Page 1

53-1002582-01
®
9 May 2012
Brocade 6910
Ethernet Access Switch
MIB Reference
Supporting R2.1.0.x
Page 2

Copyright © 2012 Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Brocade, Brocade Assurance, the B-wing symbol, BigIron, DCX, Fabric OS, FastIron, MLX, NetIron, SAN Health, ServerIron,
TurboIron, VCS, and VDX are registered trademarks, and AnyIO, Brocade One, CloudPlex, Effortless Networking, ICX, NET Health,
OpenScript, and The Effortless Network are trademarks of Brocade Communications Systems, Inc., in the United States and/or in
other countries. Other brands, products, or service names mentioned may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Notice: This document is for informational purposes only and does not set forth any warranty, expressed or implied, concerning
any equipment, equipment feature, or service offered or to be offered by Brocade. Brocade reserves the right to make changes to
this document at any time, without notice, and assumes no responsibility for its use. This informational document describes
features that may not be currently available. Contact a Brocade sales office for information on feature and product availability.
Export of technical data contained in this document may require an export license from the United States government.
The authors and Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. shall have no liability or responsibility to any person or entity with
respect to any loss, cost, liability, or damages arising from the information contained in this book or the computer programs that
accompany it.
The product described by this document may contain “open source” software covered by the GNU General Public License or other
open source license agreements. To find out which open source software is included in Brocade products, view the licensing
terms applicable to the open source software, and obtain a copy of the programming source code, please visit
http://www.brocade.com/support/oscd.
Brocade Communications Systems, Incorporated
Corporate and Latin American Headquarters
Brocade Communications Systems, Inc.
130 Holger way
San Jose, CA 95134
Tel: 1-408-333-8000
Fax: 1-408-333-8101
E-mail: info@brocade.com
European Headquarters
Brocade Communications Switzerland Sàrl
Centre Swissair
Tour B - 4è me étage
29, Route de l'Aéroport
Case Postale 105
CH-1215 Genève 15
Switzerland
Tel: +41 22 799 5640
Fax: +41 22 799 5641
E-mail: emea-info@brocade.com
Asia-Pacific Headquarters
Brocade Communications Systems China HK, Ltd.
No. 1 Guanghua Road
Chao Yang District
Units 2718 and 2818
Beijing 100020, China
Tel: +8610 6588 8888
Fax: +8610 6588 9999
E-mail: china-info@brocade.com
Asia-Pacific Headquarters
Brocade Communications Systems Co., Ltd. (Shenzhen WFOE)
Citic Plaza
No. 233 Tian He Road North
Unit 1308 – 13th Floor
Guangzhou, China
Tel: +8620 3891 2000
Fax: +8620 3891 2111
E-mail: china-info@brocade.com
Page 3
Document History
Title Publication number Summary of changes Date
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch
MIB Reference
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch
MIB Reference
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch
MIB Reference
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch
MIB Reference
53-1002582-01 Added MIB objects for
Brocade 6910 Ethernet
Access Switch Software
Release 2.1.0.2, including
fdryLinkAggregationGroup
LacpTimeout, snTrapSys
MemoryLowThreshold,
sn TrapTem per atu reO K,
snTrapPortSecurityViolation,
snTrapStackingChasPwr
SupplyOK, snTrapStacking
ChasPwrSupplyFailed,
snTrapStackingTemperature
Warning
53-1002347-03 Added documentation fixes for
Brocade 6910 Ethernet
Access Switch Software
Release 2.0.2.10
53-1002347-02 Added documentation fixes for
Brocade 6910 Ethernet
Access Switch Software
Release 2.0.2.9
53-1002347-01 New document September 2011
May 2012
January 2012
November 2011
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference iii
53-1002582-01
Page 4

iv Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 5

Contents
About This Document
In this chapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
Supported hardware and software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
Document conventions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
Text formatting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
Notes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
Related publications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
Getting technical help. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xi
Document feedback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xi
Chapter 1 Overview of the Brocade 6910 MIB
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Obtaining and installing the Brocade 6910 MIBs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Downloading the MIB from Technical Support web site . . . . . . . 1
Downloading the MIB from Brocade FTP site. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Importing the Brocade MIB into a UNIX environment . . . . . . . . . 1
Reloading MIBs into a third-party NMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Standard objects. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Proprietary objects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Structure of this guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
SNMPv3 support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Chapter 2 Supported Standard MIBs
Supported on Brocade 6910 switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
RFC compliance - management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
IEEE standards. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
LLDP MIB support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Partially supported standards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
RFC 1213: Management Information Base (MIB-II) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
RFC 1493: Definitions of managed objects for bridges . . . . . . . . . . . 7
RFC 1611: DNS Server MIB extensions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
RFC 1612: DNS Resolver MIB Extensions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
RFC 2021: Remote Network Monitoring Management
Information Base, Version 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
RFC 2096: IP forwarding table MIB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
RFC 2576: SNMP Community MIB. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference v
53-1002582-01
Page 6

RFC 2674: Definitions of managed objects for bridges with
traffic classes, multicast filtering and virtual LAN extensions . . .10
RFC 2737: Entity MIB, Version 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
RFC 2819: Remote Network Monitoring Management
Information Base. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
RFC 2863: Interfaces Group MIB. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
RFC 2925: Ping MIB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
RFC 2925: Remote Trace MIB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
RFC 3413: SNMP Notification MIB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
RFC 3635: Ethernet-like interface types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
RFC 3636: IEEE 802.3 Medium Attachment Units (MAU) MIB . . . . 14
IEEE 802.1ag: Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) MIB. . . . . . .15
RFC 4878: OAM Functions on Ethernet-Like Interfaces MIB . . . . . . 16
Chapter 3 Registration
Chapter 4 Physical Properties of a Device
Common objects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Power supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Boards. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Chassis table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
General chassis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Power supply table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Chapter 5 Basic Configuration and Management
Software Image . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Reload. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
File download and upload . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Software image details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Software configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Switch IP configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
SNTP server table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Media table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Chapter 6 User Access
Agent user access group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
General security objects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Authorization and accounting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
RADIUS general group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
RADIUS server table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
TACACS general objects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
TACACS server table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
vi Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 7

Chapter 7 Multi-Device Port Authentication
Multi-device port authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Global multi-device port authentication objects . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Clear interface multi-device port authentication objects . . . . . 37
Multi-device port authentication objects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
Multi-device port authentication clear sessions . . . . . . . . . . . .38
Chapter 8 Traffic Security
Dynamic ARP Inspection VLAN configuration table . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
DAI VLAN configuration table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Dynamic ARP Inspection Interface configuration table. . . . . . .42
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
DHCP Snooping global scalar object . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
DHCP Snooping VLAN configuration table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
DHCP Snooping Interface configuration table . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
IP Source Guard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
IP Source Guard Interface configuration table . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Chapter 9 MAC-Based VLAN
MAC-based VLAN global objects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
Chapter 10 Interfaces
Switch port information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Switch port information group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Link Aggregation Group (LAG) table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
fdryLinkAggregationGroupTable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Chapter 11 Monitoring and Logging
CPU utilization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
System DRAM information group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Global ARP statistics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Support for optical monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
System logging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
System log server table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Chapter 12 Object for Stacking
Agent temperature table for stacking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Chapter 13 Traps and Objects to Enable Traps
Objects for Brocade 6910 switch traps. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Trap information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Trap receiver table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference vii
53-1002582-01
Page 8

MIB Variable Index
Standard traps. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
System status traps. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Traps for spanning tree protocol. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Traps for RMON events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
IronWare traps. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
General traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
Port security traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Traps for stacking. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
RMON event traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
viii Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 9

About This Document
In this chapter
•Supported hardware and software. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
•Document conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
•Related publications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
•Getting technical help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xi
•Document feedback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xi
Supported hardware and software
This guide describes the Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch 2.1.0.x release.
The following hardware platforms are supported by the release of this guide:
• BR-6910-EAS-AC – Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch, 12×1 GbE combination copper
10/100/1000 Base-T (RJ45) or 100/1000 Base-X SFP ports, redundant AC power supply
• BR-6910-EAS-DC – Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch, 12×1 GbE combination copper
10/100/1000 Base-T (RJ45) or 100/1000 Base-X SFP ports, redundant DC power supply
• BR-6910-EAS-H-AC – Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch, 12×1 GbE combination copper
10/100/1000 Base-T (RJ45) or 100/1000 Base-X SFP ports, redundant AC power supply,
temperature hardened
• BR-6910-EAS-H-DC – Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch, 12×1 GbE combination copper
10/100/1000 Base-T (RJ45) or 100/1000 Base-X SFP ports, redundant DC power supply,
temperature hardened
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference ix
53-1002582-01
Page 10

Document conventions
NOTE
ATTENTION
NOTE
This section describes text formatting conventions and important notice formats used in this
document.
Text formatting
The narrative-text formatting conventions that are used are as follows:
bold text Identifies command names
italic text Provides emphasis
code text Identifies CLI output
Notes
Identifies the names of user-manipulated GUI elements
Identifies keywords
Identifies text to enter at the GUI or CLI
Identifies variables
Identifies document titles
The following notice statements are used in this manual.
A note provides a tip, guidance, or advice, emphasizes important information, or provides a
reference to related information.
An Attention statement indicates potential damage to hardware or data.
Related publications
The following Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. documents supplement the information in
this guide and can be located at http://www.brocade.com/ethernetproducts.
• Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch Installation Guide
• Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch Configuration Guide
• Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch Diagnostic Guide
For the latest edition of these documents, which contain the most up-to-date information, see
Product Manuals at http://www.brocade.com/ethernetproducts.
x Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 11

Getting technical help
To contact Technical Support, go to http://www.brocade.com/services-support/index.page for the
latest e-mail and telephone contact information.
Document feedback
Quality is our first concern at Brocade and we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and
completeness of this document. However, if you find an error or an omission, or you think that a
topic needs further development, we want to hear from you. Forward your feedback to:
documentation@brocade.com
Provide the title and version number of the document and as much detail as possible about your
comment, including the topic heading and page number and your suggestions for improvement.
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference xi
53-1002582-01
Page 12

xii Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 13

Introduction
The Management Information Base (MIB) is a database of objects that can be used by a Network
Management System (NMS) to manage and monitor devices on the network. The MIB can be
retrieved by a network management system that uses Simple Network Management Protocol
(SNMP). The MIB structure determines the scope of management access allowed by a device. By
using SNMP, a manager application can issue read or write operations within the scope of the MIB.
Obtaining and installing the Brocade 6910 MIBs
You can obtain the Brocade 6910 MIBs by downloading the file from Brocade Technical Support
site.
Chapter
1Overview of the Brocade 6910 MIB
After obtaining the MIB, follow the instructions for your network management system to be able to
use the MIB with your system.
Downloading the MIB from Technical Support web site
To download the MIB from the Brocade Technical Support Web site, you must have a user name
and password to access the Brocade support site and perform the following.
1. Go to www.brocade.com in your Web browser.
2. Login with your user name and password.
3. Click the downloads tab, then click the Knowledge Portal link.
4. Login to the Knowledge portal, then click the Software tab.
5. Click the product name. Each product release has a link for its corresponding MIB.
6. Navigate to the link for the MIB and either open the file or save it to disk.
Downloading the MIB from Brocade FTP site
You can also download the MIB from the Knowledge Portal. Contact Brocade Technical Support for
details. For the latest edition of this document, which contains the most up-to-date information,
refer to the Product Manuals tab at www.brocade.com.
Importing the Brocade MIB into a UNIX environment
You can import the Brocade 6910 MIB into third-party network management applications, such as
HP OpenView. By default, the Brocade 6910 MIB files are in DOS ASCII format that uses the
following characters:
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 1
53-1002582-01
Page 14

Standard objects
• CR/LF – Indicates the end of a line
• ^Z - Indicates the end of a file
However, in a UNIX environment, the characters LF are used to indicate the end of a line. No
character indicates the end of a file. Thus, if you need to import the Brocade 6910 MIB into a UNIX
environment, you must use a tool that converts the DOS ASCII into UNIX ASCII, such as the
dos2unix tool.
Reloading MIBs into a third-party NMS
Third party network management systems, such as HP OpenView may have problems reloading
MIB files. Ensure that you must upload the following when reloading the Brocade 6910 MIB:
• Unload the Enterprise MIBs which were installed from the previous upgrade before reloading
any new Enterprise MIB file.
• Unload the Standard MIBs which were installed from the previous upgrade before reloading
any new Standard MIB file.
Standard objects
The Brocade 6910 MIB supports certain standard MIB objects, which are derived from Request for
Comments (RFCs) documents. Refer to Chapter 2, “Supported Standard MIBs” for details on the
supported standard MIBs.
Proprietary objects
Proprietary objects are MIB objects that have been developed specifically to manage the Brocade
6910 switch. This section presents a summarized list of these objects.
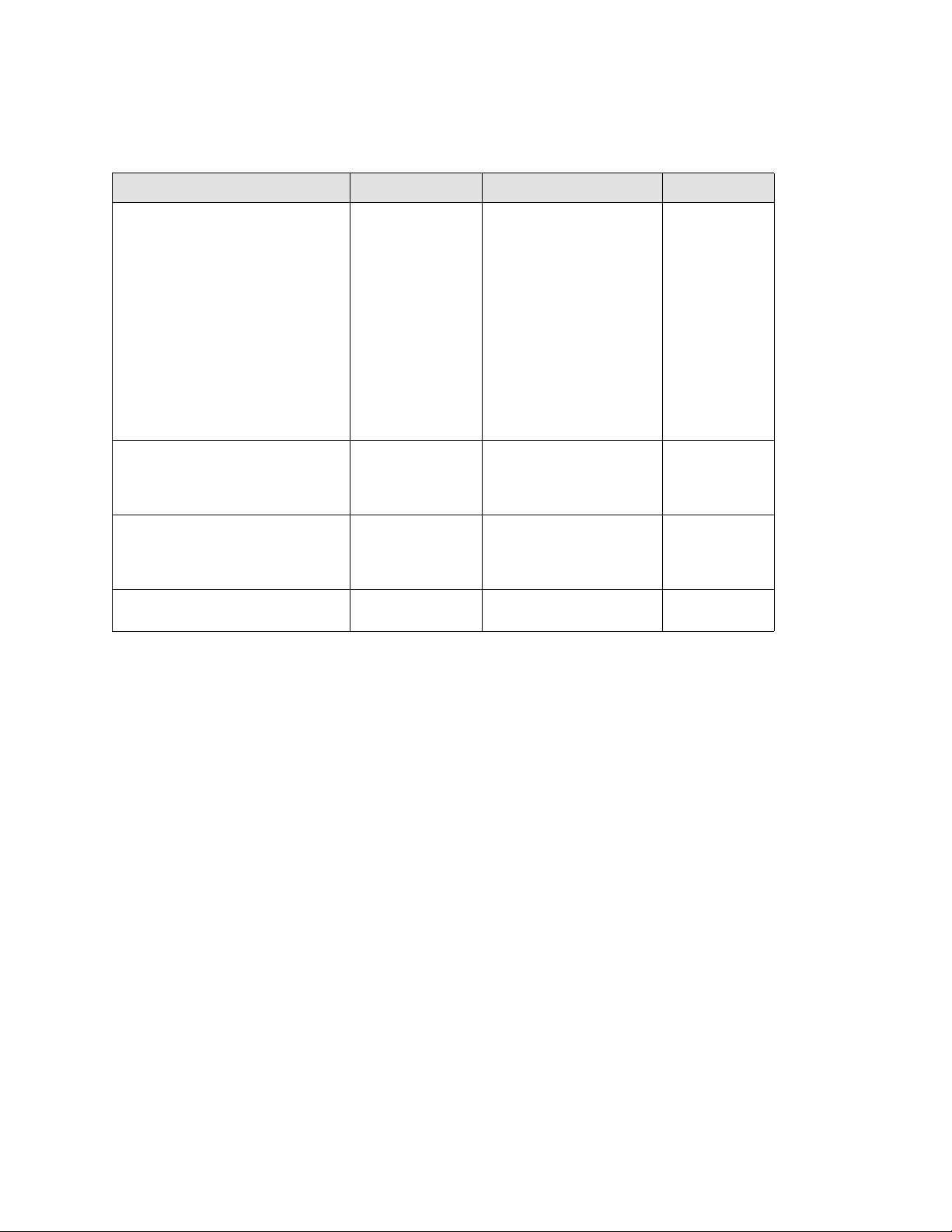
Tab le 1 shows the hierarchy of the MIB objects that are proprietary to the Brocade 6910. These
objects may also be referred to as the private (or enterprise) MIBs.
On the MIB tree, the object named “foundry” marks the start of the IronWare MIB objects. The
“foundry” object branches into the “products” branch, which branches further into three major
nodes:
• switch – Includes general SNMP MIB objects and objects related to switching functions.
• router – Contains objects for routing protocols, such as IP, OSPF. (Layer 3 routing protocols will
be supported in a future release.)
Each of these major nodes are further divided into smaller categories.
Tab le 1 contains a summary of the major categories or MIB object groups under each major node.
The MIB object groups can be divided into the individual MIB objects or additional object groups.
The column “Object Group Name” presents the name of the MIB object. The “Object Identifier”
column shows the MIB object’s identifier (OID). In this guide, the IronWare objects are presented
with their object names and object their identifiers (OIDs). As shown in Ta ble 1, OIDs are presented
in the format brcdIp.x.x.x.x, where:
• “brcdIp” represents the number 1.3.6.1.4.1.1991
• .x.x.x.x is the remainder of the number
2 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 15

