Page 1

LS50116-AE
LS50124-AE
16 and 24 port Console Servers
User Guide
MAY 2002
LS50116
LS50124
CUSTOMER
SUPPORT
INFORMATION
Order toll-free in the U.S 24 hours, 7 A.M. Monday to midnight Friday: 877-877-BBOX
FREE technical support, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week: Call 724-746-5500 or fax 724-746-0746
Mail order: Black Box Corporation, 1000 Park Drive, Lawrence, PA 15055-1018
Web site: www.blackbox.com * E-mail info@blackbox.com
Page 2

Normas Oficiales Mexicanas (NOM) Electrical Safety Statement
INSTRUCCIONES DE SEGURIDAD
1. Todas las instrucciones de seguridad y operación deberán ser leídas antes de que
el aparato eléctrico sea operado.
2. Las instrucciones de seguridad y operación deberán ser guardadas para referencia
futura.
3. Todas las advertencias en el aparato eléctrico y en sus instrucciones de operación
deben ser respetadas.
4. Todas las instrucciones de operación y uso deben ser seguidas.
5. El aparato eléctrico no deberá ser usado cerca del agua-por ejemplo, cerca de la
tina de baño, lavabo, sótano mojado o cerca de una alberca, etc.
6. El aparato eléctrico debe ser usado únicamente con carritos o pedestales que sean
recomendados por el fabricante.
7. El aparato eléctrico debe ser montado a la pared o al techo sólo como sea
recomendado por el fabricante.
8. Servicio-El usuario no debe intentar dar servicio al equipo eléctrico más allá a lo
descrito en las instrucciones de operación. Todo otro servicio deberá ser referido a
personal de servicio calificado.
9. El aparato eléctrico debe ser situado de tal manera que su posición no interfiera su
uso. La colocación del aparato eléctrico sobre una cama, sofá, alfombra o
superficie similar puede bloquea la ventilación, no se debe colocar en libreros o
gabinetes que impidan el flujo de aire por los orificios de ventilación.
10. El equipo eléctrico deber ser situado fuera del alcance de fuentes de calor como
radiadores, registros de calor, estufas u otros aparatos (incluyendo
amplificadores) que producen calor.
11. El aparato eléctrico deberá ser connectado a una fuente de poder sólo del tipo
descrito en el instructivo de operación, o como se indique en el aparato.
12. Precaución debe ser tomada de tal manera que la tierra fisica y la polarización del
equipo no sea eliminada.
13. Los cables de la fuente de poder deben ser guiados de tal manera que no sean
pisados ni pellizcados por objetos colocados sobre o contra ellos, poniendo
particular atención a los contactos y receptáculos donde salen del aparato.
14. El equipo eléctrico debe ser limpiado únicamente de acuerdo a las
recomendaciones del fabricante.
Black Box Console Server user guide 2
Page 3

15. En caso de existir, una antena externa deberá ser localizada lejos de las lineas de
energia.
16. El cable de corriente deberá ser desconectado del cuando el equipo no sea usado
por un largo periodo de tiempo.
17. Cuidado debe ser tomado de tal manera que objectos liquidos no sean derramados
sobre la cubierta u orificios de ventilación.
18. Servicio por personal calificado deberá ser provisto cuando:
a. El cable de poder o el contacto ha sido dañado; u
b. Objectos han caído o líquido ha sido derramado dentro del aparato; o
c. El aparato ha sido expuesto a la lluvia; o
d. El aparato parece no operar normalmente o muestra un cambio en su
desempeño; o
e. El aparato ha sido tirado o su cubierta ha sido dañada.
Black Box Console Server user guide 3
Page 4

FEDERAL COMMUNICATIONS COMMISSION
AND
CANADIAN DEPARTMENT OF COMMUNICATIONS
RADIO FREQUENCY INTERFERENCE STATEMENTS
This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and if not
installed and used properly, that is, in strict accordance with the manufacturer's
instructions, may cause interference to radio communication. It has been tested and
found to comply with the limits for a Class A computing device in accordance with
the specifications in Subpart J of Part 15 of FCC rules, which are designed to provide
reasonable protection against such interference when the equipment is operated in a
commercial environment. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely
to cause interference, in which case the user at his own expense will be required to
take whatever measures may be necessary to correct the interference.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class A limits for radio noise emission
from digital apparatus set out in the Radio Interference Regulation of the Canadian
Department of Communications.
Le présent appareil numérique n'émet pas de bruits radioélectriques dépassant les
limites applicables aux appareils numériques de la classe A prescrites dans le
Règlement sur le brouillage radioélectrique publié par le ministère des
Communications du Canada.
Caution: the Console Server is approved for commercial use only.
Black Box Console Server user guide 4
Page 5

About this Guide
Purpose of this manual
This manual tells you how to install, configure and use the Console Server and
associated utility software.
Who this manual is for
This manual is aimed at users who want to communicate directly via the serial port to
networked devices (such as routers, servers and so on) in order to perform system
administration tasks.
This manual requires a working knowledge of using personal computers and
associated operating systems, as well as experience in installing host cards and
peripherals.
Black Box Console Server user guide 5
Page 6

Fast Contents
ABOUT THIS GUIDE..................................................................................................... 5
AST CONTENTS ......................................................................................................... 6
F
ONTENTS ................................................................................................................... 7
C
HAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION ........................................................................................ 17
C
HAPTER 2 INSTALLATION ......................................................................................... 23
C
HAPTER 3 SYSTEM ADMINISTRATION ....................................................................... 69
C
HAPTER 4 USING YOUR CONSOLE SERVER .............................................................. 115
C
PPENDIX A CABLING INFORMATION ....................................................................... 125
A
PPENDIX B THE CLI COMMANDS ............................................................................ 141
A
PPENDIX C SNMP ................................................................................................... 203
A
PPENDIX D UPGRADING YOUR FIRMWARE .............................................................. 215
A
PPENDIX E SUMMARY OF LINE SERVICE TYPES ..................................................... 223
A
PPENDIX F BOOTP ................................................................................................. 227
A
PPENDIX G JETSET ................................................................................................. 243
A
PPENDIX H TROUBLESHOOTING ............................................................................. 251
A
NDEX.......................................................................................................................... 259
I
Black Box Console Server user guide 6
Page 7

Contents
ABOUT THIS GUIDE..................................................................................................... 5
Purpose of this manual.................................................................................................... 5
Who this manual is for..................................................................................................... 5
F
AST CONTENTS ......................................................................................................... 6
ONTENTS ................................................................................................................... 7
C
Black Box Console Server user guide 7
Page 8

CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION ....................................................................................... 17
About the Console Server ................................................................................................ 18
Typical applications summary........................................................................................ 20
Managing devices over the LAN/WAN ................................................................. 20
Managing devices without accessing the LAN/WAN............................................ 20
Network security ................................................................................................... 20
Management and diagnostics ............................................................................... 20
Console Server front and rear views.............................................................................. 21
Black Box Console Server user guide 8
Page 9

CHAPTER 2 INSTALLATION ........................................................................................ 23
General installation procedure ....................................................................................... 24
Rack mounting your Console Server............................................................................. 25
Desk mounting your Console Server............................................................................. 27
Multiple stacking your Console Server.......................................................................... 28
LED guide.......................................................................................................................... 29
Selecting AUI or 10/100 Base T interface..................................................................... 32
Setting up an IP address.................................................................................................. 33
Setting up an IP address automatically using DHCP .......................................... 33
Set up procedure.......................................................................................................... 33
About DHCP ............................................................................................................... 35
Manually setting up an IP address ....................................................................... 38
Set up procedure.......................................................................................................... 39
Server form field descriptions ..................................................................................... 42
Accessing the Console Server configuration software................................................ 45
Logging onto your Console Server ....................................................................... 45
Setting up your network parameters.............................................................................. 46
Setting up the host table........................................................................................ 46
Adding a Host.............................................................................................................. 46
Changing a Host ......................................................................................................... 48
Deleting a host ............................................................................................................ 49
Changing the Admin Password ............................................................................ 50
RADIUS configuration ......................................................................................... 51
Set up procedure.......................................................................................................... 51
RADIUS parameters description................................................................................. 54
DNS configuration ................................................................................................ 56
WINS configuration .............................................................................................. 57
Configuring network gateways ............................................................................. 58
Adding a gateway ........................................................................................................ 59
Deleting a Gateway..................................................................................................... 60
Verifying your network installation ...................................................................... 61
Saving configuration changes ........................................................................................ 62
Saving to non-volatile memory ............................................................................. 62
Saving to a file ...................................................................................................... 63
Setting date and time ........................................................................................................ 64
Performing a soft reboot.................................................................................................. 65
Restoring factory default settings ................................................................................... 66
Resetting to factory defaults using software......................................................... 66
Resetting to factory defaults using reset switch .................................................... 66
Black Box Console Server user guide 9
Page 10

CHAPTER 3 SYSTEM ADMINISTRATION ...................................................................... 69
Security............................................................................................................................... 70
Setting up the line on your Console Server................................................................... 70
Viewing and editing your line settings ........................................................................... 71
Lines set to reverse Telnet by default .................................................................... 71
Lost password.................................................................................................................... 73
Configuring a dial in line ................................................................................................ 74
Introduction to SLIP and PPP connections .......................................................... 74
Deciding whether to use SLIP or PPP ................................................................. 74
Setting up the line ................................................................................................. 75
Configuring SLIP.................................................................................................. 78
Configuring PPP .................................................................................................. 82
PPP configuration procedure ..................................................................................... 82
PPP form field descriptions ........................................................................................ 83
Configuring a modem ........................................................................................... 93
Configuring users............................................................................................................. 94
About user accounts and RADIUS........................................................................ 96
Overview ..................................................................................................................... 96
Example RADIUS user file: telnet service .................................................................. 98
Adding a user account .......................................................................................... 99
Configuring a user account .................................................................................. 100
Configuration procedure ............................................................................................. 100
User form field descriptions........................................................................................ 101
About user levels......................................................................................................... 108
CLI prompts................................................................................................................. 108
Changing a user’s password................................................................................. 109
Deleting a user account ........................................................................................ 109
Configuring Break Pass Through ................................................................................. 110
Resetting the line to default ............................................................................................. 111
Saving your settings.......................................................................................................... 112
Saving settings to non-volatile memory ................................................................ 112
Saving settings to a file......................................................................................... 112
Black Box Console Server user guide 10
Page 11

CHAPTER 4 USING YOUR CONSOLE SERVER ............................................................. 115
Introduction....................................................................................................................... 116
Accessing devices via Telnet from the LAN.................................................................. 117
Information required............................................................................................. 117
Access procedure .................................................................................................. 117
Accessing devices via SSH............................................................................................... 118
SSH Setup Procedure............................................................................................ 118
Required Information............................................................................................ 120
Access procedure .................................................................................................. 121
Accessing devices via modems using PPP .................................................................... 122
Accessing devices via modems using a dumb device................................................... 123
PPENDIX A CABLING INFORMATION ....................................................................... 125
A
RJ45 RS232 serial ports................................................................................................... 126
Pin locations RJ45 connectors ............................................................................. 126
AUI port................................................................................................................ 128
RJ45 10/100BaseT port ................................................................................................... 129
Admin Port......................................................................................................................... 130
Direct (1:1) Connections.................................................................................................. 131
Example direct connections .................................................................................. 131
Sun Microsystem servers............................................................................................. 132
CISCO RJ45 console ports with software flow control............................................... 134
Black Box 833AS......................................................................................................... 134
Black Box Series router console port.......................................................................... 134
IBM RS6000 ................................................................................................................ 135
PC serial port..................................................................................................................... 136
PC, example connections, ..................................................................................... 136
Connection from the 25-pin Admin Port to a PC ................................................. 136
Terminals............................................................................................................................ 138
Terminals (slow speed or using software flow control) ........................................ 138
Connection from the 25-pin Admin Port to a Terminal ........................................ 139
Modems.............................................................................................................................. 140
Direct connections ................................................................................................ 140
APPENDIX B THE CLI COMMANDS ............................................................................ 141
CLI commands.................................................................................................................. 142
add community...................................................................................................... 142
add DNS................................................................................................................ 142
Black Box Console Server user guide 11
Page 12

add gateway .......................................................................................................... 144
add host................................................................................................................. 144
add modem............................................................................................................ 146
add radius ............................................................................................................. 146
add trap................................................................................................................. 147
add user ................................................................................................................ 147
add WINS .............................................................................................................. 147
admin .................................................................................................................... 148
debug .................................................................................................................... 148
delete ARP ............................................................................................................ 148
delete community .................................................................................................. 148
delete DNS ............................................................................................................ 149
delete gateway ...................................................................................................... 149
delete host ............................................................................................................. 149
delete modem ........................................................................................................ 150
delete radius ......................................................................................................... 150
delete trap ............................................................................................................. 151
delete user............................................................................................................. 151
delete WINS .......................................................................................................... 151
heap ...................................................................................................................... 152
help ....................................................................................................................... 153
kill line .................................................................................................................. 153
logout .................................................................................................................... 153
netload ................................................................................................................. 154
netsave .................................................................................................................. 156
ping ....................................................................................................................... 158
reboot.................................................................................................................... 160
reset factory .......................................................................................................... 160
reset line................................................................................................................ 160
reset user............................................................................................................... 161
restart.................................................................................................................... 161
resume................................................................................................................... 161
rlogin .................................................................................................................... 163
save ....................................................................................................................... 163
screen.................................................................................................................... 164
set contact ............................................................................................................. 164
set date .................................................................................................................. 164
set ethernet interface RJ45 ................................................................................... 165
Black Box Console Server user guide 12
Page 13

