Page 1

SmartSwitch Series
2E42, 2E43, 2E48, 2E49, 2H22,
2H23, 2H28, 2H33 and 2M46
Local Management Supplement
9032971-01
Page 2

Page 3

NOTICE
Cabletron Systems reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information
contained in this document without prior notice. The reader should in all cases consult Cabletron
Systems to determine whether any such changes have been made.
The hardware, firmware, or software described in this manual is subject to change without notice.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CABLETRON SYSTEMS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INCIDENTAL,
INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES WHATSOEVER (INCLUDING BUT
NOT LIMITED TO LOST PROFITS) ARISING OUT OF OR RELATED TO THIS MANUAL OR
THE INFORMATION CONTAINED IN IT, EVEN IF CABLETRON SYSTEMS HAS BEEN
ADVISED OF, KNOWN, OR SHOULD HAVE KNOWN, THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGES.
Cabletron Systems, Inc.
35 Industrial Way
Rochester, NH 03867
1999 by Cabletron Systems, Inc.
All Rights Reserved
Printed in the United States of America
Order Number: 9032971-01 August 1999
Cabletron Systems, SPECTRUM, LANVIEW, QuickSET
trademarks and
All other product names mentioned in this manual may be trademarks or registered trademarks of
their respective companies.
SmartSwitch
is a trademark of Cabletron Systems, Inc.
, and
S
ecureFast
are registered
Local Management Supplement i
Page 4

Notice
CABLETRON SYSTEMS, INC.
PROGRAM LICENSE AGREEMENT
IMPORTANT: THIS LICENSE APPLIES FOR USE OF PRODUCT IN THE UNITED
STATES OF AMERICA AND BY UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
GOVERNMENT END USERS.
BEFORE OPENING OR UTILIZING THE ENCLOSED PRODUCT,
CAREFULLY READ THIS LICENSE AGREEMENT.
This document is an agreement (“Agreement”) between You, the end user, and Cabletron Systems,
Inc. (“Cabletron”) that sets forth your rights and obligations with respect to the Cabletron software
program (“Program”) in the package. The Program may be contained in firmware, chips or other
media. UTILIZING THE ENCLOSED PRODUCT, YOU ARE AGREEING TO BECOME BOUND
BY THE TERMS OF THIS AGREEMENT, WHICH INCLUDES THE LICENSE AND THE
LIMITATION OF WARRANTY AND DISCLAIMER OF LIABILITY. IF YOU DO NOT AGREE
TO THE TERMS OF THIS AGREEMENT, RETURN THE UNOPENED PRODUCT TO
CABLETRON OR YOUR DEALER, IF ANY, WITHIN TEN (10) DAYS FOLLOWING THE DATE
OF RECEIPT FOR A FULL REFUND.
IF YOU HAVE ANY QUESTIONS ABOUT THIS AGREEMENT, CONTACT CABLETRON
SYSTEMS +1-603-332-9400. Attn: Legal Department.
1. LICENSE.
package subject to the terms and conditions of this License Agreement.
You may not copy, reproduce or transmit any part of the Program except as permitted by the
Copyright Act of the United States or as authorized in writing by Cabletron.
2. OTHER RESTRICTIONS.
Program.
3. APPLICABLE LAW.
laws and in the state and federal courts of New Hampshire. You accept the personal jurisdiction and
venue of the New Hampshire courts.
4. EXPORT REQUIREMENTS.
regulation by agencies of the U.S. Government, including the U.S. Department of Commerce, which
prohibit export or diversion of certain technical products to certain countries, unless a license to export
the product is obtained from the U.S. Government or an exception from obtaining such license may be
relied upon by the exporting party.
If the Program is exported from the United States pursuant to the License Exception CIV under
the U.S. Export Administration Regulations, You agree that You are a civil end user of the Program
and agree that You will use the Program for civil end uses only and not for military purposes.
You have the right to use only the one (1) copy of the Program provided in this
You may not reverse engineer, decompile, or disassemble the
This License Agreement shall be interpreted and governed under the
You understand that Cabletron and its Affiliates are subject to
ii Local Management Supplement
Page 5

Notice
If the Program is exported from the United States pursuant to the License Exception TSR under
the U.S. Export Administration Regulations, in addition to the restriction on transfer set forth in
Sections 1 or 2 of this Agreement, You agree not to (i) reexport or release the Program, the source
code for the Program or technology to a national of a country in Country Groups D:1 or E:2 (Albania,
Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Bulgaria, Cambodia, Cuba, Estonia, Georgia, Iraq, Kazakhstan,
Kyrgyzstan, Laos, Latvia, Libya, Lithuania, Moldova, North Korea, the People’s Republic of China,
Romania, Russia, Rwanda, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Vietnam, or such other
countries as may be designated by the United States Government), (ii) export to Country Groups D:1
or E:2 (as defined herein) the direct product of the Program or the technology, if such foreign
produced direct product is subject to national security controls as identified on the U.S. Commerce
Control List, or (iii) if the direct product of the technology is a complete plant o r any major
component of a plant, export to Country Groups D:1 or E:2 the direct product of the plant or a major
component thereof, if such foreign produced direct product is subject to national security controls as
identified on the U.S. Commerce Control List or is subject to State Department controls under the
U.S. Munitions List.
5. UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT RESTRICTED RIGHTS.
was developed solely at private expense; (ii) contains “restricted computer software” submitted with
restricted rights in accordance with section 52.227-19 (a) through (d) of the Commercial Computer
Software-Restricted Rights Clause and its successors, and (iii) in all respects is proprietary data
belonging to Cabletron and/or its suppliers. For Department of Defense units, the Product is considered
commercial computer software in accordance with DFARS section 227.7202-3 and its successors, and
use, duplication, or disclosure by the Government is subject to restrictions set forth herein.
6. EXCLUSION OF WARRANTY.
writing, Cabletron makes no warranty, expressed or implied, concerning the Program (including its
documentation and media).
CABLETRON DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, OTHER THAN THOSE SUPPLIED TO
YOU BY CABLETRON IN WRITING, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT
NOT LIMITED TO IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE, WITH RESPECT TO THE PROGRAM, THE ACCOMPANYING
WRITTEN MATERIALS, AND ANY A CCOMP ANYING HARDWARE.
7. NO LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES.
CABLETRON OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES WHATSOEVER
(INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF BUSINESS, PROFITS,
BUSINESS INTERRUPTION, LOSS OF BUSINESS INFORMATION, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL,
CONSEQUENTIAL, OR RELIANCE DAMAGES, OR OTHER LOSS) ARISING OUT OF THE
USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS CABLETRON PRODUCT, EVEN IF CABLETRON HAS
BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. BECAUSE SOME STATES DO
NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION OF LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, OR IN THE DURATION OR LIMITATION OF IMPLIED
WARRANTIES IN SOME INSTANCES, THE ABOVE LIMITATION AND EXCLUSIONS MAY
NOT APPLY TO YOU.
Except as may be specifically provided by Cabletron in
The enclosed Product (i)
IN NO EVENT SHALL
Local Management Supplement iii
Page 6

Notice
CABLETRON SYSTEMS SALES AND SERVICE, INC.
PROGRAM LICENSE AGREEMENT
IMPORTANT: THIS LICENSE APPLIES FOR USE OF PRODUCT IN THE UNITED
STATES OF AMERICA AND BY UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
GOVERNMENT END USERS.
BEFORE OPENING OR UTILIZING THE ENCLOSED PRODUCT,
CAREFULLY READ THIS LICENSE AGREEMENT.
This document is an agreement (“Agreement”) between You, the end user, and Cabletron Systems
Sales and Service, Inc. (“Cabletron”) that sets forth your rights and obligations with respect to the
Cabletron software program (“Program”) in the package. The Program may be contained in firmware,
chips or other media. UTILIZING THE ENCLOSED PRODUCT, YOU ARE AGREEING TO
BECOME BOUND BY THE TERMS OF THIS AGREEMENT, WHICH INCLUDES THE
LICENSE AND THE LIMITATION OF WARRANTY AND DISCLAIMER OF LIABILITY. IF
YOU DO NOT AGREE TO THE TERMS OF THIS AGREEMENT, RETURN THE UNOPENED
PRODUCT TO CABLETRON OR YOUR DEALER, IF ANY, WITHIN TEN (10) DAYS
FOLLOWING THE DATE OF RECEIPT FOR A FULL REFUND.
IF YOU HAVE ANY QUESTIONS ABOUT THIS AGREEMENT, CONTACT CABLETRON
SYSTEMS +1-603-332-9400. Attn: Legal Department.
1. LICENSE.
package subject to the terms and conditions of this License Agreement.
You may not copy, reproduce or transmit any part of the Program except as permitted by the
Copyright Act of the United States or as authorized in writing by Cabletron.
2. OTHER RESTRICTIONS.
Program.
3. APPLICABLE LAW.
laws and in the state and federal courts of New Hampshire. You accept the personal jurisdiction and
venue of the New Hampshire courts.
4. EXPORT REQUIREMENTS.
regulation by agencies of the U.S. Government, including the U.S. Department of Commerce, which
prohibit export or diversion of certain technical products to certain countries, unless a license to export
the product is obtained from the U.S. Government or an exception from obtaining such license may be
relied upon by the exporting party.
If the Program is exported from the United States pursuant to the License Exception CIV under
the U.S. Export Administration Regulations, You agree that You are a civil end user of the Program
and agree that You will use the Program for civil end uses only and not for military purposes.
You have the right to use only the one (1) copy of the Program provided in this
You may not reverse engineer, decompile, or disassemble the
This License Agreement shall be interpreted and governed under the
You understand that Cabletron and its Affiliates are subject to
iv Local Management Supplement
Page 7

Notice
If the Program is exported from the United States pursuant to the License Exception TSR under
the U.S. Export Administration Regulations, in addition to the restriction on transfer set forth in
Sections 1 or 2 of this Agreement, You agree not to (i) reexport or release the Program, the source
code for the Program or technology to a national of a country in Country Groups D:1 or E:2 (Albania,
Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Bulgaria, Cambodia, Cuba, Estonia, Georgia, Iraq, Kazakhstan,
Kyrgyzstan, Laos, Latvia, Libya, Lithuania, Moldova, North Korea, the People’s Republic of China,
Romania, Russia, Rwanda, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Vietnam, or such other
countries as may be designated by the United States Government), (ii) export to Country Groups D:1
or E:2 (as defined herein) the direct product of the Program or the technology, if such foreign
produced direct product is subject to national security controls as identified on the U.S. Commerce
Control List, or (iii) if the direct product of the technology is a complete plant o r any major
component of a plant, export to Country Groups D:1 or E:2 the direct product of the plant or a major
component thereof, if such foreign produced direct product is subject to national security controls as
identified on the U.S. Commerce Control List or is subject to State Department controls under the
U.S. Munitions List.
5. UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT RESTRICTED RIGHTS.
was developed solely at private expense; (ii) contains “restricted computer software” submitted with
restricted rights in accordance with section 52.227-19 (a) through (d) of the Commercial Computer
Software-Restricted Rights Clause and its successors, and (iii) in all respects is proprietary data
belonging to Cabletron and/or its suppliers. For Department of Defense units, the Product is considered
commercial computer software in accordance with DFARS section 227.7202-3 and its successors, and
use, duplication, or disclosure by the Government is subject to restrictions set forth herein.
6. EXCLUSION OF WARRANTY.
writing, Cabletron makes no warranty, expressed or implied, concerning the Program (including its
documentation and media).
CABLETRON DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, OTHER THAN THOSE SUPPLIED TO
YOU BY CABLETRON IN WRITING, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT
NOT LIMITED TO IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE, WITH RESPECT TO THE PROGRAM, THE ACCOMPANYING
WRITTEN MATERIALS, AND ANY A CCOMP ANYING HARDWARE.
7. NO LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES.
CABLETRON OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES WHATSOEVER
(INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF BUSINESS, PROFITS,
BUSINESS INTERRUPTION, LOSS OF BUSINESS INFORMATION, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL,
CONSEQUENTIAL, OR RELIANCE DAMAGES, OR OTHER LOSS) ARISING OUT OF THE
USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS CABLETRON PRODUCT, EVEN IF CABLETRON HAS
BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. BECAUSE SOME STATES DO
NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION OF LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, OR IN THE DURATION OR LIMITATION OF IMPLIED
WARRANTIES IN SOME INSTANCES, THE ABOVE LIMITATION AND EXCLUSIONS MAY
NOT APPLY TO YOU.
Except as may be specifically provided by Cabletron in
The enclosed Product (i)
IN NO EVENT SHALL
Local Management Supplement v
Page 8

Notice
CABLETRON SYSTEMS LIMITED
PROGRAM LICENSE AGREEMENT
IMPORTANT: THIS LICENSE APPLIES FOR USE OF PRODUCT IN THE UNITED
STATES OF AMERICA AND BY UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
GOVERNMENT END USERS.
BEFORE OPENING OR UTILIZING THE ENCLOSED PRODUCT,
CAREFULLY READ THIS LICENSE AGREEMENT.
This document is an agreement (“Agreement”) between You, the end user, and Cabletron Systems
Limited (“Cabletron”) that sets forth your rights and obligations with respect to the Cabletron
software program (“Program”) in the package. The Program may be contained in firmware, chips or
other media. UTILIZING THE ENCLOSED PRODUCT, YOU ARE AGREEING TO BECOME
BOUND BY THE TERMS OF THIS AGREEMENT, WHICH INCLUDES THE LICENSE AND
THE LIMITATION OF WARRANTY AND DISCLAIMER OF LIABILITY. IF YOU DO NOT
AGREE TO THE TERMS OF THIS AGREEMENT, RETURN THE UNOPENED PRODUCT TO
CABLETRON OR YOUR DEALER, IF ANY, WITHIN TEN (10) DAYS FOLLOWING THE DATE
OF RECEIPT FOR A FULL REFUND.
IF YOU HAVE ANY QUESTIONS ABOUT THIS AGREEMENT, CONTACT CABLETRON
SYSTEMS +1-603-332-9400. Attn: Legal Department.
1. LICENSE.
package subject to the terms and conditions of this License Agreement.
You may not copy, reproduce or transmit any part of the Program except as permitted by the
Copyright Act of the United States or as authorized in writing by Cabletron.
2. OTHER RESTRICTIONS.
Program.
3. APPLICABLE LAW.
law. The English courts shall have exclusive jurisdiction in the event of any disputes.
4. EXPORT REQUIREMENTS.
regulation by agencies of the U.S. Government, including the U.S. Department of Commerce, which
prohibit export or diversion of certain technical products to certain countries, unless a license to export
the product is obtained from the U.S. Government or an exception from obtaining such license may be
relied upon by the exporting party.
If the Program is exported from the United States pursuant to the License Exception CIV under
the U.S. Export Administration Regulations, You agree that You are a civil end user of the Program
and agree that You will use the Program for civil end uses only and not for military purposes.
You have the right to use only the one (1) copy of the Program provided in this
You may not reverse engineer, decompile, or disassemble the
This License Agreement shall be governed in accordance with English
You understand that Cabletron and its Affiliates are subject to
vi Local Management Supplement
Page 9

Notice
If the Program is exported from the United States pursuant to the License Exception TSR under
the U.S. Export Administration Regulations, in addition to the restriction on transfer set forth in
Sections 1 or 2 of this Agreement, You agree not to (i) reexport or release the Program, the source
code for the Program or technology to a national of a country in Country Groups D:1 or E:2 (Albania,
Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Bulgaria, Cambodia, Cuba, Estonia, Georgia, Iraq, Kazakhstan,
Kyrgyzstan, Laos, Latvia, Libya, Lithuania, Moldova, North Korea, the People’s Republic of China,
Romania, Russia, Rwanda, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Vietnam, or such other
countries as may be designated by the United States Government), (ii) export to Country Groups D:1
or E:2 (as defined herein) the direct product of the Program or the technology, if such foreign
produced direct product is subject to national security controls as identified on the U.S. Commerce
Control List, or (iii) if the direct product of the technology is a complete plant o r any major
component of a plant, export to Country Groups D:1 or E:2 the direct product of the plant or a major
component thereof, if such foreign produced direct product is subject to national security controls as
identified on the U.S. Commerce Control List or is subject to State Department controls under the
U.S. Munitions List.
5. UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT RESTRICTED RIGHTS.
was developed solely at private expense; (ii) contains “restricted computer software” submitted with
restricted rights in accordance with section 52.227-19 (a) through (d) of the Commercial Computer
Software-Restricted Rights Clause and its successors, and (iii) in all respects is proprietary data
belonging to Cabletron and/or its suppliers. For Department of Defense units, the Product is considered
commercial computer software in accordance with DFARS section 227.7202-3 and its successors, and
use, duplication, or disclosure by the Government is subject to restrictions set forth herein.
6. EXCLUSION OF WARRANTY.
writing, Cabletron makes no warranty, expressed or implied, concerning the Program (including its
documentation and media).
CABLETRON DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, OTHER THAN THOSE SUPPLIED TO
YOU BY CABLETRON IN WRITING, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT
NOT LIMITED TO IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE, WITH RESPECT TO THE PROGRAM, THE ACCOMPANYING
WRITTEN MATERIALS, AND ANY A CCOMP ANYING HARDWARE.
7.
NO LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES. IN NO EVENT SHALL
CABLETRON OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES WHATSOEVER
(INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF BUSINESS, PROFITS,
BUSINESS INTERRUPTION, LOSS OF BUSINESS INFORMATION, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL,
CONSEQUENTIAL, OR RELIANCE DAMAGES, OR OTHER LOSS) ARISING OUT OF THE
USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS CABLETRON PRODUCT, EVEN IF CABLETRON HAS
BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. BECAUSE SOME STATES DO
NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION OF LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, OR IN THE DURATION OR LIMITATION OF IMPLIED
WARRANTIES IN SOME INSTANCES, THE ABOVE LIMITATION AND EXCLUSIONS MAY
NOT APPLY TO YOU.
Except as may be specifically provided by Cabletron in
The enclosed Product (i)
Local Management Supplement vii
Page 10

Notice
DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
Application of Council Directive(s):
Manufacturer’s Name:
Manufacturer’s Address:
European Representative Name:
European Representative Address:
Conformance to Directive(s)/Product Standards:
Equipment T ype/Environment:
W e the undersigned, hereby declare, under our sole responsibility, that the equipment packaged
with this notice conforms to the above directives.
Manufacturer Legal Representative in Europe
89/336/EEC
73/23/EEC
Cabletron Systems, Inc.
35 Industrial Way
PO Box 5005
Rochester, NH 03867
Mr. J. Solari
Cabletron Systems Limited
Nexus House, Newbury Business Park
London Road, Newbury
Berkshire RG14 2PZ, England
EC Directive 89/336/EEC
EC Directive 73/23/EEC
EN 55022
EN 50082-1
EN 60950
Networking Equipment, for use in a
Commercial or Light
Environment.
Industrial
Mr. Ronald Fotino Mr. J. Solari
___________________________________ ___________________________________
Full Name Full Name
Principal Compliance Engineer Managing Director - E.M.E.A.
___________________________________ ___________________________________
Title Title
Rochester, NH, USA Newbury, Berkshire, England
___________________________________ ___________________________________
Location Location
viii Local Management Supplement
Page 11

