Page 1

installation, start-up,
and operating instructions
DOWNFLOW 2-SPEED,
2-STAGE, INDUCED-COMBUSTION
GAS-FIRED FURNACE
NOTE: Read the entire instruction manual before starting the
installation.
This symbol → indicates a change since the last issue.
Index Page
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS .....................................................1
ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE (ESD) PRECAUTIONS
PROCEDURE........................................................................1-2
INTRODUCTION.......................................................................2-3
Dimensional Drawing ...............................................................2
Clearances to Combustibles......................................................3
LOCATION....................................................................................4
General ......................................................................................4
Location Relative to Cooling Equipment ................................4
Hazardous Locations.................................................................4
AIR FOR COMBUSTION AND VENTILATION...................4-5
Unconfined Space .....................................................................4
Confined Space......................................................................4-5
SUPPLY-AIR PLENUM INSTALLATION
(DOWNFLOW) .....................................................................5-6
Downflow Installation .............................................................5
Installation On Combustible Floor........................................5-6
FILTER ARRANGEMENT .......................................................6-7
GAS PIPING...............................................................................6-8
ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS...............................................8-9
115-v Wiring.............................................................................8
24-v Wiring............................................................................8-9
Accessories .............................................................................. 9
VENTING ......................................................................................9
START-UP, ADJUSTMENT, AND SAFETY CHECK.......10-20
General ....................................................................................10
Sequence of Operation ......................................................10-14
Adaptive Heating Mode ....................................................10-12
Non-Adaptive Heating Mode .................................................12
Cooling Mode .........................................................................13
Continuous Blower Mode.......................................................13
Heat Pump Mode...............................................................13-14
Defrost Mode ..........................................................................14
Start-Up Procedures................................................................14
Adjustments .......................................................................14-20
Set Gas Input Rate ............................................................14-19
Set Temperature Rise ........................................................19-20
Set Thermostat Heat Anticipator............................................20
Check Safety Controls.......................................................20-21
Checklist..................................................................................21
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
Installing and servicing heating equipment can be hazardous due to
gas and electrical components. Only trained and qualified personnel should install, repair, or service heating equipment.
Untrained personnel can perform basic maintenance functions
such as cleaning and replacing air filters. All other operations must
be performed by trained service personnel. When working on
heating equipment, observe precautions in the literature, on tags,
and on labels attached to or shipped with the unit and other safety
precautions that may apply.
331JAV
Series B
Cancels: II 331J-60-1 II 331J-60-2
12-97
ama
CANADIAN GAS ASSOCIATION
®
REGISTERED QUALITY SYSTEM
Follow all safety codes. In the United States, refer to the National
Fuel Gas Code (NFGC) NFPA No. 54-1996/ANSI Z223.1-1996.
In Canada, refer to the current edition of the National Standard of
Canada CAN/CGA-B149.1- and .2-M95 Natural Gas and Propane
Installation Codes (NSCNGPIC). Wear safety glasses and work
gloves. Have fire extinguisher available during start-up and
adjustment procedures and service calls.
Recognize safety information. This is the safety-alert symbol
When you see this symbol on the unit and in instructions or
manuals, be alert to the potential for personal injury.
Understand the signal words DANGER, WARNING, and CAUTION. These words are used with the safety-alert symbol. DANGER identifies the most serious hazards which will result in severe
personal injury or death. WARNING signifies hazards which
could result in personal injury or death. CAUTION is used to
identify unsafe practices which would result in minor personal
injury or product and property damage.
These instructions cover minimum requirements and conform to
existing national standards and safety codes. In some instances,
these instructions exceed certain local codes and ordinances,
especially those that may not have kept up with changing residential construction practices. We require these instructions as a
minimum for a safe installation.
ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE (ESD) PRECAUTIONS
PROCEDURE
CAUTION: Electrostatic discharge can affect electronic
components. Take precautions during furnace installation
and servicing to protect the furnace electronic control.
Precautions will prevent electrostatic discharges from
personnel and hand tools which are held during the
procedure. These precautions will help to avoid exposing
the control to electrostatic discharge by putting the
furnace, the control, and the person at the same electrostatic potential.
1. Disconnect all power to the furnace. DO NOT TOUCH
THE CONTROL OR ANY WIRE CONNECTED TO THE
CONTROL PRIOR TO DISCHARGING YOUR BODY’S
ELECTROSTATIC CHARGE TO GROUND.
APPROVED
R
.
—1—
Page 2
1
28
⁄2″
20″
13
⁄16″
7
39
⁄8″
11
⁄16″
INLET
7
⁄8″ DIA
ACCESSORY
3
⁄4″ DIA HOLE
1
GAS ENTRY
OUTLET
19″
ADDITIONAL
NOTE:
LOCATED IN THE TOP PLATE
AND BOTTOM PLATE
7
⁄8″ DIA K.O. ARE
VENT CONNECTION
13
⁄16″
1
9
⁄8″
1
10
⁄4″
1
1
⁄16″
1
2
⁄8″
1
8
⁄4″
11
⁄16″
D
E
A
AIRFLOW
1
⁄2″ DIA
2″
3
4
⁄16″
15
2
⁄16″
1
16
⁄16″
5
13
⁄16″
1
10
11
⁄16″
DIMPLES TO DRILL HOLES
FOR HANGER BOLTS (4 PLACES)
IN HORIZONTAL POSITION
⁄4″
THERMOSTAT
WIRE ENTRY
7
⁄8″ DIA
ACCESSORY
7
⁄8″ DIA HOLE
POWER ENTRY
1
1
⁄2″ DIA
R.H. GAS ENTRY
7
⁄8″ DIA
ACCESSORY
1
1
⁄16″
1
2
⁄8″
″ TYP
1
5
⁄8″ TYP
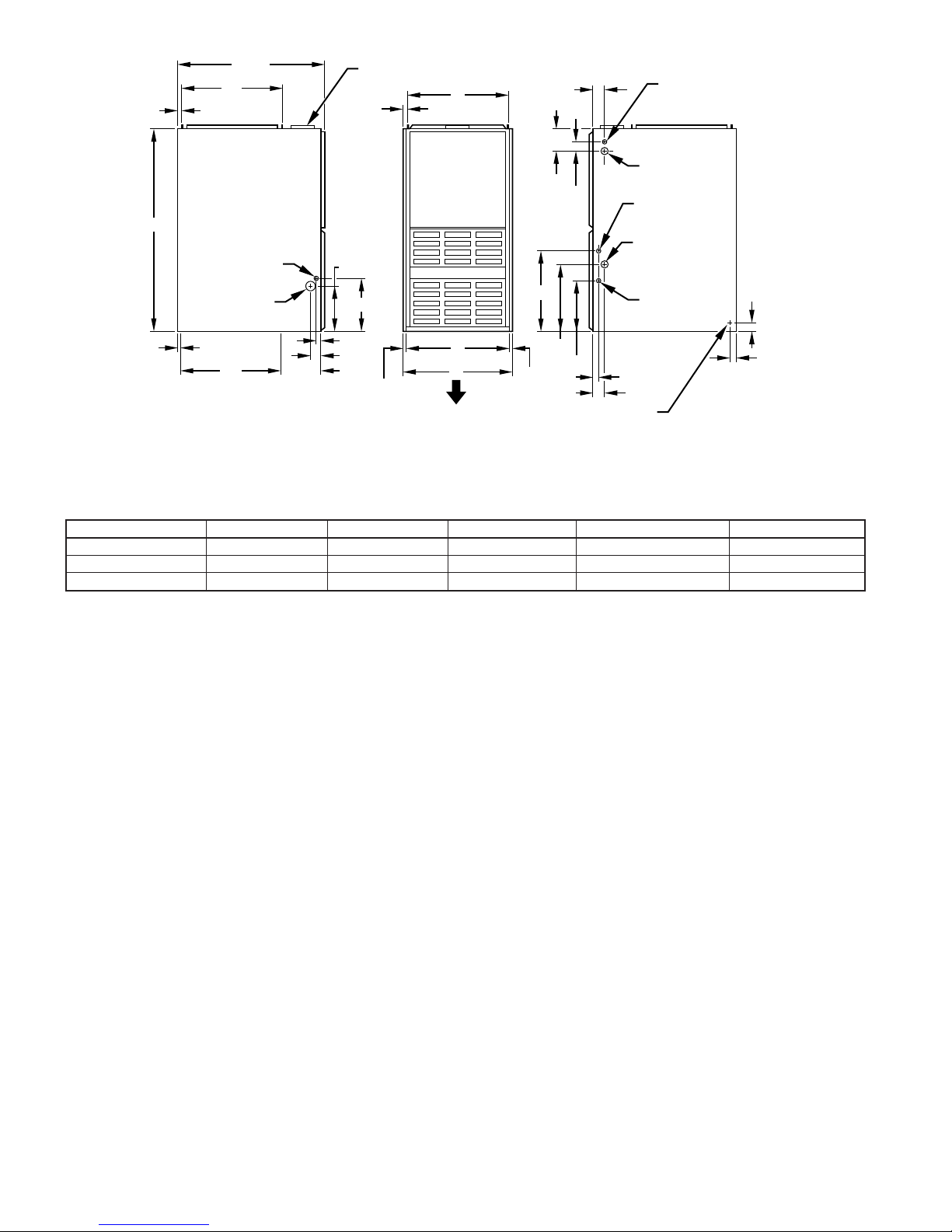
Fig. 1—Dimensional Drawing
TABLE 1—DIMENSIONS (IN.)
UNIT SIZE A D E VENT CONN SHIP. WT
036060 14-3/16 12-9/16 12-11/16 4 145
048080 17-1/2 15-7/8 16 4 154
060100 21 19-3/8 19-1/2 4 181
A88324
2. Firmly touch a clean, unpainted, metal surface of the
furnace chassis which is close to the control. Tools held in
a person’s hand during grounding will be satisfactorily
discharged.
3. After touching the chassis you may proceed to service the
control or connecting wires as long as you do nothing that
recharges your body with static electricity (for example; DO
NOT move or shuffle your feet, DO NOT touch ungrounded objects, etc.).
4. If you touch ungrounded objects (recharge your body with
static electricity), firmly touch furnace again before touching control or wires.
5. Use this procedure for installed and uninstalled (ungrounded) furnaces.
6. Before removing a new control from its container, discharge your body’s electrostatic charge to ground to protect
the control from damage. If the control is to be installed in
a furnace, follow items 1 through 5 before bringing the
control or yourself into contact with the furnace. Put all
used AND new controls into containers before touching
ungrounded objects.
7. An ESD service kit (available from commercial sources)
may also be used to prevent ESD damage.
→
INTRODUCTION
The model 331JAV Series B Furnace is available in sizes 60,000
through 100,000 Btuh input capacities.
The design of the downflow gas-fired furnace is A.G.A./C.G.A.
certified for natural and propane gases and for installation on
noncombustible flooring. The furnace is factory-shipped for use
with natural gas. The manufacturer’s accessory gas conversion kit
is required to convert furnace for use with propane gas.
These furnaces SHALL NOT be installed directly on carpeting,
tile, or any other combustible material other than wood flooring. In
downflow installations, the manufacturer’s accessory floor base
must be used when installed on combustible materials and wood
flooring. Special base is not required when this furnace is installed
on manufacturer’s Coil Assembly Part No. CD5 or CK5, or when
Coil Box Part No. KCAKC is used. This furnace is for installation
in alcoves, attics, crawlspaces, basements, closets, or utility rooms.
The design of this furnace line is not A.G.A./C.G.A. certified for
installation in mobile homes, recreation vehicles, or outdoors.
Before installing the furnace, refer to the current edition of the
NFGC and the NFPA 90B. Canadian installations must be installed
in accordance NSCNGPIC and all authorities having jurisdiction.
For a copy of the NFGC NFPA54/Z223.1, contact International
Approval Services U.S. Inc., 8501 E. Pleasant Valley Road,
Cleveland, OH 44131 or National Fire Protection Association Inc.,
Batterymarch Park, Quincy, MA 02269. For a copy of NFPA 90B,
contact National Fire Protection Association Inc., Batterymarch
Park, Quincy, MA 02269.
Before installing the furnace in Canada, refer to the current edition
of the NSCNGPIC. Contact Standards Department of Canadian
Gas Association, 55 Scarsdale Road, Don Mills, Ontario, Canada
M3B 2R3.
The duct system should be designed and sized according to
accepted national standards published by: Air Conditioning Contractors Association (ACCA), Sheet Metal and Air Conditioning
Contractors National Association (SMACNA). Or consult the
Residential Systems Design Guidelines reference tables available
from your local distributor. The duct system should be sized to
handle the maximum CFM capabilities of the equipment at the
optimum design static pressure.
—2—
Page 3

