Page 1

Installation, Start-Up
and Operating Instructions
657A
SINGLE PACKAGED
HEAT PUMP UNITS
Cancels: II 657A.24.4 II 657A.24.5
7–03
NOTE: Read the entire instruction manual before starting the
installation.
This symbol → indicates a change since the last issue.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS.....................................................1
Introduction ....................................................................................2
RECEIVING AND INSTALLATION..........................................2
Check Equipment......................................................................2
IDENTIFY UNIT................................................................2
INSPECT SHIPMENT........................................................2
Provide Unit Support................................................................3
ROOF CURB & SLAB MOUNT.......................................3
Provide Clearances....................................................................4
Select and Install Ductwork .....................................................5
Rig and Place Unit....................................................................6
INSTALLATION ................................................................8
Connect Condensate Drain.......................................................9
Install Duct Connections ..........................................................9
CONFIGURING UNITS FOR DOWNFLOW (VERTI-
CAL) DISCHARGE-STANDARD UNITS (024–042)....11
CONFIGURING UNITS FOR DOWNFLOW (VERTI-
CAL) DISCHARGE-ECM UNITS (048–060).................13
Install Electrical Connection ..................................................14
HIGH-VOLTAGE & CONTROL-VOLTAGE CONNEC-
TIONS................................................................................14
SPECIAL PROCEDURES FOR 208-V OPERATION ...15
PRE-START-UP ..........................................................................15
START-UP...................................................................................17
CHECK FOR REFRIGERANT LEAKS..........................17
START UP AND MAKE ADJUSTMENTS....................18
CHECKING COOLING CONTROL OPERATION .......18
CHECKING HEATING CONTROL OPERATION........18
CHECKING AND ADJUSTING REFRIGERANT
CHARGE...........................................................................18
INDOOR AIRFLOW AND AIRFLOW ADJUST-
MENTS..............................................................................21
For 208/230v-PSC Blower Motor.....................................21
For 208/230v-ECM Blower Motor...................................21
COOLING SEQUENCE OF OPERATION.....................22
HEATING SEQUENCE OF OPERATION.....................23
MAINTENANCE.........................................................................23
AIR FILTER......................................................................24
UNIT TOP REMOVAL....................................................24
INDOOR BLOWER AND MOTOR................................24
OUTDOOR COIL, INDOOR COIL, AND CONDENSATE
DRAIN PAN......................................................................27
OUTDOOR FAN...............................................................28
ELECTRICAL CONTROLS AND WIRING ..................28
REFRIGERANT CIRCUIT...............................................29
INDOOR AIRFLOW ........................................................29
METERING DEVICE — ACUTROL DEVICE .............29
LIQUID LINE STRAINER ..............................................29
Troubleshooting............................................................................31
Start-UpChecklist........................................................................32
NOTE TO INSTALLER — Before the installation, READ THESE
INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY AND COMPLETELY. Also,
make sure the User’s Manual and Replacement Guide are left with
the unit after installation.
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
Installation and servicing of air-conditioning equipment can be
hazardous due to system pressure and electrical components. Only
trained and qualified personnel should install, repair, or service
air-conditioning equipment.
Untrained personnel can perform basic maintenance functions of
cleaning coils and filters. All other operations should be performed
by trained service personnel. When working on air-conditioning
equipment, observe precautions in the literature, tags, and labels
attached to the unit, and other safety precautions that may apply.
Follow all safety codes. Wear safety glasses and work gloves. Use
quenching cloth for unbrazing operations. Have fire extinguisher
available for all brazing operations. Consult a qualified installer or
service agency for information or assistance. The qualified installer or agency must use only factory-authorized kits or accessories when modifying this product.
C95002
Fig. 1—Unit 657A with Optional Base Rails
WARNING: Before performing service or maintenance
operations on system, turn off power to unit. Turn off
accessory heater power switch, if applicable. Electrical
shock can cause personal injury.
Recognize safety information. This is the safety-alert symbol .
When you see this symbol in instructions or manuals, be alert to
the potential for personal injury.
Understand the signal words DANGER, WARNING, CAUTION,
and NOTE. These words are used with the safety-alert symbol.
DANGER identifies the most serious hazards which will result in
—1—
Page 2

C95003
UNIT ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
657A024 208/230-1-60 257 117 57/26 69/31 75/34 56/25 20.4/519 21.1/540 11.2/286
657A030 208/230-1-60 288 131 56/25 87/40 74/34 71/32 20.3/518 21.5/547 11.2/286
UNIT WEIGHT
lb. kg A B C D X Y Z
CORNER WT
LB/KG
CENTER OF GRAVITY
IN/MM
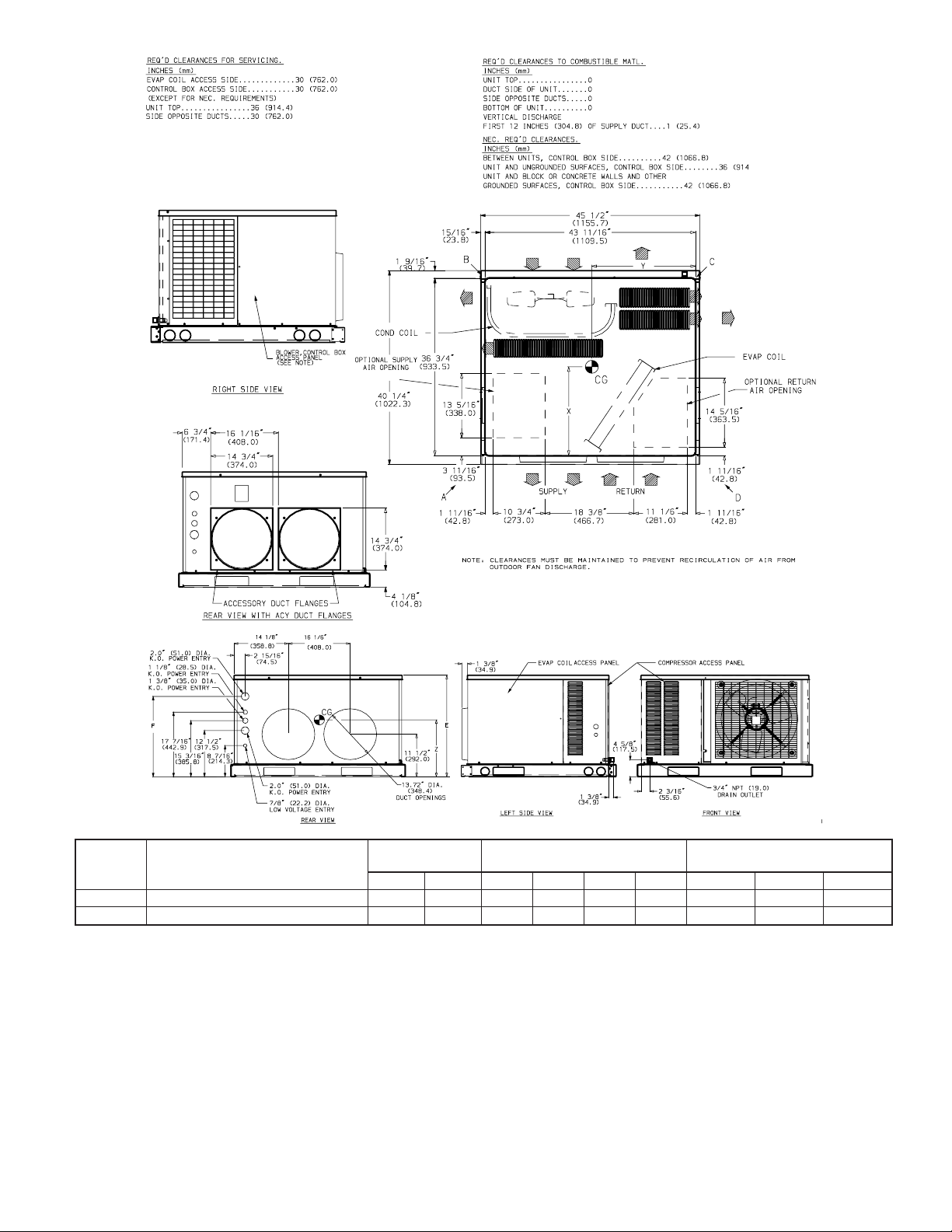
Fig. 2— 657A024-030 Unit Dimensions (without base rails)
severe personal injury or death. WARNING signifies a hazard
which could result in personal injury or death. CAUTION is used
to identify unsafe practices which would result in minor personal
injury or product and property damage. NOTE is used to highlight
suggestions which will result in enhanced installation, reliability,
or operation.
These instructions cover minimum requirements and conform to
existing national standards and safety codes. In some instances,
these instructions exceed certain local codes and ordinances,
especially those that may not have kept up with changing residential construction practices. We require these instructions as a
minimum for a safe installation.
INTRODUCTION
The 657A units (see Fig. 1) are fully self-contained, and designed
for outdoor installation. See Figs. 2–5 for unit dimensions. All
units are shipped in a horizontal-discharge configuration for
installation on a ground-level slab. All units can be converted to
down-flow discharge configurations for rooftop applications. (See
Fig. 6 for roof curb dimensions.)
RECEIVING AND INSTALLATION
I. CHECK EQUIPMENT
A. IDENTIFY UNIT
The unit model number and serial number are stamped on the unit
identification plate. Check this information against shipping papers.
B. INSPECT SHIPMENT
Inspect for shipping damage while unit is still on shipping pallet.
If unit appears to be damaged or is torn loose from its anchorage,
have it examined by transportation inspectors before removal.
—2—
Page 3
C95004
UNIT ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
657A024 208/230-1-60 277 126 62/28 74/34 80/36 61/28 20.2/515 21.3/541 13.8/351
657A030 208/230-1-60 308 140 61/28 92/42 79/36 76/35 20.2/514 21.5/547 13.8/351
UNIT WEIGHT
lb. kg A B C D X Y Z
CORNER WT
LB/KG
CENTER OF GRAVITY
IN/MM
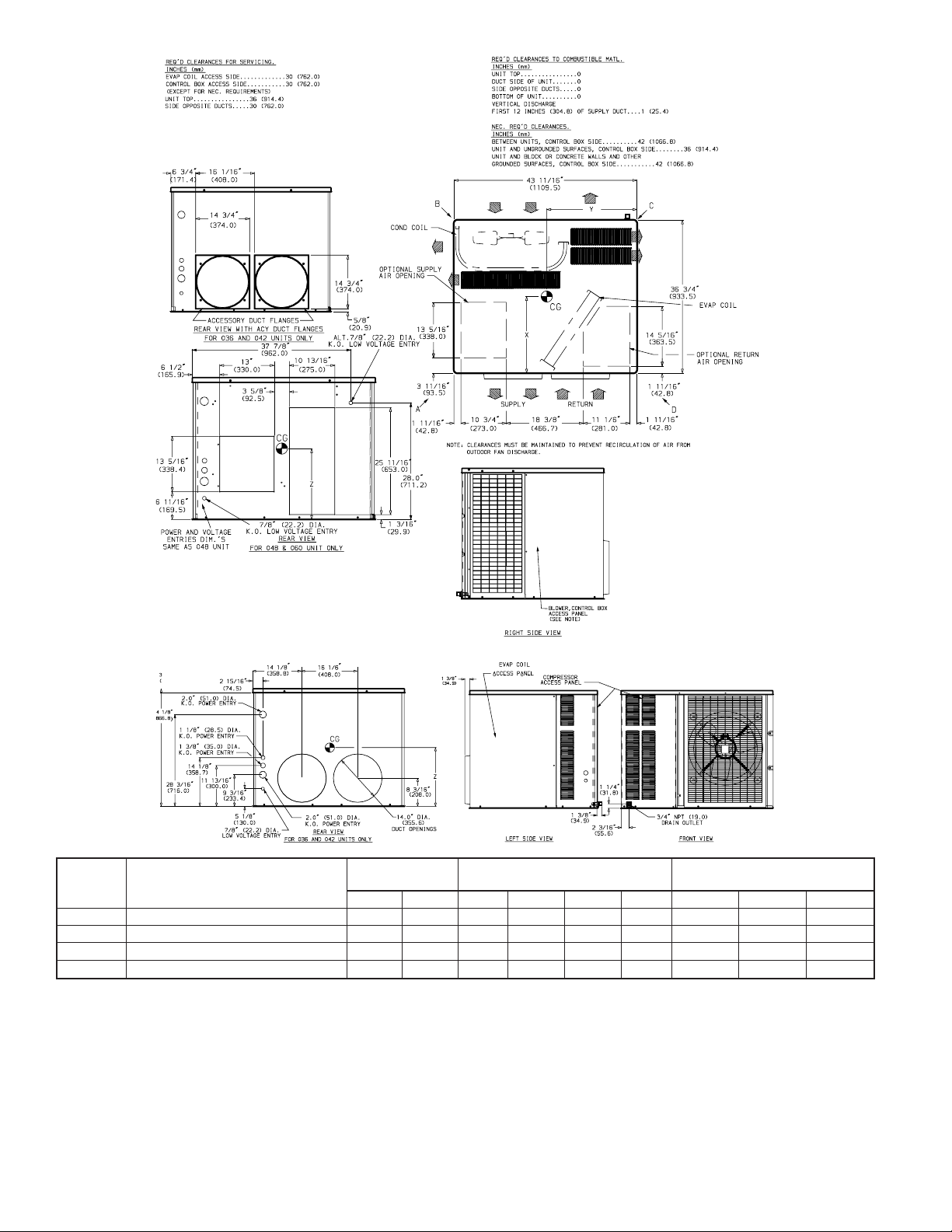
Fig. 3— 657A024-030 Unit Dimensions (with base rails)
Forward claim papers directly to transportation company. Manufacturer is not responsible for any damage incurred in transit.
Check all items against shipping list. Immediately notify the
nearest distributor if any item is missing. To prevent loss or
damage, leave all parts in original packages until installation.
II. PROVIDE UNIT SUPPORT
A. ROOF CURB & SLAB MOUNT
ROOF CURB - Install accessory roof curb in accordance with
instructions shipped with curb (See Fig. 6). Install insulation, cant
strips, roofing, and flashing. Ductwork must be attached to curb.
IMPORTANT: The gasketing of the unit to the roof curb is
critical for a watertight seal. Install gasketing material supplied
with the roof curb. Improperly applied gasketing also can result in
air leaks and poor unit performance.
Curb should be level to within 1/4 in (See Fig. 8). This is necessary
for unit drain to function properly. Refer to accessory roof curb
installation instructions for additional information as required.
SLAB MOUNT - Place the unit on a solid, level concrete pad that
is a minimum of 4 in. thick with 2 in. above grade (See Fig. 10).
The slab should extend approximately 2 in. beyond the casing on
all 4 sides of the unit. Install a 6-in. gravel apron in front of
—3—
Page 4
UNIT ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
657A036 208/230-1-60 316 144 46/21 103/47 81/37 86/39 21.2/539 20.4/520 13.6/347
657A042 208/230-1-60 316 144 46/21 103/47 81/37 86/39 21.2/539 20.4/520 13.6/547
657A048 208/230-1-60 359 163 89/40 81/37 113/51 76/35 19.7/500 20.5/522 15.0/381
657A060 208/230-1-60, 373 170 92/42 85/39 116/53 80/36 19.6/499 20.6/523 15.0/381
UNIT WEIGHT
lb. kg A B C D X Y Z
CORNER WT
LB/KG
CENTER OF GRAVITY
IN/MM
Fig. 4— 657A036-060 Unit Dimensions (without base rails)
outdoor coil-air inlet to prevent obstruction of airflow by grass or
shrubs. Do not secure the unit to the slab except when required by
local codes.
III. PROVIDE CLEARANCES
The required minimum service clearances are shown in Fig. 2-5.
Adequate ventilation and outdoor air must be provided. The
outdoor fan pushes air through the outdoor coil and discharges it
through the louvers on the top cover, the decorative grille, and the
compressor access panel. Be sure that the fan discharge does not
recirculate to the outdoor coil. Do not locate the unit in either a
corner or under an overhead obstruction. The minimum clearance
under a partial overhang (such as a normal house overhang) is 48
in. above the unit top. The maximum horizontal extension of a
partial overhang must not exceed 48 in.
IMPORTANT: Do not restrict outdoor airflow. An air restriction
at either the outdoor-air inlet or the fan discharge may be
detrimental to compressor life.
Do not place the unit where water, ice, or snow from an overhang
or roof will damage or flood the unit. Do not install the unit on
carpeting or other combustible materials. Slab-mounted units
—4—
C95005
Page 5

