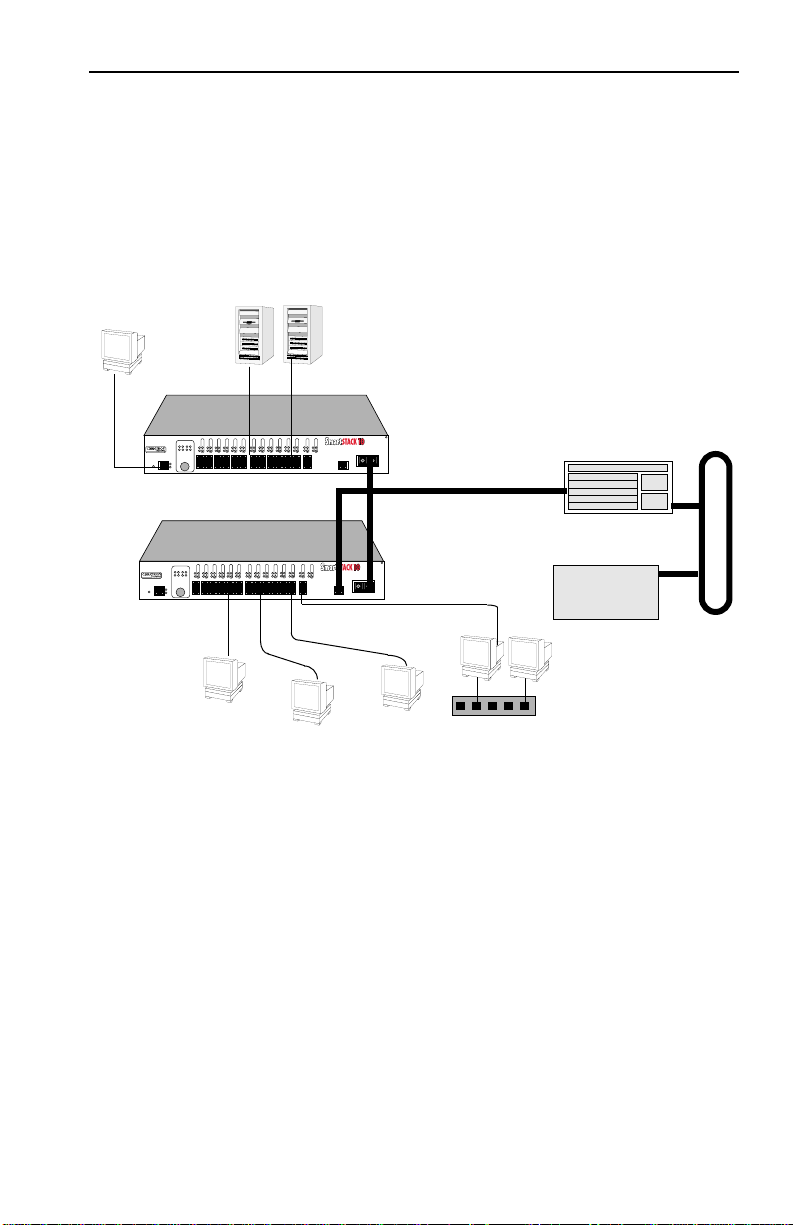
Figure 1-5 illustrates how the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 can be
used in a backbone network configuration.
Servers
Network
Management
Station
10BASE-T Cables
ELS10-26TX
PORT STATUS MODE
TXACT FDXMON
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
3412785611129
10
RXCOL 100 USR
STATUS
PWR
CPU
RESET
2X 4X 6X 8X 10X 12X 14X 16X 18X 20X 22X 24X MONX 26X
COM
Trunk Lines
ELS10-26TX
PORT STATUS MODE
TXACT FDXMON
RXCOL 100 USR
PWR
CPU
RESET
COM
LINK
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
3412785611129
10
STATUS
2X 4X 6X 8X 10X 12X 14X 16X 18X 20X 22X 24X MONX 26X
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
1314151623
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
STATUS
1314151623
17
18
LINK
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
21
19
17
22
20
18
LINK
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
21
19
22
20
ELS10-26
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
25
26
24
MON
27
FEPIM
10BASE-T/
100BASE-TX
27
ELS10-26
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
25
26
24
MON
27
FEPIM
10BASE-T/
100BASE-TX
27
10BASE-T Cables
Workgroup
Hub
Figure 1-5. SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 Backbone Configuration
SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 Fast Ethernet
Network Switch
WAN Router
The SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 has two additional ports that
provide fast Ethernet connections of 100 Mbps. Applying this
increased bandwidth to the previous example, the Manufacturing
Department’s traffic to the corporate database could be
transmitted to the corporate database at the 100 Mbps rate.