INSTALLATION
This unit is certified for downflow installation only. See Installation Manual for
important installation instructions.
MINIMUM INCHES CLEARANCE TO COMBUSTIBLE CONSTRUCTION
This forced air furnace is equipped for
use with natural gas at altitudes 0 10,000 ft
(0-3,050m).
An accessory kit, supplied by the
manufacturer, shall be used to convert to
propane gas use or may be required for
some natural gas applications.
This furnace is for indoor installation in
a building constructed on site.
This furnace may be installed on
combustible flooring in alcove or closet at
minimum clearance from combustible
material.
This furnace may be used with a Type
B-1 Vent and may be vented in common
with other gas-fired appliances.
For installation on non-combustible
†
floors only. For installation on
combustible flooring only when
installed on special base, Part No.
KGASB0201ALL, Coil Assembly,
Part No. CD5 or CK5, or Coil
Casing, Part No. KCAKC.
For furnaces wider than 14.25
#
inches (362mm) may be 0 inches.
Ø
18 inches front clearance required
for alcove.
For single wall vent type 6 inches.
##
This furnace is approved for DOWNFLOW installations only.
1"
0"
B
A
C
K
E
D
I
S
1" #
Clearance in inches.
TOP / PLENUM
E
C
A
N
R
U
F
T
N
O
R
F
F
R
O
N
T
##
BOTTOM
†
"
1
Vent Clearance to combustibles:
For Single Wall vents 6 inches (6 po).
For Type B-1 vent type 1 inch (1 po).
#
1"
E
D
I
S
S
E
R
V
I
C
E
30"
MIN
Ø
322567-101 REV. E (LIT)
→
Fig. 2—Clearances to Combustibles
CAUTION: Application of this furnace should be in-
doors with special attention given to vent sizing and
material, gas input rate, air temperature rise, and unit
sizing. Improper installation or misapplication of the
furnace can require excessive servicing or cause premature component failure.
Installation must conform to regulations of serving gas supplier
and local building, heating, and plumbing codes in effect in the
area in which installation is made, or in absence of local codes with
requirements of the NFGC.
This furnace is designed for a minimum continuous return-air
temperature of 60°F db or intermittent operation down to 55°F
such as when used with a night setback thermostat. Return-air
temperature must not exceed 85°F db.
To aid in installation, troubleshooting, and service, a status code
label is located on blower component door. This label explains
how to use the LED status indicated on furnace control which is
viewed through the sight glass on door.
A97620
WARNING: Improper installation, adjustment, alteration, service, maintenance, or use can cause carbon
monoxide poisoning, explosion, fire, electrical shock, or
other conditions which may cause personal injury, loss of
life, or property damage. Consult a qualified installer,
service agency, local gas supplier, or your distributor or
branch for information or assistance. The qualified installer or agency must use only factory-authorized and
listed kits or accessories when modifying this product. A
failure to follow this warning could result in electrical
shock, fire, personal injury, or death.
For high-altitude installation, the high-altitude conversion kit must
be installed at or above 5500 ft above sea level.
For accessory installation details, refer to applicable installation
literature.
NOTE: Remove all shipping brackets and materials before operating furnace.
—3—
Page 4
I. LOCATION
A. General
CAUTION: DO NOT install furnace in a corrosive or
contaminated atmosphere. Make sure all combustion and
circulating air requirements are followed.
DO NOT use this furnace during construction when
adhesives, sealers, and/or new carpets are being installed
and curing. If the furnace is required during construction,
use clean outside air for combustion and ventilation.
Compounds of chlorine and fluorine when burned in
combustion air form acids which will cause corrosion of
the heat exchangers and metal vent systems. Some of
these compounds are released from paneling and dry wall
adhesives, paints, thinners, masonry cleaning materials,
and many other solvents commonly used in the construction process.
Excessive exposure to contaminated combustion air will
result in safety and performance related problems.
This furnace must be installed so electrical components are
protected from water.
Locate furnace as near to center of air distribution system and
chimney or vent as possible. The furnace should be installed as
level as possible.
When furnace is installed so that supply ducts carry air to areas
outside space containing furnace, the return air must also be
handled by a duct(s) sealed to furnace casing and terminating
outside space containing furnace.
Provide ample space for servicing and cleaning. Always comply
with minimum fire protection clearances shown on unit clearance
label. This furnace shall not be installed directly on carpeting, tile,
or any combustible material other than wood flooring. The furnace
may be installed on combustible flooring when installed with
accessory downflow subbase, which is available from your distributor or branch when required.
B. Location Relative to Cooling Equipment
The cooling coil must be installed parallel with or on downstream
side of furnace to avoid condensation in heat exchangers. When
installed parallel with furnace, dampers or other means used to
control the flow of air must prevent chilled air from entering
furnace. If dampers are manually operated, they must be equipped
with means to prevent operation of either unit unless damper is in
full-heat or full-cooling position.
C. Hazardous Locations
When furnace is installed in a residential garage, it must be
installed so that burners and ignition source are at least 18 in.
above floor. The furnace should be protected from physical
damage by vehicles.
When furnace is installed in public garages, airplane hangars, or
other buildings having hazardous atmospheres, unit must be
installed in accordance with recommended good practice requirements of the National Fire Protection Association, Inc.
II. AIR FOR COMBUSTION AND VENTILATION
Provisions for adequate combustion and ventilation air must be
provided in accordance with Section 5.3, Air for Combustion and
Ventilation, of the NFGC or applicable provisions of local building
codes.
Canadian installations must be in accordance with NSCNGPIC
and all authorities having jurisdiction.
CAUTION: Air for combustion must not be contaminated by halogen compounds which include fluoride,
chloride, bromide, and iodide. These elements are found
in aerosol sprays, detergents, bleaches, cleaning solvents,
salts, air fresheners, and other household products.
CAUTION: The operation of exhaust fans, kitchen ventilation fans, clothes dryers, or fireplaces could create a
negative air pressure condition at the furnace. Make-up
air must be provided for these devices, in addition to that
required by the furnace.
All fuel-burning equipment must be supplied with air for combustion of the fuel. Sufficient air MUST be provided to ensure there
will not be a negative pressure in equipment room or space. In
addition, a positive seal MUST be made between furnace cabinet
and return-air duct to avoid pulling air from the burner area and
draft safeguard opening into circulating air.
The requirements for combustion and ventilation air depend upon
whether furnace is located in a CONFINED or UNCONFINED
space.
A. Unconfined Space
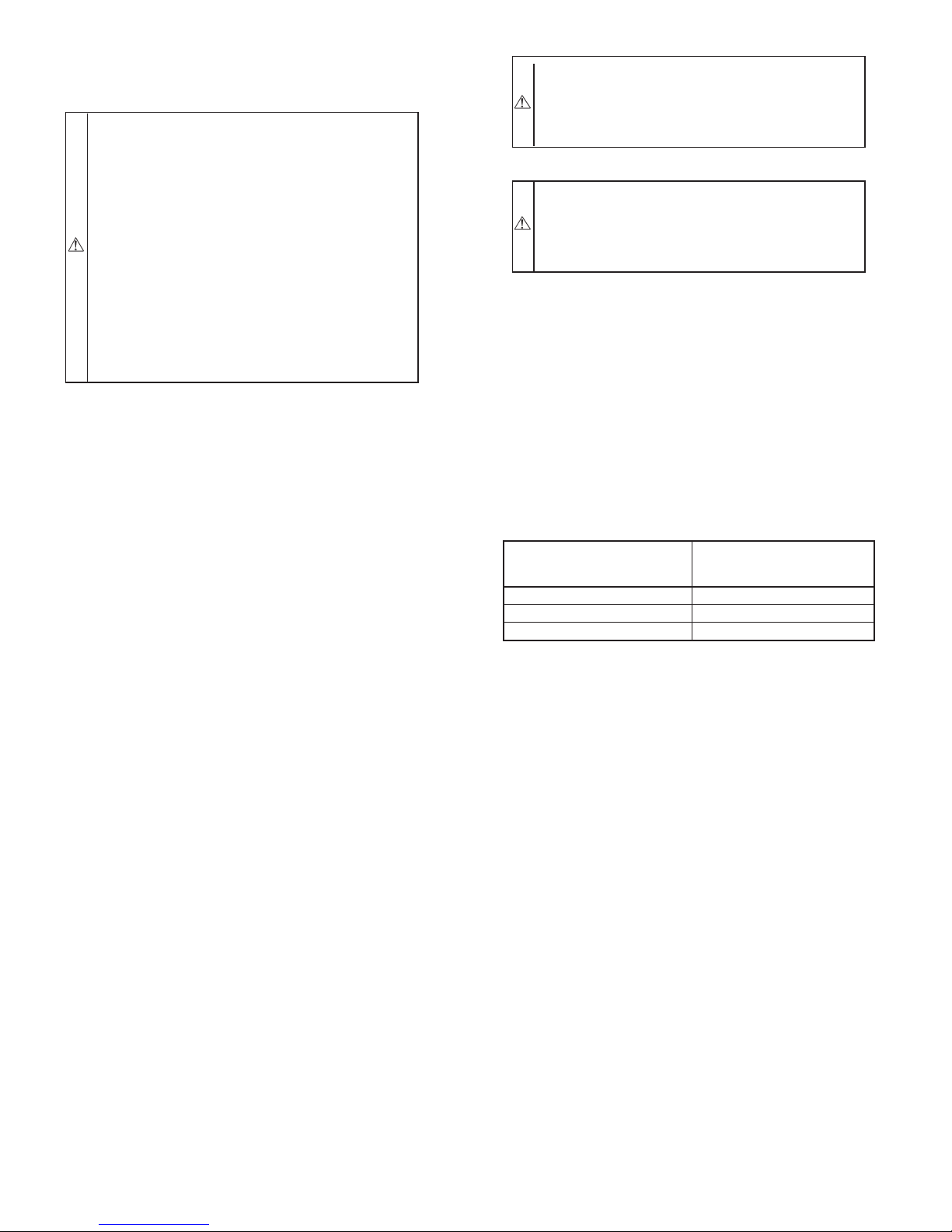
An unconfined space must have at least 50 cu ft for each 1000
Btuh of input for all appliances (such as furnaces, clothes dryer,
water heaters, etc.) in the space.
For Example:
331JAV FURNACE
HIGH-FIRE INPUT
BTUH
63,000 420
84,000 560
105,000 700
MINIMUM SQ FT
WITH
7-1/2 FT CEILING
If the unconfined space is constructed unusually tight, air for
combustion and ventilation MUST come from either the outdoors
or spaces freely communicating with outdoors. Combustion and
ventilation openings must be sized the same as for a confined
space as defined below. Return air must not be taken from the
room unless equal or greater amount of air is supplied to the room.
B. Confined Space
A confined space is defined as a space whose volume is less than
50 cu ft per 1000 Btuh of total input ratings of all appliances
installed in that space. A confined space MUST have provisions
for supplying air for combustion, ventilation, and dilution of flue
gases using 1 of the following methods.
NOTE: In determining free area of an opening, the blocking
effect of louvers, grilles, and screens must be considered. If free
area of louver or grille design is unknown, assume that wood
louvers have a 20 percent free area and metal louvers or grilles
have a 60 percent free area. Screens, when used, must not be
smaller than 1/4-in. mesh. Louvers and grilles must be constructed
so they cannot be closed.
The size of the openings depends upon whether air comes from
outside of the structure or an unconfined space inside the structure.
1. All air from an unconfined space inside the structure
requires 2 openings (for structures not usually tight):
a. Each opening MUST have at least 1 sq in. of free area
per 1000 Btuh of total input for all equipment within the
confined space, but not less than 100 sq in. per opening.
(See Fig. 3 and Table 2.) The minimum dimension of air
openings shall not be less than 3 in.
b. If the building is constructed unusually tight, a perma-
nent opening directly communicating with the outdoors
shall be provided. (See item 2 below.)
—4—
Page 5

