
BTS FREEEMG
user manual
english
version 3.1.0e

Document Number : ERFNC-00782-01e
Published: October 2010
Copyright © 2010 BTS SpA. All Rights Reserved.

BTS FREEEMG
contents
contents 1
icons, symbols and acronyms 5
disposal (WEEE) 8
intended use 9
label 9
warnings 10
copyright 13
introduction 14
general description 14
case contents 16
system components 19
physical description 19
acquisition unit 20
PDA (Personal Digital Assistant) 22
wireless EMG probes 24
wireless FSW/EGN probes 28
on-o analysis (optional) 29
electrogoniometers (optional) 30
charger 31
docking station 33
installation 38
user PC minimum conguration 38
installation of the Wi-Fi interface 38
description of the software on the user PC 40
switching on BTS FREEEMG 300 41
BTS
Bioengineering
1

BTS FREEEMG
contents
rst connection 43
connection check 43
correct data visualization check 45
acquisition protocol 47
create a new protocol 47
tting the patient 52
guide to the use of onboard software 55
initial screen 55
“Active” button 55
selecting the work mode 59
description of the main bars and menu 60
protocol 63
probes setup 64
digital oscilloscope (gane) 67
digital oscilloscope (cross check) 70
footswitches 72
“Local” button: holter mode 74
“Remote” button: lab mode 86
“Download” button 90
“Cong” button 92
“Exit” button 101
BTS FREEEMG 300 updating 102
updating the onboard software 102
creating a backup image 103
maintenance and cleaning 105
appendix A – technical specications 107
wireless probes 107
receiving unit 107
BTS
2
Bioengineering

contents
BTS FREEEMG
appendix B – environmental specications 109
appendix C – power supply and switch o 110
appendix D – battery 111
appendix E – declaration of conformity 113
appendix F – troubleshooting guide 114
1708 error - Incorrect IP address or port set up 114
1709 error - Impossibility to connect to the unit 115
backup restoring 115
BTS
Bioengineering
3

BTS FREEEMG
icons, symbols and acronyms
Symbol in the instructions for the function.
e icon represents the information which requires special attention.
Symbol in the instructions for the function.
is icon makes reference to a more detailed discussion of the subject in
hand.
Symbol on the equipment and in the users’ instructions.
Symbol for the separate disposal of electrical and electronic equipment, in
accordance with Directive 2002/96/CE (WEEE).
e equipment belongs to Group 8 (medical equipment).
In force in the nations of the European Union, Norway and Switzerland.
BTS
Bioengineering
5

BTS FREEEMG
icons, symbols and acronymi
Symbol on the equipment:
Attention, read the information in the users’ manual carefully before using
the equipment.
Symbol on the equipment:
e data appearing next to the manufacturer’s symbol refer to the place of
manufacture of the equipment itself.
Symbol on the equipment:
e gure in the square indicates the insulation class and the part types
used. In accordance with Standard ISO 60601-1, the equipment has an
internal power supply and the parts used are type BF.
Symbol on the equipment:
Symbol located next to the series number on the equipment.
BTS
6
Bioengineering

icons, symbols and acronyms
BTS FREEEMG
Symbol on the equipment:
CE mark with the code of the Notied Body. e CE mark certies that
the product conforms to the standards applicable in the member states of
the European Union (see Declaration of Conformity).
Symbol on the equipment:
e double square indicates that the product is a Class II device according to
EN 60601-1.
The device must be operated with the provided power supply unit.
Radio equipment identification
EMG probes:
FCC ID: YQH-BTSWEMG IC: 9188A-BTSWEMG
FSWEGN probes:
FCC ID: YQH-BTSWAUX IC: 9188A-BTSWEMG
Acquisition Unit contains:
FCC ID: TFB-MATRIXLP IC: 5969A-MATRIXLP
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject
to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful
interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Modifications not expressly approved by BTS SpA could void the
user's authority to operate the equipment under FCC rules.
Acronyms used in this manual:
AP Access Point
AU Acquisition Unit
EMG Electromyography
FSW Footswitch
PDA Personal Digital Assistant
RU
WS
Receiving Unit
Workstation
BTS
Bioengineering
7
BTS FREEEMG
disposal (WEEE)
In disposing of the equipment observe the legal prescriptions.
In accordance with Directive 2002/96/CE (WEEE) all equipment supplied
after 13/08/2005 may not be disposed of in general domestic waste. is
equipment belongs to Category 8 (medical equipment) and is classied in
the Business-to-Business sector.
e symbol of the crossed out rubbish bin
indicates that the equipment must not be
disposed of in normal domestic waste.
e regulations for disposal may dier between
individual countries in the EU. In cases of doubt,
refer to the respective sales outlet.
is is a battery-powered equipment.
See Appendix D for information about the batteries used. Operate
and dispose of this equipment according to the instructions set in
the “warnings” section.
BTS
8
Bioengineering

BTS FREEEMG
intended use
is equipment is an instrument for the EMG surface analysis, classied
as medical equipment in accordance with European Directive 93/42/CE
(and its amendments).
e BTS FREEEMG 300 must always be used only for this purpose, by
qualied persons, in an environment suitable for the execution of EMG
analyses and respecting the prevailing regulations in the countries in which
it is being utilised.
Acquisition Unit Regulatory label
BTS SpA
V.le Forlanini 40
Garbagnate M.se
I-20024 Italy
btsbioengineering.com
This device complies wit h Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions: (1) this device may not ca use harmful interference, and (2)
this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may
cause undesired operation.
FCC ID: YQH-BTSWEMG
IC: 9188A-BTSWEMG
XX-XX-XX
BTSWEMG
Internally powered device
0123
BTS SpA
V.le Forlanini 40
Garbagnate M.se
I-20024 Italy
btsbioengineering.com
This device complies wit h Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions: (1) this device may not ca use harmful interference, and (2)
this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may
cause undesired operation.
FCC ID: YQH-BTSWAUX
IC: 9188A-BTSWAUX
XX-XX-XX
BTSWAUX
Internally powered device
0123
Wireless Probes Regulatory labels (not on actual probes due to size constraints)
BTS
Bioengineering
9

BTS FREEEMG
warnings
We recommend to carry out any kind of operation keeping strictly
to the security regulations contained in this manual.
BTS FREEEMG 300 is a medical device (EU Directive 93/42/CE and its
amendments, including Directive 2007/47/CE) which use must be at all
times be supervised by qualied and authorized personnel, according to
the laws in force in the nation it is in use.
e results of the acquisitions must be assessed by people legally authorised
by national law, who possess the suitable necessary knowledge of anatomy
and muscular function.
e uses of the device for other purposes and with methodologies dierent
from of those indicated in this manual are not to be considered congruent
with the precise use of the device.
- Use the product according to the usage that it has been
intended.
- Avoid connecting the probes to the charger with inverted polarity
with respect to that shown on the cover of the recharger - this
could cause irreparable damage to them.
- To not wet or dip in water the parts that make up the system.
BTS
10
Bioengineering

warnings
BTS FREEEMG
- Apply the probes only on undamaged skin.
- Only use CE branded probes and hypoallergenic double-sided
tape, compatible with the usage on undamaged skin for brief
periods of time.
- Periodically verify the integrity of the system and of its
components.
- In case the device accidentally falls, tear of the probes or other
accidents always address authorized technical support.
- Do not undertake any kind of internal maintenance of the device:
in case of need always address to authorized technical support.
- e use of any components dierent from the original ones
declines the conformity of the device.
- e instrument must be used in a medical environment, since it
has a high level of sensitivity (measured voltage levels of between
1 microvolt and 6 millivolt).
- During the preparation of the patient, take particular care that
the system’s components do not impede in any way the normal
movements of the subject.
- In addition to the users’ instructions, the prescriptions regarding
accident prevention and technical regulations regarding
occupational safety must also be complied with.
BTS
Bioengineering
11

BTS FREEEMG
e appertaining national regulations and standards of the country
of use, with regards prevention of accidents and environment, are
an extension of the users’ instructions.
- BTS FREEEMG 300 is a device that is able to function
CONTINUOUSLY, this is of course limited by the battery
duration and by the memory available for the acquisition data
storing.
- the device uses lithium ion battery. For the battery replacement
and disposal please contact the technical support. At any rate,
ensure that device component (i.e. probes, receiving unit,...)
integrity is never compromised.
e information contained in this manual is subject to change
without notice and does not constitute product specications or
any obligation on the part of BTS S.p.A.
warnings
12
BTS
Bioengineering

BTS FREEEMG
copyright
e software of the system described in this manual is supplied with the
“licence to use” contract. e software may be used or copied only as
stipulated under the terms of this contract.
No part of this manual may be copied or transmitted in any form or means,
electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, without prior written
permission from BTS S.p.A.
Unless otherwise specied, any reference to companies, names, data and
addresses used in the reproduction of the screens and the examples are
purely incidental, and has the sole purpose of illustrating the use of the
BTS product. All trademarks are registered by the respective owners.
is publication contains reserved information which is the
property of BTS S.p.A.
e recipient acknowledges that the illustrations and information
supplied in this manual shall not be made available to third parties
without explicit written agreement by BTS S.p.A.
BTS
Bioengineering
13

