Page 1

INTRODUCTION
1.1 AirStation Broadband Router
Access Point (WBR-B11)
Welcome to AirStation, the easy way to wireless networking. Bring your wireless home
network closer to your fun activities!
This book, which introduces you to the
AirStation Broadband router access point, will
help you connect to your network quickly.
The AirStation Broadband Router Access
Point (AP), WBR-B11, is a 4-port router wireless small/medium business (SMB) network
device that complies with the IEEE 802.11b
standard on wireless LANs (Revision B). It
supports data rates up to 11 Mbps in the
basic mode with enhanced built-in fi rewall
functions and is used as a multi-functional
router/link between wired and wireless LAN
PCs. The WBR-B11 incorporates features of
wired and wireless networking environments.
Summary of the AirStation WBR-B11 features:
• Wi-Fi™ (Wireless Fidelity) certifi ed by the
Wi-Fi Alliance. AirStation will com mu ni cate
with other IEEE 802.11b/Wi-Fi compliant
wireless LAN products.
• Automatic Transmit Rate Select mech a nism
transmits at speeds of 11, 5.5, 2 and 1
Mbps.
• DHCP client/server function.
• Auto roaming, supports seamless roaming
over multiple channels.
• Auto VPN setup, for secure com mu ni ca tions.
• Additional Firewall Functions - DMZ, intrusion detection and notifi cation.
• Up to 128bit Wired Equivalent Privacy
(WEP) data encryption (future support for
TKIP).
• Packet fi ltering, for eliminating unwanted
communications.
• SOHO/SMB routing and fi rewall func-
tions provide a safer private networking
en vi ron ment, including MS NetMeeting and
MSN Messenger.
• Syslog transmits some or all system activities to a central Syslog server.
• Extended range, with optional add-on
antennas.
• Auto Media Dependent Interface/
Crossover (MDI/X) port, allows connection
by standard and crossover CAT5 cables.
• Supports Universal Plug and Play (UPnP).
Other features to be supported by up-
grades:
• EAP-TLS, expanding the 802.1x au then ti ca tion method.
• PPPoE multi-session, for use with multiple
stations.
1.2 AirStation Wireless Network
Features
• Enhanced security features:
- Firewall and DMZ zone functions to
prevent unknown intruders.
- Intrusion detection with a pop-up
warning for DoS, malicious attacks and
rejection.
- Dynamic packet fi ltering function
prevents specifi ed ports being open to
WAN during periods of nonuse.
- Up to 128bit WEP for protecting data.
- VPN (IPSec and PPTP) pass-through
- Packet monitoring and fi ltering by MAC
address, IP address and port.
- PPPoE support.
- Internal Network Security, for blocking
changes to AP confi guration by wireless
clients or through another AP.
• Buffalo’s easy connection method and
video guided setup instruction.
• Static and dynamic routing methods
between WAN and LAN. An economical
way to bridge multiple networks.
• Optional external antennas for boosting
range and signal quality.
• Resistance to environmental conditions.
1.3 Home Networking
11
Page 2
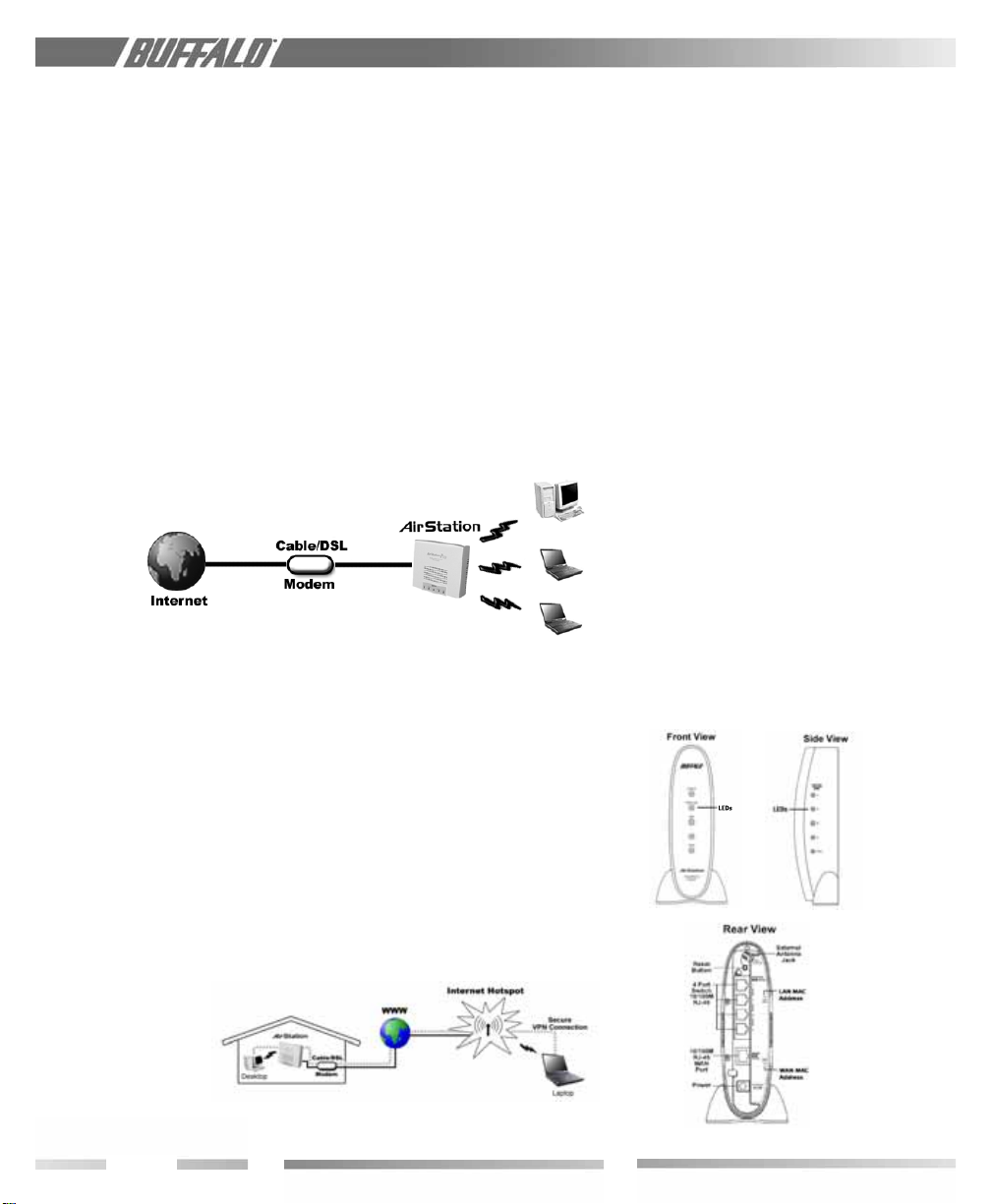
Figure 1.4
SOHO/SMB
Networking
Buffalo’s AirStation wireless access point
enables sharing broadband at your fi ngertips.
All you need to do is connect the AirStation
to a DSL or CATV modem to:
• Share fi les and printers
• Access and share the Internet
1.4 SOHO/SMB Networking
With high-speed DSL or CATV connections
