Page 1

Industrial Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch
User Manual
LIG1014A
LIE1014A
Contact
Information
Order toll-free in the U.S. or for FREE technical support: Call 877-877-BBOX
(outside U.S. call 724-746-5500)
www.blackbox.com • info@blackbox.com
Page 2
Industrial Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Trademarks Used in this Manual
Black Box and the Double Diamond logo are registered trademarks of BB Technologies, Inc.
Any other trademarks mentioned in this manual are acknowledged to be the property of the trademark owners.
We‘re here to help! If you have any questions about your application
or our products, contact Black Box Tech Support at 877-877-2269
or go to blackbox.com and click on “Talk to Black Box.”
You’ll be live with one of our technical experts in less than 60 seconds.
Page 2
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 3

Industrial Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Federal Communications Commission and Industry Canada Radio Frequency Interference
Statements
This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio-frequency energy, and if not installed and used properly, that is, in strict
accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions, may cause inter ference to radio communication. It has been tested and found to
comply with the limits for a Class A computing device in accordance with the specifications in Subpart B of Part 15 of FCC rules,
which are designed to provide reasonable protection against such interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial
environment. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause interference, in which case the user at his own
expense will be required to take whatever measures may be necessary to correct the interference.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to
operate the equipment.
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class A limits for radio noise emis sion from digital apparatus set out in the Radio
Interference Regulation of Industry Canada.
Le présent appareil numérique n’émet pas de bruits radioélectriques dépassant les limites applicables aux appareils numériques
de la classe A prescrites dans le Règlement sur le brouillage radioélectrique publié par Industrie Canada.
Disclaimer:
Black Box Network Services shall not be liable for damages of any kind, including, but not limited to, punitive, consequential or cost of cover damages, resulting
from any errors in the product information or specifications set forth in this document and Black Box Network Services may revise this document at any time
without notice.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 3
Page 4

Industrial Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Instrucciones de Seguridad
(Normas Oficiales Mexicanas Electrical Safety Statement)
1. Todas las instrucciones de seguridad y operación deberán ser leídas antes de que el aparato eléctrico sea operado.
2. Las instrucciones de seguridad y operación deberán ser guardadas para referencia futura.
3. Todas las advertencias en el aparato eléctrico y en sus instrucciones de operación deben ser respetadas.
4. Todas las instrucciones de operación y uso deben ser seguidas.
5. El aparato eléctrico no deberá ser usado cerca del agua—por ejemplo, cerca de la tina de baño, lavabo, sótano mojado o cerca
de una alberca, etc.
6. El aparato eléctrico debe ser usado únicamente con carritos o pedestales que sean recomendados por el fabricante.
7. El aparato eléctrico debe ser montado a la pared o al techo sólo como sea recomendado por el fabricante.
8. Servicio—El usuario no debe intentar dar servicio al equipo eléctrico más allá a lo descrito en las instrucciones de operación.
Todo otro servicio deberá ser referido a personal de servicio calificado.
9. El aparato eléctrico debe ser situado de tal manera que su posición no interfiera su uso. La colocación del aparato eléctrico
sobre una cama, sofá, alfombra o superficie similar puede bloquea la ventilación, no se debe colocar en libreros o gabinetes
que impidan el flujo de aire por los orificios de ventilación.
10. El equipo eléctrico deber ser situado fuera del alcance de fuentes de calor como radiadores, registros de calor, estufas u otros
aparatos (incluyendo amplificadores) que producen calor.
11. El aparato eléctrico deberá ser connectado a una fuente de poder sólo del tipo descrito en el instructivo de operación, o como
se indique en el aparato.
12. Precaución debe ser tomada de tal manera que la tierra fisica y la polarización del equipo no sea eliminada.
13. Los cables de la fuente de poder deben ser guiados de tal manera que no sean pisados ni pellizcados por objetos colocados
sobre o contra ellos, poniendo particular atención a los contactos y receptáculos donde salen del aparato.
14. El equipo eléctrico debe ser limpiado únicamente de acuerdo a las recomendaciones del fabricante.
15. En caso de existir, una antena externa deberá ser localizada lejos de las lineas de energia.
16. El cable de corriente deberá ser desconectado del cuando el equipo no sea usado por un largo periodo de tiempo.
17. Cuidado debe ser tomado de tal manera que objectos liquidos no sean derramados sobre la cubierta u orificios de ventilación.
18. Servicio por personal calificado deberá ser provisto cuando:
A: El cable de poder o el contacto ha sido dañado; u
B: Objectos han caído o líquido ha sido derramado dentro del aparato; o
C: El aparato ha sido expuesto a la lluvia; o
D: El aparato parece no operar normalmente o muestra un cambio en su desempeño; o
E: El aparato ha sido tirado o su cubierta ha sido dañada.
Page 4
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 5

Industrial Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch User Manual
Disclaimer:
Black Box Network Services shall not be liable for damages of any kind, including, but not limited to, punitive, consequential or cost of cover damages, resulting
from any errors in the product information or specifications set forth in this document and Black Box Network Services may revise this document at any time
without notice.
Quick Study: Condensed Explanation of Terms Used in this Manual
Terms related to network access rights:
ACL (Access Control List): List of Access Control Entries (ACEs). Each ACE specifies the access rights of a device.
QoS (Quality of Service): Method to allocate priority of bandwidth per device on a network.
WRR (Weighted Round-Robin): Network scheduling method that gives each packet its own packet queue.
SP-WRR (Strict Priority Weighted Round-Robin): Packets identified by QoS class and priority queues. Helps to determine
which packets are transmitted first on a network.
ToS (Type of Service): Specifies a data packet's priority for transmission over a network.
Terms related to location:
MAC (Media Access Control) Address: A computer's unique hardware identification number.
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network: A network with flexible logical connections (vs. physical connections) between LANs.
Commonly used with IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth) applications.
Dual Ring: A network redundant technology where nodes are connected using two rings with four branches. Use for small
networks that are not frequently reconfigured.
IP (internet Protocol) Address: Number that identifies a host or or network interface location.
Terms related to data security:
802.1x Authentication: Ensures integrity of the data being transferred on a network.
Dual Homing: Provides a redundant network interface for added security.
Terms related to OSI layers:
Open Systems Interconnection (OSI): Lists the communication functions of a computing system without considering internal
structure and technology.
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol): Used to discover and manage multicast groups. IGMP is part of the Network
layer in the OSI communication model.
Terms related to data traffic:
L4: In an L4 switch, data traffic is prioiritized by application, using a hardware-switching technology that can distinguish between
HT TP, FT P, o r V o IP.
POE (Power Over Ethernet): Technology that enables both data and power signals to be transmitted over one cable.
RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol): Prevents loops on an Ethernet network. Protects your network from “hanging” caused
by endless data loops.
Multicast Group: Used for streaming media applications on the internet and private networks.
Ring Protection: A ring is a network with two paths between any two nodes on the network. Ring protection ensures that one
of the two paths are not broken if the other path fails.
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol): Internet standard protocol used to collect and organize information from
managed devices on an IP network.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 5
Page 6

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
1. Specifications ................................................................................................................................................... 8
2. Overview ..................................................................................................................................................11
2.1 Introduction ..........................................................................................................................................11
2.2 Features ................................................................................................................................................11
2.3 What's Included ................................................................................................................................... 12
2.4 Additional Items You May Need .......................................................................................................... 12
2.5 Hardware Description .......................................................................................................................... 12
2. 5.1 LI G1014A .................................................................................................................................. 12
2.5.2 LI E1014A ................................................................................................................................... 13
3. Connecting to Your Industrial Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch .................................................................. 14
3.1 Connecting to Your Switch via a Serial Console .................................................................................. 14
3.2 Connecting to the Switch via Telnet .................................................................................................... 17
3.3 Connecting to the Switch via a Web Browser ..................................................................................... 18
4. Switch Functions ............................................................................................................................................ 19
4.1 VLAN Application Guide ..................................................................................................................... 19
4.1.1 Explanation of VLAN (Virtual LAN) ........................................................................................... 19
4.1.2 Example 1: Default VLAN Settings ............................................................................................ 19
4.1.3 Example 2: Port-Based VLANs .................................................................................................. 20
4.1.4 Example 3: IEEE 802.1Q Tagging ............................................................................................... 22
4.2 Security Application Guide .................................................................................................................. 24
4.2.1 Explanation of ACL (Access Control List) ................................................................................... 24
4.2.2 Case 1: ACL for MAC Addresses .............................................................................................. 24
4.2.3 Case 2: ACL for IP Addresses .................................................................................................... 35
4.2.4 Case 3: ACL for L4 Port ............................................................................................................ 35
4.2.5 Case 4: ACL for ToS .................................................................................................................. 35
4.3 Ring Protection Application Guide ....................................................................................................... 36
4.3.1 Explanation of Ring Protection .................................................................................................. 36
4.3.2 Configuration (Console) ............................................................................................................ 37
4.3.3 Configuration (Web GUI) .......................................................................................................... 38
4.3.4 Dual Ring .................................................................................................................................. 43
4.3.5 Dual Homing ............................................................................................................................. 46
4.4 QoS Application Guide ........................................................................................................................ 47
4.4.1 Explanation of QoS ................................................................................................................... 47
4.4.2 SP/SPWRR/WRR ........................................................................................................................ 47
4.4.3 Example 1: SPQ Without Shaping (Default Profile) ................................................................... 47
4.4.4 Example 2: SPQ With Shaping .................................................................................................. 50
4.4.5 Example 3: WRR ....................................................................................................................... 53
4.4.6 Example 4: SP-WRR .................................................................................................................. 57
4.5 IGMP Application Guide ...................................................................................................................... 64
4.5.1 Explanation of IGMP ................................................................................................................. 64
4.5.2 Configuring VLC on an IGMP Server......................................................................................... 68
4.5.3 Configuring VLC on an IGMP Client ......................................................................................... 71
4.6 801.1x Authentication Guide ............................................................................................................... 73
4.6.1 Explanation of 802.1x Authentication ....................................................................................... 73
4.6.2 802.1x Timer in Industrial Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch .................................................... 73
4.6.3 Configuration in RADIUS Server ................................................................................................ 73
Page 6
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 7

