Page 1

installation, start-up and
service instructions
SINGLE PACKAGE ROOFTOP
ELECTRIC COOLING/ELECTRIC HEATING UNITS
Cancels: II 551A-155-2 II 551A-155-3
Dura
Plus Series
Pac
Sizes 155-240
551A
3/1/01
CONTENTS
Page
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1-17
I. Step 1 — Provide Unit Support. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
II. Step 2 — Rig and Place Unit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
III. Step 3 — Field Fabricate Ductwork . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
IV. Step 4 — Make Unit Duct Connections . . . . . . . . . . .7
V. Step 5 — Trap Condensate Drain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
VI. Step 6 — Make Electrical Connections
VII. Step 7 — Make Outdoor-Air Inlet
Adjustments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
VIII. Step 8 — Install Outdoor-Air Hood. . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
IX. Step 9 — Install All Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
X. Step 10 — Install Humidistat for Optional
Perfect Humidity™ Dehumidification Package . . 16
START-UP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18-25
SERVICE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26-32
TROUBLESHOOTING. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33,34
START-UP CHECKLIST . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . CL-1
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
Installation and servicing of air-conditioning equipment can
be hazardous due to system pressure and electrical components. Only trained and qualified service personnel should
install, rep air, or service air-conditioning equipment.
Untrained personnel can perform basic maintenance functions of cleaning coils and filters and replacing filters. All
other operations sh o uld be perfor me d by trai ne d se rvi ce personnel. When working on air-conditioning equipment,
observe precautions in the literature, tags and labels
attached to the unit, and other safety precaution s that may
apply.
Follow all safety codes. Wear safety glasse s and work g love s.
Use quenching cloth for unbrazing operations. Have fire
extinguishers available for all brazing operations.
WARNING:
Before performing service or mainte-
. . . . . . . . . . . . 8
nance operations on unit, turn off main power switch to unit.
Electrical shock could cause personal injury.
IMPORTANT: Units have high ambient operating limits. If
limits are exceeded, the unit will automatically lock the compressor out of operation. Manual reset will be required to
restart the compressor.
INSTALLATION
I. STEP 1 — PROVIDE UNIT SUPPORT
A. Roof Curb
Assemble and install accessory roof curb or horizontal supply
roof curb in accordan ce with instructions shipped with the
accessory. Accessory roof curb and horizontal supply roof
curb and information required to field fabricate a roof curb
or horizontal supply roof curb are shown in Fig. 1 and 2.
Install insulation, cant strips, roofing, and counter flashing
as shown. Ductwork can be secured to roof curb before unit is
set in place.
IMPORTANT: The gasketing of the unit to the roof curb or
horizontal supply roof curb is critical for a leakproof seal.
Install gasket supplied with the ro of curb or h orizontal supply roof curb as shown in Fig. 1. Improperly applied gasket
can result in air leaks and poor unit performance.
Roof curb must be level. This is necessary to permit unit
drain to function properly. Unit leveling tolerance is ±
per linear ft in any direction. Refer to Accessory Roof Curb or
Horizontal Supply Roof Curb Installation Instructions for
additional information as required.
B. Alternate Unit Support
When the curb or adapter cannot be used, support unit with
sleepers using unit curb or adapter s upport area. If sl eepers
cannot be used, su ppor t l on g si des o f unit with a minimum of
3 equally spaced 4-in. x 4-in. pads on each side.
II. STEP 2 — RIG AND PLACE UNIT
Inspect unit for transportation da mage. File any claim with
transportation agency. Keep unit upright, and do not drop.
Use spreader bars over unit to prevent sling or cable damage. Rollers may be used to move unit across a roof. Level
by using unit frame as a reference; leveling tolerance is
1
±
/16 in. per linear ft in any direction. See Fig. 3 for addi-
tional information. Unit weight is shown in Table 1.
Four lifting holes are provided in ends of unit base rails as
shown in Fig. 3. Refer to rigging instructions on unit.
A. Positioning
Provide clearance around and above unit for airflow, safety,
and service access (Fig. 4 and 5).
Do not install unit in an indoor location. Do not locate air
inlets near exhaust vents or other sources of contaminated
air.
Although unit is weatherproof, guard against water from
higher level runoff and overhangs.
B. Roof Mount
Check building codes for weight distribution requirements.
1
/16 in.
Page 2

NOTES:
1. Roof curb accessory is shipped disassembled.
lb density.
2
/
1
AB
.28 .45 .28 .43
DIMENSIONS* (DEGREES AND INCHES)
UNIT
Deg. in. Deg. in.
ALL
thick neoprene coated 1
″
90 degree elbow must be installed on the supply ductwork
To prevent the hazard of stagnant water build-up in the drain pan of
A
2. Insulated panels: 1
3. Dimensions in ( ) are in millimeters.
below the unit discharge for units equipped with electric heaters.
4. Direction of airflow.
5. Roof curb: 16 ga. (VA03-56) stl.
6.
NOTE:
the indoor section, unit can only be pitched as shown.
DESCRIPTION
CURB
HEIGHT
Fig. 1 — Roof Curb Details
High
″
Standard Curb
for Units Requiring
Standard Curb
″
-2
′
1
High Installation
14
″
-0
′
2
(610)
(305)
High-Static
Side Supply and
Transition Duct
Return Curb for
High Installation
″
″
-0
-0
′
′
2
2
(610)
(610)
PKG. NO. REF.
CRRFCURB011A00
CRRFCURB010A00
CRRFCURB013A00
CRRFCURB012A00
—2—
Page 3

NOTE:
For preassembled horizontal adapter roof curb part no.
CRRFCURB013A00, the accessory kit includes a factory-designed,
high-static, regain transition duct. For horizontal curb part no.
CRRFCURB012A00, a field-supplied transition duct is required.
Fig. 2 — Horizontal Supply Roof Curb and Horizontal
Adapter Roof Curb
UNIT
551A
155
180
240
NOTES:
1. Dimensions in ( ) are in millimeters.
2. Refer to Fig. 4 and 5 for unit operating weights.
3. Remove boards at ends of unit and runners prior to rigging.
4. Rig by inserting hooks into unit base rails as shown. Use corner
post from packaging to protect coil from damage. Use bumper
boards for spreader bars.
5. Weights do not include optional EconoMi$er. Add 80 lb (36 kg) for
EconoMi$er weight.
6. Weights given are for aluminum evaporator and condenser coil
plate fins. Weights include electric heat.
7. Add 75 lb (34 kg) for crating on 551A155 and 180 units. Add 135 lb
(61 kg) for crating on 551A240 units.
8. Add 150 lb (68 kg) for copper condenser coil. Add 280 lb (127 kg)
for copper condenser and evaporator coils.
MAXIMUM
SHIPPING WEIGHT
lb kg ft-in. mm ft-in. mm
1625 737 6-11
1700 771 6-11
1800 816 6-11
DIMENSIONS
AB
1
/22121 4- 0 1219
1
/22121 3-10 1168
1
/22121 3- 7 1092
CAUTION:
All panels must be in place when rigging.
Fig. 3 — Rigging Details
—3—
Page 4
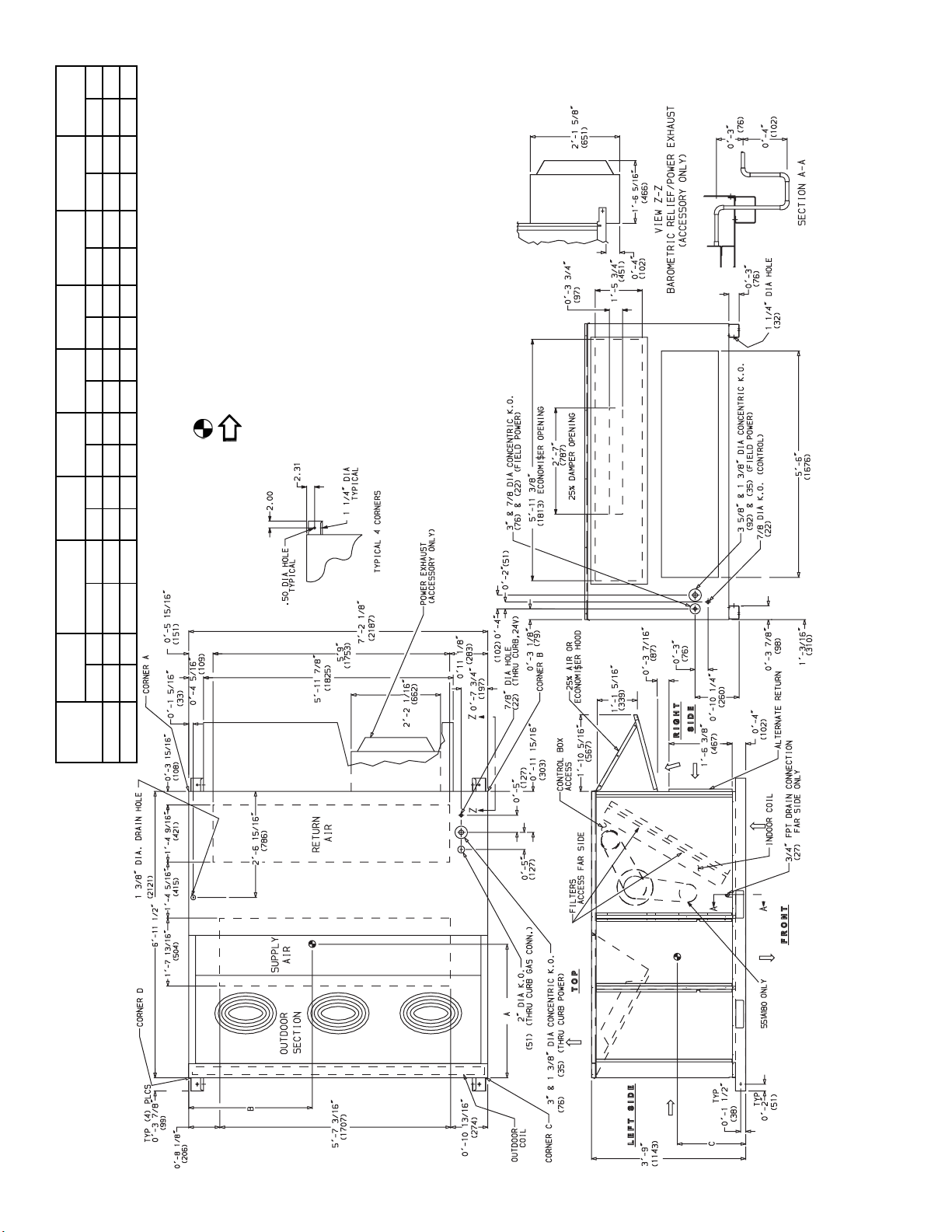
(8) on each
″
16
/
5
-
′
DIM A DIM B DIM C
D
CORNER
(2134) for coil removal. This dimension can be reduced to
C
CORNER
B
CORNER
1. Refer to print for roof curb accessory dimensions.
2. Dimensions in ( ) are in millimeters.
3. Center of Gravity.
NOTES:
4. Direction of airflow.
″
-0
′
(1219) if conditions permit coil removal from the top.
″
-0
′
4
• Rear: 7
5. Ductwork to be attached to accessory roof curb only.
6. Minimum clearance:
(1219) for proper condenser coil airflow.
″
-0
′
• Left side: 4
(1219) for proper operation of damper and power
″
-0
′
(1219) for control box access.
″
-0
′
• Front: 4
• Right side: 4
(1829) to assure proper condenser fan operation.
″
-0
′
exhaust if so equipped.
• Top: 6
• Local codes or jurisdiction may prevail.
damper/ power exhaust as stated in Note #6, a removable fence or
7. With the exception of clearance for the condenser coil and the
90 degree elbow must be installed on the supply ductwork
A
below the unit discharge for units equipped with electric heaters.
side for top cover drip edge.
barricade requires no clearance.
9. See drawing 50TJ500352 for service option details.
8. Dimensions are from outside of corner post. Allow 0
10.
A
CORNER
ECONOMI$ER
STD UNIT
WEIGHT
WEIGHT
UNIT
551A
Lb Kg Lb Kg Lb Kg Lb Kg Lb Kg Lb Kg ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm
1575 714 80 36.3 407 185 375 170 383 174 410 186 3-5 1039 3-5 1054 1-10 559
1650 748 80 36.3 375 170 375 170 449 204 452 205 3-2 963 3-7 1092 1-10 559
155
180
Fig. 4 — Base Unit Dimensions, 551A155 and 180
—4—
Page 5
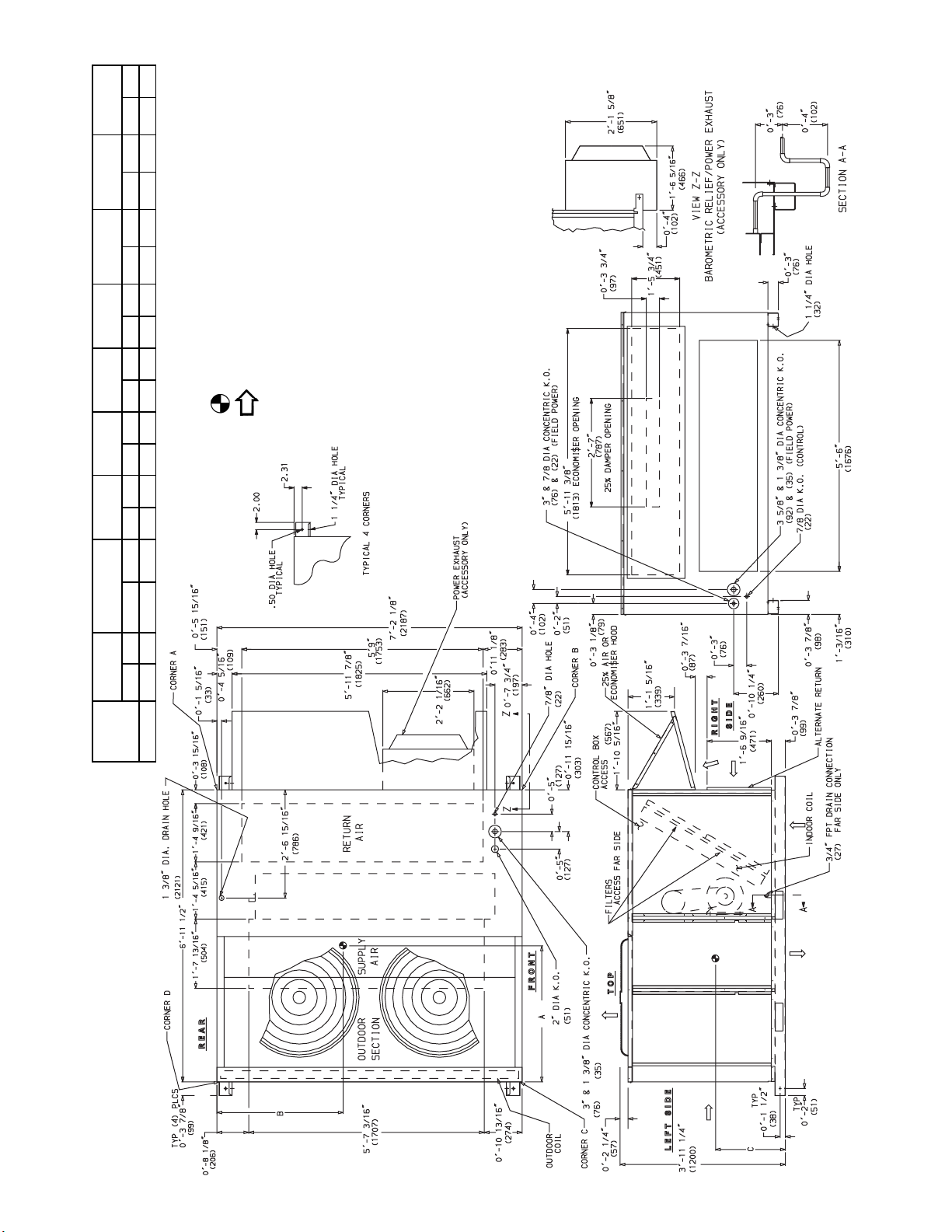
(8) on
″
16
/
5
-
′
DIM A DIM B DIM C
CORNER
CORNER
CORNER
CORNER
ECONOMI$ER
STD UNIT
UNIT
D
C
B
A
WEIGHT
WEIGHT
Lb Kg Lb Kg Lb Kg Lb Kg Lb Kg Lb Kg ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm
551A
1750 794 80 36.3 420 191 395 179 448 203 486 221 3-3 988 3-5 1054 1-8 508
240
(1219) if conditions permit coil removal from the
″
-0
(2134) for coil removal. This dimension can be
′
″
-0
′
reduced to 4
top.
1. Refer to print for roof curb accessory dimensions.
2. Dimensions in ( ) are in millimeters.
3. Center of Gravity.
NOTES:
4. Direction of airflow.
5. Ductwork to be attached to accessory roof curb only.
6. Minimum clearance:
• Rear: 7
(1219) for proper condenser coil airflow.
″
(1219) for control box access.
-0
′
″
-0
′
• Front: 4
• Left side: 4
(1219) for proper operation of damper and power
″
-0
′
(1829) to assure proper condenser fan operation.
″
-0
′
exhaust if so equipped.
• Right side: 4
• Top: 6
• Local codes or jurisdiction may prevail.
7. With the exception of clearance for the condenser coil and the
damper/ power exhaust as stated in Note #6, a removable fence
or barricade requires no clearance.
8. Dimensions are from outside of corner post. Allow 0
90 degree elbow must be installed on the supply ductwork
each side for top cover drip edge.
A
below the unit discharge for units equipped with electric
heaters.
9. See drawing 50TJ500352 for service option details.
10.
Fig. 5 — Base Unit Dimensions, 551A240
—5—
Page 6