VENT THROUGH ROOF
(CATEGORY I)
DUCTS TO
OUTDOORS
1 SQ IN.
PER 4000
BTUH
*
RETURN
AIR
INTERIOR
HEATED
SPACE
SUPPLY AIR
* Minimum opening size is 100 sq in. with
minimum dimensions of 3 in.
†
Minimum of 3 in. when type B-1 vent is used.
12″ MAX
1 SQ IN.
PER 1000
BTUH* IN DOOR
OR WALL
UNCONFINED
SPACE
6″ MIN
(FRONT)
1 SQ IN.
PER 1000
BTUH* IN DOOR
OR WALL
†
12″ MAX
A93387
Fig. 3—Confined Space: Air for Combustion and Ventilation
from an Unconfined Space
c. If furnace is installed to obtain return air is taken directly
from hallway or space adjacent to furnace, all air for
combustion must come from outdoors.
2. Air from outside the structure requires 1 of the following
methods:
a. If combustion air is taken from outdoors through 2
vertical ducts, the openings and ducts MUST have at
least 1 sq in. of free area per 4000 Btuh of total input for
all equipment within the confined space. (See Fig. 4 and
Table 2.)
b. If combustion air is taken from outdoors through 2
horizontal ducts, the openings and ducts MUST have at
least 1 sq in. of free area per 2000 Btuh of total input for
all equipment within the confined space. (See Fig. 4 and
Table 2.)
c. If combustion air is taken from outdoors through a single
opening or duct (horizontal or vertical) commencing
within 12 in. of the top of the confined space, opening
and duct MUST have at least 1 sq in. of free area per
3000 Btuh of the total input for all equipment within the
confined space and not less than the sum of the areas of
all vent connectors in the confined space. (See Fig. 4 and
Table 2.) Equipment clearances to the structure shall be
at least 1 in. from the sides and back and 6 in. from the
front of the appliances.
When ducts are used, they must be of the same cross-sectional area
as the free area of the openings to which they connect. The
minimum dimension of ducts must not be less than 3 in. (See Fig.
4.)
12″ MAX
1 SQ IN.
PER 2000
BTUH
*
DUCTS
TO
OUTSIDE
1 SQ IN.
PER 2000
BTUH
*
12″ MAX
SUPPLY AIR
Minimum dimensions of 3 in.
*
NOTE:
Use any of the following
combinations of openings:
A & B C & D D & E F & G
RETURN
A
B
AIR
D
VENT
THROUGH
ROOF
(CATEGORY I)
CONFINED
C
DUCT
TO
OUTDOORS
F
SPACE
G
E
12″ MAX
12″
MAX
1 SQ IN.
PER 4000
BTUH
OUTDOORS
1 SQ IN.
PER 4000
BTUH
12″
MAX
1 SQ IN.
PER 4000
BTUH
*
*
A93388
Fig. 4—Confined Space: Air for Combustion and Ventilation
from Outdoors
III. SUPPLY-AIR PLENUM INSTALLATION (DOWNFLOW)
A. Downflow Installation
→
NOTE: This furnace is approved for use on combustible flooring
when manufacturer’s accessory floor base Part No.
KGASB0201ALL is used. Manufacturer’s accessory floor base is
not required when this furnace is installed on manufacturer’s Coil
Assembly Part No. CD5 or CK5, or Coil Box Part No. KCAKC is
used.
1. Determine application being installed from Table 3.
2. Construct hole in floor per dimensions specified in Table 3
and Fig. 5.
3. Construct plenum to dimensions specified in Table 3.
4. If downflow subbase (KGASB) is used, install as shown in
Fig. 6.
If coil assembly CD5, CK5, or Coil Box KCAKC is used,
install as shown in Fig. 7.
B. Installation On Combustible Floor
1. Cut and frame hole in floor per dimensions in Installation
Instructions packaged with downflow subbase.
2. When completed, downflow subbase, plenum, and furnace
(or coil casing when used) should be installed as shown in
Fig. 6.
—5—
Page 6
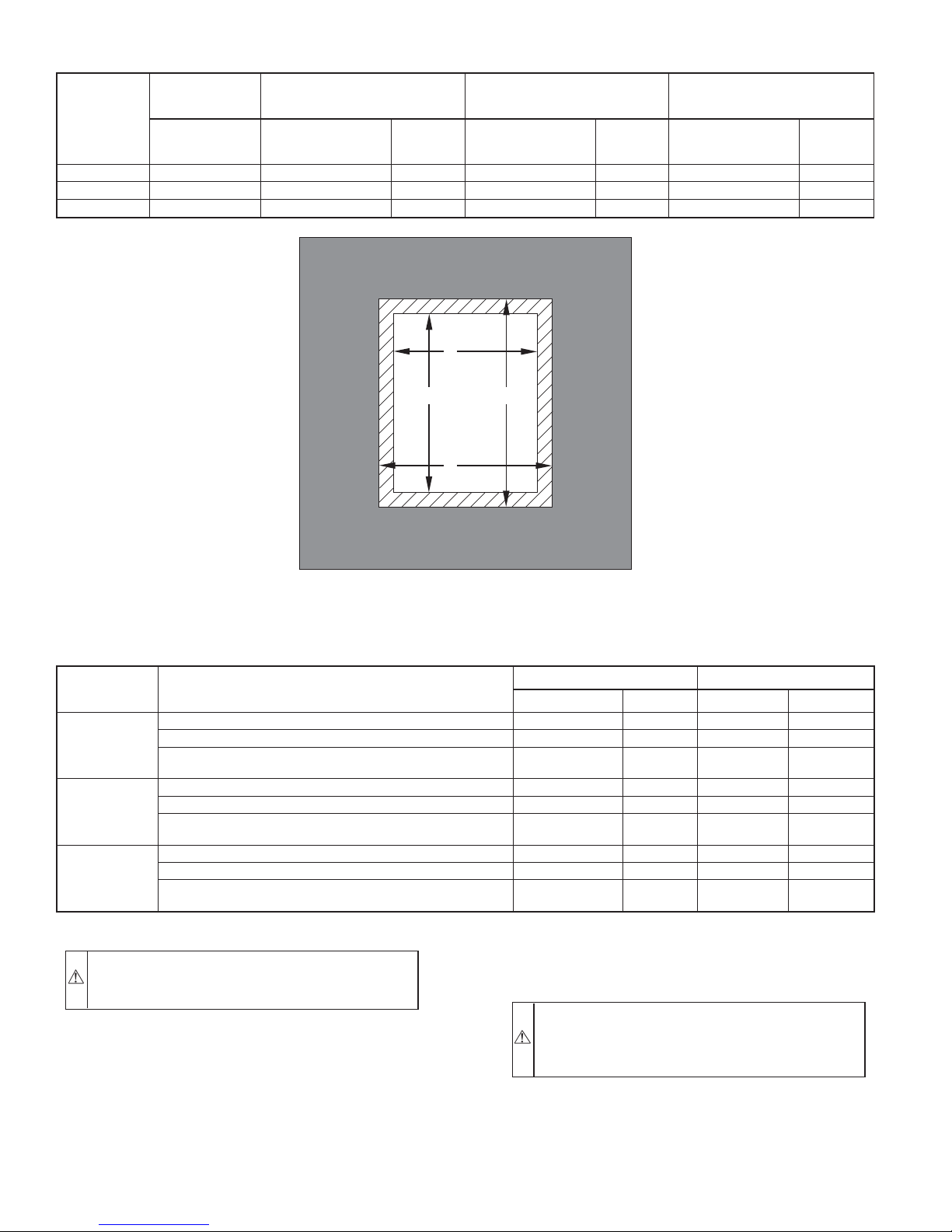
TABLE 2—FREE AREA OF COMBUSTION AIR OPENING
331JAV
FURNACE
HIGH-FIRE
INPUT
(BTUH)
63,000 100 15.8 5 31.5 7 21.0 6
84,000 100 21.0 6 42.0 8 28.0 6
105,000 105 26.3 6 52.5 9 35.0 7
AIR FROM
UNCONFINED
SPACE
Free Area
of Opening
(Sq In.)
OUTDOOR AIR THROUGH
VERTICAL DUCTS
Free Area of
Opening and Duct
(Sq In.)
(In. Dia)
Round
Pipe
OUTDOOR AIR THROUGH
HORIZONTAL DUCTS
Free Area of
Opening and Duct
(Sq In.)
(In. Dia)
Round
Pipe
OUTDOOR AIR THROUGH
SINGLE DUCT
Free Area of
Opening and Duct
(Sq In.)
A
PLENUM
OPENING
B
OPENING
D
FLOOR
C
Round
Pipe
(In. Dia)
Fig. 5—Floor and Plenum Opening Dimensions
TABLE 3—OPENING DIMENSIONS (IN.)
FURNACE
CASING
WIDTH
14-3/16
17-1/2
21
Combustible Flooring Using KGASB Subbase 11-13/16 19 13-7/16 20-3/8
Combustible Flooring with CD5 or CK5 Coil Assembly or
Combustible Flooring Using KGASB Subbase 15-1/8 19 16-3/4 20-3/8
Combustible Flooring with CD5 or CK5 Coil Assembly or
Combustible Flooring Using KGASB Subbase 18-5/8 19 20-1/4 20-3/8
Combustible Flooring with CD5 or CK5 Coil Assembly or
APPLICATION
Non-Combustible Flooring 12-11/16 19 13-3/8 19-5/8
KCAKC Coil Box
Non-Combustible Flooring 16 19 16-5/8 19-5/8
KCAKC Coil Box
Non-Combustible Flooring 19-1/2 19 20-1/8 19-5/8
KCAKC Coil Box
IV. FILTER ARRANGEMENT
WARNING: Never operate unit without a filter or with
filter access door removed. A failure to follow this
warning could result in fire, personal injury, or death.
The 2 factory-supplied filters are shipped in the blower compartment. After return-air duct has been connected to furnace, install
filters in a V-formation inside return-air plenum. (See Fig. 8.)
V. GAS PIPING
→
Gas piping must be installed in accordance with national and local
codes. Refer to the NFGC NFPA 54-1996/ANSI Z223.1-1996.
Canadian installations must be installed in accordance with NSCNGPIC and all authorities having jurisdiction.
A96283
PLENUM OPENING FLOOR OPENING
ABCD
12-5/16 19 13-5/16 20
15-1/2 19 16-1/2 20
19 19 20 20
The gas supply line should be a separate line directly from the
meter to the furnace, if possible. Refer to Table 4 for recommended gas pipe sizing. Risers should be used to connect to the
furnace and to the meter.
CAUTION: If flexible connector is required or allowed
by authority having jurisdiction, black iron pipe shall be
installed at gas valve and extend a minimum of 2 in.
outside furnace casing.
—6—
Page 7
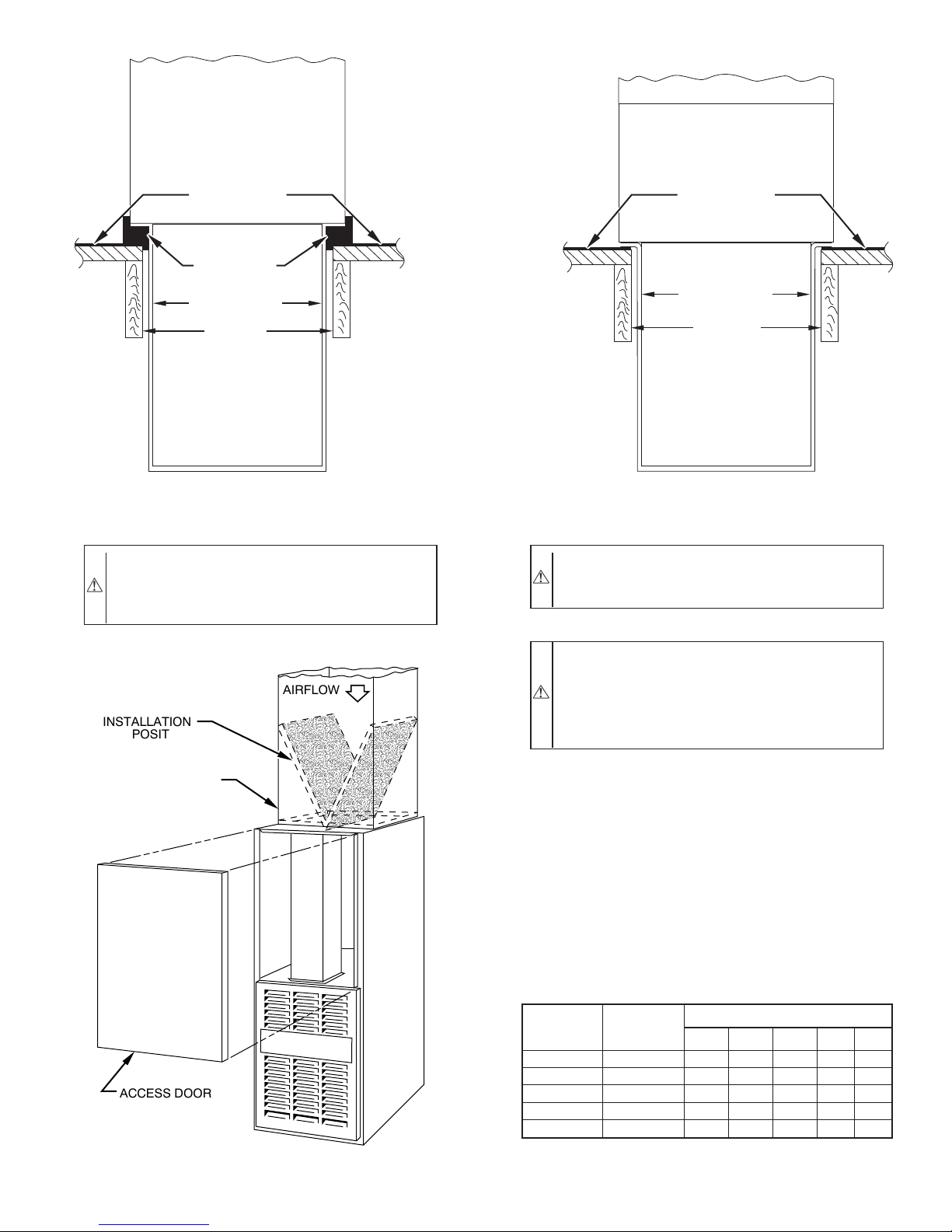
FURNACE
(OR COIL CASING
WHEN USED)
FURNACE
CD5 OR CK5
COIL ASSEMBLY
OR KCAKC
COIL BOX
COMBUSTIBLE
FLOORING
DOWNFLOW
SUBBASE
SHEET METAL
PLENUM
FLOOR
OPENING
A96285
Fig. 6—Furnace, Plenum, and Subbase Installed on
a Combustible Floor
WARNING: Use the proper length of pipes to avoid
stress on gas control manifold. A failure to follow this
warning could result in a gas leak causing fire, explosion,
personal injury, or death.
COMBUSTIBLE
FLOORING
SHEET METAL
PLENUM
FLOOR
OPENING
A96284
Fig. 7—Furnace, Plenum, and Coil Assembly or Coil Box
Installed on a Combustible Floor
CAUTION: Use a backup wrench at furnace gas control
when connecting gas pipe to furnace to avoid damaging
gas controls or manifold.
AIRFLOW
INSTALLATION
POSITION
OF FILTERS
RETURN-AIR
PLENUM
ACCESS DOOR
Fig. 8—Downflow Filter Arrangement
A88486
WARNING: Never purge a line into a combustion
chamber. Never use matches, candles, flame, or other
sources of ignition to check for gas leakage. Use a
soap-and-water solution to check for gas leaks. A failure
to follow this warning could result in fire, explosion,
personal injury, or death.
Piping should be pressure tested in accordance with local and
national plumbing and gas codes before furnace has been attached.
If test pressure exceeds 0.5 psig (14-in. wc), the gas supply pipe
must be disconnected from furnace and capped before pressure
test. If test pressure is equal to or less than 0.5 psig (14-in. wc),
turn off electric shutoff switch located on the gas valve before test.
It is recommended that ground joint union be loosened before
pressure testing.
Joint compounds (pipe dope) should be applied sparingly and only
to male threads of joints. This pipe dope must be resistant to action
of propane gas.
TABLE 4—MAXIMUM CAPACITY OF PIPE*
NOMINAL
IRON PIPE
SIZE (IN.)
1/2 0.622 175 120 97 82 73
3/4 0.824 360 250 200 170 151
1 1.049 680 465 375 320 285
1-1/4 1.380 1400 950 770 660 580
1-1/2 1.610 2100 1460 1180 990 900
* Cubic ft of gas per hr for gas pressures of 0.5 psig (14-in. wc) or less, and a
supply line pressure drop of 0.5-in. wc (based on a 0.60 specific gravity gas).
Ref: Table 10-2, NFPA 54-1996.
INTERNAL
DIAMETER
(IN.)
LENGTH OF PIPE (FT)
10 20 30 40 50
—7—
Page 8
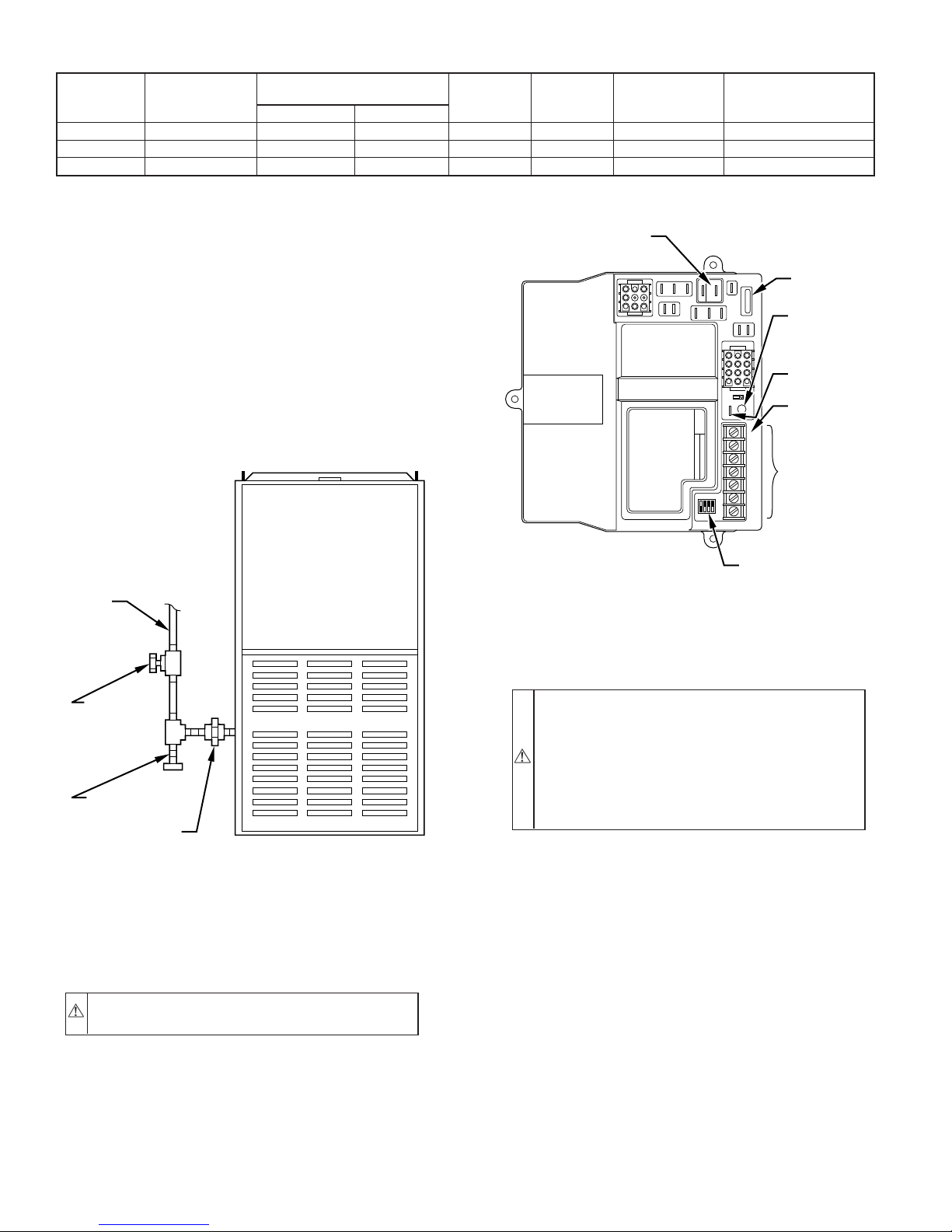
TABLE 5—ELECTRICAL DATA
UNIT
SIZE
VOLTS—
HERTZ—
PHASE
036060 115—60—1 127 104 10.5 14 35 15
048080 115—60—1 127 104 14.2 14 26 15
060100 115—60—1 127 104 17.9 12 32 20
* Permissible limits of the voltage range at which the unit will operate satisfactorily.
† Time-delay fuse is recommended.
‡ Length shown is as measured 1 way along wire path between unit and service panel for maximum 2 percent voltage drop.
Install accessible manual shutoff valve upstream of furnace gas
controls and within 72 in. of furnace. A 1/8-in. NPT plugged
tapping is provided on gas value for test gage connection.
Installation of additional 1/8-in. NPT plugged tapping, accessible
for test gage connection, installed immediately upstream of gas
supply connection to furnace and downstream of manual shutoff
valve is not required. Place ground joint union between gas control
manifold and manual shutoff.
Install sediment trap in riser leading to furnace. The trap can be
installed by connecting a tee to riser leading from furnace. Connect
capped nipple into lower end of tee. The capped nipple should
extend below level of gas controls. (See Fig. 9.)
OPERATING
VOLTAGE RANGE
Max* Min*
MAX
UNIT
AMPS
EAC - ELECTRONIC
(115-VAC 1 AMP MAX)
MIN
WIRE
GAGE
AIR CLEANER
MAX WIRE
LENGTH
78 9
456
123
FT‡
PR2
PR1
L2
L1
PARK
COM
EAC-1
EAC-2
-HEAT
-HEAT
HI-GAS
LO-GAS
HI-COOL
SEC-1
10 11 12
789
456
123
MASTER SLAVE
TWIN
TEST
1
After all connections have been made, purge lines and check for
gas leakage with regulated gas supply pressure.
1234
OFF
ON
MAX FUSE OR
HACR-TYPE
CKT BKR AMPS†
3-AMP
3
FU1
FUSE
LED -
DIAGNOSTIC
SEC-2
LIGHT
TWIN / TEST
LED
HUM
GRY/Y2W/W1
TERMINAL
HUM -
HUMIDIFIER
(24-VAC 0.5
AMP MAX)
1
24-VOLT
THERMOSTAT
TERMINALS
24 V
COM
W2
GAS
SUPPLY
MANUAL
SHUTOFF
VALVE
(REQUIRED)
SEDIMENT
TRAP
UNION
Fig. 9—Typical Gas Pipe Arrangement
VI. ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS
A. 115-v Wiring
Refer to unit rating plate or Table 5 for equipment electrical
requirements. The control system requires an earth ground for
proper operation.
CAUTION: Do not connect aluminum wire between
disconnect switch and furnace. Use only copper wire.
Make all electrical connections in accordance with the current
→
edition of the National Electrical Code (NEC) ANSI/NFPA
70-1996 and any local codes or ordinances that might apply. For
Canadian installations, all electrical connections must be made in
accordance with CSA C22.1 Canadian Electrical Code or authorities having jurisdiction.
A89414
FURNACE AND
BLOWER OFF DELAY
SETUP SWITCHES
NOTE: Proper polarity must be maintained for 115-v wiring. If
Fig. 10—Control Center
polarity is incorrect, the furnace control status LED will flash
rapidly and prevent heating operation.
→
WARNING: The cabinet must have an uninterrupted or
unbroken ground according to NEC ANSI/NFPA 701996 and Canadian Electrical Code CSA C22.1 or local
codes to minimize personal injury if an electrical fault
should occur. This may consist of electrical wire or
conduit approved for electrical ground when installed in
accordance with existing electrical codes. Do not use gas
piping as an electrical ground.
B. 24-v Wiring
Refer to ESD Precautions Procedure before proceeding with 24-v
connections.
Make field 24-v connections at the 24-v terminal block. (See Fig.
10.) Connect terminal Y/Y2 as shown in Fig. 11 or 12 for proper
operation in cooling mode. Use AWG No. 18 color-coded, copper
thermostat wire only.
When furnace is installed in horizontal position with RH discharge
air, 24-v wire connections can be made easier by removing the 2
control box mounting screws and letting control box turn so that
24-v screw terminals are visible. Be sure to reinstall control box
after connections are made.
The 24-v circuit contains an automotive-type, 3-amp fuse located
on main control. Any 24-v electrical shorts during installation,
service, or maintenance could cause this fuse to blow. If fuse
replacement is required, use ONLY a 3-amp fuse. The control will
flash code 24 when fuse needs replacement.
C. Accessories
1. Electronic air cleaner (EAC)
A93348
—8—
Page 9

