Page 1

BiGuard 50G
802.11g Dual WAN Security
Gateway
User’s Manual
Version Release 1.03 (FW:1.xx)
Page 2
BiGuard 50G User’s Manual
(Updated September, 2007)
Copyright Information
© 2007 Billion Electric Corporation, Ltd.
The contents of this publication may not be reproduced in whole or in part,
transcribed, stored, translated, or transmitted in any form or any means, without
the prior written consent of Billion Electric Corporation.
Published by Billion Electric Corporation. All rights reserved.
Disclaimer
Billion does not assume any liability arising out of the application of use of any
products or software described herein. Neither does it convey any license under its
patent rights nor the patent rights of others. Billion reserves the right to make
changes in any products described herein without notice. This publication is subject
to change without notice.
Trademarks
Mac OS is a registered trademark of Apple Computer, Inc.
Windows 98, Windows NT, Windows 2000, Windows Me and Windows XP are
registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
2
Page 3
Safety Warnings
Your BiGuard 50G is built for reliability and long service life. For your
safety, be sure to read and follow the following safety warnings.
• Read this installation guide thoroughly before attempting to set up your BiGuard
50G.
• Your BiGuard 50G is a complex electronic device. DO NOT open or attempt to
repair it yourself. Opening or removing the covers can expose you to high
voltage and other risks. In the case of malfunction, turn off the power
immediately and have it repaired at a qualified service center. Contact your
vendor for details.
• Connect the power cord to the correct supply voltage.
• Carefully place connecting cables to avoid people from stepping or tripping on
them. DO NOT allow anything to rest on the power cord and DO NOT place the
power cord in an area where it can be stepped on.
• DO NOT use BiGuard 50G in environments with high humidity or high
temperatures.
• DO NOT use the same power source for BiGuard 50G as other equipment.
• DO NOT use your BiGuard 50G and any accessories outdoors.
• If you wall mount your BiGuard 50G, make sure that no electrical, water or gas
pipes will be damaged during installation.
• DO NOT install or use your BiGuard 50G during a thunderstorm.
• DO NOT expose your BiGuard 50G to dampness, dust, or corrosive liquids.
• DO NOT use your BiGuard 50G near water.
• Be sure to connect the cables to the correct ports.
• DO NOT obstruct the ventilation slots on your BiGuard 50G or expose it to direct
sunlight or other heat sources. Excessive temperatures may damage your
device.
• DO NOT store anything on top of your BiGuard 50G.
• Only connect suitable accessories to your BiGuard 50G.
• Keep packaging out of the reach of children.
• If disposing of the device, please follow your local regulations for the safe
disposal of electronic products to protect the environment.
3
Page 4

Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Overview
1.2 Product Highlights
1.2.1 Increased Bandwidth, Scalability and Resilience
1.2.2 Virtual Private Network Support
1.2.3 Advanced Firewall Security
1.2.4 Intelligent Bandwidth Management
1.3 Package Contents
1.3.1 Front Panel
1.3.2 Rear Panel
1.3.3 Cabling
Chapter 2: Router Applications
2.1 Overview
2.2 Bandwidth Management with QoS
2.2.1 QoS Technology
2.2.2 QoS Policies for Different Applications
2.2.3 Guaranteed / Maximum Bandwidth
2.2.4 Policy Based Traffic Shaping
2.2.5 Priority Bandwidth Utilization
2.2.6 Management by IP or MAC address
2.2.7 DiffServ (DSCP Marking)
2.2.7 DSCP (Matching)
2.3 Outbound Traffic
2.3.1 Outbound Fail Over
2.3.2 Outbound Load Balancing
2.4 Inbound Traffic
2.4.1 Inbound Fail Over
2.4.2 Inbound Load Balancing
2.5 DNS Inbound
2.5.1 DNS Inbound Fail Over
2.5.2 DNS Inbound Load Balancing
2.6 Virtual Private Networking
2.6.1 General VPN Setup
4
Page 5

2.6.2 VPN Planning - Fail Over
2.6.3 Concentrator
Chapter 3: Getting Started
3.1 Overview
3.2 Before You Begin
3.3 Connecting Your Router
3.4 Configuring PCs for TCP/IP Networking
3.4.1 Overview
3.4.2 Windows XP
3.4.2.1 Configuring
3.4.2.2 Verifying Settings
3.4.3 Windows 2000
3.4.3.1 Configuring
3.4.3.2 Verifying Settings
3.4.4 Windows 98 / ME
3.4.4.1 Installing Components
3.4.4.2 Configuring
3.4.4.3 Verifying Settings
3.5 Factory Default Settings
3.5.1 Username and Password
3.5.2 LAN and WAN Port Addresses
3.6 Information From Your ISP
3.6.1 Protocols
3.6.2 Configuration Information
3.6.2.1 Windows
3.7 Web Configuration Interface
Chapter 4: Router Configuration
4.1 Overview
4.2 Status
4.2.1 ARP Table
4.2.2 Wireless Association
5
Page 6

4.2.3 Routing Table
4.2.4 Session Table
4.2.5 DHCP Table
4.2.6 IPSec Status
4.2.7 PPTP Status
4.2.8 Traffic Statistics
4.2.9 CPU Statistics
4.2.10 System Log
4.3 Quick Start
4.3.1 DHCP
4.3.2 Static IP
4.3.3 PPPoE
4.3.4 PPTP
4.3.5 Big Pond
4.4 Configuration
4.4.1 LAN
4.4.1.1 Ethernet
4.4.1.2 Wireless Security
4.4.1.3 WEP
4.4.1.4 DHCP Server
4.4.1.5 LAN Address Mapping
4.4.2 WAN
4.4.2.1 ISP Settings
4.4.2.1.1 DHCP
4.4.2.1.2 Static IP
4.4.2.1.3 PPPoE
4.4.2.1.4 PPTP
4.4.2.1.5 Big Pond
4.4.2.2 Bandwidth Settings
4.4.2.3 WAN IP Alias
4.4.3 Dual WAN
4.4.3.1 General Settings
4.4.3.2 Outbound Load Balance
4.4.3.3 Inbound Load Balance
4.4.3.4 Protocol Binding
4.4.4 System
4.4.4.1 Time Zone
4.4.4.2 Remote Access
6
Page 7

4.4.4.3 Firmware Upgrade
4.4.4.4 Backup / Restore
4.4.4.5 Restart
4.4.4.6 Password
4.4.5 Firewall
4.4.5.1 Packet Filter
4.4.5.2 URL Filter
4.4.5.3 Ethernet MAC Filter
4.4.5.4 Wireless MAC Filter
4.4.5.5 Block WAN Request
4.4.5.6 Intrusion Detection
4.4.6 VPN
4.4.6.1 IPSec
4.4.6.1.1 IPSec Wizard
4.4.6.1.2 IPSec Policy
4.4.6.2 PPTP
4.4.7 QoS
4.4.8 Virtual Server
4.4.8.1 DMZ
4.4.8.2 Port Forwarding Table
4.4.9 Advanced
4.4.9.1 Static Route
4.4.9.2 Dynamic DNS
4.4.9.3 Device Management
5 Log & Email Alert
5.1 Log Configuration
5.2 System Log Server
5.3 E-Mail Alert
6 Language
6.1 English
6.2 Simplified Chinese
6.3 Traditional Chinese
7 Save Configuration To Flash
8 Logout
Chapter 5: Troubleshooting
5.1 Basic Functionality
7
Page 8

5.1.1 Router Won’t Turn On
5.1.2 LEDs Never Turn Off
5.1.3 LAN or Internet Port Not On
5.1.4 Forgot My Password
5.2 LAN Interface
5.2.1 Can’t Access Router from the LAN
5.2.2 Can’t Ping Any PC on the LAN
5.2.3 Can’t Access Web Configuration Interface
5.2.3.1 Pop-up Windows
5.2.3.2 Javascripts
5.2.3.3 Java Permissions
5.3 WAN Interface
5.3.1 Can’t Get WAN IP Address from the ISP
5.4 ISP Connection
5.5 Problems with Date and Time
5.6 Restoring Factory Defaults
Appendix A: Product Specifications
Appendix B: Customer Support
Appendix C: FCC Interference Statement
8
Page 9

Appendix D: Network, Routing, and Firewall Basics
D.1 Network Basics
D.1.1 IP Addresses
D.1.1.1 Netmask
D.1.1.2 Subnet Addressing
D.1.1.3 Private IP Addresses
D.1.2 Network Address Translation (NAT)
D.1.3 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
D.2 Router Basics
D.2.1 Why use a Router?
D.2.2 What is a Router?
D.2.3 Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
D.3 Firewall Basics
D.3.1 What is a Firewall?
D.3.2.1 Stateful Packet Inspection
D.3.2.2 Denial of Service (DoS) Attack
D.3.2 Why Use a Firewall?
9
Page 10

Appendix E: Virtual Private Networking
E.1 What is a VPN?
E.1.1 VPN Applications
E.2 What is IPSec?
E.2.1 IPSec Security Components
E.2.1.1 Authentication Header (AH)
E.2.1.2 Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP)
E.2.1.3 Security Associations (SA)
10
Page 11

E.2.2 IPSec Mod
E.2.3 Tunnel Mode AH
E.2.4 Tunnel Mode ESP
E.2.5 Internet Key Exchange (IKE)
Appendix F: IPSec Logs and Events
F.1 IPSec Log Event Categories
F.2 IPSec Log Event Table
Appendix G: Bandwidth Management with QoS
G.1 Overview
G.2 What is Quality of Service?
G.3 How Does QoS Work?
G.4 Who Needs QoS?
G.4.1 Home Users
G.4.2 Office Users
Appendix H: Router Setup Examples
H.1 Outbound Fail Over
H.2 Outbound Load Balancing
H.3 Inbound Fail Over
H.4 DNS Inbound Fail Over
H.5 DNS Inbound Load Balancing
H.6 Dynamic DNS Inbound Load Balancing
H.7 VPN Configuration
H.7.1 LAN to LAN
H.7.2 Host to LAN
H.8 IPSec Fail Over (Gateway to Gateway)
H.9 VPN Concentrator
H.10 Protocol Binding
H.11 Intrusion Detection
H.12 PPTP Remote Access by Windows XP
H.13 PPTP Remote Access by BiGuard
11
Page 12

Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Overview
Congratulations on purchasing BiGuard 50G Router from Billion. Combining a router
with an Ethernet network switch, BiGuard 50G is a state-of-the-art device that
provides everything you need to get your network connected to the Internet over
your Cable or DSL connection quickly and easily. The Quick Start Wizard and DHCP
Server will get first-time users up and running with minimal fuss and configuration,
while sophisticated Quality of Service (QoS) and Load Balancing features grant
advanced users total control over their network and Internet connection.
This manual illustrates the many features and functions of BiGuard 50G, and even
takes you through the various ways you can apply this versatile device to your home
or office. Take the time now to familiarize yourself with BiGuard 50G.
1.2 Product Highlights
1.2.1 Increased Bandwidth, Scalability and Resilience
With integrated Dual WAN ports, BiGuard 50G combines two broadband lines such
as DSL or Cable into one Internet connection, providing optimal bandwidth sharing
for multiple PCs on your network, or allowing maximum reliability with network
redundancy. Load Balancing enables BiGuard 50G to efficiently balance network
traffic across two connections, ideal for small-to-medium businesses that require
increased bandwidth, network scalability, and resilience for mission-critical network
and Internet applications. Auto failover can also be configured to ensure smooth,
continuous service should one connection fail, providing maximum business uptime
and productivity, plus uninterrupted service for you and your customers.
1.2.2 Virtual Private Network Support
BiGuard 50G supports comprehensive IPSec & PPTP VPN protocols for businesses to
establish private encrypted tunnels over the Internet to ensure data transmission
security among multiple sites, such as a branch office or dial-up connection. IPSec
VPN is up to 30 simultaneous IPSec VPN connections are possible on BiGuard 50G,
with performance of up to 30Mbps. PPTP VPN is up to 4 simultaneous PPTP VPN
12
Page 13

connections are possible on BiGuard 50G, with performance of up to 10Mbps.
1.2.3 Advanced Firewall Security
Aside from intelligent broadband sharing, BiGuard 50G offers integrated firewall
protection with advanced features to secure your network from outside attacks.
Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI) determines if a data packet is permitted to enter
the private LAN. Denial of Service (DoS) prevents hackers from interrupting
network services via malicious attacks. In addition, BiGuard 50G firewall can be
configured to alert you via email should your network come under fire, offering both
tight network security and peace of mind.
1.2.4 Intelligent Bandwidth Management
BiGuard 50G utilizes Quality of Service (QoS) to give you full control over the
priority of both incoming and outgoing data, ensuring that critical data such as
customer information moves through your network, even while under a heavy load.
Transmission speeds can be throttled to make sure users are not saturating
bandwidth required for mission-critical data transfers. Priority types of upload data
can also be changed, allowing BiGuard 50G to automatically sort out actual speeds
for unmatched convenience.
1.3 Package Contents
BiGuard 50G iBusiness Security Gateway SMB
Getting Started CD-ROM
Quick Start Guide
AC-DC Power Adapter (12VDC, 1A)
1.3.1 Front Panel
13
Page 14

