Page 1

Broadcom® NetXtreme® BCM57XX
User Guide
Last revised: April 2017
2CS57XX-CDUM514-R
Page 2

NetXtreme User Guide
Broadcom, the pulse logo, Connecting everything, Avago, Avago Technologies, and the A logo are among the
trademarks of Broadcom and/or its affiliates in the United States, certain other countries and/or the EU.
Copyright © 2017 by Broadcom. All Rights Reserved.
The term “Broadcom” refers to Broadcom Limited and/or its subsidiaries. For more information, please visit
www.broadcom.com
.
Broadcom reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products or data herein to improve
reliability, function, or design. Information furnished by Broadcom is believed to be accurate and reliable.
However, Broadcom does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of this information, nor
the application or use of any product or circuit described herein, neither does it convey any license under its
patent rights nor the rights of others.
Last revised: April 2017
2CS57XX-CDUM514-R
Document 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 2
Page 3

NetXtreme User Guide
Table of Contents
Section 1: Installing the Hardware .................................................................................. 10
Safety Precautions .....................................................................................................................................10
Preinstallation Checklist ............................................................................................................................11
Installing the Adapter ................................................................................................................................. 11
Connecting the Network Cables................................................................................................................12
Copper................................................................................................................................................... 12
Section 2: Functionality and Features ........................................................................... 13
Functional Description............................................................................................................................... 13
Features....................................................................................................................................................... 13
Power Management ....................................................................................................................... 14
Adaptive Interrupt Frequency .........................................................................................................14
Dual DMA Channels.......................................................................................................................14
ASIC with Embedded RISC Processor ..........................................................................................15
Broadcom Advanced Control Suite ................................................................................................ 15
Supported Operating Environments......................................................................................................... 15
Network Link and Activity Indication........................................................................................................ 15
Section 3: Windows Driver and Management Application Installation ........................ 17
Installing the Driver Software .................................................................................................................... 18
Using Silent Installation .........................................................................................................................19
Modifying the Driver Software................................................................................................................... 19
Repairing or Reinstalling the Driver Software ......................................................................................... 20
Removing the Device Drivers .................................................................................................................... 20
Viewing or Changing the Properties of the Adapter ...............................................................................21
Setting Power Management Options ........................................................................................................ 21
Configuring the Communication Protocol To Use With BACS4 ............................................................ 22
Using WS-MAN ..................................................................................................................................... 22
WS-MAN Windows Server Configuration.......................................................................................22
WS-MAN Windows Client Installation ............................................................................................29
Using WMI ............................................................................................................................................. 31
Step 1: Set up Namespace Security Using WMI Control ............................................................... 31
Page 3 Document 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R
Page 4

NetXtreme User Guide
Step 2: Grant DCOM Remote Launch and Activate Permission.................................................... 31
Special Configuration for WMI on Different Systems..................................................................... 33
Section 4: Linux Driver and Management Application Installation .............................. 34
Packaging ................................................................................................................................................... 34
Installing TG3 Driver Software .................................................................................................................. 35
Installing the Source RPM Package ..................................................................................................... 35
Building the Driver from the Source TAR File ....................................................................................... 36
Network Installations ................................................................................................................................. 36
Unloading/Removing the TG3 Driver........................................................................................................ 36
Unloading/Removing the Driver from an RPM Installation.................................................................... 36
Removing the Driver from a TAR Installation........................................................................................ 36
Driver Messages......................................................................................................................................... 37
Teaming with Channel Bonding................................................................................................................ 37
Linux Management Application Installation ............................................................................................ 38
Overview ............................................................................................................................................... 38
Communication Protocols.............................................................................................................. 38
Installing WS-MAN or CIM-XML on Linux Server ................................................................................. 39
Step 1: Install OpenPegasus ......................................................................................................... 39
Step 2: Start CIM Server on the Server ......................................................................................... 41
Step 3: Configure OpenPegasus on the Server ............................................................................ 41
Step 4: Install Broadcom CMPI Provider ....................................................................................... 42
Step 5: Perform Linux Firewall Configuration, If Required............................................................. 43
Step 6: Install BACS and Related Management Applications........................................................ 44
Installing WS-MAN or CIM-XML on Linux Client................................................................................... 45
Configure HTTPS on Linux Client.................................................................................................. 45
Installing the Broadcom Advanced Control Suite..................................................................................47
Section 5: VMware Driver Software .................................................................................48
Packaging ................................................................................................................................................... 48
Drivers......................................................................................................................................................... 48
Download, Install, and Update Drivers.................................................................................................. 48
Driver Parameters................................................................................................................................. 48
Driver Parameters................................................................................................................................. 49
Driver Defaults ...................................................................................................................................... 49
Driver Messages ................................................................................................................................... 49
Document 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 4
Page 5

NetXtreme User Guide
Section 6: Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4................................................. 51
Broadcom Advanced Control Suite Overview .........................................................................................51
Starting Broadcom Advanced Control Suite ...........................................................................................52
BACS Interface............................................................................................................................................ 52
Explorer View Pane ............................................................................................................................... 53
Context View Selector ...........................................................................................................................54
Filter View....................................................................................................................................... 54
Context View Pane ................................................................................................................................54
Menu Bar ...............................................................................................................................................54
Description Pane ...................................................................................................................................55
Configuring Preferences in Windows....................................................................................................... 55
Connecting to a Host..................................................................................................................................56
Managing the Host......................................................................................................................................57
Information Tab: Host Information ......................................................................................................... 57
Managing the Network Adapter.................................................................................................................59
Viewing Adapter Information .................................................................................................................59
Viewing Driver Information ....................................................................................................................60
Viewing Resource Information...............................................................................................................61
Viewing Hardware Information ..............................................................................................................62
Testing the Network............................................................................................................................... 63
Running Diagnostic Tests .....................................................................................................................64
Analyzing Cables ..................................................................................................................................65
Setting Adapter Properties ................................................................................................................... 66
Viewing Statistics ...................................................................................................................................... 68
General Statistics ...............................................................................................................................69
Configuring Teaming..................................................................................................................................69
Team Types .......................................................................................................................................... 70
Using the Broadcom Teaming Wizard .................................................................................................. 70
Using Expert Mode ............................................................................................................................... 83
Creating a Team ...................................................................................................................................83
Modifying a Team ................................................................................................................................. 86
Adding a VLAN .....................................................................................................................................87
Viewing VLAN Properties and Statistics and Running VLAN Tests ..............................................88
Deleting a VLAN ............................................................................................................................89
Page 5 Document 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R
Page 6

NetXtreme User Guide
Configuring LiveLink for a Smart Load Balancing and Failover and SLB (Auto-Fallback Disable)
Team...................................................................................................................................... 90
Saving and Restoring a Configuration .......................................................................................... 91
Viewing BASP Statistics ...................................................................................................................... 92
Configuring With the Command Line Interface Utility............................................................................ 93
Managing VLANs........................................................................................................................................ 94
Overview ............................................................................................................................................... 94
Adding VLANs to Teams....................................................................................................................... 95
Troubleshooting BACS.............................................................................................................................. 96
Section 7: Teaming ........................................................................................................... 97
Overview ..................................................................................................................................................... 98
Load Balancing and Fault Tolerance........................................................................................................ 98
Types of Teams ............................................................................................................................. 98
Smart Load Balancing™ and Failover .................................................................................................. 99
Link Aggregation (802.3ad)................................................................................................................... 99
Generic Trunking (FEC/GEC)/802.3ad-Draft Static .............................................................................. 99
SLB (Auto-Fallback Disable) ............................................................................................................... 100
Limitations of Smart Load Balancing and Failover/SLB (Auto-Fallback Disable) Types of Teams..... 100
LiveLink™ Functionality ...................................................................................................................... 101
Teaming and Large Send Offload/Checksum Offload Support........................................................... 101
Section 8: Broadcom Gigabit Ethernet Teaming Services ..........................................102
Introduction .............................................................................................................................................. 103
Teaming Glossary............................................................................................................................... 103
Teaming Concepts.............................................................................................................................. 104
Network Addressing..................................................................................................................... 104
Teaming and Network Addresses................................................................................................ 105
Description of Teaming Types ..................................................................................................... 105
Software Components ........................................................................................................................ 109
Hardware Requirements ..................................................................................................................... 110
Ethernet Switch............................................................................................................................ 110
Router .......................................................................................................................................... 110
Supported Features by Team Type .................................................................................................... 110
Selecting a Team Type ....................................................................................................................... 112
Teaming Mechanisms.............................................................................................................................. 113
Document 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 6
Page 7

NetXtreme User Guide
Architecture ......................................................................................................................................... 113
Outbound Traffic Flow ..................................................................................................................114
Inbound Traffic Flow (SLB Only) ..................................................................................................114
Protocol Support...........................................................................................................................115
Performance.................................................................................................................................115
Driver Support by Operating System................................................................................................... 116
Supported Teaming Speeds................................................................................................................ 117
Teaming and Other Advanced Networking Properties ........................................................................ 118
Checksum Offload ...............................................................................................................................119
IEEE 802.1p QoS Tagging .................................................................................................................. 119
Large Send Offload ............................................................................................................................. 119
Jumbo Frames..................................................................................................................................... 119
IEEE 802.1Q VLANs ........................................................................................................................... 119
Wake on LAN ......................................................................................................................................120
Preboot Execution Environment (PXE) ...............................................................................................120
General Network Considerations............................................................................................................121
Teaming Across Switches ...................................................................................................................121
Switch-Link Fault Tolerance .........................................................................................................121
Spanning Tree Algorithm..................................................................................................................... 123
Topology Change Notice (TCN) ...................................................................................................124
Port Fast/Edge Port......................................................................................................................124
Teaming with Microsoft NLB/WLBS ....................................................................................................125
Application Considerations..................................................................................................................... 126
Teaming and Clustering—Microsoft Cluster Software......................................................................... 126
Teaming and Network Backup ............................................................................................................126
Load Balancing and Failover........................................................................................................ 127
Fault Tolerance ............................................................................................................................ 128
Troubleshooting Teaming Problems ......................................................................................................130
Teaming Configuration Tips ................................................................................................................130
Troubleshooting Guidelines................................................................................................................. 131
Frequently Asked Questions...................................................................................................................132
Event Log Messages ................................................................................................................................ 135
Windows System Event Log Messages ..............................................................................................135
Base Driver (Physical Adapter/Miniport)..............................................................................................135
Intermediate Driver (Virtual Adapter/Team)......................................................................................... 137
Page 7 Document 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R
Page 8

NetXtreme User Guide
Section 9: iSCSI Protocol and Broadcom Boot Agent Software .................................139
iSCSI Boot................................................................................................................................................. 139
Supported Operating Systems for iSCSI Boot .................................................................................... 139
iSCSI Boot Setup ................................................................................................................................ 139
Configuring the iSCSI Target....................................................................................................... 139
Configuring iSCSI Boot Parameters ............................................................................................ 140
MBA Boot Protocol Configuration ................................................................................................ 141
iSCSI Boot Configuration............................................................................................................. 141
Enabling CHAP Authentication .................................................................................................... 145
Configuring the DHCP Server to Support iSCSI Boot.................................................................. 145
DHCP iSCSI Boot Configurations for IPv4................................................................................... 145
DHCP iSCSI Boot Configuration for IPv6 .................................................................................... 148
Configuring the DHCP Server................................................................................................... 148
Preparing the iSCSI Boot Image.................................................................................................. 149
Booting......................................................................................................................................... 152
Other iSCSI Boot Considerations ....................................................................................................... 152
Changing the Speed & Duplex Settings in Windows Environments ............................................ 152
Locally Administered Address ..................................................................................................... 152
Virtual LANs................................................................................................................................. 153
Troubleshooting iSCSI Boot................................................................................................................ 153
Broadcom Boot Agent Driver Software.................................................................................................. 154
Overview ............................................................................................................................................. 154
Setting Up MBA in a Client Environment ............................................................................................ 154
Configuring the MBA Driver ......................................................................................................... 154
Setting Up the BIOS .................................................................................................................... 156
Section 10: Manageability ..............................................................................................157
CIM............................................................................................................................................................. 157
SNMP......................................................................................................................................................... 158
BASP Subagent........................................................................................................................... 158
BASP Extensible-Agent ............................................................................................................... 158
Section 11: Specifications ............................................................................................. 160
10/100/1000BASE-T Cable Specifications.............................................................................................. 160
Performance Specifications.................................................................................................................... 160
Document 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 8
Page 9

NetXtreme User Guide
Section 12: Troubleshooting ......................................................................................... 161
Hardware Diagnostics..............................................................................................................................161
BACS Diagnostic Tests Failures .........................................................................................................161
BACS Network Test Failures...............................................................................................................162
Troubleshooting Checklist ...................................................................................................................... 163
Checking for Network Link and Activity.................................................................................................163
Checking if Current Drivers Are Loaded ................................................................................................164
Windows....................................................................................................................................... 164
Linux............................................................................................................................................. 164
Running a Cable Length Test..................................................................................................................164
Testing Network Connectivity .................................................................................................................165
Windows .............................................................................................................................................. 165
Linux .................................................................................................................................................... 165
Broadcom Boot Agent.............................................................................................................................. 165
Broadcom Advanced Server Program (BASP) ...................................................................................... 166
Kernel Debugging over Ethernet............................................................................................................. 166
Miscellaneous ...........................................................................................................................................166
Section 13: Regulatory Information .............................................................................. 167
FCC Class B Notice ..................................................................................................................................167
VCCI Class B Notice .................................................................................................................................168
VCCI Class B Statement (Japan) ........................................................................................................168
CE Notice................................................................................................................................................... 168
Canadian Regulatory Information (Canada Only).................................................................................. 172
Industry Canada, Class B....................................................................................................................172
Industry Canada, classe B...................................................................................................................172
MIC Notice (Republic of Korea Only)......................................................................................................173
B CLASS Device .......................................................................................................................... 173
BSMI........................................................................................................................................................... 174
Page 9 Document 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R
Page 10
Section 1: Installing the Hardware
• Safety Precautions
• Preinstallation Checklist
• Installing the Adapter
• Connecting the Network Cables
Note: This section applies only to add-in NIC models of Broadcom NetXtreme Gigabit Ethernet
adapters.
Safety Precautions
Caution! The adapter is being installed in a system that operates with voltages that can be lethal.
Before you remove the cover of your system, you must observe the following precautions to protect
yourself and to prevent damage to the system components:
Installing the HardwareNetXtreme User Guide
• Remove any metallic objects or jewelry from your hands and wrists.
• Make sure to use only insulated or non-conducting tools.
• Verify that the system is powered OFF and unplugged before you touch internal components.
• Install or remove adapters in a static-free environment. The use of a properly grounded wrist strap or other
personal antistatic devices and an antistatic mat is strongly recommended.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 10
®
Page 11
Installing the HardwareNetXtreme User Guide
Preinstallation Checklist
1. Verify that your server is using the latest BIOS.
2. If your system is booted to an operating system, gracefully power down the OS.
3. When system shutdown is complete, turn off the power and unplug the power cord.
4. Holding the adapter card by the edges, remove it from its shipping package and place it on an antistatic
surface.
5. Check the adapter for visible signs of damage, particularly on the card edge connector. Never attempt to
install any damaged adapter.
Installing the Adapter
The following instructions apply to installing the Broadcom NetXtreme Gigabit Ethernet adapter (add-in NIC) in
most servers. Refer to the manuals that were supplied with your server for details about performing these tasks
on your particular server.
1. Review the Safety Precautions and Preinstallation Checklist. Before installing the adapter, ensure the
system power is OFF and unplugged from the power outlet, and that proper electrical grounding procedures
have been followed.
2. Open the system case, and select any empty PCI Express slot.
3. Remove the blank cover-plate from the slot that you selected.
4. Align the adapter connector edge with the connector slot in the system.
5. Applying even pressure at both corners of the card, push the adapter card into the slot until it is firmly seated.
When the adapter is properly seated, the adapter port connectors are aligned with the slot opening, and the
adapter faceplate is flush against the system chassis.
Caution! Do not use excessive force when seating the card as this may damage the system or the
adapter. If you have difficulty seating the adapter, remove it, realign it, and try again.
6. Secure the adapter with the adapter clip or screw.
7. Close the system case and disconnect any personal antistatic devices.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 11
®
Page 12
Installing the HardwareNetXtreme User Guide
Connecting the Network Cables
Copper
The Broadcom NetXtreme Gigabit Ethernet adapter has one or more RJ-45 connectors used for attaching the
system to an Ethernet copper-wire segment.
Note: The Broadcom NetXtreme Gigabit Ethernet adapter supports Automatic MDI Crossover (MDIX),
which eliminates the need for crossover cables when connecting machines back-to-back. A straightthrough Category 5 cable allows the machines to communicate when connected directly together.
1. Select an appropriate cable. Table 1: “10/100/1000BASE-T Cable Specifications” lists the cable
requirements for connecting to 10/100/1000BASE-T ports:
Table 1: 10/100/1000BASE-T Cable Specifications
Port Type Connector Media Maximum Distance
10BASE-T RJ-45 Category 3, 4, or 5 UTP 100 meters (328 feet)
100/1000BASE-T
1
1000BASE-T signaling requires four twisted pairs of Category 5 balanced cabling, as specified in ISO/IEC
1
RJ-45
Category 5
11801:1995 and EIA/TIA-568-A (1995) and tested using procedures defined in TIA/EIA TSB95.
2
Category 5 is the minimum requirement. Category 5e and Category 6 are fully supported.
2
UTP
100 meters (328 feet)
2. Connect one end of the cable to the adapter.
3. Connect the other end of the cable to an RJ-45 Ethernet network port.
Note: After the cable is properly connected at both ends, the port LEDs on the adapter should be
functional. See
Table 1: “10/100/1000BASE-T Cable Specifications,” on page 12 for a description of
network link and activity indications
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 12
®
Page 13
Functionality and FeaturesNetXtreme User Guide
Section 2: Functionality and Features
• Functional Description
• Features
• Supported Operating Environments
• Network Link and Activity Indication
Functional Description
Broadcom NetXtreme Gigabit Ethernet adapters connect a PCI Express™ compliant system to a Gigabit
Ethernet network. Broadcom NetXtreme Gigabit Ethernet adapters incorporate a technology that transfers data
at a maximum rate of 1 gigabit per second—10 times the rate of Fast Ethernet adapters.
Using the Broadcom teaming software, you can split your network into virtual LANs (VLANs) as well as group
multiple network adapters together into teams to provide network load balancing and fault tolerance
functionality. See Teaming and Broadcom Gigabit Ethernet Teaming Services for detailed information about
teaming. See Virtual LANs for a description of VLANs. See Configuring Teaming for instructions on configuring
teaming and creating VLANs on Windows operating systems.
Features
The following is a list of the Broadcom NetXtreme Gigabit Ethernet adapter features for all supported operating
systems:
• Integrated quad 10/100/1000BASE-T and quad 1000BASE-X/SGMII 1.25 Gbaud SerDes transceivers
• Energy Efficient Ethernet™ compliant with IEEE Std 802.3az-2010
• IEEE 802.3ap Clause 73 auto-negotiation
• Quad 10/100/1000BASE-T full-duplex/half-duplex MACs
• Quad 1000BASE-X/SGMII full-duplex/half-duplex MACs
• Automatic MDI crossover
• x2 PCI Express v2.0 at 5 GT/s or 2.5 GT/s
• MSI and MSI-X capabilities—up to 17 MSIX vectors
• I/O Virtualization support for VMware NetQueue and Microsoft VMQ
• 17 receive queues and 16 transmit queues
• 17 MSI-X vectors supporting per queue interrupt to host
• Flexible MSI-X vector to transmit/receive queue association
• Function Level Reset
• Receive Side Scaling (RSS) with per queue MSI-X vector support and support for UDP RSS hash type
• Transmit Side Scaling (TSS) and multi-Tx queue with per queue MSI-X vector support
• Jumbo frame support for up to 9000-byte payload
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 13
®
Page 14