Table 1 — Physical Data
UNIT 551A
NOMINAL CAPACITY (tons)
OPERATING WEIGHT (lb)
Unit
Al/Al*
Al/Cu*
Cu/Cu*
EconoMi$er
Roof Curb†
Perfect Humidity™ Dehumidification Package
COMPRESSOR
Quantity...Model (Ckt 1, Ckt 2)
Number of Refrigerant Circuits
Crankcase Heater Watts
Loading (% of Full Capacity)
Oil (oz) (Ckt 1, Ckt 2)
REFRIGERANT TYPE
Expansion Device
Operating Charge (lb)**
Circuit 1
Circuit 2
CONDENSER COIL
Rows...Fins/in.
Total Face Area (sq ft)
CONDENSER FAN
Nominal Cfm
Quantity...Diameter (in.)
Motor Hp...Rpm
Watts Input (Total)
EVAPORATOR COIL
Rows...Fins/in.
Total Face Area (sq ft)
EVAPORATOR FAN
Quantity...Size (in.)
Type Drive
Nominal Cfm
Std Motor Hp
Opt Motor Hp
Motor Nominal Rpm
Std Maximum Continuous Bhp
Opt Maximum Continuous Bhp
Motor Frame Size
Fan Rpm Range Low-Medium Static
Motor Bearing Type
Maximum Allowable Rpm
Motor Pulley Pitch Dia. Low-Medium Static
Nominal Motor Shaft Diameter (in.)
Fan Pulley Pitch Diameter (in.) Low-Medium Static
Nominal Fan Shaft Diameter (in.)
Belt, Quantity...Type...Length (in.) Low-Medium Static
Pulley Center Line Distance (in.)
Speed Change per Full Turn of Movable Low-Medium Static
Pulley Flange (Rpm) High Static
Movable Pulley Maximum Full Turns
From Closed Position
Factory Speed
Factory Speed Setting (Rpm) Low-Medium Static
HIGH-PRESSURE SWITCH (psig)
Cutout
Reset (Auto.)
LOW-PRESSURE SWITCH (psig)
Cutout
Reset (Auto.)
FREEZE PROTECTION THERMOSTAT (F)
Opens
Closes
High Static
High Static
High Static
High Static
High Static
OUTDOOR-AIR INLET SCREENS
Quantity...Size (in.)
RETURN-AIR FILTERS
Quantity...Size (in.)
LEGEND
Al —
Bhp —
Cu —
TXV —
Aluminum
Brake Horsepower
Copper
Thermostatic Expansion Valve
*Evaporator coil fin material/condenser coil fin material.
†Weight of 14-in. roof curb.
155 180 240
12 15 20
1575 1650 1750
1725 1800 1900
1855 1930 2030
80 80 80
200 200 200
40 40 40
1...ZR72KC, 1...ZR57KC 1...ZR94KC, 1...ZR72KC 1...ZR125KC, 1...ZR108KC
22 2
70 70 70
0, 56, 100 0, 60, 100 0, 60, 100
60, 66 85, 60 110, 110
20.7 19.5 18.5
11.9 13.45 13.3
Cross-Hatched
4...15 4...15 4...15
21.7 21.7 21.7
10,500 10,500 14,200
3...22 3...22 2...30
1
/2...1050
1100 1100 3400
Cross-Hatched
4...15 4...15 4...15
17.5 17.5 17.5
2...10 x 10 2...12 x 12 2...12 x 12
Belt Belt Belt
5200 6000 8000
2.9 5 7.5
3.7
1725 1745 1745
3.13 6.13 9.47 [208 v], 10.33 [230 v and 460 v]
4.38 N/A N/A
56H 184T 213T
834-1064 873-1021 1002 -1151
1161-1426 1025-1200 1193-1369
Ball Ball Ball
1,550 1,550 1,550
3.1/4.1 4.9/5.9 5.4/6.6
3.7/4.7 4.9/5.9 5.4/6.6
7
/
8
6.0 9.4 9.4
5.2 8.0 7.9
3
/
1
16
1...BX...42 1...BX...50 1...BX...54
1...BX...42 1...BX...48 1...BX...50
13.5-15.5 13.3-14.8 14.6-15.4
58 37 37
67 44 44
4†† 4†† 4††
3.5 3.5 3.5
978 965 1095
1327 1134 1303
3
/8-in. Copper Tubes, Aluminum Lanced, Aluminum Pre-Coated,
3
/8-in. Copper Tubes, Aluminum Lanced or Copper Plate Fins, Face Split
**Circuit 1 uses the lower por tion of condenser coil and lower por tion of evapora-
tor coils, and Circuit 2 uses the upper portion of both coils.
††Due to belt and pulley style, pulley cannot be set from 0 to 1
R-22
TXV
or Copper Plate Fins
Propeller Type
1
/2...1050 1...1075
Centrifugal Type
11/
8
17/
16
426
320
27
44
30 ± 5
45 ± 5
Cleanable
2...20 x 25 x 1
1...20 x 20 x 1
Throwaway
4...20 x 20 x 2
4...16 x 20 x 2
13/
17/
8
16
1
/2 turns open.
—6—
Page 7

III. STEP 3 — FIELD FABRICATE DUCTWORK
3/4" FPT DRAIN
CONNECTION
1-3/8"
DRAIN HOLE
INDOOR FAN MOTOR ACCESS
FILTER
ACCESS
Secure all duct s to bu ilding struct ure. Use fl exible duct con nectors between unit and ducts as required. Insulate and
weatherproof all external ductwork, joints, and roof openings
with counter flashing and m asti c i n acc ordance with applicable codes.
Ducts passing through a n unc ondit i one d spa ce must be insulated and covered with a vapor barrier.
The 551A units with electric heat require a 1-in. clearance
for the first 24 in. of ductwork.
Outlet grilles must not lie directly below unit discharge.
NOTE: A 90-degree elbow must be provided in the ductwork
to comply with UL (Underwriters’ Laboratories) codes for
use with electric heat.
WARNING:
For vertical supply and return units, tools
or parts could drop into ductwork and cause an injury.
Install a 90 degree turn in the return ductwork between the
unit and the conditioned space. If a 90 degree elbow cannot
be installed, then a grille of sufficient strength and density
should be installed to prevent objects from falling into the
conditioned space. Due to electric heater, supply duct will
require 90 degree elbow.
IV. STEP 4 — MAKE UNIT DUCT CONNECTIONS
Unit is shipped for thru-the-bottom duct conn ections. Ductwork openings a re shown in Fig. 6. Fi eld-fabricate d concentric ductwork may be connected as shown i n Fig. 7 and 8.
Attach all ductwork to roof curb and roof curb basepans.
Refer to installation instructions shipped with accessory roof
curb for more information.
V. STEP 5 — TRAP CONDENSATE DRAIN
See Fig. 4, 5, and 9 for drain location. Plug is provided in
drain hole and must be removed when unit is operating. One
3
/4-in. half-coupling is provided inside unit evaporator section for condensate drain connection. An 8
diameter nipple and a 2-in. x
coupled to standard
3
3
/4-in. diameter pipe nipple are
/4-in. diameter elbows to provide a
1
/2 in. x 3/4-in.
straight path down through holes in unit base rails (see
Fig. 10). A trap at least 4-in. deep must be used.
NOTE:
Do not drill in this area, as damage to basepan may result in
water leak.
Fig. 6 — Air Distribution — Thru-the-Bottom
(551A180 and 240 Shown)
Shaded area indicates block-off panels.
NOTE:
Dimension A, A′ and B, B′ are obtained from field-supplied ceil-
ing diffuser.
CAUTION:
units without electric heat. Personal injury or unit damage may
result.
Concentric ducts may only be installed on
Fig. 8 — Concentric Duct Details
NOTE:
Do not drill in this area, as damage to basepan may result in
water leak.
Fig. 7 — Concentric Duct Air Distribution
(551A180 and 240 Shown)
Fig. 9 — Condensate Drain Details
(551A155 Shown)
—7—
Page 8

Fig. 10 — Condensate Drain Piping Details
VI. STEP 6 — MAKE ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS
A. Field Power Supply
Unit is factory wired for voltage sh own on nameplate.
When installing units, provide a disconnect, per NEC
(National Electrical Code) requirements, of adequate size
(Table 2). Electrical heater data is shown in Table 3.
All field wiring must comply with NEC and local requirements.
Route power lines through control box access panel or unit
basepan (Fig. 4 and 5) to connections as shown on unit wiring diagram and Fig. 11.
Operating voltage to compressor must be within voltage
range indicated on unit nameplate. On 3-phase units, voltages between phases must be balanced within 2% and the
current must be balanced within 10%.
IMPORTANT: If the supply voltage phase imbalance is
more than 2%, contact your local electric utility company
immediately.
Unit failure as a res ult of ope ra tio n o n imp ro per line volt age
or excessive phase imbalance constitutes abuse and may
cause damage to electrical components.
B. Field Control Wiring
Install a Bryant-approved accessory thermostat assembly
according to the installation instruct ions included with the
accessory. Locate thermostat assembly on a solid wall in the
conditioned space to sense average temperature.
Route thermostat cable or equivalent single leads of colored
wire from subbase terminals through conduit in uni t to lowvoltage connections as shown on unit label wiring diagram
and in Fig. 12.
NOTE: For wire runs up to 50 ft, use no. 18 AWG (American
Wire Gage) insulated wire (35 C minimum). For 50 to 75 ft,
use no. 16 AWG insulated wire (35 C minimum). For over
75 ft, use no. 14 AWG insulated wire (35 C minimum). All
wire larger than no. 18 AWG cannot be directly connected to
the thermos tat and wi ll req uire a j unction box and s plice a t
the thermostat.
Set heat anticipator settings as indicated in Table 4. Settings
may be changed slightly to pr ovide a greater degree of comfort for a particular installation.
CAUTION: The correct power phasing is critical in
the operation of the scroll compressors. An incorrect
phasing will cause the compressor to rotate in the
wrong direction. This m ay lead to premature compres sor failure.
Use the following formula to determine the percentage of
voltage imbalance.
Percentage of Voltage Imbalance
= 100 x
max voltage deviation from average v oltage
average voltage
EXAMPLE: Supply voltage is 460-3-60.
AB = 452 v
BC = 464 v
AC = 455 v
Average Voltage =
455 + 464 + 455
1371
=
3
3
= 457
Determine ma ximum deviation from average voltage:
(AB) 457 – 452 = 5 v
(BC) 464 – 457 = 7 v
(AC) 457 – 455 = 2 v
Maximum deviation is 7 v.
Determine percent voltage imbalance:
Percentage of Voltage Imbalance = 100 x
7
457
= 1.53%
This amount of phase imbalance is satisfactory as it is below
the maximum allowable 2%.
UNIT
551A
All
EQUIP —
GND —
kcmil —
Equipment
Ground Code
Thousand Circular
Mils
Fig. 11 — Field Power Wiring Connections
REMOVABLE JUMPER
RC
RH
R
RED
Fig. 12 — Field Control Thermostat Wiring
TB1 MAXIMUM WIRE SIZE
VOLTAGE
208/230 460
350 kcmil 2/0
LEGEND
NEC —
TB —
THERMOSTAT ASSEMBLY
Y1 Y2
Y1
BLU
UNIT LOW-VOLTAGE CONNECTIONS
W1
W1Y2
PNK
National Electrical
Terminal Block
W2
W2
ORN
VIO
GC
G
BLK
C
BRN
L
X
X
WHT
—8—
Page 9

