Page 1
TECHNICAL:
SALES:
FAX:
ADDRESS:
WEB:
(0118) 965 6000
(0118) 965 5100
(0118) 931 5001
464 Basingstoke Road, Reading, Berkshire RG2 0QN
www.blackbox.co.uk
Compact mDSL Modem
464 Basingstoke Road, Reading, Berkshire RG2 0QN
© Copyright 2000. Black Box Catalogue, Ltd.
MDU9705A-V35
MDU9705A-X21
August 2000
Page 2

Table of Contents
Section Page
Radio and TV Interference....................................................2
CE Notice
Service
General Information...............................................................4
Features
Description
Configuration .........................................................................5
Configuring the Hardware DIP Switches
Configuration DIP Switch Set “S2”
Configuration DIP Switch Set “S3”
NetLink Plug ‘n’ Play
Installation............................................................................11
Connecting the Twisted Pair Interface
Connecting the MDU9705A-V35 Serial Interface
Connecting the MDU9705A-V35 to a DTE Device
Connecting the MDU9705A-V35 to a DCE Device
Connecting the MDU9705A-X21 Serial Interface
Connecting the MDU9705A-X21 to a DCE or DTE Device
Opening the Case
Connecting Power
Universal Power (100 - 240VAC)
120VAC Power (US)
230VAC Power (International)
48VDC Power
Operation .............................................................................16
Power-Up
LED Status Monitors
LED Descriptions Chart
Test Modes
Overview
Loops and Patterns
Using the V.52 (BER) Test Pattern Generator
Appendix A - Specifications........................................................27
Appendix B - V.35 Interface Pin Assignments............................29
Appendix C - X.21 Interface Pin Assignments...........................30
Appendix D - Transmission Distance Chart ...............................31
Radio and TV Interference
The Compact mDSL Modem generates and uses radio frequency
energy, and if not installed and used properly—that is, in strict accordance with the manufacturer's instructions—may cause interference to
radio and television reception. The Compact mDSL Modem has been
tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A computing
device in accordance with the specifications in Subpart J of Part 15 of
FCC rules, which are designed to provide reasonable protection from
such interference in a commercial installation. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If
the Compact mDSL Modem does cause interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by disconnecting the unit, the
user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of
the following measures: moving the computing equipment away from
the receiver, re-orienting the receiving antenna and/or plugging the
receiving equipment into a different AC outlet (such that the computing
equipment and receiver are on different branches).
CE Notice
The CE symbol on your Black Box equipment indicates that it is in
compliance with the Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) directive and
the Low Voltage Directive (LVD) of the European Union (EU). A
Certificate of Compliance is available by contacting Technical Support.
1
Compact mDSL Modem
2
Compact mDSL Modem
Page 3
General Information
Thank you for your purchase of this Black Box product. This product has been thoroughly inspected and tested and is warranted for
One Year parts and labor.
Features
• Multi-Rate Symmetric DSL
• CAP (Carrierless Amplitude and Phase) Modulation
• Data Rates up to 2.304Mbps
• V.35 and X.21 Interfaces
• Interoperable with the MDU9700
• SNMP Manageable via SNMP Management Module
• NetLink Plug ‘n’ Play for Easy Installations
• Universal Power Options, 120VAC, 230VAC and -48VDC Available
• Front Panel Status Indicators
• Small, Convienent Desktop Unit
• CE Marked
Description
The Black Box Compact
mDSL Modem
provides high speed 2wire connectivity to ISPs, PTTs, and corporations using mDSL (Multirate Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line) technology. Multi-rate DSL
offers the ability to deliver the maximum bit rate that a twisted pair line
can accommodate. Supporting multiple line rates from 144kbps to
2.320Mbps, the modem provides “megabyte” speeds to leased line,
LAN to LAN interconnection, and WAN access networks over 3.6
miles/5.8km (1.054Mbps on 24AWG/.5mm wire).
The MDU9705A-V35 provides a V.35 interface on an M/34 female
connector. MDU9705A-X21 provides an X.21 interface on a DB-15
female connector. Features include loopback diagnostics,
SNMP/HTTP remote management capabilities using NetLink Plug-andPlay and inband externally accessible configuration switches. All versions of the Compact mDSL Modem are compatible with Black Box’s
mDSL standalone and mDSL Access rack card.
As a symmetric DSL NTU,
mDSL
offers the same data rates in
both directions over a single pair of regular telephone lines using
Carrierless Amplitude and Phase (CAP) modulation. Line connection
is made by an RJ-45 jack. Standard versions of the Compact mDSL
Modem are powered by a 100/230VAC(Universal) supply. The DC
power supply option supports any DC input between 36-72VDC.
3
Compact mDSL Modem
4
Compact mDSL Modem
Configuration
The Compact mDSL Modem is equipped with two sets of eight
DIP switches, which allow configuration of the unit for a wide variety of
applications. This section describes switch locations and explains all
possible configurations.
