Burr Brown Corporation ADS7870EA-250, ADS7870EA-1K, ADS7870 Datasheet
1
®
ADS7870
®
ADS7870
©1999 Burr-Brown Corporation PDS-1539A Printed in U.S.A. December, 1999
FEATURES
● 16-BIT DYNAMIC RANGE
● PGA GAINS: 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 16, 20V/V
● 4-CHANNEL DIFFERENTIAL/8-CHANNEL
SINGLE ENDED MULTIPLEXER
● 2.048V OR 2.5V INTERNAL REFERENCE
● FAST SERIAL INTERFACE
● HIGH THROUGHPUT RATE: 52ksamples/s
● ERROR/OVERLOAD INDICATOR
●
2.7V TO 5.5V SINGLE-SUPPLY OPERATION
● 4-BIT DIGITAL I/O VIA SERIAL INTERFACE
● SSOP-28 PACKAGE
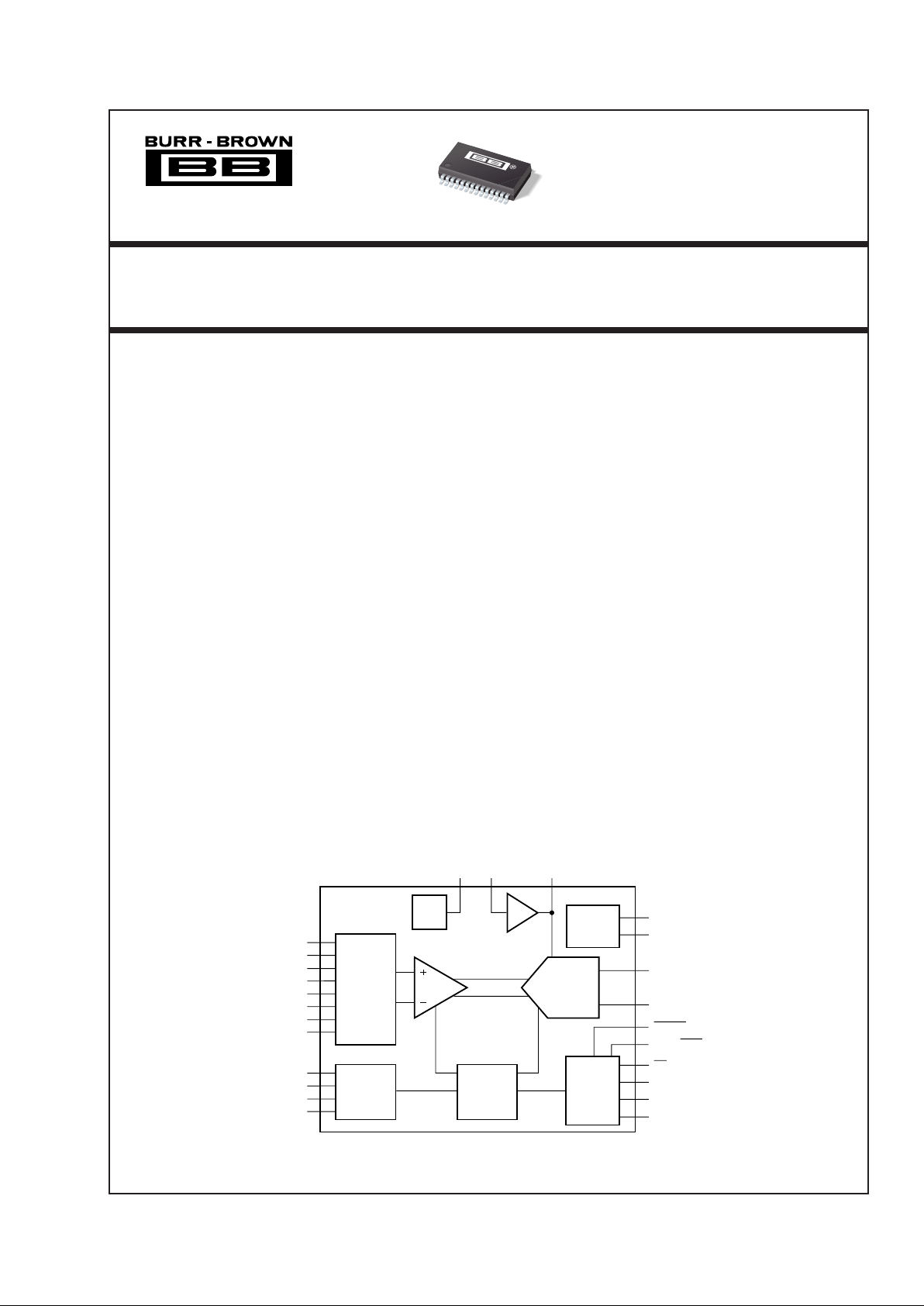
12-Bit ADC, MUX, PGA and Internal Reference
DATA ACQUISITION SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
The ADS7870
(1)
is a complete low-power data acquisition system on a single chip. It consists of a 4-channel
differential/8-channel single-ended multiplexer, precision programmable gain amplifier, 12-bit successive
approximation analog-to-digital converter and a precision voltage reference.
The programmable-gain amplifier provides high input
impedance, excellent gain accuracy, good commonmode rejection, and low noise.
For many low-level signals, no external amplification or
impedance buffering is needed between the signal
source and the A/D input.
APPLICATIONS
● PORTABLE/BATTERY POWERED
SYSTEMS
● LOW POWER INSTRUMENTATION
● LOW POWER CONTROL SYSTEMS
●
SMART SENSOR APPLICATIONS
International Airport Industrial Park • Mailing Address: PO Box 11400, Tucson, AZ 85734 • Street Address: 6730 S. Tucson Blvd., Tucson, AZ 85706 • Tel: (520) 746-1111
Twx: 910-952-1111 • Internet: http://www.burr-brown.com/ • Cable: BBRCORP • Telex: 066-6491 • FAX: (520) 889-1510 • Immediate Product Info: (800) 548-6132
ADS7870
REF
Serial
Interface
ADS7870
DIN
SCLK
CS
CONVERT
RESET
RISE/FALL
BUSY
DOUT
Clock
Divider
Oscillator
OSC ENABLE
CCLK
BUF
OUT
/REF
IN
BUF
IN
V
REF
12-Bit
A/D
BUF
MUX
8 Ch
(4 Ch Diff.)