CONTENTS
Figures ...................................................................................................xiii
Tables.....................................................................................................xiv
CHAPTER 1 CHANGES TO LOCAL MANAGEMENT SCREENS
1.1 Introduction..................................................................................1-1
1.2 Accessing Local Management.....................................................1-2
1.2.1 Navigating Local Management Screens.........................1-2
1.2.2 Screen Format................................................................1-5
1.3 Device Configuration Menu Screen.............................................1-6
1.4 System Resources Information Screen....................................... 1-8
1.4.1 Resetting the Reset Peak Switch Utilization...................1-9
1.5 FLASH Download Configuration Screen...................................1-10
1.5.1 Image File Download Using TFTP................................1-12
1.5.2 Image File Download Using Runtime ........................... 1-13
1.5.3 Image File Download Using BootP...............................1-14
1.6 Port Configuration Menu Screen...............................................1-14
1.7 Ethernet Full Duplex Configuration Screen...............................1-16
1.7.1 Setting the Operational Mode.......................................1-18
1.8 High Speed Interface Configuration Menu Screen.................... 1-19
1.9 High Speed Interface Configuration Screen.............................. 1-21
1.9.1 Configuring an FE-100FX or FE-100F3........................1-23
1.9.2 Setting the FE-100FX or FE-100F3
Operational Mode ......................................................... 1-24
1.9.3 Configuring an FE-100TX.............................................1-24
1.9.4 Setting the FE-100TX Operational Mode...................... 1-24
1.9.5 Setting the FE-100TX Advertised Ability....................... 1-25
1.10 Redirect Configuration Menu Screen ........................................1-26
1.11 Port Redirect Configuration Screen...........................................1-27
1.11.1 Changing Source and Destination Ports....................... 1-30
1.12 VLAN Redirect Configuration Screen........................................ 1-31
1.12.1 Changing Source VLAN and Destination Ports ............ 1-34
1.13 Broadcast Suppression Configuration Screen...........................1-35
1.13.1 Setting the Threshold.................................................... 1-36
1.13.2 Resetting the Reset Peak.............................................1-37
1.14 Repeater Configuration Menu Screens.....................................1-37
1.15 802.1 Configuration Menu Screen.............................................1-38
1.16 Switch Configuration Screen.....................................................1-40
1.16.1 Setting the STA............................................................. 1-42
1.16.2 Setting the Age Time Field ........................................... 1-42
1.16.3 Setting (Enabling or Disabling) the Port Status ............ 1-43
Local Management Supplement ix
Page 12

Contents
1.17 Summary of VLAN Local Management......................................1-43
1.18 802.1Q VLAN Configuration Menu Screen................................1-44
1.19 IGMP/VLAN Configuration Screen.............................................1-45
1.19.1 Configuring VLANs for IGMP ........................................1-49
1.20 Priority/Multicast Configuration Menu Screen............................1-50
1.21 Port Priority Configuration Screen .............................................1-52
1.21.1 Setting Switch Port Priority Port-by-Port .......................1-53
1.21.2 Setting Switch Port Priority on All Ports ........................1-53
1.22 Advanced Port Priority Configuration Screen ............................1-54
1.22.1 Setting the TX Mapping Queues...................................1-57
1.22.2 Setting the TX Regeneration Priorities..........................1-57
1.22.3 Setting the Default Priority of a Port..............................1-58
CHAPTER 2 LM SECURITY SCREENS FOR
2E43-51/2E43-51R DEVICES
2.1 Repeater Configuration Menu Screen .........................................2-1
2.2 Repeater Level Security Configuration ........................................2-2
2.2.1 Setting the Repeater Level Security................................2-4
2.3 Port Level Security Configuration Screen....................................2-5
2.3.1 Setting the Port Level Security........................................2-8
CHAPTER 3 LM SECURITY SCREENS FOR
2H23-50R/2H33-37R DEVICES
3.1 Repeater Configuration Menu Screen .........................................3-1
3.2 Repeater Port Configuration Screen............................................3-2
3.2.1 Setting the Port Operating Mode.....................................3-5
3.2.2 Enabling /Disabling Repeater Ports ................................3-5
3.2.3 Setting Operating Mode On All Repeater Ports ..............3-6
3.3 Module Level Security Configuration ...........................................3-7
3.3.1 Setting the Module Level Security...................................3-9
3.4 Port Level Security Configuration Screen..................................3-10
3.4.1 Setting the Port Level Security......................................3-13
x Local Management Supplement
Page 13

Contents
CHAPTER 4 GENERIC ATTRIBUTE REGISTRATION
PROTOCOL (GARP)
4.1 GARP Switch Operation.............................................................. 4-1
4.1.1 GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) ................... 4-1
4.2 GARP Multicast Registration Protocol (GMRP)...........................4-3
4.3 GARP Operation Status Screen.................................................. 4-4
4.3.1 Setting a Port to Operate in GMRP or GVRP.................4-6
4.3.2 Setting All Ports on the Switch........................................ 4-6
4.4 GMRP Configuration Screen....................................................... 4-7
4.4.1 Setting a Mode, Port-by-Port .......................................... 4-8
4.4.2 Setting a Mode for All Ports............................................4-9
CHAPTER 5 NETWORK TOOLS
5.1 Network Tools..............................................................................5-1
5.1.1 Built-in Command ........................................................... 5-2
APPENDIX A ABOUT IGMP
A.1 IGMP Overview ...........................................................................A-1
A.2 Supported Features and Functions.............................................A-1
A.3 Detecting Multicast Routers.........................................................A-2
INDEX
Local Management Supplement xi
Page 14

Page 15

FIGURES
Figure Page
1-1 802.1D Switching Mode, LM Screen Hierarchy........................1-3
1-2 802.1Q Switching Mode, LM Screen Hierarchy .......................1-4
1-3 Example of a Local Management Screen ................................1-5
1-4 Device Configuration Menu Screen..........................................1-6
1-5 System Resources Information Screen....................................1-8
1-6 Flash Download Configuration Screen...................................1-10
1-7 Port Configuration Menu Screen............................................ 1-15
1-8 Ethernet Full Duplex Configuration Screen............................ 1-17
1-9 High Speed Interface Configuration Menu Screen.................1-20
1-10 High Speed Interface Configuration Screen........................... 1-21
1-11 Redirect Configuration Menu Screen .....................................1-26
1-12 Port Redirect Configuration Screen........................................1-28
1-13 VLAN Redirect Configuration Screen..................................... 1-32
1-14 Broadcast Suppression Configuration Screen .......................1-35
1-15 802.1 Configuration Menu Screen..........................................1-38
1-16 Switch Configuration Screen..................................................1-40
1-17 802.1Q VLAN Screen Hierarchy ............................................1-43
1-18 802.1Q VLAN Configuration Menu Screen ............................1-44
1-19 IGMP/VLAN Configuration Screen.........................................1-47
1-20 Priority/Multicast Configuration Menu Screen ........................1-51
1-21 Port Priority Configuration Screen.......................................... 1-52
1-22 Advanced Port Priority Configuration Screen......................... 1-55
2-1 Repeater Configuration Menu Screen......................................2-1
2-2 Repeater Level Security Configuration Screen........................2-3
2-3 Port Level Security Configuration Screen ................................2-6
3-1 Repeater Configuration Menu Screen......................................3-1
3-2 Repeater Port Configuration Screen........................................3-3
3-3 Module Level Security Configuration Screen...........................3-7
3-4 Port Level Security Configuration Screen ..............................3-11
4-1 Example of VLAN Propagation via GVRP................................4-2
4-2 GARP Operation Status Screen...............................................4-4
4-3 GMRP Configuration Screen....................................................4-7
5-1 Network Tools Help Screen......................................................5-2
Local Management Supplement xiii
Page 16

TABLES
Table Page
1-1 User’s Guides Affected by Revisions........................................1-1
1-2 TX Queue Mapping Default Values........................................1-55
1-3 TX Priority Regeneration Default Values................................1-56
2-1 ENET/Repeater Port Relationship............................................2-6
3-1 CONN/Repeater Port Relationship...........................................3-3
3-2 CONN/Network Organization....................................................3-4
3-3 CONN/Repeater Port Relationship...........................................3-8
3-4 CONN/Repeater Port Relationship.........................................3-11
3-5 CONN/Network Organization..................................................3-12
xiv Insert BookTitle
Page 17
CHAPTER 1
CHANGES TO LOCAL MANAGEMENT SCREENS
This chapter introduces the scope of this document, new hierarchy, and
new screens (except security screens) af fected by the 4.08.xx and 4.09.xx
firmware revisions.
Chapter 2 describes the revised security screens for the 2E43-51 and
2E43-51R repeater devices. Chapter 3 describes the security screens for
the 2H23-50R and 2H33-37R repeater devices
Network Tools command, cdp.
1.1 INTRODUCTION
This supplement applies to the SmartSwitch standalone devices with
firmware revisions through 4.09.xx and documents the changes and
additions affecting the 802.1Q VLAN User’s Guide and the SmartSwitch
user’s guides listed in Table 1-1.
Table 1-1 User’s Guides Affected by Revisions
Title Part Number
.
Chapter 5 describes a new
802.1Q VLAN User’s Guide 9032599-02
2E42-27/2E42-27R/2E43-27/2E43-27R User’s Guide 9031960-05
2E43-51/2E43-51R User’s Guide 9032251-04
2E48-27R/2E49-27R User’s Guide 9032314-04
2H22-08R User’s Guide 9032385-02
2H23-50R/2H33-37R User’s Guide 9032286-04
2H28-08R User’s Guide 9032380-03
2M46-04R/2M46-04RDC User’s Guide 9032363-02
NOTE
Local Management Supplement 1-1
This document applies to several SmartSwitch models. Unless
otherwise noted, the term SmartSwitch is used in the following
text instead of a particular model number.
Page 18

Chapter 1:
Changes to Local Management Screens
1.2 ACCESSING LOCAL MANAGEMENT
Access to Local Management is controlled through the Password screen.
1.2.1 Navigating Local Management Screens
The Local Management application consists of a series of menu screens.
Navigate through Local Management by selecting items from the menu
screens.
The SmartSwitch supports two modes of switch operation. The switching
modes are as follows:
•
802.1D Switching (traditional switching)
•
802.1Q Switching (802.1Q port based VLANs)
•
SecureFast VLAN (Cabletron Systems SecureFast switching). A
separate image is required for this operation.
NOTE
Refer to the Release Notes shipped with the product to verify
which screens are supported in each of the available switching
modes.
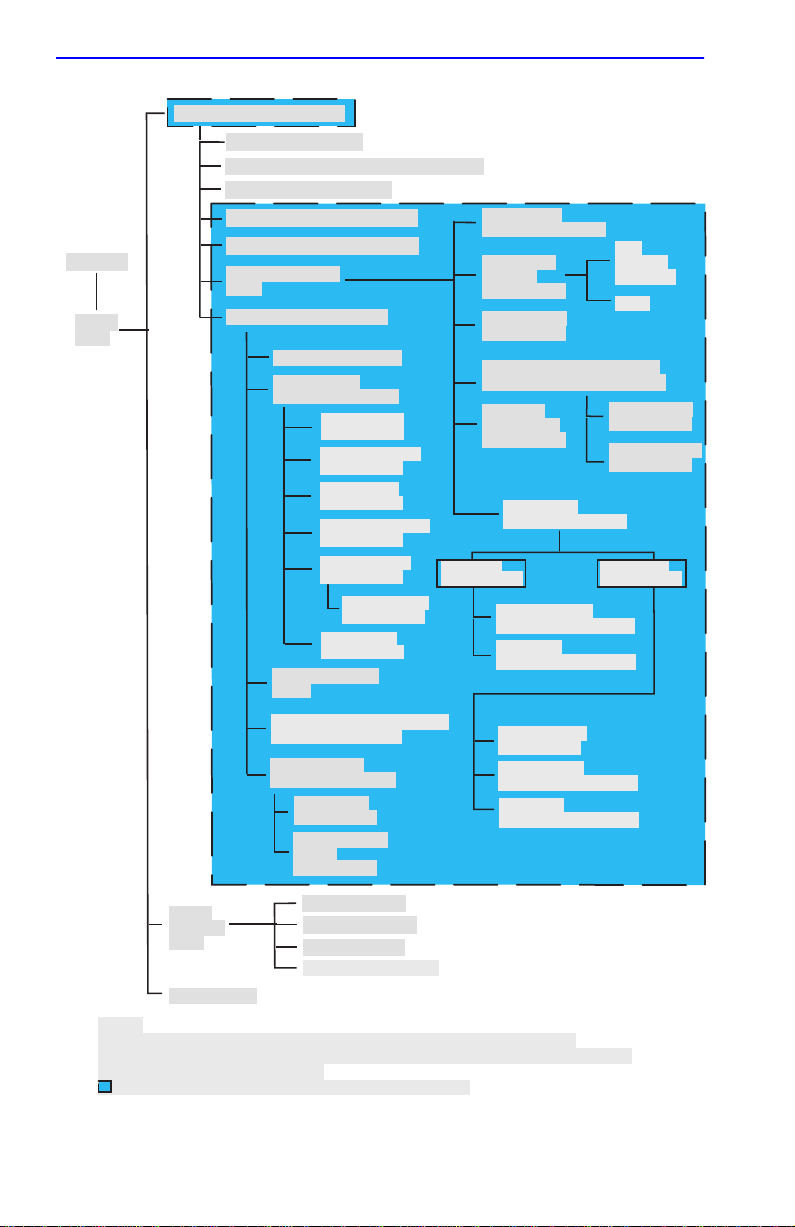
Depending on the Operational Mode set for the device, the hierarchy of
the Local Management screens differs as shown in Figure 1-1 and
Figure 1-2. Refer to the appropriate figure that relates to the Operational
Mode set for the device to see the applicable Local Management screen
hierarchy.
NOTE
The areas that changed in the hierarchy are highlighted as
shown in Figure 1-1 and Figure 1-2. The screens involved are
covered in this document.
added or revised, or changed location in the hierarchy.
These screens may have been
1-2 Local Management Supplement
Page 19

\
Password
Device
Menu
Device Configuration Menu
General Configuration
SNMP Community Names Configuration
SNMP Traps Configuration
System Resources Information
Flash Download Configuration
Port Configuration
Menu
802.1 Configuration Menu
Switch Configuration
Device
Statistics
Menu
Network Tools
Switch Statistics
Interface Statistics
RMON Statistics
** Repeater Statistics
Accessing Local Management
Ethernet Full
Duplex Configuration
High Speed
Interface
Configuration
* SmartTrunk
Configuration
Port Redirect Configuration/
Redirect Configuration Menu
Broadcast
Suppression
Configuration
** Repeater
Configuration Menu
Fast
Ethernet
Interfaces
HSIM
Port Redirect
Configuration
VLAN Redirect
Configuration
2E43-51 or
2E43-51R only
Repeater Level
Security Configuration
Port Level
Security Configuration
Notes:
* Refer to the
** This screen is only available on repeater devices (2E43-51, 2E43-51R,
2H23-50R, and 2H33-37R).
Indicates the part of the hierarchy that changed.
SmartTrunk User's Guide
for the screen hierarchy.
2H23-50R or
2H33-37R only
Repeater Port
Configuration
Module Level
Security Configuration
Port Level
Security Configuration
Figure 1-1 802.1D Switching Mode, LM Screen Hierarchy
29712_43
Local Management Supplement 1-3
Page 20
Chapter 1:
Password
Device
Menu
Changes to Local Management Screens
Device Configuration Menu
General Configuration
SNMP Community Names Configuration
SNMP Traps Configuration
System Resources Information
Flash Download Configuration
Port Configuration
Menu
802.1 Configuration Menu
Switch Configuration
802.1Q VLAN
Configuration Menu
Device/VLAN
Configuration
Port Assignment
Configuration
Port Filtering
Configuration
VLAN Forwarding
Configuration
Protocol VLAN
Configuration
Protocol Ports
Configuration
IGMP/VLAN
Configuration
GARP Operation
Status
GMRP Group Registrations/
GMRP Configuration
802.1p Priority
Configuration Menu
Port Priority
Configuration
Advanced Port
Priority
Configuration
Ethernet Full
Duplex Configuration
High Speed
Interface
Configuration
* SmartTrunk
Configuration
Port Redirect Configuration/
Redirect Configuration Menu
Broadcast
Suppression
Configuration
** Repeater
Configuration Menu
2E43-51 or
2E43-51R only
Repeater Level
Security Configuration
Port Level
Security Configuration
Repeater Port
Configuration
Module Level
Security Configuration
Port Level
Security Configuration
Fast
Ethernet
Interfaces
HSIM
Port Redirect
Configuration
VLAN Redirect
Configuration
2H23-50R or
2H33-37R only
Device
Statistics
Menu
Network Tools
Notes:
* Refer to the
** This screen is only available on repeater devices (2E43-51, 2E43-51R,
2H23-50R, and 2H33-37R).
Indicates the part of the hierarchy that changed.
SmartTrunk User's Guide
Switch Statistics
Interface Statistics
RMON Statistics
** Repeater Statistics
for the screen hierarchy.
29713-82
Figure 1-2 802.1Q Switching Mode, LM Screen Hierarchy
1-4 Local Management Supplement
Page 21

Accessing Local Management
1.2.2 Screen Format
Since the top part of the screen contains the same type of information (the
name of the screen, the SmartSwitch model number, the firmware
revision, and the BOO T PROM revision), it is not shown in the following
descriptions of the screens. Only the lower portion of the screens is shown
in the following screen descriptions. The name of the screen is shown in
the figure title for each screen. Figure 1-3 shows an example of the fields
in a screen.
Event Message Field
Event Message Line
Device Type: 2H252-25
MAC Address:
IP Address:
Subnet Mask:
Default Gateway:
TFTP Gateway IP Addr:
Operational Mode: [802.1Q SWITCHING]
Clear NVRAM [NO]
Selection Field
Display Fields
2H252-25 LOCAL MANAGEMENT
General Configuration
00-00-ID-00-00-00
0.0.0.0
255.255.0.0
NONE DEFINED
0.0.0.0
IP Fragmentation [ENABLED]
EXIT
Command Fields
Display Field
Input Fields
Firmware Revision: XX.XX.XX
BOOTPROM Revision: XX.XX.XX
Device Date:
Device Time:
Screen Refresh Time:
Screen Lockout Time:
Device Uptime XX D XX H XX M
03/15/1999
14:23:00
30 sec.
15 min.
RETURNSAVE
See
Note
Note:
This shows the location of the cutaway that is used in most of the screen graphics in this
document. The top portion of the screen is cut away to eliminate repeating the same
information in each graphic.The screen title is contained in the figure title for each screen.
2971_14
Figure 1-3 Example of a Local Management Screen
Local Management Supplement 1-5
Page 22
Chapter 1:
Changes to Local Management Screens
1.3 DEVICE CONFIGURATION MENU SCREEN
The Device Configuration Menu screen, Figure 1-4, provides access to
Local Management screens that allow you to configure and monitor
operating parameters, modify SNMP community names, set SNMP traps,
configure switch parameters and configure ports.
To access the Device Configuration Menu screen from the Device Menu
screen, use the arrow keys to highlight the
CONFIGURATION
menu item and press ENTER. The Device
Configuration Menu screen displays.
GENERAL CONFIGURATION
SNMP COMMUNITY NAMES CONFIGURATION
SNMP TRAPS CONFIGURATION
SYSTEM RESOURCES INFORMATION
FLASH DOWNLOAD CONFIGURATION
PORT CONFIGURATION MENU
802.1 CONFIGURATION MENU
DEVICE
EXIT
Figure 1-4 Device Configuration Menu Screen
RETURN
19602_66
The following briefly explains each screen accessible from the Device
Configuration Menu screen:
GENERAL CONFIGURATION
Used to monitor and configure SmartSwitch operating parameters. For
details, refer to your SmartSwitch device user’s guide.
SNMP COMMUNITY NAMES CONFIGURATION
Used to enter new, change, or review the community names used as
access passwords for device management operation. Access is limited
based on the password level of the user. For details, refer to your
SmartSwitch device user’s guide.
1-6 Local Management Supplement
Page 23

