Page 1
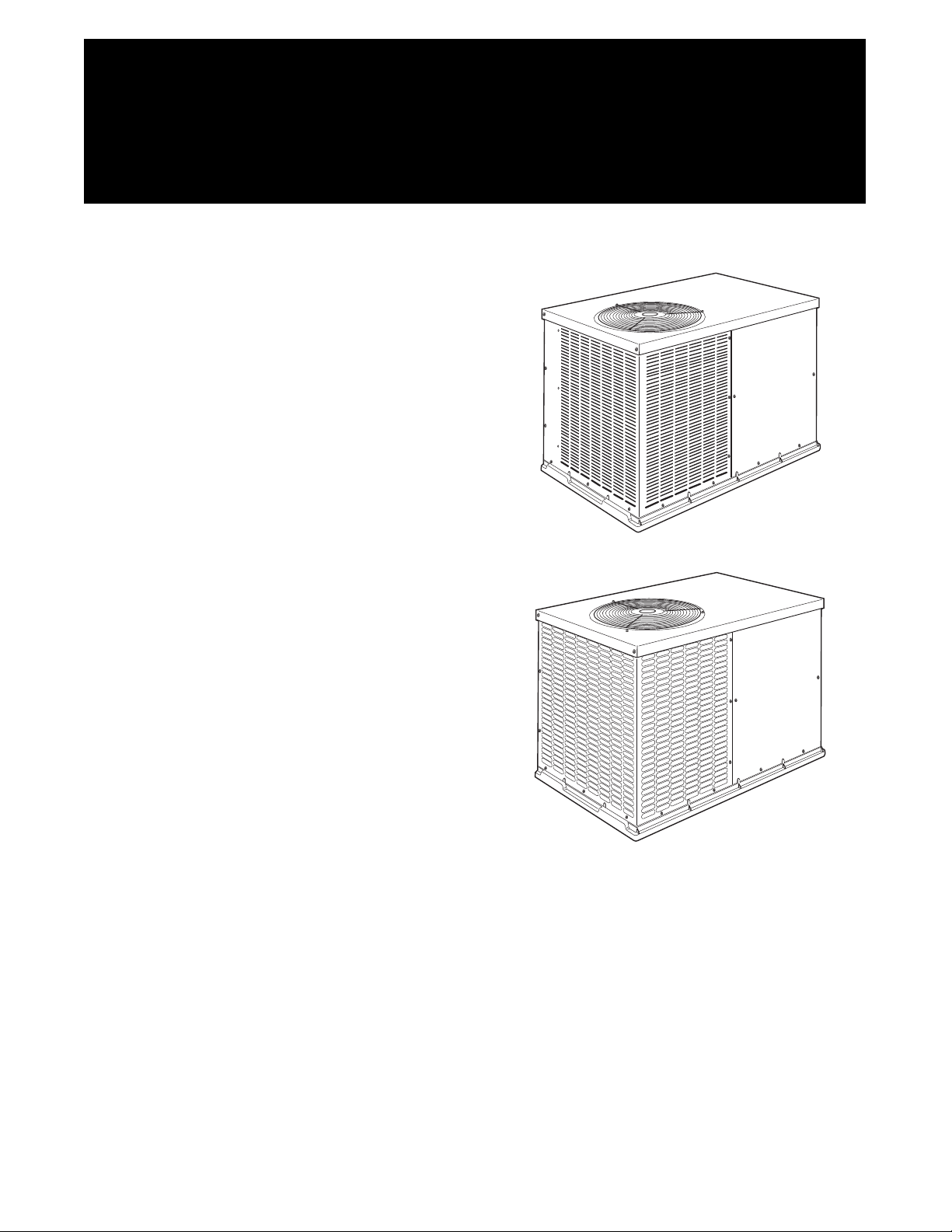
PH4Z
14 SEER SINGLE---PACKAGED HEAT PUMP SYSTEM
Installation Instructions
IMPORTANT: Effective January 1, 2015, all split system and
packaged air conditioners must be installed pursuant to applicable
regional efficiency standards issued by the Department of Energy.
NOTE: Read the entire instruction manual before starting the
installation.
NOTE: Installer: Make sure the Owner’s Manual and Service
Instructions are left with the unit after installation.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PAGE
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS 2.........................
INTRODUCTION 2...................................
RECEIVING AND INSTALLATION 2--10.................
Check Equipment 2..................................
Identify Unit 2....................................
Inspect Shipment 2.................................
Provide Unit Support 2...............................
Slab Mount 2.....................................
Ground Mount 2..................................
Provide Clearances 2.................................
Place Unit 3........................................
Select and Install Ductwork 3...........................
Installing factory--supplied duct flanges 3...............
Configuring Units for Downflow (Vertical) Discharge 9....
Connect Condensate Drain 9...........................
Install Electrical Connections 9.........................
High--Voltage Connections 9.........................
Routing Power Leads Into Unit 9......................
Connecting Ground Lead to Unit Ground 10.............
Routing Control Power Wires 10.....................
Accessory Electric Heat Wiring 10.....................
PRE--START--UP 10...................................
START--UP 11--14.....................................
Check for Refrigerant Leaks 11.........................
Start--Up Cooling and Make Adjustments 11...............
Checking Cooling and Heating Control Operation 11......
Refrigerant Charge 11................................
No Charge 11.....................................
Low Charge Cooling 11.............................
Heating Mode Charge 12............................
Indoor Airflow and Airflow Adjustments 14...............
Sequence of Operation 14.............................
Fan Operation 14..................................
Cooling Operation 14...............................
Heating Operation 14...............................
Continuous Fan 14.................................
WITH R ---410A REFRIGERANT
SINGLE PHASE
2 --- 5 N O M I N A L T ON S ( S I Z E S 2 4 --- 6 0 )
A05165
PH4Z 024--048
A150067
PH4Z 060
Fig. 1 -- PH4Z
Certified to leak 2% or less of nominal air conditioning CFM
delivered when pressurized to 1--in. W.C. with all present air
inlets, air outlets, and condensate drain port(s) sealed.
Defrost 14.......................................
Electric Resistance Heating 14........................
MAINTENANCE 18--21................................
Air Filter 18........................................
Unit Top Removal 18.................................
Indoor Blower and Motor 19...........................
Outdoor Coil, Indoor Coil, and Condensate Drain Pan 19.....
Outdoor Fan Adjustment 19............................
Electrical Controls and Wiring 20.......................
Refrigerant Circuit 20.................................
Indoor Airflow 20...................................
1
Page 2
Metering Devices 20.................................
High Flow Valves 20.................................
High Pressure Switch 20..............................
Loss of Charge Switch 20.............................
R--410A Compressor 20...............................
Refrigerant 20......................................
Compressor Oil 21...................................
Servicing Systems on Roofs with Synthetic Materials 21......
Synthetic Roof Precautionary Procedure 21................
Liquid Line Filter Drier 21.............................
R--410A Refrigerant Charging 21.......................
TROUBLESHOOTING 21..............................
START--UP CHECKLIST 21............................
!
WARNING
PERSONAL INJURY AND ENVIRONMENTAL
HAZARD
Failure to relieve system pressure could result in personal
injury and/or death.
1. Relieve pressure and recover all refrigerant before
servicing existing equipment, and before final unit disposal.
Use all service ports and open all flow--control devices,
including solenoid valves.
2. Federal regulations require that you do not vent
refrigerant into the atmosphere. Recover during system
repair or final unit disposal.
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
Installation and servicing of this equipment can be hazardous due
to mechanical and electrical components. Only trained and
qualified personnel should install, repair, or service this equipment.
Untrained personnel can perform basic maintenance functions such
PH4Z
as cleaning and replacing air filters. All other operations must be
performed by trained service personnel. When working on this
equipment, observe precautions in the literature, on tags, and on
labels attached to or shipped with the unit and other safety
precautions that may apply.
Follow all safety codes. W ear safety glasses, protective clothing,
and work gloves. Use quenching cloth for brazing operations.
Have fire extinguisher available. Read these instructions
thoroughly and follow all warnings or cautions included in
literature and attached to the unit. Consult local building codes,
the current editions of the National Electrical Code (NEC) NFPA
70 and NFPA 90B--Installation Warm Air Heating and A/C
Systems (Residential). In Canada refer to the current editions of the
Canadian Electrical Code CSA C22.1.
Recognize safety information. This is the safety--alert symbol
When you see this symbol on the unit and in instructions or manuals, be alert to the potential for personal injury. Understand these
signal words: DANGER, WARNING, and CAUTION. These
words are used with the safety--alert symbol. DANGER identifies
the most serious hazards which will result in severe personal injury
or death. WARNING signifies hazards which could result in personal injury or death. CAUTION is used to identify unsafe practices which may result in minor personal injury or product and property damage. NOTE is used to highlight suggestions which will
result in enhanced installation, reliability, or operation.
!
WARNING
ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARD
Failure to follow this warning could result in personal
injury or death.
Before installing or servicing system, always turn off main
power to system and install lockout tag. There may be
more than one disconnect switch. Turn off accessory heater
power switch if applicable.
!
CUT HAZARD
Failure to follow this caution may result in personal injury.
Sheet metal parts may have sharp edges or burrs. Use care
and wear appropriate protective clothing, safety glasses and
gloves when handling parts and servicing.
CAUTION
INTRODUCTION
This packaged heat pump is fully self-- contained and designed for
outdoor installation (See Fig. 1). Standard units are shipped in a
horizontal--discharge configuration for installation on a
ground--level slab or directly on the ground if local codes permit.
Standard units can be converted to downflow (vertical) discharge
configurations for rooftop applications with a field supplied
plenum.
RECEIVING AND INSTALLATION
Step 1 — Check Equipment
IDENTIFY UNIT
The unit model number and serial number are printed on the unit
informative plate. Check this information against shipping papers.
INSPECT SHIPMENT
Inspect for shipping damage while unit is still on shipping pallet. If
unit appears to be damaged or is torn loose from its anchorage,
have it examined by transportation inspectors before removal.
Forward claim papers directly to transportation company.
Manufacturer is not responsible for any damage incurred in transit.
.
Check all items against shipping list. Immediately notify the
nearest equipment distribution office if any item is missing. To
prevent loss or damage, leave all parts in original packages until
installation.
Step 2 — Provide Unit Support
For hurricane tie downs, contact distributor for details and PE
(Professional Engineering) Certificate, if required.
SLAB MOUNT
Place the unit on a solid, level concrete pad that is a minimum of 4
in. (102 mm) thick with 2 in. (51 mm) above grade. The slab
should extend approximately 2 in. (51 mm) beyond the casing on
all 4 sides of the unit. Do not secure the unit to the slab except
when required by local codes.
A 6--in. (152 mm) wide gravel apron should be used around the
flat surface to prevent airflow blockage by grass or shrubs. The
unit should be level within 1/4 in. (6 mm). This is necessary for the
unit drain to function properly.
GROUND MOUNT
The unit may be installed either on a slab or placed directly on the
ground if local codes permit. Place the unit on level ground
prepared with gravel for condensate discharge.
Step 3 — Provide Clearances
The required minimum service clearances are shown in Fig. 4--6.
Adequate ventilation and outdoor air must be provided.
The outdoor fan draws air through the outdoor coil and discharges
it through the top fan grille. Be sure that the fan discharge does not
recirculate to the outdoor coil. Do not locate the unit in either a
corner or under an overhead obstruction. The minimum clearance
under a partial overhang (such as a normal house overhang) is 48
2
Page 3
in. (1219 mm) above the unit top. The maximum horizontal
extension of a partial overhang must not exceed 48 in. (1219 mm).
IMPORTANT: Do not restrict outdoor airflow. An air restriction
at either the outdoor--air inlet or the fan discharge may be
detrimental to compressor life.
Do not place the unit where water, ice, or snow from an overhang
or roof will damage or flood the unit. Do not install the unit on
carpeting or other combustible materials. Slab--mounted units
should be at least 4 in. (102 mm) above the highest expected water
and runoff levels. Do not use unit if it has been under water.
Step 4 — Place Unit
Unit can be moved with the rigging holds provided in the unit
base. Refer to Table 1 for operating weights. Use extreme caution
to prevent damage when moving the unit. Unit must remain in an
upright position during all moving operations. The unit must be
level with in 1/4 in. (6 mm) for proper condensate drainage; the
ground--level pad must be level before setting the unit in place.
When a field-- fabricated support is used, be sure that the support is
level and that it properly supports the unit.
Step 5 — Select and Install Ductwork
The design and installation of the duct system must be in
accordance with the standards of the NFPA for installation of
non--residence type air conditioning and ventilating systems,
NFPA 90A or residence type, NFPA 90B and/or local codes and
ordinances.
Select and size ductwork, supply-- air registers, and return air grilles
according to ASHRAE (American Society of Heating,
Refrigeration, and Air Conditioning Engineers) recommendations.
Use the duct flanges provided on the supply-- and return-- air
openings on the side of the unit. See Fig. 4--6 for connectio n sizes
and locations. The 14--in. (356 mm) round or 14 x 20 in. (356 x
508 mm) rectangular duct collars are shipped inside the unit
attached to the base pan in the indoor blower compartment.
They are field--installed and must be removed from the indoor
blower compartment prior to start--up, even if they are not
used for installation. If a corrugated shipping block is used
under the blower housing, remove and discard the block and
label.
When designing and installing ductwork, consider the following:
!
CAUTION
UNIT DAMAGE HAZARD
Failure to follow this caution may result in damage to unit
components.
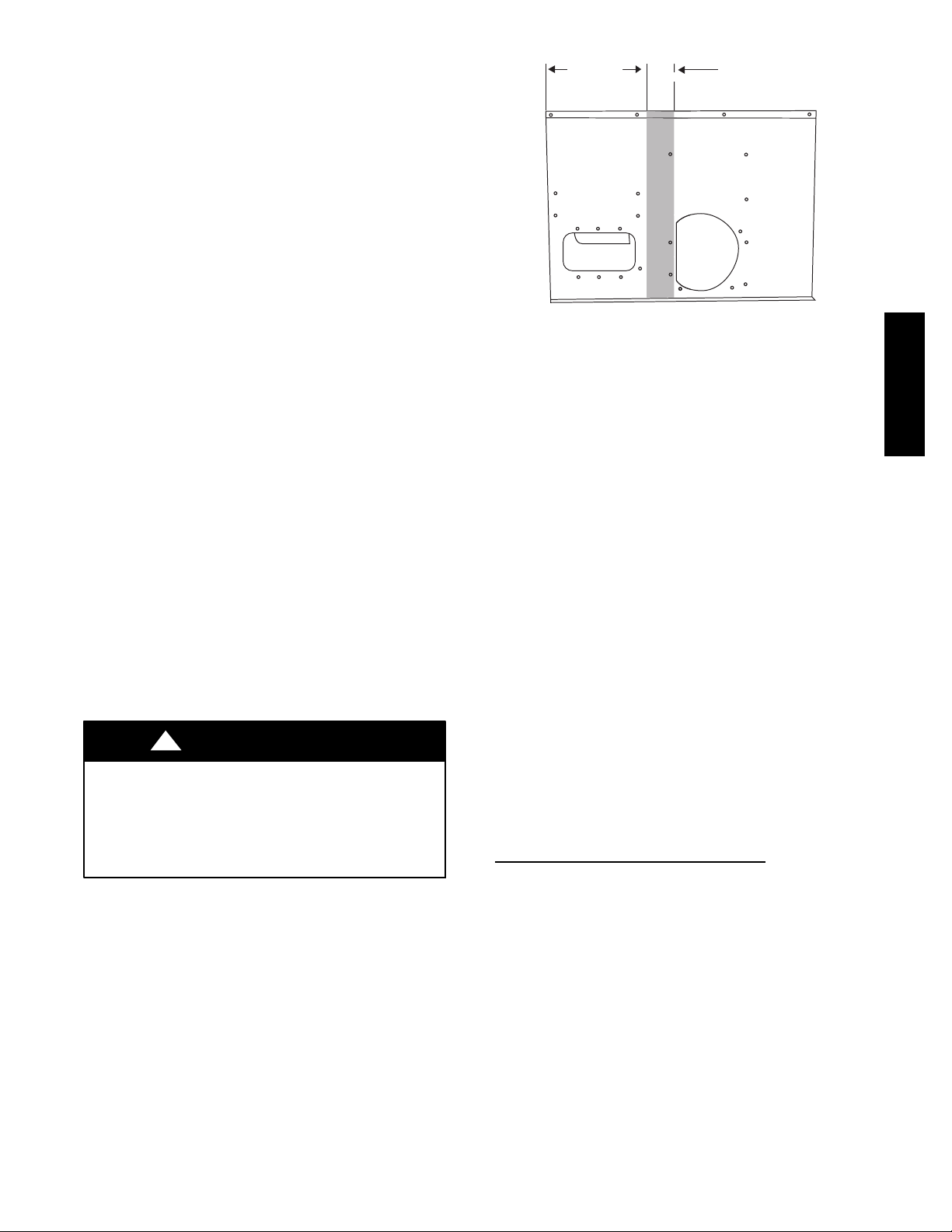
When connecting ductwork to units, do not drill deeper
than 3/4 in. (19 mm) in shaded area shown in Fig. 2 or coil
may be damaged.
19.17 in.
(487 mm)
Fig. 2 -- Area Not to be Drilled More Than 3/4--in. (19 mm)
1. All units should have field--supplied filters or accessory
filter rack installed in the return--air side of the unit.
Recommended sizes for filters are shown in Table 1.
2. Avoid abrupt duct size increases and reductions. Abrupt
change in duct size adversely affects air performance.
IMPORTANT: Use flexible connectors between ductwork and
unit to prevent transmission of vibration. Use suitable gaskets to
ensure weather tight and airtight seal. When electric heat is
installed, use fireproof canvas (or similar heat resistant material)
connector between ductwork and unit discharge connection. If
flexible duct is used, insert a sheet metal sleeve inside duct. Heat
resistant duct connector (or sheet metal sleeve) must extend 24--in.
(610 mm) from electric heater element.
3. Size ductwork for cooling air quantity (cfm). The minimum
air quantity for proper electric heater operation is listed in
Table 2. Heater limit switches may trip at air quantities
below those recommended.
4. Seal, insulate, and weatherproof all external ductwork. Seal,
insulate and cover with a vapor barrier all ductwork passing
through conditioned spaces. Follow latest Sheet Metal and
Air Conditioning Contractors National Association
(SMACNA) and Air Conditioning Contractors Association
(ACCA) minimum installation standards for residential
heating and air conditioning systems.
5. Secure all ducts to building structure. Flash, weatherproof,
and vibration--isolate duct openings in wall or roof
according to good construction practices.
Fig. 7 shows a typical duct system with unit installed.
3.92 in.
(100 mm)
Deep
A10021
Installing factory--supplied duct flanges;
For 24, 30, and 36 sizes:
S Two round 14--in. (356 mm) duct collars are factory supplied.
S Line up the 6 holes in the duct collar with the pre--drilled holes
in the side panel.
S Fasten duct collar to side panel using field--supplied screws.
For 42, 48 and 60 sizes (See Fig. 3):
S One round 14--in. (356 mm) duct collar for the supply air
connections and two “L” brackets for the 14--in. x 20 --in. (356 x
508 mm) return air connection are factory--supplied.
S Line up the 6 holes in the supply duct collar with the pre--drilled
holes in the side panel. Fasten duct collar to side panel using
field--supplied screws.
S For the return, remove the 4 screws on the left side of the return
and install one of the “L” flanges on the left side by replacing
the 4 screws. Using the 2 dimples below the return, align the
PH4Z
3
Page 4
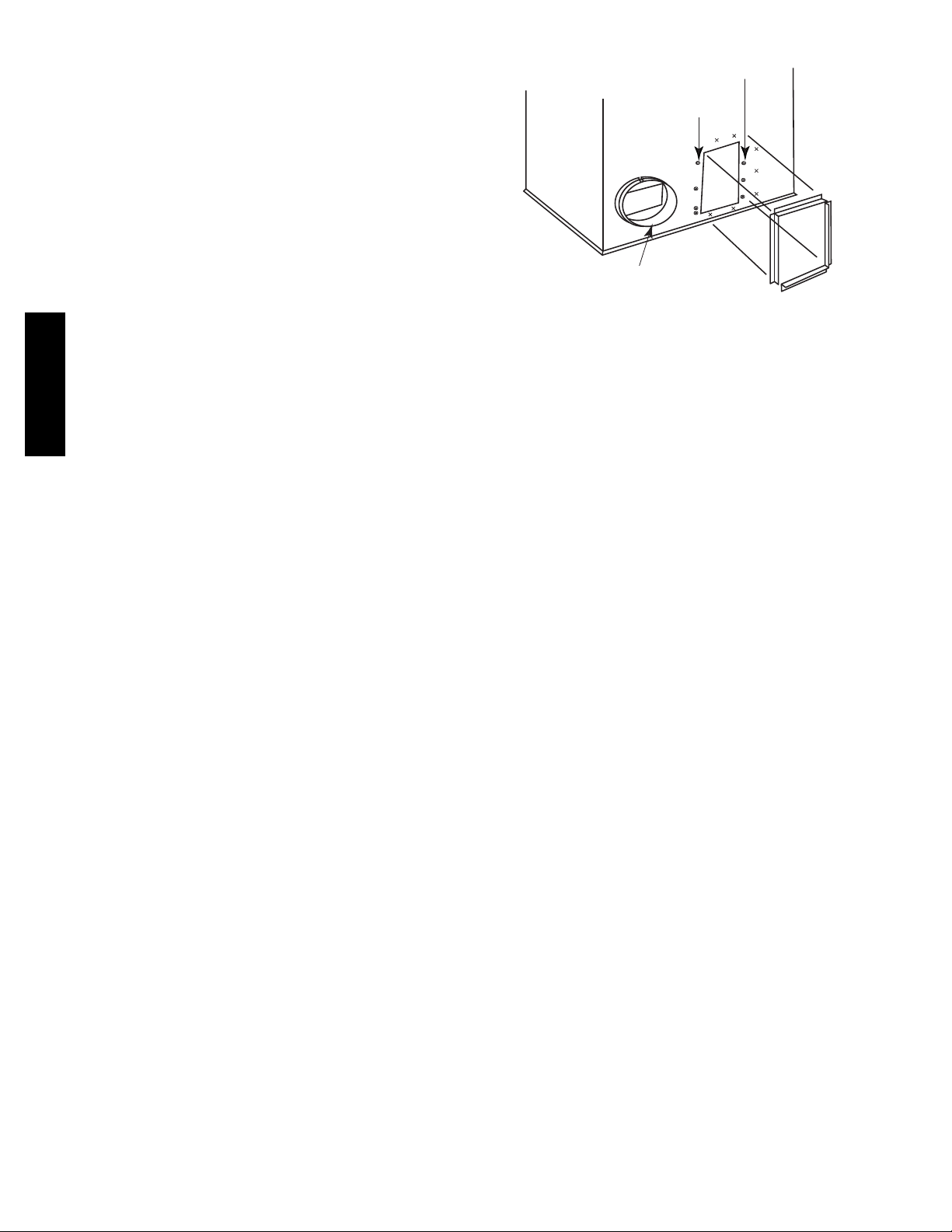
bottom of the “L” flange with the two dimples and attach using
filed--supplied thread--cutting screws.
For the second “L” flange, align flange with the three dimples to
the right of the return and the two dimples above the return and
attach using field--supplied thread--cutting screws.
NOTE: The factory--installed screws to the right of the return
should not be removed in this process.
PH4Z
3 Factory Installed Screws
(Must not be removed)
Remove 4 screws from left side
of duct opening and reuse to
install the left half of duct
flange.
Install supply duct flange
as shown into existing holes
with field-supplied screws.
X = Factory dimples for duct flange attachment.
Fig. 3 -- Installing Factory--Supplied Duct Flanges
A10081
4
Page 5
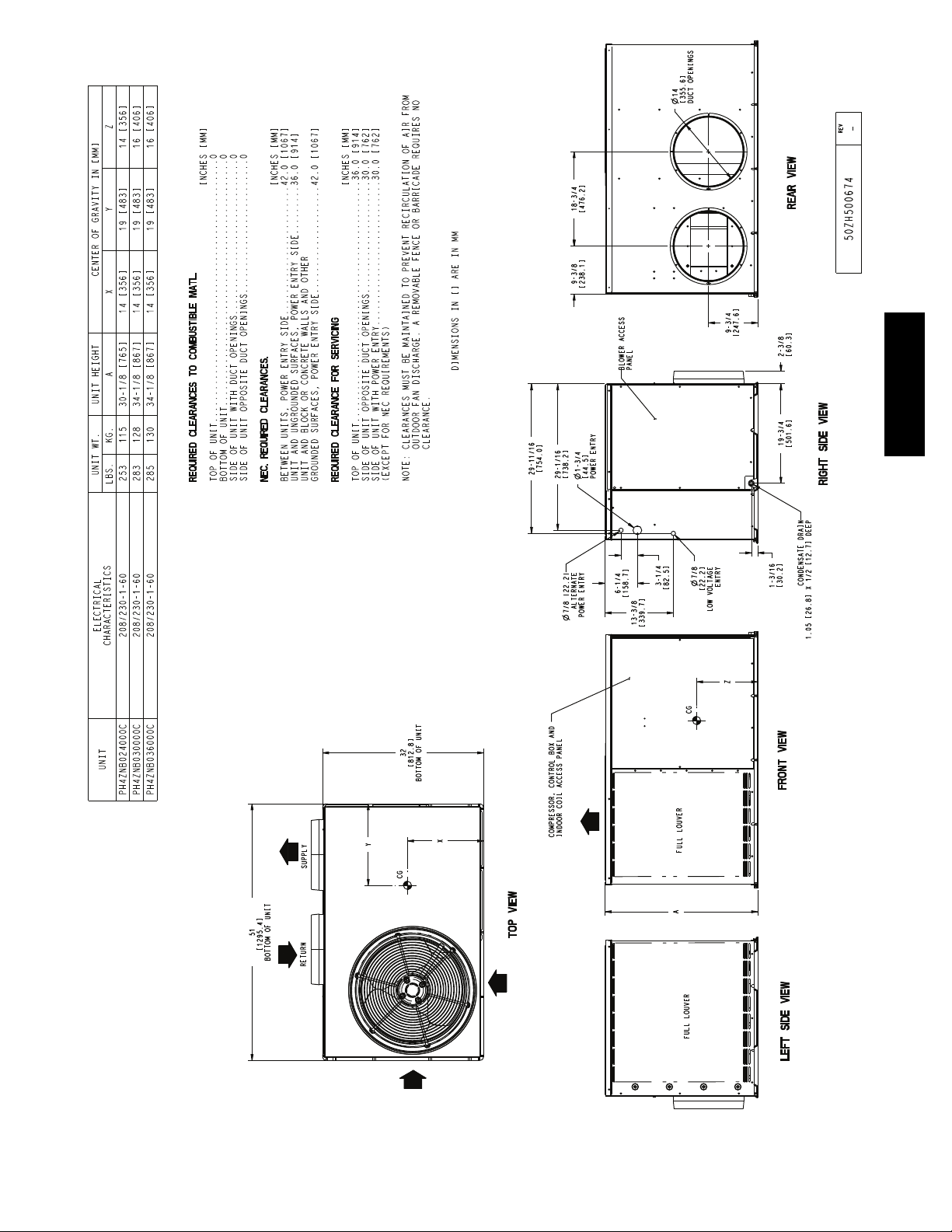
PH4Z
Fig. 4 -- Unit Base Dimensions, 024--036
5
A1456
Page 6
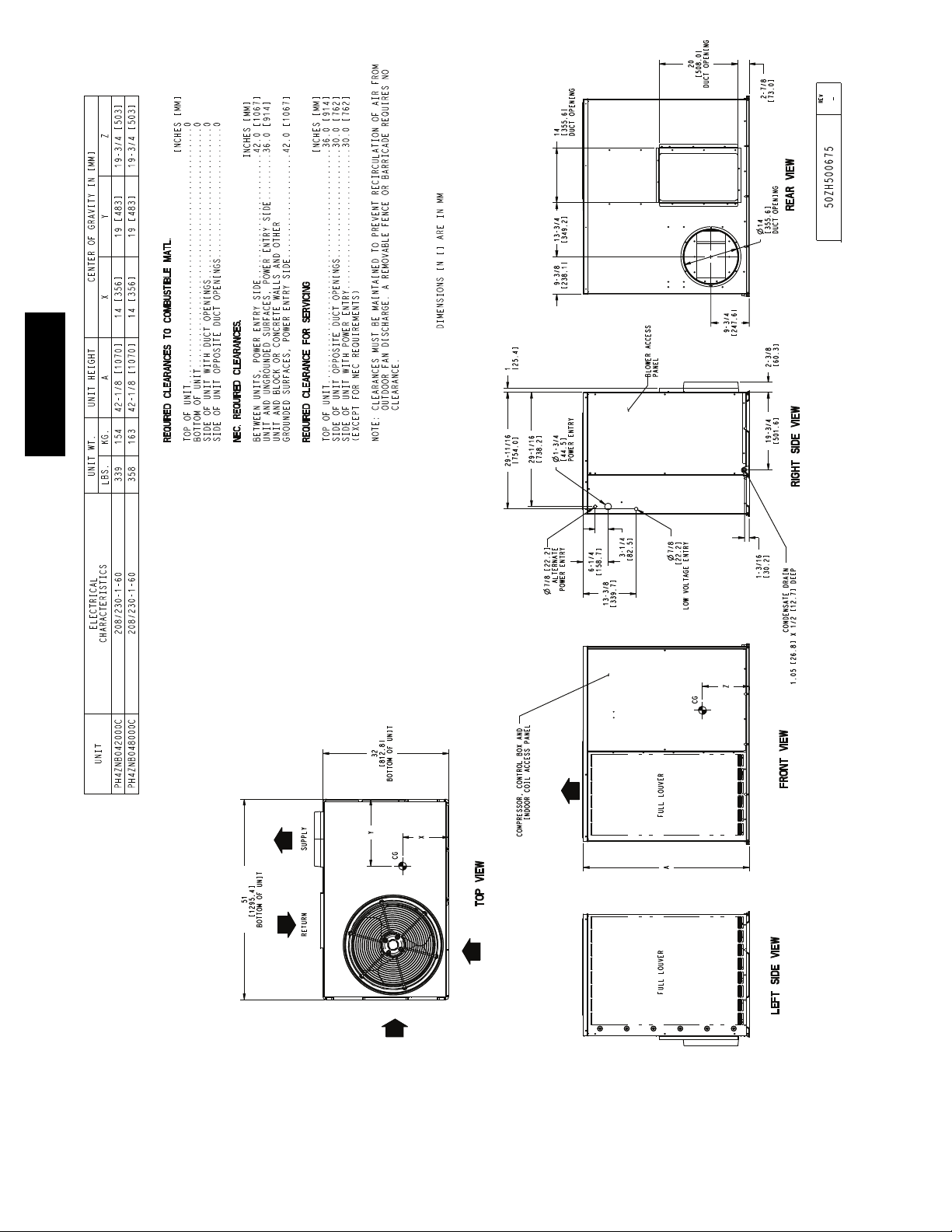
PH4Z
Fig. 5 -- Unit Base Dimensions, 042--048
6
A14557
Page 7
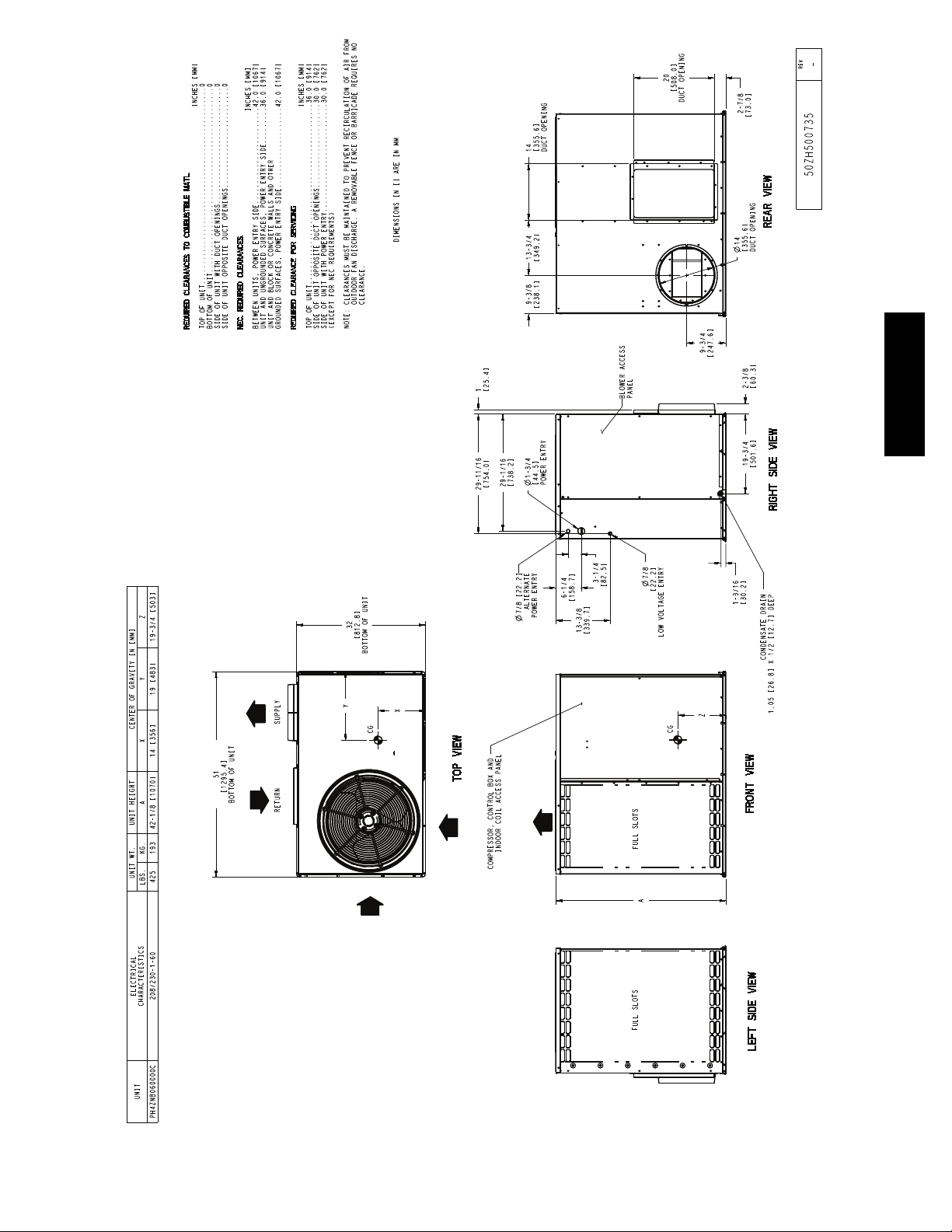
PH4Z
Fig. 6 -- Unit Base Dimensions, 060
7
A150072
Page 8
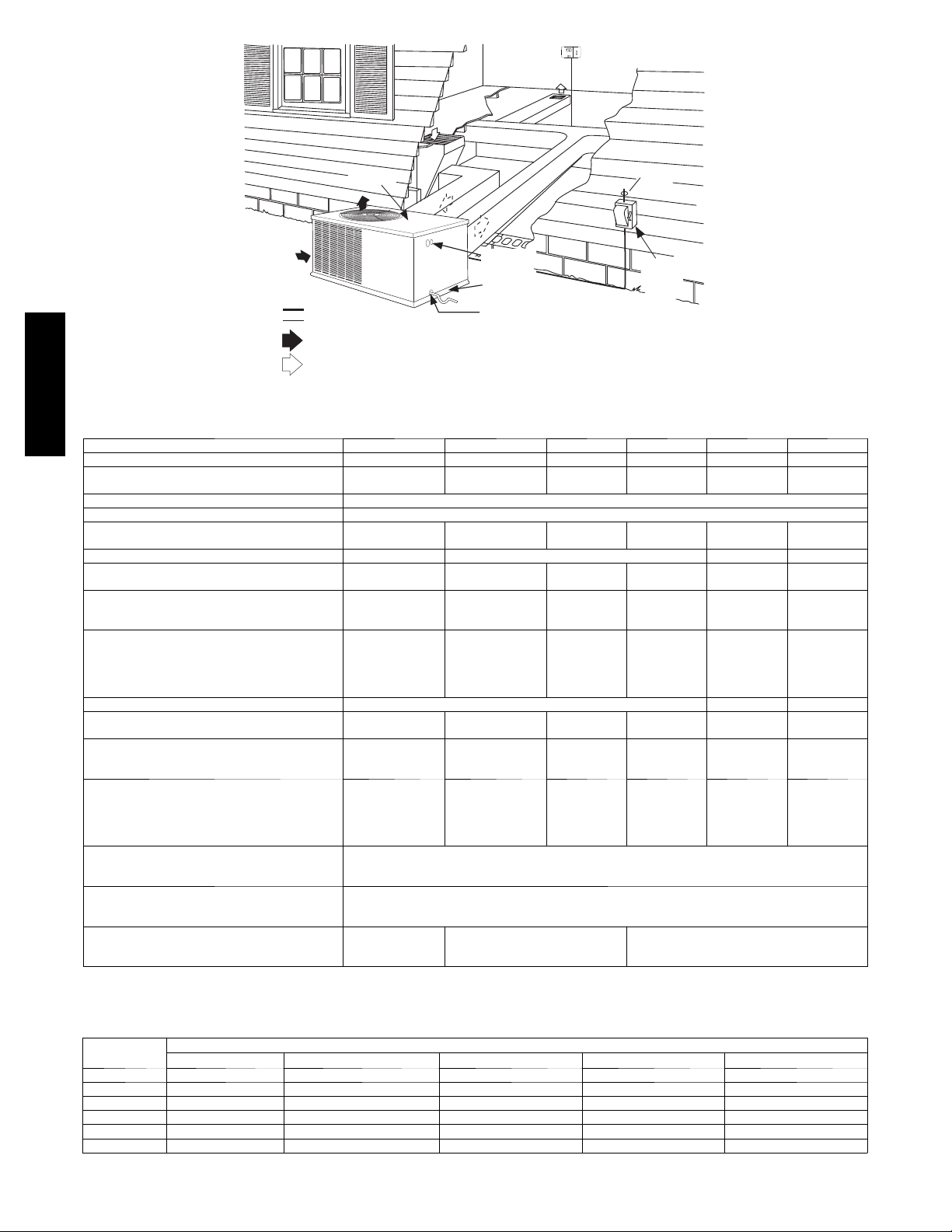
RETURN
AIR
INDOOR
THERMOSTAT
FROM
POWER
SOURCE
DISCONNECT
PER NEC
(UNIT AND
ELECTRIC
HEATER)
PH4Z
TOP COVER
Power Wiri ng
Control Wiring
Condenser Airflow
Evaporator Airflow
POWER AND
LOW-VOLTAGE
ENTRY
COMPOSITE
RUST-PROOF
BASEPAN
CONDENSATE
DRAIN
CONNECTION
Fig. 7 -- Typical Installation
Table 1 – Physical Data
UNIT SIZE 024 030 036 042 048 060
NOMINAL CAPACITY (ton) 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 5
SHIPPING WEIGHT (lb)
(kg)
COMPRESSOR TYPE SCROLL
REFRIGERANT R-410A
REFRIGERANT QUANTITIY (lb)
QUANTITY (kg)
OUTDOOR METERING DEVICE TXV Piston TXV Piston
ORIFICE OD (in.)
(mm)
OUTDOOR COIL
ROWS...FINS/in.
FACE A REA (sq. ft)
OUTDOOR FAN
NOMINAL AIRFLOW (cfm)
DIAMETER (in.)
DIAMETER (mm)
MOTOR HP (RPM)
INDOOR METERING DEVICE Piston TXV TXV
ORIFICE OD (in.)
(mm)
INDOOR COIL
ROWS...FINS/in.
FACE A REA (sq. ft)
INDOOR BLOWER
NOMINAL COOLING AIRFLOW (cfm)
NOMINAL SIZE D x L (in.)
(mm)
MOTOR (HP)
HIGH-PRESSURE SWITCH (psig)
CUTOUT
RESET (AUTO)
LOW-PRESSURE SWITCH (psig)
CUTOUT
RESET (AUTO)
RETURN-AIR FILTERS
THR OWAWAY (in.)
*Required filter sizes shown are based on the AHRI (Air Condition ing, Heating & Refrigeration Institute) rated airflow at a velocity of 300 ft/min (91 m) for throwaway type or 450 ft/ min (137 m) for high capacity type. Recommended filters are 1 ---in. (25 mm) thick.
(mm)
312
142
7.00
3.18
---
---
2...20
9.1
2000
20
508
1/8 (825)
0.059
1.499
3...12
4.3
800
10 x 8
254 x 203
1/3
20x20x1
508x508x25
333
151
7.20
3.27
0.049
1.245
2...20
10.2
2000
20
508
1/8 (825)
0.059
1.499
3...14
4.3
1000
11 x 9
279 x 229
1/3
610x762x25
24x30x1
334
152
6.30
2.86
0.057
1.448
2...20
10.2
2800
20
508
1/4 (1100)
0.067
1.702
3...12
4.9
1200
11 x 9
279 x 229
1/2
650 +/- 15
420 +/- 25
20 +/- 5
45 +/- 10
388
177
9.10
4.13
0.059
1.499
2...20
13.0
3100
20
508
1/4 (1100)
0.076
1.9304
3...14
4.9
1400
11 x 9
279 x 229
1/2
407
185
7.70
3.49
---
---
2...20
15.5
3100
20
508
1/4 (1100)
---
---
3...14
4.9
1600
11 x 9
279 x 229
3/4
24x36x1
610x914x25
A08207
475
215
11.5
5.22
0.070
1.778
2...20
15.5
3300
20
508
1/3 (1100)
---
---
3...14
4.9
1700
12 x 11
305 x 279
1
Table 2 – Minimum Airflow for Safe Electric Heater Operation
HP Unit
Size
5kW 7.5 kW 10 kW 15 kW 20 kW
24 750 800 800 X X
30 750 800 800 X X
36 750 800 800 1200 X
42 750 800 800 1200 X
48 750 800 800 1200 1800
60 750 800 800 1200 1800
X = NOT APPROVED COMBINATION
Minimum Airflow (CFM)
8
Page 9