Analog
Inputs
Digital
I/O
Registers
and
Control
I/O 0
I/O 1
I/O 2
I/O 3
PGA
The offset voltage of the PGA is auto zeroed. Gains of
1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 16 and 20V/V provide 16-bit dynamic
range and allow signals as low as 125mV to produce full
scale digital outputs.
The ADS7870 contains an internal reference, which is
trimmed for high initial accuracy and stability vs temperature. Drift is typically 10ppm/°C. An external reference can be used in situations where multiple ADS7870s
share a common reference.
The serial interface allows the use of SPI™, QSPI™,
Microwire™, and 8051-family protocols, without glue
logic.
NOTE: (1) Patent Pending.
For most current data sheet and other product
information, visit www.burr-brown.com
2
®
ADS7870
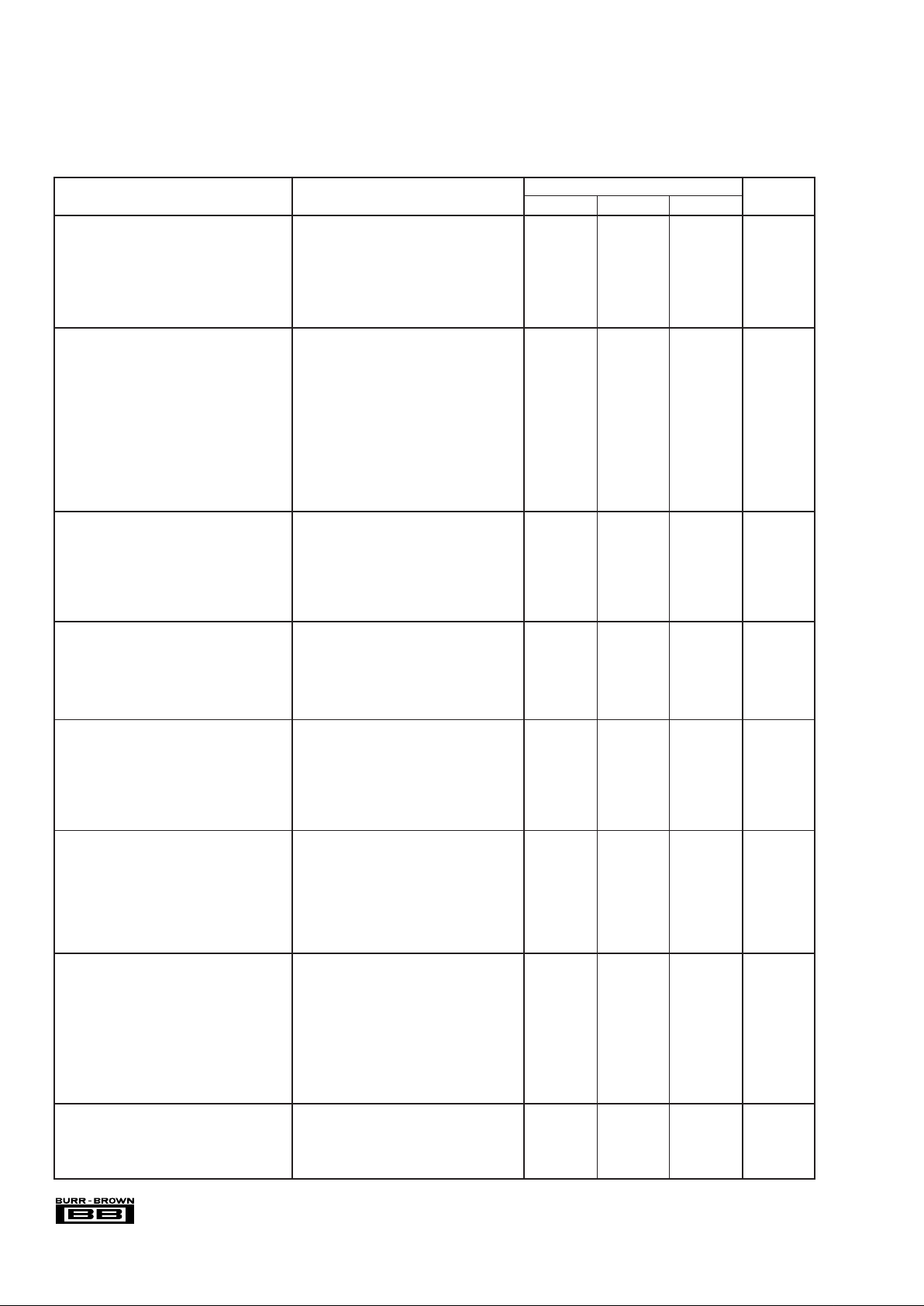
ADS7870EA
PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
ANALOG INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Input Voltage Range (LNx inputs) Linear Operation –0.2 V
DD
+ 0.2 V
Input Capacitance
(2)
4 to 9.7 pF
Input Impedance
(2)
Common-Mode 6MΩ
Differential 7MΩ
Channel-to-Channel Crosstalk V
IN
= 2Vp-p, 60Hz
(3)
100 dB
Multiplexer Leakage Current 100 pA
STATIC ACCURACY
Resolution 12 Bits
No Missing Codes G = 1 to 20V/V 12 Bits
Integral Linearity Error G = 1 to 20V/V ±1 ±2.5 LSB
Differential Linearity Error G = 1 to 20V/V ±0.5 LSB
Offset Error G = 1 to 20V/V ±1 ±6 LSB
Full Scale (Gain) Error
Ratiometric Configuration or External Ref
(4)
G = 1 to 10V/V ±0.2 %FSR
G = 16 and 20V/V ±0.25 %FSR
Internal Reference G = 1 to 10V/V ±0.35 %FSR
G = 16 and 20V/V ±0.4 %FSR
DC Common-Mode Rejection, RTI V
IN
= –0.2V to 5.2V, G = 20 V/V 92 dB
Power Supply Rejection, RTI V
DD
= 5V ±10%, G = 20 V/V 86 dB
DYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS
Throughput Rate, Continuous Mode One Channel 52 ksamp/s
Address Mode Different Channels 52 ksamp/s
External Clock, CCLK
(5)
0.100 20 MHz
Internal Oscillator Frequency 2.5 MHz