LED Function
Power A solid light indicates a steady connection to a power
source.
Status A blinking light indicates the device is writing to flash
memory.
LAN
1 – 4
Lit when connected to an Ethernet device.
10/100M : Lit green when connected at 100Mbps.
Not lit when connected at 10Mbps.
Link/ACT: Lit when device is connected.
Blinking when data is transmitting/receiving.
WAN1 Lit when connected to an Ethernet device.
10/100M : Lit green when connected at 100Mbps.
Not lit when connected at 10Mbps.
Link/ACT: Lit when device is connected.
Blinking when data is transmitting/receiving.
WAN2 Lit when connected to an Ethernet device.
10/100M : Lit green when connected at 100Mbps.
Not lit when connected at 10Mbps.
Link/ACT: Lit when device is connected.
Blinking when data is transmitting/receiving.
14
Page 15

1.3.2 Rear Panel
Port Function
1
Wireless
Antenna
2 WAN2
3 WAN1
LAN
4
1 — 4
5 RESET
One detachable 2.4GHz 5dbi SMA antenna
WAN2 10/100M Ethernet port (with auto
crossover support); connect xDSL/Cable
modem here.
WAN1 10/100M Ethernet port (with auto
crossover support); connect xDSL/Cable
modem here.
Connect a UTP Ethernet cable (Cat-5 or
Cat-5e) to one of the eight LAN ports when
connecting a PC to the network.
To reset the device and restore factory
default settings, after the device is fully
booted, press and hold RESET until the
Status LED begins to blink.
6 DC12V Connect DC Power Adapter here. (12VDC)
15
Page 16

1.3.4 Cabling
Most Ethernet networks currently use unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cabling. The
UTP cable contains eight conductors, arranged in four twisted pairs, and terminated
with an RJ45 type connector.
One of the most common causes of networking problems is bad cabling. Make sure
that all connected devices are turned on. On the front panel of BiGuard 50G, verify
that the LAN link and WAN line LEDs are lit. If they are not, check to see that you are
using the proper cabling.
16
Page 17

Chapter 2: Router Applications
2.1 Overview
Your BiGuard 50G router is a versatile device that can be configured to not only
protect your network from malicious attackers, but also ensure optimal usage of
available bandwidth with Quality of Service (QoS) and both Inbound and Outbound
Load Balancing. Alternatively, BiGuard 50G can also be set to redirect incoming and
outgoing network traffic with the Fail Over capability, ensuring minimal downtime
and increased reliability.
The following chapter describes how BiGuard 50G can work for you.
2.2 Bandwidth Management with QoS
Quality of Service (QoS) gives you full control over which types of outgoing data
traffic should be given priority by the router. By doing so, the router can ensure that
latency-sensitive applications like voice, bandwidth-consuming data like gaming
packets, or even mission critical files efficiently move through the router even under
a heavy load. You can throttle the speed at which different types of outgoing data
pass through the router. In addition, you can simply change the priority of different
types of upload data and let the router sort out the actual speeds.
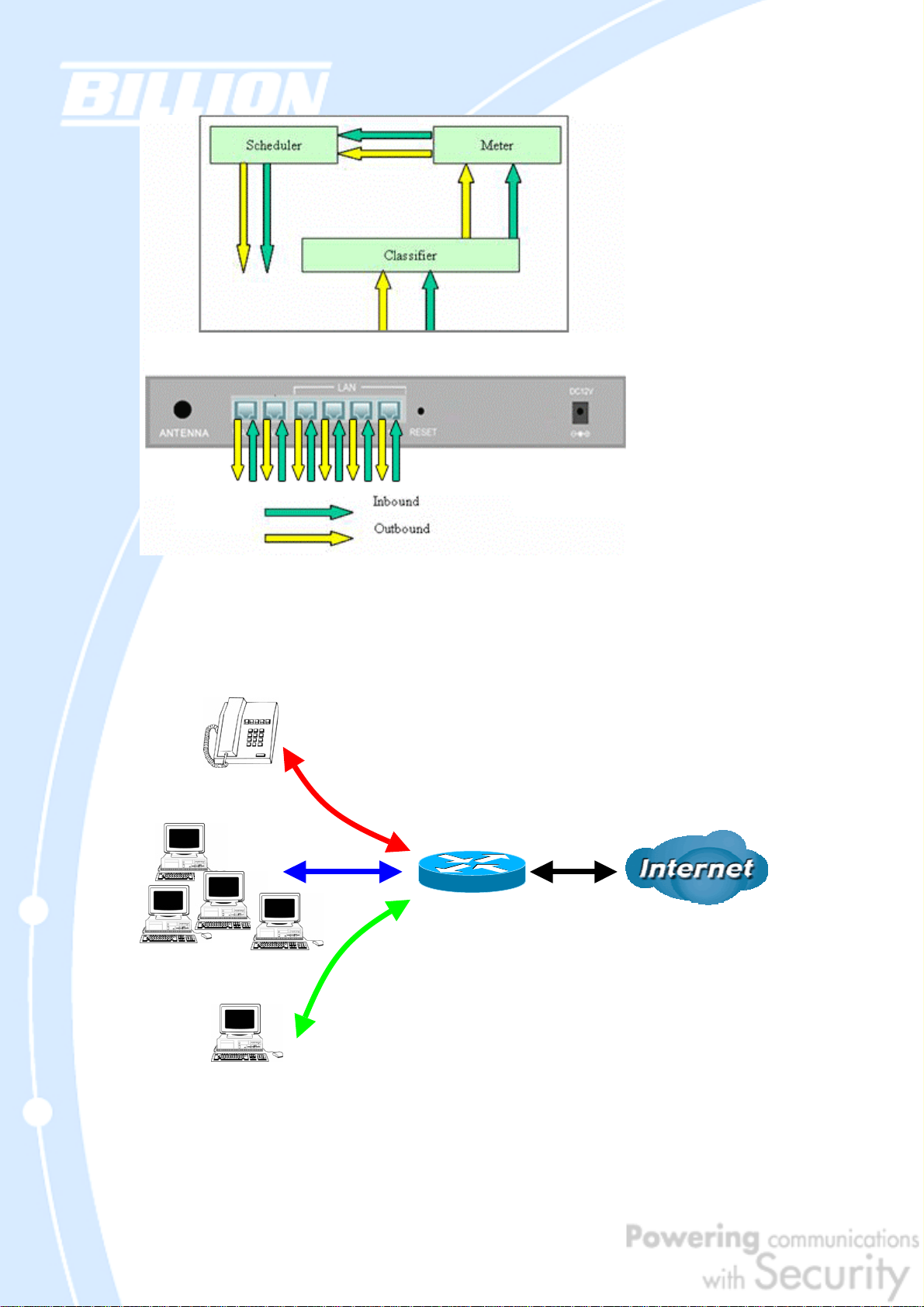
2.2.1 QoS Technology
QoS generally involves the prioritization of network traffic. QoS is comprised of
three major components: Classifier, Met er, a n d Sc h e d ul e r. E ac h o f th e s e
components has a distinct role in ensuring that incoming and outgoing data is
managed according to user specifications.
The Classifier analyses incoming packets and marks each one according to
configured parameters. The Meter communicates the drop priority to the Scheduler
and measures the temporal priorities of the output stream against configured
parameters. Finally, the Scheduler schedules each packet for transmission based on
information from both the Classifier and the Meter.
17
Page 18
2.2.2 QoS Policies for Different Applications
By setting different QoS policies according to the applications you are running, you
can use BiGuard 50G to optimize the bandwidth that is being used on your network.
VoIP
Normal PCs
Restricted PC
As illustrated in the diagram above, applications such as Voiceover IP (VoIP) require
low network latencies to function properly. If bandwidth is being used by other
18
Page 19
applications such as an FTP server, users using VoIP will experience network lag
and/or service interruptions during use. To avoid this scenario, this network has
assigned VoIP with a guaranteed bandwidth and higher priority to ensure smooth
communications. The FTP server, on the other hand, has been given a maximum
bandwidth cap to make sure that regular service to both VoIP and normal Internet
applications is uninterrupted.
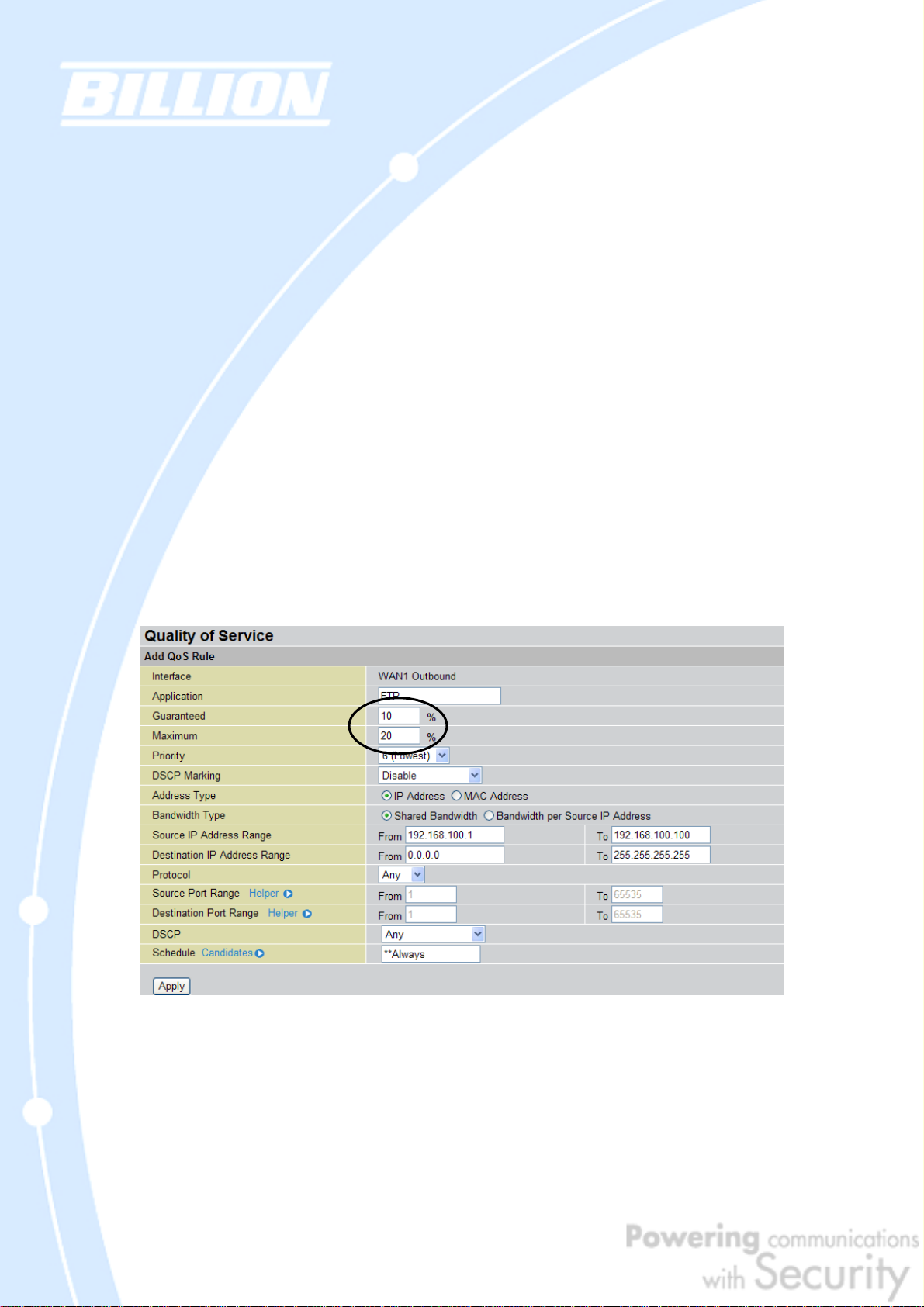
2.2.3 Guaranteed / Maximum Bandwidth
Setting a Guaranteed Bandwidth ensures that a particular service receives a
minimum percentage of bandwidth. For example, you can configure BiGuard 50G to
reserve 10% of the available bandwidth for a particular computer on the network to
transfer files.
Alternatively you can set a Maximum Bandwidth to restrict a particular application
to a fixed percentage of the total throughput. Setting a Maximum Bandwidth of 20%
for a file sharing program will ensure that no more than 20% of the available
bandwidth will be used for file sharing.
2.2.4 Policy Based Traffic Shaping
Policy Based Traffic Shaping allows you to apply specific traffic policies across a
range of IP addresses or ports. This is particularly useful for assigning different
policies for different PCs on the network. Policy based traffic shaping lets you better
19
Page 20

manage your bandwidth, providing reliable Internet and network service to your
organization.
2.2.5 Priority Bandwidth Utilization
Assigning priority to a certain service allows BiGuard 50G to give either a higher or
lower priority to traffic from this particular service. Assigning a higher priority to an
application ensures that it is processed ahead of applications with a lower priority
and vice versa.
20
Page 21

