BroMax Communications UW320 Revised Manual

USB Wireless Network
Adapter
User’s Manual
Rev 0.9

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’s Manual
Regulatory compliance
FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation.
This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
You are cautioned that changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void your authority to operate the equipment.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operation in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter.
CE Mark Warning
This is a Class B product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio
interference, in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
2

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’s Manual
About this manual
This User’s Manual describes how to install and operate your USB Wireless
Network Adapter. Please read this manual before you install the product.
This manual includes the following topics:
Product description and features.
Hardware installation procedure.
Software installation procedure.
FAQ
3

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’s Manual
Table of Contents
Regulatory compliance..............................................................................2
About this manual......................................................................................3
Chapter 1 - Introduction...................................................5
Features ..............................................................................................5
What is Wireless LAN?........................................................................6
Wireless LAN Modes...........................................................................6
Notes on Wireless LAN Configuration.................................................7
Chapter 2 - Hardware Installation....................................8
Package Contents...............................................................................8
System Requirements for the Adapter.................................................8
Connecting the USB Adapter...............................................................8
LED Indicators.....................................................................................9
Disconnecting the USB Adapter ..........................................................9
Chapter 3 – Driver Installation for Windows..................11
Driver installation for Windows 98.....................................................11
Driver installation for Windows 2000.................................................14
Driver installation for Windows ME....................................................17
Driver installation for Windows XP ....................................................19
Chapter 4 – Using the Wireless Utility...........................21
Install Wireless LAN Utility.................................................................21
In Windows XP............................................................................24
Use Windows Wireless Network Configuration .................................... 25
Use Wireless LAN Utility ...................................................................... 28
Use Wireless LAN Utility In Windows 98, 2000 and ME..............31
Configuring the USB Wireless Network Adapter ...............................31
Chapter 5 – Installing Network Protocols......................36
Installing the Network Protocols for Windows 98 and Millennium .....36
Appendix A – F AQ .........................................................39
Appendix B – Specifications..........................................40
4

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’s Manual
Chapter 1 - Introduction
Thank you for purchasing the USB Wireless Network Adapter. This high-speed USB
Wireless Network Adapter provides you with an innovative wireless networking
solution. The Adapter is easy to set up and use. With this innovative wireless
technology, you can share files and printers on the network—without inconvenient
wires! Now you can carry the LAN in your pocket!
The Adapter is a network adapter with a rate of 1, 2, 5.5, and 11 Mbps operating
in the ISM band using Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) transmission
implementing the IEEE 802.11b standard. This adapter provides Device Drivers
for Windows 98, Windows 2000, XP and Windows ME. It also provides tools for
the configuration of the adapter. The tool, as well as the installation steps of the
plug-and-play procedure for the Microsoft Windows 98, 2000, XP and Windows
ME operating systems, is described in this document.
Features
The USB Wireless Network Adapter offers compliance with the IEEE 802.11b
specification. This feature allows them to communicate with other wireless
devices that support the standard. Features of the adapter are:
Uses 2.4GHz frequency band, which complies with worldwide
requirement
Wireless interface following the IEEE 802.11b standard
Using Universal Serial Bus (USB) interface
Enciphering/deciphering of wireless data by the implementation of the
WEP algorithm
Wire-free access to networked resources from anywhere beyond the
desktop
Allows users move between Access Points without resetting their
connection reconfiguration
Delivers data rate up to 11 Mbps
Supports 11, 5.5, 2, and 1 Mbps rates
Provide USB Wireless Network Adapter Configuration utility
Antenna is built in to the Adapter with LEDs indicating Power and Link
Supports most popular operating systems: Window 98/2000/XP &
Windows ME
5
USB Wireless Network Adapter User’s Manual
p
What is Wireless LAN?
Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) systems offer a great number of
advantages over traditional wired systems. WLAN is flexible and easy to setup
and manage. They are also more economical than wired LAN systems.
Using radio frequency (RF) technology, WLAN transmit and receive data through
the air. WLAN combine data connectivity with user mobility. For example, users
can roam from a conference room to their office without being disconnected from
the LAN.
Using WLAN, users can conveniently access-shared information, and network
administrators can configure and augment networks without installing or moving
network cables.
WLAN technology provides users with many convenient and cost saving features:
• Mobility: WLAN provide LAN users with access to real-time information
anywhere in their organization, providing service opportunities that are
impossible with wired networks.
• Ease of Installation: Installing is easy for novice and expert users alike,
eliminating the need to install network cables in walls and ceilings.
• Scalability: WLAN can be configured in a variety of topologies to adapt to
specific applications and installations. Configurations are easily changed
and range from peer-to-peer networks suitable for a small number of users
to full infrastructure networks of thousands of users roaming over a broad
area
.
Wireless LAN Modes
Wireless LANs can be configured in one of two ways:
Ad-hoc
Networking
Also known as a peer-to-peer network, an ad-hoc
network is one that allows all workstations and
computers in the network to act as servers to all other
users on the network. Users on the network can share
files, print to a shared printer, and access the Internet
with a shared modem. However, with ad-hoc
networking, users can only communicate with other
wireless LAN computers that are in the wireless LAN
workgroup, and are within range.
Infrastructure
Networking
Infrastructure networking differs from ad-hoc
networking in that it includes an access point. Unlike
the ad-hoc structure where users on the LAN contend
the shared bandwidth, on an infrastructure network the
access
oint can manage the bandwidth to maximize
6
USB Wireless Network Adapter User’s Manual
bandwidth utilization.
Additionally, the access point enables users on a
wireless LAN to access an existing wired network,
allowing wireless users to take advantage of the wired
networks resources, such as Internet, email, file
transfer, and printer sharing.
Infrastructure networking has the following advantages
over ad-hoc networking:
• Extended range: each wireless LAN computer
within the range of the access point can
communicate with other wireless LAN computers
within range of the access point.
• Roaming: the access point enables a wireless
LAN computer to move through a building and still
be connected to the LAN.
• Wired to wireless LAN connectivity: the access
point bridges the gap between wireless LANs and
their wired counterparts.
Notes on Wireless LAN Configuration
When configuring a wireless LAN (WLAN), be sure to note the following points:
• Optimize the performance of the WLAN by ensuring that the distance
between access points is not too far. In most buildings, WLAN cards
operate within a range of 100 ~ 300 feet, depending on the thickness and
structure of the walls.
• Radio waves can pass through walls and glass but not metal. If there is
interference in transmitting through a wall, it may be that the wall has
reinforcing metal in its structure. Install another access point to circumvent
this problem.
• Floors usually have metal girders and metal reinforcing struts that interfere
with WLAN transmission.
This concludes the first chapter. The next chapter deals with the hardware
installation of the Adapter.
7