Table of Contents
5. Hardware Quick Setup Guide ........................................................................................................................77
5.1 What's Included ................................................................................................................................... 77
5.2 Mounting the Switch on a DIN Rail ..................................................................................................... 77
5.3 Mounting the Switch on a Wall ........................................................................................................... 78
5.4 Ethernet Interface ................................................................................................................................ 78
5.4.1 RJ - 45 ........................................................................................................................................ 78
5.4.2 Fiber SFP ................................................................................................................................... 79
5.5 Connecting the Power Terminal Block ................................................................................................. 79
5.6 Alarm Relay and Ground ..................................................................................................................... 80
5.7 Console Connection ............................................................................................................................ 81
5.8 Connect and Login to Managed Switch .............................................................................................. 81
5.9 CLI Initialization and Configuration ...................................................................................................... 81
5.10 Indicators ............................................................................................................................................. 82
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 7
Page 8
Chapter 1: Specifications
1. Specifications
Ethernet
Operating Mode Store and forward, L2 wire-speed/non-blocking switching engine
MAC Addresses 8K
Jumbo Frames 9K Bytes
Copper RJ-45 Ports
Speed 10/100/1000 Mbps
MDI/MDIX Auto-Crossover Supports straight-through or cross-pinned cables
Auto-negotiating 10/100/1000 Mbps speed auto-negotiation; Full- and half-duplex
Ethernet isolation 1500 VRMS 1 minute
SFP (Pluggable) Ports
Port Types Supported SFP (pluggable) Ports 100/1000BASE SFP slot Supports 100/1000BASE-T SFP transceiver
Fiber Port Connector LC typically for fiber (depends on module)
Optimal Fiber Cable 50- or 62.5/125-μm for multimode (MM);
8- or 9/125-μm for single mode (SM)
Network Redundancy
Fast Failover Protection Rings Link loss recovery < 20 ms,
Single and multiple rings supported
Spanning Tree Protocol IEEE 802.1D STP, IEEE 802.1w RSTP, IEEE 802.1s MSTP
Port Trunk with LACP Static trunk or Dynamic via LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol)
Bridge, VLANs, and Protocols
Flow Control IEEE 802.3x (Full Duplex) and Back-Pressure (Half Duplex)
VLAN Types Port-based VLANs,
IEEE 802.1Q tag-based VLANs,
IEEE 802.1ad Double Tagging (Q in Q)
Multicast Protocols IGMP v1, v2,
IGMP snooping and querying,
Immediate leave and leave proxy,
Throttling and filtering
LLDP IEEE 802.1ab Link layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP)
Traffic Management and QoS
Priority IEEE 802.1p QoS
Number of Queues per Port 8
Scheduling Schemes SPQ, WRR
Traffic Shaper Port-based shaping
Security
Port Security IP and MAC-based access control,
IEEE 802.1x authentication Network Access Control
Power
Power Input Redundant Input Terminals
Input Voltage Range LIG1014A, LIE1014A (without PoE): 12–58 VDC
LIE1014A (with PoE): 46–58 VDC
Maximum Power
Consumption
LIG1014A: 17 W,
LIE1014A (without PoE): 14 W,
LIE1014A (with PoE): 265 W
Page 8
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 9
Chapter 1: Specifications
Power (continued)
Reverse Power Protection Yes
Total PoE Output Power Budget 240 watts
PoE PSE Port Output Power
Management
Transient Protection > 15,000 watts peak
Indicators (LEDs)
Power Status LED Indicates power input status
Ethernet Port LED Link and Speed
Management
User Management Interfaces CLI (command-line interface),
Management Security HTTPs, SSH,
Upgrade and Restore Configuration Import/Export,
Diagnostic Syslog,
MIBs RMON 1,2,3,9; Q-Bridge MIB,,
DHCP Client, Server, Relay, Snooping, Option 82
NTP/SNTP Yes
Environment
Operating Temperature Range -40 to +167° F (-40 to +75° C) (cold startup at -40° C)
Storage Temperature Range -40 to +185° F (-40 to +85° C)
Humidity (non-condensing) 5 to 95% RH
Approvals
Certification Compliance CE / FCC; EN-50121- 4
Electrical Safety CSA C22, EN61010-1, CE
EMC FCC Part 15, CISPR 22 (EN55022) Class A,
MTBF > 25 years
RoHS and WEEE RoHS (Pb free) and WEEE compliant
Mechanical
Connectors LIG1014A: (10) RJ-45 10/100/1000BASE-T(X), (4) 100/1000BASE SFP;
Ingress Protection IP30
Installation Options DIN-Rail mounting, Wallmounting
Dimensions LIG1014A: 6"H x 2.4"W x 4.3"D (15.4 x 6 x 10.9 cm);
Weight LIG1014A: 2.4 lb. (1.1 kg);
Scheduling; power control; PoE PD power consumption monitoring
Web-based Management,
SNMP v1, v2c,
Telnet (5 sessions)
Radius Client for Management
Firmware Upgrade
Per VLAN mirroring,
SFP with DDM (Digital Diagnostic Monitoring)
RFC 1213 MIB-II, RFC 4188 Bridge MIB
IEC61000-4-2, -3, -4, -5, -6
LIE1014A: (8) RJ-45 10/100/1000BASE-T(X), (4) 100/1000BASE SFP
LIE1014A: 6.1"H x 3.0"W x 5"D (15.4 x 7.7 x 12.8 cm)
LIE1014A: 3.1 lb. (1.4 kg)
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 9
Page 10
Chapter 1: Specifications
System Statistics
Function Name System Maximum Value
VLAN ID 4096
VLAN Limitation 1024
Privilege Level of User 15
RMON Statistic Entry 65535
RMON Alarm Entry 65
RMON Event Entry 65535
IPMC Profile 64
IPMC Rule / Address Entry 128
ACE 256
ICMP Type / Code 255
RADIUS Server 5
TACACS + Server 5
MAC-based VLAN Entry 256
IP subnet-based VLAN Entry 128
Protocol-based VLAN Group 125
Voice VLAN OUI 16
QCE 256
IP Interface 8
IP Route 32
Security Access Management 16
MVR VLAN 4
MAC Learning table address 8k
IGMP Group 256
Page 10
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 11

Chapter 2: Overview
2. Overview
2.1 Introduction
The Industrial Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch is a high-quality switch that operates in a wide temperature range and an
extended power input range. The switch features advanced VLAN and QoS features. It’s ideal for harsh environments and
mission-critical applications.
Table 2-1. Available models
Component LIG1014A LIE1014A (PoE)
Total Gigabit Ethernet
Ports
10/100 /1000BASE-T(X) 10 8
100/1000BASE SFP 4 4
Power over Ethernet
The LIE1014A switch supports Power over Ethernet compliant to the IEEE 802.3af and IEEE 802.3at standard on all copper ports.
The switch can power standard PoE PD devices with up to 30 watts per port along with the Ethernet data on standard Ethernet
cabling.
Multi-rate SFP slots
Multi-rate SFP slots enable you to mix-and-match 100-Mbps and 1-Gbps SFP Modules for either multi- or single-mode as needed.
If requirements change, just replace the SFP module and protect your switch investment.
Power
The switches are powered from 12- to 58-VDC. The PoE model (LIE1014A) needs 48 VDC for 802.3af and a minimum of 53 VDC
for 802.3at.
Extended temperature range
All models are tested and released for operating temperatures from -40° up to +75° Celsius. They passed shock, vibration, and
freefall test and comply with the IEC600068-2-6, -27 and -32 standards.
Management
The switches offer powerful features including Layer 3 routing and management with all advanced filter and multicast algorithms
needed today to easily prioritize, partition, and organize a reliable high-speed network.
14 12
2.2 Features
• Provide (8) or (10) 10/100/1000 ports plus (4) multi-rate SFP slots.
• LIE1014A model uses Power over Ethernet Plus to deliver 30 watts power per port to remote PD devices.
• Extended temperature range: -40° to +75°C.
• L2 wire speed switching.
• 12- to 58-VDC dual input, reverse polarity.
• IP30 industrial design.
• DIN-rail mountable.
• Shock, vibration and freefall test to IEC60068-2-6, -27, -32.
• EMC approval acc. to IEC61000-4-2, -3, -4, -5, -6 (Level 3).
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Pa g e 11
Page 12

Chapter 2: Overview
2.3 What's Included
Your package should contain the following items. If anything is missing or damaged, contact Black Box Technical Support
at 877-877-2269 or info@blackbox.com.
LIG1014A:
• Industrial Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch with (10) 10/100/1000BASE-T(X) ports and (4) 100/1000BASE SFP ports.
• Printed Quick Start Guide
LIE1014A:
• Industrial Managed Gigabit PoE Ethernet Switch with (8) 10/100/1000BASE-T(X) ports and (4) 100/1000BASE SFP ports.
• Printed Quick Start Guide
2.4 Additional Items You Will Need
• SFP modules
Table 2-2 lists compatible SFP modules (ordered separately). These modules install in the SFP slots on the managed switch.
Table 2-2. Compatible SFP modules.
Part Number Description
LF P411 SFP/1250 Extended Diagnostics, LC multimode, 850 nm, 550 m
LFP412 SFP/1250 Extended Diagnostics, LC multimode, 1310 nm, 2 km
LFP413 SFP/1250 Extended Diagnostics, LC single-mode, 1310 nm, 10 km
LFP414 SFP/1250 Extended Diagnostics, LC single-mode, 1310 nm, 40 km
LFP401 SFP/155 Extended Diagnostics, LC multimode, 850 nm, 2 km
LFP403 SFP/155 Extended Diagnostics, LC single-mode, 1310 nm, 30 km
LFP404 SFP/155 Extended Diagnostics, LC single-mode, 1310 nm, 60 km
LFP402 SFP/155 Extended Diagnostics, LC multimode, 1310 nm, 2 km
LFP418 SFP/1250 Extended Diagnostics, LC single-mode, 1550 nm, 80 km
LFP420 Simplex SFP/1250, Extended Diagnostics, single-mode, 1550 nm TX, 1310 nm RX
2.5 Hardware Description
LIG1014A
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
9
Top
7
8
Figure 2-1. LIG1014A, Front Panel and Top Panel.
Page 12
Front
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 13

Chapter 2: Overview
LIE1014A
7
10
11
Figure 2-2. LIE1014A, Front Panel and Top Panel.
Table 2-3. Components of the LIG1014A and LIE1014A.
Number in Figures
Component LIG1014A LIE1014A (PoE) Function
2-1 and 2-2
1 (2) Power LEDs (1) P1, (1) P2 (1) P1, (1) P2 Links to power
2 (1) Alarm LED (1) ALM (1) ALM
3 Gigabit Ethernet Copper Ports (10) RJ-45 (8) RJ-45
4 Link LEDs (10) (8)
5 Speed LEDs (10) (8)
6 Gigabit Ethernet SFP ports (4) SFP slots (4) SFP slots
7 Power Input (Dual) via 6-pin
Terminal Block
8 (1) Reset Button (1) Reset
9 Console (RS -232) RJ -45 (1) RJ-45 (1) RJ-45 Links to console
10 POE LED (LIE1014A only) POE port status
11 RR/RS LEDs Device info/status
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Top
Front
(1) Power
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 13
Page 14

Chapter 3: Connecting to Your Industrial Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch
3. Connecting to Your Industrial Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch
You can connect to your switch in three ways:
1. Via a serial console.
2. Via a Telnet console.
3. Via a Web browser.
NOTE: You can’t connect to a serial console and a Telnet console at the same time. You can connect to the Web console
and a serial or Telnet console at the same time, but we do NOT recommend this.
3.1 Connecting to Your Switch via a Serial Console
You will need:
• Switch
• An RJ-45 female to DB9 or DB25 female cable (not included)
• Serial PC or terminal (not included) with terminal emulation software installed
An example below is shown using the PuTTy terminal emulation program. PuTTy is an open-source SSH and Telnet client.
STEP 1: Physically connect the switch to the serial console.
Using the RJ-45 female to DB9 or DB25 female cable (not included), connect the DB9 or DB25 serial console port to the switch.
STEP 2: Check to see if a terminal emulation program is installed on the PC. If it is not, install it now.
Launch PuTTy. Select Terminal from the menu on the left side of the screen. Select the key sequences, application keypad settings,
and extra keyboard features. Next, click Open.
Page 14
Figure 3-1. Select terminal screen.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 15
Chapter 3: Connecting to Your Industrial Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch
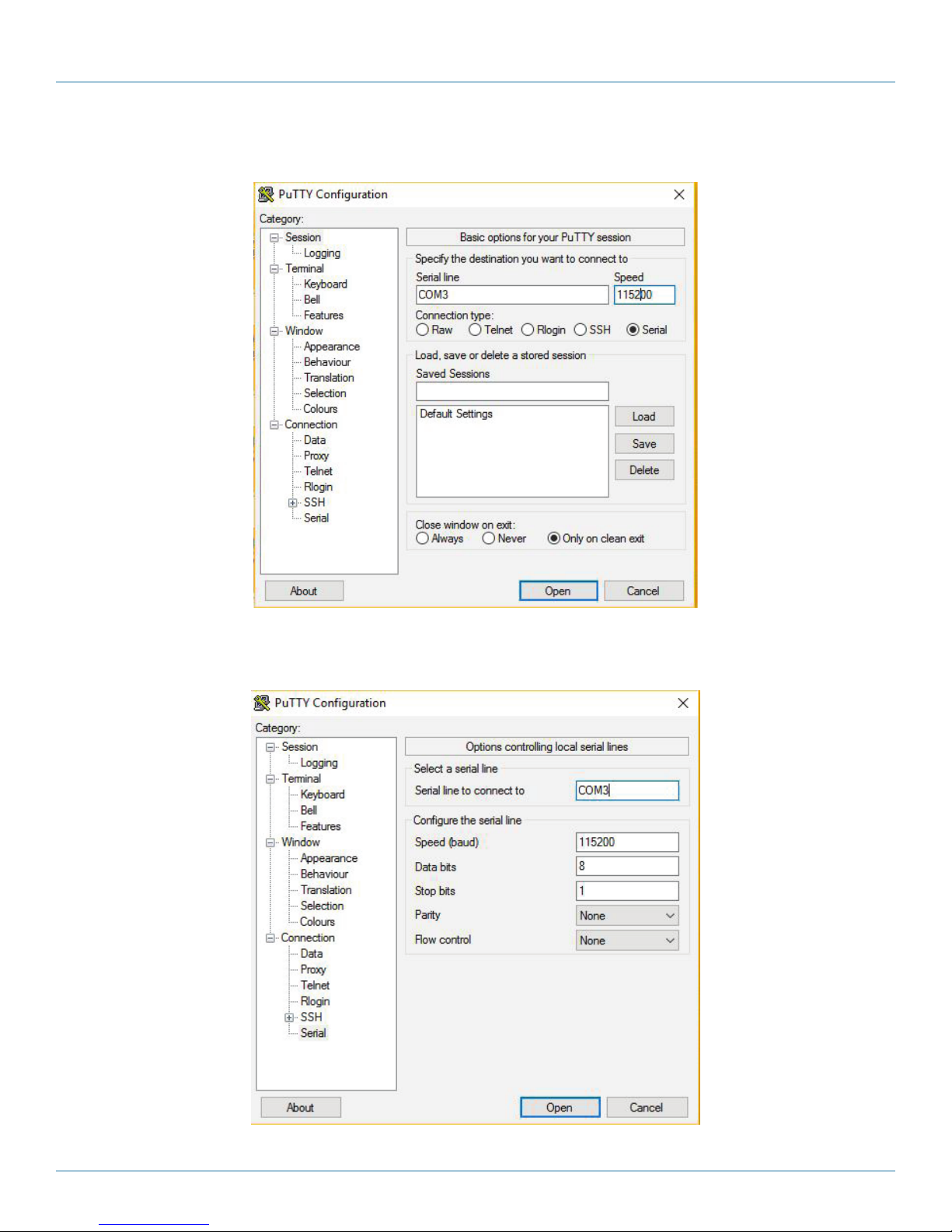
STEP 3: Once you go back to the session, select the Connection type as Serial. Fill in the Serial line and Speed fields
with COM port and speed to be used. Click Only on clean exit, then click Open.
Figure 3-2. PuTTy options screen.
STEP 4: Select Connection —> Serial from the left-hand column. The screen below appears.
Figure 3-3. Local serial lines connections options.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 15
Page 16