Configuring the Hardware DIP Switches
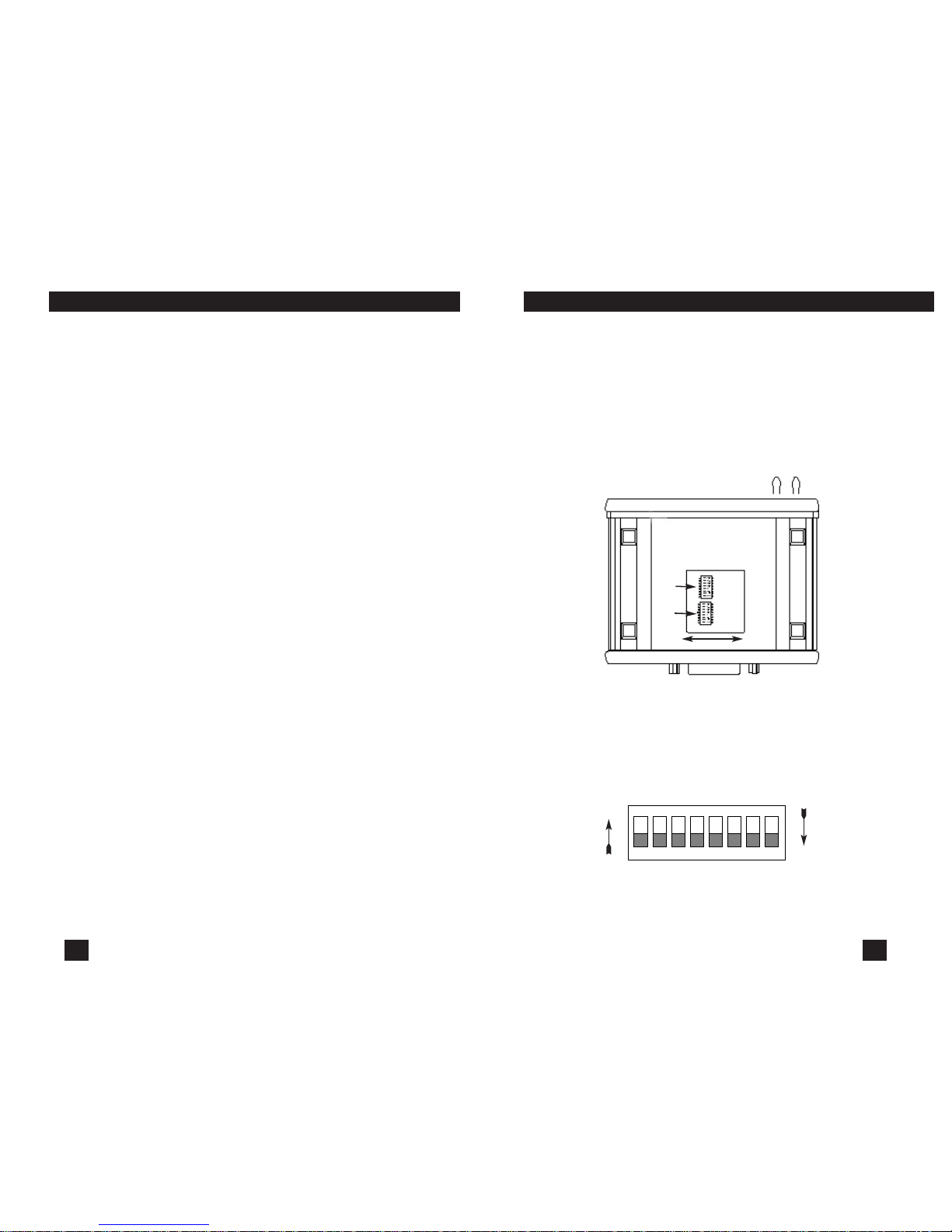
The 16 external switches are grouped into two eight-switch sets,
and are externally accessible from the underside of the Compact
mDSL Modem (See Figure 1).
The two sets of DIP switches on the underside of the Compact
mDSL Modem will be referred to as S2 and S3. As Figure 2 shows,
the orientation of all DIP switches is the same with respect to “ON” and
“OFF” positions.
Figure 2. Close Up of Configuration Switches (all sets are identical in appearance)
Figure 1. Underside of Compact mDSL Modem, Showing Location of DIP Switches
Front
Back
On
S2
S3
Off
12345678
ON
OFF
ON
Page 4

Configuration DIP Switch Set “S2”
The configuration switches on S2 allow you to specify the Clocking
Mode and to enable/disable Local and Remote Loop requests from the
V.35 DTE. Default settings of S2 are shown in the table below.
Switch S2-1, S2-2, S2-3, S2-4, and S-5:
Reserved for factory use and must remain in the OFF Position.
Switches S2-6 and S2-7: Clock Mode
Use Switches S2-6 and S2-7 to configure the 1088 for internal,
external, or receive recover clock mode.
Position Function
S2-1 Reserved
S2-2 Reserved
S2-3 Reserved
S2-4 Reserved
S2-5 Reserved
S2-6 Clock Mode On
S2-7 Clock Mode Off
S2-8 Enable Loop from DTE
Off Disabled
Off
Off
Receive
Recover
Off
Off
Off
S2 SUMMARY TABLE
Factory Default
CO/CP
Unit S2-6 S2-7 Clock Mode Description
CO On On Internal Transmit clock
generated internally
CO Off On External (DTE) Transmit clock
derived from
terminal interface
CP On Off Receive Recover Transmit clock
derived from the
received line
Off Off
Reserved
5
Compact mDSL Modem
6
Compact mDSL Modem
Switch S2-8: Enable/Disable Loop Tests from DTE
Switch S2-8 may be used to allow the MDU9705A-V35 to enter loopback diagnostic tests (Local or Remote) when the V.35 DTE raises the
appropriate loop request pin (LLB: Pin L or RDL: Pin N). When Switch
S2-8 is in the On position, the MDU9705A-V35 will enter Local
Loopback or Remote Loopback at the request of the DTE. When
Switch S2-8 is in the Off position, the MDU9705A-V35 ignores DTE
loop requests. In the Off position, loop requests may still be initiated
by the front panel switch.
