Page 1
)
((RRSS--223322//442222//448855)
VVlliinnxx W
SSeerriiaall SSeerrvveerrs
EESSRR990011WW223322,, EESSRR990011WW448855,,
EESSRR990022WW,, EESSRR990044W
Wiirreelleessss
s
MMooddeellss::
W
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m pn#6876-rev001
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m
Page 2

International Headquarters
B&B Electronics Mfg. Co. Inc.
707 Dayton Road
Ottawa, IL 61350 USA
Phone (815) 433-5100 -- General Fax (815) 433-5105
Website: www.bb-elec.com
Sales e-mail: orders@bb-elec.com
Technical Support e-mail: support@bb.elec.com
European Headquarters
B&B Electronics Ltd.
Westlink Commercial Park
Oranmore, Co. Galway, Ireland
Phone +353 91-792444 -- Fax +353 91-792445
Website: www.bb-europe.com
Sales e-mail: sales@bb-europe.com
Technical Support e-mail: support@bb-europe.com
© B&B Electronics – November 2005
-- Fax (815) 433-5109
-- Fax (815) 433-5104
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m pn#6876-rev001
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 3

©
2005 B&B Electronics. No part of this publication may be repr od uced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or
mechanical, including photograp hy, r ec or di n g, or a n y i nformation storage and retrieval s ystem without written consent. Information
in this manual is subject to change without notice, and does not represent a commitment on the part of B&B Electronics.
B&B Electronics shall not be liable for incide ntal or consequential damages resulti ng from the furnishing, perfo rmance, or use of
this manual.
All brand names used in this manu al are the registered tr ademarks of their respectiv e owners. The use of tradem arks or other
designations in this publicatio n is for reference purposes only and does not constitut e an endorsement by the t rademark holder.
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m
Page 4