FIELD 24-V WIRING
FIELD 115-, 208/230-, 460-V WIRING
FACTORY 24-V WIRING
FACTORY 115-V WIRING
1-STAGE THERMOSTAT TERMINALS
BLK
WHT
115-V FUSED
DISCONNECT
BLK
WHT
GND
JUNCTION
BOX
SWITCH
(WHEN REQUIRED)
FIVE
WIRE
TWO-WIRE
HEATING-
ONLY
CONTROL
BOX
WYRG
W2
COM
W/W1
Y/Y2
R
G
C
CONDENSING
FIELD-SUPPLIED
FUSED DISCONNECT
208/230- OR
460-V
THREE
PHASE
208/230-V
SINGLE
PHASE
GND
UNIT
24-V
TERMINAL
BLOCK
FURNACE
NOTES: 1. Connect Y-terminal as shown for proper operation.
2. Some thermostats require a "C" terminal connection as shown.
3. If any of the original wire, as supplied, must be replaced,
use same type or equivalent wire.
→ Fig. 11—Heating and Cooling Application Wiring Diagram With 1-Stage Thermostat and Condensing Unit
A97443
2-STAGE THERMOSTAT TERMINALS
SEVEN
WIRE
THREE-WIRE
HEATING-
ONLY
BLK
WHT
115-V FUSED
DISCONNECT
BLK
WHT
GND
JUNCTION
BOX
SWITCH
(WHEN REQUIRED)
CONTROL
BOX
W2
COM
W/W1
Y/Y2
GR
24-V
TERMINAL
BLOCK
FURNACE
→ Fig. 12—Heating and Cooling Application Diagram With 2-Stage Thermostat and Condensing Unit
A terminal block (EAC-1 [hot] and EAC-2 [neutral]) is
provided for EAC connection. (See Fig. 10.) The terminals
are energized with 115v, 1-amp maximum during blower
motor operation.
2. Humidifier (HUM)
Screw terminals (HUM-1 and C
OM) are provided for 24-v
humidifier connection. The terminals are energized with
24v, 0.5-amp maximum when the gas valve is energized.
VII. VENTING
→
Refer to National or Local Installation Code such as; National Fuel
Gas Code NFPA No. 54-1996/Z223.1-1996, or the Canadian
Installation Code, CAN B149.1- and .2-M95, for proper vent
FIELD 24-V WIRING
FIELD 115-, 208/230-, 460-V WIRING
FACTORY 24-V WIRING
FACTORY 115-V WIRING
W2 Y2 G Y1
W1 R
C
FIELD-SUPPLIED
FUSED DISCONNECT
208/230- OR
460-V
THREE
PHASE
208/230-V
C
Y1
Y2
GND
SINGLE
PHASE
2-SPEED
CONDENSING
UNIT
NOTES: 1. Connect Y-terminal as shown for proper operation.
2. Some thermostats require a "C" terminal connection as shown.
3. If any of the original wire, as supplied, must be replaced,
use same type or equivalent wire.
sizing and installation requirements. Use enclosed Venting Tables
for Category I Fan-Assisted Furnaces for quick, easy reference.
The horizontal portion of the venting system shall maintain a
minimum of 1/4-in. upward slope per linear ft, and it shall be
rigidly supported every 5 ft or less with hangers or straps to ensure
that there will be no movement after installation.
VIII. START-UP, ADJUSTMENT, AND SAFETY CHECK
A. General
The furnace must have a 115-v power supply properly connected
and grounded. Correct polarity must be maintained to enable gas
heating operation.
A97444
—9—
Page 10

The gas service pressure must not exceed 0.5 psig (14-in. wc), and
be no less than 0.16 psig (4.5-in. wc).
Thermostat wire connections at R and W/W1 are the minimum
required for gas heating operation. W2 must be connected for
2-stage heating thermostats. C
OM, Y/Y2, and G are required for
cooling, heat pumps, and some clock thermostats. These must be
made at 24-v terminal block on control. (See Fig. 10.)
This furnace can be installed with either single-stage heating or
2-stage heating thermostat.
For single-stage thermostats, connect thermostat W to W/W1 at
furnace control terminal block. (See Fig. 11.) For single-stage
thermostats the control determines, based on length of previous
heating on and off cycles, when to operate in low- and high-gas
heat for optimum comfort. Setup Switch-2 (SW-2) must be in the
factory-shipped OFF position. See Fig. 13 and Tables 6 and 7 for
setup switch information.
If 2-stage heating thermostat is to be used, move SW-2 to ON
position at end of furnace installation. This overrides built-in
control process for selecting high and low stage and allows 2-stage
thermostat to select gas heating modes. The W2 from thermostat
must be connected to W2 on control terminal block. (See Fig. 12.)
Before operating furnace, check each manual reset switch for
continuity. If necessary, press and release button to reset switch.
TABLE 6—SETUP SWITCH DESCRIPTION
SETUP
SWITCH NO.
SW-1
Only High-Gas Heat
SW-2
Low-Gas Heat
(Adaptive Mode)
SW-3 and
SW4
NORMAL
POSITION
OFF
(Staged Gas
Heat)
OFF
(Single-Stage
Thermostat)
ON, OFF
DESCRIPTION OF USE
Turn switch on to obtain only
high-gas-heat operation on
any call for heat regardless of
whether R-W/W1, or R-W/W1,
-W2 is closed. SW-1 overrides
SW-2.
Turn switch off for installations
with single-stage thermostats;
control selects low-gas-heat
or high-gas-heat operation
based on previous cycles.
Turn switch on for installations
with 2-stage thermostats to
permit only low-gas-heat operation in response to closing
R-W/W1. High-gas heat is
supplied only when R to
W/W1 and W2 is closed.
Switches control gas heating
blower off delay. (See Table
7.)
TABLE 7—BLOWER OFF DELAY
SETUP SWITCH POSITION
DESIRED HEATING
MODE BLOWER OFF
DELAY (SEC)
90 OFF OFF
135 OFF ON
180 ON OFF
225 ON ON
SETUP SWITCH
SW-3 SW-4
CAUTION: This furnace is equipped with 2 manual
reset limit switches in gas control area. The switches will
open and shut off power to gas valve if a flame rollout or
an overheating condition occurs in gas control area. DO
NOT bypass switches. Correct inadequate combustion air
supply, component failure, restricted flue gas passageway
before resetting switches.
B. Sequence of Operation
Using the schematic diagram follow sequence of operation through
different modes. (See Fig. 14.) Read and follow wiring diagram
very carefully.
43 2
BLOWER-
OFF
DELAY
LOW
HEAT
(ADAPTIVE
ALGORITHM)
1
OFF
ON
HIGH
HEAT
ONLY
A96402
→ Fig. 13—Setup Switches on Control Center
(Factory Settings)
NOTE: If power interruption occurs during "call for heat" (W/W1
or W/W1-and-W2), control starts 90-sec blower only on period 2
sec after power is restored if thermostat is still calling for gas
heating. The red LED flashes code 12 during 90-sec period, after
which LED will be on continuously as long as no faults are
detected. After 90-sec period, furnace responds to thermostat
normally.
Blower door must be installed for power to be conducted through
blower door interlock switch ILK to furnace control CPU, transformer TRAN, inducer motor IDM, blower motor BLWM, hot
surface ignitor HSI, and gas valve GV.
1. Adaptive Heating Mode—Single-Stage Thermostat and
2-Stage Heating
(See Fig. 11 for thermostat connections.)
NOTE: With high-heat-only switch SW-1 off, low-heat-only
switch SW-2 selects either low-heat-only operation mode when on
(see item 2 below), or adaptive heating mode when off in response
to "call for heat." (See Fig. 13.) When high-heat-only switch SW-1
is on, it always causes high-gas-heat operation when R-W/W1
circuit is closed, regardless of the setting of low-heat-only switch
SW-2.
This furnace can operate as a 2-stage furnace with a
single-stage thermostat because furnace control CPU includes a programmed adaptive sequence of controlled
operation which selects low-gas-heat or high-gas-heat operation. This selection is based upon stored history of the
length of previous gas heating on/off periods of single-stage
thermostat.
The furnace starts up in either low- or high-gas heat. If
furnace starts up in low-gas heat, control CPU determines
low-gas heat on time (from 0 to 16 minutes) which is
permitted before switching to high-gas heat.
If power is interrupted, stored history is erased, and control
CPU selects low-gas heat for up to 16 minutes and then
switches to high-gas heat as long as thermostat continues to
"call for heat." Subsequent selection is based on stored
history of thermostat cycle times.
When the wall thermostat "calls for heat," R-W1 circuit
closes. The furnace control performs a self-check, verifies
low-heat and high-heat pressure switch contacts LPS and
HPS are open, and starts inducer motor IDM in low speed
or high speed as appropriate.
—10—
Page 11

