Page 1
TECHNICAL:
SALES:
FAX:
ADDRESS:
(0118) 965 6000
(0118) 965 5100
(0118) 965 5001
464 Basingstoke Road, Reading, Berkshire RG2 0QN
www.blackbox.co.uk
Compact mDSL Modem
464 Basingstoke Road, Reading, Berkshire RG2 0QN
© Copyright 2000. Black Box Catalogue, Ltd.
MDU9705A-10BT
August 2000
Page 2

Table of Contents
Section Page
Radio and TV Interference.....................................................2
CE Notice...............................................................................2
General Information...............................................................3
Features
Description
PPP Operational Background..............................................4
Configuration.......................................................................6
Plug-and-Play
Configuring the Hardware DIP Switches
Configuration DIP Switch Set “S2”
Configuration DIP Switch Set “S3”
Installation...........................................................................12
Connecting DSL Interface
Connecting 10BaseT Ethernet Port to PC (DTE)
Connecting 10BaseT Ethernet Port to Hub (DCE)
Power Connection
Operation.............................................................................15
Power-Up
LED Status Monitors
LED Descriptions Table
Test Modes
Appendix A - Specifications........................................................21
Appendix B - Transmission Distance Chart................................22
Black Box Contact Information....................................................23
Radio and TV Interference
The Compact mDSL Modem generates and uses radio frequency
energy, and if not installed and used properly—that is, in strict accordance with the manufacturer's instructions—may cause interference to
radio and television reception. The Compact mDSL Modem has been
tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A computing
device in accordance with the specifications in Subpart J of Part 15 of
FCC rules, which are designed to provide reasonable protection from
such interference in a commercial installation. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If
the Compact mDSL Modem does cause interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by disconnecting the unit, the
user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of
the following measures: moving the computing equipment away from
the receiver, re-orienting the receiving antenna and/or plugging the
receiving equipment into a different AC outlet (such that the computing
equipment and receiver are on different branches).
CE Notice
The CE symbol on your Black Box equipment indicates that it is in
compliance with the Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) directive and
the Low Voltage Directive (LVD) of the European Union (EU). A
Certificate of Compliance is available by contacting Technical Support.
1
Compact mDSL Modem
2
Compact mDSL Modem
Page 3
3
Compact mDSL Modem
PPP Operational Background
PPP is a protocol used for multi-plexed transport over a
point-to-point link. PPP operates on all full duplex media, and is
a symmetric peer-to-peer protocol, which can be broken into
three main components: 1. A standard method to encapsulate
datagrams over serial links; 2. A Link Control Protocol (LCP) to
establish, configure, and test the data-link connection; 3. A family
of Network Control Protocols (NCPs) to establish and configure
different network layer protocols.
In order to establish communications over a point-to-point
link, each end of the PPP link must first announce its capabilities
and agree on the parameters of the link’s operation. This
exchange is facilitated through LCP Configure-Request packets.
Once the link has been established and optional facilities
have been negotiated, PPP will attempt to establish a network
protocol. PPP will use Network Control Protocol (NCP) to
choose and configure one or more network layer protocols.
Once each of the network layer protocols have been configured,
datagrams from the established network layer protocol can be
sent over the link. The link will remain configured for these communications until explicit LCP or NCP packets close the link
down, or until some external event occurs.
The PPP Bridging Control Protocol (BCP), defined in RFC
1638, configures and enables/disables the bridge protocol on
both ends of the point-to-point link. BCP uses the same
packet exchange mechanism as the Link Control Protocol
(LCP). BCP is a Network Control Protocol of PPP, bridge
packets may not be exchanged until PPP has reached the
network layer protocol phase.