2.2.6 Management by IP or MAC address
BiGuard 50G can also be configured to apply traffic policies based on a particular IP
or MAC address. This allows you to quickly assign different traffic policies to a
specific computer on the network.
DiffServ (DSCP Marking)
DiffServ (a.k.a. DSCP Marking) allows you to classify traffic based on IP DSCP values.
21
Page 22

Other interfaces can match traffic based on the DSCP markings. DSCP markings are
used to decide how packets should be treated, and is a useful tool to give
precedence to varying types of data.
2.2.8 DSCP (Matching)
Just like the DSCP Marking, DSCP is used on traffics (Both inbound rules and
outbound rules have DSCP matching). DSCP matching is used to identify traffic for
the rule. (It is just like what source IP and destination IP do). When this option of the
QoS rule is selected, the QoS rule will only be applied to the packets whose DSCP
field’s IP header matches the criteria selected. These markings can be used to
identify traffic within the network.
2.3 Outbound Traffic
This section outlines some of the ways you can use BiGuard 50G to manage
outbound traffic.
2.3.1 Outbound Fail Over
Configuring BiGuard 50G for Outbound Fail Over allows you to ensure that outgoing
traffic is uninterrupted by having BiGuard 50G default to WAN2 should WAN1 fail.
22
Page 23
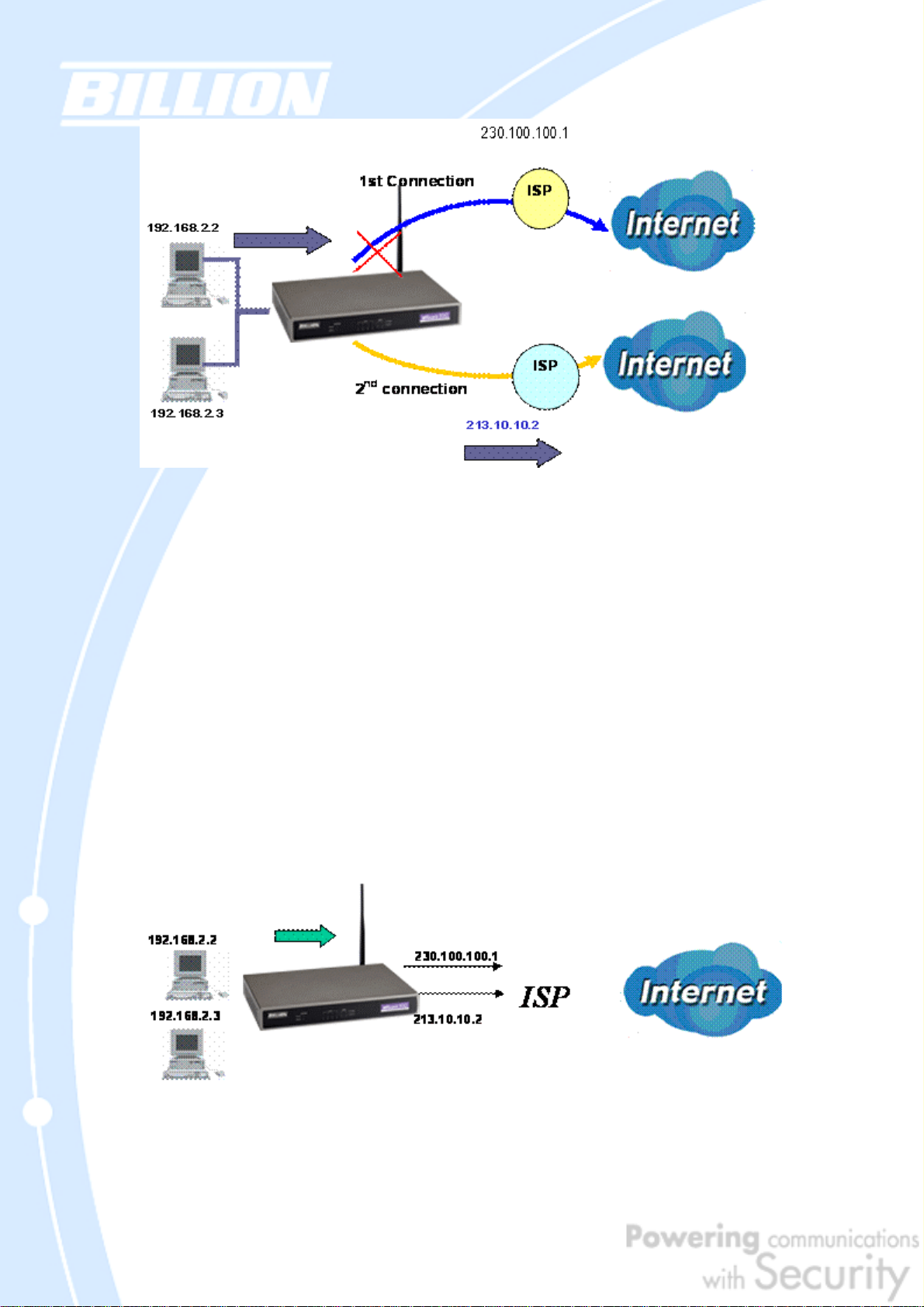
In the above example, PC 1 (IP_192.168.2.2) and PC 2 (IP_192.168.2.3) are
connected to the Internet via WAN1 (IP_230.100.100.1) on BiGuard 50G. Should
WAN1 fail, Outbound Fail Over tells BiGuard 50G to reroute outgoing traffic to WAN2
(IP_213.10.10.2). Configuring your BiGuard 50G for Outbound Fail Over provides a
more reliable connection for your outgoing traffic.
Please refer to appendix H for example settings.
2.3.2 Outbound Load Balancing
Outbound Load Balancing allows BiGuard 50G to intelligently manage outbound
traffic based on the amount of load of each WAN connection.
In the above example, PC 1 (IP_192.168.2.2) and PC 2 (IP_192.168.2.3) are
23
Page 24

connected to the Internet via WAN1 (IP_230.100.100.1) and WAN2
(IP_213.10.10.2) on BiGuard 50G. You can configure BiGuard 50G to balance the
load of each WAN port with one of two mechanisms:
1. Session (by session/by traffic/weight of link capability)
2. IP Hash (by traffic/weight of link capability)
The IP Hash mechanism will ensure that the traffic from the same source IP address
and destination IP address will go through the same WAN port. This is useful for
some server applications that need to identify the source IP address of the client.
By balancing the load between WAN1 and WAN2, your BiGuard 50G can ensure that
outbound traffic is efficiently handled by making sure that both ports are equally
sharing the load, preventing situations where one port is completely saturated by
outbound traffic.
Please refer to appendix H for example settings.
2.4 Inbound Traffic
Learn how BiGuard 50G can handle inbound traffic in the following section.
24
Page 25

2.4.1 Inbound Fail Over
Configuring BiGuard 50G for Inbound Fail Over allows you to ensure that incoming
traffic is uninterrupted by having BiGuard 50G default to WAN2 should WAN1 fail.
In the above example, an FTP Server (IP_192.168.2.2) and an HTTP Server
(IP_192.168.2.3) are connected to the Internet via WAN1 (ftp.billion.dyndns.org)
on BiGuard 50G. A remote computer is trying to access these servers via the
Internet. Under normal circumstances, the remote computer will gain access to the
network via WAN1. Should WAN1 fail, Inbound Fail Over tells BiGuard 50G to
reroute incoming traffic to WAN2 by using the Dynamic DNS mechanism.
Configuring your BiGuard 50G for Inbound Fail Over provides a more reliable
connection for your incoming traffic.
Please refer to appendix H for example settings.
25
Page 26
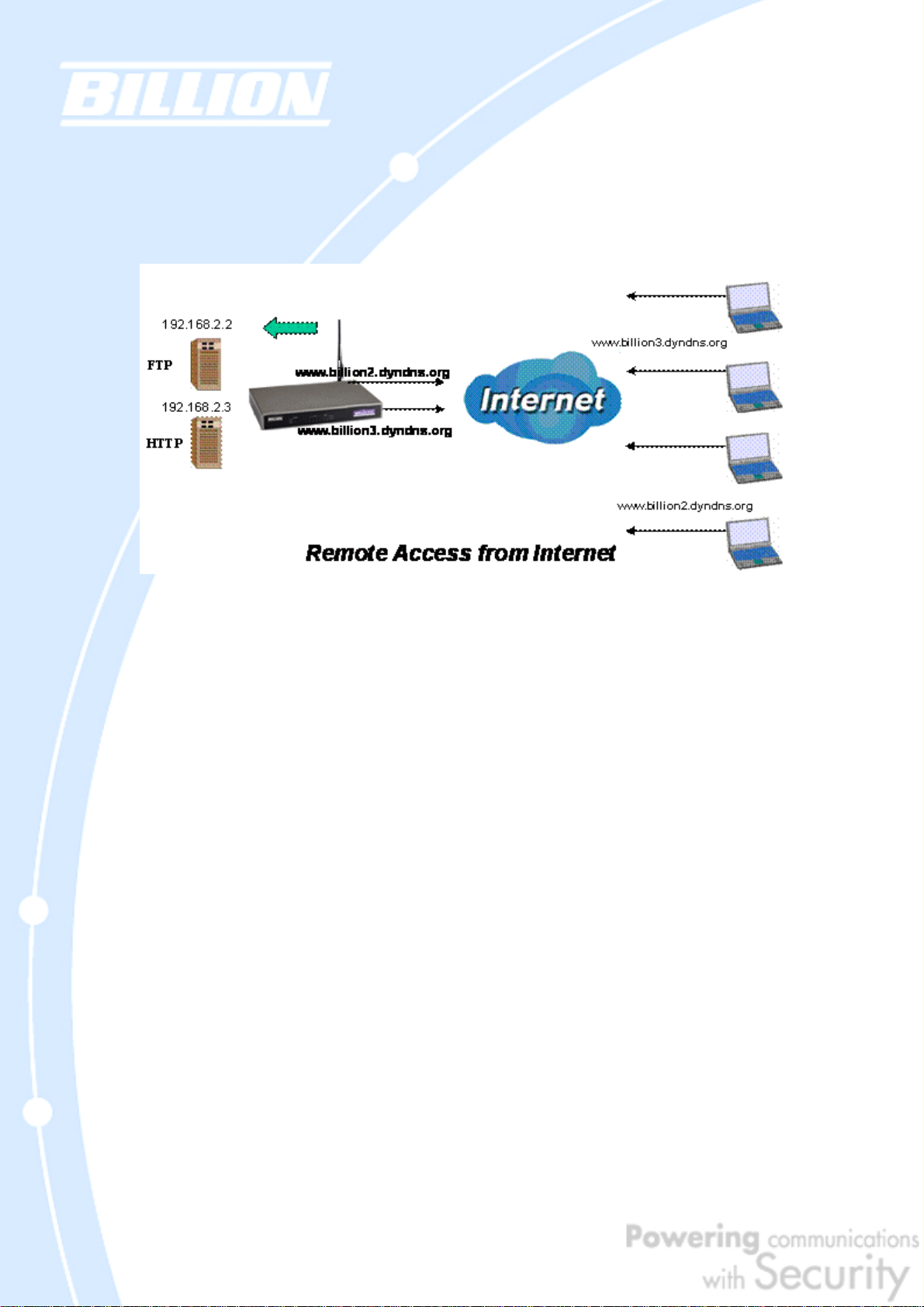
2.4.2 Inbound Load Balancing
Inbound Load Balancing allows BiGuard 50G to intelligently manage inbound traffic
based on the amount of load of each WAN connection.
In the above example, an FTP server (IP_192.168.2.2) and an HTTP server
(IP_192.168.2.3) are connected to the Internet via WAN1
(www.billion2.dyndns.org) and WAN2 (www.billion3.dyndns.org) on BiGuard 50G.
Remote PCs are attempting to access the servers via the Internet. Using Inbound
Load Balancing, BiGuard 50G can direct incoming requests to the correct WAN port
based on group assignment. For example, a sales force can be directed to
www.billion2.dyndns.org, while the R&D group can access www.billion3.dyndns.org.
By balancing the load between WAN1 and WAN2, your BiGuard 50G can ensure that
inbound traffic is efficiently handled with both ports equally sharing the load,
preventing situations where service is slow because one port is completely
saturated by inbound traffic.
Please refer to appendix H for example settings.
26
Page 27