C95006
UNIT ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
657A036 208/230-1-60 336 153 51/23 108/49 86/39 91/41 21.0/535 20.5/521 16.4/418
657A042 208/230-1-60 336 153 51/23 108/49 86/39 91/41 21.0/535 20.5/521 16.4/418
657A048 208/230-1-60 379 172 94/43 86/39 118/54 81/37 19.6/498.3 20.6/524 17.3/440
657A060 208/230-1-60, 393 179 97/44 90/41 121/55 85/39 19.5/497.3 20.6/524 17.3/440
UNIT WEIGHT
lb. kg A B C D X Y Z
CORNER WT
LB/KG
CENTER OF GRAVITY
IN/MM
Fig. 5— 657A036-060 Unit Dimensions (with base rails)
should be at least 4 in. above the highest expected water and runoff
levels. Do not use unit if it has been under water.
IV. SELECT AND INSTALL DUCTWORK
The design and installation of the duct system must be in
accordance with the standards of the NFPA (National Fire Protection Association) for installation of nonresidence-type air conditioning and ventilating systems, NFPA90A or residence type,
NFPA90B; and/or local codes and residence-type, NFPA90B;
and/or local codes and ordinances. Select and size ductwork,
supply-air registers and return-air grilles according to ASHRAE
(American Society of Heating, Refrigeration, and Air Condition-
ing Engineers) recommendations. The unit has duct flanges on the
supply- and return-air openings on the side of the unit. See Fig. 2-5
for connection sizes and locations. When designing and installing
ductwork, consider the following:
CAUTION: When connecting ductwork to units, do not
drill deeper than 1/2–in. in shaded area shown or coil may
be damaged.
1. All units should have field-supplied filters or accessory
—5—
Page 6
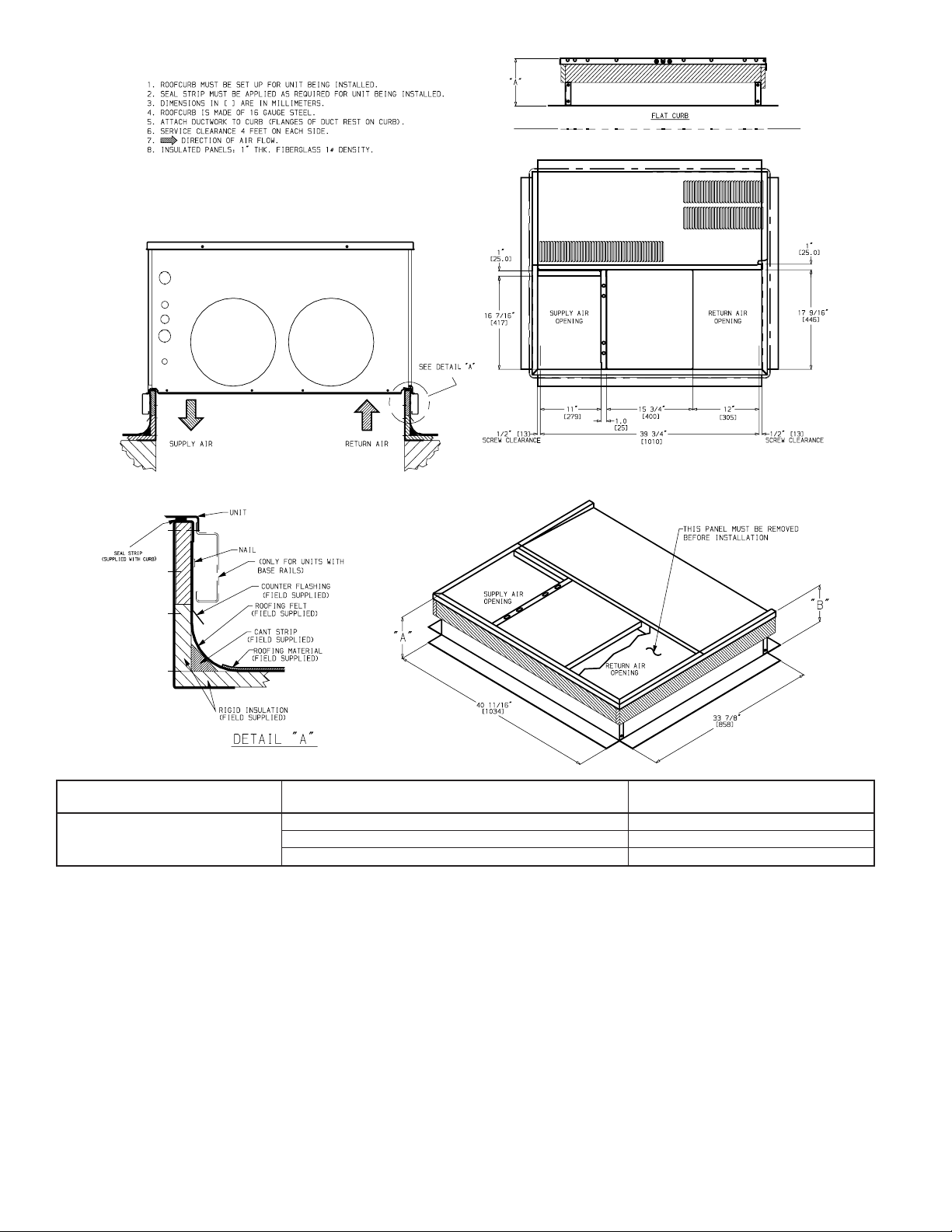
ODS CATALOG NUMBER
Flat
Curb
CPRFCURB001A00 8 (203)
CPRFCURB002A00 11 (279)
CPRFCURB003A00 14 (356)
Fig. 6— Roof Curb Dimensions
filter rack installed in the return-air side of the unit.
Recommended sizes for filters are shown in Table 1.
2. Avoid abrupt duct size increases and reductions. Abrupt
change in duct size adversely affects air performance.
IMPORTANT: Use flexible connectors between ductwork and
unit to prevent transmission of vibration. Use suitable gaskets to
ensure weathertight and airtight seal. When electric heat is
installed, use fireproof canvas (or similar heat resistant material)
connector between ductwork and unit discharge connection. If
flexible duct is used, insert a sheet metal sleeve inside duct. Heat
resistant duct connector (or sheet metal sleeve) should extend
24-in. from electric heater element.
3. Size ductwork for cooling air quantity (cfm). The minimum
air quantity for proper electric heater operation is listed in
Table 2. Heater limit switches may trip at air quantities
below those recommended.
C95007
A
IN. (MM)
NOTE: A 90-degree elbow must be provided in the supply
ductwork to comply with UL (Underwriters’ Laboratories) codes
for use with electric heat.
4. Insulate and weatherproof all external ductwork. Insulate
and cover with a vapor barrier all ductwork passing through
conditioned spaces. Follow latest Sheet Metal and Air
Conditioning Contractors National Association
(SMACNA) and Air Conditioning Contractors Association
(ACCA) minimum installation standards for residential
heating and air conditioning systems.
5. Secure all ducts to building structure. Flash, weatherproof,
and vibration-isolate duct openings in wall or roof according to good construction practices.
V. RIG AND PLACE UNIT
Use spreader bars or crate top when rigging the unit. The units
must be rigged for lifting as shown in Fig. 7. Use extreme caution
—6—
Page 7

CHART A CHART B
UNIT
SIZE
024 296 134 16.1 410 32.2 817 309 140 16.0 406 28.9 733
030 327 148 16.2 411 32.2 817 340 154 16.0 407 28.9 733
036 355 161 15.4 390 38.2 969 368 167 15.2 385 34.9 885
042 355 161 15.4 390 38.2 969 368 167 15.2 385 34.9 885
048 398 180 16.9 428 38.2 969 411 186 16.8 426 34.1 867
060 412 187 16.9 429 38.2 969 425 193 16.8 427 34.1 867
Max
Weight
LB KG IN MM IN MM LB KG IN MM IN MM
AB
Max
Weight
CD
Fig.7—657A RiggingInstructions
C95006
A
B
C
MAXIMUM ALLOWABLE
DIFFERENCE (in.)
A-B B-C A-C
1/4 1/4 1/4
Fig. 8—Unit Leveling Tolerances
to prevent damage when moving the unit. Unit must remain in an
upright position during all rigging and moving operations. The unit
must be level for proper condensate drainage; the ground-level pad
or accessory roof curb must be level before setting the unit in
place. When a field-fabricated support is used, be sure that the
support is level and that it properly supports the unit.
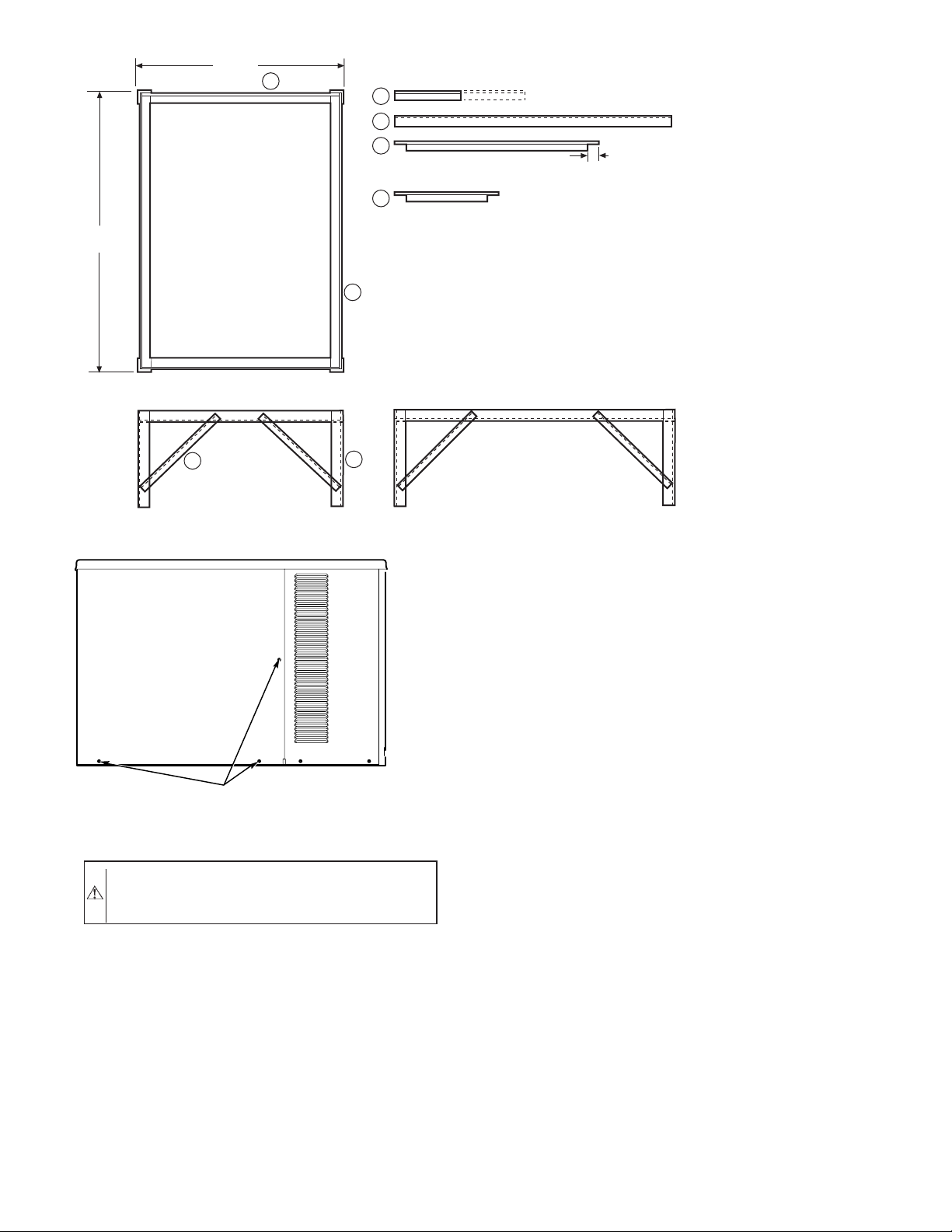
UNITS WITHOUT BASE RAILS-Accessory rigging brackets are
recommended to be used for rigging. Install brackets as follows:
C99065
—7—
Page 8

