Page 1
SignalHawk™
PC Model
Operations Manual
Model SH-36S-PC
Model SH-36S-RM
This is a preliminary manual. Specifications, limits, and text are
subject to change without notice. The information within this manual
was as complete as possible at the time of printing. Bird Electronic
Corporation is not liable for errors.
©Copyright 2010 by Bird Electronic Corporation
Instruction Book Part Number 920-SHPC-OPS Rev. C
SignalHawk is a trademark of Bird Electronic Corporation
ActiveSync, Microsoft, and Windows are registered trademarks
Adobe, Acrobat Reader are registered trademarks
of the Microsoft Corporation
of Adobe Systems Incorporated
Page 2

Page 3

Safety Precautions
The following are general safety precautions that are not necessarily
related to any specific part or procedure, and do not necessarily appear
elsewhere in this publication. These precautions must be thoroughly
understood and apply to all phases of operation and maintenance.
WARNING
Keep Away From Live Circuits
Operating Personnel must at all times observe general safety
precautions. Do not replace components or make adjustments to the
inside of the test equipment with the high voltage supply turned on.
To avoid casualties, always remove power.
WARNING
Shock Hazard
Do not attempt to remove the RF transmission line while RF power
is present.
WARNING
Do Not Service Or Adjust Alone
Under no circumstances should any person reach into an enclosure
for the purpose of service or adjustment of equipment except in the
presence of someone who is capable of rendering aid.
WARNING
Safety Earth Ground
An interruptible earth safety ground must be supplied from the
main power source to test instruments. Grounding one conductor of
a two conductor power cable is not sufficient protection. Serious
injury or death can occur if this grounding is not properly supplied.
WARNING
Resuscitation
Personnel working with or near high voltages should be familiar
with modern methods of resuscitation.
WARNING
Remove Power
Observe general safety precautions. Do not open the instrument
with the power on.
i
Page 4
Safety Symbols
WARNING
Warning notes call attention to a procedure, which if not correctly
performed, could result in personal injury.
CAUTION
Caution notes call attention to a procedure, which if not correctly
performed, could result in damage to the instrument.
Note: Calls attention to supplemental information.
Warning Statements
The following safety warnings appear in the text where there is danger to operating and maintenance personnel, and are repeated here
for emphasis.
WARNING
When using the AC adapter, connect the AC plug only to a properly
grounded receptacle. Serious injury or death can occur if not properly
grounded.
See page 5.
WARNING
Care should be taken when handling batteries.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Do not heat or dispose of batteries in fire. May burst or release toxic
materials.
Avoid forced discharge.
Do not short circuit.
Restrict charging current and time to the recommended value.
Do not solder the battery directly.
Do not disassemble, apply excessive pressure, or deform.
Avoid placing the battery in reverse polarity.
Battery disposal method should be in accordance with local and
state regulations.
See page 81.
ii
Page 5

Caution Statements
The following equipment cautions appear in the text and are repeated
here for emphasis.
CAUTION
Do not block the fan’s airflow to prevent overheating.
See page 4.
CAUTION
Spectrum Analyzer has a +20 dBm (100 mW) max. RF input.
Exceeding the maximum input will damage the SignalHawk. If
unsure of power levels, measure the test connection with a power
sensor before using the SignalHawk.
See pages 7 and 23.
CAUTION
Avoid installing the SignalHawk near equipment that exhausts or
radiates excessive heat (such as power amplifiers or DC power
supplies). Proper ventilation should always be considered as part of
the installation location.
See page 13.
CAUTION
Harsh or abrasive detergents, and some solvents, can damage the
display unit and information on the labels.
See page 81.
iii
Page 6

Safety Statements
USAGE
ANY USE OF THIS INSTRUMENT IN A MANNER NOT
SPECIFIED BY THE MANUFACTURER MAY IMPAIR THE
INSTRUMENT’S SAFETY PROTECTION.
USO
EL USO DE ESTE INSTRUMENTO DE MANERA NO
ESPECIFICADA POR EL FABRICANTE, PUEDE ANULAR LA
PROTECCIÓN DE SEGURIDAD DEL INSTRUMENTO.
BENUTZUNG
WIRD DAS GERÄT AUF ANDERE WEISE VERWENDET ALS VOM
HERSTELLER BESCHRIEBEN, KANN DIE GERÄTESICHERHEIT
BEEINTRÄCHTIGT WERDEN.
UTILISATION
TOUTE UTILISATION DE CET INSTRUMENT QUI N’EST PAS
EXPLICITEMENT PRÉVUE PAR LE FABRICANT PEUT
ENDOMMAGER LE DISPOSITIF DE PROTECTION DE
L’INSTRUMENT.
IMPIEGO
QUALORA QUESTO STRUMENTO VENISSE UTILIZZATO IN
MODO DIVERSO DA COME SPECIFICATO DAL PRODUTTORE
LA PROZIONE DI SICUREZZA POTREBBE VENIRNE
COMPROMESSA.
iv
Page 7

SERVICE
SERVICING INSTRUCTIONS ARE FOR USE BY SERVICE TRAINED PERSONNEL ONLY. TO AVOID DANGEROUS
ELECTRIC SHOCK, DO NOT PERFORM ANY SERVICING
UNLESS QUALIFIED TO DO SO.
SERVICIO
LAS INSTRUCCIONES DE SERVICIO SON PARA USO
EXCLUSIVO DEL PERSONAL DE SERVICIO CAPACITADO. PARA
EVITAR EL PELIGRO DE DESCARGAS ELÉCTRICAS, NO
REALICE NINGÚN SERVICIO A MENOS QUE ESTÉ
CAPACITADO PARA HACERIO.
WARTUNG
ANWEISUNGEN FÜR DIE WARTUNG DES GERÄTES GELTEN
NUR FÜR GESCHULTES FACHPERSONAL.
ZUR VERMEIDUNG GEFÄHRLICHE, ELEKTRISCHE SCHOCKS,
SIND WARTUNGSARBEITEN AUSSCHLIEßLICH VON
QUALIFIZIERTEM SERVICEPERSONAL DURCHZUFÜHREN.
ENTRENTIEN
L’EMPLOI DES INSTRUCTIONS D’ENTRETIEN DOIT ÊTRE
RÉSERVÉ AU PERSONNEL FORMÉ AUX OPÉRATIONS
D’ENTRETIEN. POUR PRÉVENIR UN CHOC ÉLECTRIQUE
DANGEREUX, NE PAS EFFECTUER D’ENTRETIEN SI L’ON N’A
PAS ÉTÉ QUALIFIÉ POUR CE FAIRE.
ASSISTENZA TECNICA
LE ISTRUZIONI RELATIVE ALL’ASSISTENZA SONO PREVISTE
ESCLUSIVAMENTE PER IL PERSONALE OPPORTUNAMENTE
ADDESTRATO. PER EVITARE PERICOLOSE SCOSSE
ELETTRICHE NON EFFETTUARRE ALCUNA RIPARAZIONE A
MENO CHE QUALIFICATI A FARLA.
v
Page 8

UNITS ARE EQUIPPED WITH RECHAREABLE BATTERIES.
THESE ARE TO BE REPLACED BY AUTHORIZED SERVICE PERSONNEL ONLY!!!
LAS UNIDADES VIENEN EQUIPADAS CON BATERIAS
RECARGABLES.
¡¡¡Y SOLAMENTE EL PERSONAL DE SERVICIO AUTORIZADO
PUEDE REEMPLAZARLAS!!!
GERÄTE SIND MIT WIEDER AUFLADBAREN BATTERIEN
BESTÜCKT.
BATTERIEN SIND NUR VON QUALIFIZIERTEM SERICE
PERSONAL AUSZUWECHSELN!!!
CES DISPOSITIFS SONT ÉQUIPÉS DE BATTERIES
RECHARGEABLES.
SEUL LE PERSONNEL D’ENTRETIEN AUTORISÉ EST HABILITÉ
À LES REMPLACER!
LE UNITÀ SONO DOTATE DI BATTERIE RICARICABILI,
CHE DEVONO DA COME SPECIFICATO DAL PRODUTTORE LA
PROTEZIONE DI SICUREZZA POTREBBE VENIRNE
COMPROMESSA.
vi
Page 9

USE CORRECT VOLTAGE SETTING AND FUSE - SEE MANUAL.
UTILISER UNE TENSION ET UN FUSIBLE CORRECTS - CONSULTER
LE MODE D'EMPLOI.
USE LA INSTALACION Y FUSIBLE DE VOLTAJE CORRECTO - VEA
EL MANUAL.
AUSSCHLIESSLICH VORSCHRIFTSMÄSSIGE
WECHSELSPANNUNGS-EINSTELLUNG UND SICHERUNG
BENUTZEN - SIEHE DAZU HANDBUCH.
UTILLIZZARE TENSIONE E FUSIBLE ADATTI - FARE RIFERIMENTO
AL MANUALE.
vii
Page 10

About This Manual
This manual covers the operating and maintenance instructions for
the following models:
SH-36S-PC SH-36S-RM
Changes to this Manual
We have made every effort to ensure this manual is accurate. If you
discover any errors, or if you have suggestions for improving this manual, please send your comments to our Solon, Ohio factory. This manual may be periodically updated. When inquiring about updates to
this manual refer to the part number and revision on the title page.
Literature Contents
Chapter Layout
Introduction — Describes the features of the Bird SignalHawk, lists
equipment supplied and optional equipment, and provides power-up
instructions.
Settings — Describes how to connect SignalHawk to the user’s system, describes the spectrum analyzer measurements, and provides
quick start steps for each measurement.
Measurements — Describes the power measurement feature, lists
compatible power sensors, describes how to connect SignalHawk to
the user’s system, and provides quick start steps to make power measurements.
Utilities — Describes built-in instrument utility features and how to
use them.
Maintenance — Lists routine maintenance tasks as well as trouble-
shooting for common problems. Specifications and parts information
are also included.
viii
Page 11

Table of Contents
Safety Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . i
Safety Symbols. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ii
Warning Statements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ii
Caution Statements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . iii
Safety Statements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . iv
About This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
Changes to this Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
Literature Contents. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
Chapter Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
Chapter 1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Items Supplied . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Looking at the SignalHawk. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Power Supply - PC SignalHawk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Internal Battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Power Adapters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Charge Indicator Light . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Power Supply - Rack-Mount SignalHawk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
AC Power Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
DC Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Spectrum Analyzer Quick Start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Chapter 2 PC SignalHawk Set-Up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Installing the SignalHawk Program. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Chapter 3 Rack Mount SignalHawk Set-Up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Installing the SignalHawk into a Rack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Connecting the Rack-Mount via USB Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Connecting Remotely via LAN/WAN Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Configuring a Basic Network Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Connecting a Remote Computer to the Host Computer . . . . .20
Changing the Password on Auto Logon . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Chapter 4 Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Getting Started with the SignalHawk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Setting Up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Start Menu, Menu Keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Spec Analysis Menu Key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Utilities Menu Key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Help Menu Key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
ix
Page 12

Setup Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Quick Save Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Label & Save Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Recall Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Recall Default Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Manage Setup Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Delete . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Delete All Setups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
View Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
View Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Recall Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Delete . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Top of List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Bottom of List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
View Next Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
View Previous Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Looking At The Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Freq & Span Menu. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Start / Stop Freq and Center / Span . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Wheel Step . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Full Span . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Freq List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
BW & Sweep Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Resolution & Video BW Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Resolution & Video BW . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Span/RBW . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
RBW / VBW . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Detection Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
+ Peak Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
- Peak Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Sample Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Average Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Sweep . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Single . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
External Trigger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
External - Low Level / High Level /
Rise Edge / Fall Edge / Either Edge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Gate Delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Video . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Gate Delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Ampt & Trace Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Autoscale . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Reference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
x
Page 13

Scale . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Attenuation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Preamp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Offset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Units . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Trace . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Clear Write . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Max Hold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Min Hold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Average . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Average Readings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Reset Average . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Water Fall Spectrogram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Mark & Limit Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Select Marker . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Marker On / Off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Marker to Max Peak . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Markers to Peak/Valley . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Markers Detect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Threshold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Marker to Max Peak or
Marker to Min Valley . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Marker to Next Peak Left or
Marker to Next Valley Left . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Marker to Next Peak Right or
Marker to Next Valley Right . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
All Markers to Max Peaks or
All Markers to Min Valleys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
All Markers Off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Marker Delta . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Marker Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Marker Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
All Markers Type to Icon . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
All Markers Type to Line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Marker Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Marker More . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Volume . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Marker Freq to Center . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Center Freq to Marker . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Ref Level Ampt to Marker . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Frequency Counter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
xi
Page 14