1-13
Introduction
Figure 1-6 illustrates connecting two SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26
Fast Ethernet ports to increase the bandwidth to 200 Mbps.
LAN segment
ELS10-26
ELS10-26TX
PORT STATUS MODE
TXACT FDXMON
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
21
19
1314151623
17
25
26
3412785611129
22
20
24
18
MON
27
10
RXCOL 100USR
STATUS
PWR
CPU
RESET
2X 4X 6X 8X 10X 12X 14X 16X 18X 20X 22X 24X MONX 26X
COM
Front Panel
ELS10-26
ELS10-26TX
PORT STATUS MODE
TXACT FDXMON
LINK
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
1314151623
3412785611129
10
RXCOL 100USR
STATUS
PWR
CPU
RESET
2X 4X 6X 8X 10X 12X 14X 16X 18X 20X 22X 24X MONX 26X
COM
Front Panel
Figure 1-6. SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 Trunking with 100 Mbps Ports
FEPIM
10BASE-T/
100BASE-TX
27
200 Mbps bandwidth
(Fast Ethernet, Full Duplex)
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
21
19
17
25
26
22
20
24
18
MON
27
FEPIM
10BASE-T/
100BASE-TX
27
LAN segment
1-14
Introduction
Figure 1-7 illustrates how the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 can be
used in a backbone network configuration using increased
bandwidth of the Fast Ethernet configuration.
Network
Management
Servers
Station
10BASE-T Cables
ELS10-26TX
PORT STATUS MODE
TXACT FDXMON
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
3412785611129
10
RXCOL 100 USR
STATUS
PWR
CPU
RESET
2X 4X 6X 8X 10X 12X 14X 16X 18X 20X 22X 24X MONX 26X
COM
LINK
LINK
STATUS
LINK
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
STATUS
1314151623
17
18
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
STATUS
21
19
22
20
24
ELS10-26
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
25
26
MON
27
10BASE-T/
100BASE-TX
FEPIM
27
100 Mbps (Fast Ethernet)
ELS10-26
ELS10-26TX
PORT STATUS MODE
TXACT FDXMON
