Page 1

GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway
User's Manual
High Quality, Industrial Data Acquisition, and Control Products
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 1
Page 2
Warranty
All products manufactured by ICP DAS are under warranty regarding
defective materials for a period of one year from the date of delivery to the
original purchaser.
Warning
ICP DAS assumes no liability for damages resulting from the use of this
product. ICP DAS reserves the right to change this manual at any time
without notice. The information furnished by ICP DAS is believed to be
accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by ICP DAS
for its use, or for any infringements of patents or other right of third parties
resulting from its use.
Copyright
Copyright 2008 by ICP DAS. All rights are reserved.
Trademark
The names used for identification only may be registered trademarks of
their respective companies.
List of Revision
Date Author Version Revision
2008/12/31 Raiden 1.00 Release
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 2
Page 3

Table of Contents
1. Introduction…………………………………………………………. 4
1.1 Features…………………………………………………………………………………... 5
1.2 Modules Support…………………………………………………………………………. 5
1.3 Specification……………………………………………………………………………… 5
2. Hardware……………………………………………………………. 7
2.1 Block Diagram of GW-7553…………………………………………………………….. 7
2.2 Pin Assignment…………………………………………………………………………... 7
2.3 Wiring……………………………………………………………………………………. 9
2.4 Setting the PROFIBUS Address………………………………………………………. 12
2.5 LED status indicator……………………………………………………………………. 13
2.6 Normal/Setting DIP switch…………………………………………………………….. 14
3. Communication protocol transfer theorem……………………… 16
3.1 PROFIBUS data exchange…………………………..…………………………………. 16
3.2 Modbus data exchange…………………………………………………………………. 19
3.3 Communication protocol transfer………………………………………………………. 22
4. Communication……………………………………………………. 26
4.1 Field of application…………………………………………………………………….. 26
4.2 GSD file………………………………………………………………………………… 27
4.3 The Configuration of the common parameters…………………………………………. 30
4.4 The Configuration of the modules……………………………………………………… 31
4.5 Diagnostic messages……………………………………………………………………. 34
4.6 I/O data exchange……………………………………………………………………….. 35
4.7 Establish connection with GW-7553……………………………………………………. 37
4.8 Data exchange example—Modbus RTU……………………………………………….. 39
4.9 Data exchange example—Modbus TCP………………………………………………... 49
5. Application of Utility………………………………………………. 60
5.1 Install Utility……………………………………………………………………………. 60
5.2 Utility introduction……………………………………………………………………… 63
5.3 Memory address configuration of the module………………………………………….. 65
5.4 Safe value setting……………………………………………………………………….. 67
5.5 IP setting………………………………………………………………………………… 69
5.6 Establish connection with GW-7553……………………………………………………. 70
6. Troubleshooting……………………………………………………. 73
7. Dimensions…………………………………………………………. 74
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 3
Page 4
1. Introduction
PROFIBUS and Modbus are two kinds of famous protocols and are wildly used in
the fields of factory and process automation. The GW-7553 is a PROFIBUS to
Modbus TCP gateway. By using this module, users can easily put the Modbus TCP
devices into PROFIBUS network.
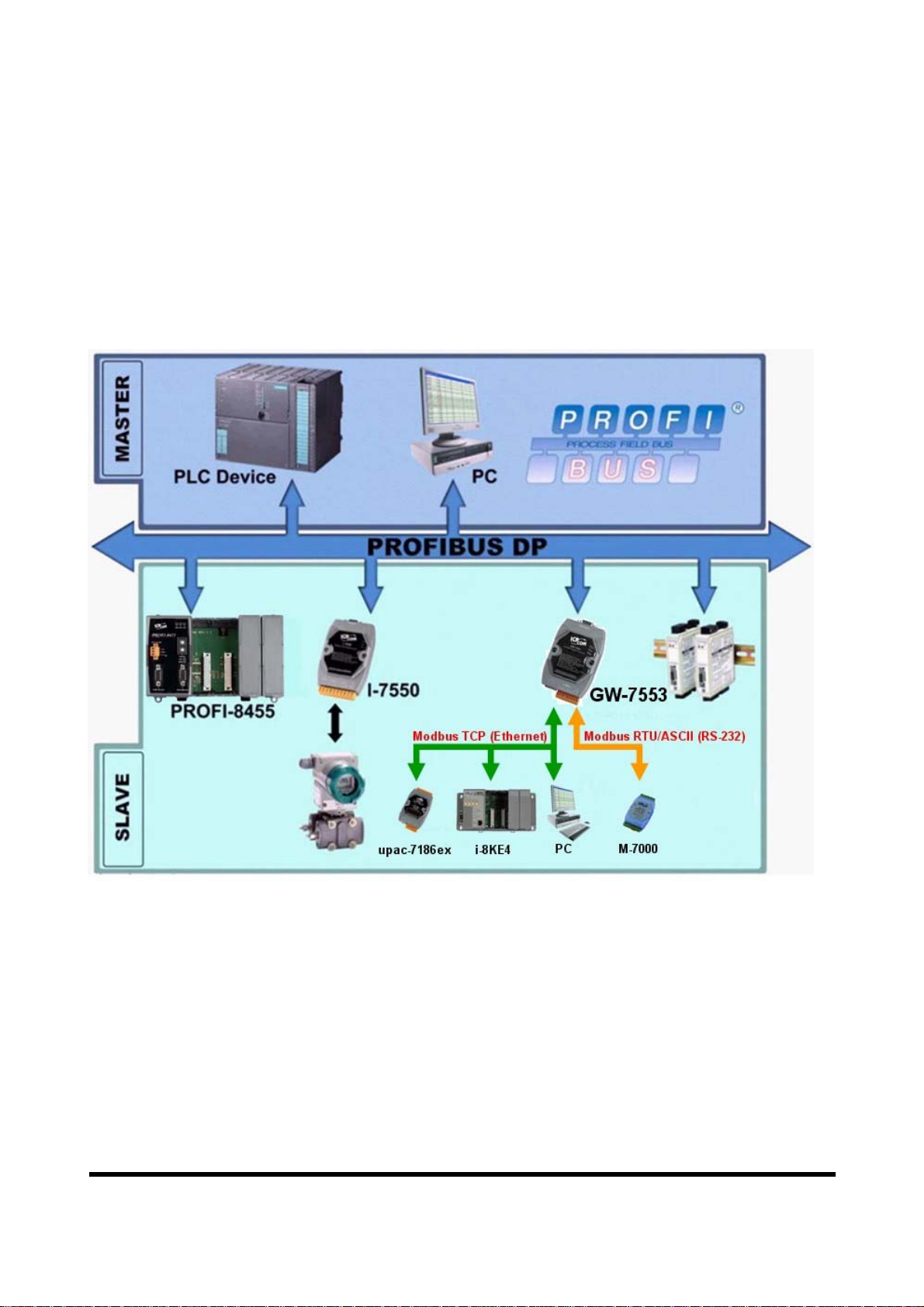
Figure 1 shows an application example for the GW-7553 module.
Figure 1 Application architecture of the GW-7553 module
The GW-7553 Gateway is specially designed for the slave device of PROFIBUS DP
protocol. In the Modbus protocol application, the GW-7553 can be a Modbus Master
device or Slave device. The Modbus devices can exchange data with the PROFIBUS
Master device via the GW-7553 module.
The main features and specification of GW-7553 are described as below:
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 4
Page 5
1.1 Features
● 16-bit Microprocessor inside with 80MHz
● Profichip VPC3+C PROFIBUS controller
● Support PROFIBUS DP-V0 slave
● PROFIBUS transmission rate detect automatically
● Max transmission speed up to 12 Mbps for PROFIBUS and 115.2 kbps for
COM Port
● Support Modbus RTU, ASCII and TCP format
● Support Modbus Master/Slave mode
● Support safe value setting
● COM Port driver has 1K bytes QUEUE input buffer & 512 bytes QUEUE