Device Configuration Menu Screen
SNMP TRAPS CONFIGURATION
Provides display and configuration access to the table of IP addresses
used for trap destinations and associated community names. For details,
refer to your SmartSwitch device user’s guide.
SYSTEM RESOURCES INFORMATION
Displays the CPU type used in the device and its operating speed;
displays the size of each memory system used (FLASH memory, DRAM
and NVRAM) in the device and the unused portion of each memory; and
displays the current CPU (switch) utilization and the peak switch
utilization. For details, refer to Section 1.4.
FLASH DOWNLOAD CONFIGURATION
Used to force the SmartSwitch to download a new image file from a TFTP
server to its FLASH memory. For details, refer to Section 1.5.
PORT CONFIGURATION MENU
Used to select the screens for configuring the SmartSwitch ports. For
details, refer to Section 1.6.
802.1 CONFIGURATION MENU
Displays only if the SmartSwitch has been configured to operate as an
IEEE 802.1Q switch. When selected, the 802.1 Configuration Menu
screen provides access to the Switch Configuration, 802.1Q VLAN
Configuration Menu, GARP Operation Status, GMRP Group
Registrations, and 802.1p Priority Configuration Menu screens. For
details, refer to Section 1.15.
Local Management Supplement 1-7
Page 24
Chapter 1:
Changes to Local Management Screens
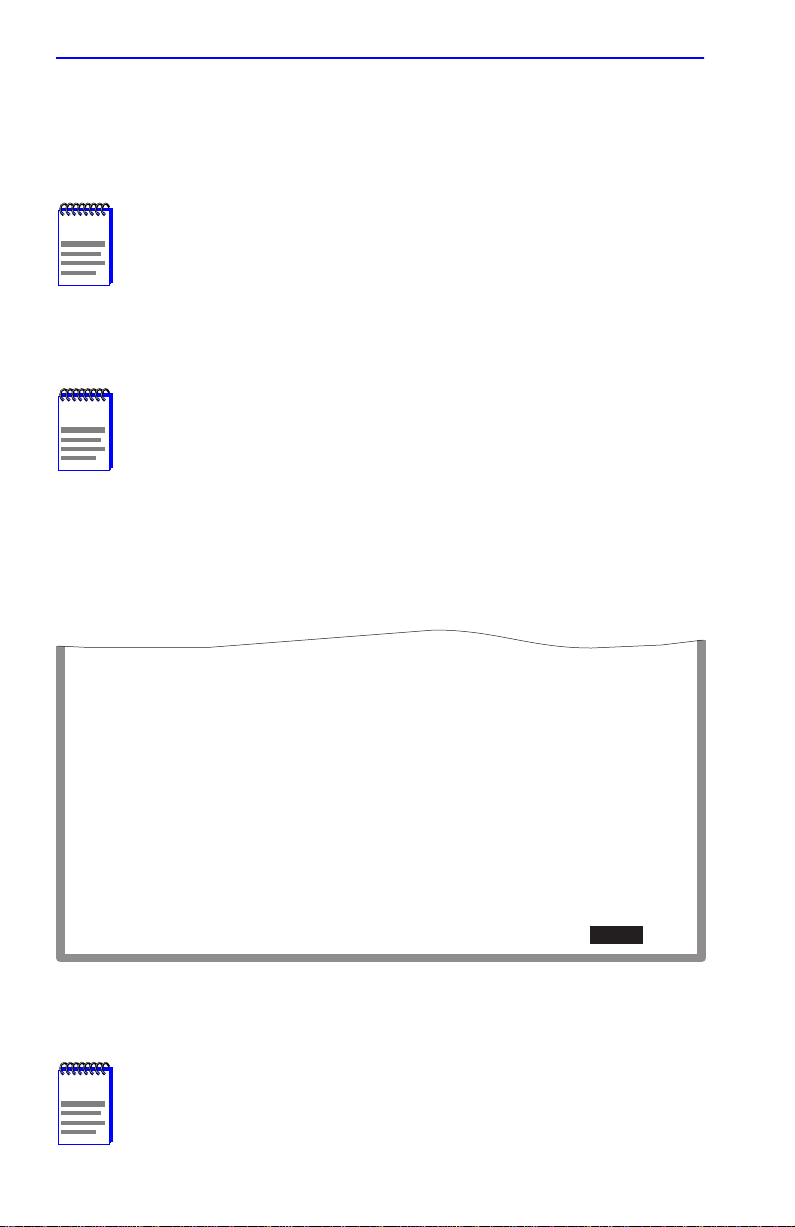
1.4 SYSTEM RESOURCES INFORMATION SCREEN
The System Resources Information screen, Figure 1-5, provides
information concerning the processor used in the SmartSwitch and the
amount of FLASH memory, DRAM, and NVRAM that is installed and
how much of that memory is available. This screen is used to monitor the
current switch utilization and the peak switch utilization.
To access the System Resources Information screen from the Device
Configuration Menu screen, use the arrow keys to highlight the
RESOURCES INFORMATION
menu item and press ENTER. The
System Resources Information screen displays.
CPU Type: i960 HX 66 Mhz
Flash Memory Installed: 4 MB
Available: XXXXX Bytes
SYSTEM
DRAM Installed: 20 MB
NVRAM Installed: XX KB
SAVE
Current Switch Utilization: 66%
Peak Switch Utilization: 75%
Reset Peak Switch Utilization: [NO]
Available: XXXXX Bytes
Available: XXXXX Bytes
EXIT
RETURN
RETURN
2762-23
Figure 1-5 System Resources Information Screen
The following briefly defines each field of the System Resources
Information screen.
CPU Type
(Read-Only)
Indicates the microprocessor used in the SmartSwitch.
Flash Memory Installed
(Read-Only)
Indicates the amount of FLASH memory installed in the SmartSwitch and
how much is currently available.
1-8 Local Management Supplement
Page 25

System Resources Information Screen
DRAM Installed (Read-Only)
Indicates the amount of DRAM installed in the SmartSwitch and how
much of it is currently available.
NVRAM Installed (Read-Only)
Indicates the amount of NVRAM installed in the SmartSwitch and how
much of it is currently available.
Current Switch Utilization (Read-Only)
Shows the percentage of the device switching capacity currently being
used.
Peak Switch Utilization (Read-Only)
Shows the peak percentage of device switching capacity used, since the
last reset.
Reset Peak Switch Utilization (Toggle)
Used to reset the Peak Switch Utilization field. The switch may be set to
either YES or NO as described in Section 1.4.1. YES resets the Peak
Switch Utilization field to the current system utilization.
1.4.1 Resetting the Reset Peak Switch Utilization
To set the Reset Peak Switch Utilization field to YES or NO, proceed as
follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Reset Peak Switch Utilization
field.
2. Press the SPACE bar to select YES or NO.
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command at the bottom of
the screen.
4. Press ENTER. The message “SAVED OK” displays and the Reset
Peak Utilization counter resets to zero.
Local Management Supplement 1-9
Page 26
Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
9
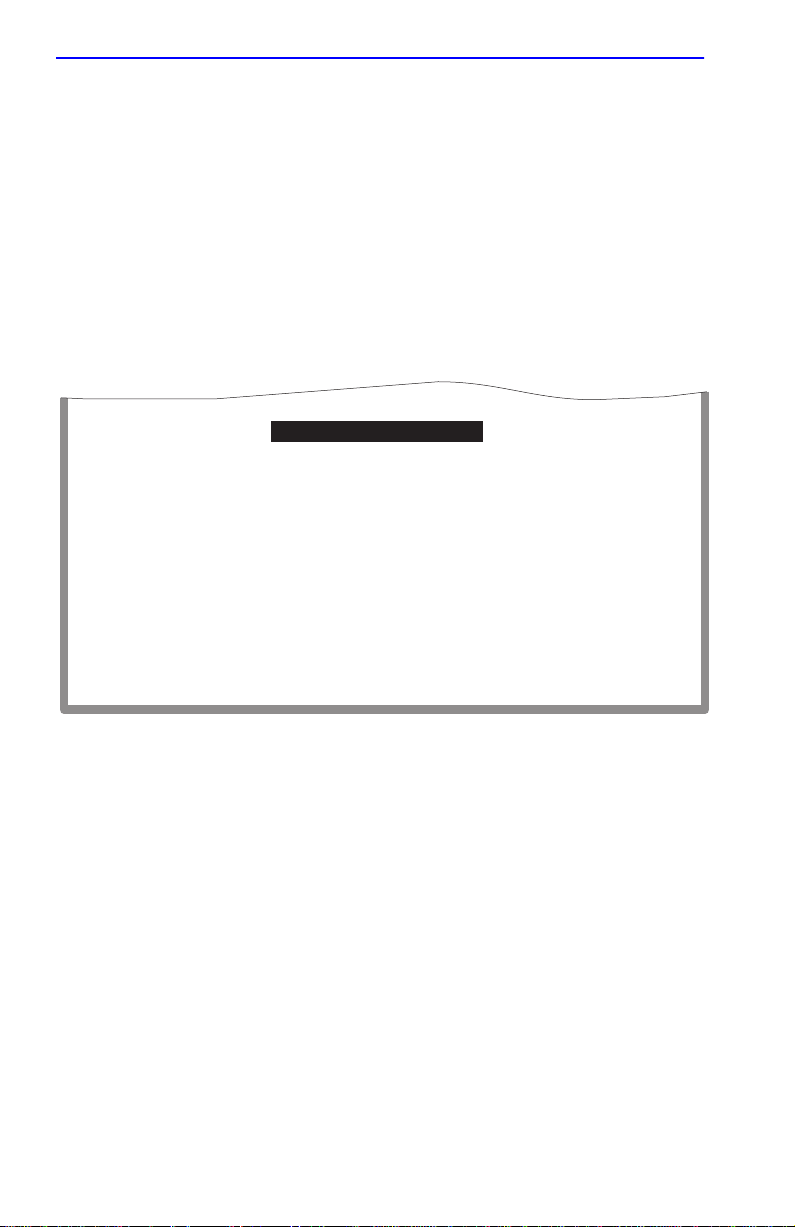
1.5 FLASH DOWNLOAD CONFIGURATION SCREEN
The Flash Download Configuration screen, shown in Figure 1-6, is used
to download a new image file from a TFTP server to Flash memory.
NOTE
the position of dipswitch 6 located inside the device. Refer to
your user’s guide for details.
Before downloading an image to the device, copy the image to the
network TFTP server .
The user may also force the do wnload of an image by changing
NOTE
For information on how to set up a workstation as a TFTP
server, refer to the specific workstation documentation.
To access the Flash Download Configuration screen from the Device
Configuration Menu screen, use the arrow keys to highlight the FLASH
DOWNLOAD CONFIGURATION menu item and press ENTER. The
Flash Download Configuration screen displays.
Download Method:
Reboot After Download:
TFTP Gateway IP Addr:
Last Image Server IP:
Last Image File Name:
Download Server IP:
Download File Name:
[RUNTIME]
[YES]
nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn
nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn
/tftpboot/xxxxx.fls
nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn
/tftpboot/xxxxx.fls
EXECUTE
EXIT
RETURN
2971-4
Figure 1-6 Flash Download Configuration Screen
Download Server IP and Download Server File Name display
NOTE
only when TFTP or RUNTIME are selected in Download
Method.
1-10 Local Management Supplement
Page 27

FLASH Download Configuration Screen
The following briefly defines each field of the Flash Download
Configuration screen:
Download Method (Selectable)
This field steps between TFTP, RUNTIME and BOOTP. If set for
BOOTP, the device sends out a BootP request to determine the IP address
of the TFTP server and the filename of the image to be downloaded. If set
for TFTP or RUNTIME, the SmartSwitch device attempts a TFTP
download based on the IP address and filename entered in the fields at the
bottom of the Flash Download Configuration screen.
Section 1.5.1 describes how to download using TFTP. Section 1.5.2
describes how to download using RUNTIME. Section 1.5.3 describes
how to download using BootP.
Reboot After Download (Modifiable when user chooses RUNTIME)
This field notifies the user that the SmartSwitch device will reboot after
the download is complete. If a RUNTIME Download is performed, this
field toggles between YES and NO. If YES is selected, the device reboots
after the download is completed. If NO is selected, the device will
continue using the existing firmware image. The device stores the new
firmware image in FLASH memory. When the device is reset, the device
will boot from FLASH memory using the new image.
TFTP Gateway IP Addr (Selectable)
This field shows the IP address of the TFTP gate w ay serv er defined in the
General Configuration screen.
Last Image Server IP (Read-only)
This field shows the IP address of the server used for the pre vious FLASH
Download.
Last Image File Name (Read-only)
This field shows the complete path and file name of the last image
downloaded to FLASH.
NOTE
Local Management Supplement 1-11
If TFTP or RUNTIME is selected as the download method, the
following two additional fields display.
Page 28

Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
Download Server IP (Selectable)
The IP address of the TFTP server to be used for the FLASH download is
entered in this field.
Download File Name (Selectable)
The complete TFTP server path and file name of the new image is entered
in this field.
1.5.1 Image File Download Using TFTP
Set the SmartSwitch device to download to FLASH using TFTP as
follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Download Method field.
2. Use the SPACE bar to select TFTP.
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the TFTP Gateway IP Addr field.
4. Set the IP address of the TFTP gateway server (this defaults to the
same IP address as that set in the TFTP Gateway IP Addr field on the
General Configuration screen).
5. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Download Server IP field.
6. Enter the IP address of the TFTP server using the DDN format.
For example: nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn
7. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Download File Name field.
8. Enter the complete path and file name of the image stored on the
download server.
For example: /tftpboot/2H23.hex
9. Use the arrow keys to highlight EXECUTE at the bottom of the screen
and press ENTER. The message “TFTP DOWNLOAD. WILL
COMMIT TO FLASH. REBOOT IN PROGRESS...” displays in the
event message line at the top of the screen and the new image is
downloaded into FLASH memory.
1-12 Local Management Supplement
Page 29

FLASH Download Configuration Screen
1.5.2 Image File Download Using Runtime
Set the SmartSwitch device to download to FLASH using RUNTIME as
follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Download Method field.
2. Use the SPACE bar to step to RUNTIME.
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Reboot After Download field.
4. Use the SPACE bar to select either YES or NO. Select YES if you
want the device to reboot after the download is complete. Select NO if
you want the device to store the new image in FLASH memory until
the device is manually reset.
5. Use the arrow keys to highlight the TFTP Gateway IP Addr field.
6. Set the IP address of the TFTP gateway server (this defaults to the
same IP address as that set in the TFTP Gateway IP Addr field on the
General Configuration screen).
7. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Download Server IP field.
8. Enter the IP address of the TFTP server using the DDN format.
For example: nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn
9. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Download File Name field.
10. Enter the complete path and file name of the image stored on the
download server.
For example: /tftpboot/2H23.fls
11. Use the arrow keys to highlight EXECUTE at the bottom of the screen
and press ENTER. The message “RUNTIME DOWNLOAD. WILL
COMMIT TO FLASH.” displays in the event message line at the top
of the screen and the new image is downloaded into FLASH memory.
Local Management Supplement 1-13
Page 30

Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
1.5.3 Image File Download Using BootP
Set the SmartSwitch device to download to FLASH using BootP as
follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Download Method field.
2. Use the SPACE bar to select BOOTP.
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the TFTP Gateway IP Addr field.
4. Set the IP address of the TFTP gateway server (this defaults to the
same IP address set in the TFTP Gateway IP Addr field in the General
Configuration screen).
5. Use the arrow keys to highlight EXECUTE at the bottom of the screen
and press ENTER. The message “BOOTP DOWNLOAD. WILL
COMMIT TO FLASH. REBOOT IN PROGRESS...” displays in the
event message line at the top of the screen and the new image is
downloaded into FLASH memory.
1.6 PORT CONFIGURATION MENU SCREEN
The Port Configuration Menu screen, Figure 1-7, is used to select screens
to perform port configuration tasks on the SmartSwitch.
To access the Port Configuration Menu screen from the Device
Configuration Menu screen, use the arrow keys to highlight the PORT
CONFIGURATION MENU item and press ENTER. The Port
Configuration Menu screen displays.
1-14 Local Management Supplement
Page 31

Port Configuration Menu Screen
ETHERNET FULL DUPLEX CONFIGURATION
HIGH SPEED INTERFACE CONFIGURATION
SMARTTRUNK CONFIGURATION
PORT REDIRECT CONFIGURATION
BROADCAST SUPPRESSION CONFIGURATION
REPEATER CONFIGURATION MENU
EXIT
Figure 1-7 Port Configuration Menu Screen
RETURN
27622-20
The following briefly defines each selectable item of the Port
Configuration Menu screen:
ETHERNET FULL DUPLEX CONFIGURATION
The Ethernet Full Duplex Configuration screen allows each 10 Mbps port
to be set for either Standard Ethernet or Full Duplex operation. The screen
also indicates whether or not each port is linked to another 10BASE-T
device and if that port is enabled. For details, refer to Section 1.7.
HIGH SPEED INTERFACE CONFIGURATION
The High Speed Interface Configuration screen selection does
NOTE
not display unless an optional interface module is installed.
The High Speed Interface Configuration screen provides access to the
Fast Ethernet Interfaces screen and the HSIM screen. For details, refer to
Section 1.8.
SMARTTRUNK CONFIGURATION
Used to logically group interfaces together to create a greater bandwidth
uplink. Refer to the Cabletron Systems SmartTrunk User’s Guide for
information about how to access and use the SmartTrunk screens.
Local Management Supplement 1-15
Page 32

Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
PORT REDIRECT CONFIGURATION
Used to access the Redirect Configuration Menu screen, which provides
access to the Port Redirect Configuration and VLAN Redirect
Configuration screens. For details, refer to Section 1.10.
BROADCAST SUPPRESSION CONFIGURATION
Used to set a desired limit of received broadcast frames that are forwarded
out other interfaces. For details, refer to Section 1.13.
REPEATER CONFIGURATION MENU
Used to access the repeater configuration screens, which enable the user
to configure operations and security at the connector and port level.
In the 2E43-51and 2E43-51R devices, the screens are the Repeater Level
Security Configuration and Port Level Security Configuration screens.
In the 2H23-50R and 2H33-37R devices, the screens are the Repeater
Configuration Menu screen and its two subordinate screens, Repeater
Level Security Configuration and Port Level Security Configuration
screens.
For details on setting the security on the repeater devices, refer to
Section 1.14.
1.7 ETHERNET FULL DUPLEX CONFIGURATION SCREEN
The Ethernet Full Duplex Configuration screen, Figure 1-8, allows the
user to set the front panel ports, individually or all at once, to either
Standard Ethernet or Full Duplex operation, and monitor each port to see
whether or not it is enabled and linked to another Ethernet device. Refer
to Section 1.7.1 to set the Operation Mode.
To access the Ethernet Full Duplex Configuration screen from the Port
Configuration Menu screen, use the arrow keys to highlight the
ETHERNET FULL DUPLEX CONFIGURATION menu item and
press ENTER. The Ethernet Full Duplex Configuration screen displays.
1-16 Local Management Supplement
Page 33