Serial Interface Clock (SCLK) 20 MHz
Data Set-Up Time 10 ns
Data Hold Time 10 ns
DIGITAL INPUTS
Logic Levels
Low Level Input Voltage, V
IL
0.8 V
High Level Input Voltage, V
IH
VDD ≤ 3.6V 2 V
V
DD
> 3.6V 3 V
Low Level Input Current, I
IL
1 µA
High Level Input Current, I
IH
1 µA
DIGITAL OUTPUTS
Data Coding Binary Two’s Complement
V
OL
I
SINK
= 5mA 0.4 V
I
SINK
= 16mA 0.8 V
V
OH
I
SOURCE
= 0.5mA VDD – 0.4 V
I
SOURCE
= 5mA 4.6 V
I
SOURCE
= 5mA, DOUT pin High-Z State, V
OUT
= 0V to V
DD
1 µA
Output Capacitance 5pF
VOLTAGE REFERENCE
BUF
IN
Input Voltage Range Input to Buffer Amplifier 0.9 VDD – 0.2 V
Input Impedance 10
12
|| 3 Ω || pF
BUF
OUT
/REF
IN
(6), (7)
Output Voltage Accuracy V
REF
= 2.048V and 2.5V ±0.05% ±0.25 %
vs Temperature T
A
= –40°C to 85°C 10 50 ppm/°C
Bandgap Voltage Reference 1.15 V
Short-Circuit Current 20 mA
POWER SUPPLY REQUIREMENTS
Specified Voltage Range, V
DD
5V
Operating Voltage Range 2.7 5.5 V
Power Supply Current
(6)
1kHz Sample Rate REF and BUF On, Internal Oscillator on 0.450 mA
50kHz Sample Rate REF and BUF On, External CCLK 1.2 1.7 mA
Power Down REF and BUF Off 1 µA
Power Dissipation
(6)
1kHz Sample Rate REF and BUF On, Internal Oscillator on 2.25 mW
50kHz Sample Rate REF and BUF On, External CCLK 6 8.5 mW
Power Down REF and BUF Off 5 µW
TEMPERATURE RANGE
Specified Range –40 +85 °C
Operating Range –55 +125 °C
Storage Range –65 +150 °C
Thermal Resistance,
θ
JA
150 °C/W
SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE TOTAL SYSTEM
(1)
(See next section for specifications for each function in the ADS7870)
At T
A
= +25°C, VDD = +5.0V, V
REF
= 2.5V connected to BUFIN (using internal reference), 2.5MHz CCLK and 2.5MHz SCLK, unless otherwise noted.
3
®
ADS7870
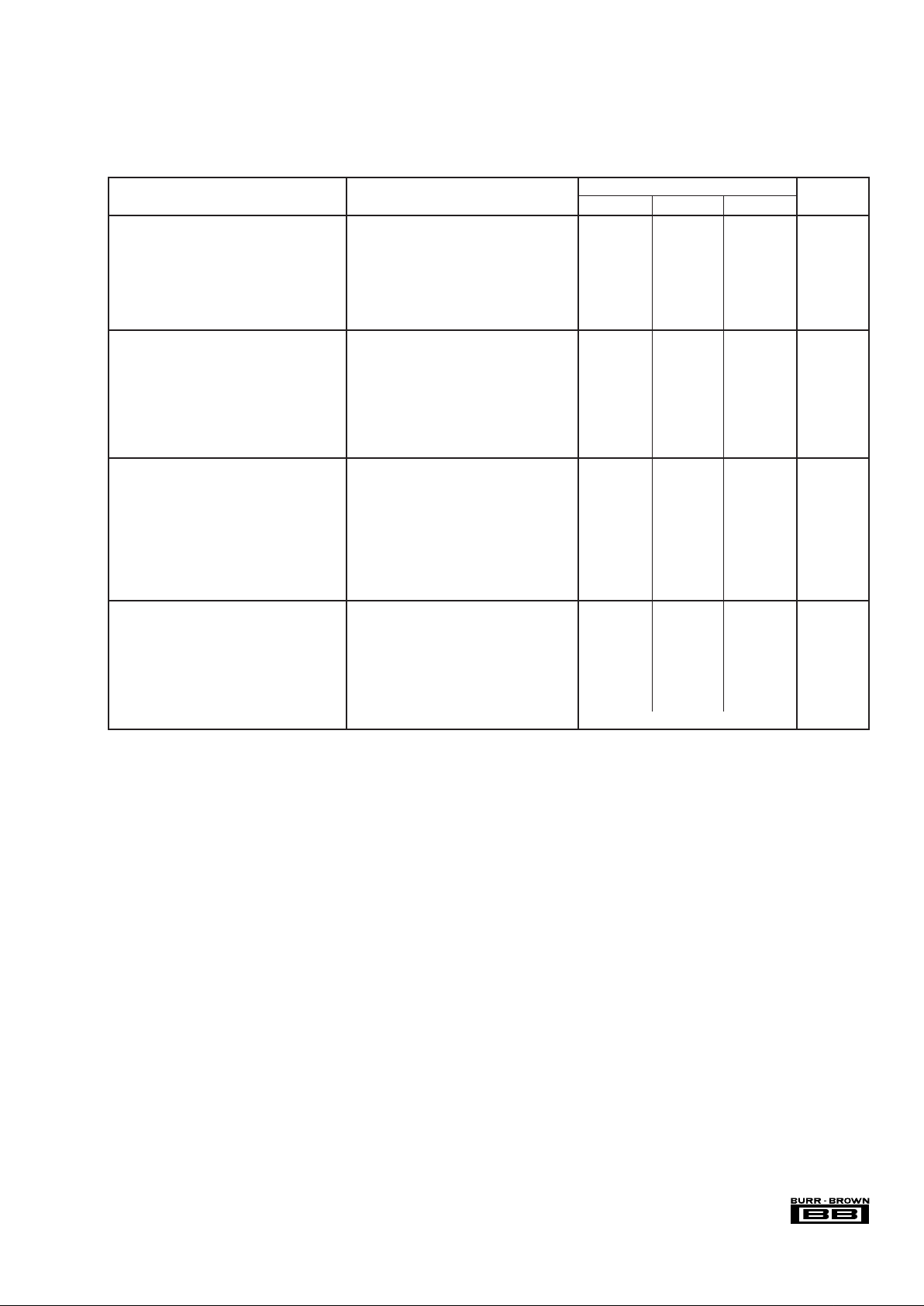
SPECIFICATIONS FOR INTERNAL FUNCTIONS
(1)
(See previous section for the TOTAL DATA ACQUISITION SYSTEM)
At T
A
= +25°C, VDD = +5.0V, V
REF
= 2.5V connected to BUFIN (using internal reference), 2.5MHz CCLK and 2.5MHz SCLK, unless otherwise noted.