Proprietary objects
For example, the OID for the object snSwitch is 1.3.6.1.4.1.1991.1.1.3, but appears as brcdIp.1.1.3
in this guide.
The Description column indicates the section in this guide that contains details for that object.
TABLE 1 Summary of MIB Objects Proprietary to the Brocade 6910
Object Group Name Object Identifier Sections to Refer To
foundry
products brcdIp.1 All sections in this manual
switch brcdIp.1.1 All sections under the switch
snSwitch brcdIp.1.1.3 “Basic Configuration and
snVLanInfo brcdIp.1.1.3.2 “VLANs” on page 65
snSwPortInfo brcdIp.1.1.3.3 “Switch port information group”
snMacFilter brcdIp.1.1.3.10 “MAC filter interface access
snRadius brcdIp.1.1.3.12 “Authorization and accounting”
snTacacs brcdIp.1.1.3.13 “TACACS general objects” on
snAAA brcdIp.1.1.3.15 “Authorization and accounting”
fdryRadius brcdIp.1.1.8
fdryRadiusMIB brcdIp.1.1.8.1 “RADIUS server table” on
router brcdIp.1.2 All sections under the router
snIp brcdIp.1.2.2 “Global Router and IP” on
snRtIpGeneral brcdIp.1.2.2.1 “IP general group” on page 67
snRtIpPortIfAccessTable brcdIp.1.2.2.19 “IP port interface access
snIgmp brcdIp.1.2.6 “IGMP” on page 69
brcdIp
All sections in this manual
branch
Management” on page 23
on page 47
tables” on page 65
on page 32 and “RADIUS
general group” on page 32
page 34
on page 32
page 33
branch
page 67
group” on page 69
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 3
53-1002582-01
Page 16

Structure of this guide
Structure of this guide
All chapters in this guide contain details about the MIB objects that are in the Brocade 6910 MIB.
Each object is presented with its object name and OID, the access type available for that object (for
example, read-write or read only), and a description. Objects are grouped according to their
function.
The chapter “Traps and Objects to Enable Traps” on page 57 contains both the objects used to
enable a particular type of trap and the objects that are available for a trap type. For example,
objects to enable Layer 4 traps as well as the Layer 4 trap objects are in the chapter.
SNMPv3 support
SNMPv3 engine is supported on the NetIron XMR/MLX. The SNMPv3 engine can accept V1, V2c,
and V3 packet formats.
4 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 17

This section summarizes the standard objects that are supported in the Brocade 6910 MIB. It does
not document all the supported standard objects, but presents those standard MIBs that are not
fully supported.
For example, although RFC1213 is supported in the Brocade 6910 MIB, some groups and tables in
that MIB are not supported. The section “RFC 1213: Management Information Base (MIB-II)” on
page 7 identifies the groups and tables that are supported and the ones not supported.
Supported on Brocade 6910 switches
RFC compliance - management
Chapter
2Supported Standard MIBs
• RFC 1213 – MIB II
• RFC 1493 – Bridge MIB
• RFC 1611 – DNS Server MIB Extensions
• RFC 1612 – DNS Resolver MIB Extensions
• RFC 1907 – SNMPv2 MIB
• RFC 2011 – SNMPv2 IP MIB
• RFC 2012 – TCP MIB
• RFC 2013 – UDP MIB
• RFC 2021 – RMON2 MIB
• RFC 2096 – IPv4 Forwarding Table MIB
• RFC 2576 – SNMP Community MIB
• RFC 2618 – RADIUS Authentication Client MIB
• RFC 2620 – RADIUS Accounting Client MIB
• RFC 2674 – 802.1Q and 802.1p Bridge MIB
• RFC 2737 – Entity MIB
• RFC 2819 – RMON MIB
• RFC 2863 – Interfaces Group MIB
• RFC 3176 – InMon Corporation's sFlow
• RFC 3411 – SNMP Frameworks MIB
• RFC 3412 – SNMP Message Processing and Dispatching (MPD) MIB
• RFC 3413 – SNMP Target MIB
• RFC 3414 – User-based Security Model for SNMPv3 MIB
• RFC 3415 – View-based Access Control Model for SNMP MIB
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 5
53-1002582-01
Page 18

LLDP MIB support
• RFC 3635 – Ethernet-like Interface Types MIB
• RFC 3636 – IEEE 802.3 Medium Attachment Units (MAU) MIB
IEEE standards
• IEEE 802.1 – Port Access Entity (PAE) MIB
• IEEE 802.1ag – Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) MIB
• IEEE 802.3 – Link Aggregation (LAG) MIB
• V-Bridge MIB draft – Bridges with RSTP and VLAN Classification Extensions (IEEE 802.1v)
LLDP MIB support
The following MIBs are in the IEEE 802.1AB standard, Station and Media Access Control
Connectivity Discovery.
• LLDP-EXT-DOT1-MIB
• LLDP-EXT-DOT3-MIB
Partially supported standards
• “RFC 1213: Management Information Base (MIB-II)” on page 7.
• “RFC 1493: Definitions of managed objects for bridges” on page 7.
• “RFC 1611: DNS Server MIB extensions” on page 7.
• “RFC 1612: DNS Resolver MIB Extensions” on page 8.
• “RFC 2021: Remote Network Monitoring Management Information Base, Version 2” on page 9.
• “RFC 2096: IP forwarding table MIB” on page 10.
• “RFC 2576: SNMP Community MIB” on page 10.
• “RFC 2674: Definitions of managed objects for bridges with traffic classes, multicast filtering
and virtual LAN extensions” on page 10.
• “RFC 2737: Entity MIB, Version 2” on page 11.
• “RFC 2819: Remote Network Monitoring Management Information Base” on page 11.
• “RFC 2863: Interfaces Group MIB” on page 12.
• “RFC 2925: Ping MIB” on page 12.
• “RFC 2925: Remote Trace MIB” on page 13.
• “RFC 3413: SNMP Notification MIB” on page 14.
• “RFC 3635: Ethernet-like interface types” on page 14.
• “RFC 3636: IEEE 802.3 Medium Attachment Units (MAU) MIB” on page 14.
• “RFC 4878: OAM Functions on Ethernet-Like Interfaces MIB” on page 16.
• “IEEE 802.1ag: Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) MIB” on page 15.
6 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 19
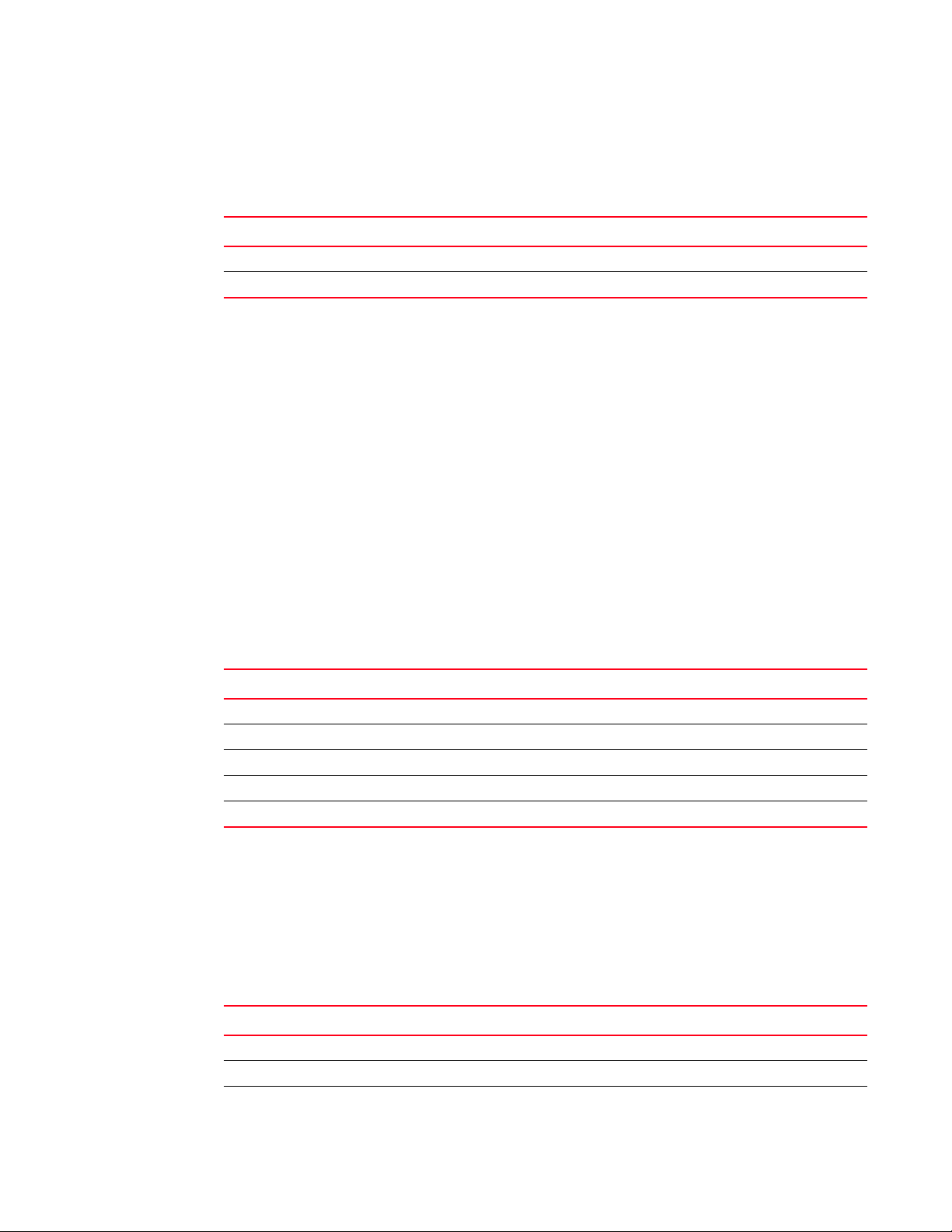
RFC 1213: Management Information Base (MIB-II)
RFC 1213: Management Information Base (MIB-II)
The following objects from RFC1213 are supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
Object Group Name Object Identifier
system 1.3.6.1.2.1.1
snmp 1.3.6.1.2.1.11
The following groups from RFC 1213 are not supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
• interfaces – Replaced by IF-MIB.interfaces
• at – atTable has been deprecated
• ip – Replaced by IP-MIB.ip
• icmp – Replaced by IP-MIB.icmp
• tcp – Replaced by IP-MIB.icmp
• udp – Replaced by UDP-MIB.udp
• egp
• transmission – Supports other relevant MIBs which are registered under this node, such as
EtherLike MIB and Entity MIB
RFC 1493: Definitions of managed objects for bridges
The following groups are supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
Object Group Name Object Identifier
dot1dBridge 1.3 .6.1.2.1.17
dot1dBas e 1.3.6.1.2.1.17.1
dot1dStp 1.3.6.1.2.1.17.2
dot1dTp 1.3 .6.1.2.1.17.4
dot1dSta tic 1.3 .6.1.2.1.17.5
The following object groups in RFC 1493 are not supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
• dot1dSr
RFC 1611: DNS Server MIB extensions
The following groups are supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
Object Group Name Object Identifier
dnsServMIBObjects 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.1.1
dnsServConfig 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.1.1.1
dnsServCounter 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.1.1.2
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 7
53-1002582-01
Page 20

RFC 1612: DNS Resolver MIB Extensions
Object Group Name Object Identifier
dnsServCounterAuthAns 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.1.1.2.2
dnsServCounterAuthNoNames 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.1.1.2.3
dnsServCounterAuthNoDataResps 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.1.1.2.4
dnsServCounterNonAuthDatas 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.1.1.2.5
dnsServCounterNonAuthNoDatas 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.1.1.2.6
dnsServCounterReferrals 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.1.1.2.7
dnsServCounterErrors 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.1.1.2.8
dnsServCounterRelNames 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.1.1.2.9
dnsServCounterReqRefusals 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.1.1.2.10
dnsServCounterReqUnparses 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.1.1.2.11
dnsServCounterOtherErrors 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.1.1.2.12
dnsServOptCounter 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.1.1.3
The following object groups in RFC 1611 are not supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
• dnsServZone
RFC 1612: DNS Resolver MIB Extensions
The following groups are supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
Object Group Name Object Identifier
dnsResMIBObjects 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.2.1
dnsResConfig 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.2.1.1
dnsResCounter 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.2.1.2
dnsResCache 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.2.1.4
dnsResCacheStatus 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.2.1.4.1
dnsResCacheMaxTTL 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.2.1.4.2
dnsResCacheGoodCaches 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.2.1.4.3
dnsResCacheBadCaches 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.2.1.4.4
dnsResOptCounter 1.3.6.1.2.1.32.2.1.6
The following object groups in RFC 1612 are not supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
• dnsResLameDelegation
• dnsResNCache
8 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 21