output buffer
● Max length of output/input data is 131/128 Bytes
● Ethernet Port: 10/100 Base-TX
● 2500Vrms High Speed iCoupler Isolation Protection for PROFIBUS network
● 3000VDC Isolation Protection on the PROFIBUS side
● Provide LED indicators
● Built-in Watchdog
● Mountable on DIN Rail
1.2 Modules Support
Only the following Modbus commands are supported by the gateway.
Table 1: Modbus function codes
Code Name Description
01 Read Coil Status Read the ON/OFF status of discrete outputs in the slave
02 Read Input Status Read the ON/OFF status of discrete inputs in the slave
03 Read Holding Registers Read the binary contents of holding registers in the slave
04 Read Input Registers Read the binary contents of input registers in the slave
05 Force Single Coil Write a single output to either ON or OFF in the slave
06 Preset Single Register Write an integer value into a single register in the slave
15 Force Multi. Coils
Write each coil in the sequence of coils to either ON or
OFF in the slave
16 Preset Multi. Registers Write a block of contiguous registers in the slave
1.3 Specification
COM Port specs:
● Serial port - RS-232
● Serial port interface: screw terminal block
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 5
Page 6
● Baud Rate:2400/4800/9600/19200/38400/57600/115200 bps
● Data Format: 7/8 data bits, None/Odd/Even parity bit, 1/2 stop bit
PROFIBUS specs:
● PROFIBUS interface connector: D-Sub 9-pin female
● Baud Rate: 9.6k/19.2k/45.45k/93.75k/187.5k/500k/1.5M/3M/6M/12Mbps
● Address Setting: 0~126 (set by DIP switch or EEPROM)
Ethernet specs:
● 10/100Base-TX (Auto-negotiating, Auto_MDIX, LED indicator)
Power requirement:
● Unregulated +10 ~ +30 VDC
● Power reverse protection, Over-Voltage brown-out protection
● Power consumption 2.5W
Module specs:
● Dimensions: 119mm x 72mm x 33mm
● Operating temperature: -25 ~ 75 ºC
● Storage temperature: -30 ~ 85 ºC
● Humidity:5 ~ 95% RH, non-condensing
● LED Status Indicators(Table 2)
Table 2: LED status indicator
− Show the power state
PWR LED
− Show data state
ERR LED
RUN LED
− Show error state
− Show communication state of PROFIBUS
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 6
Page 7
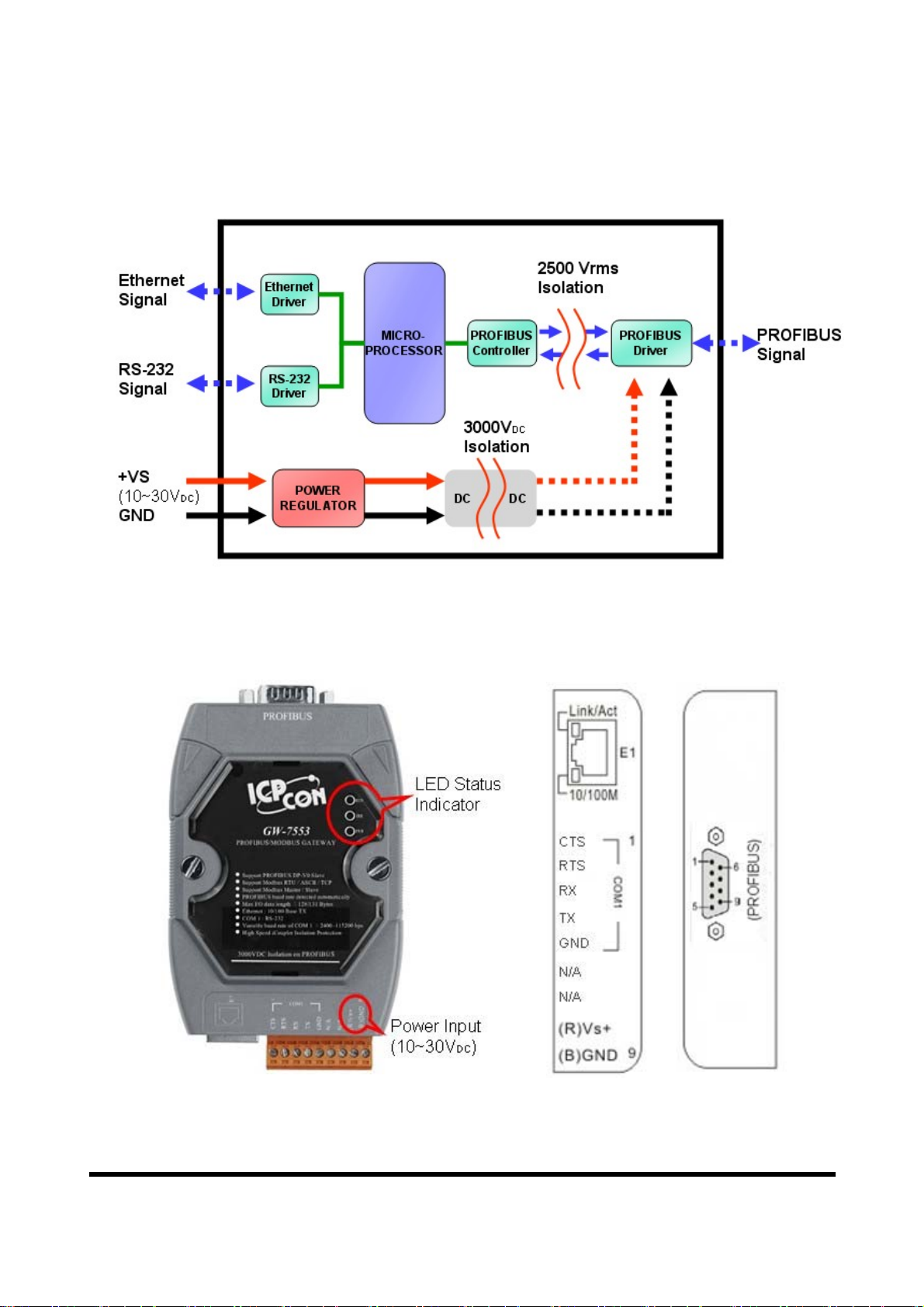
2. Hardware
2.1 Block Diagram of GW-7553
Figure 2 Block diagram of GW-7553
2.2 Pin Assignment
Figure 3 Pin assignment of GW-7553
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 7
Page 8
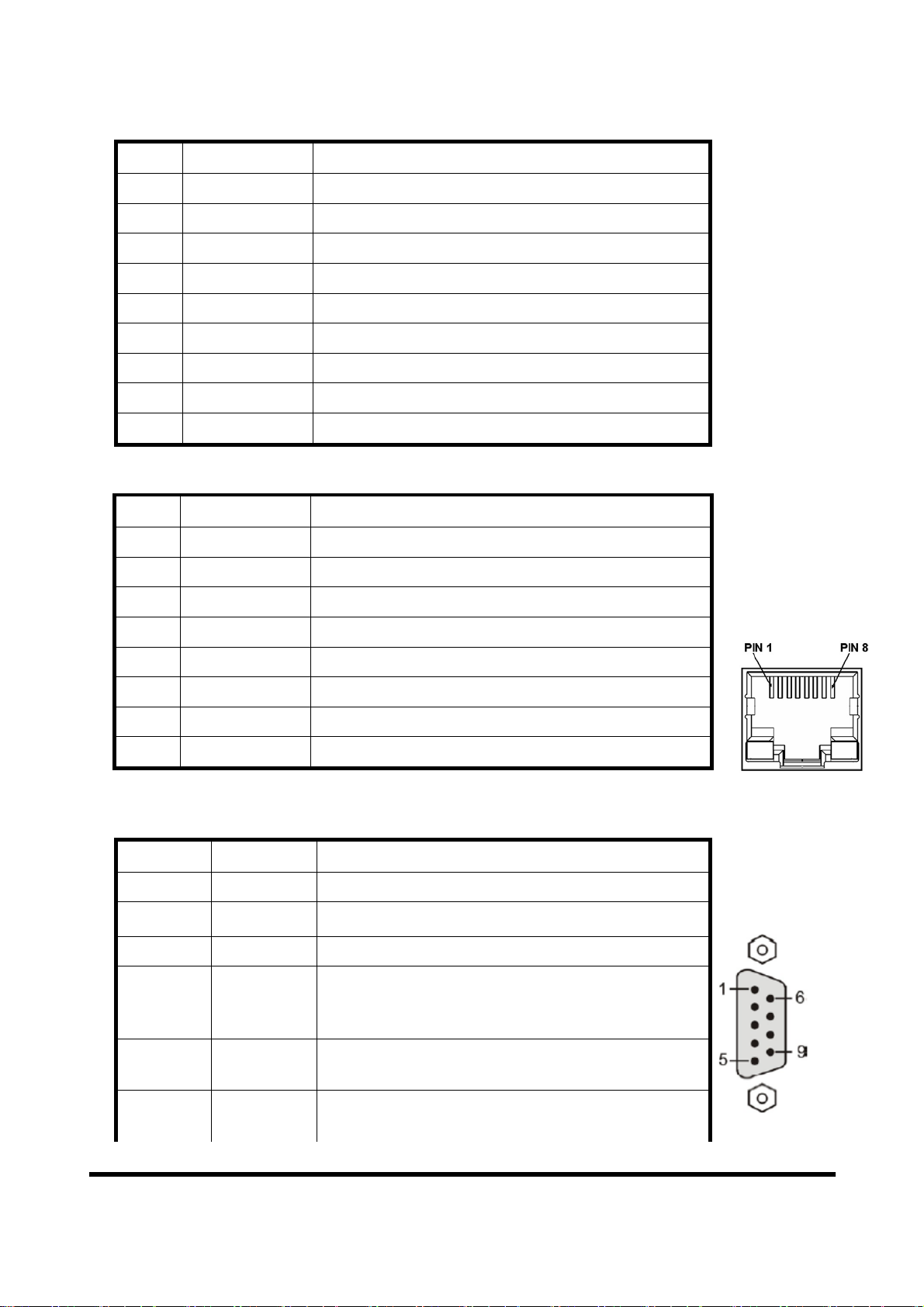
Table 3 9-pin screw terminal block
Pin Name Description
1 CTS Clear to Send of RS-232
2 RTS Request to Send of RS-232
3 RX Receive Data of RS-232
4 TX Transmit Data of RS-232
5 GND GND of RS-232
6 - N/A
7 - N/A
8 +VS V+ of Power Supply(+10 ~ +30 VDC)
9 GND GND of Power Supply
Table 4 RJ-45 socket
Pin Name Description
1 TX+ TX+ output
2 TX- TX- output
3 RX+ RX+ input
4 - N/A
5 - N/A
6 RX- RX- input
7 - N/A
8 - N/A
Table 5 PROFIBUS DB9 Female Connector
Pin Name Description
1 - N/A
2 - N/A
3 B Non-inverting Bus Line
4 ISODE Isolated DE output for use in PROFIBUS
applications where the state of the isolated drive
enable node needs to be monitored.
5 GND Power supply ground for the first node and the last
node
6 VP +5V Power Supply for the first node and the last
node
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 8
Page 9
Pin Name Description
port
7 - N/A
8 A Inverting Bus Line
9 - N/A
2.3 Wiring
GW-7553 supports PROFIBUS to Serial or Ethernet communication. It is
recommended to use only one communication interface (RS-232 or Ethernet) of
the Gateway at the same time. The following section describes the connection
interface of GW-7553.
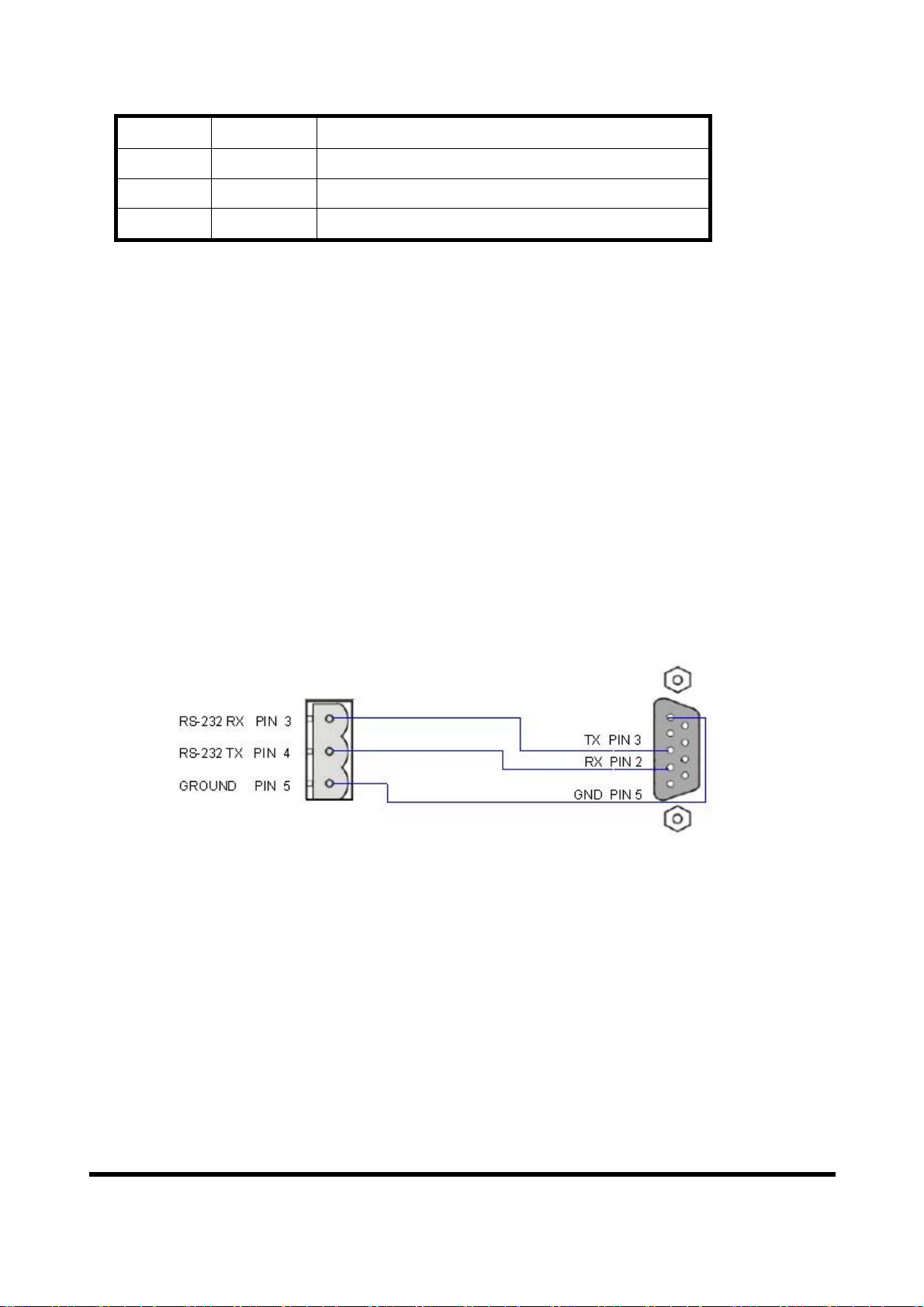
2.3.1 RS-232 connection
The RS-232 port of the GW-7553 has got three pins. The wiring of the RS-232
device with the RS-232 port of the GW-7553 is shown in figure 4.
GW-7553
RS-232
RS-232 device
Figure 4 RS-232 wiring diagram
2.3.2 Ethernet connection
The user can connect GW-7553 with the other device to the same sub network
or same Ethernet Switch, as shown in figure 5.
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 9
Page 10
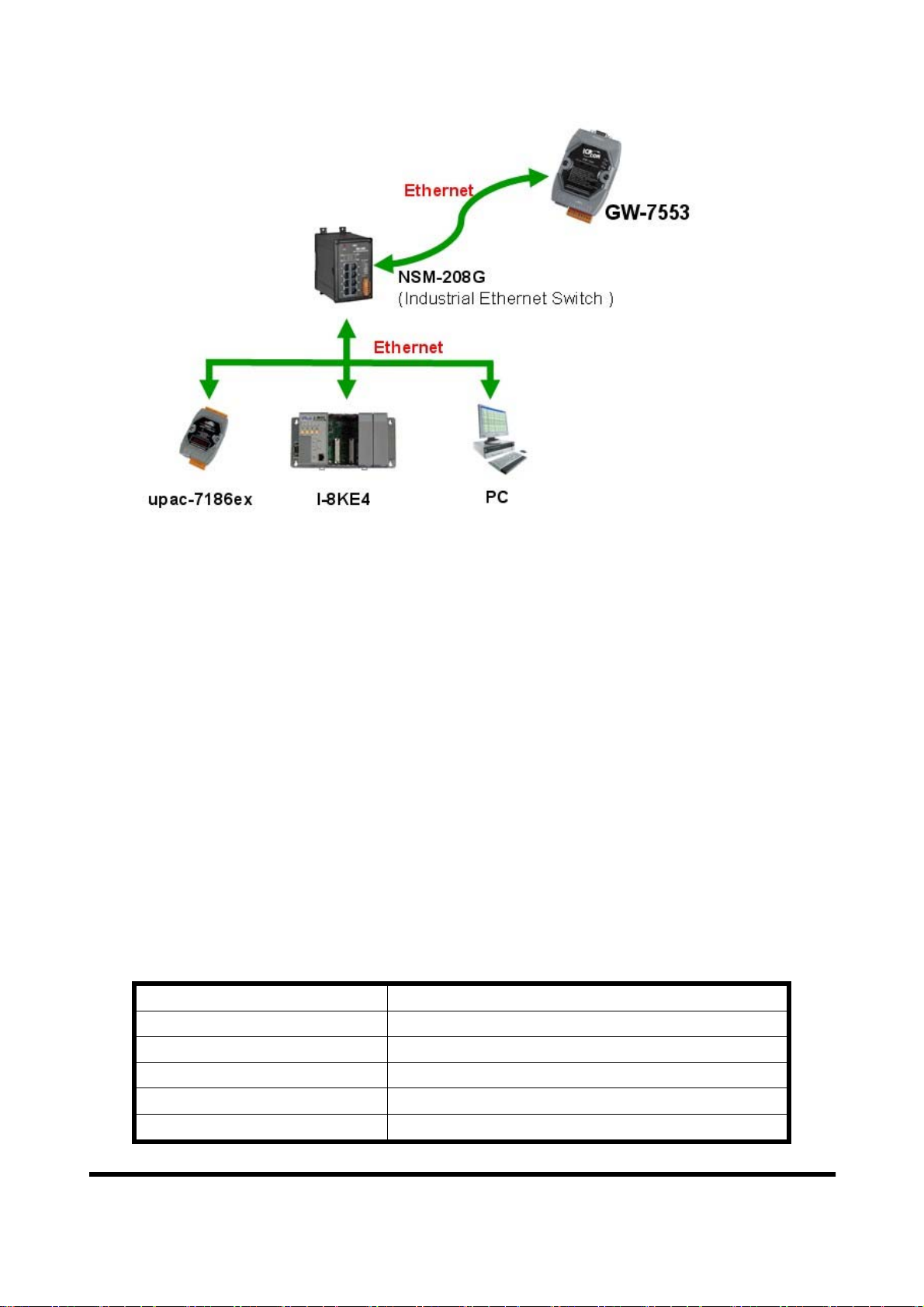
Figure 5 Ethernet connection
2.3.3 PROFIBUS Connection
The PROFIBUS interface of the GW-7553 is a DB9 female connector. The