The information provided herein is believed to be reliable; however, BURR-BROWN assumes no responsibility for inaccuracies or omissions. BURR-BROWN assumes
no responsibility for the use of this information, and all use of such information shall be entirely at the user’s own risk. Prices and specifications are subject to change
without notice. No patent rights or licenses to any of the circuits described herein are implied or granted to any third party. BURR-BROWN does not authorize or warrant
any BURR-BROWN product for use in life support devices and/or systems.
ADS7870EA
PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNITS
MULTIPLEXER
ON Resistance 500 Ω
OFF Resistance 1GΩ
OFF Channel Leakage Current V
LNx
= 5.2V
ON-Channel = 5.2V, OFF-Channel = 0V 100 pA
ON-Channel = 0V, OFF-Channel = 5.2V 100 pA
ON Channel Leakage Current ON-Channel = 5.2V, OFF-Channel = 0V 100 pA
ON-Channel = 0V, OFF-Channel = 5.2V 100 pA
PGA AMPLIFIER
Input Capacitance
(2)
4 to 9.7 pF
Input Impedance
(2)
Common-Mode 6MΩ
Differential 7MΩ
Offset Voltage 100 µV
Small-Signal Bandwidth 5/Gain MHz
Settling Time: 0.01% G = 1 0.3 µs
G = 20 6.4 µs
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
DC CHARACTERISTICS
Resolution 12 LSB
Integral Linearity Error 0.5 LSB
Differential Linearity Error 0.5 LSB
No Missing Codes 12 Bits
Offset Error REF
IN
= 2.5V 0.5 LSB
Full Scale (Gain) Error 0.02 %
Common-Mode Rejection, RTI of A/D 80 dB
Power Supply Rejection, RTI of ADS7870 External Reference, V
DD
= 5V ±10% 60 dB
PGA plus A/D CONVERTER
SAMPLING DYNAMICS f
CCLK
= 2.5 MHz, DF = 1
Throughput Rate 48 CCLK cycles 52 kHz
Conversion Time 12 CCLK cycles 4.8 µs
Acquisition Time 28 CCLK cycles 9.6 µs
Auto Zero Time 8 CCLK cycles 3.2 µs
Aperture Delay 36 CCLK cycles 12.8 µs
Small Signal Bandwidth 5 MHz
Step Response 1 Complete Conversion Cycle
NOTES:
(1) The SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE TOTAL SYSTEM are overall analog input-to-digital output specifications. The SPECIFICATIONS FOR INTERNAL
FUNCTIONS indicate the performance of the individual functions in the ADS7870.
(2) The ADS7870 uses switched capacitor techniques for the programmable gain amplifier and A/D converter. A characteristic of such circuits is that the input
capacitance at any selected LNx pin changes during the conversion cycle.
(3) One channel “on” with its inputs grounded. All other channels “off” with sinewave voltage applied to their inputs.
(4) Ratiometric configuration exists when the input source is configured such that changes in the reference cause corresponding changes in the input voltage. The
same accuracy applies when a perfect external reference is used.
(5) The CCLK is divided by the DF value specified by the contents of register ADC CONTROL Register, bits D0 and D1 to produce DCLK. The maximum value
of DCLK is 2.5MHz.
(6) REF and BUF contribute 190µA and 150 µA (950µW and 750µW) respectively. At initial power-up the default condition for both REF and BUF functions is power
off. They can be turned on under software control by writing a “1” to D3 and D2 of the REF/OSCILLATOR CONTROL Register.
(7) For V
DD
< 3.0V, V
REF
= 2.5V not usable.

4
®
ADS7870
ELECTROSTATIC
DISCHARGE SENSITIVITY
This integrated circuit can be damaged by ESD. Burr-Brown
recommends that all integrated circuits be handled with
appropriate precautions. Failure to observe proper handling
and installation procedures can cause damage.
ESD damage can range from subtle performance degradation
to complete device failure. Precision integrated circuits may
be more susceptible to damage because very small parametric
changes could cause the device not to meet its published
specifications.
Supply Voltage, VDD........................................................................... 5.5V
Analog Inputs:
Input Current, Momentary ........................................................... 100mA
Continuous ............................................................. 10mA
Input Voltage ................................................ V
DD
+ 0.5V to Gnd – 0.5V
Operating Temperature .................................................. –55°C to +125°C
Storage Temperature .....................................................–65°C to +150°C
Junction Temperature .................................................................... +150°C
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) ............................................... +300°C
NOTE: (1) Stresses above these ratings may cause permanent damage.