Syntax .......................................................................................................................... 165
See also........................................................................................................................ 165
set ethernet interface AUI..................................................................................... 165
Syntax .......................................................................................................................... 165
See also........................................................................................................................ 165
set gateway ........................................................................................................... 165
set host .................................................................................................................. 166
set line................................................................................................................... 166
set location............................................................................................................ 169
set ppp line............................................................................................................ 170
set radius............................................................................................................... 172
set server............................................................................................................... 173
set slip line ............................................................................................................ 180
set telnet ................................................................................................................ 181
set time .................................................................................................................. 182
set user .................................................................................................................. 182
show ARP.............................................................................................................. 185
show date .............................................................................................................. 185
show gateways ...................................................................................................... 186
show hardware...................................................................................................... 186
show hosts............................................................................................................. 187
show interfaces ..................................................................................................... 187
show line ............................................................................................................... 188
show modems ........................................................................................................ 191
show ppp line ........................................................................................................ 192
show radius........................................................................................................... 194
show routes ........................................................................................................... 194
show server ........................................................................................................... 196
show slip line ........................................................................................................ 197
show snmp............................................................................................................. 198
show telnet ............................................................................................................ 199
show time .............................................................................................................. 199
show user .............................................................................................................. 200
start ....................................................................................................................... 200
telnet ..................................................................................................................... 201
version .................................................................................................................. 202
Black Box Console Server user guide 13
Page 14

APPENDIX C SNMP ................................................................................................... 203
Overview............................................................................................................................. 204
Configuring SNMP support............................................................................................ 205
Summary of objects in the private MIB......................................................................... 207
Private MIB definitions ................................................................................................... 209
Network management...................................................................................................... 213
A
PPENDIX D UPGRADING YOUR FIRMWARE .............................................................. 215
Introduction....................................................................................................................... 216
Saving your existing Configuration............................................................................... 217
Example of saving a configuration file ................................................................. 217
Using TFTP from a host ....................................................................................... 217
TFTP configuration .............................................................................................. 218
Writing to FLASH memory ................................................................................... 219
Using BOOTP from a boothost...................................................................................... 220
Upgrade using JETset, the web browser interface....................................................... 221
Enabling BOOTP/DHCP after upgrading software................................................... 221
Disable BOOTP/DHCP................................................................................................... 221
A
PPENDIX E SUMMARY OF LINE SERVICE TYPES ..................................................... 223
List of line service types.................................................................................................... 224
A
PPENDIX F BOOTP ................................................................................................. 227
Introduction....................................................................................................................... 228
How BOOTP works ......................................................................................................... 229
How to setup BOOTP ...................................................................................................... 231
The bootptab file entry.......................................................................................... 231
The bootfile ........................................................................................................... 234
Black Box Console Server user guide 14
Page 15

BOOTP messages output to screen................................................................................ 236
Disabling the BOOTP reply............................................................................................ 236
Booting multiple units...................................................................................................... 238
Multiple BOOTP servers ................................................................................................. 240
Example of BOOTP......................................................................................................... 240
A
PPENDIX G JETSET ................................................................................................. 243
Introduction to JETset...................................................................................................... 244
Using JETset...................................................................................................................... 246
JETset program summary ............................................................................................... 249
A
PPENDIX H TROUBLESHOOTING ............................................................................. 251
Introduction....................................................................................................................... 252
General communication matters.................................................................................... 252
Host problems.................................................................................................................... 253
JETset problems ................................................................................................................ 254
Login problems ................................................................................................................. 255
Problems with terminals .................................................................................................. 257
Emergency recovery ......................................................................................................... 258
Problems with framed Routing....................................................................................... 258
I
NDEX.......................................................................................................................... 259
Black Box Console Server user guide 15
Page 16

Black Box Console Server user guide 16
Page 17

Chapter 1 Introduction
You need to
read this
chapter if
you want to...
You need to read this chapter if you want an overview of the Console Server product.
This chapter provides introductory information about the Console Server, its
associated components, software and configuration utilities.
This chapter includes the following sections
• About the Console Server on page 18
• Typical applications summary on page 20
• Console Server front and rear views on page 21.
For details of installation procedures, see Chapter 2 Installation.
For information about performing system administration tasks with your Console
Server, see Chapter 3 System administration.
For information on using your Console Server as a console server, see Chapter 4
Using your Console Server.
Black Box Console Server user guide 17
Page 18
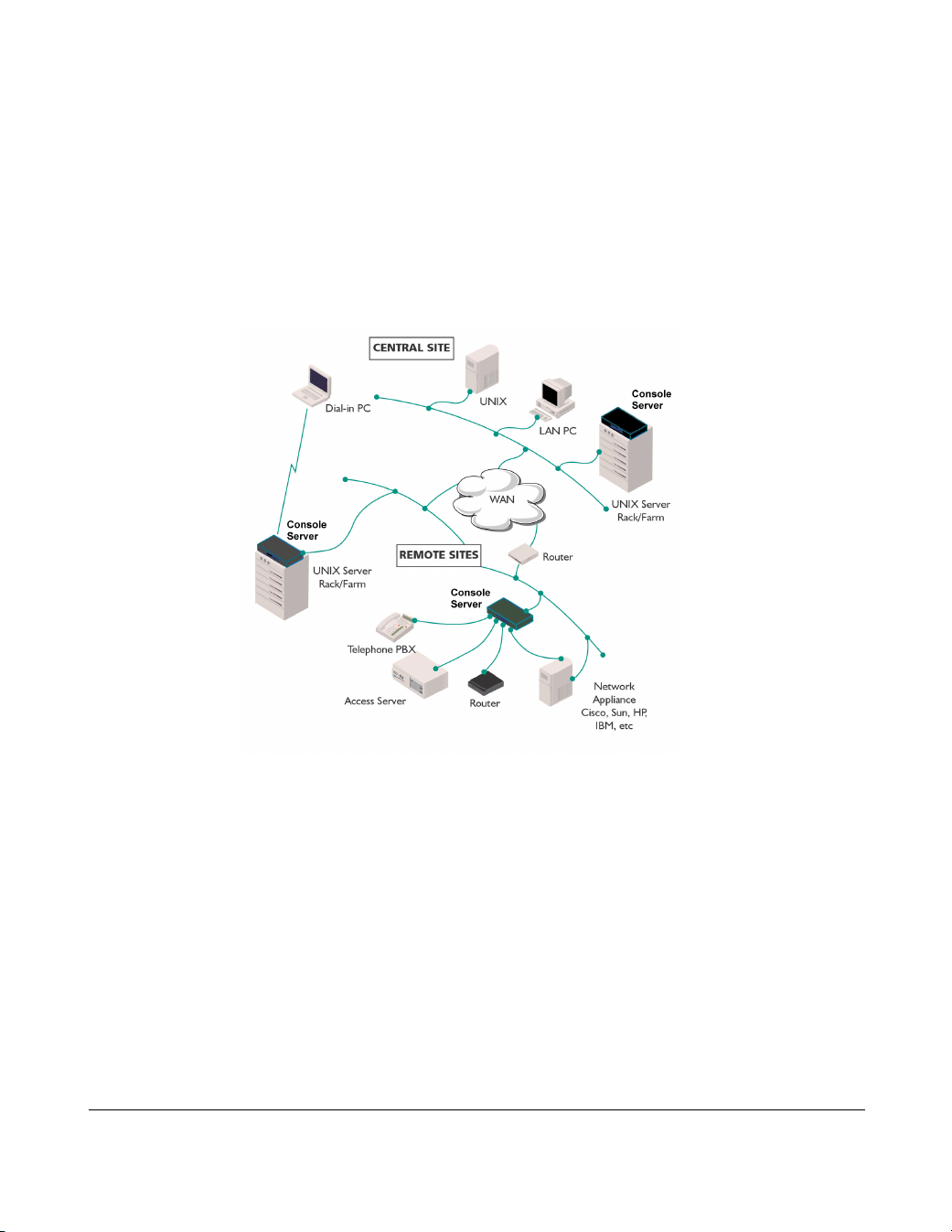
About the Console Server
The Console Server is a console server which allows you to communicate directly via
the serial port to networked devices (such as routers, servers and so on) in order to
perform system administration tasks.
The Console Server allows system administrators to diagnose and fix from anywhere
on the LAN/WAN or via a modem thus saving on administrator's time and costs to
keep system disruption to a minimum.
Typically, you use the Console Server when a server or network device fails at a
remote site or if you want to perform administration tasks from home. Using a
Console Server you can access the unit over the LAN/WAN or via dial-in.
The Console Server is available in the following variants;
• 16 port
• 24 port
Black Box Console Server user guide 18
Page 19

See also Typical applications summary on page 20 and Console Server front and rear
views on page 21.
Black Box Console Server user guide 19
Page 20