connector uses the standard PROFIBUS 9 pin assignment. It is recommended to
use a standard PROFIBUS cable and connector (DB9 male). As with every
serial bus the rate of safe data transmission in a PROFIBUS network decreases
with increasing distance between Master and Slave. Table 6 shows the
transmission rate and range for a cable with the following properties:
1. Impedance :135~165 Ω
2. Capacity : lower than 30 pF/m
3. Loop resistance : lower than 110 Ω/km
4. Wire diameter : greater than 0.65 mm
5. Core cross-section : greater than 0.34 mm
Table 6 Transmission rate decreasing with increasing transmission distance
2
Transmission Rate(kbps) Transmission Distance per Segment (meter)
9.6, 19.2, 45.45,93.75 1200
187.5 1000
500 400
1500 200
3000, 6000, 12000 100
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 10
Page 11
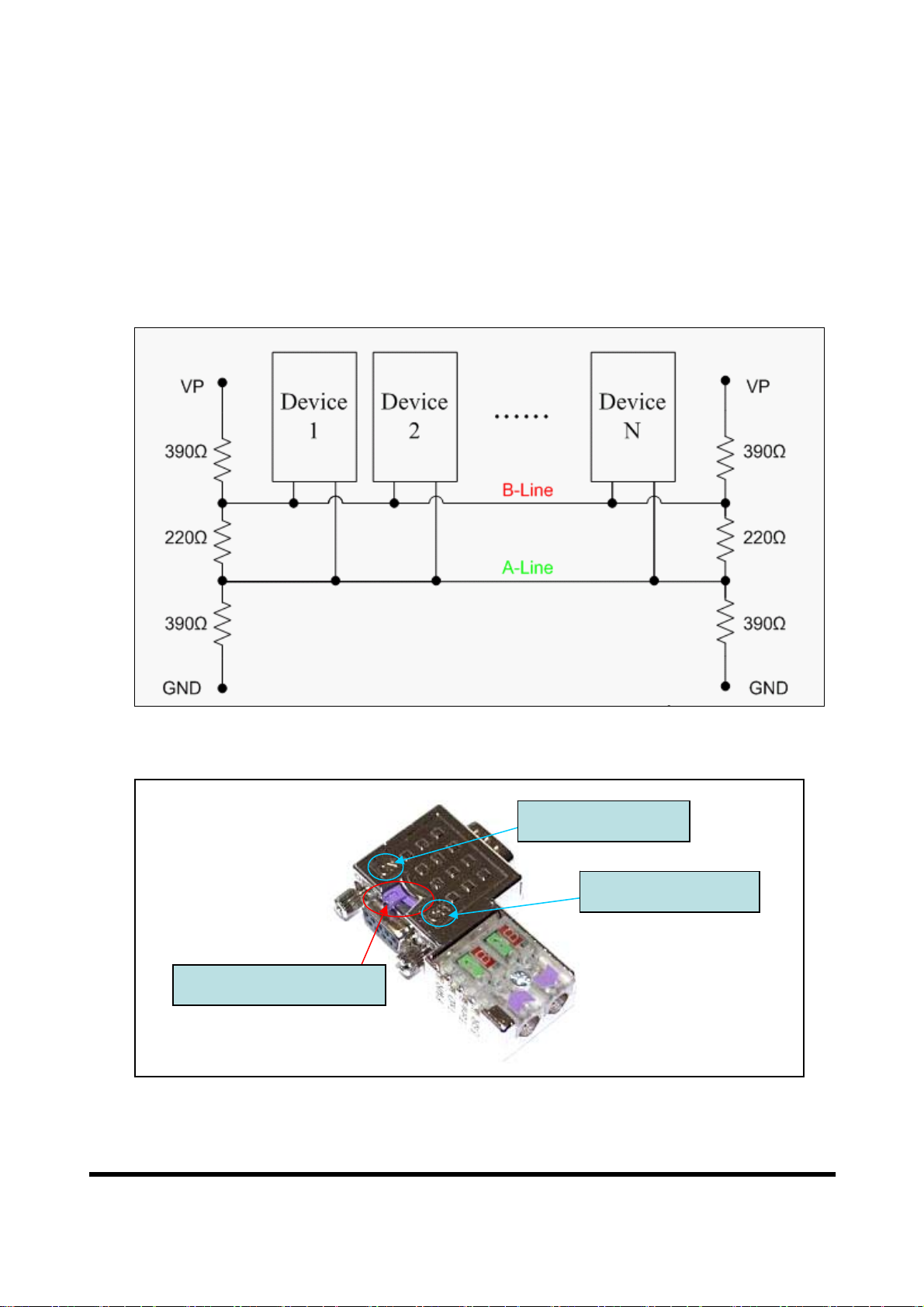
In order to minimize the reflection effect of signal transmission, both ends (first
node and last node) of a PROFIBUS segment needs to be equipped with an
active terminal resistor as shown in figure 6. A standard PROFIBUS connector
is usually already equipped with a terminal resistor. The user therefore only has
to switch on the resistor of the devices stationed at the ends of a segment as
shown in figure 7.
Figure 6 PROFIBUS connection
Terminator Switch
Figure 7 PROFIBUS connector
Terminator ON
Terminator OFF
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 11
Page 12
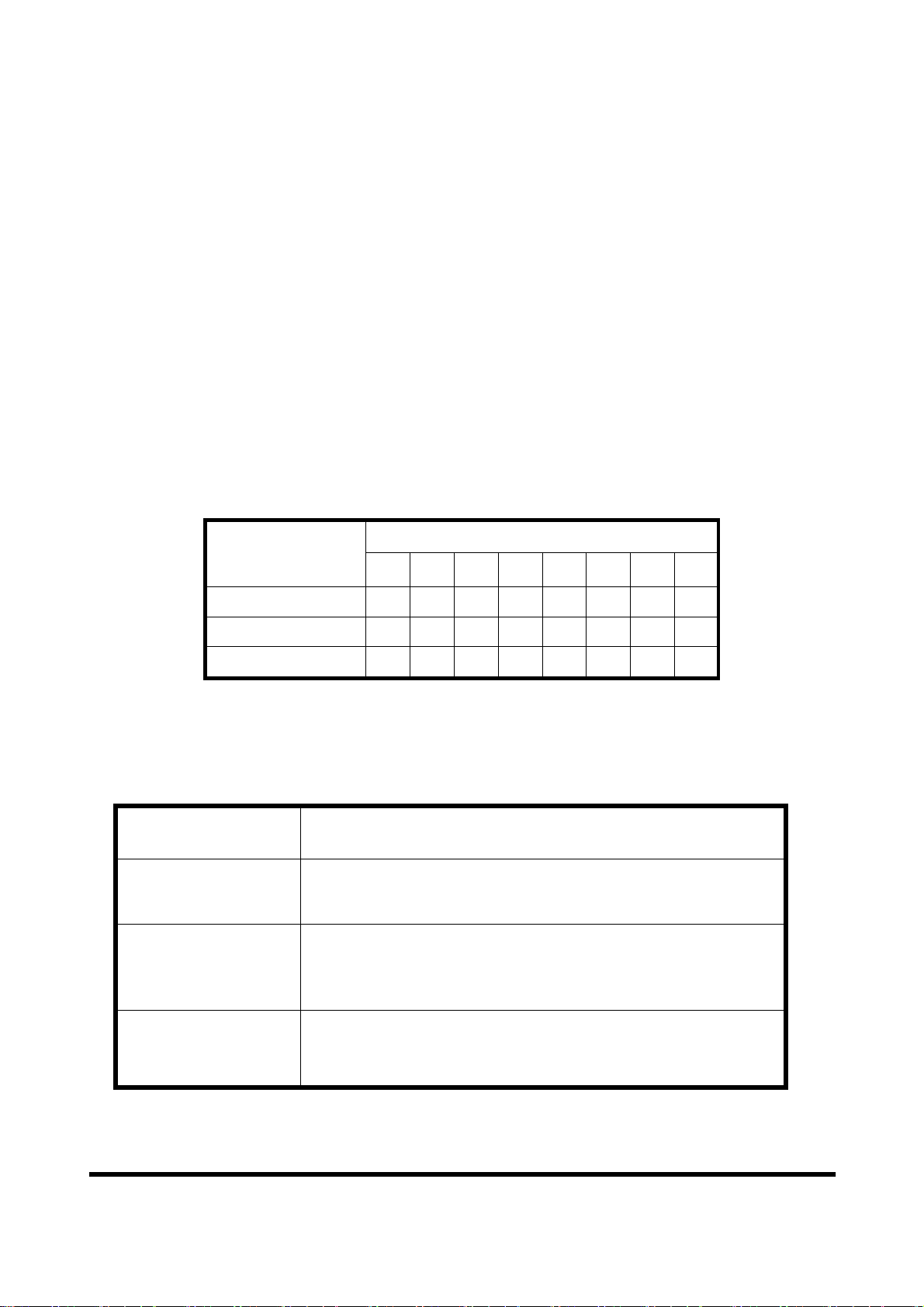
The number of stations in a PROFIBUS network is restricted to 126. According
to the PROFIBUS specification up to 32 stations are allowed per segment. A
repeater has to be used to link the bus segments.
2.4 Setting the PROFIBUS Address
The station address of GW-7553 can be set by using either the DIP switch or by
writing it directly to the EEPROM. The DIP switch covers a range from 0 to 255.
The valid address range of a PROFIBUS station spans from 0 to 126. Table 7
shows three examples of setting the station address by using the DIP switch. The
DIP switches are accessed by opening the modules housing (Figure 8). Table 8
explains which address will be used by the module after power on, if the DIP
switch address setting differs from the address stored in the EEPROM.
Table 7: DIP switch setting example
Station address
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
10 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0
126 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0
DIP switch (SW1)
Note: 1=>ON, 0=>OFF
Table 8: The Address setting of the GW-7553
DIP switch Setting Description
1. The address setting of the EEPROM is ignored.
0~125
126-254
2. The address can not be set by the PROFIBUS configuration
tool.
1. The address setting of the DIP switch is ignored.
2. If the address in the EEPROM is 126, the PROFIBUS
configuration tool can set a new address and save it to the
EEPROM.
255 1. Slave address in the EEPROM is set to 126.
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 12
Page 13
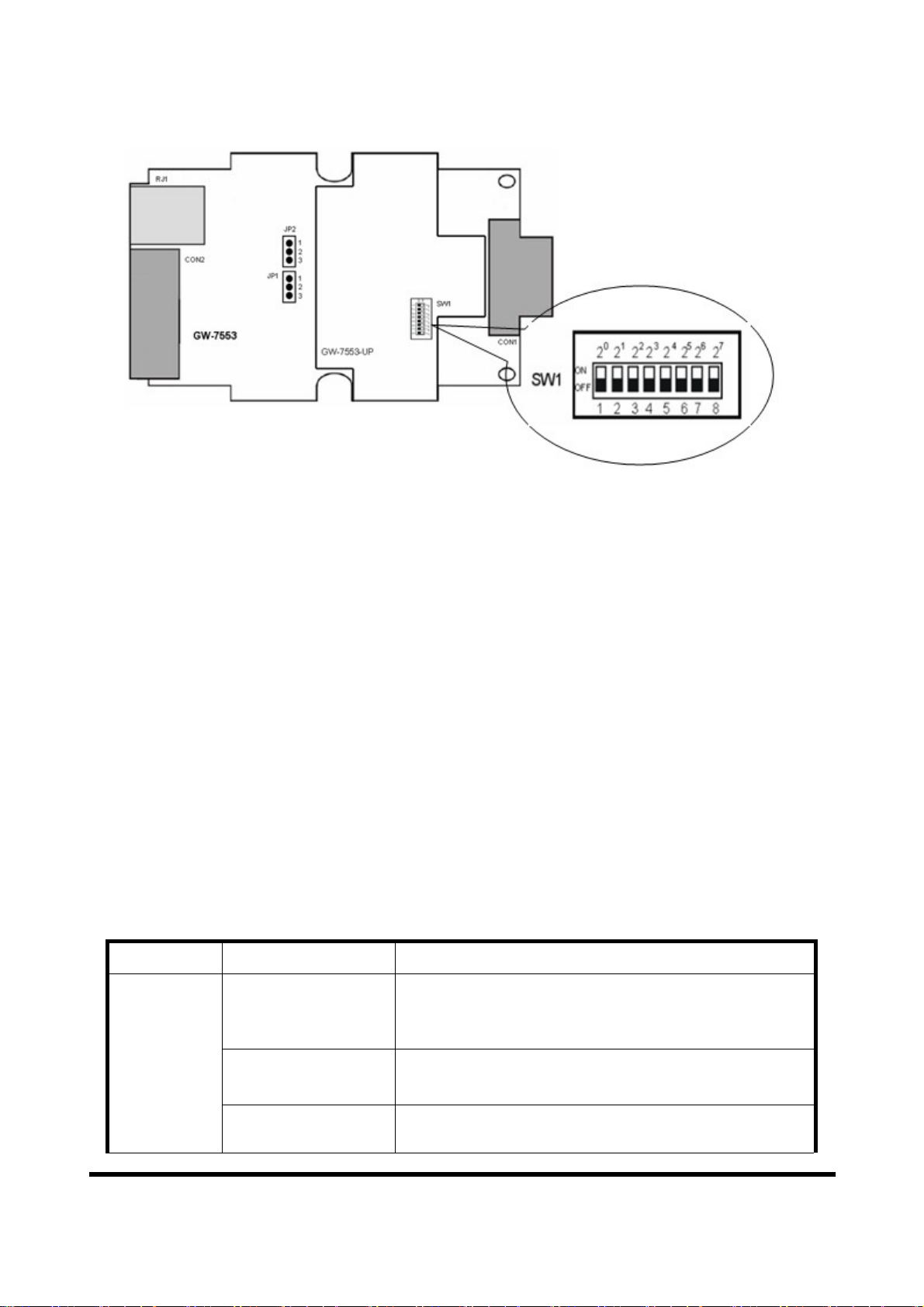
Figure 8: DIP switch
Each Slave must have a unique valid address (1 to 125) in order to be able to
communicate with the Master. To change the address by using the configuration
tool it is necessary to first set the address stored in the EEPROM to 126. This is
done by setting the DIP switch to 255 in the power off state. Switching the
module on is forcing the module to change its address in the EEROM to 126. In
the next step switch the module off and change the DIP switch setting to any
value from 126 to 254. This step is necessary in order to prevent the module to
change its address in the EEPROM to 126 every time it is powered on. The
configuration tool can now assign the Slave a new address.
2.5 LED status indicator
The GW-7553 provides three LEDs to indicate the statuses of the GW-7553
module. The position of LEDs and descriptions are shown in table 9 and figure 9.
Table 9: LED status description
LED Name Status Description
When the GW-7553 acts as a Modbus Slave device
flash
PWR
on
off Power supply has failed.
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 13
and receiving query message form Modbus Master
device, PWR led will flash.
Power supply is ok.
The firmware has loaded.
Page 14