RFC 2021: Remote Network Monitoring Management Information Base, Version 2
RFC 2021: Remote Network Monitoring Management Information
Base, Version 2
The following groups are supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
Object Group Name Object Identifier
probeConfig 1.3 .6.1.2.1.16.19
probeCapabilities 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.19.1
probeSoftwareRev 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.19.2
probeHardwareRev 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.19.3
probeDateTime 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.19.4
probeResetControl 1.3 .6.1.2.1.16.19.5
probeDownlo adFile 1. 3.6.1.2.1.16.19.6
probeDownlo adTFTPServer 1.3 .6.1.2.1.16.19.7
probeDownlo adAction 1.3 .6.1.2.1.16.19.8
probeDownlo adStatu s 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.19.9
netConfigTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.19.11
netDefaultGateway 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.19.12
The following object groups in RFC 2021 are not supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
• statistics
• history
• matrix
• filter
• tokenRing
• protocolDir
• protocolDist
• addressMap
• nlHost
• nlMatrix
• alHost
• alMatrix
• usrHistory
• trapDestTable
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 9
53-1002582-01
Page 22

RFC 2096: IP forwarding table MIB
RFC 2096: IP forwarding table MIB
The following groups are supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
Object Group Name Object Identifier
ipCidrRouteNumber 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.24.3
ipCidrRouteTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.24.4
RFC 2576: SNMP Community MIB
The following groups are supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
Object Group Name Object Identifier
snmpCommunityMIBObjects 1.3.6.1.6.3.18.1
snmpCommunityTable 1.3.6.1.6.3.18.1.1
RFC 2674: Definitions of managed objects for bridges with traffic classes, multicast filtering and virtual LAN extensions
The following groups are supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
Object Group Name Object Identifier
pBridgeMib 1.3.6.1.2.1.17.6
pBridgeMIBObjects 1.3.6.1.2.1.17.6.1
dot1dExtBase 1.3.6.1.2.1.17.6.1.1
dot1dPriority 1.3.6.1.2.1.17.6.1.2
dot1dPortPriorityTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.17.6.1.2.1
dot1dUserPrio rityRegenTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.17.6.1.2.2
dot1dTrafficClassTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.17.6.1.2.3
dot1dGarp 1.3.6.1.2.1.17.6.1.3
qBridgeMib 1.3.6.1.2.1.17.7
qBridgeMIBObjects 1.3.6.1.2.1.17.7.1
dot1qBase 1.3.6.1.2.1.17.7.1.1
dot1qTp 1.3 .6.1.2.1.17.7.1.2
dot1qFdbTabl e 1.3.6.1.2.1.17.7.1.2.1
dot1qTpFdbTable 1. 3.6.1.2.1.17.7.1.2 .2
dot1qStatic 1.3.6.1.2 .1.17.7.1.3
dot1qStaticUnicast Table 1.3 .6.1.2.1.17.7.1.3.1
10 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 23
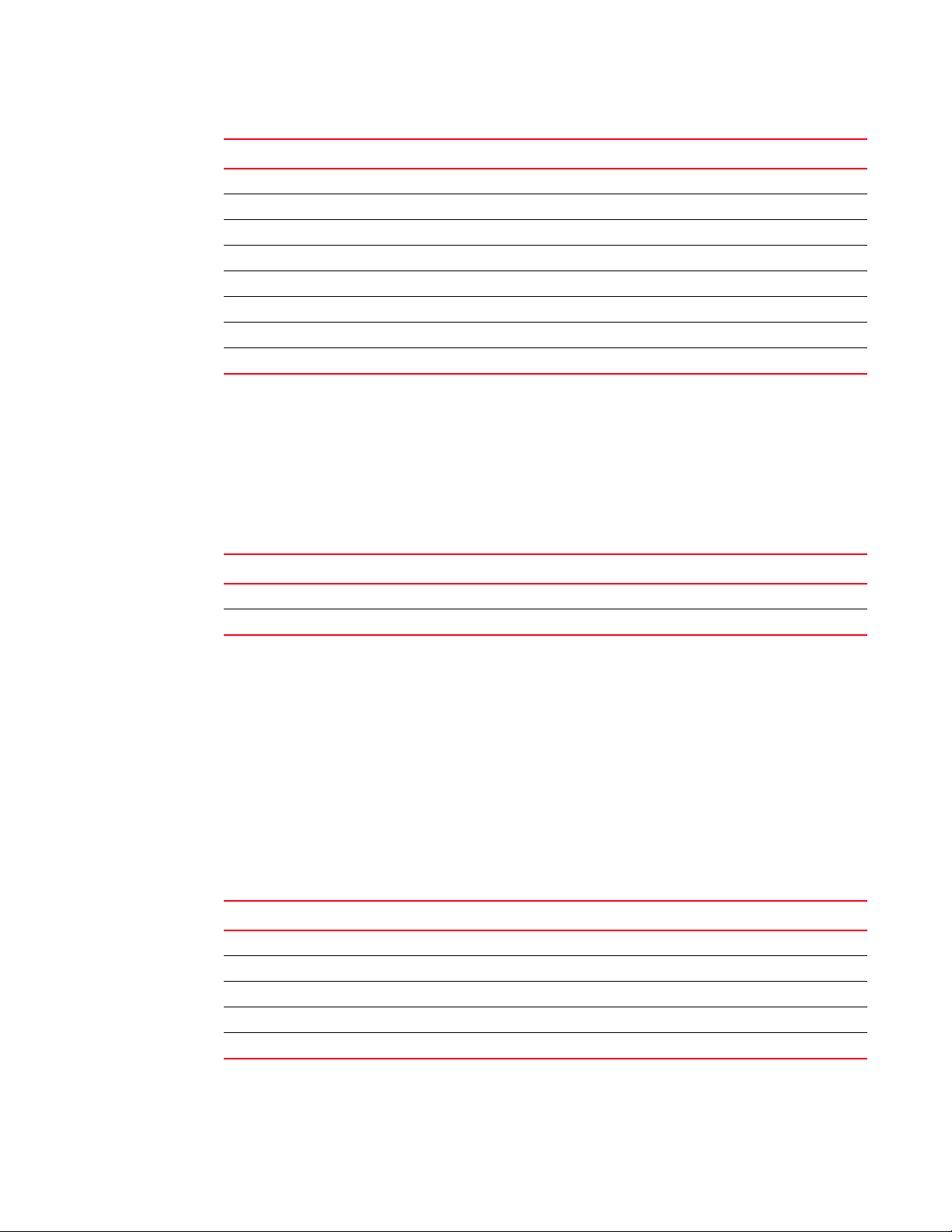
Object Group Name Object Identifier
dot1qVla n 1.3.6.1.2.1.17.7.1.4
dot1qVla nNumDeletes 1.3.6.1.2.1.17.7.1.4.1
dot1qVla nCurrentTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.17.7.1.4.2
dot1qVlanStaticTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.17.7.1.4.3
dot1qNextFreeLocalV lanIndex 1.3 .6.1.2.1.17.7.1.4.4
dot1qPortVlanTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.17.7.1.4.5
dot1qConstraintSetDefault 1.3 .6.1.2.1.17.7.1.4.9
dot1qConstraintTypeDefault 1.3.6.1.2.1.17.7.1.4.9
The following object groups in RFC 2674 are not supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
• dot1dGmrp
RFC 2737: Entity MIB, Version 2
RFC 2737: Entity MIB, Version 2
The following groups are supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
Object Group Name Object Identifier
entityMIBObjects 1.3.6.1.2.1.47.1
entityPhysical 1.3.6.1.2.1.47.1.1
The following object groups in RFC 2737 are not supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
• entityLogical
• entityMapping
• entityGeneral
RFC 2819: Remote Network Monitoring Management Information Base
The following groups are supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
Object Group Name Object Identifier
rmon 1.3.6.1.2.1.16
statistics 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1
history 1.3 .6.1.2.1.16.1
alarm 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.3
event 1.3.6.1.2.1.16. 9
The following object groups in RFC 2819 are not supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
• rmonEventsV2
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 11
53-1002582-01
Page 24

RFC 2863: Interfaces Group MIB
• hosts
• hostTopN
• matrix
• filter
• capture (packet capture)
RFC 2863: Interfaces Group MIB
The following groups are supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
Object Group Name Object Identifier
interfaces 1.3.6.1.2.1.2
ifMIB 1.3.6.1.2.1.31
ifMIBObjects 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1
ifXTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1
ifStackTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.2
ifTableLastChange 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.5
ifStackLastChange 1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.6
RFC 2925: Ping MIB
The following groups are supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
Object Group Name Object Identifier
pingObjects 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1
pingCtlTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.2
pingCtlEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.2.1
pingCtlOwnerIndex 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.2.1.1
pingCtlTestName 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.2.1.2
pingCtlTargetAddressType 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.2.1.3
pingCtlTargetAddress 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.2.1.4
pingCtlDataSize 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.2.1.5
pingCtlProbeCount 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.2.1.7
pingCtlAdminStatus 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.2.1.8
pingCtlRowStatus 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.2.1.23
pingResultsTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.3
pingResultsEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.3.1
pingResultsOperStatus 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.3.1.1
pingResultsIpTargetAddressType 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.3.1.2
12 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 25

RFC 2925: Remote Trace MIB
Object Group Name Object Identifier
pingResultsIpTargetAddress 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.3.1.3
pingResultsMinRtt 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.3.1.4
pingResultsMaxRtt 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.3.1.5
pingResultsAverageRtt 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.3.1.6
pingResultsProbeResponses 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.3.1.7
pingResultsSentProbes 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.3.1.8
pingProbeHistoryTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.4
pingProbeHistoryEntry 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.4.1
pingProbeHistoryIndex 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.4.1.1
pingProbeHistoryResponse 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.4.1.2
pingProbeHistoryStatus 1.3.6.1.2.1.80.1.4.1.3
The following object groups in RFC 2925 are not supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
• pingImplementationTypeDomains
RFC 2925: Remote Trace MIB
The following groups are supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
Object Group Name Object Identifier
traceRouteObjects 1.3.6.1.2.1.81.1
traceRouteCtlTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.81.1.2
traceRouteCtlOwnerIndex 1.3.6.1.2.1.81.1.2.1.1
traceRouteCtlTestName 1.3.6.1.2.1.81.1.2.1.2
traceRouteCtlTargetAddressType 1.3.6.1.2.1.81.1.2.1.3
traceRouteCtlTargetAddress 1.3.6.1.2.1.81.1.2.1.4
traceRouteCtlAdminStatus 1.3.6.1.2.1.81.1.2.1.21
traceRouteCtlRowStatus 1.3.6.1.2.1.81.1.2.1.27
traceRouteResultsTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.81.1.3
traceRouteProbeHistoryTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.81.1.4
The following object groups in RFC 2925 are not supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
• traceRouteHopsTable
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 13
53-1002582-01
Page 26

RFC 3413: SNMP Notification MIB
RFC 3413: SNMP Notification MIB
The following groups are supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
Object Group Name Object Identifier
snmpNotifyObjects 1.3.6.1.6.3.13.1
snmpNotifyTable 1.3.6.1.6.3.13.1.1
The following object groups in RFC 3413 are not supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
• snmpNotifyFilterProfileTable
• snmpNotifyFilterTable
RFC 3635: Ethernet-like interface types
The following groups are supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
Object Group Name Object Identifier
dot3 1.3.6.1.2.1.10.7
dot3StatsTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.10.7.2
dot3PauseTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.10.7.10
The following object groups in RFC 3635 are not supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
• dot3CollTable
• dot3Tests
• dot3Errors
• dot3ControlTable
RFC 3636: IEEE 802.3 Medium Attachment Units (MAU) MIB
The following groups are supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
Object Group Name Object Identifier
dot3IfMauBasicGroup 1.3.6.1.2.1.26.1
dot3IfMauAutoNegGroup 1.3.6.1.2.1.26.5
The following object groups in RFC 3636 are not supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
• dot3RpMauBasicGroup
14 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 27

IEEE 802.1ag: Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) MIB
IEEE 802.1ag: Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) MIB
The following groups are supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
Object Group Name Object Identifier
dot1agNotifications 1.0.8802.1.1.3.0
dot1agMIBObjects 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1
dot1agCfmStack 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.1
dot1agCfmConfigErrorList 1. 0.880 2.1.1.3.1.4
dot1agCfmMd 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.5
dot1agCfmMa 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.6
dot1agCfmMep 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7
dot1agCfmMepTable 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1
dot1agCfmMepEntry 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1
dot1agCfmMepIdentifier 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.1
dot1agCfmMepIfIndex 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.2
dot1agCfmMepDirection 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.3
dot1agCfmMepPrimaryVid 1.0. 8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.4
dot1agCfmMepActive 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.5
dot1agCfmMepFngState 1.0.8 802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.6
dot1agCfmMepCciEnabled 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.7
dot1agCfmMepCcm LtmPriority 1.0. 8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.8
dot1agCfmMepMac Addre ss 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.9
dot1agCfmMepLowPrDef 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.10
dot1agCfmMepFngAlarm Time 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.11
dot1agCfmMepFngRes etTim e 1.0. 8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.12
dot1agCfmMepHighestPrDefect 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.13
dot1agCfmMepDefects 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.14
dot1agCfmMepErrorCcmLastFailure 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.15
dot1agCfmMepXco nCcmLastFailure 1.0.880 2.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.16
dot1agCfmMepCcmSequenceErrors 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.17
dot1agCfmMepCciSentCcms 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.18
dot1agCfmMepNextLbmTransId 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.19
dot1agCfmMepLbrIn 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.20
dot1agCfmMepLbrInOutOfOrder 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.21
dot1agCfmMepLbrBadMsdu 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.22
dot1agCfmMepLtmNextSeqNumber 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.2 3
dot1agCfmMepUnexpLtrIn 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.24
dot1agCfmMepLbrOut 1.0.880 2.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.25
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 15
53-1002582-01
Page 28