2.5 DNS Inbound
Using DNS Inbound is a great way to intelligently direct network traffic.
DNS Inbound is a three step process. First, a DNS request is made to the router via
a remote PC. BiGuard 50G, based on settings specified by the user, will direct the
requesting PC to the correct WAN port by replying the selected WAN IP address
through the built-in DNS server. The remote PC then accesses the network via the
specified WAN port. How BiGuard 50G directs this traffic through the built-in DNS
server depends on whether it is configured for Fail Over or Load Balancing.
Learn how to make DNS Inbound on BiGuard 50G work for you in the following
section.
27
Page 28
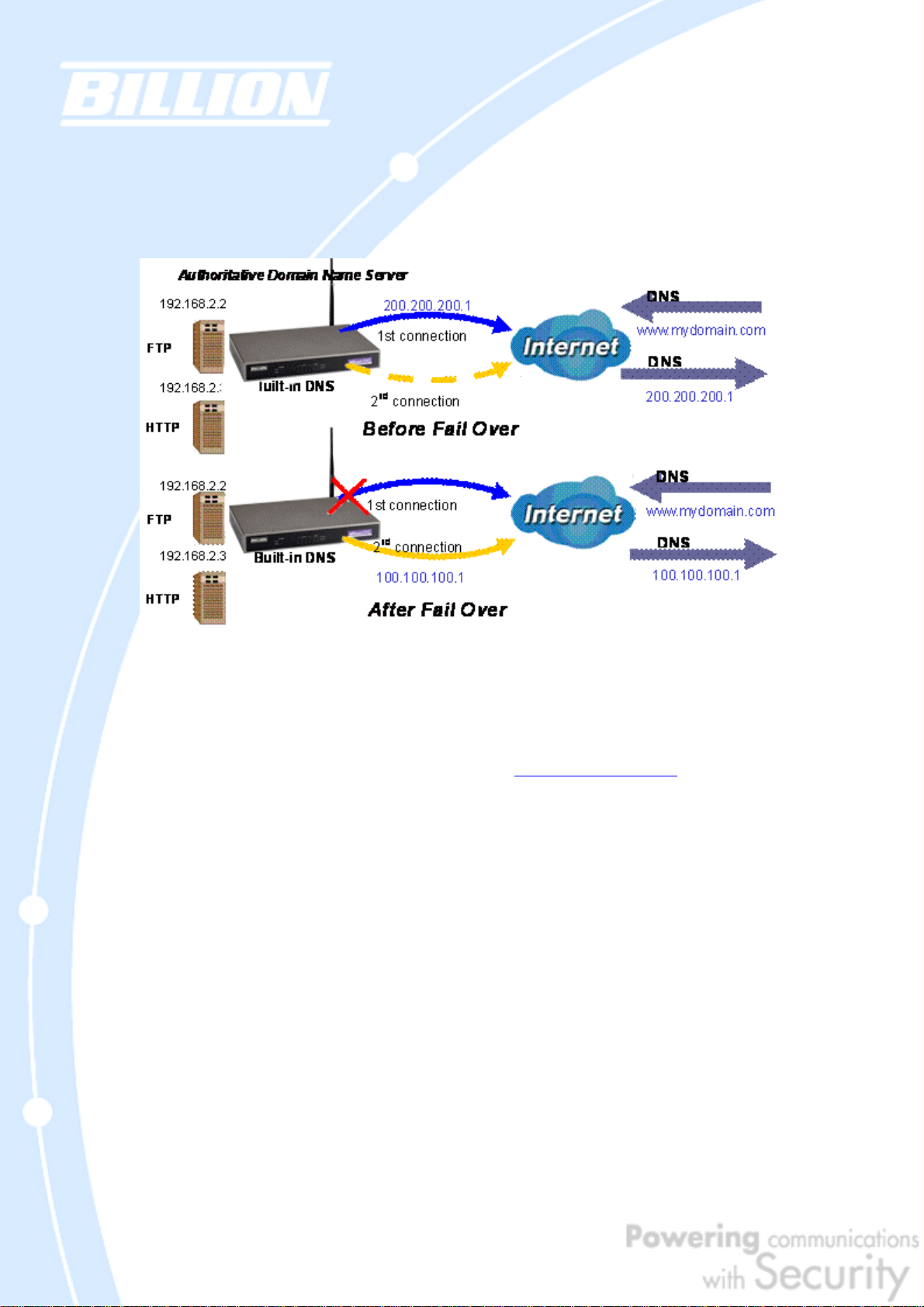
2.5.1 DNS Inbound Fail Over
BiGuard 50G can be configured to reply the WAN2 IP address for the DNS domain
name request should WAN1 fail.
In the above example, an FTP Server (IP_192.168.2.2) and an HTTP Server
(IP_192.168.2.3) are connected to the Internet via WAN1 (IP_200.200.200.1) on
BiGuard 50G. A remote computer is trying to access these servers via the Internet,
and makes a DNS request. The DNS request (www.mydomain.com
through WAN1 (200.200.200.1) to the built-in DNS server. The DNS server will reply
200.200.200.1 because this is the only active WAN port. Should WAN1 fail, BiGuard
50G will instead reply with WAN2’s IP address (100.100.100.1), and the remote PC
will gain access to the network via WAN2. By configuring BiGuard 50G for DNS
Inbound Fail Over, incoming requests will enjoy increased reliability when accessing
your network.
Please refer to appendix H for example settings.
) will be sent
28
Page 29
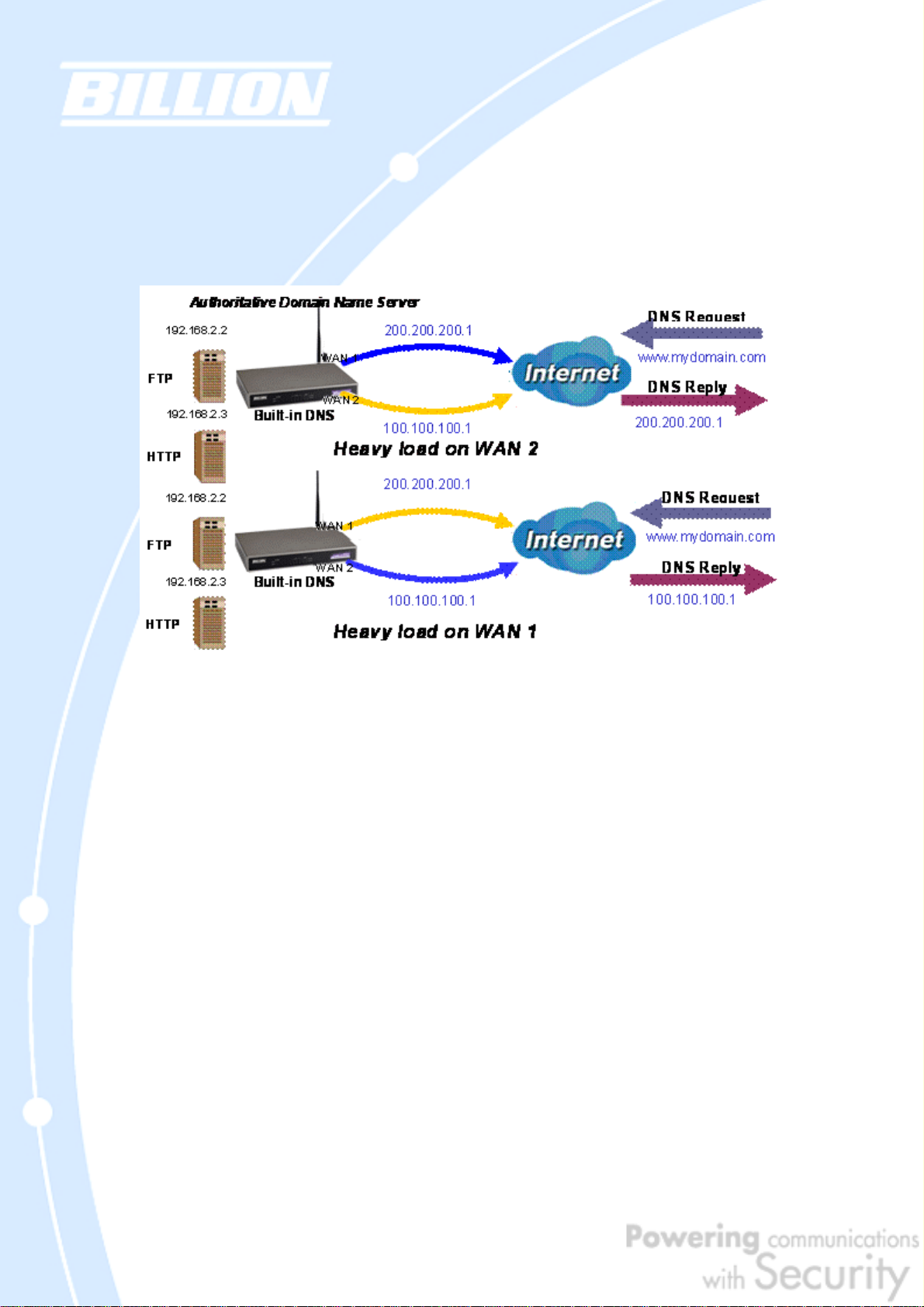
2.5.2 DNS Inbound Load Balancing
DNS Inbound Load Balancing allows BiGuard 50G to intelligently manage inbound
traffic based on the amount of load of each WAN connection by assigning the IP
address with the lowest traffic load to incoming requests.
In the above example, an FTP server (IP_192.168.2.2) and an HTTP server
(IP_192.168.2.3) are connected to the Internet via WAN1 (IP_200.200.200.1) and
WAN2 (IP_100.100.100.1) on BiGuard 50G. Remote PCs are attempting to access
the servers via the Internet by making a DNS request, entering a URL
(www.mydomain.com). Using a load balancing algorithm, BiGuard 50G can direct
incoming requests to either WAN port based on the amount of load each WAN port
is currently experiencing. If WAN2 is experiencing a heavy load, BiGuard 50G
responds to incoming DNS requests with WAN1. By balancing the load between
WAN1 and WAN2, your BiGuard 50G can ensure that inbound traffic is efficiently
handled, making sure that both ports are equally sharing the load and preventing
situations where service is slow because one port is completely saturated by
inbound traffic.
Please refer to appendix H for example settings.
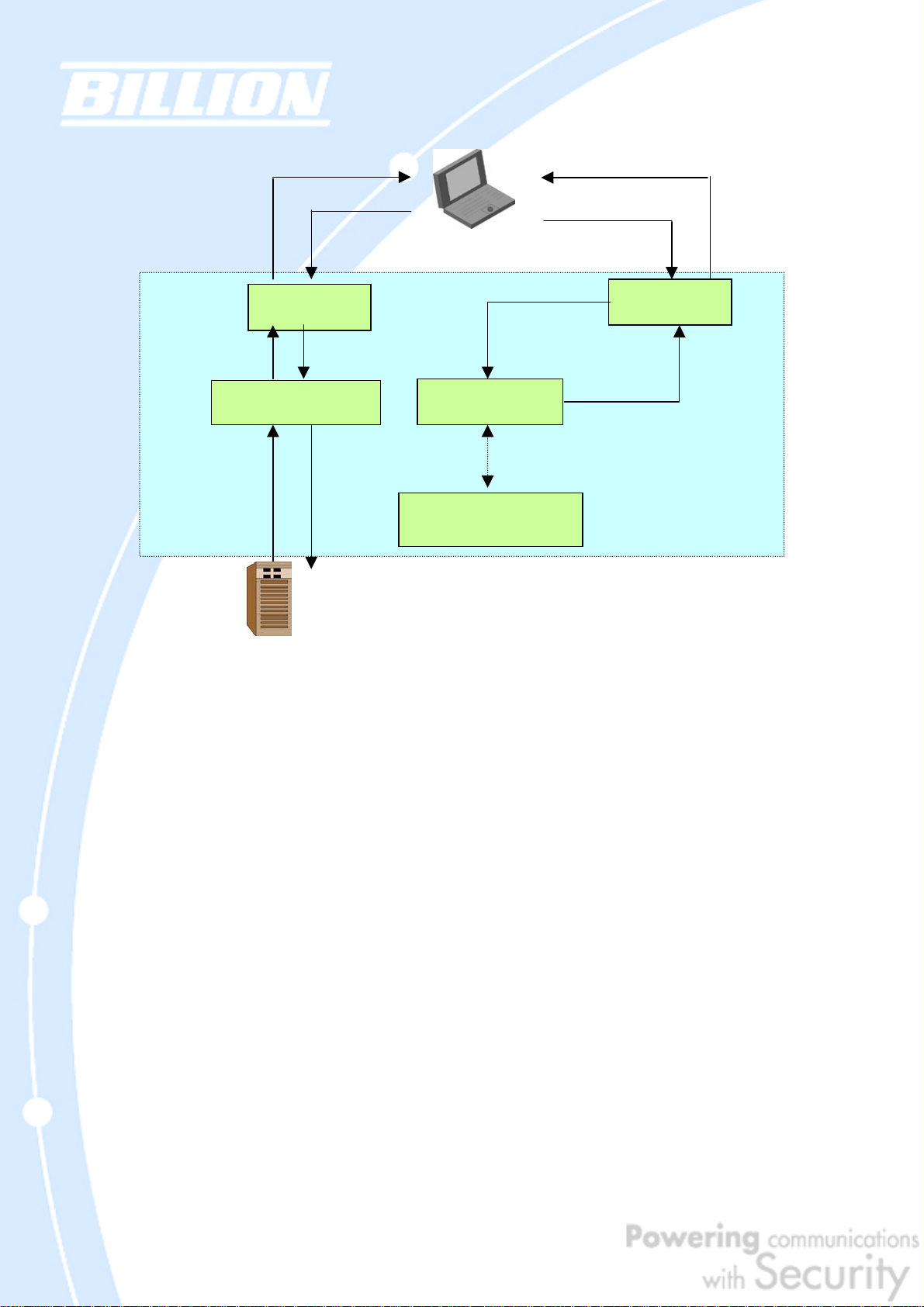
A typical scenario of how traffic is directed with DNS Inbound Load Balancing is
illustrated below:
29
Page 30
y
r
11
HTTP Repl
HTTP Request
6
WAN 1
10
7
URL Host Map
9
8
1
DNS Request
2
DNS Server
3
Bandwidth Monitor
DNS Reply
5
WAN 2
4
HTTP Serve
In the example above, the client is making a DNS request. The request is sent to the
DNS server of BiGuard 50G through WAN2 (1). WAN2 will route this request to the
embedded DNS server of BiGuard 50G (2). BiGuard 50G will analyze the bandwidth
of both WAN1 and WAN2 and decide which WAN IP to reply to the request (3). After
the decision is made, BiGuard 50G will route the DNS reply to the user through
WAN2 (4). The user will receive the DNS reply with the IP address of WAN1 (5). The
browser will initiate an HTTP request to the WAN1 IP address (6). The HTTP request
will be send to BiGuard 50G’s URL Host Map (7). The Host Map will then redirect the
HTTP request to the HTTP server (8). The HTTP server will reply (9). The URL Host
Map will route the packet through WAN1 to the user (10). Finally, the client will
receive an HTTP reply packet (11).
30
Page 31