LED Name Status Description
When the GW-7553 connects with the utility tool, it
flash
will flash fast (flash once about 55ms).
When the GW-7553 has diagnostic message, it will
flash slowly (flash once about 220ms).
ERR
RUN
− Connection error between PROFIBUS Master and
on
off
on
off GW-7553 module is not in a data exchange mode.
Slave or
− PROFIBUS system has not been configured
correctly.
Normal operation
PROFIBUS system has been configured correctly
Data exchange mode
Normal operation.
Figure 9 LED position
2.6 Normal/Setting DIP switch
There is a DIP switch on the back of the GW-7553 module, as shown in Figure 10.
The DIP switch is used to set the GW-7553 module works in operation mode or
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 14
Page 15
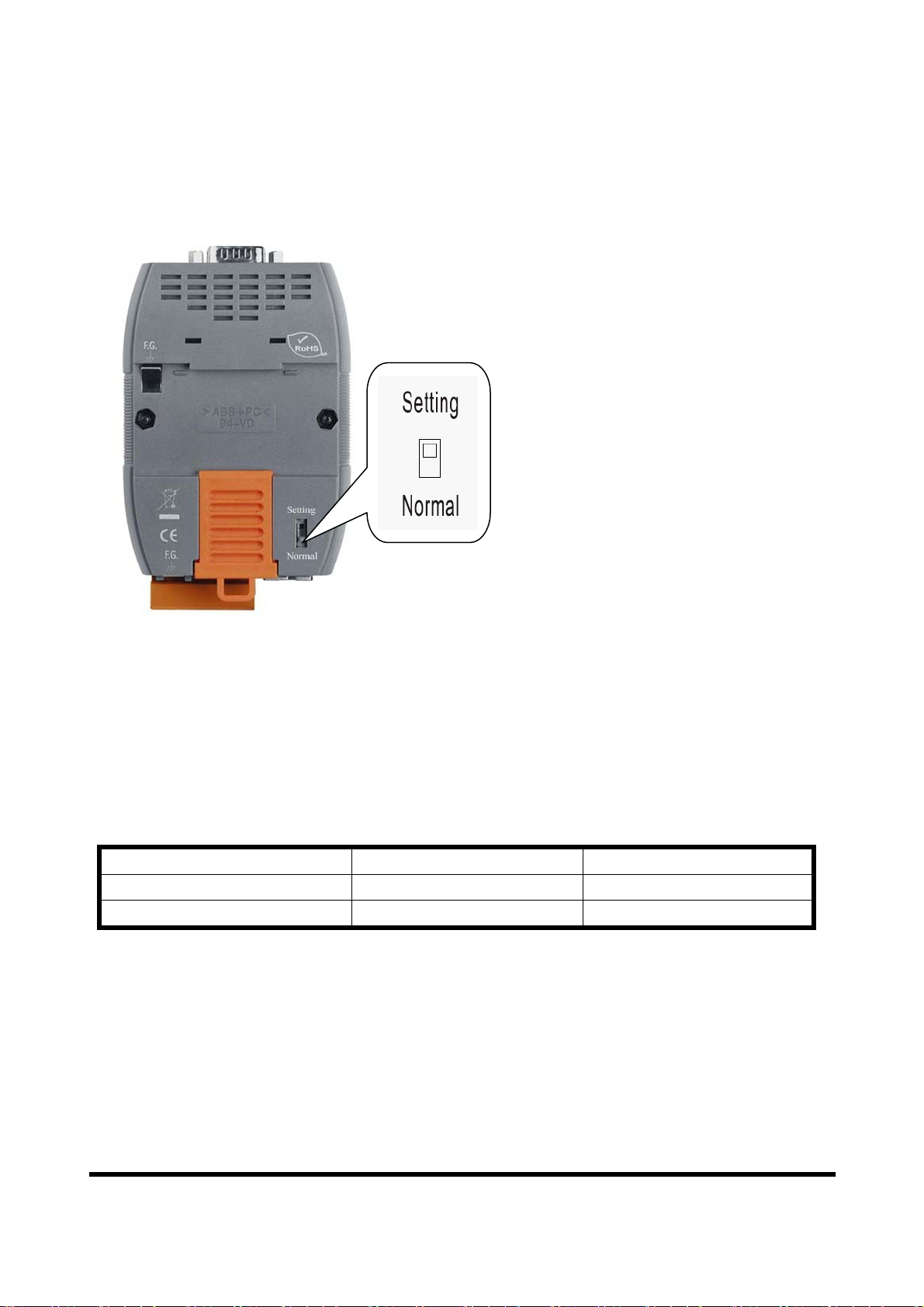
setting mode. In the normal situation, it needs to set the DIP switch to the “Normal”
position. In this case, the GW-7553 module can communicate with Modbus devices.
When the user sets the DIP switch to the “Setting” position, the GW-7553 module can
communicate with the utility to set the safe value and network configuration.
Figure 10 DIP switch of the GW-7553
PS:
There are two kinds of methods to enable the setting mode of the GW-7553. The user
can change the position of the DIP switch or set the control bit (please refer section
4.6.2 Output data area and communication command) to enable the setting mode of
the GW-7553, as shown in table 10.
Table 10 Mode of GW-7553
Mode SM(control bit)=0 SM(control bit)=1
DIP switch=Normal operation mode setting mode
DIP switch =Setting setting mode setting mode
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 15
Page 16
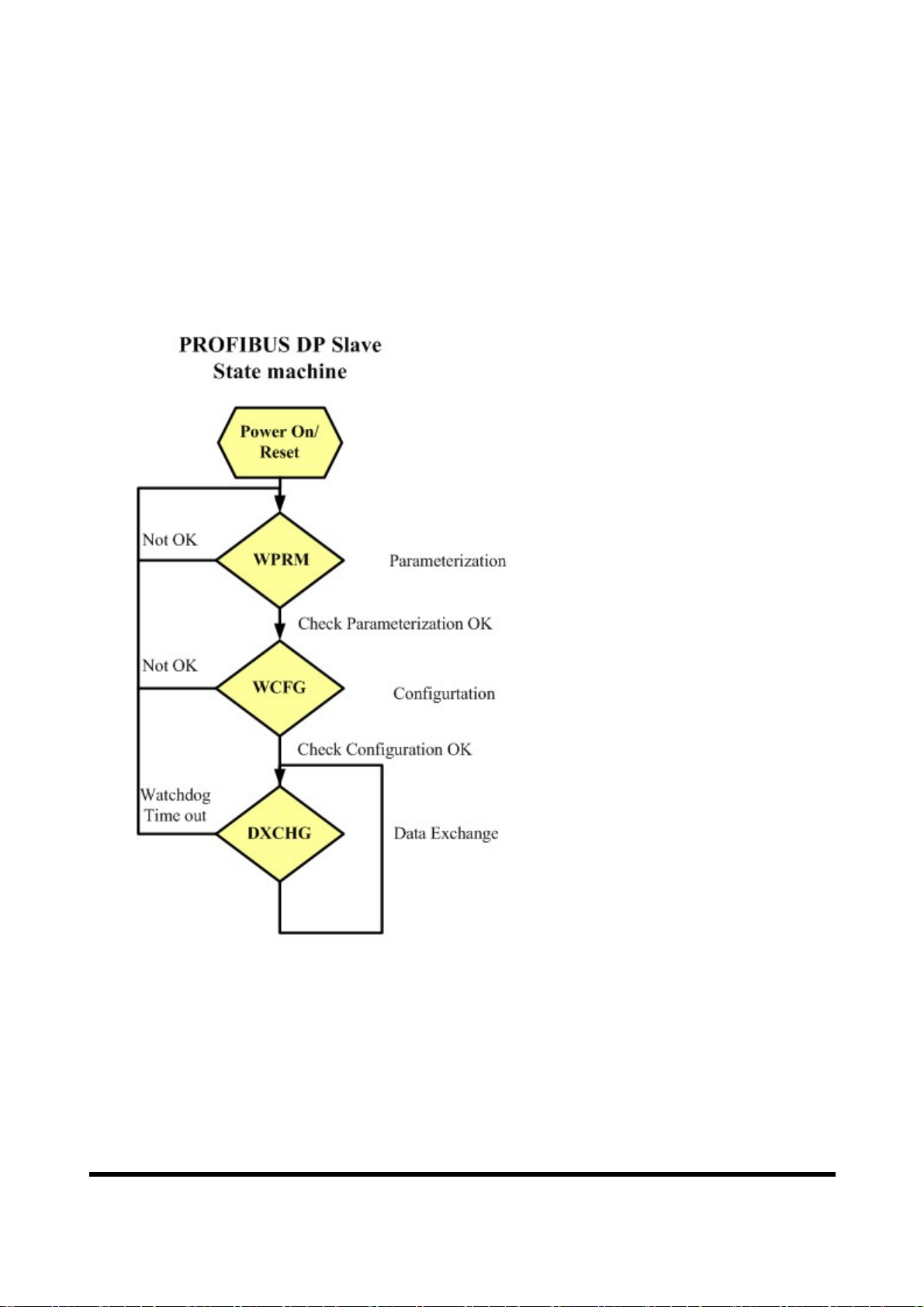
3. Communication protocol transfer theorem
3.1 PROFIBUS data exchange
The GW-7553 is a PROFIBUS DP Slave device. The GW-7553 is first
parameterized then configured and finally it goes into the data exchange mode
(Figure 11).
Figure 11 State machine of PROFIBUS DP Slave device
The GW-7553 exchanges data cyclically between internal DI、DO、AI、AO
data and PROFIBUS Master device in data exchange mode, as shown in figure 12.
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 16
Page 17
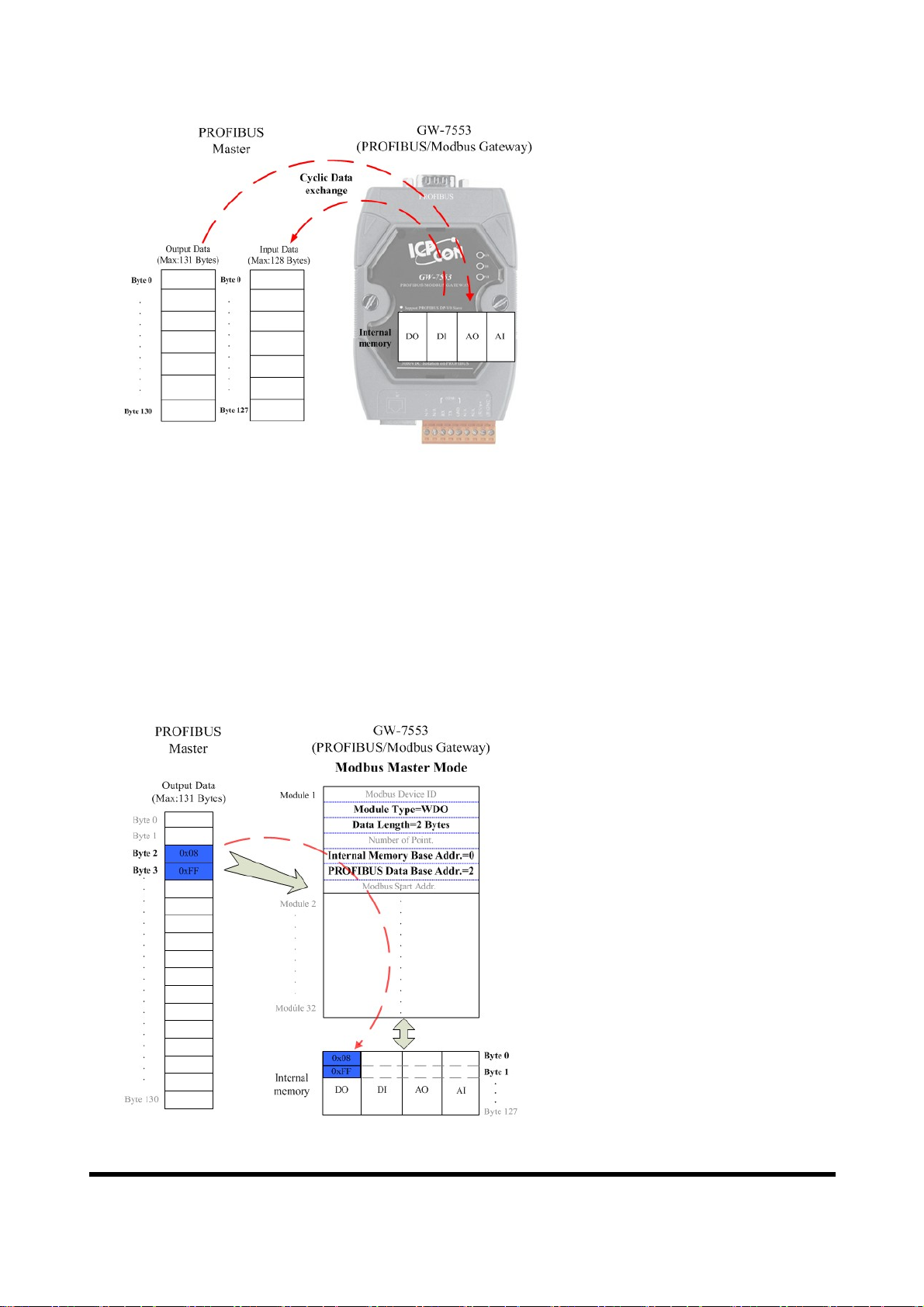
Figure 12 Data exchange between PROFIBUS Master device and GW-7553
The GW-7553 downloads the parameter and configuration from PROFIBUS
Master device to be the module parameters. The GW-7553 and PROFIBUS
Master device have different data type and data address, the GW-7553 can transfer
different data format to PROFIBUS Master device through module parameters.
When the GW-7553 acts as a Modbus Master device, it will send DI、AI data to
input data area of PROFIBUS Master device and it will save data that receives
from PROFIBUS Master device to internal DO、AO memory space, as shown in