Chapter 3: Connecting to Your Industrial Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Enter these values in the screen:
• Serial line: the COM port you are using
• Speed (baud) rate: 115,200 bps
• Data bits: 8
• Stop bits: 1
• Parity: None
• Flow control: None
Once you are done, click Open and then press Enter.
STEP 5: The serial console prompts you to log in. Enter the default username and password:
Username: admin
Password: (none)
NOTE: The password is left blank. To login, simply type admin in the Username field, then press Enter. The cursor will jump to the
Password field. Press Enter again.
STEP 6: The CLI prompt of the Switch’s serial console appears. Use the CLI Guide to find your way around the CLI.
Table 3-1. Keyboard functions.
Key Function
Up, down, right, or left arrow keys, Tab Move the cursor on-screen
Enter Press this key to select options
Space Press to toggle between settings.
Esc Go to the previous menus
Page 16
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 17

Chapter 3: Connecting to Your Industrial Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch
3.2 Connecting to the Switch via Telnet
NOTE: The PC host and the switch must be on the same logical subnet. See the table below.
Table 3-2. Default IP addresses of the switch and PC host.
IP Address Subnet Mask
Switch 192.0.2.1 255.255.255
PC Host 192.0.2.xxx 255.255.255.0
NOTE: The switch’s default IP address is 192.0.2.1
STEP 1: Using a straight-through or crossover cable, connect the switch’s RJ-45 Ethernet port to your Ethernet LAN or to your
PC’s Ethernet port.
NOTE: It does not matter if the Ethernet cable is pinned straight-through or cross-pinned; the switch supports Auto MDI-X.
STEP 2: From the Windows Run menu, click Start—>Run.
STEP 3: Type in the Switch’s default IP address: 192.0.2.1
STEP 4: A telnet prompt appears. Select the terminal type.
STEP 5: Log in using the switch’s default username and password:
Username: admin
Password: (none)
NOTE: The password is left blank. To login, simply type admin in the Username field, then press Enter. The cursor will jump to the
Password field. Press Enter again.
The main menu of the switch’s Telnet console appears.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 17
Page 18

Chapter 3: Connecting to Your Industrial Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch
3.3 Connecting to the Switch via a Web Browser
NOTE: The PC host and the switch must be on the same logical subnet. See the table below.
Table 3-3. Default IP addresses of the switch and PC host.
IP Address Subnet Mask
Switch 192.0.2.1 255.255.255
PC Host 192.0.2.xxx 255.255.255.0
STEP 1: Using a straight-through or crossover cable, connect the switch’s RJ-45 Ethernet port to your Ethernet LAN or to your
PC’s Ethernet port.
STEP 2: Open the switch’s web console. Enter the switch’s IP address in the Address or URL field.
The default IP address is 192.0.2.1.
STEP 3: The web console login screen will appear. Enter the usernameand password.
Username: admin
Password: (none)
NOTE: The password is left blank. To login, simply type admin in the Username field, then press Enter. The cursor will jump to the
Password field. Press Enter again. If you don’t want to create a password, just press Enter.
Page 18
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 19
Chapter 4: Switch Functions
4. Switch Functions
4.1 VLAN Application Guide
4.1.1 Explanation of VLAN (Virtual LAN)
You can increase the efficiency of your network by dividing it into local segments (VLANs) instead of physical segments. A VLAN
(Virtual LAN) is a group of devices that you can place anywhere on a network without being restricted by physical connections
(a limitation of a traditional physical network). VLANs enable you to segment your network into groups, for example,
departmental, hiercrchial, or usage groups. A VLAN segments a network to make it more flexible than a physical network.
VLANs make it easy to relocate devices on networks (no physical cable moves). VLANs also give your network extra security and
help control network traffic.
The Industrial Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch supports up to 2048 VLANs. Ports are grouped into broadcast domains by
assigning them to the same VLAN. Frames received on a VLAN can only be forwarded within that VLAN, and multicast frames
and unknown unicast frames are flooded only to ports in the same VLAN.
4.1.2 Example 1: Default VLAN Settings
Each port in the LIG1014A/LIE1014A Switch has a configurable default VLAN number, known as its PVID. This places all ports on
the same VLAN initially, although each port PVID is configurable to any VLAN number between 1 and 4094.
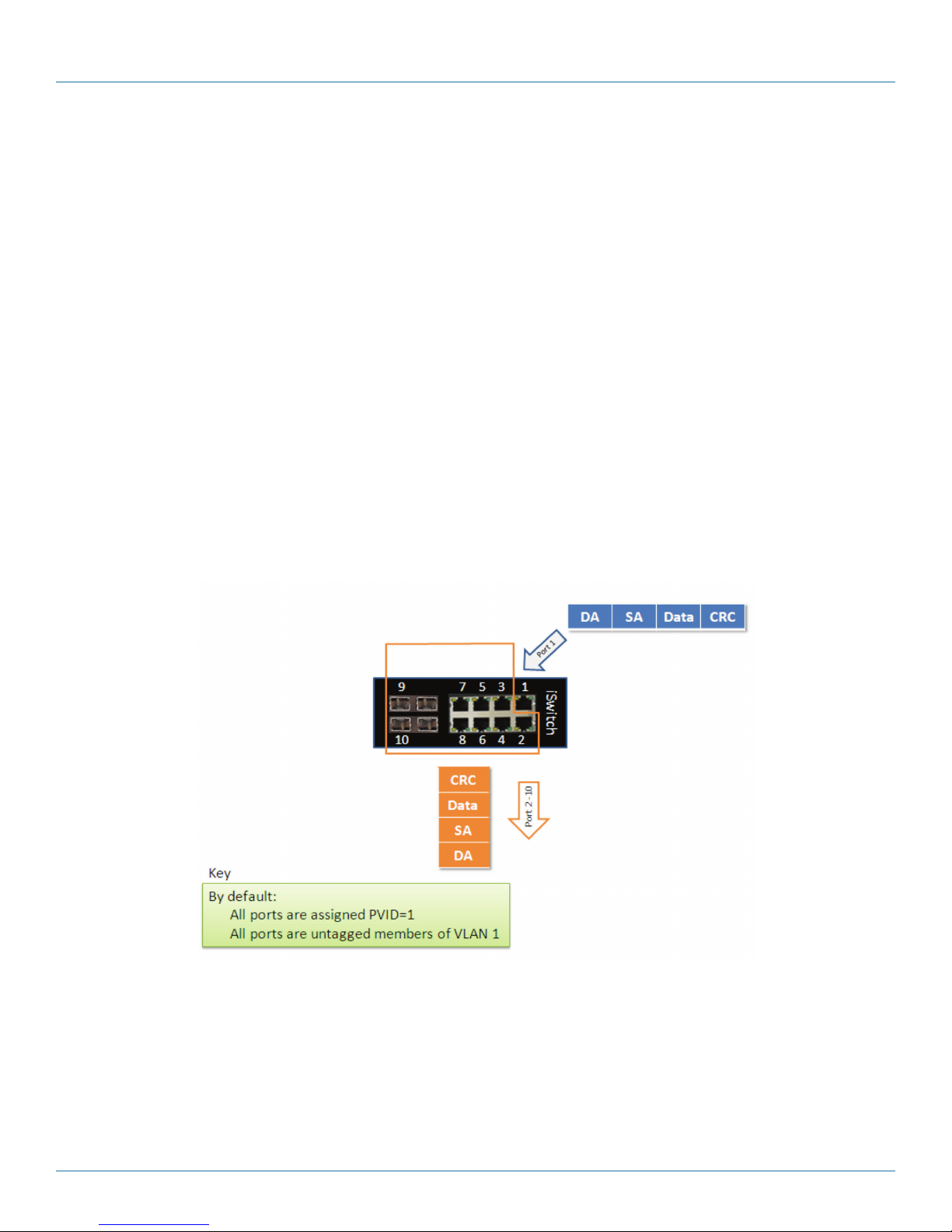
The default configuration settings for the switch have all ports set as untagged members of VLAN 1 with all ports configured as
PVID =1. In default configuration example shown in the following figure, all incoming packets are assigned to VLAN 1 by the
default port VLAN identifier (PVID=1).
Figure 4-1. Default VLAN Settings.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 19
Page 20
Chapter 4: Switch Functions
4.1.3 Example 2: Port-based VLANs
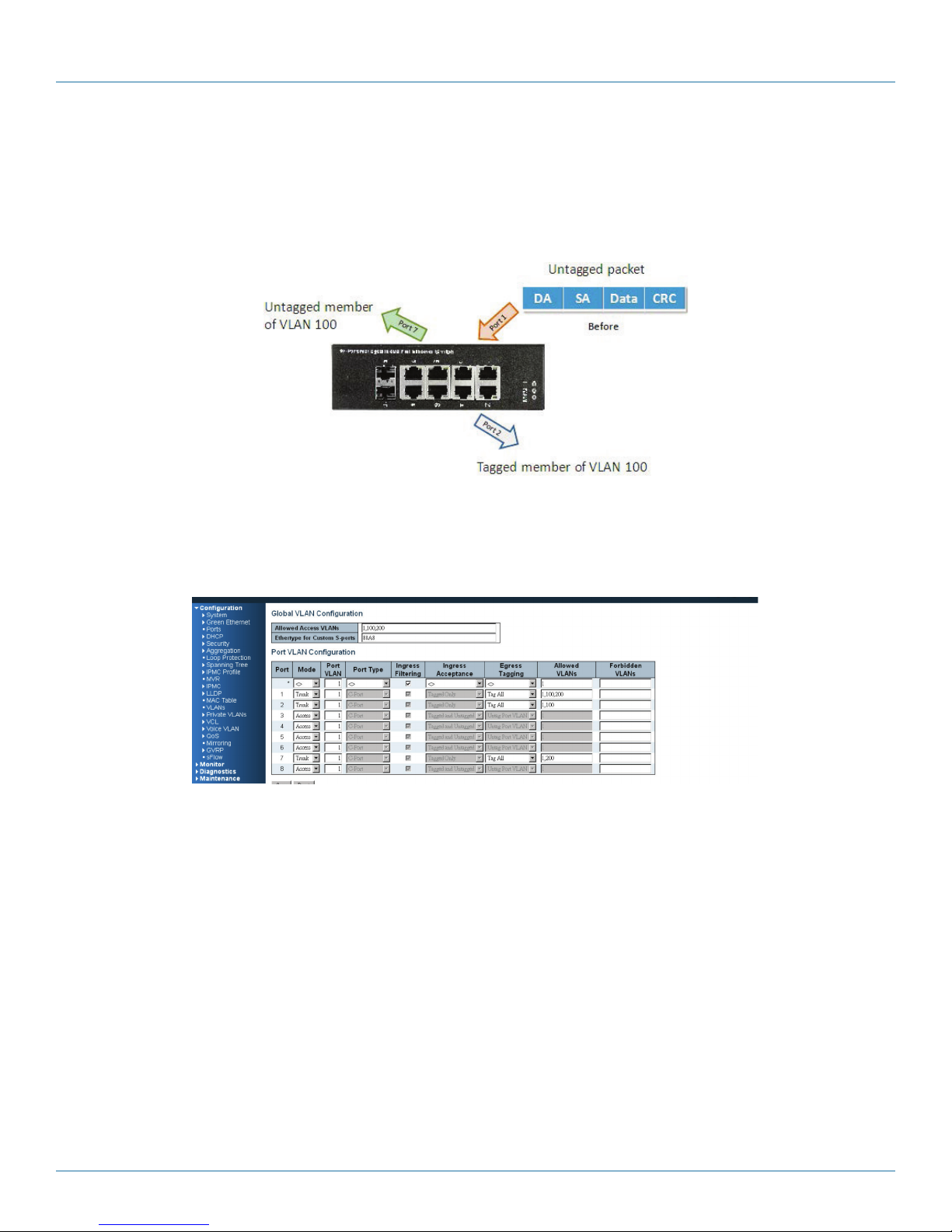
When the LIG1014/LIE1014A receives an untagged VLAN packet, it will add a VLAN tag to the frame according to the PVID
setting on a port. As shown in the following figure, the untagged packet is marked (tagged) as it leaves the LIG1014/LIE1014A
through Port 2, which is configured as a tagged member of VLAN100. The untagged packet remains unchanged as it leaves the
LIG1014/LIE1014A through Port 7, which is configured as an untagged member of VLAN100.
Figure 4-2. Port-Based VLAN.
Configuration:
STEP 1: Go to Configuration -> VLANs -> Port VLAN configuration and configure PVID 100 on Port 1, Port 2, and Port 7.
Figure 4-3. Configure PVID.
STEP 2. Select Configuration -> VLAN -> Static VLAN. Create a VLAN with VLAN ID 100. Enter a VLAN name in the Name field.
STEP 3. Assign a VLAN tag setting to or remove it from a port by toggling the checkbox under an individual port number. The
tag settings determine if packets that are transmitted from the port tagged or untagged with the VLAN ID. The possible tag
settings are:
• Tag All : Specifies that the egress packet is tagged for the port.
• Untag port vlan: Specifies that the egress packet is untagged for the port.
• Untag All: Specifies that all frames, whether classified to the Port VLAN or not, are transmitted without a tag.
Page 20
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 21