Applications
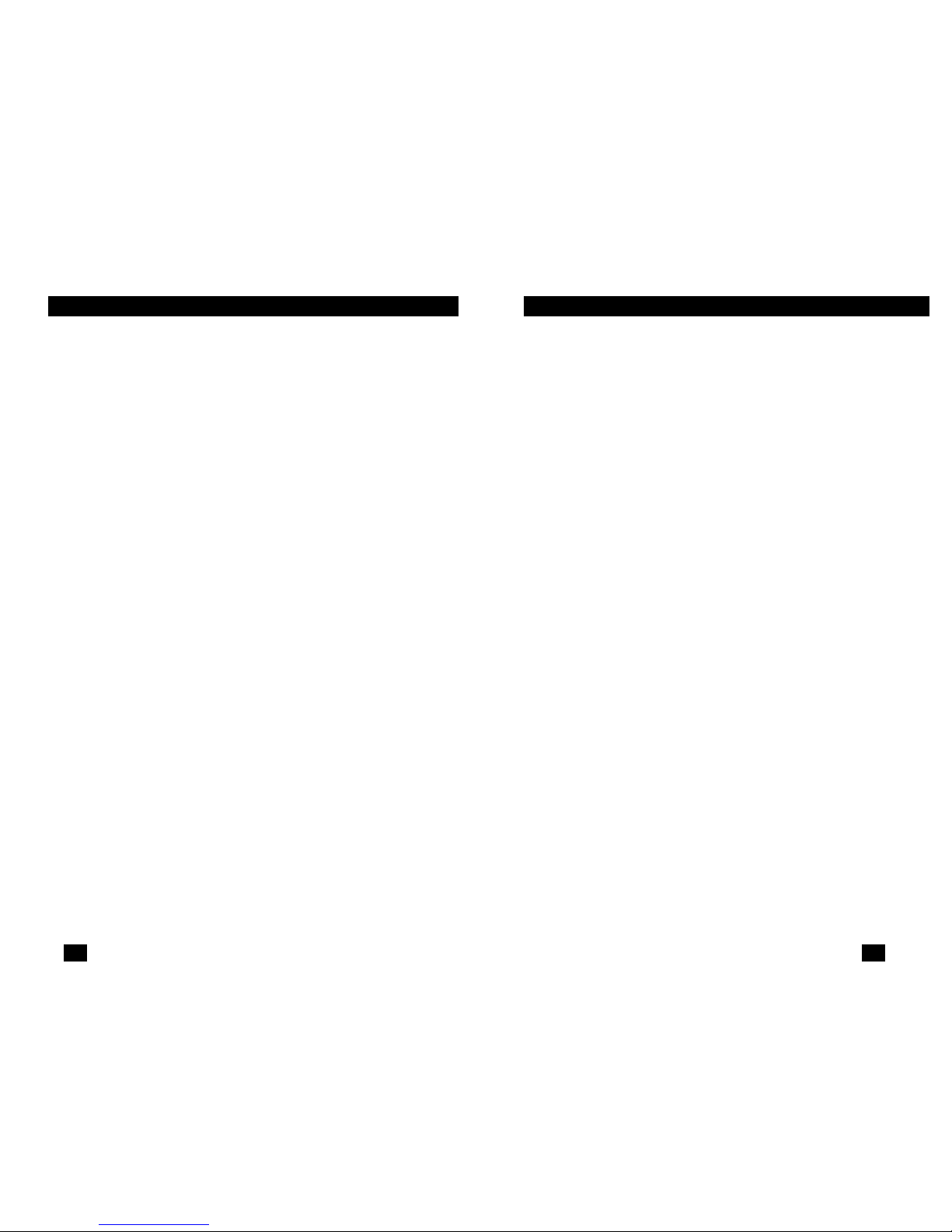
In situations where a routed network requires connectivity
to a remote Ethernet network, the interface on a router can
be configured as a PPP IP Half Bridge. The serial line to the
remote bridge functions as a Virtual Ethernet interface, effectively extending the routers serial port connection to the
remote network. The bridge device sends bridge packets
(BPDU's) to the router's serial interface. The router will
receive the layer three address information and will forward
these packets based on its IP address.
Figure 1 shows a typical Cisco router with a serial interface
configured as a PPP Half Bridge. The router serial interface uses
a remote device that supports PPP bridging to function as a node
on the remote Ethernet network. The serial interface on the
Cisco will have an IP address on the same Ethernet subnet as
the bridge.
Compact mDSL Modem
4
General Information
Thank you for your purchase of this Black Box product. This product has
been thoroughly inspected and tested and is warranted for One Year parts and
labor.
Features
• Provides MAC Level Data Link (Layer 2) connection between two peered
10BaseT Ethernet LANs
• Operates transparently to higher level protocols such as TCP/IP, DECnet,
NETBIOS and IPX
• PPP (Point to Point Protocol, RFC 1661) with Bridge Control Protocol
(RFC 1638)
•Automatically learns, loads and removes MACaddresses
•Point-to-Point Connectivity over 2-Wire mDSL up to 10km
• Plug-and-Play Slave
• HTTP/SNMP Manageable as CP (Customer Premises) Unit with mDSL
CO (Central Office) Rack Card
• Internal or receive recovered clocking between units
• LEDindicators for 10BaseT Link, DSL Link, Status, No Signal, Error and
Test Mode
Description
The Compact10BaseT mDSL Modemis a Multi-Rate DSL Modem that
provides seamless MAC Layer connectivity between 2 peered 10BaseT LANs.
Now, Enterprise users no longer need to hassle with a bridge anda CSU/DSU
or recurring leased line costs. The Compact mDSL Modem allows users to
add additional nodes to a LAN that has reached its maximum distance limits or
separate high traffic areas of a LAN. The Compact mDSL Modem connects
peered LANs and automatically forwards and receives LAN broadcasts, multicasts and frames across a 2-Wire DSL span. The Compact mDSL Modemsupports PPP (RFC 1661) and BCP (RFC 1638).
The Compact10BaseT mDSL Modem features include loopback diag-
nostics, inband SNMP/HTTP remote management capabilities using Plug-andPlay and externally accessible configuration switches. As a symmetric DSL
modem, the CompactmDSL Modemoffers the same data rates in both direc-
tions over a single pair of regular telephone lines using Carrierless Amplitude
and Phase (CAP) modulation. The Compact mDSL Modem connects to the
DSL line via an RJ-45 jack. Standard power options include 115VAC, 230VAC,
Universal (115/230VAC) and any DC input between 36-60VDC.
Page 4
Compact mDSL Modem
Configuration
There are two modes of operation for the Compact mDSL Modem:
Plug-n-Play and self configuration. Both are described below.