Functionality and FeaturesNetXtreme User Guide
• Virtual LAN (VLAN) support— IEEE 802.1q VLAN tagging
• TCP, IP, UDP checksum offload
• Large Send Offload (LSO), TCP Segmentation Offload (TSO)
• Hardware assist for IEEE 1588 and IEEE 802.1AS time synchronization implementations
• IEEE 802.3x flow control
• SMBus 2.0 Interface
• Statistics for SNMP MIB II, Ethernet-like MIB and Ethernet MIB (IEEE 802.3z, Clause 30)
• ACPI power management compliance
• Advanced power management by a Central Power Management Unit (CPMU)
• Efficient integrated switching regulator controller
• On-chip temperature monitor
• PCI Express CLKREQ support
• Power Management Offload (PM Offload)
• Serial flash and EEPROM NVRAM support; flash auto-configure
• ECC error detection and correction on internal SRAM
• JTAG boundary scan support
Power Management
Wake on LAN (Magic Packet, Wake Up Frame, specific pattern) is supported.
Note: Adapter speed connection when the system is down waiting for a wake-up signal is either 10
Mbps or 100 Mbps, but can return to 1000 Mbps when the system is up and running if connected to a
1000 Mbps capable switch. Systems intending to use Wake on LAN (WOL) should be connected to a
switch capable of both 1000 and 10/100 Mbps speeds.
Adaptive Interrupt Frequency
The adapter driver intelligently adjusts host interrupt frequency based on traffic conditions, to increase overall
application throughput. When traffic is light, the adapter driver interrupts the host for each received packet,
minimizing latency. When traffic is heavy, the adapter issues one host interrupt for multiple, back-to-back
incoming packets, preserving host CPU cycles.
Dual DMA Channels
The PCIe interface on Broadcom NetXtreme Gigabit Ethernet adapters contains two independent DMA
channels for simultaneous read and write operations.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 14
®
Page 15
Functionality and FeaturesNetXtreme User Guide
ASIC with Embedded RISC Processor
The core control for Broadcom NetXtreme Gigabit Ethernet adapters resides in a tightly integrated, highperformance ASIC. The ASIC includes a RISC processor. This functionality provides the flexibility to add new
features to the card and adapts it to future network requirements through software downloads.
Broadcom NetXtreme manageability operations such as DMTF, SMASH, DASH, and NC-SI pass-through run
on a high-performance application processor engine (APE), which is a separate from the traditional network
processing engine.
Broadcom Advanced Control Suite
Broadcom Advanced Control Suite (BACS), a component of the Broadcom teaming software, is an integrated
utility that provides useful information about each network adapter that is installed in your system. The BACS
utility also enables you to perform detailed tests, diagnostics, and analyses on each adapter, as well as to modify
property values and view traffic statistics for each adapter. BACS is used on Windows operating systems to
configure teaming and to add VLANs. See Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite for detailed information and
instructions.
Supported Operating Environments
The Broadcom NetXtreme Gigabit Ethernet adapter has software support for the following operating systems:
•Microsoft
• Linux
• VMware ESXi 6.0 or later
• Oracle Solaris
®
Windows® (32-bit and 64-bit extended) Server 2008 or later
®
(64-bit extended) RHEL 6.9, 7.1 or later; SLES 11 SP4, SLES 12 SP4 or later
Network Link and Activity Indication
For copper-wire Ethernet connections, the state of the network link and activity is indicated by the LEDs on the
RJ-45 connector, as described in Table 2: “Network Link and Activity Indicated by RJ-45 Port LEDs,” on
page 15. Broadcom Advanced Control Suite also provides information about the status of the network link and
activity (see Viewing Adapter Information).
Table 2: Network Link and Activity Indicated by RJ-45 Port LEDs
Port LED LED Appearance Network State
Link LED Off No link (cable disconnected)
Continuously illuminated Link (Green–1 Gb, Amber –10 or
100 Mb)
Activity LED Off No network activity
Blinking Network activity
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 15
®
Page 16

Functionality and FeaturesNetXtreme User Guide
Broadcom
®
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 16
Page 17

Section 3: Windows Driver and
Management Application Installation
• Installing the Driver Software
• Modifying the Driver Software
• Repairing or Reinstalling the Driver Software
• Removing the Device Drivers
• Viewing or Changing the Properties of the Adapter
• Setting Power Management Options
• Configuring the Communication Protocol To Use With BACS4
Windows Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 17
®
Page 18
Windows Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
Installing the Driver Software
Note: These instructions are based on the assumption that your Broadcom NetXtreme adapter was
not factory installed. If your controller was installed at the factory, the driver software has been installed
for you.
When Windows first starts after a hardware device (such as a Broadcom NetXtreme Adapter) has been
installed, or after the existing device driver has been removed, the operating system automatically detects the
hardware and prompts you to install the driver software for that device.
Notes:
• Before installing the driver software, verify that the Windows operating system has been upgraded
to the latest version with the latest service pack applied.
• A network device driver must be installed before the Broadcom NetXtreme Gigabit Ethernet
adapter can be used with your Windows operating system. Drivers are located on the installation
CD.
• BACS is not supported on the Server Core installation option for Microsoft Windows Server 2008
R2.
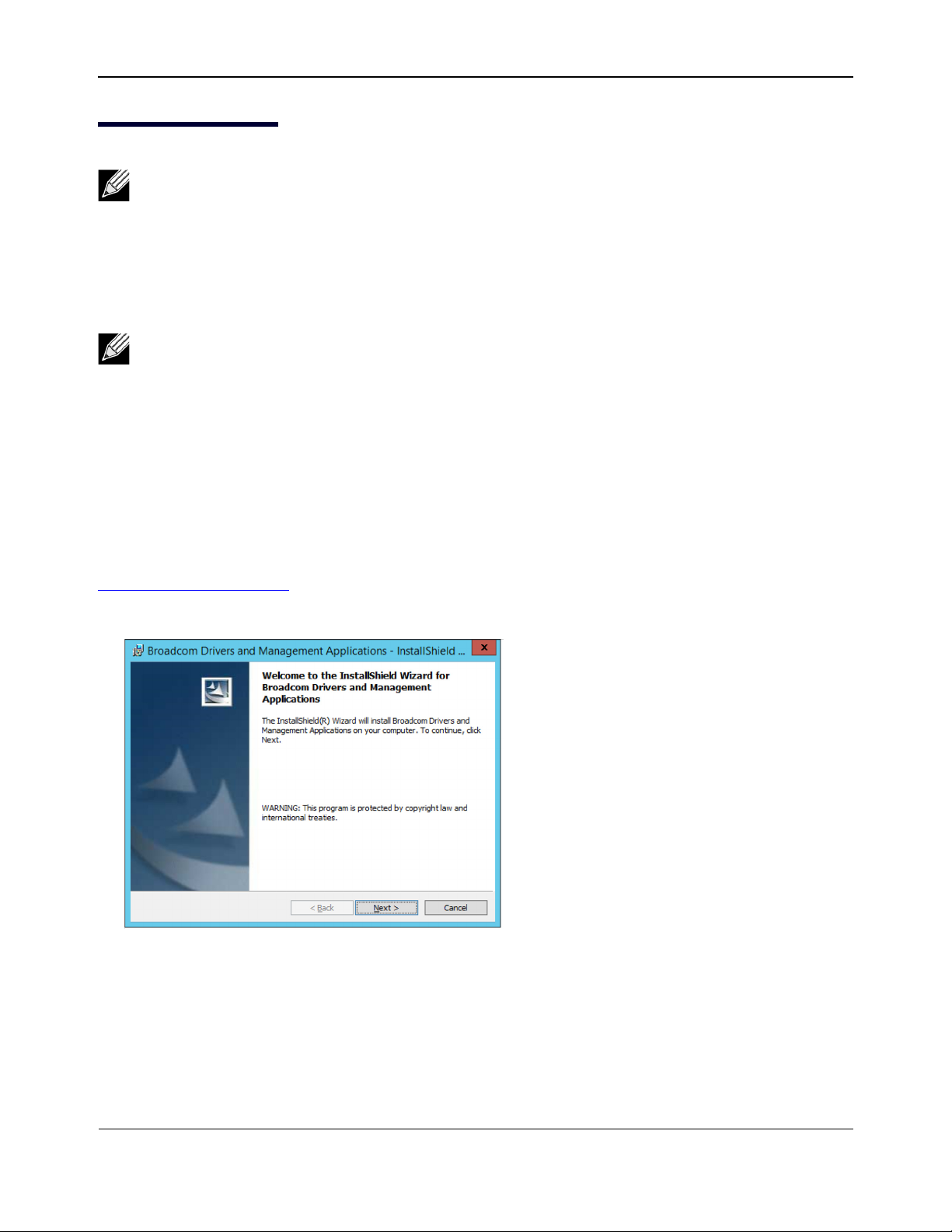
Download the driver installer from the following link:
http://www.dell.com/support
Use the self-extracting zip file.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 18
®
Page 19

Windows Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
Using Silent Installation
Refer to the readme.txt file in the installation folder for command line instructions.
Notes:
• All commands are case sensitive.
• For detailed instructions and information about unattended installs, refer to the Silent.txt file in the
Driver_Management_Apps_Installer folder.
Note: The REINSTALL switch should only be used if the same installer is already installed on the
system. If upgrading an earlier version of the installer, use
setup /s /v/qn as listed above.
Modifying the Driver Software
To modify the driver software
1. In Control Panel, double-click Add or Remove Programs.
2. Click Broadcom Drivers and Management Applications, and then click Change.
3. Click Next to continue.
4. Click Modify, Add, or Remove to change program features. This option does not install drivers for new
adapters. For information on installing drivers for new adapters, see Repairing or Reinstalling the Driver
Software.
5. Click Next to continue.
6. Click on an icon to change how a feature is installed.
7. Click Next.
8. Click Install.
9. Click Finish to close the wizard.
10. The installer will determine if a system restart is necessary. Follow the on-screen instructions.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 19
®
Page 20
Windows Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
Repairing or Reinstalling the Driver Software
To repair or reinstall the driver software
1. In Control Panel, double-click Add or Remove Programs.
2. Click Broadcom Drivers and Management Applications, and then click Change.
3. Click Next to continue.
4. Click Repair or Reinstall to repair errors or install drivers for new adapters.
5. Click Next to continue.
6. Click Install.
7. Click Finish to close the wizard.
8. The installer will determine if a system restart is necessary. Follow the on-screen instructions.
Removing the Device Drivers
When removing the device drivers, any management application that is installed is also removed.
Note: Windows Server 2008 and later provide the Device Driver Rollback feature to replace a device
driver with one that was previously installed. However, the complex software architecture of the
NetXtreme device may present problems if the rollback feature is used on one of the individual
components. Therefore, we recommend that changes to driver versions be made only through the use
of a driver installer.
To remove the device drivers
1. In Control Panel, double-click Add or Remove Programs.
2. Click Broadcom Drivers and Management Applications, and then click Remove. Follow the on-screen
prompts.
3. Reboot your system to completely remove the drivers. If you fail to reboot your system, you will not be able
to successfully install the drivers.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 20
®
Page 21
Windows Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
Viewing or Changing the Properties of the Adapter
To view or change the properties of the Broadcom network adapter
1. In Control Panel, click Broadcom Control Suite 4.
2. Click the Advanced section of the Configurations tab.
Setting Power Management Options
You can set power management options to allow the operating system to turn off the controller to save power
or to allow the controller to wake up the computer. If the device is busy doing something (servicing a call, for
example) however, the operating system will not shut down the device. The operating system attempts to shut
down every possible device only when the computer attempts to go into hibernation. To have the controller stay
on at all times, do not click the Allow the computer to turn off the device to save power check box.
Note: Power management options are not available on blade servers.
Notes:
• The Power Management tab is available only for servers that support power management.
• To enable Wake on LAN (WOL) when the computer is on standby, click Allow the device to bring
the computer out of standby box.
• If you select Only allow management stations to bring the computer out of standby, the
computer can be brought out of standby only by Magic Packet.
Caution! Do not select Allow the computer to turn off the device to save power for any adapter
that is a member of a team.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 21
®
Page 22