TTaabbllee ooff CCoonntteennttss
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION.......................................................................1
ABOUT YOUR VLINX ESR90XW WIRELESS SERIAL SERVER ................................... 1
Features................................................................................................................ 2
Communication Modes.............................................................. ...........................2
802.11 WIRELESS NETWORKING BASICS ................................................................... 3
802.11 Wireless Networking.................................................................................4
ESR90XW STARTUP PROCEDURE.............................................................................. 6
1. Package Checklist.............................................................................................6
2. Hardware Setup................................................................................................6
3. Power Up.............................................................. ............................................ 7
4. Set Up PC..........................................................................................................8
5. Configuration............................................................ ........................................8
6. Operation........................................... ...............................................................8
CHAPTER 2: VLINX ESR90XW HARDWARE............................................9
PACKAGE CHECKLIST ................................................................................................ 9
HARDWARE FEATURES............................................................................................ 10
Indicators............................................................................................................10
Reset Switch........................................................................................... ............. 10
Connectors..........................................................................................................11
RS-485 Receiver Biasing..................................................................................... 12
RS-422/485 Terminating..................................................................................... 12
CONNECTIONS FOR SERVER CONFIGURATION.......................................................... 12
OTHER HARDWARE CONNECTIONS.......................................................................... 13
CHAPTER 4: DEVICE CONFIGURATION VIA WEB CONSOLE...........15
ACCESSING THE WEB BROWSER.............................................................................. 15
CONFIGURING THE SERIAL PORT ............................................................................. 16
CONFIGURING COMMUNICATIONS MODES AND PROTOCOLS ................................... 16
CONFIGURING NETWORK PROPERTIES..................................................................... 17
CONFIGURING WIRELESS PROPERTIES..................................................................... 17
MANAGING USERS ACCOUNTS ................................................................................ 18
USING DEVICE STATUS INFORMATION .................................................................... 19
CHAPTER 5: ADJUSTING THE BEHAVIOR OF DEVICE
COMMUNICATION PORTS.................... .............................................................21
CHAPTER 6: DEVICE DISCOVERY AND VIRTUAL COM PORTS ...... 23
APPENDIX A: VLINX ESR90XW TECHNICAL DATA...................................25
APPENDIX B: RS-232/422/485 CONNECTIONS.................................................31
APPENDIX C: CONFIGURAT ION PORT CONNECTIONS............................35
DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY.................................................................357
POLLING STRINGS .................................................................................................... 22
TIMEOUTS................................................................................................................ 22
DATA QUANTITIES................................................................................................... 22
USING MULTIPLE CONDITIONS ................................................................................ 22
DEVICE DETECTION UTILITY................................................................................... 23
VCOM PORT SETUP ................................................................................................ 24
PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS....................................................................................... 25
DEFAULT SERVER PROPERTIES................................................................................ 27
VLINX ESR90XW DIMENSIONAL DIAGRAMS ......................................................... 28
DB-9 PIN-OUTS FOR RS-232 AND RS-232/422/485 CONNECTIONS ......................... 31
TERMINAL BLOCK PIN-OUT FOR RS-422 AND RS-485 (VLINX ESR901W485 ONLY)
................................................................................................................................32
RJ-45 PIN-OUT FOR CONFIGURATION PORT CONNECTION....................................... 35
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m Table of Contents i
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
ii Table of Contents Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 5
Introduction
Introduction
Features
CChhaapptteerr 11:: IInnttrroodduuccttiioonn
Thank you for purchasing a Vlinx ESR90xW Wireless Serial Server!
Like all B&B Electronics products, your serial server has been manufactured
to high standards of quality and performance to ensure your complete
satisfaction. Please read this manual and carefully follow the instructions to
achieve best results. For additional information on this and other B&B
products, and for technical support, and for technical support, call
815-433-5100 option 3, or access B&B Electronics’ website at: www.bb-
elec.com
About Your Vlinx ESR90xW Wireless Serial Server
Vlinx ESR90xW Wireless Serial Servers are part of B&B Electronics
growing family of device servers, products that allow you to connect
equipment with available serial connections into existing networks. Vlinx
ESR90xW wireless serial servers connect RS-232, RS-422 or RS-485
devices to a wireless network via wireless access points, eliminating the need
for network cabling. Devices connected to the serial ports on your Vlinx
ESR90xW can be accessed from any node on the LAN using Direct IP
Mode, Virtual COM Port, or Serial Tunneling (Paired Mode) connections.
Based on the 802.11g wireless standard, Vlinx ESR90xW servers operate at
up to 54Mbps over the 2.4 GHz band, which does not require licensing.
• Backward compatibility with 802.11b (up to 11 Mbps)
• Multi-interface serial ports
o The Vlinx 901W232 features one RS-232 serial port using a
standard DB-9M connector
o The Vlinx 901W485 features one RS-422/485 serial port using
a removable terminal block connector
o The Vlinx 902W features two serial ports (one RS-232 and one
software-selectable RS-232/422/485) using DB-9M connectors
o The Vlinx 904W features four serial ports (two RS-232 and two
software-selectable RS-232/422/485) using DB-9M connectors
• Rugged DIN rail or panel mountable IP30 enclosure
• Accepts AC or DC power over a wide voltage range
• LAN and WAN Communications via wireless access point
• TCP or UDP Client or Server operation - configurable
• Software Support - Windows 98/ME/2000/XP or NT 4.0
• Field upgradeable
• Configuration of wireless and serial port settings using:
o Vlinx Web Console, which allows configuration via the
network using a web browser.
Communication Modes
Vlinx ESR90xW Wireless Serial Servers enable communication with
serial devices over a wireless network. The three main types of
communications supported by ESR90xW Wireless Serial Servers are Direct
IP Mode, Virtual COM Mode and Serial Tunneling Mode.
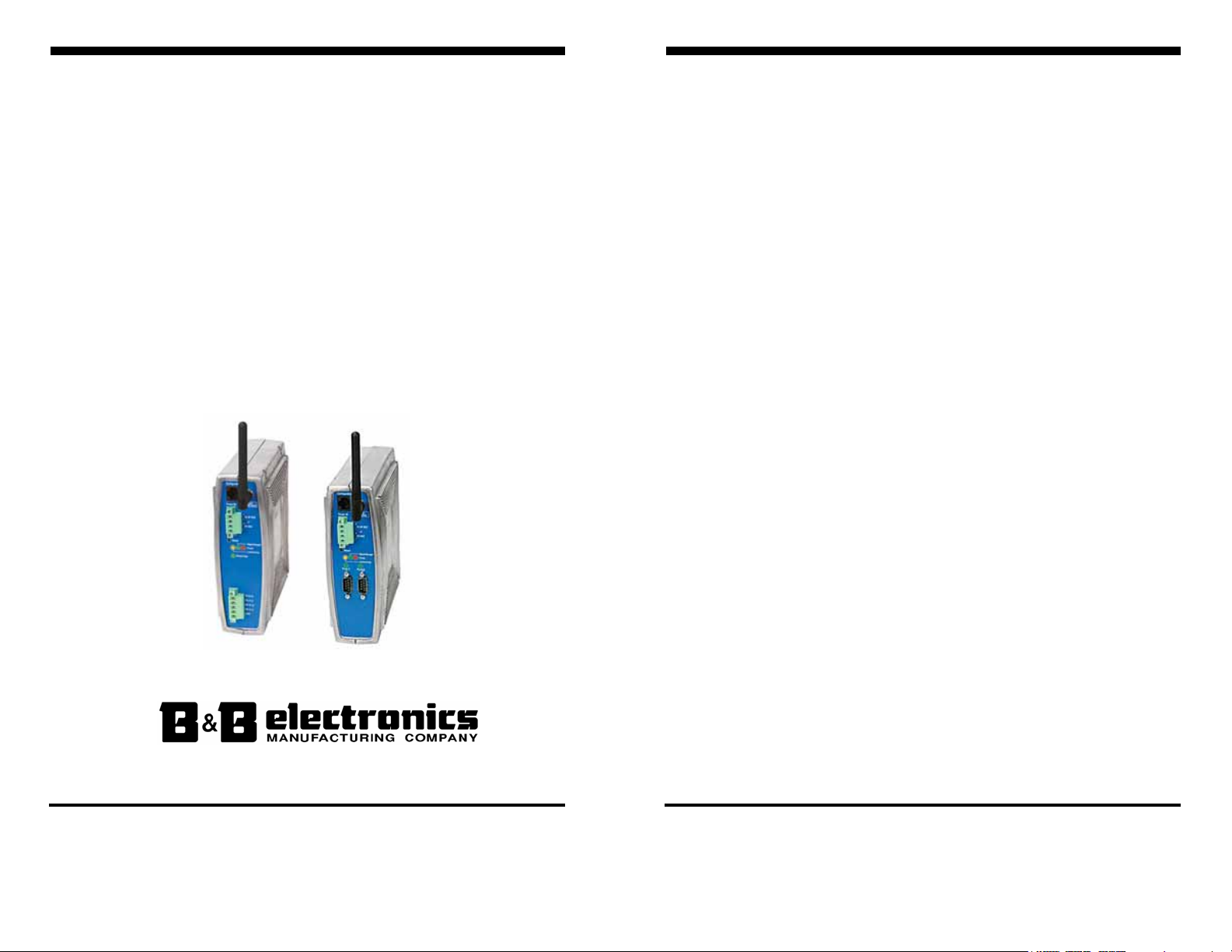
Vlinx ESR90xW Wireless Serial Servers
(ESR902W shown)
Vlinx ESR90xW wireless serial servers are built for use in industrial
environments and feature rugged DIN or panel mountable enclosures. They
operate from AC or DC power supply voltages and feature removable screw
terminal power connectors.
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m Chapter 1 1
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Direct IP Mode
Direct IP connections allow applications using TCP/IP or UDP/IP socket
programs to communicate with the asynchronous serial ports on the serial
server. In this type of application the serial server is configured as a TCP or
UDP server. The socket program running on the PC establishes a
communication connection. The data is sent directly to and from the serial
port on the server. When using UDP protocol the server can be configured to
broadcast data to and receive data from multiple IP addresses.
2 Chapter 1 Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 6