Typical applications summary
Managing devices over the LAN/WAN
The Console Server allows the administrator to Telnet to the appropriate port on the
console server. With the Console Server in band management functionality,
administrators can gain access to attached devices from anywhere on the LAN/WAN
provided they know the IP addresses. The Console Server also allows access to
multiple devices simultaneously.
Managing devices without accessing the LAN/WAN
In the event of a network failure, the Console Server allows the administrator access
via a modem attached to one of the serial ports on the unit to access attached devices.
Network security
Console Server provides a comprehensive suite of security features to allow an
organization to implement robust security planning to prevent unauthorized access.
These include SLIP and PPP Remote User dial-in and support for RADIUS.
For a secure LAN connection, the Console Server supports SSH version 1 and
version 2 protocol. Remote server connections with SSH protocol uses an encrypted
data channel with support for password and other authentications.
Management and diagnostics
Independent tests have proved Console Serverextremely easy to configure and
install. A comprehensive array of software tools allows the Console Server to be
configured, managed and upgraded either locally or remotely over the network and
even via the Internet.
These tools include JETset, for complete port management from any location via a
Web browser, and easy downloads of software upgrades to the unit's flash memory.
Command line and menu interfaces are included, as is a separate local management
port, plus industry standard control and management facilities - SNMP, BOOTP,
DHCP and DNS.
Black Box Console Server user guide 20
Page 21
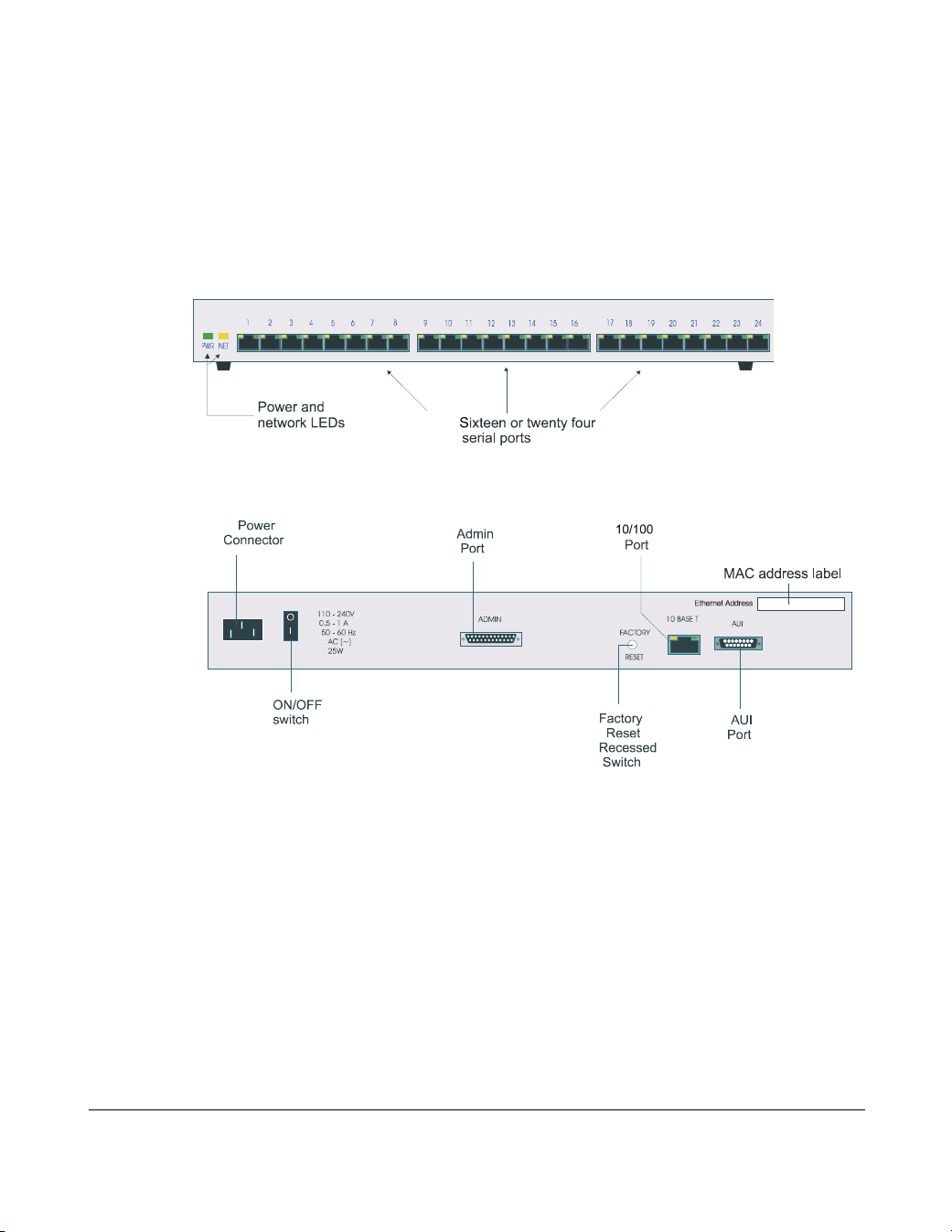
Console Server front and rear views
The Console Server is a network access server with front-mounted RJ45 serial ports. It
is designed for use in a rack. The serial ports are RS232. The product has 10/100BaseT
and AUI network connections and an Administration port for system management. The
next picture shows the front view of a 24 port unit.
Console
Server front
view
You can mount the Console Server in a 19 inch rack, on a wall or on a desk.
Console
Server rear
panel
Black Box Console Server user guide 21
Page 22

Black Box Console Server user guide 22
Page 23

Chapter 2 Installation
You need to read
this chapter if you
want to...
You need to read this chapter if you want install the Console Server.
This chapter provides task oriented information about installing the Console Server, its associated
components, software and configuration utilities.
This chapter includes the following sections;
• General installation procedure on page 24
• Rack mounting your Console Server on page 25
• Desk mounting your Console Server on page 27
• Multiple stacking your Console Server on page 28
• LED guide on page 29
• Selecting AUI or 10/100 Base T interface on page 32
• Setting up an IP address on page 33
• Accessing the Console Server configuration software on page 45
• Setting up your network parameters on page 46
• Saving configuration changes on page 62
• Setting date and time on page 64
• Performing a soft reboot on page 65
• Restoring factory default settings on page 66.
Black Box Console Server user guide 23
Page 24

General installation procedure
The general procedure for installing and setting up your Console Server is as follows;
1. Install your Console Server in a rack or on a desktop as required using the
procedures described in Rack mounting your Console Server on page 25 and
Desk mounting your Console Server on page 27.
Note If you are stacking multiple units on a desktop see Multiple stacking your Console
Server on page 28 for the maximum advisable units to stack.
2. Connect your Console Server to the network. See Appendix A Cabling
information.
3. If required, select the interface type you want. See Selecting AUI or 10/100 Base
T interface on page 32.
4. Set up your IP address using the procedures given in Setting up an IP address on
page 33.
5. Access the Console Server configuration software using the procedures given in
Accessing the Console Server configuration software on page 45
6. Set up your network parameters using the procedure given in Setting up your
network parameters on page 46.
You can now use the unit. For information on using the Console Server for system
administration purposes. See Chapter 3 System administration for further details.
For information on using your Console Server as a console server, see Chapter 4
Using your Console Server.
Black Box Console Server user guide 24
Page 25
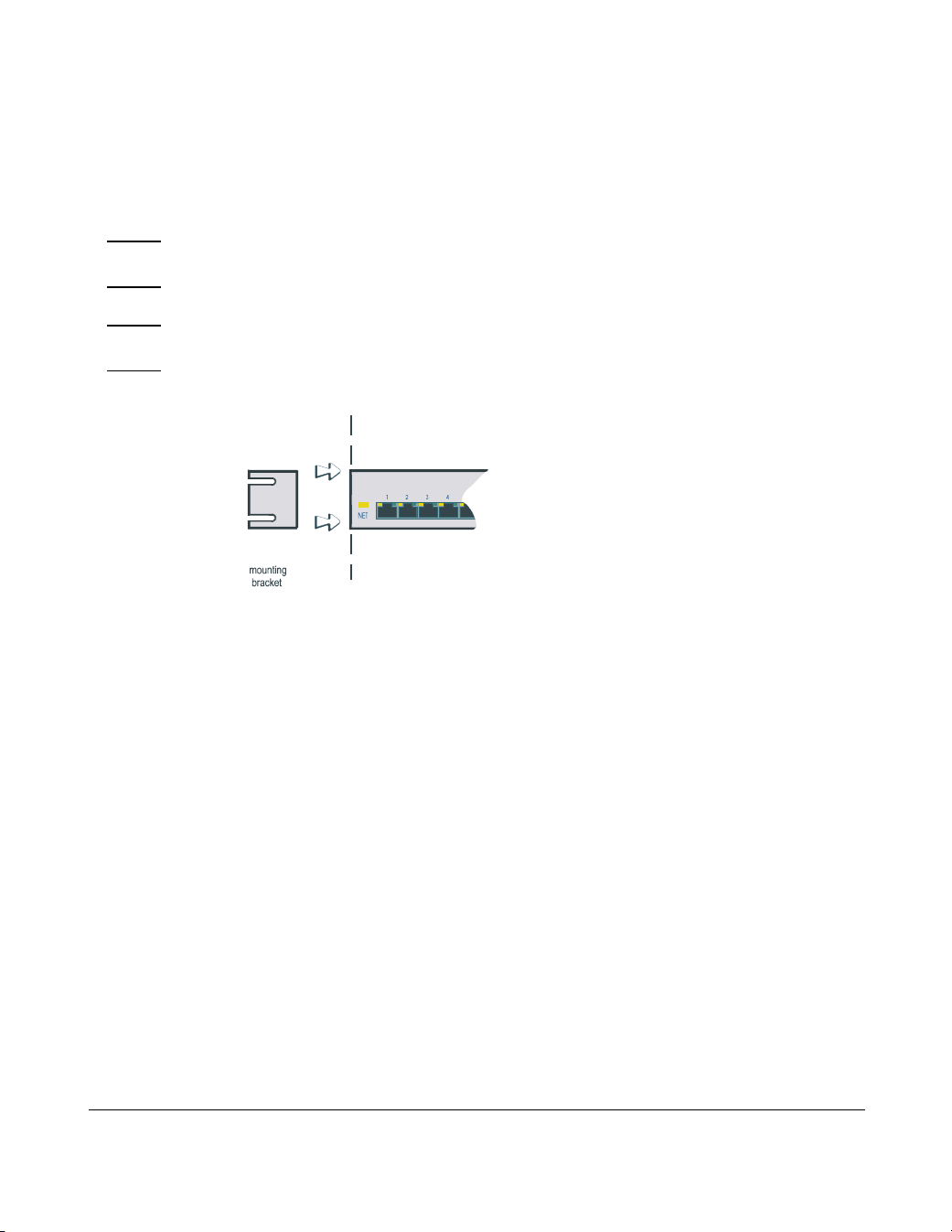
Rack mounting your Console Server
To mount a single Console Server into a 19 inch rack, use the two mounting brackets
and four screws provided with the unit.
Caution When mounting several Console Server units in a 19” rack, you must not stack more
than 3 units without leaving an air gap between them.
Caution Observe maximum ambient operating temperatures within a rack; you may have to
use forced air cooling.
Console Server
Black Box Console Server user guide 25
Page 26

Black Box Console Server user guide 26
Page 27

Desk mounting your Console Server
To prepare the Console Server for use on a desk use the four self-adhesive rubber feet
provided with the unit. Stick the four feet to the underside of the unit, one in each corner,
approximately one inch from each adjacent edge.
1 inch
(2.5 cm)
1 inch
(2.5 cm)
rubber foot
bottom panel
of unit
rubber foot
Black Box Console Server user guide 27
Page 28

Multiple stacking your Console Server
When stacking your unit on a desk we recommend that you stack no more than three
units high in a 0 to 40 degrees centigrade environment.This precaution ensures that you
keep within the maximum operating temperatures of the units.
Caution When desk mounting multiple Console Server units, make sure you fit the rubber feet
to all units before stacking to assist ventilation.
Caution When mounting several Console Server units in a 19” rack, you must not stack more
than 3 units without leaving an air gap between them.
Caution Observe maximum ambient operating temperatures within a rack; you may have to
use forced air cooling.
Black Box Console Server user guide 28
Page 29

LED guide
During bootup you should see power and network LEDs display the following
colours.
Power and
network
LEDs
Once power is on and the network is connected, the power and network LEDs will
display the following colours:
Console Server during bootup
Black Box Console Server user guide 29
Page 30

Console Server
during normal operations
Black Box Console Server user guide 30
Page 31

RJ45 LEDs There are bi-colour LEDs on the RJ45 connectors on both the front and rear panels.
These LEDs flicker briefly during bootup and then display the following colours,
Black Box Console Server user guide 31
Page 32

Selecting AUI or 10/100 Base T interface
Before performing the initial configuration of your Console Server unit, you need to
select the type of interface you want to use from either AUI or 10/100Base-T
(Default setting is 10/100Base-T). To do this proceed as follows;
Note To display the currently selected interface type, at the command prompt, type
show hardware and press the Enter key. The resulting display will include the
currently selected hardware type.
You only need to use these commands on revision 2 Console Server boards.
1. Login to your unit and display the command prompt.
2. At the command prompt, type one of the commands listed in the next table to
select the interface type you want to use.
To set this type of interface Use this command
10/100Base-T
AUI
You can now perform the initial configuration of the unit.
set ethernet interface RJ45
set ethernet interface AUI
Black Box Console Server user guide 32
Page 33