324459-101 REV. A
A97508
applications. Insulate connector if not available.
OM" terminal for about two seconds. The control will
C
COMPONENT TEST
PLUG RECEPTACLE
turn ON the inducer motor Low-Speed, inducer motor High-Speed, HSI, blower motor Low-Gas-Heat Speed, blower motor High-Gas-Heat Speed, and blower motor High-Cool Speed for 7-15 seconds each. Neither the gas valve nor the humidifier will be
turned ON.
To initiate the component test sequence with no thermostat inputs and with all inducer Post-Purge and Blower-Off Delay periods completed, short the "TWIN/TEST" terminal to the "
→ Fig. 14—Unit Wiring Diagram
LO
HI
1
2
PL3
9
4
IHI / LOR
IDR
WHT
BLK
PL3
123
BLK
WHT
BLK
YEL
ALS2
ORN
12
*
NORM
HI HT
LO HT
IDM
LS
ALS1
DSS
ALS2
NOTE #8 LPS
FRS1
(WHEN USED)
9
6
3
2
MGVR-2
TWINNING
R
HUM
TWIN
TEST
BLK
TRAN
WHT
BRN
CAP
BRN
BLK
YELMED HI
NOTE #4
COM WHT
HI
EAC-2
COMMON
L1 L2
HI-COOL
HI-GAS
GRY
BRN
HEAT
P1
GRN
BLU
ORN
RED
RED
SETTINGS
BLOWER-OFF DELAY
BLOWER-OFF DELAY
LOW-HEAT ONLY
HIGH-HEAT ONLY
*
FACTORY
34
2
1
(WHEN USED)
5
PL1
JUMPER
TJ
MASTER
SLAVE
W/W1
BLU
RED
BLWM
RED
ORN
BLU
LO
MED
RED
MED LO
NOTE #15
BLU
SPARE
EAC-1
FU1
SPARE
HEAT
LO-GAS
SEC1
SEC2
12
11 10
3
2
1
TJ
S
M
LED
TEST
TWIN
W/W1 Y/Y2 R G HUM
OFF
24V
ON
W2 Com
LEGEND
N/A
5
HPSR
24VAC
BLK
PL2
YEL
*
135 SEC
180 SEC
N/A
2
6
NOTE #5
WHT
9
87
321
2-STAGE
FURNACE
CONTROL
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
225 SEC
BLK
FRS2
N/A
12
WHT
PR1 PR2
COM
3
7
8
1
PR2
SEC2
TRAN
115VAC
PR1
SEC1
FU1
RED
BLK
WHT
OFF
4
ON
OFF
3
SWITCH
ON
90 SEC
BLOWER-
OFF DELAY
(SEC.)
HI
HPS
P
GV
M
LGPS
NOTE #8
SW1
C
1
4
10
MGVR-1
CPU
W2
Y/Y2
FSE
NOTE#7
N/A
N/A
7
8
11
G
OM
C
SW2
SW3
SW4
NOTES:
Cooling/Heat Pump 2 sec onds.
seconds.
unsuccessful trials-for-ignition. Control will automatically
9. Symbols are an electrical representation only.
10. BLOWER-ON DELAY: Gas heating 45 seconds,
1. Use only copper wire between the disconnect switch and the unit.
2. If any of the original wire, as supplied, must be replaced, use the
reset after three hours.
11. Cooling/Heat Pump BLOWER-OFF DELAY is 90
12. IGNITION-LOCKOUT will occur after four consecutive
13. Control must be grounded at pin 10 of 12-pin connector.
14. NA - Not Applicable
15. Spare terminal and wire not available on some
same or equivalent type wire.
thermal overload switches.
Installation Instructions for details on optimum speed selection.
some downflow models.
3. Inducer (IDM) and blower (BLWM) motors contain internal auto-reset
control to prove flame.
4. Blower motor speed selections are for average conditions. See
5. Repl ace only with a 3-AMP fuse.
6. Auxiliary limit switches (ALS1 & 2) used on some horizontal and
7. This wire must be connected to furnace sheet metal for
8. Factory connected when LGPS not used.
*
2 = HUMIDIFIER
*
1 = VALVE
-
PL1 12-CIRCUIT CONNECTOR
PL2 9-CIR CUIT CONNECTOR
MGVR MAIN GAS VALVE RELAY, DPST (N.O.)
ALS1 AUXILIARY LIMIT SWITCH, OVER TEMP. MANUAL RESET, SPST (N.C.)
ALS2 AUXILIARY LIMIT SWITCH, OVER TEMP. AUTO RESET, SPST (N.C.)
BHI / LOR BLOWER MOTOR SPEED CHANGE RELAY , SPDT
BHT / CLR BLOWER MOTOR SPEED CHANGE RELAY, SPDT
SPST (MANUAL)
SLAVE STATUS (MANUAL CHANGE OVER)
ALSO STATUS CODE RECALL
JUNCTION
TERMINAL
CONTROL TERMINAL
FACTORY POWER WIRING (115VAC)
FACTORY CONTROL WIRING (24VAC)
FIELD POWER WIRING (115VAC)
FIELD CONTROL WIRING (24VAC)
CONDUCTOR ON CONTROL
FIELD WIRING SCREW TERMINAL
FIELD GROUND
EQUIPMENT GROUND
FIELD SPLICE
PL3 3-CIRCUIT IDM CONNECTOR
PL6 2-CIRCU IT HSI CONNECTOR
SW1 HIGH-HEAT-ONLY SWITCH, SPST (MANUAL)
SW2 LOW-HAT-ONLY SWITCH, SPST (MANUAL)*SW3 & 4 BLOWER-OFF DELAY SETTING SWITCHES,
TJ TWINNING JUMPER, SPDT FOR MASTER OR
TRAN TRANSFORMER-115VAC/24VAC
TWIN/TEST 1-CIRCUIT TWINNING BUSS CONNECTOR,
BLWM BLOWER MOTOR, 4 or 5 -SPEED, PERMANENT-SPLIT-CAPACIT OR
BLWR BLOWER MOTOR RELA Y, SPST (N.O.)
CAP CAPACITOR
CPU MICROPROCE SSOR AND CIRCUITRY
DSS DRAFT SAFEGUARD SWITCH (N.C.)
EAC-1 ELECTRONIC AIR CLEA NER CONNECTION (115 VAC, 1 AMP MAX.)
EAC-2 ELECTRONIC AIR CLEANE R CONNECTION (COMMON)
FRS1 FLAME ROLL OUT SWITCH OVERTEMP. MANUAL RESET, SPST (N.C.)
FRS2 FLAME ROLL OUT SWITCH OVERTEMP. MANUAL RESET, SPST (N.C.)
FSE FLAME-PROVING SENSOR E LECTRODE
FU1 FUSE, 3 AMP, AUTOMOTIVE BLADE TYP E, FACTORY INSTALLED
FU2 FUSE, FIELD INSTALLED
GV GAS VALVE, REDUNDANT LOW-HEAT OPERATORS, 2-S TAGE
HPS HIGH-HEAT PRESSURE SWITCH, SPST (N.O.)
HPSR HIGH-HEAT PRESSURE SWITCH RELAY, SPST (N.C. )
HSI HOT-SURFACE IGNITE R (115 VAC)
HSIR HOT-SURFACE IGNITOR RE LAY, SPST (N.O.)
HUM 24VAC HUMIDIFIER CONNECTION (0.5 AMP. MAX. )
IDM INDU CED DRAFT MOTOR, 2-SPEED, SHADED-POLE
IDR INDUCER MOTOR RELAY, SPST (N. O.)
IHI / LOR INDUCER MOTOR SPEED C HANGE RELAY, SPDT
ILK BLOWER DOOR INTERLOCK SWITCH, SPST (N.O.)
JB JUNCTION BOX
LED LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE FOR STAT US CODES
LGPS LOW GAS-PRESSURE SWITCH, SPST (N.O.)
LPS LOW-HEAT PRESSURE SWITCH , SPST (N.O.)
LS LIMIT SWITCH, OVERTEMPER ATURE-AUTO RESET, SPST (N.C.)
L2
BLWM
BRN
CAP
HSI
BRN
COM
NOTE #4
HI
LO
NOTE #15
MED LO
LO-GAS-HEAT
HI-GAS-HEAT
BHT / CLR
MED HI
MED
SPARE
SPARE
HI-COOL
BLWR
L1
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM (NATURAL GAS & PROPANE)
NOTE #1
BHI / LOR
EQUIPMENT GROUND
ILK
2
1
PL6
3
PL2
COMMON
EAC-2
EAC-1
HSIR
TO 115VAC FIELD DISCONNECT SWITCH
GRN
C
GV
M
HI
P
BLU
BRN
GRN
HPS
IDM
BRN
GRY
CONNECTION DIAGRAM
LGPS
YEL
LPS
NOTE #8
FRS2
LS
DSS
ORN
ORN
RED
RED
RED
FU2
NOTE #1
FUSED DISCONNECT
GRN
HSI
ALS1
FRS1
(WHEN USED)
GRN
WHT
BLK
SWITCH (WHEN REQ’D)
JB
L1
L2
GRN
ILK
WHTPL6
RED
12
GRY
WHT
FSE
(WHEN USED)
NOTE #8
NOTE #6
(WHEN USED)
ORN
RED
SWITCH
HEAT
SET-UP
SWITCH
—11—
Page 12

a. Inducer prepurge period—As inducer motor IDM comes
up to low speed or high speed, the low-heat pressure
switch contacts LPS (or LPS and HPS) close to begin a
15-sec prepurge period.
b. Ignitor warm-up—At the end of prepurge period, hot
surface ignitor HSI is energized for a 17-sec ignitor
warm-up period.
c. Trial-for-ignition sequence—When ignitor warm-up pe-
riod is completed, main gas valve relay contacts
MGVR-1 and -2 close to energize low-heat gas valve
solenoid GV, gas valve opens, and 24-v power is
supplied for a field-installed humidifier at terminals
HUM and C
OM. Low-heat gas valve solenoid GV permits
gas flow to the burners where it is ignited. After 5 sec,
ignitor HSI is de-energized, and a 2-sec flame-proving
period begins.
If furnace control CPU selects high-gas-heat operation,
high-heat gas valve solenoid GV is also energized after
normally closed high-heat pressure switch relay HPSR
closes and after inducer motor IDM goes to high speed
and provides sufficient pressure to close high-heat pressure switch HPS. HPSR is open while furnace is powered in standby mode. If high-heat pressure switch HPS
fails to close and low-heat pressure switch LPS closes,
furnace operates at low-heat gas flow rate until high-heat
pressure switch closes.
d. Flame-proving—When burner flame is proved at flame-
proving sensor electrode FSE, control CPU begins
blower on delay period and continues to hold gas valve
GV open. If burner flame is not proved within 2 sec,
control CPU closes gas valve GV, and control CPU
repeats ignition sequence for up to 3 more trials-forignition before going to ignition lockout. LOCKOUT IS
RESET AUTOMATICALLY after 3 hr, or by momentarily interrupting 115-v power to furnace, or by interrupting 24-v power at SEC1 or SEC2 to control CPU
(not at W/W1, G, R, etc.). Opening thermostat R-W
circuit will not reset ignition lockout.
If flame is proved when flame should not be present,
control CPU locks out of gas heating mode and operates
inducer motor IDM on high speed until flame is no
longer proved.
e. Blower on delay—If burner flame is proven, 45 sec after
gas valve GV is opened blower motor BLWM is
energized on appropriate heating speed, low-gas-heat or
high-gas-heat speed. Simultaneously, EAC terminals
EAC-1 and EAC-2 are energized with 115v and remain
energized as long as blower motor BLWM is energized.
f. Switching from low- to high-gas heat—If furnace control
CPU switches from low-gas heat to high-gas heat,
control CPU switches inducer motor IDM speed from
low to high. The high-heat pressure switch relay HPSR
closes. When inducer motor IDM provides sufficient
pressure to close high-heat pressure switch HPS, highheat gas valve solenoid GV is energized. Blower motor
BLWM switches speed for high-gas heat 5 sec after
control CPU switches from low-gas heat to high-gas
heat.
g. Switching from high- to low-gas heat—Control CPU
will not switch from high-gas heat to low-gas heat while
thermostat R-W circuit is closed when a single-stage
thermostat is used.
h. Blower off delay—When thermostat is satisfied, R-W
circuit is opened, de-energizing gas valve GV, stopping
gas flow to burners, and de-energizing humidifier terminals HUM and C
OM. Inducer motor IDM remains ener-
gized for a 5-sec post-purge period. Blower motor
BLWM and EAC terminals EAC-1 and EAC-2 remain
energized for 90, 135, 180, or 225 sec (depending on
selection at blower off delay switches SW-3 and SW-4).
Furnace control CPU is factory set for a 135-sec blower
off delay.
2. Non-Adaptive Heating Mode—Two-Stage Thermostat and
2-Stage Heating
(See Fig. 12 for thermostat connections.)
NOTE: The low-heat-only switch SW-2 ON selects low-heatonly operation mode in response to closing thermostat R-W/W1
circuit. When high-heat-only switch SW-1 is off, closing thermostat R to W1-and-W2 circuits is required for high-gas-heat
operation. When high-heat-only switch SW-1 is on, it always
causes high-gas-heat operation when R-W/W1 circuit is closed,
regardless of setting of low-heat-only switch SW-2 and regardless
of whether R-W2 circuit is closed or open.
The start-up and shutdown functions and delays described
in item 1 above apply to 2-stage heating mode as well,
except for switching from low- to high-gas heat and vice
versa.
a. When wall thermostat "calls for heat," R-W/W1 circuit
closes for low-gas heat or R to W1-and-W2 circuits
close for high-gas heat. The furnace control performs a
self-check, verifies low-heat and high-heat pressure
switch contacts LPS and HPS are open, and starts
inducer motor IDM in low speed or high speed as
appropriate.
b. Switching from low- to high-gas heat—If thermostat
R-W/W1 circuit for low-gas heat is closed and R-W2
circuit for high-gas heat closes, control CPU switches
inducer motor IDM speed from low to high. The
high-heat pressure switch relay HPSR closes. When
inducer motor IDM provides sufficient pressure to close
high-heat pressure switch HPS, high-heat gas valve
solenoid GV is energized. Blower motor BLWM
switches speed for high-gas heat 5 sec after R-W2 circuit
closes.
c. Switching from high- to low-gas heat—If thermostat
R-W2 circuit for high-gas heat opens and R-W/W1
circuit for low-gas heat remains closed, control CPU
switches inducer motor IDM speed from high to low.
The high-heat pressure switch relay HPSR opens to
de-energize high-heat gas valve solenoid GV. When
inducer motor IDM reduces pressure sufficiently, highheat pressure switch HPS opens. The low-heat gas valve
solenoid GV remains energized as long as low-heat
pressure switch LPS remains closed. Blower motor
BLWM switches speed for low-gas heat 5 sec after
R-W2 circuit opens.
3. Cooling Mode
a. Single-Speed Cooling Outdoor Unit
(See Fig. 11 for thermostat connections.)
(1.) The thermostat closes R to G-and-Y circuits. The
R-Y circuit starts outdoor unit, and R to G-and-Y
circuits start furnace blower motor BLWM on
high-cool speed.
(2.) The EAC terminals EAC-1 and EAC-2 are ener-
gized with 115v when blower motor BLWM is
operating.
—12—
Page 13