2.6 Virtual Private Networking
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) enables you to send data between two computers
across a shared or public network in a manner that emulates the properties of a
point-to-point private link. As such, it is perfect for connecting branch offices to
headquarters across the Internet in a secure fashion.
The following section discusses Virtual Private Networking with BiGuard 50G.
2.6.1 General VPN Setup
There are typically three different VPN scenarios. The first is a Gateway to
Gateway setup, where two remote gateways communicate over the Internet via a
secure tunnel.
The next type of VPN setup is the Gateway to Multiple Gateway setup, where one
gateway (Headquarters) is communicating with multiple gateways (Branch Offices)
over the Internet. As with all VPNs, data is kept secure with secure tunnels.
The final type of VPN setup is the Client to Gateway. A good example of where this
can be applied is when a remote sales person accesses the corporate network over
a secure VPN tunnel.
31
Page 32

VPN provides a flexible, cost-efficient, and reliable way for companies of all sizes to
stay connected. One of the most important steps in setting up a VPN is proper
planning. The following sections demonstrate the various ways of using BiGuard
50G to setup your VPN.
2.6.2 VPN Planning - Fail Over
Configuring your VPN with Fail Over allows BiGuard 50G to automatically default to
WAN2 should WAN1 fail.
Because the dynamic domain name biguard.billion.com is configured for both WAN1
and WAN2, the active WAN port will announce the domain name through the WAN IP
address. The remote gateway will then be able to connect to the VPN through the
domain name.
In this Gateway to Gateway example, BiGuard 50G is communicating to a remote
32
Page 33

gateway using WAN1 through a secure VPN tunnel. Should WAN1 fail, outbound
traffic from BiGuard 50G will automatically be redirected to WAN2. This process is
completely transparent to the remote gateway, as BiGuard 50G will automatically
update the domain name (biguard.billion.com) with the WAN2 IP address.
Configuring a Gateway to Multiple Gateway setup with Fail Over is similar, as shown
below:
Configuring BiGuard 50G for Fail Over provides added reliability to your VPN.
33
Page 34

2.6.3 Concentrator
The VPN Concentrator provides an easy way for branch offices to connect to
headquarter through a VPN tunnel. All branch office traffic will be redirected to the
VPN tunnel to headquarter with the exception of LAN-side traffic. This way, all
branch offices can connect to each other through headquarter via the headquarter’s
firewall management. You can also configure BiGuard 50G to function as a VPN
Concentrator:
Please refer to appendix H for example settings.
34
Page 35

Chapter 3: Getting Started
3.1 Overview
BiGuard 50G is designed to be a powerful and flexible network device that is also
easy to use. With an intuitive web-based configuration, BiGuard 50G allows you to
administer your network via virtually any Java-enabled web browser and is fully
compatible with Linux, Mac OS, and Windows 98/Me/NT/2000/XP operating
systems.
The following chapter takes you through the very first steps to configuring your
network for BiGuard 50G. Take a look and see how easy it is to get your network up
and running.
3.2 Before You Begin
BiGuard 50G is a flexible and powerful networking device. To simplify the
configuration process and increase the efficiency of your network, consider the
following items before setting up your network for the first time:
1. Plan your network
Decide whether you are going to use one or both WAN ports. For one WAN port, you
may need a fully qualified domain name either for convenience or if you have a
dynamic IP address. If you are going to use both WAN ports, determine whether you
are going to use them in fail over mode for increased network reliability or load
balancing mode for maximum bandwidth efficiency. See Chapter 2: Router
Applications for more information.
2. Set up your accounts
Have access to the Internet and locate the Internet Service Provider (ISP)
configuration information. Each BiGuard 50G WAN port must be configured
separately, whether you are using a separate ISP for each WAN port or are having
the traffic of both WAN ports routed through the same ISP.
3. Determine your network management approach
BiGuard 50G is capable of remote management. However, this feature is not active
by default. If you reset the device, remote administration must be enabled again. If
you decide to manage your network remotely, be sure to change the default
35
Page 36

password for security reason.
4. Prepare to physically connect BiGuard 50G to Cable or DSL modems and a
computer.
Be sure to also review the Safety Warnings located in the preface of this manual
before working with your BiGuard 50G.
3.3 Connecting Your Router
Connecting BiGuard 50G is an easy three-step process:
1. Connect BiGuard 50G to your LAN by connecting Ethernet cables from your
networked PCs to the LAN ports on the router. Connect BiGuard 50G to your
broadband Internet connection via router’s WAN port.
2. Plug BiGuard 50G to an AC outlet with the included AC Power Adapter.
3. Ensure that the Power and WAN LEDs are solidly lit, and that on any LAN port that
has an Ethernet cable plugged in the LED is also solidly lit. The Status LED will
remain solid as the device boots. Once the boot sequence is complete, the LED will
shut off, indicating that BiGuard 50G is ready.
If the router does not power on, please refer to Chapter 5: Troubleshooting for
possible solutions.
36
Page 37

3.4 Configuring PCs for TCP/IP Networking
Now that your BiGuard 50G is connected properly to your network, it’s time to
configure your networked PCs for TCP/IP networking.
In order for your networked PCs to communicate with your router, they must have
the following characteristics:
1. Have a properly installed and functioning Ethernet Network Interface Card (NIC).
2. Be connected to BiGuard 50G, either directly or through an external repeater hub
via an Ethernet cable.
3. Have TCP/IP installed and configured with an IP address.
The IP address for each PC may be a fixed IP address or one that is obtained from a
DHCP server. If using a fixed IP address, it is important to remember that it must be
in the same subnet as the router. The default IP address of BiGuard 50G is
192.168.1.254 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0. Using the default
configuration, networked PCs must reside in the same subnet, and have an IP
address in the range of 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.253. However, you’ll find that the
quickest and easiest way to configure the IP addresses for your PCs is to obtain the
IP addresses automatically by using the router as a DHCP server.
If you are unable to access the web configuration interface, check to see if you have
any software-based firewalls installed on your PCs, as they can cause problems
accessing the 192.168.1.254 IP address of BiGuard 50G.
The following sections outline how to set up your PCs for TCP/IP networking. Refer
to the applicable section for your PC’s operating system.
3.4.1 Overview
Before you begin, make sure that the TCP/IP protocol and a functioning Ethernet
network adapter is installed on each of your PCs.
The following operating systems already include the necessary software
components you need to install TCP/IP on your PCs:
37
Page 38

- Windows 95/98/Me/NT/2000/XP
- Mac OS 7 and later
If you are using Windows 3.1, you must purchase a third-party TCP/IP application
package.
Any TCP/IP capable workstation can be used to communicate with or through
BiGuard 50G. To configure other types of workstations, please consult the
manufacturer’s documentation.
3.4.2 Windows XP
3.4.2.1 Configuring
1. Select Start > Settings > Network Connections.
2. In the Network Connections window, right-click Local Area Connection and
select Properties.
38
Page 39

3. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click Properties.
4a. To have your PC obtain an IP address automatically, select the Obtain an IP
39
Page 40

address automatically and Obtain DNS server address automatically radio
buttons.
4b. To manually assign your PC a fixed IP address, select the Use the followin g IP
address radio button and enter your desired IP address, subnet mask, and default
gateway in the blanks provided. Remember that your PC must reside in the same
subnet mask as the router. To designate a DNS server, select the Use the following
DNS server and fill in the preferred DNS address.
5. Click OK to finish the configuration.
40
Page 41

3.4.2.2 Verifying Settings
To verify your settings using a command prompt:
1. Click Start > Programs > Accessories > Command Prompt.
2. In the Command Prompt window, type ipconfig and then press ENTER.
If you are using BiGuard 50G’s default settings, your PC should have:
41
Page 42