UNIT
551A
155
(Standard
IFM)
155
(Optional
IFM)
180
240
Table 2 — Electrical Data
NOMINAL
VOLTAGE
(3 Ph,
60 Hz)
208/230 187 253 20.7 156 19.3 123 3 0.5 1.7 2.9
460 414 508 10 70 10 62 3 0.5 0.8 2.9 4.2
208/230 187 253 20.7 156 19.3 123 3 0.5 1.7 3.7
460 414 508 10 70 10 62 3 0.5 0.8 3.7 4.8
208/230 187 253 32.1 195 20.7 156 3 0.5 1.7 5.0
460 414 508 16.4 95 10 70 3 0.5 0.8 5.0 7.9
208/230 187 253 42 239 33.6 225 2 1 6.6 7.5
460 414 508 19.2 125 17.3 114 2 1 3.3 7.5 13.0
VO LTAG E
RANGE
Min Max RLA LRA RLA LRA Qty Hp FLA (ea) Hp FLA FLA LRA kW FLA MCA MOCP†
COMPRESSOR
No. 1 No. 2
OFM IFM
POWER
EXHAUST
—— — — 59/ 59 70/ 70
4.6 18.8 ——64/ 63 80/ 80
——14/19 39/ 45 60/ 67 70/ 70
4.6 18.8 14/19 39/ 45 66/ 73 80/ 80
8.8/
8.4
——26/34 71/ 82 100/113 100/125
4.6 18.8 26/34 71/ 82 106/119 110/125
——42/56** 117/135 157/146 175/175
4.6 18.8 42/56** 117/135 163/151 175/175
—— — — 29 35
2.3 6.0 —— 31 40
—— 15 18 29 35
2.3 6.0 15 18 31 40
—— 32 39 54 60
2.3 6.0 32 39 57 60
—— 55** 66 71 80
2.3 6.0 55** 66 74 80
—— — — 61/ 61 80/ 80
4.6 18.8 ——65/ 66 80/ 80
——14/19 39/ 45 62/ 70 80/ 80
4.6 18.8 14/19 39/ 45 68/ 76 80/ 80
11.0/
10.5
——26/34 71/ 82 102/116 110/125
4.6 18.8 26/34 71/ 82 108/122 110/125
——42/56** 117/135 159/149 175/175
4.6 18.8 42/56** 117/135 165/155 175/175
—— — — 30 35
2.3 6.0 —— 32 40
—— 15 18 30 35
2.3 6.0 15 18 32 40
—— 32 39 55 60
2.3 6.0 32 39 58 60
—— 55** 66 72 80
2.3 6.0 55** 66 75 80
—— — — 82/ 82 110/110
4.6 18.8 ——86/ 86 110/110
——26/34 71/ 82 109/122 110/125
15.8/
4.6 18.8 26/34 71/ 82 114/128 125/150
15.8
——42/56 117/135 166/155 175/175
4.6 18.8 42/56 117/135 172/161 175/175
——56/75** 156/180 176/200 200/225
4.6 18.8 56/75** 156/180 182/206 200/225
—— — — 41 50
2.3 6.0 —— 43 50
—— 32 39 59 60
2.3 6.0 32 39 62 70
—— 55 66 76 90
2.3 6.0 55 66 79 90
—— 80** 96 106 125
2.3 6.0 80** 96 109 125
—— — — 124/124 150/150
4.6 18.8 ——129/129 150/150
——26/34 71/ 82 124/134 150/150
4.6 18.8 26/34 71/ 82 129/140 150/150
25.0/
25.0
——42/56 117/135 178/166 200/175
4.6 18.8 42/56 117/135 183/172 200/175
——56/75** 156/180 187/211 200/225
4.6 18.8 56/75** 156/180 193/217 200/225
—— — — 61 80
2.3 6.0 —— 63 80
—— 32 39 65 80
2.3 6.0 32 39 68 80
—— 55 66 82 90
2.3 6.0 55 66 85 90
—— 80** 96 112 125
2.3 6.0 80** 96 115 125
ELECTRIC
HEAT*
(See Legend on page 10.)
POWER
SUPPLY
—9—
Page 10

FLA —
HACR—
IFM —
LRA —
MCA —
MOCP—
NEC —
OFM —
RLA —
*Heater capacity (kW) is based on heater voltage of 208 v, 240 v, and
†Fuse or HACR circuit breaker.
**Heaters are field installed only.
NOTES:
1. In compliance with NEC requirements for multimotor and combina-
2.
Full Load Amps
Heating, Air Conditioning and Refrigeration
Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Motor
Locked Rotor Amps
Minimum Circuit Amps
Maximum Overcurrent Protection
National Electrical Code
Outdoor (Condenser) Fan Motor
Rated Load Amps
480 v. Heaters are rated at 240 v, or 480 v. If power distribution voltage to unit varies from rated heater voltage, heater kW will vary
accordingly.
tion load equipment (refer to NEC Articles 430 and 440), the overcurrent protective device for the unit shall be fuse or HACR breaker.
Canadian units may be fuse or circuit breaker.
Unbalanced 3-Phase Supply Voltage
Never operate a motor where a phase imbalance in supply voltage is
greater than 2%.
of voltage imbalance.
% Voltage Imbalance
= 100 x
LEGEND
Use the following formula to determine the percent
max voltage deviation from average voltage
average voltage
Example: Supply voltage is 460-3-60.
AB = 452 v
BC = 464 v
AC = 455 v
=
= 457
7
457
452 + 464 + 455
3
1371
3
Average Voltage =
Determine maximum deviation from average voltage.
(AB) 457 – 452 = 5 v
(BC) 464 – 457 = 7 v
(AC) 457 – 455 = 2 v
Maximum deviation is 7 v.
Determine percent of voltage imbalance.
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x
This amount of phase imbalance is satisfactory as it is below the maximum allowable 2%.
IMPORTANT:
contact your local electric utility company immediately.
3. MCA calculation for units with electric heaters over 50 kW = (1.25 x
IFM amps) + (1.00 x heater FLA).
= 1.53%
If the supply voltage phase imbalance is more than 2%,
Table 3 — Electric Resistance Heater Data
UNIT
551A
*Maximum number of stages using accessory low-ambient kit or head pressure control device and low-ambient kit.
NOTE:
208 230 240 460 480 Cfm L/s 208 230 240 460 480
14 17 19 14 15 1 100 1
155
26 31 34 30 32 2 50/50 2 71.3 78.9 82.3 37.3 39.0
42 52 56 50 55 2 33/67 3 117.0 129.4 135.0 63.3 66.1
26 31 34 30 32 2 50/50 2
180
42 52 56 50 55 2 33/67 3 117.0 129.4 135.0 63.3 66.1
56 69 75 73 80 2 50/50 4 155.9 172.4 179.9 92.0 96.0
26 31 34 30 32 2 50/50 2
240
42 52 56 50 55 2 33/67 3 117.0 129.4 135.0 63.3 66.1
56 69 75 73 80 2 50/50 4 155.9 172.4 179.9 92.0 96.0
Heaters are rated at 240, and 480 v.
HEATER kW
Unit Voltages Heating Cfm
HEATER
STAGES
% HEAT
PER
STAGE
MAXIMUM
STAGES*
MINIMUM
39.3 43.4 45.3 17.2 17.9
3750 1770
71.3 78.8 82.3 37.3 39.0
3750 1770
71.3 78.8 82.3 37.3 39.0
5000 2360
HEATER AMPS
—10—
Page 11
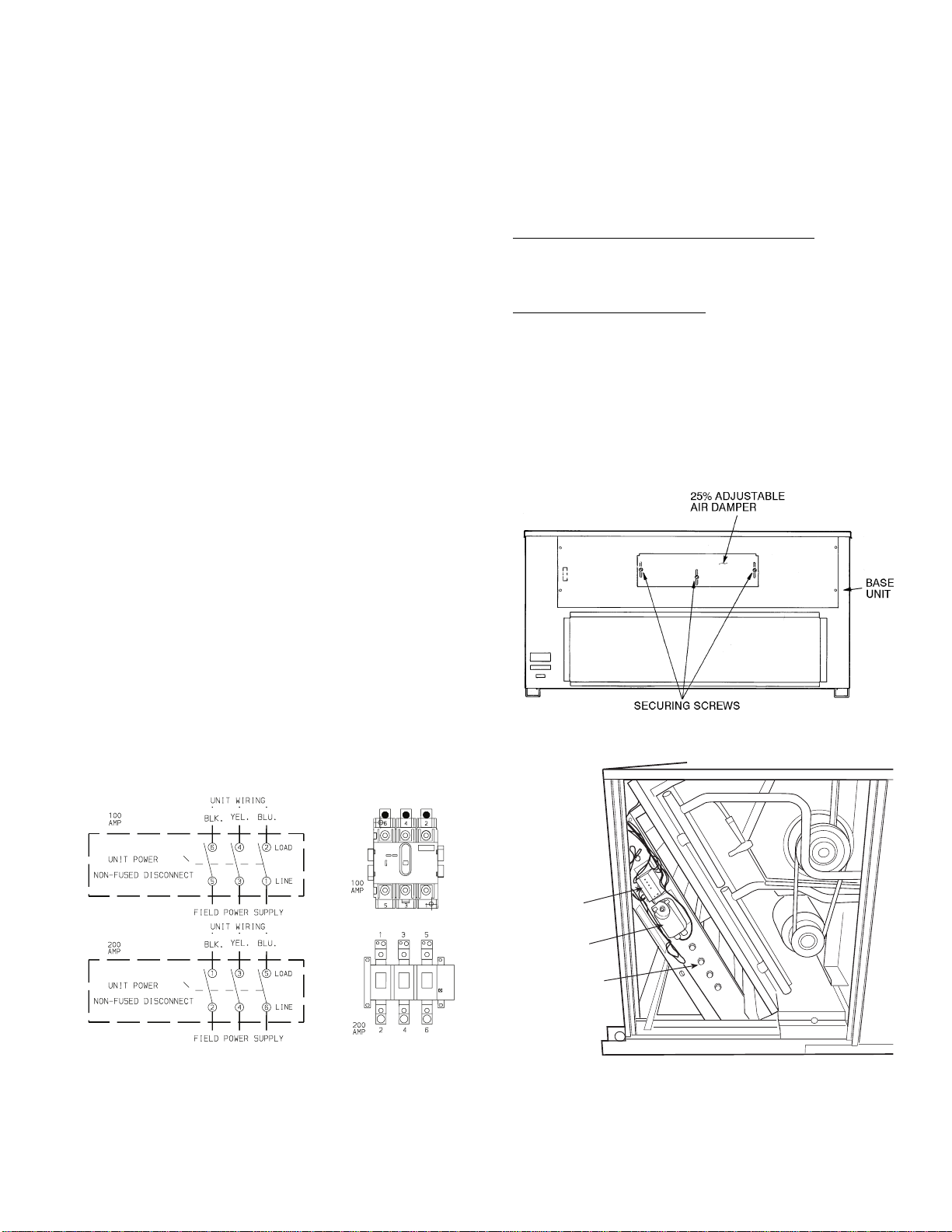
C. Optional Non-Fused Disconnect
CONTROL
MODULE
ACTUATOR
ECONOMI$ER
On units with the optional non-fused disconnect, incoming
power will be wired into the disconnect switch. Refer to
Fig. 13 for wiring for 100 and 200 amp disconnect switches.
Units with an MOCP (maximum overcurrent protection)
under 100 will use the 100 amp disconnect switch. Units
with an MOCP over 100 will use the 200 amp disconnect
switch. Refer to the applicable disconnect wiring diagram.
To prevent breakage during s hipping, the disconne ct han dle
and shaft are shipped and packaged inside the unit control
box. Install the disconnect handle before unit operation.
To install the handle and shaft, perform the following
procedure:
1. Open the co nt rol b ox do or and remove the handle and
shaft from shipping location.
2. Loosen the Allen bolt located on the disconnect
switch. The bo lt is locate d on the square hole and is
used to hold the shaft in place. The shaft cannot be
inserted until the Allen bolt is moved.
3. Insert the disconnect shaft into the square hole on
the disconnect switch. The end of the shaft is specially cut and the shaft can only be inserted in the
correct orientation.
4. Tighten the Allen bolt to lock the shaft into position.
5. Close the control box d oor.
6. Attach the handle to the external access door with
the two screws provided. When the handle is in the
ON position, the handle will be vertical. When the
handle is in the OFF position, the handle will be
horizontal.
7. Turn the handle to the OFF position and close the
door. The handle should fit over the end of the shaft
when the door is closed.
8. The handle must be in the OFF position to open the
control box door.
D. Optional Convenience Outlet
On units with optional convenience outlet, a 115-v GFI
(ground fault interrupt) convenience outlet re ce ptacle is provided for field wiring . F ield wir ing s ho uld be run th roug h th e
7
/8-in. knockout provided in the basepan near the return air
opening.
VII. STEP 7 — MAKE OUTDOOR-AIR INLET ADJUSTMENTS
A. Manual Outdoor-Air Damper
All units (except those equipped with a factory-installed
economizer) have a manual outdoor-air damper to provide
ventilation air. Damper can be preset to admit up to 25% outdoor air into return-air compartment. To adjust, loosen
securing screws and move dampe r to desired setting. Then
retighten screws to secure damper (Fig. 14).
B. Optional EconoMi$er
EconoMi$er Motor Control Module (Fig. 15-17)
Set the ECONSP dial to the ‘‘D’’ setting (Fig. 16). The control
module is located on the EconoMi$er motor. See Fig. 15 and
17.
Damper Vent Position Setting
1. Set fan switch at ON position (continuous fan operation) and close night switch if used.
2. Set system selector switch to OFF position.
3. Turn Min Pos (%) dial slowly until dampers assume
desired vent position. Do not manually operate
EconoMi$er motor since damage to motor will result.
Fig. 14 — 25% Outdoor-Air Section Details
6T3 4T2 2T1 LOAD
5L3 3L2 1L1 LINE
NOTE:
The disconnect takes the place of TB-1 as shown on the unit
wiring diagram label and the component arrangement label.
Fig. 13 — Optional Non-Fused Disconnect Wiring
Fig. 15 — EconoMi$er Damper Assembly
— End View
—11—
Page 12

Table 4 — Heat Anticipator Settings
UNIT
551A
155-240
*Heater kW is based on heater voltage of 208 v, 240 v, or 480 v.
UNIT
VO LTAG ES
208/230-3-60
460-3-60
kW* STAGE 1 STAGE 2
14/19 .40 —
26/34 .40 .66
42/56 .66 .40
56/75 .66 .66
32 .40 .40
55 .40 .66
80 .66 .66
Fig. 16 — EconoMi$er Control Module
Adjustment Potentiometers
CONTROL MODULE ACTUATOR
Fig. 17 — EconoMi$er Control Module Location
VIII. STEP 8 — INSTALL OUTDOOR-AIR HOOD
The same type of factory-installed hood is used on units with
25% air ventilation and units with an EconoMi$er.
NOTE: The hood top panel, upper and lower filter retainers,
hood drain pan, baffle (180-240), and filter support bracket
are secured opposite the condenser end of the unit. The
screens, hood side panels, remaining section of filter support
bracket, seal strip, and a ll other har dware are in a package
located inside the return-air filter access panel (Fig. 18).
1. Attach seal strip to upper filter retainer. See Fig. 19.
2. Assemble hood top panel and side panels, upper filter
retainer, and hood drain pan (Fig. 20).
3. Secure lower filter retainer and long section of filter
support bracket to unit. See Fig. 20. Leave screws
loose on size 180 and 240 units.
4. Slide baffle (size 180 and 240 units) behind lower filter retainer and tighten screws.
5. Loosen sheet metal screws for base unit top panel
located above outdoo r-air inlet opening, and rem ove
screws for hood side panels located on the sides of the
outdoor-air inlet opening.
6. Match notches in hood top panel to unit top panel
screws. Insert hood flange between unit top panel
flange and unit. Tighten screws.
7. Hold hood side panel flanges flat against unit, and
install screws removed in Step 5.
8. Insert outdo o r-air inlet screens and spacer in c ha nne l
created by lower filter retainer and filter support
bracket.
9. Attach remaining short section of filter support
bracket.
A. Outdoor Air Enthalpy Sensor Installation
Perform the following procedure to install the outdoor air
enthalpy sensor (part no. CROUTENT001A00).
1. Remove the outdoor air temperature sensor cover.
See Fig. 21. Save cover and screws.
2. Disconnect the wiring from the installed outdoor air
temperature sensor. See Fig. 22.
3. Use a
1
/4-in. nut driver to remove the 2 screws securing the outdoor air temperature sensor to the sheet
metal.
4. Mount the outdoor air enthalpy sensor in the outdoor
air temperature sensor location using the screws
removed in Step 3.
5. Connect the outdoor air enthalpy sensor wiring harness to the EconoMi$er control module and sensor.
6. Re-install sensor cover saved from Step 1.
B. Return Air Temperature Sensor or Return Air Enthalpy
Sensor Installation
Perform the following procedure to install the return air
temperature sensor (part no. CRRETTMP001A00) or return
air enthalpy sensor (part no. CRRETENT001A00).
1. Attach the sensor to the mounting bracket using
2 self-tapping
1
/2-in. screws provi ded .
2. Mount the bracket to the inside of the return air
1
opening flange using a
/4-in. nut driver and 2 no.
6 sheet metal screws.
NOTE: The sensor must be mounted in an upright position.
3. Feed the sensor wiring through the bushing in
EconoMi$er t o sec ur e wires.
4. Route sensor wiring harness from sensor to
EconoMi$er control module. Secure wiring harness to
the original har ness using tie wraps.
5. Wire the sensor to the EconoMi$er control module.
See Fig. 23 and 24.
—12—
Fig. 18 — Outdoor-Air Hood Component Location
Page 13