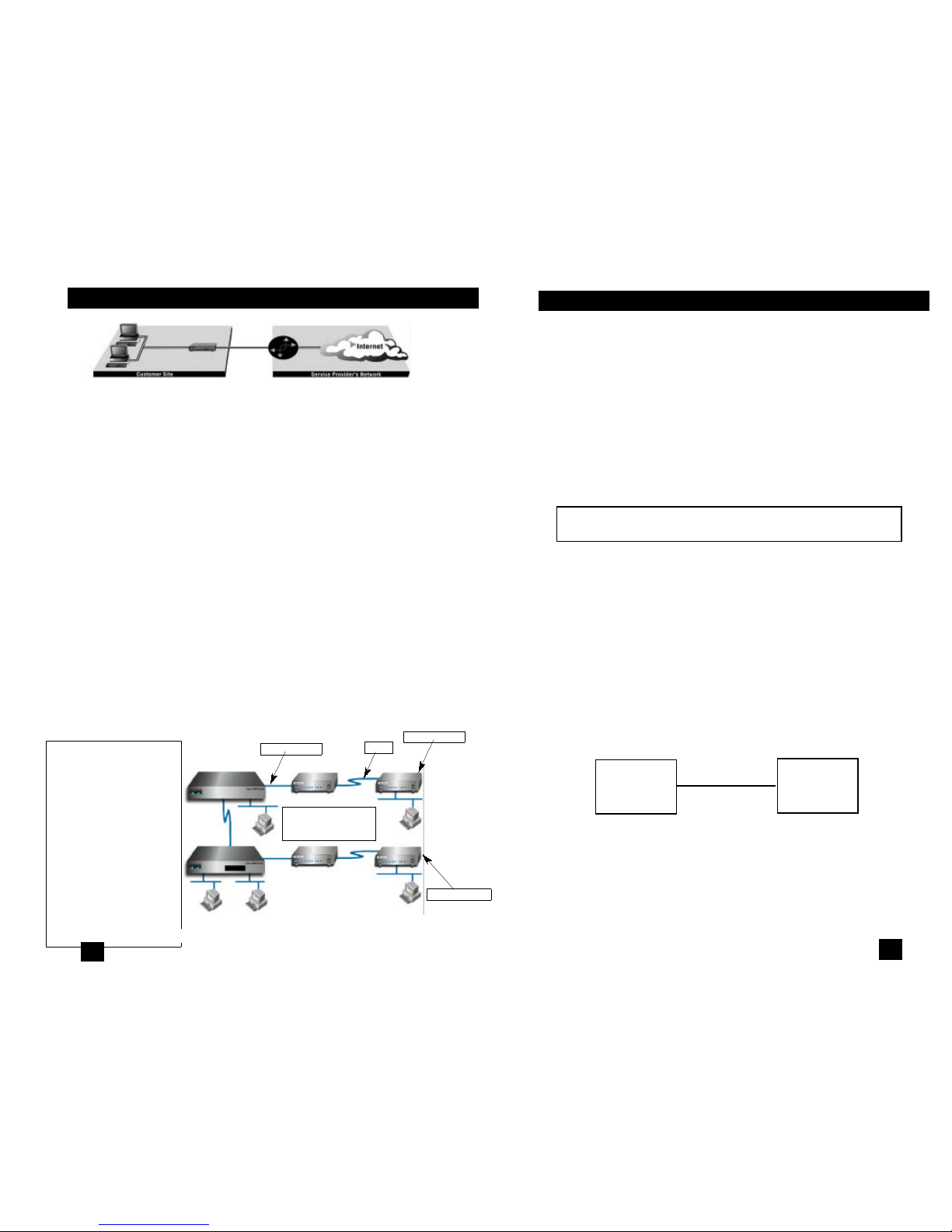
Plug-n-Play
The Plug-and-Play feature allows ISPs, carriers and PTTs to
quickly upgrade the link speed for a customer without requiring a truck
roll to configure the Customer Premise (CP) Compact mDSL Modem.
This feature also allows service providers to set up all of the configurations at the Central Office (on the rack cards) before installing the
stand alone units, saving time spent configuring or re-configuring DIP
switches.
The Plug-n-Play feature allows the user to configure the DTE rate
(bandwidth allocation, see Switches S3-1 through S3-6) of the CP unit
from the rack card at the Central Office (CO). The stand alone unit at
the Customer Premise (CP) site will automatically configure itself to the
DTE rate (Bandwidth Allocation) of the rack card. Other configuration
parameters remain in the default setting.
Follow the instructions below to activate Plug-n-Play between CO
(mDSL Rack Card) and CP (Compact mDSL Modem) units:
1. Set the mDSL Rack Card (CO) to either Internal or External
clocking mode as defined by the application.
2. Set the Compact mDSL Modem (CP) to “Plug-and-Play CP”
by setting all S2 and S3 DIP switches in the OFF position as
described in Figure 3, below.