- An IP address between 192.168.1.1 and 192.168.1.253
- A subnet mask of 255.255.255.0
To verify your settings using the Windows XP GUI:
1. Click Start > Settings > Network Connections.
42
Page 43

2. Right click one of the network connections listed and select Status from the
pop-up menu.
3. Click the Support tab.
43
Page 44

If you are using BiGuard 50G’s default settings, your PC should:
- Have an IP address between 192.168.1.1 and 192.168.1.253
- Have a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0
3.4.3 Windows 2000
3.4.3.1 Configuring
1. Select Start > Settings > Control Panel.
44
Page 45

2. In the Control Panel window, double-click Network and Dial-up Connections.
3. In Network and Dial-up Connections, double-click Local Area Connection.
45
Page 46

4. In the Local Area Connection window, click Properties.
5. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click Properties.
46
Page 47

6a. To have your PC obtain an IP address automatically, select the Obtain an IP
address automatically and Obtain DNS server address automatically radio
buttons.
6b. To manually assign your PC a fixed IP address, select the Use the following IP
address radio button and enter your desired IP address, subnet mask, and default
gateway in the blanks provided. Remember that your PC must reside in the same
subnet mask as the router. To designate a DNS server, select the Use the following
DNS server and fill in the preferred DNS address.
47
Page 48

7. Click OK to finish the configuration.
48
Page 49

3.4.3.2 Verifying Settings
1. Click Start > Programs > Accessories > Command Prompt.
2. In the Command Prompt window, type ipconfig and then press ENTER.
If you are using BiGuard 50G’s default settings, your PC should have:
- An IP address between 192.168.1.1 and 192.168.1.253
49
Page 50

- A subnet mask of 255.255.255.0
3.4.4 Windows 98 / Me
3.4.4.1 Installing Components
To prepare Windows 98/Me PCs for TCP/IP networking, you may need to manually
install TCP/IP on each PC. To do this, follow the steps below. Be sure to have your
Windows CD handy, as you may need to insert it during the installation process.
1. On the Windows taskbar, select Start > Settings > Control Panel.
2. Double-click the Network icon. The Network window displays a list of installed
components.
50
Page 51

You must have the following installed:
51
Page 52

- An Ethernet adapter
- TCP/IP protocol
- Client for Microsoft Networks
If you need to install a new Ethernet adapter, follow these steps:
a. Click Add.
b. Select Adapter, then Add.
c. Select the manufacturer and model of your Ethernet adapter, then click OK.
52
Page 53

If you need TCP/IP:
a. Click Add.
53
Page 54

b. Select Protocol, then click Add.
c. Select Microsoft. Æ TCP/IP, then OK.
If you need Client for Microsoft Networks:
a. Click Add.
54
Page 55

b. Select Client, then click Add.
c. Select Microsoft. Æ Client for Microsoft Networks, and then click OK.
3. Restart your PC to apply your changes.
3.4.4.2 Configuring
1. Select Start > Settings > Control Panel.
55
Page 56

2. In the Control Panel, double-click Network and choose the Configuration tab.
56
Page 57

3. Select TCP / IP > ASUSTek or the name of any Network Interface Card (NIC) in
your PC and click Properties.
4. Select the IP Address tab and click the Obtain an IP address automatically
radio button.
57
Page 58

5. Select the DNS Configuration tab and select the Disable DNS radio button.
6. Click OK to apply the configuration.
58
Page 59

3.4.4.3 Verifying Settings
To check the TCP/IP configuration, use the winipcfg.exe utility:
1. Select Start > Run.
2. Type winipcfg, and then click OK.
3. From the drop-down box, select your Ethernet adapter.
59
Page 60

The window is updated to show your settings. Using the default BiGuard 50G
settings, your PC should have:
- An IP address between 192.168.1.1 and 192.168.1.253
- A subnet mask of 255.255.255.0
- A default gateway of 192.168.1.254
3.5 Factory Default Settings
Before configuring your BiGuard 50G, you need to know the following default
settings:
Web Interface:
Username: admin
Password: admin
LAN Device IP Settings:
IP Address: 192.168.1.254
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
60
Page 61

ISP setting in WAN site:
Obtain an IP Address automatically (DHCP Client)
DHCP server:
DHCP server is enabled.
Start IP Address: 192.168.1.100
End IP Address: 192.168.1.199
3.5.1 User Name and Password
The default user name and password are "admin" and "admin" respectively.
If you ever forget your user name and/or password, you can restore your BiGuard
50G to its factory settings by holding the Reset button on the back of your router
until the Status LED begins to blink. Please note that doing this will also erase any
previous router settings that you have made. The Status LED will remain solid as the
device boots. Once the boot sequence is complete, the LED will shut off, indicating
that BiGuard 50G is ready.
3.5.2 LAN and WAN Port Addresses
The default values for LAN and WAN ports are shown below:
LAN Port WAN Port
IP address 192.168.1.254
The DHCP Client is enabled
to automatically get the
Subnet
Mask
DHCP server
255.255.255.0
Enabled
WAN port configuration
from the ISP.
function
IP
addresses
for
distribution
to PCs
100 IP addresses
continuing from
192.168.1.100
through
192.168.1.199
61
Page 62

3.6 Information From Your ISP
3.6.1 Protocols
Before configuring this device, you have to check with your ISP (Internet Service
Pr ovider) t o find out what kind of service is provided such as DHCP, Static IP, PPPoE,
or PPTP. The following table outlines each of these protocols:
Configure this WAN interface to use DHCP client
DHCP
Static IP
PPPoE
PPTP
protocol to get an IP address from your ISP
automatically. Your ISP provides an IP address to the
router dynamically when logging in.
Configure this WAN interface with a specific IP
address. This IP address should be provided by your
ISP.
PPPoE (PPP over Ethernet) is known as a dial-up DSL
or cable service. It is designed to integrate the
broadband services into the current widely deployed,
easy-to-use, and low-cost dial-up-access networking
infrastructure.
If your ISP provides a PPTP connection, you can use
the PPTP protocol to establish a connection to your
ISP.
Big Pond The Big Pond login for Telstra cable in Australia.
If your account uses PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE), you will need to enter your login
name and password when configuring your BiGuard 50G. After the network and
firewall are configured, BiGuard 50G will login automatically, and you will no longer
need to run the login program from your PC.
62
Page 63

3.6.2 Configuration Information
If your ISP does not dynamically assign configuration information but instead uses
fixed configurations, you will need the following basic information from your ISP:
- An IP address and subnet mask
- A gateway IP address
- One or more domain name server (DNS) IP addresses
Depending on your ISP, a host name and domain suffix may also be provided. If any
of these items are dynamically supplied by the ISP, your BiGuard 50G will
automatically acquire them.
If an ISP technician configured your computer or if you configured it using
instructions provided by your ISP, you need to copy the configuration information
from your PC’s Network TCP/IP Properties window before reconfiguring your
computer for use with BiGuard 50G. The following sections describe how you can
obtain this information.
3.6.2.1 Windows
This section uses illustrations from Windows XP. However, other versions of
Windows will follow a similar procedure. Have your Windows CD handy, as it may be
required during the configuration process.
1. Select Start > Settings > Control Panel.
63
Page 64

2. Double-click the Network icon.
3. In the Network Connections window, right-click Local Area Connection and
select Properties.
64
Page 65

4. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click Properties.
5. If an IP address, subnet mask and a Default gateway are shown, write down
the information. If no address is present, your account’s IP address is dynamically
65
Page 66

assigned. Click the Obtain an IP address automatically radio button.
6. If any DNS server addresses are shown, write them down. Click the Obtain DNS
server address automatically radio button.
7. Click OK to save your changes.
66
Page 67

3.7 Web Configuration Interface
BiGuard 50G includes a Web Configuration Interface for easy administration via
virtually any browser on your network. To access this interface, open your web
browser, enter the IP address of your router, which by default is 192.168.1.254, and
click Go. A user name and password window prompt will appear. Enter your user
name and password (the default user name and password are "admin" and "admin")
to access the Web Configuration Interface.
67
Page 68

If the Web Configuration Interface appears, congratulations! You are now ready to
configure your BiGuard 50G. If you are having trouble accessing the interface,
please refer to Chapter 5: Troubleshooting for possible resolutions.
68
Page 69

Chapter 4: Router Configuration
4.1 Overview
The Web Configuration Interface makes it easy for you to manage your network via
any PC connected to it. On the Web Configuration homepage, you will see the
navigation pane located on the left hand side. From it, you will be able to select
various options used to configure your router.
1. Click Apply if you would like to apply the settings on the current screen to the
device. The settings will be effective immediately, however the configuration is not
saved yet and the settings will be erased if you power off or restart the device.
2. Click SAVE CONFIG to save the current settings permanently to the device.
3. Click RESTART to restart the device. There are two options to restart the device.
- Select Current Settings if would like to restart using the current configuration.
- Select Factory Default Settings if you would like to restart using the factory
default configuration.
4. To exit the router’s web interface, click LOGOUT. Please ensure that you have
saved your configuration settings before you logout. Be aware that the router is
69
Page 70

restricted to only one PC accessing the web configuration interface at a time. Once
a PC has logged into the web interface, other PCs cannot gain access until the
current PC has logged out. If the previous PC forgets to logout, the second PC can
access the page after a user-defined period (5 minutes by default).
The following sections will show you how to configure your router using the Web
Configuration Interface.
4.2 Status
The Status menu displays the various options that have been selected and a number
of statistics about your BiGuard 50G.
70
Page 71

Device Information
Device Name: Displays the device name.
System Up Time: System uptime enables a user to determine how long has
the system being online or the time that an unexpected restart or fault occurred.
The system up-time is restarted when there is a power failure or upon software or
hardware reset.
Registration: Click on the Register button to open a web page on Billion’s
website to register the BiGuard 50G. Registration enables users to access new
firmware, a user’s manual, latest product news, quick customer support, and FAQ.
Failover Status: Displays the current Failover port and show whether it is
active or inactive.
Current Time: Displays the current time.
PrivateLAN MAC address: Displays the LAN MAC address for the LAN ports.
PublicWAN1 MAC address: Displays the WAN MAC address for the WAN1.
PublicWAN2 MAC address: Displays the WAN MAC address for the WAN2.
Firmware Version: Displays the current firmware version for the device.
Home URL: Displays the manufacturers website.
LAN
IP address: Displays the IP address of your device. You can click on the link
to edit the IP address and the gateway IP.
Netmask: Displays the subnet mask for the LAN.
DHCP Server: Displays whether DHCP server is enabled or not. You can click
on the link to edit the DHCP server.
WAN1
Connection Method: Displays the connection method for WAN1.
IP address: Displays the IP address for WAN1.
Netmask: Displays the subnet mask for WAN1.
Gateway: Displays the gateway for WAN1.
DNS Server: Displays the DNS Server for WAN1.
Up Time: Displays the time that WAN1 has been connected.
WAN2
Connection Method: Displays the connection method for WAN2.
IP address: Displays the IP address for WAN1.
Netmask: Displays the subnet mask for WAN2.
Gateway: Displays the gateway for WAN2.
DNS Server: Displays the DNS Server for WAN2.
Up Time: Displays the time that WAN2 has been connected.
71
Page 72

In this menu, you will find the following sections:
- ARP Table
- Wireless Association
- Routing Table
- Session Table
- DHCP Table
- IPSec Status
- PPTP Status
- Traffic Statistics
- CPU Status
- System Log
72
Page 73

4.2.1 ARP Table
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Table shows the mapping of Internet (IP)
addresses to Ethernet (MAC) addresses. This is a quick way to determine the MAC
address of your PC’s network interface to use with the router’s Firewall – MAC
Address Filter function. See the Firewall section of this chapter for more
information on this feature.
No.: Number of the list.
IP Address: A list of IP addresses of devices on your LAN.
MAC Address: The Media Access Control (MAC) addresses for each device on your
LAN.
Interface: The interface name (on the router) that this IP address connects to.
Static: Static status of the ARP table entry.
NO indicates dynamically-generated ARP table entries.
YES indicates static ARP table entries added by the user.
4.2.2 Wireless Association
The Wireless Association Table displays the wireless client’s MAC address with its
corresponding IP address.
IP Address: A list of IP addresses of devices on your WLAN.
MAC Address: The Media Access Control (MAC) addresses for each device on your
WLAN.
73
Page 74

