Burr Brown Corporation ADS7852YB-2K5, ADS7852YB-250, ADS7852Y-2K5, ADS7852 Datasheet
1
®
ADS7852
ADS7852
DESCRIPTION
The ADS7852 is an 8-channel, 12-bit analog-to-digital converter (A/D) complete with sample-and-hold,
internal 2.5V reference and a full 12-bit parallel output
interface. Typical power dissipation is 13mW at at
500kHz throughput rate. The ADS7852 features both
a nap mode and a sleep mode further reducing the
power consumption to 2mW. The input range is from
0V to twice the reference voltage. The reference voltage can be overdriven by an external voltage.
The ADS7852 is ideal for multi-channel applications
where low power and small size are critical. Medical
instrumentation, high-speed data acquisition and laboratory equipment are just a few of the applications that
would take advantage of the special features offered
by the ADS7852. The ADS7852 is available in an
TQFP-32 package and is fully specified and guaranteed over the –40°C to +85°C temperature range.
12-Bit, 8-Channel, Parallel Output
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
®
FEATURES
● 2.5V INTERNAL REFERENCE
● 8 INPUT CHANNELS
● 500kHz SAMPLING RATE
● SINGLE 5V SUPPLY
● ±1LSB: INL, DNL
● GUARANTEED NO MISSING CODES
● 70dB SINAD
● LOW POWER: 13mW
● TQFP-32 PACKAGE
APPLICATIONS
● DATA ACQUISITION
● TEST AND MEASUREMENT
● INDUSTRIAL PROCESS CONTROL
● MEDICAL INSTRUMENTS
©
1998 Burr-Brown Corporation PDS-1509C Printed in U.S.A. May, 2000
International Airport Industrial Park • Mailing Address: PO Box 11400, Tucson, AZ 85734 • Street Address: 6730 S. Tucson Blvd., Tucson, AZ 85706 • Tel: (520) 746-1111