CONFIGURING UNITS FOR DOWNFLOW (VERTICAL)
DISCHARGE
Units are dedicated side supply products. They are not convertible
to vertical air supply. A field-- supplied plenum must be used to
convert to vertical air discharge.
Step 6 — Connect Condensate Drain
NOTE: When installing condensate drain connection be sure to
comply with local codes and restrictions.
Unit removes condensate through a 1--3/64 in. (27 mm) ID hole
(using 3/4--in. (19 mm) ID piping or tubing) which is located at the
end of the unit. See Fig. 4--6 for location of condensate connection.
Condensate water can be drained directly onto the roof in rooftop
installations (where permitted) or onto a gravel apron in ground
level installations. Install a field --supplied condensate trap at end of
condensate connection to ensure proper drainage. Make sure that
the outlet of the trap is at least 1 in. (25 mm) lower than the drain
pan condensate connection to prevent the pan from overflowing
(See Fig. 8 and 9). When using a gravel apron, make sure it slopes
away from the unit.
If the installation requires draining the condensate water away from
the unit, install a 2--in. (51 mm) trap using a 3/4--in. (19 mm) ID
tubing or pipe. (See Fig. 8 and 9.) Make sure that the outlet of the
trap is at least 1 in. (25 mm) lower than the unit drain--pan
condensate connection to prevent the pan from overflowing. Prime
the trap with water. Connect a drain tube using a minimum of
3/4--in. (19 mm) PVC, 3/4 --in. (19 mm) CPVC, or 3/4--in. copper
pipe (all field supplied). Do not undersize the tube. Pitch the drain
tube downward at a slope of at least 1 in. (25 mm) for every 10 ft
(3 m) of horizontal run. Be sure to check the drain tube for leaks.
Prime trap at the beginning of the cooling season start--up.
Allowable glues for condensate trap connection are: Standard
ABS, CPVC, or PVC cement.
1” (25 mm) MIN
1" (25 mm) MIN
.
Fig. 8 -- Condensate Trap
TRAP
OUTLET
.
Fig. 9 -- PVC Condensate Trap
TRAP
OUTLET
2” (51 mm) MIN.
A08001
2" (51 mm) MIN
.
Step 7 — Install Electrical Connections
!
WARNING
ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARD
Failure to follow this warning could result in personal
injury or death.
The unit cabinet must have an uninterrupted, unbroken
electrical ground to minimize the possibility of personal
injury if an electrical fault should occur. This ground may
consist of an electrical wire connected to the unit ground
screw in the control compartment, or conduit approved for
electrical ground when installed in accordance with NEC,
ANSI/NFPA 70 American National Standards Institute/
National Fire Protection Association (latest edition) (in
Canada, Canadian Electrical Code CSA C22.1) and local
electrical codes.
!
UNIT COMPONENT DAMAGE HAZARD
Failure to follow this caution may result in damage to the
unit being installed.
1. Make all electrical connections in accordance with NEC
ANSI/NFPA 70 (latest edition) and local electrical codes
governing such wiring. In Canada, all electrical
connections must be in accordance with CSA standard
C22.1 Canadian Electrical Code Part 1 and applicable
local codes. Refer to unit wiring diagram.
2. Use only copper conductor for connections between
field--supplied electrical disconnect switch and unit. DO
NOT USE ALUMINUM WIRE.
3. Be sure that high--voltage power to unit is within
operating voltage range indicated on unit rating plate. On
3--phase units, ensure phases are balanced within 2
percent. Consult local power company for correction of
improper voltage and/or phase imbalance.
4. Do not damage internal components when drilling
through any panel to mount electrical hardware, conduit,
etc.
HIGH--VOLTAGE CONNECTIONS
The unit must have a separate electrical service with a
field--supplied, waterproof disconnect switch mounted at, or within
sight from the unit. Refer to the unit rating plate, NEC and local
codes for maximum fuse/circuit breaker size and minimum circuit
amps (ampacity) for wire sizing.
The field--supplied disconnect may be mounted on the unit over
the high--voltage inlet hole when the standard power and
low--voltage entry points are used. See Fig. 10 and Fig. 11 for
acceptable location.
Operation of unit on improper line voltage constitutes abuse and
may cause unit damage that could affect warranty.
ROUTING POWER LEADS INTO UNIT
Use only copper wire between disconnect and unit. The
high--voltage leads should be in a conduit until they enter the unit;
conduit termination at the unit must be watertight. Run the
high--voltage leads through the hole on the control box side of the
unit (See Fig. 10). When the leads are inside the unit, run leads to
the control box (See Fig. 11). Connect leads to the black and
yellow wires (See Fig. 12).
CAUTION
PH4Z
9
Page 10