When the CO and CP units connect over DSL, the CP will enter a
predefined default configuration (Receive Recovered Clocking). During
the negotiation process between the units, the CO unit will configure
the DTE rate/line rate on the CP unit as defined by the settings of the
CO unit. When additional bandwidth is required, only the configuration
For example, the customer site is assigned the addresses
192.168.1.0/24 through 192.168.1.1/24. The address
192.168.1.1/24 is also the default gateway for the remote network. The above settings remove any routing/forwarding intelligence from the CPE. The associated Cisco configuration will
set serial interface (s0) to accommodate half bridging for the
above example.
Authentication is optional under PPP. In a point-to-point
leased-line link, incoming customer facilities are usually fixed
in nature, therefore authentication is generally not required. If
the foreign device requires authentication via PAP or CHAP,
the PPP software will respond with default Peer-ID consisting
of the units Ethernet MAC address and a password which
consists of the unit’s Ethernet MAC address.
Some networking systems do not define network numbers
in packets sent out over a network. If a packet does not have
a specific destination network number, a router will assume
that the packet is set up for the local segment and will not forward it to any other sub-network. However, in cases where
two devices need to communicate over the wide-area, bridging can be used to transport non-routable protocols.
Figure 2 illustrates transparent bridging between two
routers over a serial interface (s0). Bridging will occur
between the two Ethernet Interfaces on Router A (e0 and e1)
and the two Ethernet Interfaces on Router B (e0 and e1).
Black Box
MDU9705A-10BT
Ethernet LAN
PEC Device w/ Serial I/F
Router
Figure 1.
Cisco router with serial interface, configured as PPP Half Bridge.
!
no ip routing
!
interface Ethernet0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
bridge-group 1
!
interface Serial0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
encapsulation PPP
bridge-group 1
!
interface Serial1
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
bridge-group 1
!
bridge 1 protocol ieee
!
Router A
Router B
e0
e0S1e1
S1
S0
S0
LAN
LAN
LAN
LAN
LAN
Serial Interface
Using Bridge-Groups, multiple remote LANs can be
bridged over the wide-area.
MDU9705A-10BT
MDU9705A-10BT
mDSL
Figure 2. Transparent bridging between two routers over a serial interface.
Compact mDSL Modem
5
6
NOTE: Plug-and-Play is only available when using a rack-
mounted mDSL Rack Card as the CO unit.
Compact
mDSL Modem
(CP)
DIP Switches all in OFFposition
DIP Switches or NMS configured
according to specific application
requirements
Figure 3. Typical Plug-and-Play Application
DSL Span
mDSL
Rack Card
(CO)
Page 5

of the CO unit should be changed. This feature gives ISPs, LECs and
PTTs the ability to provision bandwidth on an as needed basis to customers.
The Plug and Play application will also work in an HTTP/SNMP
managed system using the by deploying a SNMP Management Module
agent card with mDSL Rack Cards installed in Black Box’s 2U Access
Rack system. In this application, the system administrator can configure the entire rack through the Network Management Station (NMS)
before the stand alone (CP) units are installed. For more information
on the HTTP/SNMP management, please refer to the SNMP
Management Module Operations Manual.
Compact mDSL Modem
7
Configuring the Hardware DIP Switches
The Compact mDSL Modem has two sets of eight DIP switches,
which allow configuration for a wide variety of applications. This section describes switch locations and explains all settings.
The 16 external switches are grouped into two eight-switch sets,
and are externally accessible from the underside of the Compact
mDSL Modem, as shown in Figure 4, below.
The two sets of DIP switches on the underside of the Compact
mDSL Modem will be referred to in this manual as S2 and S3. As
Figure 5 shows, the orientation of all DIP switches is the same with
respect to “ON” and “OFF” positions.
OFF
ON
FRONT
REAR
Figure 4.Underside of Compact mDSL Modem, showing location of DIP switches
S2
S3
ON
OFF
Figure 5. Close Up of Configuration Switches (all sets are identical in appearance)
Compact mDSL Modem
8
Page 6

Configuration DIP Switch Set “S2”
The only setting for S2 is for Clocking Mode between the Compact
mDSL Modems. All other switches are reserved for factory usage and
must remain in the default configuration. Default settings are shown in
the table below.
Switch S2-1, S2-2, S2-3, S2-4, S2-5 and S2-8:
Switches S2-1, S2-2, S2-3, S2-4, S2-5 and S2-8 are reserved for factory use and must remain in the factory default settings as shown in
the table above.
Switches S2-6 and S2-7: Clock Mode
Use Switches S2-6 and S2-7 to configure internal, or receive
recover (clocking derived from the remote Compact mDSL Modem
across the DSL span) settings. One Compact mDSL Modem (typically
the CO, or “Central Office” unit) will be set for Internal Clock. The
remote Compact mDSL Modem (typically the CP, or Customer
Premises unit) will be set for Receive Recover clocking. See table
below.
9
Compact mDSL Modem
10
Compact mDSL Modem
Configuration DIP Switch Set “S3”
Use the DIP Switches in Switch S3 to set the DTE Rate (for LAN
Bandwidth Allocation), the transmit data sampling point and to reset
the unit to its software default settings. The following table summarizes default positions of DIP Switch S3. Detailed descriptions of each
switch follow the table.