(3.) When thermostat is satisfied, R to G-and-Y cir-
cuits are opened. The outdoor unit stops, and
furnace blower motor BLWM continues operating
on high-cool speed for an additional 90 sec.
b. Two-Speed Cooling Outdoor Unit
(See Fig. 12 for thermostat connections.)
(1.) The thermostat closes R to G-and-Y1 circuits for
low cooling or closes R to G-and-Y1-and-Y/Y2
circuits for high cooling. The R-Y1 circuits start
outdoor unit on low-cooling speed, and R-G circuit
starts furnace blower motor BLWM on low-cooling
speed (same speed as for low-gas heat). The R to
Y1-and-Y2 circuits start outdoor unit on highcooling speed, and R to G-and-Y2 circuits start
furnace blower motor BLWM on high-cooling
speed.
NOTE: Y1 is not located on furnace control, but is found in
outdoor unit. The furnace control CPU controls blower motor
BLWM speed by sensing only G for low-cooling speed and Y/Y2
for high-cooling speed.
(2.) The EAC terminals EAC-1 and EAC-2 are ener-
gized with 115v when blower motor BLWM is
operating on either cooling speed.
(3.) When thermostat is satisfied, R to G-and-Y1 or
R to G-and-Y1-and-Y/Y2 circuits open. The outdoor unit stops, and furnace blower continues operating on cooling speed for an additional 90 sec.
4. Continuous Blower Mode
a. When R to G circuit is closed by thermostat, blower
motor BLWM operates on low-gas-heat speed (identical
to low-cool speed). Terminals EAC-1 and EAC-2 are
energized with 115v as long as blower motor BLWM is
energized.
b. During "call for heat," blower motor BLWM stops
during ignitor warm-up (17 sec), ignition (7 sec), and
blower on delay (45 sec), allowing furnace heat exchangers to heat up quickly.
(1.) The blower motor BLWM reverts to continuous
blower speed after heating cycle is completed. In
high-gas heat, furnace control CPU holds blower
motor BLWM at high-gas-heat speed during selected blower off delay period before reverting to
continuous blower speed.
(2.) When thermostat "calls for low cooling," blower
motor BLWM continues to operate on low-cool
speed. When thermostat is satisfied, blower motor
BLWM continues on continuous blower speed.
(3.) When thermostat "calls for high cooling," blower
motor BLWM operates on high-cool speed. When
thermostat is satisfied, blower motor BLWM operates an additional 2 sec on high-cool speed before
reverting back to continuous blower speed.
(4.) When R to G circuit is opened, blower motor
BLWM continues operating for an additional 90 sec
if no other function requires blower motor BLWM
operation.
5. Heat Pump
NOTE: An accessory interface kit is required with single-speed
heat pumps. See interface kit Installation Instructions for singlespeed heat pump thermostat and interface connections. No interface kit is needed for 2-speed heat pumps. See 2-speed heat pump
Installation Instructions for thermostat connections.
a. Single-Speed Heat Pump Cooling
(1.) The thermostat and interface kit close R to G-and-
Y/Y2 circuit to start furnace blower motor BLWM
on high-cooling speed. (Y/Y2 input to furnace
control is necessary to provide adequate cooling
airflow.)
(2.) The EAC terminals EAC-1 and EAC-2 are ener-
gized with 115v when blower motor BLWM is
operating.
(3.) When thermostat is satisfied, furnace blower motor
BLWM continues operating on high-cooling speed
for an additional 90 sec.
b. Two-Speed Heat Pump Cooling
(1.) The thermostat R to G circuits start furnace blower
motor BLWM on low-cooling speed. Thermostat
R to G-and-Y/Y2 circuits start furnace blower motor BLWM on high-cool speed.
NOTE: The furnace control CPU controls blower motor BLWM
speed by sensing only G (for low-cooling speed) and Y2 (for
high-cooling speed).
(2.) The EAC terminals EAC-1 and EAC-2 are ener-
gized with 115v when blower motor BLWM is
operating on either cooling speed.
(3.) When thermostat is satisfied, furnace blower motor
BLWM continues operating on cooling speed for an
additional 90 sec.
c. Single-Speed Heat Pump Heating
(1.) The thermostat and accessory interface kit R to G-
and-Y/Y2 circuits start furnace blower motor
BLWM on heat pump high-heat speed (identical to
high-cool speed).
(2.) The EAC terminals EAC-1 and EAC-2 are ener-
gized with 115v when blower motor BLWM is
operating.
(3.) When thermostat is satisfied, furnace blower motor
BLWM continues operating on heat pump high-heat
speed for an additional 90 sec.
d. Two-Speed Heat Pump Heating
(1.) The thermostat closes R to G circuit for low heat
and starts furnace blower motor BLWM on heat
pump low-heat speed (identical to low-cooling
speed). Closing R-Y/Y2 circuit to furnace provides
blower motor BLWM heat pump high-heat speed.
NOTE: The furnace control CPU controls blower motor BLWM
speed by sensing only G (for heat pump low-heat speed) and Y2
(for heat pump high-heat speed).
(2.) The EAC terminals EAC-1 and EAC-2 are ener-
gized with 115v when blower motor BLWM is
operating on either heating speed.
(3.) When thermostat is satisfied, R to G or R to G-
and-Y2 circuits are opened. After opening R to
G-and-Y2 circuit, the furnace blower motor BLWM
continues operating on heating speed for an additional 90 sec.
(4.) Opening R-Y2 circuit reduces blower motor
BLWM speed to heat pump low-heat speed.
6. Defrost
a. When furnace control R to W/W1-and-Y/Y2 circuits are
closed, furnace control CPU continues blower motor
BLWM operation at heat pump heating speed until end
of prepurge period, then shuts off until end of HSI ignitor
on period (22 sec).
—13—
Page 14

b. When installed with a heat pump, furnace control CPU
automatically holds blower off time to 22 sec during HSI
ignitor on period. After 17 sec of HSI ignitor on period,
a trial-for-ignition sequence occurs as described above
for gas heating. After flame is proved and without
blower on delay, blower motor BLWM then operates on
high-gas-heat speed during defrost. For both singlespeed and 2-speed heat pumps, defrost mode is in
high-gas heat only.
c. When furnace control R to W/W1 circuit is opened,
furnace control CPU begins normal inducer post-purge
period, and blower motor BLWM remains on for blower
off delay period. If R-G circuit remains closed, blower
motor BLWM reverts to continuous operation.
C. Start-Up Procedures
→
1. Component test—The furnace features a component test
system to help diagnose a system problem in case of
component failure. To initiate component test procedure,
ensure that there are no thermostat inputs to control and that
all time delays have expired. Short TWIN/TEST terminal to
ground or C
OM for 1 to 4 sec. See Fig. 10 for terminal
locations.
NOTE: The component test feature will not operate if control is
receiving any thermostat signals and until all time delays have
expired.
The component test sequence is as follows:
a. The furnace control checks itself, operates inducer motor
on low speed for 7 sec and on high speed for 7 sec, then
stops.
b. The hot surface ignitor is then energized for 15 sec, then
de-energized.
c. The blower motor operates on low-gas-heat/heat pump
low-heat/low-cool/continuous fan speed for 7 sec, then
stops.
d. The blower motor operates on high-gas-heat speed for 7
sec, then stops. The gas valve and humidifier terminal
HUM are not energized for safety reasons.
NOTE: The EAC terminals are energized when blower is energized.
e. The blower operates on heat pump high-heat/high-cool
speed for 7 sec, then stops.
2. After all connections have been made, purge gas lines and
check for leaks.
WARNING: Never purge a line into a combustion
chamber. Never use matches, candles, flame, or other
sources of ignition to check for gas leakage. Use a
soap-and-water solution to check for gas leaks. A failure
to follow this warning could result in fire, explosion,
personal injury, or death.
3. To operate furnace, follow procedures on operating instruction label attached to furnace.
4. With furnace operating, set thermostat below room temperature and observe that furnace goes off. Set thermostat
above room temperature and observe that furnace restarts.
D. Adjustments
1. Set gas input rate.
Furnace gas input rate on rating plate is for installations at
altitudes up to 2000 ft.
In the U.S.A., input rating for altitudes above 2000 ft must
be reduced by 4 percent for each 1000 ft above sea level.
In Canada, input rating must be derated by 10 percent for
altitudes of 2000 ft to 4500 ft above sea level.
Furnace input rate must be within ±2 percent of input on
furnace rating plate.
2. Determine natural gas orifice size and manifold pressure for
correct input.
a. Obtain yearly heat value average (at installed altitude)
from local gas supplier.
b. Obtain yearly specific gravity average from local gas
supplier.
c. Verify furnace model. Table 9 can only be used for
model 331JAV Furnaces.
d. Find installation altitude in Table 9.
NOTE: For Canada altitudes of 2000 to 4500 ft, use U.S.A.
altitudes of 2001 to 3000 ft in Table 9.
e. Find closest natural gas heat value and specific gravity in
Table 9.
f. Follow heat value and specific gravity lines to point of
intersection to find orifice size and low- and high-heat
manifold pressure settings for proper operation.
EXAMPLE: (0—2000 ft altitude)
Heating value = 1075 Btu/cu ft
Specific gravity = 0.62
Therefore: Orifice No. 45
Manifold pressure: 3.7-in. wc for high heat
1.5-in. wc for low heat
* Furnace is shipped with No. 45 orifices.
In this example, all main burner orifices are the correct size
and do not need to be changed to obtain proper input rate.
g. Check and verify burner orifice size in furnace. NEVER
ASSUME ORIFICE SIZE; ALWAYS CHECK AND
VERIFY.
3. Adjust manifold pressure to obtain input rate.
a. Remove caps that conceal adjustment screws for low-
and high-heat gas valve regulators. (See Fig. 15.)
b. Move setup switch SW-2 on control center to ON
position. (See Fig. 13.) This keeps furnace locked in
low-heat operation.
c. Jumper R and W/W1 thermostat connections on control
center to start furnace.
d. Turn low-heat adjusting screw (5/64 hex Allen wrench)
counterclockwise (out) to decrease input rate or clockwise (in) to increase input rate.
NOTE: DO NOT set low-heat manifold pressure less than 1.3-in.
wc or more than 1.7-in. wc for natural gas. If manifold pressure is
outside this range, change main burner orifices.
CAUTION: DO NOT bottom out gas valve regulator
adjusting screw. This can result in unregulated manifold
pressure and result in excess overfire and heat exchanger
failures.
NOTE: If orifice hole appears damaged or it is suspected to have
been redrilled, check orifice hole with a numbered drill bit of
correct size. Never redrill an orifice. A burr-free and squarely
aligned orifice hole is essential for proper flame characteristics.
e. Move setup switch SW-2 to OFF position after complet-
ing low-heat adjustment.
f. Jumper R and W2 thermostat connections on control
center. (See Fig. 10.) This keeps furnace locked in
high-heat operation.
—14—
Page 15