HIGH-VOLTAGEPOWER
WIRINGENTRYHOLE
LOW-VOLTAGEWIRING
ENTRYHOLE
(grommethole)
PH4Z
Fig. 10 -- Unit Electrical Connection
Electric Heat Control Box
(shown uninstalled)
Electric Heat wiring
interconnection (electric
heater controls removed
for clarity)
Fig. 11 -- Control Box Wiring
UNIT GROUND
GROUND
LEAD
SINGLE-PHASE
CONNECTIONS
TO DISCONNECT
PER NEC
L
L
Fig. 12 -- Line Power Connections
CONNECTING GROUND LEAD TO UNIT GROUND
Connect the ground lead to the chassis using the unit ground in the
control box (See Fig. 11 and Fig. 12).
ROUTING CONTROL POWER WIRES (24--V)
Form a drip-- loop with the thermostat leads before routing them
into the unit. Route the thermostat leads through grommeted hole
provided in unit into unit control box (See Fig. 10). Connect
thermostat leads and unit power leads as shown in Fig. 12, Fig. 13
and Fig. 14.
The unit transformer supplies 24--v power for complete system
including accessory electrical heater. Transformer is factory wired
for 230--v operation.
Unit main harness contains a 3 amp automotive style replaceable
fuse. If transformer secondary voltage is not available at red and
EQUIP GR
BLK
YEL
A08407
A10031
A10022
brown leads in unit low voltage box, check fuse in red lead near
transformer. Replace with Littelfuse brand, part number 257003.
Unit main harness also contains a 1k ohm, 3 watt load resistor
wired across low voltage leads “G” and “C”. Purpose of resistor is
to provide a small electrical load for the indoor thermostat fan
circuit to ensure reliable operation.
ACCESSORY ELECTRIC HEAT WIRING
Refer to accessory electric heat installation instructions for
information on installing accessory electric heat. Accessory electric
heat wiring is shown in Fig. 14 and Fig. 15.
NOTE: When installing an accessory electric heater, the high
voltage wire harness pass--through must be sealed with silicone or
equivalent at the partition in order to comply with the 2% or less
air leakage certification.
PRE--START--UP
!
WARNING
FIRE, EXPLOSION, ELECTRICAL SHOCK
HAZARD
Failure to follow this warning could result in personal
injury or death and/or property damage.
1. Follow recognized safety practices and wear protective
goggles when checking or servicing refrigerant system.
2. Relieve and recover all refrigerant from system before
touching or disturbing compressor plug if refrigerant
leak is suspected around compressor terminals.
3. Never attempt to repair soldered connection while
refrigerant system is under pressure.
4. Do not use torch to remove any component. System
contains oil and refrigerant under pressure.
5. To remove a component, wear protective goggles and
proceed as follows:
a. Shut off electrical power to unit and install
lockout tag.
b. Relieve and reclaim all refrigerant from system
using both high-- and low--pressure ports.
c. Cut component connecting tubing with tubing
cutter and remove component from unit.
d. Carefully unsweat remaining tubing stubs when
necessary. Oil can ignite when exposed to torch
flame.
Proceed as follows to inspect and prepare the unit for initial
start--up:
1. Remove all access panels.
2. Read and follow instructions on all DANGER, WARNING,
CAUTION, and INFORMATION labels attached to, or
shipped with unit.
!
WARNING
PERSONAL INJURY AND ENVIRONMENTAL
HAZARD
Failure to relieve system pressure could result in personal
injury and/or death.
Relieve pressure and recover all refrigerant before system
repair or final unit disposal.
Wear safety glasses and gloves when handling refrigerant.
Keep torches and other ignition sources away from
refrigerants and oils.
10
Page 11