Limit Lines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Limit Upper/Lower . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Limit On/Off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Limit Alarm On/Off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Select Line/Mask . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
File & Help Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Quick Save Trace . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Label & Save Trace . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Log Traces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Recall Trace . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Recall Trace . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Recall & Compare . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Clear Recalled Trace . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Manage Trace Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Delete Trace . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Delete All Traces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Full Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Chapter 5 Measurements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Spectrum Analysis Measurement. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Occupied Bandwidth Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Threshold Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
% . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
dBc . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Setting Occupied Bandwidth . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Channel Power Measurement. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Setting Channel Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Adjacent Channel Power Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Time Domain (Zero Span) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Field Strength Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Received Signal
Strength Indicator (RSSI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Demodulate Signal. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Carrier-to-Interference Ratio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Out-of-Band and In-Band,
Out-of-Channel Spurious. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
xii
Page 15

Chapter 6 Utilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Utility Main Menu. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Version Info . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Utility Main Menu Selections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Spectrum Analyzer Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Custom Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Exit to Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Customizing SignalHawk Content . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Chapter 7 PC Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .71
Computer Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Downloading and Installing Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Installing the PC Tool Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Menu Bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Edit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Measurements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Communicate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Tool Bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Save . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Open . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Cut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Copy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Paste . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Delete Trace . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Return to Normal Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Zoom In . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Zoom Out . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Autoscale Graph . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Add Markers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Add to Upper Limit Line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Add to Lower Limit Line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Delete Markers or Limit Lines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Option Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Measurement Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
VNA Tool Bar. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Match . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Distance to Fault . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Smith . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
xiii
Page 16

Options Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
DTF Wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Options Dialog Box (View>Options) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Scale Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Units Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Markers Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Limits 1 Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Limits 2 Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Labels Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
GPS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Chapter 8 Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Charging the Battery. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Charging the Battery Using a Car Charger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Replacing the Battery on the PC SignalHawk. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Updating the Firmware. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Updating the Firmware on a
Remote Rack Mount SignalHawk . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Customer Service. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
SH-36S-RM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Distortion & DANL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
SH-36S-PC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Parts List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Optional Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
SH-36S-PC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Test Cables and Adapters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
SH-36S-RM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Test Cables and Adapters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
ROHS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Appendix 1 Menu Maps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Spectrum Analyzer Menu Maps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Setup Function Menu Maps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Appendix 2 Software License Terms. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Limited Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
xiv
Page 17
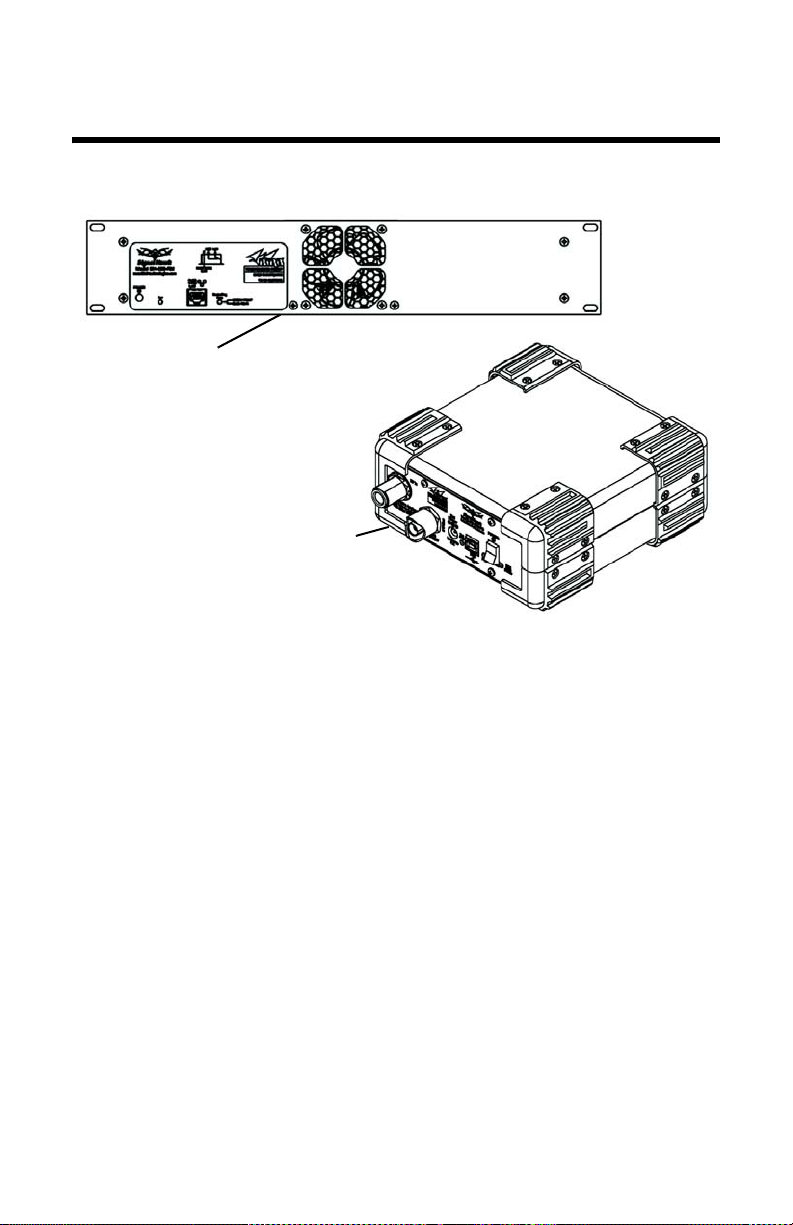
Chapter 1 Introduction
PC SignalHawk
Rack-Mount
SignalHawk
The SignalHawk is a multifunction test instrument for use in the
installation and maintenance of Radio Frequency (RF) and wireless
systems. The model number is identified on the unit and also on the
display screen at the end of the power-on sequence.
The firmware installed on the SignalHawk is updated on a regular
basis. The operator’s manual covers the most recent upgrade to the
firmware up to the date listed on the manual. See “Troubleshooting”
on page 85.
1
Page 18
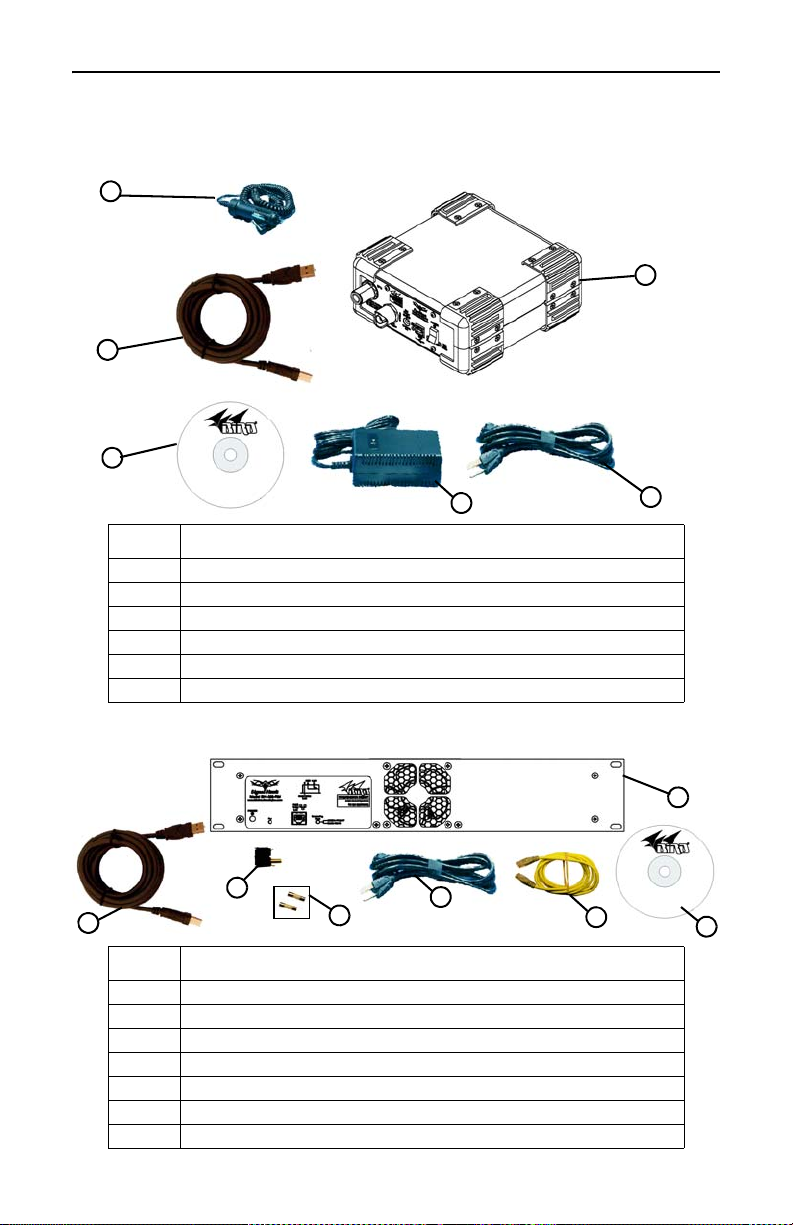
Bird Technologies
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
5
6
1
7
3
4
Items Supplied
Figure 1 SignalHawk PC Hardware and Software Supplied
Item Description
1 Car Adapter Cable
2 USB Cable
3 Software CD
4 AC Power Adapter
5 AC Power Cord
6 PC SignalHawk
Figure 2 SignalHawk Rack-Mount Hardware and Software Supplied
Item Description
1 Rack-Mount SignalHawk
2 USB Cable
3 Fuse Drawer with Shorting Bar
4 2 SLO-BLO 5mm x 20mm.63A Fuses
5 AC Power Cord
6 Ethernet Cable
7 Software CD
2
Page 19
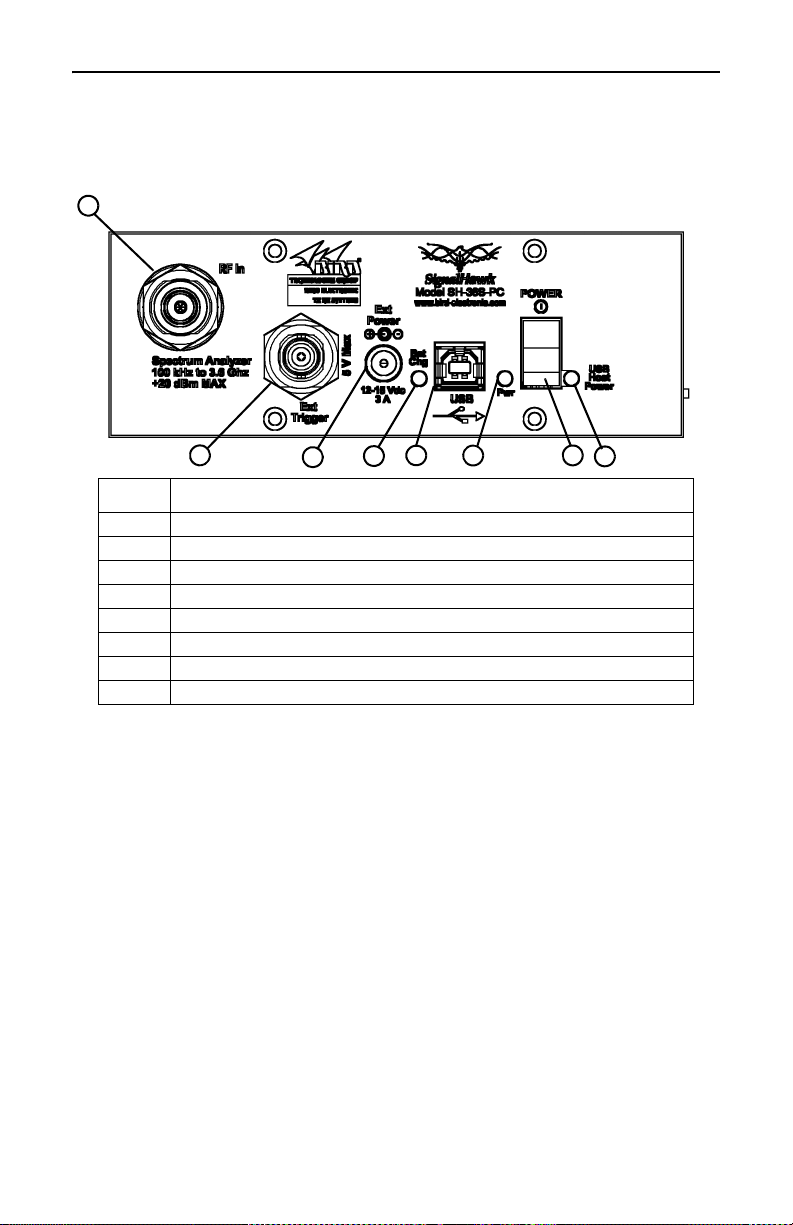
Looking at the SignalHawk
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Figure 3 PC SignalHawk Controls and Indicators
Item Description
1 Spectrum Analyzer Port, N(F) RF input, +20 dBm max.
2 BNC(F) external trigger input, 5V TTL
3 2.1mm DC jack for external power supplies
4 Battery Charge Indicator
5 USB Type B for PC connection
6 Charge Indicator Light
7 Power Switch
8 USB Host Power Indicator
Introduction
3
Page 20
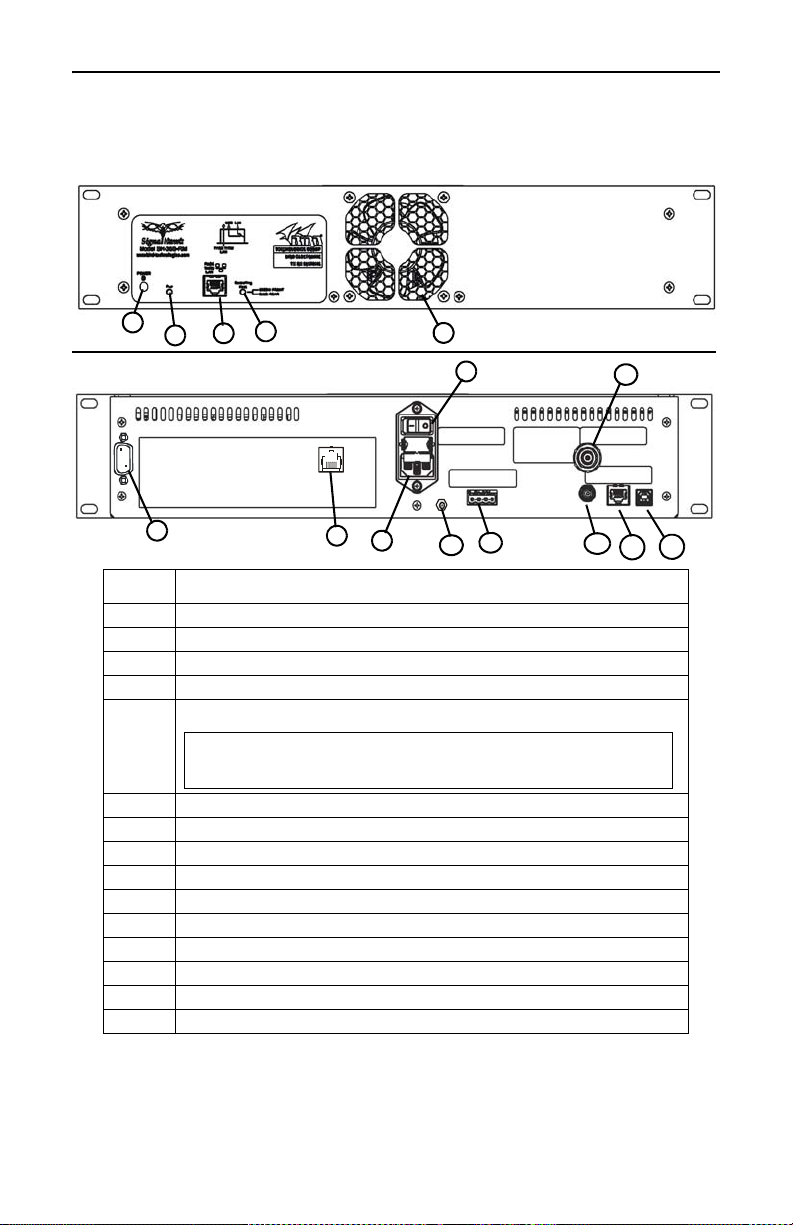
Bird Technologies
Rear
Front
13
2
1
15
14
12
11
8
9
3
4
10
7
6
5
CAUTION
Do not block the fan’s airflow to prevent overheating.
Figure 4 SignalHawk Rack-Mount Controls and Indicators
Item Description
1 Power Button
2 Power Indicator
3 Pass-Thru LAN Connector
4 Host Indicator
5Fan
6 RS-232 Connector
7 LAN Connector
8 AC Power Connector
9 AC Power Switch
10 Ground Post
11 External 12/24/48 VDC Connector
12 BNC(F) external trigger input, 5V TTL
13 Spectrum Analyzer Port, N(F) RF input, +20 dBm max.
14 Pass-Thru LAN Connector
15 USB Type B for PC connector
4
Page 21