Windows Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
Configuring the Communication Protocol To Use With BACS4
There are two main components of the BACS4 management application: the provider component and the client
software. A provider is installed on a server, or “managed host”, that contains one or more NICs. The provider
collects information on the NICs and makes it available for retrieval from a management PC on which the client
software is installed. The client software enables viewing information from the providers and configuring the
NICs.The BACS client software includes a graphical user interface (GUI) and a command line interface (CLI).
A communication protocol enables communication between the provider and the client software. Depending on
the mix of operating systems (Linux, Windows, or both) on the clients and managed hosts in your network, you
can choose an appropriate communication protocol to use. See Linux Management Application Installation for
a description of the available communication protocols for each network configuration.
The instructions in this chapter address only the scenario where Windows managed hosts are
communicating with Windows clients. In these scenarios, you can use either the WMI or the WS-MAN
(WinRM) communication protocols. When you use the driver installer described in this chapter to install both the
driver and the management applications, the provider for both WMI and WS-MAN is installed on the managed
host. Additionally, the BACS4 utility is installed on the client. The following sections provide additional
configuration steps for the communication protocol you select.
For Linux installations, the driver is installed separately from the management applications. See Linux Driver
Software and Management Application Installation for related instructions.
Using WS-MAN
To use the WS-MAN communication protocol, follow the instructions in the following sections:
• WS-MAN Windows Server Configuration
• WS-MAN Windows Client Installation
WS-MAN Windows Server Configuration
Step 1: Install the WinRM Software Component on Server
On the following operating systems, WinRM 2.0 is preinstalled:
• Windows 7
• Windows 8
• Windows 8.1
• Windows Server 2008 R2
• Windows Server 2012
• Windows 2012 R2
• Windows Server 2016
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 22
®
Page 23
Windows Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
For Windows Server 2008, install Windows Management Framework Core, which includes WinRM 2.0 and
Windows Powershell 2.0, from the following link:
http://www.microsoft.com/download/en/details.aspx?displaylang=en&id=11829
Step 2: Perform Basic Configuration on the Server
The Windows firewall must be enabled for WinRM to work properly. For detailed information about firewall
configuration, see Step 7: Additional Server Configuration. After the firewall is configured, open a command
prompt and run the following command to enable the remote management on the Windows server:
winrm quickconfig
You can use the following command to view the configuration information for the service:
winrm get winrm/config
Step 3: Perform User Configuration on the Server
To connect to WinRM, the account must be a member of the local administrators group on the local or remote
computer. The output of the
RootSDDL = O:NSG:BAD:P(A;;GA;;;BA)S:P(AU;FA;GA;;;WD)(AU;SA;GWGX;;;WD)
BA stands for BUILTIN\Administrators.
get winrm/config command will be as follows:
To add another user group to the WinRM allowed connect list, you can modify the RootSDDL to include the new
user group. You will need the SSDL ID for the new group. For example, the following command adds the new
user group with SDDL ID S-1-5-21-1866529496-2433358402-1775838904-1021.
winrm set winrm/config/Service @{RootSDDL="O:NSG:BAD:P(A;GA;;;BA)(A;;GA;;;
S-1-5-21-1866529496-2433358402-1775838904-1021)S:P(AU;FA;GA;;
WD)(AU;SA;GWGX;;;WD)"}
Step 4: Perform HTTP Configuration on the Server
To use the BACS GUI, you must configure the HTTP protocol, as follows:
Note: The default HTTP port is 5985 for WinRM 2.0.
1. Click Start (or press the Windows logo key) and select Run.
2. Enter gpedit.msc to open the local Group Policy editor.
3. Under Computer Configuration, open the Administrative Templates folder and then open the Windows
Components folder.
4. Select Windows Remote Management (WinRM).
5. Under Windows Remote Management (WinRM), select WinRm Client.
6. Under WinRM Client, double-click Trusted Hosts.
7. In the TrustedHostsList, enter the host names of the clients. If all clients are trusted then enter an asterisk
(*) only.
8. Select WinRM Service.
9. Enable Allow Basic Authentication.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 23
®
Page 24

Windows Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
10. Enable Allow unencrypted traffic.
11. Close the Group Policy wIndow.
12. From the command prompt, run the following command to configure WinRM with default settings:
winrm qc or winrm quickconfig
13. When the tool displays “Make these changes[y/n]?“, enter “y”.
14. Enter one of the following commands to check whether an HTTP listener is created:
winrm enumerate winrm/confg/listener
or
winrm e winrm/config/Listener
15. Enter the following command from the command prompt to test locally.
winrm id
Step 5: Perform HTTPS Configuration on the Server (to use HTTPS rather than HTTP)
This step consists of two distinct processes: generating a self-signed certificate, if certificate does not exist, and
importing it to a Windows server. If one does not already exist, you must configure a self-signed certificate on
the Windows server to enable HTTPS/SSL communication with the BACS GUI on the Windows client. The
Windows client also must be configured with the self-signed certificate. See Perform HTTPS Configuration (if
you plan to use HTTPS).
Note: The self-signed certificate can be created on any Windows server. The server does not require
BACS to be installed. The self-signed certificate generated on any Windows server should be copied
on the local drive of client.
1. Click Start (or press the Windows logo key) and select Run.
2. Enter gpedit.msc to open the local Group Policy editor.
3. Under Computer Configuration, open the Administrative Templates folder and then open the Windows
Components folder.
4. Select Windows Remote Management (WinRM).
5. Under Windows Remote Management (WinRM), select WinRm Client.
6. Under WinRM Client, double-click Trusted Hosts.
7. In the TrustedHostsList, enter the host names of the clients. If all clients are trusted then enter an asterisk
(*) only.
8. Select WinRM Service.
9. Enable Allow Basic Authentication.
To generate a self-signed certificate for the Windows Server:
Openssl on Windows can be used to generate the self-signed certificate, as follows:
1. Enter the following command to generate a private key:
openssl genrsa -des3 -out server.key 1024
2. You are prompted to enter a passphrase. Be sure to remember the passphrase.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 24
®
Page 25

Windows Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
3. Use the following steps to generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR).
During the generation of the CSR, you are prompted for several pieces of information. When prompted for
the “Common Name”, enter the Windows Server host name or IP address.
Enter the following command (sample responses are shown):
openssl req -new -key server.key -out server.csr
If this command does not work, try the following:
openssl req –new –key server.key –out server.csr –config openssl.cnf
The openssl.cnf file should be placed in the same directory where openssl is placed. Openssl.cnf is located
in the folder C:\Program Files (x86)\GnuWin32\share.
The following information is requested:
• Country Name (2 letter code) []:US
• State or Province Name (full name) []: California
• Locality Name (e.g., city) []: Irvine
• Organization Name (e.g., company) []: Broadcom Corporation
• Organizational Unit Name (e.g., section) []: Engineering
• Common Name (e.g., YOUR name) []: Enter the host name or IP address of the Windows server. For
iPv6, enter the Common Name in the format [xyxy:xxx:….::xxx], including the brackets [ ].
• (Optional) Email Address []:
Enter the following additional attributes to be sent with your certificate request:
• A challenge password []:password1
• An optional company name []:
4. Remove the passphrase from the key.
Enter the following commands:
cp server.key server.key.org
openssl rsa -in server.key.org -out server.key
5. Generate a self-signed certificate:
To generate a self-signed certificate which is active for 365 days, enter the following command:
openssl x509 -req -days 365 -in server.csr -signkey server.key -out server.crt
The following output displays:
Signature ok
subject=/C=US/ST=California/L=Irvine/O=Broadcom Corporation/OU=Engineering/CN=MGMTAPP-
LAB3/emailAddress=
Getting Private key
6. Enter the following command to verify the generated self-signed certificate.
openssl verify server.crt
The following output displays:
server.crt:/C=US/ST=California/L=Irvine/O=Broadcom Corporation/OU=Engineering/
CN=MGMTAPP- LAB3/emailAddress=
error 18 at 0 depth lookup:self signed certificate
OK
Ignore the error message “error 18 at 0 depth lookup:self signed certificate”. This error indicates that this is
a self-signed certificate.
7. Convert the certificate from “crt” to “pkcs12” format, as follows:
For a Windows server, the certificate should be in pkcs12 format. Enter the following command:
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 25
®
Page 26
Windows Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
openssl pkcs12 -export -in server.crt -inkey server.key -out hostname.pfx
You will be prompted for the following:
Enter Export Password:
Verifying - Enter Export Password:
Enter the password and be sure to remember it. The password is required when importing the certificate on
the Windows server and client.
8. Make a copy of the certificate file server.crt and place it on the server where BACS will be installed, so that
it can be imported. If you plan to use a Windows client to connect to the server running BACS, then the
certificate also needs to be transferred (copied and pasted) to the client system.
Note: A separate certificate must be generated for an IPv4 address, IPv6 address, and Hostname.
To install the self-signed certificate on Windows server:
Transfer the file hostname.pfx you generated on the Windows server before you install the certificate:
1. Click Start (or press the Windows logo key) and select Run.
2. Enter MMC and click OK.
3. Click File > Add/Remove Snap-in.
4. Click Add.
5. Select Certificates and click Add.
6. Select Computer account.
7. Click Next and then click Finish.
8. Click Close, then click OK.
9. Open the Certificates (Local Computer) folder and then open the Personal folder.
10. Right-click Certificates, select All Tasks and then click Import.
11. Click Next to begin the Certificate Import Wizard.
12. Browse to select hostname.pfx.
13. When you are prompted for the password for the private key, enter the same password you created in To
generate a self-signed certificate for the Windows Server:.
14. Follow the instructions, select the defaults, and continue.
The certificate is shown as installed on the right side of the window. The name will be the name you specified
while creating a self-signed certificate.
15. Right-click on the certificate and select Properties.
A dialog box displays, as follows:
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 26
®
Page 27
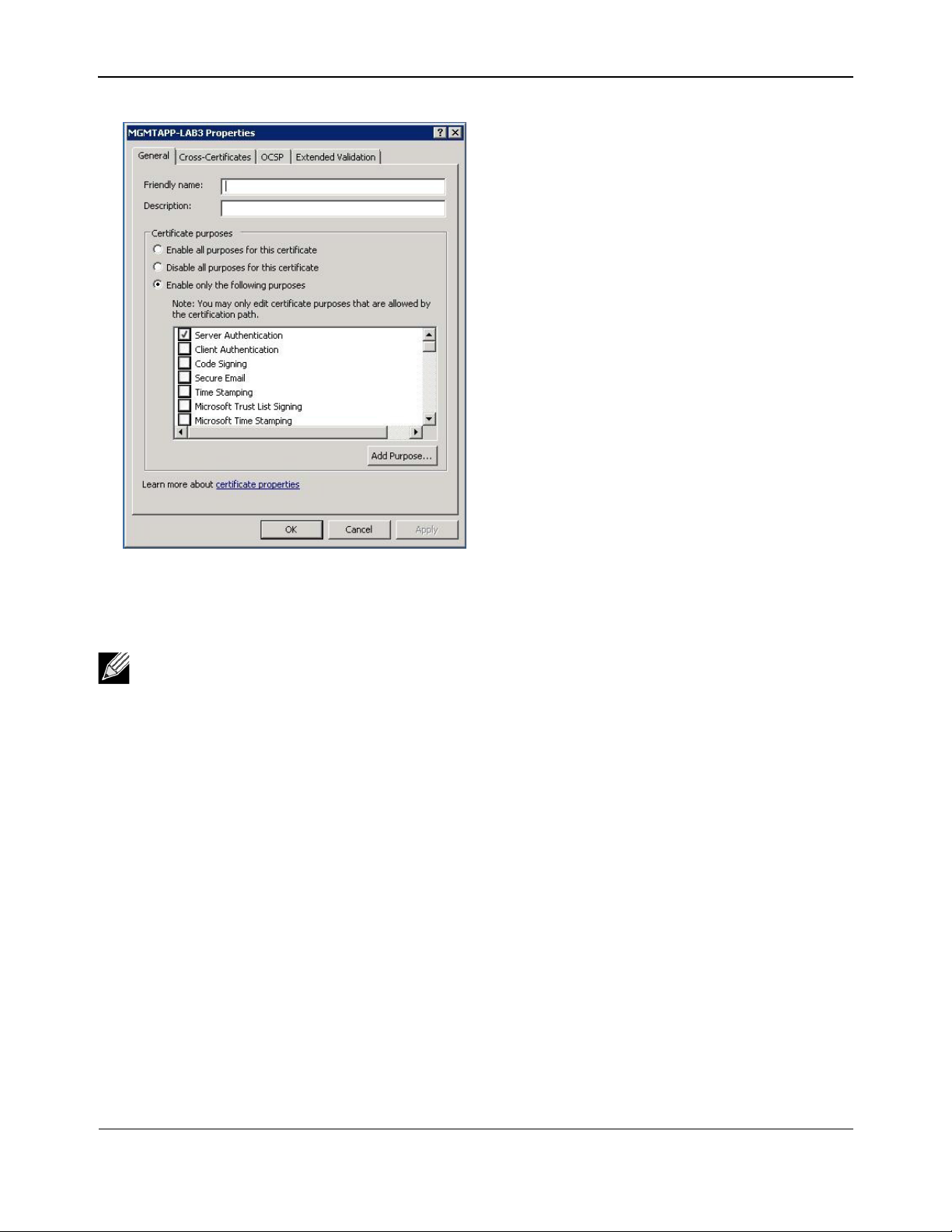
Windows Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
16. Ensure that only Server Authentication is enabled, as shown in the figure.
17. Open Trusted Root Certification Authorities and then open Certificates.
18. Follow the instructions from Step 11 on page 26 to Step 17 on page 27
Note: See Perform HTTPS Configuration (if you plan to use HTTPS) for instructions on importing the
self-signed certificate on a client.
Step 6: Configure WinRM HTTPS/SSL on the Server
1. Create WinRM Listener, as follows:
a. Click Start (or press the Windows logo key) and select Run.
b. Enter MMC and click OK.
c. Select the self-signed certificate from the Personal store.
For example, if the certificate is created with a host name, the host name will appear.
d. Double-click the certificate to open it.
e. Click the Details tab.
f. Scroll down and select the Thumbprint field.
g. Select and copy the thumbprint in the Details window so you can insert it in the next step.
h. Return to the command prompt.
i. Enter the following command:
winrm create winrm/config/Listener?Address=*+Transport=
HTTPS @{Hostname="<HostName or IPAddress>";
CertificateThumbprint="<paste from the previous step and remove the spaces>"}
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 27
®
Page 28

Windows Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
Notes:
• If the certificate was generated using the host name, enter the host name. If it was generated using
the IP address, enter the IP address. For an IPv6 address, use brackets [ ] around the address.
• If HTTPS is configured in your system, the listener must be deleted before creating a new HTTPS
listener. Use the following command:
winrm delete winrm/config/Listener?Address=*+Transport=HTTPS
a. The above command creates a listener on the HTTPS port (5986) using any/all network address of the
server, and my SelfSSL generated certificate.
b. You can use the
winrm command to modify or set the HTTPS listener, as WinRM listeners can be
configured on any user defined port.
c. From command prompt, run the following command to verify that the listener(s) that have been
configured:
winrm e winrm/config/listener
1. Test HTTPS/SSL connection on the server.
a. At the command prompt on the server, enter the following command:
winrs -r:https://yourserver:5986 -u:username -p:password hostname
b. If set up correctly, the output of the command shows the server host name.
c. To check WinRM Service Configuration, run the following command:
winrm get winrm/config/service
Step 7: Additional Server Configuration
If necessary, modify the firewall rules as follows:
Windows Server 2008 R2
1. From the Administrative Tools menu, open Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.
2. Right-click Inbound Rules and select New Rule.
The new rule wizard opens.
3. Select Port and click Next.
4. On the Protocol and Ports screen, select TCP and enter the specific port, for example, 5985 for HTTP or
5986 for HTTPS.
5. Click Next.
6. On the Action screen, select Allow the connection and click Next.
7. For Profile, you can select all three profiles if your server is in a workgroup.
8. Specify a name for the rule and click Finish.
9. Ensure that the new rule and is enabled (the green check box is selected).
Windows XP
1. Click Start > Control Panel, and then double-click Windows Firewall.
2. Click the Exceptions tab
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 28
®
Page 29

Windows Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
3. Click Add Port.
4. Enter a meaningful Name, for example “WinRM rule” and port number, for example, 5985 for HTTP or 5986
for HTTPS.
5. Click OK.
Useful WinRM Commands
Command Description
winrm quickconfig or winrm qc
winrm enumerate winrm/config/Listener or
winrm e winrm/config/Listener
winrm get winrm/config/Service
winrm delete winrm/config/
Listener?Address=*+Transport=HTTPS
Configures WinRM with default settings
Helps to check which service listener are enabled and
listening on which port and IP Address.
Checks WinRM Service Configuration.
Deletes a Listener (in this case deleting a HTTPS listener).
Useful WinRM Websites
• http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa384372%28v=vs.85%29.aspx
• http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc782312%28WS.10%29.aspx
• http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa384295%28v=VS.85%29.aspx
• The following articles on “http://support.microsoft.com:
• “Configuring WINRM for HTTPS”
• “Windows Management Framework (Windows PowerShell 2.0, WinRM 2.0, and BITS 4.0)”
WS-MAN Windows Client Installation
On the Windows client, perform following configuration steps.
1. Perform HTTP Configuration (if you plan to use HTTP)
a. Click Start (or press the Windows logo key) and select Run.
b. Enter gpedit.msc to open the local Group Policy editor.
c. Under Computer Configuration, open the Administrative Templates folder and then open the
Windows Components folder.
d. Select Windows Remote Management (WinRM).
e. Under Windows Remote Management (WinRM), select WinRm Client.
f. Under WinRM Client, double-click Trusted Hosts.
g. In the TrustedHostsList, enter the host names of the clients and click OK. If all clients are trusted then
enter “*” only.
h. Select WinRM Service.
i. Enable Allow Basic Authentication and click OK.
j. Run the following command from the command prompt to test the connection:
winrm id -remote:<remote machine Hostname or IP Address>
2. Perform HTTPS Configuration (if you plan to use HTTPS)
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 29
®
Page 30