RETURN
AIR
INDOOR
THERMOSTAT
TOP COVER
Fig. 9—Typical Unit Installation
REAR SIDE OF UNIT
PAD
UNIT OUTLINE
933 mm
(36 3/4”)
1110 mm
(43 11/16”)
984 mm
(38 3/4”)
1161 mm
(45 11/16”)
FROM
POWER
SOURCE
DISCONNECT
PER NEC
SIDE
OF UNIT
WITH DUCT
CONNECTIONS
C95013
SIDE OF UNIT WITH
ACCESS PANELS FOR
CONTROL BOX AND
INDOOR BLOWER HOUSING
NOTES:
1. Extend
2. Provide a3-ft service clearance
gravel apron around pad.
6-in.
Fig.10—Typical Slab Layout
WARNING: Secure screws and paint protectors solidly
against unit base to hold lifting brackets in position.
Never use lifting brackets when the temperature is below
-10 F (-23 C). Never exceed 200 lbs per bracket of lifting
force. Never use lifting brackets for lifting other models
of air conditioning units. Lifting point should be directly
over the unit center of gravity. Failure to follow this
warning could result in personal injury or death.
1. Position brackets as close to the corners of unit as possible.
Be sure brackets are well outside of center of gravity (See
Fig. 2-5, and 7).
2. Position paint protectors and foam strips between screws
and painted surface of unit. Tighten screws until they make
contact with the paint protectors.
3. Secure device or hook of sufficient strength to hole in
bracket as shown in detail ’’C’’ of Fig. 7.
4. If wood top is available, use it for a spreader bar to prevent
straps from damaging unit. If wood top is not available, use
spreader bars of sufficient length.
at front and rear sides of unit.
C95039
UNITS WITH OPTIONAL BASE RAILS - Keep unit upright and
do not drop. Use spreader bars or top crate when rigging unit.
Rollers may be used to move unit across roof. Level unit for proper
condensate disposal. See Fig. 7 for additional information. Lifting
holes are provided in base rails as shown in Fig. 7, See Detail “A”
or “B-B”. Refer to rigging instructions on unit.
A. INSTALLATION
1. Position the lifting bracket assembly around the base of the
unit. Leave the top shipping skid on the unit to act as a
spreader bar. Be sure the strap does not twist.
2. Place each of the four (4) metal lifting brackets into the
rigging holds in the composite pan.
3. Tighten the ratchet strap unit tight. Lifting brackets should
be secure in the rigging holds.
4. Attach the clevis or hook of sufficient strength to hole in the
lifting bracket (See Fig. 7).
5. Attach safety straps directly to the field supplied rigging
straps or clevis clip. Do not attach the safety straps to the
lifting brackets.
6. Use the top of the unit as a spreader bar to prevent the
rigging straps from damaging the unit. If the wood top is not
available, use a spreader bar of sufficient length to not
damage the unit.
—8—
Page 9
959 mm
(37 3/4 in.)
3
1
2
3
305 mm (12 in.) TO 610 mm (24 in.) (4) REQ.
1010 mm
(39 3/4 in.) (2) REQ.
909 mm (35 3/4 in.) (2) REQ.
38 mm (1 1/4 in.)
1060 mm
(41 3/4 in.)
4
NOTES:
1. Material consistsof angle iron — 31.8 mm (1-1/4 in.) to 38 mm
2
4
1
2. We ldframetogether.
3. Pa int with z inc-rich paint (rust-proof).
406 mm (16 in.) (8) REQ.
(1-1/2 in.) commerical standard.
C95013
Fig. 11—Optional Heat Pump Mounting Frame
ACCESS PANEL
(REMOVE SCREWS)
Fig. 12—Indoor Coil Access Panel
WARNING: Lifting point should be directly over the
center of gravity for the unit. Failure to follow this
warning could result in personal injury or death.
VI. CONNECT CONDENSATE DRAIN
NOTE: When installing condensate drain connection be sure to
comply with local codes and restrictions.
Unit disposes of condensate through a 3/4-in. NPT fitting which
exits through the compressor access panel. See Fig. 2–5 (Front
View) for location of condensate connection.
Condensate water can be drained directly onto the roof in rooftop
installations (where permitted) or onto a gravel apron in groundlevel installations. Install a field-supplied condensate trap at end of
condensate connection to ensure proper drainage. Make sure that
the outlet of the trap is at least 1-in. lower than the drain-pan
condensate connection to prevent the pan from overflowing. Prime
the trap with water. When using a gravel apron, make sure it slopes
C95014
away from the unit.
If the installation requires draining the condensate water away
from the unit, install a 2-in. trap using a 3/4-in. NPT connection
(See Fig. 18). Make sure that the outlet of the trap is at least 1-in.
lower than the unit drain-pan condensate connection to prevent the
pan from overflowing. Prime the trap with water. Connect a drain
tube using a minimum of 3/4-in. PVC, 3/4-in. CPVC, or 3/4-in.
copper pipe (all field supplied). Do not undersize the tube. Pitch
the drain tube downward at a slope of at least 1 in. for every 10 ft
of horizontal run. Be sure to check the drain tube for leaks. Prime
trap at the beginning of the cooling season start-up.
VII. INSTALL DUCT CONNECTIONS
The unit has duct flanges on the supply- and return-air openings on
the side and bottom of the unit. For downshot applications the
ductwork can be connected to the roof curb. See Fig. 2-5 for
connection sizes and locations.
IMPORTANT: Use flexible connectors between ductwork and
unit to prevent transmission of vibration. Use suitable gaskets to
ensure weathertight and airtight seal. When electric heat is
—9—
Page 10
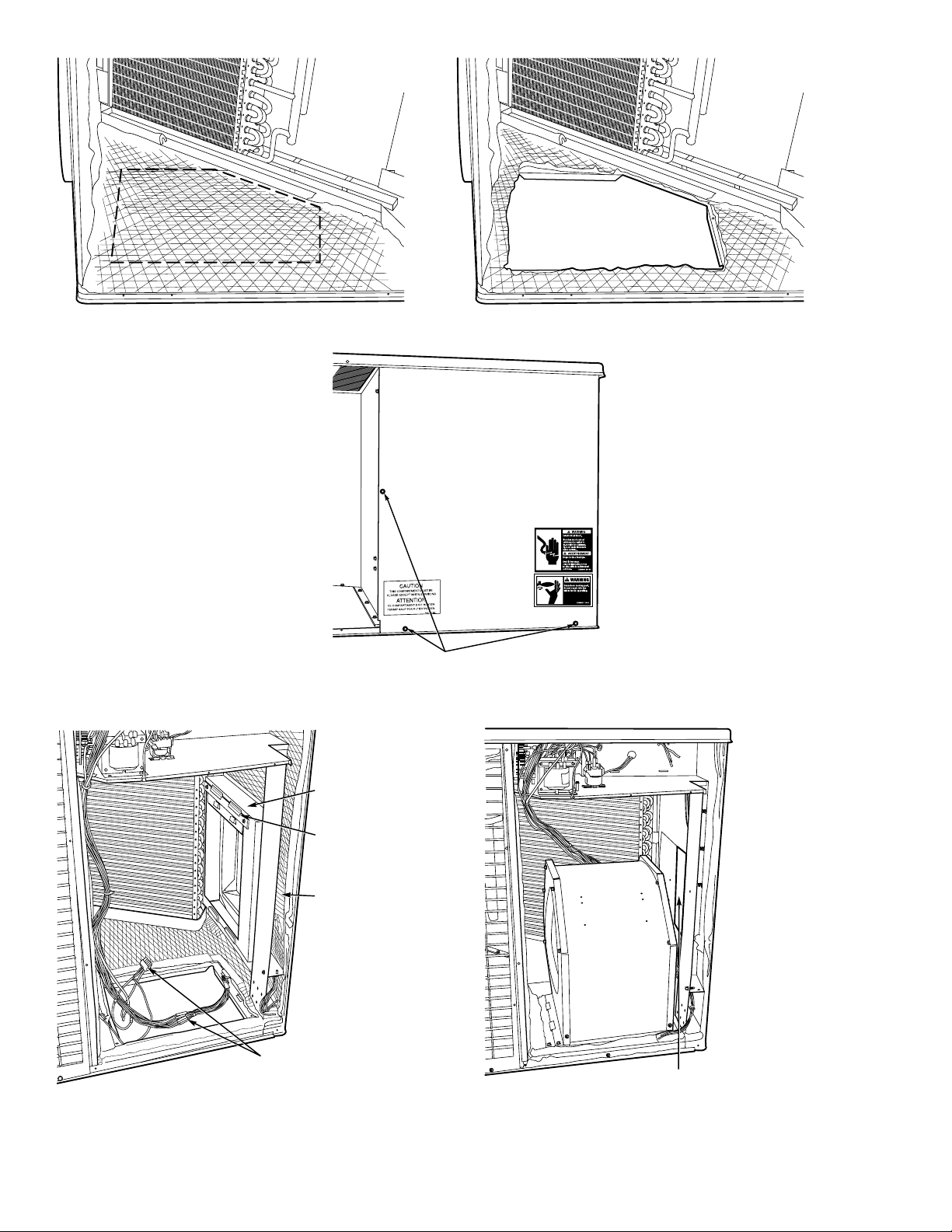
Fig. 13—Removing Insulation and Vertical Duct Cover
INDOOR BLOWER ACCESS PANEL
(REMOVE SCREWS)
Fig. 14—Indoor Blower Access Panel
C95015
C950016
BLOWER
SHELF
FILLER
BRACKET
RACEWA Y
PLUG ASSEMBLIES
HORIZONTAL DUCT OPENING
Fig. 15—Converting Blower Assembly to Vertical Airflow
—10—
C950010
Page 11

FILLER
BRACKET
REMOVE
Fig. 16—Blower Shelf and Housing
DEFROST
BOARD CONTACTOR RELAY
C95017
Fig. 17—Control Box Detail View
1” (25mm) MIN.
Fig. 18–Condensate Trap
installed, use fire proof canvas (or similar heat resistant material)
connector between ductwork and unit discharge connection. If
flexible duct is used, insert a sheet metal sleeve inside duct. Heat
resistant duct connector (or sheet metal sleeve) must extend 24-in.
from the unit discharge connection flange into the ductwork.
ACCESSORY DUCT FLANGE KIT INSTALLATION-
1. Mark hole locations (See instructions included in Flange
Kit).
CAUTION: Do not drill deeper than 1/2–in. into area
between round duct openings. Damage to refrigerant coil
could result.
2. At marked locations, drill holes using a no. 26 (.147-in.)
twist drill (See Fig. 19).
C95017
TRAP
OUTLET
2” (50mm) MIN.
C99013
3. Partially secure duct flanges using two of the no. 10, 1/2-in.
screws provided.
4. See the following caution. Using remaining holes in duct
flanges as templates, drill the remaining holes with the no.
26 (.147-in.) drill.
5. Fully secure the duct flanges using the remaining screws
provided.
NOTE: The finished kit installation accommodates a 14 3/4-in. x
14 3/4-in. duct.
A. CONFIGURING UNITS FOR DOWNFLOW (VERTICAL) DISCHARGE-STANDARD UNITS (024–042)
Units 024–042 (Units with PSC Indoor Blower Motors) are
shipped in a horizontal configuration. To convert a horizontal unit
for downflow (vertical) discharge, perform the following steps:
—11—
Page 12

TABLE 1—PHYSICAL DATA—UNIT 657A
UNIT SIZE 024 030 036 042 048 060
NOMINAL CAPACITY (ton) 2 2-1/2 3 3-1/2 4 5
OPERATING WEIGHT (lb.)
Without Base Rails
WIth Optional Rails
COMPRESSOR Scroll
REFRIGERANT (R-22)
Quantity (lb.)
REFRIGERANT METERING DEVICE Acutrol™ System
OUTDOOR COIL
Rows...Fins/in.
Face Area (sq. ft.)
OUTDOOR FAN
Nominal Cfm
Diameter (in.)
Motor Hp (Rpm)
INDOOR COIL
Rows...Fins/in.
Face Area (sq. ft.)
INDOOR BLOWER
Motor Type
Speeds
Nominal Airflow (Cfm)
Size (in.)
Motor Hp (RPM)
RETURN-AIR FILTERS (in.)
Throwaway
ECM-Electronic Computated Motor.
309
296
5.4 5.6 8.6 6.8 7.9 8.1
2...17
7.0
2200
20
1/4 (1100)
3...15
3.6
PSC
3
800
10x9
1/4 (1075)
24x24x1 24x24x1 24x30x1 24x30x1 24x30x1 24x30x1
340
327
2...17
7.0
2200
20
1/4 (1100)
3...15
3.6
PSC
3
1000
10x9
1/4 (1075)
368
355
2...17
8.7
2200
20
1/4 (1100)
4...15
4.5
PSC
3
1300
10x9
1/2 (1100)
368
355
2...17
8.7
2400
20
1/4 (1100)
4...15
4.5
PSC
3
1400
10x9
1/2 (1100)
411
398
2...17
8.7
2400
20
1/3 (1100)
4...15
4.5
ECM
Variable
1550
10x10
1.0 (Variable)
425
412
2...17
8.7
2400
20
1/3 (1050)
4...15
4.5
ECM
Variable
1800
10x10
1.0 (Variable)
19-1/2"
[495]
NOTES:
Do not drill more than 1/2-in into shaded area.
1.
Dimensions in [ ] are in mm.
2.
Fig. 19—Area Not To Be Drilled
WARNING: Before performing service or maintenance
operations on the system, turn off main power to unit and
install lockout tag or electrical shock could result.
1. Open all electrical disconnects and install lockout tag before
starting any service work.
2. Remove indoor coil access panel (See Fig. 12).
3. Locate lances in unit base insulation that are placed over the
perimeter of the vertical duct opening cover (See Fig. 13).
4. Using a straight edge and sharp knife, cut and remove the
insulation around the perimeter of the cover. Remove the
screws securing the cover to the unit base and slide out the
cover. Discard the cover.
5"
[127]
C95012
5. Remove indoor blower access panel (See Fig. 14).
6. Disconnect indoor-fan motor leads from indoor fan relay
and unit contactor (See Fig. 15). Carefully disengage wire
tie containing indoor-fan motor leads from the unit control
box (See Fig. 15 & 17).
7. Remove screws securing indoor blower housing to blower
shelf and carefully slide out blower housing. There is a filler
bracket attached to the blower shelf; remove this filler
bracket and retain for later use (See Fig. 16).
8. Locate lances in unit base insulation that are placed over the
perimeter of the vertical discharge opening cover (See Fig.
13).
9. Using a straight edge and sharp knife, cut the insulation
around the perimeter of the cover. Remove the screws
—12—
Page 13