Twx: 910-952-1111 • Internet: http://www.burr-brown.com/ • Cable: BBRCORP • Telex: 066-6491 • FAX: (520) 889-1510 • Immediate Product Info: (800) 548-6132
ADS7852
¤
For most current data sheet and other product
information, visit www.burr-brown.com
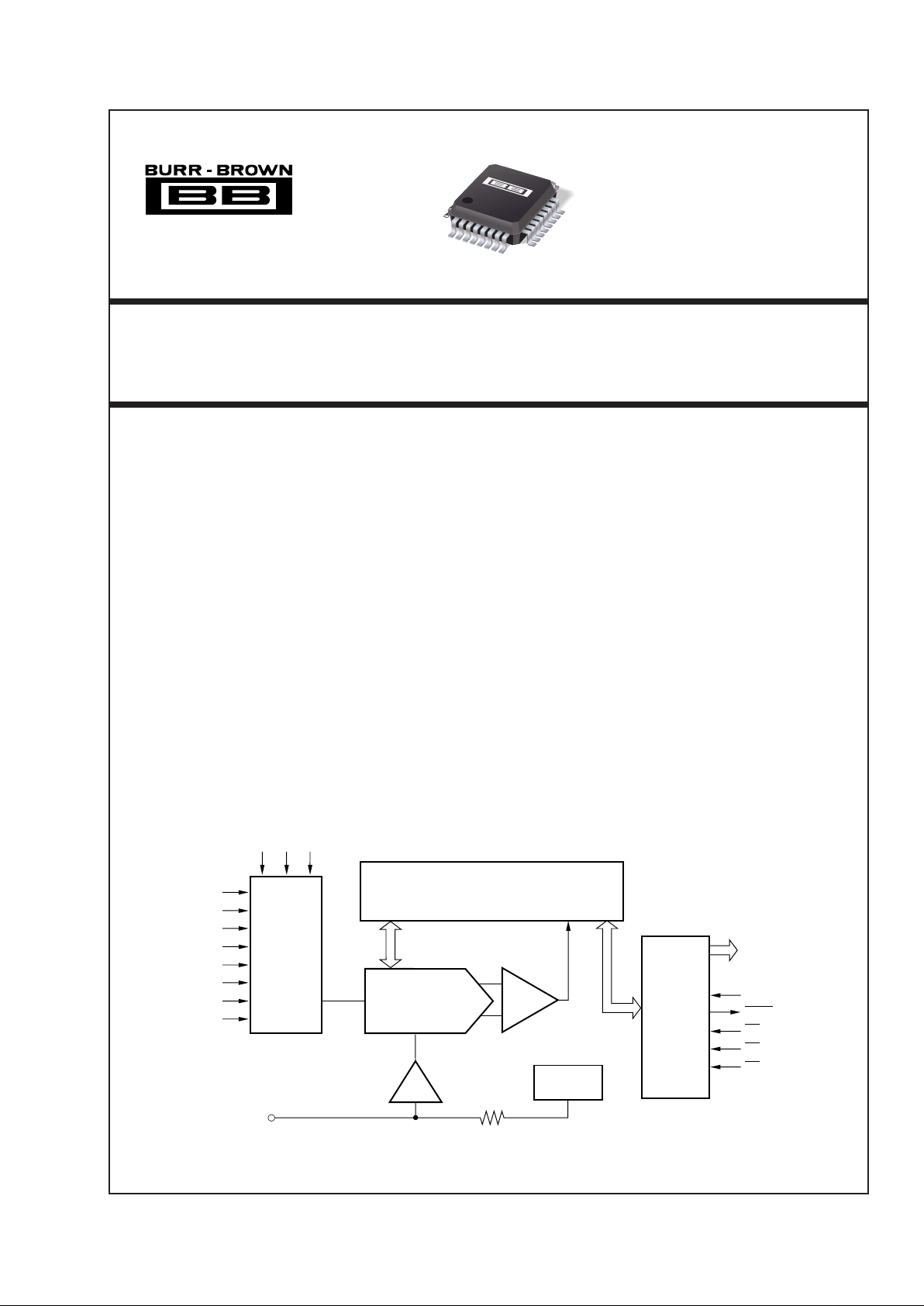
SAR
CDAC
ADS7852
Output
Latches
and
3-State
Drivers
Comparator
CLK
BUSY
WR
CS
RD
A0 A1 A2
8-Channel
MUX
Internal
+2.5V Ref
Buffer
V
REF
10kΩ
AIN0
AIN1
AIN2
AIN3
AIN4
AIN5
AIN6
AIN7
3-State
Parallel
Data Bus
2
®
ADS7852
SPECIFICATIONS
At TA = –40°C to +85°C, fS = 500kHz, f
CLK
= 16 • fS, and VSS = +5V, using internal reference, unless otherwise specified.
ADS7852Y ADS7852YB
PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX MIN TYP MAX UNITS
RESOLUTION 12 ✻ Bits
ANALOG INPUT
Input Voltage Range 0 5 ✻✻V
Input Impedance 5M ✻ Ω
Input Capacitance 15 ✻ pF
Input Leakage Current ±1 ✻ µA
DC ACCURACY
No Missing Codes 12 ✻ Bits
Integral Linearity Error ±2 ±1 LSB
(1)
Differential Linearity Error ±1 ±0.5 ±1 LSB
Offset Error ±2 ±5 ±1 ✻ LSB
Offset Error Drift ±4 ✻ ppm/°C
Offset Error Match ±1 ✻ LSB
Gain Error
(1)
Ext Ref = 2.5000V ±15 ±10 LSB
Gain Error Int Ref ±40 ±25 LSB
Gain Error Drift ±25 ✻ ppm/°C
Gain Error Match ±1 ✻ LSB
Noise 150 ✻ µVrms
Power Supply Rejection Ratio Worst-Case ∆, +V
SS
= 5V ±5% 1.2 ✻ LSB
SAMPLING DYNAMICS
Conversion Time 13.5 ✻ Clk Cycles
Acquisition Time 1.5 ✻ Clk Cycles
Throughput Rate 500 ✻ kHz
Multiplexer Settling Time 500 ✻ ns
Aperture Delay 5 ✻ ns
Aperture Jitter 30 ✻ ps
AC ACCURACY
Signal-to-Noise Ratio 72 ✻ dB
Total Harmonic Distortion
(3)