Introduction
Introduction
Virtual COM Mode
Virtual COM Mode allows application programs to effectively extend their
COM ports across the network. Data sent to that port is redirected via the
network to a COM port on the serial server. Windows programs using
standard Windows API calls are able to interface to these virtual COM ports.
When a program on the PC opens the port, it communicates with the remote
serial device connected to one of the ports on the serial server.
After connection, the LAN is transparent to the program and serial device.
Applications are able to work just as if the serial device is connected directly
to a physical COM port on the computer. The virtual COM port software
converts the application’s data into IP packets, sends it across the network to
the serial server, which converts the IP packet back to serial data and sends
the data out a serial port located on the serial server.
Serial Tunneling Mode
Serial Tunneling is also called paired mode. In this mode any two serial
devices that can communicate across the wireless link will be able to
communicate using two serial servers.
One server is configured as a TCP or UDP client and the other as a
TCP/UDP server. When setting up the server the remote IP address section
must contain the address of the client. This will allow the client’s IP address
to pass the IP address-filtering feature of the server. Conversely, the Remote
IP address of the client must contain the server’s IP address. Both
communication port numbers must be the same.
802.11 Wireless Networking
IEEE 802.11 is a set of standards that defines how multiple devices can
communicate on a wireless network. The standard has grown into a set of
several standards that define various features and functions. The 802.11g
standard defines the physical and data link layers for a wireless network
using the 2.4 GHz frequency band, a band that does not require licensing. As
a part of the IEEE family of standards, 802.11 WLANs are easily connected
to 802.3 (Ethernet) LANs. Higher layer LAN protocols, network operating
systems and internetworking protocols such as TCP/IP integrate seamlessly.
Under the IEEE 802.11 standard there can be two different types of devices
on the wireless network: stations and access points (AP). A station often is a
PC equipped with a wireless network adapter. An 802.11 access point is a
radio with an interface that allows connection to a wired LAN. Access points
run bridging software to facilitate the connection from wireless to wired
network. The access point becomes the base station for the WLAN. It
aggregates access to the wired network for multiple wireless stations. An
access point may be a standalone device or a card in a PC.
Wireless Network Configurations
The 802.11 standard defines two modes of operation: infrastructure mode
and ad hoc mode. Infrastructure mode makes use of one or more access
points connected to a wired LAN. Wireless stations communicate with access
points to gain access to each other and/or the LAN. In the Basic Service Set
(BSS) several stations communicate with one access point, which is
connected to a wired LAN. In the Extended Service Set (ESS) two or more
access points connect to the LAN creating a subnetwork.
802.11 Wireless Networking Basics
Vlinx ESR90xW wireless serial servers allow you to connect non-network-
enabled serial devices into a wireless network, giving you the capability to
gather more data and implement remote programming and management.
Serial devices no longer are limited to a physical connection to a PC. The
serial device can be connected to a Vlinx ESR90xW wireless serial server
anywhere within range of an 802.11g compatible wireless access point.
Communication occurs transparently using TCP/IP or UDP/IP over a
wireless link. This allows traditional Windows PC software access to serial
devices anywhere on the wireless network.
The enabling technology for Vlinx ESR90xW wireless serial servers is
based on the IEEE 802 standard. Some background on the standard follows.
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m Chapter 1 3
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
In ad hoc mode, also called Independent Basic Service Set (IBSS), access
points are not used. Wireless stations communicate directly with each other
in a peer-to-peer fashion. This mode allows individual computers to set up a
network where wireless infrastructure does not exist.
Vlinx ESR90xW wireless serial servers can be configured to operate in
infrastructure mode only, ad hoc mode is not supported at this time. During
device configuration a wireless configuration wizard guides you through the
process of setting up the type of network, naming the network (specifying the
SSID, or service set identifier) and other parameters.
4 Chapter 1 Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 7

Introduction
Introduction
ESR90xW Startup Procedure
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11g standard specifies a WLAN that operates on the 2.4 GHz band
at data rates up to 54 Mbps, but is backward compatible with the earlier
802.11b standard (which operates at up to 11 Mbps). Systems can
incorporate 802.11b and 802.11g equipment and they will interoperate.
However, when connected into the same network the 802.11g equipment will
operate at the 11 Mbps limitation of the 802.11b equipment.
For media access, 802.11 wireless networks use CSMA/CA, a scheme in
which a station that intends to transmit ‘listens’ for traffic on the radio carrier
frequency and sends data packets if the frequency is clear. If the receiving
station receives the packet intact it sends an acknowledgement (ACK) to
confirm the packet has been received. If the transmitting station does not
receive an ACK it assumes a collision occurred and transmits again after a
random delay period.
Communications distances vary depending on the type and thickness of
material around an 802.11g node. The transmitter power output, the type of
antenna used and the amount of attenuation through materials also affects the
useable range. Electromagnetic noise, reflections, the amount of network
traffic, other radio devices operating in the same frequency band also affect
range and overall performance. In an infrastructure network the number of
access points and their coverage pattern also affect how well the system
operates. Typically an 802.11 device operating indoors will have a range
from 100 feet minimum to about 300 feet maximum. Outdoors, some
products, using high gain antennae may achieve line-of-sight ranges of five
miles or more.
Security is a significant concern for WLAN users. Whether security threats
originate intentionally or unintentionally, wireless systems are more
susceptible than wired systems. Vlinx ESR90xW offer several security
options including WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy), LEAP (Lightweight
Extensible Authentication Protocol) and others.
Setup and configuration of your Vlinx ESR90xW wireless serial server is
fast, straightforward and simple. You have several options from which to
choose. The following procedure outlines an easy way to get your server set
up and operational.
1. Package Checklist
To begin, check to see that you have everything you will require. The
contents of your ESR90xW package should include:
• One Vlinx ESR901W232, ESR901W485, ESR902W or ESR904W
Wireless Serial Server
• One SMA antenna
• One Operation Manual
• One Quick Start Guide
• One CD containing
o Device Detection software
o Serial-IP Virtual COM Port Software
o the Operation Manual (in pdf format)
o the Quick Start Guide (in pdf format)
2. Hardware Setup
1. Connect the antenna to your ESR90xW
2. Connect a standard Ethernet (CAT5/RJ-45 straight through) cable
from the PC network adapter to the ESR90xW Configuration Port
3. Connect 24 VAC or 12 to 30 VDC power to the ESR90xW
4. Connect the serial port on the ESR90xW to the serial port on your
serial device. This is optional during the initial configuration steps
but will be required for operation.
For RS-232 operation, your ESR90xW is configured as a DTE and uses a DB9M connector. Use a straight through RS-232 cable if your serial device is
configured as a DCE. If your serial dev ice is configured as a DTE you will hav e
to use a null modem (crossover) cable.
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m Chapter 1 5
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
6 Chapter 1 Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 8