S2-8 Setting
On DTE Loopback Request Enabled
Off DTE Loopback Request Disabled
Page 5
Configuration Switch Set “S3”
Use the six DIP Switches in Switch S3 to enable the DTE bit rate.
The following table summarizes default positions of DIP Switch S3.
Detailed descriptions of each switch follow the table.
Switch S3-1: DTE Rate
Use Switch S3-1 through S3-6 to set the DTE bit rate.
S3-1 S3-2 S3-3 S3-4 S3-5 S3-6 DTE Rate (kbps)
Off Off On On On On 64
On On Off On On On 128
Off On Off On On On 192
On Off Off On On On 256
Off Off Off On On On 320
On On On Off On On 384
Off On On Off On On 448
On Off On Off On On 512
Off Off On Off On On 576
On On Off Off On On 640
Off On Off Off On On 704
On Off Off Off On On 768
Off Off Off Off On On 832
On On On On Off On 896
Off On On On Off On 960
On Off On On Off On 1024
Off Off On On Off On 1088
On On Off On Off On 1152
Off On Off On Off On 1216
On Off Off On Off On 1280
Off Off Off On Off On 1344
On On On Off Off On 1408
Off On On Off Off On 1472
S3 SUMMARY TABLE
Position Function Factory Default
S3-1 DTE Rate On
S3-2 DTE Rate Off
S3-3 DTE Rate Off
S3-4 DTE Rate Off
S3-5 DTE Rate On
S3-6 DTE Rate On
S3-7 Reset Software Defaults On
Normal Operation
S3-8
Transmit Data Sample Point
On Normal Operation
}
768 kbps
7
Compact mDSL Modem
8
Compact mDSL Modem
On Off On Off Off On 1536
On On Off Off Off On 1600
Off On Off Off Off On 1664
On Off Off Off Off On 1728
Off Off Off Off Off On 1792
On On On On On Off 1856
Off On On On On Off 1920
On Off On On On Off 1984
Off Off On On On Off 2048
On On Off On On Off 2112
Off On Off On On Off 2176
On Off Off On On Off 2240
Off Off Off On On Off 2304
Switch S3-7: Reset Software Defaults
Switch S3-7 allows the user to reset the software configured factory
defaults. This will only be needed when using the SNMP Management
Module to SNMP manage your units. For more information, please
refer to the SNMP Management Module Operations Manual.
S3-7
Setting
On Normal Operation
Off Reset
Switch S3-8: Transmit Data (TD) Sampling Point
Switch 3-8 controls the Transmit Data (TD) sampling point.
S3-8 Setting Description
On Normal TD sampled on the falling
edge of the Compact mDSL
Modem Transmit
Clock (TC)
Off Invert TD sampled on the rising
edge of the Compact mDSL
Modem Transmit
Clock.
NOTE: Based on the DTE rate chosen, the Compact mDSL
Modem will automatically select the optimum line rate depending
on distance and line conditionsfor the distance. The line selection will be based on the lowest line rate that will support the DTE
rate.
Page 6

Plug-and-Play
The Plug-and-Play feature allows ISPs, carriers and PTTs to
quickly upgrade the link speed for a customer without requiring the
customer to re-configure the Customer Premise (CP) Compact mDSL
Modem. This feature also allows service providers to set up all of the
configurations at the Central Office (on the rack cards) before installing
the stand alone units, saving time spent configuring or re-configuring
DIP switches.
The Plug-and-Play feature allows the user to configure the DTE rate
(bandwidth allocation, see Switches S3-1 through S3-6) of the CP unit
from the rack card at the Central Office (CO). The stand alone unit at
the Customer Premise (CP) site will automatically configure itself to the
DTE rate (Bandwidth Allocation) of the rack card. Other configuration
parameters remain in the default setting.
Follow the instructions below to activate Plug-and-Play between
CO (mDSL Rack Card and CP Compact mDSL Modem) units:
1. Set the mDSL Rack Card (CO) to either Internal or External
clocking mode as defined by the application.
2. Set the Compact mDSL Modem (CP) to “Plug-and-Play CP”
by setting all S2 and S3 DIP switches in the OFF position as
described in Figure 3, below.
When the CO and CP units connect over DSL, the CP will enter a
predefined default configuration (Receive Recovered Clocking). During
the negotiation process between the units, the CO unit will configure
the DTE rate/line rate on the CP unit as defined by the settings of the
CO unit. When additional bandwidth is required, only the configuration
of the CO unit should be changed. This feature gives ISPs, LECs and
PTTs the ability to provision bandwidth on an as needed basis to customers.
mDSL Rack
Card (CO)
1088 (CP)
DIP Switches all in OFF position
DIP Switches or NMS configured
according to specific application
requirements
Figure 3. Typical Plug-and-Play Application
NOTE: Plug-and-Play is only available when using a
rack-mounted mDSL Rack Card as the CO unit.
DSL Span
9
Compact mDSL Modem
10
Compact mDSL Modem
Installation
Once the Compact mDSL Modem is properly configured, it is
ready to connect to the twisted pair interface, to the serial port, and to
the power source. This section tells you how to make these connections.
Connecting the Twisted Pair Interface
The Compact mDSL Modem supports communication between two
DTE devices at distances to 5 miles (8 km) over 24 AWG (.5mm) twisted pair wire. Two things are essential:
1. These units work in pairs. Both units at the end of the twisted
pair DSL span must be set for the same DTE rate.
2. To function properly, the Compact mDSL Modem needs one
twisted pair of metallic wire. This twisted pair must be
unconditioned, dry, metallic wire, between 19 (.9mm) and 26
AWG (.4mm) (the higher number gauges will limit distance).