Windows Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
After you generate a self-signed certificate, as described in To generate a self-signed certificate for the
Windows Server:, you can import the certificate on the client to facilitate a connection between server and
client. Ensure that all steps mentioned in section To generate a self-signed certificate for the Windows
Server: are completed, including copying hostname.pfx at the location from where client can access it,
before you proceed with the following steps.
a. Click Start (or press the Windows logo key) and select Run.
b. Enter MMC and click OK.
c. Click File and select Add/Remove Snap-in.
d. Click Add.
e. Select Certificates and click Add.
f. Select Computer account and click Next.
g. Click Finish.
h. Click Close and then click OK.
i. Under Certificates (Local Computer), right-click on Trusted Root Certification Authorities, select All
Tasks, and select Import.
j. Click Next to begin the Certificate Import Wizard.
k. Browse to select the .pfx file you generated in To generate a self-signed certificate for the Windows
Server:. Change the selection in the Files of type list to Personal Information Exchange (*.pfxas,
*.p12), select the hostname.pfx file and click Open.
l. Enter the password you assigned to the private key and click Next.
3. Configure WinRM HTTPS/SSL
You can run
winrm from a client to retrieve information from the server using WinRM HTTPS connection. Use
the following steps to test the WinRM HTTPS/SSL connection from client:
a. To retrieve the server operating system information, enter the following command.
winrm e wmi/root/cimv2/Win32_OperatingSystem -r:https://yourservername -u:username
-p:password -skipCAcheck
b. To retrieve the server WinRM identity information, enter the following command.
winrm id -r:https://yourservername -u:username -p:password -skipCAcheck
c. To enumerate Windows services on the server, enter the following command.
winrm e wmicimv2/Win32_service -r:https://yourservername -u:username -p:password skipCAcheck
Note: It is important to use -skipCAcheck switch in the winrm command line testing, as the certificate
is self-generated and not imported on the client. Otherwise, the following error message displays:
WSManFault.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 30
®
Page 31

Windows Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
Using WMI
No special configuration is required to use WMI on the Windows client. Perform the steps in the following
sections to configure WMI on the Windows server.
Step 1: Set up Namespace Security Using WMI Control
The WMI Control provides one way to manage namespace security. You can start the WMI Control from the
command prompt using this command:
wmimgmt
On Windows 9x or Windows NT4 computers that have WMI installed, use this command instead:
wbemcntl.exe
Alternatively, you can access the WMI Control and the Security tab as follows:
1. Right-click on My Computer and click Manage.
2. Double-click Services and Applications and then double-click WMI Control.
3. Right-click WMI Control and then click Properties.
4. In WMI Control Properties, click the Security tab.
5. A folder named Root with a plus sign (+) next to it should now be visible. Expand this tree as necessary to
locate the namespace for which you want to set permissions.
6. Click Security.
A list of users and their permissions appears. If the user is on the list, modify the permissions as appropriate.
If the user is not on the list, click Add and add the user from the location (local machine, domain, etc.) where
the account resides.
Note: You can add these exports at the end of the .bash_profile. This file is located in the /root
directory.
• In order to view and set namespace security, the user must have Read Security and Edit Security
permissions. Administrators have these permissions by default, and can assign the permissions
to other user accounts as required.
• If this user needs to access the namespace remotely, you must select the Remote Enable
permission.
• By default, user permissions set on a namespace apply only to that namespace. If you want the
user to have access to a namespace and all subnamespaces in the tree below it, or in
subnamespaces only, click Advanced. Click Edit and specify the scope of access in the dialog
box that displays.
Step 2: Grant DCOM Remote Launch and Activate Permission
In the Windows domain environment, the Domain Administrator account has the necessary privilege level to
access the WMI component for BACS management and, therefore, no special configuration is needed. In a
large enterprise, however, a user who is accessing the local or remote host using the BACS4 client GUI may
not always have the domain administrator account privilege. It is necessary to configure WMI security access
on the remote host to allow the user to connect to it using the BACS4 client GUI.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 31
®
Page 32

Windows Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
This configuration can be easily done using the following procedure. If you do not have sufficient privileges to
configure security for WMI access, contact your Network Administrator.
1. Click Start, click Run, type DCOMCNFG, and then click OK.
2. The Component Services dialogue box displays.
3. Open Component Services and then open Computers.
4. Right-click My Computer and click Properties.
5. In My Computer Properties, click the COM Security tab.
6. Under Launch and Activation Permissions, click Edit Limits.
7. Follow these steps if your name or your group does not appear in the Groups or user names list.
a. In the Launch Permission dialog box, click Add.
b. In the Select Users, Computers, or Groups dialog box, add your name and the group in the Enter the
object names to select box, and then click OK.
c. In the Launch Permission dialog box, select your user and group in the Group or user names list.
d. In the Permissions for User area, select Allow for Remote Launch and Remote Activation, and then
click OK.
Figure 1: Launch and Activation Permission
For more information, see Securing a Remote WMI Connection on the Microsoft Developer Network site.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 32
®
Page 33

Windows Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
Special Configuration for WMI on Different Systems
In Windows Vista and Windows 7, in order to let all users in the administrator group connect using the WMI
namespace, the user might need to change the LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy as needed.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 33
®
Page 34

Linux Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
Section 4: Linux Driver and Management
Application Installation
• Packaging
• Installing TG3 Driver Software
• Network Installations
• Unloading/Removing the TG3 Driver
• Driver Messages
• Teaming with Channel Bonding
• Linux Management Application Installation
Packaging
The Linux TG3 driver is released in the following packaging formats (file names):
• Source RPM (tg3-version.3dkms.src.rpm)
• Supplemental (tg3_sup-version.tar.gz)
• Compressed tar (tg3-version.tar.gz)
Identical source files to build the driver are included in both RPM and TAR source packages. The tar file contains
additional utilities such as patches and driver disk images for network installation.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 34
®
Page 35

Linux Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
Installing TG3 Driver Software
• Installing the Source RPM Package
• Building the Driver from the Source TAR File
Installing the Source RPM Package
Prerequisites:
• Linux kernel source
• C compiler
Procedure:
1. Install the source RPM package.
rpm -ivh tg3-version.src.rpm
2. Change the directory to the RPM path and build the binary driver for your kernel (the RPM path is different
for different Linux distributions).
cd /usr/src/redhat,OpenLinux,turbo,packages,rpm …
rpm -bb SPECS/tg3.spec or rpmbuild -bb SPECS/tg3.spec
rpmbuild -bb SPECS/tg3.spec (for RPM version 4.x.x)
Note: During your attempt to install a source RPM package, the following message may be displayed:
error: cannot create %sourcedir /usr/src/redhat/SOURCE
The most likely cause of the error is that the rpm-build package has not been installed. Locate the rpm-build
package on the Linux installation media and install it using the following command:
rpm -ivh rpm-build-version.i386.rpm
Complete the installation of the source RPM.
3. Install the newly-built package (driver and man page).
rpm -ivh RPMS/x86_64/tg3-version.i386.rpm
Depending on the kernel, the driver is installed to the following path:
2.6.x kernels:
/lib/modules/kernel_version/kernel/drivers/net/tg3.ko
4. Load the driver.
modprobe tg3
To configure the network protocol and address, refer to the Linux version-specific documentation.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 35
®
Page 36

Linux Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
Building the Driver from the Source TAR File
1. Create a directory (tg3-version) and extract the TAR files to the directory.
tar xvzf tg3-version.tgz
2. Build the driver tg3.o as a loadable module for the running kernel.
CD tg3-version
make clean
make; make install
3. Test the driver by loading it.
rmmod tg3
modprobe tg3
No message should be returned if this command runs properly.
Note: See the RPM instructions above for the location of the installed driver.
4. To configure network protocol and address, refer to the manuals supplied with your operating system.
Network Installations
For network installations through NFS, FTP, or HTTP (using a network boot disk or PXE), use the tg3 driver that
is part of the Linux operating system distribution.
Unloading/Removing the TG3 Driver
• Unloading/Removing the Driver from an RPM Installation
• Removing the Driver from a TAR Installation
Unloading/Removing the Driver from an RPM Installation
To unload the driver, use ifconfig to bring down all ethX interfaces opened by the driver, and then type the
following:
rmmod tg3
If the driver was installed using rpm, do the following to remove it:
rpm -e tg3-<version>
Removing the Driver from a TAR Installation
If the driver was installed using make install from the tar file, the tg3.o driver file has to be manually deleted from
the operating system. See Installing the Source RPM Package for the location of the installed driver.
If there is an interface configuration that is related to the tg3 driver, then bring the interface down first by using
ifconfig ethx down and then rmmod tg3.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 36
®
Page 37

Linux Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
Driver Messages
The following are the most common sample messages that may be logged in the /var/log/messages file. Use
dmesg -nlevel to control the level at which messages appear on the console. Most systems are set to level 6
by default.
Driver Sign on
tg3.c:version (date)
NIC Detected
eth#: Tigon3 [partno (BCM95xxx) rev 4202 PHY (57xx) (PCI Express) 10/100/1000BaseT
Ethernet :00:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
eth#: RXcsums [1] LinkChg REG [0] MIirq [0] ASF [0] Split [0] Wirespeed [1]TSOcap [1]
eth#: dma_rwctrl [76180000]
ACPI : PCI interrupt 0000:02:02.0 [A] -> GSI 26 (level,low) -> IRQ 233
Flow Control
tg3: eth#: Flow control is configured for TX and for RX.
Link Up and Speed Indication
tg3: eth#: Link is up at 1000 Mbps, full duplex.
Link Down Indication
tg3: eth#: Link is down.
Teaming with Channel Bonding
With the TG3 driver, you can team adapters together using the bonding kernel module and a channel bonding
interface. Refer to your Linux documentation for more information on Linux Channel Bonding.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 37
®
Page 38

Linux Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
Linux Management Application Installation
• Overview
• Installing WS-MAN or CIM-XML on Linux Server
• Installing WS-MAN or CIM-XML on Linux Client
• Installing the Broadcom Advanced Control Suite
Overview
The Broadcom Advanced Control Suite version 4 (BACS4) is a management application for configuring the
NetXtreme I families of adapters. BACS4 GUI software operates on Windows and BACS CLI is used on Linux
server operating systems.
This chapter describes how to install the BACS4 management application on Linux systems. For
Windows systems, an installation program is provided which installs both the Windows drivers and the
management applications, including BACS4 (see Windows Driver and Management Application Installation for
instructions).
There are two main components of the BACS4 utility: the provider component and the client software. A provider
is installed on a server, or “managed host”, that contains one or more NICs. The provider collects information
on the NICs and makes it available for retrieval from a management PC on which the client software is installed.
The client software enables viewing information from the providers and configuring the NICs.The BACS client
software includes a command line interface (CLI).
Communication Protocols
A communication protocol enables exchanging information between provider and the client software. These are
proprietary or open-source implementations of the Web-Based Enterprise Management (WBEM) and Common
Information Model (CIM) standards from the Distributed Management Task Force (DMTF). Network
administrators can choose the best option based on the prevailing standard on their network.
The following table shows the available options based on the operating systems installed on the managed host
and the client.
And the managed host
If the client uses:
Windows Windows WMI
Windows Linux CIM-XML (OpenPegasus)
Linux Windows WS-MAN (WinRM)
Linux Linux CIM-XML (OpenPegasus)
uses:
BACS can use these communication
protocols:
WS-MAN (WinRM)
WS-MAN (OpenPegasus)
WS-MAN (OpenPegasus)
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 38
®
Page 39

Linux Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
If the client uses:
And the managed host
uses:
BACS can use these communication
protocols:
• WMI = Windows Management Instrumentation.
• WS-MAN = Web Service-Management. WinRM is a Windows-based implementation and OpenPegasus is
an open-source implementation of the that operates on Linux.
• CIM-XML = An XML-based version of OpenPegasus.
If your network includes a mix of Windows and Linux clients accessing Windows and Linux servers, then WSMAN is a suitable choice. If Linux is the only OS installed on the servers, then CIM-XML is an option. If the
network includes only Windows servers and clients, WMI is an option. WMI is very simple to configure but is
supported only on the Windows OS. (See Windows Driver and Management Application Installation for
instructions on installing and configuring the Windows protocols.)
BACS installation includes installing the provider component on the managed host and the client software on
the management station. The installation process differs based on the combination of operating systems
installed on the client and managed host and on the selected communication protocol.
Installing WS-MAN or CIM-XML on Linux Server
Step 1: Install OpenPegasus
On the Red Hat Linux OS, two installation options are available:
• From the Inbox RPM (Red Hat Only)
• From Source (Red Hat and SuSE)
On the SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 (SLES11) OS, you must use the source RPM.
Note: The Inbox RPM does not support the WS-MAN communication protocol. To use WS-MAN, you
must install OpenPegasus from source.
From the Inbox RPM (Red Hat Only)
In Red Hat Linux, an Inbox OpenPegasus RPM is available as tog-pegasus-<version>.<arch>.rpm.
1. Use the following command to install tog-pegasus:
rpm -ivh tog-openpegasus-<version>.<arch>.rpm
2. Use the following command to start Pegasus:
/etc/init.d/tog-pegasus start
Note: On SuSE Linux, the Inbox OpenPegasus RPM is not available. OpenPegasus must be installed
form source, as described in the following procedure.
Note that in inbox Pegasus, HTTP is not enabled by default. After Inbox OpenPegasus is installed successfully,
if no further configuration is required, then follow the instructions in Step 4: Install Broadcom CMPI Provider. To
enable HTTP, see Enable HTTP.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 39
®
Page 40

Linux Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
From Source (Red Hat and SuSE)
The OpenPegasus source can be downloaded from www.openpegasus.org.
Note: If not already installed, download and install the openssl and libopenssl-devel rpm. This step is
optional and required only if you are planning to use HTTPS to connect the client to the managed host.
Set the Environment Variables
Set the environment variables for building OpenPegasus as follows.
Environment Variable Description
PEGASUS_ROOT The location of the Pegasus source tree
PEGASUS_HOME The location for the built executable, repository; e.g.,
$PEGASUS_HOME/bin, PEGASUS_HOME/lib,
$PEGAUS_HOME/repository, and $PEGASUS_HOME/
mof subdirectories.
PATH $PATH:$PEGASUS_HOME/bin
PEGASUS_ENABLE_CMPI_PROVIDER_MANA
GER
PEGASUS_CIM_SCHEMA "CIM222"
PEGASUS_PLATFORM For Linux 32 bit systems: "LINUX_IX86_GNU"
PEGASUS_HAS_SSL Optional. Set to "true" for HTTPS support.
PEGASUS_ENABLE_PROTOCOL_WSMAN Optional. Set to "true" for WSMAN protocol support.
True
For Linux 64 bit systems: "LINUX_X86_64_GNU"
Additional Settings
The $PEGASUS_HOME variable must be set up in the shell environment, and $PEGASUS_HOME/bin needs
to be appended to the $PATH environment.
Examples
• export PEGASUS_PLATFORM="LINUX_X86_64_GNU"
• export PEGASUS_CIM_SCHEMA="CIM222"
• export PEGASUS_ENABLE_CMPI_PROVIDER_MANAGER=true
• export PEGASUS_ROOT="/share/pegasus-2.10-src"
• export PEGASUS_HOME="/pegasus"
• export PATH=$PATH:$PEGASUS_HOME/bin
For SSL Support, add the following environment variable:
• export PEGASUS_HAS_SSL=true
For WS-MAN Support, add the following environment variable:
• export PEGASUS_ENABLE_PROTOCOL_WSMAN=true
CIM-XML and WSMAN in OpenPegasus use the same ports for HTTP or HTTPS. The default port numbers for
HTTP and HTTPS are 5989 and 5989, respectively.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 40
®
Page 41

Linux Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
Note: You can add these exports at the end of the .bash_profile. This file is located in the /root
directory.
• The environment variables will be set when a user logs in using PuTTY.
• On the Linux system itself, for each terminal where the environment variables are not set, run the
following command:
source /root/.bash_profile
• When you logout and login, the environment variables will be set.
Build and install OpenPegasus
From $PEGASUS_ROOT (the location of the Pegasus source root directory), run the following:
make clean
make
make repository
Note: Whenever OpenPegasus is built from source, all configurations are reset to the default values.
If you are rebuilding OpenPegasus, you must redo the configuration as mentioned in Step 3: Configure
OpenPegasus on the Server.
Step 2: Start CIM Server on the Server
Use the cimserver command to start CIM server. To stop CIM server, use the command cimserver -s.
To check whether OpenPegasus has been installed properly, enter the following command:
cimcli ei -n root/PG_Interop PG_ProviderModule
Note: For OpenPegasus compiled from source, PEGASUS_HOME must be defined when you start
CIM server. Otherwise, CIM server will not load the repository properly. Consider setting
PEGASUS_HOME in the “.bash_profile” file.
Step 3: Configure OpenPegasus on the Server
Use the cimconfig command to configure OpenPegasus, as shown in the following table:
Command Description
cimconfig -l
cimconfig -l -c
cimconfig -g <property name>
cimconfig -s <property name>=<value> -p
cimconfig --help
CIM server must be started before running
effect.
cimconfig, and must be restarted for configuration changes to take
List all valid property names.
List all valid property names and its value
Query a particular property.
Set a particular property.
Find out more about the command.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 41
®
Page 42