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
Here we set tagged VLAN100 on Port 1 and Port 2, untagged VLAN100 on Port 7.
Figure 4-4. Set tagged and untagged VLAN on ports.
STEP 4: Transmit untagged unicast packets from Port 1 to Port 2 and Port 7. The LIG1014/LIE1014A should tag a packet with VID
100. The packet has access to Port 2 and Port 7. The outgoing packet is stripped of its tag to leave Port 7 as an untagged packet.
For Port 2, the outgoing packet leaves as a tagged packet with VID 100.
STEP 5: Transmit untagged unicast packets from Port 2 to Port 1 and Port 7. The LIG1014/LIE1014A should tag a packet with VID
100. The packet has access to Port 1 and Port 7. The outgoing packet is stripped of its tag to leave Port 7 as an untagged packet.
For Port 1, the outgoing packet leaves as a tagged packet with VID 100.
STEP 6: Transmit untagged unicast packets from Port 7 to Port 1 and Port 2. The LIG1014/LIE1014A should tag a packet with VID
100. The packet has access to Port 1 and Port 2. For Port 1 and Port 2, the outgoing packet leaves as a tagged packet with VID
100.
STEP 7: Repeat step 4 using broadcast and multicast packets.
CLI Commands
vlan 1
vlan 100
interface GigabitEthernet 1/1
switchport access vlan 100
switchport trunk native vlan 100
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,100
switchport trunk vlan tag native
switchport mode trunk
exit
interface GigabitEthernet 1/2
switchport access vlan 100
switchport trunk native vlan 100
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,100
switchport trunk vlan tag native
switchport mode trunk
exit
interface GigabitEthernet 1/7
switchport access vlan 100
switchport trunk native vlan 100
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,100
switchport mode trunk
exit
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 21
Page 22
Chapter 4: Switch Functions
4.1.4 Example 3: IEEE 802.1Q Tagging
LIG1014/LIE1014A is able to construct a layer-2 broadcast domain by identifying a VLAN ID specified by IEEE 802.1Q. It forwards
a frame between bridge ports assigned to the same VLAN ID and can set multiple VLANs on each bridge port.
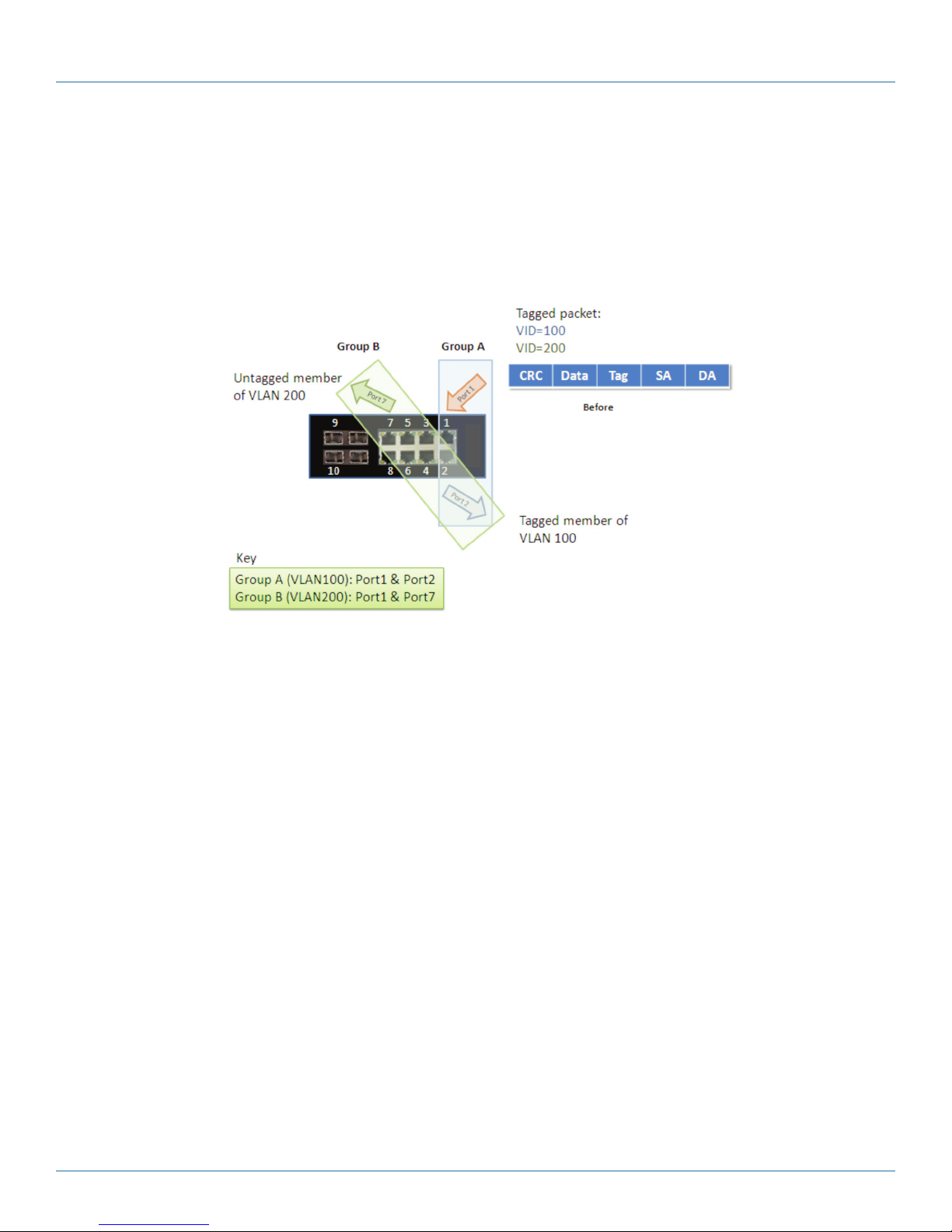
In the following figure, the tagged incoming packets are assigned directly to VLAN 100 and VLAN 200 because of the tag
assignment in the packet. Port 2 is configured as a tagged member of VLAN 100, and Port 7 is configured as an untagged
member of VLAN 200. Hosts in the same VLAN communicate with each other as if they were in a LAN. However, hosts in
different VLANs cannot communicate with each other directly.
Figure 4-5. IEEE 801.1Q Tagging.
In this case:
1. The hosts from Group A can communicate with each other.
2. The hosts from Group B can communicate with each other.
3. The hosts of Group A and Group B can’t communicate with each other.
4. Both the Group A and Group B can go to the Internet through the LIE1014A/LIG1014A.
Page 22
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 23
Chapter 4: Switch Functions
Configuration:
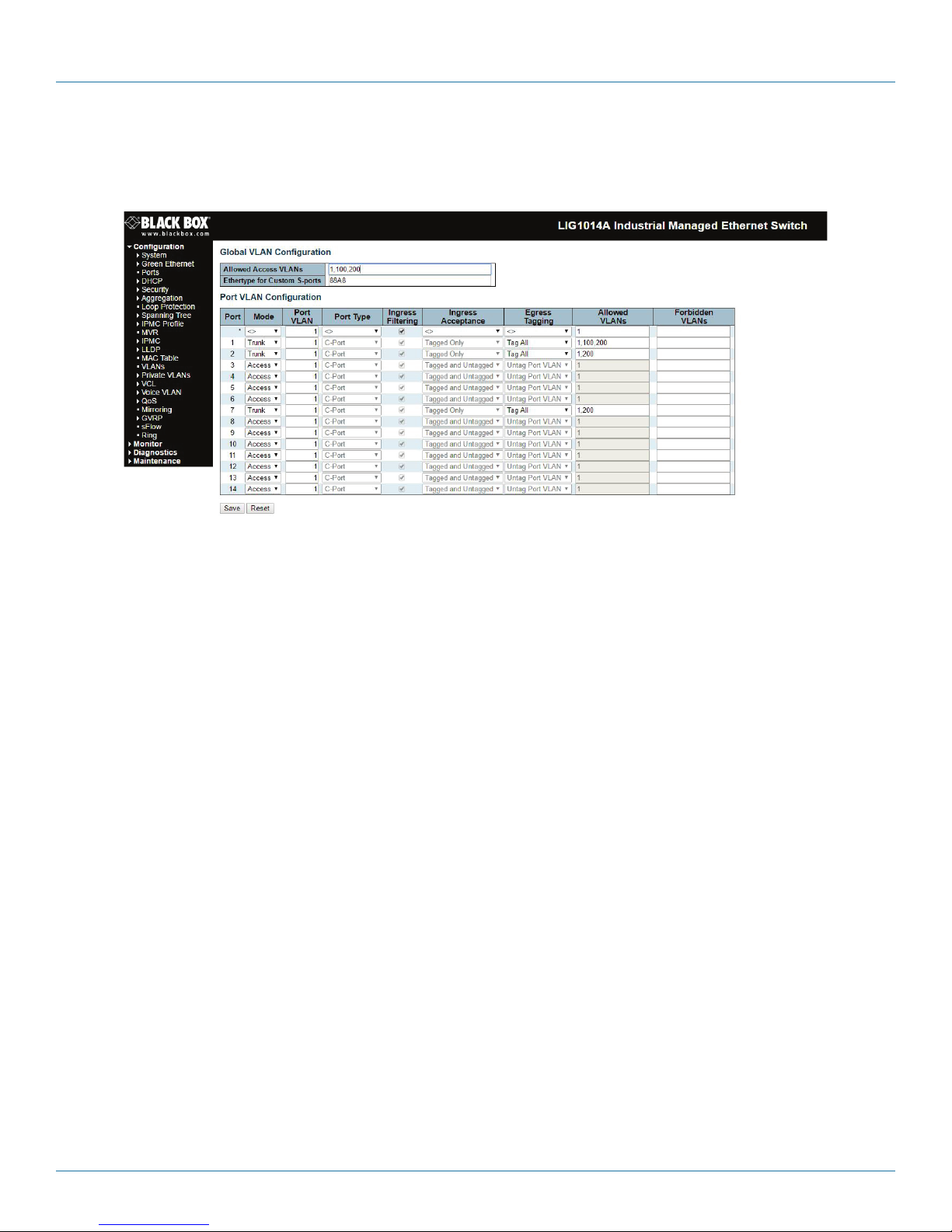
STEP 1: Go to Configuration -> VLANs -> Port VLAN configuration page and specify the VLAN membership as follows:
Figure 4-6. Specify VLAN membership.
STEP 2: Transmit unicast packets with VLAN tag 100 from Port 1 to Port 2 and Port 7. The LIG1014/LIE1014A should tag a packet
with VID 100. The packet only has access to Port 2. For Port 2, the outgoing packet leaves as a tagged packet with VID 100.
STEP 3: Transmit unicast packets with VLAN tag 200 from Port 1 to Port 2 and Port 7. The LIG1014/LIE1014A should tag a packet
with VID 200. The packet only has access to Port 7. The outgoing packet on Port 7 is stripped of its tag as an untagged packet.
STEP 4: Transmit unicast packets with VLAN tag 100 from Port 2 to Port 1 and Port 7. The LIG1014/LIE1014A should tag a packet
with VID 100. The packet only has access to Port 1. For Port 1, the outgoing packet leaves as a tagged packet with VID 100.
STEP 5: Transmit unicast packets with VLAN tag 200 from Port 7 to Port 1 and Port 2. The LIG1014/LIE1014A should tag a packet
with VID 200. The packet only has access to Port 1. The outgoing packet on Port 1 will leave as a tagged packet with VID 200.
STEP 6: Repeat the above steps using broadcast and multicast packets.
CLI Command:
vlan 1
vlan 100
interface GigabitEthernet 1/1
switchport access vlan 100
switchport trunk native vlan 100
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,100
switchport trunk vlan tag native
switchport mode trunk
exit
interface GigabitEthernet 1/2
switchport access vlan 100
switchport trunk native vlan 100
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,100
switchport trunk vlan tag native
switchport mode trunk
exit
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 23
Page 24