readily available, many users can work effectively from a home offi ce, connected securely
to a corporate network. Connect the Buffalo
AirStation Broadband router AP to a CATV
or DSL modem in order to:
• Share broadband access
• Share fi les and printers
• Bridge between multiple networks and
multiple PC platforms
• Provide easy and secure access to home
or company networks from remote locations
like VPN, allowing mobile professionals to
take their offi ces on the road effortlessly.
When no wired broadband connections are
available, wireless solutions in public spaces
coupled with VPN can connect mobile workers to their businesses. Buffalo’s access point
features make a home network system accessible from anywhere.
Buffalo’s fi rewall function provides:
• Protection of personal data/fi les by either
eliminating the intruder on the spot or
sending intruders to a nonfunctional zone
• Notifi cation of the attack (pop-up warning
and auto packet rejection)
1.6 AirStation Broadband Router
Access Point Package
The AirStation WBR-B11 package consists of
the following items.
1. WBR-B11 Access P oint
2. AC adapter with Int'l Adapters
3. CAT5 straight cable
4. WBR-B11 Utility CD
5. Warranty Statement
1.7 Product Views
Figure 1.5
Buffalo
Anywhere
Networking
1.5 Buffalo Anywhere Networking
Mobile professionals can be productive
while traveling by accessing standards-based,
secure, high-speed connections in many
hotel, airports, convention centers, and
even coffee shops. The WBR-B11 makes
ex tend ing your LAN simple, secure, scalable,
and manageable, in part through solutions
2
Page 3
1.8 About the AirStation CD
Prior to copying or installing the software,
please read the Software License Agreement
“license.txt”, located in the root folder of the
CD. By installing, copying or using the AirStation software, you are consenting to the terms
of this agreement. If you do not agree to all of
the terms of the Software License Agreement,
do not download, copy or install the AirStation software.
It is the policy of Buffalo Technology to
improve products as new technology, components, software and fi rmware become
available.
Before you proceed with the installation of this product, please consult
the AirStation website (http://
www.buffalotech.com) to download
and install the latest software for your product.
BASIC SETUP
2.1 Using AirNavigator
For easy setup, the WBR-B11 CD contains a
web-based utility, AirNavigator. Use it to set
up the wireless LAN environment for both
AP and PC (client). The system requires
Explorer 4.0 or higher, or Netscape Com mu ni ca tor 4.0 or higher.
To set up the parameters manually, refer to
Chapter 3. Before installation, verify the PC is
set up for browsing the Internet.
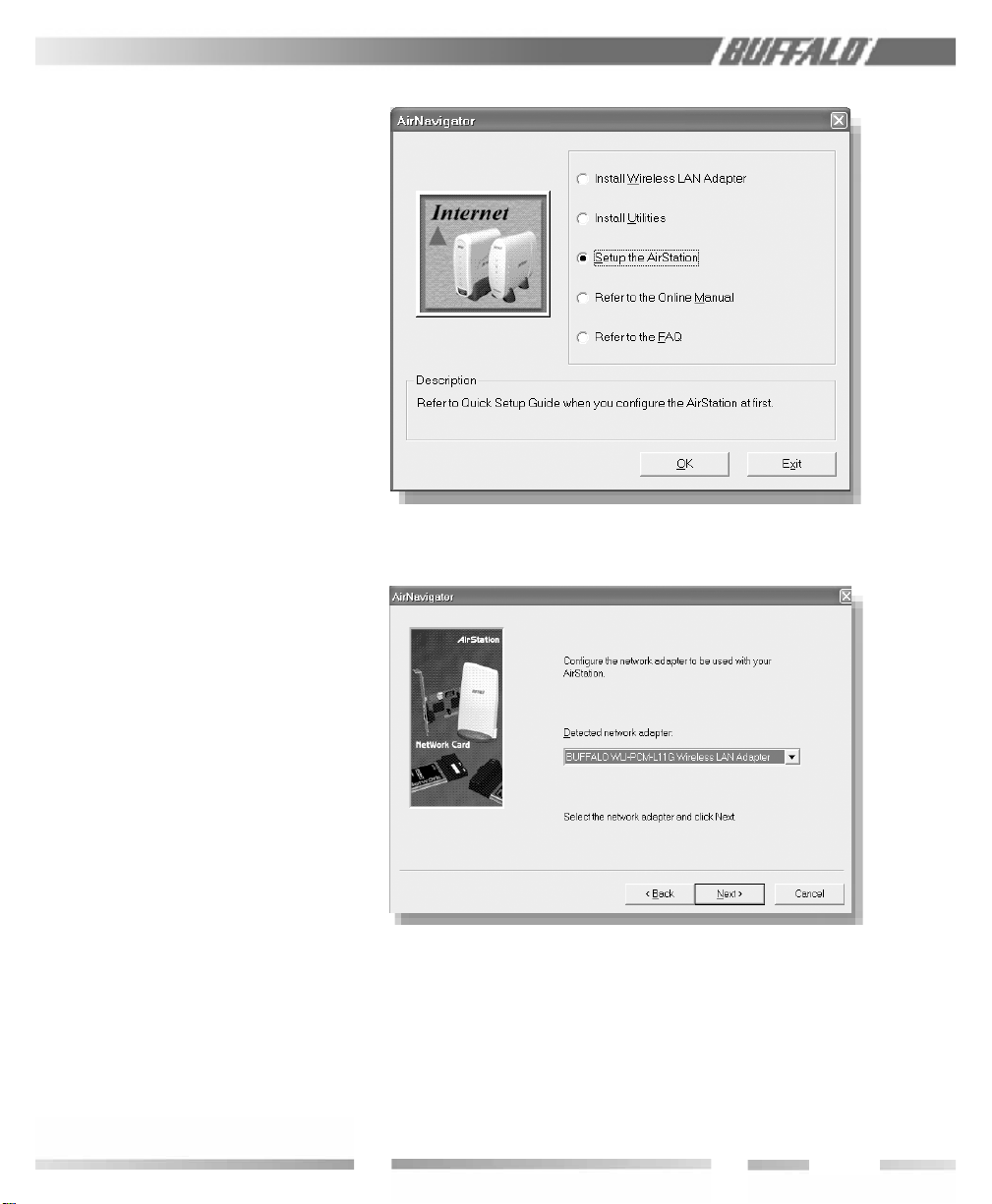
1. Insert the CD into the CD drive. The following screen will appear. For AirStation
setup, select “Setup the AirStation” and click
OK.
2. The Network Adapter confi rmation screen
will appear. Verify the adapter shown
matches that of the PC.
3. Click Next until a list of access points
shows up in the ESS-ID fi eld. Buffalo’s ESS-ID
is 12 digits and is found on the back of the
AirStation, labeled LAN MAC Address. Select
the one you want to communicate with and
highlight it. Click Next.
2.1.1
AirStation
Setup
Figure
2.1.2
AirStation
Setup:
Network
Adapter
33
Page 4