Linux Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
Enable Authentication
The following OpenPegasus properties have to be set as described in this section. Otherwise, the Broadcom
CIM Provider will not work properly. Ensure the following are set before launching BACS and connecting to the
provider.
Start CIM server if it is not already started. Then, set the following:
•
cimconfig -s enableAuthentication=true -p
• cimconfig -s enableNamespaceAuthorization=false -p
• cimconfig -s httpAuthType=Basic -p
• cimconfig -s passwordFilePath=cimserver.passwd -p
• cimconfig -s forceProviderProcesses=false -p
If you want root user to connect remotely:
•
cimconfig -s enableRemotePrivilegedUserAccess=true -p
User configuration with privilege: The Linux system users are used for OpenPegasus authentication. The
systems users have to be added to OpenPegasus using
•
cimuser -a -u <username> -w <password>
Example: cimuser -a -u root -w linux1
cimuser to connect via BACS:
Enable HTTP
1. If CIM server is not started, start it.
2. Use the following command to set up an HTTP port (optional):
cimconfig -s httpPort=5988 -p
This property is not available for Inbox OpenPegasus.
3. Use the following command to enable HTTP connection:
cimconfig -s enableHttpConnection=true -p
4. Use the cimserver -s and cimserver commands, respectively, to stop and restart CIM server for the new
configuration to take effect.
Enable HTTPS
1. If CIM server is not started, start it.
2. Set up HTTPS port with the following command (optional):
cimconfig -s httpsPort=5989 -p
This property is not available for inbox OpenPegasus.
3. Enable HTTPS connection with 'the following command:
cimconfig -s enableHttpsConnection=true -p
4. Use the cimserver -s and cimserver commands, respectively, to stop and restart CIM server for the new
configuration to take effect.
Step 4: Install Broadcom CMPI Provider
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 42
®
Page 43

Linux Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
Ensure that OpenPegasus is installed properly before installing CMPI Provider.
Install
Enter following command to install Broadcom CMPI Provider.
% rpm -i BRCM_CMPIProvider-{version}.{arch}.rpm
Uninstall
Enter following command to uninstall Broadcom CMPI Provider:
% rpm -e BRCM_CMPIProvider
Step 5: Perform Linux Firewall Configuration, If Required
Follow these procedures to open the appropriate ports in the firewall:
Red Hat
1. Click System, select Administration, and then select Firewall.
2. Select Other Ports.
3. In the Port and Protocol Dialog box, select User Defined.
4. In the Port/Port Range field, add the port number.
5. In the Protocol field, add the protocol as TCP or UDP, etc.
6. Click Apply for the firewall rules to take effect.
Example:
• For CIM-XML over HTTP, the port number is 5988 and protocol is TCP.
• For CIM-XML over HTTPS, the port number is 5989 and protocol is TCP.
SuSE
1. Click Compute and then click YaST.
2. Select Security & Users on the left pane.
3. On the right pane, double-click Firewall.
4. Select Custom Rules on the left pane.
5. On the right pane click Add.
6. Enter the following values:
• Source Network: 0/0 (means all)
• Protocol: TCP (or the appropriate protocol)
• Destination Port: <Port Number> or <Range of Port Numbers>
• Source Port: Leave blank.
7. Click Next and then click Finish for the firewall rules to take effect.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 43
®
Page 44

Linux Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
Example:
For CIM-XML, use the following values:
• Source Network: 0/0 (means all)
• Protocol: TCP
• Destination Port: 5988:5989
• Source Port: Leave blank.
Step 6: Install BACS and Related Management Applications
See Installing the Broadcom Advanced Control Suite.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 44
®
Page 45

Linux Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
Installing WS-MAN or CIM-XML on Linux Client
No special software components are required on the Linux client system to use the HTTP except installing the
BACS management application. However, for WS-MAN installations, you can optionally configure the HTTPS
protocol for use with BACS.
Configure HTTPS on Linux Client
Follow these steps if you want to use HTTPS rather than HTTP (WS-MAN only):
Generate a Self-Signed Certificate for Windows/Linux Server
Openssl on Linux or Windows can be used to generate the self-signed certificate, as follows:
Note: You can download and install openssl from http://gnuwin32.sourceforge.net/packages/
openssl.htm.
1. Enter the following command to generate a private key:
openssl genrsa -des3 -out server.key 1024
2. You are prompted to enter a passphrase. Be sure to remember the passphrase.
3. Use the following steps to generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR).
During the generation of the CSR, you are prompted for several pieces of information. When prompted for
the “Common Name”, enter the Windows Server host name or IP address.
Enter the following command (sample responses are show):
openssl req -new -key server.key -out server.csr
If this command does not work, try the following:
openssl req –new –key server.key –out server.csr –config openssl.cnf
The openssl.cnf file should be placed in the same directory where openssl is placed. Openssl.cnf is located
in the folder C:\Program Files (x86)\GnuWin32\share.
The following information is requested:
• Country Name (2 letter code) []:US
• State or Province Name (full name) []: California
• Locality Name (e.g., city) []: Irvine
• Organization Name (e.g., company) []: Broadcom Corporation
• Organizational Unit Name (e.g., section) []: Engineering
• Common Name (e.g., YOUR name) []: Enter the host name or IP address of the Windows server. For
iPv6, enter the Common Name in the format [xyxy:xxx:….::xxx], including the brackets [ ].
• (Optional) Email Address []:
Enter the following additional attributes to be sent with your certificate request:
• A challenge password []:linux1
• An optional company name []:
4. Remove the passphrase from the key.
Enter the following commands:
cp server.key server.key.org
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 45
®
Page 46

Linux Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
openssl rsa -in server.key.org -out server.key
5. Generate a self-signed certificate:
To generate a self-signed certificate which is active for 365 days, enter the following command:
openssl x509 -req -days 365 -in server.csr -signkey server.key -out server.crt
The following output displays:
Signature ok
subject=/C=US/ST=California/L=Irvine/O=Broadcom Corporation/OU=Engineering/CN=MGMTAPP-
LAB3/emailAddress=
Getting Private key
6. Enter the following command to verify the generated self-signed certificate.
openssl verify server.crt
The following output displays:
server.crt:/C=US/ST=California/L=Irvine/O=Broadcom Corporation/OU=Engineering/
CN=MGMTAPP- LAB3/emailAddress=
error 18 at 0 depth lookup:self signed certificate
OK
Ignore the error message “error 18 at 0 depth lookup:self signed certificate”. This error indicates that this is
a self-signed certificate.
7. Convert the certificate from “crt” to “pkcs12” format, as follows:
For a Windows server, the certificate should be in pkcs12 format. Enter the following command:
openssl pkcs12 -export -in server.crt -inkey server.key -out hostname.pfx
You will be prompted for the following:
Enter Export Password:
Verifying - Enter Export Password:
Enter the password and be sure to remember it. The password is required when importing the certificate on
the Windows server and client.
8. Make a copy of the certificate file server.crt and place it on the server where BACS will be installed, so that
it can be imported. If you plan to use a Windows or Linux client to connect to the server running BACS, then
the certificate also needs to be transferred (copied and pasted) to the client system.
In Linux, the certificate should have the extension “.pem”. The extension “.crt” and “.pem” are the same, so
there is no need to use the
openssl command to convert from .crt to .pem. You can simply copy the file as-is.
Note: A separate certificate must be generated for an IPv4 address, IPv6 address, and Hostname.
Import Self-Signed Certificate on Linux Client
On Linux distributions, note the following certificate directory:
• For all SuSE versions, the certificate directory is
• For Red Hat, the certificate directory can be different for each version. For some versions, it is
or /etc/pki/tls/certs. For other versions, find out the certificate directory.
certs
/etc/ssl/certs.
/etc/ssl/
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 46
®
Page 47

Linux Driver and Management Application InstallationNetXtreme User Guide
Copy hostname.pem, which you created in Generate a Self-Signed Certificate for Windows/Linux Server, into
the certificate directory of the Linux client. For example, if the certificate directory is
hostname.pem to
/etc/ssl/certs.
/etc/ssl/certs, copy
1. Change directory to
/etc/ssl/certs.
2. Create a hash value by running the following command.
openssl x509 -noout -hash -in hostname.pem
A value such as the following will be returned.
100940db
3. Create a symbolic link to the hash value by running the following command:
ln -s hostname.pem 100940db.0
Test HTTPS/SSL Connection from Linux Client
Use the following command to test whether the certificate is installed correctly on Linux:
# curl -v --capath /etc/ssl/certs https://Hostname or IPAddress:5986/wsman
If this fails, then the certificate is not installed correctly and an error message displays, indicating to take
corrective action.
Installing the Broadcom Advanced Control Suite
The Broadcom Advanced Control Suite (BACS) software can be installed on a Linux system using the Linux
RPM package. This installation includes a CLI client.
Before you begin:
• Ensure that the Broadcom network adapter(s) is physically installed and the appropriate device driver for
the NIC is installed on the system to be managed by this utility.
• Ensure that the CIM provider is installed properly on the system that is to be managed by this utility.
• For managing iSCSI on Linux hosts, ensure that the open-iscsi and sg utilities are installed on the Linux
host.
To install BACS CLI
1. Download the latest BACS management application RPM package.
2. Install the RPM package using the following command:
% rpm -i BACScli-{version}.{arch}.rpm
To use BACS CLI, refer to the file BACSCLI_Readme.txt provided with the release files.
To remove BACS CLI
To uninstall the RPM package, use the following command:
% rpm -e BACScli
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 47
®
Page 48

Section 5: VMware Driver Software
• Packaging
• Drivers
Packaging
The VMware driver is released in the following packaging format.
Table 3: VMware Driver Packaging
Format Drivers
VMware VIB vmware-esx-drivers-net-tg3-version.x86_64.vib
Drivers
VMware Driver SoftwareNetXtreme User Guide
Download, Install, and Update Drivers
To download, install, or update the VMware ESX/ESXi driver for NetXtreme I GbE network adapters, see http:/
/www.vmware.com/support.
Driver Parameters
NetQueue
The optional parameter force_netq can be used to set the number of Rx and Tx net queues. BCM57XX devices
that support NetQueue are the BCM5718, BCM5719, and BCM5720.
Allowed values for x are –1 to 15:
• 1–15 will force the number of NetQueues for the given NIC.
• 0 disables NetQueue.
• –1 specifies to use the default driver NetQueue value.
The number of “x” entries can go up to 32, which means the maximum supported NICs = 32.
Example usage:
esxcfg-module -s force_netq=-1,0,1,2 tg3]
• tg3 NIC 0: Use the default number of NetQueues.
• tg3 NIC 1: Disable the NetQueue feature.
• tg3 NIC 2: Use 1 NetQueue.
• tg3 NIC 3: Use 2 NetQueues.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 48
®
Page 49

VMware Driver SoftwareNetXtreme User Guide
Note that the NIC # above does not correspond to the vmnic<#>. The NIC number is the system vmnic probe
order number. Optimally, the number of NetQueues matches the number of CPUs on the machine.
Driver Parameters
Several optional parameters can be supplied as a command line argument to the vmkload_mod command.
These parameters can also be set via the esxcfg-module command. See the man page for more information.
Driver Defaults
Table 4: VMware Driver Defaults
Parameter Default Value
Speed Autonegotiation with all speeds advertised
Flow Control Autonegotiation with rx and tx advertised
MTU 1500 (range 46–9000)
Rx Ring Size 200 (range 0–511). Some chips are fixed at 64.
Rx Jumbo Ring Size 100 (range 0–255). Not all chips support the jumbo ring and some chips that
support jumbo frames do not use the jumbo ring.
Tx Ring Size 511 (range (MAX_SKB_FRAGS+1) – 511). MAX_SKB_FRAGS varies on
different kernels and different architectures. On a 2.6 kernel for x86,
MAX_SKB_FRAGS is 18.
Coalesce RX Microseconds 20 (range 0–1023)
Coalesce RX Microseconds
irq
Coalesce rx frames 5 (range 0–1023)
Coalesce rx frames irq 5 (range 0–255)
Coalesce TX Microseconds 72 (range 0–1023)
Coalesce tx usecs irq 20 (range 0–255)
Coalesce tx frames 53 (range 0–1023)
Coalesce tx frames irq 5 (range 0–255)
Coalesce stats usecs 1000000 (approx. 1 sec.). Some coalescing parameters are not used or have
MSI Enabled (if supported by the chip and passed the interrupt test).
WoL Disabled
20 (range 0–255)
different defaults on some chips.
Driver Messages
The following are the most common sample messages that may be logged in the file /var/log/messages. Use
dmesg -n <level> to control the level at which messages will appear on the console. Most systems are set to
level 6 by default. To see all messages, set the level higher.
Driver Sign On
tg3.c:v3.118g (Jan 4, 2012)
NIC Detected
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 49
®
Page 50

VMware Driver SoftwareNetXtreme User Guide
vmnic0#: Tigon3 [partno (BCM95xxx) rev 4202 PHY (57xx) (PCI Express) 10/100/1000BaseT
Ethernet :00:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
vmnic0#: RXcsums [1] LinkChg REG [0] MIirq [0] ASF [0] Split [0] Wirespeed [1]TSOcap [1]
vmnic0#: dma_rwctrl [76180000]
ACPI : PCI interrupt 0000:02:02.0 [A] -> GSI 26 (level,low) -> IRQ 233
Link Up and Speed Indication
tg3: vmnic0: Link is up at 1000 Mbps, full duplex.
tg3: vmnic0: Flow control is on for TX and on for RX.
Link Down Indication
tg3: vmnic0: Link is down.
Broadcom
®
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 50
Page 51

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Section 6: Using Broadcom Advanced
Control Suite 4
• Broadcom Advanced Control Suite Overview
• Starting Broadcom Advanced Control Suite
• BACS Interface
• Configuring Preferences in Windows
• Connecting to a Host
• Managing the Host
• Managing the Network Adapter
• Viewing Statistics
• Configuring Teaming
• Configuring With the Command Line Interface Utility
• Managing VLANs
• Troubleshooting BACS
Broadcom Advanced Control Suite Overview
Broadcom Advanced Control Suite (BACS) is an integrated utility that provides useful information about each
network adapter that is installed in your system. BACS also enables you to perform detailed tests, diagnostics,
and analyses on each adapter, as well as to view and modify property values and view traffic statistics for
network objects. BACS operates on Windows and Linux operating systems. BACS supports Broadcom
NetXtreme 1 and Netlink Gigabit controllers. It does not supports Broadcom NetXtreme-E 10G/25G controllers.
Broadcom Advanced Server Program (BASP), which runs within Broadcom Advanced Control Suite, is used to
configure teams for load balancing, fault tolerance, and virtual local area networks (VLANs). BASP functionality
is available only on systems that use at least one Broadcom network adapter. BASP operates on Windows
operating systems only.
Note: Some features of BACS are relevant only to particular adapters. Because a single instance of
BACS can be used to communicate with multiple hosts and adapter types, this document describes
all BACS features.
The BACS application includes a graphical user interface and a command line interface (BACSCLI). BACS GUI
and BACS CLI can operate on the following operating system families:
• Windows
• Windows Server
For information on the latest supported OS versions, refer to the release documentation provided with your
software distribution.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 51
®
Page 52

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Starting Broadcom Advanced Control Suite
In Control Panel, click Broadcom Control Suite 4, or click the BACS icon in the taskbar located at the bottom
of the Windows or Windows Server desktop.
On Linux systems, you can double-click the BACS4 desktop icon, or access the BACS program from the task
bar under System Tools. (If you are having difficulty launching BACS on a Linux system, see the related topic
in Troubleshooting BACS.)
BACS Interface
The BACS interface is comprised of the following regions:
• Explorer View pane
• Context View selector
• Context View pane
• Menu bar
• Description pane
By default, the Explorer View pane is docked and pinned on the left side of the main window, the Context View
pane on the right, the Context View selector below the menu bar, and the Description pane below the Context
View pane. Drag the splitter between any two panes to vary the size of the panes.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 52
®
Page 53

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Explorer View Pane
You can dock and pin the Explorer View pane on the left side, right side, top, or bottom of the main window.
The Explorer View pane lists the objects that can be viewed, analyzed, tested, or configured by BACS. When
an item is selected in the Explorer View pane, the tabs showing the information and options that are available
for the item appear in the Context View pane.
The organization of this panel is designed to present the manageable objects in the same hierarchical manner
as drivers and its subcomponents. This simplifies the management of various elements of the converged
network interface controller. The top level of the hierarchy is the Host container, which lists all hosts managed
by BACS. Below the hosts are the installed network adapters, with the manageable elements such as physical
port, NDIS, and iSCSI below the adapters.
The icon next to each device in the Explorer View pane shows its status. An icon next to a device name that
appears normal means the device is connected and working.
• X. A red “X” that appears on the device’s icon indicates the device is currently not connected to the
network.
• Greyed out. A device icon that appears greyed out indicates the device is currently disabled.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 53
®
Page 54