SENSOR
COVER
OUTSIDE AIR SENSOR
MOUNTING
SCREW
MOUNTING SCREW
WIRING
HARNESS
SENSOR
WIRING
CONNECTIONS
Fig. 19 — Seal Strip Location
(Air Hood Cross-Sectional View)
BAFFLE (180 AND 240 ONLY)
LOWER FILTER
RETAINER
FILTER SUPPORT
BRACKET
HOOD SIDE
HOOD TOP
PANEL
HOOD DRAIN PAN
UPPER FILTER RETAINER
NOTE:
The outdoor-air hood comes with a baffle which is used on
180 and 240 units only; discard baffle for 155 units.
PANELS (2)
BAFFLE
(180 AND
240 ONLY)
LOWER
FILTER
RETAINER
FILTER SUPPORT
BRACKET
Fig. 20 — Outdoor-Air Hood Details
C. Commissioning
The EconoMi$er saves energy when it uses outdoor air to
provide free cooling instead of mechanical air conditioning.
The EconoMi$er switchov er strategy determines if the outdoor air is suitable for free cooling. The EconoMi$er chooses
the switchover strategy with the most energy savings, provided that the required sensors are connected and functioning normally.
IMPORTANT: If a sensor stops functioning normally
(becomes unreliable), the EconoMi$er switches to the next
best strategy.
Fig. 21 — Outdoor-Air Sensor Location
Fig. 22 — Outdoor-Air Sensor Details
Refer to Table 5 to determine the sensors required for each
strategy.
Differential Enthalpy Switchover Strategy
The differential enthalpy switchover strategy must be
selected manually, if required. To enable, press and hold the
CONFIG button for 30 seconds, then release. The LED will
flash twice to indicate the change of configuration.
To return to single enthalpy mode, press and hold the CONFIG button for 30 seconds. The LED will flash once to indicate the change of configuration.
D. Discharge Air Thermistor (DAT)
The discharge air thermistor is factory-mounted on the
supply-fan housing in the fan section of the unit. The DAT is
factory-wired to the EconoMi$er Control Module.
E. CO
Control Setup
2
If a CO
sensor is not bei ng us ed, proc ee d to the n ext s ectio n.
2
If a CO2 sensor is being used, perform the following:
1. Determin e the v alue at which y ou w ant the minimu m
position of the dam pers to begin opening to allow a
greater amount of outdoor air to enter. The range is
800 to 1,400 ppm.
2. Locate the CO
SP (PPM) potentiometer and adjust
2
to the desired set point. See Fig. 16.
—13—
Page 14

F. Mechanical Cooling Lockout
Determine the outdoor-air temperature at which you want
the mechanical cooling (compressors) to be disabled. Locate
the mechanical cooling lockout (MECH CLG LOCKOUT)
potentiometer. To disable this feature, turn the potentiometer counterclockwise (CCW) to the OFF position. Otherwise,
set the value between 10 and 60 F. Mechanical cooling will
not operate when the ou tdoor air temperat ure is below this
value. See Fig. 16.
Table 5 — EconoMi$er Switchover Control Strategy
ECONOMI$ER SWITCHOVER STRATEGY
Dry Bulb
Single Enthalpy
Differential Temperature
Differential Enthalpy*
*Must be selected manually.
Outdoor Air Temperature Outdoor Air Enthalpy Return Air Temperature Return Air Enthalpy
X
XX
Table 6 — Changeover Set Points
SETTINGS A B C D
Dry Bulb (°F)
Single Enthalpy* (Btu/lb)
Differential Temperature*
(°F, Not Adjustable)
Differential Enthalpy*
(Btu/lb, Not Adjustable)
*Field-installed accessory.
73 69 66 63
27 25 24 22
2222
1111
G. Dry Bulb Changeover Set Up
Determine the dry bulb changeover set poin t from Table 6.
The settings are A, B, C and D. Locate the ECON SP potentiometer and set the dry bulb changeover set point. See
Fig. 16. When the OAT is above this set point, the damper is
limited to minimum position setting.
If a potentiometer fails, its setting will default to the values
in Table 7.
SENSORS REQUIRED
X
XX
Table 7 — Default Potentiometer Settings
POTENTIOMETER DEFAULT SETTING
CO2 SP (PPM)
MECH CLG LOCKOUT
ECON SP
MIN POS (%)
1,000
50 F
D
20
COM —
DAT —
DM —
GND —
OAH —
OAT —
POT —
RAH —
RAT —
REM —
LEGEND
Common
Discharge Air Thermistor
Damper Motor
Ground
Outdoor-Air Enthalpy Sensor
Outdoor-Air Temperature Sensor
Potentiometer
Return-Air Enthalpy Sensor
Return-Air Temperature Sensor
Remote
*OAT sensor shipped with economizer option. OAH, RAT, RAH and CO
Fig. 23 — Typical EconoMi$er Wiring
are field-installed accessories.
2
—14—
Page 15

H. Ventilation Air (Minimum Position Set Up)
If ventilatio n a i r is n ot r e qui re d, s ki p th is s ect io n. I f ven ti la tion air is requir ed, perform the following:
1. The indoor fan must be on to set the ventilation air.
Either put the thermostat in the continuous fan mode
or jumper the R and G te rminals at the ro oftop unit
connection board.
2. Locate the minimum position (MIN POS) potentiometer. Turn the potentiometer full CCW to fully close
the outdoor air dampers. Turn the potentiometer
gradually clockwise (CW) to the desired position. See
Fig. 16.
3. Replace the filter access panel. See Fig. 18. Ensure
the filter access panel is securely engaged.
4. Calculate the minimum airflow across the
EconoMi$er.
a. Calculate % of outside air using the following
formula.
% Outdoor air through EconoMi$er
% Outdoor
air
Mixture Temp – Return Air Temp
=
Outdoor Temp – Return Air Temp
b. Multiply total CFM by percentage outdoor air,
this gives outdoor air volume in CFM.
WARNING:
Personal Injury Hazard.
Avoid possible
injury by keeping fingers away from damper blades.
IX. STEP 9 — INSTALL ALL ACCESSORIES
After all the factory-installed options have been adjusted,
install all field-instal led accessories. Refer to the accessory
installation instructions included with each accessory.
A. Motormaster® I Control Installation (551A155 and 180
Only)
Install Field-Fabricated Wind Baffles
Wind baffles must be fi eld-fabricat ed for all units to en sure
proper cooling cycle oper ation at low ambient temperatu res.
See Fig. 25 for baffle de tails. Use 20-gage, galvani zed sheet
metal, or similar corrosion-resistant metal for baffles. Use
field-supplied screws to attach baffles to unit. Screws should
1
be
/4-in. diameter and 5/8-in. long. Dri ll requ ired screw ho les
for mounting baffles.
CAUTION:
To avoid damage to the refrigerant coils
and electrical components, use recommended screw sizes
only. Use care when drilling holes.
Outdoor Air Enthalpy
CROUTENT001A00
OAT
COM
OAH
+15V
RAT
COM
RAH
+15V
CO
(+)
2
CO
2
COM
DAT
COM
REM
POT
COM
LED
COM
Tan
Violet
White
Red
Tan
Violet
White
Red
T
Violet
O
C
U
O
T
T
M
PW
C
O
M
Remote
Minimum Position
1k ohm Potentiometer
T
PW
O
U
TT
Unoccupied Control
(Part number on the control
must be AD-DME1701-1
or AD-DME1711-1.)
Unoccupied
Contact
24 VAC must be present
on BI for the system to be
Violet
470 ohm
5watt
Resistor
unoccupied.
Return Air Enthalpy
CRRETENT001A00
CO2 Sensors:
CRCDXSEN004A00
NOT
USED
2
1
2to10VDCat
0 to 2000 ppm
Line
20 VA
24 VAC
Voltage
20 mA LED
Remote
LED
-
Field-supplied Wiring Wiring Included
Fig. 24 — Typical EconoMi$er Sensor Wiring
—15—
Page 16

Install Motormaster® I Controls
Only one Motormaster I control is required per unit. The
Motormaster I control must be used in c onjunction with the
Accessory 0° F Low Ambient Kit (purchased separately). The
Motormaster I device contro ls outdoor fan no. 1 while outdoor fans no. 2 and 3 are sequenced off by the Accessory 0° F
Low Ambient Kit.
Accessory 0° F Low Ambient Kit — Install the Accessory 0° F
Low Ambient Kit per instruction supplied with accessory.
Sensor Assembly — Install the sensor assembly in the location shown in Fig. 26.
Motor Mount — To ensure proper fan height, replace the
existing motor mount with the new motor m ount provided
with accessory.
Transformer (460-v Units Only) — On 460-volt units a transformer is required. The transformer is provided with the
accessory and must be field-installed.
Motormaster I Control — Recommended mounting location
is on the inside of the panel to the left of the control box. The
control should be mounted on the inside of the panel, vertically, with leads prot ruding from bottom of extrusion.
B. Motormaster III Control Installation (551A240 Only)
Install Field-Fabricated Wind Baffles
Wind baffles must be field-fabricated for all units to ensure
proper cooling cycle operation at low ambient temperatures.
See Fig. 25 for ba ffle detai ls. Use 20-gage, g alvanized s heet
metal, or similar corrosion-resistant metal for baffles. Use
field-supplied screws to attach baffles to unit. Screws should
1
be
/4-in. diameter and 5/8-in. long. Drill r equir ed scre w holes
for mounting baffles.
NOTE:
Dimensions in ( ) are in mm.
Fig. 25 — Wind Baffle Details
CAUTION:
To avoid damage to the refrigerant coils
and electrical components, use recommended screw sizes
only. Us e care when drilling holes.
Replace Outdoor Motor
Replace outdoor fan motor no. 1 with motor included in
accessory kit. Existing motor is not Motormaster® III
compatible.
Install Motormaster III Controls
Only one Motormaster III control is required per unit.
Sensor — Install the se nsor for thermistor input con trol in
the location shown in Fig. 26. Connect sensor leads to the
purple and grey c ontrol si gnal leads o n the Motor master III
control.
Signal Selection Switch — Remove the cover of the M otormaster III control. Set t he switch to accept the thermistor
sensor input signal. Set the frequency to match the unit
power supply (60 Hz).
Motormaster III Control — Recommended mounting location
is beneath the control box, mounted to the partition that separates the control box section from the indoor section.
NOTE: If unit power is supplied through the roof curb and
basepan of the unit, mount the Motormaster III contro l on
the corner post adjacent to the conduit running from the
basepan to the bottom of the control box.
X. STEP 10 — INSTALL HUMIDISTAT FOR OPTIONAL PERFECT HUMIDITY™ DEHUMIDIFICATION PACKAGE
Perfect Humidity dehumidification package operation can be
controlled by field installation of a Bryant-approved humidistat. To install the humidistat perform the following
procedure:
1. Locate humidistat on a solid interior wall in the conditioned space. Location should be a well ventilated
area to sense average humidity.
2. Route thermostat cable or equivalent single leads of
colored wire from humidistat termi nals through conduit in unit to the low voltage connection on the
2-pole ter minal strip (TB3 ) as shown in Fig. 27 and
Fig. 28.
—16—
Page 17

MOTORMASTER
SENSOR
NOTES:
1. All sensors are located on
the eighth hairpin up from
the bottom.
2. Field-installed tubing insulation is required to be
installed over the TXV bulb
and capillary tube for
proper operation at low
ambients. Tubing insulation is only required on the
portion of suction line
located between indoor
and outdoor section.
LOCATION
HAIRPIN END
Fig. 26 — Motormaster® I and Motormaster III
Sensor Locations
Fig. 28 — Typical Perfect Humidity Dehumidification
Package Control Box
CB —
LLSV —
LPS —
TB —
TRAN —
LEGEND
Circuit Breaker
Liquid Line Solenoid Valve
Low-Pressure Switch
Terminal Block
Transformer
Fig. 27 — Typical Perfect Humidify™ Dehumidification Package
Humidistat Wiring Schematic (460V Unit Shown)
—17—
Page 18