Fig ure 2.1.3
AirStation
Selection
Figure 2.1.4
Confi gure IP
Address
4. If the client IP range is different thanthe
default AirStation IP of 192.168.11.1, an IP
confi guration screen will appear next. Select
Automatically set up the IP address, or Specify an IP address for
manual setup.
5. Install Client Manager now or remove the
check from the box and click Next.
Figure 2.1.5
Login
6. .A login screen will appear.
• Enter “root” as the User name.
• Leave the Password box blank (do not
enter anything into the Password box) and
click OK.
If the following screen is shown, con nec tion to
the access point is complete.
4
Page 5
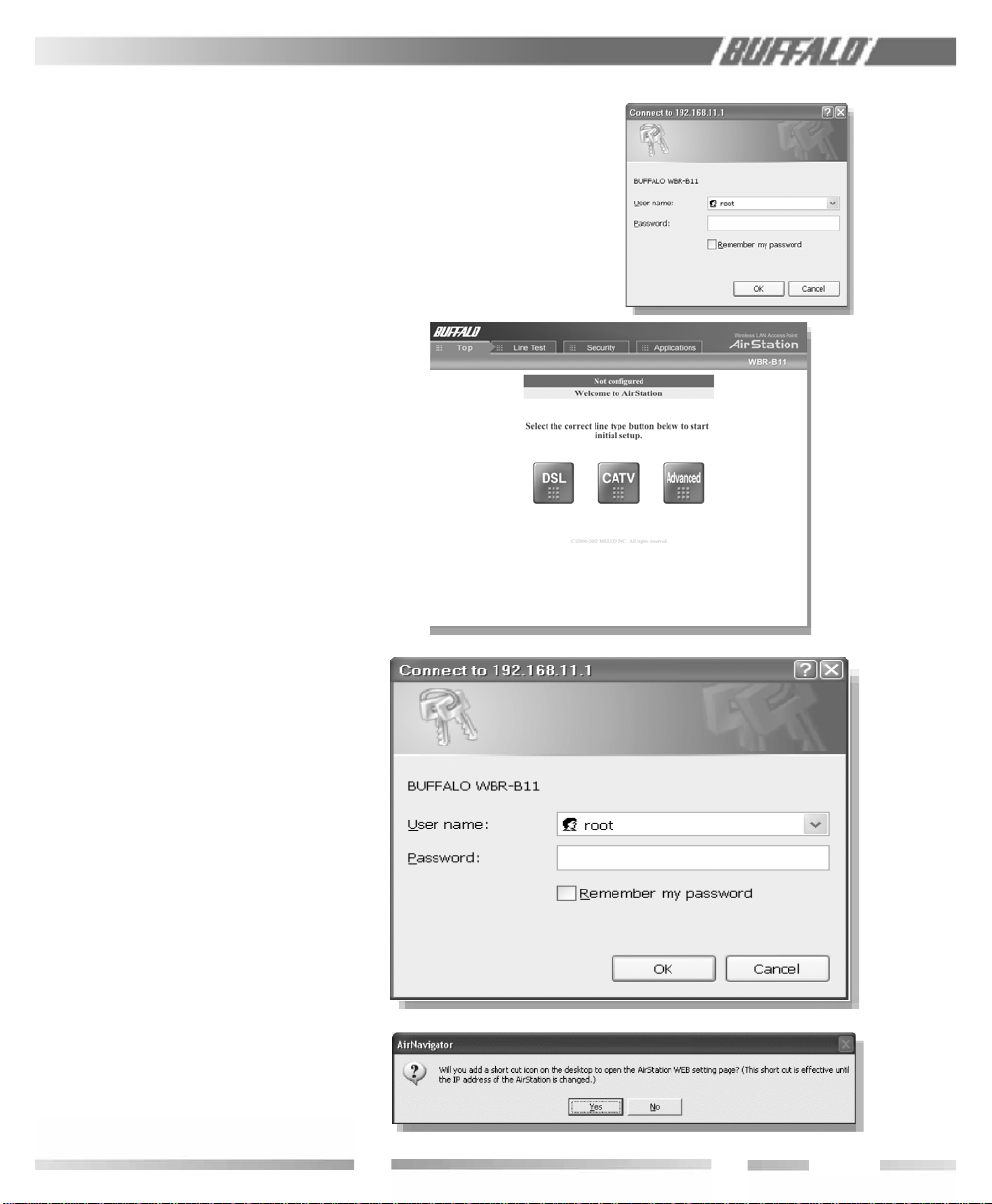
7. Click Finish.
8. To place a shortcut icon on the desktop,
click Yes. Oth er wise, click No.
Figure 2.1.6A
Login Screen
Fig ure 2.1.6B
AirStaton
Initial Setup
Screen
Figure 2.1.7
AirStation
Setup:
Com plete
STANDARD SETTINGS
3.1 Introduction
Setting up the AirStation parameters using
Buffalo’s utility tool, Client Manager, requires
basic wireless confi guration knowledge.
Setup includes manual wireless confi guration
and basic administrative management.
For explanation of each parameter and its
use, see Chapter 4.
3.2 Setup Preparation
Make note of the WBR-B11’s wired MAC
address (found on the back of the WBR-B11).
Figure 2.1.8
AirSta-
tion Setup:
Shortcut
55
Page 6
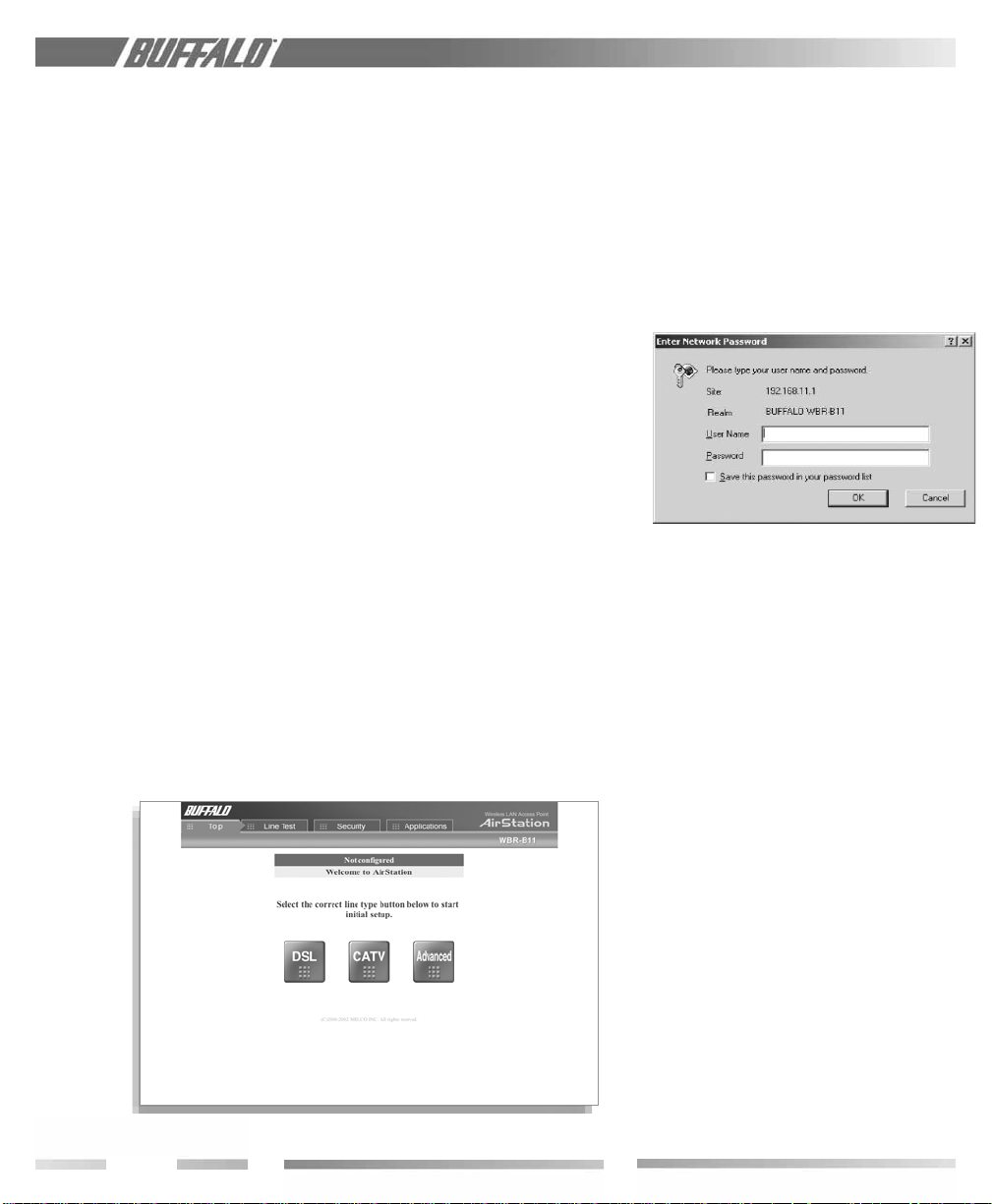
Fig ure 3.5
Initial Settings Screen
It is also recommended you record any other
broadband access information such as global
IP address, subnet mask address, default
gateway address, DNS server address and
PPPoE parameters.
3.3 Setup Overview
The WBR-B11 CD contains the Client Manager program. The Client Manager is used
for setting up and confi guring the access
point and for monitoring the wireless signal
between the AP and client.
Specialized setups for security, fi ltering and
other features will be explained in later sections.
3.4 Open the Setup Screen
• Connect the WBR-B11 according to the
wiring instructions.
(Install the setup utility, Client Manager, from
the CD.
• The WBR-B11 has a default LAN IP address of 192.168.11.1 and Subnet Mask of
255.255.255.0.
Ex: The setting PC can use 192.168.11.2 as
an IP and 255.255.255.0 as the Subnet Mask
during setup unless a different IP range is
entered for the AirStation.
1. Click Start and select Programs
4AirStation Utility4Client Man ag er
2. Select Edit4Search AirStation to
fi nd the nearest AirStation.
3. Highlight the WBR-B11, click the Ad-
min menu button, then the Confi gure
AirStation tab to open the setup screen.
4. The AirStation log-in screen will appear.
5. Enter “root” for User Name
and leave Password blank
3.5 Input Parameters Through the
Client Manager
1. Click the appropriate button to select the
type of broadband access. (Users more
experienced in networking may choose to
select the Advanced button and skip to
Chapter 4.)
2. For supplementary tools, use the tabs along
the top of the screen.
3.5.1 DSL Button
Select the appropriate connection method.
Automatic IP Assignment by ISP
- The DHCP server of the ISP assigns an IP
address automatically.
Enter IP address manually - Enter the
IP address given by the ISP.
PPPoE Connection - Enter the PPPoE
information provided by the ISP.
6
Page 7