Setting up an IP address
Setting up an IP address automatically using DHCP
This section includes the following;
• Set up procedure on page 33
• About DHCP on page 35
Set up procedure
To set up an IP address automatically using DHCP proceed as follows;
Note For details of the BOOTP/DHCP tags (client information items) that are supported
by both BOOTP and DHCP see Appendix F BOOTP. In addition on Microsoft
Windows NT, DHCP allows for the configuration of WINS server names.
If automatic configuration of Console Server clients is required, only one service
DHCP, BOOTP or RARP should be enabled on your network server.
We strongly recommend that you do not run both the BOOTP and DHCP services
on the same network to configure Console Server clients unless you are very
familiar with the potential interactions that may result.
For information on BOOTP see Appendix F BOOTP.
1. Set up your DHCP server as required.
See your system documentation for details of configuring the DHCP service on
your server's operating system.
Black Box Console Server user guide 33
Page 34

2. Connect your Console Server to the network and turn on the unit.
The IP address and any other configuration information will now be set up
automatically.For more information see About DHCP on page 35.
Black Box Console Server user guide 34
Page 35

DHCP
request and
response
About DHCP
You can use DHCP to perform the following actions on a single or multiple Console
Server (the ‘unit(s)’)s on its/their boot-up:
auto-configure with minimal information; e.g. only an ip address
auto-configure with basic setup information (ip address, subnet mask, broadcast
address, etc.)
download a new version of software
download a full configuration profile (saved from another unit)
DHCP is particularly useful for multiple installations: you can do all the unit’s
configuration in one DHCP file, rather than configure each unit manually.
Another advantage of DHCP is that you can connect a unit to the network, turn on its
power and let auto-configuration take place. All the configuration is carried out for you
during the DHCP process.
The the unit’s implementation of DHCP is compatible with RFC 951.
On bootup or power-up, the unit will send a broadcast request to the DHCP server(s) on
the network. The request contains the ethernet address of the unit; it asks for network
configuration details (internet address, subnet mask, etc.). This process is shown in
DHCP request and response on page 35.
You can stop the DHCP server from replying to the unit; see Appendix F BOOTP
Black Box Console Server user guide 35
Page 36

The DHCP server checks the ethernet address and looks for a matching address in its
DHCP tables:
- if a matching ethernet address is found the DHCP server will reply to the unit; the
reply will contain network configuration information. This information is listed in
the DHCP tables for that particular unit (identified by its hardware address). The
unit then boots using the information sent to it.
- if no matching ethernet address is found the DHCP server does not reply; the unit
boots from internal memory.
Refer to DHCP request and response on page 35 for an explanation of the following text:
the DHCP response contains network configuration information; e.g. ip address,
subnet mask, broadcast address. It may also contain details of a bootfile (not
mandatory)
a bootfile (if you specify one) contains a unit’s specific boot information; e.g.
authentication method of users, access permission for the GUI. It may also contain
details of other files (not mandatory); e.g. software version, language files and a
general configuration file
a configuration file (if you specify one) contains general configuration parameters;
these parameters will have been created from another unit and saved to a file
in the DHCP response the minimum parameters to specify are :ht and :ha
there is no minimum number of parameters to specify in the bootfile or
configuration file; unspecified parameters will remain unchanged in the unit’s
memory
After processing the DHCP response the unit will download additional files, as follows:
if a bootfile is specified, the unit will then download that bootfile (using tftp).
if the bootfile specifies other files e.g. a software file, the unit will compare that
filename with the filename in its memory; if it has changed the unit will then
download that other file using tftp. If the filename has not changed the unit will not
download it.
The DHCP protocol provides an industry standard alternative to BOOTP and provides
a more sophisticated method of managing IP addresses and configuration parameters. It
should be particularly useful when managing the unit from a Windows NT server
environment and some versions of UNIX such as UnixWare 7.
DHCP is a superset of the BOOTP configuration service which it completely replaces.
DHCP is backward compatible with BOOTP in that the entire suite of BOOTP tags is
supported within DHCP. DHCP is now often used in favour of BOOTP as it is supported
on a wide range of network operating systems, however to ensure compatibility with
existing installations, the Console Server will continue to fully support BOOTP.
Black Box Console Server user guide 36
Page 37

The major differences between BOOTP and DHCP are:
• BOOTP is largely reliant on a network client's low level Ethernet address (MAC
address) for client information look-up, DHCP has no such limitation, although it
is still possible to associate a specific IP address to a specific MAC address.
• Client information supplied by DHCP is supplied on a lease basis, that is to say
that the client negotiates with the server for the lease of an IP address for a specific
period of time. This allows for the allocation of a fixed pool of client addresses
that are allocated by the DHCP server on a “first come first served” basis.
No additional configuration is required in the unit to enable DHCP, however your
network server will need to have it's DHCP service configured for Console Server
clients and if boot file download is required, then the TFTP service should be configured
and running. DHCP/BOOTP can also be disabled completely by setting the configurable
server DHCP parameter to off.
Black Box Console Server user guide 37
Page 38

Manually setting up an IP address
This section includes the following;
• Set up procedure on page 39
• Server form field descriptions on page 42.
Black Box Console Server user guide 38
Page 39

Set up procedure
To manually set up an IP address proceed as follows;
1. Set up a terminal or PC running terminal emulation. For examples of connection
pinouts see Appendix A Cabling information.
If you connect via the Admin Port you will see a display of diagnostic and bootup
messages.
Note that if you cannot emulate VT100, you will have to use the Command Line
Interface (cli); (the cli commands are described in full in Appendix B The CLI
commands).
2. At the console, with the login prompt displayed, type admin and press <return>.
3. At the password prompt, now displayed type superuser and press <return>. This
is the default admin user password.
The command line prompt will now be displayed:
4. At the command prompt type screen and press <return> to enter Full Screen
mode.
The main menu is now displayed:
5. At the main menu, select ‘server configuration’. (alternatively, use the cli
command set server)
The server form will be displayed as shown in the next picture:
Black Box Console Server user guide 39
Page 40

6. Within the server form, complete the fields by moving between the fields using
the arrow keys. Use the <del> key to backspace if necessary.
For a description of the fields in this form see Server form field descriptions on
page 42.
Example settings for all the Console Server configuration fields are shown in the
next picture:
7. When you have completed the form, press <return>.
You will be presented with the following display:
Black Box Console Server user guide 40
Page 41

8. Accept the form; you will be returned to the Main Menu.
You may want to save your configuration changes permanently; see Saving
configuration changes on page 62
9. Reboot the unit. Rebooting will ensure that other network devices can
communicate with it.
Note If you set the port to authenticate by RADIUS only, users will not be able to dial in
and connect if the network connection is down (no access to RADIUS server).
Tip If you are not using the RADIUS service, you can leave authentication set to ‘both’.
You will have entered users in the Console Server’s user table. The unit will
authenticate users via its own user table and, provided user names and passwords
are valid, should not need recourse to a RADIUS host.
Black Box Console Server user guide 41
Page 42

Server form field descriptions
The server form fields are described in the next table. You can use this information to
assist with setting values in Set up procedure on page 39.
Parameter Description
servername
(also known as hostname or alias)
Internet Address (IP Address) The Console Server’s unique address in the network.
Broadcast Address The address used by the Console Server for sending
Subnet Mask Allows interconnected local networks to coexist with the
Domain Name Unique name which describes your domain - your location in
Authentication You can authenticate all users connecting to the Console Server
The familiar name for your Console Server.
information to all hosts on your network simultaneously.
Once you have entered an IP address and subnet mask, the
broadcast address will default to the IP address with the host
part(s) set to 255.
same network ID. This hides complicated local environment
and routing information from external hosts and gateways. If
you want the Console Server to belong to the same subnet as
other hosts, give it the same subnet mask as them.We
recommend you set a subnet mask on initial configuration
the global network. Like Hostname, it is a symbolic rather
than a numerical identifier.
in one of three ways:
Black Box Console Server user guide 42
Page 43

Parameter Description
both - (the default) firstly with the unit’s own user table. If
the username is found in unit but the password is incorrect,
an authentication request is sent to the RADIUS host. If the
username is not found in the unit, authentication is passed up
to the RADIUS host. (The exception is the ‘admin’ user; if
you supply an incorrect password, the unit will not go to the
RADIUS host; it will fail the authentication).
When the unit uses the RADIUS host, it will try firstly the
primary RADIUS host and then - if one is specified - the
secondary RADIUS host; (see RADIUS configuration on
page 51).
local - with the unit’s user table (only)
RADIUS - with the RADIUS host’s user table (only); does
not apply to username ‘admin’ who is always authenticated
locally.
DHCP You can use the auto configuration method for configuring
the Console Server from a DHCP server. You must turn on
this feature by selecting 'on' and disable this feature by
selecting 'off'. Default is 'off' or DHCP is disabled.
SSH protocol In order to provide a secure connection from the LAN to a
device on the Console Server, you must enable the
appropriate SSH protocol version. By default, ssh protocol is
'disabled'. To support SSH version 1, select 'ssh-1'. To
support SSH version 2 only, select 'ssh-2'. To enable both
version of ssh support, select 'both (ssh-1+ssh-2)'. If you are
configuring ssh for the first time, you will be prompted to
generate the appropriate encryption keys used for negotiating
a secure connection. This key generation process could take
several minutes. Once generated, the Console Server will
then support the ssh protocol selected.
Black Box Console Server user guide 43
Page 44

Parameter Description
gui access this parameter controls access to the Console Server’s
graphical configuration programme JETset.
The default is ‘off’. When set to ‘on’ the admin user can
access the JETset from a Web browser, using the unit’s
internet address. Entry to the programme is then controlled
by password.
If you are not using the JETset to configure the unit, we
suggest you set this parameter to ‘off’; access will be denied
to any person who tries to connect to the unit from their
browser.
How to access the JETset is described in Appendix G JETset.
Black Box Console Server user guide 44
Page 45

Accessing the Console Server configuration software
Logging onto your Console Server
1. From your host, telnet to Console Server. For example, telnet 192.65.1434.15
2. A login prompt is now displayed.
3. At the console, with the login prompt displayed, type admin and press <return>.
At the password prompt, type superuser and press <return>. This is the default
admin user password. The command line prompt will be displayed: <product
name (abbreviated)> e.g. xxxxxx, followed by the hash # sign, indicating that you
are now logged in as the system administrator.
4. To enter Full Screen mode (the text-based menus), type screen and press
<return>. The main menu will be displayed:
Black Box Console Server user guide 45
Page 46

Setting up your network parameters
Setting up the host table
The Console Server needs to know the hostnames and internet addresses of the other
hosts in the network (or any hosts anywhere on the Internet) which you want to
communicate with on a regular basis. For example, gateways, RADIUS, servers and
so on. These hostnames are added to the unit’s Host Table. You can add up to twenty
hosts. To do this;
1. From the Main menu, select ‘Network Configuration’.
The Network Configuration menu is now displayed.
2. Within the Network Configuration menu, select ‘Host Table’;
The Host Table menu will be displayed:
You can now add (Adding a Host on page 46), change (Changing a Host on page
48)or delete (Deleting a host on page 49) a host as required.
Adding a Host
To add a host (cli syntax add host):
1. Within the Host Table menu, select ‘Add Host’ from the Host Table menu; this
option enables you to add the hostname of a host to the host table.
You will be asked to enter the hostname:
Black Box Console Server user guide 46
Page 47

2. Type in the name of the host (14 characters maximum) and press <return>.
Black Box Console Server user guide 47
Page 48

Changing a Host
This option enables you to add or change a host’s internet address:
To change a host (set host, show host):
1. Within the Host Table menu, Select ‘Change Host’ from the Host Table menu;
This form will list all hosts added to the host table. The default internet address is
0.0.0.1.
2. Enter the correct internet address of each host. Use the <del> key to backspace if
necessary.
Black Box Console Server user guide 48
Page 49

Deleting a host
This option enables you to delete an entry from the host table. If a host is referenced
by a pre-defined session, or is defined as a gateway or name server, you won’t be
allowed to delete it.
To delete a host (cli command delete host)
1. Within the Host Table menu, When you select ‘Delete Host’, the host table will be
displayed:
2. Select the host that you want to delete and press <return>.
You will be asked to confirm the deletion:
3. Type ‘y’ to delete the host, ‘n’ to cancel the command.
Black Box Console Server user guide 49
Page 50