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
3412785611129
RXCOL 100 USR
STATUS
PWR
CPU
RESET
2X 4X 6X 8X 10X 12X 14X 16X 18X 20X 22X 24X MONX 26X
COM
STATUS
LINK
10
LINK
STATUS
STATUS
1314151623
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
LINK
STATUS
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
21
19
17
25
26
22
20
24
18
MON
27
FEPIM
10BASE-T/
100BASE-TX
27
10BASE-T Cables
Workgroup
Hub
Figure 1-7. SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 Backbone Configuration
Virtual Workgr oups
Network Switch
WAN Router
The SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 allows you to define ports for
logical groups of associated devices (virtual workgroups) to
provide a more efficient flow of traffic across your Ethernet
network. You can define a maximum of eight virtual workgroups.
Virtual workgroups offer you the ability to limit broadcasts to
logical domains within the network. Workgroup destinations are
recognized by the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 and broadcast packets
are routed directly to hosts within the workgroup, eliminating the
need to perform a general broadcast across each segment of the
network to find specific host addresses.
1-15
Introduction
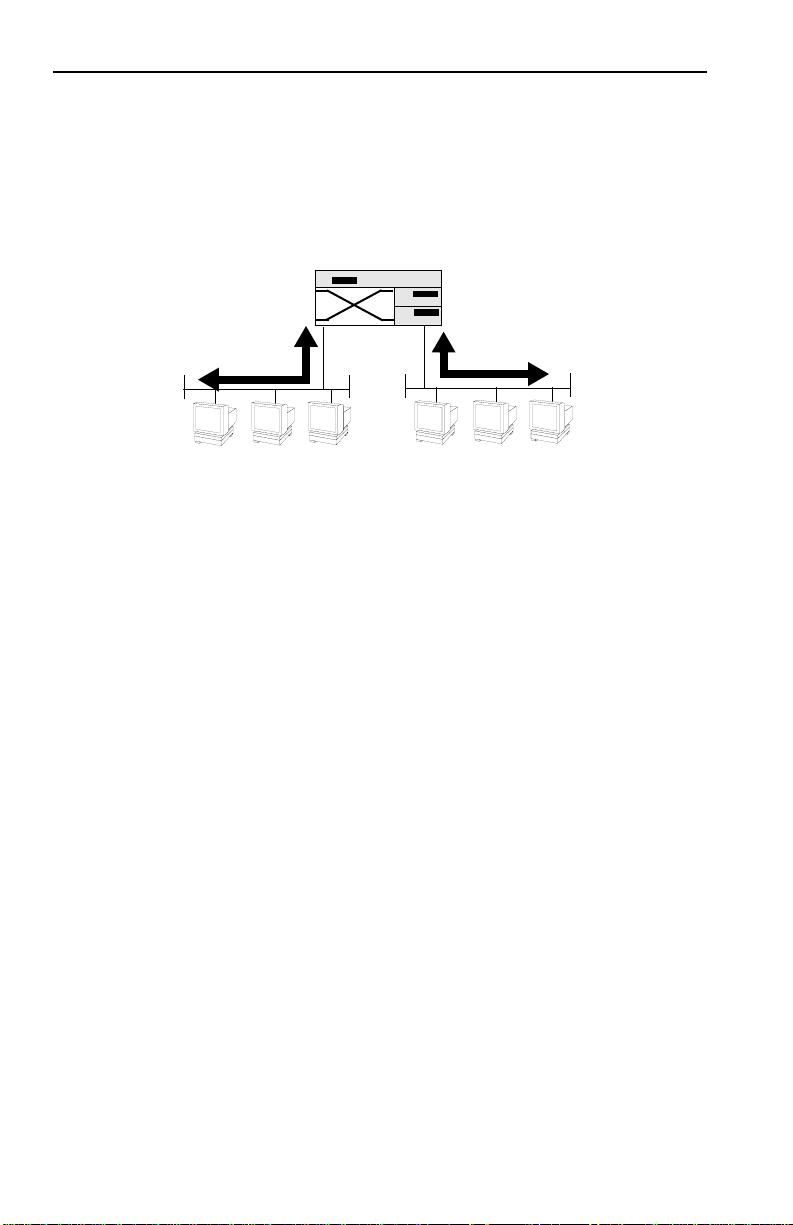
Figure 1-8 shows two Ethernet segments, A and B, that do not
include a SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26.
Repeater
Traffic
Figure 1-8. Multiple Ethernet Segments Sharing 10 Mbps Bandwidth
A
B
Traffic
Each host on segments A and B is limited to sharing a network
bandwidth of 10 Mbps.
1-16
Introduction
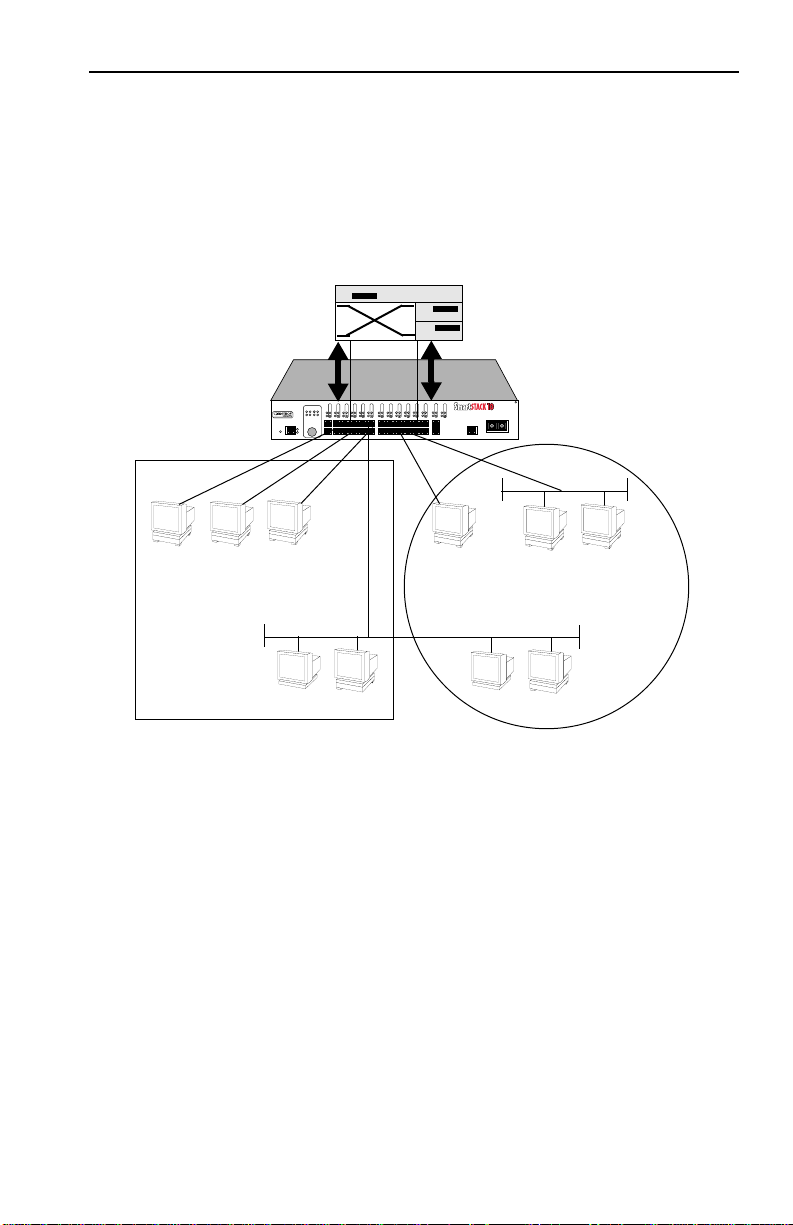
Figure 1-9 shows two Ethernet segments that take advantage of the
virtual workgroup feature of the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 and the
increased bandwidth applied to each A and B host.