3.5.2 CATV Button
Select the appropriate connection method.
Automatic IP Assignment by ISP
- The DHCP server of the ISP assigns an IP
address automatically.
Enter IP address manually - Enter
the IP address given by the ISP.
The IP address is acquired au to mat i cal ly but DNS server address
entered manually - Enter the DNS
server in for ma tion manually even though the
IP address is acquired automatically.
3.5.3 Line Test tab
Tests the connection to the Internet.
3.5.4 Security tab
Set security parameters. Follow the in struc -
tions in each screen.
Fig ure
3.5.1 DSL
Button
Fig ure 3.52
CATV
Button
77
Fig ure 3.5.4
Line T est T ab
Page 8

Fig ure 3.5.4
Security T ab
Fig ure 3.5.5
Ap pli ca tion
Tab
Fig ure 4.1.1
LAN Setting
3.5.5 Application tab
Set up special applications such as games, MS
NetMeeting and MSN Messenger. Follow
the instructions in each screen.
USING AIRSTATION
FOR ADVANCED
CONFIGURATIONS
Although your AirStation will function fi ne
using only the settings from Section 3, you
may wish to explore more advanced options.
This chapter explains each parameter in the
Advanced button. Click the Top tab
and click the Advanced button.
4.1 LAN Setting
Set up LAN connections.
4.1.1 Wireless
Wireless LAN operation setup.
ESS-ID - Allows administrator to alter the
ESS-ID of the AirStation. To communicate
with a specifi c AP only , the AP’s ESS-ID
must be entered in the client PC. The client
PC looks for the specifi c AP (or ESS-ID)
for wireless communication. Use up to 32
al pha nu mer ic characters for the ESS-ID (case
sensitive).
■ Note: Roaming - When m ultiple AirSta-
tions have an identical ESS-ID, WEP, and DS
channel, client PCs may Roam between the
AirStations.
Wireless Channel - Select the channel
used for wireless communication. There are
11 overlapping channels. Channels 1, 6 and
11 are non-overlapping.
If there are multiple APs in close proximity
using the same channel, there may be interference. In this case, change to a non-overlapping channel.
■ Note: This parameter is automatically set
8
Page 9

in the client computer.
Encryption Key (WEP) - Select Encrypt or Do not encrypt. Create and
enter an encryption code to protect wireless
com mu ni ca tions. It is possible to enter up to
4 different WEPs. The WEP key must match
between two parties for secure com mu ni ca tions.
Examples of WEP key:
64bit ASCII: 5 digits of alphanumeric charac-
ters, “ab34Y”
128bit ASCII: 13 digits of alphanumeric char-
acters, “123456abcdef7”
■ Note: ASCII WEP is case sensitive.
64bit HEX: 10 digits, using characters 0-9 and
a-f, “00234ABCDE”
128bit HEX: 26 digits, using characters 0-9
and a-f, “20123456789abcdeabcdeabcde”
BSS (Basic Service Set) Basic Rate
Set - The transmission data rate between
devices. If one device supports 2Mbps only,
the data rate for the entire network should
be limited to 2Mbps (“Default” selection).
Otherwise, use 11Mbps max (“All” selection).
DTIM Period - An access point transmits
beacon signals to nearby clients at a preset
interval. This parameter sets the beacon
transmission interval time (1-255 sec.).
Se lec tion of a larger number may conserve
energy for the client PC (when client power
management is enabled), but may delay wireless communication. The default value of 1 is
recommended.
ANY Connection - Enables a client
PC to connect to the nearest WBR-B11 by
entering the word “any” for the ESS-ID. If
the “ANY Connection” is not selected, the
WBR-B11 will not be found unless the
specifi c WBR-B11’s ESS-ID is entered in the
client PC.
LAN Side IP address - Allows ad min is tra tor to specify a static IP and Subnet Mask
for the LAN side of the AirStation.
■ Note: If the AP’s IP address is changed to
a different range, the setting PC’s IP must
be changed to the same range to continue
confi guration. Then restart the setup session
from the AirStation utility screen.
DHCP Server Function Simple Setting - Allows administrator to enable/disable
the DHCP server function for the AirStation
LAN side. Select Use to enable and Do
not use to disable the function. Once Use
is selected, the assigned IP address range can
be specifi ed. Enter the starting LAN IP ad-
dress and total number of PCs.
4.1.3 DHCP Server
Allows a more advanced confi guration of the
DHCP server functions.
DHCP Server Function - Allows ad min is tra tor to enable/disable the DHCP server
function for the AirStation LAN side. Select
Use to enable or Do not use to disable this
function.
Assigned IP address (Range As sign ment) - Sets the beginning address
and range of addresses to be assigned by the
AirStation’s DHCP server function. Select up
to 253 consecutive addresses (nodes). The
Fig ure 4.1.2
LAN Port
4.1.2 LAN port
Set LAN interface parameters.
99
Page 10