BTS FREEEMG
introduction
General description
BTS FREEEMG 300 is an indispensable instrument for laboratories
which are concerned with the study of muscular activity in the elds
of rehabilitation, sports medicine, ergonomics, clinical research, and
assessment of functional ability and muscular fatigue.
BTS FREEEMG 300 makes the selection of muscles, the setting of
duration and frequency of acquisition, amplication gain and the correct
positioning of electrodes, simple and rapid.
BTS FREEEMG 300 can be applied in research, sports, occupational
medicine, gnatology, neurology, and orthopaedics.
With the software tools available, BTS FREEEMG 300 becomes an
advanced diagnostic tool to evaluate neurological and orthopaedic
disorders, pharmacological therapy, progression of motor decits, use
of ortheses, rehabilitative follow-up, and to optimize sports training
programmes,...
BTS FREEEMG 300 is generally supplied with Myolab the easy to
use BTS software programmes for displaying, processing and reporting
electromyograph signals.
BTS Myolab is an extremely exible solution with numerous analysis tools
available making it possible to perform even advanced elaborations of,
BTS
14
Bioengineering

introduction
BTS FREEEMG
for example, the study of myoelectric manifestations of localized muscle
fatigue, even for cyclical movements.
BTS EMGenius and BTS EMG-Analyzer are also available as option:
• BTS EMGenius is the application software for functional evaluation
of cyclical movements such as ambulation, through automatic
identication of gait phases, and in movements such as “hand to
mouth, “sit-to-stand”, exion-extension of the hand, reaching, etc...
BTS EMGenius has been designed and developed to be easy to learn
how to use in very short time: e friendly and intuitive interface
makes the analysis laboratory immediately productive.
• BTS EMG-Analyzer is the most complete software solution for
analysing electromyographic signals. It includes predened templates
for evaluations in the clinical, sports, and research eld: Jump,
plyometrics, walking, fatigue analysis, isokinetic, etc...
BTS EMG-Analyzer also has an editor for creating elaboration
protocols: thanks to an innovative object interface, that translates
the biomechanical analysis language into graphical form, the user can
develop quickly and eectively customized analysis protocols.
BTS FREEEMG 300 seamlessly integrates with BTS motion analysis
systems, through the SMART (and ELITE) dedicated software.
BTS
Bioengineering
15

BTS FREEEMG
Case contents
Standard components:
• Receiving Unit
Acquisition Unit
• Probes Kit
• up to 16 wireless probes (identicative labels available in 4
dierent colors)
introduction
• Acquisition Unit
• HP iPAQ hx4700 Pocket PC
• Belts for attachment to patient
• Stylus (located in the Pocket PC)
Pocket PC
• Access Point
• Set of disposable electrodes
BTS
16
Bioengineering

introduction
BTS FREEEMG
• Probes Chargers:
• up to 2 “Charger” units: each charger handles up to 8 probes
and 2 FSW/EGN). e second unit is included in the standard
kit only for FREEEMG with at least 12 probes, or available as
an option.
• e optional “Docking Station” version is also available
• Accessories
• USB-PDA cable •AC adaptor
(RoHS conform)
• Manuals
• BTS FREEEMG 300 user • HP iPAQ PocketPC manual
manual complete of CD and Companion CD
BTS
Bioengineering
17

BTS FREEEMG
introduction
Optional components:
• Footswitch Kit
• 2 FSW/EGN Wireless Probes • 2 Connectors of 4 Switches
• 10 single Switches
• Electrogoniometer Kit
• 1 FSW/EGN Wireless Probe • 1 Electrogoniometer
• 1 Connector
• Supplementary Receiving Unit
• Secure Digital
You will receive the instructions for use for other possible optional components not mentioned in this manual.
BTS
18
Bioengineering
BTS FREEEMG
system components
BTS FREEEMG 300 electromyograph consists of a receiving unit which
utilises a PocketPC platform and wireless probes designed and developed
by BTS SpA.
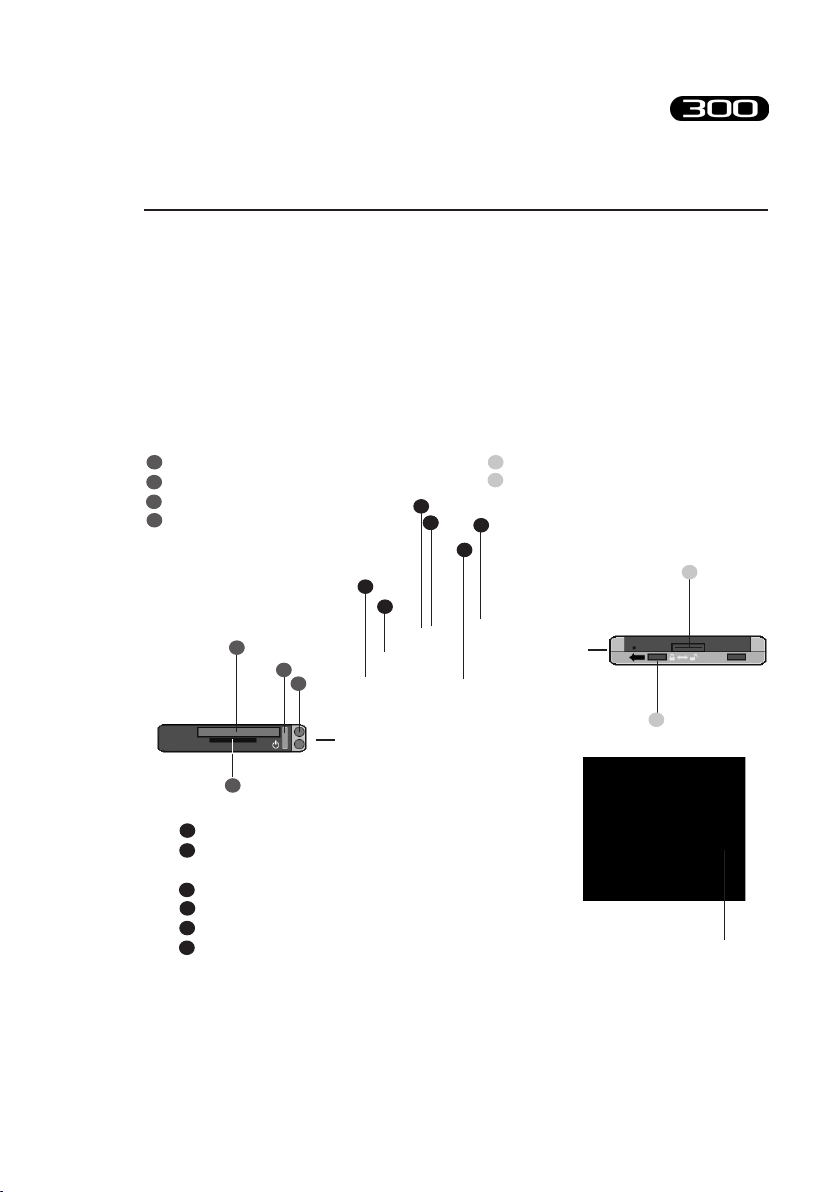
Physical description
power button (on/o)
1
Compact Flash (CF) slot type II
2
Secure Digital (SD) slot
3
stylus pen
4
2
1
4
1
2
2
5
6
activesync connector
1
battery door lock (in lock position to
2
switch on BTS FREEEMG 300)
4
3
1
3
LED - WIFI (solid blu = WiFi Active)
1
LED - charging and notication indicators
2
(blinking amber = charging; solid amber = full charge)
VGA color display
3
antenna
4
service slot
5
grip
6
2
wireless probes
BTS
Bioengineering
19

BTS FREEEMG
Acquisition unit
e acquisition unit consists of:
• a digital card
• a receiver card
• a plastic casing
• a guide for the PDA insertion.
system components
e digital card is connected to the palmtop, via the Compact Flash port,
when this is made to slide in the proper guide.
When the acquisition unit is connected to the palmtop, the card
communicates, “describing” itself to the driver in operation and thereby
allowing the system to self-congure and to carry out a self-diagnosis.
In addition to serving as a Compact Flash interface the card allows control
BTS
20
Bioengineering

system components
BTS FREEEMG
of the receiver card and handles acquisition of data coming from the
probes.
e receiver card is comprised of 4 elements that act as coordinators
of the wireless connection network with the probes, thus managing
communications with the probes, both for activation and data acquisition.
e acquisition unit is able to handle:
• up to 16 probes, used for acquisition of the activity of the same
number of electromyographic signals
• up to two probes of 4 auxiliary channels for switch connection,
used for the basographic acquisition.
• As an alternative to the EMG channels it is possible to acquire
up to 4 electrogoniometers (each EGN occupies 2 analogue
channels).
In particular, the following probe combinations are possible:
EGN EMG FSW
0 up to 16 probes 2 probes of 4 switches
1-2 up to 12 probes 2 probes of 4 switches
3-4 up to 8 probes 2 probe of 4 switches
BTS
Bioengineering
21

BTS FREEEMG
system components
PDA (Personal Digital Assistant)
HP iPAQ hx4700 Pocket PC is based on
Microsoft® Windows®.
It uses the Intel® PXA270 processor and
the new transective display VGATFT, 4”
with 64k colors, to provide exceptional
graphics power and performance to display
large dimension images at highest quality
resolution.
HP hx4700 is tted with excellent expansion capacity (Compact Flash
Type II and SD slot) to provide more storage space and greater function
range.
64 MB of SDRAM and 128 MB of ROM memory allow a greater number
of programmes and les to be stored, while the 1800 mAh lithium ion
battery ensures longer uninterrupted use of the Pocket PC.
22
BTS
Bioengineering