VIN = 5Vp-p at 50kHz –74 –72 –77 –76 dB
Signal-to-(Noise+Distortion) V
IN
= 5Vp-p at 50kHz 68 70 71 72 dB
Spurious Free Dynamic Range V
IN
= 5Vp-p at 50kHz 76 74 78 77 dB
Channel-to-Channel Isolation V
IN
= 5Vp-p at 50kHz 95 ✻ dB
REFERENCE OUTPUT
Internal Reference Voltage 2.48 2.50 2.52 ✻✻✻ V
Internal Reference Drift 30 ✻ ppm/°C
Input Impedance CS = GND 5 ✻ GΩ
CS = V
SS
5 ✻ GΩ
Source Current
(4)
Static Load 50 ✻ µA
REFERENCE INPUT
Range 2.0 2.55 ✻✻V
Resistance
(5)
to Internal Reference Voltage 10 ✻ kΩ
DIGITAL INPUT/OUTPUT
Logic Family CMOS ✻
Logic Levels:
V
IH
IIH = +5µA3+V
SS
+ 0.3 ✻✻V
V
IL
IIL = +5µA –0.3 0.8 ✻✻V
V
OH
IOH = 250µA 3.5 ✻ V
V
OL
IOL = 250µA 0.4 ✻ V
Data Format Straight Binary ✻
POWER SUPPLY REQUIREMENT
+V
SS
Specified Performance 4.75 5.25 ✻✻V
Quiescent Current 2.6 3.5 ✻✻ mA
Normal Power 13 17.5 ✻✻ mW
Nap Mode Current
(6)
600 800 ✻✻ µA
Sleep Mode Current
(6)
10 30 ✻✻ µA
TEMPERATURE RANGE
Specified Performance –40 +85 ✻✻°C
Storage –65 +150 ✻✻°C
✻ Specifications same as ADS7852Y.
NOTES: (1) LSB means Least Significant Bit, with V
REF
equal to +2.5V, one LSB is 1.22mV. (2) Measured relative to an ideal, full-scale input of 4.999V. Thus,
gain error includes the error of the internal voltage reference. (3) Calculated on the first nine harmonics of the input frequency. (4) If the internal reference is required
to source current to an external load, the reference voltage will change due to the internal 10kΩ resistor. (5) Can vary ±30%. (6) See Timing Diagrams for further
detail.
The information provided herein is believed to be reliable; however, BURR-BROWN assumes no responsibility for inaccuracies or omissions. BURR-BROWN assumes