Fig ure 4.1.3A
DHCP
Server
Fig ure 4.1.3B
DHCP Server
10
IPs to be excluded from the range spec i fi c-
a tion should be entered in the specifi ed fi eld.
Lease period - Specifi es the number of
hours (1-999) an assigned IP address is valid.
The client PC will request a renewal of IP address at the end of the valid time period.
Default Gateway - Allows administrator to use the Default Gateway address
(the AirStation’s IP address), assign a specifi c
Gateway address, or block clients from Gateway notifi cation.
DNS server - Allows administrator to use
the default DNS address (the AirStation’s IP
address), assign specifi c DNS addresses, or
block clients from DNS address notifi cation.
WINS server - Allows administrator to
use a WINS address. Select auto assignment
of the IP address, enter a specifi c WINS IP ad-
dress, or block clients from the WINS address
notifi cation.
Domain name - Allows administrator to
use an assigned domain name, assign a specifi c
domain name, or block clients from domain
name no ti fi ca tion. Domain names will be
sent to LAN PCs when an IP address is assigned. Enter a maximum of 64 al pha nu mer ic
characters.
Manual IP and MAC Address As sign ment - Allows administrator to add ad-
ditional leased IP addresses tied to a specifi c
MAC address. When a specifi c MAC address
connects to the AP, the IP address specifi ed
will be given to that client.
Display/delete lease information
- List of IP addresses, MAC addresses, lease
periods and status is displayed.
4.1.4 Wireless LAN Computer Lim i ta tion
This option limits the PCs allowed a wireless
connection to the AirStation. It is used to
control the wireless connections to the access
point.
Wireless PC’s Connection - Select
Limit to restrict the connection and Do not
Limit for open access. Register your client
PC’s MAC address before selecting Set.
Register for allowable PC’s MAC
address - MAC access restriction set up in
LAN. Input the MAC addresses that to be
allowed to communicate.
MAC address list - Display a table list of
all MAC addresses.
4.2 WAN Settings
4.2.1 W AN P ort
Communication Method of Wired
WAN - Select port speed and type of
duplex connecting to the WAN port. If
unknown, select Auto negotiation.
Page 11

MAC Address of WAN - Set the
AirStation MAC address to be used for WAN
com mu ni ca tion.
IP Address of WAN - Allows administrator to select DHCP server, PPPoE, or
manual setting for the WAN port of the
AirStation.
Auto IP assignment from DHCP
server - acquire the IP address automatically
from the DHCP server.
Use PPPoE client - If selected, the in for -
ma tion listed below must be entered.
Manual setting - Enter the appropriate IP
address and subnet mask.
PPPoE Setting (for enabling PPPoE
Client function) - Allows administrator
to use PPPoE as specifi ed by the ISP. The fol-
lowing parameters should be entered:
User Name - Enter the user name (up
to 64 alphanumeric characters) for PPPoE
au tho ri za tion.
Password - Enter password provided by
ISP (up to 64 alphanumeric characters). Reenter password in the Confi rmation box.
Service Name - Enter the PPPoE service
name (up to 64 alphanumeric characters). If
ISP doesn’t require service name, leave blank.
Connection Type - Select from:
• Continuous Connection - Connects
im me di ate ly after setting and never dis con nects.
• Connect on Demand - Reconnects
when the Disconnect time elapses.
• Manual - Disables Automatic Con-
nec tion. Connects to Internet using the
Connect button on the initial settings
page.
The Connect button will not appear until
PPPoE is set.
Disconnection Time - Specify the number of minutes (0-1440) before automatic
dis con nect is performed. If “0” is entered,
dis con nect function is disabled. If Con-
tin u ous Connection is selected, the
Figure 4.1.4
Wire-
less LAN
Computer
Limitation
Figure
4.2.1A
WAN Port
Settings
Figure
4.2.1B
WAN Port
Settings
1111
Page 12

Fig ure 4.2.2
Network
Setup of
WAN
timer is disabled.
Authorization - Authorization method
for accessing the ISP PPPoE server. If unknown, select Auto authorization.
MTU (Maximum Transmit Unit)
Size - Maximum Transmit Unit (578-1492)
when using PPPoE.
MRU (Maximum Receive Unit)
Size - Maximum Receive Unit (578-1492)
when using PPPoE.
Keep Alive - Enables the PPPoE client to
send a Link Control Protocol (LCP) echo request to the PPPoE server once per minute.
If there is no reply within six minutes, the client disconnects. Set to Disable if frequent
disconnection occurs.
4.2.2 Network WAN
WAN side (Internet) parameters.
Host Name - Enter the host name as
desired.
Default Gateway - A default gateway
IP should be assigned to the AirStation. If
unknown, leave blank. If Auto IP as sign -
ment from DHCP Server was selected
in section 4.1.3, a gateway IP is assigned
automatically, provided the DHCP server is
set to provide one.
DNS Server Address - Enter the
primary and secondary DNS address(es) of
the server to be used by the WBR-B11 for
DNS resolution. If DNS was set to Do not
use (Section 4.1.3), leave blank. If Auto
IP as sign ment from DHCP Server
was selected, DNS addresses are assigned
automatically, provided the DHCP server is
set to provide them.
Port Number for WEB Setting - Set
a specifi c port number when remote setup of
the AirStation is planned.
PING from WAN - Allows a PING test
from WAN side. Select Do not respond
or Respond.
4.3 Network Setting
4.3.1 Routing Setup
RIP transmission to WAN - Allows
RIP transmission or None (no RIP) to WAN
RIP reception from WAN - Allows RIP
reception or None (no RIP) from WAN
RIP transmission to LAN - Allows RIP
transmission or None (no RIP) to LAN
RIP reception from LAN - Allows RIP
reception or None (no RIP) from LAN
Add Routing Table Entry
• Destination address - Network IP
address and subnet mask.
• Gateway - Address through which
the packet passes before it reaches the
des ti na tion address.
• Metric - Number of routers (1-15) to
be passed before the packet reaches its
destination.
Display/Delete Routing Table
(Entries) - Allows administrator to delete
routing information.
12
4.3.2 Address Translation
Page 13