system components
BTS FREEEMG
For further details please refer to the HP iPAQ hx4700 Pocket PC
Manual included.
BTS
Bioengineering
23
BTS FREEEMG
system components
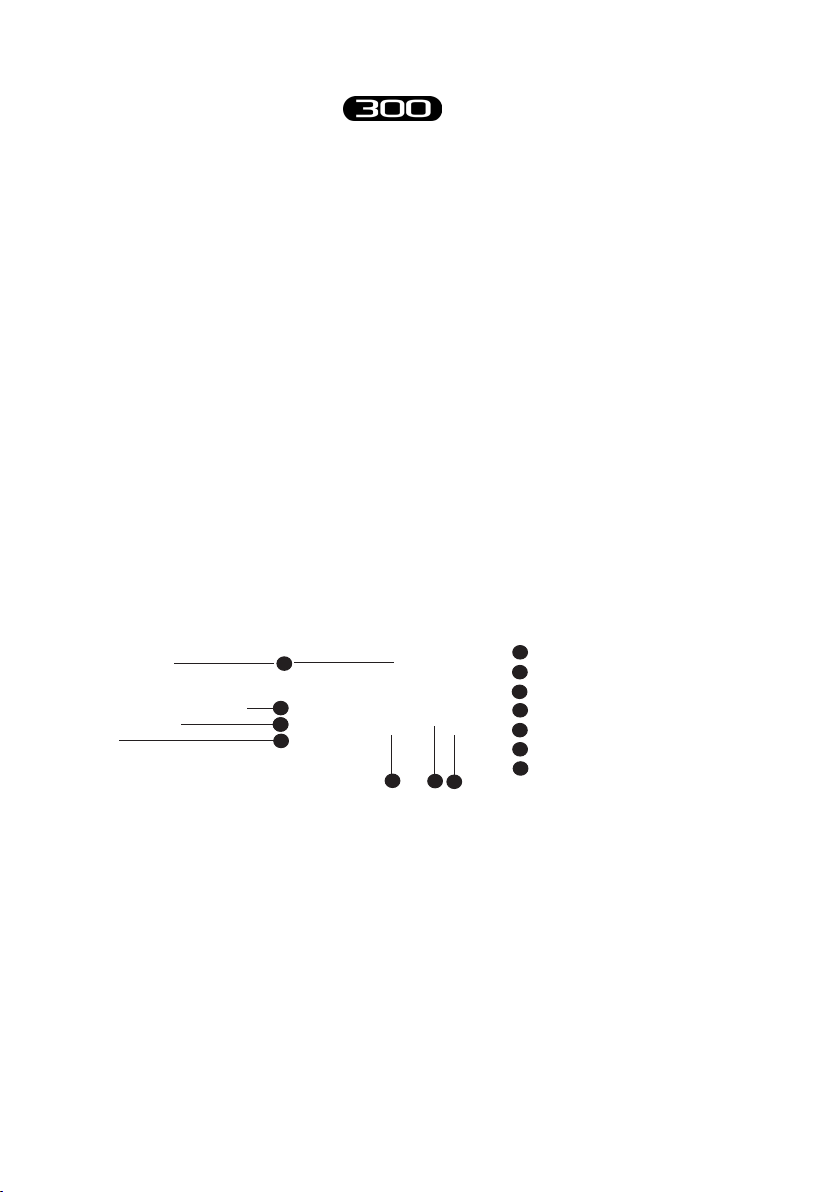
Wireless EMG Probes
BTS FREEEMG 300 utilises miniaturised probes with active electrodes
weighing less than 9 grams.
e special design ensures maximum space-saving and comfort for the
patient who is free to move around without obstacles.
e probes can be hooked on directly to the pre-gelled electrodes without
requiring additional xing with plasters or double-sided tape.
is together with the total absence of cables enables a much faster patient
preparation, drastically reducing the time of each session.
Each receiving unit can control up to 16 probes, for a total therefore of
16 analysable muscles in a single exam (standard conguration with one
receiving unit).
LED
6
1
2
2
3
4
5
7
1
mother electrode
2
satellite electrode
3
mother electrode clip
4
satellite electrode clip
5
exible cable
6
probe ID
7
Each probe consists of a mother electrode and a satellite electrode, each
tted with a clip.
e two parts, connected via a exible cable, may be positioned as needed
by the user at adjustable distance (electrodes with variable geometry).
BTS
24
Bioengineering

system components
BTS FREEEMG
In the mother electrode there are the A/D converter, the antenna and the
battery.
In the satellite electrode there is the Signal Conditioning (preamplier and
lter) and is reported the probe ID.
All probes are also equipped with a solid state memory buer, to prevent
data loss for problems due to the Wi-Fi network or due to exceeding the
useful operating range.
Each probe is tted with an LED indicating its state. e probes can be in
one of a number of dierent states:
• Charge: steady red LED.
During recharging the red LED is on, the probe is completely
passive and does not respond to any command. When the
battery is fully recharged or when the probe is removed from
the charger, if suciently recharged it passes to the “Inactive”
mode.
• Inactive: green LED which cyclically lights with a steady light
for a few seconds every 3 minutes.
In the “Inactive” mode the probes cannot be used directly by the
patient unit but are in constant standby to be activated by the
activation software. When the probe is inactive, it carries out a
scan of the radio frequencies: during the scan the green LED is
lit continuously.
• Active-Scanning: green LED which cyclically lights for a few
seconds.
In this mode the probe is searching for a patient unit on the
channel assigned during the activation phase. At intervals of
BTS
Bioengineering
25

BTS FREEEMG
about 3 seconds its carries out a scan of the frequencies. During
the scan the green LED ashes quickly.
• Active-Connected: Green LED which ashes slowly.
When the probe and the receiving station establish a connection,
the green LED begins to pulse slowly: the probe is waiting for
commands. If the connection is interrupted, the probe returns
to “Active-Scanning” mode and attempts to re-establish the
connection.
• Active-Capturing: Green LED which lights and goes out at
regular intervals.
During acquisition the green LED ashes at regular intervals of
approximately one second. At the conclusion of the acquisition,
the probe returns to the “Active-Connected” condition. If during
the acquisition, connection to the receiver unit is lost, the probe
continues to acquire, storing the data locally for one minute and
at the same time scans the assigned channel trying to reconnect
to the receiving unit.
If after one minute the scan is unsuccessful, the probe returns
to the “Active-Scanning” condition interrupting the storage of
data.
system components
• Probe discharged: LED is o.
If the probe is completely discharged the LED does not display
any ashing cycle and is o.
e probes are charged by a dedicated charger to which the probes are
connected via their respective clips.
BTS
26
Bioengineering

system components
BTS FREEEMG
Refer to the cover of the charger to identify the correct polarity.
e probes cannot be recharged if the polarities are inverted.
e EMG probes can be used also to acquire the EMG signal by means of
Fine-Wire electrods.
With this aim, there are available, in option, adaptors allowing for the
connection with Fine-Wire electrods. e EMG probes can be connected
to them using the clips. Each adaptor can be xed to the subject by means
of proper elastics.
For these applications the acquisition frequency must be setted
on 4 KHz (the giudelines recommend for Fine-Wire electrods an
acquisition frequency major or equal to 2 KHz).
BTS
Bioengineering
27

BTS FREEEMG
system components
FSW/EGN Wireless Probes (optional)
For collecting the on-o analysis signals coming from the Footswitch
or for collecting data from the Electrogoniometers (optional system
components) BTS FREEEMG 300 uses wireless probes which must be
connected to the FSW or EGN probes using a special connector.
e probe will work dierently if used with one or the other
probe and will receive from the same receiving unit information
on its work modality during activation.
e probe consists of a single parallelepiped-shaped block.
e upper face has an ID tag characterized by a colour (Green, Red, Yellow,
Blue) and a letter (A, B, C, D, E or F) and a status LED which operates
similar to that described for the EMG probes (see previous paragraph).
e two lateral faces have two connectors; the one on the ID tag side
serves to charge the probe, and a cable will be connected to this to enable
connection to the charger (Charger or Docking Station).
BTS
28
Bioengineering

system components
BTS FREEEMG
e one on the other side is for the probe connections (FSW or EGN).
Finally, the ID identier of the probe is on the bottom left corner of the
back side.
On-o analysis (optional)
e footswitches are useful in dening the contact points during the
contact phases of deambulation.
e footswitches consist of a resistive membrane, (FSR technology), of
diameter 18 mm and thickness less than 0.5 mm, expressly designed for
applications in the analysis of movement.
e compact size of the instrument permits a maximum of exibility in
positioning on the patient’s foot.
For applications other than gait analysis, there are available on request
smaller diameter (8 mm) switch probes (appliable, for example, to the
nger), and square (useful for tapping tests), 44 mm x 44 mm.
BTS FREEEMG 300 permits up to 8 basographic zones to be measured,
through 2 connectors from 4 single switches (usually right and left side)
that are connected to the two FSW/EGN wireless probes.
BTS
Bioengineering
29

BTS FREEEMG
system components
e footswitch channels are supplementary to the 16
electromyographic channels.
Refer to § “Acquisition unit” for the list of probe combinations
possible in case of acquisition also with EGN.
Electrogoniometers (optional)
e electrogoniometer is an easy to use device that allows the measurement
of joint angle progress over time.
ere are primarily two types of electrogoniometers: the potentiometer
and the strain gauge. BTS FREEEMG 300 uses the strain gauge
electrogoniometer of Biometrics LTD.
ere are single-axle models for the neck (axial rotation) and the forearm
(prone-supination) and biaxial models for other main joints: wrist, elbow,
knee, ankle, hip and back.
e strain gauge electrogoniometers are made up of two sensors, connected
to each other, that are xed to the bone segments involved in the joint to
value.
e measure of the angle is provided by the relative angle between the
axes of the two sensors and, unlike the potentiometric electrogoniometers,
BTS
30
Bioengineering

system components
BTS FREEEMG
it doesn’t depend on the linear slidings in which the two extremities can
incur.
Each electrogoniometer is connected to a FSW/EGN wireless probe
using the appropriate connector. Each receiving unit can handle up to 4
electrogoniometers.
e electrogeniometer channels are not supplementary to the 16
electromyographic channels, but each electrogoniometer used
engages 2 EMG channels. Refer to § “Acquisition unit” for the
detailed list of probe combinations possible.
Charger
e Charger, included with the product, charges the FREEEMG probes.
e Charger can simultaneously charge 8 EMG probes and 2 FSW/EGN
probes.
BTS
Bioengineering
31

BTS FREEEMG
system components
Two units are provided for systems with more than 12 channels
More units can be connected in series for simultaneous power
supply through the same AC adapter, using the cable included.
e EMG probes are connected to the charger using the same clips that
normally collect the EMG signal, while the FSW/EGN probes connect to
the charger using the special connector as shown in the gure below:
For correct connection simply follow the outline of the probes shown on
the base of the Charger.
e Charger comes with an output short circuit protection
system also in case of reversed recharging poles. At any rate, poles
connected incorrectly will not recharge.
To recharge connect all the probes that you would like to charge to the
Charger (follow the instructions described above) and connect the AC/
DC adaptor to the mains and turn on the switch located on the rear panel.
When the Charger is properly connected to the mains and has been turned
on, the status LED “Power” will show a steady GREEN light.
BTS
32
Bioengineering

system components
BTS FREEEMG
e charging status of the probes is indicated by the status LED of the
probes (see § “Wireless Probes”).
When connecting the probes to the Charger (connected to the
mains and turned on) if they are charged less than 90% they will
be automatically reset; to use them again for acquisitions you
need to repeat the activation procedure.
Docking Station (optional)
As in alternative to the Charger an optional Docking Station is available.
is unit has additional features that are described below.
Each Docking Station can simultaneously charge 8 EMG probes and 2
FSW/EGN probes.
Unlike the standard Charger, each Docking Station will have to
be powered separately; therefore two units cannot be connected in
series for contemporary power supply.
BTS
Bioengineering
33