Ethernet Full Duplex Configuration Screen
SAVE
PORT #
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
OPERATION MODE
[STANDARD ENET]
[STANDARD ENET]
[STANDARD ENET]
[STANDARD ENET]
[STANDARD ENET]
[STANDARD ENET]
[STANDARD ENET]
[STANDARD ENET]
[STANDARD ENET]
[STANDARD ENET]
[STANDARD ENET]
[STANDARD ENET]
SET ALL PORTS: FULL
LINK STATUS
Link
Link
Link
No Link
Link
Link
Link
Link
Link
Link
Link
Link
EXIT
PORT STATUS
ENABLED
ENABLED
ENABLED
ENABLED
ENABLED
ENABLED
ENABLED
ENABLED
ENABLED
ENABLED
ENABLED
ENABLED
[13-24]
RETURN
RETURN
19601-21
Figure 1-8 Ethernet Full Duplex Configuration Screen
This section explains each field of the Ethernet Full Duplex Configuration
screen.
PORT # (Read-only)
Identifies the number of the port.
OPERATION MODE (Toggle)
Allows the user to set the specified port to transmit and receive data
separately (Standard) or simultaneously (Full Duplex). Set this field to
one of the following values:
• STANDARD ENET – The port is running in half duplex (default) and
either transmits data or receives data, but not both at the same time. To
set Ethernet ports for Standard operation, refer to Section 1.7.1.
• FULL DUPLEX – Depending on the SmartSwitch, the port transmits
and receives data simultaneously at 10 or 100 Mbps, thus enabling the
port to effectiv ely switch at 20 or 200 Mbps. To set Ethernet ports for
Full Duplex operation, refer to Section 1.7.1.
Local Management Supplement 1-17
Page 34

Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
LINK STATUS (Read-only)
Indicates whether there is a physical connection from this port to another
Ethernet device. One of the following values displays:
• Link – A link signal is present; there is a valid physical connection
from this port to another device.
• No Link – No link signal is present; there is no valid physical
connection from this port to another device.
PORT STATUS (Read-only)
Indicates whether the port was turned on or off administratively (by the
user). One of the following values is displayed:
• ENABLED – The port is turned on administratively.
• DISABLED – The port is turned off administratively.
NOTE
SET ALL PORTS (Toggle)
Enabling or disabling ports from the Switch Configuration
screen is described in Section 1.16.3.
All front panel ports can be set at once to either STANDARD or FULL
DUPLEX from this field. To set ports, refer to Section 1.7.1.
[1-12], [13-24], [25-36], or [37-48] (Navigation Key)
When the Full Duplex Configuration screen displays, the current
operation mode and status information are displayed for the first 12 ports.
This field allows the user to step to another screen for the same type of
information for ports 13 through 24, 25 through 36, and 37 through 48, if
available. The number of ports av ailable is dependent on the SmartSwitch
model. To navigate to the next screen, highlight the
[xx-xx] field and press
ENTER. The user can change the Operation Mode fields while in any of
the selected screens.
1.7.1 Setting the Operational Mode
The Operational Mode may be set to Standard Ethernet or Full Duplex
either one port at a time or all at once. The following steps describe
setting the port Operational Mode for individual ports followed by steps
to set the Operational Mode for all ports.
1-18 Local Management Supplement
Page 35

High Speed Interface Configuration Menu Screen
To set the Operational Mode for individual ports, proceed as follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Operation Mode field adjacent to
the number of the port(s) that you plan to change.
NOTE
The Operation Mode for the first 12 ports can be changed on
the first screen. To display the Operation Mode for additional
groups of twelve ports (13 – 24, 25 – 36, and 37 – 48), use the
arrow keys to highlight the Ports [xx-xx] field and press
ENTER.
2. Press the SPACE bar until the appropriate mode, FULL DUPLEX or
STANDARD ENET displays in the field.
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command on the bottom
line of the screen.
4. Press ENTER. The message “SAVED OK” displays.
To set the Operation Mode for all ports (1-24, or higher), proceed as
follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SET ALL PORTS field.
2. Press the SPACE bar until you see FULL or STANDARD.
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command on the bottom
line of the screen.
4. Press ENTER. The message “SAVED OK” displays.
1.8 HIGH SPEED INTERFACE CONFIGURATION MEN U
SCREEN
NOTE
The High Speed Interface Configuration Menu screen, Figure 1-9, applies
to the Fast Ethernet Interface Modules and the High Speed Interface
Module.
Local Management Supplement 1-19
This High Speed Interface Configuration Menu screen does not
display unless an optional interface module is installed: one or
two Fast Ethernet Interface Modules, or High Speed Interface
Module (HSIM), depending on what the host SmartSwitch
supports.
Page 36

Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
To access the High Speed Interface Configuration Menu screen from the
Port Configuration Menu screen, use the arrow keys to highlight the
HIGH SPEED INTERFACE CONFIGURATION menu item and
press ENTER. The High Speed Interface Configuration Menu screen,
Figure 1-9, displays.
FAST ETHERNET INTERFACES
HSIM
SAVE
Figure 1-9 High Speed Interface Configuration Menu Screen
EXIT
RETURN
19601-53
The following briefly explains each screen accessible from the High
Speed Interface Configuration Menu screen.
FAST ETHERNET INTERFACES
Displays the types of fast Ethernet interfaces installed in the device, their
current operating mode, and indicates if the ports are linked. This screen
also allows the user to enable or disable Auto-Negotiation and set the
Advertised Ability. For details, refer to Section 1.9.
HSIM
Displays the types of interfaces installed in the High Speed Interface
Module (HSIM) slot. The HSIM screens are depicted in their respective
user’s guides.
1-20 Local Management Supplement
Page 37

High Speed Interface Configuration Screen
1.9 HIGH SPEED INTERFACE CONFIGURATION
SCREEN
NOTE
applies only to installed optional Fast Ethernet Interface
Modules. This screen supports the FE-100TX, FE-100FX,
FE-100F3, and FE-100LH Fast Ethernet Interface Modules that
operate at 100 Mbps.
The High Speed Interface Configuration screen displays the types of
installed Fast Ethernet Interface Modules, their current operating mode,
and indicates if the ports are linked. This screen also allows the user to
enable or disable Auto-Negotiation and set the Advertised Ability.
To access the High Speed Interface Configuration screen from the High
Speed Interface Configuration Menu screen, use the arrow keys to
highlight the FAST ETHERNET INTERFACES menu item and press
ENTER. The High Speed Interface Configuration screen displays.
The High Speed Interface Configuration screen, Figure 1-10,
Port Type
Link Status
Current Oper. Mode
Desired Oper. Mode
Advertised Ability
Port 25
FE-100TX
Link
100Base-TXFD
[Auto-Negotiation]
[100Base-TXFD] [Disabled]
Port 26
Unknown
N/A
[N/A]
[N/A]
[N/A]
EXIT
RETURNSAVE
19601-24
Figure 1-10 High Speed Interface Configuration Screen
Local Management Supplement 1-21
Page 38

Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
The following briefly explains each field of the High Speed Interface
Configuration screen.
Port Type (Read-only)
Displays the type of interface (FE-100FX, FE-100TX, FE-100F3,
FE-100LH, or Unknown) installed. Figure 1-10 shows that there is an
FE-100TX interface installed in one optional port slot and no interface
indicated by Unknown in another optional port slot. This example does
not apply to all devices because the number of ports vary, depending on
the SmartSwitch model.
Link Status (Read-only)
Indicates whether or not there is a physical connection from this port to
another 10BASE-T or 100BASE-TX/FX device. One of the following
values displays:
• Link – There is a link signal present and a valid physical connection
to another device.
• No Link – There is no link signal present and no valid physical
connection to another device.
Current Oper. Mode (Read-only)
This field displays the current operating mode of interfaces installed in
the optional port slot(s). Depending on whether a 100BASE-FX, or
100BASE-TX is installed, this field displays the following:
• With a 100BASE-FX interface: 100Base-FX, 100Base-FXFD (full
duplex), or N/A when port is empty.
• With a 100BASE-TX interface: Unknown, 10Base-T, 10Base-TFD
(full duplex), 100Base-TX, 100Base-TXFD (full duplex) or N/A when
port is empty.
Desired Oper. Mode (Selectable)
This field allows the user to select the desired operational mode for an
interface in one of the optional port slots. The field toggles between
100BASE-FX and 100BASE-FXFD (full duplex) when an FE-100FX or
FE-100F3 is installed. Section 1.9.1 describes how to configure a port
with an FE-100FX or FE-100F3.
1-22 Local Management Supplement
Page 39

High Speed Interface Configuration Screen
NOTE
In normal operation, the port with an FE-100TX installed
automatically establishes a link with the device at the other end
of the segment without requiring user setup. However, Local
Management provides the user with the option of manually
configuring that port.
If an FE-100TX is installed, the field steps to Auto-Negotiation,
10Base-T, 10Base-TFD (full duplex), 100Base-TX, and 100Base-TXFD
(full duplex). In normal operation, the port with an FE-100TX installed is
capable of auto-negotiating the operational mode and no further user
setup is required. Section 1.9.3 describes how to manually configure an
FE-100TX.
In Auto-Negotiation, the FE-100TX negotiates to the highest common
denominator of the two interfaces. The order of priority of negotiation is
100BASE-TXFD, 100BASE-TX, 10BASE-TFD, and 10BASE-T.
Advertised Ability (Selectable)
During auto-negotiation, the FE-100TX “tells” the device at the other end
of the segment about its capabilities. The capabilities of a port with an
FE-100TX installed are 10Base-T, 10Base-TFD (full duplex mode),
100Base-TX and 100Base-TXFD (full duplex mode). In normal
operation, with all capabilities enabled, the FE-100TX “advertises” that it
has the ability to operate in any mode. The Network Manager (or user)
may choose to set up the port so that only a portion of the available
capabilities are advertised and the others are disabled. For example, only
100Base-TX and 100Base-TXFD might be enabled so that only devices
that operate at 100 Mbps can communicate with that port. Section 1.9.5
describes how to enable or disable advertised modes.
1.9.1 Configuring an FE-100FX or FE-100F3
When an FE-100FX or FE-100F3 is installed, it must be manually set to
operate in the same technology as the device at the other end of the
connected segment. Section 1.9.2 provides instructions for manually
configuring the port with an FE-100FX or FE-100F3 interface.
Local Management Supplement 1-23
Page 40

Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
1.9.2 Setting the FE-100FX or FE-100F3 Operational Mode
Use this field to set the active technology. This field toggles between
100Base-FX and 100Base-FXFD (full duplex). To set the active
technology through Local Management, proceed as follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Desired Operational Mode field.
2. Use the SPACE bar to select 100Base-FX or 100Base-FXFD (full
duplex).
3. Press ENTER. The port now operates in the chosen mode.
4. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command. Press ENTER.
The message “SAVED OK” displays and Local Management saves
the changes to memory.
1.9.3 Configuring an FE-100TX
In normal operation, an FE-100TX interface automatically establishes a
link with the device at the other end of the segment and no user setup is
required. Section 1.9.4 and Section 1.9.5 provide instructions for
manually configuring the port with an FE-100TX installed.
1.9.4 Setting the FE-100TX Operational Mode
Use this field to set the active technology. This field steps between
Auto-Negotiation, 10Base-T, 10Base-TFD (full duplex), 100Base-TX,
and 100Base-TXFD (full duplex). If Auto-Negotiation is selected, the
FE-100TX automatically sets the active technology.
To manually set the active technology through Local Management,
proceed as follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Desired Oper. Mode field.
2. Use the SPACE bar to select the desired mode. Press ENTER. If any
mode other than Auto-Negotiation is selected, the port only operates
in the chosen mode and Auto-Negotiation is disabled.
1-24 Local Management Supplement
Page 41

High Speed Interface Configuration Screen
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command. Press ENTER.
The message “SAVED OK” displays and Local Management saves
the changes to memory. The selected mode is displayed in both the
Desired Operational Mode field and the Current Operational Mode
field.
1.9.5 Setting the FE-100TX Advertised Ability
In normal operation, an FE-100TX auto-negotiates to the highest speed
possible. Under some circumstances, the Network Administrator may
want the port to advertise only some of the available modes and not
advertise in other modes. This field steps to 10Base-T, 10Base-TFD (full
duplex), 100Base-TX, and 100Base-TXFD (full duplex). To set the
advertised ability, proceed as follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Desired Oper. Mode field.
2. Use the SPACE bar to select the desired mode.
3. Use the LEFT-ARROW key to move back to the Advertised Ability
selection and use the SPACE bar to select the next mode to enable or
disable.
4. Use the RIGHT-ARROW key to move across to the
Enabled/Disabled field to the right of the selection.
5. Use the SPACE bar to select Enabled or Disabled. Press ENTER.
Continue this process until you have completed enabling or disabling
the advertised modes.
6. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command. Press ENTER.
The message “SAVED OK” displays and Local Management saves
the changes to memory.
Local Management Supplement 1-25
Page 42
Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
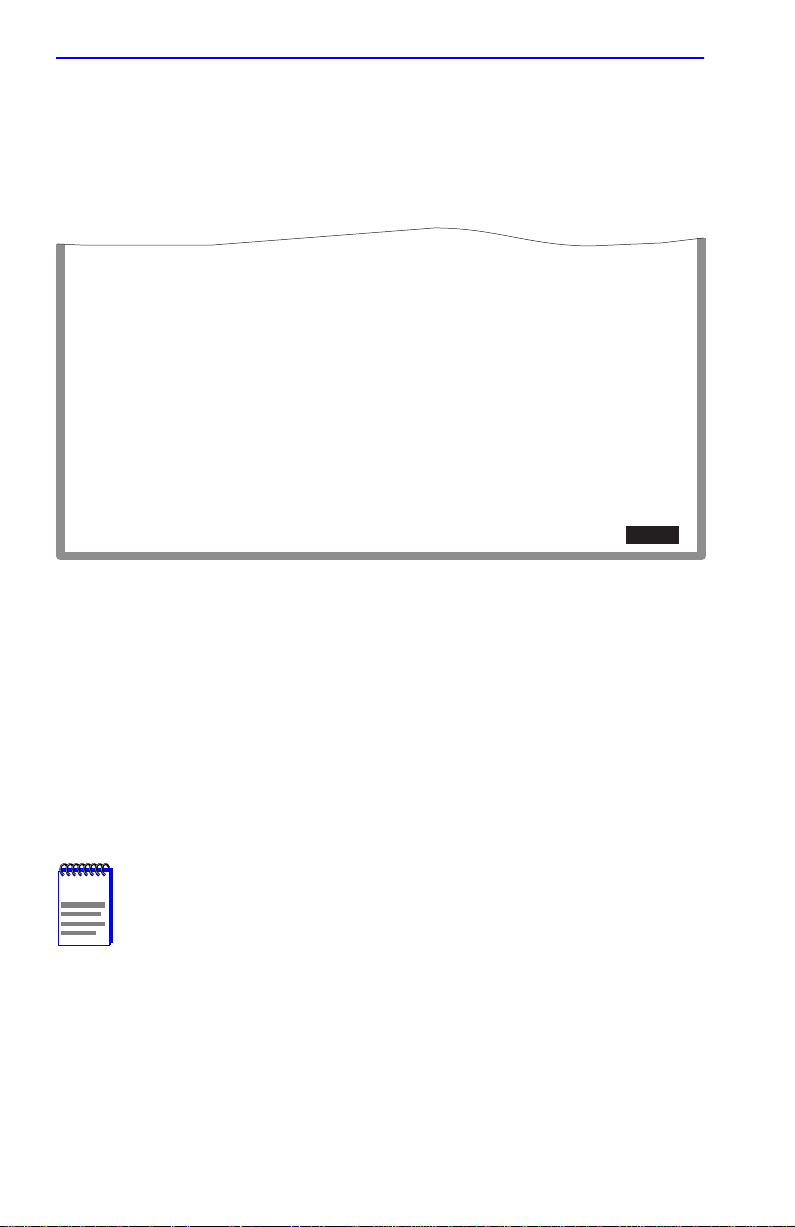
1.10 REDIRECT CONFIGURATION MENU SCREEN
The Redirect Configuration Menu screen (Figure 1-11) provides access to
the Port Redirect Configuration and VLAN Redirect Configuration
screens. Any combination, up to 128, of port and/or VLAN redirect
instances can be configured.
To access the Redirect Configuration Menu screen from the Port
Configuration Menu screen, use the arrow keys to highlight the PORT
REDIRECT CONFIGURATION menu item and press ENTER. The
Redirect Configuration Menu screen displays.
PORT REDIRECT CONFIGURATION
VLAN REDIRECT CONFIGURATION
EXIT
Figure 1-11 Redirect Configuration Menu Screen
RETURN
2971_94
The following defines each selectable item of the Redirect Configuration
Menu screen:
PORT REDIRECT CONFIGURATION
The Port Redirect Configuration screen is used to redirect traffic from a
source switch port to a destination switch port. For details, refer to
Section 1.11.
VLAN REDIRECT CONFIGURATION
The VLAN Redirect Configuration screen is used to configure the device
to direct traffic from a VLAN to a particular switch port. F or details, refer
to Section 1.12.
1-26 Local Management Supplement
Page 43

Port Redirect Configuration Screen
1.11 PORT REDIRECT CONFIGURATION SCREEN
The Port Redirect Configuration screen, Figure 1-12, enables the user to
redirect frames from one source port to one destination port. Frames
received on the source port can be redirected and transmitted in the frame
format in which they are received (normal), or the y can be redirected with
a VLAN Tag (TAGGED) or without a VLAN Tag (UNTAGGED). Also,
any errored frames received can be either dropped or forwarded to the
destination port. For example, port 1 can be set as the source port with
port 2 as the destination port. Frames from port 1 are then automatically
redirected to port 2 according to the configured frame format, and frames
with errors can be either forwarded or dropped according to the screen
settings.
NOTE
If an optional ATM interface is installed, up to 128 ports may be
set to redirect frames. This includes ATM P ort Virtual Channels
(PVCs).
The port redirect function is very useful for troubleshooting purposes, as
it allows traffic to be sent to a particular port where, with the use of an
analyzer or RMON probe, all current traffic from the source port can be
examined.
NOTE
Although all traffic from the source port (including, if desired,
errored frames) is sent to the destination port, normal switching
is still performed for all frames on the source port.
Local Management Supplement 1-27
Page 44
Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
To access the Port Redirect Configuration screen from the Redirect
Configuration Menu screen, use the arrow keys to highlight the PORT
REDIRECT CONFIGURATION menu item and press ENTER. The
Port Redirect Configuration screen displays.
Source Port
-------------------- ---------------------- -------------------- 1
3
6
--
--
--
--
--
Source Port [1]
Destination Port [1]
SAVE
Destination Port
2
4
9
--
--
--
--
--
Frame Format [UNTAGGED]
Redirect Errors [OFF]
PREVIOUS
Frame Format
---------------------
NORMAL
TAGGED
UNTAGGED
--
--
--
--
--
NEXT
Redirect Errors
ON
ON
OFF
--
--
--
--
--
Status [ADD]
RETURN
EXIT
RETURN
2971-22
Figure 1-12 Port Redirect Configuration Screen
The following definitions briefly explain each field of the Port Redirect
Configuration screen:
Source Port (Read-Only)
Shows which ports are currently set as source ports.
Destination Port (Read-Only)
Shows which ports are currently set as destination ports.
NOTE
1-28 Local Management Supplement
Only one destination port may be assigned to a source port.
Page 45

