Page 1
CUSTOMER
SUPPORT
INFORMATION
Order toll-free in the U.S. 24 hours, 7 A.M. Monday to midnight Friday: 877-877-BBOX
FREE technical support, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week: Call 724-746-5500 or fax 724-746-0746
Mail order: Black Box Corporation, 1000 Park Drive, Lawrence, PA 15055-1018
Web site: www.blackbox.com • E-mail: info@blackbox.com
JUNE 2000
IC111C
IC181C
Four Port RS-232 Serial Interface
Page 2

FOUR PORT RS-232 SERIAL INTERFACE
FEDERAL COMMUNICATIONS COMMISSION
AND
INDUSTRY CANADA
RADIO FREQUENCY INTERFERENCE STATEMENTS
This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy a
nd if not installed and used properly, that is, in strict accordance with the
manufacturer’s instructions, may cause interference to radio communication.
It has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A
computing device in accordance with the specifications in Subpart J of
Part 15 of FCC rules, which are designed to provide reasonable protection
against such interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial
environment. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to
cause interference, in which case the user at his own expense will be required
to take whatever measures may be necessary to correct the interference.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible
for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class A limits for radio noise emission from
digital apparatus set out in the Radio Interference Regulation of Industry Canada.
Le présent appareil numérique n’émet pas de bruits radioélectriques dépassant les limites
applicables aux appareils numériques de la classe A prescrites dans le Règlement sur le
brouillage radioélectrique publié par Industrie Canada.
TRADEMARKS USED IN THIS MANUAL
IBM is a registered trademark, and XT is a trademark of IBM Corporation.
U.L. is a registered trademark of Underwriters Laboratories, Inc.
Page 3

FOUR PORT RS-232 SERIAL INTERFACE
Contents
Chapter Page
1. Specifications...................................................................................................1
2. Introduction ....................................................................................................2
2.1 Overview..................................................................................................2
2.2 What’s Included......................................................................................2
2.3 Features...................................................................................................3
2.4 Technical Description............................................................................4
3. Address Selection............................................................................................5
4. Option Selection .............................................................................................6
4.1 Port Enable/Disable...............................................................................6
4.2 Interrupt-Mode Options ........................................................................8
5. Installation.....................................................................................................10
5.1 Software Installation .............................................................................10
5.1.1 Windows 3.1x...............................................................................10
5.1.2 Windows 95/98 ...........................................................................10
5.1.3 Windows NT ................................................................................10
5.2 Hardware Installation ...........................................................................10
Appendix A: Circuit-Board Design ...................................................................11
Appendix B: Troubleshooting ..........................................................................12
Page 4

1
CHAPTER 1: Specifications
Protocol — Asynchronous
Number of Ports — 4
Speed — IC111C: Up to 115.2 Kbps; IC181C: 460.8 kbps and higher
Operation — RS-232
Connectors — DB37M on card; (1) 3-ft. (0.9-m) DB37F-to-4x DB25M octopus
cable, included
Maximum Distance — 50 ft. (15.2 m) @ 19.2 Kbps with 2500 pF max. cable
capacitance (lower capacitance will allow greater distances)
Communications Chip — IC111C: 16550 UART; IC181C: 16850 UART
MTBF — >150,000 hours
MTTR — <0.25 hours
Materials — Boards are built to U.L.®94V0 rating and are 100% electrically
tested. Boards are solder mask over bare copper or tin nickel
Manufacturing — IPC 610-A Class-III standards are adhered to with a 0.1
visual A.Q.L. and 100% functional testing
Operating Temperature — 32° to 122°F (0° to 50°C)
Storage Temperature — -4° to 158°F (-20° to 70°C)
Humidity — 10 to 90% relative humidity, noncondensing
Power — +5 VDC @ 200 mA ±12 V @ 50 mA
Size — 4.2"W x 8.6"D (10.7 x 21.9 cm)
Weight — 0.4 lb. (0.2 kg)
1. Specifications
Page 5