14 11/16” (372)
13 3/4” (348)
3 3/4” (94)
9 11/16” (245)
0
21 9/16” (547)
11/32” DIA (8 Places/Holes)
11/16” (17) TYP
0 10 5/8” (270)
22-GAGE SHEET
METAL COVER (SEE ABOVE)
SEAL ALL FOUR CORNERS
WITH SILICONE SEALER
Fig. 20—Field-Fabricated Duct Cover
9/32” (7) TYP
19” (482)
4 ADHESIVE-BACKED SPONGE RUBBER
SEAL STRIPS-1/8” (3.2) THICK
1//2-IN. THICK, 1-lb. DENSITY FIBERGLASS INSULATION
WITH ALUMINUM FOIL BACKING; SECURE WITH ADHESIVE
31 3/16” (792)
1 3/4” (43) 0
C95019
TABLE 2—MINIMUM AIRFLOW FOR SAFE ELECTRIC HEATER
OPERATION (CFM)
SIZE
024 030 036 042 048 060
700 875 1225 1225 1400 1750
securing the cover to the unit base and slide out the cover.
Discard the cover. Install filler bracket removed in Step 7.
10. If unit ductwork is to be attached to vertical opening flanges
on the unit base (jackstand applications only), do so at this
time.
11. It is recommended that the unit base insulation around the
perimeter of the vertical opening be secured to the unit base
with aluminum tape to prevent the insulation from tearing
or bunching up when the blower housing is installed in the
vertical discharge position.
12. Orient blower housing for vertical airflow (blower motor
adjacent to horizontal duct opening) and slide into vertical
opening making sure the flanges on the blower side plates
engage the tabs in the unit base (See Fig. 15). Resistance
will be felt as the blower housing contacts the unit base
insulation; this can be overcome by applying a slight force
to the base of the blower. Continue sliding blower in until
hole in side plate flange aligns with the hole in the unit base.
Secure using screw removed in Step 7. Reconnect indoorfan motor leads and insert wire tie back into unit control
box.
13. Cover the horizontal duct openings. Duct covers can be
ordered as an accessory or field fabricated (See Fig. 20).
14. Reinstall the indoor coil and indoor blower access panels.
15. After completing unit installation, perform all safety checks
and power up unit.
B. CONFIGURING UNITS FOR DOWNFLOW (VERTICAL) DISCHARGE-ECM UNITS (048–060)
Units 048–060 (Units with ECM Indoor Blower Motors) are
shipped in a horizontal configuration. To convert a horizontal unit
for downflow (vertical) discharge, perform the following steps:
—13—
Page 14

WARNING: Before performing service or maintenance
operations on the system, turn off main power to unit and
install lockout tag or electrical shock could result.
1. Open all electrical disconnects and install lockout tag before
starting any service work.
2. Remove indoor coil access panel (See Fig. 12).
3. Locate lances in unit base insulation that are placed over the
perimeter of the vertical duct opening cover (See Fig. 13).
4. Using a straight edge and sharp knife, cut and remove the
insulation around the perimeter of the cover. Remove the
screws securing the cover to the unit base and slide out the
cover. Discard the cover.
5. Remove indoor blower access panel (See Fig. 14).
6. Disconnect the plug assemblies from the indoor-fan motor
(See Fig. 15 & 17).
7. Remove screws securing indoor blower housing to blower
shelf and carefully slide out blower housing. There is a filler
bracket attached to the blower shelf; remove this filler
bracket and retain for later use (See Fig. 16).
8. Locate lances in unit base insulation that are placed over the
perimeter of the vertical discharge opening cover (See Fig.
13).
9. Using a straight edge and sharp knife, cut the insulation
around the perimeter of the cover. Remove the screws
securing the cover to the unit base and slide out the cover.
Discard the cover. Install filler bracket removed in Step 6.
10. If unit ductwork is to be attached to vertical opening flanges
on the unit base (jackstand applications only), do so at this
time.
11. It is recommended that the unit base insulation around the
perimeter of the vertical opening be secured to the unit base
with aluminum tape to prevent the insulation from tearing
or bunching up when the blower housing is installed in the
vertical discharge position.
12. Remove screws securing the high-voltage raceway to duct
panel. Temporarily place raceway on top of unit until
blower housing is installed.
13. Orient blower housing for vertical airflow (blower motor
adjacent to horizontal duct opening) and slide into vertical
opening making sure the flanges on the blower side plates
engage the tabs in the unit base (See Fig. 15). Resistance
will be felt as the blower housing contacts the unit base
insulation; this can be overcome by applying a slight force
to the base of the blower. Continue sliding blower in until
hole in side plate flange aligns with the hole in the unit base.
Secure using screw removed in Step 6.
14. Reinstall the high-voltage raceway removed in Step 12.
15. Cover the horizontal duct openings. Duct covers can be
ordered as an accessory or field fabricated (See Fig. 20).
16. Reinstall the indoor coil and indoor blower access panels.
17. After completing unit installation, perform all safety checks
and power up unit.
VIII. INSTALL ELECTRICAL CONNECTION
WARNING: The unit cabinet must have an uninter-
rupted, unbroken electrical ground to minimize the possibility of personal injury if an electrical fault should
occur. This ground may consist of an electrical wire
connected to the unit ground lug in the control compartment, or conduit approved for electrical ground when
installed in accordance with NEC (National Electrical
Code) ANSI/NFPA (latest edition) and local electrical
codes. In Canada, follow Canadian Electrical Code CSA
(Canadian Standards Association) C22.1 and local electrical codes. Failure to adhere to this warning could result
in personal injury or death.
CAUTION: Failure to follow these precautions could
result in damage to the unit being installed:
1. Make all electrical connections in accordance with
NEC ANSI/NFPA (latest edition) and local electrical
codes governing such wiring. In Canada, all electrical
connections must be in accordance with CSA standard
C22.1 Canadian Electrical Code Part 1 and applicable
local codes. Refer to unit wiring diagram.
2. Use only copper conductor for connections between
field-supplied electrical disconnect switch and unit.
DO NOT USE ALUMINUM WIRE.
3. Be sure that high-voltage power to unit is within
operating voltage range indicated on unit rating plate.
4. Do not damage internal components when drilling
through any panel to mount electrical hardware, conduit, etc. On 3-phase units, ensure phases are balanced
within 2 percent. Consult local power company for
correction of improper voltage and/or phase imbalance.
A. HIGH-VOLTAGE & CONTROL-VOLTAGE CONNECTIONS
The unit must have a separate electrical service with a fieldsupplied, waterproof, disconnect switch mounted at, or within
sight from, the unit. Refer to the unit rating plate for maximum
fuse/circuit breaker size and minimum circuit amps (ampacity) for
wire sizing. See Table 3 for electrical data.
The field-supplied disconnect switch box may be mounted on the
unit over the high-voltage inlet hole when the standard power and
low-voltage entry points are used. See Fig. 21 for acceptable
location.
See unit wiring label and Fig. 23, 24 & 26-27 for reference when
making high voltage connections. Proceed as follows to complete
the high-voltage connections to the unit.
If the unit has an electric heater, a second disconnect may be
required. Consult the Installation Instructions provided with
the accessory heater for electrical service connections.
1. ROUTING POWER LEADS INTO UNIT-Use only copper
wire between disconnect and unit. The high-voltage leads
should be in a conduit until they enter the duct panel;
conduit termination at the duct panel must be watertight.
Run the high-voltage leads through the knockout on the
duct panel (see Fig. 21 for location and size). When the
leads are inside the unit, run leads up the high-voltage
raceway to the line wiring splice box (Fig. 22). For
single-phase units, connect leads to the black and yellow
wires (see Fig. 24 & 26-27).
2. CONNECTING GROUND LEAD TO WIRE-BINDING
SCREW - Refer to Fig. 22. Connect the ground lead to the
chassis using the wire-binding screw in the wiring splice
box.
—14—
Page 15

HIGH
VOLTAGE
POWER
ENTRY
(KNOCKOUT)
2 DIA.
1 1/8 DIA.
1 3/8 DIA.
2 DIA.
7/8 DIA.
CONTROL
POWER
ENTRY*
*Knockout on rectangular-duct panel units; entry hole on round-duct
panel units.
NOTE: For rectangular duct knockout sizes, see Fig. 2-9.
Fig. 21–Typical Duct Panel Knockouts
3. ROUTING CONTROL POWER WIRES - STD NONECM UNITS (24 v) -Form a drip-loop with the thermostat
leads before routing them into the unit. Route the thermostat
leads through grommeted hole provided in unit (see Fig. 21)
into unit control power splice box. Connect thermostat leads
to unit control power leads as shown in Fig. 23.
4. ROUTING CONTROL POWER WIRES - ECM UNITS
(24 v) - Remove knockout in the duct panel (see Fig. 21).
Remove the rubber grommet from the installer’s packet
(included with unit) and install it in the knockout opening.
Route thermostat wires through grommet providing a drip
loop at the panel. Connect low-voltage leads to the thermostat as shown in Fig. 23.
The Easy Select interface board is located in the return-air
section and is attached to the duct panel. The Easy Select
interface board is factory wired to the motor and factory
default selections are preset.
5. The unit transformer supplies 24-v power for complete
system including accessory electrical heater. Transformer is
factory wired for 230-v operation. If supply voltage is 208
v, rewire transformer primary as described in the Special
Procedures for 208-v Operation section.
NOTE: Do not use any type of power-stealing thermostat. Unit
control problems may result.
Use no. 18 American Wire Gage (AWG) color-coded, insulated
(35 C minimum) wires to make the control voltage connections
between the thermostat and the unit. If the thermostat is located
more than 100 ft. from the unit (as measured along the control
voltage wires), use no. 16 AWG color-coded, insulated (35 C
minimum) wires.
B. SPECIAL PROCEDURES FOR 208-V OPERATION
WARNING: Make sure that the power supply to the unit
is switched OFF and lockout tag installed before making
any wiring changes. Electrical shock can cause serious
injury or death.
C95036
6. Wrap the wire nut with electrical tape so that the metal
terminal cannot be seen.
NOTE: Indoor blower motor speeds may need to be changed for
208-v operation. Refer to Indoor Airflow and Airflow Adjustment
Section.
PRE-START-UP
WARNING: Failure to observe the following warnings
could result in serious personal injury:
1. Follow recognized safety practices and wear protective
goggles when checking or servicing refrigerant system.
2. Do not operate compressor or provide any electric
power to unit unless compressor terminal cover is in
place and secured.
3. Do not remove compressor terminal cover until all
electrical sources are disconnected.
4. Relieve and recover all refrigerant from system before
touching or disturbing anything inside terminal box if
refrigerant leak is suspected around compressor terminals.
5. Never attempt to repair soldered connection while
refrigerant system is under pressure.
6. Do not use torch to remove any component. System
contains oil and refrigerant under pressure. To remove
a component, wear protective goggles and proceed as
follows:
a. Shut off electrical power to unit.
b. Relieve and reclaim all refrigerant from system using
both high- and low-pressure ports.
c. Cut component connecting tubing with tubing cutter
and remove component from unit.
d. Carefully unsweat remaining tubing stubs when
necessary. Oil can ignite when exposed to torch
flame.
1. Disconnect the orange transformer-primary lead from the
contactor. See unit wiring label
2. Remove the wire nut from the terminal on the end of the red
transformer-primary lead.
3. Save the wire nut.
4. Connect the red lead to the contactor terminal from which
the orange lead was disconnected.
5. Using the wire nut removed from the red lead, insulate the
loose terminal on the orange lead.
Proceed as follows to inspect and prepare the unit for initial
startup:
1. Remove access panel.
2. Read and follow instructions on all WARNING, CAUTION, and INFORMATION labels attached to, or shipped
with, unit.
3. Make the following inspections:
a. Inspect for shipping and handling damages such as
broken lines, loose parts, disconnected wires, etc.
—15—
Page 16