、
figure 13
14.
Figure 13 The output data of PROFIBUS Master device send to the GW-7553
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 17
Page 18
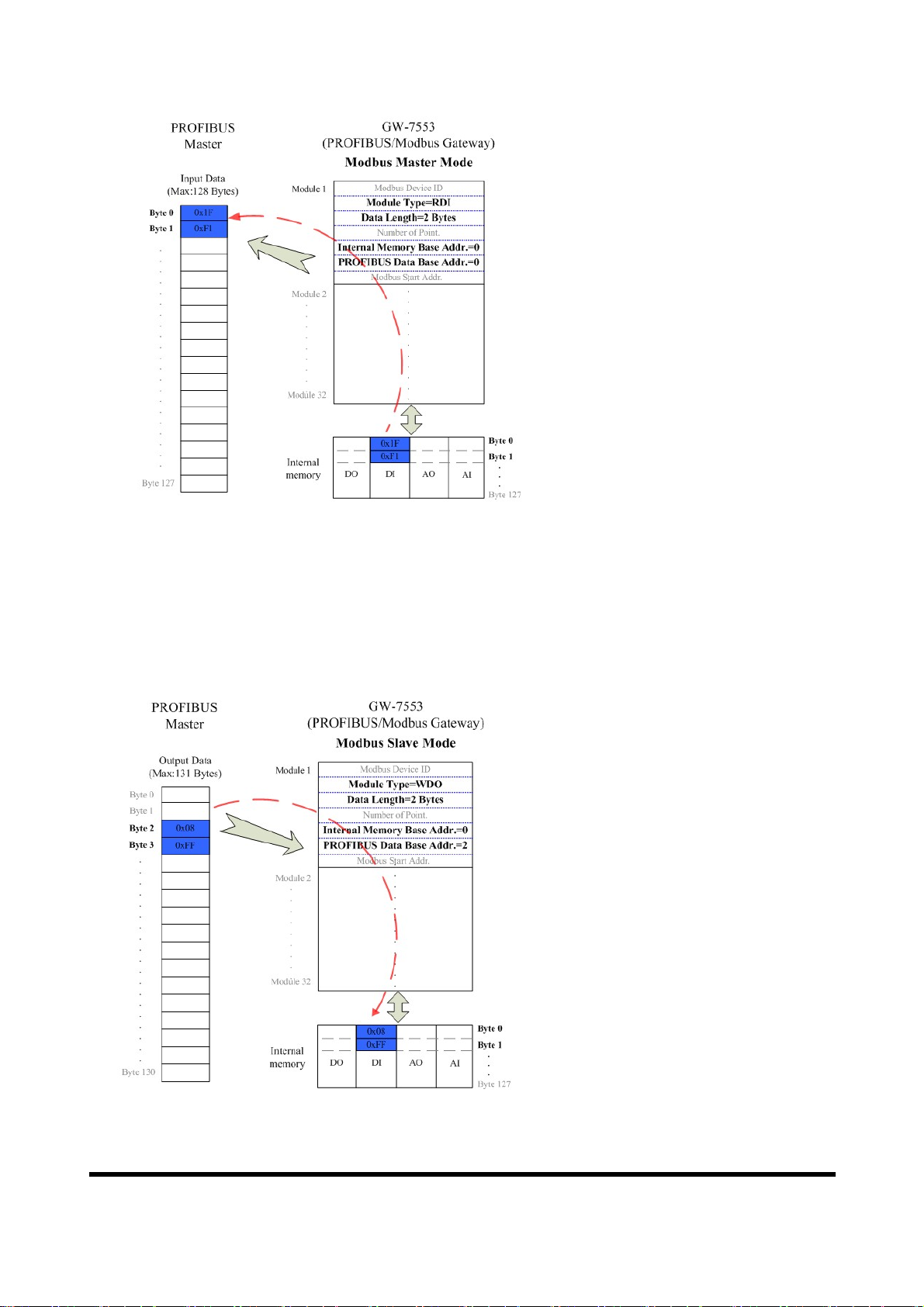
Figure 14 The input data of PROFIBUS Master device receive from the GW-7553
When the GW-7553 acts as a Modbus Slave device, it will send DO、AO data to
input data area of PROFIBUS Master device and it will save data that receives
from PROFIBUS Master device to internal DI、AI memory space, as shown in
figure 15
、
16.
Figure 15 The output data of PROFIBUS Master device send to the GW-7553
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 18
Page 19
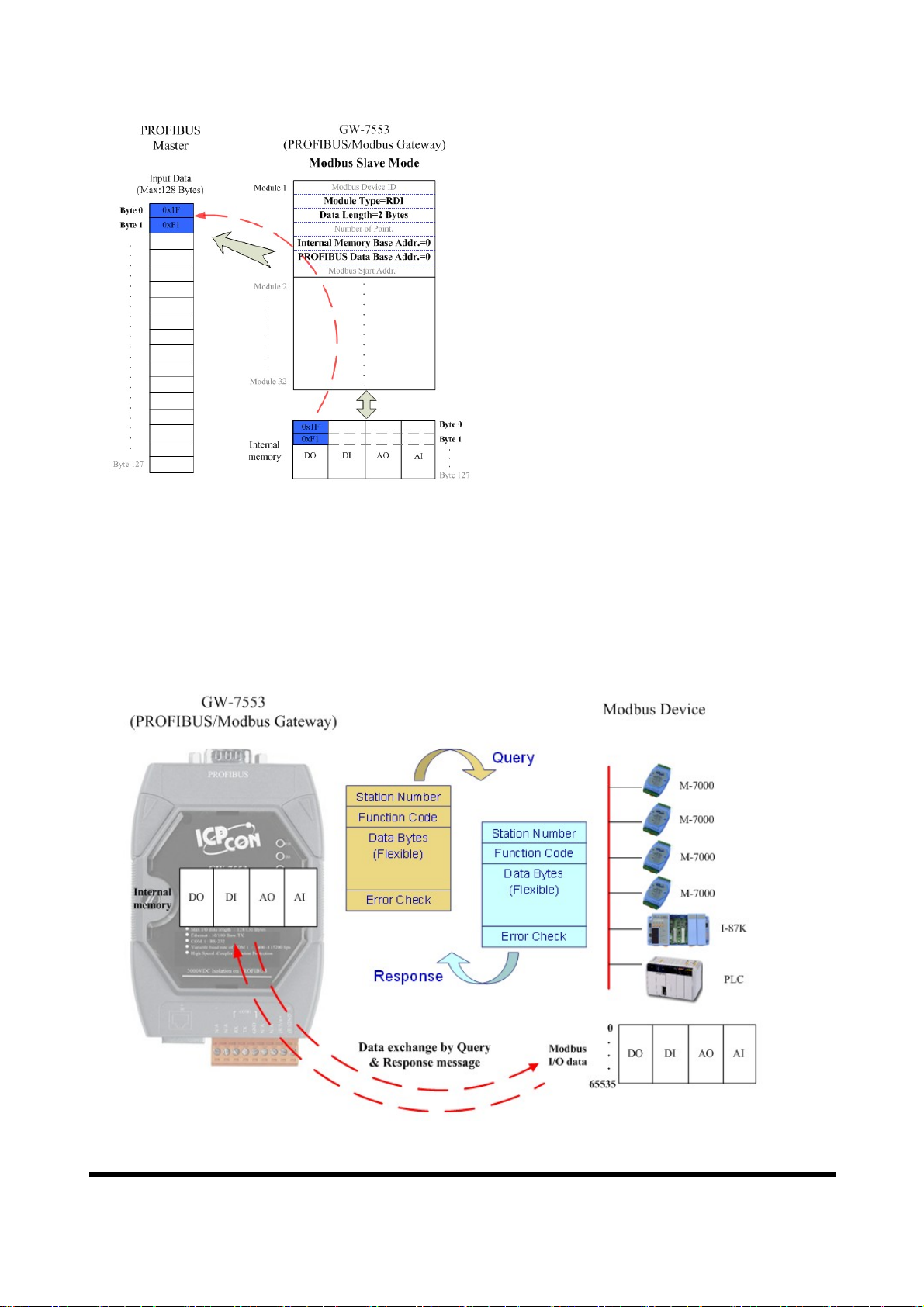
Figure 16 The input data of PROFIBUS Master device receive from the GW-7553
3.2 Modbus data exchange
Modbus protocol belongs to Master-Slave communication and it uses query and
response message to arrive at data exchange and device control, as shown in
figure 17.
Figure 17 Data exchange between the Modbus devices and the GW-7553
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 19
Page 20
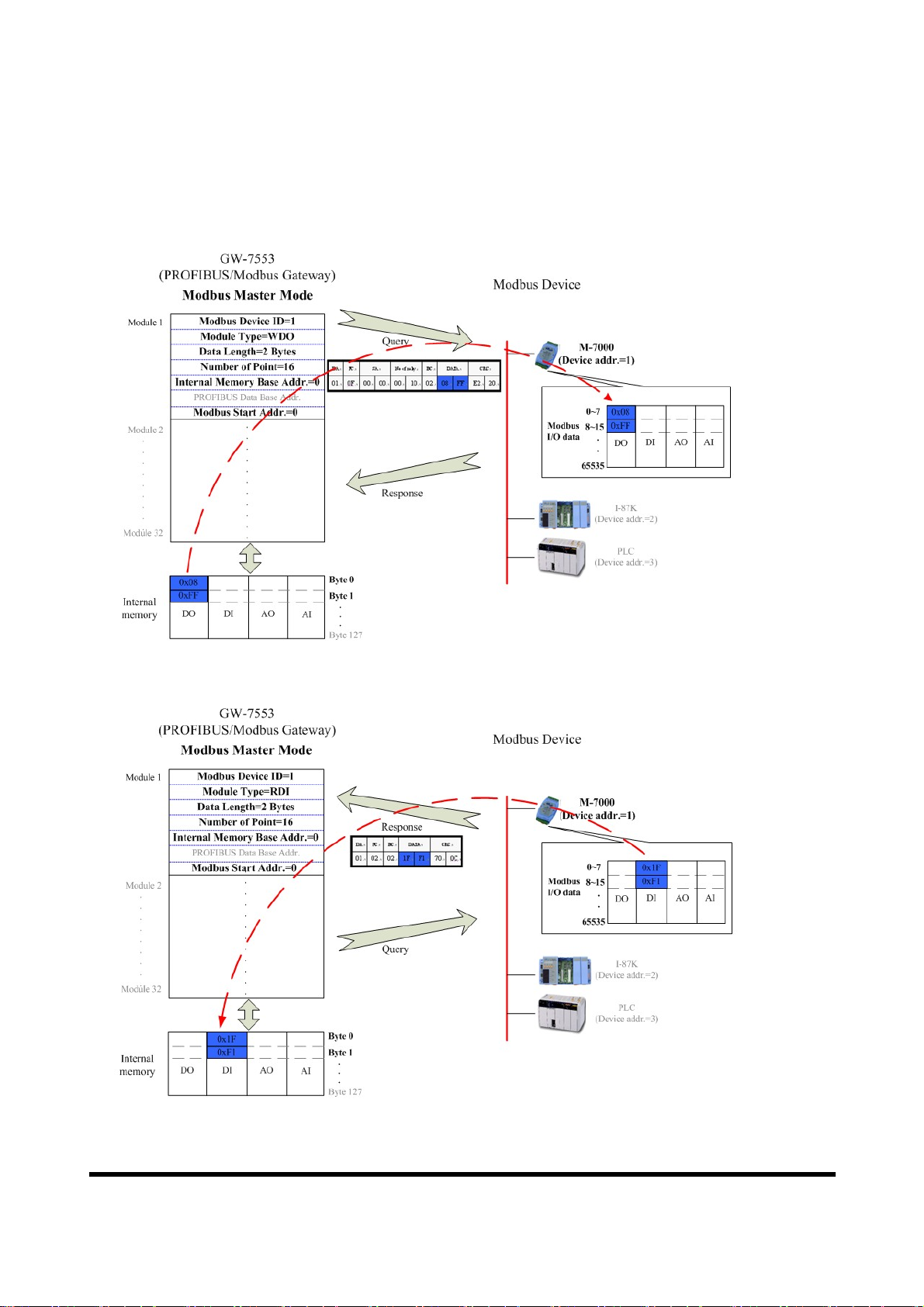
When the GW-7553 acts as a Modbus Master device, it can get query message
through module parameter and DO、AO data and send query message to Modbus
Slave device. It can also receive response message form Modbus Slave device and
then saving to internal DI、AI memory space, as shown in figure 18
、
19.
Figure 18 GW-7553 output data to Modbus Slave devices
Figure 19 GW-7553 receive data from Modbus Slave devices
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 20
Page 21
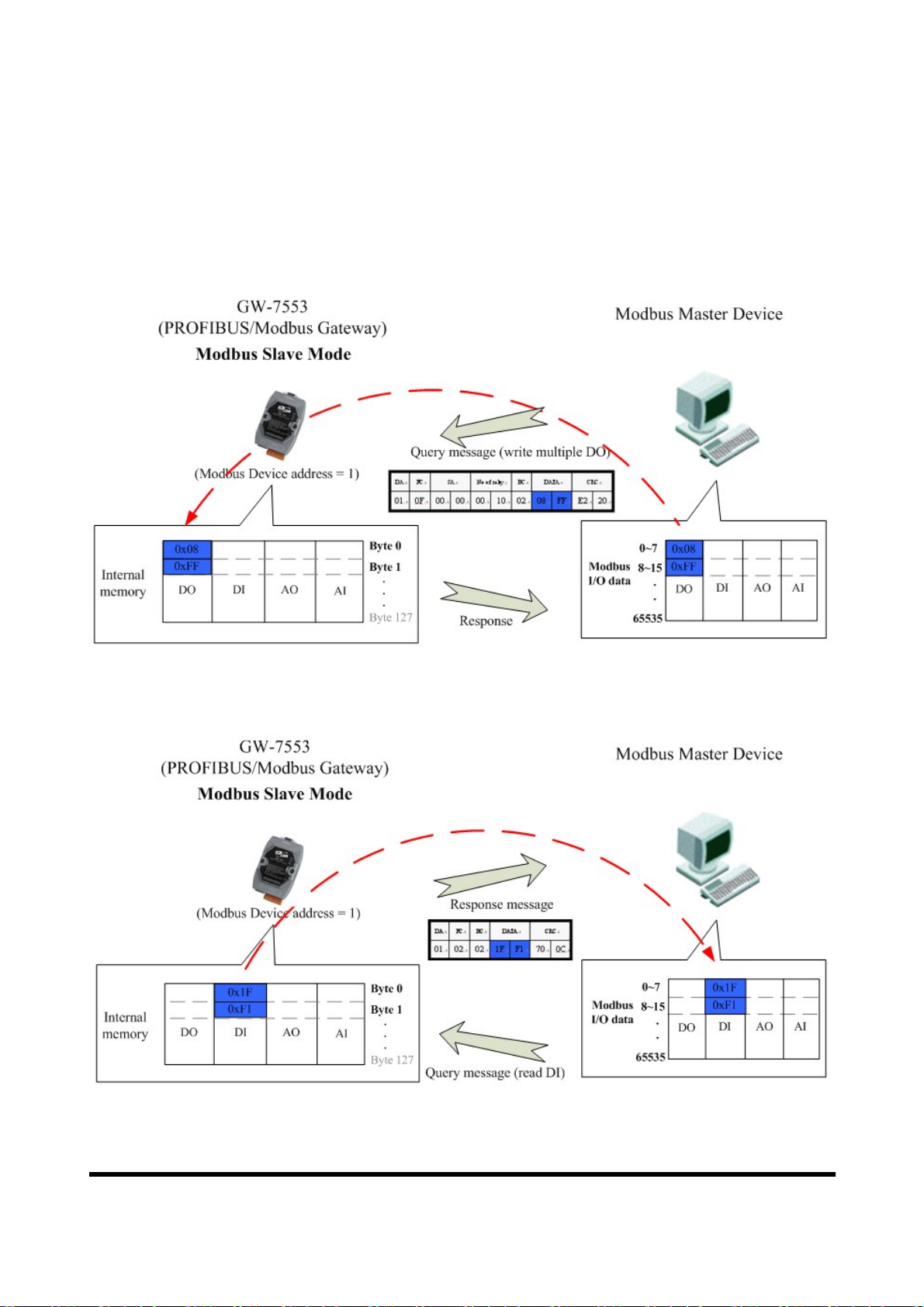
hen the GW-7553 acts as a Modbus Slave device, it can receive query message
W
from Modbus Master device and then saving to internal DO、AO memory space.
It can also send response message to Modbus Master device through internal DI、
AI data, as shown in figure 20
、
21.
Figure 20 The GW-7553 receive data from Modbus Master device
Figure 21 The GW-7553 output data to Modbus Master device
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 21
Page 22
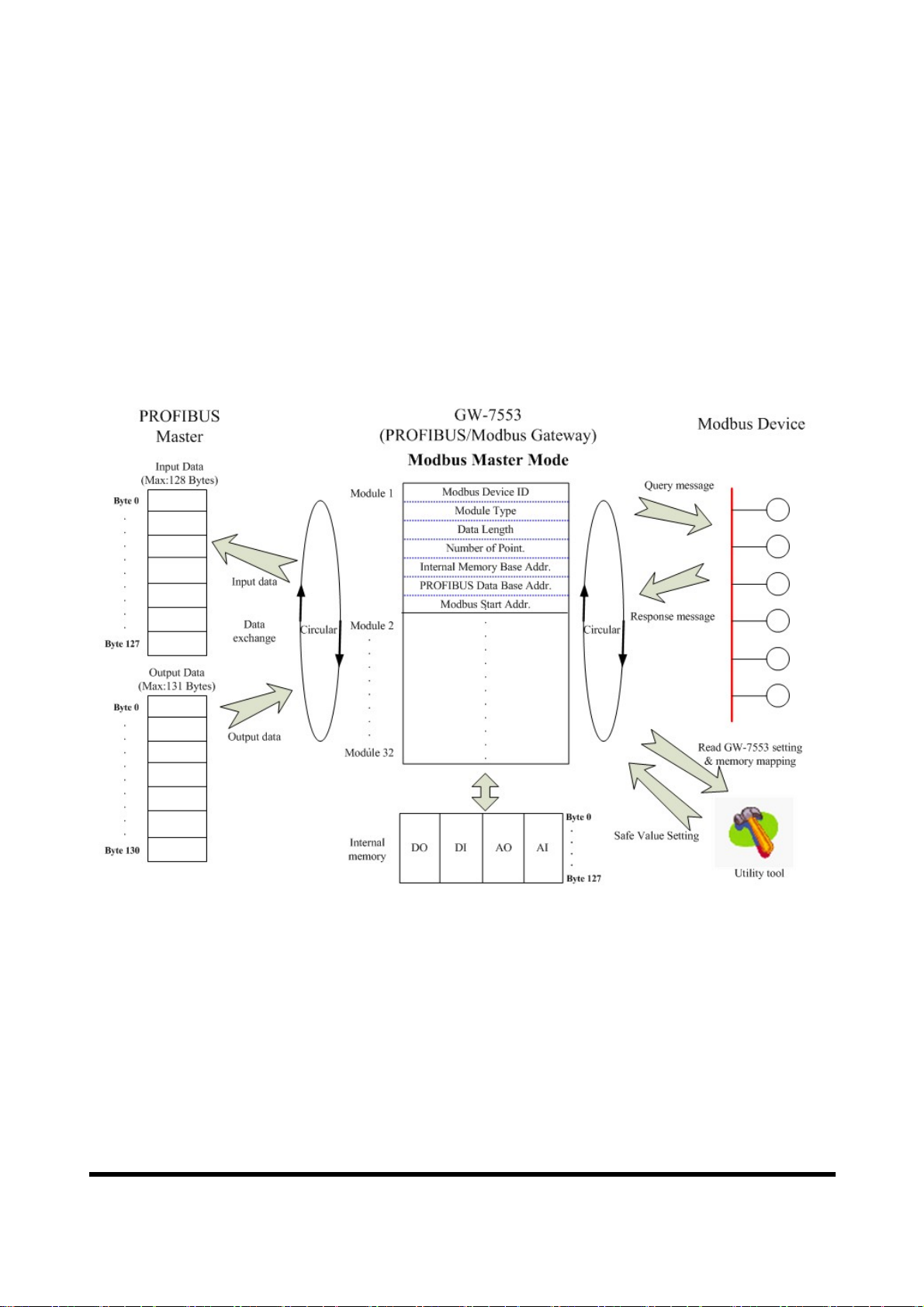
3.3 Communication protocol transfer
In section 3.1 and 3.2, we can understand that data exchange is through DI、
DO、AI、AO memory space of the GW-7553 between PROFIBUS Master、
Modbus and the GW-7553. When the GW-7553 acts as a Modbus Master device,
the data exchange runs continuously between PROFIBUS Master、Modbus and
the GW-7553, as shown in figure 22
、
23.
Figure 22 GW-7553 (master mode) communication protocol transfers
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 22
Page 23
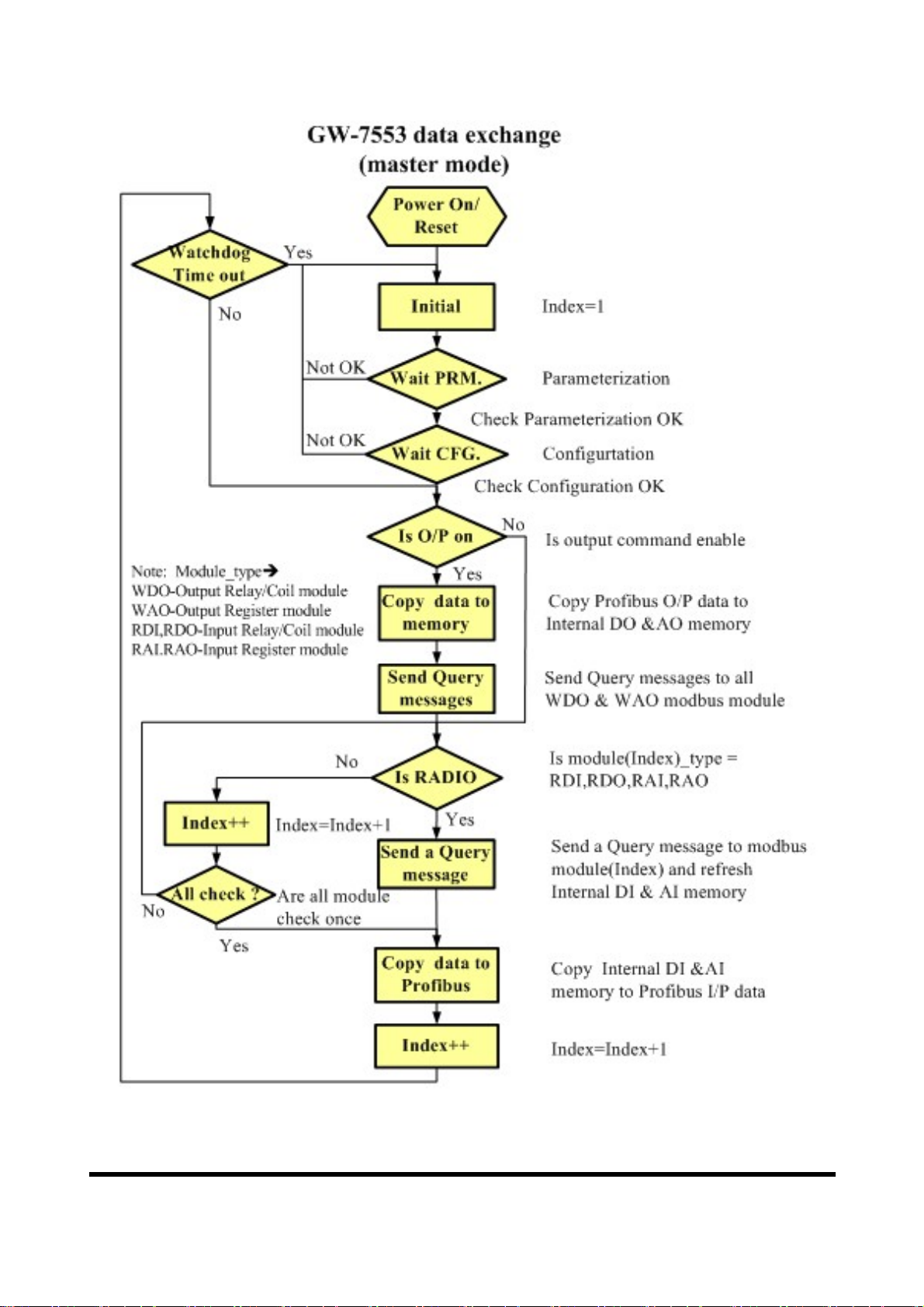
Figure 23 GW-7553 (master mode) flowchart
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 23
Page 24