2
FOUR PORT RS-232 SERIAL INTERFACE
2.1 Overview
The Four Port RS-232 Serial Interface provides your PC system with four RS232 asynchronous ports. Connect to any device that uses the RS-232 protocol,
such as modems, data-entry terminals, and plotters.
The Serial Interface also includes a serial utility diskette with Seacom, a DOS
interrupt and driver package. Seacom allows data to be buffered, eliminating
data loss in high-speed data transfers. It also allows more than
4 ports (256 max.) to be configured and utilized under DOS.
The README file on the serial utility diskette contains information about the
latest changes and revisions. To view this file, insert the diskette into drive A
or B and type A:TYPE READ.ME|MORE [ENTER] or B:TYPE
READ.ME|MORE [ENTER].
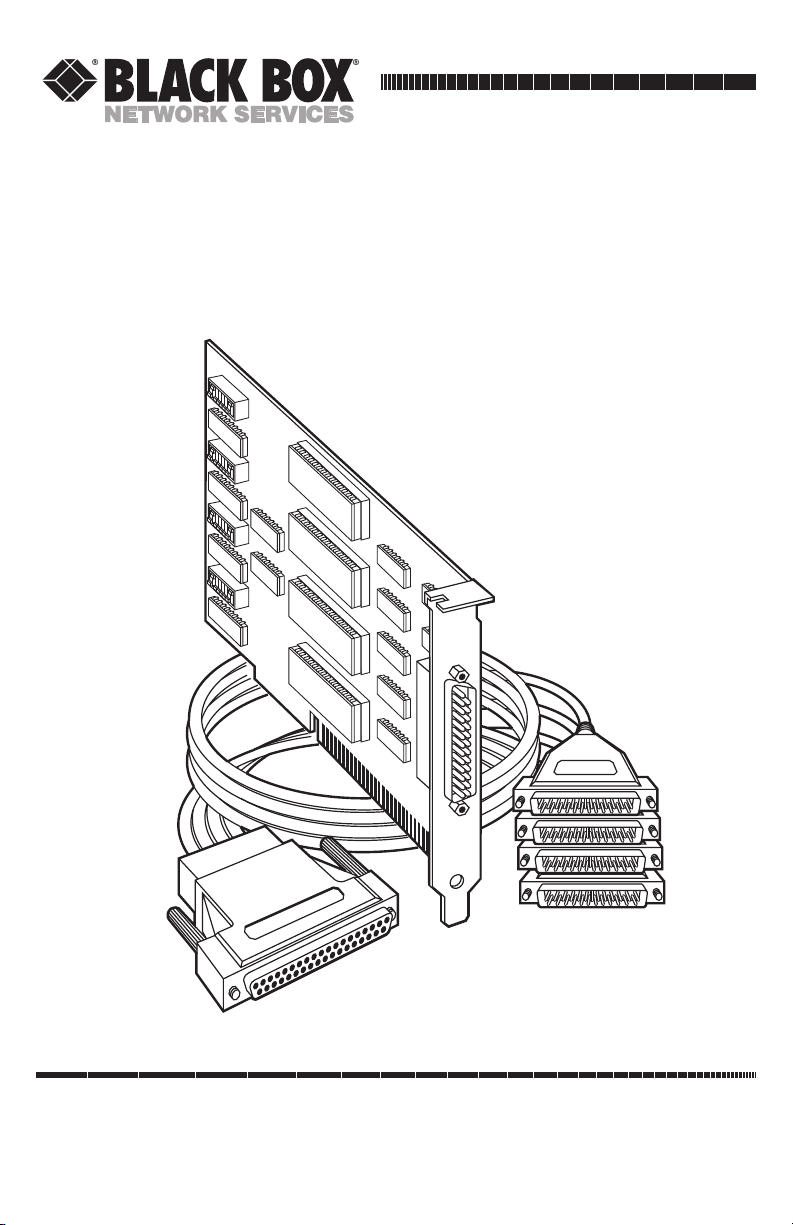
2.2 What’s Included
Your Serial Interface should come with the following items. If any of these
items are missing or damaged, contact your supplier.
(1) Four Port RS-232 Serial Interface with 1x DB37F,
(1) Octopus cable, (1) 3-ft. (0.9-m) to 4x DB25M,
(2) 3.5" serial utility diskettes,
This manual
2. Introduction
Page 6