UNIT POWER
LEAD
UNIT LINE WIRE
SPLICE BOX
Fig. 22—Wiring Splice Boxes
WIRE-BINDING
SCREW
CONTROL POWER
SPLICE BOX
C95022
→
VOLTAGE
RANGE
UNIT
657A
SIZE
(–SERIES,
IF
USED)
024–311 208/230-1 187 253 11.2 56.0 1.4 2.0
024–321 208/230-1 187 253 12.1 54.0 1.4 2.0
030 208/230-1 187 253 15.0 73.0 1.4 2.6
036 208/230-1 187 253 16.0 88.0 1.2 2.6
042 208/230-1 187 253 20.0 104.0 1.4 3.1
048–301 208/230-1 187 253 26.4 129.0 2.1 7.2
048–311 208/230-1 187 253 20.8 109.0 2.1 7.2
060 208/230-1 187 253 32.1 169.0 2.1 7.2
(See legend following Electrical Data chart)
V-PH
(60 HZ)
Min Max RLA LRA FLA FLA kW FLA
COMPRESSOR OFM IFM
TABLE 3—ELECTRICAL DATA—657A
ELECTRIC
HEAT
3.75/5.00
5.60/7.50
7.50/10.0
3.75/5.00
5.60/7.50
7.50/10.0
3.75/5.00
5.60/7.50
7.50/10.0
11.30/15.0
3.75/5.00
5.60/7.50
7.50/10.0
11.30/15.0
3.75/5.00
5.60/7.50
7.50/10.0
11.30/15.0
15.0/20.0
3.75/5.00
5.60/7.50
7.50/10.0
11.30/15.0
15.0/20.0
3.75/5.00
5.60/7.50
7.50/10.0
11.30/15.0
15.0/20.0
3.75/5.00
5.60/7.50
7.50/10.0
11.30/15.0
15.0/20.0
18.1/20.8
27.1/31.3
36.1/41.7
18.1/20.8
27.1/31.3
36.1/41.7
18.1/20.8
27.1/31.3
36.1/41.7
54.1/62.0
18.1/20.8
27.1/31.3
36.1/41.7
54.1/62.0
18.1/20.8
27.1/31.3
36.1/41.7
54.1/62.0
72.2/83.3
18.1/20.8
27.1/31.3
36.1/41.7
54.1/62.0
72.2/83.3
18.1/20.8
27.1/31.3
36.1/41.7
54.1/62.0
72.2/83.3
18.1/20.8
27.1/31.3
36.1/41.7
54.1/62.0
72.2/83.3
SINGLE-POINT
POWER SUPPLY
Single-
Point
Wiring
MCA
40.3/43.4
51.0/56.5
62.5/69.5
41.4/44.5
52.2/57.7
63.7/70.7
45.3/48.8
56.6/61.8
67.9/74.8
90.4/100.3
48.3/51.7
56.6/61.8
67.9/74.8
90.4/100.3
52.1/55.5
63.3/68.6
74.6/81.6
97.1/107.0
119.8/133.7
65.2/68.3
75.9/81.4
87.4/94.4
110.2/120.4
131.8/145.9
58.2/61.3
68.9/74.4
80.4/87.4
103.2/113.4
124.8/138.9
72.0/75.5
83.3/88.5
94.6/101.5
117.1/126.9
139.6/153.5
Single-
Point
Max
Fuse
or
Ckt
Bkr
45/45
60/60
—
45/45
60/60
—
50/50
60/–
—
—
60/60
60/–
—
—
60/60
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
60/-
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
Single-
Point
MOCP
—
—
70/80
—
—
70/80
—
–/70
70/80
100/100
—
–/70
80/80
100/110
—
70/80
80/90
100/110
125/150
70/70
80/90
90/100
125/125
150/150
-/70
70/80
90/90
110/125
125/150
90/100
100/100
100/110
125/150
150/175
Heater
Only
DualPoint
Wiring
MCA
22.5/26.0
33.7/39.1
45.1/50.8
22.5/26.0
33.7/39.1
45.1/50.8
22.5/26.0
33.7/39.1
45.1/50.1
67.9/78.1
22.5/26.0
33.7/39.1
45.1/50.1
67.9/78.1
22.5/26.0
33.7/39.1
45.1/50.8
67.9/78.1
90.1/104.2
22.5/26.0
33.7/39.1
45.1/50.8
67.9/78.1
90.1/104.2
22.5/26.0
33.7/39.1
45.1/50.8
67.9/78.1
90.1/104.2
22.5/26.0
33.7/39.1
45.1/50.8
67.9/78.1
90.1/104.2
DUAL-POINT
POWER SUPPLY
(INCLUDING UNIT ONLY)
Heater
Only
Dual-
Heater
Point
Max
Fuse
or
Ckt
Bkr
25/30
35/40
50/60
25/30
35/40
50/60
25/30
35/40
50/60
—
25/30
35/40
50/60
—
25/30
35/40
50/60
—
—
25/30
35/40
50/60
—
—
25/30
35/40
50/60
—
—
25/30
35/40
50/60
—
—
100/110
100/110
100/110
100/110
Unit
Only
Only
Dual-
Dual-
Point
Point
MOCP
MCA
—
——17.4 25/25 —
—
——18.5 25/25 —
—
—
22.8 30/30 —
—
70/80
—
—
23.8 35/35 —
—
70/80
—
—
—
29.5 45/45 —
70/80
—
—
—
42.3 50/50 —
70/80
—
—
—
35.3 45/45 —
70/80
—
—
—
48.7 — 80/80
70/80
Unit
Only
Dual-
Point
Max
Fuse
or
Ckt
Bkr
Unit
Only
DualPoint
MOCP
b. Inspect for oil at all refrigerant tubing connections and
on unit base. Detecting oil generally indicates a refrigerant leak. Leak test all refrigerant tubing connections
using electronic leak detector, halide torch, or liquidsoap solution. If a refrigerant leak is detected, see Check
for Refrigerant Leaks section.
—16—
Page 17

LEGEND
FLA — Full Load Amps
LRA — Locked Rotor Amps
MCA — Minimum Circuit Amps
MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection
RLA — Rated Load Amps
CKT BKR
NOTES:
1. In compliance with NEC (National Electrical Code) requirements
2. Minimum wire size is based on 60 C copper wire. If other than
3. Unbalanced 3-Phase Supply Voltage
—
Circuit Breaker
for multimotor and combination load equipment (refer to NEC
Articles 430 and 440), the overcurrent protective device for the
unit shall be Power Supply fuse. Canadian units may be
fuse or circuit breaker.
60 C wire is used, or if length exceeds wire length in table,
determine size from NEC.
Never operate a motor where a phase imbalance in supply voltage is greater than 2%.
the percentage of voltage imbalance.
% Voltage imbalance
= 100 x
max voltage deviation from average voltage
Use the following formula to determine
average voltage
®
EXAMPLE: Supply voltage is 460-3-60.
Determine maximum deviation from average voltage.
(AB) 457
(BC) 464
(AC) 457
Maximum deviation is 7 v.
Determine percent of voltage imbalance.
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x
This amount of phase imbalance is satisfactory as it is below the
maximum allowable 2%.
IMPORTANT: If the supply voltage phase imbalance is
more than 2%, contact your local electric utility company
immediately.
AB = 452 v
BC = 464 v
AC = 455 v
Average Voltage =
452=5v
457=7v
455=2v
= 1.53%
457
=
= 457
7
452 + 464 + 455
3
1371
3
C99024
C
O
R
G
Y
E
W2
THERMOSTAT
AND SUBBASE
Fig. 23—Control-Voltage Connections
c. Inspect all field- and factory-wiring connections. Be sure
that connections are completed and tight.
d. Ensure electrical wiring does not contact refrigerant
tubes or sharp metal edges.
e. Inspect coil fins. If damaged during shipping and han-
dling, carefully straighten fins with a fin comb.
4. Verify the following conditions
a. Make sure that outdoor-fan blade is correctly positioned
in fan orifice. Leading edge of outdoor-fan blade should
be 2 in. back from inlet grille or 1/2–in. maximum from
the fan deck.
b. Make sure that air filter(s) is in place.
c. Make sure that condensate drain trap is filled with water
to ensure proper drainage.
d. Make sure that all tools and miscellaneous loose parts
have been removed.
5. Compressors are internally spring mounted. Do not loosen
or remove compressor hold-down bolts.
BRN
ORN
RED
GRN
YEL
WHT
UNIT CONTROL POWER
SPLICE BOX
C99056
6. Each unit (system) has 2 Schrader-type ports, one low-side
fitting located on the suction line, and one high-side fitting
located on the compressor discharge line. Be sure that caps
covering these Schrader fittings are tight.
START-UP
A. CHECK FOR REFRIGERANT LEAKS
Proceed as follows to locate and repair a refrigerant leak and to
charge the unit:
1. Locate leak and make sure that refrigerant system pressure
has been relieved and reclaimed from both high- and
low-pressure ports.
2. Repair leak following accepted practices. NOTE: Install a
filter drier whenever the system has been opened for repair.
3. Add a small charge of R-22 refrigerant vapor to system and
leak-test unit.
4. Recover refrigerant from refrigerant system and evacuate to
500 microns if no additional leaks are not found.
5. Charge unit with R-22 refrigerant, using a volumetriccharging cylinder or accurate scale. Refer to unit rating
plate for required charge. Be sure to add extra refrigerant to
compensate for internal volume of filter drier.
—17—
Page 18

GROUND
LEAD
GROUND LUG
(IN SLPICE BOX)
SINGLE-PHASE
CONNECTIONS
TO DISCONNECT
PER NEC
3-PHASE
CONNECTIONS
LEGEND
NEC – National Electrical Code
Field Wiring
Splice Connections
Fig. 24—High-Voltage Connections
1/2 IN. MAX
FR OM FAN DECK
MOTOR SHAFT
MOTOR
C95027
Fig. 25—Fan Blade Clearance
B. START UP AND MAKE ADJUSTMENTS
CAUTION: Complete the required procedures given in
the Pre-Start- Up section before starting the unit. Do not
jumper any safety devices when operating the unit. Do
not operate the compressor when the outdoor temperature
is below 40°F (unless accessory low-ambient kit is
installed). Do not rapid-cycle the compressor. Allow 5
minutes between “on” cycles to prevent compressor
damage.
C. CHECKING COOLING CONTROL OPERATION
Start and check the unit for proper cooling control operation as
follows:
1. Place room thermostat SYSTEM switch in OFF position.
Observe that blower motor starts when FAN switch is
placed in ON position and shuts down when FAN switch is
placed in AUTO position.
2. Place SYSTEM switch in COOL position and FAN switch
in AUTO position. Set cooling control below room temperature. Observe that compressor, outdoor fan, and indoor
blower motors start. Observe that compressor and outdoor
fan shut down when control setting is satisfied and that
indoor blower shuts down after fan time delay expires.
L1
L2
L3
BLK
YEL
BLU
NOTE: Use copper wire only.
3. When using an auto-changeover room thermostat, place
both SYSTEM and FAN switches in AUTO positions.
Observe that unit operates in heating mode when temperature control is set to “call for heating” (above room
temperature) and operates in cooling mode when temperature control is set to “call for cooling” (below room
temperature).
D. CHECKING HEATING CONTROL OPERATION
Start and check the unit for proper cooling control operation as
follows:
1. Place room thermostat SYSTEM switch in OFF position.
Observe that blower motor starts when FAN switch is
placed in ON position and shuts down when FAN switch is
placed in AUTO position.
2. Place SYSTEM switch in HEAT position and FAN switch
in AUTO position. Set cooling control above room temperature. Observe that compressor, outdoor fan, and indoor
blower motors start. Observe that compressor and outdoor
fan shut down when control setting is satisfied and that
indoor blower shuts down after fan time delay expires.
3. When using an auto-changeover room thermostat, place
both SYSTEM and FAN switches in AUTO positions.
Observe that unit operates in heating mode when temperature control is set to “call for heating” (above room
temperature).
4. If system is equipped with supplemental or emergency heat
(resistance heaters), observe that when thermostat is placed
in EMERGENCY HEAT mode and temperature control is
set above room temperature that heaters and indoor blower
come on. Observe that heaters shut off when control setting
is satisfied and that the indoor blower shuts off after fan
time delay expires.
E. CHECKING AND ADJUSTING REFRIGERANT
CHARGE
The refrigerant system is fully charged with R-22 refrigerant,
tested, and factory-sealed.
NOTE: Adjustment of the refrigerant charge is not required
unless the unit is suspected of not having the proper R-22 charge.
A superheat charging chart is attached to the outside of the
compressor access panel. The chart includes the required suction
line temperature at given suction line pressures and outdoor
ambient temperatures (See Table 13A-H and Fig. 30).
An accurate superheat, thermocouple- or thermistor-type thermometer, a sling psychrometer, and a gauge manifold are required
when using the superheat charging method for evaluating the unit
charge. Do not use mercury or small dial-type thermometers
because they are not adequate for this type of measurement.
C99057
—18—
Page 19

Fig. 26—Wiring Diagram–024 to 042 (208/230-60-1)
—19—
C95037
Page 20

Fig. 27—Wiring Diagram–048 to 060 (208/230-60-1 with ECM Indoor)
—20—
C95038
Page 21

TRANSFORMER CONTAINS A MANUAL
RESET OVERCURRENT PROTECTOR
IT WILL NOT AUTOMATICALLY RESET
DISCONNECT POWER AND INSTALL
LOCKOUT TAG PRIOR TO SERVICING
THIS COMPARTMENT MUST BE CLOSED
EXCEPT WHEN SERVICING
Fig. 28—Transformer Label
NOTE: Allow system to operate in the cooling mode for a
minimum of 10 minutes before checking or adjusting refrigerant
charge.
CAUTION: When evaluating the refrigerant charge, an
indicated adjustment to the specified factory charge must
always be very minimal. If a substantial adjustment is
indicated, an abnormal condition exists somewhere in the
cooling system, such as insufficient airflow across either
coil or both coils. Failure to adjust charge properly or
correct the abnormal conditions will cause damage to the
unit.
C95025
WARNING: Disconnect electrical power to the unit and
install lockout tag before changing blower speed. Electrical shock can cause serious injury or death.
Airflow can be changed by changing the lead connections of the
blower motor.
Unit 657A three-speed motors (024–042) are factory wired for low
speed operation.
G. For 208/230v-PSC Blower Motor
For color coding on the 208/230V motor leads, see Table 4.
Proceed as follows:
1. Remove caps from low- and high-pressure service fittings.
2. Using hoses with valve core depressors, attach low- and
high-pressure gauge hoses to low- and high-pressure service
fittings, respectively.
3. Start unit in Cooling mode and let unit run until system
pressures stabilize.
4. Measure and record the following:
a. Outdoor ambient-air temperature (°F db).
b. Indoor coil inlet-air temperature (°F wb).
c. Suction-tube temperature (°F) at low-side service fitting.
d. Suction (low-side) pressure (psig).
5. Using “Superheat Charging Charts” compare outdoor-air
temperature (°F db) with the Indoor coil air inlet temperature (°F wb) to determine desired system operating superheat temperature. See Table 13A–H and Fig. 30.
6. Using ’’Required Suction-Tube Temperature (F)’’ table,
compare desired superheat temperature with suction (lowside) operating pressure (psig) to determine proper suctiontube temperature. See Fig. 30.
7. Compare actual suction-tube temperature with proper
suction-tube temperature. Using a tolerance of ±3° F, add
refrigerant if actual temperature is more than 3° F higher
than proper suction-tube temperature, or remove refrigerant
if actual temperature is more than 3° F lower than required
suction-tube temperature.
NOTE: If the problem causing the inaccurate readings is a
refrigerant leak, refer to Check for Refrigerant Leaks section.
F. INDOOR AIRFLOW AND AIRFLOW ADJUSTMENTS
NOTE: For cooling operation, the recommended airflow is 350 to
450 cfm for each 12,000 Btuh of rated cooling capacity.
Table 8 shows cooling airflows at various external static pressures.
Table 9 shows Fan Only and Cooling modes for ECM units
(048-060). Refer to these tables to determine the airflow for the
system being installed.
NOTE: Be sure that all supply- and return-air grilles are open,
free from obstructions, and adjusted properly.
TABLE 4—COLOR CODING FOR 208/230–V MOTOR
LEADS
3-SPEED
black = high speed
blue = medium speed
red = low speed
To change the speed of the indoor fan motor (IFM), remove the fan
motor speed leg lead from the indoor fan relay (IFR) and replace
with lead for desired blower motor speed. Insulate the removed
lead to avoid contact with chassis parts.
H. For 208/230v-ECM Blower Motor
To configure the 657A 048-60 unit, move the 5 Easy Select board
wires to the terminals which control the airflow. Refer to the Easy
Select interface board (Fig. 29) located next to the terminal.
Perform the following steps for basic system configuration.
1. AUX HEAT RANGE (VIO) NOTE: If no heater is installed, this step can be omitted. The airflow for electric
heat is selected with the AUX HEAT RANGE terminals.
Refer to Table 2 and the installation instructions for electric
heaters for minimum airflow required for safe heater
operation. Refer to table below for the available airflows.
Each select pin is configured for a certain airflow. The
airflow will be supplied in the Heating mode on air
conditioners when electric heat is the primary heating
source. The preset factory default selection is the highest
airflow.
2. AC/HP SIZE (BLU) - The preset factory default selection
for AC/HP SIZE (air conditioner/heat pump) is set to 400
cfm/ton. The selection pins are configured for 350 cfm/ton
and 400 cfm/ton.
3. TYPE (ORN) - The TYPE is a preset factory default
selection. The preset factory default setting is AC for the
657A units. Default setting should not be altered.
4. AC/HP CFM ADJUST (BLK) - The preset factory default
selection is MED. Selections HI and LO will adjust the
airflow supplied for all operational modes (see table below).
The selection options allow installer to adjust airflow to
meet such individual needs as noise and static compensation, etc.
—21—
Page 22