Introduction
Introduction
4. Set Up PC
1. Configure the PC to work in the 192.168.0.x private address range
2. Open a web browser
3. Enter 192.168.0.200 into the address bar of the browser
Figure 1. Direct Connection for Configuration
3. Power Up
1. Apply power to the ESR90xW
2. Front panel LED will illuminate with the following sequence:
a. Power LED will always be lit while device is powered
b. Signal Strength LED – White for 5 seconds, blink
yellow/Red and go dark.
c. The Link/Activity LED will be red when the device is
associating with an access point (if configured to do so)
d. The Link/Activity LED will be green when the device is
associated with an access point (if configured to do so)
Note: The device by default is not configured to associate with an access point
Operating System Boot Completion Indication
e. Once the device has booted successfully into the operating
system all of the LEDs with the exception of Power will
blink once to indicate a completed boot sequence.
f. When this sequence starts all of the LEDs will be lit for
5. Configuration
1. Enter your Username and Password to Login. The default username is
“Administrator” with no password.
2. Navigate to Wireless Settings, provide SSID name, configure security settings
3. Navigate to Serial Configuration, set up serial parameters to match your serial
device
4. Click Apply and restart the ESR90xW
6. Operation
1. ESR90xW will boot up and attempt to connect to the designated access point
2. The Link LED will light when it makes the connection
3. Communications will occur between the PC and serial device
one half of a second after which they will resume their
previous state.
Figure 3. Web Console Device Information Page
Figure 2. ESR90xW LEDs
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m Chapter 1 7
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Figure 4. Infrastructure Mode Operation
8 Chapter 1 Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 9

Vlinx ESR90xW Hardware
Vlinx ESR90xW Hardware
Hardware Features
CChhaapptteerr 22:: VVlliinnxx EESSRR9900xxWW HHaarrddwwaarree
Package Checklist
Vlinx ESR90xW Wireless Serial Servers are shipped with the following
items included:
9 A Vlinx ESR901W232, ESR901W485, ESR902W or ESR904W
Wireless Serial Server
9 This Operation Manual
9 CD-ROM disc with Device Detection Software and Serial/IP™ for
Windows 98/ME/2000/XP/NT 4.0, Operation Manual and Quick Start
Guide (in pdf format)
Indicators
Power LED
Red: Indicates the device is receiving power from an external source
Signal Strength LED
Tri-color: Indicates the connection quality:
• Dark: no connection or 0% signal strength
• Red: poor signal, represents 1% to 60% signal strength
• Blue: acceptable signal, represents 61% to 85% signal strength
• Green: good signal, represents 86% to 100% signal strength
Link/Activity LED
• Dark: no wireless connection is being attempted
• Solid Red: Indicates that a connection to a wireless access point or
device is being attempted.
• Blinking Red: When link is established, LED blinks.
• Solid Green: Indicates that a connection to a wireless access point or
device has been established.
• Green With Red: Red flashes on and off when data is present on the
wireless network.
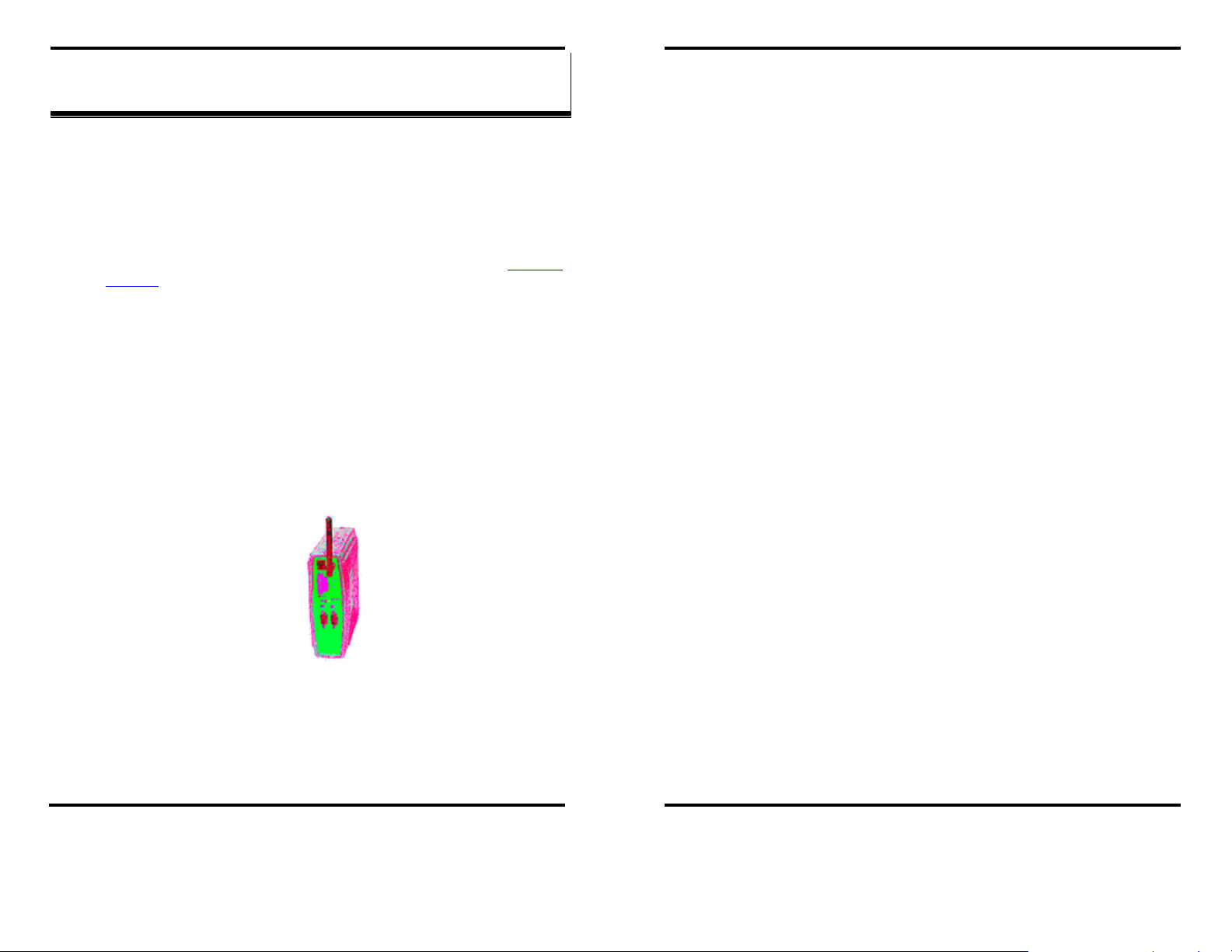
Figure 5. Front View of the Vlinx ESR901W232, ESR901W485,
ESR902W and ESR904W Wireless Serial Servers
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m Chapter 2 9
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Serial Port LEDs (for each port)
• Blinking Red: Indicates the serial port is communicating.
Reset Switch
The Reset switch is a recessed switch located on the front of the Vlinx
ESR90xW. It can perform more than one function:
• Press 0 to 1 second: no effect
• Press and hold 1 to 10 seconds: reset serial server operating system
• Press and hold 10+ seconds: reset serial server to factory default
settings.
10 Chapter 2 Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 10