BTS FREEEMG
system components
e EMG probes are connected to the charger using the clips for collecting
the electromyographic signal, while the FSW/EGN probes connect to the
charger using the special connector.
For correct positioning simply follow the outline shown on the base of the
Docking Station as shown in the following gure:
e Docking Station comes with an output short circuit protection
system also in case of reversed recharging poles.
At any rate, poles connected incorrectly will not recharge.
e Docking Station also allows for recharging the receiving unit by
connecting it with the relevant cable (USB/PDA cable) in the USB port
located on the rear panel.
It should be noted that you can use the Docking Station to
recharge the PDA only when by pressing the power button the
palmtop turns on.
Otherwise you will need to recharge the PDA with the supplied
HP by connecting it to the network. In order to go back and
recharge using the Docking Station, simply charge with the
power supply unit for about one minute, and then check that it is
BTS
34
Bioengineering

system components
BTS FREEEMG
suciently charged by unplugging it from the power supply unit
and turning it o and then back on.
ere are two ways to recharge the probes:
• using the medical power supply unit from the network
• using the internal battery
e rst method involves the connection of the Docking Station by means
of the AC/DC adaptor to the mains.
In this case not only the connected probes will be charged but also the
internal batter of the unit itself.
e second method lets you recharge the probes and/or the receiving
unit when you are not at the laboratory and a mains power network is
unavailable.
In particular with the battery fully charged you can fully recharge all the
probes and receiving unit or fully charge the probes only twice.
To recharge a probe simply connect it as described in the method above.
Connection to the Docking Station resets the probe if charged
less than 90%, to use it again for acquisitions you must repeat the
activation procedure.
e Docking System is equipped with an “Activate” button and 3 status
LEDs: “Charge”, “Battery” and “Power”.
BTS
Bioengineering
35

BTS FREEEMG
system components
e “Activate” button allows immediate activation of all the probes
connected to the Docking Station and selected to activate the receiving
unit (see § “Active” Button); you do not need to wait for the software cycle
of the “inactive” state probe to be complete. By pressing the button the
probe will immediately scan the radio frequencies and enter immediately
in communication with the receiving unit.
e “Charge” LED gives information on the probes charging and consists
of a BLUE light which signals the following:
• BLUE LED “breathing”: indicates that the probes are charging.
Two situations can be veried in this case:
• Status LED of the RED probe on: e probe is charged
less than 90%
• Status LED of the RED probe o: e probe is more
than 90% charged but still not complete.
It is important to remember that RED LED
of the probe stays on until it is 90% charged.
is function allows you to have an indication
on the full charge of the probe, therefore
increasing the autonomy of the probe by about
10%.
• BLUE LED o: indicates that all probes are fully recharged.
• BLUE LED on: indicates that the “activate” button has been
pressed and the probes are active. In this case the probes are not
powered by the Docking Station but by the probe’s battery.
e “Battery” LED is an indicator of the state of the auxiliary battery
BTS
36
Bioengineering

system components
BTS FREEEMG
and consists of a two-tone RED- GREEN LED, whose signals have the
following signicance:
• LED o (both the RED light and the GREEN light are o): in
this case the battery is in sleep mode or has been removed from
the Docking Station
• GREEN light of LED on: the auxiliary battery is charging.
• Steady RED light of LED on: the auxiliary battery is fully
charged.
• Blinking RED light of LED on: indicates battery malfunction
or a battery charging problem.
e “Power” LED is on (GREEN light) when the switch located on the
rear panel of the Docking Station is ON and it is connected to the mains
or, if this is not the case, the auxiliary battery is suciently charged.
e Docking Station has a lid, which opens automatically by means of
a spring- brake mechanism, which works by pressing close to the word
“Push”, located on the left shoulder of the unit..
e probes should be put back in the Docking Station when not
in use for acquisition sessions. Moreover, if left for a long period,
we recommend turning of the unit by moving the switch located
on the rear panel of the Docking Station to OFF. Close the lid for
better protection of the probes.
BTS
Bioengineering
37

BTS FREEEMG
installation
User PC minimum conguration
Operating system Windows XP
Microsoft.NET framework 1.1
Processor P IV 1600 MHz
RAM 256 MB
Video card 32 MB, Open GL
Disk space 100 MB for the application,
not including storage for acquired data
USB 2.0
Installation of the Wi-Fi Interface
e real time data transmission between the BTS FREEEMG 300 and the
Workstation occurs thanks to the Wi-Fi network. is type of connection
is permitted using an Access Point supplied with the system.
An AP is an Ethernet device which works with devices present in a small
area.
e AP, starting point of the service, operates from bridges between the
wireless devices and the systems physically connected to the network with
an RJ45 connector.
e AP transmits the signals to the surrounding area via radio waves. All
the wireless devices within the area can receive signals and communicate
with the AP, and through them, with all the other devices, creating a
network without cables.
BTS
38
Bioengineering

installation
BTS FREEEMG
Connecting a Workstation (PC laptop or desktop), not provided with a
Wi-Fi interface, to Access Point with a normal network cable is created
through the wireless connection with BTS FREEEMG 300.
Receiving Unit
Wireless Probes
Access Point
Workstation
e access point included in the system is already congured with the
network name (SSID) “BTSFREEEMG300” with transmission on
channel 6. e base conguration prepared in BTS (factory settings) uses
the following IP addresses:
Access Point 192.168.1.1
BTS FREEEMG 300 192.168.1.2
Workstation assigned automatically
by the Access Point
You should always use the AP included even if the Workstation is
equipped with a Wi-Fi interface.
BTS
Bioengineering
39

BTS FREEEMG
installation
Description of the software on the user PC
e BTS portfolio has 3 applications dedicated to electromyography:
• BTS Myolab: general purpose tool for acquisition, display,
processing, and reporting of electromyographic signals and joint
angle measurements.
• BTS EMGenius (optional): system for the functional evaluation
of cyclical movements, such as walking. is software is
designed to use in clinics, oering automatic procedures, guided
and consolidated, targeted especially at cyclical analysis (using a
Footswitch).
• BTS EMG-Analyzer (optional): A complete and highly exible
solution for making advanced elaborations of electromyographic
signals and angular measurements of body segments. Includes
predened templates for evaluations in clinics, sports, and
research and an editor to develop customized elaboration
protocols.
For more details concerning the use of these software, please refer
to their specic manuals.
However BTS FREEEMG 300 is manageable by all BTS applications of
SMART family dedicated to the motion analysis with which is possible
to acquire and process the electromyography signals in a integrate and
synchronous way with the other devices connected.
e SMART Analyzer software allows to perform advanced elaborations of
the EMG signals, integrating the electromyography information with the
BTS
40
Bioengineering

installation
BTS FREEEMG
cinematic and kinetic data. It is possible to construct customized analysis
protocols complete of advanced multimedial report.
Switching on BTS FREEEMG 300
e patients unit consists of two main components: the PDA and the
Acquisition Unit and is usually given with the two parts already connected.
Anyway, to connect the Acquisition Unit to the palmtop, run the PDA
along the AU guides, being particularly careful that the CF enters the
appropriate slot without being forced or receives any sudden impact, and
avoid any excessive pressure on the palmtop screen.
To avoid damaging the Compact Flash we suggest only to remove
the PDA from the AU only if necessary and in any case, even if
expressly requested, it is suggested not to move it completely from
its place, but to let it slip just enough to disconnect it from the
digital card (more or less 1 cm) event that will be signalled by an
audio beep.
e recharge of the battery and the transfer of data with the USB
can also be done through the specic cable, without disconnecting
the AU or the PDA.
It is also advisable to perform a connecting/separating operation
of these parts only when the device is turned o.
BTS
Bioengineering
41

BTS FREEEMG
installation
Check the connection between PDA and AU, switch on the BTS
FREEEMG 300: check that the slot switch, located on the side of the BTS
FREEEMG 300 shown in the diagram, is in the position closest to the
closed lock symbol. If not, move it to this position.
Switch on by actuating the button on the opposite side of the BTS
FREEEMG 300, as shown here:
At this point wait until the application BTS FREEEMG 300 is completely
charged. On the BTS FREEEMG 300 display the following screen will be
visualized:
42
BTS
Bioengineering

installation
BTS FREEEMG
First Connection
e BTS FREEEMG 300 is supplied with the onboard PDA software
preinstalled and congured. In any case for the rst connection we suggest
to perform some verications.
Connection check
e user PC communicates with the BTS FREEEMG 300 by means of
Wi-Fi protocol trought the Access Point (see § “Installation of the Wi-Fi
Interface”).
Verify that the local net resources are laid out, like assumed in the
conguration of default according to BTS, the PC user IP address must
assigned automatically by the Access Point.
Verify the software conguration installed on the PC.
To do so, launch the program that you want to congure and on the menu
bar at the voice “EMG Device” select “IP and Port Cong”.
BTS
Bioengineering
43

BTS FREEEMG
installation
Verify that the IP address and the port are set with the following connection
parameters:
IP Address: 192.168.1.2
Port: 8000
Moreover, if there is a second BTS FREEEMG 300 receiving unit available
(mind that in this case it is possible to manage up to 8 channels with each
unit), select the option “Activate Second Unit (only for BTS FREEEMG)”
and check that the IP address and the port for the second device are set up
with the following connection parameters:
IP Address: 192.168.1.3
Port: 9000
If the values do not correspond change them and click on “Update” before
closing the window.
Switch-on the BTS FREEEMG 300 (see § “switching on BTS FREEEMG
300”), wait until the application of the acquisition management is
completely loaded and select the remote application clicking on “Remote”.
If the Wi-Fi connection between the Receiving Unit and the Workstation
is assigned in the correct way, after clicking on the “Remote” button, the
connection led of the Wi-Fi net, that you can nd on the front of the BTS
FREEEMG 300 and that presents the Wi-Fi logo ( ), will result on
(solid blue).
44
BTS
Bioengineering

installation
BTS FREEEMG
During the start-up of the Remote mode dierent wireless nets
can be found present in the working area.
Always use the “BTSFREEEMG 300” net ignoring the other nets.
From the Workstation launch the application that you want to use (for
example Myolab.
Wait until, in the application being used, the respective LED indicating
the state of the Wi-Fi connection between the receiving unit and the
workstation changes from red to ashing green.
Correct data visualization check
During the initial connection, check the correct operation of the probes in
use, and the correct display of data on the BTS FREEEMG 300.
To do this, activate all the EMG probes and, if the system is also provided
with footswitches, two FSW/EGN probes, enabled as FSW, to be tested
all previously charged, as indicated in § ““Active” Button”. When all the
probes are shown to be active on the display, select the Remote mode
by clicking on the “Remote” button. Select the defaul protocol and then
“Setup Probes” from the menu and wait for all the activated probes to be
acknowledged (the respective box must be green).
To verify the correct functioning of the EMG probes, position a pair of
electrodes (see § “Fitting the Patient”) and connect Probe 1. Next, select
“Gains” from the menu and check the progress of the EMG1 signal.
Repeat the procedure connecting the other probes one at a time.
BTS
Bioengineering
45