Switch S3-1 through S3-6: DTE Rate
Use Switch S3-1 through S3-6 to provision bandwidth to the LAN
in 64kbps increments up to 2.304Mbps. Peak bandwidth utilization on
the local domain on an Ethernet LAN runs typically between 15% to
20% (1.5Mbps to 2Mbps) of the maximum bit rate of 10Mbps. Traffic
between LANs typically runs even lower -- between 2% to 7%
(200kbps to 700kbps) of the maximum bit rate depending upon application and environmental conditions. This is the amount of traffic that
will run across the DSL span.
Set Switches 3-1 through S3-6 to allocate bandwidth based upon
expected LAN to LAN traffic rates. As an example, set applications
with low LAN to LAN bandwidth content between 64kbps and 576kbps.
Applications with high bandwidth LAN to LAN content should be set
between 576kbps and 2.304Mbps as required.
S3-1S3-2S3-3S3-4S3-5S3-6 DTE Rate (kbps)
OffOffOnOnOnOn 64
OnOnOffOnOnOn 128
OffOnOffOnOnOn 192
OnOffOffOnOnOn 256
OffOffOffOnOnOn 320
OnOnOnOffOnOn 384
OffOnOnOffOnOn 448
OnOffOnOffOnOn 512
CO/CP
UnitS2-6S2-7 Clock Mode Description
Compact mDSL Modem
generates internal,
CO On On Internal crystal controlled timing.
Compact mDSL Modem
CP On OffReceive Recoverreceives its timing
from the CO unit
over the DSL span.
Position Function
S2-1 Reserved
S2-2 Reserved
S2-3 Reserved
S2-4 Reserved
S2-5 Reserved
S2-6 Clock Mode On
S2-7 Clock Mode Off
S2-8 Reserved
Off
Off
Off
S2 SUMMARY TABLE
Factory Default
Off
Off
Off
Receive
Recover
S3 SUMMARY TABLE
Position Function Factory Default
S3-1 DTE Rate On
S3-2 DTE Rate Off
S3-3 DTERate Off
S3-4 DTE Rate Off
S3-5 DTE Rate On
S3-6 DTE Rate On
S3-7 Reset Software DefaultsOn
Normal Operation
S3-8
Reserved
On
}
768 kbps
Page 7

OffOffOnOffOnOn 576
OnOnOffOffOnOn 640
OffOnOffOffOnOn 704
OnOffOffOffOnOn 768
OffOffOffOffOnOn 832
OnOnOnOnOffOn 896
OffOnOnOnOffOn 960
OnOffOnOnOffOn 1024
OffOffOnOnOffOn 1088
OnOnOffOnOffOn 1152
OffOnOffOnOffOn 1216
OnOffOffOnOffOn 1280
OffOffOffOnOffOn 1344
OnOnOnOffOffOn 1408
OffOnOnOffOffOn 1472
OnOffOnOffOffOn 1536
OnOnOffOffOffOn 1600
OffOnOffOffOffOn 1664
OnOffOffOffOffOn 1728
OffOffOffOffOffOn 1792
OnOnOnOnOnOff 1856
OffOnOnOnOnOff 1920
OnOffOnOnOnOff 1984
OffOffOnOnOnOff 2048
OnOnOffOnOnOff 2112
OffOnOffOnOnOff 2176
OnOffOffOnOnOff 2240
OffOffOffOnOnOff 2304
Switch S3-7: Reset Software Defaults
Use Switch S3-7 to reset the software configured factory defaults.
This feature is applicable only using the SNMP Management Module to
SNMP through the mDSL Modem central office to manage your units.
For more information, please refer to the SNMP Management Module
Operations Manual.
S3-7 Setting
On Normal Operation
Off Reset
Switch S3-8: Reserved
Switch S3-8 is reserved for factory use and must remain in the On
position.
Installation
When the Compact mDSL Modem has been properly configured, it
may be connected to the DSL twisted pair interface, the 10BaseT
Ethernet Interface, and the power source. This section describes
these connections.
Connecting DSL Interface
The MDU9705A-10BT supports communication between 10BaseT
Hubs or Workstations at distances to 5 miles (8 km) over 24 AWG
(.5mm) twisted pair wire. There are two requirements for installing the
Compact mDSL Modem:
1. These units operate as a pair. Both units at the end of the
twisted pair DSL span must be set for the same DTE rate.
2. To function properly, the Compact mDSL Modem needs one
twistedpair of metallic wire. This twisted pair must be
unconditioned, dry, metallic wire, between 19 (.9mm) and 26
AWG (.4mm) (the higher number gauges will limit distance).
Standard dial-up telephone circuits, or leased circuits that run
through signal equalization equipment, or standard, flat modular telephone type cable, are not acceptable.
The RJ-45 connector on the Compact mDSL Modem’s twisted pair
interface is polarity insensitive and is wired for a two-wire interface.
The signal/pin relationships are shown in Figure 6 below.
NOTE: The Compact mDSL Modem will automatically select
the optimum line rate for the required distance based on the DTE
rate set by Switches S3-1 through S3-6. This selection is based
on the lowest line rate that will support the DTE rate.
12
Compact mDSL Modem
11
Compact mDSL Modem
Figure 6.Compact mDSL Modem twisted pair lineinterface.