Vlinx ESR90xW Hardware
Vlinx ESR90xW Hardware
Connectors
Configuration Port Connector
One standard RJ-45 receptacle that allows the serial server to be connected to
personal computer for programming, troubleshooting and device
configuration. A standard straight-through RJ-45 (male) Ethernet cable can
be used for this purpose. (This port is not intended to connect directly to an
Ethernet network.)
Antenna Connector
The antenna connector is a reverse SMA connector.
(An omni-directional antenna is supplied with ESR90xW wireless serial
servers. All ESR90xW serial servers are FCC-certified when the supplied
antenna is used.)
Serial Port Connector(s)
• ESR901W232: One DB-9M connector
• ESR901W485: One five-terminal removable terminal block
• ESR902W: Two DB-9M connectors
o Port 1: RS-232
o Port 2: software selectable for RS-232, RS-422 or RS-485
• ESR904W: Four DB-9M connectors
o Ports 1 & 3: RS-232
o Ports 2 & 4: software selectable for RS-232, RS-422 or RS-
485
Power Connector
The power connector is a removable terminal block with four terminals.
From top to bottom the terminals are:
RS-485 Receiver Biasing
Vlinx ESR90xW wireless serial servers provide built-in receiver biasing on
RS-485 ports (includes the 902W485 port, 902W Port 2 and 904W Ports 2
and 4). The Data(+) line is pulled up to 3.3V supply using a 4.7 kΩ resistor
and the Data(-) line is pulled down to ground, also using a 4.7 kΩ resistor.
RS-422/485 Terminating
If a terminating resistor is deemed necessary, for RS-422 operation typically
a 120 Ω resistor would be connected across the Receive Data(+) and Receive
Data(-) lines. For RS-485 operation the resistor would be connected across
the Data(+) and Data(-) lines.
For more information on Receiver B iasing and RS-422/485 Termina ting access the
B&B Electronics RS-422/ 48 5 Ap pl ic at i o n Note a v ai la ble at www.bb-elec.com)
Connections for Server Configuration
Vlinx ESR90xW Wireless Serial Servers can be configured via:
• A wired connection to a RJ-45 Ethernet connector on the ESR90xW
front panel.
• The wireless network
The wired connection is recommended for configuration, especially when
configuring wireless settings, to ensure communication is not lost while
changing settings.
Terminal
Number
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m Chapter 2 11
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Terminal
Name
1
2
1
2 DC power
AC In
AC In
DC GND
supply
One side of AC power supply (if AC
Other side of AC power supply (if
Negative side of DC power supply
Positive side of DC power supply (if
Connect to Description
power used)
AC power used)
(if DC power used)
DC power used)
Internally, the chassis ground of the
Server is connected to this terminal.
24 VAC
+12VDC to 30 VDC
Figure 6. Wired Connection for Configuration
12 Chapter 2 Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 11