no responsibility for the use of this information, and all use of such information shall be entirely at the user’s own risk. Prices and specifications are subject to change
without notice. No patent rights or licenses to any of the circuits described herein are implied or granted to any third party. BURR-BROWN does not authorize or warrant
any BURR-BROWN product for use in life support devices and/or systems.
3
®
ADS7852
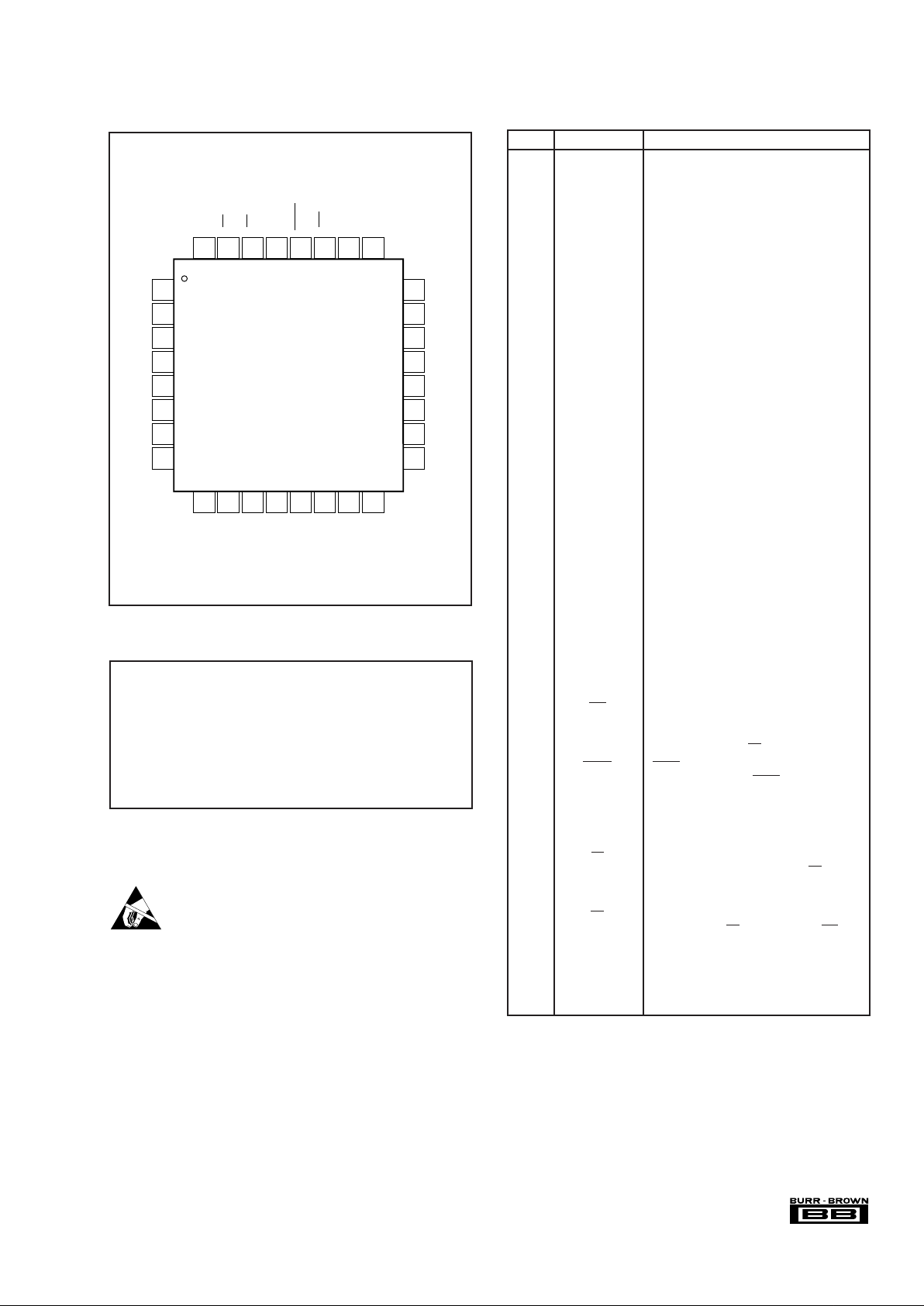
Top View TQFP
PIN NAME DESCRIPTION
1 AIN0 Analog Input Channel 0
2 AIN1 Analog Input Channel 1
3 AIN2 Analog Input Channel 2
4 AIN3 Analog Input Channel 3
5 AIN4 Analog Input Channel 4
6 AIN5 Analog Input Channel 5
7 AIN6 Analog Input Channel 6
8 AIN7 Analog Input Channel 7
9 AGND Analog Ground, GND = 0V
10 V
REF
Voltage Reference Input and Output. See
Specification Table for ranges. Decouple to
ground with a 0.1µF ceramic capacitor and
a 2.2µF tantalum capacitor.
11 DGND Digital Ground, GND = 0V
12 A2 Channel Address. See Channel Selection
Table for details.
13 A1 Channel Address. See Channel Selection
Table for details.
14 A0 Channel Address. See Channel Selection
Table for details.
15 DB11 Data Bit 11 (MSB)
16 DB10 Data Bit 10
17 DB9 Data Bit 9
18 DB8 Data Bit 8
19 DB7 Data Bit 7
20 DB6 Data Bit 6
21 DB5 Data Bit 5
22 DB4 Data Bit 4
23 DB3 Data Bit 3
24 DB2 Data Bit 2
25 DB1 Data Bit 1
26 DB0 Data Bit 0 (LSB)
27 WR Write Input. Active LOW. Use to start a
new conversion and to select an analog
channel via address inputs A0, A1 and A2
in combination with CS.