1 (N/C)
2 (N/C)
3 (N/C)
4 (2-Wire TIP)
5 (2-Wire RING)
6 (N/C)
7 (N/C)
8 (N/C)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
DSL
Interface
10BaseT
Interface
Page 8

Connecting 10Base-T Ethernet Port to PC (DTE)
The 10Base-T interface is configured as DTE (Data Terminal
Equipment). If the Compact mDSL Modemis to connect to another
DTE device such as a 10Base-T network interface card, construct a
10Base-T crossover cable and connect the wires as shown in the diagram below.
10BaseT Port 10Base-T DTE
RJ-45 Pin No. RJ-45 Pin No.
1 (TD+) 1 (TD+)
2 (TD-) 2 (TD-)
3 (RD+) 3 (RD+)
6 (RD-) 6 (RD-)
Connecting 10Base-T Ethernet Port to Hub (DCE)
The 10Base-T interface is configured as DTE (Data Terminal
Equipment), just like a 10Base-T network interface card in a PC.
Therefore, it “expects” to connect to a 10Base-T Hub using a straightthrough RJ-45 cable. Use the diagram below to construct a cable to
connect the 10 BaseT interface to a 10Base-T Hub.
10BaseT Port 10Base-T Hub
RJ-45 Pin No. RJ-45 Pin No.
1 (TD+) 1 (RD+)
2 (TD-) 2 (RD-)
3 (RD+) 3 (TD+)
6 (RD-) 6 (TD-)
13
Compact mDSL Modem
14
Compact mDSL Modem
Power Connection
Universal ACPower (100-240VAC)
The Compact mDSL Modem uses a 5VDC, 2A universal input
100-240VAC, power supply (center pin is +5V). The universal input
power supply has a male IEC-320 power entry connector. This power
supply connects to the Compact mDSL Modem by means of a barrel
jack on the rear panel. Many international power cords are available
for the universal power supply.
The Compact mDSL Modem powers up as soon as it is plugged
into an AC outlet. The Compact mDSL Modem does not have a power
switch.
120 VAC Power (US)
The 100-132VAC adapter supplied with the U.S. version of the
Compact mDSL Modem is a wall mount type and may be plugged into
any approved 120 VAC wall jack.
230 VAC Power (International)
The 230VAC adapter supplied with the International version of the
Compact mDSL Modem is a wall mount type and may be plugged into
any approved 230 VAC wall jack.
DC Power
The 36-60VDC DC to DC adapter supplied with the DC version of
the Compact mDSL Modem plugs in a DC source (nominal 48VDC)
and plugs into the barrel power supply jack on the rear of the
MDU9705A-10BT. Please refer to Figure 8, below, to make the proper
connection.
1 TD+(data output from mDSL Modem)
2 TD- (data output from mDSL Modem)
3 RD+ (data input to mDSL Modem)
4 (no connection)
5 (no connection)
6 RD- (data input to mDSL Modem)
7 (no connection)
8 (no connection)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Figure 7.mDSL Modem 10BaseT Ethernet RJ-45 Connector Pinout
WARNING!There are no user-serviceable parts in the
power supply section of the MDU9705A-10BT.
Figure 8.Connecting DC Power to the 48VDC Power Supply.
-Vin
To Power
Supply Jack
To -48VDC
Source
+Vin
Page 9

Operation
When the Compact mDSL Modem has been properly configured
and installed, it should operate transparently. This sections describes
power-up, LED status monitors, and the built-in loopback test modes.
Power-Up
Before applying power to the Compact mDSL Modem, please read
the Power Connectionsectionand ensurethat the unit is connected
to the appropriate power source.
LED Status Monitors
The Compact mDSL Modem features six front panel LEDs that
monitor connections on the DSL and 10BaseT links, signaling, error
and test modes. Figure 9 (below) shows the front panel location of
each LED. Descriptions of each LED follow Figure 9.
DSL Link(Active Green) Solid green (On) indicates that the
end to end DSL Framer Link is up, signifying that
the link across the DSL span is active. The DSL
Link LEDis Off when the link is down.
Status Blinks yellow from one to eleven times to indicate
system status. Each pulse pattern is separated by
a 2 second “off” period. Greater pulse patterns
have higher priority (buffer saturation has greater
priority than an empty MAC table). Valid system
statuses are:
1 pulse = system status is okay
2 pulses = no MAC entries in the MAC
Address Table
3 pulses = Clear to Send (CTS) or Carrier
Detect (DCD) from base unit are not
asserted
4 pulses = IM1/I buffer is saturated
5 pulses = WAN receive frame(s) too large
6 pulses = WAN receive frame(s) not octet
aligned
7 pulses = WAN receive frame(s) aborted
8 pulses = Detected WAN receive frame(s) with
15
Compact mDSL Modem
16
Compact mDSL Modem
CRC
9 pulses = Detected LAN receive frame(s) too
large
10 pulses = Detected LAN receive frame(s) not
octet aligned
11 pulses = Detected LAN receive frame(s) with
bad CRC
10BT Link(Active Green) Solid green indicates that the
10BaseT Ethernet interface has detected a valid
SQE heartbeat, signifying a valid 10BaseT connection.
NS (Active Red) Solid red indicates that the Digital
Signal Processors (DSPs) are not linked.