Vlinx ESR90xW Hardware
For wireless configuration, or for typical infrastructure mode operation, the
Vlinx ESR90xW communicates with a wireless access point, which is
connected to a PC via a wired network.
Figure 7. Connection via the Wireless LAN
Other Hardware Connections
Serial tunneling can occur between two ESR90xW serial servers
communicating with individual access points and across a wired network.
Vlinx ESR90xW Hardware
Figure 8. Serial Tunneling via Infrastructure
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m Chapter 2 13
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
14 Chapter 2 Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 12

Web Console
CChhaapptteerr 44:: DDeevviiccee CCoonnffiigguurraattiioonn vviiaa
WWeebb CCoonnssoollee
Web Console
You can change the Device Name of the serial server by typing in a different
name
For changes to take effect on this or any other W eb Console page, you must
click the Apply button before navigating away from the page.
The Web Console can be used to configure your Vlinx ESR90xW Wireless
Serial Server from any web browser software (such as Internet Explorer,
Mozilla Firefox or Netscape). Server properties can be set up using six
browser pages: Main, Serial, Network, Wireless, User and Status.
Accessing the Web Browser
In your browser, type the IP Address of the serial server into the address field
at the top of the window and press the
appears.
Enter key. The following window
Configuring the Serial Port
To configure the serial server serial port parameters to match the serial
device connected to the serial server’s port click
banner. The Serial Configuration page appears. In the Serial
Configuration page you can select each serial port on the serial server and
view or change its parameters.
Figure 10. The Web Console Serial Configuration Page
Select the port to be configured from the Port dropdown list. The selections
available in the Interface Type dropdown will change depending on the
capabilities of the selected port. Select the communications parameters based
on the requirements of the serial device to be connected to the serial server.
Serial on the Web Console
Figure 9. The Web Console Main Page
Enter your Username and Password to Login. The default username is
“Administrator” with no password. After you have logged in you will be able
to navigate through the web console pages and change properties as required
using the mouse and keyboard.
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m Chapter 4 15
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Configuring Communications Modes and
Protocols
To configure serial server communications modes and protocols, click the
Advanced button on the Serial Configuration page. The Advanced Serial
Configuration page appears. On this page you can configure:
• Connection Mode (TCP or UDP)
16 Chapter 4 Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 13

Web Console
Web Console
• Connection Protocol (RAW Client, RAW Server, Virtual COM Port
Server, RFC2217 Client)
• Server (Remote) IP Address
• Server (Remote) Port
• Local Port
• Send Serial Data to Ethernet… conditions
For explanations of these configuration parameters see Adjusting the
behavior of device communication ports.
Configuring Network Properties
To view or change network properties, click Network on the Web Console
banner. The Device Network Settings appears. This page contains the
Ethernet settings for the wired Configuration Port and the wireless serial
server. If you are configuring the ESR90xW via the hardwired
Configuration Port select Wired Port in the dropdown list box. To
configure via the wireless network, select Wireless in the dropdown list box.
Figure 12. The Vlinx Web Console Wireless Interface
You can choose between dynamic or static IP addressing and view or set up
static addressing parameters.
On this page you can specify the SSID, or name of the network you want to
connect to. Several other text boxes display useful information about the
devices wireless network configuration:
Configuration Page
Figure 11. The Web Console Device Network Settings Page
Configuring Wireless Properties
To view or change wireless properties, click Wireless on the Web Console
banner. The Wireless Interface Configuration page appears.
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m Chapter 4 17
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
• Wireless Output Power
• Security Method
o WEP
o LEAP
Managing Users Accounts
As administrator, you can configure multiple user accounts, setting up rights
for each user. User Accounts can be added and removed, and user details
viewed in the Users page. User Details (rights) include: Manage User
Accounts, Modify Device Network Settings, Modify Device Serial Port
Settings, Manage Log, Update Device Firmware and Reset Device.
To view or change user properties, click
The following page will appear:
18 Chapter 4 Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
User on the Web Console banner.
Page 14

Web Console
Web Console
Figure 13. The Vlinx Web Console Users Page
Using Device Status Information
To view or change device status properties, click Status on the Web Console
banner. The following page will appear:
Figure 14. The Vlinx Web Console Status Page
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m Chapter 4 19
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
20 Chapter 4 Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 15

Device Communication Ports
Device Communication Ports
Polling Strings
CChhaapptteerr 55:: AAddjjuussttiinngg tthhee BBeehhaavviioorr ooff
DDeevviiccee CCoommmmuunniiccaattiioonn PPoorrttss
There is a significant difference between serial and Ethernet data communications.
Data that comes in through the Ethernet is presented to the device in the form of very
distinct packets. On the other hand without information about the format of the data
coming in through the serial port the device may not know at what point to package
up the data and hand it off to the Ethernet network. It is for this reason that the
ESR90xW series of devices allow you to define when the device converts serial
stream data into Ethernet packets. The following examples are provided to illustrate
the power behind these options:
Configuration #1: The ESR90xW is connected to a device used to monitor air
temperature. Software that interfaces with this hardware polls the device for the
current status once a minute. This data is returned in the form of a single byte
containing the temperature in Celsius.
Configuration #2: This ESR90xW is connected to a machine is connected to an
ATM machine. When a customer starts a transaction with the ATM a large burst of
serial data is passed onto the central bank.
Obviously in both of the configurations the data is critical and needs to be passed over
the network in the quickest manner possible. For configuration #1 the best behavior
for the device would be to send the incoming byte of temperature information out over
the network as soon as it comes in. On the other hand if the device acted the same way
for the second configuration it would flood the network with all of the Ethernet
overhead. In this case the device would be better to wait for a moment and send a full
Ethernet packet rather than a packet for each byte of data.
There are a number of different conditions that your ESR90xW can be configured to
watch for when dealing with the data coming in through it’s serial communication
port(s).
Polling strings are used when you want the ESR90xW to look for a specific data
pattern before taking the data in it’s serial buffer and creating an Ethernet packet with
it. Polling strings can be configured to monitor not only the serial traffic but the
Ethernet traffic as well.
Timeouts
Polling strings are used when you want the ESR90xW to look for a specific data
pattern before taking the data in its serial buffer and creating an Ethernet packet with
it.
There are two different types of timeouts. Total Message and Inter-character timeouts.
A Total Message timeout counter starts when the first byte is received. Once the
specified amount of time has elapsed since this initial byte the trigger is fired and the
device will transmit the buffered data.
The second type of timeout is an Inter-character timeout. This is used to trigger after a
defined amount of inactivity.
Data Quantities
In addition to the two previously mentioned methods of Ethernet packet transmission
triggers you can also setup a specific data amount that the device will wait for before
acting on the incoming data.
Using Multiple Conditions
You can use the data trigger conditions individually or it is also possible to use them
in combination with each other. When more than one condition is specified they are
treated as a “logical AND”. This means that if any of the conditions specified is true
then the data buffer is transmitted.
• Polling Strings
• Timeouts
• Data Quantities
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m Chapter 5 21
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
22 Chapter 5 Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 16