Thermostat
G
Y
W2
R
RED
GREEN
O
ORANGE
C
BROWN
WHITE
and subbase
Fig. 13 -- Control Connections
3. Make the following inspections:
a. Inspect for shipping and handling damages, such as
broken lines, loose parts, disconnected wires, etc.
b. Inspect all field-- and factory--wiring connections. Be
sure that connections are completed and tight.
c. Ensure wires do not touch refrigerant tubing or sharp
sheet metal edges.
d. Inspect coil fins. If damaged during shipping and
handling, carefully straighten fins with a fin comb.
4. Verify the following conditions:
a. Make sure that outdoor--fan blade is correctly posi-
tioned in fan orifice. See Outdoor Fan Adjustment
section.
b. Make sure that air filter is in place.
c. Make sure that condensate drain pan and trap are filled
with water to ensure proper drainage.
d. Make sure that all tools and miscellaneous loose parts
have been removed.
Unit Control
Power
A10026
START--UP
Step 1 — Check for Refrigerant Leaks
Proceed as follows to locate and repair a refrigerant leak and to
charge the unit:
1. Locate leak and make sure that refrigerant system pressure
has been relieved and reclaimed from both high-- and
low--pressure ports.
2. Repair leak following accepted practices.
NOTE: Install a filter drier whenever the system has been opened
for repair.
3. Add a small charge of R--410A refrigerant vapor to system
and leak--test unit.
4. Recover refrigerant from system and evacuate to 500
microns if no additional leaks are found.
5. Charge unit with R--410A refrigerant, using an accurate
scale. Refer to unit rating plate for required charge.
Step 2 — Start--Up Cooling and Make Adjustments
Complete the required procedures given in the Pre--Start--Up
section before starting the unit. Do not jumper any safety devices
when operating the unit. Do not operate the unit in cooling mode
when the outdoor temperature is below 40F(4.4C) (unless
accessory low--ambient kit is installed). Do not rapid cycle the
compressor. Allow 5 min. between “on” cycles to prevent
compressor damage.
CHECKING COOLING AND HEATING CONTROL
OPERATION
Start and check the unit for proper cooling control operation as
follows:
1. Place room thermo stat SYSTEM switch in OFF position.
Observe that blower motor starts when FAN switch is
placed in ON position and shuts down within 60 sec. when
FAN switch is placed in AUTO position.
2. Place SYSTEM switch in COOL position and FAN switch
in AUTO position. Set control below room temperature.
Observe that compressor, outdoor fan, and indoor blower
motors start and that reversing valve shifts. Observe that
cooling cycle shuts down when control setting is satisfied.
Reversing valve (RV) remains energized.
3. Place system switch in HEAT position. Observe that
compressor, indoor fan and outdoor fan energize (Reversing
Valve is deenergized in heat pump heating mode). Set
control above room temperature. Observe that heating cycle
shuts down when control setting is satisfied.
4. When using an automatic changeover room thermostat,
place both SYSTEM and FAN switches in AUTO positions.
Observe that unit operates in Cooling mode when
temperature control is set to call for Cooling (below room
temperature), and unit operates in Heating mode when
temperature control is set to call for Heating (above room
temperature).
Step 3 — Refrigerant Charge
Refrigerant Charge — The refrigerant system is fully charged with
R--410A refrigerant and is tested and factory sealed. Amount of
refrigerant charge is listed on unit nameplate and in Table 1. Unit
must operate a minimum of 15 minutes before checking charge.
NOTE: Adjustment of the refrigerant charge is not required unless
the unit is suspected of not having the proper R--410A charge.
NOTE: Unit sizes 024--042 have fixed orifice refrigerant metering
devices. There is a different charging procedure for both expansion
devices. Refer to the correct procedure for your unit.
NO CHARGE
Use standard evacuating techniques. After evacuating system,
weigh in the specified amount of refrigerant (refer to Table 1).
LOW CHARGE COOLING
024--042 Units, Fixed Metering Device:
1. Operate unit a minimum of 10 minutes before checking
charge.
2. Measure suction pressure by attaching an accurate gauge to
compressor suction side service port.
3. Measure suction side temperature by attaching an accurate
thermisitor type or electronic thermometer to suction line
about 10 in. from compressor.
4. Measure outdoor air dry--bulb temperature with thermometer.
5. Measure indoor air (return air) wet--bulb temperature with a
sling psychrometer or electronic equivalent.
6. Using Superheat Charging Table (Table 3) find outdoor
temperature and indoor air wet--bulb temperature. At this
intersection note superheat. Where a dash (----) appears on
PH4Z
11
Page 12