3
CHAPTER 2: Introduction
2.3 Features
Listed below are the special features your Serial Interface offers.
• Each port is independently addressable.
• Eleven interrupt options, including AT interrupts, for simple integration
into existing systems.
• IRQs can be shared or individually set for each port.
• Supports Interrupt Sharing—only one interrupt line required for multiple
ports.
• Supports any character set defined by binary notation.
• 16550 UARTs (IC111C) or 16850 UARTs (IC181C) help ensure against
data loss.
• Faster baud rates—up to 115.2 Kbps.
• Provides COM1: through COM4: Turnkey Solution.
• Individually selectable address and interrupts (IRQs 2[9]–7 and 10, 11, 12,
and 15).
• Four DB25 male connectors provided using the octopus cable.
Page 7

4
FOUR PORT RS-232 SERIAL INTERFACE
2.4 Technical Description
The Four Port RS-232 Serial Interface provides four additional serial ports for
terminals, modems, printers, etc. The Serial Interface can be configured as
COM1: through COM4:, or as any other I/O address (up to 3FF Hex),
providing total compatibility with most communications software and
languages. The Four Port RS-232 Serial Interface (IC111C) uses the 16550
UART chip, which features programmable baud rate, data format, interrupt
control, and a 16-byte FIFO. The IC181C uses the 16850 UART.
Modem Control Signal Considerations
Some software packages require the use of the modem handshake signals
such as CTS or DCD. Consult your software manual to determine the
requirements of your modem control signals. If no requirements are
mentioned, or if you are not sure, a safe configuration is to tie DTR to DSR
and DCD (6-8-20), and tie RTS to CTS (4-5). This will typically satisfy the
modem control-signal requirements for most communications software.
Pin Number Signal Name Mode
2 Transmit Data (TD) Output RS-232
4 Request To Send (RTS) Output RS-232
20 Data Term Ready (DTR) Output RS-232
7 Ground (GND) ––––––––––––
3 Receive Data (RD) Input RS-232
8 Data Carrier Detect (DCD) Input RS-232
6 Data Set Ready (DSR) Input RS-232
5 Clear To Send (CTS) Input RS-232
22 Ring Indicator (RI) Input RS-232
Table 2-1. P1 through P4 pinouts as found on the
octopus cable (standard RS-232C DTE)
Page 8

5
CHAPTER 3: Address Selection
NOTE
Be sure to set the address selections and jumper options before
installation.
Each serial port on the Four Port RS-232 Serial Interface occupies 8 consecutive I/O locations. DIP switch SW4 sets the base address for Port 1, SW3
for Port 2, SW2 for Port 3, and SW1 for Port 4. Be careful when selecting the
base address as some selections conflict with existing PC ports. The following
table shows several examples that usually do not cause a conflict.
Address Binary Switch Position Setting
Hex A9 A0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
280-287 1010000XXX OFF ON OFF ON ON ON ON
2A0-2A7 1010100XXX OFF ON OFF ON OFF ON ON
2E8-2EF 1011101XXX OFF ON OFF OFF OFF ON OFF
2F8-2FF 1011111XXX OFF ON OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF
3E8-3EF 1111101XXX OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF
300-307 1100000XXX OFF OFF ON ON ON ON ON
328-32F 1100101XXX OFF OFF ON ON OFF ON OFF
3F8-3FF 1111111XXX OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF
Typically COM1:=3F8h; COM2:=2F8h; COM3:=3E8h; COM4:=2E8h
The following illustration shows the correlation between the DIP-switch
setting and the address bits used to determine the base address. In the figure
below, the address 300 hex through 307 hex is selected (300 hex =11 0000
0XXX in binary representation, where X is a non-selectable address bit). Note
that setting the switch ON (or closed) corresponds to a “0” in the address,
while leaving it OFF (or open) corresponds to a “1.”
A9 A3
ON
OFF
EN
0
1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
3. Address Selection
Page 9