Standard dial-up telephone circuits, or leased circuits that run
through signal equalization equipment, or standard, flat modular telephone type cable, are
not acceptable
.
The RJ-45 connector on the Compact mDSL Modem’s twisted pair
interface is polarity insensitive and is wired for a two-wire interface.
The signal/pin relationships are shown in Figure 5 below.
Figure 4. Compact mDSL Modem RJ-45 twisted pair line interface.
1 (N/C)
2 (N/C)
3 (N/C)
4 (2-Wire TIP)
5 (2-Wire RING)
6 (N/C)
7 (N/C)
8 (N/C)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Page 7

Connecting the Compact mDSL Modem (V.35) Serial Interface
The MDU9705A-V35 supports V.35 serial port connections. This
section describes how to connect the serial ports to your V.35 equipment.
Connecting the Compact mDSL Modem (V.35) to a “DTE” Device
The MDU9705A-V35 provides a V.35 DCE (Data Circuit
Terminating Equipment) interface on an M/34 female connector. As a
DCE, this interface is designed to connect to DTE equipment, such as
a router. When connecting the V.35 interface of the Compact mDSL
Modem to your DTE device, use a V.35 straight through cable (See
Figure 4, below). Appendix C describes pin assignments and signal
sources for the Compact mDSL Modem V35 interface. When purchasing or constructing an interface cable, please refer to the pin diagrams
in Appendix C as a guide.
Connecting the Compact mDSL Modem (V.35) to a “DCE” Device
The MDU9705A-V35 provides a V.35 DCE (Data Circuit
Terminating Equipment) interface on an M/34 female connector. As a
DCE, this interface is designed to connect to DTE equipment, such as
a router. However, tail-circuit applications require connection to another DCE equipment, such as a multiplexer. When connecting the V.35
interface of the Compact mDSL Modem to your DCE device, use a
V.35 null modem cable. Some applications may also require the
installation of a V.35 tail-circuit buffer to account for small differences
in clock frequency between the MDU9705A-V35 and the V.35 DCE
(Multiplexer).
Figure 5. Connecting the MDU9705A-V35 to V.35 Serial DCE
Straight-Through M/34
Cable
DSL Span
MDU9705A-V35 (DCE)
Remote Compact
mDSL Modem
V.35 Router (DTE)
DSL Span
Remote Compact
mDSL Modem
MDU9705A-V35
(DCE)
V.35 Multiplexer (DCE)
Figure 4. Connecting the MDU9705A-V35 to V.35 Serial DTE
11
Compact mDSL Modem
12
Compact mDSL Modem
Connecting the Compact mDSL Modem (X.21) Serial Interface
The MDU9705A-X21 supports X.21 serial port connections. This
section describes how to connect the serial ports to your X.21 equipment.
Connecting the MDU9705A-X21 to a “DCE” or “DTE” Device
The MDU9705A-X21 provides an X.21 interface on a DB-15
female connector. The X.21 interface default configuration is DCE
(Data Circuit Terminating Equipment) for connection to DTE (Data
Terminal Equipment) such as a router. However, the X.21 interface on
the Compact mDSL Modem may be configured as DTE (Data Terminal
Equipment) for connection to DCE such as a modem or multiplexer.
When connecting the X.21 interface of the MDU9705A-X21 to your
DTE device, use a X.21 straight through cable (See Figure 6, below).
To change the DCE/DTE orientation from the
default position (DCE), you must open the case Compact mDSL
Modem case.
Opening the Case
To open the Compact mDSL Modem case, insert a flat head
screw driver into an open slot on both sides of the case, as in Figure 7.
Twist the screw driver head slightly and the top half of the case will
separate from the lower half, as in Figure 7, below. Take caution not to
Figure 6. Connecting the MDU9705A-X21 to X.21 DTE or DCE
Straight-Through 15-pin
D-Sub Cable
DSL Span
Router (DTE)
OR
Mux (DCE)
MDU9705A-X21
(DCE or DTE)
Remote Compact
mDSL Modem
Figure 7. Opening the case with a small screwdriver
Page 8

damage the pc-board mounted components.
The DCE/DTE strap is located on the top side of the MDU9705AX21 pc board (See Figure 8, below). The arrows on the top of the
strap indicate the configuration of the X.21 port (for example, if the
DCE arrows are pointing toward the DB-15 connector, the X.21 port is
wired as a DCE). Change the DCE/DTE orientation by pulling the
strap out of its socket, rotating it 180º, then plugging the strap back
into the socket. You will see that the DCE/DTE arrows now point in
the opposite directions, showing the new configuration of the X.21 port.
To close the case, fit the 2 halves together snugly and snap them back
in place.
Connecting Power
The Compact mDSL Modem (all versions) are available with
Universal AC (100-240VAC), 120VAC, 230VAC or -48VDC power
options. This section describes these options.
Universal AC Power (100-240VAC)
The Compact mDSL Modem uses a 5VDC, 2A universal input
100-240VAC, power supply (center pin is +5V). The universal input
power supply has a male IEC-320 power entry connector. This power
supply connects to the Compact mDSL Modem by means of a barrel
jack on the rear panel. Many international power cords are available
for the universal power supply (Please refer to Appendix B for countryspecific power cords.
The Compact mDSL Modem powers up as soon as it is plugged
into an AC outlet--there is no power switch.
DCE/DTE Strap
DB-15 Connector
Figure 8. Setting the DCE/DTE Strap
13
Compact mDSL Modem
14
Compact mDSL Modem
120 VAC Power (US)
The 100-132 VAC adapter supplied with the U.S. version of the
Compact mDSL Modem is a wall mount type and may be plugged into
any approved 120 VAC wall jack.