Address Translation - Select Use or Do not
Use. Address Translation must be enabled
for client PCs to connect to the Internet. Selecting Use enables the following functions:
• IP Masquerade - When the LAN
PC connects to the WAN side, the IP
address of LAN PC is dynamically translated to become the WAN IP address
of the AirStation. Multiple LAN PCs can
share one WAN IP address to access
the Internet.
• Static IP address translation
-When the WAN requests connection
to the LAN, the WAN IP address of the
AirStation is translated into the IP address of the LAN PC.
Log Output - Allows NAT log to be
gen er at ed and issued. Select Discard Packet
to disable.
IP address of DMZ - Allows administrator to set the DMZ address.
Incoming packets containing no recognizable
destination port information will be re di rect ed to the DMZ’s IP address.
IP address of WAN - Select AirStation’s IP address of WAN or Manual
setting. For Manual setting, enter the IP
address used by the WAN PC to connect
to the local PC. Some network applications
(online games or streaming software) require
adding Address T ranslation tables).
Protocol (WAN):
• All - Selects all IP protocols.
• ICMP - Network Diagnostic Protocol (1).
• Manual - Specify the protocol number
(0-255).
• TCP/UDP - Enter port number.
IP address of LAN - Select Manual and
enter the destination IP address of the LAN
PC; or select AirStations’s IP address
of LAN.
• Select Add to NAT table.
Protocol (LAN) - Enter destination
port number. If left blank, the packets are
transferred to the same port number as the
Figure4.3.1A
Routing
Setup
Figure4.3.1B
Routing
Setup
Figure4.3.2A
Address
Traanslation
1313
Page 14

Fig ure
4.3.2B
Address
Translation
Fig ure
4.3.3A
Packet
Filter
Fig ure
4.3.3B
Packet
Filter
source port number.
Display/Delete NAT Table - Allows
ad min is tra tor to delete NAT tables.
4.3.3 Packet Filter
Log Output - Activates the packet fi lter
log.
Filter setting - Choose type from pull-
down menu.
For Manual setting:
• Operation - Packets from WAN (or
LAN), select ignored, rejected, or ac-
cepted.
IP Address - Filter for the specifi c IP ad-
dress
• Destination IP Address - The IP ad-
dress for the packet to arrive at.
• Source IP Address - The IP address for
the packet sender.
Warning: If administrator selects Packet
from LAN is Deny or Reject, the ad min is tra tor will no longer have access to the
AirStation confi guration screens. This function
prohibits setup from a wireless PC. The
WBR-B11 can be returned to the factory
default settings (ALL of them!) by holding
down the INIT button on the back of the unit
for three seconds.
Protocol - Mark and select a specifi c
protocol. Select from all protocols, ICMP,
arbitrary protocol number and TCP/
UDP protocol number.
• All - Selects all IP protocols.
• ICMP - Network Diagnostic Protocol (1).
• Manual - Enter protocol number (0-255).
• TCP/UDP Destination Port - Select
TCP or UDP, then enter port number.
Source MAC address - Enter the source
MAC address to be fi ltered.
■ Note: If confi guring from a wireless PC,
add your MAC address to the list of au tho rized wireless LAN PCs. The MAC address
must be in two-digit groups separated by
colons (Section 4.1.4).
14
Page 15

Example: 00:40:26:00:11:22
Display/delete packet fi lter in for -
ma tion - Allows the administrator to delete
or initialize the packet fi ltering.
4.3.4 Intrusion Detector
Intrusion Detector - Select Do not
use, Use or Use (Apply Packet fi lter
setting for Intrusion Detector setting).
IP Spoofi ng - Check Block to prevent IP
spoofi ng.
Threshold Value - Enter the number (1-
999) of packets before notifi cation occurs.
Notify by email
• Notifi cation email address - Enter
des ti na tion email address
• Sender email server address - En-
ter SMTP server address
• Receiving email server au tho ri z-
a tion - Enter POP3 Server address, User
name and Password
• Send test - Click Send to test no ti -
fi ca tion
Pop-up notifi cation - Client Manager
must be on to use this feature
• Destination IP address - Enter ad-
dress to be notifi ed
Fig ure 4.3.4A
Intrusion
Detector
Fig ure 4.3.4B
Intrusion
Detector
4.3.5 UPnP
Select Use to enable UPnP (Universal Plug
and Play). When a computer with UPnP
support connects to the AirStation, that computer automatically receives confi guration
information from the AirStation.
4.3.6 Log Information
Display log info level - Select Error and/or
Notice to specify the types of reports to be
logged by the AirStation.
Display log info - Select the specifi c
reports to be logged.
Log information - Displays recorded logs.
4.3.7 Syslog transmitting
Select Use or Do not use
• Syslog Server - Enter the IP address of
the Syslog server.
• Log Information Level - Select Er-
ror and/or Notice to specify the types of
reports to be sent to the Syslog server.
• Log Information - Select the specifi c
reports to be sent to the Syslog server.
4.4 Management
(Network Diagnosis Settings)
1515
Page 16

Figure
4.3.7
Syslog
Trans mit ting
Figure
4.4.1 Unit
In for ma tion
Figure 4.4.2
Time Setup
4.4.1 Unit information
AirStation name - When using Client
Manager and multiple AirStations, select a
unique name to make it easier to identify
each AirStation.
Administrator name - “root”, cannot be
changed
Administrator password - Allows the
administrator to enter an administrator password to restrict access to the setting screens.
• New Password - Enter new password.
Enter up to eight alphanumeric characters
(case sensitive)
• Confi rm Password - Reenter the new
password for confi rmation
4.4.2 Time setup
Time setup - Enter the current date and
time, and click Set
NTP - Select Use or Do not use
■ Note: If NTP is used, time is set au to -
mat i cal ly.
NTP server name - Enter the NTP
server name
Check Interval - Enter the time interval
for time check frequency
Time Zone - Select local time zone
Click Set.
4.4.3 System Information
Displays System Settings and information.
16
Page 17

4.4.4 Transfer Packet Condition
Displays number of packets sent and received
for wired WAN-LAN and wireless LAN
traffi c.
Figure
4.4.3A
System
In for ma tion
Figure
4.4.3B
System
Information
4.4.5 PING Test
Destination - Enter IP address for test and
click OK
Figure 4.4.4
Transfer
Packet In-
formatiion
1717
Page 18

Figure 4.4.5
Ping T est
4.4.6 Initialization/reboot
Initialization sets all parameters back to factory defaults. After initialization, the AirStation must be restarted.
Figure 4.4.6
Initialization
Reboot
Figure 4.4.7
Firmware
Update
4.4.7 Firmware Update
Firmware fi le name - Enter the path
and fi lename for new fi rmware or select
Browse to search for the path
Click Firmware Update to load fi rm-
ware to the AirStation.
■ Note: Firmware update does not erase
current user settings.
ADDITIONAL
INFORMATION
For more information, please consult one of
the following:
• The on-line help system of your
AirStation wireless system - for in for ma tion about software and driver func tion al ity.
• The AirStation website at: http:
//www.buffalotech.com - for
frequently asked questions (FAQ’s) and
Software Updates.
18
Page 19