Device Communication Ports
Device Communication Ports
VCOM Port Setup
CChhaapptteerr 66:: DDeevviiccee DDiissccoovveerryy aanndd
VViirrttuuaall CCOOMM PPoorrttss
Device Detection Utility
To find devices on a wireless network, run the Device Detection Utility. This
program will be installed in the start menu at B&B Electronics\Tools.
To use, click “Scan For Devices”. The software will send a broadcast and all
devices on that subnet will be displayed in the list. The device will be displayed
with a friendly name and the IP Address that it was found on.
A typical scan would look something like this:
To install and manage Virtual COM ports, Serial IP software will be provided.
The software will be installed in the start menu at Serial-IP. To run the setup
software, choose Control Panel and this screen will be displayed:
After completing a network scan, use the IP Address to browse to the Web Server
to configure the device.
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m Chapter 6 23
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
To setup and assign a port, follow these steps:
1. Click “Select Ports” to assign a VCOM
2. Check “Connect to server”
3. Assign IP Address and Port number of device
4. Click “Configuration Wizard”
5. Click “Start”
6. If Configuration Wizard completes successfully, click “Use Settings”
7. Close Serial IP Control Panel
24 Chapter 6 Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 17

Vlinx ESR90xW Technical Data
Vlinx ESR90xW Technical Data
Parity: None, Even, Odd, Mark, Space
AAppppeennddiixx AA:: VVlliinnxx EESSRR9900xxWW TTeecchhnniiccaall DDaat
Product Specifications
Serial Server Model: Vlinx ESR901W232, Vlinx ESR901W485, Vlinx ESR902W or Vlinx
ESR904W
Manual: Paper copy of this manual, PDF available
Dimensions 6.85 x 5.72 x 2.27 in (17.4 x 14.5 x 5.77 cm)
Power Supply Voltage Requirements: 12V to 30 VDC or 24VAC
Power Consumption: 12W max, on air
Operating Temperature: 0 to 60 °C (32 to 140 °F)
Storage Temperature: −40 to 85 °C (−40 to 185 °F)
Humidity: 5% to 98% R.H. non-condensing
Approvals: CE, FCC (using the supplied antenna)
Serial Port Activity Indicator: Red LED
Link/Activity Indicator: Red LED
Port Indicator: Red LED
Set Up Connector: Single RJ-45 female (auto configuring)
Serial Connector(s): Vlinx ESR901W232: one 9 pin D-type male (DB-9M)
Vlinx ESR901W485 one removable five terminal screw-type terminal block
Vlinx ESR902W: Two 9 pin D-type male (DB-9M)
Vlinx ESR904W: Four 9 pin D-type male (DB-9M)
Power Supply: (AC or DC) Removable four terminal screw-type terminal block
RS-232 Interface Lines Supported: TXD, RXD, RTS, CTS, DTR, DSR, DCD, RI, GND
t
aa
Configuration Modes: Direct TCP Server, Client
Wireless Network Interface: 2.4 GHz IEEE 802.11g DSSS
Wireless Data Rates: 54, 48, 36, 24, 18, 12, 9, 6, 11, 5.5, 2, 1 Mbps
Stability & Troubleshooting Features: Internal device application logging, Fault logging
Advanced Data Management: Buffer level triggering
Data Bits: 5, 6, 7 or 8
Stop Bits: 1, 1.5 or 2
Set-up Options: Vlinx Web Console Configuration
Virtual COM Port Connection
Pair Mode
Configuration Port: Ethernet RJ-45, Auto-MDX
RF Power: +15 dBm Nominal (without antenna gain)
Security: WEP standard encryption, 64/128 bit, administration/configuration
password protection
Antenna: Omni-directional antenna included, reverse SMA connector
Protocols: TCP, IP, ARP, DHCP, HTTP, UDP, ICMP
Hardware watchdog timer
LEDs indicators for Power, Signal strength, LAN-link, Data
Serial and network delimiter triggering
Serial line status triggering
Total message timeout
Inter-character message timeout
Accessories: Lightning arrestor
Panel mount bracket
Serial Memory: 1K byte per port
Network Memory: 1K byte
RS-422 Interface Lines Supported: TXDB(+), TXDA(−), RXDB(+), RXDA(−) and GND
RS-485 Interface Lines Supported: Data B (+), Data A (–) and GND
Serial Data Rates: 110, 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 14400, 19200, 28800, 38400,
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m Appendix A 25
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
57600, 115200, 230400 bps
26 Appendix A Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 18