230 VAC Power (International)
The 230 VAC adapter supplied with the International version of the
Compact mDSL Modem is a wall mount type and may be plugged into
any approved 230 VAC wall jack.
DC Power
The 36-60 VDC DC to DC adapter supplied with the DC version of
the Compact mDSL Modem plugs in a DC source (nominal 48VDC)
and plugs into the barrel power supply jack on the rear of the Compact
mDSL Modem. Please refer to Figure 9, below, to make the proper
connection.
Figure 9. Connecting DC Power to the 48VDC Power Supply.
WARNING! There are no user-serviceable parts in the
power supply section of the Compact mDSL Modem. Fuse
replacement should only be performed by qualified service
personnel.
To Power
Supply Jack
-Vin
+Vin
To -48VDC
Source
Page 9

Operation
Once the Compact mDSL Modem is properly configured and
installed, it should operate transparently. This sections describes
power-up, reading the LED status monitors, and using the built-in loopback test modes.
Power Up
To apply power to the Compact mDSL Modem, first be sure that
you have read Section 4.4, and that the unit is connected to the
appropriate power source. Then power-up the unit.
LED Status Monitors
The Compact mDSL Modem features six front panel LEDs that
monitor power, the DTE signals, network connection and test modes.
Figure 10 (below) shows the front panel location of each LED.
Following Figure 10 is a description of each LEDs function. See also,
LED description chart on page 17.
DSL Link (Active Green) Solid green (On) indicates that the
end to end DSL Framer Link is up, signifying that
the link across the DSL span is active. The DSL
Link LED is Off when the link is down.
TD & RD Glows yellow to indicate an idle condition of Binary
“1” data on the respective terminal interface signals. Green indicates Binary “0” data
NS (No Signal) glows red to indicate that the local
Compact mDSL Modem is not connected with the
remote Compact mDSL Modem.
ER - blinks ON/OFF after a 511/511E test has timed
out. See Section 5.3.3 (Test Pattern Generator) for
more information.
-flashes once to indicate that a CRC error has
occurred (during normal operation) or bit errors
have occurred (during 511/511E tests).
Figure 10. Compact mDSL Modem Front Panel
Compact mDSL Modem - V.35
15
Compact mDSL Modem
16
Compact mDSL Modem
-only at power up, blinks once every 200 ms if the
DTE Rate is set to an unsupported settings
TM glows yellow to indicate that the Compact mDSL
Modem has been placed in Test Mode. The unit can be
placed in test mode by the local user or by the remote
user. The TM LED will flash for 400msec when a valid
packet is received from the SNMP Management
Module.
Test Modes
The Compact mDSL Modem offers two proprietary loopback test
modes, plus a built-in V.52 BER test pattern generator to evaluate the condition of the modems and the communication link. These tests can be activated physically from the front panel or via the DTE interface.
Overview
Figure 11 shows the major elements used in the loop-back and pattern
tests available in the Compact mDSL Modem. Each block has several functions. Following Figure 11 are descriptions that show how the elements are
used during Test Modes.
Clock (CO) Internal 768Kb No DTE Clock (CP) R/R No DTE
TD RD DSL NS ER TM TD RD DSL NS ER TM
Power ON G O off ON off off O O off ON off off
DSL Link G O G off off off O G G off off off
Link Brk G O off off off off O O off off off off
Brk+ 10s G G off ON off off O O off ON off off
RDL G G G off off ON O G G off off ON
RDL+511 G G off off off ON O G off off off ON
With DTE Connected With DTE Connected
Mark O O G off off off O O G off off off
Space G G G off off off G G G off off off
Data GO GO G off off off GO GO G off off off
Link Brk = DSL Link Broken
Brk+10s = 10 Seconds following Link Break
G=GREEN
O=ORANGE
ON= ON
off= OFF
Y=yellow
5.2.1 Compact mDSL Modem LED Descriptions Chart
Page 10

Figure 11: Block Diagram Compact mDSL Modem
Framer The framer is used to determine the status of
the line. In normal operation the framer transmits
and expects to receive framed packets from the
far end. If the framer receives framed packets
from the far end, CTS and CD will be active. If
framed packets are not received, CTS and CD
will be inactive. The restart procedure uses this
information to determine if a valid connection is
made (cable disconnect, poor cable quality, etc).
In normal Data Mode, if the Compact mDSL
Modem receives 4 seconds of unframed packets
it will restart and begin trying to re-establish a
connection with the far end. The distinction
between framed packets and unframed packets
becomes important when we discuss the Pattern
Generator.
Pattern Gen/Det This part of the Processor generates and
detects the 511/511E patterns. When transmitting 511 patterns, the information is unframed
(because it originates after the framer) and is
intended to be evaluated only by another
Processor. If the units are in Data Mode and the
pattern generator is enabled on one end of the
link, the far end will begin receiving unframed
packets and assume that the line has gone
down. During test modes, we force the pattern
generator to time out before it can cause the link
to be killed.
Loop Control This part of the Processor is used to control
loop-backs. In a Local Loop, the data is looped
back towards the local DTE. In a Remote Loop,
the data is looped back to the line, but it is also
allowed to pass through to the framer and to the
remote DTE.