Port Redirect Configuration Screen
Frame Format (Read-Only)
Displays the current frame format setting: NORMAL, TAGGED or
UNTAGGED The default is NORMAL.
• NORMAL – Frames are redirected in the format that they were
received or transmitted on the source port.
• TAGGED – Frames are transmitted on the destination port with a
VLAN tag inserted according to the frame classification.
• UNT A GGED – Frames are transmitted on the destination port without
a VLAN tag regardless of the format of the received frame.
Redirect Errors (Read-Only)
Displays whether the corresponding source ports are configured ON to
send errored frames to the destination ports, or OFF to drop all errored
frames and only forward valid frames to the destination ports. All
redirected error frames display in the way they were received or
transmitted on the source port, regardless of the frame format setting.
Source Port [n] (Selectable)
Used to select the port [n] that is to be changed to a source port. If a port
is currently being redirected, it will not display as a selectable port. For
details, refer to Section 1.11.1.
Destination Port [n] (Selectable)
Used to select the port [n] that is to be changed to a destination port. If a
port is currently being redirected, it will not display as a selectable port.
For details, refer to Section 1.11.1.
Frame Format (Selectable)
Used to select the frame format for the transmission of redirected frames
on the destination port. NORMAL, TAGGED, or UNTAGGED may be
selected. Refer to the previously described read-only Frame Format field
for details about each format. The default setting is NORMAL.
Redirect Errors (Toggle)
Used to set each source port to either ON, to send errored frames to its
destination port, or OFF to drop errored frames, and send only valid
traffic to its destination port. The default setting is OFF.
Status (Toggle)
Used to add or delete source and destination ports selected in the Source
Port [n] and Destination Port [n] fields.
Local Management Supplement 1-29
Page 46

Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
1.11.1 Changing Source and Destination Ports
T o add or delete source port and destination port entries and set the Frame
Format and Redirect Errors functions, proceed as follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Source Port field near the bottom
of the screen.
2. Press the SPACE bar or BACKSPACE one or more times to increment
or decrement the port number displayed in the brackets [n] until the
appropriate port number displays.
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Destination Port field near the
bottom of the screen.
4. Use the SPACE bar or BACKSPACE to step to the appropriate port
number for the destination port.
5. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Frame Format field near the
bottom of the screen.
6. Use the SPACE bar or BACKSPACE to step to the appropriate frame
format setting (NORMAL, TAGGED, or UNTAGGED) for the
selected Destination Port.
7. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Redirect Errors field near the
bottom of the screen.
8. Use the SPACE bar to select either the ON or OFF option and press
ENTER. ON forces the source port to forward errored frames to the
destination port(s). OFF forces the errored frames to be dropped
before forwarding traffic.
9. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Status field.
10. Use the SPACE bar to select either the ADD or DEL (delete) option.
Press ENTER. This adds or deletes the selections for the Source Port,
Destination Port, Frame Format, and Redirect Errors made in steps 1
through 8 and also updates the screen.
NOTE
1-30 Local Management Supplement
A destination port can only be assigned to one source port.
Page 47

VLAN Redirect Configuration Screen
If more than one port is being redirected, repeat steps 1
TIP
through 10 for each additional setting. Then go to step 11 to
save all the new settings at once.
If an entry is to be changed, delete the entry, save the screen,
then recreate the entry with its new settings.
Any combination, up to 128, of port redirect instances
(configured on the Port Redirect Configuration screen) and/or
VLAN redirect instances (configured on the VLAN Redirect
Configuration screen) can be configured.
11. Use the arrow keys to highlight SAVE at the bottom of the screen.
Press ENTER. The message “SAVED OK” displays. This saves the
new settings and updates the Source Port and Destination Port
read-only fields.
1.12 VLAN REDIRECT CONFIGURATION SCREEN
The VLAN Redirect Configuration screen, Figure 1-13, enables the user
to select a source VLAN identification (ID) and a destination port. For
example, VLAN ID 1 can be set as the source VLAN with port 2 as the
destination port. Traffic from VLAN 1 is then automatically redirected to
port 2 according to the Frame Format setting for that source VLAN. The
Frame Format setting determines the format in which the frames received
belonging to the source VLAN are redirected to the destination port. The
frames can be forwarded in the frame format as received, tagged, or
untagged.
The VLAN redirect function is very useful for troubleshooting purposes.
It allows traffic associated with a particular VLAN to be sent to a
particular port where, with the use of an analyzer or RMON probe, all
current traffic from the source VLAN can be examined.
NOTE
Local Management Supplement 1-31
Although traffic associated with a particular VLAN is sent to the
destination port, normal switching is still performed for all
frames on the source port.
The Redirect Errors function is not supported on this screen.
Page 48

Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
5
To access the VLAN Redirect Configuration screen from the Redirect
Configuration Menu screen, use the arrow keys to highlight the VLAN
REDIRECT CONFIGURATION menu item and press ENTER. The
VLAN Redirect Configuration screen displays.
Source VLAN
-------------------- 1
3
6
--
--
--
--
--
Source VLAN [1]
Destination Port [1]
SAVE
Destination Port
---------------------- -------------------- 2
4
9
--
--
--
--
--
Frame Format [UNTAGGED]
Redirect Errors Unsupported
PREVIOUS
Frame Format
--------------------
RECEIVED
TAGGED
UNTAGGED
--
--
--
--
--
NEXT
Redirect Errors
UNSUPPORTED
UNSUPPORTED
UNSUPPORTED
--
--
--
--
--
Status [ADD]
RETURN
EXIT
RETURN
2971-9
Figure 1-13 VLAN Redirect Configuration Screen
The following definitions briefly explain each field of the VLAN Redirect
Configuration screen:
Source VLAN (Read-Only)
Shows the VLAN ID of the VLANs that are currently set as source
VLANs.
Destination Port (Read-Only)
Shows which ports are currently set as destination ports.
NOTE
The Redirect Errors function is not supported on this screen.
1-32 Local Management Supplement
Multiple VLANs may be assigned to a destination port.
Page 49

VLAN Redirect Configuration Screen
Frame Format (Read-Only)
Displays the current frame format setting: RECEIVED, TAGGED or
UNTAGGED. The default is RECEIVED.
• RECEIVED – Frames are redirected in the format that they were
received by the SmartSwitch device.
• TAGGED – Frames are transmitted on the destination port with a
VLAN tag inserted according to the frame classification of the
receiving port.
• UNT A GGED – Frames are transmitted on the destination port without
a VLAN tag regardless of the format of the received frame.
Redirect Errors
Unsupported.
Source VLAN [n] (Modifiable)
Used to enter the VLAN ID of the VLAN that is to be changed to a source
VLAN. If a VLAN is currently being redirected, it will not display as a
selectable VLAN. For details, refer to Section 1.11.1.
Destination Port [n] (Selectable)
Used to select the port number that is to be changed to a destination port.
If a port is currently being redirected, it will not display as a selectable
port. For details, refer to Section 1.11.1.
Frame Format (Selectable)
Used to select the frame format for the transmission of redirected frames
on the destination port. RECEIVED, TAGGED, or UNTAGGED may be
selected. Refer to the previously described read-only Frame Format field
for details about each format. The default setting is RECEIVED.
Redirect Errors
Unsupported.
Status (Toggle)
Used to add or delete source and destination ports selected in the Source
VLAN [n] and Destination Port [n] fields.
Local Management Supplement 1-33
Page 50

Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
1.12.1 Changing Source VLAN and Destination Ports
To add or delete source VLAN and destination port entries and set the
Frame Format, proceed as follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Source VLAN field near the
bottom of the screen.
2. Type in the VLAN ID number of the source VLAN to be configured.
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Destination Port field near the
bottom of the screen.
4. Use the SPACE bar or BACKSPACE to step to the appropriate port
number for the destination port.
5. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Frame Format field near the
bottom of the screen.
6. Use the SPACE bar or BACKSPACE to step to the appropriate frame
format setting (RECEIVED, TAGGED, or UNTAGGED) for the
selected Destination Port.
7. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Status field.
8. Use the SPACE bar to select either the ADD or DEL (delete) option.
Press ENTER. This adds or deletes the selections for the Source
VLAN, Destination Port, and Frame Format made in steps 1
through 6 and also updates the screen.
NOTE
TIP
1-34 Local Management Supplement
Multiple VLANs may be assigned to a destination port.
If more than one VLAN is being redirected, repeat steps 1
through 8 for each additional setting. Then go to step 9 to save
all the new settings at once.
If an entry is to be changed, delete the entry, save the screen,
then recreate the entry with its new settings.
Any combination, up to 128, of port redirect instances
(configured on the Port Redirect Configuration screen) and/or
VLAN redirect instances (configured on the VLAN Redirect
Configuration screen) can be configured.
Page 51

Broadcast Suppression Configuration Screen
9. Use the arrow keys to highlight SAVE at the bottom of the screen.
Press ENTER. The message “SAVED OK” displays. This saves the
new settings and updates the Source Port and Destination Port
read-only fields.
1.13 BROADCAST SUPPRESSION CONFIGURATION SCREEN
The Broadcast Suppression Configuration screen, Figure 1-14, enables
the user to set a desired limit of receive broadcast frames that are switched
out to the other ports.
NOTE
dropped.
To access the Broadcast Suppression Configuration screen from the Port
Configuration Menu screen, use the arrow keys to highlight the
BROADCAST SUPPRESSION CONFIGURATION menu item and
press ENTER. The Broadcast Suppression Configuration screen displays.
Broadcast frames received above the threshold setting are
PORT #
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
SAVE
Total RX
12345678910
12345678910
12345678910
12345678910
12345678910
12345678910
12345678910
12345678910
12345678910
12345678910
12345678910
12345678910
Peak Rate
150000
150000
150000
150000
150000
150000
150000
150000
150000
150000
150000
150000
Time Since Peak
999:23:59
999:23:59
999:23:59
999:23:59
999:23:59
999:23:59
999:23:59
999:23:59
999:23:59
999:23:59
999:23:59
999:23:59
Threshold
150000
150000
150000
150000
150000
150000
150000
150000
150000
150000
150000
150000
EXIT[13 - 24]
Reset Peak
[NO]
[NO]
[NO]
[NO]
[NO]
[NO]
[NO]
[NO]
[NO]
[NO]
[NO]
[NO]
RETURN
RETURN
2971-56
Figure 1-14 Broadcast Suppression Configuration Screen
Local Management Supplement 1-35
Page 52

Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
The following explains each field of the Broadcast Suppression screen:
PORT # (Read-Only)
Identifies the number of the port.
Total RX (Read-Only)
Displays the total number of broadcast frames received.
Peak Rate (Read-Only)
Displays the highest number of broadcast frames received in a one-second
interval.
Time Since Peak (Read-Only)
Displays the time since peak rate was achieved.
Threshold (Modifiable)
Used to set the desired limit of receive broadcast frames that will be
forwarded per port per second. For details on how to set the threshold,
refer to Section 1.13.1.
Reset Peak (Toggle)
Used to reset the Peak Rate. Resetting the Peak Rate also resets the Time
Since Peak field. The Reset Peak field toggles between YES and NO. For
details, refer to Section 1.13.2.
1.13.1 Setting the Threshold
To set the Threshold, proceed as follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Threshold field for the selected
port.
2. Type in the numbers for the desired limit. Only enter values in
increments of ten (for example: 10, 20, 30, etc.).
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command at the bottom of
the screen.
4. Press ENTER. The message “SAVED OK” displays.
1-36 Local Management Supplement
Page 53

Repeater Configuration Menu Screens
[13 - 24] (Navigation Key)
When the Switch Configuration screen displays, the current screen
settings are displayed for the first 12 ports. This field is used to step to the
next screen for the same type of information for the next twelve ports, if
available. (The number of ports available is dependent on the
SmartSwitch model.) To navigate to the next screen, highlight the
[xx-xx]
field and press ENTER. The user can change the field settings while in
any of the selected screens.
1.13.2 Resetting the Reset Peak
To reset the peak level of the broadcast traffic, proceed as follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Reset Peak field for the selected
port.
2. Press the SPACE bar to select YES or NO.
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command at the bottom of
the screen.
4. Press ENTER. The message “SAVED OK” displays and the Time
Since Peak field is also reset.
1.14 REPEATER CONFIGURATION MENU SCREENS
The Repeater Configuration Menu screen and its subordinate security
screens are only displayed when using the repeater device 2E43-51,
2E43-51R, 2H23-50R, or 2H33-37R. The screens that will display
depend on the repeater device.
In the 2E43-51and 2E43-51R devices, the screens are the Repeater Level
Security Configuration and Port Level Security Configuration screens.
In the 2H23-50R and 2H33-37R devices, the screens are the Repeater
Configuration Menu screen and its two subordinate screens, Repeater
Level Security Configuration and Port Level Security Configuration
screens.
For a description of the screens associated with the 2E43-51 and
2E43-51R devices, refer to Chapter 2; for the 2H23-50R and 2H33-37R
devices, refer to Chapter 3. The screens enable the user to configure
operations and security at the connector and port level.
Local Management Supplement 1-37
Page 54

Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
1.15 802.1 CONFIGURATION MENU SCREEN
The 802.1 Configuration Menu screen, Figure 1-15, provides access to the
Switch Configuration, 802.1Q VLAN Configuration Menu, GARP
Operation Status, GMRP Group Registrations, and 802.1p Priority
Configuration Menu screens.
To access the 802.1 Configuration Menu screen from the Device
Configuration Menu screen, use the arrow keys to highlight the 802.1
CONFIGURATION MENU item and press ENTER. The 802.1
Configuration Menu screen displays.
NOTE
mode, SWITCH CONFIGURATION is the only menu item that
displays.
When the SmartSwitch is operating in the 802.1D switching
SWITCH CONFIGURATION
802.1Q VLAN CONFIGURATION MENU
GARP OPERATION STATUS
GMRP GROUP REGISTRATIONS
802.1p PRIORITY CONFIGURATION MENU
EXIT
Figure 1-15 802.1 Configuration Menu Screen
RETURN
29711_89
The following briefly describes each screen that is accessible from the
802.1 Configuration Menu screen.
SWITCH CONFIGURATION
Provides the basic setup options for customizing the operation of a switch
device in the network. For details, refer to Section 1.16.
1-38 Local Management Supplement
Page 55

802.1 Configuration Menu Screen
802.1Q VLAN CONFIGURATION MENU
Displays only if the SmartSwitch has been configured to operate as an
IEEE 802.1Q switch. When selected, this menu item opens the 802.1Q
VLAN Configuration Menu screen.
The IGMP/VLAN Configuration screen has been added to the 802.1Q
VLAN Configuration Menu screen. The revised menu screen is shown in
this supplement along with a description of how to use the IGMP/VLAN
Configuration screen. Refer to Section 1.19 for details.
For details about the other VLAN Local Management screens and how to
use them to configure VLANs in the SmartSwitch, refer to the Cabletron
Systems 802.1Q VLAN User’s Guide.
GARP OPERATION STATUS
Used to enable/disable GVRP and GMRP on the switch and set each port
to operate as a GVRP- or GMRP-aware port so it can send/receiv e frames
from other GVRP- or GMRP-aware devices. GVRP and GMRP enables
the switch to dynamically create VLANs and Multicast Registration
across a switched network. For more information about GVRP and
GMRP, refer to Section 4.1.
For details about the GARP Configuration screen, refer to Section 4.3.
GMRP GROUP REGISTRATIONS
Used to select individual ports or all of the ports and apply one of four
modes of operation according to, or regardless of, multicast address
registration. For more information about GVRP and GMRP, refer to
Section 4.1.
For details about the GMRP Group Registrations/GMRP Configuration
screen, refer to Section 4.1.
802.1p PRIORITY CONFIGURATION
Used to select the Priority/Multicast Configuration Menu screen, which in
turn enables the selection of the Port Priority Configuration and Adv anced
Port Priority Configuration screens. For details, refer to Section 1.20.
Local Management Supplement 1-39
Page 56

Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
1.16 SWITCH CONFIGURATION SCREEN
The Switch Configuration screen, Figure 1-16, provides the basic setup
options to make a switch operational in your network.
To access the Switch Configuration screen from the 802.1 Configuration
Menu screen, use the arrow keys to highlight the SWITCH
CONFIGURATION menu item and press ENTER.
Switch Address: 00-00-1D-00-00-00
Number of Ports: 27
Port #
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
MAC Address
00-00-1D-00-00-00
00-00-1D-00-00-01
00-00-1D-00-00-02
00-00-1D-00-00-03
00-00-1D-00-00-04
00-00-1D-00-00-05
00-00-1D-00-00-06
00-00-1D-00-00-07
EXIT
Type of STA: [DEC]
Age Time (sec): 300
State
learning
listening
standby
learning
listening
standby
listening
listening
[9-16]
Status
[ENABLED]
[DISABLED]
[ENABLED]
[DISABLED]
[ENABLED]
[DISABLED]
[ENABLED]
[DISABLED]
RETURNSAVE
19601-18
Figure 1-16 Switch Configuration Screen
The following describes each field of the Switch Configuration screen:
Switch Address (Read-Only)
Displays the MAC address of the SmartSwitch device.
Number of Ports (Read-Only)
Displays the total number of switched ports on the SmartSwitch device.
Type of STA (Toggle)
Allows the user to set the method that the switches use to decide which
switch is the controlling (Root) switch when two or more switches exist in
parallel (Spanning Tree Algorithm). Valid entries include IEEE, DEC, and
NONE. To set the STA, refer to Section 1.16.1.
1-40 Local Management Supplement
Page 57

Switch Configuration Screen
Age Time (Modifiable)
Allows the user to set the amount of time (in seconds) that the
SmartSwitch keeps an address in its switch table before discarding it. An
address is automatically discarded when a valid frame is not received
from that address within the time specified in the Age Time field. To
change the Age Time field from the default value of 300 seconds, refer to
Section 1.16.2.
Port # (Read-Only)
Lists each switched port on the device. If the number of ports is greater
than eight, then the additional ports are listed on subsequent screens.
MAC Address (Read-Only)
Displays the base hardware address assigned to each listed port.
State (Read-Only)
Disabled: Management disabled this interface. No traffic is received or
forwarded while the interface is disabled.
• Listening – The switch is not adding information to the Transparent
Database. The switch is monitoring BPDU traffic while preparing to
move from the learning to the forwarding state.
• Learning – The switch is learning the addresses on this interface. The
switch enters the learning state when the Transparent Database is
created (during start-up or after being deleted), or when the Spanning
Tree Algorithm detects a network topology change.
• Forwarding – The switch is operating and this interface is forw arding
traffic.
• Standby – This interface will not forward any traf fic through the switch
because a loop condition has been detected by the STA.
Status (Toggle)
Allows the user to enable or disable a port by setting the status of the
listed interface to either ENABLED or DISABLED. To set the port status,
refer to Section 1.16.3.
Local Management Supplement 1-41
Page 58

Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
[1-8], [9-16], [17-24], [25-32], [33-40], or [41-48] (Navigation Key)
When the Switch Configuration screen displays, the current screen
settings are displayed for the first 8 ports. This field is used to step to
another screen for the same type of information for ports 9 through 16, 17
through 24, 25 through 32, 33 through 40, and 41 through 48, if available.
(The number of ports available is dependent on the SmartSwitch model.)
To navigate to the next screen, highlight the
[xx-xx] field and press
ENTER. The user can change the field settings while in any of the
selected screens.
1.16.1 Setting the STA
The Spanning Tree Algorithm (STA) setting allows the user to set the
method that the switches use to decide which is the controller (Root)
switch when two or more switches are in parallel. The av ailable selections
are IEEE, DEC, and NONE.
To set the STA, proceed as follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Type of STA field.
2. Use the SPACE bar to step to the appropriate setting (IEEE, DEC, or
NONE).
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command at the bottom of
the screen.
4. Press ENTER. The message “SAVED OK” displays.
1.16.2 Setting the Age Time Field
To set the Age Time, proceed as follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Age Time field.
2. Type in the desired Age Time in increments of 10. The available Age
Time range is 10 to 1,000,000 seconds with the default value being
300 seconds.
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command at the bottom of
the screen.
4. Press ENTER. The message “SAVED OK” displays.
1-42 Local Management Supplement
Page 59