Changing the Admin Password
cli syntax:
set user
password
To change the Admin password proceed as follows;
1. Within the Users menu, select ‘Set Password’.
2. From the list now displayed, select ‘admin’ user.
You will be prompted to enter a password. This can be up to sixteen characters.
Use the <del> key to backspace if necessary.
3. At the prompt, enter the password and press <return>.
You are now prompted to enter the password a second time to confirm your
choice.
4. At the prompt, re-enter the password and press <return>.
The password change will take effect next time you log in.
Note The factory default password is superuser.
Black Box Console Server user guide 50
Page 51

RADIUS configuration
This section includes the following:
• Set up procedure on page 51
• RADIUS parameters description on page 54.
Set up procedure
To configure how the Console Server interacts with the RADIUS host or hosts:
1. From the Main menu, select ‘radius configuration’:
2. Within the radius configuration menu, select from one of add/delete
authentication/accounting host.
A list of hosts from the unit’s host table is now displayed (see Setting up the host
table on page 46):
:
3. Highlight your selection and press <return>.
You will be asked to enter a ‘secret’ (a password):
Black Box Console Server user guide 51
Page 52

4. Key a maximum of sixteen alphanumeric characters.
To change the secret you must delete the host and then add it again; when you add
a host you are prompted for a secret.The first host entered becomes the primary
authentication/accounting host, the next host entered becomes the secondary host.
You can enter a maximum of two hosts in each of the fields.
You must enter the same secret in the RADIUS host (see your RADIUS
documentation); the secret is not transmitted over the network. Note that to set
RADIUS authentication on/off, go to back to the Main Menu and select ‘server
configuration’. See Setting up an IP address on page 33.
5. Select ‘change radius settings’, you are presented with the following (shown in
the next picture):
The RADIUS parameters are described in RADIUS parameters description on
page 54.
6. When you have completed the form, press <return>. You will be presented
with the following display:
Black Box Console Server user guide 52
Page 53

7. Accept the form; you will be returned to the menu.
Tip You may want to save your configuration changes permanently; see Saving
configuration changes on page 62
Black Box Console Server user guide 53
Page 54

RADIUS parameters description
The RADIUS parameters are as follows:
retry
(for authentication) the number of times the unit will re-send a request to a
RADIUS authentication host, before re-presenting another login to the user.
(for accounting) the number of times the unit will re-send a request to a RADIUS
accounting host, before understanding that the accounting request has failed.
The default retry value is 5; the unit will try the primary host up to 5. You can
enter values between 0 (don’t retry) and 255. If you have different authentication
and accounting hosts unit will retry first the authentication host(s) and then the
accounting host(s).
timeout - the time in seconds between unit sending a request to a RADIUS
accounting or authentication host and receiving a reply. If no reply is received
before the expiry of the timeout period, the unit will retry the same host up to and
including the number of retry attempts specified under ‘retry’.
The default timeout period is 3 seconds (you can enter values between 1 and 255).
accounting - turns accounting on or off within the unit; the default is off.
RADIUS
accounting
RADIUS host
specified
no off - no accounting
yes on up accounting in both Console Server and
accounting flag
state of RADIUS
host
result
RADIUS host
yes on down accounting in Console Server only
Notes on Table above:
‘accounting’ within the Console Server is an increment of the session id (see
below).
‘accounting’ in the RADIUS accounting host means that you should be able to
see accounting information by interrogating the host (see your RADIUS
documentation).
acct_port - the UDP port number for RADIUS accounting. The default value is
1646 which should match most RADIUS implementations. Change this value if
your RADIUS host is using a different UDP port number.
Black Box Console Server user guide 54
Page 55

auth_port - the UDP port number for RADIUS authentication. The default value
is 1645 which should match most RADIUS implementations. Change this value if
your RADIUS host is using a different UDP port number.
acct_authenticator - a flag to instruct the unit to check the authenticator field in
the accounting reply transmission from a RADIUS host to the unit. The
authenticator field contains the secret, encrypted. The options are ‘on’ (the unit will
check this field) or ‘off’ (the unit will not check this field); the default is ‘on’. Make
sure the setting in your RADIUS host is the same as the unit.
session id - displays in real-time the hexadecimal value of the current session
(incrementing with each session). The current session is the most recent connection
into the unit when the line service is set to ‘cslogin’ (the default line service).
You can reset the session id to zero; enter 0s from your keyboard.
An explanation of the eight digit value displayed in the session id field is as follows:
the first two digits show the number of reboots which have taken place. The
maximum number which will be shown is ff (255); on the next reboot, this
value will reset itself to 01 (1).
the last six digits show the number of user sessions which have started since
the last reboot (on reboot these six digits are reset to zero). The first session
will be 000001, the second session will be 000002, etc. The maximum
number of sessions is approximately 16 million, i.e. ffffff, at which point
the counter would reset itself to all zeros, i.e. 000000.
An example of all eight digits in a session id is:
0a000006
which means there have been 10 reboots (0a) of this unit (since the counter
was reset or wrapped around) and 6 (000006) sessions started since that
reboot.
Sessions are measured through the RJ45 ports on the front panel; connections
through any of the ports on the rear panel are not shown.
Black Box Console Server user guide 55
Page 56

DNS configuration
You can enter the addresses of two DNS hosts in the Console Server (the ‘unit’); one
will be the primary host, the other a secondary host. The DNS hosts do not have to be
the same hosts as entered in your unit’s host table. On a remote access connection the
unit will transmit these addresses to a dial-up Windows NT/95 client. Therefore, your
remote user does not have to configure DNS parameters in his/her computer. For
more information on DNS see Appendix D RADIUS & Networking.
To configure DNS host proceed as follows;
1. From the Main menu select ‘network configuration’:
Cli syntax:
add DNS
delete DNS 5. If required, change the DNS entry by deleting it, then entering the replacement
2. From the network configuration menu, select DNS.
The Add/Delete DNS menu is now displayed.
3. Within the Add/Delete DNS menu select the Add DNS option.
You are now prompted to enter an internet address;
4. Enter this address in dot decimal notation. If you wish, it can be the same address
as a machine already entered in the unit’s host table.
The first host entered becomes the primary DNS host, the next host entered
becomes the secondary host. You can enter a maximum of two DNS hosts.
value.
Black Box Console Server user guide 56
Page 57

WINS configuration
WINS (Windows Internet Name Service) is a database of hostnames and
corresponding internet addresses. It is a Microsoft specific name resolution service.
The basic function of WINS is the similar to DNS, i.e. it maps computer names to
TCP/IP addresses for client computers on a network. For more information on WINS
see Appendix D RADIUS & Networking.
You can enter the addresses two WINS hosts in the unit; one will be the primary host,
the other a secondary host. On a remote access connection the unit will transmit these
addresses to a dial-up Windows NT/95 client. Therefore, your remote user does not
have to configure WINS parameters in his/her computer.
1. From the Main menu select ‘network configuration’:
Cli syntax:
add WINS
delete WINS 4. If required, change the WINS entry by deleting it, then entering the replacement
Black Box Console Server user guide 57
2. From the network configuration menu, select WINS.
You are now prompted to enter an internet address;
3. Enter this address in dot decimal notation. If you wish, it can be the same address
as a machine already entered in the unit’s host table.
The first host entered becomes the primary WINS host, the next host entered
becomes the secondary host. You can enter a maximum of two WINS hosts.
value.
Page 58

Configuring network gateways
Gateways are hosts that connect Local Area Networks (LANs) together. If you want
to access a host which isn’t on your local network you will be connected via a
gateway. Gateways route data via other gateways until the destination local network
is reached. There are three types:
• Default - this is a gateway which provides general access beyond your local
network.
• Host - this a gateway reserved for accessing a specific host external to your local
network.
• Network - this is a gateway reserved for accessing a specific network external to
your local network.
The unit allows you enter a maximum of twenty gateways.
Particularly useful when checking routes to/from gateways is the show routes
command;.
Active and
passive
gateways
The unit supports both active and passive gateways. The default is active. Definitions
of these types are as follows:
Active gateway: a gateway which is temporarily listed in the unit’s routing table
(while RIP packets are received). If the unit detects that the gateway
is no longer operating (no RIP packets received) it will be deleted
from the routing table.
Passive gateway: a gateway which is permanently listed in the unit’s routing table. It
is thus always available.
See the following for how to configure gateways:
• Adding a gateway on page 59
• Deleting a Gateway on page 60.
Black Box Console Server user guide 58
Page 59

Adding a gateway
To add a gateway proceed as follows:
1. From the Network Configuration menu, select ‘Gateway’.
2. From the Gateway menu, select ‘Add Gateway’.
3. From the host table now displayed, select a host.
Note that you can define a host only once as a gateway.
When you have added a gateway, you must define its type.
4. From the Gateway menu, select ‘Change Gateway’.
The Gateways form is now displayed (for example):
This form lists all gateways defined for your network. In this example, only one
has been defined.
5. Complete the Type field; the values are ‘host’, ‘network’ or ‘default’.
If you set the field to ‘host’ or ‘network’, you must include the internet address of
the target host or network. If you change a gateway from ‘host’ or ‘network’ to
‘default’, the internet address will be ignored.
6. Complete the ‘Status’ field; the values are ‘active’ or ‘passive’.
Note the gateways configured in this table will be ignored if you have used DHCP or
BOOTP to download a single passive gateway into the unit; see Appendix F
BOOTP.
Black Box Console Server user guide 59
Page 60

delete
gateway
Deleting a Gateway
If a host on your network is retired from gateway duty, you can use this option to delete
it from the list of gateways. Note that the host will NOT be deleted from the host table.
To delete a gateway proceed as follows:
1. From the Network Configuration menu, select ‘Gateway’.
2. From the Gateway menu, select ‘Delete Gateway’ to list your gateways:
3. Delete the gateway you require from the list.
Black Box Console Server user guide 60
Page 61

Verifying your network installation
To check that you have installed the Console Server (the ‘unit’) successfully proceed
as follows;
1. At the command prompt, try to ping a remote host by typing the following
command:
ping hostname
Choose a host that you have defined in the host table. If no packet loss is reported,
your unit is ready to use.If the command returns an error, refer to the ping cli
command. See Appendix B The CLI commands;
Black Box Console Server user guide 61
Page 62

Saving configuration changes
Saving to non-volatile memory
To save your configuration settings to non volatile memory proceed as follows;
1. After making changes to the configuration exit the text menu screen (form) you
are using.
The ‘options’ form now appears:
2. Within the options form select ‘accept and exit form’ to retain your changes in
RAM (volatile memory).
3. To save your changes permanently exit the text menu system completely then
return to the Main Menu and select ‘command line mode’;
The exit full screen mode form is now displayed:
4. Within the ‘exit full screen mode’ form select ‘exit and save changes’.
All the changes made since last entering the menus will be saved to FLASH
(permanent, non-volatile) memory.
You will now be at the command line prompt.
5. To return the menus, at the command prompt, type: screen
Black Box Console Server user guide 62
Page 63

Saving to a file
cli syntax:
netsave
You can also save your configuration information to a file on a host. This can only be
done in the cli; See Appendix B The CLI commands.
Black Box Console Server user guide 63
Page 64

Setting date and time
The Console Server (the ‘unit’) has a real-time clock which you can set and view. It is
battery-backed and therefore will operate when power is off and over reboots. The clock
is year 2000 compliant.
To set the date and time on your unit proceed as follows;
1. From the Main Menu select Hardware.
The hardware form is now displayed. Only the date and time fields are
user editable.
:
2. Identify your unit using the hardware information displayed.
(To view hardware details in command line mode (cli) use the command show
hardware).
3. Within the ‘hardware’ form. move the cursor to the start of the field using the
‘delete’ key; then enter information in the format (for the date):
DD/MM/YYYY e.g. 30/03/2001
and in the format (for the time):
HH:MM:SS e.g. 20:32:00
Note that you do not have to enter the number of seconds.
4. Alternatively, in command line mode (cli) enter the commands ‘set date’ and ‘set
time’;
To view the date and time select ‘hardware’ from the Main Menu and check the
‘hardware’ form; In command line mode, enter the commands Show date, Show time,
or Show hardware.
Black Box Console Server user guide 64
Page 65