table do not attempt to charge unit under these conditions or
refrigerant slugging may occur. In this situation refrigerant
must be evacuated and weighed in. See rating plate for
charge quantity.
7. Refer to Required Suction Tube Temp. Table (Table 3).
Find superheat temperature located in Step 6 and suction
pressure. At this intersection note suction line temperature.
8. If unit has a higher suction line temperature than charted
temperature, add refrigerant until charted temperature is
reached.
9. If unit has a lower suction line temperature than charted
temperature, reclaim refrigerant until charted temperature is
reached.
10. If outdoor air temperature or pressure at suction port
changes, charge to new suction line temperature indicated
on chart.
048--060 Units, TXV
1. Measure Discharge line pressure by attaching a gauge to the
service port.
2. Measure the Liquid line temperature by attaching a tempera-
PH4Z
ture sensing device to it.
3. Insulate the temperature sensing device so that the Outdoor
Ambient doesn’t affect the reading.
4. Refer to the required Subcooling in Table 4 based on the
model size and the Outdoor Ambient temperature.
5. Interpolate if the Outdoor ambient temperature lies in between the table values.
6. Find the Pressure Value in the table corresponding to the
measured Pressure of the Compressor Discharge line.
7. Read across from the Pressure reading to obtain the Liquid
line temperature for a required Subcooling.
8. Add Charge if the measured temperature is higher than the
table value.
9. Remove charge if the measured temperature is lower than
the table value.
HEATING MODE CHARGE
Do not attempt to adjust charge by cooling methods while in heat
pump heating mode. Recover refrigerant and weigh in according to
unit data plate refrigerant data.
12
Page 13