Summary of VLAN Local Management
1.16.3 Setting (Enabling or Disabling) the Port Status
To set the status of an interface (port), proceed as follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Status field of the port.
2. Use the SPACE bar to toggle to either ENABLED or DISABLED.
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command at the bottom of
the screen.
4. Press ENTER. The message “SAVED OK” displays.
1.17 SUMMARY OF VLAN LOCAL MANAGEMENT
The VLAN configuration process is an extension of normal Local
Management operations. A series of Local Management screens provides
access to the functions and commands necessary to add, change, or delete
VLANs and to assign ports to those VLANs. The IGMP/VLAN
Configuration screen has been added to the SmartSwitch device to enable
the operation of IGMP on selected VLANs.
A switch supporting 802.1Q VLANs provides the VLAN Configuration
screens as a standard part of its Local Management hierarchy when the
switch is configured to operate in 802.1Q Mode. The hierarchy of the
Local Management screens pertaining to 802.1Q VLAN configuration is
shown in Figure 1-17. This supplement shows the revised hierarchy
(Figure 1-17) and 802.1Q VLAN Configuration Menu screen
(Figure 1-18), and describes how to use the IGMP/VLAN Configuration
screen (Figure 1-19). For information concerning the other VLAN
screens, refer to the 802.1Q VLAN User’s Guide (P/N 9032599-02).
802.1Q VLAN
Configuration Menu
Figure 1-17 802.1Q VLAN Screen Hierarchy
Local Management Supplement 1-43
Device VLAN Configuration
Port Assignment Configuration
Port Filtering Configuration
VLAN Forwarding Configuration
Protocol VLAN Configuration
Protocol Ports Configuration
IGMP/VLAN Configuration
25995_03
Page 60

Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
1.18 802.1Q VLAN CONFIGURATION MENU SCREEN
To access the 802.1Q VLAN Configuration Menu screen from the 802.1
VLAN Configuration Menu screen, use the arrow keys to highlight the
802.1Q VLAN CONFIGURATION MENU item and press ENTER.
The 802.1Q VLAN Configuration Menu screen, Figure 1-18, displays.
DEVICE VLAN CONFIGURATION
PORT ASSIGNMENT CONFIGURATION
PORT FILTERING CONFIGURATION
VLAN FORWARDING CONFIGURATION
PROTOCOL VLAN CONFIGURATION
IGMP/VLAN CONFIGURATION
EXIT
Figure 1-18 802.1Q VLAN Configuration Menu Screen
RETURN
25995-04
The following describes the screen menu items:
DEVICE VLAN CONFIGURATION
Used to view , add, name, enable, or disable VLANs within the de vice, and
also associate the VLANs to a Filter Database ID (FID). It also enables
the user to configure attributes that apply to the entire switch and/or
VLANs. Refer to your SmartSwitch device user’s guide for additional
information.
PORT ASSIGNMENT CONFIGURATION
Displays a list of ports and enables the user to assign a Port VLAN ID
(PVID) to each port. The screen also allows the user to change the
operational mode of a port. Refer to your SmartSwitch device user’s
guide for additional information.
1-44 Local Management Supplement
Page 61

IGMP/VLAN Configuration Screen
PORT FILTERING CONFIGURATION
Used to set the switch to filter out inbound frames to prevent them from
being forwarded by the switch out a particular port. This screen also lists
the VLANs that ha v e frames eligible to be transmitted out that port. Refer
to your SmartSwitch device user’s guide for additional information.
VLAN FORWARDING CONFIGURATION
Used to view which ports are included in the VLAN’s Forwarding List
and whether to include a Tag Header in a frame being transmitted. Refer
to your SmartSwitch device user’s guide for additional information.
PROT OCOL VLAN CONFIGURATION
Used to assign VLAN IDs to protocol types of received frames and to
access the Protocol Ports Configuration screen to add or delete
transmitting ports associated with a specific VLAN ID and protocol type.
Refer to your SmartSwitch device user’s guide for additional information.
IGMP/VLAN CONFIGURATION
Used to enable or disable IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol)
on selected VLANs. For details, refer to Section 1.19.
1.19 IGMP/VLAN CONFIGURATION SCREEN
The IGMP/VLAN Configuration screen, Figure 1-19, is used to enable or
disable IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol, RFC 2236) on
selected VLANs.
IGMP provides a solution for handling multicast streams in layer 2
switching devices. IGMP is for hosts on multi-access networks to inform
locally attached switches of their Multicast group membership
information. This is performed by hosts multicasting IGMP Host
Membership Reports. Multicast switches listen for these messages and
then pass them to the routers. This allows distribution trees to be formed
to deliver multicast datagrams.
Information from the IGMP packets is used to send the multicast stream
only to the end stations that request it.
Local Management Supplement 1-45
Page 62

Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
IGMP is enabled or disabled by VLAN, not port by port.
NOTE
Certain versions of firmware will not allow the switch to be a
querier. Please check your release notes for further
information. Refer to RFC 2236, Section 8, for more
information on IGMP.
The following multicast routing protocols are transparently supported and
are used only to detect the location of the routers (see the Release Notes
for any changes or additions to this list):
• DVMRP (Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol, RFC 1075)
• PIM (Protocol Independent Multicast) version 1 and 2
• CBT (Core Based Trees)
• MOSPF (Multicast OSPF, RFC 1583)
For additional information about IGMP, refer to Appendix A.
NOTE
The IGMP/VLAN Configuration screen does not display when
the operational mode of the device is set to SECURE FAST
VLAN.
Your SmartSwitch device user’s guide provides instructions for
setting the operational mode.
To access the IGMP/VLAN Configuration screen from the Layer 3
Extensions Menu screen, use the arrow keys to highlight the
IGMP/VLAN CONFIGURATION menu item and press ENTER. The
IGMP/VLAN Configuration screen displays.
1-46 Local Management Supplement
Page 63

IGMP/VLAN Configuration Screen
Configuration Statistics
------------------- ----------- IGMP Version: [ 2 ] Querier Address: 0.0.0.0
Query Interval: 120 Querier Uptime: 0 D 0 H 0 M
Query Response Time: 10 Querier Expire Time: 24500 S
Interface Robustness: 2
Last Member Query Interval: 10
VLAN ID: [ 1]
IGMP State: [ DISABLED ]
Default for new VLANS: [ DISABLED ]
SAVE EXIT RETURN
3026_201
Figure 1-19 IGMP/VLAN Configuration Screen
The following describes each field of the IGMP/VLAN Configuration
screen:
IGMP Version (T oggle)
Displays the current configured IGMP version running on the VLAN
selected in the VLAN ID field (version 1 or 2). The default is version 2.
The IGMP Version field can be toggled to configure the switch in either
version 1 or 2 to match the router configuration. For IGMP to function
correctly, all switches on a LAN must be configured to run the same
version of IGMP.
Query Interval (Modifiable)
If the switch is the querier, the value in the Query Interval field indicates
how often IGMP Host-Query frames are transmitted on the VLAN
selected in the VLAN ID field. This value is also used in calculations for
other timers. The default value is 125 seconds. The range of possible
entries is 1 to 300 seconds. An entry outside of the range will cause the
error message “PERMISSIBLE RANGE: 1...300” to display in the Event
Message field.
Local Management Supplement 1-47
Page 64

Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
Query Response Time (Modifiable)
Used to enter the maximum query response time advertised in IGMPv2
general queries on this VLAN. This v alue is used in calculations for other
timers. The default value is 10 seconds. The range of possible entries is 1
to 300 seconds. The value entered in this field cannot be bigger than the
Query Interval.
Interface Robustness (Modifiable)
Allows tuning for the expected frame loss on a subnet. If a subnet is
expected to be high loss, the Robustness Variable may be increased.
IGMP is robust to (Robustness Variable-1) packet losses. This value is
used in calculations for other timers. The default value is 2.
If the Interface Robustness is adjusted higher than the default
TIP
Last Member Query Interval (Modifiable)
value, depending on the network, this may be an indication of
problems with the network that need to be resolved.
Displays the Max Response Time inserted into Group-Specific Queries
sent in response to the Leave Group messages, and is also the amount of
time between Group-Specific Query messages. This value may be tuned
to modify the leave latency of the network. A reduced value results in
reduced time to detect the loss of the last member of a group. The interval
is in tenths of seconds. This value is not used if the switch is not the
querier.
Querier Address (Read-Only)
Displays the address of the IGMP Querier on the IP subnet to which this
VLAN is attached.
Querier Uptime (Read-Only)
Displays the number of seconds that the current IGMP Querier has been
operational since the last change in Queriers.
Querier Expire Time (Read-Only)
The number of seconds remaining before the Other Querier Present Timer
expires. If the local system (current device displayed) is the querier, the
value of this object is zero.
1-48 Local Management Supplement
Page 65

IGMP/VLAN Configuration Screen
VLAN ID (Selectable)
Displays the Identifying number for the VLANs a vailable to be modified.
The information under Configuration and Statistics applies only to this
VLAN ID number. Use the SPACE bar to step through all available
VLAN IDs.
IGMP State (Selectable)
Displays the current state of the VLAN indicated in the VLAN ID field,
which can be modified. Use the SPACE bar to step through the choices:
ENABLED, DISABLED, ENABLE ALL, DISABLE ALL. The
commands ENABLED and DISABLED will act only on the VLAN
whose ID is in the VLAN ID field. The commands ENABLE ALL and
DISABLE ALL act on all VLANs available to the switch.
Default for new VLANS (Toggle)
New VLANs can be set up by default to be either ENABLED or
DISABLED. A VLAN is set up, by choosing the number for that VLAN
1.19.1 Configuring VLANs for IGMP
To set up IGMP protocol for VLANs, proceed as follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the VLAN ID field, and use the
SPACE bar to toggle through the VLAN choices to find the correct
VLAN to be configured. ALL may be chosen to affect all VLANs seen
by the device.
2. Use the arrow keys to highlight the IGMP State field.
3. Use the SPACE bar to select ENABLED, DISABLED,
ENABLE ALL or DISABLE ALL. ENABLED and DISABLED are
used to enable or disable the VLAN chosen in step 1. ENABLE ALL
and DISABLE ALL are used to enable or disable all available VLANs
at one time.
4. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Default for new VLANS field.
5. Use the SPACE bar to toggle the setting to either ENABLED or
DISABLED to set the default for new VLANs.
Local Management Supplement 1-49
Page 66

Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
6. Use the arrow keys to highlight the IGMP Version field. Then use the
SPACE bar to select the proper IGMP version for the VLAN shown in
the VLAN ID field.
When configuring IGMP, it is advisable to follow the IGMP
TIP
configuration rules in RFC 2236 concerning switches and
routers.
7. Use the arrow keys to highlight the remaining fields: Query Interval,
Query Response Time, Interface Robustness, and Last Member
Query Interval. Enter the desired numbers in each field.
8. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command and press the
ENTER key to save the information in all the fields that were changed.
The event message line will indicate “SAVED OK” and the screen can
now be exited. To set up a VLAN, refer to the Cabletron Systems 802.1Q
VLAN User’s Guide.
1.20 PRIORITY/MULTICAST CONFIGURATION MENU
SCREEN
The Priority/Multicast Configuration Menu screen, Figure 1-20, provides
access to the Port Priority Configuration, and Advanced Port Priority
Configuration screens These screens are used for the following:
• Setting the default priority of frames received without a priority
setting.
• Mapping the frame priorities to transmit queues for each front panel
port. The number of ports is dependent on the SmartSwitch model.
NOTE
The 802.1p Priority Configuration Menu item cannot be
selected from the Port Priority Configuration screen when the
operational mode of the device is set to 802.1D SWITCHING.
To access the Priority/Multicast Configuration Menu screen from the
802.1 Configuration Menu screen, use the arrow keys to highlight the
802.1p PRIORITY CONFIGURATION MENU item and press
ENTER. The Priority/Multicast Configuration Menu screen displays.
1-50 Local Management Supplement
Page 67

Priority/Multicast Configuration Menu Screen
PORT PRIORITY CONFIGURATION
ADVANCED PORT PRIORITY CONFIGURATION
EXIT
Figure 1-20 Priority/Multicast Configuration Menu Screen
RETURN
27623-86
The Priority/Multicast Configuration Menu screen displays the following
menu items:
PORT PRIORITY CONFIGURATION
Used to set the port default transmit priority (0 through 7) of each port for
frames that are received without priority information in their tag header.
For details, refer to Section 1.21.
ADVANCED PORT PRIORITY CONFIGURATION
Used to map priorities to transmit queues for each port. This screen is also
used to change priority on a port by port basis and to reprioritize frames
received in one priority so they can be transmitted at a different priority.
For details, refer to Section 1.22.
Local Management Supplement 1-51
Page 68
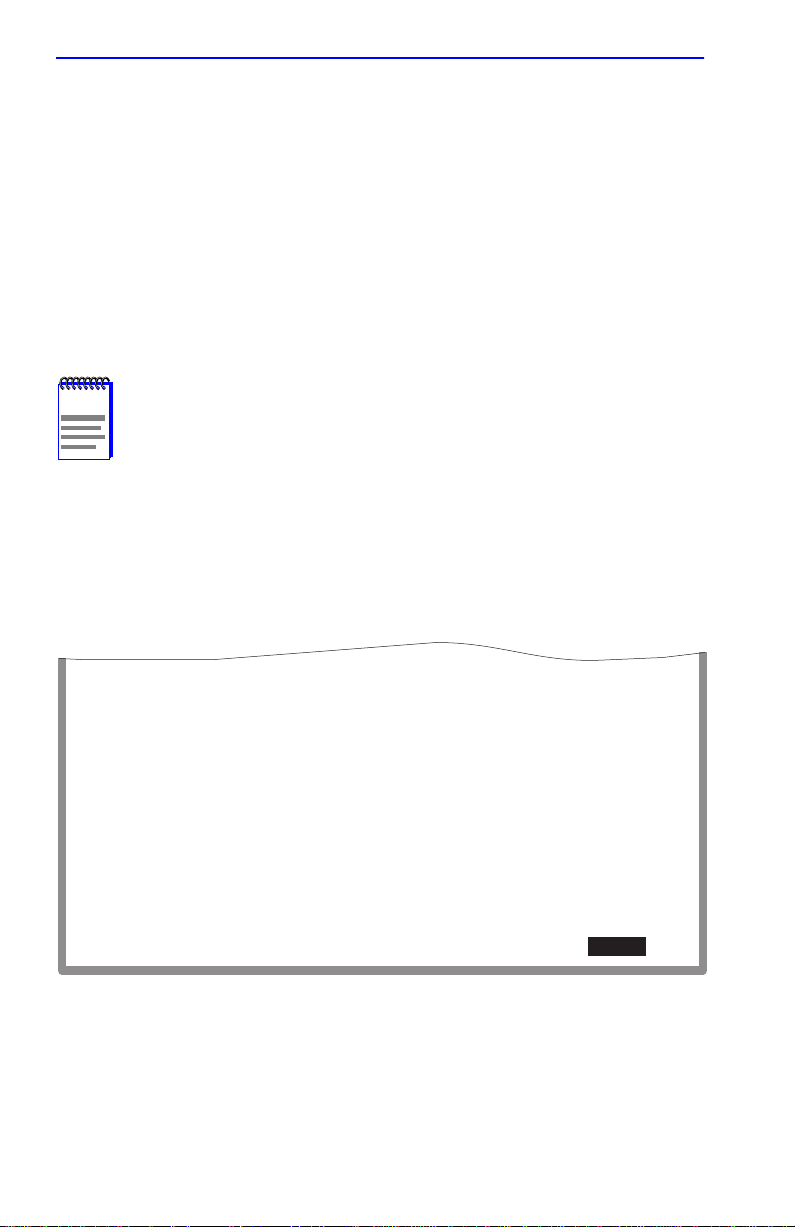
Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
1.21 PORT PRIORITY CONFIGURATION SCREEN
The Port Priority Configuration screen, Figure 1-21, is used to set the
priority (0 through 7) on each port. A port receiving a frame without
priority information in its tag header is assigned a priority according to
the priority setting on the port. For example, if the priority of a port is set
to 5, all frames received through that port without priority indicated in
their tag header are classified as a priority 5.
A frame with priority information in its tag header is transmitted
according to that priority.
NOTE
the operational mode of the device is set to 802.1D
SWITCHING.
To access the Port Priority Configuration screen from the
Priority/Multicast Configuration Menu screen, use the arrow keys to
highlight the PORT PRIORITY CONFIGURATION menu item and
press ENTER. The Port Priority Configuration screen displays.
The Port Priority Configuration screen does not display when
Port #
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
SAVE EXIT
Priority
[0]
[2]
[2]
[3]
[3]
[4]
[4]
[0]
[5]
[6]
[6]
[7]
Set All Switch Port's Priority [3]
PREVIOUS NEXT
Port #
13
14
14
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
Priority
[4]
[4]
[4]
[4]
[4]
[6]
[6]
[6]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
RETURN
2762-87
Figure 1-21 Port Priority Configuration Screen
1-52 Local Management Supplement
Page 69

Port Priority Configuration Screen
The following describes each field of the Port Priority Configuration
screen:
Port # (Read-Only)
Lists each switched port on the device.
Priority (Selectable)
Used to select the transmit priority of frames received without the priority
indicated in their tag header. A priority of 0 through 7 (with 0 being the
lowest priority and 7 the highest) can be selected for each port. All ports
are set to the default value of “0” when the device is initialized.
To set the transmit priority for each port, refer to Section 1.21.1.
Set All Switch Port’s Priority (Selectable)
Used to set all ports to one default transmit priority. A value of 0 through
7 (with 0 being the lowest priority and 7 the highest) can be selected that
will apply to all ports. To set the default transmit priority for all ports,
refer to Section 1.21.2.
1.21.1 Setting Switch Port Priority Port-by-Port
To set the default port priority on a particular port, proceed as follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Priority field for the particular
port.
2. Press the SPACE bar to step to the appropriate value: 0 through 7.
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command at the bottom of
the screen.
4. Press ENTER. The message “SAVED OK” displays and the setting is
saved.
1.21.2 Setting Switch Port Priority on All Ports
To set the port priority on all ports, proceed as follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Set All Switch Port’s Priority
field.
2. Press the SPACE bar to select a priority from 0 through 7 (0 is the
lowest priority).
Local Management Supplement 1-53
Page 70

Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command at the bottom of
the screen.
4. Press ENTER. The message “SAVED OK” displays and the setting is
saved.
1.22 ADVANCED PORT PRIORITY CONFIGURATION
SCREEN
The Advanced Port Priority Configuration screen, Figure 1-22, is used to
set the Priority/Queue Mapping and Priority Regeneration for a particular
port or change the default port priority . Priority/Queue Mapping is used to
set the transmit (TX) queue (0 or 1, with 0 being the lowest level TX
queue) for each frame priority.
For example, if the TX queue is set to 1 for those frames with a priority 1,
then those frames would be transmitted before any frames with a priority
that has the TX queue set to 0.
Priority Regeneration is used to classify different types of traffic by
reprioritizing received frames to a different transmit priority. For
example, the frames associated with a particular type of traffic that hav e a
received (RX) transmit priority, or a port default priority, of 3 could be
changed to have a transmit priority of 5.
NOTE
The Advanced Port Priority Configuration screen does not
display when the operational mode of the device is set to
802.1D SWITCHING.
To access the Advanced Port Priority Configuration screen from the
Priority/Multicast Configuration Menu screen, use the arrow keys to
highlight the ADVANCED PORT PRIORITY CONFIGURATION
menu item and press ENTER. The Advanced Port Priority Configuration
screen displays.
1-54 Local Management Supplement
Page 71