Introduction
Power Supply - PC SignalHawk
Internal Battery
The PC SignalHawk has an internal, rechargeable, lithium-ion battery
pack that will operate the unit for a minimum of 3 hours of continuous
use. Recharging time, from a full discharge, is approximately 4 hours.
Note: When the unit is shipped from the factory, the
battery may not be fully charged. Use an AC adapter when
operating the unit for the first time.
Power Adapters
WARNING
When using the AC adapter, connect the AC plug only to a properly
grounded receptacle. Serious injury or death can occur if not
properly grounded.
The PC SignalHawk can be operated using the supplied AC adapter or
a 12V automobile cigarette lighter adapter. Using these adapters will
also charge the internal battery.
Note: The charge LED will be steady amber while charg-
ing and steady green when fully charged.
Charge Indicator Light
The charge indicator light on the PC SignalHawk has a dual function.
Power Source Light Color Condition
External Power Amber Charging battery.
Green Battery fully charged.
Battery Power None (light is off) 100% to 30% Power Available
Yellow Below 30% Power Available
When the yellow light comes on, the PC SignalHawk has approximately 1 to 1.5 hrs of operation left depending on temperature and
battery age. At this time, the unit should be charged or the battery
should be replaced. See “Charging the Battery” on page 81 or "Replacing the Battery on the PC SignalHawk" on page 81.
Note: To avoid damage to the battery pack, the unit will
shut-off completely when the battery charge falls below 10%. If
this occurs, the battery must be charged to a minimum voltage
before the unit is allowed to resume operation. Full recharging
is recommended.
Note: When using the supplied car charging adaptor, a
minimum voltage of 11.5V is required overcome the safety circuit and allow it to be operational. To ensure complete charging, at least 13V must be present at the DC input.
5
Page 22

Bird Technologies
Power Supply - Rack-Mount SignalHawk
AC Power Connector
The AC Power connector provides operating power for the Rack-Mount
SignalHawk. The AC power supply cord is also the line disconnect
device for this product. Use the supplied AC power cord or an approved
power cord to connect to the Rack-Mount SignalHawk, such as domestic
type SVT, 300 VAC, 18 AWG, 10 A, 3 conductor (including ground) or
international type H05VV-F, 300 VAC, 1.00 mm, 10 A, 3 conductor
(including ground).
Note: The Rack-Mount SignalHawk is shipped from the
factory configured for 110VAC operation, 2-pole fuse (fused line
and neutral). If the Rack-Mount SignalHawk will be installed
with 220VAC supply, follow these instructions:
1. Remove the fuse drawer from the power entry module on the rear
of the unit.
2. Remove fuses from drawer & set aside.
Note: There are two different fuse drawers supplied with
the Rack-Mount SignalHawk. One is a 2-pole fuse tray (fuse on
both lines) the other is a single fuse tray (line fuse, shorting bar
on neutral). Check with local regulations to determine whether
single or dual pole fuse protection is required.
3. Install one or both fuses into the appropriate fuse drawer:
z 110VAC operation: 5x20mm SLO BLO 1.25A
z 220VAC operation: 5x20mm SLO BLO 0.63A
4. Replace fuse drawer into the power entry module
5. Insert AC power cord into the IEC receptacle on the power entry
module.
DC Supply
The Rack-Mount SignalHawk can also be powered by a direct DC voltage wired into the terminal lugs on the rear of the unit. This is useful
if the installation site has DC power readily available or it can be connected in addition to the AC power if the DC source is part of a battery
back-up system. There are two separate DC power inputs on the terminal connector. The combination of the two allows a wide range of
DC voltage sources. Refer to the specifications page for voltage range
and current requirements.
Note: Ensure proper polarity is observed on the DC supply
and input voltage is connected to the correct pair of terminal lugs.
6
Page 23
Introduction
Spectrum Analyzer Quick Start
CAUTION
Spectrum Analyzer has a +20 dBm (100 mW) max. RF input.
Exceeding the maximum input will damage the SignalHawk. If
unsure of power levels, measure the test connection with a power
sensor before using the SignalHawk.
1. Measure the output power, or signal power, at the system’s test
port using a power meter, service monitor, or equivalent.
Note: Ensure the output power is less than +20 dBm
(100 mW).
2. Connect the SignalHawk’s “RF Input” connector:
z For low-power connections, connect directly to the output
of the signal source. See the below graph:
z For high-power connections, use a directional coupler or
attenuator to reduce the output level of the signal source. See
the below graph:
3. Power up the SignalHawk.
4. In the Start Menu, use the arrow keys to highlight the desired
measurement, and press Enter.
5. In the Freq & Span Menu, set the frequency range (See “Freq &
Span Menu” on page 31).
6. Wait for one sweep, then go into the Amplitude Menu and click on
Autoscale (see “Ampt & Trace Menu” on page 41).
7
Page 24

Bird Technologies
7. In the Start menu, select the desired measurement.
z "Spectrum Analysis Measurement" on page 52.
z "Occupied Bandwidth Measurement" on page 53.
z "Channel Power Measurement" on page 55.
z "Adjacent Channel Power Measurement" on page 57.
z "Time Domain (Zero Span)" on page 59
z "Field Strength Measurement" on page 60.
z "Demodulate Signal" on page 62
z "Carrier-to-Interference Ratio" on page 63.
z "Out-of-Band and In-Band, Out-of-Channel Spurious" on page 65.
z "Water Fall Spectrogram" on page 43.
8. Turn on markers or limit lines if needed (see “Marker On / Off” on
page 44 and "Limit Lines" on page 46).
9. Make a sweep.
10. In the File & Help Menu, click on Quick Save Trace to save the
data (see “File & Help Menu” on page 48).
8
Page 25

Chapter 2 PC SignalHawk Set-Up
Installing the SignalHawk Program
Note: Install the PC software before connecting the PC
SignalHawk for the first time.
1. Insert installation CD.
2. Select Install Software when prompted.
Note: Set-up will inspect the computer for any missing
operating system prerequisites. If all are present, skip to step 6.
3. Select “Next” and the install utility begins the Prerequisites
Installation process.
4. Review the End-User License Agreement, check “I accept the
terms of the License Agreement” and select “Install.”
Note: The install Utility will install the prerequisites. This
may take several minutes
Note: When completed, check with Microsoft
ter for any security updates. Typically, if “Automatic Updates”
are configured on the host PC, these will be automatically
flagged and selected for download and installation.
Note: The installation utility will launch after the OS pre-
requisites are installed.
5. Do one of the following:
z Accept the default installation location.
z Select a different folder.
6. Select “Next” and the installer will complete.
7. Select “Finish” to launch the SignalHawk program.
8. Connect PC SignalHawk to a PC using the supplied USB cable.
Note: The “USB Host Power” LED will illuminate when the
host port is active and has power. It is not an indication of proper
USB connectivity to the host. Refer to software installation
instructions for how to address the PC SignalHawk from the host.
9. Turn power on.
10. Select “Install the software automatically…” in the Found New
Hardware Wizard window.
®
support cen-
9
Page 26
Bird Technologies
Figure 5 Found New Hardware Wizard
11. Click “Next”.
12. Follow the instructions that are presented.
13. Click “Finish” in the Completing the Found New Hardware Wizard
window.
Figure 6 Completing the Found New Hardware Wizard
14. Launch the SignalHawk program.
Note: PC SignalHawk can be used in any orientation.
15. Select the unit from the DSP Device List, if necessary.
16. Connect RF signal.
17. Connect a TTL trigger source to the BNC connector, if necessary.
10
Page 27
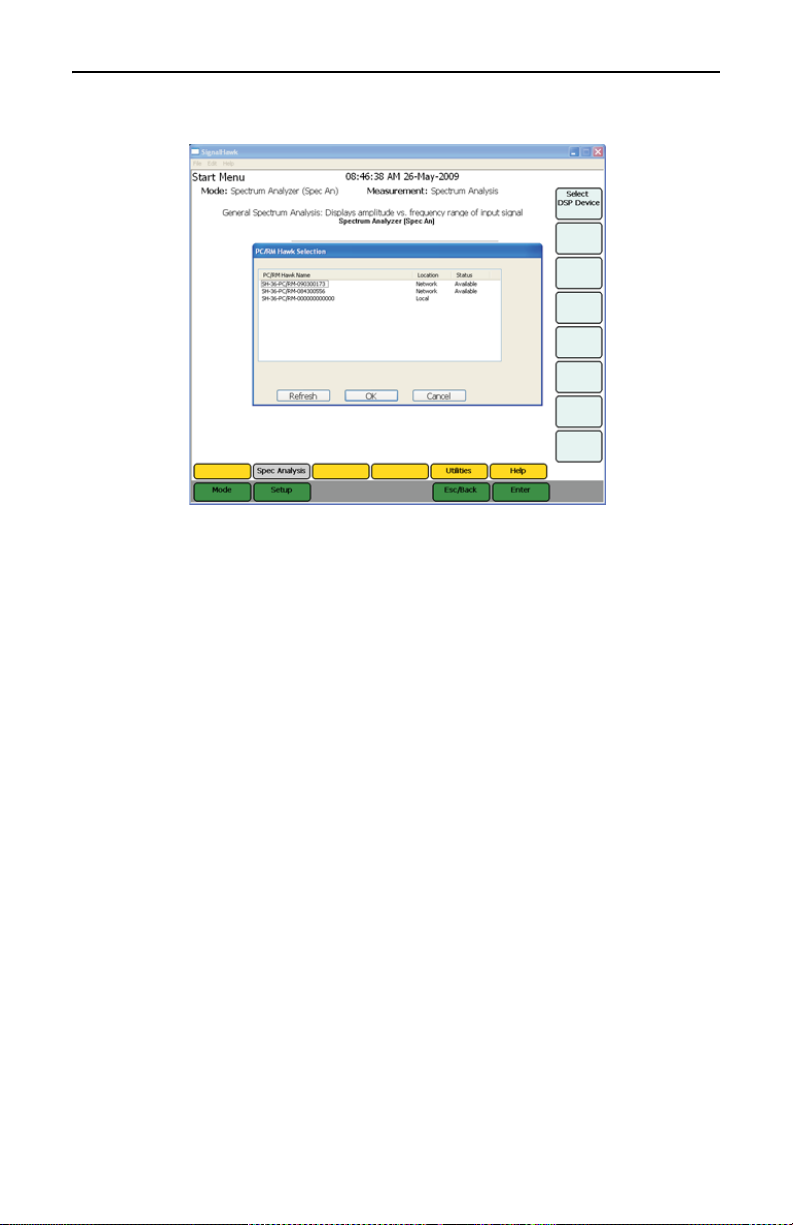
Figure 7 Select DSP Device List
PC SignalHawk Set-Up
11
Page 28