BTS FREEEMG
installation
After checking the electromyograph channels, if the system is also provided
with footswitches, attach the connectors with the 4 switches already inserted
to the 2 corresponding FSW/EGN probes. After selecting from the menu
the item “Footswitch” (as shown later in § “Guide to using the software
on the BTS FREEEMG 300”), check each contact is functioning correctly
by pressing rmly each switch and observing the corresponding red LED
light on the display of the BTS FREEEMG 300 (see § “Footswitch”).
If your system has one or more electrogoniometers, repeat the probe
activation procedures deactivating all the EMG probes and enabling
as EGN a number of FSW/EGN probes equal to the number of
electrogoniometers included (maximum 4), refer to § “Active” Button”.
When all the probes required are active go back to Remote mode by
clicking on the “Remote” button. From the Workstation prepare an
acquisition protocol that entails the use of a number of EGN equal to
those provided with your system and transfer it on the receiving unit (see §
“Create a new protocol”). Selection the newly transferred protocol, select
“Probes setup” on the menu and assign each channel to an EGN probe,
checking that they are all recognized (the respective box must be green)
(see § “Probes Setup”).
Finally, connect each electrogoniometer to a connector and then to a
FSW/EGN probe. Select “Gains” from the menu and check the related
signal to the EGN channel that is testing. Repeat the procedure for each
electrogoniometer provided.
46
BTS
Bioengineering

BTS FREEEMG
acquisition protocol
Create a new protocol
Now we will describe how to create a new protocol using the Myolab
software (standard equipment).
e procedure may be dierent if performed with other
applications. In this case, refer to the specic manual of the
software you are using.
To create a new protocol select “Prepare protocol” from the menu voice
“FREEEMG” of Myolab.
A window will open, which allows to create or modify protocols.
BTS
Bioengineering
47

BTS FREEEMG
With BTS FREEEMG 300 it is possibile to acquire:
- up to 16 analog channels: electromyographic signals - EMG
(each EMG employs 1 analog channel), electrogoniometer signals
- EGN (each EGN employs 2 analog channels)
- 8 on-o analysis areas - FSW.
Refer to § “Acquisition unit” for the detailed list of probe
combinations possible.
If you are working with two receiving units the FSW will always
be assigned to the rst unit.
In this case the protocol preparation window will appear as shown
below:
acquisition protocol
To create a new protocol:
BTS
48
Bioengineering

acquisition protocol
- in case a protocol has already been loaded it is possible to empty
out all the elds of the table for the protocol creation by clicking
on the “Clear All” button
-select the current eld, i.e. “Field 1”
- enable the eld putting the check near “Enable”
- choose the probe type “Channel type” to associate to the eld
selected among the available options
BTS FREEEMG
Note that the protocols to use with BTS FREEEMG 300
must contain only EMG, EGN, FSW, however if you
select EMG it can only be the Surface type.
- specify the eld “Signal description”, clicking on the arrow to
enter the list
- select the body side which the signal is refering to
- click on the “Assign” button.
BTS
Bioengineering
49

BTS FREEEMG
acquisition protocol
If all these operations are correctly executed, in corrispondence of the
current eld the label name of the acquiring signal will appear (i.e. R_
ADD, Right Adductor Longus).
Repeat the described operations for every signal that belongs to the
protocol.
e FSW must be put in the right side of the list.
To modify the information of a eld already inserted, click on the
correspondant “Field”, select the channel type and the side and click on
“Assign”. e current eld is modied.
To delete the information in one eld, choose the equivalent “Field” and
click on the “Clear eld” button.
To modify an existing protocol:
- in the box “Select Protocol” the protocols previously created on the
PC are saved, click on the arrow and select the desired protocol.
- for the addition or modication of the signals, follow the
procedures recommended for the protocol creation.
- to return to the original protocol (the one selected in “Select
protocol”) delete the changes done clicking on “Reload
Protocol”.
When every signal of the protocol is inserted, proceed saving the protocol,
following these instructions:
- indicate a name for the protocol specifying it on the “Protocol
Name” box
- it is possibile to insert also a short description of the protocol
BTS
50
Bioengineering

acquisition protocol
using the appropriate box “Description”
- make sure that the BTS FREEEMG 300 is in the Lab Modality (to
access this modality from the main page, click on the “Remote”
button; if two BTS FREEEMG 300 units are being used, make
sure that both the unit have the Remove Mode activated)
- click on “Write by WiFi” to save the protocol on the PC and
transfer it on to the BTS FREEEMG 300.
If two receiving units are being used, it is necessary to wait for
the protocol to be transferred to both units. At the end of the
transfer, the protocol will be visible in both, but in each unit will
be displayed only the respective signals from the channels they are
connected to.
For example, if a protocol with 10 EMG channels has been
created ( 8 associated with the rst unit, 2 with the second) and
the footswitches, the protocol on the rst unit will register 8
EMG channels and the FSWs, while the protocol on the second
unit will register only 2 EMG channels.
BTS FREEEMG
Only the enable signals (“Enable” checked ) will be memorized
in the protocol.
If for example a 4 signals plus FS protocol has already been dened
to create a protocol including only the 4 EMG signals it is enough
to remove the checks on “Enable” from the FS elds.
If required it’s possibile to transfer the protocol through a cable:
- connect the PC and the RU through a USB-PDA cable
- click on “Write Protocol” to save on PC and transfer the protocol
on the BTS FREEEMG 300.
BTS
Bioengineering
51

BTS FREEEMG
acquisition protocol
Fitting the patient
Carefully prepare the skin of the subject in the area to be examined before
positioning the pre-gelled electrodes on the muscles.
Note that the condition of the skin where the electrodes are
applied inuences the quality of the acquired signal.
erefore you should pay careful attention to this phase in
preparing the subject.
Attach the probes, previously activated (see § ““Active” Button), to the
electrodes using the appropriate clips.
anks to the special hardware architecture of the probes and the
much reduced weight, normally no extra xing is required.
If the analysis protocol being used requires it, proceed to the positioning
of the footswitches to the respective contact areas.
When FSWs are used, these are xed to the skin of the subject used tape
or hyper-allergenic bi-adhesive tape.
Never apply the tape on the black membrane of the sensor,
removing the tape could cause the detachment of the membrane
making the switch unusable.
BTS
52
Bioengineering

acquisition protocol
BTS FREEEMG
After positioning the sensors, connect them by means of the appropriate
connector to the corresponding preactivated probe.
Finally, attach the probe and the switch box with the hypo-allergenic
adhesive tape close to the same switches (i.e. close to the ankle when the
sensor have been placed on the foot sole) at all times taking care to leave
the patient the greatest degree of freedom of movement.
Finally, If the analysis protocol being used requires it, proceed to the
positioning of the Electrogoniometers.
Each EGN should be positioned straddling the joint with the two sti
ends positioned on the sagittal plane, parallel to the axes of the two body
segments that make up the joint under investigation, securing them to the
patient’s skin using the plaster or hypoallergenic double-sided tape.
After positioning the sensors, connect them by means of the appropriate
connector to the corresponding preactivated probe.
Finally, attach the probe and the switch box with the hypo-allergenic
adhesive tape close to the sensor on the side where the connection cable
comes out.
roughout the dressing procedure of the patient or at the end of it you
can use the receiving unit to check, using the oscilloscope of the “Gains”
function of the RU, the correct placement of the electrodes and control
that the acquisition gain of the EMG channels is properly set.
It’s possibile also to compare two channels at a time using the “Cross
check” function (see § “Guide to the use of the onboard software”).
BTS
Bioengineering
53

BTS FREEEMG
acquisition protocol
After making all the checks, it is possible to procede with the acquisition
session.
54
BTS
Bioengineering

BTS FREEEMG
guide to the use of onboard software
Initial screen
At the start-up of the BTS FREEEMG 300 you see the initial screen
comprised of six buttons: “Local”, “Remote”, “Download”, “Cong”,
“Activate” and “Exit”.
In the lower right hand corner of the main screen there is the version number of the software installed on board.
“Active” button
e “Active” button allows only those probes to be activated which are
to be used during the acquisition and to assign each of these to a specic
channel.
Click on this button to call up the following display:
BTS
Bioengineering
55

BTS FREEEMG
guide to the use of onboard software
e probes are divided by type: EMG, up to 16 probes for collecting
electromyographic signals, FSW, up to 4 probes for collecting basographic
signals (up to 2 can be selected at the same time), and EGN, up to 4
probes for collecting signals from the electrogoniometers.
A number (or letter) and the colour corresponding to the ID tag of the
probe is shown next to each probe.
By clicking on Options and then “Show probe ID” you can pass from
viewing by label to that for viewing by “ProbeID” identication code, the
code shown on the clip of each probe and vice versa:
56
BTS
Bioengineering

guide to the use of onboard software
BTS FREEEMG
To activate, select the probe that you would like to use for the acquisition
by enabling the check mark in the appropriate box:
It is important to remember that only certain probe congurations
can be activated (for the detailed list of possible congurations,
see § “acquisition unit”).
is procedure will be guided by the software disabling, upon
reaching a conguration limit, all the checkboxes that can no
longer be selected, furthermore, in the notication area at the
bottom, any time the maximum conguration for a type of probe
(EMG, EGN, or FSW) is reached, a warning message will appear
as shown in the following gure:
BTS
Bioengineering
57