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
interface GigabitEthernet 1/7
switchport access vlan 100
switchport trunk native vlan 100
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,100
switchport mode trunk
exit
4.2 Security Application Guide
4.2.1 Explanation of ACL (Access Control List)
Access Control List (ACL) is a traffic filter for ingress and egress packets. It checks each Ethernet packet and filters/forwards it to
its destination. ACL settings might include the packet's source or destination IP address, packet's source or destination MAC
address, IP protocols, and more. ACL examines these values to permit or access a packet.
The LIG1014A/LIE1014A's ACL function supports access control security for MAC address, IP address, Layer 4 Port, and Type of
Service. Each has five actions: Deny, Permit, Queue Mapping, CoS Marking, and Copy Frame. You can set the default ACL rule to
Permit or Deny. For details about the switch's ACL function, see the following table.
Table 4-1. Default ACL Rule Actions.
Deny Permit Queue Mapping CoS Marking Copy Frame
Permit (a) (b) (c) (d) (e)
Deny (f) (g) (h) (i) (j)
Below is a description of the ACL rules listed in Table 4-1 that the switch uses:
(a): Permit all frames, but deny frames set in ACL entry.
(b): Permit all frames.
(c): Permit all frames, and map queues of the transmitting frames.
(d): Permit all frames, and change the CoS value of the transmitting frames.
(e): Permit all frames, and copy a frame set in ACL entry to a defined GE port.
(f): Deny all frames.
(g): Deny all frames, but permit frames set in ACL entry.
(h): Deny all frames.
(i): Deny all frames.
(j): Deny all frames, but to copy frame which set in ACL entry to a defined GE port.
4.2.2 Case 1: ACL for MAC address
The MAC address ACL filters source MAC address, destination MAC address, or both. When it filters both MAC addresses,
packets for both rules take effect. In other words, the switch does not filter MAC addresses if it only complies with the rule for
one of the two MAC addresses.
To filter only one directional MAC address, set the other MAC address to all zeros. The switch can also filter VLAN and Ether type.
If you don't want to filter VLAN and Ether type, set them both to all zeros.
Page 24
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 25

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
• Case 1: Permit all frames, but deny frames set in ACL entry.
Set the default ACL Rule of GE port to “Permit”, then bind a suitable profile with “deny” for ACL. The GE port can pass through
all packets except for the ACL entry of the bound profile.
Filter One MAC Address, but Deny Filtering for One VLAN
To filter one directional MAC address with one VLAN denied filtering, follow the steps listed next:
STEP 1: Create a new ACL Profile. (Profile Name: DenySomeMac)
Figure 4-7. Create new ACL profile screen.
STEP 2: Create a new ACL Entry rule under this ACL profile. (Deny MAC: 11 and VLAN: 4)
STEP 3: Bind this ACL profile to a GE port. (Port 4)
Figure 4-8. Bind the ACL profile to a Gigabit Ethernet port screen.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 25
Page 26

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
STEP 4: Send frames between Port 3 and Port 4, and see the test result.
LIE1014A
LIE1014A
Figure 4-9. Test result: frames sent betwen Port 3 and Port 4.
CLI Commands:
access-list ace 1 ingress interface GigabitEthernet 1/4 policy 1 vid 4
frametype etype smac 00-00-00-00-00-11 action deny
exit
interface GigabitEthernet 1/3
switchport trunk allowed vlan 4,5
switchport trunk vlan tag native
!
interface GigabitEthernet 1/4
switchport trunk allowed vlan 4,5
switchport trunk vlan tag nativevlan 4
exit
Filter Two Directional MAC Addresses, with Filtering Denied to All VLANs
LIE1014A
Follow these steps:
STEP 1: Create a new ACL Profile. (Profile Name: DenySomeMac)
Figure 4-10. Create new ACL profile.
Page 26
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 27

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
STEP 2: Create a new ACL Entry rule under this ACL profile. (Deny SrcMAC: 13 and DesMAC: 11)
STEP 3: Bind this ACL profile to a GE port. (Port 3)
Figure 4-11. Bind ACL profile to a Gigabit Ethernet port.
STEP 4: Send frames between Port 3 and Port 4, and see the test result.
LIE1014A
Figure 4-12.
CLI Commands:
access-list ace 2 ingress interface GigabitEthernet 1/3 policy 0 frametype etype smac
00-00-00-00-00-13 dmac 00-00-00-00-00-11 action deny
exit
interface GigabitEthernet 1/3
switchport trunk allowed vlan 4,5
switchport trunk vlan tag native
!
interface GigabitEthernet 1/4
switchport trunk allowed vlan 4,5
switchport trunk vlan tag nativevlan 4
exit
LIE1014ALIE1014A
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 27
Page 28

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
• Case 1: (b) Permit all frames.
In this case, ACL function is disabled. All frames will pass through.
• Case 1: (c) Permit all frames, and map queues of the transmitting frames.
Set the default Gigabit Ethernet port ACL Rule to “Permit”, then bind a suitable profile with “Queue Mapping” for some ACL
functions. Map queues 0–7 of the frame received from this port.
• Case 1: (d) Permit all frames, and change the CoS value of the transmitting frames.
Set the default Gigabit Ethernet port ACL Rule as “Permit”, then bind a suitable profile with “CoS Marking” action for some ACL
functions. Change the CoS values of the VLAN frames received from this port.
To set one directional MAC address with CoS Marking:
STEP 1: Create a new ACL Profile. (Profile Name: CoSMarkingTest)
STEP 2: Create a new ACL Entry rule under this ACL profile.
(Filter SrcMAC: 11 and VLAN ID: 4 frame to CoS: 2)
STEP 3: Bind this ACL profile to a GE port. (Port 4)
STEP 4: Send frames between Port 3 and Port 4, and see the test result.
LIE1014A LIE1014A
Page 28
Figure 4-13.
LIE1014A
Figure 4-14.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 29

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
CLI Commands:
access-list ace 1 next 2 ingress interface GigabitEthernet 1/4 policy 1 vid 4 frametype etype
smac 00-00-00-00-00-11 action deny
exit
interface GigabitEthernet 1/3|
switchport trunk allowed vlan 4,5
switchport trunk vlan tag native
!
interface GigabitEthernet 1/4
switchport trunk allowed vlan 4,5
switchport trunk vlan tag native
exit
• Case 1: (e) Permit all frames, and copy a frame set in ACL entry to a defined GE port.
Set the default ACL Rule of GE port to “Permit”, then bind a suitable profile with “Copy Frame” for a mirror analyzer used.The
system will copy frames from a binding GE Port to analyzer port.
To set two directional MAC addresses with Copy Frame:
STEP 1: Create a new ACL Profile. (Profile Name: CopyFrameTest)
STEP 2: Create a new ACL Entry rule under this ACL profile. (SrcMAC: 13 and DesMAC: 11)
STEP 3: Set the analyzer port to enable and mirror the analyzer port.
STEP 4: Bind this ACL profile to a GE port. (Port 3)
Figure 4-15.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 29
Page 30

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
STEP 5: Send frames between Port 3 and Port 4, and see the test result.
LIE1014A
LIE1014A
LIE1014A
Figure 4-16.
CLI Commands:
access-list ace 2 next 3 ingress interface GigabitEthernet 1/3 policy 0 frametype etype smac
00-00-00-00-00-13 dmac 00-00-00-00-00-11 action deny mirror redirect interface
GigabitEthernet 1/5
exit
interface GigabitEthernet 1/3
switchport trunk allowed vlan 4,5
switchport trunk vlan tag native
!
interface GigabitEthernet 1/4
switchport trunk allowed vlan 4,5
switchport trunk vlan tag native
exit
• Case 1: (f) Deny all frames.
All frames will not pass through.
• Case 1: (g) Deny all frames, but permit frames set in ACL entry.
Set the default ACL Rule of a GE port as “Deny”, then bind a suitable profile with “Permit” for ACL. The GE port cannot pass
through any packets except the ACL entry of the bound profile.
To set one directional MAC address with one VLAN filtered:
STEP 1: Create a new ACL Profile. (Profile Name: AllowSomeMac)
STEP 2: Create a new ACL Entry rule under this ACL profile. (Allow MAC: 11 and VLAN: 4)
Page 30
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 31

STEP 3: Bind this ACL profile to a GE port. (Port 4)
Chapter 4: Switch Functions
Figure 4-17.
STEP 4: Send frames between Port 3 and Port 4, and see the test result.
LIE1014A
LIE1014A
LIE1014A
Figure 4-18.
CLI Commands:
access-list ace 4 ingress interface GigabitEthernet 1/4 policy 3 tag tagged vid 4 frametype etype
smac 00-00-00-00-00-11
exit
interface GigabitEthernet 1/3
switchport trunk allowed vlan 4,5
switchport trunk vlan tag native
!
interface GigabitEthernet 1/4
switchport trunk allowed vlan 4,5
switchport trunk vlan tag native
exit
To set two directional MAC addresses with all VLANs filtered:
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 31
Page 32

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
STEP 1: Create a new ACL Profile. (Profile Name: AllowSomeMac)
STEP 2: Create a new ACL Entry rule under this ACL profile. (Allow SrcMAC: 13 and DesMAC: 11)
STEP 3: Bind this ACL profile to a GE port. (PORT-3)
Figure 4-19.
STEP 4: Send frames between Port 3 and Port 4, and see the test result.
LIE1014A LIE1014A
CLI Commands:
00-00-00-00-00-13 dmac 00-00-00-00-00-11
exit
interface GigabitEthernet 1/3
switchport trunk allowed vlan 4,5
switchport trunk vlan tag native
!
interface GigabitEthernet 1/4
switchport trunk allowed vlan 4,5
switchport trunk vlan tag native
exit
LIE1014A
Figure 4-20.
Page 32
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 33

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
• Case 1: (h) Deny all frames.
The default ACL Rule of GE port is “Deny”, so Queue Mapping is not needed in this case.
• Case 1: (i) Deny all frames.
Deny all frames.
The default ACL Rule of GE port is “Deny”, so CoS Marking action is not needed in this case.
• Case 1: (j) Deny all frames.
Set the default ACL Rule of GE port as “Deny”, then bind a suitable profile with “Copy Frame” action for the mirror analyzer
used. The system will copy frames from the binding GE Port to analyzer port. No frames are received from the denied GE port but
Only mirror analyzer port frames are received from the denied GE port.
To set one directional MAC address with Copy Frame:
STEP 1: Create a new ACL Profile. (Profile Name: CopyFrameTest)
STEP 2: Create a new ACL Entry rule under this ACL profile. (SrcMAC: 13 and DesMAC: 11)
STEP 3: Bind this ACL profile to a GE port. (Port 3)
Figure 4-21.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 33
Page 34

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
STEP 4: Set the analyzer port to enable and mirror the analyzer port.
Figure 4-22.
STEP 5: Send frames between Port 3 and Port 4, and see the test result.
LIE1014A
LIE1014A
LIE1014A
Figure 4-23.
CLI Commands:
access-list ace 5 next 6 ingress interface GigabitEthernet 1/3 policy 5 frametype etype smac
00-00-00-00-00-13 dmac 00-00-00-00-00-11
Exit
monitor destination interface GigabitEthernet 1/5
monitor source cpu both
exit
interface GigabitEthernet 1/3
switchport trunk allowed vlan 4,5
switchport trunk vlan tag native
!
interface GigabitEthernet 1/4
switchport trunk allowed vlan 4,5
switchport trunk vlan tag native
exit
Page 34
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 35