When the GW-7553 acts as a Modbus Slave device, the data exchange runs
continuously between PROFIBUS Master and the GW-7553 and the data
exchange runs between Modbus Master device and the GW-7553, when GW-7553
、
receive query message from Modbus Master device, as shown in figure 24
25.
Figure 24 GW-7553 (slave mode) communication protocol transfer
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 24
Page 25

Figure 25 GW-7553 (slave mode) flowchart
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 25
Page 26

4. Communication
4.1 Field of application
A master station can be a PLC, PC or any other smart device. The system can be a
mono-master system (Figure 26) or a multi-master system (Figure 27). The GW-
7553 enables the integration of the Modbus devices into a PROFIBUS DP
network.
Figure 26 Mono-master system
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 26
Page 27

Figure 27 Multi-master system
4.2 GSD file
The characteristic (ex: baud rate, message length, number of input / output data.....)
of each PROFIBUS DP device is described in the GSD file. The GSD file of the
GW-7553 is in the ICP DAS companion CD-ROM (PATH--> CD:
\profibus\gateway\gw-7553\gsd\). The user can copy GSD file ( IPDS0C0D.gsd )
and the Bitmap file ( ICP_7553.bmp,GW_7553.bmp ) to the PROFIBUS
configuration tool.
4.2.1 The example of how to load GSD file
In the following examples the CIF50-PB PROFIBUS Master card from Hilscher
is used. The configuration and communication is done by the program “SyCon”
provided by Hilscher.
Step 1: Copy the GSD file (IPDS0C0D.gsd) and the Bitmap file
(ICP_7553.bmp,GW_7553.bmp) from CD of the GW-7553 module
into the PROFIBUS configuration tool.
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 27
Page 28

File->CopyGSD
(Directory: --> CD: \profibus\gateway\gw-7553\gsd\)
Step 2: Click “insert slave” button in the PROFIBUS configuration tool.
Figure 28 Insert PROFIBUS Slave device
Step 3: Select GW-7553 and click “Add” button to assign the GW-7553.
Figure 29 Assign the GW-7553
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 28
Page 29

Step 4: Set the address of the GW-7553 and click “OK” button.
Figure 30 Set the address of the GW-7553
Step 5: The GW-7553 icon is shown in the window. It adds the GW-7553
successfully in the software.
Figure 31 Finish adding the GW-7553
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 29
Page 30

4.3 The Configuration of the common parameters
GW-7553 has twelve common parameters. The user can configure the common
parameters to set the communication mode and data format by the PROFIBUS
configuration tool. The common parameters are described below.
● COM Port baud rate:2400/4800/9600/19200/38400/57600/115200
● COM Port parity:None/Even/Odd
● COM Port data length:7/8 data bit
● COM Port stop bit:1/2 stop bit
● Modbus Type:Master/Slave
● Modbus Format:RTU/ASCII/TCP
● I/O Safe Mode:Retain last value/Switch safe value
● Byte Order : Little-Endian/Big-Endian
● Modbus Device ID(S):1~247
● Polling Modbus Device Interval(ms) (M):1~65535ms
● Query Message Timeout Value(ms)(M):1~65535ms
PS:
● TCP_Connect_Num(T)(M):1~8
a. When stop bit of COM Port is 2, data bit of COM Port must be 7 or else stop bit
of COM Port will be set to 1.
b. I/O Safe Mode
When GW-7553 acts as a Modbus Master (Modbus Type=Master):
i. Data exchange between PROFIBUS Master and GW-7553 is interrupted
“I/O Safe Mode” will be activated when the data exchange between
PROFIBUS Master and GW-7553 is interrupted (e.g. no physical
connection, PROFIBUS Master leaves the data exchange mode, etc.).
• I/O safe mode = “Switch Safe Value”
The GW-7553 will set internal DIO and AIO data to safe value and
send the safe values to the Modbus Slave device.
• I/O safe mode = “Retain Last Value”
Internal DIO and AIO data retain last value
ii. Connection between Modbus Slave and the GW-7553 is interrupted
• I/O safe mode = “Switch Safe Value”
The GW-7553 will set the internal DI and AI data to safe value and send
safe values to PROFIBUS Master device.
• I/O safe mode = “Retain Last Value”
Internal DIO and AIO data retain last value
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 30
Page 31

When GW-7553 acts as a Modbus Slave (Modbus Type=Slave):
i. Data exchange between PROFIBUS Master and GW-7553 is interrupted
“I/O Safe Mode” will be activated when the data exchange between
PROFIBUS Master and GW-7553 is interrupted.
• I/O safe mode = “Switch Safe Value”
The GW-7553 will set internal DIO and AIO data to safe value.
• I/O safe mode = “Retain Last Value”
Internal DIO and AIO data retain last value
ii. Connection between Modbus Master and the GW-7553 is interrupted
Internal DIO and AIO data retain last value received
Please refer section 5.4 about the safe value settings
c. Byte order is an important factor related to the memory allocation. Big-
endian byte order (Motorola format) allocates more significant byte in lower
memory address. On the other hand, little-endian byte order (Intel format)
allocates more significant byte in higher memory address.
d. Modbus device ID is a Modbus address of the GW-7553, when the GW-7553
acts as a Modbus Slave device.
e. We recommend the user to set the “query message timeout value” bigger than
3ms in order to identify the response message.
f. The user can set the maximum number of Modbus TCP Slave device by
“TCP_Connect_Num”. These Modbus TCP Slave devices can have different
IP Address for connection.
g. (M) means the parameter is effective, when Modbus Type of GW-7553 is
Master.
(S) means the parameter is effective, when Modbus Type of GW-7553 is
Slave.
(T) means the parameter is effective, when Modbus Format of GW-7553 is
TCP.
4.4 The Configuration of the modules
The user can set the number and size of the I/O modules in the PROFIBUS
configuration tool. The settings of the modules are described below.
● Max. I/O modules:32 modules
● System setting module:3 byte out
● Output module:Output Relay/Coil => 1~32 Bytes
Output Register => 1~64 Words
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 31
Page 32

● Input module:Input Relay/Coil => 1~32 Bytes
Input Register
● Max. length of I/O data:259 Bytes
● Output length:0~131 Bytes
● Input length:0~128 Bytes
=> 1~64 Words
The modules have module parameters about the communication settings. The
module parameters are shown in the below:
A. Output Relay/Coil module parameters:
● Modbus Slave Device ID(M):0~247
● Start Address(M):0~65535
● NO. of Relay/Coil(M):8*(n-1)+1 ~ 8*n Bits
n=Module size/Byte
● TCP_Connect_Index(T)(M):1~8
B. Output Register module parameters:
● Modbus Slave Device ID (M):0~247
● Start Address(M):0~65535
● TCP_Connect_Index(T)(M):1~8
C. Input Relay/Coil module parameters:
● Modbus Slave Device ID (M):0~247
● Start Address(M):0~65535
● NO. of Relay/Coil(M):8*(n-1)+1 ~ 8*n Bits
● Module Type(M):Read DI/DO
n=Module size/Byte
● TCP_Connect_Index(T)(M):1~8
D. Input Register module parameters:
● Modbus Slave Device ID (M):0~247
● Start Address(M):0~65535
● Module Type(M):Read AI/AO
● TCP_Connect_Index(T)(M):1~8
Example 1:
If the user wants to read a Modbus digital input module (DI module), Device ID is
1, data address is 10010~10019, and data count is 10 via the first TCP connection.
In this case, the user can select an “Input Relay/Coil=> 2 Bytes module”, module
parameters are shown in the below:
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 32
Page 33

Input Relay/Coil module parameters:
● Modbus Slave Device ID(M):1
● Start Address(M):9
● NO. Of Relay/Coil(M):10
● Module Type(M):Read DI
● TCP_Connect_Index(T)(M):1
Example 2:
If the user wants to write a Modbus analog output module (AO module), Device
ID is 2, data address is 40001~ 40004 and data count is 4 via the second TCP
connection.
In this case, the user can select an “Output Register => 4 Words module”, module
parameters are shown in the below:
Output Register module parameters:
● Modbus Slave Device ID(M):2
● Start Address(M):0
● TCP_Connect_Index(T)(M):2
PS:
a. Relay/Coil module is digital module (DI/DO module), the unit is Byte;
Register module is analog module (AI/AO module), the unit is Word.
b. Modbus Slave Device ID:It is a Modbus Slave device address.
c. Start Address:The GW-7553 and Modbus Slave device exchange data
from this starting address.
d. NO. of Relay/Coil:It is data size that the GW-7553 and Modbus Slave
device exchange.
e. Module type:The user can select data type for data exchange by this
setting.
Write DO(WDO)-- Write Digital Output
Write AO(WAO)-- Write Analog Output
Read DI(RDI)- Read Digital Input
Read DO(RDO)- Read Digital Output
Read AI(RAI)-Read Analog Input
Read AO(RAO)-Read Analog Output
f. TCP_Connect_Index:The user can select TCP connection of the module.
The module will transmit and receive data from this connection.
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 33
Page 34