BTS FREEEMG
guide to the use of onboard software
Before proceeding to activation, connect the probes to the Charger (or to
the Docking Station) included, use two units if required.
is operation resets the probes, deactivating any probes already active,
except for those probes that are more than 90% charged (in case of
Charger to reset these probes you must wait for the battery level to below
the threshold of 90%).
It is advisable to connect all the probes and not just those used
during acquisition to ensure that you reset any previously activated
probes, which will not be used.
An already active probe can be reused and does not require
reactivation. In this case it must be selected in the activation
program, but do not connect it to the Charger or Docking Station
so it doesn’t reset.
It is in any case necessary that the probes are suciently charged
for the activation to succeed.
Click Start to initiate the probe activation procedure.
Now we would like to distinguish between operations to perform based on
if you use the Charger or Docking Station:
- Charger procedures:
e probes will be activated only when removed from the Charger.
Remove the probes, therefore, from the charger, and wait for the BTS
FREEEMG 300 to activate all the selected probes.
BTS
58
Bioengineering

guide to the use of onboard software
BTS FREEEMG
To facilitate the activation and to verify that all the required probes
are active, we suggest detaching the probes from the charger one
at a time.
- Docking Station procedures:
Click on the Docking Station “Activate” button.
Immediately all the probes selected in the activation probe will be
automatically activated and all the other probes will be reset, regardless
of the charge level.
When a probe has been recognised and activated, it will be highllight by a
green rectangle, as showen in the following gure:
When all the EMG, EGN and FSW probes selezionate risultano attive, are
indicated as activated, click “Stop” to terminate the activation procedure.
Finally, click “Exit” to return to the initial screen.
Selecting the work mode
e rst two buttons (Red and Yellow) allows the user to select the desired
BTS
Bioengineering
59

BTS FREEEMG
guide to the use of onboard software
working mode: button “Local” Holter mode, button “Remote” Lab
mode.
Local Acquisition
(Holter Mode)
Remote Acquisition
(Lab Mode)
Clicking on the button for the desired mode, you can enter the software
of relative management.
In particular by clicking on the “Local” and “Remote” buttons you will see
the following screens:
Description of the main bars and menu
All of the BTS FREEEMG 300 pages have a button bar on the right and
a status bar at the top.
Button Bar
BTS
60
Bioengineering

guide to the use of onboard software
e side arrows (Toggles) can be used to change the active eld.
e up and down buttons make it possible to:
• change the value in the active eld
• navigate around the main menu
e menu button opens the main menu
Status Bar
e status bar displays:
• active page
• the condition of the 4 transmitters indicated with A, B, C, D.
One transmitter can serve more than one probe. When a probe
is transmitting the LED of its corresponding transmitter turns
steady green
• e status of the FSWs (steady green LED if at least 1 FSW probe
is active and recognised by the system)
• battery level
BTS FREEEMG
Main Menu
Clicking on the “menu” button of the buttons bar you enter the main
menu.
ere are two menus: one for the Holter mode and one for the Lab mode.
e two are dierent for the items: “Database” and “PlayBack” which exist
soley in the Holter mode.
BTS
Bioengineering
61

BTS FREEEMG
e main menu allows you to:
- explore the functions of the BTS FREEEMG 300.
To enter a page select the corresponding icon by clicking with
the stylus on the desired function or by usnig the Up and Down
Buttons.
- lock up the palm by clicking with the stylus on the icon “Lock”.
Accomplishing this function will result in the following screen:
guide to the use of onboard software
Lab Mode Menu
Holter Mode Menu
To unlock the palm, clik on the “Unlock” button, this will
BTS
62
Bioengineering

guide to the use of onboard software
BTS FREEEMG
immediately move to another position.
To complete this procedure it is necessary to press it again before
it goes back to the original position.
- close the application by clicking on the “Exit” button.
e following describes the menu functions starting from the ones that
you can nd both in the Holter Mode and in the Lab Mode that have the
same characteristics.
Protocol
is item allows the user to select a protocol from the ones previously
created by the user (see § “Acquisition protocol”).
In any case if a protocol hasn’t yet been created it is possible to use the
default protocol.
Selecting a protocol is achieved by scrolling through the list on the left
panel by clicking on the Up and Down buttons of the buttons bar. e
protocol you select will be highlighted in blue.
BTS
Bioengineering
63

BTS FREEEMG
guide to the use of onboard software
Probes Setup
When a new protocol is dened, the user needs to associate with the items
of the protocol (muscles, joints and foot areas) the channel that physically
acquires the data.
By clicking “Probes setup” from the menu you will see the following
screens:
In particular we can identify two zones:
• the probe-protocol association table
• e “Probes” area
e table, for each signal of the acquisition protocol, previously selected in
the “protocol” section shows:
• the identier of the assigned probe (comprised of the colour and
number/letter of the label), if no probe has been assigned the eld is
set on “--”
• the type of probe: Surface, Footswitch, Electrogoniometer,...
• the state of the probe:
• OK: Signal/probe properly assigned, the probe has been
BTS
64
Bioengineering

guide to the use of onboard software
BTS FREEEMG
selected in the activator and is connected to the RU.
• NOT CONNECTED: Signal/probe properly assigned, the
probe has been selected in the activator, but does not appear
to be connected to the RU.
• “--” : no assigned probe.
• NOT ACTIVATED: the probe is assigned to the protocol
signal, but has not been selected in the activator.
• ERROR: the signal/probe has not been properly assigned as
the type of probe expected by the protocol does not match
the actual probe
In the “Probes” area (rectangle at the bottom) where the selected probes in
the activator are listed and the state is described.
In particular, the boxes associated to channels can have dierent colours:
• Green:
the selected probe in the activator is connected to the RU and is
assigned to a protocol signal (the “Status” eld of the protocol is
“OK”)
• Grey:
the selected probe in the activator is connected to the RU but is not
assigned to any protocol signal
• Orange:
the selected probe in the activator is not connected to the RU but
is assigned to a protocol signal (the “Status” eld of the protocol is
“NOT CONNECTED”)
• White:
the selected probe in the activator is not connected to the RU and has
not been assigned to any protocol signal
BTS
Bioengineering
65

BTS FREEEMG
guide to the use of onboard software
• Red:
the selected probe in the activator is connected to the RU and assigned
to a protocol signal, but the type of probe expected by the protocol
does not match the actual probe (the “Status” eld of the protocol is
“ERROR”).
To make the association probe-signal:
1. use Up and Down buttons to select a signal
2. use toggle to select the “Probe” eld
3. choose among the available ones (all the probes present in
the probe area will be proposed), the probe to pair to the
highlighted signal
4. use toggle to select the description (the whole row)
5. move on the next description with the arrow Down and restart
from point 2 to assign the channel to the next item.
Active elds (Toggle) Value range (Select)
66
Description Signals List
Probe 1, 2, ..., 15, 16, for EMG channels
BTS
Bioengineering
A.1, A.2, A.3, A.4, B.1, B.2, B.3, B.4,
C.1, C.2, C.3, C.4, D.1, D.2, D.3, D.4,
E.1, E.2, E.3, E.4, F.1, F.2, F.3, F.4,
for EGN and FSW
all available in 4 colors:
Green, Red, Blue, Yellow

guide to the use of onboard software
BTS FREEEMG
Each Electrogoniometer generates two signals, it is important that
you assign two channels of the same probe to the signals generated
by the same EGN, e.g. C.1, C.2
To properly assign the basographic signals to the FSW probe
channels please remember to match the 4 signals related to one
probe to the protocol signals related to the physically close contact
area, e.g. A.1, A.2, A,3, A.4 for the Right foot and B.1, B.2, B.3,
B.4 for the Left foot.
Before starting acquisition, the user needs to conrm that the
“Status” of each protocol voice is OK.
Digital Oscilloscope (gain)
With BTS FREEEMG 300 the user can set up to 3 dierent ranges of
values to see the muscular contractions better.
To setting this value see § “ Cong” Button”.
e selectable values are:
• S1: 6,34mV;
• S2: 3,17mV;
• S3: 1,62mV.
By accessing the gains page it is possible to verify that electrodes have
been well positioned (no noise or motion artefacts) and that the signals are
properly displayed and if they are not you can change the range of value
BTS
Bioengineering
67

BTS FREEEMG
guide to the use of onboard software
set in the conguration section.
To do this, simply view via the oscilloscope the real-time muscular activity
of each muscle you would like to analyse for a few seconds, asking the
patient to perform several contractions.
If the intensity of the muscle is very low, so that it is dicult to distinguish
between when the muscle is in contraction from when it is at rest, the range
needs to be reduced (the system will increase the gain correspondingly).
If, on the other hand, the signal in the current amplitude tends to saturate
(meaning during the contraction there are peaks in the orange zone or
beyond), it is necessary to increase the range (the system will reduce the
signal gain accordingly).
Keep in mind that the base range value will be the same for all
signals acquired.
erefore select the value that lets you best see the channels
simultaneously without saturation.
If the selected range is insucient to contain the entire signal
dynamic, the acquisition data will tend to saturate during
the contraction, which will appear as unnatural plateaus in
measurement values at the limits of the selected range.
On the other hand, if the signal is very weak, maintaining a high
range is not a mistake. It is recommended, however, that the range
be reduced whenever possible, in order to make better use of the
digitalisation of the acquisition card.
BTS
68
Bioengineering

guide to the use of onboard software
BTS FREEEMG
e gain used in the acquisition of the EMG signals is managed
by the application on the basis of the range selected, the choice
of range should be done with great care since it aects not only
the display but also the acquisition signal (it is not a just a simple
zoom!).
By clicking the voice “Gain” from the menu you will see the following
screens:
To scroll the diferent signals, click on the Toggle to activate the “Signal”
active eld and select the protocol item desired by actuating the Up and
Down buttons.
To make the signal visualization easier it is possible to use the “Time”
active eld (by selecting it with the Toggle) this allows to adjust the speed
at which the signals run on the screen (this is only for display purposes,
and will have no eect on the capture).
It is possible to set the time value interval shown on the axes of the
oscilloscope abscissas, selecting from a range of values from 1 to 10
seconds, that can be selected with the Up and Down buttons.
BTS
Bioengineering
69