Performing a soft reboot
To perform a soft re-boot (cli syntax: reboot);
1. From the Network Configuration menu, select ‘Reboot’.
You will be asked whether you wish to save your configuration changes to nonvolatile memory:
2. At the prompt, type y and press the Enter key.
The unit will close all connections and then reboot.
Black Box Console Server user guide 65
Page 66

Restoring factory default settings
Resetting to factory defaults using software
This feature enables you to reset the unit to its default settings. This will clear all
configuration data entered by the admin user, and all user accounts, except the
default admin user, will be deleted.
To reset to factory default settings from within the software (cli syntax: reset
factory):
1. From the Network Configuration menu, select ‘Reset’.
You will be asked to confirm the reset:
2. At the prompt, type ‘y’ to reset the unit, or ‘n’ to cancel the command.
Resetting to factory defaults using reset switch
To reset to factory defaults using the reset switch, proceed as follows;
Black Box Console Server user guide 66
Page 67

1. Use the tip of a pen or pencil to press the reset switch located on the rear of the
unit.
The Console Server will then reboot and reset itself to factory default settings.
Black Box Console Server user guide 67
Page 68

Black Box Console Server user guide 68
Page 69

Chapter 3 System administration
You need to read
this chapter if you
want to...
You need to read this chapter if you want to do system administration with the Console Server.
This chapter provides task oriented information on system administration with the Console Server.
This chapter includes the following sections;
• Security on page 70
• Setting up the line on your Console Server on page 70
• Viewing and editing your line settings on page 71
• Lost password on page 73
• Configuring a dial in line on page 74
• Configuring users on page 94
• Configuring Break Pass Through on page 110
• Resetting the line to default on page 111
• Saving your settings on page 112
Black Box Console Server user guide 69
Page 70

Security
The Console Server has a number of security features built in that can be enabled or
disabled depending on the security level required.
These features include:
• Telnet access - Login and password required.
See set line on page 166 in Appendix B The CLI commands.
• SSH access - Makes ports only accesible via SSH connections.
See Accessing devices via SSH on page 118 in Chapter 4 Using your Console
Server.
• Radius authentication - Allows user names and passwords to be authenticated by
an external Radius server.
See About user accounts and RADIUS on page 96 in Chapter 3 System
administration.
• Disable Daemons - Allows unused Daemons to be disabled to prevent
unauthorised access by hackers.
See set server on page 173 in Appendix B The CLI commands.
• Trusted host filtering - Prevents the unit from being seen on the network by non-
authorised systems
See set server on page 173 in Appendix B The CLI commands.
Setting up the line on your Console Server
The default use of the Console Server is as a Console server. Therefore all lines are
set with a service of “Reverse Telnet”. This allows a user on the LAN to be able to
telnet into the ports and access the attached devices.
Each port also requires a TCP socket number in order to work. By default, the unit is
set to use numbers 10001 to 10024. You can change these to any other socket number
as long as there is no conflict on the network.
For an explanation of other line services see Appendix E Summary of Line Service
Types.
Black Box Console Server user guide 70
Page 71

Viewing and editing your line settings
Lines set to reverse Telnet by default
cli syntax:
set line
A Typical
Reverse
Te ln et
Configuratio
n
A reverse telnet connection enables a TCP/IP host on the local network to establish a
login connection via a Console Server (the ‘unit’) port on a non-TCP/IP machine
external to the network, such as routers, servers and so on.
To set up a reverse telnet connection, follow these steps:
1. Select Line Settings from the Line Configuration menu then select the line that
you want to configure.
2. Set ‘service’ to rev tel (default setting).
Note when field is highlighted, pressing L will list all available options.
Black Box Console Server user guide 71
Page 72

3. Assign a TCP port number to the unit port using the ‘CS Port’ field. This TCP
port number will be used by any host wanting to access the unit port. If you select
a TCP port being used by another process, a connection will not be established
(By default, lines are set to TCP port 10001 to 10024 for each port. For example,
Line 1 10001, Line 16 10016).
4. Do not configure the idle and session timers; these timers have no effect on
reverse telnet connections.
5. The ‘Hostname’ and ‘Host Port’ fields may contain default or last-used values,
but these will be ignored.
Black Box Console Server user guide 72
Page 73

6. The line should now be configured similar to that shown in the next picture:
7. Press <return> to exit; if you do not wish to save your changes press the <escape>
key.
8. If you want to configure all lines with the same parameters, refer to Resetting the
line to default on page 111.
Lost password
If you are an admin user, and you lose your password, there is no way of logging in
without it. This restriction is for security reasons. Unless there is another user with
admin level privileges (who will have the ability to change your password) you will have
to reset the Console Server (the ‘unit’) to its factory default settings.
cli syntax:
set user
If a user forgets his/her password, you can assign a new password; go to the Users Menu
and select ‘set password’.
Black Box Console Server user guide 73
Page 74

Configuring a dial in line
Introduction to SLIP and PPP connections
This section deals with setting up SLIP and PPP connections on a line. There is also
a summary of the configurable features of modems.
Deciding whether to use SLIP or PPP
If you require any of the features listed below, use PPP, otherwise SLIP should be
sufficient.
IP Address Negotiation. SLIP provides no mechanism for informing the other end of a
link of its IP address, whereas PPP will do so.
Error Checking. SLIP does not error check whereas PPP does. This is not necessarily a
problem in SLIP since most upper layer protocols have their own error checking.
Some systems exchange UDP packets with checksum disabled, which would cause
problems should that part of an IP packet get corrupted.
Authentication. Once SLIP has started you cannot authenticate the remote device,
whereas as PPP provides the option of using security protocols PAP or CHAP. See
Configuring PPP on page 82, then sub-section ‘Security’ for further details.
Software Flow Control. You cannot use software flow control on SLIP links since there
is no way of escaping control characters from the data stream. PPP has a facility (called
ACCM) which allows specific control characters to be escaped from the data stream.
See Configuring PPP on page 82 for more details.
For more information on the SLIP and PPP protocols see Configuring a dial in line on
page 74.
Black Box Console Server user guide 74
Page 75

Setting up the line
cli syntax:
set line,
show line
1. From the Line Configuration menu, select ‘Line Settings’.
2. Within the Line settings menu, select a particular line; e.g. line 3.
The line form will be displayed (default values shown in the next example):
3. Within the line form, set the Service field using one of the options given in the
next table;
Black Box Console Server user guide 75
Page 76

Service option Description
PPP When you want a remote access service connection using PPP, or when you
want to use the unit as a router with PPP. In both cases the user (whether real or
dummy) will be authenticated within PPP (provided you use Security - PAP or
CHAP).
cslogin When you want a remote access service connection using SLIP. Do not use the
option ‘SLIP’ because there would be no authentication of the user; (instead,
you will set SLIP for a particular user - see Configuring a user account on page
100).
Choosing the ‘cslogin’ option, the unit will present the login prompt: the user
will be required to enter a name and password and hence will be authenticated.
SLIP When you want to use the unit as a router with SLIP. There will be no
authentication of each unit by the other unit.
Option Description
Line name
Speed, Bits,
Parity and
Line name can be configured to uniquely identify the line.
Change as necessary from the default line configuration of 9600 baud, 8 data
bits, no parity, 1 stop bit.
Stop
Flow Flow Control field to either ‘soft’ (software) or ‘hard’ (hardware). For SLIP set to
‘hard’ only. For PPP set to either ‘soft’ or ‘hard’ (‘hard’ recommended). If you
select ‘soft’ you must set the parameter ACCM when you configure PPP for the
line (in Configuring PPP on page 82)
Host port field. This is the host TCP port number and is set by default to 23. In most cases you
can use the default value.
Dial Set to ‘in’ if your user is remote and will be dialling in via modem or ISDN TA;
set to ‘in’ or ‘out’ if using the unit as a router, depending on which end of the
link your unit is situated.
Phone Number When dial is set to ‘out’ and the line ‘service’ is set to ‘slip’ or ‘ppp’ enter a
phone number for the unit to dial (you should only have this combination of
settings when you are using two units back-to-back, i.e. as routers.
Idle Timer
router use only
Enter a period in seconds for which the idle timer will run. Use this timer to
close a connection because of inactivity. When the idle timer expires the unit
will end the connection. The default value is 300 seconds, meaning the idle
timer will expire 300 seconds after the last activity. The maximum value is
4294967 seconds (equal to 49 days, approximately). A value of 0 (zero) means
the idle timer will not expire, so the connection is open permanently.
Black Box Console Server user guide 76
Page 77

Service option Description
Session Timer
router use only
Enter a period in seconds for which the session timer will run. Use this timer to
forcibly close the session (connection). When the session timer expires the unit
will end the connection. The default value is 0 (zero), meaning that the session
timer will not expire (the session is open permanently, or until you kill the line.
The maximum value is 4294967 seconds (equal to 49 days, approximately).
4. Ignore the other fields in this form. Press <return> to exit; if you do not wish to
save your changes press the <escape> key.
cli syntax:
add modem
5. Now go to the Line Configuration Menu:
6. Within the Line Configuration Menu, select ‘Add Modem’.
7. Enter the name of the modem/ISDN TA attached to the unit. You can enter a
maximum of twenty names, each with nineteen alphanumeric characters.
8. Within the Line Configuration Menu, select ‘Change Modem’. Select your
modem/ISDN TA name. Enter the initialisation string; see your modem/ISDN TA
documentation.
9. Press <return> to exit; if you do not wish to save your changes press the <escape>
key.
set line 10. Go back to the ‘Line Settings’ menu. Select your line. When the line parameters
form appears go the field ‘modem name’. Press ‘L’ (upper or lower case) or the
spacebar. Choose the modem name which you entered at Step 5.
11. Press <return> to exit; if you do not wish to save your changes press the <escape>
key.
You can copy the settings for this line to other lines (an option as you exit this
line);
You can reset this line to default (an option as you exit this form); refer to
Resetting the line to default on page 111
12. You may want to save your configuration permanently; if so, refer to Saving
settings to non-volatile memory on page 112.
Black Box Console Server user guide 77
Page 78

Configuring SLIP
cli syntax:
set slip line,
show slip
line
Option Description
Local ip address This is the IP address of the unit end of the SLIP link. For routing to work you
To configure the SLIP parameters proceed as follows;
1. From the Line Configuration menu, select ‘SLIP’ and then select a line.
The SLIP form is now displayed (default values shown):
2. Within the SLIP form, set the parameters listed in the next table:
must enter an IP address in this field. Choose an address which is part of the
same network or subnetwork as the remote end; e.g. if the remote end is address
192.101.34.146, your local ip address may be 192.101.34.145; (in the cli,
example syntax would be:
set slip li 1 lipaddr 192.101.34.145)
Do not use the unit’s (main) ip address in this field; if you do so, routing will not
take place correctly.
Black Box Console Server user guide 78
Page 79

Option Description
Remote ip address This is the IP address of the remote end of the SLIP link. This must be specified.
Choose an address which is part of the same network or subnetwork as the unit
(see comment in ‘Local ip address’ above). Enter the remote ip address in dot
notation, e.g.192.101.34.146
(or in the cli, example syntax would be: set slip li 5 ripaddr 192.101.34.146)
If your user is authenticated by the unit this remote ip address will be overridden
if you have set a ‘framed ip’ address for the user with values other than
255.255.255.254 or 255.255.255.255; see Configuring a user account on page
100, sub-section ‘framed ip’.
If your user is authenticated by RADIUS and the RADIUS parameter ‘FramedAddress’ is set in the RADIUS file the unit will use the value in the RADIUS
file in preference to the ‘Remote ip address’ value configured here.
Subnet Mask this is the subnet mask of the node on the remote end of the SLIP link. This field
is optional. This parameter should be entered in dot notation e.g.
255.255.255.224
If your user is authenticated by RADIUS and the RADIUS parameter ‘FramedNetmask’ is set in the RADIUS file the unit will use the value in the RADIUS
file in preference to the ‘Subnet Mask’ value configured here.
Maximum
transmission unit
The Maximum Transmission Unit (mtu) parameter restricts the size of
individual SLIP packets being sent by the unit. Enter a value in bytes between
256 and 1006, e.g. 512 (in the cli, example syntax would be: set slip li 1 mtu
512). The default value is 256. For more information on this parameter see
Configuring a user account on page 100, sub-section ‘framed mtu’.
If your user is authenticated by the unit this mtu value will be overridden when
you have set a ‘framed mtu’ value for the user; see Configuring a user account on
page 100, sub-section ‘framed mtu’.
If your user is authenticated by RADIUS and the RADIUS parameter ‘FramedMTU’ is set in the RADIUS file the unit will use the value in the RADIUS file
in preference to the ‘mtu’ value configured here.
Suppress icmp This option causes ICMP (Internet Control Management Protocol) packets
directed to this SLIP link to be discarded. The possible values are ‘on’ and ‘off’;
the default is off.
Interactive
priority
This determines whether interactive traffic (e.g. telnet sessions) is given priority
over batch type traffic (e.g. ftp) thus avoiding the situation where a user has to
wait for their character to be echoed while several large ftp packets are
transferred. The possible values are ‘on’ and ‘off’; the default is on.
Black Box Console Server user guide 79
Page 80