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
4.2.3 Case 2: ACL for IP address
For IP address ACL, the switch can filter source IP address, destination IP address, or both. You can set an IP range ACL. When the
switch filters both IP addresses, packets that coincide with both rules will take effect. In other words, the switch does filter ACL
for IP address if it only coincides with one rule.
To filter only one directional IP address, set the other IP address to all zeros. The switch also filters Protocols (TCP=6, UDP=17, etc.)
Certain Protocols under these IP addresses will take effect. If you don't want the switch to filter Protocol, set it to zero. For details
about testing, refer to MAC ACL above.
4.2.4 Case 3: ACL for L4 Port
For Layer 4 port ACL, the switch can filter (1) source IP address, (2) source L4 port, (3) destination IP address, (4) destination L4
port, and (5) UDP or TCP Protocol. You can filter (1)– (4) for all or some specific values, but you should select exactly one Protocol
from UDP or TCP.
When it filters both directional IP address and L4 port, packets that coincide with both rules will take effect. In other words, the
switch does not filter if it only coincides with one rule.
To filter only one directional IP address or L4 port, set the other IP address and the L4 port to all zeros. For details about testing,
refer to MAC ACL above.
4.2.5 Case 4: ACL for ToS
For Type of Service (ToS) ACL, the switch can filter (1) source IP address with ToS type, (2) destination IP address with ToS type, or
(3) both, or (4) neither (if you select neither, the switch just filters ToS). When it filters both IP addresses, packets that coincide
with both rules will take effect. In other words, the switch does not filter if it only coincides with one rule.
To filter only one directional IP address, set the other IP addresses to all zeros. For details about testing, refer to Case 1: MAC ACL
above.
Valid Values: Precedence: 0–7, ToS: 0–15, DSCP: 0–63
This value (7) is reserved and set to 0.
Ex: Pre (001) means 1
Pre (100) means 4
ToS (00010) means 1
ToS (10000) means 8
DSCP (000001) means 1
DSCP (100000) means 32
Figure 4-24.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 35
Page 36

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
4.3 Ring Protection Application Guide
4.3.1 Explanation of Ring Protection
A reliable network is very important in industrial Ethernet applications.
The LIG1014A/LIE1014A switch provides millisecond-grade failover ring protection; this feature offers a seamless working
network even if connections create issues. Ring Protection works with both Ethernet and fiber cable.
Page 36
Figure 4-25.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 37

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
4.3.2 Configuration (Console)
To configure ring protection on the LIG1014A/LIE1014A switch:
1. Login as “admin” in the console interface.
2. Go to Configure mode via the ”configure terminal” command.
3. Go to Configure Ring Protection via the “ring protect” command.
4. Go to configure ring protection group1 via the “group1” command.
5. Before configuring the console, you must disable ring protection status using the “mode disable” command.
6. To set all necessary parameters:
• For Node 1 and Node 2, choose the ports that you want to connect to the other switch.
• For example, if you choose Port 1 and Port 2, then Port 1 and Port 2 are both connected to the other switch.
• Choose one of ring connection devices as “Master.” The “Node 2 port” will be the blocking port for the master device.
id 1
node1 interface GigabitEthernet 1/1
node2 interface GigabitEthernet 1/2
Role Master node1 interface GigabitEthernet 1/1
node2 interface GigabitEthernet 1/2
• To finish this configuration, you must enable ring protection status by selecting the “mode enable” command.
NOTE: Pay attention to the of “Previous Command Result” status after every action.
configure terminal
ring protect
group1
mode disable
id 1
node1 interface GigabitEthernet 1/1
node2 interface GigabitEthernet 1/2
Role Master
mode enable
exit
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 37
Page 38

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
4.3.3 Configuration (Web UI)
Figure 4-26.
STEP 1: Set RSTP on the central switch.
NOTE: The administrator must configure STP mode on the central switch “SWM.”
Figure 4-27.
1. Go to the “Configuration—>Spanning Tree—>Bridge Setting” Web page.
2. Select “Protocol Version” as “RSTP.”
3. Click the “Save” button.
Page 38
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 39

Figure 4-28.
1. Go to the “Configuration—>Spanning Tree—>CIST ports” Web page.
Chapter 4: Switch Functions
2. Do not enable Port 7 or 8, check box for ring 1.
3. Do not enable Port 9 or 10, check box for ring 2.
4. Check “Auto Edge” on Port 11 and 12.
5. Click the“Save” button.
STEP 2: Set ring protection on the central switch.
1. Go to the “Configuration—>Ring” Web page.
2. Select “Ring Group 1”
3. Ring ID 1
Check “Ring Enable,” and ”Master.”
Set Port 7 as Node 1 and Port 8 as Node 2.
Figure 4-29.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 39
Page 40

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
4. Click the “Save” button.
Figure 4-30.
1. Go to the “Configuration—>Ring” Web page.
2. Select “Ring Group 2.”
3. Ring ID 2
Check “Ring Enable,”, and ”Master.”
Set Port 9 as Node 1 and Port 10 as Node 2.
4. Click the “Save” button.
Follow the instructions in the screen shown next to save running configuration.
Figure 4-31.
Page 40
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 41

STEP 3: Configure ring protection on switches SW11, SW12, SW13, and SW14.
Figure 4-32.
1. Go to the Configuration —>Spanning Tree—>CIST ports Web page.
2. Do not enable the STP check box for ring configuration.
Chapter 4: Switch Functions
3. Click the “Save” button.
1. Go to the “Configuration—>Ring” Web page.
2. Select “Ring Group 1.”
3. Ring ID 1
Figure 4-33.
Check “Ring Enable.”
Set Node 1 as Port 7, and node 2 as Port 8.
4. Click the “Save” button.
Then save the running configuration.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 41
Page 42

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
STEP 4: Configure ring protection on switches SW21, SW22, SW23, and SW24.
Figure 4-34.
1. Go to the Configuration —>Spanning Tree—>CIST ports Web page.
2. Do not enable the STP check box for ring configuration.
3. Click the “Save” button.
1. Go to the “Configuration—>Ring” Web page.
2. Select “Ring Group 2.”
3. Ring ID 2
Figure 4-35.
Check “Ring Enable.”
Set Node 1 as Port 9, and node 2 as Port `0.
4. Click the “Save” button.
Then save the running configuration.
Page 42
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 43

4.3.4 Dual Ring
Feature: Interconnection ports can belong to two neighbor ring groups.
Advantage: You can run the ring function on just one port.
Chapter 4: Switch Functions
Figure 4-36.
Configure Steps:
1. Disable RSTP on all ring ports.
2. Select a master port in every ring group.
3. Configure ring protection on the ring 2 group.
4. Configure ring protection on the other ring group device.
NOTE: Rules:
• Any device with a master port cannot connect with another device with a master port.
• The NSF ports are member ports of the middle ring group.
• The ring groups can up to three in a dual-ring scenario.
• Any device that belongs to two ring groups is an inter-connection device.
Configure ring protection on the middle ring group (ring2).
On device 4 (ring 2 master):
1. Go to the “Configuration—>Ring” Web page.
2. Select “Ring Group 2.”
3. Ring ID 2
Check “Ring Enable,” ”Interconnection,” and ”Master.”
Protect Port and NSF is on “Node 1 (port 9).”
Node 1 is “Port 9,” and node 2 is ”Port 10.”
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 43
Page 44

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
4. Click the “Save” button.
Figure 4-37.
On devices 3, 5, and 6 (ring 2 slave):
1. Select “Ring Group 2.”
3. Ring ID 2
Check “Ring Enable” and ”Interconnection,”
NSF is on “Node 1 (port 9).”
Node 1 is “Port 9,” and node 2 is ”Port 10.”
3. Click the “Save” button.
Page 44
Figure 4-38.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 45

Configure ring protection on the side ring group (ring 1 and 3).
On device 2 and 7 (master):
1. Select “Ring Group 1 (or 3)”
2. Ring ID 1 (or 3)
Check “Ring Enable”, and ”Master”.
Protect Port is on “Node1 (port 9)”
Node 1 will be “Port 9”, and node 2 will be “Port 10.”
3. Click the “Save” button.
On device 1 and 8 (slave):
1. Select “Ring Group 1 (or 3)”
2. Ring ID 1(or 3)
Check “Ring Enable”
Node 1 will be “Port 9”, and node 2 will be ”Port 8”
3. Click the “Save” button.
Chapter 4: Switch Functions
On device 3–6 (slave) + Inter-connection:
1. Select “Ring Group 1 (or 3)”
2. Ring ID 1(or 3)
3. Check “Ring Enable,” and ”Inter-connection”
Node 1 will be “Port 9”, and node 2 will be ”Port 8”
4. Click the “Save” button.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 45
Page 46

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
4.3.5 Dual Homing
Feature: Dual homing devices (switch 6) enable two ring groups.
Advantage: Recovery time is less than “dual ring,” and you can connect two dual ring systems.
Configure Steps:
1. Disable RSTP on all ring ports.
2. Select a master port in every ring group.
3. Configure ring protection on ring 2 group.
4. Configure ring protection on other ring group devices.
Compare to Dual Ring, but only modify devices 5 and 6.
On device 5 (slave):
1. Select “Ring Group 3.”
2. Ring ID
Check “Ring Enable.”
Node 1 will be “Port 9, and node 2 will be “Port 8.”
3. Click the “Save” button.
On device 6 (slave):
1. Select “Ring Group 3.”
2. Ring ID 3
Check “Ring Enable.”
3. Node 1 will be “Port 9”, and node 2 will be ”Port 8.”
4. Select “Ring Group 2.”
5. Ring ID 2
Check “Ring Enable”
Node 1 will be “Port 7,” and node 2 will be “Port 10.”
Figure 4-39.
6. Click the “Save” button.
Page 46
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 47

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
4.4 QoS Application Guide
4.4.1 Explanation of QoS
Quality of Service (QoS) features allow you to allocate network resources to mission-critical applications at the expense
of applications that are less sensitive to factors such as time delays or network congestion. You can configure your network
to prioritize specific types of traffic, ensuring that each type receives the appropriate Quality of Service (QoS) level.
4.4.2 SP/SPWRR/WRR
The LIG1014A/LIE1014A can be configured to have 8 output Class of Service (CoS) queues (Q0–Q7) per port, into which each
packet is placed. Q0 is the highest priority Queue. Each packet’s 802.1p priority determines its CoS queue. You need to bind
VLAN priority/queue mapping profile to each port, and, for every VLAN priority, assign a traffic descriptor. The traffic descriptor
defines the shapping parameter on every VLAN priority for Ethernet interface. Currently LIG1014A/LIE1014A supports Strict
Priority (SP)/SPWRR (SP+WRR)/WRR (Weighted Round Robin) scheduling methods on each port.
Table 4-2. Default Priority and Queue mapping.
Priority0 Priority1 Priority2 Priority3 Priority4 Priority5 Priority6 Priority7
Queue0 Queue1 Queue2 Queue3 Queue4 Queue5 Queue6 Queue7
WRR WRR WRR WRR SPQ SPQ SPQ SPQ
Application Examples
Several examples for various QoS combinations are listed next. You can configure QoS using the Web-based management system,
CLI (Command Line Interface), or SNMP.
4.4.3 Example 1: SPQ without Shaping (Default profile)
Send 2 Streams (Stream 0, Stream 1) from Port 1 to Port 2. Both streams are running at 100 Mbps. Stream 0 includes VLAN
Priority 0, Stream 1 includes VLAN Priority 7. Set Port 2 link speed to 100 Mbps.
Expected Result:
Port 2 only can receive 100 Mbps of Stream 1, and Stream 0 will be discarded.
Gigabit port VLAN Priority & Queue mapping:
Figure 4-40.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 47
Page 48

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
• Stream 0:
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:01
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:01
Vlan:100
Vlan prio: 0
Send rate: 100 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
• Stream 1:
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:02
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:02
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 7
Send rate: 100 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
Web management:
Step 1. Go to Configuration —> Ports —> set port 2 link speed to 100 Mbps full duplex.
Page 48
Figure 4-41.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 49

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
Step 2. Select Configuration—> VLANs —>Create a VLAN with VLAN ID 100. Enter a VLAN name in the Name field. Here we set
tagged VLAN 100 on Port 1 and Port 2.
Figure 4-42.
CLI configuration commands:
interface GigabitEthernet 1/2
speed 100
duplex full
exit
vlan 100
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 49
Page 50