Exposure to absolute maximum conditions for extended periods may degrade
device reliability.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
(1)
PACKAGE SPECIFIED
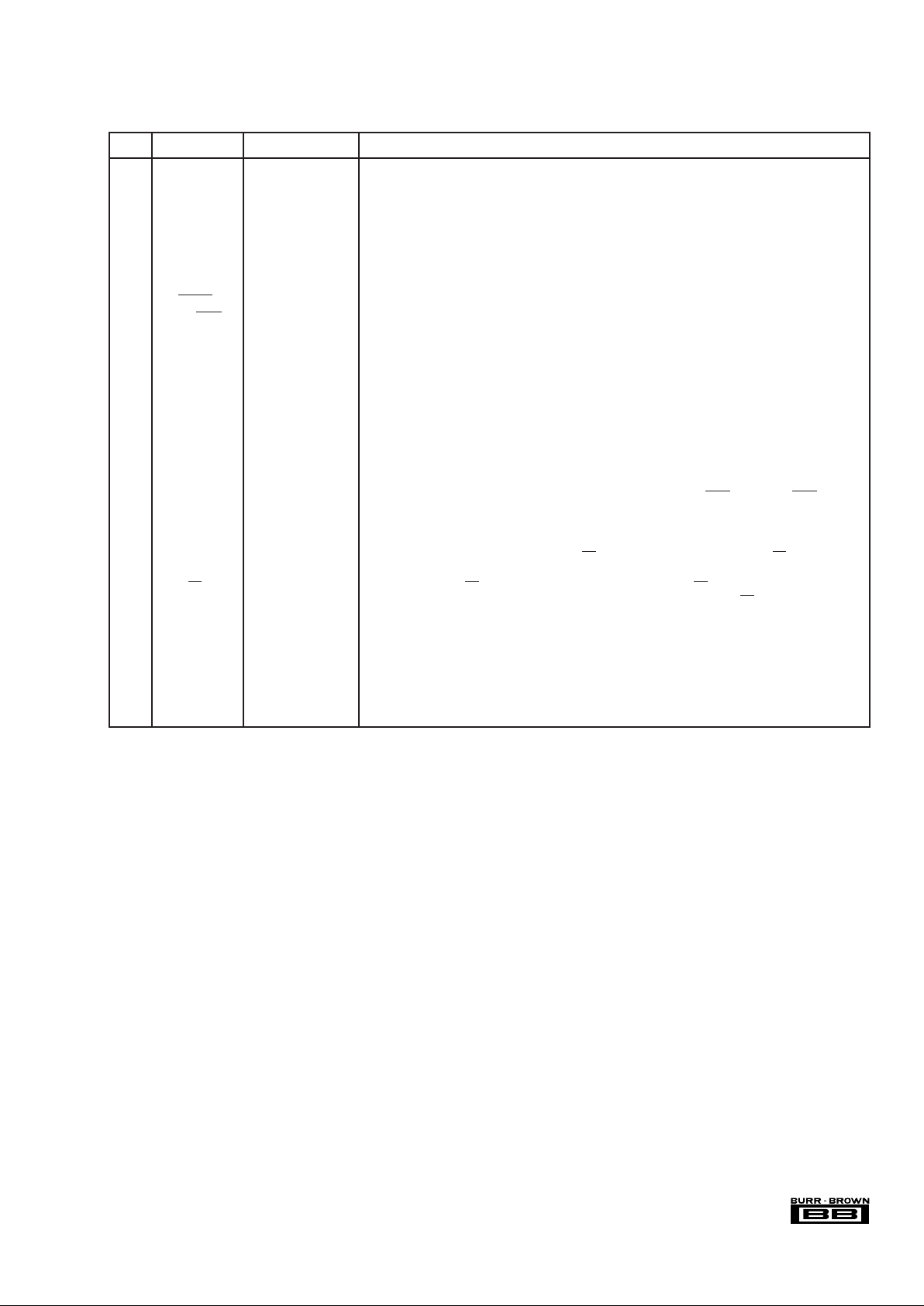
DRAWING TEMPERATURE PACKAGE ORDERING TRANSPORT
PRODUCT PACKAGE NUMBER RANGE MARKING NUMBER(1) MEDIA
ADS7870EA SSOP-28 Surface Mount 324 –40°C to +85°C ADS7870EA ADS7870EA Rails
ADS7870EA SSOP-28 Surface Mount 324 –40°C to +85°C ADS7870EA ADS7870EA/250 Tape and Reel
"""""ADS7870EA/1K Tape and Reel
NOTES: (1) Models with a slash (/) are available only in Tape and Reel in the quantities indicated (e.g., /1K indicates 1000 devices per reel). Ordering 1000 pieces
of “ADS7870EA/1K” will get a single 1000-piece Tape and Reel. For detailed Tape and Reel mechanical information, refer to Appendix B of Burr-Brown IC Data
Book.
PACKAGE/ORDERING INFORMATION
BUF
OUT
/REF
IN
BUF
IN
V
REF
GND
V
DD
CS
DOUT
DIN
SCLK
CCLK
OSC ENABLE
BUSY
CONVERT
NC
LN0
LN1
LN2
LN3
LN4
LN5
LN6
LN7
RESET
RISE/FALL
I/O0
I/O1
I/O2
I/O3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
ADS7870
PIN CONFIGURATION
Top View SSOP
5
®
ADS7870
PIN # NAME I/O DESCRIPTION
1 LN 0 Analog Input MUX Input Line 0
2 LN 1 Analog Input MUX Input Line 1
3 LN 2 Analog Input MUX Input Line 2
4 LN 3 Analog Input MUX Input Line 3
5 LN 4 Analog Input MUX Input Line 4
6 LN 5 Analog Input MUX Input Line 5
7 LN 6 Analog Input MUX Input Line 6
8 LN 7 Analog Input MUX Input Line 7
9 RESET Digital Input Master Reset zero’s all registers.
10 RISE/FALL Digital Input
Sets the active edge for SCLK. “0” sets SCLK active on falling edge. “1” sets SCLK active on rising edge.
11 I/O 0 Digital Input/Output Digital Input or Output signal
12 I/O 1 Digital Input/Output Digital Input or Output signal
13 I/O 2 Digital Input/Output Digital Input or Output signal
14 I/O 3 Digital Input/Output Digital Input or Output signal
15 NC No Connection Do not connect to this pin.
16 CONVERT Digital Input “0” to “1” transition starts a conversion cycle.
17 BUSY Digital Output “1” indicates converter is busy
18 OSC ENABLE Digital Input “0” sets CCLK as input, “1” sets CCLK as output and turns oscillator on.
19 CCLK Digital Input/Output If OSC ENABLE = “1” then Internal Oscillator is output to this pin. If OSC ENABLE = “0” then this is
the input pin for an external conversion clock.
20 SCLK Digital Input Serial Data Input/Output Transfer Clock. Active edge set by the RISE/FALL pin. If RISE/FALL is low,
SCLK is active on the falling edge.
21 DIN Digital Input Serial Data Input. In the 3-wire mode, this pin is used for serial data input. In the 2-wire mode serial
data, output appears on this pin as well as the DOUT pin.
22 DOUT Digital Output Serial Data Output. This pin is driven when CS is low and is high impedance when CS is high. This
pin behaves the same in both 3-wire and 2-wire modes.
23 CS Digital Input Chip Select. When CS is low the serial interface is enabled. When CS is high the serial interface is
disabled, the DOUT pin is high impedance, and the DIN pin is an input. The CS pin only effects the
operation of the serial interface. It does not directly enable/disable the operation of the signal
conversion process.
24 V
DD
Power Power Supply Voltage, +2.7V to +5.5V.
25 GND Power Power Supply Ground.
26 V
REF
Analog Output 2.048V/2.5V On-Chip Voltage Reference
27 BUF
IN
Analog Input Input to Reference Buffer Amplifier
28 BUF
OUT
/REFINAnalog Output/Input Output from Reference Buffer Amplifier and Reference Input to ADC.