START-UP
Use the following information and Start-Up Checklist on
page CL-1 to check out unit PRIOR to start-up.
I. UNIT PREPARATION
Check that unit has been installed in accordance with these
installation instructions and all applicable codes.
II. COMPRESSOR MOUNTING
Compressors are internally spring mounted. Do not loosen or
remove compressor holddown bolts.
III. REFRIGERANT SERVICE PORTS
Each refrigerant system has a total of 3 Schrader-type service
gage ports. One port is located on the suction line, one on the
compressor discharge line, and one on the liquid line. In addition Schrader-type valves are located underneath the lowpressure switches. Be sure that caps on the ports are tight.
IV. COMPRESSOR ROTATION
It is important to be c ertain the c ompressors are rotating in
the proper direction. To determine whether or n ot compressors are rotating in the proper direction:
1. Connect ser vice gage s to suctio n and dis charge pres sure fittings.
2. Energize the compressor.
3. The suction pressu re should drop and th e discharge
pressure should rise, as is normal on any start-up.
If the suction pressure does not drop and the discharge pressure does not rise to normal levels:
1. Note that the evaporator fan is probably also rotating
in the wrong direction.
2. Turn off power to the unit.
3. Reverse any two of the incoming power leads.
4. Turn on power to the compressor.
The suction and discharge pressure levels should now move
to their normal start-up levels.
NOTE: When compressors are rotati ng in the wrong direction, the unit will have increased noise levels and will not
provide heating and cooling.
After a few minutes o f re vers e o per ation , th e s cro ll co m pressor internal overload protection will open, which will activate the unit’s lockout and requires a manual reset. Reset is
accomplished by turning the thermostat on and of f.
V. INTERNAL WIRING
Check all electrical connections in unit control boxes; tighten
as required.
VI. CRANKCASE HEATERS
Heaters are energized as long as there is power to unit and
compressor is not operating.
IMPORTANT: Unit power must be on for 24 hours prior to
start-up. Otherwise, damage to compressor may result.
VII. EVAPORATOR FAN
Fan belt and variable pulleys are factory installed. Remove
tape from the fan pulley. See Table 8 for Air Quantity Limits .
See Tables 9-12 for Fan Performance data. Be sure that fans
rotate in the proper direction. See Tables 13 and 14 for
Static Pressure information for accessories and options. See
Table 15 for fan rpm at various fan motor pulley settings.
See Table 16 for Evaporator-Fan Motor Specifications. To
alter fan performance, see Evaporator-Fan Performance
Adjustment section, page 26.
Table 8 — Air Quantity Limits
UNIT
551A
155
180
240
MINIMUM CFM MAXIMUM CFM
3600 6,000
4500 7,500
6000 10,000
VIII. CONDENSER FANS AND MOTORS
Condenser fans and motors are factory set. Refer to
Condenser-Fan Adjustment section (page 28) as required. Be
sure that fans rotate in the correct direction.
IX. RETURN-AIR FILTERS
Check that correct filters are installed in filter tracks. See
Table 1. Do not operate unit without return-air filters.
X. OUTDOOR-AIR INLET SCREENS
Outdoor-air inlet screen s must be in place bef ore operating
unit.
XI. ACCESSORY ECONOMI$ER ADJUSTMENT
Remove filter access panel. Check that outdoor-air damper
blades are closed and return-air damper blades are open.
EconoMi$er operation and adjustment is described in Base
Unit Operation and EconoMi$er Adjustment sections (this
page and page 28), respectively.
XII. BASE UNIT OPERATION
A. Cooling, Units Without EconoMi$er
When thermos tat calls for cool ing, terminals G and Y1 are
energized. The indoor (evaporator) fan contactor (IFC),
and compressor contactor no. 1 (C1) are energized and
evaporator-fan motor, compressor no. 1 and condenser fans
start. The condenser-fan motors run continuously while unit
is cooling. If the thermostat calls for a second stage of cooling
by energizing Y2, compressor contactor no. 2 (C2) is energized and compressor no. 2 starts.
B. Heating, Units Without EconoMi$er (If Accessory or
Optional Heater is Installed)
Upon a call for heating through terminal W1, IFC and
heater contactor no. 1 (HC1) are energized. On units
equipped for 2 stages of heat, when additional heat is
needed, HC2 is energized through W2.
C. Cooling Units With EconoMi$er
When the OAT is above the ECON SP set point and the room
thermostat calls for Stage 1 cooling (R to G + Y1), the indoorfan motors (IFM) i s energized and the Econ oMi$er damper
modulates to minimum position. The compressor contactor
and OFC are energized to start the comp ressor and outdo orfan motor (OFM). After the thermostat is satisfied, the
damper modulates to the fully closed position when the IFM
is deenergized.
When the OAT is below the ECON SP setting and the room
thermostat calls for Stage 1 cooling (R to G + Y1), the
EconoMi$er modulates to the minimum position when the
IFM is energized. The Econ oMi$er provides Sta ge 1 of cooling by modulating the return and outdoor air dampers to
maintain a 55 F supply air set point. If the supply-air temperature (SAT) is greater than 57 F, the Econ oMi$er modulates open, allowing a greater amount of outdoor air to enter
the unit. If the SA T drops bel ow 53 F, the outdoo r air d amp er
modulates closed to reduce the amou nt of outd oor air. When
the SAT is between 53 and 57 F, the EconoMi$er maintains
its position.
—18—
Page 19

If outdoor air alone cannot satisfy the cooling requirements
of the conditione d space, and the OAT is above the MECH
CLG LOCKOUT set point, the EconoMi$er integrates free
cooling with mechanic al coo lin g. This is acco mpl ishe d b y the
strategies below.
NOTE: Compressors have a two-minute Minimum On and
Minimum Off, which are accomplished by the strategies
below.
1. If Y1 is energized, and th e room thermosta t calls for
Y2 (2-stage thermostat), the compressor and OFC are
energized. The position of the EconoMi$er damper is
maintained at its current value.
2. If Y1 is ene rgized for mor e than 2 0 minute s , and Y2 is
not energized (whether or not a 2-stage thermostat is
used), the compressor and OFC are energized. The
position of the EconoMi$er damper is maintained at
its current value.
3. If Y1 is energized, and compressor no. 1 is already
energized (see S tep 2) and the ro om thermosta t calls
for Y2, compressor no. 1 continues to operate. If Y2
remains energized for more than 20 minutes, compressor no. 2 is energized.
NOTE: Compressor no. 2 cannot be energized unless there is
a signal for Y2 from the space thermostat.
4. If compressor no. 2 is energized, and the Y2 signal
from the thermostat is satisfied, compressors 1 and 2
are deenergized. Re-asserting Y2 will start compressor no. 1 and (after a 20-minute interstage delay)
compressor no. 2.
5. If compresso r no. 1 is energized and the thermostat is
satisfied, compressor no. 1, the OFM, and IFM are
deenergized and the EconoMi$er modulates closed.
When the OAT is below the MECH CLG LOCKOUT set
point, the compressors re main off.
D. Freeze Protection Thermostat(s)
A freeze protection thermostat (FPT) is located on the top
and bottom of the evaporator coil. It detects frost build-up
and turns off the compress or, allowi ng the coil to clear. Once
frost has melted, the compressor can be reenergized by resetting the compressor lockout.
E. Heating, Units With EconoMi$er (If Accessory or
Optional Heater is Installed)
When the room the rmostat calls for heat, the heat ing controls are energized as described in the Heating, Units Without EconoMi$er section. The IFM is energized and the
EconoMi$er damper modulates to the minimum position.
When the thermostat is satisfied, the damper modulates
closed.
F. Units With Perfect Humidity™ Dehumidification Package
When thermostat calls for cooling, terminals G and Y1 and/
or Y2 and the compressor contactor C1 and/or C2 are energized. The indoor (evaporator) fan motor (IFM), compressors,
and outdoor (condenser) fan motors (OFM) start. The OFMs
run continuously while the unit is in cooling. As shipped
from the factory, both Perfect Humidity dehumidification circuits are always energized.
If Perfect Humidity circuit modulation is desired, a fieldinstalled, w all- mou nted hu midi stat is re quired . If th e Perfect
Humidity humidistat is installed and calls for the Perfect
Humidity subcooler coil to operate, the humidistat internal
switch closes. This energizes the 3-way liquid line solenoid
valve coils (LLSV1 for circuit 1 and LLSV2 for circuit 2) of
the Perfect Humidity circuits, forcing t he warm liquid refrigerant of the liquid line to enter the subcooler coils. See
Fig. 29.
As the warm liquid passes through the subcooler coils, it is
exposed to the cold supply airf low comi ng off the e vaporato r
coils and the liquid is further cooled to a temperature
approaching the evaporator coil leaving-air temperature.
The state of the refrigerant leaving the subcooler coils is a
highly subcooled liquid refrigerant. The liquid then enters a
thermostatic expansion valve (TXV) where the liquid is
dropped to the evaporator pressure. The TXVs can throttle
the pressure drop of the liquid refrigerant and maintain
proper conditions at the compressor suction valves over a
wide range of operating conditions. The liquid proceeds to
the evaporator coils at a temperature lower than normal
cooling operati on. This low er temperatu re is what i ncreases
the latent and sensible capacity of the evaporator coils.
The 2-phase refrige rant pass es th roug h the e vapo rator s an d
is changed into a vapor. The air passing over the evaporator
coils will become col der than during normal operation as a
result of the colde r refrigeran t temperatures. However, as it
passes over the subcooler coils, the air will be warmed,
decreasing the sensible capacity and reducing the sensible
heat of the roof- top unit.
As the refrigerant leaves the evaporator, the refrigerant
passes a subcooler control low-pressure switch (S-LPS1 for
circuit 1 or S-LPS2 for circuit 2) in the suction line. This lowpressure switch will deactivate the Perfect Humidity package when the suction pressure reaches 60 psig. The subcooler control low-press ure switch is an added safety device
to protect against evaporator coil freeze-up during low ambient operation. T he subcooler control low-pressure switch will
only deactivate the 3-way liquid line solenoid valve in the
Perfect Humidity circuit. The compressors will continue to
run as long as th ere is a call for cooling, regardles s of the
position of the subcooler control low-pressure switch. The
3-way solenoid valve and th e Perfect Humidity package will
be reactivated o nly when the call for co oling has been satisfied, the subcooler control low-pressure switch has closed
above 80 psig, and a new call for cooling exists. The crankcase heaters on the scroll compressors provide additional
protection for the compressors due to the additional refrigerant charge in the subcooler.
When the humidistat is satisfied, the humidistat internal
switch opens, cutting power to and deenergizing the LLSVs.
The refrigerant is routed back through the evap orators and
the subcooler coils are removed from the refrigerant loops.
When the thermostat is satisfied, C1 and C2 are deenergized
and the comp ressors, IFM, a nd O FMs shut off. I f t he thermostat fan selector switch is in the ON position, the IFM will
run continuously.
—19—
Page 20

Table 9 — Fan Performance — 551A155 (With Standard Indoor Fan Motor)
551A155 (12 TONS)*
Available External Static Pressure (in. wg)
Cfm
Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp
3750
4000
4250
4500
4750
5000
5250
5500
5750
6000
6250
551A155 (12 TONS) (cont)*
Cfm
3750
4000
4250
4500
4750
5000
5250
5500
5750
6000
6250
Bhp —
FIOP —
Watts —
*Standard low-medium static drive range is 834 to 1064 rpm. Alternate
high-static drive range is 1161 to 1426. Other rpms require a fieldsupplied drive.
NOTES:
1. Maximum continuous bhp for the standard motor is 3.13. The max-
753 915 1.05 786 972 1.12 892 1170 1.35 991 1378 1.58 1084 1595 1.83
747 977 1.12 810 1090 1.25 911 1292 1.49 1007 1503 1.73 1097 1723 1.98
741 1041 1.20 835 1220 1.40 932 1426 1.64 1024 1640 1.89 1111 1863 2.14
761 1158 1.33 861 1360 1.56 954 1570 1.81 1043 1788 2.06 1127 2014 2.32
792 1305 1.50 887 1512 1.74 977 1726 1.99 1063 1948 2.24 1145 2177 2.50
823 1464 1.68 915 1676 1.93 1002 1894 2.18 1084 2120 2.44 1164 2352 2.70
855 1635 1.88 943 1852 2.13 1027 2075 2.39 1107 2304 2.65 1184 2539 2.92
887 1819 2.09 972 2041 2.35 1053 2268 2.61 1130 2501 2.88 ———
920 2016 2.32 1002 2242 2.58 1079 2473 2.84 ——————
953 2226 2.56 1031 2457 2.83 1107 2692 3.10 ——————
986 2449 2.82 1062 2685 3.09 —————————
Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp
1172 1822 2.10 1256 2057 2.37 1337 2299 2.64 1414 2549 2.93 ———
1182 1952 2.24 1264 2188 2.52 1343 2432 2.80 1418 2683 3.09 ———
1194 2093 2.41 1274 2332 2.68 1351 2577 2.96 ——————
1208 2247 2.58 1286 2487 2.86 —————————
1223 2412 2.77 1299 2655 3.05 —————————
1240 2590 2.98 ————————————
— — —— — —— — —— — —— — —
— — —— — —— — —— — —— — —
— — —— — —— — —— — —— — —
— — —— — —— — —— — —— — —
— — —— — —— — —— — —— — —
Brake Horsepower
Factory-Installed Option
Input Watts to Motor
imum continuous watts is 2700. Do not adjust motor rpm such that
motor maximum bhp and/or watts is exceeded at the maximum
operating cfm.
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
Available External Static Pressure (in. wg)
1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0
LEGEND
2. Static pressure losses (i.e., EconoMi$er) must be added to external static pressure before entering Fan Performance table.
3. Interpolation is permissible. Do not extrapolate.
4. Fan performance is based on wet coils, clean filters, and
casing losses. See Table 13 for accessory/FIOP static pressure
information.
5. Extensive motor and drive testing on these units ensures that the
full bhp and watts range of the motor can be utilized with confidence. Using your fan motors up to the watts or bhp rating shown
will not result in nuisance tripping or premature motor failure. Unit
warranty will not be affected.
6. Use of a field-supplied motor may affect wiring size. Contact your
Bryant representative for details.
—20—
Page 21

551A155 (12 TONS)*
Cfm
Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp
3750
4000
4250
4500
4750
5000
5250
5500
5750
6000
6250
551A155 (12 TONS) (cont)*
Cfm
3750
4000
4250
4500
4750
5000
5250
5500
5750
6000
6250
753 942 1.08 786 998 1.15 892 1192 1.37 991 1395 1.60 1084 1606 1.85
747 1006 1.16 810 1118 1.29 911 1315 1.51 1007 1520 1.75 1097 1733 1.99
741 1073 1.23 835 1248 1.44 932 1448 1.67 1024 1657 1.91 1111 1872 2.15
761 1191 1.37 861 1389 1.60 954 1593 1.83 1043 1804 2.07 1127 2022 2.33
792 1339 1.54 887 1541 1.77 977 1749 2.01 1063 1963 2.26 1145 2183 2.51
823 1499 1.72 915 1705 1.96 1002 1916 2.20 1084 2133 2.45 1164 2356 2.71
855 1671 1.92 943 1880 2.16 1027 2095 2.41 1107 2316 2.66 1184 2541 2.92
887 1854 2.13 972 2068 2.38 1053 2286 2.63 1130 2510 2.89 1205 2739 3.15
920 2050 2.36 1002 2268 2.61 1079 2490 2.86 1154 2717 3.12 1227 2948 3.39
953 2258 2.60 1031 2480 2.85 1107 2706 3.11 1179 2936 3.38 1249 3171 3.65
986 2480 2.85 1062 2706 3.11 1135 2935 3.38 1205 3169 3.64 1273 3406 3.92
Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp
1172 1825 2.10 1256 2051 2.36 1337 2284 2.63 1414 2523 2.90 1488 2768 3.18
1182 1954 2.25 1264 2181 2.51 1343 2415 2.78 1418 2655 3.05 1491 2901 3.34
1194 2094 2.41 1274 2323 2.67 1351 2558 2.94 1424 2799 3.22 1496 3045 3.50
1208 2246 2.58 1286 2476 2.85 1360 2713 3.12 1432 2955 3.40 1502 3202 3.68
1223 2410 2.77 1299 2642 3.04 1371 2880 3.31 1442 3123 3.59 1510 3372 3.88
1240 2585 2.97 1313 2819 3.24 1384 3059 3.52 1453 3304 3.80 1520 3554 4.09
1258 2773 3.19 1329 3009 3.46 1398 3250 3.74 1465 3497 4.02 1530 3748 4.31
1276 2972 3.42 1346 3211 3.69 1413 3455 3.97 1479 3703 4.26 ———
1296 3185 3.66 1364 3426 3.94 1430 3671 4.22 ——————
1317 3410 3.92 1383 3653 4.20 —————————
1339 3648 4.20 ————————————
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0
Table
10 — Fan Performance — 551A155 (Wi
Available External Static Pressure (in. wg)
Available External Static Pressure (in. wg)
th Optional Indoor Fan Motor)
LEGEND
Bhp —
FIOP —
Watts —
*Standard low-medium static drive range is 834 to 1064 rpm. Alternate
high-static drive range is 1161 to 1426. Other rpms require a fieldsupplied drive.
NOTES:
1. Maximum continuous bhp for the optional motor is 4.38. The maxi-
Brake Horsepower
Factory-Installed Option
Input Watts to Motor
mum continuous watts is 3775. Do not adjust motor rpm such that
motor maximum bhp and/or watts is exceeded at the maximum
operating cfm.
2. Static pressure losses (i.e., EconoMi$er) must be added to external static pressure before entering Fan Performance table.
3. Interpolation is permissible. Do not extrapolate.
4. Fan performance is based on wet coils, clean filters, and
casing losses. See Table 13 for accessory/FIOP static pressure
information.
5. Extensive motor and drive testing on these units ensures that the
full bhp and watts range of the motor can be utilized with confidence. Using your fan motors up to the watts or bhp rating shown
will not result in nuisance tripping or premature motor failure. Unit
warranty will not be affected.
6. Use of a field-supplied motor may affect wiring size. Contact your
Bryant representative for details.
—21—
Page 22