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
4.4.4 Example 2: SPQ with Shaping
Send two Streams (Stream 0, Stream 1) from port 1 to port 2. Both streams are running at 100 Mbps. Stream 0 includes VLAN
Priority 0, Stream 1 includes VLAN Priority 7. Stream 3 and Stream 4 are used only for learning which to make sure the traffic
does not flood.
Expected Result:
Port 2 only can receive 20 Mbps of Stream 1, and 80 Mbps of Stream 0.
VDSL port VLAN Priority & Queue mapping:
• Stream 0:
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:01
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:01
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 0
Send rate: 100Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
• Stream 1:
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:02
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:02
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 7
Send rate: 100 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
• Stream 3: (for Learning)
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:01
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:01
Vlan : 100
Figure 4-43.
Page 50
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 51

Vlan prio: 0
Send rate: 10 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
• Stream 4: (for Learning)
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:02
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:02
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 0
Send rate: 10Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
Web management:
STEP 1: Go to Configuration —> Qos—>Port Shaping, to create a Qos profile on Port 2.
Chapter 4: Switch Functions
Figure 4-44.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Pag e 51
Page 52

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
STEP 2: Select schedule mode as “”Strict Priority” and set shaping rate for queue 0 and queue 7 as described next.
Figure 4-45.
CLI configuration commands:
vlan 100 v100
interface gigabit 1
vlan 100 tag
exit
interface gigabit 2
qos shaper 100000
qos queue-shaper queue 0 80000
qos queue-shaper queue 7 20000
exit
Page 52
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 53

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
4.4.5 Example 3: WRR
Send three Streams (Stream 0, Stream 1, and Stream 2) from Port 1 to Port 2. These Streams each have 100 Mbps. Stream 0
includes VLAN Priority 0, Stream1 includes VLAN Priority 3, Stream2 includes VLAN Priority 7. Stream 3, Stream 4, and Stream 5
are used only for learning to make sure the traffic is not flooding. WRR supports weight assignment; the range of weight value is
from 1 to 255. LIG1014A/LIE1014A applies WRR scheduling and weight 1 for all the Gigabit Ethernet ports. In the following case,
assign Weight 2 for Priority 0, Weight 3 for Priority 3, and Weight 5 for Priority 7.
Expected Result:
Port 2 can receive about 20 Mbps of Stream 30 Mbps of Stream 1 and 50 Mbps of Stream 2.
Gigabit port VLAN Priority & Queue mapping:
• Stream 0:
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:01
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:01
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 0
Send rate: 100 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
• Stream 1:
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:04
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:04
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 3
Send rate: 100 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
Figure 4-46.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 53
Page 54

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
• Stream 2:
Dst Mac : 00:00:00:00:20:08
Src Mac : 00:00:00:00:10:08
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 7
Send rate: 100 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
• Stream 3: (for Learning)
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:01
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:01
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 0
Send rate: 10 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
• Stream4: (for Learning)
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:04
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:04
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 0
Send rate: 10 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
• Stream 5: (for Learning)
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:08
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:08
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 0
Send rate: 10 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
Page 54
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 55

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
Web management:
STEP 1: Go to Configuration—> Qos—> Port shaping, and click on Port 2 to create a Qos profile.
Figure 4-47.
STEP 2: Select schedule mode to “”Weighted” and set weight value for queue 0, queue 3, and queue 7 as described next.
Figure 4-48.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 55
Page 56

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
CLI configuration command:
interface GigabitEthernet 1/1
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,100
switchport hybrid allowed vlan 1,100
switchport trunk vlan tag native
switchport mode trunk
exit
interface GigabitEthernet 1/2
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,100
switchport trunk vlan tag native
switchport mode trunk
qos shaper 100000
qos queue-shaper queue 6 50000 excess
qos queue-shaper queue 7 50000 excess
qos wrr 2 1 1 3 1 1
exit
Page 56
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 57

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
4.4.6 Example 4 SP-WRR
Send 4 Streams (Stream 0, Stream 1, Stream 2, and Stream 3) from Port 1 to Port 2. These Streams each have 100 Mbps. Stream
0 includes VLAN Priority 0, Stream 1 includes VLAN Priority 1, Stream 2 includes VLAN Priority 2, Stream 3 includes VLAN Priority
3, and Stream 4 includes VLAN Priority 6. Stream 5, Stream 6, Stream 7, Stream 8, and Stream 9 are used only for learning to
make sure traffic is not flooding. WRR supports a range of weight values from 1 to 255. LIG1014A/LIE1014A applies WRR
scheduling and weight 1 for all the Gigabit Ethernet Port. In the following case, we will assign Weight 1 for Priority 0, Weight 2
for Priority 1, Weight 3 for Priority 2, and Weight 4 for Priority 3. In SP-WRR mode, queue 0 to queue 3 belongs to WRR, and
queue 4 to queue 6 belongs to SP.
Expected Result:
In Case 1, Port 2 can receive about 10 Mbps of Stream 0, 20 Mbps of Stream 1, 30 Mbps of Stream 2, and 40 Mbps of Stream 3
if we send Stream 0 to Stream 3 to Port1. In Case 2, we expect Port 2 only can receive 100 Mbps of Stream 6, and Stream 0 to
Stream 3 will be discarded.
Case 1:
Gigabit port VLAN Priority & Queue mapping:
• Stream 0:
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:01
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:01
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 0
Send rate: 100 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
Figure 4-49.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 57
Page 58

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
• Stream 1:
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:02
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:02
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 3
Send rate: 100 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
• Stream 2:
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:03
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:03
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 7
Send rate: 100 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
• Stream 3:
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:04
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:04
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 7
Send rate: 100 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
• Stream 5: (for Learning)
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:01
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:01
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 0
Send rate: 10 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
• Stream 6: (for Learning)
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:02
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:02
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 0
Send rate: 10 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
• Stream 7: (for Learning)
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:03
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:03
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 0
Send rate: 10Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
Page 58
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 59

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
• Stream 8: (for Learning)
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:04
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:04
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 0
Send rate: 10Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
Web management:
STEP 1: Go to Configuration—> Qos —> Port shaping, and click on PORT-2 to create a Qos profile.
Figure 4-50.
STEP 2: Select schedule mode to “”Weighted” and set the weight value for queue 0, and set weight value for queue 0–queue 3
as described next.
Figure 4-51.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 59
Page 60

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
STEP 3: Go to Configuration—> Queue and Scheduler —> Binding, and bind profile 2 on Port 2.
CLI configuration commands:
interface GigabitEthernet 1/2
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,100
switchport hybrid allowed vlan 100,4095
switchport trunk vlan tag native
switchport mode trunk
qos shaper 100000
qos queue-shaper queue 0 500
qos queue-shaper queue 1 500
qos queue-shaper queue 2 500
qos queue-shaper queue 3 500
qos wrr 1 2 3 4 1 1
exit
Case 2:
Gigabit port VLAN Priority & Queue mapping
• Stream 0:
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:01
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:01
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 0
Send rate: 100 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
Page 60
Figure 4-52.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 61

• Stream 1:
Dst Mac : 00:00:00:00:20:02
Src Mac : 00:00:00:00:10:02
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio : 3
Send rate : 100Mbps
Packet length: 1518bytes
• Stream 2:
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:03
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:03
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 7
Send rate: 100 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
• Stream 3:
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:04
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:04
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 7
Send rate: 100 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
Chapter 4: Switch Functions
• Stream 4:
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:07
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:07
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 7
Send rate: 100 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
• Stream 5: (for Learning)
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:01
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:01
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 0
Send rate: 10 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
• Stream 6: (for Learning)
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:02
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:02
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 0
Send rate: 10 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 61
Page 62

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
• Stream 7: (for Learning)
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:03
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:03
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 0
Send rate: 10 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
• Stream 8: (for Learning)
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:04
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:04
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 0
Send rate: 10 Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
• Stream 9: (for Learning)
Dst Mac: 00:00:00:00:10:07
Src Mac: 00:00:00:00:20:07
Vlan : 100
Vlan prio: 0
Send rate: 10Mbps
Packet length: 1518 bytes
Web management:
STEP 1: Go to Configuration —> Qos —> Port shaping, and click on Port 2 to create a Qos profile.
Figure 4-53.
Page 62
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 63

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
STEP 2: Select schedule mode to “”Weighted” and set the weight value for queue 0, and set weight value for queue 0–queue 3
as described next.
Figure 4-54.
CLI configuration command:
interface GigabitEthernet 1/2
switchport trunk allowed vlan 1,100
switchport hybrid allowed vlan 100,4095
switchport trunk vlan tag native
switchport mode trunk
qos shaper 100000
qos wrr 1 2 3 4 1 1
exit
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 63
Page 64

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
4.5 IGMP Application Guide
4.5.1 Explanation of IGMP
IGMP is an acronym for Internet Group Management Protocol. It is a communications protocol used to manage the membership
of Internet Protocol multicast groups. IGMP is used by IP hosts and adjacent multicast routers to establish multicast group
memberships. It is an integral part of the IP multicast specification, similar to ICMP for unicast connections. IGMP can be used for
online video and gaming, and allows more efficient use of resources when supporting these uses.
Figure 4-55.
Example 1:
The administrator can set every client to get the multicast stream. Go to “Configuration—>IPMC—>Basic Configuration” and
select the “Snooping Enable” checkbox, and click on OK.
Figure 4-56.
Page 64
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 65

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
Example 2:
LIE1014A
Figure 4-57.
1. Go to “Configuration—>IPMC—>Basic Configuration” to select the “Snooping Enable” checkbox
2. De-select the ”Unregistered IPMCv4 Flooding Enabled” checkbox.
3. If the Multicast stream is from an L3 switch, then the uplink port must be “Router Port.”
NOTE: If an aggregation member port is selected as a router port, the whole aggregation will act as a router port.
Figure 4-58.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 65
Page 66

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
4. Go to “Configuration—>IPMC—>VLAN Configuration” to select the “Snooping Enable” checkbox and set Port 14's VLAN ID.
Figure 4-59.
Example 3:
LIE1014A
Figure 4-60.
In this scenario, these clients belong to multiple vlans, so you have to create more than one vlan to be the agent for all client
vlans.
1. To create a vlan: go to ”Configuration—>VLANs—>Allow Access VLANs”, then set port 14 to be the vlan200 member port.
Page 66
Figure 4-61.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 67

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
2. Go to “Configuration—>IPMC—>VLAN Configuration” to select the ”Snooping Enable” checkbox and set Port 14’s VLAN ID.
Figure 4-62.
3. If there is no querier on the L3 switch, select “Querier Election,” and set the “Querier Address.” The IP address is in the same
network as the uplink interface.
4. Select the IGMP version as the server.
Figure 4-63.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 67
Page 68

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
4.5.2 Configuring VLC on an IGMP Server
1. In the Media area of the top tool bar, select “Stream.”
2. Select a video or voice file to play.
Figure 4-64.
Page 68
Figure 4-65.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 69

3. Confirm that the file is correct, then click “Next” twice.
Chapter 4: Switch Functions
Figure 4-66.
4. Select the stream type as “UDP” and click the “Add” button.
Figure 4-67.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 69
Page 70

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
5. Set the stream IP; the range is 224.0.0.1 to 239.255.255.254, and the protocol port is 1234.
For this example, we set stream IP as 255.0.0.1.
Figure 4-68.
6. Select ”Sort out all stream” and click the “Stream” button, then the stream starts sending to switch.
Figure 4-69.
Page 70
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 71

4.5.3 Configuring VLC on an IGMP Client
1. In the Media area of the top tool bar, select Open Network Stream.
Chapter 4: Switch Functions
Figure 4-70.
2. Set the stream IP and protocol port as the previous setting on the server. The protocol type is “UDP,” and the format should be
the same as below the circle, then click the “PLAY” button.
Figure 4-71.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 71
Page 72

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
To return to the management switch:
Go to “Monitor—>IPMC—>Groups Information,” and you will see the IP stream in the table.
Figure 4-72.
Page 72
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 73