A
WBR-B11 Access Point Specifi cations
Physical Specifi cations AA
Dimensions (LxWxH) 205 x 170 x 76 mm
Weight 620 grams
Temperature & Humidity
Operation 0¡ to 40¡ C
Maximum humidity 80%
Transit/Storage 0¡ to 40¡ C maximum humid-
ity 80% (no condensation)
Power Characteristics
Transmit Mode 1.1A (Nominal),
1919
Page 20

WBR-B11 ACCESS POINT SPECIFICATIONS
Physical Specifi cations
Dimensions (LxWxH) 205 x 170 x 76 mm
Weight 620 grams
Temperature & Humidity
Operation 0° to 40°C
Maximum humidity 80%
Transit/Storage 0° to 40° C maximum humidity 80% (no condensation)
Power Characteristics
Transmit Mode 1.1A (Nominal),
Power Supply 3.3 V
Regulatory Information
Wireless communication is often subject to local radio regulations. Although AirStation wireless
networking products have been designed for operation in the license-free 2.4 GHz band, local radio
regulations may impose limitations on the use of wireless communication equipment.
Networking Characteristics
Compatibility
• IEEE 802.11 Standard for Wireless LANs (DSSS)
• Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity) certifi ed by the Wi-Fi Alliance.
Host Operating System
• Microsoft Windows® ME/98/NT4.0/2000/XP, Unix/Linux/MacOS
Media Access Protocol
• CSMA/CA (Collision Avoidance) with Acknowledgment (ACK)
Radio Characteristics
R-F Frequency Band 2.4 GHz (2400-2483 MHz)
11 selectable sub-channels
Modulation Technique Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
• CCK for High & Medium Transmit Rate
• DQPSK for Standard Transmit Rate
• DBPSK for Low Transmit Rate
Spreading 11-chip Barker Sequence
Bit Error Rate (BER) Better than 10 -5
Nominal Output Power 15 dBm
Transmit Rate / Range
High Speed 11 Mbps
Medium Speed 5.5 Mbps
Standard Speed 2 Mbps
Low Speed 1 Mbps
Open Offi ce Environment
160 m (525 ft.) 270 m (885 ft.) 400 m (1300 ft.) 550 m (1750 ft.)
Semi-Open Offi ce Environment
50 m (165 ft.) 70 m (230 ft.) 90 m (300 ft.) 115 m (375 ft.)
Closed Offi ce
25 m (80 ft.) 35 m (115 ft.) 40 m (130 ft.) 50 m (165 ft.)
20
Page 21

Receiver Sensitivity -83 dBm -87 dBm -91 dBm -94 dBm (depends on data rate)
Delay Spread (at FER of <1%) 65 ns 225 ns 400 ns 500 ns (depends on data rate)
• The range of wireless devices can be affected by metal surfaces, solid high-density materials
and obstacles in the signal path.
Table “Radio Characteristics” lists the typical ranges when used indoors:
• In Open Offi ce environments, clients can “see” each other, i.e. there are no physical ob struc -
tions between them.
• In Semi-open Offi ce environments, work space is separated by room dividers; client cards
are at desktop level.
• In Closed Offi ce environments, workspace is separated by fl oor-to-ceiling brick walls.
■ NOTE: The range values listed in Table “Radio Char ac ter is tics” are typical distances as
measured at Buffalo Technology AirStation laboratories. These values are provided for your
guidance but may vary according to the actual radio conditions at the location where the
AirStation product is installed.
AirStation IEEE 802.11 Channel Sets
The range of the wireless signal is related to the Transmit Rate of the wireless communication.
Communications at a lower Transmit range may
travel longer distances.
Center Channel ID FCC
1 2412 4 2427 7 2442 10 2457
2 2417 5 2432 8 2447 11 2462
†
3 2422 6 2437 9 2452
†
De fault Channel10 2457
2121
Page 22

B. 1 Common Troubleshooting Tips
Common Problems:
• Out of range, client cannot connect to the AirStation.
• Confi guration mismatch, client cannot connect to the AirStation.
• Absence or confl ict with the Client Driver.
• Confl ict of another device with the AirStation hardware.
B.1.1 LED Activity B
Monitoring LED activity helps identify problems.
• Power LED should be GREEN,
• Wireless LED should be GREEN if the line is active. If is it blinking GREEN, wireless com mu ni ca tion is active.
• Ethernet LED should be GREEN (100Mbps) or AMBER (10Mbps) while the com mu ni ca tion is
active.
DIAG LED Activity
Unplug the power for three seconds. Plug the power back in to monitor the DIAG LEDs during
start-up.
If the symptom matches Table B.1.1, email techsupport@buffalotech.com
or call 800-688-7466
between the hours of 8:30 am and 7:30pm, CST.
DIAG LED Display Time Description/Action
Continuous Red Starting RAM Error Red fl ash, 2 times Starting Flash ROM Error
Red fl ash, 3 times Starting A problem in the wired LAN side
Red fl ash, 4 times Starting A problem in the wireless LAN side
B. 1.2 LEDs Work But Client PC Cannot Connect to Network
If the LEDs indicate that the network is working properly (Power LED is on, Transmit/Receive
LED blinks), check the TCP/IP settings of the network.
Changing Client TCP/IP Settings in Windows
Consult the LAN Administrator for TCP/IP settings.
To add or change the TCP/IP Settings:
1. On the Windows task bar click Start.
2. Select Settings, then Control Panel.
3. Double-click on the Network icon to view the Network Properties.
4. From the list of installed components, verify the TCP/IP -> Buffalo WLI-USB-L11G wireless
LAN adapter protocol (or appropriate wireless LAN adapter) is installed.
• If this protocol is not yet installed, click the Add button and select the TCP/IP protocol
from the list. Refer to Windows Help for more information.
• If this protocol is installed, select this protocol and click the Properties button. Verify
the parameters match the settings provided by your LAN Administrator. Make changes if
necessary, and click OK.
5. When prompted, restart your computer.
B. 1.3 Other Problems
Please refer to www.buffalotech.com and www.airstation.com for further reference
materials.
Glossary
22
Page 23