Table 3 – Superheat Charging
PH4Z
Table 4 – Required Subcooling
A12098
13
A150075
Page 14

Step 4 — Indoor Airflow and Airflow Adjustments
!
WARNING
UNIT OPERATION HAZARD
Failure to follow this caution may result in equipment
damage or improper operation.
For cooling operation, the recommended airflow is 350 to
450 cfm for each 12,000 Btuh of rated cooling capacity.
Table 5 shows wet coil air delivery for horizontal discharge units.
NOTE: Be sure that all supply-- and return--air grilles are open,
free from obstructions, and adjusted properly.
!
WARNING
ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARD
PH4Z
Failure to follow this warning could result in personal
injury or death.
Disconnect electrical power to the unit and install lockout
tag before changing blower speed.
Blower speed tap can be changed by replacing the factory installed
blue low speed tap wire (cooling) with the unused black high speed
wire in unit control box. The red medium speed wire is factory
installed to operate with a call for supplemental electric heat. See
unit wiring diagram.
Be sure new airflow meets the range noted above and minimum
electric heat CFM, if equipped. Refer to Table 2 and 5.
All model sizes are factory wired or rated airflow operation.
Step 5 — Sequence of Operation
FAN O P E R ATION
The FAN switch on the thermostat controls indoor fan operation.
When the F AN switch is placed in the ON position, the indoor
(evaporator) fan motor (IFM) is energized through the G terminal
on the thermostat. The motor’s internal logic then provides power
to the indoor (evaporator) fan motor (IFM). The IFM will run
continuously when the FAN switch is set to ON.
When the FAN switch is set to AUTO, the thermostat deenergizes
the IFM (provided there is not a call for cooling). The contacts
open and the IFM is deenergized. The IFM will be energized only
when there is a call for cooling, in heat pump heating mode or if
the unit is equipped with accessory electric heat, the indoor--fan
motor will also run while the accessory electric heat is energized.
NOTE: Motors on this product are programmed for 60 second
time delay on tap 1 and 30 second time delay on tap 2. There is no
time delay on tap 3. The indoor fan will remain ON for the set time
delay after G or W2 is de--energized.
COOLING OPERATION
With a call for cooling (Y), the compressor, outdoor fan, and
indoor fan start immediately. When the cooling demand is met, Y
de--energizes, shutting the compressor, indoor fan and the outdoor
fan.
HEATING OPERATION
With a call for heating (Y), the compressor, outdoor fan, and
indoor fan start immediately. If Y cannot satisfy the heating
demand, the auxiliary or backup heat (W2) energizes. In case of
staged heating, W3 is energized if the demand is not met. When
heating demand is met, W3, W2 and Y sequentially de--energize
shutting the compressor, indoor fan and the outdoor fan.
CONTINUOUS FAN
With the continuous indoor fan option selected on the thermostat,
G is continuously energized. The continuous fan speed will be the
same as the cooling fan speed.
DEFROST
Defrost board (DB) is a time and temperature control, which
includes a field--selectable time period between checks for defrost
(30, 60, 90 and 120 minutes). The time period is factory--set at 60
minutes and should only be adjusted by a trained service person.
Electronic timer and defrost cycle start only when contactor is
energized and defrost thermostat (DFT) is closed.
Defrost mode is identical to Cooling mode. The outdoor fan motor
stops because of “OF1” and “OF2” contacts opening on the defrost
board, a bank of optional electric heat turns on to warm air
supplying the conditioned space.
ELECTRIC RESISTANCE HEATING
If accessory electric heaters are installed, on a call for “Emergency
Heat” the thermostat energizes W which energizes the heater relay
and in turn energizes the electric heaters. The IFM is energized
which starts the indoor--fan motor. If the heaters are staged, W2 is
energized when the second stage of heating is required. When the
need for heating is satisfied, the heater and IFM are de--energized.
14
Page 15

PH4Z
Fig. 14 -- Connection Electrical Diagram
15
A14563
Page 16

PH4Z
Fig. 13 Cont. -- Ladder Electrical Diagram
16
A14564
Page 17

Wires to be removed
A14444
Fig. 15 -- Accessory Electric Heater Wiring
Table 5 – Wet Coil Air Delivery*
(Deduct 10 percent for 208 Volt Operation)
230 VOLT HORIZONTAL DISCHARGE
UNIT
SIZE
024
030
036
042
048
060
*Air delivery values are based on operating voltage of 230v, wet coil, without filter or electric heater. Deduct filter and electric hea ter pressure drops to obtain
static pressure available for ducting.
NOTES:
1. Do not operate the unit at a cooling airflow that is less than 350 cfm for each 12,000 Btuh of rated cooling capacity. Evaporator coil frosting may occuratairflows below this point.
2. Standard Cubic Feet per Minute
SPEED TAP AIR DELIVERY
1 SCFM 933 799 758 707 675 608 549 497 435 394
2 SCFM 1016 921 882 854 809 761 711 668 599 552
3 SCFM 1079 1041 1003 970 944 909 866 810 764 724
1 SCFM 1052 1018 984 943 914 879 833 795 732 678
2 SCFM 1141 1107 1069 1036 1006 974 932 899 856 784
3 SCFM 1246 1213 1181 1144 1108 1078 1043 1015 973 931
1 SCFM 1311 1253 1195 1136 1083 1023 958 895 818 729
2 SCFM 1413 1364 1313 1256 1203 1148 1084 1022 969 882
3 SCFM 1571 1525 1473 1423 1364 1313 1261 1210 1156 1090
1 SCFM 1499 1434 1394 1349 1307 1273 1232 1169 1108 1038
2 SCFM 1568 1532 1497 1459 1407 1381 1346 1304 1252 1185
3 SCFM 1635 1593 1560 1523 1484 1439 1406 1369 1335 1264
1 SCFM 1657 1625 1590 1554 1517 1486 1448 1417 1381 1340
2 SCFM 1707 1673 1644 1614 1586 1549 1515 1479 1449 1407
3 SCFM 1931 1900 1870 1840 1809 1778 1749 1714 1683 1646
1 SCFM 1774 1746 1717 1678 1639 1590 1538 1492 1461 1418
2 SCFM 1857 1820 1784 1752 1720 1671 1625 1579 1532 1509
3 SCFM 2183 2144 2115 2079 2049 2018 1986 1933 1859 1733
2
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE (IN. W.C.)
PH4Z
17
Page 18