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
4.6 802.1x Authentication Application Guide
4.6.1 Explanation of 802.1x Authentication
IEEE 802.1x derives keys that you can use to provide per-packet authentication, integrity, and confidentialily. Typically, you would
use the keys along with well-known key derivation algorithms (e.g., TLS, SRP, MD5-Challenge, etc.). The LIG1014A/LIE1014A
switch supports the 802.1x authentication function per port (Port 1–Port 10). Enable the system's 802.1x function, then choose
the ports and type you want to apply. If you enable 802.1x authentication control for a certain Ethernet port on the switch, this
port should be authenticated before using any service from the network.
4.6.2 802.1x Timer in the Industrial Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Table 4-3. 802.1x Timer in the LIG1014A/LIE1014A switch.
Item Parameter (sec) Description
1 ReAuth Period LIG1014A/LIE1014A will restart authentication after each Reauth-Period when authentication
is successful and the ReAuth option is enabled.
2 Quiet Period LIG1014A/LIE1014A will wait the length of the QuietPeriod to restart the authentication
process again when authentication failed the previous time.
3 Tx Period LIG1014A/LIE1014A will send the EAP-request to the Supplicant every TxPeriod
when authentication is running and the Quiet Period is not running.
4 Supplicant Timeout LIG1014A /LIE1014A will wait the length of the SupplicantTmeout to receive a response
from the Supplicant.
5 Server Timeout LIG1014A/LIE1014A will wait ServerTimeout to receive response from RADIUS server.
4.6.3 Configuration in a RADIUS Server
STEP 1: Prepare a Linux PC with a RADIUS server installed.
STEP 2: Edit the secret key for the Radius server.
Setting:
client 20.20.20.0/24 {
secret = a1b2c3d4
STEP 3: Edit the user name and password for supplicant to authenticate with the server.
Setting:
test123 Cleartext-Password := “test123”
aaaa Cleartext-Password := “aaaa”
STEP 4: Set a static IP address for this Radius Server.
Setting: 20.20.20.20
STEP 5: Start Radius Server
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 73
Page 74

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
Example:
To learn how to activate 802.1x Authentication via LIG1014A/LIE1014A to be authenticated by a RADIUS server, read the
following example. In this basic example, Port 1 is a testing port that enables 802.1x in the LIG1014A/LIE1014A.
With the default configuration, use the following Web UI setting:
Figure 4-73.
STEP 1: Go to Configuration—> Security —> Networks —> NAS.
Figure 4-74.
Page 74
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 75

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
Select “Enable” to enable authentication, and set Port 1 and Port 2 as “Port Base 802.1x.”
STEP 2: Go to Configuration —> Security —> AAA —> Radius.
Click “Add New Server,” and type in “20.20.20.20” for the server, and “a1b2c3d4” for the secret key. Then click the “Save”
button.
CLI Command:
Configure ter
interface vlan 1
ip address 20.20.20.120 255.0.0.0
exit
exit
radius-server host 20.20.20.20 timeout 5 retransmit 3 key a1b2c3d4
dot1x re-authentication
dot1x system-auth-control
interface GigabitEthernet 1/1
dot1x port-control auto
Configuration
Supplicant’s NIC Setting
STEP 1: Configure a static IP address 20.20.20.10 and a net mask 255.255.255.0 for the supplicant.
(If a DHCP server will assign an IP address for supplicant, you can ignore this step.)
STEP 2: Select the IEE E802.1x Authentication Enable check box, then configure the EAP type as MD5-Challenge.
After setting this function in the NIC, the supplicant should enter a correct pair of account and password to use this Ethernet port
service from the LIG1014A/LIE1014A.
Figure 4-75.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 75
Page 76

Chapter 4: Switch Functions
Authentication Behavior
The supplicant should pass authentication process to use any service. After the supplicant enters the correct account and
password stored in RADIUS server, it can be authenticated successfully. The authentication process is described in the following
diagram.
LIE1014 A
Figure 4-76.
.
Page 76
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 77

Chapter 5: Hardware Quick Setup Guide
5. Hardware Quick Setup Guide
5.1 What’s Included
Your package should contain the following items. If anything is missing or damaged, contact Black Box Technical Support
at 877-877-2269 or info@blackbox.com.
• (1) Industrial Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch - (10) RJ-45, (4) SFP (LIG1014A)
OR
(1) Industrial Managed Gigabit Ethernet PoE+ Switch - (8) RJ-45, (4) SFP (LIE1014A)
• (2) wallmount brackets
• (1) DIN-rail clip
• (4) M3 screws (for the wallmount brackets or DIN-rail clip)
• (1) DC power terminal block
• (10) or (8) RJ-45 connector dust covers
• (4) SFP port dust covers
• This Quick Start Guide
WARNING! When a connector is removed during installation, testing, or servicing, or when an energized fiber
is broken, your eyes might be exposed to to hazardous laser output power.
5.2 Mounting the Switch on a DIN Rail
1. Screw the DIN rail bracket onto the switch with the included bracket and screws.
2. Hook the switch-DIN-rail-bracket assembly over the DIN rail.
3. Push the bottom of the assembly towards the DIN rail until it snaps into place.
Figure 5-1. Din-rail mounting.
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 77
Page 78

Chapter 5: Hardware Quick Setup Guide
5.3 Mounting the Switch on a Wall
Screw the wall mount brackets on using the included M3 screws.
M4 screw
P1 P2 ALM
Figure 5-2. Wallmounting.
5.4 Ethernet Interface
The switch has two types of Ethernet interfaces: electrical (RJ-45) and optical (SFP) interfaces.
5.4.1 R J- 45
• To connect the switch to a PC, use straight-through or cross-over Ethernet cables.
• To connect the switch to an Ethernet device, use UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) or STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) Ethernet cables.
The RJ- 45 pinout is shown in the following figure and tables.
LED B
LED A
Pin 8
Figure 5-3. RJ-45 connector pinout.
Table 5-1. RJ-45 pinout descriptions
Pin Assignment PoE Assignment
1, 2 TX/RX+, TX/RX- Positive V
3, 6 TX/RX+, TX/RX- Negative V
4, 5 TX/RX+, TX/RX- Not used
7, 8 TX/RX+, TX/RX- Not used
Pin 1
(LIE1014A only)
port
port
Page 78
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 79

Chapter 5: Hardware Quick Setup Guide
5.4.2 Fiber, SFP
For both 100/1000 Mbps fiber speed connections, the SFP slots are available. The SFP slot accepts the fiber transceivers
that typically have an LC connector.
The fiber transceivers have options of multimode, single mode, long-haul or specialapplication transceivers.
DANGER:
Never attempt to view optical connectors that might be emitting laser energy.
Do not power up the laser product without connecting the laser to the optical fiber and putting the dust cover
in position, because laser outputs will emit infrared laser light at this point.
Table 5-2. Compatible SFP modules.
Part
Number Description
LF P411 SFP/1250 Extended Diagnostics, LC multimode, 850 nm, 550 m
LFP412 SFP/1250 Extended Diagnostics, LC multimode, 1310 nm, 2 km
LFP413 SFP/1250 Extended Diagnostics, LC single-mode, 1310 nm, 10 km
LFP414 SFP/1250 Extended Diagnostics, LC single-mode, 1310 nm, 40 km
LFP401 SFP/155 Extended Diagnostics, LC multimode, 850 nm, 2 km
LFP403 SFP/155 Extended Diagnostics, LC single-mode, 1310 nm, 30 km
LFP404 SFP/155 Extended Diagnostics, LC single-mode, 1310 nm, 60 km
LFP402 SFP/155 Extended Diagnostics, LC multimode, 1310 nm, 2 km
LFP418 SFP/1250 Extended Diagnostics, LC single-mode, 1550 nm, 80 km
LFP420 Simplex SFP/1250, Extended Diagnostics, single-mode, 1550 nm TX, 1310 nm RX
5.5 Connecting the Power Terminal Block
The switch can be powered from two power supplies (input range 12V – 58V). Insert the positive and negative wires into V+ and
V- contacts on the terminal block respectively and tighten the wire-clamp screws to prevent the wires from loosening.
LIG1014A
First power supply
PWR1 ALM PW R2
Consol e
Reset
Figure 5-4. Terminal block, LIG1014A.
Second power supply
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 79
Page 80

Chapter 5: Hardware Quick Setup Guide
LIE1014 A
Second power supply
Consol e
Figure 5-5. Terminal block, LIE1014A.
5.6 Alarm Relay and Ground
The alarm relay output contacts are in the middle of the DC terminal block connector as shown in the figure below.
The alarm relay out is “Normal Open”, and it will be closed when detected any predefined failure such as power failures or
Ethernet link failures.
First power supply
PWR1 ALM PW R2
Reset
The relay output has current carrying capacity of 0.5 A @ 24 VDC.
Extra power system
PWR1 ALM PW R2
Consol e
Figure 5-6. Alarm relay, LIG1014A or LIE1014A.
Alarm system
Ground
connector
Page 80
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 81

Chapter 5: Hardware Quick Setup Guide
5.7 Console Connection
The Console port is for local management by using a terminal emulator or a computer with terminal emulation software.
• DB9 connector connect to computer COM port
• Baud rate: 115200bps
• 8 data bits, 1 stop bit
• No Priority
• No flow control
PWR1 ALM PW R2
Reset
Consol e
Figure 5-7. Console connector, LIG1014A or LIE1014A.
An RJ-45 (male) connector-to-RS-232 DB9 (female) connector cable is required. The RJ-45 connector of the cable is connected to
the console connector on the switch. The pin assignment of the console cable is shown on the next page.
5.8 Connect and Login to Managed Switch
1. Connecting to the Ethernet port (RJ45 Ethernet port) of Managed Switch.
2. Factory default IP: 192.0.2.1
3. Login with default account and password.
Username: admin
Password: (none)
5.9 CLI Initialization and Configuration (Optional)
1. Connecting to the Ethernet port(RJ45 Ethernet port) of Managed Switch
2. Type in the command under Telnet: telnet 192.0.2.1
3. Login with the default account and password.
Username: admin
Password: (none)
4. Change the IP with commands listed below:
CLI Command:
enable
configure terminal
interface vlan 1
ip address xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
exit
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 81
Page 82

Chapter 5: Hardware Quick Setup Guide
5.10 Ind ic ator s
Table 5-3. Front-panel LEDs on the LIG1014A.
LED Name Status Condition
(1) P1 LED ON, Green P1 power line has power
OFF P1 power line is disconnected or does not have power
(1) P2 LED ON, Green P2 power line has power
OFF P2 power line is disconnected or does not have power
(1) Alarm LED ON, Red Failure alarm occurs
OFF No power failure alarm
(10) Link/Act LEDs for RJ-45 ports On, Green Ethernet link is up but no traffic is detected
OFF Ethernet link is down
(10) Speed LEDs for R J- 45 ports O N, Yel low 1000-Mbps connection is detected.
OFF No link, a 10-Mbps or 100-Mbps connection is detected
(4) Link /Act LED for SFP port ON, Green Ethernet link is up
OFF Ethernet link is down
(4) Speed LED for SFP port ON, Ye llow SFP port speed 1000 -Mbps connection is detected
OFF No link, or an SFP port speed 100-Mbps connection is detected
Page 82
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 83

Chapter 5: Hardware Quick Setup Guide
Table 5-4. Front-panel LEDs on the LIE1014A.
LED Name Status Condition
(8) PoE LEDs ON, Green PoE is working
OFF PoE is not working
(1) P1 LED ON, Green P1 power line has power
OFF P1 power line is disconnected or does not have power
(1) P2 LED ON, Green P2 power line has power
OFF P2 power line is disconnected or does not have power
(1) Alarm LED ON, Red Power failure alarm occurs
OFF No power failure alarm
(8) Link/Act LEDs for RJ-45 PoE+ ports On, Green Ethernet link is up but no traffic is detected
OFF Ethernet link is down
(8) Speed LEDs for RJ-45 PoE+ ports ON, Yellow 1000-Mbps connection is detected.
OFF No link, a 10-Mbps or 100-Mbps connection is detected
(4) Link /Act LED for SFP port ON, Green Ethernet link is up
OFF Ethernet link is down
(4) Speed LED for SFP port O N, Yel low SFP port speed 1000-Mbps connection is detected
OFF No link, or an SFP port speed 100-Mbps connection is detected
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
Page 83
Page 84

Black Box Tech Support: FREE! Live. 24/7.
Tech support the
way it should be.
Great tech support is just 60 seconds away at 877-877-2269 or blackbox.com.
About Black Box
Black Box provides an extensive range of networking and infrastructure products. You’ll find everything from cabinets and racks
and power and surge protection products to media converters and Ethernet switches all supported by free, live 24/7 Tech support
available in 60 seconds or less.
© Copyright 2016. Black Box Corporation. All rights reserved. Black Box® and the Double Diamond logo are registered trademarks of BB Technologies, Inc.
Any third-party trademarks appearing in this manual are acknowledged to be the property of their respective owners.
lig1014a_lie1014a_user_rev2
877-877-2269 | blackbox.com
 Loading...
Loading...