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’s Manual
Chapter 2 - Hardware Installation
This chapter covers connecting your USB Wireless Network Adapter to USB port
of desktop / notebook PC.
Package Contents
Please make sure that items below are included on package.
One USB Wireless Network Adapter
One USB cable
One CD containing drivers and documentation
One Quick Installation Guide
System Requirements for the Adapter
Operating System: MS Windows 98, Windows 2000, XP & Windows ME
Desktop PC or notebook PC with CD-ROM drive
One free USB port
Pentium-Class 90MHz or higher
Connecting the USB Adapter
NOTE: These instructions apply to most desktop/notebook computers. For
detailed information on inserting USB adapters into your desktop/notebook PC,
consult the desktop/notebook PC User’s Manual.
The Adapter’s USB port is located on the back of the Adapter.
USB port
And your Adapter comes with a USB cable that has two different types of
connectors – type A & type B. Type A connector of the USB cable plugs into your
notebook/desktop PC’s USB port. And type B connector of the USB cable
connects to the USB port of your USB Wireless Network Adapter.
8

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’s Manual
USB Type A USB Type B
LED Indicators
POWER LINK
The following table describes the meaning of LED indicators:
LED MEANING
POWER
LINK
Indicates that the Adapter is powered on when the LED
lights up.
Indicates link status. The LED lights up while the wireless
connection is linked. If the light is blinking, it is
disconnected, and is scanning the wireless network.
Disconnecting the USB Adapter
In Win 98/ME operating systems, you do not have to power down your
notebook/desktop PC to remove the Adapter. The Adapter is hot swappable—you
9