Bird Technologies
12
Page 29

Chapter 3 Rack Mount SignalHawk Set-Up
Installing the SignalHawk into a Rack
CAUTION
Do not block the fans airflow to prevent overheating.
The Rack-Mount SignalHawk is a short-depth, 2 rack-unit (RU) device
designed for installation into standard 19" equipment test racks. It
can also be used free-standing. Use installation hardware available for
the rack to mount the SignalHawk.
Note: For maximum stability, use four screws to secure the
SignalHawk into the rack.
CAUTION
Avoid installing the SignalHawk near equipment
that exhausts or radiates excessive heat (such as
power amplifiers or DC power supplies). Proper
ventilation should always be considered as part of
the installation location.
1. Install the Rack-Mount SignalHawk into the equipment or test rack.
2. Connect proper power supply. See “Power Supply - Rack-Mount
SignalHawk” on page 6.
3. Connect the SignalHawk to a host PC though one of the following:
z Rear USB
z Rear LAN
Note: See “Rack-Mount SignalHawk Connection Dia-
gram” on page 19. There are three RJ45 (Ethernet) jacks on the
unit. Use the rear LAN connection jack for remote access.
Note: Host control priority is given in the order shown above.
Example - If the normal remote connection is via a Rear LAN
connection, and the Rear USB is connected to a local host the
remote LAN connection will be disconnected & the local host
connection will be allowed control. The remote LAN connection will be restored upon disconnection from the local host.
4. There are two additional connectors on the front and rear of the
unit used for a “Pass-thru LAN” connection. The rear jack may be
connected to an on-site router or hub. This now enables convenient, local connection to a network while on-site without having
to have physical access to an on-site hub.
13
Page 30
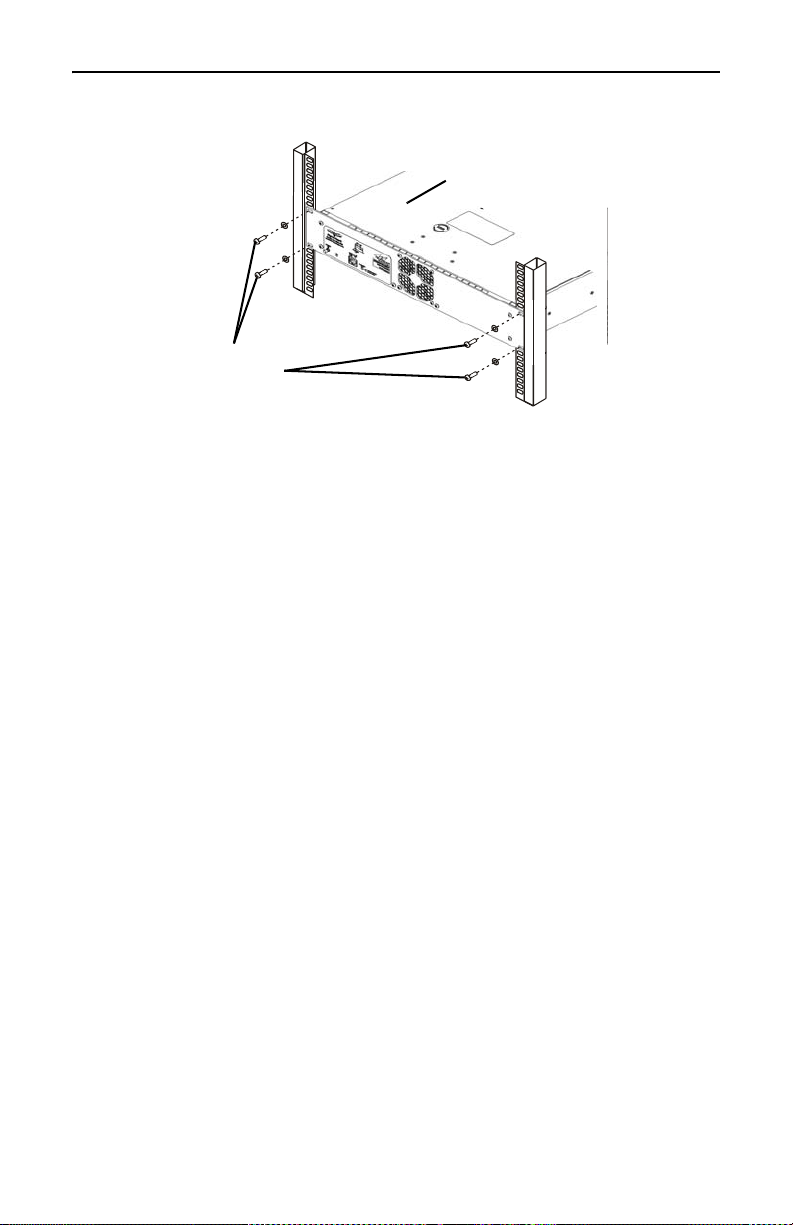
Bird Technologies
Mounting
Screws and
Washers
Rack Mount
SignalHawk
Figure 8 Installing the SignalHawk into a Rack
Connecting the Rack-Mount via USB Connection
1. Insert installation CD into host PC.
2. Select Install Software when prompted.
Note: Install the PC software before connecting the Rack
Mount SignalHawk for the first time.
Note: Set-up will inspect the computer for any missing
operating system prerequisites. If all are present, skip to step 6.
3. Select “Next” and the install utility begins the Prerequisites
Installation process.
4. Review the End-User License Agreement, check “I accept the
terms of the License Agreement” and select “Install.”
Note: The install utility will install the prerequisites. This
may take several minutes.
Note: When completed, check with Microsoft
ter for any security updates. Typically, if “Automatic Updates”
are configured on the host PC, these will be automatically
flagged and selected for download and installation.
®
support cen-
Note: The installation utility will launch after the OS pre-
requisites are installed.
5. Do one of the following:
z Accept the default installation location.
z Select a different folder.
6. Select “Next” and the installer will complete.
7. Select “Finish” to launch the SignalHawk program.
8. Connect Rack Mount SignalHawk to a PC using the supplied USB cable.
Note: The “USB Host Power” LED will illuminate when host
port is active and has power. It is not an indication of proper USB
connectivity to the host. Refer to software installation instructions
for how to address the PC SignalHawk from the host.
14
Page 31

Rack Mount SignalHawk Set-Up
9. Turn power on.
10. Select “Install the software automatically…” in the Found New
Hardware Wizard window.
Note: This procedure is performed when connecting either
a PC or Rack-Mount SignalHawk for the first time. Driver
installation is required for every distinct SH-36S-PC or SH36S-RM connected to the computer.
Figure 9 Found New Hardware Wizard
11. Click “Next”.
12. Follow the instructions that are presented.
13. Click “Finish” in the Completing the Found New Hardware Wizard
window.
Figure 10 Completing the Found New Hardware Wizard
14. Launch the SignalHawk program.
15. Select the SignalHawk unit from the Select DSP Device list.
15
Page 32

Bird Technologies
Connecting Remotely via LAN/WAN Connection
Note: The Rack-Mount SignalHawk provides the follow-
ing connections to a network:
• 10/100 auto sensing RJ45 Ethernet connector
• Half and full duplex support
• IP address: 192.168.1.10
• Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Configuring a Basic Network Connection
1. Do one of the following:
z For connecting to a stand alone computer - Connect the
Rack Mount to the computer with a crossover cable.
z For connecting to a network - Connect the Rack Mount to
the network using the cable supplied.
Note: Do not use the ‘Pass-thru LAN’ RJ-45 connector next
to the BNC trigger connector for direct remote access. Use the
RJ-45 connector in the PC back-panel.
Note: Before making changes to the client computer, it is
highly recommended to create a “System Restore Point”:
a. Click Start
b. Go to Programs or All Programs.
c. Go to Accessories.
d. Go to System Tools.
e. Select System Restore.
Note: Permissions affiliated with being an administrator
or a member of the Administrators group are needed in order to
complete this procedure. If the computer is connected to a network, network policy settings might also prevent you from completing this procedure.
2. Install TCP/IP Services on the client computer controlling the Rack
Mount by doing the following:
a. Open Add or Remove Programs in Control Panel.
b. Click Add/Remove Windows Components.
c. In Components, select Networking Services, and then
select Details.
d. In Subcomponents of Networking Services, select Simple
TCP/IP Services, and then click OK.
e. Click Next.
Note: If prompted to do so, type the path where the Win-
dows XP distribution files are located, and then click OK.
16
Page 33

Rack Mount SignalHawk Set-Up
f. Click Finish.
g. Click Close.
3. Configure TCP/IP settings on the client computer:
Note: The client computer may have TCP/IP settings pre-
viously configured. Changing settings may prevent access to
other network resources such as the Internet or file sharing.
Consult with your network administrator before making any
changes.
a. Open Network Connections in Control Panel.
b. Select Local Area Connection and then, under Network
Tasks, click Change settings of this connection.
c. On the General tab, under This connection uses the follow-
ing items, click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click
Properties.
d. Specify an IP address:
z Click Use the following IP address, and in IP address,
type the following IP address:
192.168.1.11
e. Specify a subnet mask:
z In Subnet Mask, type the following:
255.255.255.0
Note: Default IP settings for the Rack Mount are IP
address: 192.168.1.10 and Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0. DHCP
is NOT enabled by default on the Rack Mount.
Note: Use automated IP settings (DHCP) whenever possi-
ble for the majority of client computers. DHCP is enabled by
default and when automated IP settings are used for all connections, they eliminate the need to configure settings (i.e.
DNS, WINS, etc.).
4. Create a Remote Desktop Connection on the client computer:
a. Open Remote Desktop Connection:
i. Click Start
ii. Select Programs or All Programs
iii. Select Accessories
iv. Click Remote Desktop Connection.
b. In the Computer box, type the following default IP address
for the Rack Mount:
192.168.1.10
c. Click Connect.
Note: If a connection cannot be achieved, disable the
computers wireless networking function.
17
Page 34