4.5 Diagnostic messages
The GW-7553 can show maximally 10 diagnostic messages at the same time. If
the number of the diagnostic messages is bigger than 10, the GW-7553 will not
process other diagnostic message. The diagnostic messages have four types. They
are “Module Error”, “System Setting Module Error”, “EEPROM Error” and
“Input Data Error”. The diagnostic messages are shown in table 11.
Table 11 Diagnostic messages
Messages Description Note
ILLEGAL FUNCTION!
ILLEGAL DATA ADDRESS!
ILLEGAL DATA VALUE!
SLAVE DEVICE FAILURE!
ACKNOWLEDGE!
SLAVE DEVICE BUSY!
NEGATIVE ACKNOWLEDGE!
Module 1~32 Error *
MEMORY PARITY ERROR!
Please refer
Modbus
Exception
Code
definition for
detail.
System setting module
Error
EEPROM Error
Data Error
Modbus NOT DEFINED ERROR!
GATEWAY PATH UNAVAILABLE!
GATEWAY TARGET DEVICE FAILED
TO RESPOND!
CRC (LRC) Error!
Response Message Timeout!
Response Message error!
Connection error!
Not find System setting module.
Position is not correct!
Read safe value error.
Read IP error!
Write IP error!
PROFIBUS lose input data.
Lose PROFIBUS output data.
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 34
Page 35

“*” These error messages are not supported when the GW-7553 act as a Modbus
Slave.
PS:
Data Error:
a. GW-7553 acts as a Modbus Master
If the polling speed between the GW-7553 device and the Modbus Slave is
faster than the data exchange rate between PROFIBUS Master and the GW7553 then the PROFIBUS Master will not get all the data from the Modbus
Slave and therefore a diagnostic message (“PROFIBUS lose input data”) will be
send by the GW-7553 to the PROFIBUS Master
b. GW-7553 acts as a Modbus Slave
If the GW-7553 receives more telegram from the Modbus Master than it
transmits to the PROFIBUS Master then a diagnostic message (“PROFIBUS
lose input data”) will be send by the GW-7553 to the PROFIBUS Master.
c. When the GW-7553 receives a “data output command” (output byte 0) from
system setting module, and this command didn’t increase in order (ex: 0->1, 1>2,…, 255->0), the GW-7553 will think that it lose some output data of the
PROFIBUS Master and a diagnostic message (“Lose PROFIBUS output data”)
will be sent by the GW-7553 to the PROFIBUS Master.
4.6 I/O data exchange
The I/O data exchange is decided by Modbus type of the GW-7553 (please refer
section 4.3 The Configuration of the common parameters) between PROFIBUS
Master device and the GW-7553. Output data area of PROFIBUS Master device is
mapped into DO/AO memory of the GW-7553 and input data area of PROFIBUS
Master device is mapped into DI/AI memory of the GW-7553, when Modbus type
is Master. In the other way, Output data area of PROFIBUS Master device is
mapped into DI/AI memory of GW-7553 and input data area of PROFIBUS
Master device is mapped into DO/AO memory of GW-7553, when Modbus type
is Slave (please refer section 3.1 PROFIBUS data exchange ).
4.6.1 Input data area
The maximum length of input data is 128 bytes. Before arrange the input
module, the user must arrange and configure the system setting module. The
user can get data and control I/O of Modbus Slave device or get DI/DO/AI/AO
of the GW-7553 by read input module.
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 35
Page 36

Table 12 Input data area
Module Byte Data Description
Input
module
0~127 Data Receive data
4.6.2 Output data area and communication command
The maximum length of output data is 131 bytes. Before arrange the output
module, the user must arrange and configure the system setting module. The
first three bytes belong to communication commands, as shown in table 13. The
user can change data and I/O state of Modbus Slave device or DI/DO/AI/AO
data of GW-7553 by modify data of output module.
Table 13 Output data area
Module Byte
0
System
setting
module
1
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Data output command
- - - - - - SM DC Control bit
Bit Position
Description
Output module select
Output data
Output
module
2
3~130
● Data output command(byte 0)
a. When Modbus type is Master
When this byte is changed, PROFIBUS Master device will send data
of output module to DO/AO data of GW-7553 and then GW-7553
will send query message to Modbus Slave device for change data or
output state of Modbus Slave device.
b. When Modbus type is Slave
When this byte is changed, PROFIBUS Master device will send data
of output module to DO/AO data of GW-7553.
PS: When the user use this byte to trigger “data output command”, the
user must increase this byte in order (ex: 0->1, 1->2,…, 255->0) or else
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 36
Page 37

the GW-7553 will send a diagnostic message to the PROFIBUS Master
(please refer section 4.5 Diagnostic messages).
● Control bit(byte 1)
DC(bit 0):When this bit is set (DC=1), diagnostic messages sent by the
GW-7553 module will all be cleared.
SM(bit 1):When this bit is set (SM=1), the GW-7553 will enter setup
mode. The utility can communicate with the GW-7553 in
this mode.
When this bit is ''0'' (SM=0), the GW-7553 will enter normal
operation mode. The GW-7553 can communicate with
Modbus device in this mode.
Bit 2~7:The remaining bits have to be set to zero.
● Output module select(byte 2)
When this byte is ‘0’ and the user change data output command(byte 0),
it will trigger all data output command of output modules.
When this byte isn’t ‘0’ and the user change data output command(byte
0), it will trigger single data output command of the output module and
this byte
represent that the user want to trigger data output command of the third
module )
represent module address of the output module (ex: “byte 2”=3, it
4.7 Establish connection with GW-7553
Before establishing a connection between the DP-Master and the GW-7553, user
should execute the following steps first.
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 37
Page 38

Figure 32 Establish connection with GW-7553
First, users must load the electronic device description file (GSD file) of the GW7553 into the DP-Master, and then set the parameters. Finally change your DPMaster from Offline state to Operate state. While DP-Master changes to operate
mode, GW-7553 will initial the modules. Then GW-7553 allocates the memory
space and waits for Set_Prm telegram. The next step is waiting for Check_Cfg
telegram in order. If there is no error occurs, GW-7553 proceeds into data
exchange state. Users can observe the status indicator LED to know the state of
GW-7553. At the meantime, if there is any error occurs, GW-7553 will return to
wait parameterization.
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 38
Page 39

4.8 Data exchange example—Modbus RTU
In this example a Modbus Master device simulated by a PC program sends query
message and receives response message from a PROFIBUS Master via the GW7553 gateway.
In the following examples the CIF50-PB PROFIBUS Master card from Hilscher is
used. The configuration and communication is done by the program “SyCon”
provided by Hilscher.
Step 1: Copy the GSD file and assign the GW-7553 a valid station address
(Please refer to the section 4.2 GSD file).
Step 2: Connect the RS-232 port of the GW-7553 module to a COM port of
the PC and the PROFIBUS port to a PROFIBUS Master (Figure 33).
Figure 33 Wiring diagram between PC and GW-7553
Step 3: Set the parameters of the GW-7553. We just need to change
“Modbus Type” to Slave and the default setting is being used in the
other parameters for this example. Please refer to section 4.3 the
Configuration of the common parameters. The users can set
parameters as shown in the below.
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 39
Page 40

Figure 34 Double click the GW-7553 icon to open the
“Slave configuration” window
Figure 35 Click “Parameter Data…” button to open the
“Parameter Data” window
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 40
Page 41

Figure 36 The user needs to change “Modbus Type” to
Slave for this example and click “OK” button
Step 4: Set the GW-7553 modules, as shown in figure 37 and 38.
− Select “System setting” module: “System setting” module always has
to be selected otherwise no communication can be established
between the gateway and the Modbus network.
− Select “Output Relay/Coil” module: In this example a “Output
Relay/Coil--2 Byte” module is selected.
− Select “Input Relay/Coil” module: In this example a “Input
Relay/Coil--2 Byte” module is selected.
Figure 37 Double click the GW-7553 icon to open the
“Slave configuration” window
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 41
Page 42

Figure 38 Select modules
Step 5: Close the “Slave Configuration” window by clicking the “OK”
button.
Step 6: Now the setting done by the configuration tool has to be
downloaded to the PROFIBUS Master.
Click on the Master area in the graphic window then
Online -> Download…
Figure 39 Click “Online->Download” to download the
setting into PROFIBUS Master
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 42
Page 43

4.8.1 Receiving data from a Modbus Master device
-- Start the test utility “MBRTU” (figure 40) on the PC.
This utility simulates a Modbus Master device and is on the web site in the
following directory:
http://ftp.icpdas.com.tw/pub/cd/8000cd/napdos/modbus/modbus_utility/
(1) Set the COM Port number of the PC
(2) Set the Baud rate to 115200
(3) Set the Line control to N,8,1
(4)Open the connection
Figure 40 MBRTU Utility
--Send Command to write DO of the GW-7553
The user needs to input command (” 01 0F 00 00 00 10 02 FF FF”) here and
click <Send Command> button to send Modbus command: “01 0F 00 00 00
10 02 FF FF E3 90” and then MBRTU can receive response message (” 01 0F
00 00 00 10 54 07”). The user can find byte 0, 1 of the input data area in the
configuration program “SyCon” have changed into “0xFF” at this time, as
shown in the below.
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 43
Page 44

Figure 41 Send Modbus command (output data: 0xFF, 0xFF)
Figure 42 Receive “0xFF” in the input data area
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 44
Page 45

Table 14 Receive “0xFF” in the input data area
Module Byte Data type Representation Value
Input module
PS:
Modbus command:
Query message
SA
DA FC
(Hi)
01 0F 00 00 00 10 02 FF FF E3 90
Response message
SA
DA FC
(Hi)
01 0F 00 00 00 10 54 07
Input 0 Byte Hex 0xFF
Input 1 Byte Hex 0xFF
SA
NO
NO
BC DATA
(Lo)
SA
(Lo)
(Hi)
NO
(Hi)
(Lo)
NO
(Lo)
CRC
check
CRC
check
z DA: Device Address-0x01
z FC: Function Code-0x0F=>Write multi-DO
z SA(Hi): Start Address(Hi byte)-0x00
z SA(Lo): Start Address(Lo byte)-0x00
z NO(Hi): No. Of points (Hi byte)-0x00
z NO(Lo): No. Of points (Lo byte)-0x10
z BC: Byte Count-0x02
4.8.2 Receiving data from the PROFIBUS Master device
--Send Command to read DI of the GW-7553
The user needs to input command (” 01 02 00 00 00 10”) in MBRTU and
click <Send Command> button to send Modbus command: “01 02 00 00 00
10 79 C6” and then MBRTU can receive response message (” 01 02 02 00 00
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 45
Page 46

B9 B8”). In this message, the user can know the value of DI0 & DI1 is “0” in
the GW-7553.
--Send output data to write DI of the GW-7553 by the PROFIBUS Master
The user needs to set “0xFE” & “0xDC” in byte 3 & byte 4 of output data
area in the configuration program “SyCon” and then set the value of the first
byte from 0 to 1 to trigger the data output command.
--Send Command to read DI of the GW-7553 again
Now the user can input command (” 01 02 00 00 00 10”) in MBRTU and
click <Send Command> button to send Modbus command: “01 02 00 00 00
10 79 C6” again. Then MBRTU can receive response message (” 01 02 02 FE
DC F8 41”). In this message, the user can know the value of DI0 & DI1 have
changed into “0xFE” & “0xDC” in the GW-7553, as shown in figure 43, 44,
45 & table 15.
Figure 43 Send Modbus command to read DI of the GW-7553
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 46
Page 47

Figure44 Set output data and trigger output data command in
the output data area
Table 15 Set output data and trigger output data command
Module Byte Data type Representation Value
System
module
Output
module
Output 0 Byte Hex
Output 1 Byte Hex 0x00
Output 2 Byte Hex 0x00
Output 3 Byte Hex
Output 4 Byte Hex
0x00 → 0x01
0x00→ 0xFE
0x00→ 0xDC
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 47
Page 48

Figure 45 Send Modbus command to read DI of the GW-7553 and
receive data (0xFE, 0xDC)
PS:
Modbus command:
Query message
SA
SA
NO
NO
CRC
DA FC
(Hi)
(Lo)
(Hi)
(Lo)
check
01 02 00 00 00 10 79 C6
Response message
CRC
DA FC BC DATA
check
01 02 02 FE DC F8 41
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 48
Page 49

z DA: Device Address-0x01
z FC: Function Code-0x02:read DI
z SA(Hi): Start Address(Hi byte)-0x00
z SA(Lo): Start Address(Lo byte)-0x00
z NO(Hi): No. Of points(Hi byte)-0x00
z NO(Lo): No. Of points (Lo byte)-0x10
z BC: Byte Count-0x02
4.9 Data exchange example—Modbus TCP
In this example a Modbus Master device simulated by a PC program sends query
message and receives response message from a PROFIBUS Master via the GW7553 gateway.
In the following examples the CIF50-PB PROFIBUS Master card from Hilscher is
used. The configuration and communication is done by the program “SyCon”
provided by Hilscher.
Step 1: Copy the GSD file and assign the GW-7553 a valid station address
(Please refer to the section 4.2 GSD file).
Step 2: Connect GW-7553 and PC by Figure 46.
Figure 46 Wiring diagram between PC and GW-7553
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 49
Page 50

Step 3: Set the parameters of the GW-7553. We need to change “Modbus
Type” to Slave and “Modbus Format” to Modbus TCP. The default
setting is being used in the other parameters for this example. Please
refer to section 4.3 the Configuration of the common parameters.
The users can set parameters as shown below.
Figure 47 Double click the GW-7553 icon to open the
“Slave configuration” window
Figure 48 Click “Parameter Data…” button to open the
“Parameter Data” window
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 50
Page 51

Figure 49 The user needs to change “Modbus Type” to
Slave and “Modbus Format” to Modbus TCP for this
example and click “OK” button
Step 4: Set the GW-7553 modules, as shown in figure 50 and 51.
− Select “System setting” module: “System setting” module always has
to be selected otherwise no communication can be established
between the gateway and the Modbus network.
− Select “Output Relay/Coil” module: In this example a “Output
Relay/Coil--2 Byte” module is selected.
− Select “Input Relay/Coil” module: In this example a “Input
Relay/Coil--2 Byte” module is selected.
Figure 50 Double click the GW-7553 icon to open the
“Slave configuration” window
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 51
Page 52

Figure 51 Select modules
Step 5: Close the “Slave Configuration” window by clicking the “OK”
button.
Step 6: Now the setting done by the configuration tool has to be
downloaded to the PROFIBUS Master.
Click on the Master area in the graphic window then
Online -> Download…
Figure 52 Click “Online->Download” to download the
setting into PROFIBUS Master
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 52
Page 53

Step 7: Set the network settings of the GW-7553 by PROFIBUS/Modbus
gateway utility (please refer section 5.5 & 5.6). The settings of the GW7553 must have the same domain and different IP with the PC (ex: PC’s
IP=192.168.0.106, MASK=255.255.0.0; GW-7553’s IP=192.168.0.107,
MASK=255.255.0.0).
Step 8: Reset the power of the GW-7553 for an active setting.
4.9.1 Receiving data from a Modbus Master device
-- Start the test utility “MBTCP” (figure 53) on the PC.
This utility simulates a Modbus Master device and is on the web site in the
following directory:
http://ftp.icpdas.com.tw/pub/cd/8000cd/napdos/modbus/modbus_utility/
(1) Set the IP address of the GW-7553
(2) Click the connect button
Figure53 MBTCP Utility
--Send Command to write DO of the GW-7553
The user needs to input command (” 01 0F 00 00 00 10 02 FF FF”) here and
click <Send Command> button to send Modbus command: “01 0F 00 00 00
10 02 FF FF” and then MBTCP can receive response message (” 01 0F 00 00
00 10”). The user can find byte 0, 1 of the input data area in the configuration
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 53
Page 54

program “SyCon” have changed into “0xFF” at this time, as shown below.
Figure 54 Send Modbus command (output data: 0xFF, 0xFF)
Figure 55 Receive “0xFF” in the input data area
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 54
Page 55