USB Wireless Network Adapter User’s Manual
can remove the Adapter when your notebook/desktop PC is powered on. However,
Microsoft recommends that you stop the Adapter before removing the Adapter. Refer
to your Win 98/ME online help for information on stopping the USB Adapter.
WARNING: Do not remove the USB Wireless Network Adapter when a data
transmission is taking place. Exit your communications program normally, stop
the Adapter if necessary, and then remove the adapter.
10
USB Wireless Network Adapter User’s Manual
Chapter 3 – Driver Installation for Windows
The f ollowing sections cover the USB Wireless Network Adapter driver installatio n in the
Windows 98/2000/ME/XP operating systems.
Note: You have to install your hardware first before you begin to install the drivers.
Driver installation for Windows 98
Follow the steps below to install the USB Wireless Network Adapter drivers for
Windows 98.
1. Connecting the USB Wireless Network Adapter to the USB port of a notebook or
desktop PC. (Refer to Chapter 2 – Hardware installation. )
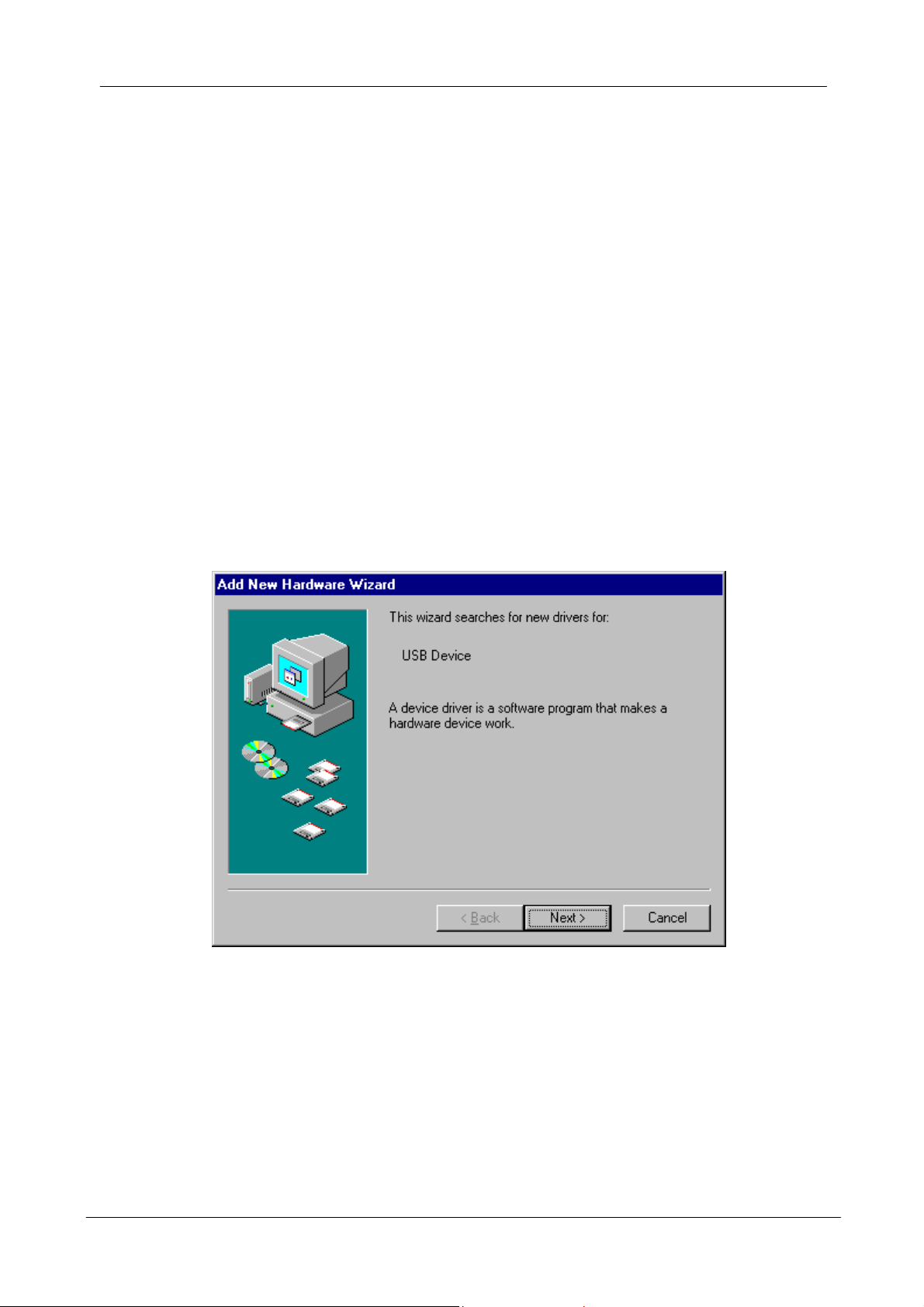
2. After Windows 98 detects the USB Wireless Network Adapter, the Add New
Hardware Wizard window appears. Clicks Next to continue the installation.
11
USB Wireless Network Adapter User’s Manual
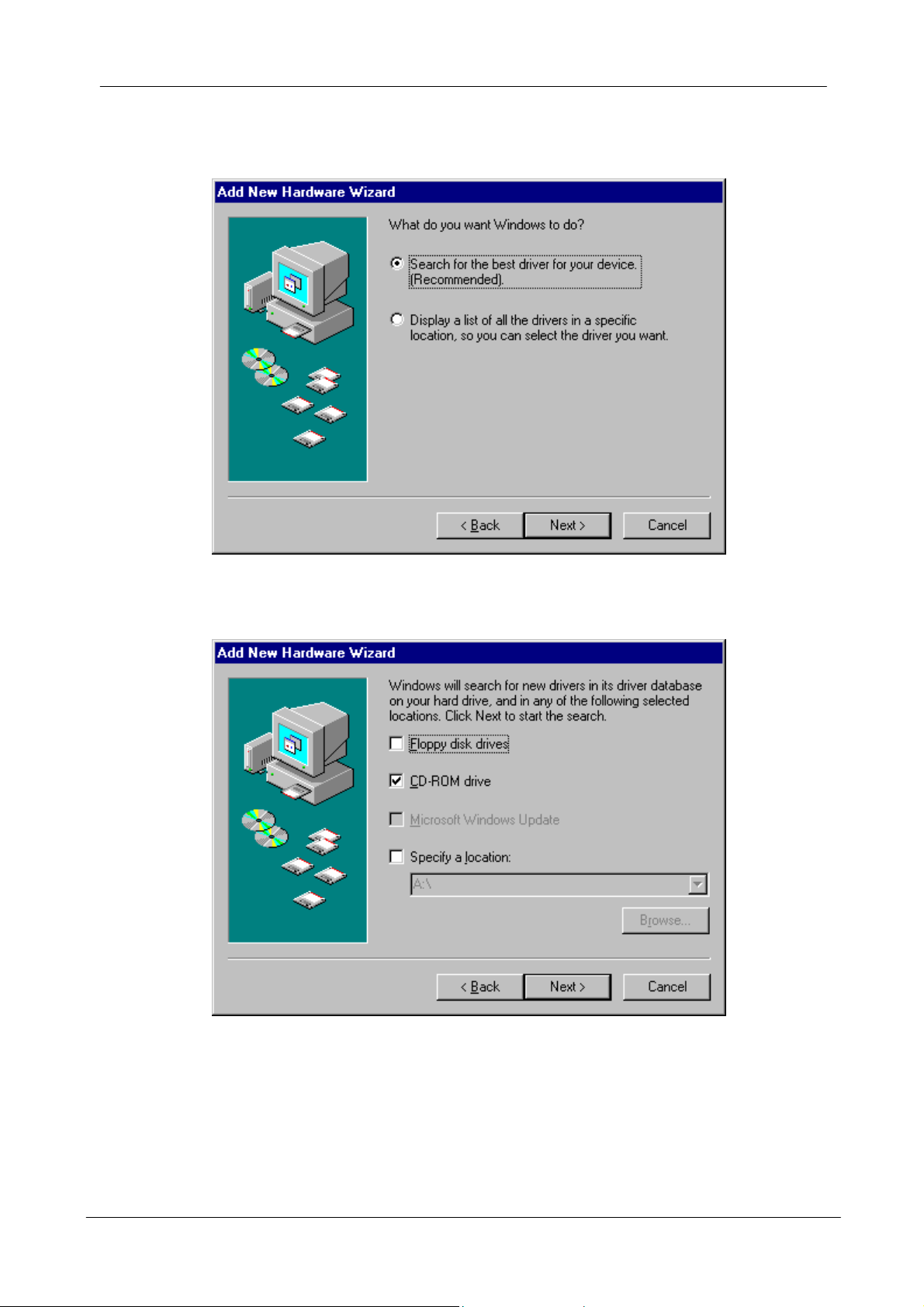
3. A screen appears prompting you to select an installation method. Select Search
for the best driver for your device. (Recommended) and click Next to continue.
4. Ensure that the CD-ROM drive is selected. Inserts the driver CD-ROM into your
CD-ROM drive and clicks Next to continue.
12
 Loading...
Loading...