Vlinx ESR90xW Technical Data
Vlinx ESR90xW Technical Data
Default Server Properties
Server Name Vlinx ESR901W232 or Vlinx ESR901W485 or Vlinx ESR902W or Vlinx
ESR904W
Serial Number: (printed on bottom of unit)
Password: Blank
DHCP: Disable
IP Address: 192.168.0.200
Net Mask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway: 192.168.0.254
MAC Address: Fixed – see bottom label
Version&Date: current firmware version number & date
Serial server port: 1
Baud Rate: 9600
Data//Stop: 8-1
Parity: None
Flow Control: None
TCP/UDP Protocol: TCP
Vlinx ESR90xW Dimensional Diagrams
Figure 15. Dimensional Diagram of the Vlinx ESR901W232
Serial timeout: 0 seconds
TCP alive timeout: 0 minutes
Connection Mode: Server
TCP/UDP port: Vlinx ESR901W/902/904 Port 1: 4000
Vlinx ESR902W/904 Port 2: 4001
Vlinx ESR904W Port 3: 4002
Vlinx ESR904W Port 4: 4003
Serial port mode: Vlinx 901W/902/904 (all ports): RS-232
Max connection: 1
Remote IP Address: 255.255.255.255
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m Appendix A 27
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Figure 16. Dimensional Diagram of the Vlinx ESR901W485
28 Appendix A Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 19

Vlinx ESR90xW Technical Data
Figure 17. Dimensional Diagram of the Vlinx 902W
Vlinx ESR90xW Technical Data
Figure 18. Dimensional Diagram of the Vlinx 904W
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m Appendix A 29
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
30 Appendix A Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 20

RS-232/422/485 Connections
RS-232/422/485 Connections
AAppppeennddiixx BB:: RRSS--223322//442222//448855 CCoonnnneeccttiioonnss
Terminal Block Pin-out for RS-422 and RS-485
DB-9 Pin-outs for RS-232 and RS-232/422/485
Connections
DB-9M
Pin
1 Carrier Detect DCD In TXDA(-)
2 Receive Data RXD In TXDB(+)
3 Transmit Data TXD Out RXDB(+) DATA B(+)
4 Data Terminal Ready DTR Out RXDA(-) DATA A(-)
5 Signal Ground GND --- GND GND
6 Data Set Ready DSR In
7 Request To Send RTS Out
8 Clear To Send CTS In
9 Ring Indicator RI In
RS-232
RS-232 DTE RS-422 RS-485
Signal Name
Figure 19. DB-9 Pin-outs for RS-232/422/485
(Vlinx ESR901W485 only)
T
X
D
T
X
R
D
X
D
B
(
+
)
/
D
a
R
X
D
A
(
-
)
/
D
a
G
N
Terminal
2
1 (+) Transmit Data (+) -- -2
(-) Transmit Data (-) -- -3 (+) Receive Data (+) Data(+) Data(+)
4
(-) Receive Data (-) Data(-) Data(-)
5
Signal Ground GND Ground
RS-422
Signal Name
B
(
+
)
A
(
-
)
t
a
(
+
)
t
a
(
-
)
D
1
2
3
4
5
RS-485
RS-485
Signal Name
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m Appendix B 31
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Figure 20. Terminal Block Pin-out for Vlinx ESR901W485 Serial
Connection
32 Appendix B Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 21

RS-232/422/485 Connections
RS-232/422/485 Connections
1
2
3
4
Signal Name Terminal
AC Power Supply
(24 VAC)
AC Power Supply
(24 VAC)
DC Gnd 3
DC Power Supply
(+12 VDC to 30 VDC)
Figure 21. Terminal Block Pin-out for Vlinx ESR90xW Power
Supply Connection
1
2
4
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m Appendix B 33
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
34 Appendix B Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 22

Configuration Port Connections
AAppppeennddiixx CC:: CCoonnffiigguurraattiioonn PPoorrtt CCoonnnneeccttiioonns
RJ-45 Pin-out for Configuration Port Connection
The Configuration Port on the Vlinx ESR90xW Wireless Serial Servers is
wired as a standard Ethernet connector. However, this port is intended for
direct connection to a PC for configuration purposes only and is not to be
connected to a network.
A standard Ethernet cable can be used to connect the PC to the Configuration
Port.
RJ-45 Pin Signal Wire Color RJ-45 Pin
1 TX+ White-Green 1
2 TX- Green 2
3 RX+ White-Orange 3
4 Not used Blue 4
5 Not used White-Blue 5
6 RX- Orange 6
7 Not used White-Brown 7
8 Not used Brown 8
Figure 22. Pin-out for a Standard Ethernet Cable
s
Configuration Port Connections
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m Appendix C 35
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
36 Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 23

Declaration of Conformity
Manufacturer’s Name: B&B Electronics Manufacturing Company
DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
Manufacturer’s Address: P.O. Box 1040
707Dayton Road
Ottawa, IL 61350 USA
Model Numbers: ES R9 01W232, ESR901W485, ESR902W, ESR904W
Description: Wireless Serial Servers
Type: Light industrial ITE equipment
Application of Counci l Direc tive: 89/336-EEC
Standards: EN 55022
EN 61000-6-1
EN 61000 (-4-1, -4-3, -4-4, -4-5, -4-6, -4-8, -4-11)
Robert M. Paratore, Director of Engineering
International Headquarters
B&B Electronics Mfg. Co. Inc.
707 Dayton Road
Ottawa, IL 61350 USA
Phone (815) 433-5100 -- General Fax (815) 433-5105
Website: www.bb-elec.com
Sales e-mail: orders@bb-elec.com
Technical Support e-mail: support@bb.elec.com
Phone +353 91-792444 -- Fax +353 91-792445
Technical Support e-mail: support@bb-europe.com
European Headquarters
B&B Electronics Ltd.
Westlink Commercial Park
Oranmore, Co. Galway, Ireland
Website: www.bb-europe.com
Sales e-mail: sales@bb-europe.com
© B&B Electronics – November 2005
-- Fax (815) 433-5109
-- Fax (815) 433-5104
Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m 37
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
38 Documentation Number: ESR90xW-4905m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
 Loading...
Loading...