ER (Active Red) Flashing red indicates CRC Errors on
DSL (Framer) side if DSL Link is active or if bit
errors are received during loop/BER test.
- ER flashes once to indicate a CRC error (during
normal operation) or bit errors (during Remote
Loopback 511/511E tests).
TM (Active Yellow) Solid Yellow indicates an Active
Test Mode. The unit may be placed in test mode
by the local user or by the remote user.
LED Descriptions Table
Link Brk = DSL Link Broken
Brk+10s = 10 Seconds following Link Break
G=GREEN
O=ORANGE
ON= ON
off= OFF
F=Flashing
G*=Green if a valid 10Base-T connection is detected.
Figure 9.Compact mDSL Modem Front Panel
Link
DSL
10BT
ERNS
Status
TM
-511E/RDL
-Normal
-511/RDL
Compact mDSL Modem - 10BaseT
LOCAL REMOTE
10BaseT DSL Status NS ER TM 10Base-T DSL Status NS ER TM
Power ON G* off F ON off off G* off F ON off off
DSL Link G* G F off off off G* off F off off off
Link Brk G* off F off off off G* off F off off off
Brk+ 10s G* off F ON off off G* off F ON off off
RDL G* G F off off ON G* off F off off ON
RDL+511 G* off F off off ON G* off F off off ON
With DTE Connected With DTE Connected
Mark G* G F off off off G* G F off off off
Space G* G F off off off G* G F off off off
Data G* G F off off off G* G F off off off
Page 10

Test Modes
The Compact mDSL Modem offers a proprietary Remote
Loopback test modes, plus a built-in V.52 BER test pattern generator
to evaluate the communication status between units. Activate this test
mode by toggling the Test Mode Switch on the front panel of the unit.
Overview
Figure 10 below shows the major elements used in the loop-back
and 511 pattern tests available in the Compact mDSL Modem. Each
block has several functions. Following Figure 10 are descriptions of the
elements during Test Modes.
Framer The framer determines the status of the line. In
normal operation the framer transmits and
expects to receive framed packets from the far
end. If the framer receives framed packets from
the far end, the DSL Link LED will turn on. If
framed packets are not received, the DSL Link
LED will turn off. The restart procedure uses this
information to determine if a valid connection is
made (cable disconnect, poor cable quality, etc).
In normal Data Mode, if the box receives 4 seconds of unframed packets it will restart the box
and begin trying to re-establish a connection
with the the remote Compact mDSL Modem.
The distinction between framed packets and
unframed packets becomes important when we
discuss the Pattern Generator.
Pattern Gen/DetThis part of the Processor generates and
detects the 511/511E patterns. When transmitting 511 patterns, the information is unframed
(because it originates after the framer) and is
17
Compact mDSL Modem
18
Compact mDSL Modem
intended to be evaluated only by another Processor.
If the units are transmitting data and the pattern gen
-
erator is enabled on one end of the link, the far end
will begin receiving unframed packets and assume
that the line has gone down. During test modes, the
pattern generator is forced to time out before it can
cause the DSL link to go down.
Loop Control This part of the Processor is used to control Remote
Loopback test mode. In a Remote Loop, the
511/511/Edata is looped back to the line and to the
remote unit over the DSL span.
Restart ProcedureThe restart procedure is in place to allow the
and Time Outs units to re-establish a connection after the framer
begins seeing unframed packets. The Test Mode
Timing Chart below shows the amount of time the
framer must see consecutive unframed packets
before the unit will restart and try to establish a new
line connection. The reason that there are different
Restart Times will become apparent after reading the
rest of the document. The 511/511E Time Out shown
refers to the amount of time the 511/511E pattern will
be valid. At the end of this time the pattern will auto
-
matically turn itself off and the normal data path will
be re-established. The ER led will flash indicating to
the user that the test has timed out. The ER led will
stop flashing once the 511/511E switch is placed into
the normal position.
Symbol Indicators
This symbol designates the origination or the termination of a data path. The direction of the arrow con
-
nected distinguish the two data paths.
This symbol designates an invalid data path. If there
is data present it should be ignored.
Pattern
Gen/Det
Loop
Contr
ol
Loop
Contro
l
Pattern
Gen/Det
Processor
Processor
Framer
Framer
DSL
Span
Figure 10: Block Diagram- Two Compact mDSL Modems Communicating Over the DSL Span
Test Mode Timing
Item Elapsed Time (seconds)
Start Up 50
Data Mode 4
511/511E Generator Enabled 60 (The generator will stop after 45 seconds.)
Remote End of an RDL 60
511/511E Time Out 45 (The pattern generator will automatically turn
off after 45 seconds. The ER LED will flash until
the user turns off the 511/511E switch.)
Page 11

Loops and Patterns
The following section describes the Remote Loopback/BER test
modes.