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Context View Selector
The Context View selector appears below the menu bar and includes the filter and tab categories. Although you
can expand and collapse the categories that appear on tabs in the Context View pane, you can alternatively
display a category by selecting the box next to the category name.
Filter View
In a multiple-host environment using several C-NICs, there can be a large number of manageable elements per
adapter that can be difficult and cumbersome to view, configure, and manage all elements. Use the filter to
select a particular device function. Possible filter views include:
•All
•Team view
• NDIS view
• iSCSI view
• iSCSI Target view
Context View Pane
The Context View pane displays all the parameters that you can view for the object selected in the Explorer View
pane. The parameters are grouped by tabs and categories, depending on the parameter type. The available tabs
are Information, Configuration, Diagnostics, and Statistics. Because the BACS interface is context-sensitive,
only the parameters that apply to the selected object can be viewed or configured in the Context View pane.
Menu Bar
The following appear on the menu bar, but because the menu items are context-sensitive, not all items will be
available at all times:
File menu
• Team Save As: Saves the current team configurations to a file.
• Team Restore: Restores any saved team configuration from a file.
Action menu
• Remove Host: Removes the selected host.
• Refresh Host: Refreshes the selected host.
View menu
• Explorer View: Displays/hides the Explorer View pane.
• Tool Bar: Displays/hides the tool bar.
• Status Bar: Displays/hides the status bar.
• Broadcom Logo: Displays/hides the Broadcom Logo on BACS to optimize the maximum viewable space.
Tools menu
• Options: Used for configuring BACS preferences.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 54
®
Page 55

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Teams (Windows only)
• Create Teams: Creates new teams with either the Teaming Wizard or in Advanced mode.
• Manage Teams: Manages existing teams with either the Teaming Wizard or in Advanced mode.
Description Pane
The Description pane provides information, configuration instructions, and options for the selected parameter in
the Context View pane.
Configuring Preferences in Windows
To enable or disable the BACS tray icon in Windows
On Windows systems, BACS places an icon in the Windows taskbar when the program is installed. Use the
Options window to turn this icon on or off.
1. From the Tools menu, select Options.
2. Select or clear Enable BACSTray (the option is enabled by default).
3. Click OK.
Setting the teaming mode in Windows
1. From the Tools menu, select Options.
2. Select Expert Mode if you do not need the assistance of the teaming wizard to create teams; otherwise,
select Wizard Mode.
3. Click OK.
Setting the Explorer View refresh time in Windows
1. From the Tools menu, select Options.
2. Select Auto to set the Explorer View refresh time to 5 seconds. Otherwise, select Custom and select a time,
in seconds.
3. Click OK.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 55
®
Page 56

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Connecting to a Host
You can add one or more Windows or Linux hosts to manage from BACS.
To add a local host
1. From the Action menu, click Add Host.
2. For both Windows and Linux hosts, do not change the default settings. The User name and Password are
not required while connecting to the local host.
3. Select Persist if you want BACS to save the information for this host.
4. Click Ok. BACS can now be used to view information and manage the host.
To add a remote host
1. From the Action menu, click Add Host.
2. Type the remote host’s name or IP address in the Host box.
3. Select the protocol from the Protocol list. The protocol options for Windows are WMI, WSMan, or Try All.
The protocol options for Linux are CimXML, WSMan, or Try All. The Try All option forces the GUI client to
try all options.
4. Select the HTTP scheme, or the HTTPS scheme for added security.
5. Type the Port Number value you used to configure the host, if it is different than the default value of 5985.
6. Type the User name and Password.
7. Select Persist if you want BACS to save the information for this host. The host will appear in the Explorer
Pane whenever you reopen BACS, and you will not need to enter the host IP address or host name when
connecting to the host. For security reasons, you must enter the User name and Password every time.
8. Click OK.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 56
®
Page 57

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Managing the Host
At the host level, you can view host information and configure parameters from the following tabs:
• Information
• Configuration
To view host information
Select the host in the Explorer View pane, and then select the Information tab to view host-level information.
Information Tab: Host Information
Host Name. Displays the name of the host.
OS Version Info. Displays the operating system, including the version.
Platform. Displays the hardware architecture platform (for example, 32-bit or 64-bit)
To configure the host
Select the host in the Explorer View pane, and then select the Configuration tab to configure host-level
parameters.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 57
®
Page 58

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Broadcom
®
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 58
Page 59

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Managing the Network Adapter
The installed network adapters appear one level below the host in the hierarchical tree in the Explorer View
pane. At the adapter level, you can view information and configure parameters from the following tabs:
• Information
• Configuration
Viewing Adapter Information
The Vital Signs section of the Information tab has useful information about the network adapters that are
installed in your system, such as the link status of the adapter and general network connectivity.
Select the network adapter in the Explorer View pane, and then select the Information tab to view adapterlevel information.
Notes:
• Information about Broadcom network adapters may be more comprehensive than information
about network adapters made by others.
• Some information may not be available for all Broadcom network adapters.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 59
®
Page 60

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Viewing Driver Information
The Driver Information section of the Information tab displays data about the driver for the selected network
adapter.
To view Driver Information for any installed network adapter, click the name of the adapter listed in the Explorer
View pane, then click the Information tab.
Driver Status. The status of the adapter driver.
• Loaded. Normal operating mode. The adapter driver has been loaded by Windows and is functioning.
• Not Loaded. The driver associated with the adapter has not been loaded by Windows.
• Information Not Available. The value is not obtainable from the driver that is associated with the adapter.
Driver Name. The file name of the adapter driver.
Driver Version. The current version of the adapter driver.
Driver Date. The creation date of the adapter driver.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 60
®
Page 61

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Viewing Resource Information
The Resources section of the Information tab displays information about connections and other essential
functions for the selected network adapter.
To view Resources for any installed network adapter, click the name of the adapter listed in the Explorer View
pane, then click the Information tab.
Note: Some information may not be available for all Broadcom network adapters.
Bus Type. The type of input/output (I/O) interconnect used by the adapter.
Slot No. The slot number on the system board occupied by the adapter. This item is not available for PCI
Express type adapters.
Bus Speed (MHz). The bus clock signal frequency used by the adapter. This item is not available for PCI Express
type adapters.
Bus Width (bit). The number of bits that the bus can transfer at a single time to and from the adapter. This item
is not available for PCI Express type adapters.
Bus No. Indicates the number of the bus where the adapter is installed.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 61
®
Page 62

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Device No.
Function No. The port number of the adapter. For a single-port adapter, the function number is 0. For a two-port
The number assigned to the adapter by the operating system.
adapter, the function number for the first port is 0, and the function number for the second port is 1.
Interrupt Request. The interrupt line number that is associated with the adapter. Valid numbers range from 2 to
25.
Memory Address. The memory mapped address that is assigned to the adapter. This value can never be 0.
Viewing Hardware Information
The Hardware section of the Information tab displays information about the hardware settings for the selected
network adapter.
To view Hardware for any installed network adapter, click the name of the adapter listed in the Explorer View
pane, then click the Information tab.
Note: Some information may not be available for all Broadcom network adapters.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 62
®
Page 63

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
ASIC Version.
The chip version of the Broadcom adapter (this information is not available for adapters made by
others).
Firmware Version. The firmware version of the Broadcom adapter (this information is not available for adapters
made by others). This information is only available for Broadcom NetXtreme adapters.
Vendor ID. The vendor ID.
Device ID. The adapter ID.
Subsystem Vendor ID. The subsystem vendor ID.
Subsystem ID. The subsystem ID.
Testing the Network
The Network Test option on the Diagnostics tab lets you verify IP network connectivity. This test verifies if the
driver is installed correctly and tests connectivity to a gateway or other specified IP address on the same subnet.
The network test uses TCP/IP to send ICMP packets to remote systems, then waits for a response.
Note: The network test option is not available on adapters that are grouped into a team (see
Configuring Teaming).
To run the network test
1. Click the name of the adapter to test in the Explorer View pane.
2. From the Select a test to run list, select Network Test. If the Network Test option is not available, then
from the Context View tab on the right side of the window, select Diagnostics and then select Network
Test.
3. To change the destination IP address, select IP address to ping. In the Network Test window, enter a
Destination IP address, then click OK.
4. Click Test.
The results of the network test are displayed in the Status field.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 63
®
Page 64

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Running Diagnostic Tests
The Diagnostic Tests option on the Diagnostics tab lets you check the state of the physical components on a
Broadcom network adapter. You can trigger the tests manually, or choose to have BACS 3 continuously perform
them. If the test are performed continuously, then the number of passes and fails in the Result field for each test
increments every time the tests are performed. For example, if a test is performed four times and there are no
fails, the value in the Result field for that test is 4/0. However, if there were 3 passes and 1 fail, the value in the
Result field is 3/1.
Notes:
• You must have administrator privileges to run diagnostic tests.
• The network connection is temporarily lost while these tests are running.
• Not all Broadcom adapters support each test.
To run the diagnostic tests once
1. Click the name of the adapter to test in the Explorer View pane and select the Diagnostics tab.
2. From the Select a test to run list, select Diagnostic Tests.
3. Select the diagnostic tests you want to run. Click Select All to select all tests or Clear All to clear all test
selections.
4. Select the number of times to run the tests from Number of loops.
5. Click Run test(s).
6. In the error message window that warns of the network connection being temporarily interrupted, click Yes.
The results are displayed in the Result field for each test.
Control Registers. This test verifies the read and write capabilities of the network adapter registers by writing
various values to the registers and verifying the results. The adapter driver uses these registers to perform
network functions such as sending and receiving information. A test failure indicates that the adapter may not
be working properly.
MII Registers. This test verifies the read and write capabilities of the registers of the physical layer (PHY). The
physical layer is used to control the electrical signals on the wire and to configure network speeds such as 1000
Mbit/s.
EEPROM. This test verifies the content of the electrically erasable programmable read-only memory (EEPROM)
by reading a portion of the EEPROM and computing the checksum. The test fails if the computed checksum is
different from the checksum stored in the EEPROM. An EEPROM image upgrade does not require a code
change for this test.
Internal Memory. This test verifies that the internal memory of the adapter is functioning properly. The test writes
patterned values to the memory and reads back the results. The test fails if an erroneous value is read back.
The adapter cannot function if its internal memory is not functioning properly.
On-Chip CPU. This test verifies the operation of the internal CPUs in the adapter.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 64
®
Page 65

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Interrupt.
This test verifies that the Network Device Driver Interface Specification (NDIS) driver is able to receive
interrupts from the adapter.
LoopBack MAC. This test verifies that the NDIS driver is able to send packets to and receive packets from the
adapter.
LoopBack PHY. This test verifies that the NDIS driver is able to send packets to and receive packets from the
adapter.
Test LED. This test causes all of the port LEDs to blink 5 times for the purpose of identifying the adapter.
Analyzing Cables
The Cable Analysis option on the Diagnostics tab lets you monitor the conditions of each wire pair in an
Ethernet Category 5 cable connection within an Ethernet network. The analysis measures the cable quality and
compares it against the IEEE 802.3ab specification for compliance.
Notes:
• You must have administrator privileges to run the cable analysis test.
• The network connection is temporarily lost during an analysis.
• For Broadcom NetXtreme adapters, the cable analysis test can only run for gigabit link speed
connections and when there is no connection.
• This option is not available for all Broadcom network adapters.
To run a cable analysis
1. Connect the cable to a port on a switch where the port is set to Auto and the Speed & Duplex driver settings
are also set to Auto.
2. Click the name of the adapter to test in the Explorer View pane.
3. From the Select a test to run list, select Cable Analysis. If the Cable Analysis option is not available, then
from the Context View tab on the right side of the window, select Diagnostics and then select Cable
Analysis.
4. Click Run.
5. In the error message window that warns of the network connection being temporarily interrupted, click Yes.
Distance. The valid cable distance in meters (except when the Noise result is returned).
Status. This shows the type of link on this cable pair.
• Good. Good cable/PCB signal paths, but no gigabit link.
• Crossed. Pin short or crosstalk along two or more cable/PCB signal paths.
• Open. One or both pins are open for a twisted pair.
• Short. Two pins from the same twisted pair are shorted together.
• Noise. Persistent noise present (most likely caused by Forced 10/100).
• GB Link. Gigabit link is up and running.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 65
®
Page 66

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
• N/A. Algorithm failed to reach a conclusion.
Link. The link connection speed and duplex mode.
Status. The status after the test is run, either completed or failed.
There are several factors that could have an effect on the test results:
• Link partner. Various switch and hub manufacturers implement different PHYs. Some PHYs are not IEEE
compliant.
• Cable quality. Category 3, 4, 5, and 6 may affect the test results.
• Electrical interference. The testing environment may affect the test results.
Setting Adapter Properties
Advanced on the Configurations tab allow you to view and change the values of the available properties of
the selected adapter. The potentially available properties and their respective settings are described below.
Notes:
• You must have administrator privileges to change the values for a property.
• The list of available properties for your particular adapter may be different.
• Some properties may not be available for all Broadcom network adapters.
To set adapter properties
1. Click the name of the adapter in the Explorer View pane, and click the Configurations tab.
2. From the Advanced section, select the property you want to set.
3. To change the value of a property, select an item from the property’s list or type a new value, as appropriate
(selection options are different for different properties).
4. Click Apply to confirm the changes to all properties. Click Reset to return the properties to their original
values.
802.1p QOS. Enables quality of service, which is an Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IEEE)
specification that treats different types of network traffic diversely to ensure required levels or reliability and
latency according to the type of traffic. This property is disabled by default. Unless the network infrastructure
supports QoS, do not enable this property. Otherwise, problems may occur.
Flow Control. Enables or disables the receipt or transmission of PAUSE frames. PAUSE frames allow the
network adapter and a switch to control the transmit rate. The side that is receiving the PAUSE frame
momentarily stops transmitting.
• Auto (default). PAUSE frame receipt and transmission are optimized.
• Disable. PAUSE frame receipt and transmission are disabled.
• Rx PAUSE. PAUSE frame receipt is enabled.
• Rx/Tx PAUSE. PAUSE frame receipt and transmission are enabled.
• Tx PAUSE. PAUSE frame transmission is enabled.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 66
®
Page 67

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Speed & Duplex.
The Speed & Duplex property sets the connection speed and mode to that of the network. Note
that Full-Duplex mode allows the adapter to transmit and receive network data simultaneously.
• 10 Mb Full. Sets the speed at 10 Mbit/s and the mode to Full-Duplex.
• 10 Mb Half. Sets the speed at 10 Mbit/s and the mode to Half-Duplex.
• 100 Mb Full. Sets the speed at 100 Mbit/s and the mode to Full-Duplex.
• 100 Mb Half. Sets the speed at 100 Mbit/s and the mode to Half-Duplex.
• Auto (default). Sets the speed and mode for optimum network connection (recommended).
Notes:
• Auto is the recommended setting. This setting allows the network adapter to dynamically detect
the line speed of the network. Whenever the network capability changes, the network adapter
automatically detects and adjusts to the new line speed and duplex mode. A speed of 1 Gbit/s is
enabled by selecting Auto, when that speed is supported.
• 1 Gb Full Auto must be attached to a link partner that is also capable of a 1 Gb connection. Since
the connection is limited to a 1 Gb connection only, the Ethernet@Wirespeed feature will be
disabled. If the link partner supports a 1 Gb connection only, the Wake on LAN feature may not
work. Additionally, management traffic in the absence of an operating system may also be affected.
• 10 Mb Half and 100 Mb Half settings force the network adapter to connect to the network in HalfDuplex mode. Note that the network adapter may not function if the network is not configured to
operate at the same mode.
• 10 Mb Full and 100 Mb Full settings force the network adapter to connect to the network in FullDuplex mode. The network adapter may not function if the network is not configured to operate at
the same mode.
Wake Up Capabilities. Enables the network adapter to wake up from a low-power mode when it receives a
network wake-up frame. Two types of wake-up frames are possible: Magic Packet and Wake Up Frame.
This property is only available for Broadcom NetXtreme adapters.
• Both (default). Selects both Magic Packet and Wake Up Frame as wake-up frames.
• Magic Packet. Selects Magic Packet as the wake-up frame.
• None. Selects no wake-up frame.
• Wake Up Frame. Selects Wake Up Frame as the wake-up frame and allows the network adapter to wake
the system when an event such as a ping or an Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) request is received.
This option works in conjunction with the operating system power mode saving and does not work if the
Power Save setting does not enable WOL.
Priority & VLAN. Allows enabling both the prioritization of network traffic and VLAN tagging. VLAN tagging only
occurs when the VLAN ID setting is configured with a value other than 0 (zero).
• Priority & VLAN Enabled (default). Allows for packet prioritization and VLAN tagging.
• Priority & VLAN Disabled. Prevents packet prioritization and VLAN tagging.
• Priority Enabled. Allows packet prioritization only.
• VLAN Enabled. Allows VLAN tagging only.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 67
®
Page 68