BURNER
ORIFICE
A93059
CAUTION: DO NOT redrill orifices. Improper drilling
(burrs, out-of-round holes, etc.) can cause excessive
burner noise and misdirection of burner flames. This can
result in flame impingement of burners and heat exchangers, causing failures.
g. Turn high-heat adjusting screw (5/64 hex Allen wrench)
counterclockwise (out) to decrease input rate or clockwise (in) to increase rate.
NOTE: DO NOT set high-heat manifold pressure less than 3.2-in.
wc or more than 3.8-in. wc for natural gas. If manifold pressure is
outside this range, change main burner orifices.
h. When correct input is obtained, replace caps that conceal
gas valve regulator adjustment screws. Main burner
flame should be clear blue, almost transparent. (See Fig.
16.)
i. Remove jumper R to W2.
4. Verify natural gas input rate by clocking gas meter.
a. Calculate high-altitude adjustment (if required).
UNITED STATES
At altitudes above 2000 ft, this furnace has been approved for a 4 percent derate for each 1000 ft above sea
level. See Table 8 for derate multiplier factor and
example.
EXAMPLE:
80,000 Btuh input furnace installed at 4300 ft.
Furnace Input
Rate at
Sea Level
80,000 X 0.82 = 65,600
X
Multiplier
Derate
Factor
Furnace Input Rate
=
at Installation
Altitude
CANADA
At installation altitudes from 2000 to 4500 ft, this
furnace must be derated 10 percent by an authorized Gas
Conversion Station or Dealer. To determine correct input
rate for altitude, see example above and use 0.82 as
derate multiplier factor.
b. Check that gas valve adjustment caps are in place for
proper input to be clocked.
c. Obtain yearly heat value average for local gas supply.
NOTE: Be sure heating value of gas used for calculations is
correct for your altitude. Consult local gas utility for altitude
adjustment of gas heating value.
d. Check and verify orifice size in furnace. NEVER AS-
SUME THE ORIFICE SIZE. ALWAYS CHECK AND
VERIFY.
e. Turn off all other gas appliances and pilots.
f. Move setup switch SW-2 to ON position. (See Fig. 13.)
This keeps furnace locked in low-heat operation.
g. Jumper R to W/W1.
h. Let furnace run for 3 minutes in low-heat operation.
i. Measure time (in sec) for gas meter to complete 1
revolution. Note reading.
j. Refer to Table 10 for cubic ft of gas per hr.
k. Multiply gas rate cu ft/hr by heating value (Btu/cu ft).
l. Move setup switch SW-2 to OFF position and jumper R
and W2 thermostat connections. (See Fig. 13.) This keeps
furnace locked in high-heat operation. Repeat items h
through k for high-heat operation.
EXAMPLE: (High-heat operation at 0—2000 ft altitude)
Furnace input from rating plate is 80,000 Btuh
Btu heating input = Btu/cu ft X cu ft/hr
Heating value of gas = 1050 Btu/cu ft
Time for 1 revolution of 2-cu ft dial = 92 sec
Gas rate = 80 cu ft/hr (from Table 10)
Btu heating input = 78 X 1050 = 81,900 Btuh
In this example, the orifice size and manifold pressure
adjustment is within ±2 percent of the furnace input rate.
TABLE 8—ALTITUDE DERATE MULTIPLIER FOR U.S.A.
ALTITUDE
(FT)
0—2000 0 1.00
2001—3000 8—12 0.90
3001—4000 12—16 0.86
4001—5000 16—20 0.82
5001—6000 20—24 0.78
6001—7000 24—28 0.74
7001—8000 18—32 0.70
8001—9000 32—36 0.66
9001—10,000 36—40 0.62
* Derate multiplier factor is based on midpoint altitude for altitude range.
%OF
DERATE
DERATE MULTIPLIER
FACTOR FOR U.S.A.*
NOTE: Measured gas inputs (high heat and low heat) must be
within ±2 percent of that stated on furnace rating plate when
installed at sea level or derated per that stated above when installed
at higher altitudes.
m. Remove jumper across R, W/W1, and W2 thermostat
connections to terminate call for heat.
5. Set temperature rise.
Place SW-2 in ON position. Jumper R to W/W1 and W2 to
check high-gas-heat temperature rise. To check low-gasheat temperature rise, remove jumper to W2. Determine air
temperature rise for both high and low heat using the
following steps. DO NOT exceed temperature rise ranges
specified on unit rating plate for high and low heat.
—15—
Page 16

TABLE 9—MODEL 331JAV ORIFICE SIZE AND MANIFOLD PRESSURE FOR CORRECT INPUT
(TABULATED DATA BASED ON 21,000 BTUH HIGH HEAT/13,500 BTUH LOW HEAT PER BURNER,
DERATED 4% FOR EACH 1000 FT ABOVE SEA LEVEL)
ALTITUDE
RANGE
(FT)
0 925 43 3.4/1.4 43 3.5/1.5 43 3.6/1.5 43 3.8/1.6 42 3.2/1.3
to 975 44 3.5/1.5 44 3.6/1.5 44 3.8/1.6 43 3.4/1.4 43 3.5/1.4
2000 1025 44 3.2/1.3 44 3.3/1.4 44 3.4/1.4 44 3.5/1.5 44 3.6/1.5
U.S.A. and Canada
ALTITUDE
RANGE
(FT)
U.S.A. 775 43 3.7/1.5 42 3.2/1.3 42 3.3/1.4 42 3.4/1.4 42 3.5/1.4
Altitudes 800 43 3.5/1.4 43 3.6/1.5 43 3.7/1.5 42 3.2/1.3 42 3.3/1.3
2001 825 44 3.8/1.6 43 3.4/1.4 43 3.5/1.5 43 3.6/1.5 43 3.7/1.5
to 850 44 3.6/1.5 44 3.7/1.5 44 3.8/1.6 43 3.4/1.4 43 3.5/1.5
3000 875 44 3.4/1.4 44 3.5/1.4 44 3.6/1.5 44 3.7/1.5 44 3.8/1.6
or 900 44 3.2/1.3 44 3.3/1.4 44 3.4/1.4 44 3.5/1.4 44 3.6/1.5
Canada 925 46 3.8/1.6 45 3.8/1.6 44 3.2/1.3 44 3.3/1.4 44 3.4/1.4
Altitudes 950 46 3.6/1.5 46 3.7/1.5 45 3.7/1.5 45 3.8/1.6 44 3.2/1.3
U.S.A. and Canada
2000 975 46 3.4/1.4 46 3.5/1.5 46 3.7/1.5 46 3.8/1.6 45 3.7/1.5
to 1000 47 3.7/1.5 47 3.8/1.6 46 3.5/1.4 46 3.6/1.5 46 3.7/1.5
4500 1025 47 3.5/1.5 47 3.6/1.5 47 3.8/1.6 46 3.4/1.4 46 3.5/1.5
ALTITUDE
RANGE
(FT)
3001 825 44 3.3/1.4 44 3.4/1.4 44 3.5/1.5 44 3.7/1.5 44 3.8/1.6
to 875 46 3.7/1.5 45 3.7/1.5 44 3.2/1.3 44 3.3/1.3 44 3.4/1.4
U.S.A. Only
4000 925 47 3.8/1.6 46 3.5/1.4 46 3.6/1.5 46 3.7/1.5 46 3.8/1.6
AVG GAS
HEAT VALUE
AT ALTITUDE
(BTU/CU FT)
850 42 3.3/1.4 42 3.4/1.4 42 3.5/1.5 42 3.7/1.5 42 3.8/1.6
875 43 3.8/1.6 42 3.2/1.3 42 3.3/1.4 42 3.5/1.4 42 3.6/1.5
900 43 3.6/1.5 43 3.7/1.5 42 3.2/1.3 42 3.3/1.3 42 3.4/1.4
950 44 3.7/1.5 44 3.8/1.6 43 3.5/1.4 43 3.6/1.5 43 3.7/1.5
1000 44 3.3/1.4 44 3.5/1.4 44 3.6/1.5 44 3.7/1.5 44 3.8/1.6
1050 45 3.7/1.5 45 3.8/1.6 44 3.2/1.3 44 3.4/1.4 44 3.5/1.4
1075 46 3.7/1.5 46 3.8/1.6 45 3.7/1.5 44 3.2/1.3 44 3.3/1.4
1100 46 3.5/1.5 46 3.6/1.5 46 3.8/1.6 45 3.7/1.5 45 3.8/1.6
AVG GAS
HEAT VALUE
AT ALTITUDE
(BTU/CU FT)
AVG GAS
HEAT VALUE
AT ALTITUDE
(BTU/CU FT)
750 43 3.5/1.4 43 3.6/1.5 43 3.7/1.5 42 3.2/1.3 42 3.3/1.4
775 44 3.8/1.6 43 3.4/1.4 43 3.5/1.4 43 3.6/1.5 43 3.7/1.5
800 44 3.5/1.5 44 3.7/1.5 44 3.8/1.6 43 3.4/1.4 43 3.5/1.4
850 45 3.8/1.6 44 3.2/1.3 44 3.3/1.4 44 3.4/1.4 44 3.6/1.5
900 46 3.5/1.5 46 3.7/1.5 46 3.8/1.6 45 3.7/1.5 44 3.2/1.3
950 47 3.6/1.5 47 3.7/1.5 46 3.4/1.4 46 3.5/1.5 46 3.6/1.5
975 47 3.4/1.4 47 3.5/1.5 47 3.7/1.5 47 3.8/1.6 46 3.4/1.4
1000 48 3.7/1.5 48 3.8/1.6 47 3.5/1.4 47 3.6/1.5 47 3.7/1.5
0.58 0.60 0.62 0.64 0.66
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
0.58 0.60 0.62 0.64 0.66
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
0.58 0.60 0.62 0.64 0.66
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
SPECIFIC GRAVITY OF NATURAL GAS
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
SPECIFIC GRAVITY OF NATURAL GAS
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
SPECIFIC GRAVITY OF NATURAL GAS
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
—16—
Page 17

TABLE 9—MODEL 331JAV ORIFICE SIZE AND MANIFOLD PRESSURE FOR CORRECT INPUT Continued
(TABULATED DATA BASED ON 21,000 BTUH HIGH HEAT/13,500 BTUH LOW HEAT PER BURNER,
DERATED 4% FOR EACH 1000 FT ABOVE SEA LEVEL)
ALTITUDE
RANGE
(FT)
4001 800 45 3.7/1.5 44 3.2/1.3 44 3.3/1.4 44 3.4/1.4 44 3.5/1.5
to 850 46 3.5/1.4 46 3.6/1.5 46 3.7/1.5 46 3.8/1.6 45 3.8/1.6
U.S.A. Only
5000 900 47 3.5/1.5 47 3.6/1.5 47 3.8/1.6 46 3.4/1.4 46 3.5/1.5
ALTITUDE
RANGE
(FT)
5001 800 46 3.4/1.4 46 3.5/1.5 46 3.7/1.5 46 3.8/1.6 45 3.7/1.5
to 850 47 3.4/1.4 47 3.6/1.5 47 3.7/1.5 47 3.8/1.6 46 3.5/1.4
U.S.A. Only
6000 900 48 3.5/1.4 48 3.6/1.5 48 3.7/1.5 47 3.4/1.4 47 3.5/1.4
ALTITUDE
RANGE
(FT)
6001 725 46 3.6/1.5 46 3.7/1.5 45 3.7/1.5 45 3.8/1.6 44 3.2/1.3
to 775 47 3.6/1.5 47 3.7/1.5 47 3.8/1.6 46 3.5/1.4 46 3.6/1.5
U.S.A. Only
7000 825 48 3.6/1.5 48 3.7/1.5 48 3.8/1.6 47 3.5/1.4 47 3.6/1.5
AVG GAS
HEAT VALUE
AT ALTITUDE
(BTU/CU FT)
725 44 3.8/1.6 43 3.4/1.4 43 3.5/1.4 43 3.6/1.5 43 3.7/1.5
750 44 3.5/1.5 44 3.6/1.5 44 3.8/1.6 43 3.4/1.4 43 3.5/1.4
775 44 3.3/1.4 44 3.4/1.4 44 3.5/1.5 44 3.6/1.5 44 3.7/1.5
825 46 3.7/1.5 46 3.8/1.6 45 3.8/1.6 44 3.2/1.3 44 3.3/1.4
875 47 3.7/1.5 46 3.4/1.4 46 3.5/1.5 46 3.6/1.5 46 3.7/1.5
925 48 3.8/1.6 47 3.4/1.4 47 3.6/1.5 47 3.7/1.5 47 3.8/1.6
950 48 3.6/1.5 48 3.7/1.5 48 3.8/1.6 47 3.5/1.4 47 3.6/1.5
AVG GAS
HEAT VALUE
AT ALTITUDE
(BTU/CU FT)
700 44 3.5/1.5 44 3.6/1.5 44 3.8/1.6 43 3.4/1.4 43 3.5/1.4
725 44 3.3/1.4 44 3.4/1.4 44 3.5/1.4 44 3.6/1.5 44 3.7/1.5
750 45 3.7/1.5 44 3.2/1.3 44 3.3/1.4 44 3.4/1.4 44 3.5/1.4
775 46 3.6/1.5 46 3.8/1.6 45 3.7/1.5 44 3.2/1.3 44 3.3/1.4
825 47 3.7/1.5 47 3.8/1.6 46 3.4/1.4 46 3.6/1.5 46 3.7/1.5
875 48 3.7/1.5 48 3.8/1.6 47 3.5/1.4 47 3.6/1.5 47 3.7/1.5
925 48 3.3/1.4 48 3.4/1.4 48 3.5/1.5 48 3.6/1.5 48 3.8/1.6
950 49 3.7/1.5 49 3.8/1.6 48 3.3/1.4 48 3.5/1.4 48 3.6/1.5
975 49 3.5/1.4 49 3.6/1.5 49 3.7/1.5 48 3.3/1.4 48 3.4/1.4
1000 49 3.3/1.4 49 3.4/1.4 49 3.6/1.5 49 3.7/1.5 49 3.8/1.6
AVG GAS
HEAT VALUE
AT ALTITUDE
(BTU/CU FT)
650 44 3.5/1.5 44 3.7/1.5 44 3.8/1.6 43 3.4/1.4 43 3.5/1.4
675 44 3.3/1.4 44 3.4/1.4 44 3.5/1.4 44 3.6/1.5 44 3.7/1.5
700 45 3.7/1.5 44 3.2/1.3 44 3.3/1.3 44 3.4/1.4 44 3.5/1.4
750 47 3.8/1.6 46 3.5/1.4 46 3.6/1.5 46 3.7/1.5 46 3.8/1.6
800 48 3.8/1.6 47 3.5/1.4 47 3.6/1.5 47 3.7/1.5 47 3.8/1.6
850 48 3.4/1.4 48 3.5/1.4 48 3.6/1.5 48 3.7/1.5 47 3.4/1.4
875 49 3.8/1.6 48 3.3/1.4 48 3.4/1.4 48 3.5/1.5 48 3.6/1.5
0.58 0.60 0.62 0.64 0.66
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
0.58 0.60 0.62 0.64 0.66
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
0.58 0.60 0.62 0.64 0.66
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
SPECIFIC GRAVITY OF NATURAL GAS
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
SPECIFIC GRAVITY OF NATURAL GAS
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
SPECIFIC GRAVITY OF NATURAL GAS
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
—17—
Page 18