RFC 4878: OAM Functions on Ethernet-Like Interfaces MIB
Object Group Name Object Identifier
dot1agCfmMepTransmitLbmStatus 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.26
dot1agCfmMepTransmitLbmDestMacAddress 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.27
dot1agCfmMepTransmitLbmD estMepId 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.29
dot1agCfmMepTransmitLbmMessages 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.30
dot1agCfmMepTransmitLbmVlanPriority 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.32
dot1agCfmMepTransmitLbmResultOK 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.34
dot1agCfmMepTransmitLbmSeqNum ber 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.35
dot1agCfmMepTransmitLtmStatus 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.36
dot1agCfmMepTransmitLtmF lags 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.37
dot1agCfmMepTransmitLtmTargetMacAddress 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.38
dot1agCfmMepTransmitLtmTargetMepId 1. 0.880 2.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.39
dot1agCfmMepTransmitLtmTargetIsMepId 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.40
dot1agCfmMepTransmitLtmTtl 1.0.8 802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.41
dot1agCfmMepTransmitLtmResult 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.42
dot1agCfmMepTransmitLtmSeqNum ber 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1. 7.1.1.43
dot1agCfmMepRowStatus 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.1.1.49
dot1agCfmLtrTable 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.2
dot1agCfmMepDbTable 1.0.8802.1.1.3.1.7.3
The following object groups in RFC 3636 are not supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
• dot1agCfmDefaultMd
• dot1agCfmVlan
RFC 4878: OAM Functions on Ethernet-Like Interfaces MIB
The following groups are supported on Brocade 6910 switches.
Object Group Name Object Identifier
dot3OamThresholdEvent 1.3.6.1.2.1.158.0.1
dot3OamTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.158.1.1
dot3OamPeerTable 1. 3.6.1.2.1.158.1.2
dot3OamLoopback Table 1. 3.6.1.2.1.158.1.3
dot3OamStatsTable 1.3.6.1.2 .1.15 8.1.4
dot3OamErrFrameWindow 1.3.6.1.2.1.158.1.5.1.9
dot3OamErrFrameT hreshold 1.3.6.1.2.1.15 8.1.5.1.10
dot3OamErrFrameE vNotifEnable 1.3.6.1.2.1.158.1.5.1.11
16 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 29

RFC 4878: OAM Functions on Ethernet-Like Interfaces MIB
Object Group Name Object Identifier
dot3OamDyingGaspEnable 1.3.6.1.2.1.158.1.5.1.15
dot3OamEventLogTable 1.3.6.1.2.1.158.1.6
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 17
53-1002582-01
Page 30

RFC 4878: OAM Functions on Ethernet-Like Interfaces MIB
18 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 31

Chapter
Registration objects identify the Brocade product that is being managed. The following table
presents the objects for product registration. The sysOID will return one of these values.
Object Name and Identifier Description
3Registration
ethernetAccessSwitchBr6910
brcdip.1.16.1
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 19
53-1002582-01
Page 32

Registration
20 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 33

Common objects
This chapter presents the global objects for the general management of a device’s physical
properties, such as the current status of the power supply and fan.
Refer to the configuration guide for details on power supplies, fans, and other features discussed in
this chapter.
Power supply
The following object applies to all devices. Refer to the chapter, “Physical Properties of a Device” on
page 21, for information on power supply traps.
Chapter
4Physical Properties of a Device
Boards
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
snChasMainBrdDescription
brcdIp.1.1.1.1.5
Syntax: DisplayString
snChasMainPortTotal
brcdIp.1.1.1.1.6
Syntax: Integer
Read only The main board description string. This object can have up to 128
characters.
Read only Shows the total number of ports on the main board.
Valid values: 1 – 24
Chassis table
The snChasUnitTable manages the temperature for the devices.
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
snChasUnitTable
brcdIp.1.1.1.4.1
snChasUnitEntry
brcdIp.1.1.1.4.1.1
snChasUnitIndex
brcdIp.1.1.1.4.1.1.1
Syntax: Integer32
snChasUnitSerNum
brcdIp.1.1.1.4.1.1. 2
Syntax: DisplayString
N/A A table of chassis information for each unit. Only activechassis
appears in a table row.
N/A A row in the chassis table.
Read only The index to the table
Read only The serial number of the unit. If the serial number is unknown
or unavailable, then the value should be a zero length string
There can be up to 128 characters for the serial number.
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 21
53-1002582-01
Page 34

Common objects
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
snChasUnitPartNum
brcdIp. 1.1.1.4.1.1.7
Syntax: DisplayString
snChasUnitActualTemperature
brcdIp.1.1.1.4.1.1. 4
Syntax: Integer
Read only The part number of the chassis for each unit. If the part
number is unknown or unavailable then the value should be a
zero length string.
Read only Shows the average of all sensors in the current unit. Each unit
is 0.5 degrees Celsius.
Values are from -110 to 250.
General chassis
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
snChasSerNum
brcdIp.1.1.1.1.2
Syntax: DisplayString
snChasNumSlots
brcdIp.1.1.1.1.24
Syntax: Integer32
Read only The serial number of the chassis. If the serial number is unknown
or unavailable thenthe value should be a zero length string.
This object can have up to 128 characters.
Read only Shows the maximum number of units in a stack.
Power supply table
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
snChasPwrSupply2Table
brcdIp.1.1.1.2.2
snChasPwrSupply2Entry
brcdIp.1.1.1.2.2.1
snChasPwrSupply2Unit
brcdIp.1.1.1.2.2.1.1
snChasPwrSupply2Index
brcdIp.1.1.1.2.2.1.2
Syntax: Integer32
snChasPwrSupplyOperStatus
brcdIp.1.1.1.2.2.1.4
Syntax: Integer
N/A A table containing power supply information. Only installed power
supplies appear in the table.
N/A A row in the power supply table. One row appears for each power
supply.
Read only The index to power supply table.
Read only The index to power supply table.
Read only Shows the status of the power supply:
• other(1) – Status is neither normal(2) or failure(3).
• normal(2)
• failure(3)
Temperature
Refer to the chapter “Traps and Objects to Enable Traps” on page 57 for objects dealing with traps.
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
snChasActualTemperature
brcdIp.1.1.1.1.18
Syntax: Integer
22 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
Read only Shows the average temperature of all sensors in all units. Each
unit is 0.5 degrees Celsius.
Values are from -110 – 250
NOTE: For per-unit (per thermal sensor), see
UnitActualTemperature and snAgentTemp2Value instead.
53-1002582-01
Page 35

Software Image
This chapter describes objects to manage the software image and configuration in a device. Refer
to the configuration guide for detailed explanation on the features discussed in this chapter.
• “Reload” on page 23
• “File download and upload” on page 24
• “Software image details” on page 26
Reload
The following object allows you to reload the agent.
Chapter
5Basic Configuration and Management
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
snAgReload
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.1
Syntax: Integer
Read-write Reboots the agent.
The following values can only be read:
• other(1) – Agent is in unknown or other state
• running(2) – agent running
• busy(4) – reload not allowed at this time, flash is busy
The following value can be written:
• reset(3) – Do a hard reset
The agent will return a response before the action occurs.
snAgEraseNVRAM
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.2
Syntax: Integer
Read-write The following values can only be read:
• normal(1)
• error(2) – Operation failed or the flash is bad
• erasing(4) – agent is erasing NVRAM flash
• busy(5) – operation not allowed at this time, flash is busy.
The following value can be written:
• erase(3) – NVRAM is set to be erased.
The agent will return a response even before the erase is
done.And the value of this object will be erasing(4) until the
erase is done. And the erase request will be rejected until the
value of this object is either normal(1) or error(2).
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 23
53-1002582-01
Page 36

Software Image
NOTE
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
snAgWriteNVRAM
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.3
Syntax: Integer
Read-write Saves all configuration information to NVRAM of the agent. The
following values can only be read:
• normal(1)
• error(2) – Operation failed or the flash is bad
• writing(4) – Agent is writing NVRAM flash
The following value can be written:
NOTE: write(3) – Write operation. The agent will return a
response even before the write operation is complete. The
read values will be written until the write operation is
finished. New write requests will be rejected until an
error(2) or normal(1) value is obtained.
snAgConfigFromNVRAM
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.4
Syntax: Integer
Read-write Configures the switch from NVRAM of the agent.
The following value can be written:
• config(3) – Do configuration.
The agent will return a response after configuration is done.
The following values can only be read:
• normal(1)
• error(2) – Operation failed or bad flash
• busy(5) – Operation not allowed at this time, flash is busy
File download and upload
The following objects manage file downloads and uploads.
NOTES: When uploading or downloading configuration files to and from the TFTP server using
SNMP, check the following:
• Make sure that user has administrative access (privilege=15) on the device; otherwise,
the user will not be able to upload files to the TFTP server.
For a successful download or upload, first write snAgTftpServerAddrType, snAgTftpServerAddr,
snAgImgFname, and then snAgImgLoad.
24 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 37

Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
Software Image
snAgImgFname
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.6
Syntax: DisplayString
snAgImgLoad
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.7
Syntax: Integer
snAgCfgFname
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.8
Syntax: DisplayString
snAgCfgLoad
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.9
Syntax: Integer
Read-write Shows the name of the image file, including the path, that is
currently associated with the system. When the object is not used,
the value is a zero length string. It can have up to 127 characters.
Read-write Downloads or uploads a new software image to the agent.
The following values can be read:
Error values: from normal(1) to operationError(17) and
tftpWrongFileType(23).
loading(18) – Operation is in process.
The following values can be set:
• uploadMPPrimar y(19) – Upload the Startup image from MP
flash to TFTP server.
• downloadMPPrimary(20) – Swaps the roles of the startup
and non-startup images in flash.
• uploadMPSecondary(21) – Upload the Non-Startup image
from MP flash to TFTP server.
• downloadMPSecondary(22) – Download the Non-Startup
image from TFTP server to MP flash.
MP is the management processor.
The image filename is defined in snAgImgFname. The TFTP server
address is defined in snAgTftpServerAddrType and
snAgTftpServerAddr. The write request will be rejected during
loading until error or normal.
Read-write Name of the config file including path currently associated with
the system. When the object is not used, the value is a zero length
string. This object can have up to 127 characters.
Read-write Downloads or uploads a configuration file to the agent.
Error values: from normal(1) to operationError(17) and
tftpWrongFileType(29).
loading(18) – Operation is in process.
The following values can be set for operations with the TFTP
server:
• uploadFromFlashToServer(20) – Upload the config from
flash to TFTP server.
• downloadToFlashFromServer(21) – Download the config to
flash from TFTP server.
• uploadFromDramToServer(22) – Upload the config from
DRAM to TFTP server.
• downloadToDramFromServer(23) – Download the config to
DRAM from TFTP server.
The config filename is defined in snAgCfgFname.
The TFTP server address is defined in snAgTftpServerAddr.
The write request will be rejected during loading until error or
normal.
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 25
53-1002582-01
Page 38

Software Image
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
snAgTftpServerAddrType
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.65
Syntax: InetAddressType
Read-write Shows the IP address type of the TFTP server that will be used to
download and upload image and configuration files. Supported
address types are:
• ipv4(1)
• ipv6(2)
• ipv6z(4)
Default: IPv4
snAgTftpServerAddr
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.66
Syntax: InetAddress
Read-write Shows the IP address of the TFTP server that will be used to
download and upload image and configuration files.
Software image details
The following objects show information about software images in a device. These objects are
available in all devices.
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
snAgImgVer
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.11
Syntax: DisplayString
snAgSoftwareFeature
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.41
Syntax: OctetString
Read-only Shows the version of the running software. The software image
file name is displayed in the format:
major.0.minor.maintenance
It can have up to 32 characters.
Read-only A bit string representing the software feature of the running
switch/router image. Each bit can have one of the following
values:
• 0 – The feature is not available
• 1 – The feature is available
Bit 0 is the least significant bit of an octet, and bit 7 is the most
significant bit of an octet.
• Octet 0, bit 0 – RMON
• Octet 0, bit 1 – IPX switching
• Octet 0, bit 2 – Server Load Balancing
• Octet 0, bit 3 – Layer 3 filter in switch
• Octet 0, bit 4 – IPX routing
• Octet 0, bit 5 – AppleTalk routing
• Octet 0, bit 6 – IP multicast routing
• Octet 0, bit 7 – Local access control
• Octet 1, bit 0 – BGP routing
• Octet 1, bit 1 – Loopback interface
• Octet 1, bit 2 – BigIron multi-management module
• Octet 1, bit 3 – BigIron SYSIF II
• Octet 1, bit 4 – BigIron POS support
• Octet 1, bit 5 – AppleTalk cable VLAN
• Octet 1, bit 6 – 64 subnet
• Octet 1, bit 7 – multi-slot trunk
• Octet 2, bit 0 – TACACS
• Octet 2, bit 1 – Gigabit Ethernet port auto-negotiation mode
• Octet 2, bit 2 – FSRP
• Octet 2, bit 3 – Exodus requested OSPF enhancement
• Octet 2, bit 4 – OSPF NSSA
• Octet 2, bit 5 – POS
26 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 39

Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
Software Image
snAgSoftwareFeature
(continued)
snAgBuildDate
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.47
Syntax: DisplayString
snAgBuildtime
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.48
Syntax: DisplayString
snAgBuildVer
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.49
Syntax: DisplayString
• Octet 2, bit 6 – QoS
• Octet 2, bit 7 – Single Span
• Octet 3, bit 0 – Fast Span
• Octet 3, bit 1 – Base L3
• Octet 3, bit 2 – static log buffer
• Octet 3, bit 3 – L2 POS
• Octet 3, bit 4 – BI15K
• Octet 3, bit 5 - L2 ATM
• Octet 3, bit 6 - ATM
• Octet 3, bit 7 - NETFLOW
• Octet 4, bit 0 - SFLOW
• Octet 4, bit 1 - GVRP
• Octet 4, bit 2 - GARP
• Octet 4, bit 3 - Dynamic trunk
• Octet 4, bit 4 - IGC 8G
• Octet 4, bit 5 - Rate limit
• Octet 4, bit 6 - IPC rate limit
• Octet 4, bit 7 - MPLS
• Octet 5, bit 0 - ISIS
• Octet 5, bit 1 - Link aggregation
• Octet 5, bit 2 - Port dual mode
• Octet 5, bit 3 - Private VLAN
• Octet 5, bit 4 - MBGP
• Octet 5, bit 5 - IPv6 protocol VLAN
• Octet 5, bit 6 - X10G
• Octet 5, bit 7 - FastIron Edge switch/router
• Octet 6, bit 0 - FDP
• Octet 6, bit 1 – port tag type
• octet 6, bit 2 - wireless capable
• octet 6, bit 3 - snSwPortVlanId object has changed from
read-only to read-write
• octet 6, bit 4 - LLDP
Additional bits are added for new features. Check the MIB file for
the software version you are running.
Read only Shows the date when the software was built. It can display up to
32 characters.
Read only Shows the time when the software was built. It can display up to
32 characters.
Read only Shows the version of the software in the format:
major.0.minor.maintenance
It can display up to 32 characters.
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 27
53-1002582-01
Page 40