BTS FREEEMG
guide to the use of onboard software
Active elds (Toggle) Value range (Select)
Signal Protocol signals
Time 1 sec - 10 sec
Oscilloscopio digitale (cross check)
e Cross Check is very useful during the patient setup phase, allows the
operator to verify, prior to the actual acquisition of the signals, that the
electrodes have been positioned correctly.
e possibility of displaying two traces simultaneously prevents the
problem of cross-talk: this phenomenon occurs as a detection of electrical
activity on the trace of a muscle during a movement which should not
involve the muscle in question.
Cross-talk is occurring if, for example, during the movement of extension
of the wrist, one observes the activity of the ulnar carpus exor.
BTS
70
Bioengineering

guide to the use of onboard software
BTS FREEEMG
is is due to an incorrect positioning of the electrodes, as a consequence
of which the channel dedicated to a certain muscle is in reality measuring
the activity of another muscle.
In the above example, the activity measured on the trace of the ulnar
carpus exor is not in reality being produced by that muscle, but by one
deeper down or by its antagonist.
To appoint the signals to visualize select the “Signal 1” and then “Signal
2” eld with the Toggle and scroll the signal list included in the protocol
using the Up and Down buttons.
e current display can be enlarged or reduced via the zoom function: this
does not aect in any way the data being read.
e “Time” eld can be used to vary the speed at which the signal runs
on the screen (again, this has no eect on the reading, but only on the
display).
It is possible to x the time intervals represented on the axis of the abscissas
of the oscilloscope, choosing from a range of values from 1 to 10 seconds.
Active elds (Toggle) Value range (Select)
Signal 1 Protocol signals
Signal 2 Protocol signals
Zoom From 1/10 to x10
Time From 1 sec to 10 sec
BTS
Bioengineering
71

BTS FREEEMG
guide to the use of onboard software
Footswitches
e Footswitches page shows in real time the activation of the contact
zone during the deambulation contact phase.
When a zone is active, the foot is resting on it - the corresponding circle
colors is red.
If there isn’t correspondence between the contact points indicated
on the display and the movements done by the subject (for
example if with the right foot in stance the areas under the left
foot of the display became red) we suggest you to review the FSW
channels setup selecting the menu voice “Probes Setup”.
Usually the Footswitches are used for studying the sole of the foot during
ambulation.
Four points have been identied for this purpose in order to be able to
distinguish the foot tread while walking.
ese 4 areas are:
BTS
72
Bioengineering

guide to the use of onboard software
BTS FREEEMG
• Internal Contact,
• External Contact,
• Heel Contact
• Toe Contact.
However, while preparing the protocol you can indicate the general
contact areas:
• “Contact area 1”,
• “Contact area 2”,
• “Contact area 3”
• ,...
e Footswitch probes can also be used for other applications and
placed on other parts of the body where you would like to record
the moment of contact (for example on a nger during pointing
exercises).
In this case you should use a general “Contact Area 1”, “Contact
Area 2” in the protocol, and in the FSW page refer to the rectangles
located under the gure showing the foot to check that the probes
are properly activated.
“Local” button: Holter Mode
In this mode the RU is completely independent and it’s possibile to acquire
the data independently of the WS.
Session preparation:
selecting “Local” you can enter the patient’s database on the palm.
BTS
Bioengineering
73

BTS FREEEMG
List of patients already included in the
database of the BTS FREEEMG 300
List of sessions for the highlighted
patient
List of the tests of the highlighted
session
guide to the use of onboard software
To add a new patient click with the stylus on “New subject” button.
A window will open which allows you to insert general information about
the patient.
To insert the patient data:
• move up to the eld to insert
• insert the value with the keypad, (each tap on the gender eld
will change from F to M and viceversa)
• press OK to insert the patient into the database
BTS
74
Bioengineering

guide to the use of onboard software
BTS FREEEMG
It is possible to modify or to delete the data of a patient already inserted.
By clicking on the line of that patient, it will be underlined in light blue
and the “Delete” and “Modify” buttons will appear.
Clicking on “Modify” a window will open that allows to modify the general
information of this patient.
Click on “Delete” and immediately a window with the request to conrm
the deletion will appear:
Clicking on “Yes” the trial will be removed from the database, with all
the related sessions and trials, while if you choose “No” the deletion will
be aborted.
BTS
Bioengineering
75

BTS FREEEMG
guide to the use of onboard software
To create a new test session click on “New Session”.
A window will open that allows to the user to insert data linked to the
session:
• patient weight
• patient height
• pathology
• possible notes of the session
Press “OK” to add the session of the selected patient.
e default protocol is linked to the session; to change the
protocol click on the Menu button and enter the “Protocol” item
(see § “Protocol”).
Cautious that it is not possible, rather than, to change protocol of
a session when this has already got some acquisitions.
To continue working with the same patient but with a dierent
protocol it is necessary to create a new acquisition session for that
patient.
BTS
76
Bioengineering

guide to the use of onboard software
BTS FREEEMG
To modify or to delete the data of a session created previously click on the
correspondent line, it will be underlined in light blue and the “Delete” and
“Modify” buttons will appear.
Clicking on “Modify” a window will open that allows to modify the data
related to this session:
Click on “Delete” and immediately a window with the request to conrm
the deletion of the session and the relate trials will appear:
Clicking on “Yes” the session and the trials will be removed from the
database, with all the related sessions and trials, while if you choose “No”
the deletion will be aborted.
BTS
Bioengineering
77

BTS FREEEMG
guide to the use of onboard software
Latter it is possible to delete single trials. To do that click on the
correspondent line, it will be underlined in light blue and the “Delete”
buttons will appear.
Click on “Delete” and immediately a window with the request to conrm
the deletion of the trial will appear:
Clicking on “Yes” the selected trial will be removed from the database, with
all the related sessions and trials, while if you choose “No” the deletion will
be aborted.
Acquisition:
to proceed with the acquisition in “Local” mode it is necessary to have
created a new session and to have selected an analysis protocol or to have
selected a session already in the database.
Proceed then with the operations described in the previous paragraphs:
“Probes Setup”, “Range”, “Digital Oscilloscope”, “Footswitches”.
Once nished all the preliminary operations and the necessary checking it
is possible to proceed with the acquisitions.
To do that, select the item “Capture” from the Menu.
BTS
78
Bioengineering

guide to the use of onboard software
BTS FREEEMG
A screen will appear, which gives the setup for that acquisition:
For every test it’s possibile to indicate the Start and Stop mode, the
acquisition frequency and the type and notes of the test.
To edit the notes click on “Edit Notes”, a window will open which allows
you to edit the notes.
Introduce the note using the keyboard and then click on “OK” to conrm
or on “Cancel” to come back to the previous screen without saving the
text just typed.
BTS
Bioengineering
79

BTS FREEEMG
guide to the use of onboard software
To modify the other acquisition parameters select the relative eld with
the Toggle and then use the Up and Down buttons.
Active elds (Toggle) Value range (Select)
Acq. Frequency 1KHz, 2KHz, 3KHz, 4KHz
Flag MMT, Resting, Walking, Undened, Extra
If you want to process the acquired tests using Myolab Clinic, the
“Flag” eld must be dierent from “Undened”. All the other
BTS Software don’t make use of this data.
e acquisition starts by clicking on the “Start” button.
At the start-up of the acquisition the BTS FREEEMG 300 automatically
goes into Lock mode, showing the following:
To unlock the palm click on the “Unlock” button, this will immediately
move to another position. To complete this procedure it is necessary to
BTS
80
Bioengineering

guide to the use of onboard software
BTS FREEEMG
press it again before it goes back to the original position.
Before quitting this mode the screen with the acquiring setup reappears
but the “Start” (or “Arm”) button is substituted with the “Unlock” and
“Stop” buttons.
e “Unlock” button allows to come back to the previous screen.
Clicking on “Stop”, instead, will end the acquisition.
At this point the following screen will be visualized:
BTS
Bioengineering
81

BTS FREEEMG
guide to the use of onboard software
To save data on BTS FREEEMG 300 select “Store” whereas to cancel the
data just acquired click on “Delete”.
In this case a conrmation for the cancellation will be asked of the user,
select “Yes” if you want to delete the new acquired data. Click“No” button”
and then “Store” to save the test.
After the storing or the cancellation of the last acquired test you are
redirected to the screen containing the “Start” button.
To continue with another acquisition click on “Start” and repeat the
operations just described. If any other acquisition won’t be executed, select
“Exit” from the menu.
Playback
In the Holter mode it is possible to visualize a preview of the data acquired
and saved in the database.
To do that, from the menu select the voice “Database” and select the
patient, the session and the trial that you want to visualize clicking with
the stylus on the correspondent line, that will be underlined in light blue.
Once the trial is selected, from the menu select the voice “Playback”.
At the end of an acquisition session it is possible to go directly to the
“Playback” page, without passing from the “database”: in this circumstance
all the trials saved in the last session acquired will be loaded.
In both these circumstances the following screen will appear:
BTS
82
Bioengineering

guide to the use of onboard software
BTS FREEEMG
From the lower panel select the trial to visualize by tapping on the
correspondent line.
It is possible to visualize two signals at the same time.
To do that select the eld “Signal 1” and than “Signal 2” using the Toggle
and scroll the list of the available signals operating on the Up and Down
buttons.
After that to improve the signal visualization, adjust the active elds
“Zoom” and “Time” selecting them with the Toggle and changing their
value with the Up and Down buttons.
In particular the “Zoom” eld allows increasing or reducing the current
view area (it acts on the axis of ordinates), while the “Time” eld allows
changing the temporal value range showed on the axis of the abscissas,
choosing among a range of value in between 1 and 10 seconds.
is means that the selected trial will not be entirely visualized, but only
bits of the length of 1, 2, 5 or 10 seconds according with the “Time”
eld.
BTS
Bioengineering
83