TABLE 5—TERMINAL CONFIGURATION
TERMINAL 1234
Available
Airflow (CFM)
1365 1470 1680 1840
Y1
AUX HEAT
RANGE
VIO
1
BLU
BRN
BLK
GR Y
AC/HP SIZE
1
AC HPC HP
AC/HP CFM ADJUST
LO MED HI
AC/HP TIME DELAY
1 2 3 4
RED
2 3 4
2 3 4
TYPE
JW1 JW2
D4
D5
W3
W2
1
P2
JW3
JW 4
E
G
/W1
G
W2
Y/Y2
JW 5
D3
D1
D2
Y
C
R
O
Y1
/Y2
IFO
O
SEC-1
SEC-2
R1
L
R2
R3
F1
5
P1
1
L
5 AMP FUSE
Fig. 29—Easy Select Interface Board for Units 048-060 with ECM Blower Motor
TABLE 6—CFM ADJUST (PERCENT OF CFM)
MODE FAN ONLY COOLING HEATING
LO-Adjust
–15 –10 –10
C95024
HI-Adjust
15 10 10
5. AC/HP TIME DELAY (GRY) - Four motor operation delay
options are provided to customize system operation. See
listing below:
Unit Controls— All compressors have the following internalprotection controls.
1. High-Pressure Relief Valve - This valve opens when the
pressure differential between the low and high side becomes
excessive.
2. Compressor Overload - This overload interrupts power to
the compressor when either the current or internal temperature become excessive, and automatically resets when the
internal temperature drops to a safe level.
This overload may require up to 60 minutes (or longer) to
reset; therefore, if the internal overload is suspected of
being open, disconnect the electrical power to the unit and
check the circuit through the overload with an ohmmeter or
continuity tester.
I. COOLING SEQUENCE OF OPERATION
PSC BLOWER MOTOR UNITS (024–042)
NOTE: With the FAN switch in the ON position, 24-v is supplied
to the IFR through the G terminal on the thermostat. This voltage
energizes the coil of the contactor, closing the normally-open set of
contacts which provide continuous power to the indoor (evapora-
tor) fan motor (IFM). Moving the FAN switch back to the AUTO.
position, providing there is not a call for cooling, deenergizes the
IFR, opens the IFR contacts, and deenergizes the IFM. The FAN
switch in AUTO. position cycles upon a call for cooling.
On a call for cooling, 24 v is supplied to the compressor contactor
(C) and IFR simultaneously through the Y and G terminals of the
thermostat, respectively. On units with a compressor time delay
relay, there is a built-in, 5-minute (± 45 seconds) delay between
compressor starts. Energizing the contactor closes the normallyopen set of contacts supplying power to both the compressor and
outdoor (condenser) fan motor (OFM). Energizing the IFR closes
the normally-open set of contacts providing power to the IFM. On
the loss of the call for cooling, 24 v is removed from both the Y
and G terminals of the thermostat (providing the FAN switch is in
the AUTO. position), deenergizing both the contactor and IFR and
opening both the contacts supplying power to compressor/OFM
and IFM.
ECM BLOWER MOTOR UNITS (048–060)
Indoor Fan - With the fan switch in the ON position, 24-v is
supplied to the ECM motor through the ’’G’’ terminal on the
thermostat. This voltage provides continuous power to the indoor
(evaporator) fan motor (IFM). If the fan switch is moved back to
the AUTO position and there is not a call for heating or cooling,
24-v is removed from the ’’G’’ terminal and the indoor fan
—22—
Page 23

OPTION DESCRIPTION
30-Sec On/60-Sec Off Delay
Profile (Terminal 1)
No Delay Option
(Terminal 2)
30-Sec Off Delay
(Terminal 3)
45-Sec Off Delay
(Terminal 4)
TABLE 7—ECM BOARD PIN SELECTION
Used when it is desirable to allow system coils time to heat
up or cool down prior to airflow
Used for servicing or when other components are used to
perform the delay function
Preset factory setting for 657A units
Enhances system efficiency
remains energized for the delay timing. When the fan switch is in
AUTO, the fan cycles with either the call for heating or cooling.
Cooling- On a call for cooling, 24 v is supplied to the compressor
contactor (C) and IFM simultaneously through the ’’Y’’ and ’’G’’
terminals of the thermostat. Energizing the contactor closes the
normally open set of contacts supplying power to both the
compressor and outdoor (condenser) fan motor (OFM). On the loss
of the call for cooling, 24 v is removed from the ’’Y’’ and ’’G’’
terminals of the thermostat, deenergizing the compressor and
OFM. The indoor fan remains energized for the delay timing.
NOTE: Once the compressor has started and then stopped, it
cannot be restarted again until 5 minutes have elapsed.
J. HEATING SEQUENCE OF OPERATION
PSC BLOWER MOTOR UNITS (024–042)
Heat Pump Heating - On a call for heat, thermostat makes circuits
R-Y and R-G. When compressor time delay (5 +/- 2 minutes) is
completed, a circuit is made to C, starting COMP and OFM.
Circuit R-G also energizes IFR and starts IFM after 1-sec. delay.
Should room temperature continue to fall, circuit R-W is made
through second-stage thermostat bulb. If optional electric heat
package is used, a relay is energized, bringing on first bank of
supplemental electric heat. When thermostat is satisfied, contacts
open, deenergizing contactor and relay; motors and heaters deenergize. The IFM may be controlled by a time-delay relay that will
extend IFM operation for a matter of sec.
Defrost Mode - Defrost board (DB) is a time and temperature
control, which includes a field-selectable time period between
checks for defrost (30, 50 or 90 minutes). Electronic timer and
defrost cycle start only when contactor is energized and defrost
thermostat (DFT) is closed.
Defrost mode is identical to Cooling mode, except outdoor-fan
motor stops and a bank of optional electric heat turns on to warm
air supplying the conditioned space.
Auxiliary Heating - If accessory electric heaters are installed, on
a call for heat, circuit R-W is made through the thermostat
contacts. Circuit R-G is made which energizes the IFR. If the
heaters are staged, then the thermostat closes a second set of
contacts W2 when second stage is required. When thermostat is
satisfied, contacts open, deenergizing the heater relay and the IFR.
ECM BLOWER MOTOR UNITS (048–060)
Heat Pump Heating - On a call for heat, thermostat makes circuits
R-Y and R-G. When compressor time delay (5 +/- 2 minutes) is
completed, a circuit is made to C, starting COMP and OFM.
Circuit R-G also energizes IFR and starts IFM after 1-sec. delay.
Should room temperature continue to fall, circuit R-W is made
through second-stage thermostat bulb. If optional electric heat
package is used, a relay is energized, bringing on first bank of
supplemental electric heat. At this time, the airflow (CFM) will be
either the AUX HEAT RANGE (VIO) setting or the AC/HP SIZE
(BLU) setting, whichever is greater. This may be a noticeable
change in airflow. When thermostat is satisfied, contacts open,
deenergizing contactor and relay; motors and heaters deenergize.
The IFM has a time delay relay that keeps the fan on for 30-sec.
Defrost Mode - Defrost board (DB) is a time and temperature
control, which includes a field-selectable time period between
checks for defrost (30, 50 or 90 minutes). Electronic timer and
defrost cycle start only when contactor is energized and defrost
thermostat (DFT) is closed.
Defrost mode is identical to Cooling mode, except outdoor-fan
motor stops and a bank of optional electric heat turns on to warm
air supplying the conditioned space.
Auxiliary Heating - If accessory electric heaters are installed, on
a call for heat, circuits R-W and R-G are made through the
thermostat contacts, energizing the heater relay and IFM. If the
heaters are staged, then the thermostat closes the second set of
contacts, W2, when the second stage is required. When the
thermostat is satisfied, contacts open, deenergizing the heater relay
and the IFM.
MAINTENANCE
To ensure continuing high performance, and to minimize the
possibility of premature equipment failure, periodic maintenance
must be performed on this equipment. This cooling unit should be
inspected at least once each year by a qualified service person. To
troubleshoot cooling of units, refer to tables at the back of the
book.
NOTE TO EQUIPMENT OWNER: Consult your local dealer
about the availability of a maintenance contract.
WARNING: The ability to properly perform maintenance on this equipment requires certain expertise, mechanical skills, tools, and equipment. If you do not
possess these, do not attempt to perform any maintenance
on this equipment other than those procedures recommended in the User’s Manual. FAILURE TO HEED
THIS WARNING COULD RESULT IN SERIOUS PERSONAL INJURY AND POSSIBLE DAMAGE TO THIS
EQUIPMENT.
WARNING: Failure to follow these warnings could
result in serious personal injury:
1. Turn off electrical power to the unit and install lockout
tag before performing any maintenance or service on
the unit.
2. Use extreme caution when removing panels and parts.
As with any mechanical equipment, personal injury
can result from sharp edges, etc.
3. Never place anything combustible either on, or in
contact with, the unit.
CAUTION: Errors made when reconnecting wires may
cause improper and dangerous operation. Label all wires
prior to disconnection when servicing.
The minimum maintenance requirements for this equipment are as
follows:
—23—
Page 24

TABLE 8—DRY COIL AIR DELIVERY (DEDUCT 10 PERCENT FOR 208V)*
HORIZONTAL AND DOWNFLOW DISCHARGE
UNIT 657A024-042
230 AND 460 VOLT
Unit
024 & 030
036
042
* Air delivery values are based on operating voltage of 230-v dry coil, without filter or electric heater. Deduct wet coil, filter and electric heater pressure drops to obtain static
pressure available for ducting.
NOTES:
1. Do not operate the unit at a cooling airflow that is less than 350 cfm for each 12,000 Btuh of rated cooling capacity. Indoor coil frosting may occur at airflows below this
point.
2. Dashes indicate portions of table that are beyond the blower motor capacity or are not recommended.
Motor
Speed
Low
Med
High
Low
Med
High
Low
Med
High
0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
Watts 280 275 265 255 250 245 240 ————
Cfm820810755700660600560————
Watts 365 360 350 345 340 330 320 310 300 — —
Cfm 1025 1010 975 940 900 850 800 720 630 — —
Watts — — 490 480 470 460 445 430 410 390 380
Cfm — — 1300 1255 1200 1150 1080 1005 915 790 620
Watts 520 495 474 458 445 425 —————
Cfm 1375 1335 1290 1240 1200 1140 —————
Watts 575 560 535 510 480 460 440 425 — — —
Cfm 1520 1490 1450 1400 1380 1300 1200 1080 — — —
Watts ————650614575540510480—
Cfm————1560 1500 1380 1280 1170 1060 —
Watts 490 480 470 460 450 430 410 390 — — —
Cfm 1400 1380 1340 1300 1250 1200 1140 1070 — — —
Watts 590 580 560 545 525 505 480 450 420 — —
Cfm 1600 1560 1540 1470 1430 1360 1300 1220 1120 — —
Watts —————700670640600560500
Cfm—————1780 1670 1600 1480 1340 1100
External Static Pressure (in. wg)
TABLE 9—048 & 060 ECM AIRFLOW (CFM)
UNIT 657A
048 1400 1600
060 1750 2000
1. Inspect air filter(s) each month. Clean or replace when
necessary.
2. Inspect indoor coil, drain pan, and condensate drain at least
each cooling season for cleanliness. Clean when necessary.
3. Inspect blower motor and wheel for cleanliness and check
lubrication each heating and cooling season. Clean when
necessary.
4. Check electrical connections for tightness and controls for
proper operation each heating and cooling season. Service
when necessary.
5. Ensure electric wires are not in contact with refrigerant
tubing or sharp metal edges.
A. AIR FILTER
CAUTION: Never operate the unit without a suitable air
filter in the return-air duct system. Always replace the
filter with the same size as originally installed. See Table
1 for recommended filter sizes.
Inspect air filter(s) at least once each month and replace
(throwaway-type) or clean (cleanable-type) at least twice during
each heating and cooling season or whenever the filter(s) becomes
clogged with dust and lint.
B. UNIT TOP REMOVAL
NOTE: When performing maintenance or service procedures that
require removal of the unit top, be sure to perform all of the routine
maintenance procedures that require top removal, including coil
inspection and cleaning, and condensate drain pan inspection and
cleaning.
FAN ONLY
(CFM)
COOLING
(CFM)
Only qualified service personnel should perform maintenance and
service procedures that require unit top removal. Refer to the
following top removal procedures:
1. Remove 7 screws on unit top cover surface. (Save all
screws.)
2. Remove 4 screws on unit top cover flange. (Save all
screws.)
3. Lift top from unit carefully. Set top on edge and make sure
that top is supported by unit side that is opposite duct (or
plenum) side.
4. Carefully replace and secure unit top to unit, using screws
removed in Steps 1 and 2, when maintenance and/or service
procedures are completed.
C. INDOOR BLOWER AND MOTOR
NOTE: Motors without oilers are prelubricated. Do not attempt to
lubricate these motors.
For longer life, operating economy, and continuing efficiency,
clean accumulated dirt and grease from the blower wheel and
motor annually.
Lubricate the motor every 5 years if the motor is used intermittently (thermostat FAN switch in AUTO. position), or every 2
years if the motor is used continuously (thermostat FAN switch in
ON position).
—24—
Page 25