28 BUSY BUSY output goes LOW and stays LOW
during a conversion. BUSY rises when a
conversion is complete.
29 CLK
External Clock Input. The clock speed
determines the conversion rate by the
equation: f
CLK
= 16 • f
SAMPLE
.
30 RD Read Input. Active LOW. Use to read the
data outputs in combination with CS. Also
use (in conjunction with A0 or A1) to place
device in power-down mode.
31 CS Chip Select Input. Active LOW. The
combination of CS taken LOW and WR
taken LOW initiates a new conversion and
places the outputs in tri-state mode.
32 V
SS
Voltage Supply Input. Nominally +5V.
Decouple to ground with a 0.1µF ceramic
capacitor and a 10µF tantalum capacitor.
PIN ASSIGNMENTS
PIN CONFIGURATION
ELECTROSTATIC
DISCHARGE SENSITIVITY
Electrostatic discharge can cause damage ranging from performance degradation to complete device failure. BurrBrown Corporation recommends that all integrated circuits
be handled and stored using appropriate ESD protection
methods.
ESD damage can range from subtle performance degradation to complete device failure. Precision integrated circuits
may be more susceptible to damage because very small
parametric changes could cause the device not to meet
published specifications.
Analog Inputs to AGND, Any Channel Input ..............–0.3V to (VD + 0.3V)
REF
IN
.........................................................................–0.3V to (VD + 0.3V)
Digital Inputs to DGND ..............................................–0.3V to (V
D
+ 0.3V)
Ground Voltage Differences: AGND, DGND..................................... ±0.3V
+V
SS
to AGND..........................................................................–0.3V to 6V
Power Dissipation .......................................................................... 325mW
Maximum Junction Temperature ................................................... +150°C
Operating Temperature Range ......................................... –40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range .......................................... –65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) ............................................... +300°C
NOTE: (1) Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may
cause permanent damage to the device. Exposure to absolute maximum conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
(1)
AIN0
AIN1
AIN2
AIN3
AIN4
AIN5
AIN6
AIN7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
DB2
DB3
DB4
DB5
DB6
DB7
DB8
DB9
ADS7852Y
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
V
SS
CS
RD
CLK
BUSYWRDB0 (LSB)
DB1
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
AGND
V
REF
DGND
A2
A1
A0
DB11 (MSB)
DB10
4
®
ADS7852
PACKAGE/ORDERING INFORMATION
MAXIMUM MAXIMUM
RELATIVE GAIN PACKAGE SPECIFICATION
ACCURACY ERROR DRAWING TEMPERATURE PACKAGE ORDERING TRANSPORT
PRODUCT (LSB) (LSB) PACKAGE NUMBER
(1)
RANGE MARKING
(2)
NUMBER
(3)
MEDIA
ADS7852Y ±2 ±25 TQFP-32 351 –40°C to +85°C A52 ADS7852Y/250 Tape and Reel
ADS7852Y
""""""ADS7852Y/2K5 Tape and Reel
ADS7852YB ±1 ±40 TQFP-32 351 –40°C to +85°C A52 ADS7852YB/250 Tape and Reel
ADS7852YB
""""""ADS7852YB/2K5 Tape and Reel
NOTE: (1) For detail drawing and dimension table, please see end of data sheet or Package Drawing File on Web. (2) Performance Grade information is marked
on the reel. (3) Models with a slash(/) are available only in Tape and reel in quantities indicated (e.g. /250 indicates 250 units per reel, /2K5 indicates 2500 devices
per reel). Ordering 2500 pieces of ”ADS7852Y/2K5“ will get a single 2500-piece Tape and Reel. For detailed Tape and Reel mechanical information, refer to the
www.burr-brown.com web site under Applications and Tape and Reel Orientation and Dimensions.
A2 A1 A0 CHANNEL SELECTED
0 0 0 Channel 0
0 0 1 Channel 1
0 1 0 Channel 2
0 1 1 Channel 3
1 0 0 Channel 4
1 0 1 Channel 5
1 1 0 Channel 6
1 1 1 Channel 7
ADS7852 CHANNEL SELECTION
 Loading...
Loading...