Remote Digital When Remote Loop/511 or Remote Loop/511/E
is enabled via the front panel switch, the
Remote unit’s Restart Timer is set to one
minute. This is because when the 511/511E
generator is initiated on the local unit, the
Remote framer begins seeing unframed packets. The Remote unit can not distinguish the
511/511E pattern from the line being disconnected, so the Restart Timer has been lengthened to
allow the pattern generator to function. Once the
511/511E test is started, the Local unit changes
its' Restart Timer to one minute. The pattern
originates within the Processor and is sent to
the Remote unit. It is then looped back to the
Local unit where it is evaluated for errors. After
45 seconds, the Pattern Generator will timeout
and stops sending the pattern. The ER led will
begin blinking until the user turns off the
511/511E switch.
Using the V.52 (BER) Test Pattern Generator
To use the V.52 BER tests in conjunction with the Remote Digital
Loopback tests, follow these instructions:
1. Locate the Remote Loop/511 & Remote Loop/511E toggle
switch on the front panel of the unit and move it DOWN.
This activates the Remote Loop with V.52 BER and transmits
a “511” test pattern into the loop. If any errors are present,
the local unit’s red “ER” LED will blink sporadically.
2. If the above test indicates no errors are present, move the
19
Compact mDSL Modem
20
Compact mDSL Modem
test switch V.52 toggle switch UP, activating the “511/E”
test with intentional errors present. If the test is working prop
erly, the local unit’s red “ER” LED will blink. A successful
“511/E” test will confirm that the link is in place, and that the
Compact mDSL Modem’s built-in “511” generator and detec
tor are working properly.
Pattern
Gen/Det
Loop
Contr
ol
Loop
Contro
l
Pattern
Gen/Det
Processor
Processor
Framer
Framer
Line
Page 12

Appendix A
10BASE-T mDSL
SPECIFICATIONS
Clocking Modes: Internal or Receive Recovered
DTE Rate: All 64k increments from 64 to 2304 kbps
Diagnostics: V52 compliant (511/511E) pattern generator
and detector with error injection mode and
Remote Loopback control by a single front
panel switch
LEDStatus: The following LEDs are displayed on the
front panel:
DSL Link (Green Active) - DSL Link Active
10BT Link (Green Active) - Valid Ethernet
Connection
Status (Flashing Yellow) - Status indication from the Ethernet port
NS (Red Active) - No signal on DSP Link
ER (Flashing Red) - CRC error during nor-
mal operation, bit error during pattern generation test
TM (Active Yellow) - Test Mode Enabled
Configuration: Externally accessible dip switches or
SNMP/HTTP managed through MDU9700C
Power: +5V External desk top power supply, 100-
240VAC, 50-60 Hz (Universal Input), 10W
or -48 VDC
Compliance: FCC Part 15, CE mark
Transmission Line: Single Twisted Pair (2 wires)
Line Coding: CAP(Carrierless Amplitude and Phase
Modulation)
Line Rates (DSL line): 144, 272, 400, 528, 784, 1040, 1552, 2064,
2320 kbps
Line Interface: Transformer coupled, 1500 VAC isolation
mDSL Physical
ETHERNET SPECIFICATIONS
Connection: RJ-45, 10Base-T 802.3 Ethernet
Protocol: PPP (RFC 1661) with Bridging Control
(RFC 1638)
Address Aging: Entries are deleted after 8 minutes of inac-
tivity
Frame Latency: 1 Frame
Frame Buffer: 512 Frames
Ethernet Physical
Connection:
pin 1 TD Data +
pin 2 TD Data pin 3 RD Data +
pin 6 RD Data +
pins 4, 5, 7, 8 no connection
21
Compact mDSL Modem
Compact mDSL Modem
Page 13

How To Contact your Local Black Box
Italy: Australia:
Black Box Italia S.P.A
Black Box Catalog AustraliaPTYLTD
Tel: 0227400280 Tel: 0398797100
Fax: 0227400219 Fax: 0398702955
www.blackbox.it
Germany: Brazil:
Black Box Deutschland Black Box Do Brasil
Tel: 0811/5541-0 Tel: (011) 5515-4000
Fax: 0811/5541-499 Fax: (011) 5515-4002
www.blackbox-deutschland.com www.blackbox.com.br
Switzerland: Canada:
Datacom Black Box Services AG Black Box Canada Corp.
Tel: 0554517070 Tel: 0416-736-8000
Fax: 0554517075 Fax: 0416-736-7348
www.black-box.xh www.blackbox.com
Netherlands: Mexico:
Black Box Datacom BV
Black Box De Mexico S.A. de C.V
Tel: 03032417799 Tel: 05-420-0100
Fax: 0302414746 Fax: 05-420-0123
www.blackbox.nl/ www.blackbox.com.mx
Belgium: Japan:
Black Box Black Box Catalog
Tel: 027258550 Tel: 03-3820-5011
Fax: 027259212 Fax: 03-3820-5010
www.blackbox.be www.blackbox.co.jp
France: U.S.A:
Black Box Catalogue Black Box Corporation
Tel: 0145606700 Tel: 724-746-5500
Fax: 0145606747 Fax: 724-746-0746
www.blackbox.fr www.blackbox.com
Spain: Chile:
Black Box Comunicaciones S.A. Black Box Chile
Tel: 34 91 663 0200 Tel: 00 562 223 8811
Fax: 34 91 661 84 35 Fax: 00 562 225 1002
www.blackbox.es www.blackbox.cl
23
Compact mDSL Modem
 Loading...
Loading...