Advanced Port Priority Configuration Screen
Priority/Queue Mapping
-------------------------------
Priority
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
SAVE PREVIOUS EXITNEXT
TX Queue
[0]
[0]
[0]
[0]
[1]
[1]
[1]
[1]
Default Priority [7]
Priority Regeneration
----------------------------
RX Priority
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Port #: xxx
TX Priority
[0]
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
[7]
RETURN
Figure 1-22 Advanced Port Priority Configuration Screen
The following describes each field of the Advanced Port Priority
Configuration screen:
Priority (Read-Only)
Lists the eight priorities, 0 through 7.
TX Queue (Toggle)
Enables the frames with a certain priority to be mapped to transmit
according to one of two TX queues (0 or 1) with 0 being the lowest
transmit level. Refer to Table 1-2 for the TX Queue default values
according to frame priority.
2971_88
Table 1-2 TX Queue Mapping Default Values
Priority 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
TX Queue
00001111
To set the TX Mapping Queues, refer to Section 1.22.1.
RX Priority (Read-Only)
Lists the eight priorities, 0 through 7.
Local Management Supplement 1-55
Page 72

Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
TX Priority (Selectable)
Enables the frames with a certain RX priority to be changed to transmit
according to a different TX priority (0 through 7).
The following describes how the frames of learned traffic are handled.
When a frame is received, it is checked to see if it has a priority. If it does,
it is forwarded to the appropriate output port. If it does not, the frame is
assigned the default RX priority and then forwarded to the appropriate
output port. At the output port, the RX priority of the frame is checked
against the TX Regeneration table and may be transmitted at a different
TX priority according to the table. For example, all frames with an RX
priority of 3 could be regenerated with a TX priority of 5. The new value
would also be inserted in the VLAN tag if the frame is tagged as
outbound.
The regenerated priority is used to determine the correct queue as defined
in the Priority/Queue Mapping. The default values for the TX Priority
settings are listed in Table 1-3 according to RX priority.
Table 1-3 TX Priority Regeneration Default Values
RX Priority 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
TX Priority
01234567
To set the TX Regeneration Priorities, refer to Section 1.22.2.
Default Priority (Selectable)
Used to set the default port priority (0 through 7) of the port selected in
the Port command. To set the default port priority, refer to Section 1.22.3.
Port # (Modifiable)
Used to enter the number of the port to be configured. Using an arrow key
or pressing ENTER after entering a port number, causes the screen to
refresh and show the current settings for that port.
1-56 Local Management Supplement
Page 73

Advanced Port Priority Configuration Screen
1.22.1 Setting the TX Mapping Queues
To set the TX queue for frames with a particular priority, proceed as
follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Port # field.
2. Type in the number of the port to which the TX queue setting will be
applied.
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Default Priority field. The screen
refreshes and displays the current settings of the port in the Port #
field.
4. Use the arrow keys to highlight the TX Queue field for the particular
frame priority.
5. Press the SPACE bar to step to the appropriate value, 0 or 1. The 0
selection is the lowest level TX queue.
6. If more than one TX queue is to be changed, repeat steps 4 and 5 until
all the appropriate TX queue settings are changed.
7. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command at the bottom of
the screen.
8. Press ENTER. The message “SAVED OK” displays and the setting is
saved.
1.22.2 Setting the TX Regeneration Priorities
To set the TX priority for frames with a particular RX priority, proceed as
follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Port # field.
2. Type in the number of the port to which the TX priority setting will be
applied.
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Default Priority field at the
bottom of the screen. The screen refreshes and displays the current
settings of the port in the Port # field.
4. Use the arrow keys to highlight the TX Priority field for the particular
RX frame priority.
Local Management Supplement 1-57
Page 74

Chapter 1: Changes to Local Management Screens
5. Press the SPACE bar to step to the appropriate value, 0 through 7. The
0 selection is the lowest level TX priority value.
6. If more than one TX priority is to be changed, repeat steps 4 and 5 until
all the appropriate TX priority settings are changed.
7. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command at the bottom of
the screen.
8. Press ENTER. The message “SAVED OK” displays and the setting is
saved.
1.22.3 Setting the Default Priority of a Port
To set the default port priority, proceed as follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Port # field.
2. Type in the number of the port having the default priority changed.
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Default Priority field at the
bottom of the screen. The screen refreshes and displays the current
settings of the port in the Port # field.
4. Press the SPACE bar to step to the appropriate value, 0 through 7. The
0 selection is the lowest level priority.
5. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command at the bottom of
the screen.
6. Press ENTER. The message “SAVED OK” displays and the setting is
saved. This new setting will be reflected in the Port Priority
Configuration screen the next time it is displayed.
1-58 Local Management Supplement
Page 75

CHAPTER 2
LM SECURITY SCREENS FOR
2E43-51/2E43-51R DEVICES
The information in this chapter replaces the information about the
Repeater Configuration Menu and Repeater Port Configuration screens
provided in the 2E43-51/2E43-51R SmartSwitch 2100 User’s Guide.
2.1 REPEATER CONFIGURATION MENU SCREEN
The Repeater Configuration Menu screen, Figure 2-1, is used to access
the Repeater Level Security Configuration, or Port Level Security
Configuration screen.
To access the Repeater Configuration Menu screen from the Port
Configuration Menu screen, select the REPEATER
CONFIGURATION MENU item and press ENTER. The Repeater
Configuration Menu screen displays.
REPEATER LEVEL SECURITY CONFIGURATION
PORT LEVEL SECURITY CONFIGURATION
RETURNEXIT
27462_104w
Figure 2-1 Repeater Configuration Menu Screen
Local Management Supplement 2-1
Page 76

Chapter 2: LM Security Screens for 2E43-51/2E43-51R Devices
The following introduces each screen that is accessible from the Repeater
Configuration Menu screen.
REPEATER LEVEL SECURITY CONFIGURATION
Used to set the state of security of all ports on each connector,
simultaneously. The ports can be set to receive all frames (NonSecure
state), lock on the source address of the next frame received
(LockOnNext), or lock on the address of the last frame received
(LockedOnAddr). For details, refer to Section 2.2.
PORT LEVEL SECURITY CONFIGURATION
Used to set the security for each port of a connector, individually. For
details, refer to Section 2.3.
2.2 REPEATER LEVEL SECURITY CONFIGURATION
The Repeater Level Security Configuration screen, Figure 2-2, is used to
set the state of security according to connector. All ports on a connector
can be set to receive all frames (NonSecure state), lock on the source
address of the next frame received (LockOnNext), or lock on the source
address of the last frame received (LockedOnAddr). When either of the
last two options are set, the switch can be set to enable or disable the
reception of frames and send or not send traps when an intruder is
detected.
T o access the Repeater Le vel Security Configuration screen, use the arro w
keys to highlight the REPEATER LEVEL SECURITY
CONFIGURATION menu item on the Repeater Configuration Menu
screen and press ENTER. The Repeater Level Security Configuration
screen displays.
2-2 Local Management Supplement
Page 77

Repeater Level Security Configuration
Interface Security State Action On Intruder
1 [NonSecure]
[NonSecure]
2
3 [LockOnNext] [DisablePort] [SendTrap]
4 [LockedOnAddr] [DisablePort] [NoTrap]
SAVE EXIT RETURN
2971_112w
Figure 2-2 Repeater Level Security Configuration Screen
The following section defines the fields on the Repeater Level Security
Configuration screen.
Interface (Read-Only)
Indicates the interface connector (ENET 1 through 4) selected in the
Interface field.
Security State (Selectable)
Used to set all ports on an interface connector to the same security state.
PortMismatch displays for an interface connector when all the ports on
the interface connector are not set to the same state. The selectable states
are as follows:
• NonSecure – Allows the ports on the connector to receive all frames.
The source address of received frames is not examined and the frames
are processed in a non-secure state.
• LockedOnAddr – The Security State of all ports on the specified
interface connector are set to LockedOnAddr. This setting is for
convenience, so that all ports on an interface connector can be set to
LockedOnAddr at one time. Until the address is set at the port level,
the port defaults to the locked on address of “00-00-00-00-00-00” as
indicated by “XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX” in the address field shown in
the Port Level Security Screen, see Figure 2-3.
Local Management Supplement 2-3
Page 78

Chapter 2: LM Security Screens for 2E43-51/2E43-51R Devices
The port will lock down on the address that is currently configured in
the Port Level Security Configuration screen (if one is entered), or on
the source address of the last received frame. When a port is locked on
an address, the device executes the actions selected in the Action On
Intruder field (Port Level Security Configuration screen) when a frame
is received that violates security.
• LockOnNext – The next frame received by each port on the interface
connector is examined to learn its source address. After the source
address of a frame is learned on a port, it is now locked on that address
and only those frames received with that same source address are
allowed on that port. All frames received that do not have that same
source address will cause the device to execute the actions selected in
the Action On Intruder field.
Action On Intruder (Toggle)
Used to select the actions taken for the selected security state. There are
two fields in which to select the actions. Both toggle to activate or
deactivate the action.
• DisablePort/NoDisablePort – DisablePort causes the switch to turn off
the port that had a security violation. With NoDisable set, the port is
not turned off.
• SendTrap/NoT rap – SendTrap causes the switch to send an SNMP trap
when a port detects a security violation. With NoTrap set, no SNMP
trap is sent.
2.2.1 Setting the Repeater Level Security
To set the security on all repeater ports of each connector, proceed as
follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Security State field for the
interface connector.
2. Use the SPACE bar to step to the appropriate security level
(NonSecure, LockedOnAddr, or LockOnNext).
3. If the security level chosen causes the DisablePort and SendTrap
fields to display under Action On Intruder, use the arrow keys to
highlight the DisablePort field. If the security level chosen does not
cause the fields to display under Action On Intruder, proceed to step 7.
2-4 Local Management Supplement
Page 79

Port Level Security Configuration Screen
4. To change the DisablePort setting to NoDisablePort, press the
SPACE bar to toggle the setting.
5. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SendTrap field.
6. To change the SendTrap setting to NoTrap, press the SPACE bar to
toggle the setting.
7. To change the security on all interface ports on more than one
connector, repeat step 1 through step 6 for each connector. Then
proceed to step 8 to save all settings at once.
8. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command.
9. Press ENTER. The message “SAVED OK” displays and all ports of
the connector are set to the selected operating mode.
NOTE
If LockedOnAddr is chosen as the Security State, the address
of the repeater ports must be configured in the Port Level
Security Configuration screen. Refer to Section 2.3.
2.3 PORT LEVEL SECURITY CONFIGURATION
SCREEN
The Port Level Security Configuration screen, Figure 2-3, functions
similarly to the Repeater Level Security Configuration screen, except that
it is used to set the security of each port of a selected connector.
To access the Port Level Security Configuration screen, use the arrow
keys to highlight the PORT LEVEL SECURITY CONFIGURATION
menu item on the Repeater Configuration Menu screen and press ENTER.
The Port Level Security Configuration screen displays.
Local Management Supplement 2-5
Page 80

Chapter 2: LM Security Screens for 2E43-51/2E43-51R Devices
Port Security State Action On Intruder Address
1 [LockedOnAddr] [NoD
2 [NonSecure] [00-00-00-00-00-00]
3 [LockedOnAddr] [DisablePort] [SendTrap] [xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx]
4 [LockOnNext] [DisablePort] [SendTrap]
5 [NonSecure] [00-00-00-00-00-00]
6 [NonSecure] [00-00-00-00-00-00]
7 [NonSecure] [00-00-00-00-00-00]
8 [NonSecure] [00-00-00-00-00-00]
9 [NonSecure] [00-00-00-00-00-00]
10 [NonSecure] [00-00-00-00-00-00]
11 [NonSecure] [00-00-00-00-00-00]
12 [NonSecure] [00-00-00-00-00-00]
SAVE INTERFACE #: [1] EXIT RETURN
isablePort] [SendTrap] [xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx]
27462_113w
Figure 2-3 Port Level Security Configuration Screen
The following section defines the fields on the Port Level Security
Configuration screen.
Port (Read-only)
Lists the repeater ports on the ENET interface connector (ENET 1
through 4) selected in the INTERFACE # field. Refer to Table 2-1 for the
ENET/repeater port relationship on the device.
Table 2-1 ENET/Repeater Port Relationship
ENET 1 = Repeater ports 1 – 12 ENET 3 = Repeater ports 25 – 36
ENET 2 = Repeater ports 13 – 24 ENET 4 = Repeater ports 37 – 48
Security State (Selectable)
Used to select the security state of each repeater port on the connector for
frames received. The states are as follows:
• NonSecure – Allows the ports on the connector to receive all frames.
The source address of received frames is not examined and the frames
are processed in a non secure state.
The last source address detected is displayed in the address column.
This provides a quick and easy way to see what address belongs to
what port.
2-6 Local Management Supplement
Page 81

Port Level Security Configuration Screen
• LockOnNext – The next frame received by each port is examined to
learn its source address. After the source address of a frame is learned
on a port, it is now locked on that address and only those frames
received with that same source address are allowed on that port. All
frames received that do not have that same source address will cause
the device to execute the actions selected in the Action On Intruder
field.
• LockedOnAddr – The port locks down on the address that is currently
configured in the Port Level Security Configuration screen (if one is
entered) or on the source address of the currently received frame. If an
address was not configured or received, the device defaults to the
locked on address of “00-00-00-00-00-00” as indicated by
“XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX” in the address field shown in Figure 2-3.
When a port is locked on an address and the frame received violates
the set security , the actions selected in the Action On Intruder field are
executed.
Action On Intruder (Toggle)
Used to select the actions taken for the selected security state. There are
two fields to select the actions. Both toggle to activate or deactivate the
action.
• DisablePort/NoDisablePort– DisablePort causes the switch to turn off
the port that had a security violation. W ith NoDisablePort set, the port
is not turned off.
• SendTrap/NoT rap – SendTrap causes the switch to send an SNMP trap
when a port detects a security violation. With NoTrap set, no SNMP
trap is sent.
Address (Modifiable)
Used to enter the source MAC address for the LockedOnAddr security
state setting. Once a secure address is defined on a port, only those frames
received with that same source address are allo wed on that port. Any other
frame detected with a different address is considered as an intruder,
causing the actions selected in the Action On Intruder field to be e xecuted.
When the security state setting is NonSecure, the field displays the source
address of the last frame.
Local Management Supplement 2-7
Page 82

Chapter 2: LM Security Screens for 2E43-51/2E43-51R Devices
INTERFACE # (Selectable)
Used to select the front panel interface connector (ENET 1 to ENET 4) to
which the port security settings will be applied.
2.3.1 Setting the Port Level Security
To set the security for each repeater port on a connector, proceed as
follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the INTERFACE # field.
2. Use the SPACE bar to step to the appropriate interface connector
number (ENET 1 to ENET 4).
3. Press ENTER to display the ports on the chosen interface connector.
4. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Security State field for the
interface connector.
5. Use the SPACE bar to step to the appropriate security level
(NonSecure, LockOnNext, or LockedOnAddr).
6. If the security level chosen causes the DisablePort and SendTrap
fields to display under Action On Intruder, use the arrow keys to
highlight the DisablePort field. If the security level chosen does not
cause the fields to display under Action On Intruder, proceed to
step 12.
7. To change the DisablePort setting to NoDisablePort, press the
SPACE bar to toggle the setting.
8. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SendTrap field.
9. To change the setting to NoTrap, press the SPACE bar to toggle the
setting.
10. If the security state selected is LockedOnAddr, use the arrow keys to
highlight the Address field for the port. Otherwise go to step 12.
11. Enter the MAC address, using the numerical keys. It is not necessary
to separate the numbers with dashes when entering the address.
12. To change the security on more than one port, repeat step 4 through
step 11 for each port. Then proceed to step 13 to save all settings at
once.
2-8 Local Management Supplement
Page 83

Port Level Security Configuration Screen
13. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command.
14. Press ENTER. The message “SAVED OK” displays and all ports of
the connector are set to the selected operating mode.
15. To change the security on a different interface connector, repeat step 1
through step 14 as needed.
Local Management Supplement 2-9
Page 84

Chapter 2: LM Security Screens for 2E43-51/2E43-51R Devices
2-10 Local Management Supplement
Page 85

CHAPTER 3
LM SECURITY SCREENS FOR
2H23-50R/2H33-37R DEVICES
The information in this chapter replaces the information about the
Repeater Configuration Menu and Repeater Port Configuration screens
provided in the 2H23-50R/2H33-37R SmartSwitch 2100 User’s Guide.
3.1 REPEATER CONFIGURATION MENU SCREEN
The Repeater Configuration Menu screen, Figure 3-1, is used to access
the Repeater Port Configuration, Module Level Security Configuration, or
Port Level Security Configuration screen. To access the Repeater
Configuration Menu screen from the Port Configuration Menu screen,
select the REPEATER CONFIGURATION MENU item and press
ENTER. The Repeater Configuration Menu screen displays.
REPEATER PORT CONFIGURATION
MODULE LEVEL SECURITY CONFIGURATION
PORT LEVEL SECURITY CONFIGURATION
RETURNEXIT
2745_104w
Figure 3-1 Repeater Configuration Menu Screen
Local Management Supplement 3-1
Page 86

Chapter 3: LM Security Screens for 2H23-50R/2H33-37R Devices
The following introduces each screen that is accessible from the Repeater
Configuration Menu.
REPEATER PORT CONFIGURATION
Used to monitor the link status and current operating mode of each port
on the 10-Mbps or 100-Mbps network of a front panel connector, and also
turn each port on or off. For details, refer to Section 3.2.
MODULE LEVEL SECURITY CONFIGURATION
Used to set the state of security for each port of a connector,
simultaneously. All ports on a connector can be set to receive all frames
(NonSecure state), lock on the source address of the next frame received
(LockOn Next), or lock on the address of the last frame received (Lock ed
On Addr). For details, refer to Section 3.3.
PORT LEVEL SECURITY CONFIGURATION
Used to set the security for all ports of a connector. For details, refer to
Section 3.4.
3.2 REPEATER PORT CONFIGURATION SCREEN
The Repeater Port Configuration screen, Figure 3-2, is used to monitor
the link status and current operating mode of each repeater port on a
10-Mbps or 100-Mbps network of a front panel connector. The screen is
also used to change the operating mode, and turn each repeater port on
(enable) or off (disable).
To access the Repeater Port Configuration screen, use the arrow keys to
highlight the REPEATER PORT CONFIGURATION menu item from
the Repeater Configuration Menu screen and press ENTER. The Repeater
Port Configuration screen displays.
3-2 Local Management Supplement
Page 87

Repeater Port Configuration Screen
PORT# NETWORK# LINK STAT. CURRENT OPER. MODE DESIRED OPER. MODE PORT STAT.
1 1 No Link Unknown [Auto-Neg] [Disabled]
2 2 No Link Unknown [Auto-Neg] [Enabled]
3 1 Link 10Base-T [Auto-Neg] [Enabled]
4 2 No Link Unknown [Auto-Neg] [Enabled]
5 2 No Link Unknown [Auto-Neg] [Enabled]
6 2 No Link Unknown [Auto-Neg] [Enabled]
7 2 No Link Unknown [Auto-Neg] [Enabled]
8 2 No Link Unknown [Auto-Neg] [Enabled]
9 2 No Link Unknown [Auto-Neg] [Enabled]
10 2 No Link Unknown [Auto-Neg] [Enabled]
11 2 No Link Unknown [Auto-Neg] [Enabled]
12 2 No Link Unknown [Auto-Neg] [Enabled]
SAVE SET ALL PORTS: [Auto-Neg] CONNECTOR #: [1] EXIT RETURN
2276_111w
Figure 3-2 Repeater Port Configuration Screen
The following are definitions for each field of the Repeater Port
Configuration screen:
PORT # (Read-only)
Indicates the repeater port on the connector selected in the CONNECTOR
field. Refer to Table 3-1 for the connector (CONN) /repeater port
relationship on the device.
Table 3-1 CONN/Repeater Port Relationship
2H23-50R 2H33-37R
CONN 1 = Repeater ports 1 – 12 CONN 1 = Repeater ports 1 – 12
CONN 2 = Repeater ports 13 – 24 CONN 2 = Repeater ports 13 – 24
CONN 3 = Repeater ports 25 – 36 CONN 3 = Repeater ports 25 – 36
CONN 4 = Repeater ports 37 – 48
Local Management Supplement 3-3
Page 88