TABLE 9—MODEL 331JAV ORIFICE SIZE AND MANIFOLD PRESSURE FOR CORRECT INPUT Continued
(TABULATED DATA BASED ON 21,000 BTUH HIGH HEAT/13,500 BTUH LOW HEAT PER BURNER,
DERATED 4% FOR EACH 1000 FT ABOVE SEA LEVEL)
ALTITUDE
RANGE
(FT)
7001 700 47 3.8/1.6 46 3.4/1.4 46 3.6/1.5 46 3.7/1.5 46 3.8/1.6
to 750 48 3.7/1.5 47 3.4/1.4 47 3.5/1.5 47 3.6/1.5 47 3.7/1.5
U.S.A. Only
8000 800 48 3.3/1.4 48 3.4/1.4 48 3.5/1.5 48 3.6/1.5 48 3.7/1.5
ALTITUDE
RANGE
(FT)
8001 650 47 3.8/1.6 46 3.4/1.4 46 3.5/1.5 46 3.7/1.5 46 3.8/1.6
to 700 48 3.7/1.5 48 3.8/1.6 47 3.5/1.4 47 3.6/1.5 47 3.7/1.5
U.S.A. Only
9000 750 49 3.8/1.6 48 3.3/1.4 48 3.4/1.4 48 3.5/1.5 48 3.7/1.5
ALTITUDE
RANGE
(FT)
9001 625 47 3.4/1.4 47 3.6/1.5 47 3.7/1.5 47 3.8/1.6 46 3.5/1.4
to 675 48 3.4/1.4 48 3.5/1.4 48 3.6/1.5 48 3.7/1.5 48 3.8/1.6
U.S.A. Only
10,000 725 49 3.4/1.4 49 3.5/1.5 49 3.7/1.5 49 3.8/1.6 48 3.3/1.4
AVG GAS
HEAT VALUE
AT ALTITUDE
(BTU/CU FT)
625 44 3.3/1.4 44 3.4/1.4 44 3.5/1.5 44 3.6/1.5 44 3.7/1.5
650 45 3.7/1.5 45 3.8/1.6 44 3.3/1.3 44 3.4/1.4 44 3.5/1.4
675 46 3.6/1.5 46 3.7/1.5 46 3.8/1.6 45 3.8/1.6 44 3.2/1.3
725 47 3.5/1.5 47 3.6/1.5 47 3.8/1.6 46 3.4/1.4 46 3.5/1.5
775 48 3.5/1.5 48 3.6/1.5 48 3.8/1.6 47 3.4/1.4 47 3.5/1.4
825 49 3.6/1.5 49 3.8/1.6 48 3.3/1.4 48 3.4/1.4 48 3.5/1.5
850 49 3.4/1.4 49 3.5/1.5 49 3.7/1.5 49 3.8/1.6 48 3.3/1.4
AVG GAS
HEAT VALUE
AT ALTITUDE
(BTU/CU FT)
600 45 3.7/1.5 44 3.2/1.3 44 3.3/1.4 44 3.4/1.4 44 3.5/1.4
625 46 3.6/1.5 46 3.7/1.5 46 3.8/1.6 45 3.8/1.6 44 3.2/1.3
675 47 3.5/1.4 47 3.6/1.5 47 3.7/1.5 47 3.8/1.6 46 3.5/1.4
725 48 3.4/1.4 48 3.6/1.5 48 3.7/1.5 48 3.8/1.6 47 3.4/1.4
775 49 3.5/1.5 49 3.7/1.5 49 3.8/1.6 48 3.3/1.4 48 3.4/1.4
800 49 3.3/1.4 49 3.4/1.4 49 3.5/1.5 49 3.7/1.5 49 3.8/1.6
AVG GAS
HEAT VALUE
AT ALTITUDE
(BTU/CU FT)
575 46 3.6/1.5 46 3.7/1.5 46 3.8/1.6 45 3.8/1.6 44 3.2/1.3
600 47 3.7/1.5 46 3.4/1.4 46 3.5/1.5 46 3.6/1.5 46 3.8/1.6
650 48 3.6/1.5 48 3.8/1.6 47 3.4/1.4 47 3.5/1.5 47 3.6/1.5
700 49 3.7/1.5 49 3.8/1.6 48 3.3/1.4 48 3.5/1.4 48 3.6/1.5
750 50 3.8/1.6 49 3.3/1.4 49 3.4/1.4 49 3.5/1.5 49 3.6/1.5
775 50 3.5/1.5 50 3.7/1.5 50 3.8/1.6 49 3.3/1.4 49 3.4/1.4
0.58 0.60 0.62 0.64 0.66
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
0.58 0.60 0.62 0.64 0.66
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
0.58 0.60 0.62 0.64 0.66
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
SPECIFIC GRAVITY OF NATURAL GAS
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
SPECIFIC GRAVITY OF NATURAL GAS
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
SPECIFIC GRAVITY OF NATURAL GAS
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Orifice
No.
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
Manifold
Pressure
High/Low
—18—
Page 19

TABLE 10—GAS RATE (CU FT/HR)
SECONDS
FOR 1
REVOLUTION
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
SIZE OF TEST DIAL
1
cu ft2cu ft5cu ft
360
720
327
655
300
600
277
555
257
514
240
480
225
450
212
424
200
400
189
379
180
360
171
343
164
327
157
313
150
300
144
288
138
277
133
267
129
257
124
248
120
240
116
232
113
225
109
218
106
212
103
206
100
200
97
195
95
189
92
185
90
180
88
176
86
172
84
167
82
164
80
160
78
157
76
153
75
150
73
147
1800
1636
1500
1385
1286
1200
1125
1059
1000
947
900
857
818
783
750
720
692
667
643
621
600
581
563
545
529
514
500
486
474
462
450
439
429
419
409
400
391
383
375
367
SECONDS
FOR 1
REVOLUTION
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
62
64
66
68
70
72
74
76
78
80
82
84
86
88
90
92
94
96
98
100
102
104
106
108
110
112
116
120
SIZE OF TEST DIAL
1
cu ft2cu ft5cu ft
72
71
69
68
67
65
64
63
62
61
60
58
56
54
53
51
50
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
38
37
36
35
35
34
33
33
32
31
30
a. Place duct thermometers in return and supply ducts as
near furnace as possible. Be sure thermometers do not
see heat exchangers so that radiant heat will not affect
thermometer readings. This is particularly important
with straight-run ducts.
144
141
138
136
133
131
129
126
124
122
120
116
112
109
106
103
100
97
95
92
90
88
86
84
82
80
78
76
75
74
72
71
69
68
67
65
64
62
60
360
355
346
340
333
327
321
316
310
305
300
290
281
273
265
257
250
243
237
231
225
220
214
209
205
200
196
192
188
184
180
178
173
170
167
164
161
155
150
BURNER FLAME
BURNER
MANIFOLD
Fig. 16—Burner Flame
A89020
b. When thermometer readings stabilize, subtract return-air
temperature from supply-air temperature to determine
temperature rise.
NOTE: If temperature rise is outside this range, first check:
(1.) Gas input for low- and high-heat operation.
(2.) Derate for altitude if applicable.
(3.) Return and supply ducts for excessive restrictions
causing static pressures greater than 0.50-in. wc.
c. Adjust air temperature rise by adjusting blower speed.
Increase blower speed to reduce temperature rise. Decrease blower speed to increase temperature rise. For
high heat, speed selection can be med-high, med (5speed blowers only), or med-low (factory setting). For
low heat, speed tap selection can be low (factory setting),
med-low, or med (5-speed blowers only).
WARNING: Disconnect electrical power before changing speed tap (or removing cap on 5-speed motors). A
failure to follow this warning can cause personal injury or
death.
ON/OFF
SWITCH
INLET
PRESSURE
TAP
O
F
F
ON
MANIFOLD
PRESSURE
TAP
→ Fig. 15—Redundant Automatic Gas Control Valve
LOW-FIRE
ADJUSTMENT
ALLEN SCREW
(UNDER CAP)
HIGH-FIRE
ADJUSTMENT
ALLEN SCREW
(UNDER CAP)
A97358
NOTE: For furnaces with 5-speed motors, ensure that unused
speed tap is either capped or placed on SPARE terminal on control
center before power is restored.
d. To change motor speed selection for high heat, remove
blower motor lead from control HIGH-GAS-HEAT
terminal. (See Fig. 10 and Fig. 14.) Select desired blower
motor speed lead from 1 of the other terminals and
relocate it to HIGH-GAS-HEAT terminal. See Table 11
for lead color identification. Reconnect original lead to
PARK terminal (or cover with insulating cap, if used in
furnaces using 5-speed blower motors). Follow this same
procedure for proper selection of cool and low-gas-heat
speed selection.
6. Set thermostat heat anticipator.
a. When using a nonelectronic thermostat, the thermostat
heat anticipation must be set to match amp draw of
electrical components in R-W/W1 circuit. Accurate amp
draw readings can be obtained at wires normally connected to thermostat subbase terminals R and W/W1.
Fig. 17 illustrates an easy method of obtaining actual
amp draw. The amp reading should be taken after blower
motor has started and furnace is operating in low heat.
To operate furnace in low heat, first move SW-2 to ON
position, THEN connect ammeter wires as shown in Fig.
—19—
Page 20

→
COLOR SPEED AS SHIPPED‡
Orange† Med SPARE or Capped
* Continuous fan speed.
† Available on 5-speed blowers only.
‡ Terminal on control center.
TABLE 11—SPEED SELECTION
White Common C
Black High Cool
Yellow Med-High SPARE
Blue Med-Low High-Gas-Heat
Red Low* Low-Gas-Heat
OM
CAUTION: Recheck temperature rise. It must be within
limits specified on unit rating plate. Recommended operation is at midpoint of rise range or above.
17. The thermostat anticipator should NOT be in this
circuit while measuring current. If thermostat has no
subbase, thermostat MUST be disconnected from R and
W/W1 wires during current measurement. Return SW-2
to final desired location after completing reading. See
thermostat manufacturer’s instructions for adjusting heat
anticipator and for varying heating cycle length.
b. When using an electronic thermostat, set cycle rate for 3
cycles per hr.
THERMOSTAT SUBBASE
TERMINALS WITH
THERMOSTAT REMOVED
(ANITICIPATOR, CLOCK, ETC.,
MUST BE OUT OF CIRCUIT.)
HOOK-AROUND
AMMETER
R Y W G
10 TURNS
FROM UNIT 24-V
CONTROL TERMINALS
EXAMPLE:
5.0 AMPS ON AMMETER
10 TURNS AROUND JAWS
0.5 AMPS FOR THERMOSTAT
=
ANTICIPATOR SETTING
Fig. 17—Amp Draw Check With Ammeter
E. Check Safety Controls
The flame sensor, gas valve, and pressure switches were all
checked in the Start-Up section as part of normal operation.
1. Check primary limit control.
This control shuts off combustion control system and
energizes circulating-air blower motor if furnace overheats.
The preferred method of checking limit control is to
gradually block off return air after furnace has been
operating for a period of at least 5 minutes. As soon as limit
has shut off burners, return-air opening should be unblocked. By using this method to check limit control, it can
be established that the limit is functioning properly and will
operate if there is a motor failure.
2. Check draft safeguard switch.
A96316
The purpose of this control is to permit safe shutdown of he
furnace during certain blocked vent conditions.
a. Disconnect power to furnace and remove vent connector
from furnace flue collar. Be sure to allow time for vent
connector pipe to cool down before removing.
b. Restore power to furnace and set room thermostat above
room temperature.
c. After normal start-up, allow furnace to operate for 2
minutes, then block flue outlet 100 percent. Furnace
should cycle off within 2 minutes.
d. Remove blockage and reconnect vent connector to
furnace flue collar.
e. Wait 5 minutes and then reset draft safeguard switch.
3. Check flow-sensing pressure switches.
This control proves operation of draft inducer blower.
a. Turn off 115-v power to furnace.
b. Remove gas control door and disconnect inducer motor
lead wires from wire harness.
c. Turn on 115-v power to furnace
d. Close thermostat switch as if making normal furnace
start. If hot surface ignitor does not glow within several
minutes and control flashes code 32, pressure switches
are functioning properly.
e. Turn off 115-v power to furnace.
f. Reconnect inducer motor wires, replace gas control door,
and turn on 115-v power to furnace.
4. Check auxiliary limits.
a. Turn off 115-v power to furnace.
b. Remove blower access door.
c. Disconnect red motor lead at blower speed selector.
Mark terminal for proper reconnection.
d. Replace blower access door.
e. Turn on 115-v power to furnace. Be sure room thermo-
stat is calling for low heat.
f. Allow furnace to operate until auxiliary limit activates,
but DO NOT operate furnace longer than 4 minutes.
g. If furnace operates for 4 minutes, check/replace limit
switch(es).
h. Turn off 115-v power to furnace.
i. Remove blower access door.
j. Reconnect red motor lead, reset switch, and replace door.
k. Turn on 115-v power to furnace.
F. Checklist
1. Put away tools and instruments, and clean up debris.
2. Check SW-1 through SW-4 after completing installation to
ensure desired settings for thermostat type (SW-1 and
SW-2) and blower off delay (SW-3 and SW-4). Refer to
Tables 6 and 7.
3. Verify manual reset switches have continuity.
4. Ensure blower and gas control access doors are properly
installed.
5. Cycle test furnace with room thermostat.
6. Check operation of accessories per manufacturer’s instructions.
7. Review User’s Manual with owner.
8. Leave literature packet near furnace.
—20—
Page 21

—21—
Page 22

—22—
Page 23

SERVICE TRAINING
Packaged Service Training programs are an excellent way to increase your
knowledge of the equipment discussed in this manual, including:
• Unit Familiarization • Maintenance
• Installation Overview • Operating Sequence
A large selection of product, theory, and skills programs is available, using popular
video-based formats and materials. All include video and/or slides, plus companion
book.
Classroom Service Training plus "hands-on" the products in our labs can mean
increased confidence that really pays dividends in faster troubleshooting, fewer
callbacks. Course descriptions and schedules are in our catalog.
CALL FOR FREE CATALOG 1-800-644-5544
[ ] Packaged Service Training [ ] Classroom Service Training
A94328
—23—
Page 24

© 2008 Bryant Heating & Cooling Systems 7310 W. Morris St. Indianapolis, IN 46231
—24—
Printed in U.S.A. 331j602 Catalog No. 5333-100
 Loading...
Loading...