Software configuration
NOTE
Software configuration
Switch IP configurations
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
snAgGblIfIpAddr
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.13
Syntax: Integer
snAgGblIfIpMask
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.14
Syntax: Integer
snAgDefGwayIp
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.10
Syntax: Integer
Read-write Shows the IP address of the interface.
Read-write Shows the IP address mask of the interface.
Read-write Shows the IP address of the default gateway router.
SNTP server table
These objects provide information on the SNTP server.
In a specific configuration and with IPv4 SNTP servers only, SNMP may stop working when the SNTP
server table is viewed. If this occurs, add rfc4001-inetAddressMIB.mib or rfc4001.mib.
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
fdrySntpServerTable
brcdIp.1.1.7.1.1.1
fdrySntpServerEntry
brcdIp.1.1.7.1.1.1.1
fdrySntpServerIndex
brcdIp.1.1.7.1.1.1.1.1
Syntax: Unsigned32
fdrySntpServerAddrType
brcdIp.1.1.7.1.1.1.1.2
Syntax: InetAddressType
None Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) server table.
None An entry in the SNTP server table. This table uses running index as
the Index to the table.Reasons to go for running index Scheme
rather than IP addresses:
1 The table will be Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF)
independent so that multiple VRFs can share the same
address type and address.
2 Index with address type and address could be potentially 17
unsigned integer, dp parsing and finding the next index takes
CPU time. The PDU gets to be huge too!
3 IP address is just another attribute; they are supposed to be
a list of servers.
None The index to the SNTP server table. A maximum of three SNTP
servers are supported.
Read-create The SNTP server IP address type:
• ipv4(1)
• ipv6(2)
• ipv6z(4)
Default: IPv4
28 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 41

Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
Media table
Media table
fdrySntpServerAddr
brcdIp.1.1.7.1.1.1.1.3
Syntax: InetAddress
fdrySntpServerVersion
brcdIp.1.1.7.1.1.1.1.4
Syntax: Integer32
fdrySntpServerRowStatus
brcdIp.1.1.7.1.1.1.1.5
Syntax: RowStatus
Read-create The SNTP server IP address.
Read only The SNTP server version.
Read-create This variable is used to create, or delete a row in this table. When
a row in this table is in active(1) state, no objects in that row can
be modified except this object.
When a row in this table is in active(1) state, the switch supports
writing active(1) or destroy(6), the former of which has no effect,
and the latter of which deletes this entry.
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
snIfMediaInfoTable
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.9.1
snIfMediaInfoEntry
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.9.1.1
snIfMediaType
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.9.1.1.1
Syntax: DisplayString
snIfMediaVendorName
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.9.1.1.2
Syntax: DisplayString
snIfMediaVersion
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.9.1.1.3
Syntax: DisplayString
snIfMediaPartNumber
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.9.1.1.4
Syntax: DisplayString
snIfMediaSerialNumber
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.9.1.1.5
Syntax: DisplayString
N/A This table lists the information for the media device (SFP, XFP, or
copper) installed in the physical Ethernet port. Only the ifIndices
of Ethernet ports that are associated with the operational cards
are included in this table.
N/A An entry in the Interface Media Information table. The ifIndex of
the Ethernet interface is used to index this table.
Read only The type of the media installed in the physical port.
This object displays up to 128 characters.
Read only The media vendor name. The full name of the corporation is
displayed. This object displays up to 128 characters.
Read only The media vendor product version number.
This object displays up to 128 characters.
Read only The media vendor part number.
This object displays up to 128 characters.
Read only The vendor serial number of the media device.
This object displays up to 128 characters.
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 29
53-1002582-01
Page 42

Media table
30 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 43

Agent user access group
This chapter presents the objects used to control user access to devices.
The objects in this section apply to user accounts
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
Chapter
6User Access
snAgWebMgmtServerTcpPort
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.64
Syntax: Integer
General security objects
The following objects are used to manage general security functions.
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
snAgGblTelnetTimeout
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.37
Syntax: Integer
snAgGblEnableWebMgmt
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.38
Syntax: Integer
snAgGblEnableTelnetServer
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.45
Syntax: Integer
snAgGblTelnetLoginTimeout
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.60
Syntax: Integer
Read-write This object allows you to specify which TCP port will be used for
the Web management interface.
Enter a number from 1 – 65535.
Read-write Shows how many minutes a Telnet session can remain idle
before it times out. The value of this object can be up to 1093
minutes.
Read-write Enables or disables access to the device from the Web
management interface:
• disable(0)
• enable(1)
Default: enable(1)
Read-write Enables or disables the Telnet server in a device:
• Disable(0)
• Enable(1)
Default: enable(1)
Read-write
Indicates how many minutes you have to log in before Telnet is
disconnected.
Valid values: 1 – 5 minutes.
Default: 5 minutes
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 31
53-1002582-01
Page 44

Authorization and accounting
Authorization and accounting
The following objects are for authorization, and accounting functions.
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
snAuthorizationExec
brcdIp.1.1.3.15.2.3
Syntax: OctetString
snAccountingExec
brcdIp.1.1.3.15.3.3
Syntax: OctetString
RADIUS general group
You can use a Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS) server to secure the following
types of access to the switch or router:
Read-write Shows the authorization method for exec programs. This object
can have zero to one octet. The octet represents a method for
Telnet or SSH login authorization. The octet can have one of the
following values:
• tacplus(5) – Send EXEC authorization request to TACACS+
server
• none(6) – No EXEC authorization method
Setting a zero length octet string invalidates all authorization
methods.
Read-write Shows the accounting method for exec programs. This object
can have zero to one octet. The octet represents a method for
Telnet or SSH login accounting. The octet can have one of the
following values:
• radius(2) – Send accounting information to the RADIUS
server
• tacplus(5) – Send accounting information to the TACACS+
server
• none(6) – No accounting method
Setting a zero length octet string invalidates all accounting
methods.
• Telnet access
• SSH access
• Web management access
• Access to the Privileged EXEC level and CONFIG levels of the CLI
The following objects provide information on RADIUS authentication.
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
snRadiusGeneral
brcdIp.1.1.3.1 2.1
snRadiusRetransmit
brcdIp.1.1.3.1 2.1.3
Syntax: Integer
snRadiusTimeOut
brcdIp.1.1.3.1 2.1.4
Syntax: Integer
32 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
Read-write Indicates the number of authentication query retransmissions
that can be sent to the RADIUS server.
Valid values: 1 – 30
Default: 2
Read-write Specifies the number of seconds to wait for authentication reply
from the RADIUS server.
Valid values: 1 – 65535
Default: 5
53-1002582-01
Page 45

Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
RADIUS server table
snRadiusKey
brcdIp.1.1.3.1 2.1.6
Syntax: DisplayString
snRadiusLoginMethod
brcdIp.1.1.3.1 2.1.7
Syntax: OctetString
snRadiusWebServerMethod
brcdIp.1.1.3.1 2.1.9
Syntax: OctetString
Read-write Shows the authentication key as encrypted text.
Write operation can only be done if the SET request uses SNMPv3
with data encrypted using privacy key.
This object can have up to 64 characters as encrypted text.
Read-write Shows the sequence of authentication methods for the RADIUS
server. Each octet represents a method for authenticating the
user at login. Each octet can have one of the following values:
• radius(2) – Authenticate by requesting the RADIUS server
• local(3) – Authenticate by local user account table
• tacplus(5) – Authenticate by requesting TACACS Plus server
Setting a zero length octet string invalidates all previous
authentication methods.
NOTE: snRadiusLoginMethod and snRadiusWebServerMethod
effectively set the same object.
Read-write Shows the sequence of authentication methods. Each octet
represents a method for authenticating the user who is accessing
the Web-server. Each octet can have one of the following values:
• radius(2) – Authenticate by requesting the RADIUS server
• local(3) – Authenticate by local user account table
• tacplus(5) – Authenticate by requesting TACACS Plus server
Setting a zero length octet string invalidates all previous
authentication methods.
NOTE: snRadiusLoginMethod and snRadiusWebServerMethod
effectively set the same object.
RADIUS server table
The following objects provide information on the RADIUS server.
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
fdryRadiusServerTable
brcdIp.1.1.8.1.1.1
fdryRadiusServerEntry
brcdIp.1.1.8.1.1.1.1
Syntax: FdryRadiusServerEnt
fdryRadiusServerIndex
brcdIp.1.1.8.1.1.1.1.1
Syntax: Unsigned32
fdryRadiusServerAddrType
brcdIp.1.1.8.1.1.1.1.2
Syntax: InetAddressType
fdryRadiusServerAddr
brcdIp.1.1.8.1.1.1.1.3
Syntax: InetAddress
N/A RADIUS server table listing the RADIUS authentication servers.
N/A An entry in the RADIUS server table.
N/A
Read-create
Read-create The RADIUS server IP address.
The index to the RADIUS server table. A maximum of five RADIUS
servers are supported.
The RADIUS server IP address type – ipv4(1)
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 33
53-1002582-01
Page 46

TACACS general objects
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
fdryRadiusServerAuthPort
brcdIp.1.1.8.1.1.1.1.4
Syntax: Unsigned32
fdryRadiusServerAcctPort
brcdIp.1.1.8.1.1.1.1.5
Syntax: Unsigned32
fdryRadiusServerRowKey
brcdIp.1.1.8.1.1.1.1.6
Syntax: DisplayString
fdryRadiusServerRowStatus
brcdIp.1.1.8.1.1.1.1.8
Syntax: RowStatus
TACACS general objects
The Terminal Access Controller Access Control System (TACACS) or security protocols can be used
to authenticate the following types of access to devices:
• Telnet access
• SSH access
• Securing Access to Management Functions
• Web management access
• Access to the Privileged EXEC level and CONFIG levels of the CLI
Read-create The authentication UDP port number.
Default: 1812
Read-create The account UDP port number.
Default: 1813
Read-create The authentication key displayed as encrypted text.
Valid values: Up to 64 characters as encrypted text.
Read-create This variable is used to create, or delete a row in this table. When
a row in this table is in active(1) state, no objects in that row can
be modified except this object.
When a row in this table is in active(1) state, the switch supports
writing active(1) or destroy(6), the former of which has no effect,
and the latter of which deletes this entry.
The TACACS and protocols define how authentication, authorization, and accounting information is
sent between a device and an authentication database on a TACACS server.
The following objects provide information on TACACS authentication.
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
snTacacsGeneral
brcdIp.1.1.3.13.1
snTacacsKey
brcdIp.1.1.3.13.1.4
Syntax: DisplayString
34 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
Read-write Authentication key displayed as encrypted text.
Write operation can only be done if the SET request usesSNMPv3
with data encrypted using privacy key.
Valid values: Up to 64 characters as encrypted text.
53-1002582-01
Page 47

TACACS server table
The following objects provide information on the TACACS server.
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
TACACS server table
fdryTacacsServerTable
brcdIp.1.1.9.1.1.1
fdryTacacsServerEntry
brcdIp.1.1.9.1.1.1.1
fdryTacacsServerIndex
brcdIp.1.1.9.1.1.1.1.1
Syntax: Unsigned32
fdryTacacsServerAddrType
brcdIp.1.1.9.1.1.1.1.2
Syntax: InetAddresstype
fdryTacacsServerAddr
brcdIp.1.1.9.1.1.1.1.3
Syntax: Inetaddress
fdryTacacsServerAuthPort
brcdIp.1.1.9.1.1.1.1.4
Syntax: Unsigned32
fdryTacacsServerRowKey
brcdIp.1.1.9.1.1.1.1.5
Syntax: DisplayString
(size(0..64))
fdryTacacsServerRowStatus
brcdIp.1.1.9.1.1.1.1.7
Syntax: RowStatus
None The TACACS server table listing the TACACS authentication
servers.
None An entry in the TACACS server table. This table uses a running
index as the index to the table.
None The index to the TACACS server table. Only one TACACS server is
supported.
Read-create
Read-create The TACACS server IP address.
Read-create The UDP port used for authentication.
Read-create The authentication key displayed as encrypted text.
Read-create This variable is used to create, or delete a row in this table. When
The RADIUS server IP address type – ipv4(1)
Default: 49
Valid values: Up to 64 characters as encrypted text.
a row in this table is in active(1) state, no objects in that row can
be modified except this object.
When a row in this table is in active(1) state, the switch supports
writing active(1) or destroy(6), the former of which has no effect,
and the latter of which deletes this entry.
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 35
53-1002582-01
Page 48

TACACS server table
36 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 49

Multi-device port authentication
Multi-Device Port Authentication is also known as MAC Authentication. The following tables
describe the Multi-Device Port Authentication MIB objects.
Global multi-device port authentication objects
The following global objects are available for Multi-Device Port Authentication.
TABLE 2 MAC Authentication Global Objects
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
Chapter
7Multi-Device Port Authentication
snMacAuthClearGlobalCmd
brcdIp.1.1.3.28.1.1
Syntax: Integer
Read-write valid(0) - An SNMP-GET of this MIB shows that it is a valid command.
clear(1) - Represents clear MAC Authentication table for all ports.
Clear interface multi-device port authentication objects
The following clear interface objects are available for Multi-Device Port Authentication.
TABLE 3 MAC Authentication Clear Interface Objects
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
snMacAuthClearIFCmdTable
brcdIp.1.1.3.28.2
Syntax: Sequence of
SnMacAuthClearIfCmdEntry
snMacAuthClearIfCmdEntry
brcdIp.1.1.3.28.2.1
Syntax: SnMacAuthClearIfCmdEntry
snMacAuthClearIfCmdIndex
brcdIp.1.1.3.28.2.1.1
Syntax: InterfaceIndex
snMacAuthClearIfCmdAction
brcdIp.1.1.3.28.2.1.2
Syntax: InterfaceIndex
N/A The status of clearing a MAC authentication entry for an
interface.
N/A An entry clearing a MAC authentication entry for an
interface.
N/A The ifIndex value of the local interface on which a clear
command is issued and monitored.
Read-write valid(0) - An SNMP-GET of this command shows that it is
valid.
clear(1) - Represents clearing a MAC authentication entry for
an interface.
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 37
53-1002582-01
Page 50

Multi-device port authentication
Multi-device port authentication objects
The following objects are available for Multi-Device Port Authentication.
TABLE 4 Multi-Device Port Authentication Objects
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
snMacAuthTable
brcdIp.1.1.3.28.3
Syntax: Sequence of
SnMacAuthEntry
snMacAuthEntry
brcdIp.1.1.3.28.3.1
Syntax: SnMacAuthEntry
snMacAuthIfIndex
brcdIp.1.1.3.28.3.1.1
Syntax: InterfaceIndex
snMacAuthVlanId
brcdIp.1.1.3.28.3.1.2
Syntax: Integer
snMacAuthMac
brcdIp.1.1.3.28.3.1.3
Syntax: MacAddress
snMacAuthTimeStamp
brcdIp.1.1.3.28.3.1.5
Syntax:TimeStamp
snMacAuthAge
brcdIp.1.1.3.28.3.1.6
Syntax: Integer
N/A Displays the MAC Authentication table.
N/A An entry in the MAC Authentication table.
N/A In order to identify a particular interface, this object identifies the
instance of the ifIndex object, defined in RFC 2863.
N/A The ID of a VLAN of which the port is a member. This object is not
supported, and therefore returns 0, which is an invalid VLAN ID
value.
N/A MAC Address to be authenticated.
Read only Timestamp at which the MAC was authenticated or failed to be
authenticated.
Read only Age of the mac session in which the MAC address is authenticated.
Multi-device port authentication clear sessions
The following clear sessions objects are available for Multi-Device Port Authentication.
TABLE 5 MAC Authentication Clear Mac Session MIBs
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
snMacAuthClearMacSessionTable
brcdIp.1.1.3.28.4
Syntax: Sequence of
SnMacAuthClearMacSessionEntry
snMacAuthClearMacSessionEntry
brcdIp.1.1.3.28.4.1
Syntax:
SnMacAuthClearMacSessionEntry
snMacAuthClearMacSessionIfIndex
brcdIp.1.1.3.28.4.1.1
Syntax: InterfaceIndex
38 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
N/A The status of clearing a MAC Session entry indexed by a MAC
address.
N/A An entry of clearing a MAC Session entry indexed by a MAC
address.
N/A The ifIndex value of the local interface on which a clear
command is issued and monitored.
53-1002582-01
Page 51

Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
Multi-device port authentication
snMacAuthClearMacSessionMac
brcdIp.1.1.3.28.4.1.2
Syntax: MacAddress
snMacAuthClearMacSessionAction
brcdIp.1.1.3.28.4.1.3
Syntax: Integer
N/A A MAC Session entry indexed by a MAC address.
Read-write valid(0) - An SNMP-GET of this MIB shows that it is a valid
command.
clear(1) - Represents clearing a MAC Session entry indexed
by a MAC address.
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 39
53-1002582-01
Page 52

Multi-device port authentication
40 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 53

This chapter presents the SNMP MIB objects for various traffic security features such as Dynamic
ARP Inspections, DHCP Snooping, and IP Source Guard.
Dynamic ARP Inspection VLAN configuration table
Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) is a security mechanism which validates all ARP packets in a subnet
and discard those packets with invalid IP to MAC address bindings. To configure the feature using
SNMP MIB objects, do the following:
1. Enable DAI on a VLAN
DAI on a VLAN is disabled by default. To enable DAI on an existing VLAN, set the object
fdryDaiVlanDynArpInspEnable in the fdryDaiVlanConfigTable to true. Set it to false to disable it.
2. Enable trust on a port
Chapter
8Traffic Security
The default trust setting for a port is untrusted. To enable trust on a port, set the object
fdryDaiIfTrustValue in the fdryDaiIfConfigTable to true. Set it to false to disable trust on a port.
3. Configure a DAI ARP entry
To configure a DAI ARP entry, set the fdryDaiArpInspectIpAddr, fdryDaiArpInspectMacAddr and
fdryDaiArpInspectRowStatus (value as createAndGo) in the fdryDaiArpInspectTable. This table
displays all DAI entries. A row instance contains the configuration to map a device IP address
with its MAC address and its type, state, age and port.
DAI VLAN configuration table
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
fdryDaiVlanConfigTable
brcdIp.1.1.3.35.1.1
fdryDaiVlanConfigEntry
brcdIp.1.1.3.35.1.1.1
fdryDaiVlanVLanId
brcdIp.1.1.3.35.1.1.1.1
Syntax: VlanIndex
fdryDaiVlanDynArpInspEnable
brcdIp.1.1.3.35.1.1.1.2
Syntax: TruthValue
N/A This table provides the mechanism to control Dynamic ARP
Inspection per VLAN.
N/A When a VLAN is created on a device supporting this table, a
corresponding entry of this table is added.
This entry represents a row that contains the configuration to
enable or disable Dynamic ARP Inspection on the existing VLAN.
It is indexed by fdryDaiVlanVLanId.
N/A This object indicates the VLAN number on which the Dynamic ARP
Inspection feature is configured.
Read-write This object indicates whether Dynamic ARP Inspection is enabled
in this VLAN.
If this object is set to “true”, Dynamic ARP Inspection is enabled.
If this object is set to “false”, Dynamic ARP Inspection is disabled.
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 41
53-1002582-01
Page 54

Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Dynamic ARP Inspection Interface configuration table
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
fdryDaiIfConfigTable
brcdIp.1.1.3.35.2.1
fdryDaiIfConfigEntry
brcdIp.1.1.3.35.2.1.1
fdryDaiIfTrustValue
brcdIp.1.1.3.35.2.1.1.1
Syntax: TruthValue
N/A This table allows you to configure the trust state for
N/A A row in the fdryDaiConfigTable. Each row contains the
Read-write This object indicates whether the interface is trusted
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) snooping enables the device to filter untrusted DHCP
packets in a subnet. DHCP snooping can prevent man-in-the-middle (MiM) attacks, such as a
malicious user who is posing as a DHCP server and is sending false DHCP server reply packets with
the intention of misdirecting other users. It can also stop unauthorized DHCP servers and prevent
errors due to misconfiguration of DHCP servers.
SNMP DHCP snooping MIB objects describes how to configure the DHCP snooping feature using
SNMP. It consists of the following:
Dynamic ARP Inspection at each physical interface.
configuration to enable or disable the trust state for
Dynamic ARP Inspection at each physical interface
capable of this feature.
for Dynamic ARP Inspection.
If this object is set to 'true', the interface is trusted. ARP
packets coming to this interface will be forwarded
without being checked.
If this object is set to “false”, the interface is not
trusted. ARP packets received on this interface will be
subjected to ARP inspection.
• fdryDhcpSnoopGlobalClearOper: A scalar used to clear all entries in the DHCP binding
database
• fdryDhcpSnoopVlanConfigTable: A table that provides the mechanism to control DHCP
snooping per VLAN. When a VLAN is created on a device that supports this table, a
corresponding entry of this table will be added.
• fdryDhcpSnoopIfConfigTable: A table that provides the mechanism to configure the trust state
for DHCP snooping at each physical interface.
• fdryDhcpSnoopBindTable: A table that provides the information for DHCP snooping binding
database learned by the device. The DHCP binding database is integrated with the enhanced
ARP table. It contains the information of a DHCP entry, such as IP address, MAC address, type,
state, port, VLAN ID, and lease time. (To be provided at a later date.)
42 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 55

Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
DHCP Snooping global scalar object
One scalar object can clear all entries in the DHCP binding database.
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
fdryDhcpSnoopGlobalClearOper
brcdIp.1.1.3.36.1.1.
Syntax: ClearAction
Read-write Determines if all entries in the DHCP database is
cleared:
• valid(0) - this values is always returned when the
variable is read.
• clear(1) - clears all entries in the DHCP binding
database.
DHCP Snooping VLAN configuration table
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
fdryDhcpSnoopVlanConfigTable
brcdIp.1.1.3.36.2.1
fdryDhcpSnoopVlanConfigEntry
brcdIp.1.1.3.36.2.1.1
fdryDhcpSnoopVlanVLanId
brcdIp.1.1.3.36.2.1.1.1
Syntax: VlanIndex
fdryDhcpSnoopVlanDhcpSnoopEnable
brcdIp.1.1.3.36.2.1.1.2
Syntax: TruthValue
N/A A table controls DHCP Snooping per VLAN. When a
VLAN is created in a device supporting this table, a
corresponding entry of this table will be added.
N/A A row in the table. It contains the configuration to either
enable or disable DHCP Snooping on the existing VLAN.
It is indexed by fdryDhcpSnoopVlanVLanId.
N/A This object indicates the VLAN number on which DHCP
Snooping feature is configured.
Read-write This object indicates whether DHCP Snooping is
enabled in this VLAN.
If set to “true”, DHCP snooping is enabled.
If set to “false” it is disabled.
DHCP Snooping Interface configuration table
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
fdryDhcpSnoopIfConfigTable
brcdIp.1.1.3.36.3.1
fdryDhcpSnoopIfConfigEntry
brcdIp.1.1.3.36.3.1.1
fdryDhcpSnoopIfTrustValue
brcdIp.1.1.3.36.3.1.1.1
Syntax: TruthValue
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 43
53-1002582-01
N/A This table allows you to configure the trust state for
DHCP Snooping at each physical interface.
N/A A row instance contains the configuration to enable or
disable the trust state for DHCP Snooping at each
physical interface capable of this feature. It is indexed
by the ifIndex.
Read-write This object indicates whether the interface is trusted
for DHCP Snooping.
If this object is set to “true”, the interface is trusted.
DHCP packets coming to this interface will be
forwarded without checking.
If this object is set to “false”, the interface is not
trusted. DHCP packets received on this interface will be
subjected to DHCP checks.
Page 56

IP Source Guard
IP Source Guard
IP Source Guard is a security feature that restricts IP traffic on untrusted ports. IP Source Guard
filters traffic based on the DHCP snooping binding database or the manually configured IP source
bindings.
When IP Source Guard is first enabled, only DHCP packets are allowed and all IP traffic is blocked.
When the system learns a valid IP address, IP Source Guard then allows IP traffic. Only the traffic
with valid source IP addresses is permitted.
SNMP IP Source Guard MIB objects manage information for the configuration of the IP Source
Guard feature. There are three tables for IP Source Guard:
• fdryIpSrcGuardIfConfigTable - enables or disables IP Source Guard on each physical interface.
• fdryIpSrcGuardPortVlanConfigTable - enables or disables IP Source Guard on a port on a VLAN.
(Not provided by this switch.)
• fdryIpSrcGuardBindTable - provides the IP addresses used for IP Source Guard purposes at
each physical interface, with or without specific VLAN memberships. (To be provided at a later
date.)
IP Source Guard Interface configuration table
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
fdryIpSrcGuardIfConfigTable
brcdIp.1.1.3.37.1.1
fdryIpSrcGuardIfConfigEntry
brcdIp.1.1.3.37.1.1.1
fdryIpSrcGuardIfEnable
brcdIp.1.1.3.37.1.1.1.1
Syntax: TruthValue
N/A This table enables or disables IP Source Guard on each
physical interface.
N/A A row indicates if IP Source Guard is enabled or
disabled on each physical interface. It is indexed by
ifIndex.
Read-write This object indicates whether IP Source Guard is
enabled on this interface.
If this object is set to “true”, IP Source Guard is
enabled. Traffic coming to this interface will be
forwarded if it is from the list of IP addresses obtained
from DHCP snooping. Otherwise it is denied.
If this object is set to “false”, IP Source Guard is
disabled.
44 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 57

MAC-based VLAN global objects
The following MAC-Based VLAN global objects have been created to provide support through SNMP.
TABLE 6 MAC-Based VLAN MIB Global Objects
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
Chapter
9MAC-Based VLAN
fdryMacVlanGlobalObjects
brcdIp.1.1.3.32.1
fdryMacVlanGlobalClearOper
brcdIp.1.1.3.32.1.1
Syntax: Integer
N/A Displays the Global MAC VLAN Objects table.
Read-write valid(0) - This value is always returned when the variable is
read.
clear(1) - Setting the variable to this value clears the
operational MAC-based VLAN information for all ports.
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 45
53-1002582-01
Page 58

MAC-based VLAN global objects
46 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 59

Switch port information
This chapter presents the objects used to define interfaces on a device. Refer to the configuration
guide for details on the features discussed in this chapter.
The following table contains information about the switch port groups.
Switch port information group
The snSwIfInfoTable contains information about the switch port groups.
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
Chapter
10Interfaces
snSwIfInfoTable
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.5
snSwIfInfoEntry
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.5
snSwIfInfoPortNum
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.5.1.1
Syntax: InterfaceIndex
snSwIfInfoTagMode
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.5.1.4
Syntax: Integer
snSwIfInfoChnMode
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.5.1.6
Syntax: Integer
N/A The Switch Port Information Table.
N/A An entry in the snSwIfInfo table indicates the configuration for a
specified port.
Read only Shows the port or interface index.
Read-write Indicates if the port has an 802.1Q tag:
• tagged(1) – Ports can have multiple VLAN IDs since these
ports can be members of more than one VLAN.
• untagged(2) – There is only one VLAN ID per port.
• dual(3) – Ports can have multiple VLANs per port.
Read-write Indicates if the port operates in half- or full-duplex mode:
• halfDuplex(1) – Half duplex mode.
• fullDuplex(2) – Full duplex mode. 100BaseFx, 1000BaseSx,
and 1000BaseLx ports operate only at fullDuplex(2).
The read-back channel status from hardware can be:
• halfDuplex(1) – Half duplex mode.
• fullDuplex(2) – Full duplex mode.
The port media type (expansion or regular) and port link type
(trunk or feeder) determine whether this object can be written
andthe value of this object.
Note that “writing” this variable writes the forced-mode
configuration, which is used when autonegotiation is disabled,
and has nothing to do with the current operation mode when
autonegotiation is enabled.
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 47
53-1002582-01
Page 60

Switch port information
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
snSwIfInfoSpeed
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.5.1.7
Syntax: Integer
snSwIfInfoMediaType
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.5.1.8
Syntax: Integer
snSwIfInfoConnectorType
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.5.1.9
Syntax: Integer
snSwIfStpPortEnable
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.5.1.15
Syntax: Integer
snSwIfInfoAutoNegotiate
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.5.1.19
Syntax: Integer
snSwIfInfoFlowControl
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.5.1.20
Syntax: Integer
snSwIfInfoGigType
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.5.1.21
Syntax: Integer
snSwIfFastSpanPortEnable
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.5.1.22
Syntax: Integer
Read-write Indicates the speed configuration for a port:
• s10M(2) – 10Mbits per second.
• s100M(3) – 100Mbits per second.
The read-back hardware status are the following:
• s10M(2) – 10Mbits per second.
• s100M(3) – 100Mbits per second.
• s1G(4) – 1Gbits per second.
The port media type (expansion or regular) and port link type
(trunk or feeder) determine whether this object can be written
and the valid values for this object.
Note that “writing” this variable writes the forced-mode
configuration, which is used when autonegotiation is disabled,
and has nothing to do with the current operation mode when
autonegotiation is enabled.
Read only Shows the media type for the port:
• other(1) – other or unknown media.
• m100BaseTX(2) – 100Mbits per second copper.
• m100BaseFX(3) – 100Mbits per second fiber.
• m1000BaseTX(7) – 1Gbits per second copper.
Read only Shows the type of connector that the port offers:
• other(1) – Other or unknown connector
• copper(2) – Copper connector
• fiber(3) – Fiber connector
This describes the physical connector type
Read-write Indicates if STP is enabled for the port:
• disabled(0)
• enabled(1)
Refer to the document IEEE 802.1D-1990: Section 4.5.5.2,
dot1dStpPortEnable.
Read-write Applies only to Gigabit Ethernet ports.
Indicates if auto-negotiation mode is enabled on the port.
• disable(0) – The port will be placed in non-negotiation mode.
• enable(1) – The port will start auto-negotiation indefinitely
until it succeeds.
Default: enable(1)
Read-write Indicates if port flow control is enabled:
• disable(0)
• enable(1)
Default: enabled(1)
Read only Applies only to Gigabit Ethernet ports.
Shows the media type for the port:
• m1000BaseSX(0) – 1-Gbps fiber, with a short wavelength
transceiver
• m1000BaseLX(1) – 1-Gbps fiber, with a long wavelength
transceiver (3km)
• m1000BaseTX(5) – 1-Gbps copper (100meter).
• notApplicable(255) – a non-gigabit port.
Read-write Indicates if fast span is enabled on the port.
• disable(0)
• enable(1)
48 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 61

Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
Link Aggregation Group (LAG) table
snSwIfGBICStatus
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.5.1.27
Syntax: Integer
snSwIfStatsMacStations
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.5.1.44
Syntax: Integer32
Read only Indicates if the Gigabit port has a GBIC or miniGBIC port:
Read only Shows the total number of MAC Stations connected to the
Link Aggregation Group (LAG) table
fdryLinkAggregationGroupTable
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
fdryLinkAggregationGroupTable
brcdIp.1.1.3.33.1.1
fdryLinkAggregationGroupEntry
brcdIp.1.1.3.33.1.1.1
fdryLinkAggregationGroupName
brcdIp.1.1.3.33.1.1.1.1
Syntax: DisplayString (Size(1..64))
fdryLinkAggregationGroupType
brcdIp.1.1.3.33.1.1.1.2
Syntax: Integer
fdryLinkAggregationGroupIfList
brcdIp.1.1.3.33.1.1.1.4
Syntax: OctetString
fdryLinkAggregationGroupLacpTimeout
brcdIp.1.1.3.33.1.1.1.8
Syntax: Integer
fdryLinkAggregationGroupIfIndex
brcdIp.1.1.3.29.2.1.1.9
Syntax: InterfaceIndex
fdryLinkAggregationGroupPortCount
brcdIp.1.1.3.33.1.1.1.10
Syntax: Unsigned32
N/A The fdryLinkAggregation table.
N/A An entry of the Link Aggregation table,
N/A Displays the name of a LinkAggregationGroup.
Read/create Displays the LinkAggregationGroup type.
Read/create Displays a list of interface indices which are the port
Read/create The LACP timeout value this LACP LAG will use.
Read only After a LAG is deployed, this object dIsplays information
Read only Displays the number of member ports belong to this
• GBIC(1) – GBIC
• miniGBIC(2) – MiniGBIC
• empty(3) – GBIC is missing
• other(4) – Not a removable Gigabit port
interface.
Possible Values:
• static(1)
• dynamic(2)
membership of a trunk group. Each interface index is a
32-bit integer in big endian order.
NOTE: This object accepts 32-bit integer only.
for the LAG entry in the ifTable. Use this variable to
access the entry in the ifTable and ifXTable. Zero is
returned for LAGs that have not been deployed.
LAG.
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 49
53-1002582-01
Page 62

Link Aggregation Group (LAG) table
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
fdryLinkAggregationGroupRowStatus
brcdIp.1.1.3.33.1.1.1.11
Syntax: RowStatus
fdryLinkAggregationGroupId
brcdIp.1.1.3.33.1.1.1.12
Syntax: Unsigned 32
Read/create This variable is used to create or delete a trunk whose
fdryLinkAggregationGroupType(2) is static(1). Set this
to active(1) to create, and set this to notInService(2) to
delete.
However, reading this as active(1) may mean a link
aggregation whose fdryLinkAggregationGroupType(2) is
static(1) or dynamic(2).
Read only The numeric identifier assigned to this LAG.
50 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 63

CPU utilization
The following objects monitor CPU utilization in all devices. Refer to the configuration guide for
additional information on this feature.
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
Chapter
11Monitoring and Logging
snAgGblCpuUtilData
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.35
Syntax: Gauge
snAgGblCpuUtil5SecAvg
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.51
Syntax: Gauge32
snAgGblCpuUtil1MinAvg
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.52
Syntax: Gauge32
Read only The statistics collection of utilization of the CPU in the device.
Read only Shows CPU utilization every 5 seconds.
Read only Shows CPU utilization every one minute.
System DRAM information group
This group displays memory utilization statistics for protocols that use dynamic memory allocation.
It shows the same information that a show memory command displays.
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
snAgSystemDRAM
brcdIp.1.1.2.1 2.4
snAgSystemDRAMUtil
brcdIp.1.1.2.1 2.4.1
Syntax: Integer
snAgSystemDRAMTotal
brcdIp.1.1.2.1 2.4.2
Syntax: Integer
snAgSystemDRAMFree
brcdIp.1.1.2.1 2.4.3
Syntax: Integer
NA The System DRAM Information Group
Read only The amount of system dynamic memory that is currently
Read only The total amount of system dynamic memory, in bytes.
Read only The amount of free system dynamic memory, in bytes.
This object reads the same value as snAgGblCpuUtil5SecAvg.
utilized, in percentage.
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 51
53-1002582-01
Page 64

Global ARP statistics
Global ARP statistics
The following are the MIB objects display statistics for ARP.
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
snArpStatsTotalReceived
brcdIp.1.1.3.22.1.1
Syntax: Counter32
snArpStatsRequestReceived
brcdIp.1.1.3.22.1.2
Syntax: Counter32
snArpStatsRequestSent
brcdIp.1.1.3.22.1.3
Syntax: Counter32
snArpStatsRepliesSent
brcdIp.1.1.3.22.1.4
Syntax: Counter32
Support for optical monitoring
The following objects are for support in Ethernet optical monitoring. They are equivalent to the
show interfaces transceiver CLI command.
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
snIfOpticalMonitoringInfoTable
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.6
snIfOpticalMonitoringInfoEntry
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.6.1
Syntax: Unsigned32
snIfOpticalMonitoringTemperature
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.6.1.1
Syntax: DisplayString
snIfOpticalMonitoringTxPower
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.6.1.2
Syntax: DisplayString
snIfOpticalMonitoringRxPower
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.6.1.3
Syntax: DisplayString
snIfOpticalMonitoringTxBiasCurrent
brcdIp.1.1.3.3.6.1.4
Syntax: DisplayString
Read only The total number of ARP packets received from the interfaces,
including those received in error.
Read only The total number of input ARP request packets received from
the interfaces.
Read only The total number of output ARP request packets sent from the
interfaces.
Read only The total number of output ARP reply packets sent from the
interfaces.
N/A This table lists the instrumented parameters of all optical
interfaces.
N/A The snIfOpticalMonitoringInfoEntry specifies the optical
parameters of the specified interface. Only the ifIndices of
optical interfaces whose parameters need to be monitored
will be used to index this table.
Read only This object holds the value of the transmitter laser diode
temperature for the interface. This object indicates the
health of the transmitter.
The format is [-]xxx.yyyy C(elsius), followed by whether the
measured value is normal, high/low alarm or high/low
warning.
Read only This object holds the value of the transmitter optical signal
power for the interface, measured in dBm, followed by
whether this is a normal value, or high/low warning or alarm.
Read only This object holds the value of the receiver optical signal
power for the interface, measured in dBm, followed by
whether this is a normal value, or high/low warning or alarm.
Read only Tx Bias Current. It is measured in mA, and is followed by
whether this is a normal value, or high/low warning or alarm.
52 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 65

System logging
The objects in this section manage system logging functions (Syslog) using SNMP.
System log server table
The System Log (Syslog) Server Table shows which servers will receive Syslog messages. Every
server in this table will receive all Syslog messages.
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
System logging
brcdSysLogServerTable
brcdIp.1.1.11.1.1.1
brcdSysLogServerEntry
brcdIp.1.1.11.1.1.1.1
brcdSysLogServerAddrType
brcdIp.1.1.11.1.1.1.1.1
brcdSysLogServerAddr
brcdIp.1.1.11.1.1.1.1.2
brcdSysLogServerUDPPort
brcdIp.1.1.11.1.1.1.1.3
brcdSysLogServerRowStatus
brcdIp.1.1.11.1.1.1.1.5
N/A System Log Server Table
N/A A row in the System Log Server table
N/A The System Log server address type. The supported address
types are:
• ipv4(1)
• ipv6(2)
• ipv6z(4)
Default: IPv4
N/A IP address of System Log server.
N/A UDP port number of the System Log server.
Read/create Controls the management of the table rows.
Setting this object to createAndGo(4) adds new row. Setting
this object to destroy(6) deletes a row. The value active(1) is
returned for get and get-next requests.
Other values in the enumeration are not used.
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 53
53-1002582-01
Page 66

System logging
54 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 67

Agent temperature table for stacking
The Agent Temperature Table shows temperature information for a module’s temperature sensor in
the Stacking devices.
Name, Identifier, and Syntax Access Description
Chapter
12Object for Stacking
snAgentTemp2Table
brcdIp.1.1.2.13.2
snAgentTemp2Entry
brcdIp.1.1.2.13.2.1
snAgentTemp2UnitNum
brcdIp.1.1.2.13.2.1.1
Syntax: Integer
snAgentTemp2SlotNum
brcdIp.1.1.2.13.2.1.2
Syntax: Integer
snAgentTemp2SensorId
brcdIp.1.1.2.13.2.1.3
Syntax: Integer
snAgentTemp2Value
brcdIp.1.1.2.13.2.1.5
Syntax: Integer
N/A This table lists the temperature of each unit in the stack.
N/A A row in the unit temperature table.
N/A The unit number which contains the temperature sensor
represented by this row.
N/A The slot number of module which contains the temperature
sensor represented by this row. (The value of this object is
always 1.)
N/A The temperature sensor ID of the member module that is
represented by this row.
The first detector is located between the physical layer ASICs
on the main board. The second and third detector are located
on right and left side of daughter board.
Read only Temperature of the sensor represented by this row. Each unit is
0.5 degrees Celsius.
Values are from -110 to 250.
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 55
53-1002582-01
Page 68

Agent temperature table for stacking
56 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 69

Objects for Brocade 6910 switch traps
This section present the objects available to enable or disable traps.
Trap information
The following objects provide general information on traps.
Name, OID, and Syntax Access Description
Chapter
13Traps and Objects to Enable Traps
snAgTrpRcvrCurEntry
brcdIp.1.1.2.1.16
Syntax: Integer
Read only Shows the total number of entries that are currently in the Trap
Receiver Table. There can be up to 5 entries.
Trap receiver table
This table allows you to configure trap receivers on the Brocade 6910 switch:
Name, OID, and Syntax Access Description
fd ryTrapRec eiv erTabl e
brcdIp.1.1.10.1.1.1
fdryTrapReceiverEntry
brcdIp.1.1.10.1.1.1.1
fdryTrapReceiverIndex
brcdIp.1.1.10.1.1.1.1.1
Syntax: Unsigned32
fd ryTrapRec eiv erAdd rType
brcdIp.1.1.10.1.1.1.1.2
Syntax: InetAddressType
None The Trap Receiver Table.
None An entry in the Trap Receiver Table. This table uses a running
index as the index to the table.
Reasons to use the running index scheme rather than IP
addresses:
1 The table will be Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF)
independent so that multiple VRFs can share the same
address type and address.
2 An index with address type and address could be
potentially 17 unsigned integers, causing parsing and
finding the next index to take much CPU time. The PDU
gets to be huge too.
3 An IP address is just another attribute, and they are
supposed to be a list of servers.
None The index to the Trap Receiver Table.
Read-create Trap Receiver IP address Type. Supported address types are:
• ipv4(1)
• ipv6(2)
• ipv6z(4)
Default: ipv4
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 57
53-1002582-01
Page 70

Standard traps
Name, OID, and Syntax Access Description
fdryTrapReceiverAddr
brcdIp.1.1.10.1.1.1.1.3
Syntax: InetAddress
fdryTrapReceiver
CommunityOrSecurityName
brcdIp.1.1.10.1.1.1.1.4
Syntax: OctetString
(size(0..32))
fdryTrapReceiverUDPPort
brcdIp.1.1.10.1.1.1.1.5
Syntax: Integer32
(0..65535)
fdryTrapReceiverSecurityModel
brcdIp.1.1.10.1.1.1.1.6
Syntax: SecurityModel
fdryTrapReceiverSecurityLevel
brcdIp.1.1.10.1.1.1.1.7
Syntax: SecurityLevel
fdryTrapReceiverRowStatus
brcdIp.1.1.10.1.1.1.1.8
Syntax: RowStatus
Read-create The IP address of the SNMP manager that will receive the trap.
Read-create The community string to use to access the trap receiver. This
object can have up to 32 octets. In the case of USM (SNMPv3)
security model, this object is used to provide the security name.
Writing a null string sets the name to “public”.
Read-create The UPD port number of the trap receiver.
Valid value: 0 – 65535
Default: 162
Read-create The version of trap format to be used.
Default: v1
Read-create Used for USM (SNMPv3) security model to specify the level of
security. The security name is provided by
fdryTrapReceiverCommunityOrSecurityName.
Default: noAuth
Read-create This variable is used to create, or delete a row in this table.
When a row in this table is in active(1) state, no objects in that
row can be modified except this object.
When a row in this table is in active(1) state, the switch
supports writing active(1) or destroy(6), the former of which has
no effect, and the latter of which deletes this entry.
Standard traps
This section present the standard traps supported on devices.
System status traps
Brocade supports the following traps from RFC 1215:
Trap Name and Number Varbind Description
coldStart
1.3.6.1.6.3.1.1.5.1
warmStar t
1.3.6.1.6.3.1.1.5.2
authenticationFailure
1.3.6.1.6.3.1.1.5.5
(None) Indicates that the sending protocol entity is re-initializing itself: the
agent's configuration or the protocol entity implementation may
be altered.
(None) Indicates that the sending protocol entity is re-initializing itself;
however, the agent configuration nor the protocol entity
implementation is not altered.
(None) Indicates that the sending protocol entity is the addressee of a
protocol message that is not properly authenticated. While
implementations of the SNMP must be capable of generating this
trap, they must also be capable of suppressing the emission of
such traps through an implementation-specific mechanism.
58 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 71

Brocade supports the following traps from RFC 2863:
Trap Name and Number Varbind Description
Standard traps
linkDown
1.3.6.1.6.3.1.1.5.3
linkUp
1.3.6.1.6.3.1.1.5.4
ifIndex(1)
ifAdminStatus(7)
ifOperStatus(8)
ifIndex(1)
ifAdminStatus(7)
ifOperStatus(8)
A failure in one of the communication links.
For example,
Interface <port-name> <port-num>, state down
The communication link is up.
For example,
Interface <port-name> <port-num>, state up
Traps for spanning tree protocol
Brocade supports for the following traps for Spanning Tree Protocol from RFC 1493.
Trap Name and Number Description
newRoot
1.3.6.1.2.1.17.0.1
topologyChange
1.3.6.1.2.1.17.0.2
Indicates that the sending agent has become the new root of the Spanning
Tree. The trap is sent by a bridge soon after its election as the new root, for
example, upon expiration of the Topology Change Timer immediately
subsequent to its election.
Is sent by a bridge when any of its configured ports transitions from the
Learning state to the Forwarding state, or from the Forwarding state to the
Blocking state. The trap is not sent if a newRoot trap is sent for the same
transition.
Traps for RMON events
Brocade supports for the following traps for RMON from RFC 2819.
Trap Name and Number Varbind Description
risingAlarm
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.0.1
fallingAlarm
1.3.6.1.2.1.16.0.2
alarmIndex,
alarmVariable,
a l ar m S am p l e Ty p e,
alarmValue,
alarmRisingThreshold
alarmIndex,
alarmVariable,
a l ar m S am p l e Ty p e,
alarmValue,
alarmFallingThreshold
The SNMP trap that is generated when an alarm entry
crosses its rising threshold and generates an event that is
configured for sending SNMP traps.
The SNMP trap that is generated when an alarm entry
crosses its falling threshold and generates an event that is
configured for sending SNMP traps.
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 59
53-1002582-01
Page 72