6
FOUR PORT RS-232 SERIAL INTERFACE
NOTE
Be sure to set the address selections and jumper options before
installation.
The board contains several jumper straps for each port which must be set for
proper operation.
4.1 Port Enable/Disable
Each port on the Four Port RS-232 can be enabled or disabled with switch
position 8 on the DIP switch. The port is enabled with the switch ON (or
closed) and disabled when OFF (or open). If any port is disabled, be sure to
also disable the interrupt request for that port by removing the IRQ jumper.
Headers E1–E4 select the IRQ for each serial port. If COM1: is selected, this
jumper must be on the IRQ4 setting. If COM2: is selected, this jumper must
be on IRQ3.
NOTE
Most communications software applications default COM3: to IRQ4 and
COM4: to IRQ3. This requires the sharing of interrupts between COM1:
and COM3:, and between COM2: and COM4:. While this is the default, it
is not always the best setting. Check your software configuration
instructions to determine the most appropriate IRQ setting.
4. Option Selection
Page 10

7
CHAPTER 4: Option Selection
Any two or more ports can share a common IRQ by placing the jumpers on
the same IRQ setting, and setting the appropriate selections at E1. Consult
your particular software for IRQ selection. If no interrupt is desired, remove
the jumper.
NOTE
IRQ 2 on AT class machines is not available. IRQ 9 is substituted in place
of IRQ 2. To select IRQ 9, place jumper in the IRQ 2 position.
Figure 4-1. IRQ Selection.
Figure 4-1 shows the correlation between jumper block E5 and the interrupt
jumpers (E1–E4). This example shows the Four Port RS-232 Serial Interface
shipping configuration with COM1: and COM3: sharing interrupt 4 and
COM2: and COM4: sharing interrupt 3. See Section 4.2 for more information
on the different configuration options available with Jumper E5.
E5
23456
7
101112
15
1 2
3 4
M
S
N
M
S
N
PORT 1 (COM1)
PORT 2 (COM2)
PORT 3 (COM3)
PORT 4 (COM4)
E4
E3
E2
E1
23456
7
101112
15
23456
7
101112
15
23456
7
101112
15
Page 11

8
FOUR PORT RS-232 SERIAL INTERFACE
4.2 Interrupt-Mode Options
Jumper E5 selects the interrupt mode for each port. Each port must be set
in the correct mode to ensure proper installation.
“N” indicates the normal, single interrupt per port mode (Figure 4-2). “S”
indicates the shared interrupt mode, which allows more than one port to
access a single IRQ (Figure 4-4). “M” indicates the inclusion of a 1K ohm
pull-down resistor required on one port when sharing interrupts
(Figure 4-3).
Figure 4-2. E5 in normal mode.
Set jumpers to “S” for shared interrupt mode on all blocks sharing an IRQ
except one. Set that port block for “M.” This provides the pull-down resistor
circuit that makes sharing of IRQs possible. If you are using more than one
Four Port RS-232 Serial Interface or a compatible card in a bus, you should
have only one port set to “M.” Figure 4-3 shows all four ports sharing a single
IRQ.
Figure 4-3. E5, sharing a single IRQ.
1 2
3 4
M
S
N
M
S
N
1 2
3 4
M
S
N
M
S
N
Page 12

9
Set jumper to “S” if you are using more than one Four Port RS-232 Serial
Interface in a bus or you wish to remove the pull-down resistor completely
for hardware compatibility.
NOTE
Setting the board in this configuration when it is not accompanied by a
pull-down resistor will prevent the ports from triggering an interrupt. The
factory default for this board is COM1: and COM3: sharing IRQ4, and
COM2: and COM4: sharing IRQ3.
Figure 4- 4. E5, sharing multiple serial interface cards.
1 2
3 4
M
S
N
M
S
N
CHAPTER 4: Option Selection
Page 13