Chapter 3: LM Security Screens for 2H23-50R/2H33-37R Devices
NETWORK # (Read-only)
Indicates the network on the connector selected in the CONNECTOR
field. Table 3-2 shows the association between the connector (CONN) and
Networks on the device.
Table 3-2 CONN/Network Organization
2H23-50R 2H33-37R
CONN 1 = Network 1, 10 Mbps
Network 2, 100 Mbps
CONN 2 = Network 3, 10 Mbps
Network 4, 100 Mbps
CONN 3 = Network 5, 10 Mbps
Network 6, 100 Mbps
CONN 4 = Network 7, 10 Mbps
Network 8, 100 Mbps
CONN 1 = Network 1, 10 Mbps
Network 2, 100 Mbps
CONN 2 = Network 3, 10 Mbps
Network 4, 100 Mbps
CONN 3 = Network 5, 10 Mbps
Network 6, 100 Mbps
HSIM = 7
LINK STAT. (Read-only)
Displays the Link status (Link or No Link) of the port.
CURRENT OPER. MODE (Read-only)
Displays the current operating mode of the port.
DESIRED OPER. MODE (Selectable)
Steps through the following operating mode options: Auto-Neg (Auto
Negotiation), 10Base-T, and 100Base-TX.
• When Auto-Ne g. is selected, the port automatically negotiates with the
device to which it is attached to determine its Operating Mode
(10 Mbps or 100 Mbps).
• When 10Base-T is selected, the port is forced to operate in standard
Ethernet mode (10 Mbps) only.
• When 100Base-TX is selected, the port is forced to operate in Fast
Ethernet mode (100 Mbps) only.
To set the port operating mode, refer to Section 3.2.1.
3-4 Local Management Supplement
Page 89

Repeater Port Configuration Screen
PORT STAT. (Toggle)
Used to enable (turn on) or disable (turn off) the port. To enable or disable
the port, refer to Section 3.2.2.
SET ALL PORTS (Selectable)
Used to select operating mode for all the ports on the connector
simultaneously. This field steps through the following selections:
Auto-Neg., 10Base T, and 100Base-TX. To set all the ports to the same
operating mode, refer to Section 3.2.3.
CONNECTOR # (Selectable)
Selects the front panel connector to which the settings will be applied.
3.2.1 Setting the Port Operating Mode
To set the operating mode for one or more repeater ports, proceed as
follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the CONNECTOR # field.
2. Use the SPACE bar to step to the appropriate connector number.
3. Press ENTER to display the repeater port settings on that connector.
4. Use the arrow keys to highlight the DESIRED OPER. MODE field
of the repeater port being configured.
5. Use the SPACE bar to step to the appropriate Operating Mode
(Auto-Neg, 10Base-T, or 100Base-TX).
6. If setting the operating mode on other repeater ports, repeat steps 4 and
5 for each one and then proceed to step 7.
7. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command.
8. Press ENTER. The message “SAVED OK” displays and all operating
mode settings are saved.
3.2.2 Enabling /Disabling Repeater Ports
To enable or disable one or more repeater ports, proceed as follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the CONNECTOR # field.
2. Use the SPACE bar to step to the number of the connector containing
the repeater port(s) to be enabled or disabled.
Local Management Supplement 3-5
Page 90

Chapter 3: LM Security Screens for 2H23-50R/2H33-37R Devices
3. Press ENTER to display the repeater port settings on that connector.
4. Use the arrow keys to highlight the PORT STAT. field of the repeater
port being enabled or disabled.
5. Use the SPACE bar to toggle to the appropriate setting (Enable or
Disable).
6. If setting more than one repeater port, repeat steps 4 and 5 for each one
and then proceed to step 7.
7. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command.
8. Press ENTER. The message “SAVED OK” displays and all settings
are saved.
3.2.3 Setting Operating Mode On All Repeater Ports
The repeater ports on a connector can be set to the same operating mode
simultaneously using the SET ALL PORTS field, as follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the CONNECTOR # field.
2. Use the SPACE bar to step to the appropriate connector number.
3. Press ENTER to display the repeater port settings on that connector.
4. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SET ALL PORTS field.
5. Use the SPACE bar to step to the appropriate Operating Mode
(Auto-Neg, 10Base-T, or 100Base-TX).
6. Press ENTER.
7. Enable or disable each repeater port as needed. Refer to Section 3.2.2
for instructions.
8. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command.
9. Press ENTER. The message “SAVED OK” displays and all repeater
ports of the connector are set to the selected operating mode.
NOTE
3-6 Local Management Supplement
If LockedOnAddr is chosen as the Security State, the individual
port must be configured in the Port Level Security
Configuration screen. Sections 3.4 provides instructions for
configuring individual ports.
Page 91

Module Level Security Configuration
3.3 MODULE LEVEL SECURITY CONFIGURATION
The Module Level Security Configuration screen, Figure 3-3, is used to
set the state of security according to connector. All repeater ports on a
connector can be set to receive all frames (NonSecure state), lock on the
source address of the next frame received (LockOnNext) or the source
address of the last frame received (LockedOnAddr). When either of the
last two options are set, the switch can be set to enable or disable the
reception of frames and send or not send traps when an intruder is
detected.
To access the Module Level Security Configuration screen, use the arrow
keys to highlight the MODULE LEVEL SECURITY
CONFIGURATION menu item on the Repeater Configuration Menu
screen and press ENTER. The Module Level Security Configuration
screen displays.
Connector Security State Action On Intruder
1 [LockOnNext] [DisablePort] [SendTrap]
2 [PortMismatch]
3 [NonSecure]
4 [LockedOnAddr] [DisablePort] [SendTrap]
SAVE EXIT RETURN
2276_112w
Figure 3-3 Module Level Security Configuration Screen
Local Management Supplement 3-7
Page 92

Chapter 3: LM Security Screens for 2H23-50R/2H33-37R Devices
The following section defines the fields on the Module Level Security
Configuration screen.
Connector (Read-Only)
Indicates the connector. Refer to Table 3-3 for the connector
(CONN)/repeater port relationship on the device.
Table 3-3 CONN/Repeater Port Relationship
2H23-50R 2H33-37R
CONN 1 = Repeater ports 1 – 12 CONN 1 = Repeater ports 1 – 12
CONN 2 = Repeater ports 13 – 24 CONN 2 = Repeater ports 13 – 24
CONN 3 = Repeater ports 25 – 36 CONN 3 = Repeater ports 25 – 36
CONN 4 = Repeater ports 37 – 48
Security State (Selectable)
Used to set all ports on an interface connector to the same security state.
PortMismatch is a Read-Only field that indicates not all ports on the
interface connector are set to the same state. The selectable states are as
follows:
• NonSecure – Allows the ports on the connector to receive all frames.
The source address of received frames is not examined and the frames
are processed in a non secure state.
• LockOnNext – The next frame received by each port is examined to
learn its source address. After the source address of a frame is learned
on a port, it is now locked on that address and only those frames
received with that same source address are allowed on that port. All
frames received that do not have that same source address will cause
the device to execute the actions selected in the Action On Intruder
field.
3-8 Local Management Supplement
Page 93

Module Level Security Configuration
• LockedOnAddr – The Security State of all ports on the specified
connector are set to LockedOnAddr . This setting is for conv enience, so
that all ports on an interface connector can be set to LockedOnAddr at
one time. Until the address is set at the repeater port level, the port will
default to the locked on address of “00-00-00-00-00-00” as indicated
by “XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX” in the address field shown in
Figure 3-4. If an address is configured or received, the port locks do wn
on the address that is currently configured in the Port Level Security
Configuration screen (if one is entered) or on the source address of the
currently received frame. If the port locks on address and a frame is
received that violates security, the actions selected in the Action On
Intruder field are executed.
Action On Intruder (Toggle)
Used to select the actions taken for the selected security state. There are
two fields to select the actions. Both toggle to activate or deactivate the
action.
• DisablePort/NoDisable – DisablePort causes the switch to turn off the
port that had a security violation. With NoDisable set, the port is not
turned off.
• SendTrap/NoT rap – SendTrap causes the switch to send an SNMP trap
when a port detects a security violation. With NoTrap set, no SNMP
trap is sent.
3.3.1 Setting the Module Level Security
To set the module security simultaneously for all ports on a connector,
proceed as follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Security State field for the
connector.
2. Use the SPACE bar to step to the appropriate security level.
3. If the security level chosen causes the DisablePort and SendTrap
fields to display under Action On Intruder, use the arrow keys to
highlight the DisablePort field. If the security level chosen does not
cause the fields to display under Action On Intruder, proceed to step 7.
4. To change the DisablePort setting to NoDisable, press the SPACE
bar to toggle the setting.
Local Management Supplement 3-9
Page 94

Chapter 3: LM Security Screens for 2H23-50R/2H33-37R Devices
5. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SendTrap field.
6. To change the SendTrap setting to NoTrap, press the SPACE bar to
toggle the setting.
7. To change the security on more than one connector, repeat steps 1
through 6 for each connector. Then proceed to step 8 to save all
settings at once.
8. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SAVE command.
9. Press ENTER. The message “SAVED OK” displays and all ports of
the connector are set to the selected operating mode.
NOTE
If LockedOnAddr is chosen as the Security State, the address
of the repeater ports must be configured in the Port Level
Security Configuration screen. Refer to Section 3.4.
3.4 PORT LEVEL SECURITY CONFIGURATION
SCREEN
The Port Level Security Configuration screen, Figure 3-4, is used to set
the security of each port of a selected connector.
To access the Port Level Security Configuration screen, use the arrow
keys to highlight the PORT LEVEL SECURITY CONFIGURATION
menu item on the Repeater Configuration Menu screen and press ENTER.
The Port Level Security Configuration screen displays.
3-10 Local Management Supplement
Page 95

Port Level Security Configuration Screen
Port Network Security State Action On Intruder Address
1 1
2 2 [NonSecure] [00-00-00-00-00-00]
3 1 [LockedOnAddr] [DisablePort] [SendTrap] [xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx]
4 2 [NonSecure] [00-00-00-00-00-00]
5 2 [NonSecure] [00-00-00-00-00-00]
6 2 [NonSecure] [00-00-00-00-00-00]
7 2 [NonSecure] [00-00-00-00-00-00]
8 2 [NonSecure] [00-00-00-00-00-00]
9 2 [NonSecure] [00-00-00-00-00-00]
10 2 [NonSecure] [00-00-00-00-00-00]
11 2 [NonSecure] [00-00-00-00-00-00]
12 2 [NonSecure] [00-00-00-00-00-00]
SAVE CONNECTOR #: [1] EXIT RETURN
Figure 3-4 Port Level Security Configuration Screen
[LockOnNext] [DisablePort] [SendTrap]
2276_113w
NOTE
have changed, such as from LockOnNext to LockedOnAddr,
the screen must be exited (Return may be used) and
re-entered to see the changed state.
The following section defines the fields on the Port Level Security
Configuration screen.
The screen will not refresh automatically. To check if the states
Port (Read-only)
Indicates the repeater port on the connector selected in the
CONNECTOR # field. Refer to Table 3-4 for the connector
(CONN)/repeater port relationship on the device.
Table 3-4 CONN/Repeater Port Relationship
2H23-50R 2H33-37R
CONN 1 = Repeater ports 1 – 12 CONN 1 = Repeater ports 1 – 12
CONN 2 = Repeater ports 13 – 24 CONN 2 = Repeater ports 13 – 24
CONN 3 = Repeater ports 25 – 36 CONN 3 = Repeater ports 25 – 36
CONN 4 = Repeater ports 37 – 48
Local Management Supplement 3-11
Page 96

Chapter 3: LM Security Screens for 2H23-50R/2H33-37R Devices
Network (Read-only)
Indicates the network to which the port is currently attached. Table 3-5
shows the association between the connector (CONN) and Network on
the device.
Table 3-5 CONN/Network Organization
2H23-50R 2H33-37R
CONN 1 = Network 1, 10 Mbps
Network 2, 100 Mbps
CONN 2 = Network 3, 10 Mbps
Network 4, 100 Mbps
CONN 3 = Network 5, 10 Mbps
Network 6, 100 Mbps
CONN 4 = Network 7, 10 Mbps
Network 8, 100 Mbps
Security State (Selectable)
CONN 1 = Network 1, 10 Mbps
Network 2, 100 Mbps
CONN 2 = Network 3, 10 Mbps
Network 4, 100 Mbps
CONN 3 = Network 5, 10 Mbps
Network 6, 100 Mbps
HSIM = Port 7
Used to select the state of security for frames received by a specific port
on the connector. The states are as follows:
• NonSecure – Allows the ports on the connector to receive all frames.
The source address of received frames is not examined and the frames
are processed in a non secure state.
• LockOnNext – The next frame received by each port is examined to
learn its source address. After the source address of a frame is learned
on a port, it is now locked on that address and only those frames
received with that same source address are allowed on that port. All
frames received that do not have that same source address will cause
the device to execute the actions selected in the Action On Intruder
field.
• LockedOnAddr – The device locks down on the address that is
currently configured in the Port Level Security Configuration screen
(if one is entered) or on the source address of the currently received
frame. If an address was not configured or received, the de vice defaults
to the locked on address of “00-00-00-00-00-00” as indicated by
“XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX” in the address field shown in Figure 3-4.
3-12 Local Management Supplement
Page 97

Port Level Security Configuration Screen
When a port is locked on an address, the device executes the actions
selected in the Action On Intruder field when a frame is received that
violates security.
Action On Intruder (Toggle)
Used to select the actions taken for the selected security state. There are
two fields to select the actions. Both toggle to activate or deactivate the
action.
• DisablePort/NoDisable – DisablePort causes the switch to turn off the
port that had a security violation. With NoDisable set, the port is not
turned off.
• SendTrap/NoT rap – SendTrap causes the switch to send an SNMP trap
when a port detects a security violation. With NoTrap set, no SNMP
trap is sent.
Address (Modifiable)
Used to enter the source MAC address for the LockedOnAddr security
state setting. Once a secure address is defined on a port, only those frames
received with that same source address are allo wed on that port. Any other
frame detected with a different address is considered as an intruder,
causing the actions selected in the Action On Intruder field to be e xecuted.
When the security state setting is NonSecure, the field displays the source
address of the last frame.
The Address column will display the MAC address used for the security
states, NonSecure or LockedOnAddr. This could be the last address seen
(NonSecure) or the address manually entered for the LockedOnAddr
security state.
CONNECTOR # (Selectable)
This command field selects the front panel connector to which the port
security settings will be applied.
3.4.1 Setting the Port Level Security
To set the security for each repeater port on a connector, proceed as
follows:
1. Use the arrow keys to highlight the CONNECTOR # field.
Local Management Supplement 3-13
Page 98

Chapter 3: LM Security Screens for 2H23-50R/2H33-37R Devices
2. Use the SPACE bar to step to the appropriate connector (CONN)
number.
3. Press ENTER to display the 12 repeater ports of the selected
connector.
4. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Security State field for the desired
repeater port.
5. Use the SPACE bar to step to the appropriate security level
(NonSecure, LockOnNext, or LockedOnAddr).
6. If the security level chosen causes the DisablePort and SendTrap
fields to display under Action On Intruder, use the arrow keys to
highlight the DisablePort field.
If the security level chosen does not cause the fields to display under
Action On Intruder, proceed to step 10.
7. To change the DisablePort setting to NoDisable, press the SPACE
bar to toggle the setting.
8. Use the arrow keys to highlight the SendTrap field.
9. To change the setting to NoTrap, press the SPACE bar to toggle the
setting.
10. If the security state selected is LockedOnAddr, use the arrow keys to
highlight the Address field for the repeater port. Otherwise go to
step 12.
11. Enter the MAC address to lock on, using the numerical keys. When
entering the address, it is not necessary to include dashes in the
number.
12. To change the security on more than one repeater port, repeat steps 4
through 11 for each port.
13. After configuring the repeater ports, use the arrow keys to highlight
the SAVE command.
14. Press ENTER. The message “SAVED OK” displays and all
configured settings for all repeater ports of the connector are saved.
15. If the ports on another connector need to be configured, repeat steps 1
through 14.
3-14 Local Management Supplement
Page 99

CHAPTER 4
GENERIC ATTRIBUTE REGISTRATION
PROTOCOL (GARP)
This appendix provides the following information:
• Describes the switch operation when its ports are configured to operate
under the Generic Attribute Registration Protocol (GARP)
applications – GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) and/or
GARP Multicast Registration Protocol (GMRP).
• Describes the GARP Configuration screen and how to use it to
enable/disable GVRP and GMRP on the switch and set each port to
operate as a GVRP- and/or GMRP-aware port.
• Describes the GMRP Configuration screen and how to use it to select
individual ports, or all of the ports, and apply one of four modes of
operation according to, or regardless of, the multicast address
registration.
4.1 GARP SWITCH OPERATION
Some or all ports on the switch may be activated to operate under the
GARP applications, GVRP and/or GMRP. A description of how GVRP
and GMRP handle frames under GARP is described in Section 4.1.1 and
Section 4.2.
4.1.1 GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP)
The process of the forwarding decision and tagging frames is the same as
for 802.1Q as described in the Cabletron Systems 802.1Q VLAN User’s
Guide. However, the GVRP protocol frames will not have a tag even
when transmitted out a 1Q Trunk Port.
Local Management Supplement 4-1
Page 100

Chapter 4: Generic Attribute Registration Protocol (GARP)
The purpose of GVRP is to dynamically create VLANs across a switched
network. When a VLAN is declared, the information is transmitted out
GVRP configured ports on the switch in a GARP formatted frame using
the GVRP multicast MAC address (01-80-C2-00-00-21). A switch that
receives this frame, examines the frame, and extracts the VLAN IDs.
GVRP then creates the VLANs and adds the receiving port to its tagged
member list for the extracted VLAN ID(s). The information is then
transmitted out the other GVRP configured ports of the switch. Figure 4-1
shows an example of how VLAN blue from end station A would be
propagated across a switch network.
In Figure 4-1, Switch 4, port 1 is registered as being a member of VLAN
Blue and then declares this fact out all its ports (2 and 3) to Switch 1 and
Switch 2. These two switches register this in the Port VLAN Lists of the
ports (Switch 1, port 1 and Switch 2 Port 1) that received the frames with
the information. Switch 2, which is connected to Switch 3 and Switch 5
declares the same information to those two switches and the Port VLAN
List of each port is updated with the new information, accordingly.
3
D
Switch 1 Switch 2
RR
1
2
3
D
Switch 4 Switch 5
R
1
End
Station A
Figure 4-1 Example of VLAN Propagation via GVRP
R
= Port registered as a member of VLAN Blue
D
= Port declaring VLAN Blue
D
1
2
RD
1
R
Switch 3
1
2599_19
4-2 Local Management Supplement
 Loading...
Loading...