551A180 (15 TONS)*
Cfm
Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp
4500
4800
5100
5700
6000
6300
6600
6900
7200
7500
551A180 (15 TONS) (cont)*
Cfm
4500
4800
5100
5700
6000
6300
6600
6900
7200
7500
753 1307 1.53 753 1307 1.53 784 1397 1.64 859 1635 1.92 928 1880 2.20
747 1384 1.62 747 1384 1.62 806 1563 1.83 878 1808 2.12 946 2060 2.42
741 1465 1.72 752 1500 1.76 828 1745 2.05 898 1996 2.34 964 2255 2.65
735 1659 1.95 805 1895 2.22 876 2156 2.53 942 2423 2.84 1004 2696 3.16
759 1854 2.18 832 2118 2.48 901 2388 2.80 965 2663 3.12 1026 2943 3.45
790 2088 2.45 860 2360 2.77 926 2638 3.09 988 2920 3.43 1048 3208 3.76
821 2340 2.74 888 2621 3.07 952 2906 3.41 1013 3196 3.75 1070 3491 4.10
852 2611 3.06 917 2900 3.40 979 3194 3.75 1038 3492 4.10 1094 3794 4.45
883 2903 3.40 946 3200 3.75 1006 3501 4.11 1063 3807 4.47 1118 4117 4.83
914 3215 3.77 975 3521 4.13 1033 3830 4.49 1089 4143 4.86 1142 4461 5.23
Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp
993 2133 2.50 1055 2394 2.81 1114 2662 3.12 1170 2938 3.45 1224 3220 3.78
1009 2319 2.72 1070 2585 3.03 1127 2859 3.35 1183 3139 3.68 1236 3427 4.02
1026 2521 2.96 1086 2794 3.28 1142 3073 3.60 1196 3359 3.94 1248 3650 4.28
1064 2975 3.49 1120 3260 3.82 1174 3551 4.17 1226 3848 4.51 1277 4151 4.87
1083 3228 3.79 1139 3520 4.13 1192 3817 4.48 1243 4119 4.83 1292 4427 5.19
1104 3501 4.11 1158 3799 4.46 1210 4102 4.81 1260 4410 5.17 1309 4724 5.54
1125 3791 4.45 1178 4095 4.80 1229 4405 5.17 1278 4720 5.54 1326 5039 5.91
1147 4101 4.81 1199 4412 5.18 1249 4728 5.55 1297 5050 5.92 ———
1170 4431 5.20 1221 4749 5.57 1270 5072 5.95 ——————
1193 4781 5.61 1243 5107 5.99 —————————
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0
Table 11 — Fan Perfor
Available External Static Pressure (in. wg)
Available External Static Pressure (in. wg)
ance
m
— 551A180
551A180 (15 TONS) (cont)*
Available External Static Pressure (in. wg)
Cfm
Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp
4500
4800
5100
5700
6000
6300
6600
6900
7200
7500
Bhp —
FIOP —
Watts —
*Standard low-medium static drive range is 873 to 1021 rpm. Alternate
high-static drive range is 1025 to 1200. Other rpms require a fieldsupplied drive.
NOTES:
1. Maximum continuous bhp for the standard motor is 6.13. The max-
1276 3509 4.12 1326 3805 4.46 1375 4107 4.82 1421 4414 5.18 1467 4728 5.55
1287 3721 4.36 1336 4020 4.72 1384 4326 5.07 1430 4638 5.44 1475 4955 5.81
1299 3949 4.63 1347 4253 4.99 1395 4563 5.35 1440 4879 5.72 ———
1325 4458 5.23 1373 4772 5.60 1418 5091 5.97 ——————
1340 4741 5.56 1387 5060 5.93 —————————
1356 5043 5.91 ————————————
— — —— — —— — —— — —— — —
— — —— — —— — —— — —— — —
— — —— — —— — —— — —— — —
— — —— — —— — —— — —— — —
Brake Horsepower
Factory-Installed Option
Input Watts to Motor
imum continuous watts is 5180. Do not adjust motor rpm such that
motor maximum bhp and/or watts is exceeded at the maximum
operating cfm.
2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3.0
LEGEND
2. Static pressure losses (i.e., EconoMi$er) must be added to external static pressure before entering Fan Performance table.
3. Interpolation is permissible. Do not extrapolate.
4. Fan performance is based on wet coils, clean filters, and casing
losses. See Table 13 for accessory/FIOP static pressure
information.
5. Extensive motor and drive testing on these units ensures that the
full bhp and watts range of the motor can be utilized with confidence. Using your fan motors up to the watts or bhp rating shown
will not result in nuisance tripping or premature motor failure. Unit
warranty will not be affected.
6. Use of a field-supplied motor may affect wiring size. Contact your
Bryant representative for details.
—22—
Page 23

Table 12 —
551A240 (20 TONS)*
Cfm
Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp
6,000
6,500
7,000
7,500
8,000
8,500
9,000
9,500
10,000
551A240 (20 TONS) (cont)*
Cfm
6,000
6,500
7,000
7,500
8,000
8,500
9,000
9,500
10,000
551A240 (20 TONS) (cont)*
Cfm
6,000
6,500
7,000
7,500
8,000
8,500
9,000
9,500
10,000
Bhp —
FIOP —
Watts —
*Standard low-medium static drive range is 1002 to 1151 rpm. Alternate
high-static drive range is 1193 to 1369. Other rpms require a fieldsupplied drive.
NOTES:
1. Maximum continuous bhp for the standard motor is 9.47 (for 208-v
units) and 10.33 (for 230 and 460-v units). The maximum continuous watts is 7915 (for 208-v units) and 8640 (for 230 and 460-v
units). Do not adjust motor rpm such that motor maximum bhp
and/or watts is exceeded at the maximum operating cfm.
753 2385 2.83 816 2579 3.06 884 2807 3.33 949 3040 3.61 1010 3277 3.89
793 2738 3.25 861 2959 3.51 925 3186 3.78 987 3418 4.05 1045 3653 4.33
844 3151 3.74 908 3372 4.00 968 3598 4.27 1026 3828 4.54 1082 4062 4.82
895 3596 4.27 955 3817 4.53 1013 4042 4.80 1068 4271 5.07 1121 4504 5.34
947 4073 4.83 1004 4294 5.09 1058 4518 5.36 1111 4747 5.63 1162 4978 5.91
999 4583 5.44 1053 4803 5.70 1105 5027 5.96 1155 5255 6.23 1204 5485 6.51
1052 5125 6.08 1103 5345 6.34 1152 5569 6.61 1200 5796 6.88 1247 6025 7.15
1105 5699 6.76 1153 5919 7.02 1200 6142 7.29 1246 6369 7.56 1291 6598 7.83
1158 6306 7.48 1204 6526 7.74 1249 6750 8.01 1293 6975 8.27 1336 7203 8.55
Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp
1069 3517 4.17 1125 3761 4.46 1180 4006 4.75 1232 4255 5.05 1283 4506 5.35
1102 3891 4.62 1156 4132 4.90 1208 4377 5.19 1259 4623 5.48 1308 4871 5.78
1136 4299 5.10 1188 4538 5.38 1239 4780 5.67 1288 5025 5.96 1335 5271 6.25
1173 4739 5.62 1223 4977 5.90 1272 5217 6.19 1319 5460 6.48 1365 5705 6.77
1211 5212 6.18 1259 5449 6.46 1306 5688 6.75 1352 5929 7.03 1396 6172 7.32
1251 5718 6.78 1297 5954 7.06 1342 6192 7.35 1386 6431 7.63 1429 6673 7.92
1292 6257 7.42 1337 6492 7.70 1380 6729 7.98 1423 6967 8.27 1464 7207 8.55
1335 6830 8.10 1377 7063 8.38 1419 7299 8.66 1460 7536 8.94 1501 7776 9.22
1378 7434 8.82 1419 7667 9.10 1460 7902 9.37 1499 8138 9.65 1538 8377 9.94
Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp Rpm Watts Bhp
1332 4750 5.65 1380 5015 5.95 1427 5272 6.25 1472 5531 6.56 1517 5793 6.87
1356 5122 6.08 1402 5375 6.38 1447 5630 6.68 1492 5886 6.98 1535 6144 7.29
1381 5519 6.55 1427 5770 6.84 1471 6022 7.14 1514 6276 7.45 ———
1409 5951 7.06 1453 6199 7.35 1496 6449 7.65 1538 6701 7.95 ———
1440 6417 7.61 1482 6663 7.90 1523 6911 8.20 ——————
1471 6916 8.20 1513 7161 8.49 —————————
1505 7449 8.84 1545 7693 9.13 —————————
1540 8016 9.51 ————————————
———————————————
LEGEND
Brake Horsepower
Factory-Installed Option
Input Watts to Motor
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0
2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3.0
Fan Perform
Available External Static Pressure (in. wg)
Available External Static Pressure (in. wg)
Available External Static Pressure (in. wg)
ance — 551A240
2. Static pressure losses (i.e., EconoMi$er) must be added to external static pressure before entering Fan Performance table.
3. Interpolation is permissible. Do not extrapolate.
4. Fan performance is based on wet coils, clean filters, and casing
losses. See Table 13 for accessory/FIOP static pressure
information.
5. Extensive motor and drive testing on these units ensures that the
full bhp and watts range of the motor can be utilized with confidence. Using your fan motors up to the watts or bhp rating shown
will not result in nuisance tripping or premature motor failure. Unit
warranty will not be affected.
6. Use of a field-supplied motor may affect wiring size. Contact your
Bryant representative for details.
—23—
Page 24

Table 13 — Accessory/FIOP Static Pressure (in. wg)
UNIT
551A
155,180
240
LEGEND
FIOP —
NOTES:
1. Heaters are rated at 240 v, and 480 v.
2. The factory assembled horizontal adapter substantially improves
Factory-Installed Option
fan performance.
HEATER
RATED
VO LTAG E
208/240-3-60
480-3-60
208/240-3-60
480-3-60
CFM
3,750 0.05 (14/19, 26/34) 0.06 (42/56) 0.07 (56/75) 0.03
4,000 0.05 (14/19, 26/34) 0.06 (42/56) 0.07 (56/75) 0.04
5,000 0.07 (14/19, 26/34) 0.08 (42/56) 0.10 (56/75) 0.05
6,000 0.09 (14/19, 26/34) 0.12 (42/56) 0.15 (56/75) 0.07
7,200 0.11 (14/19, 26/34) 0.16 (42/56) 0.20 (56/75) 0.09
7,500 0.12 (14/19, 26/34) 0.17 (42/56) 0.21 (56/75) 0.10
3,750 0.05 (15, 32) 0.06 (55) 0.07 (80) 0.03
4,000 0.05 (15, 32) 0.06 (55) 0.07 (80) 0.04
5,000 0.07 (15, 32) 0.08 (55) 0.10 (80) 0.05
6,000 0.09 (15, 32) 0.12 (55) 0.15 (80) 0.07
7,200 0.11 (15, 32) 0.15 (55) 0.20 (80) 0.09
7,500 0.12 (15, 32) 0.17 (55) 0.21 (80) 0.10
5,000 0.08 (26/34) 0.11 (42/56) 0.14 (56/75) 0.06
6,000 0.09 (26/34) 0.12 (42/56) 0.15 (56/75) 0.07
7,200 0.11 (26/34) 0.16 (42/56) 0.20 (56/75) 0.09
9,000 0.15 (26/34) 0.19 (42/56) 0.24 (56/75) 0.11
10,000 0.17 (26/34) 0.21 (42/56) 0.26 (56/75) 0.12
11,250 0.20 (26/34) 0.24 (42/56) 0.29 (56/75) 0.14
5,000 0.08 (32) 0.11 (55) 0.14 (80) 0.06
6,000 0.09 (32) 0.12 (55) 0.15 (80) 0.07
7,200 0.11 (32) 0.15 (55) 0.20 (80) 0.09
9,000 0.15 (32) 0.19 (55) 0.24 (80) 0.11
10,000 0.17 (32) 0.21 (55) 0.26 (80) 0.12
11,250 0.20 (32) 0.24 (55) 0.29 (80) 0.14
ELECTRIC HEATERS
PRESSURE DROP
(kW)
3. The static pressure must be added to external static pressure. The
sum and the evaporator entering-air cfm should then be used in
conjunction with the Fan Performance table to determine blower
rpm, bhp, and watts.
ECONOMI$ER
PRESSURE
DROP
Fig. 29 — Perfect Humidity™ Operation Diagram
—24—
Page 25

Table 14 — Perfect Humidity™ Dehumidification
Package Static Pressure Drop (in. wg)
UNIT SIZE
551A
155
180
240
UNIT NOMINAL
TONS
12 .026 .045 .071
15 .040 .071 .111
20 .071 .126 .197
Table 15 — Fan RPM at Motor Pulley Settings*
551A 0 0.5 1 1
155†
155**
180†
180**
240†
240**
†† †† †† †† 1064 1035 1006 978 949 920 891 863 834
†† †† †† †† 1426 1393 1360 1327 1294 1261 1227 1194 1161
†† †† †† †† 1021 1002 984 965 947 928 910 891 873
†† †† †† †† 1200 1178 1156 1134 1112 1091 1069 1047 1025
†† †† †† †† 1151 1132 1114 1095 1077 1058 1040 1021 1002
†† †† †† †† 1369 1347 1325 1303 1281 1259 1237 1215 1193
/
22
2
1
*Approximate fan rpm shown.
†Indicates standard drive package.
**Indicates alternate drive package.
††Due to belt and pulley style, pulley cannot be set to this number of turns open.
1
/
2
CFM PER TON
300 400 500
33
1
/
2
44
1
/
2
55
1
/
2
6
BHP —
UNIT
551A
155
(Standard
Motor)
155
(Optional
Motor)
180
240
LEGEND
Brake Horsepower
Table 16 — Evaporator Fan Motor Specifications
NOMINAL
HP
VOLTAGE
2.9 208 2700 85.8 3.13 2.34 9.46
2.9 230 2700 85.8 3.13 2.34 8.6
2.9 460 2700 85.8 3.13 2.34 4.3
3.7 208 3775 85.8 4.38 3.27 10.5
3.7 230 3775 85.8 4.38 3.27 10.5
3.7 460 3775 85.8 4.38 3.27 4.8
5 208 5180 87.5 6.13 4.57 15.8
5 230 5180 87.5 6.13 4.57 15.8
5 460 5180 87.5 6.13 4.57 7.9
7.5 208 7915 88.5 9.47 7.06 22
7.5 230 8640 88.5 10.33 7.71 22
7.5 460 8640 88.5 10.33 7.71 13
MAX
WATTS
EFF.
%
MAX
BHP
MAX
BkW
MAX
AMPS
—25—
Page 26