10
FOUR PORT RS-232 SERIAL INTERFACE
IMPORTANT
You MUST set up the operating system BEFORE you physically install
the Card.
5.1 Software Installation
If you are installing an ISA adapter in DOS, OS/2®, or QNX, please refer to the
appropriate directory on one of the Serial Utilities Disks for instructions.
5.1.1 W
INDOWS
3.1
X
Please refer to the /WINDOWS sub-directory on the Serial Utilities Diskette for
help files and current information on the installation of the Card in this operating
environment.
5.1.2
W
INDOWS
95/98 U
SERS
For the ISA card, run setup on disk two of the Serial Utilities Diskettes before
installing the card. Make note of the resources that Windows assigns the adapter,
and set the adapter to match those resources. Power down the computer and
install the adapter as described in Section 5.2. If you wish to change any resources
assigned to the adapter, refer to the help file installed in the Black Box folder in
the Start, Programs menu.
5.1.3 W
INDOWS
NT
For the ISA card, run setup on disk two of the Serial Utilities Diskettes before
installing the card. After installing the software, refer to the help file that
automatically comes up for installation instructions.
5. Installation
Page 14

11
CHAPTER 5: Installation
5.2 Hardware Installation
The ISA Card can be installed in any of the PC expansion slots. The Card contains
several jumper straps for each port that you must set for proper operation.
1. Turn off PC power. Disconnect the power cord.
2. Remove the PC case cover.
3. Locate an available slot and remove the blank metal slot cover.
4. Gently insert the Card into the slot. Make sure that the Card is seated
properly.
5. Replace the screw.
6. Replace the cover.
7. Connect the power cord.
Installation is complete.
Page 15

12
FOUR PORT RS-232 SERIAL INTERFACE
Appendix A: Circuit-Board Design
= User
Configurable
3.9"
PORT 4
C1
U1
PORT 3
U2
PORT 2
C2
U3
PORT 1
U4
A9 A3ON=0
E
SW4
R4
D4
R7
R8
E4
2
3
4
PORT 1
5
6
7
10
11
12
15
C7
U10
PORT 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
10
11
12
15
PORT 4
SW2
R2
N
3
4
D2
E2
C3
PORT 3
U5
C5
U8
E5
R9
PORT 3
SW3
R3
MSNMS
12
E3
D3
2
3
U6
4
PORT 2
5
6
7
10
11
12
15
C6
U9
PORT 2
SW1
R1
R5
R6
D1
E1
2
3
4
PORT 4
5
6
7
10
11
12
15
C4
U7
P2
8.66"
C8
P1
U11
C14
C11
+
U15
1
20
C9 C10
U12
C12
U17
U16
P3
19
37
Y1
U14U13
C13
U18
C19
C15
4.2"
Page 16

13
APPENDIX B: Troubleshooting
By using the supplied serial utility diskette and following these simple steps,
most common problems can be eliminated.
1) Identify all I/O adapters currently installed in your system. This includes
your onboard serial ports, controller cards, and sound cards. The I/O
address used by these adapters, as well as the IRQ (if any) should be
identified.
2) Configure your serial interface so that there is no conflict with currently
installed adapters. No two adapters can occupy the same I/O address.
3) Make sure the Serial Interface is using a unique IRQ. While the Interface
does allow the sharing of IRQs, many other adapters (such as SCSI
adapters and onboard serial ports) do not. The IRQ is typically selected
via an onboard header block. Refer to Chapters 3 and 4 for help in
choosing an I/O address and IRQ.
4) Make sure the Four Port RS-232 Serial Interface is securely installed in a
motherboard slot.
5) Use the supplied diskette and this manual to verify that the Serial
Interface is configured correctly. The supplied diskette contains a
diagnostic program (SSD) that will verify if an adapter is configured
properly. This diagnostic program is written with the user in mind and is
easy to use. Refer to the README file on the diskette for detailed
instructions on how to use the SSD program.
6) These are know I/O conflicts:
• The 278 and 378 settings may conflict with your printer I/O adapter.
• 3B0 cannot be used if a monochrome adapter is installed.
• 3F8-3FF is typically reserved for COM1:.
• 2F8-2FF is typically reserved for COM2:.
• 3E8-3EF is typically reserved for COM3:.
• 2E8-2EF is typically reserved for COM4:.
7) Refer to the diskette for any post-production manual updates and
application-specific information.
Appendix B. Troubleshooting
Page 17

1000 Park Drive • Lawrence, PA 15055-1018 • 724-746-5500 • Fax 724-746-0746
© Copyright 2000. Black Box Corporation. All rights reserved.
 Loading...
Loading...