Bird Technologies
Note: Depending on which version of Windows is
being used, the Windows Security or the Log On to Windows dialog box appears at this time.
d. In the Windows Security or Log On to Windows dialog box,
type user credentials.
Example - User name, password, and domain. Default
user credentials for the Rack Mount are:
Username: Bird
Password: Bird
e. Click OK or Submit.
Note: To change the connection settings, (such as screen
size, automatic logon information, and performance options),
click Options before connecting. For more information, see “To
Change Connection Settings” in the Remote Desktop Help.
Advanced network settings such as configuring the Rack Mount on a
domain, can be configured by using the remote desktop connection or
by logging in locally to the Rack Mount using an external monitor,
keyboard and mouse (not included) connected to the I/O ports on the
back panel of the unit. Consult the network administrator for proper
configuration.
Note: Other programs may be used on the Rack Mount
Hawk as long as they directly support its specific use or provide
system utilities, resource management, anti-virus or similar protection. Software such as email, word processing, spreadsheet,
database, scheduling or personal finance software cannot run on
this device, however, you may use terminal services protocols to
access such software running on a server. For more information,
refer to the User End License Agreement in the Appendix.
Note: The Rack Mount operating system has Windows
Firewall ‘On’ by default but does not have any anti-virus/antispyware installed. Use caution when connecting the Rack
Mount to a WAN or Internet gateway. Consult with the network
administrator.
18
Page 35

Rack Mount SignalHawk Set-Up
RF MODULE
Mini ITX PC
USB
USB
ETHERNET
ETHERNET
Local Broadcast
Site
WAN/LAN
Rack-Mount
Signal Hawk
Local PC
Laptop
Remote PC
RF
IN
ETHERNET
HUB
ROUTER
Pass-thru connection:
allows convenient
access to hub through
front panel
Figure 11 Rack-Mount SignalHawk Connection Diagram
19
Page 36

Bird Technologies
Connecting a Remote Computer to the Host Computer
To connect your home computer, which is the client (or remote) computer to the Rack Mount, follow these steps:
1. On your home computer, click Start, point to All Programs, and
then point to Accessories.
2. In the Accessories menu, point to Communications, and then click
Remote Desktop Connection.
3. In the Computer box, type the computer name of your host computer.
Note: The default computer name of the Rack Mount is
'SH-36S-RM' and the default IP address and Subnet mask is
192.168.1.10 and 255.255.255.0
4. Click Connect.
5. When the Log On to Windows dialog box appears, type your user
name, password, and domain (if required), and then click OK.
6. The Remote Desktop window opens, and you see the desktop settings, files, and programs that are on your host computer, which in
this example is the Rack Mount. Your host computer remains
locked, and nobody can access it without a password. In addition, no
one will be able to see the work you are doing remotely.
To end your Remote Desktop session:
1. Click Start, and then click Log Off at the bottom of the Start menu.
2. When prompted, click Log Off.
20
Page 37

Rack Mount SignalHawk Set-Up
Changing the Password on Auto Logon
1. Go to the Start Menu.
2. Select All Programs
3. Select Bird Technologies Group.
4. Go to Utilities.
5. Go to Automatic Logon Utility.
6. Enter a username and new password.
7. Click Ok.
Figure 12 Automatic Logon Utility
21
Page 38

Bird Technologies
22
Page 39

Chapter 4 Settings
In order to obtain the most accurate information possible, it is very
important to use the proper settings. The SignalHawk can be configured
in various ways, allowing for a wide range of measurement capabilities.
Getting Started with the SignalHawk
CAUTION
Spectrum Analyzer has a +20 dBm (100 mW) max. RF input.
Exceeding the maximum input will damage the SignalHawk. If
unsure of power levels, measure the test connection with a power
sensor before using the SignalHawk.
Press the Power button to turn on the unit.
Setting Up
See “PC SignalHawk Set-Up” on page 9. Use this chapter to adjust the
Settings.
Start Menu, Menu Keys
Menu keys are the six rectangular yellow keys located below the display
screen. Click a menu key to move the highlight selection bar to the
desired menu list. When using a menu list, use the mouse scroll wheel
or the up- and down-arrow keys to move the highlight bar through the
list. Use the left- and right-arrow keys to move to a different list box.
Spec Analysis Menu Key
Click here to enter the Spectrum Analyzer mode.
Utilities Menu Key
Click here to display the Utility Menu main screen. The Utilities
menu provides information about the instrument software, amount of
available memory, battery charge status, system date and time, and
how to contact Bird Technologies Group.
Help Menu Key
Displays the Help options but does not exit the current screen. Click on the
Back... selection to display the default selections for the current menu.
23
Page 40

Bird Technologies
Operations Manual (Quick Start Guide) - This manual contains quick
start steps for measurements and for the Menu keys.
Menu List - Displays the list of all measurements available in the
active operating mode. This list can be expanded and collapsed to
reveal or hide more detail about the measurement, such as setup
parameters and custom configurations.
Reference Manual (User Manual) - This manual expands upon the
information in the Operations Manual to include complete descriptions
of features, measurement setup parameters, and system setup options.
Back... - Clicking here exits Help and returns to the features for the
currently active menu.
24
Page 41

Figure 13 SignalHawk Start Menu - Spectrum Analyzer
Item Description
1 Name of measurement being used
2 Menu Selection labels
3 Go to the Help menu. Select Esc/Back to return here. There
are two functions in the help menu.
4 Enter goes to a menu. Esc will exit a menu.
5 Go to the Utilities menu. See Chapter 6, page 67.
6 Go to setup screen
7 Go to mode selection screen
8 Menu key labels
9 Selected measurement (highlighted)
10 Name and brief description of highlighted measurement
11 Current active operating mode
-- Mouse scroll wheel will increase values.
-- Keyboard can be used to manually enter values.
-- Function Keys correlate with the selections on side of the display.
Settings
25
Page 42

Bird Technologies
Setup Menu
The Setup Menu allows access to saved setups and settings used previously
on the SignalHawk. Click on Setup to access the menu.
Figure 14 Setup Menu
Quick Save Setup
The saved settings are stored as a file in the internal drive of the host
PC. Each quick save is stored in a separate file that is named using the
date-time file naming format GeneralSA(MM-DD-hh-mm-ss).shs where
YYYY is the year, the first MM is the month, DD is the day, HH is the
hour, the second MM is the minute, and SS is the second of the time
when the file was saved.
26
Page 43

Label & Save Setup
Figure 15 Setup Menu - Save
Labels and saves the settings for a setup for future use.
Settings
To save a Setup:
1. Click on Save Trace.
2. Enter a file name.
Recall Setup
Recalls a saved setup and sets the instrument parameters to run the
recalled setup.
Recall Default Setup
Recalls the factory default setup and sets the instrument parameters
to run this setup.
Manage Setup Files
Allows access to the file management of the saved Setups.
27
Page 44

Bird Technologies
Figure 16 Setup - Manage Setup Files
Delete
Deletes the selected Setup on the list.
Delete All Setups
Deletes all of the Setups on the list.
View S etup
See “View Setup” on page 28 in the Setup Menu.
View S etup
Displays the properties of a selected saved Setup on the list.
Figure 17 Setup - View Setup
28
Page 45

Settings
Recall Setup
Recalls a saved setup and sets the instruments parameters to run the
recalled setup.
Delete
Deletes the displayed Setup.
Top of List
Displays the Setup from the top of list of saved Setups.
Bottom of List
Displays the Setup from the bottom of list of saved Setups.
View N ext Setup
Displays the next Setup on the list of saved Setups.
View Previous Setup
Displays the previous Setup on the list of saved Setups.
29
Page 46

Bird Technologies
12
1
4
6
7
5
3
2
8
10
11
9
Looking At The Screen
Figure 18 General Screen Features
Item Description
1 Name of selected measurement
2 Sweep display area
3 Marker
4 Date and time
5 Name of setup file being used
6 Menu selection labels
7 Menu key labels
8 Help tips for the current screen
9 Measurement settings
10 Sweep progress bar
11 Data trace
12 System key labels
30
Page 47

Freq & Span Menu
Figure 19 Freq & Span Menu
Settings
In the Freq & Span Menu the range of frequencies to sweep are specified.
The SignalHawk can sweep frequencies between 100 kHz and 3.6 GHz.
Frequencies can be selected at spans from 1 kHz up to the entire
range of the instrument. These frequencies can be set to sweep by one
of the following methods:
z Set the Center Freq and Freq Span.
z Set the Start Freq and Stop Freq.
z Select the Full Span of the instrument.
z Select a band from the Freq List.
The most common of these methods is to set the center frequency and a
frequency span (a range) and let SignalHawk calculate the start and
stop frequencies for the sweep. Reducing the span, by default (with RBW
and VBW, both on auto mode) will usually speed up the sweep, provide
more detail, and lower the noise floor. Unless specified otherwise, set the
center frequency to the center of the signal being measured.
31
Page 48

Bird Technologies
Start / Stop Freq and Center / Span
These settings control the frequency range being swept.
Note: “Center / Span” are used in this manual, but using
“Start / Stop Freq” achieves the same results.
After clicking the menu selection, it will highlight the active function.
Then the following can be performed:
z Up/Down Arrow Keys: Increase and decrease the frequency
or span in small steps.
z Left/Right Arrow Keys: Increase and decrease the frequency
or span in large steps.
z Mouse Scroll Wheel: Each click of the mouse scroll wheel
changes the frequency or span by the value of the “Wheel Step”.
z Number Keys: Press any key except +/- to open a box to type
in a new frequency.
Note: If a mistake happens, press Esc/Back. When done,
press enter (to keep the same frequency units) or click the menu
selection corresponding to the desired units.
Wheel Step
When another frequency function is active and the mouse scroll wheel
is turned, the value will change in steps of the “Wheel Step”. After
clicking “Wheel Step” to highlight it, the following is enabled:
z Up/Down Arrow Keys and Mouse Scroll Wheel: Change
the step value by a small amount.
z Left/Right Arrow Keys: Change the step value by a large
amount.
z Number Keys: Press any key except +/- to open a box to type
in a new frequency. If a mistake is made, press Esc/Back.
When done, press enter, or click the menu selection corresponding to the desired units.
Full Span
Click on this to set the Start Freq to 0, and the Stop Freq to the max
freq of the unit, currently 3.6 GHz.
Note: The start frequency can be set to 0 as a convenience.
However, the accuracy spec does not apply below the minimum
freq of the unit (100 kHz).
Freq List
Selecting this opens up a list of predefined frequency bands. Use the
up/down arrows or mouse scroll wheel to scroll to the desired band,
then press Enter to use it. Recently used bands are displayed at the
top of the list.
Note: Channelized bands are denoted on the Frequency
List by a plus sign; “+”.
32
Page 49

Figure 20 Example, Freq List
Recently Used Bands
Settings
33
Page 50

Bird Technologies
Actual Input
RBW > Separation
RBW = Separation
Separation
3 dB
BW & Sweep Menu
The bandwidth menu includes functions that control sweep speed and
accuracy, and has the interface for customizing sweep triggers.
When two signals are separated by a freq distance equal to the Resolution BW, a 3 dB dip between them will appear on the screen. This is
the minimum resolvable frequency spacing. The menu selections legend displays the current value.
Figure 21 Signal Representation
Lowering the RBW will lower the noise floor, which can make lowpower signals easier to see, and makes readings close to the noise floor
more accurate.
Figure 22 Example, BW & Sweep Menu
34
Page 51

Settings
Click on the Resolution BW selection then use the arrow keys or the
mouse wheel to enter the desired bandwidth.
RBW goes from 100 Hz - 1 MHz, steps of 1 / 3 / 10 (e.g.: 1 kHz to 3 kHz
to 10 kHz to 30 kHz, etc.)
Video BW Mode (VBW) determines how much smoothing takes place.
Note: VBW goes from 10 Hz to 300 kHz.
z Wide (high) VBW setting: Faster sweep times, but can
obscure signal details.
z Narrow (lower) VBW setting: Better trace smoothing for
signals present in high noise levels.
As the VBW is reduced, longer sweep times will be necessary to obtain
a measurement. To be useful, VBW must be narrower than RBW. No
smoothing takes place when VBW is greater than or equal to RBW.
Resolution & Video BW Modes
Click on these to toggle RBW or VBW, respectively, between automatic and manual control. In automatic, they are controlled by the
current span and the values of Span/RBW and RBW/VBW. If either
the RBW or VBW is changed, these will switch to manual.
Auto RBW sets the RBW based upon the frequency span. When in
Auto mode, the RBW is set according to the nearest ratio of the Span/
RBW selection. The default ratio is 300. When the frequency span is
reduced, the RBW will also be reduced accordingly.
Example - When the span is changed to 3600 MHz, the RBW
will automatically be set to 1 MHz. When the span is reduced to
100 MHz, the RBW will automatically reduce to 300 kHz.
Auto VBW sets the VBW based upon the RBW value. When in Auto
mode, the VBW is set according to the nearest ratio as set using the
VBW/RBW selection. The default ratio is 3. As the RBW span is
reduced the VBW will be reduced accordingly.
Example - When the RBW is changed to 1MHz, the VBW will
automatically be set to 300kHz. When the RBW is reduced to
30kHz, the VBW will automatically be set to 10kHz.
35
Page 52