SERVICE
WARNING:
Before performing service or maintenance operations on unit, turn off main power switch to unit
and install lockout tag on disconnect switch. Turn off accessory heater power switch if applicable. Electrical shock
could cause personal injury.
I. CLEANING
Inspect unit interior at beginning of each heating and cooling
season and as operating conditions require. Remove unit top
panel and/or side panels for access to unit interior.
A. Evaporator Coil
Clean as required with a commercial coil cleaner.
B. Condenser Coil
Clean condenser coil annually and as required by location
and outdoor-air conditions. Inspect coil monthly — clean as
required.
C. Condensate Drain
Check and clean each year at start of cooling season. In winter, keep drains and trap dry.
D. Filters
Clean or replace at start of each heating and cooling season,
or more often if opera ting c ondit ions re quire. Refer to T able 1
for type and size.
E. Outdoor-Air Inlet Screens
Clean screens with steam or hot water and a mild detergent.
Do not use throwaway filters in place of screens.
II. LUBRICATION
A. Compressors
Each compressor is charged with the correct amount of oil at
the factory. Conventional white o il (Sontext 200LT) is used.
White oil is compatible with 3GS oil, and 3GS oil may be
used if the additi on of oil is requi red. See c ompressor n ameplate for original oi l charge. A complete recharge should be
four ounces less than the original oil charge. When a compressor is exchanged in the field it is possible that a major
portion of the oil from the repl aced compresso r may still be
in the system. While this will not affect the reliability of the
replacement compressor, the extra oil will add rotor drag and
increase power usa ge. To remove this excess o il, an access
valve may be added to the lower portion of the suction line at
the inlet of the compressor. The compressor should then be
run for 10 minutes, shut down, and the access valve opened
until no oil flows. This should be repeated twice to make sure
the proper oil le vel has been achieved.
B. Fan Shaft Bearings
For size 155 units, bearings are permanently lubricated. No
field lubrication is required. For size 180 and 240 units, the
bearings are of the pillow block type and have grease fittings. The bearing opposite the motor end has an extended
tube line so it can be lubrica ted from the motor side. Lubri cate the bearings twice annually.
Typical lubricants are given below:
MANUFACTURER LUBRICANT
Texaco
Mobil
Sunoco
Texaco
*Preferred lubricant because it contains rust and oxidation inhibitors.
Regal AFB-2*
Mobilplex EP No. 1
Prestige 42
Multifak 2
C. Condenser and Evaporator-Fan Motor Bearings
The condenser and ev ap orat or-fan motor s have pe rman en tly
sealed bearings, so no field lubrication is necessary.
III. EVAPORATOR FAN PERFORMANCE ADJUSTMENT
(Fig. 30-32)
Fan motor pulleys are factory set for speed shown in Table 1.
To change fan speeds:
1. Shut off unit power supply.
2. a. Size 155 Only: Loosen belt by loosening fan motor
mounting plate nuts.
b. Size 180 and 240 Only: Loosen nuts on the 2 car-
riage bolts in the motor mounting base. Install
jacking bolt and plate under motor base (bolt and
plate are shipped in installer’s packet). See F ig. 32.
Using bolt and plate, raise motor to top of slide and
remove belt. Secure motor in this position by tightening the nuts on the carriage bolts.
3. Loosen movable-pulley flange setscrew (see Fig. 30).
4. Screw movable flange toward fixed flange to increase
speed and away from fixed flange to decrease speed.
Increasing fan speed increases load on motor. Do not
exceed maximum speed specified in Table 1.
See Table 8 for air quantity limits.
5. Set movable flange at nearest keyway of pulley hub
and tighten setsc rew. (See Table 1 for speed change
for each full turn of pulley flange.)
6. Replace and tighten belts. See Belt Tension Adjust-
ment section on page 27.
To align fan and motor pulleys:
1. Loosen fan pulley setscrews.
2. Slide fan pulley along fan shaft.
3. Make angular alignment by loosening motor from
mounting plate.
IV. EVAPORATOR FAN SERVICE AND REPLACEMENT
A. 551A155 Units (See Fig. 31)
NOTE: To remove belts only, follow Steps 1-6.
1. Remove filter and supply-air section panels.
2. Remove unit top panel.
3. Loosen carriage nuts A and B holdin g motor mount
assembly to fan scroll side plates.
4. Loosen sc re w C.
5. Rotate motor mount assembly (with motor attached)
as far as possible away from evaporator coil.
6. Remove belt.
7. Rotate motor mount assembly back past original
position toward evaporator coil.
8. Remove motor mounting nuts D and E (both sides).
9. Lift motor up through top of unit.
10. Reverse above procedure to reinstall motor.
11. Check and adjust belt tension as necessary.
B. 551A180,240 Units (See Fig. 32)
The 551A180,240 units use a fan motor mounting system
that features a slide-out motor mounting plate. To replace or
service the motor, slide out the bracket.
1. Remove the evaporator-fan access panel and the
heating control access panel.
2. Remove the center post (located betwe en the ev apor a-
tor fan and heating control access panels) and all
screws securing it.
—26—
Page 27

Fig. 30 — Evaporator-Fan Pulley Alignment
and Adjustment
3. Loosen nuts on the two carriage bolts in the motor
mounting base.
4. Using jacking bolt under motor base, raise motor to
top of slide and remove belt. Secure motor in this
position by tightening the nuts on the carriage bolts.
5. Remove the belt drive.
6. Remove jacking bolt and tapped jacking bolt plate.
7. Remov e the 2 screws that secure the motor mounti ng
plate to the motor support channel.
8. Remove the 3 screws from the end of the motor sup-
port channel that interfere with the motor slide path.
9. Slide out the motor and motor mounting plate.
10. Disconnect wiring connections and remove the 4
mounting bolts.
11. Remove the motor.
12. To install the new motor, reverse Steps 1-11.
Fig. 31 — 551A155 Evaporator-Fan
Motor Section
NOTE:
packet. They should be added to the motor support channel below the
motor mounting plate to aid in raising the motor. The plate part number
is 50DP503842. The adjustment bolt is
1
A 3
/2-in. bolt and threaded plate are included in the installer’s
3
/8- 16 x 21/2 LG.
Fig. 32 — 551A180,240 Evaporator-Fan
Motor Section
V. BELT TENSION ADJUSTMENT
To adjust belt tension:
1. Loosen fan motor bolts.
2. Adjust belt tension:
a. Size 155 Units: Move m oto r mo unt in g pla te up or
down for proper belt tension (
1
/2 in. deflection
with one finger).
b. Size 180, 240 Units: Turn motor jacking bolt to
move motor mounting plate up or down for
proper belt tension (
3
/8 in. deflection at midspan
with one finger [9 lb force]).
3. Tighten nuts.
4. Adjust bolts and nut on mounting plate to secure
motor in fixed position.
—27—
Page 28

VI. CONDENSER-FAN ADJUSTMENT
A. 551A155 and 180 Units (Fig. 33)
1. Shut off unit power supply.
2. Remove access panel(s) closest to the fan to be
adjusted.
3. Loosen fan hub setscrews .
4. Adjust fan height on shaft using a straightedge
placed across the fan orifice.
5. Tighten setscrews and replace panel(s).
6. Turn on unit power.
B. 551A240 Units (Fig. 34)
1. Shut off unit power supply.
2. Remove fan top-grille assembly and loosen fan hub
screws.
3. Adjust fan height on unit, using a straightedge
placed across the fan orifice.
4. Tighten setscrews and replace rubber hubcap to prevent hub from rusting to motor shaft.
5. Fill hub recess with permagum if rubber hubcap is
missing.
NOTE: Dimensions are in inches).
Fig. 33 — Condenser-Fan Adjustment,
551A155,180
NOTE: Dimensions are in inches.
Fig. 34 — Condenser-Fan Adjustment,
551A240
VII. ECONOMI$ER ADJUSTMENT
A. LED Indication
The EconoMi$er controller features an onboard diagnostic
LED (light-emitting diode) that flashes to indicate its status.
See Table 17 for flash codes. The controller also has terminal
connections (REM LED) for remotely mounting an LED, if
desired. The flash code priorities are as follows:
1. On/Off or continuous flash
2. Critical fault
3. Non-critical fault
If any sensors are opened, shorted, or removed, the
EconoMi$er determines whether the failure is critical or
non-critical and flashes the appropriate code . If a non-critical
sensor fault occurs (i.e., outdoor air humidity), the
EconoMi$er automatically reconfigures its control strategy
to a more appropriate m ode. If a critical sensor fault occurs
(i.e., supply air sensor), the EconoMi$er reverts to a safe
mode of operation until the sensor problem is resolved.
B. Manual Configuration Pushbutton
The EconoMi$er cont roller also featur es an onboard button
(CONFIG) to help troub leshoot the sy stem. See Fig. 16. The
button can perform 3 different functions.
Pressing the CONFIG button for more than three seconds,
but less than ten seconds and then releasing will start the
automatic test procedure. The damper will modulate fully
open, wait, and modulate closed. This process takes three
minutes to complete. Use this feature to determine if the
actuator can be commanded.
If the CONFIG button is pressed and held for ten seconds
and less than 30 seconds then released, th e EconoMi$er controller reconfigures its mode of operation based on the sensors that are connected and functioning normally, and
cancels the automatic test procedure.
If the EconoMi$er co ntrol ler reco gni zed a non- cr itica l se nso r
fault, and flashed a code (i.e., FLASH 6, outdoor air
humidity sensor fault) the FLASH CODE will be cleared,
and normal operation begins. Ensure faulty sensor is
removed before clearing faults.
If the EconoMi$er controller recognizes a critical sensor
fault, and flashes a code (i.e., FLASH 4, discharge air thermostat fault) the FLASH code will not be cleared, and the
EconoMi$er will remain in the safe operation mode. The
sensor fault must be corrected to enable EconoMi$er to
revert to normal operation.
Table 17 — EconoMi$er Control Module Flash Code Identification
FLASH CODE CAUSE ACTION TAKEN BY ECONOMI$ER
Constant On
Constant Off
Continuous
Flash
Flash One
Flash Two
Flash Three
Flash Four
Critical Fault
Flash Five
Flash Six
Flash Seven
Flash Eight
Flash Nine
Non-Critical Fault
Flash Ten
Normal operation Normal operation.
No power No operation.
CONFIG button pushed and held
between 3 and 9 seconds
Control board fault System shutdown.
Thermostat fault (i.e., Y2 without Y1) System shutdown until corrected.
Actuator fault Revert to mechanical cooling only.
Discharge air thermistor fault
Outdoor air temperature sensor fault
Outdoor air humidity sensor fault Continue operation with dry bulb or dry bulb differential switchover.
Return air temperature sensor fault
Return air humidity sensor fault
Carbon Dioxide (CO
Onboard adjustment potentiometer fault Continue operation with default potentiometer settings.
) sensor fault Continue operation without ventilation control.
2
Outdoor air damper is stroked fully open, then closed
(automatic test procedure takes 3 minutes to complete).
Continue operation with damper at minimum position.
Revert to mechanical cooling only.
Continue operation with damper at minimum position.
Disable mechanical cooling lockout.
Continue operation with single enthalpy EconoMi$er
switchover or dry bulb EconoMi$er switchover (without
humidity sensor).
Continue operation with single enthalpy, differential dry
bulb, or dry bulb EconoMi$er switchover.
—28—
Page 29

If the CONFIG button is pressed and held for more than
30 seconds and released, the EconoMi$er controller will
enable the enthalpy comparison strategy (with outdoor air
enthalpy and return air enthalpy sensors installed).
VIII. POWER FAILURE
Dampers have a spring return. In event of power failure,
dampers will return to fully closed position until power is
restored. Do not manually operate damper motor.
IX. REFRIGERANT CHARGE
Amount of refrigerant charge is listed on unit nameplate and
in Table 1. Refer to Carrier GTAC II; Module 5; Charging,
Recovery, Recycling, and Reclamation section for charging
methods and procedures. Unit panels must be in place when
unit is operating during charging procedure.
NOTE: Do not use recycled refrigerant as it may contain
contaminants.
A. No Charge
Use standard evacuating techniques. After evacuating system, weigh in the specified amount of re frigerant (refer to
Table 1).
B. Low Charge Cooling
Using cooling charging chart (see Fig. 35), add or remove
refrigerant until conditions of the chart are m et. Note that
charging chart is different from those normally used. An
accurate pressure gage and temperature-sensing device is
required. Chargi ng is accomplished by ens uring the proper
amount of liquid subcooling. Measure liquid line pressure at
the liquid line service valve using pressure gage. Connect
temperature sensing device to the liquid line near the liquid
line service valve and insulate it so that outdoor ambient
temperature does not affect reading.
C. To Use The Cooling Charging Chart
Use the above temperature and pressure readings, and find
the intersection point on the cooling charging chart. If intersection point on chart is a bove line, add refrige rant. If intersection point on chart is below line, carefully recover some of
the charge. Recheck suction pressure as charge is adjusted.
BOTH CIRCUITS
REDUCE CHARGE IF BELOW CURVE
150
200
250
300
350
400
140
120
100
80
60
LIQUID TEMPERATURE AT LIQUID VALVE (DEG F)
40
50
ALL OUTDOOR FANS MUST BE OPERATING
ADD CHARGE IF ABOVE CURVE
100
LIQUID PRESSURE AT LIQUID VALVE (PSIG)
Fig. 35 — Cooling Charging Chart
NOTE: Indoor-air CFM must be within normal operating
range of unit. All o utdoor fans must be operating.
The TXV (thermostatic expansion valve) is set to main-
tain between 15 and 20 degrees of superheat at the compressors. The valves are factory set and should not require
re-adjustment.
D. Perfect Humidity™ System Charging
The system charge for units with the Perfect Humidity
option is greater than that of the standard unit alone. The
charge for units with this option is indicated on the unit
nameplate drawing. To charge systems using the Perfect
Humidity Dehumidification package, fully evacuate, recover,
and re-charge the system t o the namepla te specifie d charge
level. To check or adjust refrige rant charge on systems using
the Perfect Humidity Dehumidification package, charge per
the standard subcooling charts. The subcooler MUST be
deenergized to use the charging charts. The charts reference
a liquid pressure (psig) and temperature at a point between
the condenser coil and the s ubcooler coil. A tap is provided
on the unit to measure liquid pressure entering the subcooler (leaving t he condenser).
X. FILTER DRIER
Replace whenever refrigerant system is exposed to
atmosphere.
XI. PROTECTIVE DEVICES
A. Compressor Protection
Overtemperature
Each compressor has an internal protector to protect it
against excessively high discharge gas temperatures.
Overcurrent
Each compressor has internal line break motor protection.
Crankcase Heater
All units are equipped with a 70-watt crankcase hea ter to
prevent absorptio n of liquid refrigera nt by oil in the crankcase when the compressor is idle. The crankcase heater is
energized whenev er there is a main power to the unit and
the compressor is not energized.
IMPORTANT: After prolonged shutdown or servicing, energize the crankcase heaters for 24 hours before starting the
compressors.
Compressor Lockout
If any of the safeties (high-pressure, low-pressure, freeze
protection thermostat, compressor internal thermostat) trip,
or if there is loss of power to the compressors, the C LO (compressor lockout) will lock th e comp ressors o ff. To reset, manually move the thermostat setting.
B. Evaporator Fan Motor Protection
A manual reset, calibrated trip, magnetic circuit breaker
protects against ov ercurrent. Do not bypass connections or
increase the size of the breaker to correct troubl e. Determine
the cause and correct it before r esetting the breaker.
C. Condenser-Fan Motor Protection
Each condenser-fan motor is internally protected against
overtemperature.
D. High- and Low-Pressure Switches
If either switch trips, or if the compressor overtemperature
switch activates, that refrigerant circuit will be automatically locked out by the CLO. To reset, manually move the
thermostat setting.
—29—
Page 30