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Note: If an intermediate driver is managing the network adapter for VLAN tagging, the Priority &
VLAN Disabled and Priority Enabled settings should not be used. Use the Priority & VLAN
Enabled setting and change the VLAN ID to 0 (zero).
VLAN ID.
Enables VLAN tagging and configures the VLAN ID when Priority & VLAN Enabled is selected as the
Priority & VLAN setting. The range for the VLAN ID is 1 to 4094 and must match the VLAN tag value on the
connected switch. A value of 0 (default) in this field disables VLAN tagging.
Risk Assessment of VLAN Tagging through the NDIS Miniport Driver
Broadcom's NDIS 6.0 miniport driver provides the means to allow a system containing a Broadcom adapter
to connect to a tagged VLAN. Unlike BASP, however, the NDIS 6 driver's support for VLAN participation is
only for a single VLAN ID.
Also unlike BASP, the NDIS 6.0 driver only provides VLAN tagging of the outbound packet, but does not
provide filtering of incoming packets based on VLAN ID membership. This is the default behavior of all
miniport drivers. While the lack of filtering packets based on VLAN membership may present a security
issue, the following provides a risk assessment based on this driver limitation for an IPv4 network:
A properly configured network that has multiple VLANs should maintain separate IP segments for each
VLAN. This is necessary since outbound traffic relies on the routing table to identify which adapter (virtual
or physical) to pass traffic through and does not determine which adapter based on VLAN membership.
Since support for VLAN tagging on Broadcom's NDIS 6.0 driver is limited to transmit (Tx) traffic only, there
is a risk of inbound traffic (Rx) from a different VLAN being passed up to the operating system. However,
based on the premise of a properly configured network above, the IP segmentation and/or the switch
VLAN configuration may provide additional filtration to limit the risk.
In a back-to-back connection scenario, two computers on the same IP segment may be able to
communicate regardless of their VLAN configuration since no filtration of VLAN membership is occurring.
However, this scenario assumes that the security may already be breached since this connection type is
not typical in a VLAN environment.
If the risk above is not desirable and filtering of VLAN ID membership is required, then support through an
intermediate driver would be necessary.
Viewing Statistics
The information provided on the Statistics tab allows you to view traffic statistics for both Broadcom network
adapters and network adapters made by others. Statistical information and coverage are more comprehensive
for Broadcom adapters.
To view Statistics information for any installed network adapter, click the name of the adapter listed in the
Explorer View pane, then click the Statistics tab.
Click Refresh to get the most recent values for each statistic. Click Reset to change all values to zero.
Notes:
• Team statistics are not compiled for a Broadcom network adapter if it is disabled.
• Some statistics may not be available for all Broadcom network adapters.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 68
®
Page 69

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
General Statistics
General Statistics show the transmitted and received statistics to and from the adapter.
Frames Tx OK. A count of the frames that were successfully transmitted. This counter is incremented when the
transmit status is reported as Transmit OK.
Frames Rx OK. A count of the frames that were successfully received. This does not include frames received
with frame-too-long, frame check sequence (FCS), length, or alignment errors, nor frames lost due to internal
MAC sublayer errors. This counter is incremented when the receive status is reported as Receive OK.
Directed Frames Tx. A count of directed data frames that were successfully transmitted.
Multicast Frames Tx. A count of frames that were successfully transmitted (as indicated by the status value
Transmit OK) to a group destination address other than a broadcast address.
Broadcast Frames Tx. A count of frames that were successfully transmitted (as indicated by the transmit status
Transmit OK) to the broadcast address. Frames transmitted to multicast addresses are not broadcast frames
and are excluded.
Directed Frames Rx. A count of directed data frames that were successfully received.
Multicast Frames Rx. A count of frames that were successfully received and are directed to an active
nonbroadcast group address. This does not include frames received with frame-too-long, FCS, length, or
alignment errors, nor frames lost because of internal MAC sublayer errors. This counter is incremented as
indicated by the Receive OK status.
Broadcast Frames Rx. A count of frames that were successfully received and are directed to a broadcast group
address. This count does not include frames received with frame-too-long, FCS, length, or alignment errors, nor
frames lost because of internal MAC sublayer errors. This counter is incremented as indicated by the Receive
OK status.
Frames Rx with CRC Error. The number of frames received with CRC errors.
Configuring Teaming
The teaming function allows you to group any available network adapters together to function as a team.
Teaming is a method of creating a virtual NIC (a group of multiple adapters that functions as a single adapter).
The benefit of this approach is that it enables load balancing and failover. Teaming is done through the
Broadcom Advanced Server Program (BASP) software. For a comprehensive description of the technology and
implementation considerations of the teaming software, refer to the "Broadcom Gigabit Ethernet Teaming
Services" section of your Broadcom network adapter user guide.
Teaming can be accomplished by either of the following methods:
• Using the Broadcom Teaming Wizard
• Using Expert Mode
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 69
®
Page 70

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Notes:
• For further information regarding teaming protocols, see “Teaming” in your Broadcom network
adapter user guide.
• If you do not enable LiveLink™ when configuring teams, disabling Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
at the switch is recommended. This minimizes the downtime due to spanning tree loop
determination when failing over. LiveLink mitigates such issues.
• BASP is available only if a system has one or more Broadcom network adapters installed.
• The Large Send Offload (LSO) and Checksum Offload properties are enabled for a team only
when all of the members support and are configured for the feature.
• You must have administrator privileges to create or modify a team.
• The load balance algorithm in a team environment in which members are connected at different
speeds favors members connected with a Gigabit Ethernet link over members connected at lower
speed links (100 Mbps or 10 Mbps) until a threshold is met. This is normal behavior.
• Wake on LAN (WOL) is a feature that allows a system to be awakened from a sleep state by the
arrival of a specific packet over the Ethernet interface. Because a virtual adapter is implemented
as a software only device, it lacks the hardware features to implement WOL and cannot be enabled
to wake the system from a sleeping state via the virtual adapter. The physical adapters, however,
support this property, even when the adapter is part of a team.
Team Types
You can create four types of load balance teams:
• Smart Load Balance and Failover
• Link Aggregation (802.3ad)
• Generic Trunking (FEC/GEC)/802.3ad-Draft Static
• SLB (Auto-Fallback Disable) – The Auto-Fallback Disable feature is configured for Smart Load Balance
and Failover type teams in the Teaming Wizard.
For a description of these types, see “Load Balancing and Fault Tolerance” in the Broadcom® NetXtreme®
BCM57XX User Guide.
Using the Broadcom Teaming Wizard
You can use the Broadcom Teaming Wizard to create a team, configure an existing team if a team has already
been created, or create a VLAN.
1. Create or edit a team:
To create a new team, select Create a Team from the Team menu, or right-click one of the devices in the
“Unassigned Adapters” section and select Create a Team. This option is not available if there are no devices
listed in the “Unassigned Adapters” sections, which means all adapters are already assigned to teams.
To configure an existing team, right-click one of the teams in the list and select Edit Team. This option is
only available if a team has already been created and is listed in the Team Management pane.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 70
®
Page 71

Note: If you prefer to work without the wizard for now, click Expert Mode. If you want to always use
Expert Mode to create a team, select Default to Expert Mode on next start. See Using Expert Mode.
2. To continue using the wizard, click Next.
Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
3. Type the team name and then click Next. If you want to review or change any of your settings, click Back.
Click Cancel to discard your settings and exit the wizard.
Note: The team name cannot exceed 39 characters, cannot begin with spaces, and cannot contain
any of the following characters: & \ / : * ? < > |
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 71
®
Page 72

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
4. Select the type of team you want to create. If the team type is an SLB type team, click Next. If the team type
is not an SLB type team, then a dialog box appears. Verify that the network switch connected to the team
members is configured correctly for the team type, click OK, and continue.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 72
®
Page 73

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
5. From the Available Adapters list, click the adapter you want to add to the team and then click Add. Remove
team members from the Team Members list by clicking the adapter and then clicking Remove. Click Next.
Note: There must be at least one Broadcom network adapter assigned to the team.
The Large Send Offload (LSO) and Checksum Offload (CO) columns indicate if the LSO, and/or the CO
properties are supported for the adapter. The LSO, and CO properties are enabled for a team only when all
of the members support and are configured for the feature. If this is the case, then the team offload
capabilities appear on the bottom of the screen.
Note: Adding a network adapter to a team where its driver is disabled may negatively affect the
offloading capabilities of the team. This may have an impact on the team’s performance. Therefore, it
is recommended that only driver-enabled network adapters be added as members to a team.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 73
®
Page 74

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
6. If you want to designate one of the adapters as a standby member (optional), select Use the following
member as a standby member, then choose the standby member from the list of adapters.
7. The Auto-Fallback Disable mode feature allows the team to continue using the standby member rather than
switching back to the primary member if the primary member comes back online. To enable this feature,
select Enable Auto-Fallback Disable mode. Click Next.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 74
®
Page 75

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
8. If you want to configure LiveLink, select Yes, otherwise select No, then click Next.
Broadcom
®
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 75
Page 76

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
9. Select the probe interval (the number of seconds between each retransmission of a link packet to the probe
target) and the maximum number of probe retries (the number of consecutively missed responses from a
probe target before a failover is triggered).
10. Set the Probe VLAN ID to allow for connectivity with probe targets residing on a tagged VLAN. The number
set must match the VLAN ID of the probe targets as well as the port(s) on the switch to which the team is
connected.
Note: Each LiveLink enabled team can only communicate with Probe Targets on a single VLAN. Also,
VLAN ID 0 is equivalent to an untagged network. If the Probe VLAN ID is set to a value other than 0,
then a VLAN must be created with an identical VLAN tag value (see Step 16 on page 79).
11. Click the probe target at the top of the list, click Edit Target IP Address, type the target IP address in the IP
Address box for one or all probe targets, and then click OK. Click Next.
Note: Only the first probe target is required. You can specify up to three additional probe targets to
serve as backups by assigning IP addresses to the other probe targets.
12. Select a listed team member, click Edit Member IP Address, and then type the member IP address in the
IP Address box. Repeat for all listed team members and then click OK. Click Next.
Note: All of the member IP addresses must be in the same subnet as the subnet of the probe targets.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 76
®
Page 77

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
13. If you want to create a VLAN on the team, select Add VLAN, or if you want to change the settings of an
existing VLAN, select Edit VLAN, then click Next. If you do not want to create or edit a VLAN, select Skip
Manage VLAN, then click Next, and continue with the wizard from the Finish screen (see Step 18 on
page 80 of this procedure).
VLANs enable you to add multiple virtual adapters that are on different subnets. The benefit of this is that
your system can have one network adapter that can belong to multiple subnets.
Note: VLANs can only be created when all team members are Broadcom adapters.
14. Type the VLAN name and then click Next.
Note: The team name cannot exceed 39 characters, cannot begin with spaces, and cannot contain
any of the following characters: & \ / : * ? < > |
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 77
®
Page 78

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
15. To tag the VLAN, select Tagged and then click Next. Otherwise, click Untagged, click Next, and continue
with the wizard to add additional VLANs (see Step 17 on page 80 of this procedure).
Broadcom
®
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 78
Page 79

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
16. Type the VLAN tag value and then click Next. The value must be between 1 and 4094.
Broadcom
®
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 79
Page 80

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
17. Select Yes to add or manage another VLAN and then click Next. Repeat until you do not want to add or
manage any additional VLANs.
Note: You can define up to 64 VLANs per team (63 VLANs that are tagged and 1 VLAN that is not
tagged). Adding several VLANS may slow down the reaction time of the Windows interface due to
memory and processor time usage for each VLAN. The degree to which Windows performance may
suffer depends on system configuration.
18. To apply and commit the changes to the team, select Commit changes to system and Exit the wizard. To
apply your changes but continue using the wizard, select Save changes and continue to manage more
teams. Click Finish.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 80
®
Page 81

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Note: At any point in the Broadcom Teaming Wizard procedure, click Preview to get a visual
representation of what the team will look like before committing any changes.
Broadcom
®
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 81
Page 82

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
19. Click the team name in the Team Management pane to view the team's properties in the Information tab,
transfer and receive data in the Statistics tab.
Broadcom
®
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 82
Page 83

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Using Expert Mode
Use Expert Mode to create a team, modify a team, add a VLAN, and configure LiveLink for a Smart Load
Balance and Failover and SLB (Auto-Fallback Disable) team. To create a team using the wizard, see Using the
Broadcom Teaming Wizard.
To set the default Teaming Mode, select Options from the Tools menu, then select Expert Mode or Wizard
Mode (the default is Wizard Mode).
Creating a Team
Note: Enabling Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is not recommended for members of an
SLB type of team.
1. From the Teams menu, select Create Team, or right-click one of the devices in the “Unassigned Adapters”
section and select Create a Team. This option is not available if there are no devices listed in the
“Unassigned Adapters” sections, which means all adapters are already assigned to teams.
2. Click Expert Mode.
Note: If you want to always use Expert Mode to create a team, click Default to Expert Mode on next
start.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 83
®
Page 84

3. Click the Create Team tab.
Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Note: The Create Team tab appears only if there are teamable adapters available.
4. Click the Team Name field to enter a team name.
5. Click the Team Type field to select a team type.
6. Assign any available adapter or adapters to the team by selecting the adapter from the Load Balance
Members list. There must be at least one adapter selected in the Load Balance Members list.
7. You can assign any other available adapter to be a standby member by selecting it from the Standby
Member list.
Note: There must be at least one Broadcom network adapter assigned to the team.
The Large Send Offload (LSO), Checksum Offload (CO), and RSS indicate if the LSO, CO, and/or RSS
properties are supported for the team. The LSO, CO, and RSS properties are enabled for a team only when
all of the members support and are configured for the feature.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 84
®
Page 85

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Note: Adding a network adapter to a team where its driver is disabled may negatively affect the
offloading capabilities of the team. This may have an impact on the team’s performance. Therefore, it
is recommended that only driver-enabled network adapters be added as members to a team.
8. Type the value for Team MTU.
9. Click Create to save the team information.
10. Repeat steps Step 4 through Step 9 to define additional teams. As teams are defined, they can be selected
from the team list, but they have not yet been created. Click the Preview tab to view the team structure
before applying the changes.
11. Click Apply/Exit to create all the teams you have defined and exit the Manage Teams window.
12. Click Yes when the message is displayed indicating that the network connection will be temporarily
interrupted.
Notes:
• The team name cannot exceed 39 characters, cannot begin with spaces, and cannot contain any
of the following characters: & \ / : * ? < > |
• Team names must be unique. If you attempt to use a team name more than once, an error
message is displayed indicating that the name already exists.
• The maximum number of team members is 8.
• When team configuration has been correctly performed, a virtual team adapter driver is created for
each configured team.
• If you disable a virtual team and later want to reenable it, you must first disable and reenable all
team members before you reenable the virtual team.
• When you create Generic Trunking and Link Aggregation teams, you cannot designate a standby
member. Standby members work only with Smart Load Balancing and Failover and SLB (AutoFallback Disable) types of teams.
• For an SLB (Auto-Fallback Disable) team, to restore traffic to the load balance members from the
standby member, click the Fallback button on the Team Properties tab.
• When configuring an SLB team, although connecting team members to a hub is supported for
testing, it is recommended to connect team members to a switch.
• Not all network adapters made by others are supported or fully certified for teaming.
1. Configure the team IP address.
a. From Control Panel, double-click Network Connections.
b. Right-click the name of the team to be configured, and then click Properties.
c. On the General tab, click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click Properties.
d. Configure the IP address and any other necessary TCP/IP configuration for the team, and then click OK
when finished.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 85
®
Page 86

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Modifying a Team
After you have created a team, you can modify the team in the following ways:
• Change the type of team
• Change the members assigned to the team
• Add a VLAN
• Modify a VLAN (using Expert Mode)
• Remove a team or a VLAN (using Expert Mode)
To modify a team
1. From the Team menu, click Edit Team, or right-click one of the teams in the list and select Edit Team. This
option is only available if a team has already been created and is listed in the Team Management pane.
2. The wizard Welcome screen appears. Click Next to continue modifying a team using the wizard or click
Expert Mode to work in Expert Mode.
Note: The Edit Team tab in Expert Mode appears only if there are teams configured on the system.
3. Click the Edit Team tab.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 86
®
Page 87

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
4. Make the desired changes, and then click Update. The changes have not yet been applied; click the
Preview tab to view the updated team structure before applying the changes.
5. Click Apply/Exit to apply the updates and exit the Manage Teams window.
6. Click Yes when the message is displayed indicating that the network connection will be temporarily
interrupted.
Adding a VLAN
You can add virtual LANs (VLANs) to a team. This enables you to add multiple virtual adapters that are on
different subnets. The benefit of this is that your system can have one network adapter that can belong to
multiple subnets. With a VLAN, you can couple the functionality of load balancing for the load balance members,
and you can employ a failover adapter.
You can define up to 64 VLANs per team (63 VLANs that are tagged and 1 VLAN that is not tagged). VLANs
can only be created when all teams members are Broadcom adapters. If you try to create a VLAN with a nonBroadcom adapter, an error message is displayed.
To configure a team with a VLAN
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 87
®
Page 88

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
1. From the Teams menu, select Add VLAN.
2. The Welcome screen appears.
3. Click Expert Mode.
4. On the Create Team tab of the Manage Teams window, click Manage VLAN(s).
5. Type the VLAN name, then select the type and ID.
6. Click Create to save the VLAN information. As VLANs are defined, they can be selected from the Team
Name list, but they have not yet been created.
7. Continue this process until all VLANs are defined, then click OK to create them.
8. Click Yes when the message is displayed indicating that the network connection will be temporarily
interrupted.
Note: To maintain optimum adapter performance, your system should have 64 MB of system memory
for each of the eight VLANs created per adapter.
Viewing VLAN Properties and Statistics and Running VLAN Tests
To view VLAN properties and statistics and to run VLAN tests
1. Select one of the listed VLANs.
2. Click the Information tab to view the properties of the VLAN adapter.
3. Click the Statistics tab to view the statistics for the VLAN adapter.
4. Click the Diagnostics tab to run a network test on the VLAN adapter.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 88
®
Page 89