IronWare traps
NOTE
IronWare traps
This section presents the IronWare traps supported on devices running IronWare software.
The Traps in the IronWare MIBs include the following lines in their description:
--#TYPE "Brocade Trap: Power Supply Failure"
--#SUMMARY "Power supply fails, error status %d."
--#ARGUMENTS { 0 }
--#SEVERITY MINOR
--#STATE OPERATIONAL
These lines are used by the HP OpenView network management system.
General traps
The table below lists the general traps generated by devices. Refer to the previous sections in this
chapter to determine if traps for a feature need to be enabled.
Trap Name and Number Varbind Severity Description
snTrapUserLogin
brcdIp.0.75
snTrapUserLogout
brcdIp.0.76
snTrapClientLoginReject
brcdIp.0.110
snAgGblTrapMessage Informational The SNMP trap that is generated
when a user logs in to a device.
Sample Trap Message:
Security: telnet login
from src IP 10.37.21.63 to
USER EXEC mode.
snAgGblTrapMessage Informational The SNMP trap that is generated
when a user logs out of a device.
Sample Trap Message:
Security: telnet logout
from src IP 10.37.21.63
from USER EXEC mode.
snAgGblTrapMessage Informational The SNMP trap that is generated
when a login attempt by a telnet or
SSH client fails.
Format:
Security: {snmp | ssh|telnet| web}
access [by user <name>] from src [IP
<ipv4> | IPv6 <ipv6>] rejected, <n>
attempts
60 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 73

IronWare traps
NOTE
Trap Name and Number Varbind Severity Description
snTrapSysMemoryLowThreshold
brcdIp.0.180
snTrapTemperatureOK
brcdIp.0.1001
snAgGblTrapMessage Informational The SNMP trap that is generated
when memory utilization reaches the
memory rising threshold (set by the
CLI memory command).
snAgGblTrapMessage Informational The SNMP trap that is generated
when the actual temperature reading
falls from the rising threshold and
reaches the falling threshold.
Sample Trap Message:
System: Stack unit
<unitNumber> temperature
<actual-temp> C degrees is
normal
Port security traps
The Port Security feature enables a device to learn a limited number of “secure” MAC addresses on
an interface. The interface will forward only those packets with source MAC addresses that match
these secure addresses. If the interface receives MAC addresses that are included in its secure
MAC list, the device generates the following traps:
These traps appy to ports that have the Port Security feature enabled.
Trap Name and Number Varbind Severity Description
snTrapPortSecurityViolation
brcdIp.0.77
snAgGblTrapMessage Minor The SNMP trap that is generated
when insecure MAC addressesare
received from a port with MAC
security feature enabled.
Sample Trap Message:
Brocade Trap: Port
Security Violation
Traps for stacking
Brocade supports for the following traps for stacking.
Trap Name and Number Varbind Severity Description
snTrapStackingChasPwrSupplyOK
brcdIp.0.166
snChasUnitIndex,
snChasPwrSupplyIndex,
snAgGblTrapMessage
Minor The SNMP trap that is generated
when a power supply operational
status changed from failure to
normal for a stacking system.
Sample Trap Message
System: Stack unit
<unitNumber>
Power supply
<snChasPwrSupplyIndex> is
up
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 61
53-1002582-01
Page 74

Examples
Trap Name and Number Varbind Severity Description
Examples
snTrapStackingChasPwrSupplyFailed
brcdIp.0.167
snTrapStackingTemperatureWarning
brcdIp.0.171
snChasUnitIndex,
snChasPwrSupplyIndex,
snAgGblTrapMessage
snChasUnitIndex,
snAgGblTrapMessage
Minor The SNMP trap that is generated
when a power supply operational
status changed from normal to
failure for a stacking system.
Sample Trap Message
System: Stack unit
<unitNumber>
Power supply
<snChasPwrSupplyIndex> is
down
Critical The SNMP trap that is generated
when the actual temperature
reading rises from the falling
threshold and reaches the rising
threshold.
Sample Trap Message
System: Stack unit
<unitNumber> Temperature
<actual-temp> C degrees,
warning level
<warning-temp> C degrees
RMON event traps
The following is an example of how to generate an SNMP trap for an RMON event.
If you want to configure a device to send an SNMP trap when the number of broadcast packets
exceeds 100, do the following:
1. Configure an RMON alarm with an ID of 1 that checks etherStatsBroadcastPkts for Port 1 every
15 seconds to see if it exceeds a specified delta threshold (i.e., a change compared to the last
reading). In every sample, check if etherStatsBroadcastPkts exceeds 100 packets compared to
the last measurement. If it does, send an event (id 1) with “Tom” as the owner name. The event
trigger is re-armed, when the falling-threshold value falls below 30 packets since the last
reading.
Console(config)#rmon alarm 1 1.3.6.1.2.1.16.1.1.1.6.1 15 delta
rising-threshold 100 1 falling-threshold 80 1 owner Tom
The rising and the falling thresholds are used for the presence and absence of one specific
condition, with an oscillation buffer in between (e.g. warning versus no warning, not opposite
events like “too much” and “too little”), and should be near each other to be meaningful. The
data monitored may oscillate between these thresholds over time, triggering multiple events,
e.g. when using the settings of 100 and 80 as in the preceding example.
62 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 75

Examples
2. Configure an RMON event with an ID of 1, which sends an send a SNMP trap that contains the
community string “public”, some description, and owner Tom whenever broadcasts exceed
100 packets.
Console(config)#rmon event 1 trap public description broadcast_above_100 owner
Tom
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 63
53-1002582-01
Page 76

Examples
64 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 77

MIB Variable Index
A
authenticationFailure, 58
B
brcdSysLogServerAddr, 53
brcdSysLogServerAddrType
brcdSysLogServerEntry
brcdSysLogServerRowStatus
brcdSysLogServerTable
brcdSysLogServerUDPPort
, 53
, 53
, 53
, 53
, 53
C
coldStart, 58
E
ethernetAccessSwitchBr6910, 19
F
fallingAlarm, 59
fdryDaiIfConfigEntry
fdryDaiIfConfigTable
fdryDaiIfTrustValue
fdryDaiVlanConfigEntry
fdryDaiVlanConfigTable
fdryDaiVlanDynArpInspEnable
fdryDaiVlanVLanId
fdryDhcpSnoopGlobalClearOper
fdryDhcpSnoopIfConfigEntry
fdryDhcpSnoopIfConfigTable
fdryDhcpSnoopIfTrustValue
fdryDhcpSnoopVlanConfigEntry
fdryDhcpSnoopVlanConfigTable
, 42
, 42
, 42
, 41
, 41
, 41
, 41
, 43
, 43
, 43
, 43
, 43
, 43
fdryDhcpSnoopVlanDhcpSnoopEnable
fdryDhcpSnoopVlanVLanId
fdryIpSrcGuardIfConfigEntry
fdryIpSrcGuardIfConfigTable
fdryIpSrcGuardIfEnable
fdryLinkAggregationGroupEntry
fdryLinkAggregationGroupId
fdryLinkAggregationGroupIfIndex
fdryLinkAggregationGroupIfList
fdryLinkAggregationGroupLacpTimeout
fdryLinkAggregationGroupName
fdryLinkAggregationGroupPortCount
fdryLinkAggregationGroupRowStatus
fdryLinkAggregationGroupTable
fdryLinkAggregationGroupType
fdryMacVlanGlobalClearOper
fdryMacVlanGlobalObjects
fdryRadiusServerAcctPort
fdryRadiusServerAddr
fdryRadiusServerAddrType
fdryRadiusServerAuthPort
fdryRadiusServerEntry
fdryRadiusServerIndex
fdryRadiusServerRowKey
fdryRadiusServerRowStatus
fdryRadiusServerTable
fdrySntpServerAddr
fdrySntpServerAddrType
fdrySntpServerEntry
fdrySntpServerIndex
fdrySntpServerRowStatus
fdrySntpServerTable
fdrySntpServerVersion
fdryTacacsServerAddr
fdryTacacsServerAddrType
fdryTacacsServerAuthPort
fdryTacacsServerEntry
fdryTacacsServerIndex
fdryTacacsServerRowKey
fdryTacacsServerRowStatus
fdryTacacsServerTable
, 29
, 43
, 44
, 44
, 44
, 49
, 50
, 49
, 49
, 49
, 49
, 50
, 49
, 49
, 45
, 45
, 34
, 33
, 33
, 34
, 33
, 33
, 34
, 34
, 33
, 28
, 28
, 28
, 29
, 28
, 29
, 35
, 35
, 35
, 35
, 35
, 35
, 35
, 35
, 43
, 49
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 65
53-1002582-01
Page 78

fdryTrapReceiver CommunityOrSecurityName, 58
fdryTrapReceiverAddr
fdryTrapReceiverAddrType
fdryTrapReceiverEntry
fdryTrapReceiverIndex
fdryTrapReceiverRowStatus
fdryTrapReceiverSecurityLevel
fdryTrapReceiverSecurityModel
fdryTrapReceiverTable
fdryTrapReceiverUDPPort
, 58
, 57
, 57
, 57
, 58
, 58
, 58
, 57
, 58
L
linkDown, 59
linkUp
, 59
N
newRoot, 59
R
risingAlarm, 59
S
snAccountingExec, 32
snAgBuildDate
snAgBuildtime
snAgBuildVer
snAgCfgFname
snAgCfgLoad
snAgConfigFromNVRAM
snAgDefGwayIp
snAgEraseNVRAM
snAgGblCpuUtil5SecAvg
snAgGblCpuUtilData
snAgGblEnableTelnetServer
snAgGblEnableWebMgmt
snAgGblIfIpAddr
snAgGblIfIpMask
snAgGblTelnetLoginTimeout
snAgGblTelnetTimeout
snAgImgFname
, 27
, 27
, 27
, 25
, 25
, 24
, 28
, 23
, 51
, 51
, 31
, 31
, 28
, 28
, 31
, 31
, 25
snAgImgLoad
snAgImgVer
snAgReload
snAgSoftwareFeature
snAgSystemDRAM
snAgSystemDRAMFree
snAgSystemDRAMTotal
snAgSystemDRAMUtil
snAgTftpServerAddr
snAgTftpServerAddrType
snAgTrpRcvrCurEntry
snAgWebMgmtServerTcpPort
snAgWriteNVRAM
snArpStatsRepliesSent
snArpStatsRequestReceived
snArpStatsRequestSent
snArpStatsTotalReceived
snAuthorizationExec
snChasActualTemperature
snChasMainBrdDescription
snChasMainPortTotal
snChasNumSlots
snChasPwrSupply2Entry
snChasPwrSupply2Index
snChasPwrSupply2Table
snChasPwrSupply2Unit
snChasPwrSupplyOperStatus
snChasSerNum
snChasUnitActualTemperature
snChasUnitEntry
snChasUnitIndex
snChasUnitPartNum
snChasUnitSerNum
snChasUnitTable
snIfMediaInfoEntry
snIfMediaInfoTable
snIfMediaPartNumber
snIfMediaSerialNumber
snIfMediaType
snIfMediaVendorName
snIfMediaVersion
snIfOpticalMonitoringInfoEntry
snIfOpticalMonitoringInfoTable
snIfOpticalMonitoringRxPower
snIfOpticalMonitoringTemperature
snIfOpticalMonitoringTxBiasCurrent
snIfOpticalMonitoringTxPower
snMacAuthAge
, 25
, 26
, 23
, 26
, 51
, 51
, 51
, 51
, 26
, 26
, 57
, 31
, 24
, 52
, 52
, 52
, 52
, 32
, 22
, 21
, 21
, 22
, 22
, 22
, 22
, 22
, 22
, 22
, 22
, 21
, 21
, 22
, 21
, 21
, 29
, 29
, 29
, 29
, 29
, 29
, 29
, 52
, 52
, 52
, 52
, 38
, 52
, 52
66 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
Page 79

snMacAuthClearGlobalCmd, 37
snMacAuthClearIfCmdAction
snMacAuthClearIfCmdEntry
snMacAuthClearIfCmdIndex
snMacAuthClearIFCmdTable
snMacAuthClearMacSessionAction
snMacAuthClearMacSessionEntry
snMacAuthClearMacSessionIfIndex
snMacAuthClearMacSessionMac
snMacAuthClearMacSessionTable
snMacAuthEntry
snMacAuthIfIndex
snMacAuthMac
snMacAuthTable
snMacAuthTimeStamp
snRadiusGeneral
snRadiusKey
snRadiusLoginMethod
snRadiusRetransmit
snRadiusTimeOut
snRadiusWebServerMethod
snSwIfFastSpanPortEnable
snSwIfGBICStatus
snSwIfInfoAutoNegotiate
snSwIfInfoChnMode
snSwIfInfoConnectorType
snSwIfInfoEntry
snSwIfInfoFlowControl
snSwIfInfoGigType
, 38
, 38
, 38
, 38
, 32
, 33
, 32
, 32
, 49
, 47
, 47
, 48
, 37
, 37
, 37
, 37
, 39
, 38
, 33
, 33
, 48
, 48
, 48
, 48
, 39
, 38
, 38
, 38
snSwIfInfoMediaType
snSwIfInfoPortNum
snSwIfInfoSpeed
snSwIfInfoTable
snSwIfInfoTagMode
snSwIfStatsMacStations
snSwIfStpPortEnable
snTacacsGeneral
snTacacsKey
snTrapClientLoginReject
snTrapPortSecurityViolation
snTrapStackingChasPwrSupplyFailed
snTrapStackingChasPwrSupplyOK
snTrapStackingTemperatureWarning
snTrapSysMemoryLowThreshold
snTrapTemperatureOK
snTrapUserLogin
snTrapUserLogout
, 34
, 48
, 47
, 48
, 47
, 47
, 49
, 48
, 34
, 60
, 61
, 61
, 61
, 61
, 60
, 60
T
topologyChange, 59
W
warmStart, 58
, 62
, 62
Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference 67
53-1002582-01
Page 80

68 Brocade 6910 Ethernet Access Switch MIB Reference
53-1002582-01
 Loading...
Loading...