Pattern
Gen/Det
Loop
Contr
ol
Loop
Contro
l
Pattern
Gen/Det
Processor
Processor
Framer
Framer
Line
17
Compact mDSL Modem
18
Compact mDSL Modem
Restart Procedure The restart procedure is in place to allow the
and Time Outs units to re-establish a connection after the
framer begins seeing unframed packets. The
Test Model Timing Chart below shows the
amount of time the framer must see consecutive
unframed packets before the unit will restart and
try to establish a new line connection. The reason that there are different Restart Times will
become apparent after reading the rest of the
document. The 511/511E Time Out shown refers
to the amount of time the 511/511E pattern will
be valid. At the end of this time the pattern will
automatically turn itself off and the normal data
path will be re-established. The ER led will flash
indicating to the user that the test has timed out.
The ER led will stop flashing once the 511/511E
switch is placed into the normal position.
Symbol Indicators
This symbol designates the origination or the
termination of a data path. The direction of the
arrow connected distinguish the two data paths.
This symbol designates an invalid data path. If
there is data present it should be ignored.
Test Mode Timing
Item Elapsed Time (seconds)
Start Up 50
Data Mode 4
511/511E Generator Enabled 60 (The generator will stop after 45 seconds.)
Remote End of an RDL 60
511/511E Time Out 45 (The pattern generator will automatically turn
off after 45 seconds. The ER LED will flash until
the user turns off the 511/511E switch.)
Page 11

Loops and Patterns
The following section describes the Test Modes used in the
Compact mDSL Modem. At the bottom of each Test Mode, a figure is
included to show the data path.
Local Loop There are two different modes of operation for a
Local Loop depending on the status of the units
at the time that the Local Loop is initiated. If the
units are not in linked (NS LED on) and the
Local Loop is initiated, either by the front panel
switch or the DTE interface, the unit will enter
mode 1. If the units are linked, NS LED off, then
the unit will enter a mode 2 Local Loop.
A Mode 1 Local Loop is shown in Figure 12.
When the Local Loop is initiated, either by the
front panel switch or the DTE interface, the loop
will be activated within the local Processor. The
data present at the local DTE interface will be
looped back to the local DTE by the Loop
Control block within the Processor. Any data
present on the line or at the far end DTE interface is invalid. The remote unit will remain in the
StartUP mode, NS LED on, CTS LED yellow,
and CD LED yellow, until the local unit is taken
out of the Local Loop mode. After the Local
Loop is deselected, the units will both be in
StartUP mode and the link will be established.
A mode 2 Local Loop is shown in Figure 13.
When the Local Loop is initiated, either by the
front panel switch or the DTE interface, two separate loop paths will be started. In the first path,
data presented to the local DTE interface will be
looped back to the local DTE within the framer.
In the second path, data presented at the far
end DTE will be transmitted to the local DTE
and then looped back within the local DTE Loop
Control block with the Processor. After the Local
Loop is deselected, the units will be placed back
into DataMode and the normal data paths will be
re-established.
19
Compact mDSL Modem
20
Compact mDSL Modem
Figure 12. Block Diagram Local Loop Mode 1
Figure 13. Block Diagram Local Loop Mode 2
Local Loop When the unit is placed into a Mode 1. Local
with 511/511E Loop and the 511/511E pattern generator is acti-
vated, the local pattern generator begins sending out a 511/511E pattern to the Loop Control
block. The Loop Control block will loop this data
back to the 511/511E pattern detector block,
which will evaluate the data for errors. Because
the 511/511E pattern generator is contained
within the Processor the data is unframed so the
framer will begin seeing unframed packets. The
framer receives this unframed data and can not
distinguish this information from a line disconnection (this would cause the units' Restart procedure to start). What we have done to allow
this mode to work is to add time outs for the
pattern generators. When the 511/511E is initiated, the line restart procedure is changed to one
minute. The 511/511E pattern will timeout after
45 seconds. So if the 511/511E is turned on during a local loop, the restart procedure is set to
one minute, but the 511/511E pattern will time
out after 45 seconds, allowing the framer to
begin seeing framed packets (and not restart
the box).
Pattern
Gen/Det
Loop
Contr
ol
Loop
Contro
l
Pattern
Gen/Det
Processor
Processor
Framer
Framer
Line
Pattern
Gen/Det
Loop Contr
ol
Loop Contro
l
Pattern
Gen/Det
Processor
Processor
Framer
Framer
Line
Page 12

Local Loop After the 511/511E pattern times out, the ER led
with 511/511E will begin flashing. It will remain this way until
(continued) the pattern generator switch is turned off. Note
that the data at the local DTE and the remote
DTE are not valid. Because the data is
unframed there is no way for the framer to send
this data out to the DTE. This is an important
distinction because other Black box units will
send out the 511 pattern.
When the unit is placed into a Mode 2 Local
Loop, the 511/511E pattern generator on the
local unit is unavailable for transmission. As can
be seen from Figure 11, the 511/511E pattern
generator has no data path connections available. The 511/511E pattern generator is still
available on the remote unit. For more information on the proper operation of this pattern generator please refer to the "Remote Digital Loop
with 511/511E" section.
Figure 14. Block Diagram Local Loop Mode 1 with 511/511E
Figure 15. Block Diagram Local Loop Mode 2 with 511/511E
Pattern
Gen/Det
Loop
Contr
ol
Loop
Contro
l
Pattern
Gen/Det
Processor
Processor
Framer
Framer
Line
Pattern
Gen/Det
Loop
Contr
ol
Loop
Contro
l
Pattern
Gen/Det
Processor
Processor
Framer
Framer
Line
21
Compact mDSL Modem
22
Compact mDSL Modem
Remote Digital The Remote Loop uses the EOC channel (an
Loop out-of-band signaling channel) to establish the
remote link. Upon the RDL switch being thrown
or DTE initiation, a RDL_ON Request signal is
sent to the remote unit. The Remote unit then
responds with an RDL Acknowledge command
and the link is established. Data originates at
the local DTE and is looped at the Remote
PROCESSOR back to the Local DTE. Note that
the data is also passed through to the Remote
DTE and is not squelched. When a Remote unit
enters RDL, it changes its' Restart timeout to
one minute (the reason will be explain in the
RDL with 511/511E section). If the line is disconnected, the local unit will Restart (NS led activated) after 4 - 6 seconds, but the Remote unit will
wait for one minute before it Restarts. Note that
the transmit data at the Remote DTE is ignored.