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Deleting a VLAN
The procedure below applies when you are in Expert Mode.
To delete a VLAN
1. Select the VLAN to delete.
2. From the Teams menu, select Remove VLAN.
3. Click Apply.
4. Click Yes when the message is displayed indicating that the network connection will be temporarily
interrupted.
Note: If you delete a team, any VLANs configured for that team are also deleted.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 89
®
Page 90

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Configuring LiveLink for a Smart Load Balancing and Failover and SLB (Auto-Fallback Disable) Team
LiveLink is a feature of BASP that is available for the Smart Load Balancing (SLB) and SLB (Auto-Fallback
Disable) type of teaming. The purpose of LiveLink is to detect link loss beyond the switch and to route traffic only
through team members that have a live link.
Read the following notes before you attempt to configure LiveLink.
Notes:
• Before you begin configuring LiveLink™, review the description of LiveLink. Also verify that each
probe target you plan to specify is available and working. If the IP address of the probe target
changes for any reason, LiveLink must be reconfigured. If the MAC address of the probe target
changes for any reason, you must restart the team (see “Troubleshooting”).
• A probe target must be on the same subnet as the team, have a valid (not a broadcast, multicast,
or unicast), statically-assigned IP address, and be highly available (always on).
• To ensure network connectivity to the probe target, ping the probe target from the team.
• You can specify up to four probe targets.
• The IP address assigned to either a probe target or team member cannot have a zero as the first
or last octet.
To configure LiveLink
1. From the Teams menu, select Edit Team.
2. Click Expert Mode (to configure LiveLink using the Teaming Wizard, see Using the Broadcom Teaming
Wizard).
3. In the Manage Members window, click the Edit Team tab.
4. Select Enable LiveLink. The LiveLink Configuration options appear below.
5. It is recommended to accept the default values for Probe interval (the number of seconds between each
retransmission of a link packet to the probe target) and Probe maximum retries (the number of
consecutively missed responses from a probe target before a failover is triggered). To specify different
values, click the desired probe interval in the Probe interval (seconds) list and click the desired maximum
number of probe retries in the Probe maximum retries list.
6. Set the Probe VLAN ID to correspond with the VLAN where the probe target(s) resides. This will apply the
appropriate VLAN tag to the link packet based on the shared configuration of the attached switch port(s).
Note: Each LiveLink enabled team can only communicate with Probe Targets on a single VLAN. Also,
VLAN ID 0 is equivalent to an untagged network.
7. Select Probe Target 1 and type the target IP address for one or all probe targets.
Note: Only the first probe target is required. You can specify up to 3 additional probe targets to serve
as backups by assigning IP addresses to the other probe targets.
8. Select one of the listed team members and type the member IP address.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 90
®
Page 91

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Note: All of the member IP addresses must be in the same subnet as the probe targets.
9. Click Update. Repeat these steps for each of the other listed team members.
10. Click Apply/Exit.
Saving and Restoring a Configuration
To save a configuration
1. From the File menu, select Team Save As.
2. Type the path and file name of the new configuration file, and then click Save (a .bcg extension is added).
The configuration file is a text file that can be viewed by any text editor. The file contains information about
both the adapter and the team configuration.
To restore a configuration
1. From the File menu, select Team Restore.
2. Click the name of the file to be restored, and then click Open.
Note: If necessary, go to the folder where the file is located.
3. Click Apply.
4. Click Yes when the message is displayed indicating that the network connection will be temporarily
interrupted.
5. If a configuration is already loaded, a message is displayed that asks if you want to save your current
configuration. Click Yes to save the current configuration. Otherwise, the configuration data that is currently
loaded is lost.
Note: The team may take a very long time to restore if the team is configured with many VLANs and
a static IP address.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 91
®
Page 92

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Viewing BASP Statistics
The Statistics section shows performance information about the network adapters that are on a team.
To view BASP Statistics information for any team member adapter or the team as a whole, click the name of the
adapter or team listed in the Team Management pane, then click the Statistics tab.
Click Refresh to get the most recent values for each statistic. Click Reset to change all values to zero.
Tx. Packet. This is the number of packets transmitted.
Tx. Packet Discarded. This is the number of packets discarded.
Tx. Packet Queued. This is the number of packets queued.
Rx. Packet. This is the number of packets received.
Rx. Packet Discarded. This is the number of packets discarded.
Probes Retried. This is the number of consecutively missed responses from a probe target before a failover is
triggered.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 92
®
Page 93

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Configuring With the Command Line Interface Utility
An alternate method to BACS for configuring Broadcom network adapters is with BACSCLI, which is a
Broadcom utility that allows you to view information and configure network adapters using a console in either a
non-interactive command line interface (CLI) mode or an interactive mode. As with BACS, BACSCLI provides
information about each network adapter, and enables you to perform detailed tests, run diagnostics, view
statistics, and modify property values. BACSCLI also allows you the ability to team network adapters together
for load balancing and failover.
For a complete list of available commands and examples, see the BACSCLI ReadMe text file on the Dellprovided CD.
BACSCLI is installed when BACS is installed with the installer.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 93
®
Page 94

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Managing VLANs
Overview
Virtual LANs (VLANs) allow you to split your physical LAN into logical parts, to create logical segmentation of
workgroups, and to enforce security policies for each logical segment. Each defined VLAN behaves as its own
separate network with its traffic and broadcasts isolated from the others, increasing bandwidth efficiency within
each logical group. Up to 64 VLANs (63 tagged and 1 untagged) can be defined for each Broadcom adapter on
your server, depending on the amount of memory available in your system.
VLANs can be added to a team to allow multiple VLANs with different VLAN IDs. A virtual adapter is created for
each VLAN added.
Although VLANs are commonly used to create individual broadcast domains and/or separate IP subnets, it is
sometimes useful for a server to have a presence on more than one VLAN simultaneously. Broadcom adapters
support multiple VLANs on a per-port or per-team basis, allowing very flexible network configurations.
Figure 2: Example of Servers Supporting Multiple VLANs with Tagging
Figure 2 shows an example network that uses VLANs. In this example network, the physical LAN consists of a
switch, two servers, and five clients. The LAN is logically organized into three different VLANs, each
representing a different IP subnet. The features of this network are described in Table 5:
Table 5: Example VLAN Network Topology
Component Description
VLAN #1 An IP subnet consisting of the Main Server, PC #3, and PC #5. This subnet
represents an engineering group.
VLAN #2 Includes the Main Server, PCs #1 and #2 via shared media segment, and PC #5.
This VLAN is a software development group.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 94
®
Page 95

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Table 5: Example VLAN Network Topology (Cont.)
Component Description
VLAN #3 Includes the Main Server, the Accounting Server and PC #4. This VLAN is an
accounting group.
Main Server A high-use server that needs to be accessed from all VLANs and IP subnets. The
Main Server has a Broadcom adapter installed. All three IP subnets are accessed
via the single physical adapter interface. The server is attached to one of the switch
ports, which is configured for VLANs #1, #2, and #3. Both the adapter and the
connected switch port have tagging turned on. Because of the tagging VLAN
capabilities of both devices, the server is able to communicate on all three IP
subnets in this network, but continues to maintain broadcast separation between all
of them.
Accounting Server Available to VLAN #3 only. The Accounting Server is isolated from all traffic on
VLANs #1 and #2. The switch port connected to the server has tagging turned off.
PCs #1 and #2 Attached to a shared media hub that is then connected to the switch. PCs #1 and
#2 belong to VLAN #2 only, and are logically in the same IP subnet as the Main
Server and PC #5. The switch port connected to this segment has tagging turned
off.
PC #3 A member of VLAN #1, PC #3 can communicate only with the Main Server and PC
#5. Tagging is not enabled on PC #3 switch port.
PC #4 A member of VLAN #3, PC #4 can only communicate with the servers. Tagging is
not enabled on PC #4 switch port.
PC #5 A member of both VLANs #1 and #2, PC #5 has an Broadcom adapter installed. It
is connected to switch port #10. Both the adapter and the switch port are configured
for VLANs #1 and #2 and have tagging enabled.
Note: VLAN tagging is only required to be enabled on switch ports that create trunk links to other
switches, or on ports connected to tag-capable end-stations, such as servers or workstations with
Broadcom adapters.
Adding VLANs to Teams
Each team supports up to 64 VLANs (63 tagged and 1 untagged). With multiple VLANs on an adapter, a server
with a single adapter can have a logical presence on multiple IP subnets. With multiple VLANs in a team, a
server can have a logical presence on multiple IP subnets and benefit from load balancing and failover. For
instructions on adding a VLAN to a team, see Adding a VLAN for Windows operating systems.
Note: Adapters that are members of a failover team can also be configured to support VLANs.
Because VLANs are not supported for a third-party NIC, if an third-party NIC is a member of a failover
team, VLANs cannot be configured for that team.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 95
®
Page 96

Using Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 4NetXtreme User Guide
Troubleshooting BACS
Problem: When attempting to open BACS on a Linux System, the following error message displays:
“Another instance of the BACS client appears to be running on this system. Only one instance of the BACS
client can be running at a time. If you are sure that no other BACS client is running, then a previous instance
may have quit unexpectedly.”
Solution: This message displays if you try to run a second instance of BACS. If you receive this message but
are certain that no instance of BACS is currently running, a previous instance of BACS may have quit
unexpectedly. To clear that instance, remove the file “/dev/shm/sem.Global-BACS-{C50398EE-84A7-4bc39F6E-25A69603B9C0}.”
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 96
®
Page 97

Section 7: Teaming
• Overview
• Load Balancing and Fault Tolerance
Note: See Broadcom Gigabit Ethernet Teaming Services for detailed information on the following
topics:
• Glossary of Terms and Acronyms
• Teaming Concepts
• Software Components
• Hardware Requirements
• Supported Features by Team Type
• Selecting a Team Type
• Teaming Mechanisms
• Architecture
• Types of Teams
• Driver Support by Operating System
• Supported Teaming Speeds
• Teaming and Other Advanced Networking Features
• General Network Considerations
• Application Considerations
• Troubleshooting Teaming Problems
• Frequently-Asked Questions
• Event Log Messages
TeamingNetXtreme User Guide
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 97
®
Page 98

TeamingNetXtreme User Guide
Overview
Adapter teaming allows you to group network adapters together to function as a team. The benefits of teaming
include allowing membership to VLANs, providing load balancing between adapters, and offering fault
tolerance. These benefits can be combined such that you can couple the functionality of load balancing for the
load balance members and the capability of employing a failover with having the team participate on different
VLANs.
Broadcom Advanced Server Program (BASP) is the Broadcom teaming software. For Windows operating
systems, BASP is configured through the Broadcom Advanced Control Suite (BACS) utility. For Linux operating
systems, teaming is done with channel bonding (see Teaming with Channel Bonding).
BASP supports four types of load balancing teams:
• Smart Load Balancing and Failover
• Link Aggregation (802.3ad)
• Generic Trunking (FEC/GEC)/802.3ad-Draft Static
• SLB (Auto-Fallback Disable)
Load Balancing and Fault Tolerance
Teaming provides traffic load balancing and fault tolerance (redundant adapter operation in the event that a
network connection fails). When multiple adapters are installed in the same system, they can be grouped with
up to 16 teams.
Each team can consist of up to eight adapters, with one adapter used as a standby for Smart Load Balancing
and Failover (SLB) or SLB (Auto-Fallback Disabled) team types. If traffic is not identified on any of the adapter
team member connections due to failure of the adapter, cable, or switch, the load will be distributed to the
remaining team members with an active connection. In the event that all primary adapters fail, traffic will be
distributed to the standby adapter. Existing sessions are maintained with no impact on the user.
Types of Teams
The available types of teams for the supported operating systems are shown in the following table:
Table 6: Types of Teams
Operating System Available Types of Teams
Windows Server 2008 and
Windows Server 2012
Smart Load Balancing and Failover
Link Aggregation (802.3ad)
Generic Trunking (FEC/GEC)/802.3ad-Draft Static
SLB (Auto-Fallback Disable)
NOTE: Windows Server 2012 provides built-in teaming support, called NIC
Teaming. It is not recommended that users enable teams through NIC Teaming
and BASP at the same time on the same adapters.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 98
®
Page 99

TeamingNetXtreme User Guide
Table 6: Types of Teams
Operating System Available Types of Teams
Linux Team adapters using the bonding kernel module and a channel bonding interface.
See your Linux documentation for more information.
Smart Load Balancing™ and Failover
Smart Load Balancing™ and Failover is the Broadcom implementation of load balancing based on IP flow. This
feature supports balancing IP traffic across multiple adapters (team members) in a bidirectional manner. In this
type of team, all adapters in the team have separate MAC addresses. This type of team provides automatic fault
detection and dynamic failover to other team member or to a hot standby member. This is done independently
of the Layer 3 protocol (IP); rather, it works with existing Layer 2 and Layer 3 switches. No switch configuration
(such as trunk, link aggregation) is necessary for this type of team to work.
Notes:
• If you do not enable LiveLink™ when configuring SLB teams, disabling Spanning Tree Protocol
(STP) at the switch or port is recommended. This minimizes the downtime due to spanning tree
loop determination when failing over. LiveLink mitigates such issues.
• If a team member is linked at 1000 Mbit/s and another team member is linked at 100 Mbit/s, most
of the traffic is handled by the 1000 Mbit/s team member.
Link Aggregation (802.3ad)
This mode supports link aggregation and conforms to the IEEE 802.3ad (LACP) specification. Configuration
software allows you to dynamically configure which adapters you want to participate in a given team. If the link
partner is not correctly configured for 802.3ad link configuration, errors are detected and noted. With this mode,
all adapters in the team are configured to receive packets for the same MAC address. The outbound loadbalancing scheme is determined by our BASP driver. The team link partner determines the load-balancing
scheme for inbound packets. In this mode, at least one of the link partners must be in active mode.
Generic Trunking (FEC/GEC)/802.3ad-Draft Static
The Generic Trunking (FEC/GEC)/802.3ad-Draft Static type of team is very similar to the Link Aggregation
(802.3ad) type of team in that all adapters in the team are configured to receive packets for the same MAC
address. The Generic Trunking (FEC/GEC)/802.3ad-Draft Static) type of team, however, does not provide LACP
or marker protocol support. This type of team supports a variety of environments in which the adapter link
partners are statically configured to support a proprietary trunking mechanism. For instance, this type of team
could be used to support Lucent's OpenTrunk or Cisco's Fast EtherChannel (FEC). Basically, this type of team
is a light version of the Link Aggregation (802.3ad) type of team. This approach is much simpler, in that there is
not a formalized link aggregation control protocol (LACP). As with the other types of teams, the creation of teams
and the allocation of physical adapters to various teams is done statically through user configuration software.
The Generic Trunking (FEC/GEC/802.3ad-Draft Static) type of team supports load balancing and failover for
both outbound and inbound traffic.
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 99
®
Page 100

TeamingNetXtreme User Guide
SLB (Auto-Fallback Disable)
The SLB (Auto-Fallback Disable) type of team is identical to the Smart Load Balancing and Failover type of
team, with the following exception—when the standby member is active, if a primary member comes back on
line, the team continues using the standby member, rather than switching back to the primary member.
If any primary adapter assigned to a team is disabled, the team functions as a Smart Load Balancing and
Failover type of team in which auto-fallback occurs.
All primary interfaces in a team participate in load-balancing operations by sending and receiving a portion of
the total traffic. Standby interfaces take over in the event that all primary interfaces have lost their links.
Failover teaming provides redundant adapter operation (fault tolerance) in the event that a network connection
fails. If the primary adapter in a team is disconnected because of failure of the adapter, cable, or switch port, the
secondary team member becomes active, redirecting both inbound and outbound traffic originally assigned to
the primary adapter. Sessions will be maintained, causing no impact to the user.
Limitations of Smart Load Balancing and Failover/SLB (AutoFallback Disable) Types of Teams
Smart Load Balancing™ (SLB) is a protocol-specific scheme.
Table 7: Smart Load Balancing
Operating System Failover/Fallback — All Broadcom Failover/Fallback — Multivendor
Protocol IP IP
Windows Server 2008 Y Y
Windows Server 2008 R2 Y Y
Windows Server 2012 Y Y
Operating System Load Balance — All Broadcom Load Balance — Multivendor
Protocol IP IP
Windows Server 2008 Y Y
Windows Server 2008 R2 Y Y
Windows Server 2012 Y Y
Windows Server 2012 R2 Y Y
Legend: Y = yes
N = no
N/S = not supported
Broadcom
April 2017 • 2CS57XX-CDUM514-R Page 100
®
 Loading...
Loading...