PIN ASSIGNMENTS
6
®
ADS7870
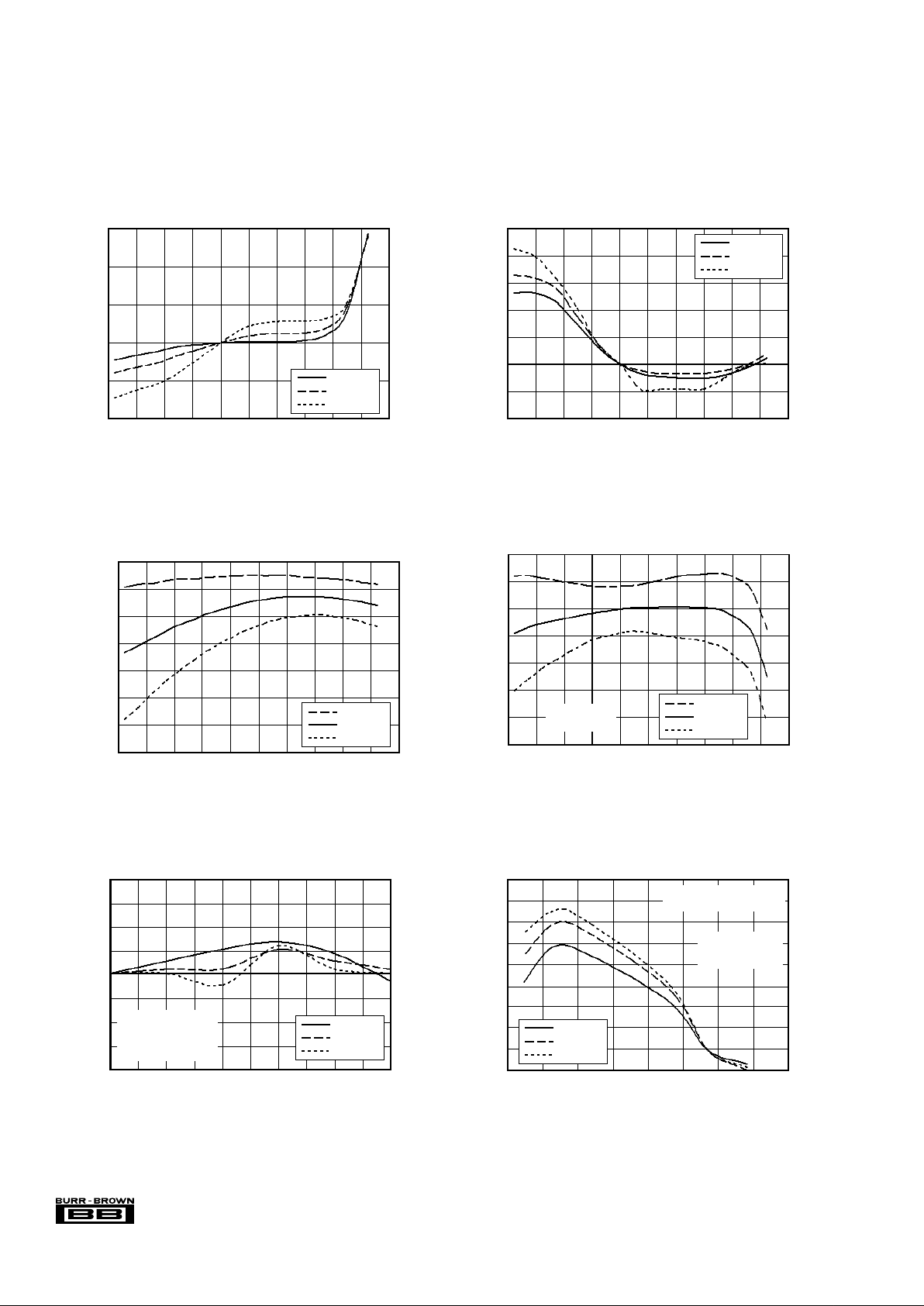
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CURVES
At TA = +25°C, VDD = +5.0V, V
REF
= 2.5V connected to BUFIN (using internal reference), 2.5MHz CCLK and 2.5MHz SCLK, unless otherwise noted.
15
10
5
0
–5
–10
Error (LSB)
–60 –40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
Temperature (°C)
GAIN ERROR vs TEMPERATURE
Gain= 1
Gain = 8
Gain = 20
10
8
6
4
3
0
–2
–4
Output Offset Error (LSB)
–60 –40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
Temperature (°C)
OUTPUT OFFSET ERROR vs TEMPERATURE
Gain= 1
Gain = 8
Gain = 20
2.55
2.50
2.45
2.40
2.35
2.30
2.25
2.20
CCLK (MHz)
–60 –40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
Temperature (°C)
INTERNAL OSCILLATOR FREQUENCY
vs TEMPERATURE
+3 Sigma
Avg
–3 Sigma
0.4
0.2
0.0
–0.2
–0.4
–0.6
–0.8
–1.0
V
REF
Error (% )
–60 –40 –20 0 20 40 60 00 100 120 140
Temperature (°C)
VOLTAGE REFERENCE ERROR
vs TEMPERATURE
V
REF
= 2.048V
or 2.5V
+3 Sigma
V
REF
–3 Sigma
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
–0.5
–1
–1.5
–2
Output Offset Error (LSB)
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5
Common-Mode Voltage (V)
OUTPUT OFFSET ERROR
vs COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE
1 LSB =
–72dB for Gain = 1
–98dB for Gain = 20
Gain= 1
Gain = 10
Gain = 20
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
–1
Output Offset Error (LSB)
2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6
V
DD
(V)
OUTPUT OFFSET ERROR
vs POWER SUPPLY VOLTAGE
4 LSB =
86dB (Gain = 20)
60dB (Gain = 1)
50kS/s, CCLK = 2.5MHz,
V
REF
= 2.048V
Gain= 1
Gain = 10
Gain = 20
7
®
ADS7870
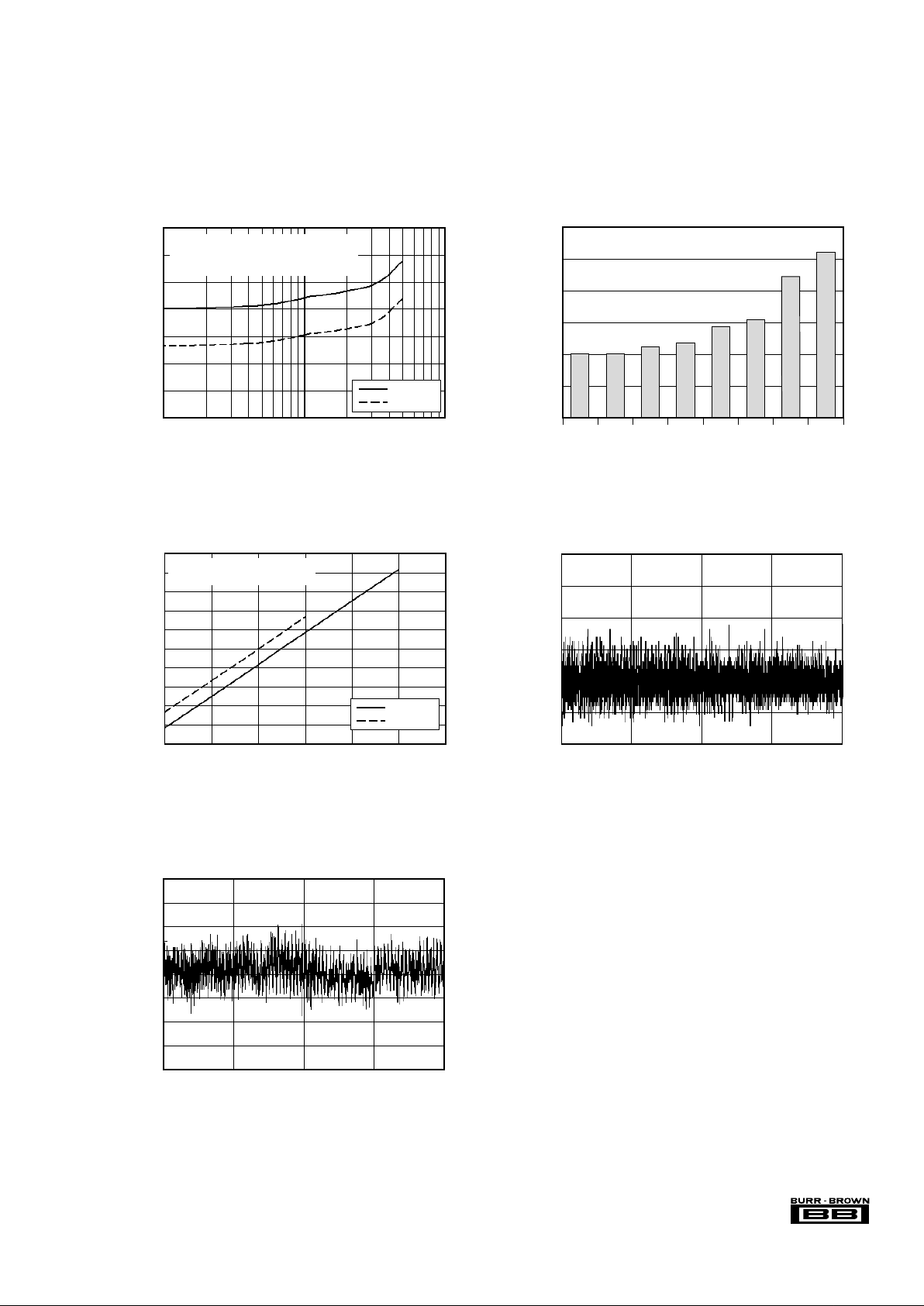
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CURVES (cont.)
At TA = +25°C, VDD = +5.0V, V
REF
= 2.5V connected to BUFIN (using internal reference), 2.5MHz CCLK and 2.5MHz SCLK, unless otherwise noted.
1.4
1.2
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
Quiescent Current (mA)
1 10 100
Sample Rate (kS/s)
QUIESCENT CURRENT vs SAMPLING RATE
V
REF
and Buffer ON, Oscillator OFF
Serial Data clocked during the 48 clock
count conversion cycle, CCLK = SCLK
VDD = 5V
V
DD
= 3V
6.0
5.0
4.0
3.0
2.0
1.0
0
Peak-to-Peak Output Noise (LSB)
12458 201610
Gain
OUTPUT NOISE vs GAIN
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
–0.1
–0.2
–0.3
–0.4
Input Bias Current (µA)
0123456
Input Voltage (V)
INPUT BIAS CURRENT vs INPUT VOLTAGE
VDD = 5V