Option Description
VJ Compression This determines whether Van Jacobson compression is used on this link; i.e.
whether you are using SLIP or C-SLIP (compressed SLIP). The choices are ‘on’
(C-SLIP) or ‘off’ (SLIP); the default is ‘on’. Select ‘on’ will turn on VJ
compression. C-SLIP greatly improves the performance of interactive traffic,
such as Telnet or Rlogin; see Configuring a dial in line on page 74 for more
information.
In the cli, example syntax would be: set slip li 1 vj on.
If your user is authenticated by the unit this VJ compression value will be
overridden if you have set a ‘framed compression’ value for a user; see
Configuring a user account on page 100, sub-section ‘framed compression’.
If your user is authenticated by RADIUS and the RADIUS parameter ‘FramedCompression’ is set in the RADIUS file the unit will use the value in the
RADIUS file in preference to the ‘VJ compression’ value configured here.
TX parameters Meaning Transmit parameters. This will output to the screen of the user all the
SLIP parameters configured for that line/port. TX parameters are useful in some
applications such as Trumpet Winsock. Options are ‘on’ or ‘off’.
Black Box Console Server user guide 80
Page 81

Configuring PPP
This section describes how to configure a dial in line using PPP and includes the
following:
• PPP configuration procedure on page 82
• PPP form field descriptions on page 83.
An example of a remote access connection using PPP, including the setup of a remote
user is described in Configuring a dial in line on page 74.
PPP configuration procedure
cli syntax:
set PPP line,
show PPP
line
To configure a line using PPP proceed as follows;
1. Within the Line Configuration menu, select ‘PPP’.
2. Now select a line.
The PPP form for the selected line is now displayed as shown in the next picture
(default values shown in this example):
3. Within the PPP form set all the fields to the values you require. See PPP form
field descriptions on page 83 for details of how to set each field within the PPP
form.
Black Box Console Server user guide 81
Page 82

PPP form field descriptions
This section describes the fields and settings used in the PPP form referred to in PPP
configuration procedure on page 82. The following fields are described in this section.
• Local ip address on page 84
• Remote ip address on page 84
• Subnet Mask on page 84
• ACCM on page 85
• Max. receive unit on page 85
• Security on page 85
• User on page 87
• Password on page 87
• Remote User on page 87
• Remote Password on page 88
• Address/Control comp on page 88
• Protocol compression on page 89
• VJ Comp on page 89
• Magic No. negotiation on page 89
• IP address negotiation on page 89
• Configure req. timeout on page 90
• Terminate req. timeout on page 90
• Configure req. retries on page 90
• Terminate req. retries on page 90
• Configure NAK retries on page 90
• Authentication timeout on page 90
• Roaming callback on page 90
• Challenge_ interval on page 92
Black Box Console Server user guide 82
Page 83

Local ip
address
This is the IP address of the unit end of the PPP link. For routing to work you must
enter a local IP address. Choose an address which is part of the same network or
subnetwork as the remote end; e.g. if the remote end is address 192.101.34.146, your
local ip address may be 192.101.34.145; (in the cli, example syntax would be:
set ppp li 6 lipaddr 192.101.34.145)
To see an example of ip address usage, refer to ‘Setting up an IP address on page 33’.
Do not use the unit’s (main) ip address in this field; if you do so, routing will not take
place correctly.
Remote ip
address
This is the IP address of the remote end of the PPP link. This must be specified.
Choose an address which is part of the same network or subnetwork as the unit (see
comment in ‘Local ip address’ above). Enter the remote ip address in dot notation,
e.g.192.101.34.146; (or in the cli, example syntax would be: set ppp li 6 ripaddr
192.101.34.146).
If you set the PPP parameter ‘IP address negotiation’ to ‘on’ the unit will ignore the
remote ip address value you enter here and will allow the remote end to specify its ip
address.
If your user is authenticated by the unit this remote ip address will be overridden if
you have set a ‘framed ip’ address for the user other than 255.255.255.254; see
Configuring a user account on page 100, sub-section ‘framed ip’.
If your user is authenticated by RADIUS and the RADIUS parameter ‘FramedAddress’ is set in the RADIUS file the unit will use the value in the RADIUS file in
preference to the ‘Remote ip address’ value configured here. The exception to this
rule is a Framed-Address value in the RADIUS file of 255.255.255.254; this value
allows the unit to use the remote ip address value configured here.
Subnet Mask This is the subnet mask of the node on the remote end of the PPP link. This field is
optional. This parameter should be entered in dot notation e.g. 255.255.255.224
(or in the cli, e.g., set ppp li 9 255.255.255.224).
If your user is authenticated by RADIUS and the RADIUS parameter ‘FramedNetmask’ is set in the RADIUS file the unit will use the value in the RADIUS file in
preference to the ‘Subnet Mask’ value configured here.
Black Box Console Server user guide 83
Page 84

ACCM This allows the specification of an accm (asynchronous control character map) of
characters that should be escaped from the data stream. This is entered as a 32 bit
hexadecimal number with each bit specifying whether or not the corresponding
character should be escaped.
The bits are specified most significant bit first and are numbered 31-0. Thus if bit 17
is set, the 17th character should be escaped i.e. 0x11 (XON). So entering the value
000a0000 (in the cli, e.g.: set ppp li 1 accm 000a0000) will cause the control
characters 0x11 (XON) and 0x13 (XOFF) to be escaped on the link, thus allowing the
use of XON/XOFF (software) flow control.
If you have selected software flow control on the line (see Setting up the line on page
75) you must enter a value of 000a0000 for the ACCM.
The default value is 00000000, which means no characters will be escaped.
Max. receive
unit
The Maximum Receive Unit (mru) parameter specifies the maximum size of PPP
packets that the unit’s port will accept. Enter a value in bytes between 64 and 1500;
e.g. 512 (in the cli, example syntax would be: set ppp li 1 mru 512). The default value
is 1500. For more information on this parameter see Configuring a user account on
page 100, sub-section ‘framed mtu’.
If your user is authenticated by the unit the ‘mru’ value will be overridden when you
have set a ‘framed mtu’ value for the user; see Configuring a user account on page
100, sub-section ‘framed mtu’.
If your user is authenticated by RADIUS and the RADIUS parameter ‘FramedMTU’ is set in the RADIUS file the unit will use the value in the RADIUS file in
preference to the ‘mru’ value configured here.
Security This specifies what type of authentication will be done on the link: none, PAP or
CHAP. The default is CHAP.
You can use PAP and/or CHAP to:
• authenticate a port or user on the unit, from a remote location, or
• authenticate a remote client/device, from the unit.
PAP is a one time challenge of a client/device requiring that it respond with a valid
username and password. A timer operates during which successful authentication
must take place. If the timer expires before the remote end has been authenticated
successfully the link will be terminated.
Black Box Console Server user guide 84
Page 85

CHAP challenges a client/device at regular intervals to validate itself with a
username and a response, based on a hash of the ‘secret’ (password). A timer
operates during which successful authentication must take place. If the timer expires
before the remote end has been authenticated successfully the link will be terminated.
With both PAP and CHAP make sure the unit and the remote client/device have the
same setting. e.g. if the unit is set to PAP but the remote end is set to CHAP the
connection shall be refused.
In the cli, to turn on PAP (for example) the syntax would be:
set ppp li 7 security pap
If you have selected a line service of ‘cslogin’, PAP or CHAP will not take place
since the user will have already been authenticated. In this case setting security to
PAP or CHAP will have no effect.
Black Box Console Server user guide 85
Page 86

User Complete this field only if you:
• have specified PAP or CHAP (security protocols) in the ‘Security’ field, and
• you wish to dedicate this line to a single remote user, and this user will be
authenticated by the unit, or
• you are using the unit as a router (back-to-back with another unit).
‘User’ is the name the remote device will use to authenticate a port on this unit (the
opposite of the parameter ‘Remote User’). The remote device will only authenticate
your unit’s port when PAP or CHAP are operating. You can enter a maximum of
sixteen alphanumeric characters, e.g. kevinc8 (or, in the cli, example syntax would
be set ppp li 1 user kevinc8)
When connecting together two networks, enter a dummy user name; e.g. CS_HQ.
Note If you want a reasonable level of security the user name and password should not
be similar to a user name or password used regularly to login to the unit.
Password Complete this field only if you:
• have specified PAP or CHAP (security protocols) in the ‘Security’ field, and
• you wish to dedicate this line to a single remote user, and this user will be
authenticated by the unit, or
• you are using the unit as a router (back-to-back with another unit).
‘Password’ means the following:
in the ‘Security’ field, when you have specified PAP ‘Password’ is the password the
remote device will use to authenticate the port on this unit (the opposite of the
parameter ‘Remote Password’). The remote device will only authenticate your unit’s
port when PAP or CHAP are operating.
in the ‘Security’ field, when you have specified CHAP ‘Password’ is the secret
(password) known to both ends of the link upon which responses to challenges shall
be based. The remote device will only authenticate your unit’s port when PAP or
CHAP are operating.
In both cases, you can enter a maximum of 16 alphanumeric characters; (in the cli,
example syntax would be: set ppp I 7 password ******)
Remote User Complete this field only if you:
• have specified PAP or CHAP (security protocols) in the ‘Security’ field, and
Black Box Console Server user guide 86
Page 87

• you wish to dedicate this line to a single remote user, and your user will be
authenticated by the unit, or
• you are using the unit as a router (back-to-back with another unit).
‘Remote User’ is the name the unit will use to authenticate the port on the remote
device (the opposite of the parameter ‘User’). Your unit will only authenticate the
port on the remote device when PAP or CHAP are operating. You can enter a
maximum of sixteen alphanumeric characters;
(in the cli, example syntax would be: set ppp I 6 ruser kevin)
When connecting together two networks, enter a dummy user name; e.g. CS_SALES.
Note If you want a reasonable level of security the user name and password should not
be similar to a user name or password used regularly to login to the unit.
Remote
Password
Address/
Control
comp
Complete this field only if you:
• have specified PAP or CHAP (security protocols) in the ‘Security’ field, and
• you wish to dedicate this line to a single remote user, and this user will be
authenticated by the unit, or
• you are using the unit as a router (back-to-back with another unit).
‘Remote password’ means the following:
in the ‘Security’ field when you have specified PAP, ‘Remote Password’ is the
password the unit will use to authenticate the remote device.
in the ‘Security’ field when you have specified CHAP, ‘Remote Password’ is the
secret (password) known to both ends of the link upon which responses to challenges
shall be based.
In summary ‘Remote Password’ is the opposite of the parameter ‘Password’. Your
unit will only authenticate the remote device when PAP or CHAP are operating.
In both cases, you can enter a maximum of sixteen alphanumeric characters;
(or, in the cli, e.g., set ppp li 1 rpassword ******)
This determines whether compression of the PPP Address and Control fields shall
take place on the link. The choices are ‘on’ or ‘off’; the default is ‘on’. For most
applications this should be enabled; i.e. ‘on’. In the cli example syntax would be:
set ppp li 1 address_comp on
Black Box Console Server user guide 87
Page 88