BTS FREEEMG
guide to the use of onboard software
Active elds (Toggle) Value range (Select)
Signal 1 Protocol signals
Signal 2 Protocol signals
Zoom
Time From 1 sec to 10 sec
# Trial Trials of the selected session
However it is possible to scroll the whole trial changing time after time the
frame from where the visualization starts.
To do that click with the stylus on the grey band that represents the whole
trial in the point correspondent to the rst frame to visualize.
On the grey band at the two extremities, are indicated the beginning of
the trial (that is 0:00) and the total length of it (like in the example in the
gure 0:34, that means 0 minutes and 34 seconds).
In the spot in which you tap, a grey rectangle will appear in which will be
indicated the correspondent time of the selected rst frame (like in the
example in the gure 0:21).
erefore, if the “Time” eld is set, for example, on “5sec”, we are
visualizing 5 seconds of trial starting from the 21st second.
It is possible, if you regard it relevant, delete some trials.
BTS
84
Bioengineering

guide to the use of onboard software
BTS FREEEMG
Click on the trial, choosing it in the lower panel, that you want to delete.
It will be underlined in light blue and the “Delete” button will appear.
Click on “Delete” and immediately a window with the request to conrm
the deletion will appear:
Clicking on “Yes” the trial will be removed from the database, while if you
choose “No” the deletion will be aborted.
Importing data to Myolab
e data acquired in Holter mode is saved in a local database in the BTS
FREEEMG 300. To execute the elaboration and the analisys of the data,
you need to import the test using the software Myolab software.
To do this, proceed as described further in § “Download button”.
BTS
Bioengineering
85

BTS FREEEMG
guide to the use of onboard software
“Remote” button: Lab mode
In this mode the connection between RU and WS is always available.
e specic characteristics are:
• sending data boxes to the WS for the visualization in the remote
oscilloscope, available in the applicative software.
• data transfer at the end of acquisition.
• the duration of acquisition and the Start/Stop are controlled by
the PC.
Selecting “Capture” from the main menu the following screen appears:
is screen displays some information concerning the system:
• Status: Ready mode
• Mode: Stand Alone
• Data: None
To make an acquisition in Lab mode, there must be no
data saved on the BTS FREEEMG 300.
BTS
86
Bioengineering

guide to the use of onboard software
BTS FREEEMG
is possibility can happen only with a loss of WiFi connection between
BTS FREEEMG 300 and Workstation during the last acquisition, or if
the data transfer has not gone well.
In this case the screen displayed after having selected “Capture” from the
main menu will contain instead of the “Arm” button, the “Delete” button
and the “Data” eld will be “Ready”.
If you want, it is possible to recover the lost data saved in the RU
before proceeding with the new acquisitions downloading them on the
Workstation using the Myolab software.
To know the download procedure consult the manual of
Myolab.
Otherwise the data will have to be deleted and cannot be retrieved in the
future.
To delete the data, click on the “Delete” button; by doing this the system
will ask you a conrmation for the deletion, select “Yes” if you really want
to delete the data in a permanent way, otherwise click on “No” to come
back to the previous screen.
BTS
Bioengineering
87

BTS FREEEMG
guide to the use of onboard software
Once deleted the le, the “Arm” button appears again and the “Data”
eld will again become “None”; so it’s possibile to proceed with the
acquisition.
Before arming the system it is possible to set the acquisition
frequency using the Up and Down button of the button bar.
Active elds (Toggle) Value range (Select)
Acq. Frequency 1KHz, 2KHz, 3KHz, 4KHz
To prepare the system for capture it is necessary to “arm” it by simply
tapping the “Arm” button that will be replaced by the “Lock” and the
“Cancel” buttons; now it is possible to make the acquisition via remote
control.
At this level it is not possible to change the acquisition
frequency.
BTS
88
Bioengineering

guide to the use of onboard software
BTS FREEEMG
Tapping on the “Cancel” button the previous screen appears, returns
control to the RU.
To procede with the next acquisition, the system needs to be armed
again.
It is possible to lock the system by clicking on “Lock” directly by this
window, therefore at the beginning of the acquisition the BTS FREEEMG
300 locks automatically displaying:
e acquisition starts-up through the remote control, directly by
the Workstation.
is display will remain on the BTS FREEEMG 300 until the acquiring
session is over.
It’s possibile to interrupt the acquisition remotely and proceed with the
next ones.
At the end of every acquisition an automatical data download will be
BTS
Bioengineering
89

BTS FREEEMG
guide to the use of onboard software
executed.
Only at the end of the download is it possibile to launch another remote
acquisition.
Once the acquisition session is over, unlock the BTS FREEEMG 300.
In order to do so, press the “Unlock” button, this will immediately move
to another position.
To complete this procedure it is necessary to press it again before it goes
back to the original position.
Finally to quit from the “Armed” status click on the “Cancel” button.
For the details of the remote management of the acquisition from
the WS refer to the specic manual of the software meant to be
used.
Download Button
If the Holter mode is chosen (local acquisition), the acquisitions are saved
in a local database to BTS FREEEMG 300.
To elaborate the acquired data with the dedicate softwares installed on the
Workstation, the user needs to download them with Myolab following
these instructions:
• Select from the main page the download mode clicking on the
“Download” button
• BTS FREEEMG 300 keeps waiting, showing the following
screen:
BTS
90
Bioengineering

guide to the use of onboard software
• From Myolab, select the “Download” item from the “FREEEMG”
menu
• A window will appear that will allow you to explore and modify
the active database on the BTS FREEEMG 300, and download
all the les that you are interested in.
For further details concerning the data download refer
to the user manuals of Myolab software.
BTS FREEEMG
e data import takes place with a wireless connection;
if the import operation fails, you need to verify that
the RU and WS are connected (see § “Appendix C –
troubleshooting guide”).
• When the download is nished on the BTS FREEEMG 300
keep pressing the “Exit” button to go back to the main screen.
BTS
Bioengineering
91

BTS FREEEMG
guide to the use of onboard software
“Cong” button
e “Cong” button launches an application that allows the modication
of some system settings.
It uses ve tabs to reach the dierent information and features:
• Info:
Main screen that contains information of the installed versions.
• General:
General settings (i.e. language, audio settings...).
• Radio:
Associates the ID identier of each EMG and FSW/EGN probe
to its label identied by colour and number/letter;
setting of the signal range;
setting the radio channels utilising the probes.
• Database:
Datbase managment.
• Maintenance:
section permitted only to BTS Technician sta, for assistance.
For this reason to access this area a Password is required.
To execute any changes of the parts that can type on it is possible to use
the touch-screen features of the display and where necessary, activate the
keyboard, clicking on the low right corner icon represented by a little
keyboard.
To exit this application and come back to the main screen, you must tap
on the “Ok” button, placed in the top right corner.
One tap on this button will conrm all the changes made.
BTS
92
Bioengineering

guide to the use of onboard software
BTS FREEEMG
It won’t be possible to undo the changes made, apart setting again,
manually the previous values.
All the changes made are immediately activated, therefore, in some
circumstance, it will be necessary to restart the BTSFREEEMG300
application to see these changes applied (for example when you change
the language).
Let’s analyze now, more in depth, the four tabs that the user can modify.
Info
Clicking on the “Cong” button on the main screen, it automatically
selects the application screen in which the tab Info is selected:
On this page it is possible to read all the information about the versions of
each installed component, hardware or software.
BTS
Bioengineering
93

BTS FREEEMG
guide to the use of onboard software
General
Selecting “General”, the following screen will be visualized:
It is possible to set:
• e language
• “DHCP”, for automatic host conguration, the “IP address”
and “Netmask”, available only with the “DHCP” not checked,
to manually assign the connection parameters and the “Port
Number”.
• “Quite mode”: Checking this voice, the program will play
without any noise (instead of what normally happens when for
example you Tap on a button or activate an acquisition…)
• “Lock on Capture”: Checking this voice when an acquisition
starts the BTS FREEEMG 300 will be automatically locked
showing the “Unlock” button
• “Video o on Capture”: if checked, the display automatically
will switch-o at the acquisition beginning. To activate the
screen again a click on one of the PocketPC button is enough
• e use of a Secure Digital memory card to store the temp le
generated during the acquisition (check this voice only if there is
a Secure Digital board in the related port).
94
BTS
Bioengineering

guide to the use of onboard software
BTS FREEEMG
Radio
When “Radio” is selected the following page is displayed:
e “EMG probes” and “FSW/EGN probes” sections allow to associate
the ID that uniquely identies each probe manufactured by BTS S.p.A.
with the probe’s label.
e ID is shown on the clip of every EMG probe and on the back of every
FSW/EGN probe.
Up to 16 EMG probes and up to 4 FSW/ EGN probes can be registered.
Probes that are not registered in this section will not be recognized
by the Receiving Unit and therefore may not be used for
acquisitions.
Generally, the system is distributed to the customer with this association
already made.
However it could be useful if new probes are purchased or if probes are
replaced due to a malfunction.
BTS
Bioengineering
95

BTS FREEEMG
guide to the use of onboard software
However when you receive the system it is advisable to check
that the association has been made correctly. If a probe has been
incorrectly associated to a label or the ID number does not match
that on the clip the probe may not work. Instead, changing
two IDs compared to the label could cause an exchange of
acquisition signals as well and therefore cause false results in the
Electromyographic examination.
Follow the procedure below, to register a probe that has not been
introduced:
• Enter the ID of the probe using the keypad that can be activated
on the bottom right-hand side of the page.
If the string entered is not admissible or has already
been entered the software will highlight it in red.
• Select the colour of the probe’s label (the colours can be Red,
Green, Blue, and Yellow) using the drop down menu.
BTS
96
Bioengineering

guide to the use of onboard software
• Finally, select the number or letter shown on the probe’s label
(number selection from 1- 16, letter selection from A-F).
BTS FREEEMG
If the label (identied by the colour/ number or letter
combination) has already been used the software will
highlight the ID string in red.
BTS
Bioengineering
97

BTS FREEEMG
guide to the use of onboard software
From the Radio page two other sections may be accessed.
e “Signal” section allows to select the Range for electromyographic
signals. 3 dierent value are available:
• 6,34mV;
• 3,17mV;
• 1,62mV
From the “Radio Channels” section the ZigBee channel with which to
work can be assigned to the activator and the four transmitters.
BTS
98
Bioengineering
 Loading...
Loading...