V
DD
= 3V
Input Impedance Inversly proportional
to Sampling Rate.
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
–0.5
–1.0
Error (LSB)
0
1000
2000
3000
4096
Output Code
DIFFERENTIAL LINEARITY ERROR
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
–0.5
–1.0
–1.5
–2.0
Error (LSB)
0
1000
2000
3000
4096
Output Code
INTEGRAL LINEARITY ERROR

8
®
ADS7870
OVERVIEW
The ADS7870 is a complete data acquisition device composed of an input analog multiplexer (MUX), a programmable gain amplifier (PGA) and an analog-to-digital converter (A/D). Four lines of digital input/output (I/O) are also
provided. Additional circuitry provides support functions
including conversion clock, voltage reference, and serial
interface for control and data retrieval.
Control and configuration of the ADS7870 is accomplished
by command bytes written to internal registers through the
serial port. Command register device control includes MUX
channel selection, PGA gain, A/D start conversion command, and I/O line control. Command register configuration
control includes internal voltage reference setting and oscillator control.
Operational modes and selected functions can be activated
by digital inputs at corresponding pins. Pin settable configuration options include SCLK active-edge selection, master
reset, and internal oscillator clock enable.
The ADS7870 has eight analog-signal input pins, LN0
through LN7. These pins are connected to a network of
analog switches (the “MUX” block in Figure 1). The inputs
can be configured as 8 single ended or 4 differential inputs.
The four general-purpose digital I/O pins (I/O3 through
I/O0) can be made to function individually as either digital
inputs or digital outputs. These pins give the user access to
four digital I/O pins through the serial interface without
having to run additional wires to the host controller.
The programmable gain amplifier (PGA) provides gains of
1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 16, and 20V/V.
The 12-bit A/D converter in the ADS7870 is a successive
approximation type. The output of the converter is 2’s
complement format and can be read MSB first or LSB first.
The ADS7870’s internal voltage reference can be software
configured for output voltages of 1.15V, 2.048V or 2.5V.
The reference circuit is trimmed for high initial accuracy and
low temperature drift. A separate buffer amplifier is provided to buffer the high impednace V
REF
output.