Bird Technologies
Resolution & Video BW
Click on the selection to highlight it. Then:
z Up/Down Keys - Change the bandwidth incrementally.
z Left/Right Keys - Change the bandwidth from min to max.
z Mouse Scroll Wheel - Change the bandwidth incrementally.
Span/RBW
Click on the Span/RBW selection then enter the desired ratio. Values range
from 10 to 3600 in steps of one.
The ratio of frequency span to RBW determines how the RBW tracks
with frequency span when the Resolution BW mode is in Auto. This
value is ignored when Resolution BW Mode is in Manual mode. The
menu selection legend displays the current value.
z Up and Down Arrow Keys - Press these keys to increase or
decrease the ratio in steps of one.
z Left and Right Arrow Keys - Press these keys to enter the
minimum ratio (left-arrow) or the maximum ratio (right-arrow).
z Mouse Scroll Wheel - Rotate the wheel to increase or
decrease the ratio in steps of one.
RBW / VBW
Clicking on the key brings up a list of allowed values for RBW / VBW. When
VBW is set to auto, the RBW is divided by this value and set as the VBW.
Figure 23 Example, RBW/VBW
36
Page 53

Settings
Detection Mode
Depending on measurement settings, many more data points are collected than there are pixels on the screen. Detection modes allow the
user to choose how the collected data in each pixel is represented.
+ Peak Detection
Returns the maximum value of the data collected for each display pixel.
Recommended for pure sine waves or narrow bandwidth signals. In
zero-span mode, this mode acts like a peak detector and can be used to
show AM band frequencies.
- Peak Detection
Returns the minimum value of the data collected for each display pixel.
Recommended for displaying the difference between CW and pulsed signals.
Sample Detection
Returns a sample of the data collected for each display pixel. Use this
method for noise-like signals.
Average Power
Returns the average of the data collected for each display pixel. Recommended for noise-reduction.
Figure 24 Example, Detection Mode
37
Page 54

Bird Technologies
Sweep
Sweep sets up the properties of individual sweeps that the SignalHawk performs. It can set whether the sweeping is continuous or
single, and the properties of video triggers (if enabled).
Figure 25 Example, Sweep More
Figure 26 Example, Trigger Rep
38
Page 55

Settings
Single
Performs a single sweep. Before a single sweep is triggered, the SignalHawk will display the previous sweep. To begin a sweep, press the
Manual Trigger soft key. After the sweep finishes, it will display the
results and stop sweeping.
Trigger - Sets the type of trigger that initiates a sweep. There are four
types of trigger to choose from:
z Internal Continuous - Sweeps continuously and is con-
trolled by the SignalHawk.
z Internal Single - Sweeps once when triggered. Controlled by
the SignalHawk through the Arm Trigger soft key.
z External Continuous - See “External Trigger” below.
z External Single - See “External Trigger” below.
Note: Useful for signals that are time varying. Ones that
change slow enough to trigger manually as well as carrier/interference ratios. See “Carrier-to-Interference Ratio” on page 63.
Arm Trigger - Manually initiates a sweep. External Trigger
External - Low Level / High Level /
Rise Edge / Fall Edge / Either Edge
z Low Level - Triggers if input = 0 ± 0.5 V (TTL “Low”).
z High Level - Triggers if input = 4.2 ± 0.8 V (TTL “High”).
z Rise Edge - Triggers if the input goes from “Low” to “High”.
z Fall Edge - Triggers if the input goes from “High” to “Low”.
z Either Edge - Triggers if the input goes from either “High” to
“Low” OR “Low” to “High”.
Gate Delay
Length of wait after the trigger signal and before beginning a sweep.
The range is 100 µs to 1 s.
39
Page 56

Bird Technologies
Figure 27 Example, Low Level / High Level /
Rise Edge / Fall Edge / Either Edge
Video
Note: This can only be used if the Time Domain measure-
ment is enabled. See “Time Domain (Zero Span)” on page 59.
Trigger control and sweeping both happen on the radio frequency
connector. Once a sweep is done, it will be displayed until a trigger
condition occurs again and it performs another sweep. This is used in
zero-span mode.
In order to use this function, the trigger condition needs to be set up:
1. Monitor the RF data to determine the trigger condition.
2. Set the power level at center freq.
3. Set the trigger level:
z High Level - Trigger if dBm rises ABOVE the power level.
z Low Level - Trigger if dBm falls BELOW the power level.
z Pwr Level - Set the power level using the keypad.
4. Enable the trigger.
Gate Delay
Length of wait after the trigger signal and before beginning a sweep
The range is 100 µs to 1 s.
40
Page 57

Settings
Ampt & Trace Menu
Figure 28 Example, Ampt & Trace Menu
Autoscale
Resizes the graph to fit the whole trace on the screen. This function
will change the reference and scale of a trace.
Reference
Sets the y-axis value at the top of the graph.
Scale
Sets the dB value of each partition of the graph on a scale from 1 to 15.
The graph is partitioned into 10 divisions, giving a set number of dB
per division.
Note: This soft key is not displayed if the Units of measure
is in Volt or Watt. See “Units” on page 42.
Attenuation
Controls the built-in attenuator on the signal input. This reduces the
amplitude of a high-powered signal. The attenuation can be set to Auto,
or at levels of 0, 10, 20, and 30 dB. The reported value of the signal is
automatically corrected for the selected attenuation.
Note: When the Reference (see “Reference”) is set to a higher
setting, Attenuation will automatically set itself above this setting.
Example - Reference is set to 25 dBm, Attenuation automatically sets itself to 30 dB and cannot be lowered.
41
Page 58

Bird Technologies
dBm 10 Log Power Watts()[]30dB+×=
dBm dBuV 10
∗
50log()90––=
dBm dBmV 10
∗
50log 30–()–=
dBm dBV 10
∗
50log 30+()–=
dBm 20 Log Power Volts()[]×=30dB+
Watts 10ΛdBm 30–()10⁄()=
Preamp
Controls the built-in amplifier on the signal input. This lowers the noise
floor, allowing very low power signals be detected, by giving a 24 dB
nominal gain boost.
Note: Attenuation is automatically disabled to 0 when
Preamp is activated.
Note: The preamp should not be used with input signals
greater than -30 dBm.
Offset
Shifts the signal to compensate for external factors (attenuation, couplers, amplifiers, etc.) This allows for a true signal level reading.
1. Measure the total amount of loss for all attached signal devices.
2. Enter the measured amount as the Offset value or gain.
Example - The system has 10 dB of loss due the use of a coupler;
enter the value of 10 in the Offset. Offset range is -100 to +100.
Units
dBm
dBuV
dBmV
dBV
Volts
Watts
Trace
Opens a trace submenu with the following options:
Clear Write
Switches off the Average and Max Hold functions.
Max Hold
Holds and displays the highest point of a any given sweep until Max
Hold is turned off.
42
Page 59

Settings
STEP 4
STEP 5
Waterfall
Display
Min Hold
Holds and displays the lowest point of any given sweep until Min Hold
is turned off.
Average
Displays the running average of multiple readings which is used to
smooth a signal and decrease noise amplitude.
Average Readings
Sets the number of averaged readings. The valid range is from 2 to 1024.
Reset Average
Resets the current running average of multiple readings.
Water Fall Spectrogram
The Water Fall Spectrogram shows how the spectral density of a signal
varies with time and presents it in a visual image. Also known as spectral waterfalls, sonograms, voiceprints, or voicegrams, spectrograms are
used to identify phonetic sounds and specific noise disturbances.
1. Go to the Ampt & Trace menu.
2. Click on the Trace selection.
3. Click on the Water Fall selection.
4. Turn the Water Fall spectrogram on.
5. Select the dual screen display, if desired
Figure 29 Example, Water Fall Spectrogram
43
Page 60

Bird Technologies
Mark & Limit Menu
Figure 30 Example, Mark & Limit Menu
Select Marker
Changes the active marker. There are six markers to choose from (measurements that use some of the markers for data display have less selectable
markers). Pressing the soft key will cycle through each of the six markers.
Marker On / Off
Turns a Marker on and off.
Marker to Max Peak
Moves the active marker to the highest point on the trace.
Markers to Peak/Valley
Figure 31 Markers to Peak/Valley
44
Page 61

Settings
Markers Detect
Toggles the functionality of the submenu between finding peaks or
finding valleys.
Threshold
The threshold offset, displayed on the first line, is used to calculate the
threshold level, displayed on the second line, above the noise floor.
Note: The low level peaks below the threshold level are fil-
tered out. Only peaks above or at the threshold level are detected.
Marker to Max Peak or Marker to Min Valley
Sets the marker to the either the maximum peak or minimum valley
depending on the functionality chosen in Markers Detect. See “Markers Detect” on page 45.
Marker to Next Peak Left or Marker to Next Valley Left
Cycles the active marker to the left through the points on the trace
either from highest peaks or lowest valleys (see “Markers Detect” on
page 45) progressing to the left.
Marker to Next Peak Right or Marker to Next Valley Right
Cycles the active marker to the right through the points on the trace
either from highest peaks or lowest valleys (see “Markers Detect” on
page 45) progressing to the right.
All Markers to Max Peaks or All Markers to Min Valleys
Sets all the markers to either the maximum peaks or minimum valleys depending on the functionality chosen in Markers Detect. See
“Markers Detect” on page 45.
All Markers Off
Turns off all markers on the trace.
Marker Delta
Turns On/Off and displays the delta of the one to five markers.
Marker Display
Marker Type
Sets the current marker to either be displayed as a line or floating
numbered icon.
All Markers Type to Icon
Sets all markers to be displayed as floating numbered icons.
All Markers Type to Line
Sets all markers to be displayed as numbered lines.
Marker Display
Turns On/Off and sets the location of the delta display into one of the
four corners of the screen.
45
Page 62

Bird Technologies
Marker More
Sets the properties of active markers through the following attributes:
RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator)
Turns the audio indicator On or Off (an electronic ping). See “Received
Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI)” on page 61.
Volume
Sets the volume of the electronic ping generated from the RSSI.
Marker Freq to Center
Moves the current marker to the center frequency.
Center Freq to Marker
Sets the center frequency to the frequency of the active marker.
Ref Level Ampt to Marker
Sets the top-line amplitude reference level to the amplitude of the
active marker.
Frequency Counter
Turns the Frequency Counter on or off. This enables the frequency
read out of all displayed markers to read the exact frequency of the
peak within the pixel to a resolution of 1 Hz.
Note: Signals that vary in frequency must be within the
RBW to obtain accurate results.
Limit Lines
Limit lines give notification of when a signal has reached or gone over a
set measurement amount. Limit lines can be moved with arrow keys.
Note: All valid traces are black, and any part of any trace
that is outside of a limit is red. Red indicates a failed limit.
Limit Upper/Lower
Pick between upper & lower limit line.
Limit On/Off
Pick between limit line on or off.
Limit Alarm On/Off
Pick whether a limit line fail makes the unit beep.
Select Line/Mask
Creates a specific set of limit lines and presents a list of these
predefined masks to choose from.
Note: Custom Masks can be saved to the Mask list. See
“Customizing SignalHawk Content” on page 68.
46
Page 63

Settings
Figure 32 Example, Mask List
Once a mask is selected, it is controlled by the following options:
Freq Lock - Locks the mask onto the selected band even if the
frequency is changed.
EM to Max Peak - Sets mask’s reference level to the maximum peak in
each sweep.
Figure 33 Example, Limit Line Mask
47
Page 64

Bird Technologies
File & Help Menu
When File & Help is clicked, menu selections for saving the current
trace, selecting the utility option, activating the logging feature, and
accessing help features (Fig. 34) are enabled. A trace is saved as a file
and stored in the default file location of the host PC.
Figure 34 Example, File & Help Menu
Quick Save Trace
Saves the trace that is displayed on the screen.
1. Click on File & Help.
2. Click on Quick Save Trace.
Note: The trace is stored as a file in the default file loca-
tion of the host PC. Each quick save is stored in a separate file
that is named using the measurement and date-time file naming format: Measurement name(MM-DD HH-MM-SS).shf.
Where the first MM is the month, DD is the day, HH is the
hour, the second MM is the minute, and SS is the second of the
time when the file was saved.
Label & Save Trace
Labels and saves the trace for future use.
1. Click on Save Trace.
2. Enter a file name.
48
Page 65