Router
A
A
Workgroup A
ELS10-26TX
PORT STATUS MODE
TXACT FDXMON
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
3412785611129
RXCOL 100 USR
STATUS
PWR
CPU
RESET
2X 4X 6X 8X 10X 12X 14X 16X 18X 20X 22X 24X MONX 26X
COM
A
A
A
AB
LINK
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
21
19
1314151623
17
22
20
18
10
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
LINK
STATUS
25
26
24
MON
27
B
ELS10-26
FEPIM
10BASE-T/
100BASE-TX
27
B
Workgroup B
B
B
B
Figure 1-9. Using the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 to Create Virtual
Workgroups
to Help Optimize Bandwidth
A host from workgroup A can limit a broadcast to all hosts within
workgroup A and prevent the broadcast from going across the
network and adding to the amount of contention for the limited
10 Mbps bandwidth.
Ports that are not part of a workgroup will receive and transmit
packets from any ports. However, if you configure the
SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 with workgroup A and B, as shown in
Figure 1-9, broadcast traffic from workgroup A ports will not be
seen on workgroup B ports, and vice versa.
1-17

Introduction
As illustrated in the previous diagram, virtual workgroups allow
you to associate multiple ports and define a workgroup. In reality,
you are assigning workgroup IDs to SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26
ports.
1.6 LOCAL CONSOLE MANAGER
The Local Console Manager (LCM) is a command-line interface
built into the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26. The LCM t enables you to
monitor, manage, and configure the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26
through the out-of-band RS232C connection attached to any nonintelligent terminal or workstation running terminal emulation.
You can also use a Cabletron Systems Network Management
System, or a standard SNMP-based Network Management System,
to manage the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26. For a list of available
SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 network management tools, see Section
4.1, SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 Management Tools.
The following sections describe LCM command syntax and the
basic LCM commands for logging in, logging out, and getting
help.
• LCM commands used for configuring the SmartSTACK 10
ELS10-26 are described in Chapter 3, Configuring Your
SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26.
• LCM commands used for monitoring and managing the
SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 are described in Chapter 4,
Monitoring and Managing Your SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26.
Note: The Getting Started with the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 guide
lists the available LCM commands, including each command’s
options.
1-18

Introduction
1.6.1 Command Syntax Conventions
The following conventions apply as you use LCM commands:
• Press the Enter key to execute a command after you type it in.
•A port range is either a single port number, or a list of port
numbers separated by commas or hyphens. For example, 3 is
3; 3,7 are ports 3 and 7; 3-5 are ports 3,4, and 5; and 3-5,7
port
are ports
• To quit any command, press the Control-C keys (^C or Ctrl-C).
• You can abbreviate any command where there is no ambiguity;
if there is ambiguity, LCM responds with an error message.
• Commands are not case sensitive.
• Any invalid commands or misspellings will receive an error
message.
• A previous command can be repeated by typing !!
3,4,5, and 7.
• MAC addresses are displayed in little-endian Ethernet (least
significant bit) bit order, with each octet separated by a colon.
For example:
ELS10-26 >address 00:40:27:04:1a:0f
• Information that you need to enter with an LCM command is
enclosed in square brackets [ ]. For example, you must enter a
port number and an IP address to execute the
NUMBER] [IP ADDRESS]
ELS10-26 >ipaddr 6 192.138.217.40
command:
ipaddr [PORT-
• Parameters that appear in all capital letters, for example bridge
[PORT-RANGE]
, indicate that you must enter a value for that
parameter. If a string of parameters is displayed between braces,
for example
[{off|on|noBPDU}], you must select one of the
displayed options. For example, if you wanted to enable
bridging on a port, or a range of ports, you would enter:
ELS10-26 >bridge 2-4 on
1-19

Introduction
1.6.2 Basic LCM Commands
If you are going to manage the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 using
LCM, you first must connect the SmartSTACK 10 ELS10-26 to an
ASCII terminal or terminal emulator. See Section 2.5, Connecting
the Local Console Manager, for instructions.
When you want to use LCM, begin by pressing the Enter key
several times to get the LCM prompt (
ELS10-26 >).
Help
Displays the menu of available commands. Help can also be
displayed by typing a question mark (?). The output from the
command is displayed below.
help
1-20
 Loading...
Loading...