UNIT SIZE
024
030
036
042
048
060
TABLE 10—WET COIL PRESSURE DROP
AIRFLOW
(CFM)
600 0.039
700 0.058
800 0.075
900 0.088
900 0.088
1000 0.095
1200 0.123
1000 0.068
1200 0.088
1400 0.108
1600 0.123
1000 0.048
1200 0.069
1400 0.088
1600 0.102
1400 0.068
1550 0.073
1600 0.075
1800 0.088
1700 0.082
1900 0.095
2100 0.108
2300 0.123
PRESSURE DROP
(IN. WG)
TABLE 11—ACCESSORY ELECTRIC HEATER PRESSURE DROP (IN. WG)
HEATER
KW
600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000 2200
5–20 0.030 0.033 0.037 0.042 0.047 0.052 0.060 0.067 0.075
CFM
TABLE 12—FILTER PRESSURE DROP (IN. WG)
UNIT SIZE
024–036 24 x 24 x 1 — — 0.06 0.06 0.07 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.10 ——————————
042–060 24 x 30 x 1 — — — — — — — — 0.08 0.09 0.09 0.10 0.11 0.12 0.13 0.14 0.15 0.17 0.18
FILTER
SIZE
(IN.)
500 600 700 800 900 1000 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 1600 1700 1800 1900 2000 2100 2200 2300
TABLE 13A—SUPERHEAT CHARGING TABLE, UNIT 024–311
TEMP (F)
AIR ENT
COND
65
70 — — 19.5 24.4 29.3 29.9 30.4 29.5 28.6 28.2 27.8
75 — — 15.0 21.4 27.8 28.6 29.4 28.5 27.7 27.2 26.7
80 — — 7.5 14.4 21.4 24.5 27.6 27.1 26.5 26.1 25.6
85 — — — 7.5 15.0 20.4 25.8 25.6 25.4 24.9 24.5
90 — — — — 7.5 14.0 20.4 22.3 24.2 23.8 23.4
95 — — — — — 7.5 15.0 19.0 23.1 22.7 22.3
100 ——————7.513.5 19.5 20.3 21.1
105 ———————8.016.0 18.0 20.0
110 ————————12.4 15.7 18.9
115 ————————8.913.3 17.8
Ewb-Entering Wet Bulb
SPH-Superheat at Compressor (F)
– -Do not attempt to charge system under these conditions as refrigerant slugging may occur.
SPH
56 58 60 62 64 66 68 70 72 74 76
— — 24.0 27.4 30.8 31.1 31.5 30.5 29.5 29.2 28.9
EVAP AIR – CFM
800
EVAP AIR – Ewb (F)
WARNING: Disconnect and tag electrical power to the
unit before cleaning the blower motor and wheel. Failure
to adhere to this warning could cause personal injury or
death.
To clean the blower motor and wheel:
1. Remove and disassemble blower assembly as follows:
a. Remove unit access panel.
b. For PSC Blower Motors Disconnect motor lead from
indoor fan relay (IFR). Disconnect yellow lead from
terminal L2 of the contactor.
—25—
Page 26

TABLE 13B—SUPERHEAT CHARGING TABLE, UNIT 024–321
TEMP (F)
AIR ENT
COND
65
70 33.3 32.3 33.2 33.9 36.9 36.0 35.2 34.4 33.4 32.5 31.8
75 24.6 25.6 24.1 25.0 33.3 34.8 33.8 32.6 31.8 31.0 30.2
80 16.4 17.6 21.4 16.8 23.2 31.8 32.2 31.3 30.4 29.5 28.6
85 — — 9.4 8.6 14.7 21.6 29.4 29.8 28.9 27.8 27.0
90 —————11.6 18.9 26.4 27.3 26.4 25.5
95 —————3.710.8 18.0 24.1 25.0 24.1
100 ———————8.016.3 22.1 22.6
105 ————————7.214.8 20.1
110 —————————5.213.8
115 ——————————5.1
Ewb-Entering Wet Bulb
SPH-Superheat at Compressor (F)
– -Do not attempt to charge system under these conditions as refrigerant slugging may occur.
SPH
56 58 60 62 64 66 68 70 72 74 76
38.0 37.3 37.4 37.5 38.3 37.7 36.8 35.9 35.0 34.3 33.5
EVAP AIR – CFM
750
EVAP AIR – Ewb (F)
TABLE 13C—SUPERHEAT CHARGING TABLE, UNIT 030
TEMP (F)
AIR ENT
COND
65
70 — — — 10.5 17.5 24.5 24.8 25.1 25.4 25.1 24.8
75 — — — 8.4 15.5 22.5 22.8 23.1 23.4 23.8 24.2
80 — — — 6.8 12.9 18.9 20.3 21.5 22.9 23.0 23.0
85 — — — 5.1 10.2 15.4 17.7 20.1 22.3 22.1 21.8
90 — — — — 7.9 11.9 15.2 18.5 21.8 21.5 21.2
95 — — — — 5.6 8.4 12.7 17.0 21.2 20.8 20.6
100 — — — — — — 9.2 14.1 191 19.5 19.9
105 — — — — — — 5.7 11.4 17.1 18.2 19.3
110 — — — — — — 5.0 10.0 15.1 16.9 18.6
115 ———————8.713.0 15.5 18.0
Ewb-Entering Wet Bulb
SPH-Superheat at Compressor (F)
– -Do not attempt to charge system under these conditions as refrigerant slugging may occur.
SPH
56 58 60 62 64 66 68 70 72 74 76
5.5 5.5 5.5 12.5 19.6 26.6 26.9 27.2 27.5 26.5 25.4
EVAP AIR – CFM
1000
EVAP AIR – Ewb (F)
TABLE 13D—SUPERHEAT CHARGING TABLE, UNIT 036
TEMP (F)
AIR ENT
COND
65
70 23.8 23.8 25.5 27.2 29.5 32.3 32.0 30.9 29.7 28.6 27.6
75 19.0 19.1 20.6 22.2 25.7 30.4 30.6 29.7 28.7 27.5 26.3
80 15.0 15.0 15.8 16.5 21.1 26.5 27.7 27.8 27.8 26.6 25.3
85 10.9 10.9 10.9 10.9 16.6 22.6 24.8 25.9 26.9 25.6 24.3
90 7.7 7.7 7.0 8.3 12.6 19.1 21.5 23.4 25.3 24.4 23.6
95 ————8.614.5 16.5 20.9 23.6 23.3 22.9
100 —————11.3 14.3 17.4 20.4 21.1 21.8
105 —————7.110.5 13.9 17.2 19.0 20.8
110 ——————7.111.7 16.4 18.2 19.9
115 ———————9.615.5 17.3 19.1
Ewb-Entering Wet Bulb
SPH-Superheat at Compressor (F)
– -Do not attempt to charge system under these conditions as refrigerant slugging may occur.
SPH
56 58 60 62 64 66 68 70 72 74 76
28.6 28.6 30.4 32.1 33.3 34.3 33.4 32.0 30.7 29.8 28.9
c. On all units remove blower assembly from unit. Remove
screws securing blower and slide assembly out. Be
careful not to tear insulation in blower compartment.
EVAP AIR – CFM
1150
EVAP AIR – Ewb (F)
d. Allow time for oil to be absorbed by each bearing, then
wipe excess oil from motor housing.
e. Replace dust caps or plugs in oil ports.
d. Ensure proper reassembly by marking blower wheel and
motor in relation to blower housing before disassembly.
e. Loosen setscrew(s) that secures wheel to motor shaft,
remove screws that secure motor mount brackets to
housing, and slide motor and motor mount out of
housing.
2. Lubricate motor as follows:
a. Thoroughly clean all accumulations of dirt or grease
from motor housing.
b. Remove dust caps or plugs from oil ports located at each
end of motor.
c. Use a good grade of SAE 20 non-detergent motor oil and
put one teaspoon (1.16 oz. or 16 to 25 drops) in each oil
port.
3. Remove and clean blower wheel as follows:
a. Ensure proper reassembly by marking wheel orientation.
b. Remove screws holding cut-off plate, and remove plate
from housing.
c. Lift wheel from housing. When handling and/or cleaning
blower wheel, be sure not to disturb balance weights
(clips) on blower wheel vanes.
d. Remove caked-on dirt from wheel and housing with a
brush. Remove lint and/or dirt accumulations from
wheel and housing with vacuum cleaner, using soft
brush attachment. Remove grease and oil with mild
solvent.
e. Reassemble wheel and cut-off plate into housing.
—26—
Page 27

TABLE 13E—SUPERHEAT CHARGING TABLE, UNIT 042
TEMP (F)
AIR ENT
COND
65
70 11.4 11.4 11.5 15.1 18.7 22.3 23.6 25.1 26.4 26.1 25.8
75 9.4 9.4 9.4 13.0 16.5 20.1 21.6 23.0 24.4 24.5 24.6
80 8.9 8.9 8.9 12.4 16.0 19.4 21.0 22.4 23.8 24.0 24.0
85 8.2 8.2 8.2 11.8 15.3 18.7 20.2 21.8 23.3 23.4 23.4
90 7.7 7.7 7.7 10.8 13.7 16.7 18.7 20.7 22.7 22.7 22.9
95 7.2 7.2 7.2 9.7 12.2 14.6 17.2 19.7 22.2 22.3 22.3
100 6.6 6.6 6.6 9.6 12.6 15.5 17.6 19.7 21.6 21.7 21.7
105 6.1 6.1 6.1 9.6 13.1 16.5 18.0 19.5 21.1 21.1 21.2
110 — — — 7.0 9.9 13.0 15.0 17.1 19.1 19.8 20.6
115 ————6.99.411.9 14.5 17.0 18.5 20.0
Ewb-Entering Wet Bulb
SPH-Superheat at Compressor (F)
– -Do not attempt to charge system under these conditions as refrigerant slugging may occur.
SPH
56 58 60 62 64 66 68 70 72 74 76
13.5 13.5 13.5 17.1 20.7 24.3 25.7 27.1 28.5 27.8 27.0
EVAP AIR – CFM
1400
EVAP AIR – Ewb (F)
TABLE 13F—SUPERHEAT CHARGING TABLE, UNIT 048–301
TEMP (F)
AIR ENT
COND
65
70 24.0 23.8 23.6 25.0 26.4 27.8 28.4 29.0 29.7 29.6 29.5
75 19.7 19.7 19.7 21.4 23.2 25.0 25.9 26.8 27.6 27.9 28.2
80 15.8 15.8 15.8 17.6 19.4 21.2 22.7 24.1 25.6 26.2 26.9
85 12.0 12.0 12.0 13.8 15.6 17.5 19.5 21.5 23.5 24.5 25.6
90 7.5 7.5 7.5 9.4 11.3 13.2 16.3 19.3 22.4 23.3 24.2
95 — — — 5.0 7.0 9.0 13.1 17.1 21.2 22.0 22.8
100 ——————9.414.3 19.1 20.3 21.4
105 ——————5.711.4 17.1 18.6 20.1
110 ———————9.013.5 15.8 18.0
115 ———————6.710.0 13.0 16.0
Ewb-Entering Wet Bulb
SPH-Superheat at Compressor (F)
– -Do not attempt to charge system under these conditions as refrigerant slugging may occur.
SPH
56 58 60 62 64 66 68 70 72 74 76
26.3 27.0 27.6 28.6 29.6 30.5 30.9 31.3 31.7 31.2 30.7
EVAP AIR – CFM
1600
EVAP AIR – Ewb (F)
TABLE 13G—SUPERHEAT CHARGING TABLE, UNIT 048–311
TEMP (F)
AIR ENT
COND
65
70 35.3 35.8 36.8 37.6 37.7 37.8 38.4 38.2 38.4 38.0 37.6
75 31.7 31.4 32.6 34.0 34.5 35.1 35.3 35.5 35.6 35.8 35.5
80 28.1 28.0 28.8 29.8 30.9 31.6 32.8 32.9 32.7 33.0 33.4
85 24.7 24.0 24.6 26.1 27.5 28.3 29.9 30.3 30.5 30.2 30.7
90 21.2 20.8 19.3 21.0 23.4 25.0 26.6 27.4 27.9 28.1 28.0
95 16.5 16.1 16.3 16.5 18.8 21.2 22.7 23.9 25.4 25.7 25.9
100 12.4 7.5 5.6 11.5 14.9 16.8 19.1 21.4 22.0 23.3 23.5
105 ————9.712.7 15.2 18.3 19.5 20.2 21.1
110 —————7.711.2 13.7 16.7 17.8 18.5
115 ———————7.3. 10.2 11.8 14.3
Ewb-Entering Wet Bulb
SPH-Superheat at Compressor (F)
– -Do not attempt to charge system under these conditions as refrigerant slugging may occur.
SPH
56 58 60 62 64 66 68 70 72 74 76
39.4 39.4 40.4 40.6 40.6 40.8 41.0 40.8 40.7 40.2 39.9
f. Reassemble motor into housing. Be sure setscrews are
tightened on motor shaft flats and not on round part of
shaft.
g. Reinstall unit access panel.
4. Restore electrical power to unit. Start unit and check for
proper blower rotation and motor speeds during heating and
cooling cycles.
D. OUTDOOR COIL, INDOOR COIL, AND CONDENSATE DRAIN PAN
Inspect the outdoor coil, indoor coil, and condensate drain pan at
least once each year. See Unit Top Removal section.
The coils are easily cleaned when dry; therefore, inspect and clean
the coils either before or after each cooling season. Remove all
obstructions, including weeds and shrubs, that interfere with the
EVAP AIR – CFM
1550
EVAP AIR – Ewb (F)
grease, clean the coils with a mild detergent-and-water solution.
Rinse coils with clear water, using a garden hose. Be careful not to
splash water on motors, insulation, wiring, or air filter(s). For best
results, spray outdoor coil fins from inside to outside the unit. On
units with an outer and inner (2 row) outdoor coil, be sure to clean
between the coils. Be sure to flush all dirt and debris from the unit
base.
Inspect the drain pan and condensate drain line when inspecting
the coils. Clean the drain pan and condensate drain by removing all
foreign matter from the pan. Flush the pan and drain tube with
clear water. Do not splash water on the insulation, motor, wiring,
or air filter(s). If the drain tube is restricted, clear it with a
“plumbers snake” or similar probe device. Ensure that the auxiliary
drain port above the drain tube is also clear
airflow through the outdoor coil.
Straighten bent fins with a fin comb. If coated with dirt or lint,
clean the coils with a vacuum cleaner, using the soft brush
attachment. Be careful not to bend the fins. If coated with oil or
—27—
Page 28