Settings
Figure 35 Example, Save Trace
Log Traces
Saves a sweep every 60 seconds and assigns a default name to each save.
Recall Trace
Opens up a submenu with three options:
Recall Trace
Displays a saved trace on the screen.
Recall & Compare
Displays a saved trace overlapping over the current trace on the screen.
Note: The Saved trace is orange. The current trace is black.
Clear Recalled Trace
Deletes the highlighted trace.
Manage Trace Files
Copy trace files to and from network drives, and delete traces.
Delete Trace
Deletes a selected trace.
Delete All Traces
Deletes all traces in the directory.
Full Screen
Enlarges the graph area to the size of the whole screen. Press escape
to go back to regular screen.
Utility
See “Utility Main Menu” on page 68.
Help
Brings up the menu selections that will enable either the Quick Start
Guide or the User Manual, saved in the unit.
49
Page 66

Bird Technologies
50
Page 67

Chapter 5 Measurements
Spectrum Analysis, measuring the power at each frequency in the
sweep range, is the basic measurement. The other measurements
interpret that data to provide useful results.
In the Spectrum Analyzer mode, the following measurements can be used:
z "Spectrum Analysis Measurement" on page 52.
z "Occupied Bandwidth Measurement" on page 53.
z "Channel Power Measurement" on page 55.
z "Adjacent Channel Power Measurement" on page 57.
z "Time Domain (Zero Span)" on page 59
z "Field Strength Measurement" on page 60.
z "Carrier-to-Interference Ratio" on page 63.
z "Out-of-Band and In-Band, Out-of-Channel Spurious" on page 65.
z "Water Fall Spectrogram" on page 43.
51
Page 68

Bird Technologies
Spectrum Analysis Measurement
Spectrum Analysis measures the power at each frequency in the range
shown on the screen. From the Spectrum Analyzer list on the Start Menu,
select Spectrum Analysis then press the Enter key.
Figure 36 Example, Spectrum Analysis, Frequency and Span Screen
52
Page 69

Measurements
Measurement
Settings
Occupied Bandwidth Measurement
Occupied Bandwidth measures the frequency band bandwidth that
contains a specified percentage of the total power of the signal.
It gives best results with single-peaked signals. Bandwidth can be
defined in two ways. Both give measurement results in Hz units.
Threshold Modes
%
The calculated occupied bandwidth represents the user specified percent
of the total power of the displayed span. Best for Watts power units.
dBc
The bandwidth is calculated by finding the frequencies above and below
the center or carrier frequency that is the user specified dB below the
carrier level. This method is best for measuring dBm power units.
Setting Occupied Bandwidth
Note: For the best accuracy, set the center frequency so the
main or carrier signal is centered on the screen before taking
measurements.
1. Select either % or dBc under Threshold Mode.
2. Do one of the following:
z If the % Threshold has been selected, go the % soft key
and set the desired threshold via either the mouse scroll wheel
or keyboard.
z If the dBc Threshold has been selected, go the dBc and set the
desired threshold via either the mouse scroll wheel or keyboard.
Note: The threshold and the measured bandwidth will be
displayed in the “measurement settings” area at the bottom of
the display. Markers 1 and 2 will be turned on, and placed at
the band edges.
Figure 37 Example, Occupied Bandwidth
53
Page 70

Bird Technologies
STEP 1
STEP 2
STEP 1
STEP 2
Figure 38 Example, Occupied Bandwidth - %
Note: Limit can be set without changing the Threshold Mode.
Figure 39 Example, Occupied Bandwidth - dBc
54
Note: Limit can be set without changing the Threshold Mode.
Page 71

Measurements
STEP 1
Measurement
Settings
Channel Power Measurement
Channel Power measures the Integration Bandwidth, the total power
over a frequency range, concentrated on the center frequency of the
sweep. It is useful for channelized (frequency-division multiplexed)
signals. Results are shown in both total power in the channel (in dBm
or Watts), and spectral density (dBm or Watts per Hz).
Setting Channel Power
Note: For best accuracy, set the center frequency so the signal
is roughly centered before taking measurements. In addition, the
span should be 1½ – 5 times as large as the desired channel width.
1. Select the Integration Bandwidth (IBW).
Note: The IBW is automatically set when a channelized
frequency band is selected from the Frequency list.
2. Enter the desired bandwidth.
3. Select the desired unit.
Note: The default unit is MHz.
Note: The integration bandwidth, channel power, and
power density will be displayed in the “measurement settings”
area at the bottom of the display. Markers 1 and 2 will be
turned on, and placed at the band edges.
Figure 40 Example, Channel Power
55
Page 72

Bird Technologies
STEP 2
STEP 3
Figure 41 Example, Channel Power, Integration Bandwidth
56
Page 73

Measurements
Adjacent Channel Power Measurement
Adjacent Channel Power measures the relative power of frequency
bands adjacent to a central channel. This is often used to identify
power leakage from the center channel into the adjacent channels.
The total power in the central (main) channel is displayed in dBm
(Ch Power), and the power in the adjacent channels is displayed as dB
below and above the main channel power (Dn ACPR and Up ACPR).
Note: For best accuracy, set the central frequency so the sig-
nal is centered before taking measurements. In addition, set the
span so the central, upper, and lower channels are all shown on
the screen.
Note: If a channelized band is selected from the Frequency
list, these parameters are automatically set.
1. Set the width of the central channel.
Note: The central channel can be set to a different fre-
quency width than the adjacent channels, but both adjacent
channels have the same width.
2. Set both adjacent channels.
3. Set the Center-to-Center channel spacing.
Note: Channel spacing is the distance from the central chan-
nel’s center frequency to the adjacent channel’s center frequency. If
there is no guardband between channels, the channel spacing
should be half (channel width + adjacent channel width).
4. Enter the desired bandwidth in each variable.
5. Select the desired unit of measurement.
Note: Pressing Enter will default the Unit to MHz.
Note: All 6 markers will be used to show the edges of the
central, upper, and lower channels.
57
Page 74

Bird Technologies
STEP
1
STEP
2
STEP
3
Measurement
Settings
Width
Adjacent
Channel
Adjacent
Channel
Guardband
Guardband
STEP 4
STEP 5
Figure 42 Example, Adjacent Channel Power
Figure 43 Example, Adjacent Channel Power, Bandwidth Settings
58
Page 75

Measurements
STEP 1
Measurement
Settings
STEP 2
Time Domain (Zero Span)
In Time Domain, the amplitude of a single frequency is measured,
rather than sweeping a range of frequencies. The SignalHawk measures and displays the amplitude of the frequency for a specified
period (sweep time) and refreshes during the next sweep. The Time
Domain trace resembles the horizontal line display on an oscilloscope.
Note: The center frequency will being measured.
1. Activate the measurement by doing one of the following:
z Select Time Domain in the Start Menu.
z Select Time Domain in the Measurement Menu.
z Set the Frequency Span to 0 Hz. See “Freq & Span Menu” on
page 31.
2. Press the Sweep Time soft key and enter how long a single sweep
should be using one of these methods:
Note: Time range can be set from 1 ms to 100 s.
z Up/Down Arrows: Step increments of one second.
z Right/Left Arrows: Step increments of one millisecond.
z Mouse Scroll Wheel: Step increments of one second per click.
z Number Keys: Enter the time in seconds.
Note: There are a limited number of pixels, so longer
sweep times mean less detail in the display.
Note: This enables the Video Trigger in the BW & Sweep
menu. To use the Video Trigger, see “Resolution & Video BW”
on page 36.
Figure 44 Example, Time Domain
59
Page 76

Bird Technologies
Measurement
Settings
STEP 2
Field Strength Measurement
Field Strength measures the signals reaching an antenna. The SignalHawk
automatically corrects the sweep data for the antenna’s gain and frequency
dependence and displays it in dBm / m.
1. Connect an antenna to the RF In connector on the SignalHawk.
Note: Use an antenna with known gain characteristics.
For best accuracy, set the start and stop frequencies to the measurement range of the chosen antenna.
2. Select Antenna and select the antenna type from the drop down list.
Note: The antenna type, valid frequency range, and gain
in dB (relative to an isotropic radiator) are shown in the
measurement settings area.
3. Measure the strength of the signal emanating from a transmission
antenna (within the frequency range of the antenna connected to
the RF In port).
4. Move to various positions relative to the transmitting source and
observe the signal value.
Figure 45 Example, Field Signal Strength
60
Page 77

Measurements
Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI)
RSSI provides an audible indication at the frequency of the current
marker. It will beep faster as the received signal strength goes up and
slows as it goes down.
Similar to Water Fall, power is linearly mapped to a range of 0-210
using the same range as for the Water Fall for simplicity. The beep
rate and volume are proportional to the mapped power value at the
current marker index. Values of zero are equivalent to continuous
beeps and -210 are equivalent to a beep every 4 seconds.
Figure 46 Example, Field Signal Strength - RSSI
61
Page 78

Bird Technologies
STEP 1
STEP 2
STEP 3
Volum e
Control
Demodulate Signal
Removes the carrier and sends the signal to the internal speaker or
headphones. The SignalHawk can demodulate AM, narrowband FM,
and wideband FM signals. It can also set the specific frequency and
volume.
1. Set the type of demodulation:
a. Select the Demodulate Type.
b. Select the type of demodulation desired.
2. Set the demodulation carrier frequency:
a. Select the Demod Freq button.
b. Enter the carrier frequency using the number keys.
c. Select the frequency units.
3. Set the time to demodulate the signal:
a. Select the Demodulate Time button.
b. Enter a value.
c. Select the time units.
d. Allow audio to play for the demodulate time.
e. Repeat as necessary.
Figure 47 Example, Demodulate Signal
62
Page 79

Measurements
Measurement
Settings
STEP 2
STEP 3
Note: In the status area, the carrier power, interferer power
will be displayed in selected power units, and the ratio in dB.
Carrier-to-Interference Ratio
Calculates the ratio of the carrier signal power to the power level of
the noise and interference signals.
To determine the ratio, two measurements need be done. First sweep
should be the carrier and interferer. The second sweep should be the
interferer alone.
Note: Because the transmitted carrier must be turned off
for the second portion of this measurement, access to the transmitter is needed to complete this procedure.
1. Do one of the following:
z Move marker to the desired frequency.
Note: The default marker placement assumes the carrier
to be measured is the center of the frequency span. It can be
moved via the arrow keys and/or wheel.
z Select Marker to Max Peak to quickly identify the signal to be
measured.
2. Measure the carrier signal.
3. Turn off the transmitter.
4. Measure the noise and interference signal levels as follows:
Note: The carrier power and interferer power will be displayed
in selected power units, and the ratio in dB.
Figure 48 Example, Carrier-to-Interference Ratio - Carrier On
63
Page 80

Bird Technologies
STEP 4
Measurement
Settings
Figure 49 Example, Carrier-to-Interference Ratio - Carrier Off
64
Page 81

Measurements
Out-of-Band and In-Band, Out-of-Channel Spurious
Note: These two measurement methods are not listed on
the interface.
Out-of-Band & In-Band, Out-of-Channel Spurious measures the
distortion and interference inside or outside a system band.
1. Click on Mark & Limit.
2. Click on the Marker 1 2 3 4 5 6 selection to select marker 1.
Note: The bracketed number indicates the active marker.
3. Click on On/Off.
4. Use the arrow keys, the number keys or mouse scroll wheel to
move the marker over one of the spurs.
5. Compare the value of the marker to the specified allowable level of
Out-of-Band (In-Band, Out-of-Channel) spurious emissions for the
corresponding channel transmit frequency.
65
Page 82

Bird Technologies
66
Page 83

Chapter 6 Utilities
With SignalHawk’s built-in utilities, information about the instrument
is displayed. The Menu keys provide information about the software,
hardware, and data files.
Utilities can be accessed by clicking on Utilities from the Start Menu
screen, or by clicking on File & Help from a measurement screen then
click on Utility.
To exit the Utility mode, press the Esc/Back function key to return to the
previous screen, or press the Mode key to go to the Start Menu screen.
Utility
Click on Utility to go to the Utility Menu. When the utility menu is
accessed, new menu keys and selections for getting help and exiting to
the Windows operating system are activated. The Utility Menu screen
displays status information about the instrument and about the operating system.
Figure 50 Utility Menu, Main Screen, Version Info Screen
67
Page 84

Bird Technologies
Utility Main Menu
Version Info
Click on this to view general information such as how to contact Bird
Technologies Group.
The selections for this menu provide access to user help and the Windows operating system.
Utility Main Menu Selections
Spectrum Analyzer Help
Click on this selection to display the SignalHawk Start-up Instructions.
Press the up- and down-arrow keys or use the mouse scroll wheel to scroll
through the displayed text. Click on Exit Menu or Esc to return to the
Utility Menu.
Custom Help
Displays user created help files that have been uploaded to the
SignalHawk.
Exit to Windows
Click on this to exit the SignalHawk program.
Customizing SignalHawk Content
1. Go to the Utilities menu.
2. Press the Exit to Windows soft key.
Note: The SignalHawk will ask for verification.
3. Go to My Computer on the PC.
4. Click on the following:
a. Hard Drive
b. Program Files
c. Bird Technologies Group
d. PC SignalHawk
e. My Lists
68
Page 85