Table 16 Receive “0xFF” in the input data area
Module Byte Data type Representation Value
Input module
PS:
Modbus command:
Query message
SA
DA FC
(Hi)
01 0F 00 00 00 10 02 FF FF
Response message
SA
DA FC
(Hi)
01 0F 00 00 00 10
Input 0 Byte Hex 0xFF
Input 1 Byte Hex 0xFF
SA
NO
NO
BC DATA
(Lo)
SA
(Lo)
(Hi)
NO
(Hi)
(Lo)
NO
(Lo)
z DA: Device Address-0x01
z FC: Function Code-0x0F=>Write multi-DO
z SA(Hi): Start Address(Hi byte)-0x00
z SA(Lo): Start Address(Lo byte)-0x00
z NO(Hi): No. Of points (Hi byte)-0x00
z NO(Lo): No. Of points (Lo byte)-0x10
z BC: Byte Count-0x02
4.9.2 Receiving data from the PROFIBUS Master device
--Send Command to read DI of the GW-7553
The user needs to input command (” 01 02 00 00 00 10”) in MBTCP and click
<Send Command> button to send Modbus command: “01 02 00 00 00 10”
and then MBTCP can receive response message (” 01 02 02 00 00”). In this
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 55
Page 56

message, the user can know the value of DI0 & DI1 is “0” in the GW-7553.
--Send output data to write DI of the GW-7553 by the PROFIBUS Master
The user needs to set “0xFE” & “0xDC” in byte 3 & byte 4 of output data
area in the configuration program “SyCon” and then set the value of the first
byte from 0 to 1 to trigger the data output command.
--Send Command to read DI of the GW-7553 again
Now the user can input command (” 01 02 00 00 00 10”) in MBTCP and click
<Send Command> button to send Modbus command: “01 02 00 00 00 10”
again. Then MBTCP can receive response message (” 01 02 02 FE DC”). In
this message, the user can know the value of DI0 & DI1 have changed into
“0xFE” & “0xDC” in the GW-7553, as shown in figure 56, 57, 58 & table 17.
Figure 56 Send Modbus command to read DI of the GW-7553
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 56
Page 57

Figure 57 Set output data and trigger output data command
in the output data area
Table 17 Set output data and trigger output data command
Module Byte Data type Representation Value
System
module
Output
module
Output 0 Byte Hex
Output 1 Byte Hex 0x00
Output 2 Byte Hex 0x00
Output 3 Byte Hex
Output 4 Byte Hex
0x00 → 0x01
0x00→ 0xFE
0x00→ 0xDC
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 57
Page 58

Figure 58 Send Modbus command to read DI of the GW-7553 and
receive data (0xFE, 0xDC)
PS:
Modbus command:
Query message
SA
SA
NO
NO
DA FC
(Hi)
(Lo)
(Hi)
(Lo)
01 02 00 00 00 10
Response message
DA FC BC DATA
01 02 02 FE DC
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 58
Page 59

z DA: Device Address-0x01
z FC: Function Code-0x02:read DI
z SA(Hi): Start Address(Hi byte)-0x00
z SA(Lo): Start Address(Lo byte)-0x00
z NO(Hi): No. Of points(Hi byte)-0x00
z NO(Lo): No. Of points (Lo byte)-0x10
z BC: Byte Count-0x02
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 59
Page 60

5. Application of Utility
5.1 Install Utility
Step 1:
Download the PROFIBUS/Modbus gateway utility setup file from the
CD-ROM disk following the path of “CD:\profibus\gateway\gw7553\utilities\” or the web site
“
ftp://ftp.icpdas.com.tw/pub/cd/fieldbus_cd/profibus/gateway/gw-
7553/utilities/”
Step 2:
Execute the Setup.exe file to install the PROFIBUS/Modbus Gateway
Utility.
Figure 59 Install the utility
Step 3:
Click the “Next” button to continue. If you want to change the installation
destination, click “Browse” button to set the installation path.
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 60
Page 61

Step 4:
Figure 60 Set the installation path
Click the “Next” button to confirm installation
Figure 61 Confirm installation
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 61
Page 62

Step 5:
Step 6:
Click the “Close” button to finish and exit the installation program
Figure 62 Installation complete
After finishing the installation of the PROFIBUS/Modbus Gateway
Utility, users can find the Utility as shown in the following screen shot.
Figure 63 The path of Utility
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 62
Page 63

5.2 Utility introduction
By this utility, the user can understand the module address of PROFIBUS、
Modbus and the GW-7553. The utility also support users set safe value and
network setting easily. It introduces main window of the utility first as shown in
figure 64.
Figure 64 Main window of the utility
Main window of the utility has 6 parts, they are (1)Menu、 (2)COM Port
settings、(3)Module state、(4)Module parameters、(5)Connection status of GW7553 and COM Port、(6) Status bar, as shown in the below.
5.2.1 Menu:
1. Communication =>
a. Connect:Open COM Port and connect with the GW-7553
b. Disconnect:Close COM Port and disconnect with the GW-7553
c. Exit:Exit from the utility
2. IP Setting =>
a. New Setting:Open a new IP setting.
b. Load from file:Load a IP setting from the file.
c. Load from device:Load a IP setting from the GW-7553.
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 63
Page 64

3. Safe Value Setting =>
a. New Setting:Open a new safe value setting.
b. Load from file:Load a safe value setting from the file.
c. Load from device:Load a safe value setting from the GW-7553.
4. View =>
a. Space configuration in device:Display memory address configuration
of select module in the GW-7553.
b. Space configuration in PROFIBUS:Display memory address
configuration of select module in PROFIBUS Master station.
c. Space configuration in Modbus:Display memory address
configuration of select module in the Modbus.
5. Help =>
a. Get Firmware Version From Module:Show firmware version of the
GW-7553.
b. About Utility:Show about version of the utility.
5.2.2 COM Port settings:
1. Port: COM1~COM8
2. Baud rate: 2400/4800/9600/19200/38400/57600/115200
3. Parity: None/Odd/Even
4. Data bit: 8 data bit
5. Stop bit: 1 stop bit
5.2.3 Module state:
It can display the number of modules in the GW-7553 and display module
parameters in the window of the module parameter by click the module’s icon.
5.2.4 Module parameters:
Display module parameters of the GW-7553.
5.2.5 Connection status of device and COM Port:
Module state:Display connection status between the utility and the GW-7553.
The green color means connected and the red color means
disconnected.
COM Port state:Display state of the PC’s COM Port. The green color means
COM Port is open and the red color means COM Port is close.
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 64
Page 65

5.2.6 Status bar:
Display messages about COM Port connection、the GW-7553 connection and
the progress of data transmission.
5.3 Memory address configuration of the module
There are 3 kinds of memory address configuration. They are (1)Space
configuration in device 、 (2) Space configuration in PROFIBUS 、(3)Space
configuration in Modbus, as shown in figure 65.
Figure 65 The menu of space configuration
5.3.1 Space configuration in device:
The user can select check box of the module to show memory address
configuration of DI/DO/AI/AO in the GW-7553, as shown in figure 66.
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 65
Page 66

Figure 66 Space configuration in device
5.3.2 Space configuration in PROFIBUS:
The user can select check box of the module to show memory address
configuration of I/O data area in the PROFIBUS Master station, as shown in
figure 67.
Figure 67 Space configuration in PROFIBUS
5.3.3 Space configuration in Modbus:
The window of “Space Configuration in Modbus” divided into 3 parts to explain,
as shown in figure 68.
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 66
Page 67

) Select module:
(1
The user can select
check box of the module to show memory address
configuration of DI/DO/AI/AO in Modbus network.
(
2) Display interface:
The user can click “W
rite Output” button to show DO/AO memory
address configuration of output modules in Modbus network, click “Read
Input” button to show DI/AI memory address configuration of input
modules in Modbus network, click “Read Output” button to show DO/AO
memory address configuration of input modules in Modbus network.
(
3) Color display:
The user can disc
riminate states of Modbus address configuration by
different color. White means the address is not used. Light blue means the
address was configured by a module. Mazarine means the address was
configured by many modules, but Modbus ID is not repeat in these
modules. Red means the address was configured by many modules and
Modbus ID is repeat in these modules. The data may be read and written
by different modules at this time, it may make the data transmit and
device control error easy because address configuration and Modbus ID
overlap.
Figure 68 Space configuration in Modbus
5.4 Safe value setting
There are 3 kinds of safe valu
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 67
e setting. They are (1) Open a new setting、(2)Load
Page 68

from file、(3)Load from device, as shown in figure 69.
Figure 69 The menu of safe value setting
The window of “Safe Value Setting” divided into 6 parts to explain, as shown in
figure 70.
1) Select module:
(
The user can sele
ct check box of the module to know memory address
configuration of the module for set safe value of the module.
(2) DI/O table:
The user can do
uble click left button of mouse at the value of DI/DO to change
the value from “H” to “L” or “L” to “H”.
(3) All DI/O setting:
The user can click “A
ll set to H” button to set all of DI/DO to “H” and click “All
set to L” button to set all of DI/DO to “L”.
(4)AI/O table:
The user can d
ouble click left button of mouse at the value of AI/AO to change
the value into 0x0000~0xFFFF.
(5) All AI/O setting:
The user can click “A
ll set to F” button to set all of AI/AO to “0xFFFF” and click
“All set to 0” button to set all of AI/AO to “0x0000”.
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 68
Page 69

(6) Display and Save interface
The user can click “Output” b
“Input” button to show safe value setting of DI/AI, click “Save to File” button to
open “save file dialog” to save safe value setting for backup, click “Save to
Device” button to save safe value setting to EEPROM of the GW-7553.
utton to show safe value setting of DO/AO, click
Figure 70 Safe value setting
5.5 IP setting
There are 3 kinds o
file、(3)Load from device, as shown in figure 71.
f IP setting. They are (1) Open a new setting、(2)Load from
Figure 71 The menu of IP setting
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 69
Page 70

3 parts to explain, as shown in figure 72.
The window of “IP Setting” divided into
1) Local IP Setting:
(
The user can set local
(2) Rem
The user can set IP add
TCP Slave in this part. When GW-7553 acts as a Modbus TCP Master, these
settings are effective. GW-7553 can connect Modbus TCP Slave devices by these
IP settings and the maximum of Modbus TCP Slave device is 8.
(3
) Save interface
The user can click
setting for backup, click “Save to Device” button to save IP setting to EEPROM
of the GW-7553.
ote IP Setting:
IP setting of GW-7553 in this part.
ress, time out value and reconnecting time of the Modbus
“Save to File” button to open “save file dialog” to save IP
Figure 72 IP setting
5.6 Establish connection with GW-7553
he connection of Utility and GW-7553 is shown in figure 73. Please follow the
T
steps to establish connection.
S
tep 1:
ire COM Port of PC to RS-232 port of GW-7553.
W
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 70
Page 71

Step 2:
C
onnect PROFIBUS cable between PROFIBUS Master station and GW7553 and enter data exchange mode (please refer step 1~6 of section 4.8
PROFIBUS and Modbus data exchange demo for detail). The RUN LED
of GW-7553 is going to light at this time.
Figure 73 The connection of Utility and GW-7553
Step 3:
S
et bit 2 of byte 1 to High in output data area of the PROFIBUS Master
station (set the GW-7553 to setting mode; please refer section 4.6.2
Output data area and communication command) or turn the switch on the
back of the GW-7553 to setting mode (please refer section 2.6
Normal/Setting DIP switch).
Step 4:
Open Utility.exe on PC.
Figure 74 Open Utility
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 71
Page 72

Step 5:
Step 6:
Set COM Port communication setting of Utility (please refer section 5.2.2
COM Port settings) the same as COM Port setting of GW-7553(please
refer section 4.3 The Configuration of the common parameters)
Click “Communication=>Connect” button in menu.
Step 7:
Figure 75 Communication menu
Module state shows green in the Utility now, it means the connection is
complete.
Figure 76 Display connection state
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 72
Page 73

6. Troubleshooting
The troubleshooting list can help users to resolve the problems when using the GW-
7553. If the problem still can't be solved, please contact with technical staff of ICP
DAS.
Table 18 Errors and solutions
Item Trouble state Solution
'PWR' LED indication of
1
the GW-7553 is always
turned off
'ERR' LED indication of the
2
GW-7553 is always turned
on
'ERR' LED indication of the
3
GW-7553 is flashing fast
'ERR' LED indication of the
4
GW-7553 is flashing slow
PROFIBUS Master station
can not communicate with
the Modbus device, when
5
“RUN LED” of the GW7553 is light and “ERR
LED” of the GW-7553 is
dark.
The power supply of GW-7553 has some problems. Please check
the wire connection of the power and the voltage is between
10~30V
That means the GW-7553 isn't connecting to the PROFIBUS
Master station. Please check the wire connection and the
PROFIBUS Master s
GW-7553 in the PROF
It means the GW-7553 is in setting mode and connects with
Utility. Please close Utility and set the GW-7553 to operation
mode (please refer section 2.6 Normal/Setting DIP switch and
section 4.6.2 Output data area and communication command).
It means the GW-7553 has diagnostic messages. Please check
diagnostic messages in the PROFIBUS Master station.
a. Please confirm the GW-7553 is working in operation mode
b. Please confirm the connection between the GW-7553 and
c. Please confirm COM Port setting (please refer section 4.3
d. Please confirm module ID of the GW-7553 (please refer
e. Please confirm Setting of Start Address and NO. of
f. Please confirm the output data put in correct address and have
DC.
tation. T configuration and address of
IBUS Master station are not correct.
and avoid clearing diagnostic message by communication
command (please refer section 2.6 Normal/Setting DIP
switch and section 4.6.2 Output data area and communication
command).
Modbus device.
The Configuration of the common parameters) or IP setting
(please refer section 5.5 IP setting) of the GW-7553 the same
as the Modbus device.
section 4.3 The Configuration of the common parameters and
section 4.4 The Configuration of the modules) the same as
Modbus address of Modbus device.
Relay/Coil is correct (please refer section 4.4 The
Configuration of the modules).
changed value of byte 0 to trigger the output command, when
output data can not send to Modbus device in output data area
of PROFIBUS Master (please refer section 4.6.2 Output data
area and communication command).
he
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 73
Page 74

7. Dimensions
GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 74
Page 75

GW-7553 PROFIBUS/Modbus TCP Gateway User Manual (Version 1.00, Dec/2008) PAGE: 75
 Loading...
Loading...