When the switch is thrown or the DTE removes
the RDL request, the local unit will transmit an
RDL_OFF Request to the Remote unit. The
local unit will keep its' TM led active until this
request has been completely sent out. If the
switch is thrown again before the completion of
the termination phase the switch will be ignored
until it is placed back into the normal position.
Figure 16. Block Diagram Remote Loop
Pattern
Gen/Det
Loop
Contr
ol
Loop
Contro
l
Pattern
Gen/Det
Processor
Processor
Framer
Framer
Line
Page 13

Remote Digital The Remote Digital Loop with 511/511E is
Loop with shown above. After RDL is established the
511/511E Remote units' Restart Timer is set to one
minute. This has been done because when the
511/511E generator is started on the local unit,
the Remote framer begins seeing unframed
packets. The Remote unit can not distinguish
the 511/511E pattern from the line being disconnected so the Restart Timer has been lengthened to allow the pattern generator to function.
Once the 511/511E test is started, the Local unit
changes its' Restart Timer to one minute. The
pattern originates within the Processor and is
sent to the Remote unit. It is then looped back
to the Local unit where it is evaluated for errors.
After 45 seconds, the Pattern Generator will
timeout and stops sending the pattern. The ER
led will begin blinking until the user turns off the
511/511E switch.
Figure 17. Block Remote Loop with 511/511E
Pattern
Gen/Det
Loop
Contr
ol
Loop
Contro
l
Pattern
Gen/Det
Processor
Processor
Framer
Framer
Line
23
Compact mDSL Modem
24
Compact mDSL Modem
Data Mode with When the units enter DataMode it is possible to
511/511E Pattern turn on the 511/511E pattern generators on
Generators both ends of the link. Once a 511/511E pattern
is selected on one end of the link, the pattern
generator will begin transmitting unframed
511/511E through the line to the Remote end. A
possible problem with this test can occur due to
the Restart procedure. Once the Local 511/511E
is turned on, the Remote unit begins receiving
an unframed 511 pattern. If the Remote unit
does not turn on the 511/511E-pattern generator
within 4 seconds, the Remote unit will Restart
and enter the StartUp mode. Note that once the
511/511E-pattern generator is started the
Restart timer is changed to one minute (only on
the unit which has the pattern enabled). If both
units enable the 511/511E pattern within 4 seconds of each other, both units will be transmitting and receiving the 511/511E pattern. Both
framers are now receiving unframed data and
will restart after one minute. The 511/511E pattern generators will TimeOut after 45 seconds
re-enabling the normal data path. The ER led
will begin flashing until the user terminates the
test.
Figure 18. Block Diagram DataMode with 511/511E
Pattern
Gen/Det
Loop
Contr
ol
Loop
Contro
l
Pattern
Gen/Det
Processor
Processor
Framer
Framer
Line
Page 14

Using the V.52 (BER) Test Pattern Generator
To use the V.52 BER tests in conjunction with the Remote Digital
Loopback tests (or with Local Line Loopback tests), follow these
instructions:
1. Locate the “511/511E” toggle switch on the front panel of the
Compact mDSL Modem and move it UP. This activates the
V.52 BER test mode and transmits a “511” test pattern into the
loop. If any errors are present, the local modem’s red “ER”
LED will blink sporadically.
2. If the above test indicates no errors are present, move the
V.52 toggle switch DOWN, activating the “511/E” test with
errors present. If the test is working properly, the local
modem's red “ER” LED will glow. A successful “511/E” test
will confirm that the link is in place, and that the Compact
mDSL Modem built-in “511” generator and detector are work
ing properly.
NOTE: The above V.52 BER tests can be used independently
of the Remote Digital Loopback tests. This requires two operators: (1) to initiate and monitor the tests at the local Compact
mDSL Modem, and (2) to do the same at the remote Compact
mDSL Modem. In this case, the test pattern sent by each
Compact mDSL Modem will not be looped back, but will be
transmitted down the line to the other Compact mDSL Modem.
While one operator initiates test, the other monitors for errors.