The voltage reference, PGA, and A/D converter use the
conversion clock (CCLK) and signals derived from it. CCLK
can be either an input or output signal. The ADS7870 can
divide the CCLK signal by a constant before it is applied to
the A/D converter or PGA. This allows a higher frequency
system clock to be used to control the A/D converter
operation. Division factors (DF) of 1, 2, 4 and 8 are available. The signal that is actually applied to the PGA and
A/D converter is DCLK, where DCLK = CCLK/DF.
The ADS7870 is designed so that its serial interface can be
conveniently used with a wide variety of micro-controllers.
It has four conventional serial interface pins: SCLK (serial
data clock), DOUT (serial data out), DIN (serial data in,
which may be set bi-directional in some applications), and
CS (chip select function).
The ADS7870 has ten internal user accessible registers
which are used in normal operation to configure and control
the device (see Table II, Register Address Map).
REF
Serial
Interface
ADS7870
DIN
SCLK
CS
CONVERT
RESET
RISE/FALL
BUSY
DOUT
Clock
Divider
Oscillator
OSC ENABLE
CCLK
BUF
OUT
/REF
IN
BUF
IN
V
REF
282726
12-Bit
A/D
BUF
MUX
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
19
18
17
16
9
10
23
20
21
22
LN0
LN1
LN2
LN3
LN4
LN5
LN6
LN7
11
12
13
14
Digital
I/O
Registers
and
Control
I/O 0
I/O 1
I/O 2
I/O 3
V
DD
24
PGA
Gnd
25
FIGURE 1. Basic Circuit Diagram.

9
®
ADS7870
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
MULTIPLEXER
The ADS7870 has eight analog-signal input pins, LN0
through LN7. These pins are connected to a network of
analog switches (the “MUX” block in Figure 1). The switches
are controlled by four bits in the Gain/Mux register.
LN0 through LN7 can be configured as 8 single ended inputs
or 4 differential inputs. Some mux combination examples
are shown in Figure 7. The differential polarity of the input
pins can be changed with the M2 bit in the MUX address.
This feature allows reversing the polarity of the conversion
result without having to physically reverse the input connections to the ADS7870.
For linear operation, the input signal at any of the LN0
through LN7 pins can range between GND – 0.2V and V
DD
+ 0.2V. The polarity of the differential signal can be changed
through commands written to Gain/Mux register, but each
line must remain within the linear input common mode
voltage range as described below.
Inputs LN0 through LN7 have ESD protection circuitry as
the first active elements on the chip. These contain protection diodes connected to VDD and GND that remain reverse
biased under normal operation. If input voltages are expected beyond the absolute maximum voltage range it is
necessary to add resistance in series with the input to limit
the current to 10mA or less.
CONVERSION CLOCK
The conversion clock (CCLK) and signals derived from it
are used by the voltage reference, the PGA, and the A/D
converter. The PGA and the A/D use the same clock signal.
These clocks are associated with the OSC ENABLE and
CCLK pins as well as the OSCE and OSCR bits in the
Ref/Oscillator Configuration Register (register 7). CCLK
can be either an input pin or an output pin. When the OSC
ENABLE pin is low (OSC ENABLE = “0”), the CCLK pin
is an input and the ADS7870 uses an applied external clock
for the conversion process. When OSC ENABLE = “1”, the
ADS7870 uses an internal 2.5MHz oscillator as the conversion clock. This clock signal appears as an output on the
CCLK pin.
The ADS7870 can be programmed to divide the CCLK
before it is applied to the A/D converter and PGA. This
allows a higher frequency system clock, such as the SCLK,
to be used synchronously to control the A/D converter
operation. The frequency division constant is controlled by
2 bits (CDF1 and CDF0) in the ADC Control Register.
Division factors (DF) of 1, 2, 4, and 8 are available. The
signal that is actually applied to the PGA and A/D is DCLK,
where DCLK = CCLK/DF.
The CCLK pin can be made either an input or an output and
is convenient in situations where several ADS7870s are used
in the same application. One ADS7870 can be made the
conversion clock master (CCLK made an output) and all the
other ADS7870s can be slaved to it (their pins made inputs).
This can potentially reduce A/D conversion errors caused by
clock and other systems noise.
The ADS7870 has both maximum and minimum DCLK
frequency constraints (DCLK = CCLK/DF). The maximum
DCLK is 2.5MHz. The minimum DCLK frequency applied
to the PGA, reference and A/D is 100kHz.
VOLTAGE REFERENCE AND BUFFER AMPLIFIER
The internally generated V
REF
of the ADS7870 is based on
a band-gap voltage reference. The ADS7870 uses a unique
(patent pending) switched capacitor implementation of the
band-gap reference. The circuit has curvature correction for
V
REF
drift. The reference may be software configured for
output voltages of 1.15V, 2.048V or 2.5V.
The amplifier inside the reference circuit has very limited
output current capability. A separate buffer amplifier must
be used to supply any load current. The internal buffer
amplifier can supply typically up to 20mA and sink up to
20µA. The temperature compensation of the onboard reference is adjusted with the reference buffer in the circuit.
Performance is specified in this configuration.
PROGRAMMABLE GAIN AMPLIFIER
The programmable gain amplifier (PGA) provides gains of
1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 16, and 20V/V. The PGA is a single supply,
rail-to-rail input, auto-zeroed, capacitor based instrumentation amplifier. PGA gain is set by bits G2 through G0 of
Register 4.
Register 2 is a read only register that is used to report any out
of range conditions at the PGA input or output during the
convert cycle. The logical “OR” of these signals is available
as the least significant bit of the A/D output register 0.
Testing bit D0 of the A/D output register will indicate out of
range conditions as described in the section which details the
register contents.
A/D CONVERTER
The 12-bit A/D converter in the ADS7870 is a successive
approximation type. The output of the converter is 2’s
complement format and can be read through the serial
interface MSB first or LSB first. A plot of Output Codes vs
Input Voltage is shown in Figure 2. With the input multiplexer configured for differential input the A/D output codes
range from –2048 for VIN = –V
REF
/G to 2047 for VIN =
(+V
REF
–1V
LSB
)/G. With the input multiplexer configured
for single-ended inputs the A/D output codes range from
0 to 2047 for VIN = 0 to (+V
REF
– 1V
LSB
)/G.
CONVERSION CYCLE
A conversion cycle requires 48 DCLK cycles (DCLK =
CCLK/DF). These signals are described in the Conversion
Clock section that follows.
Operation of the PGA requires 36 DCLK cycles. During the
PGA portion, the common mode voltage of the input source
 Loading...
Loading...