Ta ble 6 – Filter Pressure Drop (IN. W.C.)
FILTER SIZE
in. (mm)
20X20X1
(508X508X25)
20X24X1
(508X610x25)
24X30X1
(610X762x25)
24X36X1
(610X914X25)
HEATER kW
5--20 0.033 0.037 0.042 0.047 0.052 0.060 0.067 0.075
500 600 700 800 900 1000 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 1600 1700 1800 1900 2000 2100 2200
0.05 0.07 0.08 0.10 0.12 0.13 0.14 0.15 — — — — — — — — — —
— — — 0.08 0.09 0.10 0.11 0.13 0.14 0.15 0.16 — — — — — — —
— — — 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.10 — — — — — — —
— — — — — — — 0.06 0.07 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.09 0.10 0.11 0.12 0.13 0.14
Table 7 – Accessory Electric Heat Pressure Drop (IN. W.C.)
800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000 2200
CFM
CFM
MAINTENANCE
To ensure continuing high performance, and to minimize the
possibility of premature equipment failure, periodic maintenance
must be performed on this equipment. This cooling unit should be
inspected at least once each year by a qualified service person. To
PH4Z
troubleshoot unit, refer to Table 9, Troubleshooting Chart.
NOTE TO EQUIPMENT OWNER: Consult your local dealer
about the availability of a maintenance contract.
!
WARNING
PERSONAL INJ URY AND UNIT DAMAGE
HAZARD
Failure to follow this warning could result in personal
injury or death and possible unit component damage.
The ability to properly perform maintenance on this
equipment requires certain expertise, mechanical skills,
tools and equipment. If you do not possess these, do not
attempt to perform any maintenance on this equipment,
other than those procedures recommended in the Owner’s
Manual.
!
WARNING
ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARD
Failure to follow this warning could result in personal
injury or death.
1. Turn off electrical power to the unit and install lockout
tag before performing any maintenance or service on this
unit.
2. Use extreme caution when removing panels and parts.
3. Never place anything combustible either on or in contact
with the unit.
1. Inspect air filter(s) each month. Clean or replace when
necessary.
2. Inspect indoor coil, drain pan, and condensate drain each
cooling season for cleanliness. Clean when necessary.
3. Inspect blower motor and wheel for cleanliness each
cooling season. Clean when necessary.
4. Check electrical connections for tightness and controls for
proper operation each cooling season. Service when
necessary.
5. Ensure electric wires are not in contact with refrigerant
tubing or sharp metal edges.
Air Filter
IMPORTANT: Never operate the unit without a suitable air filter
in the return --air duct system. Always replace the filter with the
same dimensional size and type as originally installed. See Table 1
for recommended filter sizes.
Inspect air filter(s) at least once each month and replace
(throwaway--type) or clean (cleanable--type) at least twice during
each cooling season and twice during the heating season if electric
heat is installed, or whenever the filter becomes clogged with dust
and lint.
Unit Top Removal
NOTE: When performing maintenance or service procedures that
require removal of the unit top, be sure to perform all of the routine
maintenance procedures that require top removal, including coil
inspection and cleaning, and condensate drain pan inspection and
cleaning.
!
WARNING
ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARD
Failure to follow this warning could result in personal
injury or death.
Disconnect electrical power, and install lockout tag to the
unit before removing top.
!
UNIT OPERATION HAZARD
Failure to follow this caution may result in equipment
damage or improper operation.
Errors made when reconnecting wires may cause improper
and dangerous operation. Label all wires prior to
disconnecting when servicing.
The minimum maintenance requirements for this equipment are as
follows:
CAUTION
Only qualified service personnel should perform maintenance and
service procedures that require unit top removal.
Refer to the following top removal procedures:
1. Unplug all three wires from the outdoor fan motor.
2. Remove screws on unit top cover flange. (Save all screws.)
3. Lift top from unit carefully. Set top on edge and make sure
that top is supported by unit side that is opposite duct (or
plenum) side.
4. Carefully replace and secure unit top to unit, using screws
removed in Steps 1 and 2, when maintenance and/or service
procedures are completed.
18
Page 19

Indoor Blower and Motor
NOTE: All motors are pre--lubricated. Do not attempt to lubricate
these motors.
For longer life, operating economy, and continuing efficiency,
clean accumulated dirt and grease from the blower wheel and
motor annually.
!
WARNING
ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARD
Failure to follow this warning could result in personal
injury or death.
Disconnect electrical power, and install lockout tag to the
unit before cleaning and lubricating the blower motor and
wheel.
To clean the blower wheel:
1. Remove the blower housing:
a. Remove the screws on the external side of the duct
panel that fasten the housing to the duct panel assembly.
b. Remove the side access panel and unscrew the
mounting bracket that fastens the blower housing to the
internal partition panel of the control box assembly.
c. Make sure that the blower housing is supported by hand
before completely removing the mounting bracket.
d. Slide the blower housing from the rails of the duct panel
and place it outside the unit.
2. Remove the blower wheel from the housing:
a. Loosen the set screw which secures the wheel to the
motor shaft.
b. Loosen the three mounting legs of the motor by
removing the bolts that fasten the mounting legs to the
housing.
c. Slide out the motor assembly (motor, belly band and the
3 mounting legs) from the hub of the wheel.
d. Remove the filler panel at the discharge end of the
blower housing by removing the two screws that fasten
it to the housing.
e. Ensure proper reassembly by marking wheel orientation.
Remove the wheel from the housing.
3. Remove the caked on dirt from the wheel and the motor
using a brush.
4. Remove lint and dirt accumulations from the wheel and
housing with a vacuum cleaner, using a soft brush
attachment.
5. Remove grease and oil with a mild solvent.
6. Reassemble
a. Slip the wheel back in the housing with the hub set
screw parented in the correct direction.
b. Install the filler panel.
c. Reinsert the motor assembly in the wheel hub and align
the mounting legs with the housing mounting hold
locations.
d. Tighten the mounting bolts to fasten the motor assembly
with the housing.
e. Center the wheel in the housing by sliding it, align the
flat end of the shaft with the set screw and tighten the
set screw.
f. Slide back the blower housing into the mounting rails in
the duct panel and install the mounting bracket back in
its position.
g. Install the screws on the external side of the duct panel
to fasten duct panel with the housing.
h. Replace the side access panel.
Outdoor Coil, Indoor Coil, and Condensate Drain Pan
Inspect the condenser coil, evaporator coil, and condensate drain
pan at least once each year.
The coils are easily cleaned when dry; therefore, inspect and clean
the coils either before or after each cooling season. Remove all
obstructions, including weeds and shrubs, that interfere with the
airflow through the condenser coil.
Straighten bent fins with a fin comb. If coated with dirt or lint,
clean the coils with a vacuum cleaner, using the soft brush
attachment. Be careful not to bend the fins. If coated with oil or
grease, clean the coils with a mild detergent and water solution.
Rinse coils with clear water, using a garden hose. Be careful not to
splash water on motors, insulation, wiring, or air filter(s). For best
results, spray condenser coil fins from inside to outside the unit. On
units with an outer and inner condenser coil, be sure to clean
between the coils. Be sure to flush all dirt and debris from the unit
base.
Inspect the drain pan and condensate drain line when inspecting
the coils. Clean the drain pan and condensate drain by removing all
foreign matter from the pan. Flush the pan and drain trough with
clear water. Do not splash water on the insulation, motor, wiring, or
air filter(s). If the drain trough is restricted, clear it with a
“plumbers snake” or similar probe device.
Outdoor Fan Adjustment
!
UNIT OPERATION HAZARD
Failure to follow this caution may result in damage to unit
components.
Keep the condenser fan free from all obstructions to ensure
proper cooling operation. Never place articles on top of
unit.
1. Shut off unit power supply and install lockout tag.
2. Remove outdoor--fan assembly (grille, motor, motor cover,
and fan) by removing screws and flipping assembly onto
unit top cover.
3. Inspect the fan blades for cracks or bends.
4. If fan needs to be removed, loosen the setscrew and slide the
fan off the motor shaft.
5. When replacing fan blade, position blade as shown in Fig.
16. Tighten setscrews.
Fig. 16 -- Outdoor Fan Adjustment
CAUTION
FAN
HUB
MOTOR
SHAFT
HP UNIT
SIZE
024
030
036
A
042
048
060
A
in. (mm)
13/16 (20.6)
13/16 (20.6)
0
0
1/2 (12.7)
1/2 (12.7)
A150076
PH4Z
19
Page 20

Electrical Controls and Wiring
Inspect and check the electrical controls and wiring annually. Be
sure to turn off the electrical power to the unit.
Remove access panel to locate all the electrical controls and wiring.
Check all electrical connections for tightness. Tighten all screw
connections. If any smoky or burned connections are noticed,
disassemble the connection, clean all the parts, re--strip the wire
end and reassemble the connection properly and securely.
Check to ensure no wires are touching refrigerant tubing or sharp
sheet metal edges. Move and secure wires to isolate from tubing
and sheet metal edges.
After inspecting the electrical controls and wiring, replace all the
panels. Start the unit, and observe at least one complete cooling
cycle to ensure proper operation. If discrepancies are observed in
operating cycle, or if a suspected malfunction has occurred, check
each electrical component with the proper electrical
instrumentation. Refer to the unit wiring label when making these
checks. (See Fig. 14)
Refrigerant Circuit
Inspect all refrigerant tubing connections and the unit base for oil
accumulation annually. Detecting oil generally indicates a
PH4Z
refrigerant leak.
!
WARNING
EXPLOSION, SAFETY AND ENVIRONMENTAL
HAZARD
Failure to follow this warning could result in personal
injury, death or equipment damage.
This system uses R--410A refrigerant which has higher
operating pressures than R--22 and other refrigerant. No
other refrigerant may be used in this system. Gauge set,
hoses, and recovery system must be designed to handle
R--410A. If you are unsure, consult the equipment
manufacturer.
If oil is detected or if low cooling performance is suspected, leak
test all refrigerant tubing using an electronic leak detector, halide
torch or liquid-- soap solution. If a refrigerant leak is detected, refer
to Check for Refrigerant Leaks section.
If no refrigerant leaks are found and low cooling performance is
suspected, refer to Checking and Adjusting Refrigerant Charge
section.
Indoor Airflow
The airflow does not require checking unless improper
performance is suspected. If a problem exists, be sure that all
supply-- and return--air grilles are open and free from obstructions,
and that the air filter is clean.
Metering Devices
Refrigerant cooling metering device is a piston located upstream of
the indoor coil distributor assembly. Refrigerant heating mode
metering device is a piston located upstream of the outdoor coil
distributor assembly.
High Flow Valves
High flow valves are located on the compressor hot gas and suction
tubes. Large black plastic caps distinguish these valves with
O--rings located inside the caps. Ensure the plastic caps are in place
and tight or the possibility of refrigerant leakage could occur. To
replace valve core body without removing charge, service tool p/n
SCFT20A is required.
High Pressure Switch
The high--pressure switch is located in the discharge line and
protects against excessive condenser coil pressure. It opens at 650
psig (4482 kPA). High pressure may be caused by a dirty
condenser coil, failed fan motor, or condenser air recirculation.
To check switch:
1. Turn off all power to unit.
2. Disconnect leads on switch.
3. Apply ohmmeter leads across switch. You should have
continuity on a good switch.
Loss of Charge Switch
The loss of charge switch is located in the liquid line and will
protect the compressor against a loss of charge condition. It opens
at 20 psig (138 kPa). If switch is open check system pressures. If
pressures are normal, check continuity and wiring of switch. Repair
or replace as required.
R--410A Compressor
The compressor used in this product is specifically designed to
operate with R--410A refrigerant and cannot be interchanged.
The compressor is an electrical (as well as mechanical) device.
Exercise extreme caution when working near compressors. Power
should be shut off, if possible, for most troubleshooting techniques.
Refrigerants present additional safety hazards.
!
WARNING
EXPLOSION HAZARD
Failure to follow this warning could result in personal
injury or death and/or property damage.
Wear safety glasses and gloves when handling refrigerants.
Keep torches and other ignition sources away from
refrigerants and oils.
Compressors vary in type by unit size. See Table 8 below for
compressor type by size.
Table 8 – Compressor Type
UNIT
All compressors in these units have internal overload protection.
This protection will interrupt motor current under fault conditions
such as running current overload. The Copeland Scroll
compressors also have internal pressure relief that will relieve from
the high side to the low side if the differential is between 550 and
625 psig.
COMPRESSOR
TYPE
024 Copeland Scroll 3MAF Polyolester Oil (POE)
030 Copeland Scroll 3MAF Polyolester Oil (POE)
036 LG Scroll RB32G Polyolester Oil (POE)
042 LG Scroll RB32G Polyolester Oil (POE)
048 LG Scroll RB32G Polyolester Oil (POE)
060 Copeland Scroll 3MAF Polyolester Oil (POE)
MANUFACTURER SUGGESTED
OIL TYPE
Refrigerant
!
EXPLOSION, ENVIRONMENTAL SAFETY
HAZARD
Failure to follow this warning could result in personal
injury, death or equipment damage.
This system uses R--410A refrigerant which has higher
operating pressures than R--22 and other refrigerants. No
other refrigerant may be used in this system. Gauge set,
hoses, and recovery system must be designed to handle
R--410A. If you are unsure, consult the equipment
manufacturer.
WARNING
20
Page 21