25
Compact mDSL Modem
26
Compact mDSL Modem
APPENDIX A
BLACK BOX COMPACT MDU9705A-V35
AND MDU9705A-X21 SPECIFICATIONS
Clocking Modes: Internal, External, or Receive Recovered
DTE Rate: All 64k steps from 64 to 2304 kbps
DTE Interface: V.35 (Compact mDSL Modem), DCE
Orientation;
X.21 (Compact mDSL Modem), DCE or
DTE Orientation depending upon orientation
of pc-board mounted daughter board
DTE Connector: M/34 Female (Compact mDSL Modem)
D-Sub-15 Female (Compact mDSL
Modem)
Diagnostics: V52 compliant (511/511E) pattern generator
and detector with error injection mode controlled by front panel switch, Local and
Remote Loopback control by either a front
panel switch or from the DTE interface
LED Status: The following LEDs are displayed on the
front panel:
DSL Link (Green Active) - DSL Link Active
TD, RD (Yellow/Green) - Idle Yellow
NS (Red Active) - No signal DSL Link
ER (Flashing Red) - CRC error during nor-
mal operation, bit error during pattern generation test
TM (Active Yellow) - Test Mode Enabled
Configuration: Externally accessible dip switches or SNMP
managed through mDSL Rack Card
Power: +5 VDC external desk top power supply, 90-
260VAC, 50-60 Hz (Universal Input), 10W
or -48 VDC
Compliance: FCC Part 15, CE, CTR1
Transmission Line: Single Twisted Pair
Line Coding: CAP (Carrierless Amplitude and Phase
Modulation
Line Rates (DSL line): 144, 272, 400, 528, 784, 1040, 1552, 2064,
2320 kpbs
Line Interface: Transformer coupled, 1500 VAC isolation
mDSL Physical
Connection: RJ-45, 2 wire, polarity insensitive pins 4
and 5
Environment: Operating temperature 0-50°C; humidity 5-
95% non-condensing; altitude, 0-15, 000
feet (0-4600 m)
Page 15

APPENDIX B
BLACK BOX MDU9705A-V35
INTERFACE PIN ASSIGNMENTS
V.35 INTERFACE
(M/34 Female Connector)
(DCE Orientation)
Pin #
Signal
B ...........................SGND (Signal Ground)
C ...........................RTS (Request to Send) (DTE Source)
D ...........................CTS (Clear to Send) (DCE Source)
E ...........................DSR (Data Set Ready) (DCE Source)
F............................CD (Carrier Detect) (DCE Source)
H ...........................DTR (Data Terminal Ready) (DTE Source)
L............................LLB (Local Line Loop) (DTE Source)
M...........................TM (Test Mode) (DTE Source)
N ...........................RDL (Remote Digital Loop) (DTE Source)
P ...........................TD (Transmit Data) (DTE Source)
R ...........................RD
(Receive Data) (DCE Source)
S ...........................TD/ (Transmit Data-B) (DTE Source)
T............................RD/ (Receive Data-B) (DCE Source)
U ...........................XTC (External Transmit Clock) (DTE
.....................................Source)
V ...........................RC(Receiver Clock) (DCE Source)
W...........................XTC/ (External Transmit Clock) (DTE
.....................................Source)
X ...........................RC/ (Receiver Clock) (DCE Source)
Y ...........................TC (Transmitter Clock-A) (DCE Source)
AA ..........................TC/ (Transmit Clock-B) (DCE Source)
27
Compact mDSL Modem
Compact mDSL Modem
APPENDIX C
BLACK BOX MDU9705A-X21
INTERFACE PIN ASSIGNMENTS
X.21 INTERFACE
(D-Sub-15 Female Connector)
(DTE /DCE Orientation)
Pin #
Signal
1 ......................Frame Ground
2 ......................T (Transmit Data-A) (DTE Source)
3 ......................C (Control-A) (DTE Source)
4 ......................R (Receive Data-A) (DCE Source)
5 ......................I (Indication-A) (DCE Source)
6 ......................S (Signal Element Timing-A) (DCE
........................Source)
7 ......................BT (Byte Timing-A) (DCE Source)
8 ......................SGND (Signal Ground)
9 ......................T/ (Transmit Data-B) (DTE Source)
10 ......................C/ (Control-B) (DTE Source)
11......................R/ (Receive Data-B) (DCE Source)
12 ......................I/ (Indication-B) (DCE Source)
13 ......................S/ (Signal Element Timing-B) (DCE
........................Source)
14 ......................BT/ (Byte Timing-B) (DCE Source)
Page 16

APPENDIX E
BLACK BOX COMPACT MDU9705A-V35
AND MDU9705A-X21
TRANSMISSION DISTANCE CHART
Copyright ©2000
Black Box Company
All Rights Reserved
Line Rate DTE Rates
kbps feet miles km feet miles km
144 64, 128 21400 4.0 6.6 30700 5.8 9.4
272 192, 256 20300 3.8 6.2 30600 5.8 9.4
400 320, 384 18600 3.5 5.7 29100 5.5 9
528 448, 512 17400 3.3 5.4 26100 4.9 8.0
784 576, 640, 704, 768 15800 3.0 4.9 22600 4.3 7.0
1040 832, 896, 960, 1024 15500 2.9 4.8 22100 4.2 6.8
1552 1088 - 1536 13600 2.6 4.2 19200 3.6 5.9
2064 1600 - 2048 12200 2.3 3.8 17200 3.3 5.3
2320 2112 - 2304 11500 2.2 3.5 15800 3.0 4.9
Line Rate DTE Rates
kbps feet miles km feet miles km
144 64, 128 16992 3.2 5.2 25000 4.7 7.7
272 192, 256 15088 2.9 4.6 22000 4.2 6.8
400 320, 384 13264 2.6 4.2 20000 3.8 6.2
528 448, 512 12300 2.3 3.8 18000 3.4 5.5
784 576, 640, 704, 768 10216 1.9 3.1 14000 2.6 4.3
1040 832, 896, 960, 1024 8417 1.6 2.6 12000 2.3 3.7
1552 1088 - 1536 7107 1.3 2.2 10000 1.9 3.1
2064 1600 - 2048 5920 1.1 1.8 8000 1.5 2.5
2320 2112 - 2304 5416 1.0 1.7 73000 1.4 2.2
Cross Talk (49 adjacent CAP pairs)
26 AWG (0.4mm)
24 AWG (0.5mm)
No Cross Talk
26 AWG (0.4mm)
24 AWG (0.5mm)
Transmission Distance - Black Box Compact mDSL Modem
29
Compact mDSL Modem
30
Compact mDSL Modem
 Loading...
Loading...