Protocol
compression
This determines whether compression of the PPP Protocol field shall take place on
this link. The choices are ‘on’ or ‘off’; the default is ‘on’. For most applications this
should be enabled; i.e. ‘on’. In the cli example syntax would be:
set ppp li 1 proto_comp on.
VJ Comp This determines whether Van Jacobson Compression is used on this link. The choices
are ‘on’ or ‘off’; the default is ‘on’. Select ‘on’ will turn on VJ compression. Select
‘on’ will turn on VJ compression. C-SLIP greatly improves the performance of
interactive traffic, such as Telnet or Rlogin; see Configuring a dial in line on page 74
for more information. In the cli, example syntax would be: set ppp li 1 vj on.
If your user is authenticated by the unit this VJ compression value will be overridden
if you have set a ‘framed compression’ value for a user; see Configuring a user
account on page 100, sub-section ‘framed compression’.
If your user is authenticated by RADIUS and the RADIUS parameter ‘FramedCompression’ is set in the RADIUS file the unit will use the value in the RADIUS
file in preference to the ‘VJ compression’ value configured here.
Magic No.
negotiation
IP address
negotiation
This is a mechanism whereby a line can determine if it has been looped back. The
choices are ‘on’ or ‘off’; the default is ‘off’. If enabled (on) this option allows the
sending of random numbers on the link. The random numbers should be different,
unless the link has been looped back. In the cli, example syntax would be: set ppp li 1
magic_neg off.
This parameter specifies whether or not IP address negotiation shall take place. IP
address negotiation is where the unit allows the remote end to specify its ip address.
The values are ‘on’ or ‘off’. The default value is ‘off’.
If set to ‘on’ the unit allows the remote end to specify its ip address; the ip address
specified by the remote end will then be used in preference to the Remote ip address
set for a line.
If set to ‘off’ the unit will not allow the remote end to specify its ip address. The
Remote ip address set for the line will be used.
In the cli, example syntax would be: set ppp li 7 ipaddr_neg on.
When configuring your user (Configuring a user account on page 100), if you set
‘framed ip’ address to 255.255.255.255, the unit will override the value for IP
address negotiation set here. The result is that the unit will allow the remote end to
specify its ip address.
Black Box Console Server user guide 88
Page 89

Configure
req. timeout
This parameter specifies the maximum time in seconds that LCP (Link Control
Protocol) will wait before it considers a ‘configure request’ packet to have been lost.
(in the cli example syntax would be: set ppp li 8 cr_tmout 3).
Te rm in at e
req. timeout
Configure
req. ret ries
Te rm in at e
req. ret ries
Configure
NAK retries
Authenticatio
n timeout
Roaming
callback
This parameter specifies the maximum time in seconds that LCP (Link Control
Protocol) will wait before it considers a ‘terminate request’ packet to have been lost;
(in the cli example syntax would be: set ppp li 24 tr_tmout 3).
This parameter specifies the maximum number of times a ‘configure request’ packet
will be sent before the link is terminated;
(in the cli example syntax would be: set ppp li 23 cr_retry 10)
This parameter specifies the maximum number of times a ‘terminate request’ packet
will be sent before the link is terminated;
(in the cli example syntax would be: set ppp li 13 tr_retry 2)
This parameter specifies the maximum number of times a ‘configure nak’ packet will
be sent before the link is terminated;
(in the cli example syntax would be: set ppp li 2 nak_retry 10)
The timeout in minutes during which successful PAP or CHAP authentication must
take place; (you must have PAP or CHAP turned on). If the timer expires before the
remote end has been authenticated successfully the link will be terminated.
(in the cli example syntax would be: set ppp li 5 auth_tmout 1)
allows the user to specify a telephone number which the unit should use to callback
him/her. This feature is particularly useful for a mobile user. The possible values are
‘on’ and ‘off’; the default is ‘off’. The operation of roaming callback is shown
diagrammatically in Roaming callback on page 90.
Roaming callback can only work with a user whose (fixed) callback parameter is set
to ‘on’. See Configuring a user account on page 100. Roaming callback therefore
overrides (fixed) callback.To use roaming callback, the remote end must be a
Microsoft Windows which support Microsoft’s Callback Control Protocol (CBCP)
The user is allowed 30 seconds to input a telephone number after which the unit ends
the call.
Black Box Console Server user guide 89
Page 90

PPP line
uration
area
ROAMING
CALLBACK
OFF ON
Valueother actions necessaryresult parameter Config-
-
for the particular user you must set
(fixed) callback to ‘on’. See Configuring
a user account on page 100. Unless fixed
callback is set to on for user, he/she
cannot receive roaming callback.
the user must initially dial into the unit on
a line where roaming callback is set to
‘on’. You must therefore provide the user
with the telephone number for this type of
line(s).
the unit can still provide
fixed callback - provided you
have set the (fixed) callback
parameter to ‘on’ for that
particular user; see
Configuring a user account on
page 100.
Black Box Console Server user guide 90
after successful authentication the unit will
prompt the user for a telephone number to
call him/her back. After receipt of the
number, the unit will drop the line, call the
user back on that telephone number. The
user will be authenticated again (a
precaution).
Page 91

Challenge_
interval
sets the interval in minutes at which the unit will issue a CHAP re-challenge to the
remote end. The default value is 0 (zero) meaning CHAP re-challenge is disabled.
During CHAP authentication an initial CHAP challenge takes place, and is unrelated
to CHAP re-challenges. The initial challenge takes place even if re-challenges are
disabled.
Some PPP client software does not work with CHAP re-challenges so you may wish
to leave the parameter disabled in the unit.
Black Box Console Server user guide 91
Page 92

Configuring a modem
A summary of the configurable features for modems is listed below.
Note all references to modems apply equally to ISDN Terminal Adaptors
cli syntax:
set line
set line • when dial is set to ‘out’ and the line service is set to ‘slip’ or ‘ppp’ you can enter a
add modem
set modem
• you can set the ‘dial’ parameter to ‘in’, ‘out’ or ‘none’ (default ‘none’) in the line
parameters sub-menu. Setting ‘in’ or ‘out’ tells the unit that there is a modem on
that line. The unit will communicate with the modem through various RS232
signals. The ‘dial’ parameter can be set for all line services (e.g. cslogin, silent
raw).
‘phone number for the unit to dial (line parameters sub-menu). This combination
of circumstances occurs when you have two units connected back-to-back; i.e.
they are acting as routers.
• when the ‘dial’ parameter to ‘in’ and the line service is set to ‘cs_login’, ‘slip’ or
‘ppp’ the unit can initialise a modem. You enter a modem name and initialisation
string in the modems sub-menu. The unit will initialise that modem before any
new connection is started.
See add modem on page 146 in Appendix B The CLI commands.
Black Box Console Server user guide 92
Page 93

Configuring users
You need to configure user accounts on the Console Server (the ‘unit’) for those
users who are tasked with administering the attached devices or Remote Access
connections. If you are using a RADIUS host you may not need user accounts for
those users who are authenticated by the RADIUS host; see Configuring a dial in line
on page 74.
When you set up a User account you will see, as an example, the following form in
the text menus:
More detail on this form is contained in Configuring a user account on page 100.
When telneting or using SSH to connect to a port, the user will need to supply a user
name and password.
The remote access connections where you will need to configure user accounts
are where users:
• are being provided a remote access service, i.e. a SLIP or PPP connection, and
they are being authenticated by unit.
As the system administrator you will have your own user account (default name
‘admin’).
The unit’s login accounts are password-protected and assigned a user level; this level
restricts the user to certain commands; see About user levels on page 108. A maximum
of 32 user accounts can be created.
This section includes the following:
• About user accounts and RADIUS on page 96
• Adding a user account on page 99
• Configuring a user account on page 100
Black Box Console Server user guide 93
Page 94

Black Box Console Server user guide 94
Page 95

About user accounts and RADIUS
Overview
You can have a maximum of 32 user accounts on the Console Server. You will also be
able to configure user accounts on the RADIUS host. Therefore some users can be
authenticated by the unit, other users by RADIUS. You could have other combinations
of maintaining user accounts; i.e. duplicated on both the unit and the RADIUS host or,
alternatively all user accounts stored on the RADIUS host only.
Caution when a user is authenticated by RADIUS the unit starts a user service - such as telnet
or SLIP - based on instructions passed down by the RADIUS host. User parameters such as ‘service’ or ‘ip_host’ are taken entirely from the RADIUS host.
When
RADIUS
authenticates
users
Caution If you set the port to authenticate by RADIUS only, users will not be able to dial in and
connect if the network connection is down (no access to RADIUS server).
Black Box Console Server user guide 95
Page 96

Black Box Console Server user guide 96
Page 97

Example RADIUS user file: telnet service
davePassword = "garage"
User-Service = Callback-login,
Login-Host = 192.101.34.199,
Login-Service = Telnet,
Login-TCP-Port = 23,
Class = "Indirect Sales Group",
Session-Timeout = 1800,
Idle-Timeout = 600,
CallBack-Number = "3592"
An explanation of the file shown in Example RADIUS user file: telnet service on page
98 is as follows:
- the file contains a mixture of user parameters (e.g. callback-number) and line
parameters (e.g. login-host).
- this user has been authenticated by RADIUS; therefore, all user parameters are
passed down to the unit in this file.
- if you also have user ‘dave’ listed in the unit’s user table (i.e. a duplicate entry we do not recommend this action) all the user parameters configured in the unit for
user ‘dave’ will be overridden by the parameters in the RADIUS file; (for the user
to be authenticated by the RADIUS host, where you have a duplicate entry, the
password for ‘dave’ in the unit would have to be different to that entered in the
RADIUS user’s database or authentication in the unit would have to be set to
RADIUS (i.e. RADIUS only)).
- Class = "Indirect Sales Group" is a RADIUS class attribute. The unit
can only process a string of maximum 32 characters; therefore limit your string to
this size. In this example "Indirect Sales Group" is 20 characters (including spaces).
- line parameters override those configured in the unit; see Configuring a dial in line
on page 74 for a more detailed discussion on line parameters.
Black Box Console Server user guide 97
Page 98

Adding a user account
To add a user account, proceed as follows;
1. Within the Users menu, select ‘Add User’ (cli syntax: add user).
2. Enter a username, maximum sixteen characters (do not use spaces). If your user is
equipment allocate an appropriate name, e.g. barcode2.
3. Enter a password, maximum sixteen characters (do not use spaces). Re-enter the
password.
Admin users can change user passwords using the ‘Set Password’ feature described
in Changing a user’s password on page 109. Normal users can change their own
passwords; see Changing a user’s password on page 109.
Black Box Console Server user guide 98
Page 99

Configuring a user account
The section includes the following:
• Configuration procedure on page 100
• User form field descriptions on page 101.
• About user levels on page 108
• CLI prompts on page 108.
Configuration procedure
To configure a user account, proceed as follows;
Tip Your configuration will only be used if the user is authenticated by the unit. If the
user is authenticated by RADIUS, the unit will use configuration details for users
sent by the RADIUS host; see Configuring a dial in line on page 74.
1. Select ‘Change User’ from the Users menu (cli syntax: set user).
2. Choose your user from the list of names now displayed.
A user form will now be displayed as shown in the next example (uses default
values):
3. Within the user form, set the fields you require.See User form field descriptions
on page 101 for a description of how to set each field in more detail.
4. Press <return> to exit; accept or discard the form as you wish.
Note Changes you make in this form, as the system administrator, will only take effect for
a user when the user next logs in to the unit.
Black Box Console Server user guide 99
Page 100

User form field descriptions
This section describes the fields within the user form detailed in Configuration
procedure on page 100.The following fields are included:
• Service on page 102
• TCP Port No on page 103
• phone number on page 103
• idle timer on page 103
• session timer on page 103
• Level on page 103
• IP Host on page 103
• callback on page 104
• Callback for a user on page 105
• framed ip on page 107
• framed netmask on page 107
• framed mtu on page 107
• framed compression on page 108.
Black Box Console Server user guide 100
 Loading...
Loading...