4.2.3 Routing Table
The Routing Table displays the current path for transmitted packets. Both static and
dynamic routes are displayed.
No.: Number of the list.
Destination: The IP address of the destination network.
Netmask: The destination netmask address.
Gateway/Interface: The IP address of the gateway or existing interface that this
route will use.
Cost: The number of hops counted as the cost of the route.
4.2.4 Session Table
The NAT Session Table displays a list of current sessions for both incoming and
outgoing traffic with protocol type, source IP, source port, destination IP and
destination port, each page shows 10 sessions.
No.: Number of the list.
Protocol: Protocol type of the Session.
From IP: Source IP of the session.
From Port: source port of the session.
To IP: Destination IP of the session.
To Port: Destination port of the session.
74
Page 75

Sessions:
Filter: when the presented field is filled, please click Filter button.
From IP: please input the source IP you would like to filter.
From Port: please input the source port you would like to filter.
To IP: please input the destination IP you would like to filter.
To Port: please input the destination port you would like to filter.
First: To the first page.
Previous: To the previous page.
Next: To the next page.
Last: To the last page.
Jump to the session: please input the session number you would like to see and
press “GO”
4.2.5 DHCP Table
The DHCP Table displays a list of IP addresses that have been assigned to PCs on
your network via Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
No.: Number of the list.
IP Address: A list of IP addresses of devices on your LAN.
Device Name: The host name (computer name) of the client.
MAC Address: The MAC address of client.
Lease Time: The connection time to the DHCP server.
4.2.6 IPSec Status
The IPSec Status window displays the status of the IPSec Tunnels that are currently
configured on your BiGuard 50G.
75
Page 76

Name: The name you assigned to the particular IPSec entry.
Enable: Whether the IPSec connection is currently Enable or Disable.
Status: Whether the IPSec is Active, Inactive or Disable.
Local Subnet: The local IP address or subnet used.
Remote Subnet: The subnet of the remote site.
Remote Gateway: The remote gateway IP address.
SA: The Security Association for this IPSec entry.
Action: Manually connect or drop the tunnel.
4.2.7 PPTP Status
The PPTP Status window displays the status of the PPTP Tunnels that are currently
configured on your BiGuard 50G.
Name: The name you assigned to the particular PPTP entry.
Enable: Whether the PPTP connection is currently Enable or Disable.
Status: Whether the PPTP is Active, Inactive or Disable.
Type: Whether the Connection type is Remote Access or LAN to LAN
Peer Network: The Remote subnet for LAN to LAN as connection type.
Connect by: The remote address when connected.
Action: Manually drop the tunnel.
4.2.8 Traffic Statistics
The Traffic Statistics window displays both sent and received sent data (in Bytes/sec)
over a one hour duration. The line in red represents WAN1, while the line in blue
represents WAN2.
76
Page 77

WAN1: Transmitted (Tx) and Received (Rx) bytes and packets for WAN1.
WAN2: Transmitted (Tx) and Received (Rx) bytes and packets for WAN2.
Display: Allows you to change the units of measurement for the traffic graph.
4.2.9 CPU Statistics
This page displays the router’s system information.
Processor: The router’s processor type and model.
MemTotal: The router’s physical memory size.
77
Page 78

MemFree: The router’s current free memory size.
CPU status: The CPU’s usage shown in percentage each minute.
When the CPU percentage in use is higher than 80% the line will turn red.
When the CPU percentage in use is lower than 80% the line will turn blue.
4.2.10 System Log
This window displays BiGuard 50G’s System Log entries. Major events are logged on
this window.
Display: There are several options in display, All logs all o w s th e s yst e m t o sh o w all
types of system logs, and there are also specific event logs such as; System
Maintenance, System Errors, Access Control, Packet Filter, LAN MAC Filter,
URL Filter, Intrusion Detection, Call Data Record, PPP, Remote Access, and
IPSEC.
Refresh: Refresh the System Log.
Clear Log: Clear the System Log.
Send Log: Send the System Log to your email account. You can set the email
address in Configuration > System > Email Alert. See the Email Alert section
for more details.
Save Log: Save the System log to a text file.
There are several links at the bottom right of the table indicating ‘<<First’,
‘<Previous’, a dropdown menu for the number of pages, ‘Next>’ and ‘Last>>’.
78
Page 79

st
First directs the page number for the table to the 1
page number for the table to the one page before, the dropdown menu allows the
user to specifically select the page number to view, next directs the page number
for the table to the one page after current page, and last directs the page number
for the table to the last page of the table.
page, previous directs the
Please refer to Appendix F: IPSec Log Events for more information on log events.
4.3 Quick Start
The Quick Start menu allows you to quickly configure your network for Internet
access using the most basic settings. The Quick Start can be applied to both WAN1
or WAN2.
Connection Method: Select your router’s connection to the Internet. Selections
include Obtain an IP Address Automatically, Static IP Settings, PPPoE
Settings, PPTP Settings, and Big Pond Settings.
4.3.1 DHCP
The following is information regarding your ISP that you will need to enter in order
to properly configure your Internet connection. If you select to Obtain an IP
Address Automatically, these will be automatically set for you, provided that your
ISP dynamically assigns an IP address.
79
Page 80

4.3.2 Static IP
IP assigned by your ISP: Enter the assigned IP address from your IP.
IP Subnet Mask: Enter your IP subnet mask.
ISP Gateway Address: Enter your ISP gateway address.
Primary DNS: Enter your primary DNS.
Secondary DNS: Enter your secondary DNS.
Click Apply to save your changes. To reset to defaults, click Reset.
4.3.3 PPPoE
Username: Enter your user name.
Password: Enter your password.
Retype Password: Retype your password.
Connection: Select whether the connection should Always Connect or Trigger
on Demand. If you want the router to establish a PPPoE session when starting up
and to automatically re-establish the PPPoE session when disconnected by the ISP,
select Always Connect. If you want to establish a PPPoE session only when there
80
Page 81

is a packet requesting access to the Internet (i.e. when a program on your computer
attempts to access the Internet), select Trigger on Demand .
Idle Time: Auto-disconnect the router when there is no activity on the line for a
predetermined period of time. Select the idle t i m e from the drop d o w n m e n u. Active
if Trigger on Demand is selected.
Click Apply to save your changes. To reset to defaults, click Reset.
4.3.4 PPTP
Username: Enter your user name.
Password: Enter your password.
Retype Password: Retype your password.
PPTP Client IP: Enter the PPTP Client IP provided by your ISP.
PPTP Client IP Netmask: Enter the PPTP Client IP Netmask provided by your ISP.
PPTP Client IP Gateway: Enter the PPTP Client IP Gateway provided by your ISP.
PPTP Server IP: Enter the PPTP Server IP provided by your ISP.
Connection: Select whether the connection should Always Connect or Trigger
on Demand. If you want the router to establish a PPTP session when starting up
and to automatically re-establish the PPTP session when disconnected by the ISP,
select Always Connect. If you want to establish a PPTP session only when there is
a packet requesting access to the Internet (i.e. when a program on your computer
attempts to access the Internet), select Trigger on Demand .
Idle Time: Auto-disconnect the router when there is no activity on the line for a
81
Page 82

predetermined period of time. Select the idle t i m e from the drop d o w n m e n u. Active
if Trigger on Demand is selected.
Click Apply to save your changes. To reset to defaults, click Reset.
4.3.5 Big Pond
Username: Enter your user name.
Password: Enter your password.
Retype Password: Retype your password.
Login Server: Enter the IP of the Login server provided by your ISP.
Click Apply to save your changes. To reset to defaults, click Reset.
For detailed instructions on configuring WAN settings, please refer to the WAN
section of this chapter.
4.4 Configuration
The Configuration menu allows you to set many of the operating parameters of
BiGuard 50G. In this menu, you will find the following sections:
- LAN
- WAN
- Dual WAN
- System
- Firewall
- VPN
82
Page 83

- QoS
- Virtual Server
- Advanced
These items are described below in the following sections.
4.4.1 LAN
There are three items within this section: Ethernet, Wireless, Wireless Securtiy,
DHCP Server and LAN Address Mapping.
4.4.1.1 Ethernet
83
Page 84

IP Address: Enter the internal LAN IP address for BiGuard 50G (192.168.1.254 by
default).
Subnet Mask: Enter the subnet mask (255.255.255.0 by default).
RIP: RIP v2 Broadcast and RIP v2 Multicast. Check to enable RIP.
Wireless
WLAN Service: Default setting is set to Disable. If you have any wireless, both
802.11g and 802.11b, device in your network, you can select Enable.
Mode: The default setting is 802.11b+g (Mixed mode). If you do not know or have
both 11g and 11b devices in your network, then keep the default in mixed mode.
From the drop-down manual, you can select 802.11g if you have only 11g card. If
you have only 11b card, then select 802.11b.
ESSID: The ESSID is the unique name of a wireless access point (AP) to be
distinguished from another. For security propose, change to a unique ID name to the
AP which is already built-in to the router’s wireless interface. It is case sensitive and
must not excess 32 characters. Make sure your wireless clients have exactly the
ESSID as the device, in order to get connected to your network.
Note: ESSID is case sensitive and must not excess 32 characters.
84
Page 85

Hide ESSID: It is function in which transmits its ESSID to the air so that when
wireless client searches for a network, router can then be discovered and recognized.
Default setting is Disable.
Enable: Select Enable if you do not want broadcast your ESSID. When select
Enable, no one will be able to locate the Access Point (AP) of your router.
Disable: When Disable is selected, you can allow anybody with a wireless client
to be able to locate the Access Point (AP) of your router.
Regulation Doma in: There are five Regulation Domains for you to choose from,
including North America (N.America), Europe, France, etc. The Channel ID will
be different based on this setting.
WMM(QOS): Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) QoS, the specification provides basic
prioritization of data packets through the wireless network. When enabled, you will
be less likely to hear delays during phone conversations, or higher quality live
streaming whilst watching videos. The improvement is due to the delay of other
network traffics which are not as critical and can be expensed, such as downloading
files where a small delay is generally acceptable. For WMM QoS to work properly
after it is enabled, both the servers and network cards communicating with each
other must support WMM.
WMM-APSD: Enable WMM-APSD if you want to turn on the power saving mode.
WMM Automatic Power Save Delivery (APSD) provides efficient power management
method to the router. It does so by waking up the wireless module of the router
when there is a need to send or receive, then it goes back to sleep mode once the
communication has ended. This mechanism will save more power through the
router than the traditional ‘always on’ method.
Channel ID: Select the ID channel that you would like to use.
Tx Power Level: It is function that enhances the wireless transmitting signal
strength. User may adjust this power level from minimum 0 up to maximum 255.
Note: The Power Level maybe different in each access network user premises
environment and choose the most suitable level for your network.
AP MAC Address: It is a unique hardware address of the Access Point.
AP Firmware Version: The Access Point firmware version.
Wireless Distribution System (WDS)
It is a wireless access point mode that enables wireless link and communication with
other access point. It is easy to be installed, simply define the peer’s MAC address
85
Page 86

of the connected AP. WDS takes advantages of cost saving and flexibility which no
extra wireless client device is required to bridge between two access points and
extending an existing wired or wireless infrastructure network to create a larger
network.
In addition, WDS enhances its link connection security in WEP mode, WEP key
encryption must be the same for both access points.
WDS Service: The default setting is Disable. Check Enable radio button to
activate this function.
1. Peer WDS MAC Address: It is the associated AP’s MAC Address. It is important
that your peer’s AP must include your MAC address in order to acknowledge and
communicate with each other.
2. Peer WDS MAC Address: It is the second associated AP’s MAC Address.
3. Peer WDS MAC Address: It is the third associated AP’s MAC Address.
4. Peer WDS MAC Address: It is the fourth associated AP’s MAC Address.
Note: For MAC Address, Semicolon ( : ) or Dash (-) must be included.
4.4.1.2 Wireless Security
You can disable or enable with WPA or WEP for protecting wireless network. The
default mode of wireless security is disabled.
WPA Pre-Shared Key
WPA Algorithms: TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) / AES(Advanced
86
Page 87