Utilities
Figure 51 PC SignalHawk Directory
5. Copy the csv file of the list to be edited to the desktop of the PC.
6. Open the csv file.
7. Add custom information into the list.
8. Copy the csv file back into the My Lists directory.
Note: The computer will ask for verification to overwrite
the file in the directory.
9. Close the My Lists directory window.
10. Launch the PC SignalHawk program.
69
Page 86

Bird Technologies
70
Page 87

Chapter 7 PC Tool
Bird’s SignalHawk PCTool enables the use of a PC to store measurement data, transfer it between units, and do individual analysis. Traces
can be transferred from the SignalHawk to the PC and back. One or
more saved traces can be opened and compared. They can also be copied
and pasted into other open files, as well as adding markers or limit
lines. In addition, labels can be added and modifications saved to files.
Note: Not all sections of this chapter apply to the PC and
Rack Mount SignalHawks.
Computer Requirements
The PC must meet the following minimum requirements:
z Windows 98 or later operating system
z Internet Explorer version 6 or later
z Hard disk with 30 MB of free space
Downloading and Installing Software
Note: These files are on the CD supplied with the Signal-
Hawk, and can also be downloaded from the website.
Note: For the latest versions of the PCTool, Microsoft
ActiveSync
Technologies SignalHawk website.
For PC:
http://birdtechnologies.thomasnet.com/item/all-categories-testequipment/-categories-test-equipment-sh-36-signalhawk-series/
sh-36s-pc
For Rack Mount:
http://birdtechnologies.thomasnet.com/item/all-categories-testequipment/-categories-test-equipment-sh-36-signalhawk-series/
sh-36s-rm
®
, and USB Drivers download them from the Bird
®
Installing the PC Tool Software
1. Download and install Microsoft ActiveSync.
2. Click on “Install PC Interface Tool.”
3. Save the compressed file to the PC’s desktop.
4. Double click the compressed file on the PC desktop.
5. Click-and-drag the SHPCTool icon (Setup file) out of the compressed file window and onto the PC desktop.
6. Double-click the Setup file.
7. Follow the instructions in the Install Wizard to complete the installation.
71
Page 88

Bird Technologies
Menu Bar
File
Presents commands to Open, Close, Save, Export, and Print SignalHawk files that are stored on the PC.
Note: By default, traces will be saved to the “My Traces”, which
is a subfolder under the folder where the PCTool was installed.
Edit
Presents commands to copy the active trace from a graph and paste it
into another graph. Traces can also be deleted from a graph.
Note: The last trace remaining on a graph cannot be removed.
View
Presents commands to manipulate the trace - Zoom In, Zoom Out, Add,
and Delete Markers or Limit Lines, Autoscale the Trace, Set to Normal
Mode, and Set Options. Normal mode is identified by the standard
Windows “selection” cursor (arrow pointing to the upper left). DTF Settings (Cable Vp & Loss, Start & Stop Distance, etc) can also be viewed.
Tools
Presents access to the units converter.
Figure 52 Units Converter
Measurements
Note: This option will only appear for VNA traces.
Presents the various measurement types to display the reading. The
types of measurement depend on the type of trace file being read. VNA
files will give Match Measurement, Distance-to-Fault, Cable Loss, and
Smith Chart as options.
Communicate
Presents commands to get files from and/or send files to the SignalHawk. In
addition, use this function to upgrade the SignalHawk software/firmware.
72
Page 89

PC Tool
Tool Bar
Use the tool icons to perform the tasks that are available on the Menu bar.
Save
Saves a copy of a graph.
Open
Opens a graph.
Cut
Cuts a trace from a graph.
Copy
Copies a trace from a graph.
Paste
Pastes a trace onto a graph.
Note: A trace from one measurement type cannot be placed
onto a graph from another measurement type (Occupied Bandwidth, Channel Power, etc). The graphs do not match.
Delete Trace
Deletes a trace from a graph.
Note: The last trace on a graph cannot be deleted.
Return to Normal Mode
Returns the display back to the start menu.
Zoom In
Increases the focus on a specific area of a graph.
73
Page 90

Bird Technologies
Zoom Out
Decreases the focus from a specific area of a graph.
Autoscale Graph
Resizes the axis to fit all traces on the graph.
Add Markers
Drops a marker onto a graph.
Add to Upper Limit Line
Adds a limit line to the graph.
z First click will create a point on the graph with a highlighted line.
z Second click will create another point that connects to the first
point via a line.
z Third click connects to the second, and so on.
Add to Lower Limit Line
Adds a limit line to the graph.
z First click will create a point on the graph with a line.
z Second click will create another point that connects to the first
point via a line.
z Third click connects to the second, and so on
Delete Markers or Limit Lines
Deletes a marker, a limit line, or a point on a limit line. When deleting
points, the icon will change to an eraser graphic when the icon floats over
something that can be deleted.
Option Dialog Box
Opens the pop-up Option Dialog box. "Options Dialog Box (View>Options)"
on page 76.
Measurement Types
The measurement types for that file are displayed, depending on the
type of file being read.
74
Page 91

VNA Tool Bar
Note: There is an addendum, with additional options, to
the menu bar when the PC Tool is reading a VNA file.
Note: This section does not apply to PC and Rack Mount
SignalHawks.
Match
Sets the current trace to a Match measurement display.
Distance to Fault
Sets the current trace to a Distance to Fault display.
Cable
Sets the current trace to a Cable Loss display.
PC Tool
Smith
Sets the current trace to display a Smith Chart.
Options Dialog Box
Opens the pop up Option Dialog box. "Options Dialog Box
(View>Options)" on page 76.
DTF Wizard
Opens the Distance to Fault Wizard.
Figure 53 DTF Wizard
75
Page 92

Bird Technologies
Autoscale
Boxes
Options Dialog Box (View>Options)
The Options dialog box contains six tabs - Scale, Units, Markers,
Limits1, Limits 2, and Labels. Select a tab and enter or edit specific
values for the currently active graph.
Scale Tab
1. Enter the x- and y- axis.
2. Enter the y- axis offset.
3. Do one of the following:
z Select the Autoscale box.
z Manually enter values for the scales.
Note: The Offset setting for a specific trace is displayed.
The setting changes when the Trace changes.
Figure 54 Example, Scale Tab
Units Tab
1. Select the units of measure for the y axis.
2. Set the size of text for the entire graph.
3. Set whether or not to display grid lines.
Figure 55 Example, Units Tab
76
Page 93

PC Tool
Markers Tab
When a frequency or distance for a marker is entered, the marker will
be set to the datapoint closest to that frequency or distance. The actual
frequency of the marker will replace the value entered and will also
display on the screen below the graph area.
For each marker:
1. Specify or change the frequency.
2. Specify the symbol type.
3. Specify a delta with another marker.
4. Turn a marker on or off.
Note: After turning a marker on in the Options window,
the marker can be moved by clicking on the marker and dragging it to a desired location.
Figure 56 Example, Markers Tab
Limits 1 Tab
Defines and turns on or off upper/lower limit lines.
Note: The options displayed on this tab will change
slightly depending on the type of graph opened.
Note: The upper limit fails any datapoints that are above
the line.
Note: The lower limit fails any datapoints that are below
the line.
Note: The limit line will be flat across the graph at the
power level specified.
1. Click on the line
2. Drag the line to move it up and down.
Note: There is a drop down menu of predefined limits that
is available to be utilized.
77
Page 94

Bird Technologies
-120
-110
-100
-90
-80
-70
95.0 95.2 95.4 95.6 95.8
LIMIT TEST FAILED
Power (dBm)
Frequency (MHz)
Limit Line
Figure 57 Example, Limits 1 Tab
Limits 2 Tab
Note: The options displayed on this tab will change
slightly depending on the type of graph opened.
Note: The upper limit fails any datapoints that are above
the line.
Note: The lower limit fails any datapoints that are below
the line.
Note: Up to thirty points, for both upper and lower limit
lines can be set up. Using multiple points, a bracketed area
may be created.
1. Click on a segment
2. Drag each segment at its set point to move it up or down.
Note: If a limit line point is disabled, it is removed from
the list in the Options dialog box.
Figure 58 Example, Limits 2 Tab
Figure 59 Multiple limit line points used to create a bracketed area
78
Page 95

PC Tool
GPS
Location
GPS
Time
Labels Tab
Creates a title, subtitle, and a trace name for the displayed trace.
The title will be in larger letters and centered above the graph. The sub-
title will be smaller.
Edit a trace name by typing in the list of traces on this tab. The trace
and date will be located above the graph and on the left.
Note: If a specific trace name is not created, the PC tool
will create one automatically.
Other options are to display or hide the title, subtitle, trace name, and
trace date on the graph.
Figure 60 Example, Labels Tab
GPS
If a GPS sensor is attached to the SignalHawk, it will display a location and GPS time reading at the bottom of the trace.
Note: This section does not apply to PC and Rack Mount
SignalHawks.
Figure 61 GPS Reading
79
Page 96

Bird Technologies
80
Page 97

Chapter 8 Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for proper and accurate performance
of the SignalHawk. These procedures cover the basic maintenance of
the SignalHawk. For more advanced issues, please contact Bird
Technologies customer service.
Cleaning
CAUTION
Harsh or abrasive detergents, and some solvents, can damage the
unit and labels.
Clean the Bird SignalHawk only with a soft cloth dampened with mild
detergent and water. Do not use any other type of cleaning solution.
Charging the Battery
The internal battery pack will automatically recharge when the
SignalHawk is powered from the AC or cigarette lighter adapter.
Recharging time, from a full discharge, is approximately 4 hours.
Charging the Battery Using a Car Charger
The vehicle must be operational when charging the unit.
Note: The unit will not completely charge unless at least
12.6-13V is present at the DC input.
Replacing the Battery on the PC SignalHawk
WARNING
Care should be taken when handling batteries.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Do not heat or dispose of batteries in fire. May burst or release toxic
materials.
Avoid forced discharge.
Do not short circuit.
Restrict charging current and time to the recommended value.
Do not solder the battery directly.
Do not disassemble, apply excessive pressure, or deform.
Avoid placing the battery in reverse polarity.
Battery disposal method should be in accordance with local and
state regulations.
1. Remove the four screws securing the back cover to the SignalHawk.
2. Remove the back cover.
3. Remove the battery.
4. Detach the power cord from the battery connector.
5. Reverse Steps 1 to 4 to install a new battery.
81
Page 98

Screws
Back
Cover
Battery
Battery
Power
Cord
Battery
Plug
Detail
“A”
Detail
“B”
Bird Technologies
Updating the Firmware
Note: There are two different firmware files: one contain-
ing the DSP image and the other containing the FPGA image.
1. Navigate to Bird Technologies Group>PC SignalHawk in the Start
menu.
2. Click on Firmware Update Wizard.
Note: The wizard will launch and provide step-by-step
instructions.
3. Select the DSP and FPGA images to be updated.
Figure 62 DSP and FPGA Image Selection
82
Page 99

Maintenance
4. Connect the unit to the PC via USB cable.
5. Turn on the SignalHawk.
6. Select “Install the software automatically...” if the “Found New
Hardware Wizard” is presented.
Note: Both program wizards will run co-currently. See
“Installing the SignalHawk Program” on page 9 for the PC
SignalHawk.
7. Click “Next.”
Figure 63 DSP List
8. Select the unit from the list presented.
9. Select the images that need updating.
10. Click “Next” repeatedly until the update is completed.
Figure 64 Image Selection
11. Cycle power when prompted by the program wizard.
83
Page 100

Bird Technologies
Updating the Firmware on a Remote Rack Mount SignalHawk
1. Go to http://birdtechnologies.thomasnet.com/item/all-categories-testequipment/-categories-test-equipment-sh-36-signalhawk-series/sh36s-rm.
2. Download the Rack Mount SignalHawk software upgrade to a
local PC.
3. Connect the remote computer to the host computer. See “Connecting a Remote Computer to the Host Computer” on page 20.
4. Click on “Options-Local Resources” at the start of the Remote
Desktop Connection window.
Figure 65 Remote Desktop Connection Window
5. Select “Disk drives”.
Note: This will enable access of the local drives to the
remote Rack Mount SignalHawk.
Figure 66 Options-Local Resources
6. Click on the “Connect”.
7. Click “OK” to access the local drives from the remote computer.
84
 Loading...
Loading...