This system uses R --410A refrigerant which has higher operating
pressures than R--22 and other refrigerants. No other refrigerant
may be used in this system. Gauge set, hoses, and recovery system
must be designed to handle R--410A. If you are unsure, consult the
equipment manufacturer. Failure to use R--410A compatible
servicing equipment or replacement components may result in
property damage or injury.
Compressor Oil
Use only manufacturer suggested compressor oil, see Table 8 for
correct oil.
NOTE: Alternate manufacturer approved compressor oil for
Copeland Scroll compressor: Uniqema RL32--3MAF, Copeland
Ultra 32 CC, Mobil Arctic EAL22 CC, ICI Emkarate RL22 or ICI
Emkarate 32CF.
This oil is extremely hygroscopic, meaning it absorbs water
readily. POE/PVE oils can absorb 15 times as much water as other
oils designed for HCFC and CFC refrigerants. Take all necessary
precautions to avoid exposure of the oil to the atmosphere.
Servicing Systems on Roofs with Synthetic Materials
POE/PVE (polyolester) compressor lubricants are known to cause
long term damage to some synthetic roofing materials. Exposure,
even if immediately cleaned up, may cause embrittlement (leading
to cracking) to occur in one year or more. When performing any
service that may risk exposure of compressor oil to the roof, take
appropriate precautions to protect roofing. Procedures which risk
oil leakage include, but are not limited to, compressor replacement,
repairing refrigerant leaks, replacing refrigerant components such
as filter drier, pressure switch, metering device, coil, accumulator,
or reversing valve.
Synthetic Roof Precautionary Procedure
1. Cover extended roof working area with an impermeable
polyethylene (plastic) drip cloth or tarp. Cover an
approximate10x10ft (3x3m)area.
2. Cover area in front of the unit service panel with a terry
cloth shop towel to absorb lubricant spills, prevent run--offs,
and protect drop cloth from tears caused by tools or
components.
3. Place terry cloth shop towel inside unit immediately under
component(s) to be serviced and prevent lubricant run--offs
through the louvered openings in the unit base.
4. Perform required service.
5. Remove and dispose of any oil contaminated material per
local codes.
Liquid Line Filter Drier
The filter drier is specifically designed to operate with R--410A.
Use only factory--authorized components. Filter drier must be
replaced whenever the refrigerant system is opened. When
removing a filter drier, use a tubing cutter to cut the drier from the
system. Do not unsweat a filter drier from the system. Heat from
unsweating will release moisture and contaminants from drier into
system.
R--410A Refrigerant Charging
Refer to unit informatio n plate and charging chart. Some R --410A
refrigerant cylinders contain a dip tube to allow liquid refrigerant to
flow from cylinder in upright position. For cylinders equipped
with a dip tube, charge R--410A units with cylinder in upright
position and a commercial metering device in manifold hose.
Charge refrigerant into suction--line.
TROUBLESHOOTING
Refer to the Troubleshooting Chart (Table 9) for troubleshooting
information.
START--UP CHECKLIST
Use the Start-- Up Checklist at the back of this manual.
PH4Z
21
Page 22

AIR CONDITIONER WITH R--410A QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE
R--410A refrigerant operates at 50--70 percent higher pressures than R--22. Be sure that servicing equipment and replacement components
are designed to operate with R --410A. R--410A refrigerant cylinders are rose colored.
S R--410A refrigerant cylinders manufactured prior to March 1, 1999, have a dip tube that allows liquid to flow out of cylinder in upright
position.
Cylinders manufactured March 1, 1999 and later DO NOT have a dip tube and MUST be positioned upside down to allow liquid to flow.
S Recovery cylinder service pressure rating must be 400 psig. DOT 4BA400 or DOT BW400.
S R--410A systems should be charged with liquid refrigerant. Use a commercial type metering device in the manifold hose.
S Manifold sets should be minimum 700 psig high--side and 180 psig low-- side with 550 psig low--side retard.
S Use hoses with minimum 700 psig service pressure rating.
S Leak detectors should be designed to detect HFC refrigerant.
S R--410A, as with other HFCs, is only compatible with POE/PVE oils.
S Vacuum pumps will not remove moisture from oil.
S Only use factory specified liquid--line filter driers with rated working pressures no less than 600 psig.
S Do not install a suction--line filter drier in liquid line.
S POE/PVE oils absorb moisture rapidly. Do not expose oil to atmosphere.
S POE/PVE oils may cause damage to certain plastics and roofing materials.
S Wrap all filter driers and service valves with wet cloth when brazing.
PH4Z
S A R--410A liquid--line filter drier is required on every unit.
S Do not use an R--22 TXV.
S Never open system to atmosphere while it is under a vacuum.
S When system must be opened for service, break vacuum with dry nitrogen and replace filter driers.
S Always replace filter drier after opening system for service.
S Do not vent R--410A into the atmosphere.
S Observe all warnings, cautions, and bold text.
S Do not leave R--410A suction line driers in place for more than 72 hrs.
22
Page 23

Table 9 – Troubleshooting Chart
SYMPTOM CAUSE REMEDY
Power failure Call power company
Fuse blown or circuit breaker tripped Replace fuse or reset circuit breaker
Compressor and outdoor fan
will not start
Compressor will not start but condenser fan
runs
Compressor cycles (other than normally satisfying) cooling/heating calls
Compressor operates continuously
Excessive head pressure
Head pressure too low
Excessive suction pressure
Suction pressure too low
Defective contactor, transformer, control relay, or
high--pressure, loss-of--charge or low--pressure switch
Insufficient line voltage Determine cause and correct
Incorrect or faulty wiring Check wiring diagram and rewire correctly
Thermostat setting too low/too high Reset Thermostat setting
Faulty wiring or circuit
Loose connections in compressor
Compressor motor burned out, seized, or Determine cause
internal overload open Replace compressor
Defective run capacitor, overload, or PTC (positive
temperature coefficient) thermistor
Low input voltage Determine cause and correct
Refrigerant overcharge or undercharge
Defective compressor Replace and determine cause
Insufficient line voltage Determine cause and correct
Blocked outdoor coil Determine cause and correct
Defective run/start capacitor, overload or start relay Determine cause and replace
Faulty outdoor fan motor or capacitor Replace
Restriction in refrigerant system Locate restriction and remove
Dirty air filter Replace filter
Unit undersized for load Decrease load or increase unit size
Thermostat temperature set too low Reset Thermostat setting
Low refrigerant charge Locate leak, repair, and recharge
Air in system
Outdoor coil dirty or restricted Clean c oil or remove restriction
Dirty air filter Replace filter
Dirty indoor or outdoor coil Clean coil
Refrigerant overcharged Recover excess refrigerant
Air in system
Indoor or outdoor air restricted or air short-- cycling Determine cause and correct
Low refrigerant charge Check for leaks, repair and recharge
Restriction in liquid tube Remove restriction
High Heat load Check for source and eliminate
Reversing valve hung up or leaking internally Replace valve
Refrigerant overcharged Recover excess refrigerant
Dirty air filter Replace filter
Low refrigerant charge Check for leaks, repair and recharge
Metering device or low side restricted Remove source of restriction
Insufficient coil airflow Check filter–replace if necessary
Temperature too low in conditioned area Reset Thermostat setting
Outdoor ambient below 55F(13C) Install low--ambient kit
Filter drier restric ted Replace
Replace component
Check wiring and repair or replace
Determine cause and replace
Recover refrigerant, evacuate system, and recharge to capacities shown on rating plate
Recover refrigerant, evacuate system, and recharge
Recover refrigerant, evacuate system, and recharge
PH4Z
23
Page 24

START--UP CHECKLIST
(REMOVE AND STORE IN JOB FILE)
I. PRELIMINARY INFORMATION
Model No ............................................................................................................................................................
Serial No .............................................................................................................................................................
Date .....................................................................................................................................................................
Technician ..........................................................................................................................................................
Customer Information(Name/Address) .....................................................................................................................
II. PRE--START--UP
____ Verify that all packing materials have been removed from unit.
____ Verify that condensate connection is installed per installation instructions.
____ Check all electrical connections and terminals for tightness.
____ Check wire proximity to refrigerant tubes and sheet metal edges.
____ Check that indoor (indoor) air filter is clean and in place.
____ Verify that unit installation is level.
____ Check fan wheel propeller for location in housing and setscrew tightness.
III. START--UP
Supply Voltage: L1--L2 __________
Compressor Amps: L1(C) __________ L2(S) __________ L3(R) __________
Indoor Fan Amps: __________ Outdoor Fan Amps: __________
PH4Z
TEMPERATURE--Cooling Mode
Outdoor Air Temperature: __________ DB ____________WB
Return--Air Temperature: __________ DB __________ WB
Cooling Supply Air: __________DB___________WB
PRESSURES--Cooling Mode
Refrigerant Suction __________ psig
Suction Line Temp* ___________
Refrigerant Discharge __________ psig
Discharge Temp {__________
TEMPERATURE--Heating Mode
Outdoor Air Temperature: __________ DB ____________WB
Return--Air Temperature: __________ DB __________ WB
Supply Air: __________DB___________WB
PRESSURES--Heating Mode
Refrigerant Suction __________ psig
Suction Line Temp* ___________
Refrigerant Discharge __________ psig
Discharge Temp {__________
*Measured at suction inlet to compressor
{Measured at liquid line leaving outdoor coil
Copyright 2016 CAC / BDP D 7310 W. Morris St. D Indianapolis, IN 46231 Edition Date: 5/16
Manufacturer reserves the right to change, at any ti me, specifications and designs without notice and without obligations.
24
C a t a l o g N o : I M --- P H 4 Z --- 0 4
R e p l a c es : I M --- P H 4 Z --- 0 3
 Loading...
Loading...