Encryption Standard) utilizes a stronger encryption method and incorporates
Message Integrity Code (MIC) to provide protection against hackers.
WPA Shared Key: The key for network authentication. The input format is in
character style and key size should be in the range between 8 and 63 characters.
Group Key Renewal: The period of renewal time for changing the security key
automatically between wireless client and Access Point
(AP).
WPA2 Pre-Shared Key
WPA2 Algorithms: TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) / AES(Advanced
Encryption Standard) utilizes a stronger encryption method and incorporates
Message Integrity Code (MIC) to provide protection against hackers.
WPA2 Shared Key: The key for network authentication. The input format is in
character style and key size should be in the range between 8 and 63 characters.
Group Key Renewal: The period of renewal time for changing the security key
automatically between wireless client and Access Point (AP).
87
Page 88

4.4.1.3 WEP
WEP Encryption: To prevent unauthorized wireless stations from accessing data
transmitted over the network, the router offers highly secure data encryption,
known as WEP. If you require high security for transmissions, there are two
alternatives to select from: WEP 64 and WEP 128. WEP 128 will offer increased
security over WEP 64.
Default Used WEP Key: Select the encryption key ID; please refer to Key (1~4)
below.
Passphrase: This is used to generate WEP keys automatically based upon the input
string and a pre-defined algorithm in WEP64 or WEP128. You can input the same
string in both the AP and Client card settings to generate the same WEP keys. Please
note that you do not have to enter Key (1-4) as below when the Passphrase is
enabled..
Key (1-4): Enter the key to encrypt wireless data. To allow encrypted data
transmission, the WEP Encryption Key values on all wireless stations must be the
same as the router. There are four keys for your selection. The input format is in HEX
style, 5 and 13 HEX codes are required for WEP64 and WEP128 respectively
no any
separator is included.
4.4.1.4 DHCP Server
In this menu, you can disable or enable the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
(DHC P ) s e rve r. Th e DHC P pr o to c ol a l lo w s y o u r B i Gu a rd 5 0 G t o dy n am i c al l y a s si g n I P
addresses to PCs on your network if they are configured to automatically obtain IP
addresses.
88
Page 89

To disable the router’s DHCP Server, select the Disable radio button, and then click
Apply. When the DHCP Server is disabled, you will need to manually assign a fixed
IP address to each PC on your network, and set the default gateway for each PC to
the IP address of the router (192.168.1.254 by default).
To configure the router’s DHCP Server, select the Enable radio button, and then
configure parameters of the DHCP Server including the IP Pool (starting IP address
and ending IP address to be allocated to the PCs on your network), DNS Server,
WINS Server, and Domain Name. These details are sent to each DHCP client when
they request an IP address from the DHCP server. Click Apply to enable this
function.
Fixed Host allows specific computer/network clients to have a reserved IP address.
89
Page 90

Name: Enter the name you want to give for the IP+Mac Address Fixed Host
account.
Active: Select whether you want to Enable or Disable this particular Fixed Host
account.
IP Address: Enter the IP address that you want to reserve for the above MAC
address.
MAC Address: Enter the MAC address of the PC or server you wish to be assigned
a reserved IP.
Candidates: You can also select the Candidates which are referred from the ARP
table for automatic input.
Click the Apply button to add the configuration into the Host Table.
90
Page 91

4.4.1.5 LAN Address Mapping
LAN Address Mapping is a function that can support multiple subnet and also
multiple NAT, you can specify a subnet and LAN Gateway IP Address and select
associated WAN IP Address specified in WAN IP Alias in Configuration -> WAN ->
WAN IP Alias.
Please click Create to create a LAN Address Mapping rule.
Name: Please input the name of the rule.
IP Address: Please input the LAN Gateway IP Address you would like to use.
Netmask: Please input the Netmask you would like to use.
WAN IP Address: Please click Candidates to select the WAN IP address you would
like to use from WAN Alias list.
Click the Apply button to add the configuration into the LAN Address Mapping.
91
Page 92

4.4.2 WAN
WAN refers to your Wide Area Network connection. In most cases, this means your
router’s connection to the Internet through your ISP. BiGuard30 features Dual WAN
capability. There are three items within this section:
The WAN menu contains two items: ISP Settings, Bandwidth Settings and WAN
IP Alias.
4.4.2.1 ISP Settings
This ISP Settings Table displays the different WAN connections that are configured
on BiGuard 50G. To edit any of these connections, click Edit. You will be taken to the
following menu.
92
Page 93

Connection Method: Select how your router will connect to the Internet. Selections
include Obtain an IP Address Automatically, Static IP Settings, PPPoE
Settings, PPTP Settings, and Big Pond Settings. For each WAN port, the factory
default is DHCP. If your ISP does not use DHCP, select the correct connection
method and configure the connection accordingly. Configurable items will vary
depending on the connection method selected.
4.4.2.1.1 DHCP
Host Name: Some ISPs authenticate logins using this field.
93
Page 94

MAC Address: If your ISP requires you to input a WAN Ethernet MAC, check the
checkbox and enter your MAC address in the blanks below.
Candidates: You can also select the MAC address from the list in the Candidates.
DNS: If your ISP requires you to manually setup DNS settings, check the checkbox
and enter your primary and secondary DNS.
RIP: To activate RIP, select Send, Receive, or Both from the drop down menu. To
disable RIP, select Disable from the drop down menu.
MTU: Enter the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) for your network.
Network Address Translation: Enables or Disables the NAT function. To apply this
interface as router mode please select Disable. Due to default firewall feature, if you
would like to use router mode, you have to input the packet filter rules you would
like to forward in Configuration -> Firewall -> Packet filter
Click Apply to save your changes. To reset to defaults, click Reset.
4.4.2.1.2 Static IP
IP assigned by your ISP: Enter the static IP assigned by your ISP.
IP Subnet Mask: Enter the IP subnet mask provided by your ISP.
ISP Gateway Address: Enter the ISP gateway address provided by your ISP.
MAC Address: If your ISP requires you to input a WAN Ethernet MAC, check the
checkbox and enter your MAC address in the blanks below.
Candidates: You can also select the MAC address from the list in the Candidates.
94
Page 95

Primary DNS: Enter the primary DNS provided by your ISP.
Secondary DNS: Enter the secondary DNS provided by your ISP.
RIP: To activate RIP, select Send, Receive, or Both from the drop down menu. To
disable RIP, select Disable from the drop down menu.
MTU: Enter the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) for your network.
Network Address Translation: Enables or Disables the NAT function. To apply
this interface as router mode please select Disable. Due to default firewall feature,
if you would like to use router mode, you have to input the packet filter rules you
would like to forward in Configuration -> Firewall -> Packet filter
Click Apply to save your changes. To reset to defaults, click Reset.
4.4.2.1.3 PPPoE
Username: Enter your user name.
Password: Enter your password.
Retype Password: Retype your password.
Connection: Select whether the connection should Always Connect or Trigger
on Demand. If you want the router to establish a PPPoE session when starting up
and to automatically re-establish the PPPoE session when disconnected by the ISP,
95
Page 96

select Always Connect. If you want to establish a PPPoE session only when there
is a packet requesting access to the Internet (i.e. when a program on your computer
attempts to access the Internet), select Trigger on Demand .
Idle Time: Auto-disconnect the router when there is no activity on the line for a
predetermined period of time. Select the idle t i m e from the drop d o w n m e n u. Active
if Trigger on Demand is selected.
IP Assigned by your ISP: If your IP is dynamically assigned by your ISP, select the
Dynamic radio button. If your IP assigns a static IP address, select the Static radio
button, and input your IP address in the blank provided.
MAC Address: If your ISP requires you to input a WAN Ethernet MAC, check the
checkbox and enter your MAC address in the blanks below.
Candidates: You can also select the MAC address from the list in the Candidates.
DNS: If your ISP requires you to manually setup DNS settings, check the checkbox
and enter your primary and secondary DNS.
RIP: To activate RIP, select Send, Receive, or Both from the drop down menu. To
disable RIP, select Disable from the drop down menu.
MTU: Enter the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) for your network.
Network Address Translation: Enables or Disables the NAT function. To apply
this interface as router mode please select Disable. Due to default firewall feature,
if you would like to use router mode, you have to input the packet filter rules you
would like to forward in Configuration -> Firewall -> Packet filter
Click Apply to save your changes. To reset to defaults, click Reset.
96
Page 97

4.4.2.1.4 PPTP Settings
Username: Enter your user name.
Password: Enter your password.
Retype Password: Retype your password.
PPTP Client IP: Enter the PPTP Client IP provided by your ISP.
PPTP Client IP Netmask: Enter the PPTP Client IP Netmask provided by your ISP.
PPTP Client IP Gateway: Enter the PPTP Client IP Gateway provided by your ISP.
PPTP Server IP: Enter the PPTP Server IP provided by your ISP.
Connection: Select whether the connection should Always Connect or Trigger
on Demand. If you want the router to establish a PPTP session when starting up
and to automatically re-establish the PPTP session when disconnected by the ISP,
select Always Connect. If you want to establish a PPTP session only when there is
a packet requesting access to the Internet (i.e. when a program on your computer
attempts to access the Internet), select Trigger on Demand .
Idle Time: Auto-disconnect the router when there is no activity on the line for a
predetermined period of time. Select the idle t i m e from the drop d o w n m e n u. Active
if Trigger on Demand is selected.
IP Assigned by your ISP: If your IP is dynamically assigned by your ISP, select the
Dynamic radio button. If your IP assigns a static IP address, select the Static radio
97
Page 98

button. This will take you to another page for inputting the IP address information.
MAC Address: If your ISP requires you to input a WAN Ethernet MAC, check the
checkbox and enter your MAC address in the blanks below.
Candidates: You can also select the MAC address from the list in the Candidates.
DNS: If your ISP requires you to manually setup DNS settings, check the checkbox
and enter your primary and secondary DNS.
RIP: To activate RIP, select Send, Receive, or Both from the drop down menu. To
disable RIP, select Disable from the drop down menu.
MTU: Enter the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) for your network.
Network Address Translation: Enables or Disables the NAT function. To apply
this interface as router mode please select Disable. Due to default firewall feature,
if you would like to use router mode, you have to input the packet filter rules you
would like to forward in Configuration -> Firewall -> Packet filter
Click Apply to save your changes. To reset to defaults, click Reset.
4.4.2.1.5 Big Pond Settings
Username: Enter your user name.
Password: Enter your password.
Retype Password: Retype your password.
Login Server: Enter the IP of the Login server provided by your ISP.
98
Page 99

MAC Address: If your ISP requires you to input a WAN Ethernet MAC, check the
checkbox and enter your MAC address in the blanks below.
Candidates: You can also select the MAC address from the list in the Candidates.
DNS: If your ISP requires you to manually setup DNS settings, check the checkbox
and enter your primary and secondary DNS.
RIP: To activate RIP, select Send, Receive, or Both from the drop down menu. To
disable RIP, select Disable from the drop down menu.
MTU: Enter the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) for your network.
Network Address Translation: Enables or Disables the NAT function. To apply
this interface as router mode please select Disable. Due to default firewall feature,
if you would like to use router mode, you have to input the packet filter rules you
would like to forward in Configuration -> Firewall -> Packet filter
Click Apply to save your changes. To reset to defaults, click Reset.
A simpler alternative is to select Quick Start from the main menu. Please see the
Quick Start section of this chapter for more information.
4.4.2.2 Bandwidth Settings
Under Bandwidth Settings, you can easily configure both inbound and outbound
bandwidth for each WAN port.
WAN1: Enter your ISP inbound and outbound bandwidth for WAN1.
WAN2: Enter your ISP inbound and outbound bandwidth for WAN2.
NOTE: These values entered here are referenced by both QoS and Load Balancing
functions.
99
Page 100

WAN IP Alias
WAN IP Alias allows you to input additional WAN IP addresses. WAN IP Alias can be
used for Multiple NAT settings, including LAN Address Mapping settings and Virtual
Server settings.
Please click Create to create a LAN Address Mapping rule.
Name: Please input the name of the rule.
IP Address: Please input the additional WAN IP address you would like to use.
Interface: Please select the WAN Interface that you would like to add the additional
WAN IP to.
Click the Apply button to add the configuration into the WAN IP Alias.
4.4.3 Dual WAN
In this section, you can setup the fail over or load balance function, outbound load
balance or inbound load balance function, or setup specific protocol to bind with
100
 Loading...
Loading...