E. Freeze Protection Thermostat (FPT)
An FPT is located on the top and bottom of the evaporator
coil. It detects frost build-up and turns off the compressor,
allowing the coil to clear. Once the frost has melted, the compressor can be reenergized.
XII. RELIEF DEVICES
All units have relief devices to protect against damage from
excessive pressures (e.g ., fire). These devices protect the high
and low side.
XIII. CONTROL CIRCUIT, 24-V
This control circuit is protected against overcurrent by a
3.2-amp circuit breaker. Breaker can be reset. If it trips,
determine cause of trouble before resetting. See Fig. 36 and
37.
XIV. REPLACEMENT PARTS
A complete list of replacement parts may be obtained from
any Bryant distributor upon reque st.
XV. ECONOMI$ER LEDs
The EconoMi$er control module has LEDs for diagnostic
purposes. The flash code identification is shown in Table 17.
LEGEND AND NOTES FOR FIG. 36 AND 37
AHA —
BRK W/AT —
C —
CAP —
CB —
CC —
CH —
CLO —
COMP —
CR —
DAT —
DM —
DU —
EC —
EQUIP —
FL —
FPT —
FU —
GND —
Adjustable Heat Anticipator
Breaks with Amp Turns
Contactor, Compressor
Capacitor
Circuit Breaker
Cooling Compensator
Crankcase Heater
Compressor Lockout
Compressor Motor
Control Relay
Discharge Air Thermistor
Damper Motor
Dummy Terminal
Enthalpy Control
Equipment
Fuse Link
Freeze Protection Thermostat
Fuse
Ground
HC —
HPS —
HTR —
IFC —
IFCB —
IFM —
IFR —
L —
LPS —
LS —
NEC —
OAT —
OFC —
OFM —
OP —
PL —
PRI —
QT —
SW —
Heater Contactor
High-Pressure Switch
Heater
Indoor-Fan Contactor
Indoor-Fan Circuit Breaker
Indoor-Fan Motor
Indoor-Fan Relay
Light
Low-Pressure Switch
Limit Switch
National Electrical Code
Outdoor-Air Thermostat
Outdoor-Fan Contactor
Outdoor-Fan Motor
Overcurrent Protection
Plug Assembly
Primary
Quadruple Terminal
Switch
XVI. OPTIONAL HINGED ACCESS DOORS
When the optional serv ice package is ordered or the if the
hinged access d oors option is ordered, the u nit will be provided with external and internal hinged access doors to facilitate service.
Four external hinged access door s are pro vided. All extern al
doors are provided with 2 large
1
/4 turn latches with folding
bail-type handles. (Compressor access doors have one latch.)
A single door is provided for filter and drive access. One door
is provided for control box access. The control box access door
is interlocked with the non-fused disconnect which must be
in the OFF position to open the door. Two doors are provided
for access to the compressor compartment.
Two internal access doors are provided in side the filter/drive
access door. The filter access door (on the left) is secured by 2
1
small
/4 turn latches with folding bail-type handles. This
door must be opened prior to opening the drive access door.
The drive access door is shipped with 2 sheet metal screws
holding the door closed. Upon initial opening of the door,
these screws may be removed and discarded. The door is
then held shut by the filter access door, which closes over it.
LEGEND
TB —
TC —
TH —
TRAN —
Terminal Block
Thermostat Cooling
Thermostat Heating
Transformer
Terminal (Marked)
Terminal (Unmarked)
Terminal Block
Splice
Factory Wiring
Field Wiring
Option/Accessory Wiring
To indicate common potential
only; not to represent wiring.
NOTES:
1. Compressor and/or fan motor(s) thermally protected; 3-phase motors protected
against primary single-phasing conditions.
2. If any of the original wire furnished must be replaced, it must be replaced with type
90° C wire or its equivalent.
3. Jumpers are omitted when unit is equipped with EconoMi$er.
5. IFCB must trip amps is equal to or less than 140% FLA.
6. The CLO locks out the compressor to prevent short cycling on compressor overload and safety devices. Before replacing CLO, check these devices.
7. Number(s) indicates the line location of used contacts. A bracket over (2) numbers
signifies a single-pole, double-throw contact. An underlined number signifies a
normally closed contact. Plain (no line) number signifies a normally open contact.
—30—
Page 31

Fig. 36 — Typical Wiring Schematic (551A180, 460v Shown)
—31—
Page 32

Fig. 36 — Typical Wiring Schematic (551A180, 460v Shown) (cont)
Fig. 37 — Typical Component Arrangement (551A180 Shown)
—32—
Page 33

PROBLEM CAUSE REMEDY
Compressor and
condenser fan
will not start.
Compressor will not start
but condenser fan runs.
Compressor cycles
(other than normally
satisfying thermostat).
Compressor operates
continuously.
Excessive head pressure.
Head pressure too low.
Excessive suction
pressure.
Suction pressure too low.
TXV —
Thermostatic Expansion Valve
LEGEND
TROUBLESHOOTING
Refer to Tables 18-20 for troubleshooting details.
Table 18 — Cooling Service Analysis
Power failure. Call power company.
Fuse blown or circuit breaker tripped. Replace fuse or reset circuit breaker.
Defective thermostat, contactor, transformer, or control
relay.
Insufficient line voltage. Determine cause and correct.
Incorrect or faulty wiring. Check wiring diagram and rewire correctly.
Thermostat setting too high. Lower thermostat setting below room temperature.
Faulty wiring or loose connections in compressor circuit. Check wiring and repair or replace.
Compressor motor burned out, seized, or internal
overload open.
Defective overload. Determine cause and replace.
Compressor locked out Determine cause for safety trip and reset lockout.
One leg of 3-phase power dead. Replace fuse or reset circuit breaker.
Refrigerant overcharge or undercharge. Recover refrigerant, evacuate system, and recharge
Defective compressor. Replace and determine cause.
Insufficient line voltage. Determine cause and correct.
Blocked condenser. Determine cause and correct.
Defective overload. Determine cause and replace.
Defective thermostat. Replace thermostat.
Faulty condenser-fan motor. Replace.
Restriction in refrigerant system. Locate restriction and remove.
Dirty air filter. Replace filter.
Unit undersized for load. Decrease load or increase unit size.
Thermostat set too low. Reset thermostat.
Low refrigerant charge. Locate leak, repair, and recharge.
Air in system. Recover refrigerant, evacuate system, and recharge.
Condenser coil dirty or restricted. Clean coil or remove restriction.
Dirty air filter. Replace filter.
Dirty condenser coil. Clean coil.
Refrigerant overcharged. Recover excess refrigerant.
Faulty TXV. 1. Check TXV bulb mounting and secure tightly to
Air in system. Recover refrigerant, evacuate system, and recharge.
Condenser air restricted or air shor t-cycling. Determine cause and correct.
Low refrigerant charge. Check for leaks, repair, and recharge.
Restriction in liquid tube. Remove restriction.
High heat load. Check for source and eliminate.
Faulty TXV. 1. Check TXV bulb mounting and secure tightly to
Refrigerant overcharged. Recover excess refrigerant.
Dirty air filter. Replace filter.
Low refrigerant charge. Check for leaks, repair, and recharge.
Metering device or low side restricted. Remove source of restriction.
Faulty TXV. 1. Check TXV bulb mounting and secure tightly to
Insufficient evaporator airflow. Increase air quantity. Check filter and replace if
Temperature too low in conditioned area. Reset thermostat.
Field-installed filter drier restricted. Replace.
Replace component.
Determine cause. Replace compressor.
Determine cause.
to nameplate.
suction line.
2. Replace TXV if stuck open or closed.
suction line.
2. Replace TXV if stuck open or closed.
suction line.
2. Replace TXV if stuck open or closed.
necessary.
—33—
Page 34

Table 19 — EconoMi$er Troubleshooting
PROBLEM POTENTIAL CAUSE REMEDY
Damper Does Not
Open
EconoMi$er
Operation Limited to
Minimum Position
Damper Position
Less than Minimum
Position Set Point
Damper Does Not
Return to Minimum
Position
Damper Does Not
Close on Power Loss
LEGEND
IFM —
PL —
Indoor Fan Motor
Plug
Indoor (Evaporator) Fan is
Off
Check to ensure that 24 vac is present at Terminal C1 (Common Power)
on the IFC (Indoor [Evaporator] Fan Contactor) or that 24 vac is present at
the IFO (Indoor [Evaporator] Fan On) terminal. Check whether 24 vac is
present at PL6-1 (red wire) and/or PL6-3 (black wire). If 24 vac is
not present, check wiring (see unit label diagram).
Check proper thermostat connection to G on the connection board.
No Power to EconoMi$er
Controller
Check to ensure that 24 vac is present across Terminals 24 VAC and
24 V COM on the EconoMi$er control. If 24 vac is not present, check wiring
(see unit label diagram). If 24 vac is present, STATUS light should be on
constantly.
No Power to G Terminal If IFM is on, check to ensure 24 vac is present on G Terminal of the
EconoMi$er controller. If 24 vac is not present, check wiring (see unit
label diagram).
Controller Fault If STATUS light is flashing one flash, the EconoMi$er controller is
experiencing a fault condition. Cycle power to the controller. If condition
continues, replace the EconoMi$er controller.
Thermostat Fault If STATUS light is flashing two flashes, the EconoMi$er controller senses that
the thermostat is wired incorrectly. Check wiring between the thermostat
and the connection board in the electrical panel. The fault condition is
caused by Y2 being energized before Y1.
Actuator Fault Check the wiring between the EconoMi$er controller and the actuator.
Hold CONFIG button between 3 and 10 seconds to verify the
actuator’s operation. (This process takes 3 minutes to complete.)
Minimum Position Set
Incorrectly
EconoMi$er Changeover
Set Point Set Too High or
Verify that the MIN POS (%) is set greater than zero. Adjust MIN POS (%)
to 100% to verify operation, and then set to correct setting.
Set at correct value. See Table 6.
Too Low
Discharge Air
Thermistor Faulty
Outdoor Air Temperature
Sensor Faulty
Supply Air Low Limit
Strategy Controlling
If STATUS light is flashing 4 flashes, Discharge Air Thermistor is
faulty. Check wiring or replace sensor.
If STATUS light is flashing 5 flashes, Outdoor Air Temperature Sensor is
faulty. Check wiring or replace sensor.
The supply-air temperature is less than 45 F, causing the minimum
position to be decreased. Refer to the Start-Up instructions. Verify correct
setting of MIN POS (%). If correct, EconoMi$er is operating correctly.
Ventilation Strategy
CO
2
Controlling
Damper Travel is
Restricted
If a CO2 sensor is being used, and the damper position is greater than
minimum position, the ventilation control strategy is controlling. Refer to
the Start-Up instructions. EconoMi$er is operating correctly.
Check to ensure the damper is not blocked.
Table 20 — Perfect Humidity™ Dehumidification Subcooler Service Analysis
PROBLEM CAUSE REMEDY
Subcooler will not energize
Subcooler will not deenergize
Low system capacity
Copyright 2001 Bryant Heating & Cooling Systems CATALOG NO. 5355-105
No power to subcooler
control transformer.
No power from subcooler control transformer
to liquid line three way valve.
Liquid line three-way valve
will not operate.
Liquid Line three-way valve
will not close.
Low refrigerant charge or
frosted coil.
Check power source. Ensure all wire connections
are tight.
1. Fuse open; check fuse. Ensure continuity of wiring.
2. Subcooler control low-pressure switch open.
Cycle unit off and allow low-pressure switch
to reset. Replace switch if it will not close.
3. Transformer bad; check transformer.
1. Solenoid coil defective; replace.
2. Solenoid valve stuck closed; replace.
Valve is stuck open; replace.
1. Check charge amount. See system charging
section.
2. Evaporator coil frosted; check and replace
subcooler control low pressure switch if necessary.
Page 35

Page 36

START-UP CHECKLIST
MODEL NO.:
SERIAL NO.:
DATE: TECHNICIAN:
I. PRE-START-UP:
VERIFY THAT ALL PACKING MATERIALS HAVE BEEN REMOVED FROM UNIT
VERIFY INSTALLATION OF INDOOR FAN MOTOR ADJUSTMENT BOLT (155 UNITS) OR ADJUSTMENT
BOLT AND PLATE (180, 240 UNITS)
VERIFY INSTALLATION OF OUTDOOR AIR HOOD
VERIFY THAT CONDENSATE CONNECTION IS INSTALLED PER INSTRUCTIONS
VERIFY THAT ALL ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS AND TERMINALS ARE TIGHT
CHECK THAT FILTERS AND SCREENS ARE CLEAN AND IN PLACE
VERIFY THAT UNIT IS LEVEL
CHECK FAN WHEEL AND PROPELLER FOR LOCATION IN HOUSING/ORIFICE, AND VERIFY SETSCREW
IS TIGHT
VERIFY THAT FAN SHEAVES ARE ALIGNED AND BELTS ARE PROPERLY TENSIONED
VERIFY THAT SCROLL COMPRESSORS ARE ROTATING IN THE CORRECT DIRECTION
VERIFY THAT CRANKCASE HEATER HAS BEEN ENERGIZED FOR 24 HOURS
II. START-UP:
ELECTRICAL
SUPPLY VOLTAGE L1-L2 L2-L3 L3-L1
COMPRESSOR AMPS — COMPRESSOR NO. 1 L1 L2 L3
— COMPRESSOR NO. 2 L1 L2 L3
SUPPLY F AN AMPS
EXHAUST FAN AMPS
CUT ALONG DOTTED LINE
ELECTRIC HEAT AMPS (IF SO EQUIPPED) L1 L2 L31
TEMPERATURES
OUTDOOR-AIR TEMPERATURE
RETURN-AIR TEMPERATURE
COOLING SUPPLY AIR
ELECTRIC HEAT SUPPLY AIR (IF SO EQUIPPED)
F DB (Dry-Bulb)
F DB F WB (Wet-Bulb)
F
F
PRESSURES
REFRIGERANT SUCTION CIRCUIT NO. 1 PSIG CIRCUIT NO. 2 PSIG
REFRIGERANT DISCHARGE CIRCUIT NO. 1
VERIFY REFRIGERANT CHARGE USING CHARGING CHART ON PAGE 29.
PSIG CIRCUIT NO. 2 PSIG
GENERAL
ECONOMI$ER MINIMUM VENT AND CHANGEOVER SETTINGS TO JOB REQUIREMENTS
VERIFY INSTALLATION OF ALL OPTIONS AND ACCESSORIES
CUT ALONG DOTTED LINE
Copyright 2001 Bryant Heating & Cooling Systems
CL-1
CATALOG NO. 5355-105
 Loading...
Loading...