10BaseT or 100BaseTx: 802.3 based
Ethernet network that uses UTP (Unshielded
twisted pair) cable and a star topology. 10 is
10 Mbps and 100 is 100 Mbps.
802.1x: The standard for wireless LAN authentication used between an AP and a client.
802.1x with EAP will initiate key handling.
Ad-Hoc Network: The wireless network
based on a peer-to-peer communications
session. Also referred to as AdHoc.
Bandwidth: The transmission capacity of a
computer or a communication channel, stated
in Megabits per second (Mbps).
BSS (Basic Service Set): An 802.11
net work ing framework that includes an Access Point.
Bus Mastering: A system in which the
specifi ed Input/Output device (e.g. NIC Card)
can perform tasks without the intervention
of the CPU.
Client: A PC or workstation on a network.
Cross-Over Wiring: A UTP cable that
has its transmit and receive pair crossed to
allow com mu ni ca tions between two devices.
DCE (Data Communications Equip ment): Hardware used for communica-
tion with a Data Terminal Equipment (DTE)
device.
Default Gateway: The IP Address of
either the nearest router or server for the
LAN.
Default Parameter: Parameter set by
the manufacturer.
Destination Address: The address portion of a packet that identifi es the intended
recipient station.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Confi gura-
tion Protocol): Based on BOOTP, it uses a
pool of IP addresses, which it assigns to each
device connected to it, and retrieves the address when the device becomes dormant for
a period of time.
DNS (Domain Name System): Sys-
tem used to map readable machine names
into IP addresses
Driver: Software that interfaces a computer
with a specifi c hardware device.
DSSS (Direct Sequence Spread
Spectrum): Method of spreading a wireless
signal into wide frequency bandwidth.
DTE (Data Terminal Equipment):
Device that controls data fl owing to and from
a computer.
Dynamic IP Address: An IP address that
is automatically assigned to a client station in a
TCP/IP network, typically by a DHCP server.
ESS (Extended Service Set): A set of
two or more BSSs that form a single sub-network. ESS-ID is user identifi cation used in the
ESS LAN confi guration.
Ethernet: The most widely used ar chi tec ture for Local Area Networks (LANs). It
is a shared-media network architecture. The
IEEE 802.3 standard details its functionality.
Ethernet cable: A wire similar to tele phone cable that carries signals between
Ethernet devices.
File and Print Sharing: A Microsoft application that allows computers on a network
to share fi les and printers.
Firmware: Programming inserted into programmable read-only memory, thus becoming
a permanent part of a computing device.
Frame: A fi xed block of data, transmitted as
a single entity. Also referred to as packet.
Full-Duplex: To transmit on the same
channel in both directions simultaneously.
Gbps (Giga Bits per second): One
billion bits per second.
Half-duplex: To transmit on the same
channel in both directions, one direction at a
time.
Hub: A device which allows connection of
computers and other devices to form a LAN.
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and
Electronics Engineers): The professional
2323
Page 24

24
organization which promotes development
of electronics technology.
IP (Internet Protocol) Address: A
unique 32-binary-digit number that identifi es
each sender or receiver of information sent
in packets.
Infrastructure: A wireless network or
other small network in which the wireless
network devices are made a part of the
network through the Access Point.
ISP (Internet Service Provider): A
company that provides access to the Internet
and other related services.
IV (Initialization Vector): The header
section of a message packet.
LAN (Local Area Network): A group
of computers and peripheral devices connected to share resources.
LED (Light Emitting Diode): The
lights on a hardware device representing the
activity through the ports.
MAC (Medium Access Control) Address: A unique number that dis tin guish es
network cards.
Mbps (Mega Bits Per Second): A
mea sure ment of millions of bits per second.
MDI/X (Media Dependent
Interface/Cross-over): Port on a
network hub or switch that crosses the
incoming transmit lines with the outgoing
receive lines.
MHz (MegaHertz): One million cycles
per second.
MIB II: A database containing performance
information and statistics on each device in a
network.
MIPS (Million Instructions Per Second): A measurement of processing speed.
NAT (Network Address Translation): An internet standard that enables
a LAN to use one set of IP addresses for
internal traffi c and a second set for external
traffi c.
NIC (Network Interface Card): An
expansion card connected to a computer
so the computer can be connected to a
network.
Packet: A block of data that is transferred
as a single unit, also called a frame or a block.
Packet Filtering: Discarding unwanted network traffi c based on its originating address
or its type.
PCI (Peripheral Component In ter con nect): A bus that is connected directly
to the CPU.
PCMCIA (Personal Computer
Mem o ry Card International As so ci a tion) Card: Removable module that
adds features to a portable computer.
Ping (Packet Internet Groper): An
Internet utility used to determine whether a
particular IP address is online.
Plug and Play: Hardware that, once
installed (“plugged in”), can immediately be
used (“played”), as opposed to hardware that
requires manual confi guration.
PoE (Power over Ethernet): A mech a nism to send DC power to a device using a
CAT5 Ethernet cable.
PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol
over Ethernet): A specifi cation for con-
necting users on an Ethernet line to the Internet through a common broadband medium.
Protocol: A standard way of exchanging
information between computers.
RADIUS (Remote Authentication
Dial In User Service): A server that
issues authentication key to clients.
RAM (Random Access Memory):
Non-permanent memory.
Repeater Hub: A device that collects,
strengthens and transmits information to all
connected devices, allowing the network to
be extended to accommodate additional
workstations.
RC4: The encryption algorithm that is used
in WEP.
Page 25

RJ-45 connector: An 8-pin connector
used between a twisted pair cable and a data
transmission device.
ROM (Read Only Memory): Permanent memory.
Router: Device that can connect individual
LANs and remote sites to a server.
Roaming: The ability to use a wireless
device while moving from one access point
to another without losing the connection.
Script: A macro or batch fi le contain-
ing instructions and used by a computer to
perform a task.
Server: Any computer that makes fi les or
peripheral devices available to users of the
network and has a resident Network OS.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol): The protocol used to defi ne and
deliver electronic mail (e-mail) from one
location to another.
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol: An application layer
protocol that outlines the formal structure
for com mu ni ca tion among network devices.
Static IP Address: A permanent IP
address is assigned to a node in a TCP/IP
network. Also known as global IP.
STP (Shielded Twisted Pair): Twisted
Pair cable wrapped in a metal sheath to provide extra protection from external interfering signals.
Subnet Mask: An eight-byte address
divided into 4 parts separated by periods.
TCP/IP (Transmission Control
Pro to col/Internet Protocol): Proto-
col used by computers when communicating
across the Internet or Intranet.
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol): Simple form of FTP (File Transfer
Protocol), which Uses UDP (User Datagram
Protocol), rather than TCP/IP for data transport and provides no security features.
TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity
Pro to col): An encryption method replacing
WEP. TKIP uses random IV and frequent key
exchanges.
Topology: The shape of a LAN (Local Area
Network) or other communications system.
Twisted Pair: Cable that comprises 2 or
more pair of insulated wires twisted together.
UDP (User Datagram Protocol): A
com mu ni ca tion method (protocol) that offers
a limited amount of service when messages
are exchanged between computers in a network. UDP is used as an alternative to TCP/IP.
Uplink: Link to the next level up in a communication hierarchy.
UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair)
cable: Two or more unshielded wires
twisted together to form a cable.
WAN (Wide Area Network): A net-
working system covering a wide geo graph i cal
area.
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy):
An encryption method based on 64 or 128bit
algorithm.
Web Browser: A software program that
allows viewing of web pages.
Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity): An or ga -
tion that tests and assures interoperability
ni za
among WLAN devices.
Wire Speed: The maximum speed at
which a given packet can be transferred using
Ethernet and Fast Ethernet standard specifi ca-
tions.
WLAN (Wireless LAN): A LAN topology using wireless devices.
VPN (Virtual Private Network): A
security method to connect remote LAN users to a corporate LAN system.
2525
 Loading...
Loading...