TABLE 13H—SUPERHEAT CHARGING TABLE, UNIT 060
TEMP (F)
AIR ENT
COND
65
70 16.5 16.5 16.5 18.8 21.1 23.5 25.2 27.0 28.8 28.2 27.6
75 12.0 12.0 12.0 14.8 17.6 20.4 22.7 24.9 27.2 26.9 26.6
80 10.5 10.5 10.5 12.7 14.9 17.1 19.8 22.5 25.2 25.4 25.5
85 9.0 9.0 9.0 10.6 12.3 13.9 17.0 20.0 23.1 23.8 24.5
90 4.5 4.5 4.5 6.5 8.5 10.5 14.3 18.1 21.9 22.7 23.5
95 ————4.87.211.7 16.2 20.7 21.6 22.5
100 —————3.68.613.6 18.6 20.0 21.4
105 ——————5.511.1 16.6 18.5 20.4
110 ———————10.0 15.5 17.5 19.4
115 ———————9.214.7 16.5 18.5
Ewb-Entering Wet Bulb
SPH-Superheat at Compressor (F)
– -Do not attempt to charge system under these conditions as refrigerant slugging may occur.
SPH
56 58 60 62 64 66 68 70 72 74 76
21.0 21.0 21.0 22.8 24.7 26.5 27.8 29.1 30.4 29.5 28.6
EVAP AIR – CFM
1800
EVAP AIR – Ewb (F)
Required Suction Tube Temperature
SUPERHEAT
TEMP (F)
0 35 37 39 41 43 45 47 49 51
2 37 39 41 43 45 47 49 51 53
4 39 41 43 45 47 49 51 53 55
6 41 43 45 47 49 51 53 55 57
8 43 45 47 49 51 53 55 57 59
10 45 47 49 51 53 55 57 59 61
12 47 49 51 53 55 57 59 61 63
14 49 51 53 55 57 59 61 63 65
16 51 53 55 57 59 61 63 65 67
18 53 55 57 59 61 63 65 67 69
20 55 57 59 61 63 65 67 69 71
22 57 59 61 63 65 67 69 71 73
24 59 61 63 65 67 69 71 73 75
26 61 63 65 67 69 71 73 75 77
28 63 65 67 69 71 73 75 77 79
30 65 67 69 71 73 75 77 79 81
32 67 69 71 73 75 77 79 81 83
34 69 71 73 75 77 79 81 83 85
36 71 73 75 77 79 81 83 85 87
38 73 75 77 79 81 83 85 87 89
40 75 77 79 81 83 85 87 89 91
NOTE: Measure suction tube temperature with accurate superheat ther-
mometer or thermistor-type thermometer
61.5 64.2 67.1 70 73 76 79.2 82.4 85.7
SUCTION PRESSURE AT SERVICE PORT (Psig)
Fig. 30—Required Suction Tube Temperature (F) *
C95030
E. OUTDOOR FAN
CAUTION: Keep the outdoor fan free from all obstruc-
tions to ensure proper cooling operation. Never place
articles on top of the unit. Damage to unit may result.
1. Remove 2 screws at bottom of outdoor air intake grille and
remove plastic grille.
2. Inspect the fan blades for cracks or bends.
3. If fan needs to be removed, loosen the setscrew and slide
the fan off the motor shaft.
4. When replacing fan blade, position blade so that the leading
edge is 2-in. back from outdoor inlet grille or 1/2-in.
maximum fro fan deck (See Fig. 25).
5. Ensure that setscrew engages the flat area on the motor shaft
when tightening
6. Replace grille.
F. ELECTRICAL CONTROLS AND WIRING
Inspect and check the electrical controls and wiring annually. Be
sure to turn off the electrical power to the unit and install lockout
tag.
Remove the control/blower and compressor compartment access
panels to locate all the electrical controls and wiring. Check all
electrical connections for tightness. Tighten all screw connections.
If any smoky or burned connections are noticed, disassemble the
connection, clean all the parts, restrip the wire end and reassemble
the connection properly and securely.
After inspecting the electrical controls and wiring, replace the
access panel. Start the unit, and observe at least one complete
heating cycle and one complete cooling cycle to ensure proper
operation. If discrepancies are observed in either or both operating
cycles, or if a suspected malfunction has occurred, check each
electrical component with the proper electrical instrumentation.
Refer to the unit wiring label when making these checkouts.
NOTE: Refer to the heating and/or cooling sequence of operation
in this publication as an aid in determining proper control
operation
—28—
Page 29

OUTDOOR COIL
INDOOR COIL
B
A
ACCUMULATOR
COMPRESSOR
Check Valves
A
Closed
B
Open
C
Closed
D
Open
LCS Loss of Charge Switch
1. Hot gas from compressor flows through the 4-way valve and is
directed to the heating liquid line check valve. It is then condensedandsubcooledthroughconverging circuits. Refrigerant leaves
the outdoor coil by way of the strainer and the check valve in the
cooling liquid line.
2. The refrigerant then feeds the indoor coil through the Acutrol
metering device on each circuit.
LEGEND
Acutrol Metering Device
Check Valve (Arrow indicates direction of flow)
Fig. 31—Typical Heat Pump Operation-Cooling Mode
G. REFRIGERANT CIRCUIT
Inspect all refrigerant tubing connections and the unit base for oil
accumulations annually. Detecting oil generally indicates a refrigerant leak.
WARNING: System under pressure. Relieve pressure
and recover all refrigerant before system repair or final
unit disposal to avoid personal injury or death. Use all
service ports and open all flow-control devices, including
solenoid valves.
COOLING CYCLE
3. Each circuit evaporates the refrigerant and the circuits are com-
4. The refrigerant then flows through the 4-way valve, accumulator,
LCS
STRAINER
D
STRAINER
C
bined in the indoor coil header with some of the circuits flowing
through the check valve.
and back to the compressor.
C95044
I. METERING DEVICE — ACUTROL DEVICE
This unit uses metering devices that are of the fixed orifice type
(located in the header to the indoor and outdoor coils).
J. LIQUID LINE STRAINER
The liquid line strainer (to protect metering device) is made of wire
mesh and located in the liquid line on the inlet side of the metering
device.
TROUBLESHOOTING
If oil is detected or if low cooling performance is suspected,
leak-test all refrigerant tubing using an electronic leak-detector,
halide torch, or liquid-soap solution. If a refrigerant leak is
detected, refer to Check for Refrigerant Leaks section.
If no refrigerant leaks are found and low cooling performance is
suspected, refer to Checking and Adjusting Refrigerant Charge
section.
H. INDOOR AIRFLOW
The heating and/or cooling air-flow does not require checking
unless improper performance is suspected. If a problem exists, be
sure that all supply- and return-air grilles are open and free from
obstructions, and that the air filter is clean. When necessary, refer
to Indoor Airflow and Airflow Adjustments section to check the
system airflow.
UsetheTroubleshooting–Cooling&Heatingguide(seeTable14)
if problems occur with these units.
START-UP CHECKLIST
Use the Start-Up checklist to ensure proper start-up procedures are
followed.
—29—
Page 30

OUTDOOR COIL
INDOOR COIL
B
A
ACCUMULATOR
COMPRESSOR
Check Valves
A
Open
B
Closed
C
Open
D
Closed
LCS Loss of Charge Switch
LEGEND
Acutrol Metering Device
Check Valve (Arrow indicates direction of flow)
HEATING CYCLE
1. Hot gas from compressor flows through the 4-way valve and is
directed to the cooling liquid line check valve. It is then condensed
and directed through subcooling circuits and out to the strainer
and the check valve in the heating liquid line.
2. The refrigerant then feeds the outdoor coil through the Acutrol
metering device on each circuit.
Fig. 32—Typical Heat Pump Operation-Heating Mode
LCS
STRAINER
D
STRAINER
C
3. Each circuit evaporates the refrigerant and the circuits are combinedintheoutdoorheaderwithsomeofthecircuits flowing through
the check valve.
4. The refrigerant then flows through the 4-way valve, accumulator,
and back to the compressor.
C95045
—30—
Page 31

SYMPTOM CAUSE REMEDY
Compressor and outdoor fan
will not start
Compressor will not start but condenser fan
runs
Compressor cycles (other than normally
satisfying thermostat)
Compressor operates continuously
Excessive head pressure
TABLE 14—TROUBLESHOOTING CHART
Power Failure Call power company
Fuse blown or circuit breaker tripped Replace fuse or reset circuit breaker
Defective thermostat, contactor, transformer,
control relay, defrost board, or high pressure or lossof-charge/low pressure switch
Insufficient line voltage Determine cause and correct
Incorrect or faulty wiring Check wiring diagram and rewire correctly
Thermostat setting too high
Faulty wiring or loose connections in compressor
circuit
Compressor motor burned out, seized, or
internal overload open
Defective run capacitor, overload, or PTC
(positive temperature coefficient) thermistor
Low input voltage (20 percent low) Determine cause and correct
Refrigerant overcharge or undercharge
Defective compressor Replace and determine cause
Insufficient line voltage Determine cause and correct
Blocked outdoor coil Determine cause and correct
Defective run/start capacitor, overload or start
relay
Defective thermostat Replace thermostat
Faulty outdoor-fan motor or capacitor Replace
Damaged reversing valve Determine cause and correct
Restriction in refrigerant system Locate restriction and remove
Dirty air filter Replace filter
Unit undersized for load Decrease load or increase unit size
Thermostat set too low Reset thermostat
Low refrigerant charge Locate leak, repair, and recharge
Frosted coil with incorrect defrost operation
Air in system
Outdoor coil dirty or restricted Clean coil or remove restriction
Dirty air filter Replace filter
Dirty indoor or outdoor coil Clean coil
Refrigerant overcharged Recover excess refrigerant
Air in system
(Heat) Indoor air restricted or recirculating Determine cause and correct
Indoor or outdoor air restricted or air short-cycling Determine cause and correct
Replace component
Lower thermostat setting below room
temperature
Check wiring and repair or replace
Determine cause.
Replace compressor
Determine cause and replace
Recover refrigerant, evacuate system, and
recharge to capacities shown on nameplate
Determine cause and replace
Check defrost time settings
Reset as necessary
Check defrost temperature switch
Replace as necessary
Recover refrigerant, evacuate system,
and recharge
Recover refrigerant, evacuate system,
and recharge
SYMPTOM CAUSE REMEDY
Head pressure too low
Excessive suction pressure
Suction pressure too low
Compressor runs but
outdoor fan does not
IFM does not run
IFM operation is intermittent
IFM (048–060) runs when
it should be off
IFM–Indoor Fan Motor
TABLE 14—TROUBLESHOOTING CHART (CONT’D)
Low refrigerant charge Check for leaks, repair and recharge
Restriction in liquid tube Remove restriction
(Heat) Outdoor coil frosted
(Cool) High Heat load Check for source and eliminate
Reversing valve hung up or leaking internally Replace valve
Refrigerant overcharged Recover excess refrigerant
(Cool) Dirty air filter Replace filter
(Heat) Outdoor coil frosted
Low refrigerant charge Check for leaks, repair and recharge
Metering device or low side restricted Remove source of restriction
(Cool) Insufficient coil airflow
(Cool) Temperature too low in conditioned area Reset thermostat
(Cool) Outdoor ambient below 40°F Install low-ambient kit
Filter-drier restricted Replace
NC (normally closed) contacts on defrost board
open
Blower wheel not secured to shaft Properly tighten blower wheel to shaft
Insufficient voltage at motor Determine cause and correct
Power connectors not properly sealed Connectors should snap easily; do not force
Water dripping into motor Verify proper drip loops in connector wires
Connectors not firmly sealed
Motor programmed with a delay profile Allow a few minutes for motor to shut off
With thermostat in “off” mode, the voltage on
G, Y1, Y2, W with respect to common, should be
1/2 of actual low voltage supply
Move timer on control board to 30 minutes
between defrost cycles
Move timer on control board to 30 minutes
between defrost cycles
Increase air quantity
Check filter–replace if necessary
Check condition of relay on board
Replace if necessary
Gently pull wires individually to be sure they are
crimped into the housing
If measured voltage is more that 1/2, the thermostat
is incompatible with motor. If voltage is less than
1/2, the motor has failed
—31—
Page 32

I. PRELIMINARY INFORMATION
Model No .............................................................................................................................................................
Serial No ..............................................................................................................................................................
Date .....................................................................................................................................................................
Technician ...........................................................................................................................................................
Job/ Location...............................................................................................................................................
II. PRE-START-UP
____ Verify that all packing materials have been removed from unit
____ Verify that condensate connection is installed per installation instructions
____ Check all electrical connections and terminals for tightness
____ Check that indoor (evaporator) air filter is clean and in place
____ Verify that unit installation is level
____ Check fan wheel propeller for location in housing and setscrew tightness
III. START-UP
SupplyVoltage:C-S__________S-R__________R-C__________
Compressor Amps: C __________ S __________ R __________
Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Amps: __________
TEMPERATURE
Outdoor (Condenser) Air Temperature: __________ DB
Return-Air Temperature: __________ DB __________ WB
Cooling Supply Air: __________ DB __________ WB
PRESSURES
Refrigerant Suction __________ psig
Suction Line Temp*__________
Refrigerant Discharge __________ psig
Discharge Temp† __________
____ Verify Refrigerant charge using charging tables
START-UP CHECKLIST
(REMOVE AND STORE IN JOB FILE)
* Measured at suction inlet to compressor
† Measured at liquid line leaving outdoor coil
© 2003 Bryant Heating & Cooling Systems 7310 W. Morris St. Indianapolis, IN 46231
—32—
Printed in U.S.A. ii657a245 Catalog No. 5365-702
 Loading...
Loading...