Page 1

iMcV-E1-Mux/4
Operation Manual
Page 2

FCC Radio Frequency Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B computing device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial
environment. This equipment generates uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to
cause harmful interference in which the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the manufacturer could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
The use of non-shielded I/O cables may not guarantee compliance with FCC RFI limits. This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class B
limits for radio noise emission from digital apparatus set out in the Radio Interference Regulation of the Canadian Department of
Communications.
Le présent appareil numérique n’émet pas de bruits radioélectriques dépassant les limites applicables aux appareils numériques de classe B
prescrites dans le Règlement sur le brouillage radioélectrique publié par le ministère des Communications du Canada.
Warranty
IMC Networks warrants to the original end-user purchaser that this product, EXCLUSIVE OF SOFTWARE, shall be free
from defects in materials and workmanship under normal and proper use in accordance with IMC Networks' instructions
and directions for a period of six (6) years after the original date of purchase. This warranty is subject to the limitations set
forth below.
At its option, IMC Networks will repair or replace at no charge the product which proves to be defective within such
warranty period. This limited warranty shall not apply if the IMC Networks product has been damaged by unreasonable
use, accident, negligence, service or modification by anyone other than an authorized IMC Networks Service Technician
or by any other causes unrelated to defective materials or workmanship. Any replaced or repaired products or parts carry
a ninety (90) day warranty or the remainder of the initial warranty period, whichever is longer.
To receive in-warranty service, the defective product must be received at IMC Networks no later than the end of the
warranty period. The product must be accompanied by proof of purchase, satisfactory to IMC Networks, denoting
product serial number and purchase date, a written description of the defect and a Return Merchandise Authorization
(RMA) number issued by IMC Networks. No products will be accepted by IMC Networks which do not have an RMA
number. For an RMA number, contact IMC Networks at PHONE: (800) 624-1070 (in the U.S and Canada) or (949) 4653000 or FAX: (949) 465-3020. The end-user shall return the defective product to IMC Networks, freight, customs and
handling charges prepaid. End-user agrees to accept all liability for loss of or damages to the returned product during
shipment. IMC Networks shall repair or replace the returned product, at its option, and return the repaired or new
product to the end-user, freight prepaid, via method to be determined by IMC Networks. IMC Networks shall not be
liable for any costs of procurement of substitute goods, loss of profits, or any incidental, consequential, and/or special
damages of any kind resulting from a breach of any applicable express or implied warranty, breach of any obligation
arising from breach of warranty, or otherwise with respect to the manufacture and sale of any IMC Networks product,
whether or not IMC Networks has been advised of the possibility of such loss or damage.
EXCEPT FOR THE EXPRESS WARRANTY SET FORTH ABOVE, IMC NETWORKS MAKES NO OTHER WARRANTIES,
WHETHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WITH RESPECT TO THIS IMC NETWORKS PRODUCT, INCLUDING WITHOUT
LIMITATION ANY SOFTWARE ASSOCIATED OR INCLUDED. IMC NETWORKS SHALL DISREGARD AND NOT BE
BOUND BY ANY REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES MADE BY ANY OTHER PERSON, INCLUDING EMPLOYEES,
DISTRIBUTORS, RESELLERS OR DEALERS OF IMC NETWORKS, WHICH ARE
INCONSISTENT WITH THE WARRANTY SET FORTH ABOVE. ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES INCLUDING THOSE OF
MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE HEREBY LIMITED TO THE DURATION OF THE
EXPRESS WARRANTY STATED ABOVE.
Every reasonable effort has been made to ensure that IMC Networks product manuals and promotional materials
accurately describe IMC Networks product specifications and capabilities at the time of publication. However, because of
ongoing improvements and updating of IMC Networks products, IMC Networks cannot guarantee the accuracy of printed
materials after the date of publication and disclaims liability for changes, errors or omissions.
ii
Page 3

Table of Contents
FCC Radio Frequency Interference Statement ------------------------------------------------- ii
Warranty ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ii
About the iMcV-E1-Mux/4 ------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1
Managed Modules----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2
Port Interfaces ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 3
LED
Operation ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5
10/100BaseT Connector --------------------------------------------------------------------- 5
E1 RJ-48 Connectors -------------------------------------------------------------------------- 6
SFP
Ports ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 6
Connector Pinout and DIP Switch Assignments ----------------------------------------------- 7
DIP Switch Assignments---------------------------------------------------------------------- 7
10/100BaseT Ethernet Mating Connector Pinout--------------------------------------- 8
E1 Port Mating Connector Pinout ---------------------------------------------------------- 8
RS-232 Port Mating Connector Pinout---------------------------------------------------- 8
RS-232 Serial Console Port ------------------------------------------------------------------ 9
Installation Instructions -----------------------------------------------------------------------------10
Configuration Options------------------------------------------------------------------------------11
Ethernet Line Setup ------------------------------------------------------------------------- 11
Packet Size ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 11
Auto Negotiation----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 11
Forcing the Speed, Duplex Mode, and Flow Control-------------------------------- 11
FX LinkLoss and
FX LinkLoss (FXLL) --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 12
Link Fault Pass-Through (
E1 Ports Setup -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 12
Alarm Level ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 12
Loopback -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 12
Console Screens -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13
Login Screen ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 13
Main Menu--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 14
Menu Options-------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 14
Unit Configuration Screen -------------------------------------------------------------------- 14
Port Alarm Status Screen ---------------------------------------------------------------------- 15
SFP
Line Status Screen ------------------------------------------------------------------------- 15
Ethernet Port Configuration Screen --------------------------------------------------------- 16
Ethernet Port Status Screen ------------------------------------------------------------------- 16
E1 Port Configuration Screen----------------------------------------------------------------- 17
E1 Port Status Screen--------------------------------------------------------------------------- 17
Troubleshooting -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------18
Fiber Optic Port Verification------------------------------------------------------------------ 19
E1 Port Verification ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- 20
LFPT
----------------------------------------------------------------------- 11
LFPT
)------------------------------------------------------------ 12
iii
Page 4

Normal Operation ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 20
Fiber Optic Cleaning Guidelines------------------------------------------------------------- 21
Electrostatic Discharge Precautions --------------------------------------------------------------22
Specifications -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------23
Standards/Compliance -----------------------------------------------------------------------------23
IMC Networks Technical Support----------------------------------------------------------------24
Definition of Terms/Acronyms --------------------------------------------------------------------25
Certifications -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------27
iv
Page 5

About the iMcV-E1-Mux/4
Overview
The iMcV-E1-Mux/4 is a media converter that transports four independent E1 lines
1+1
over an existing single (or dual, “
”) standard 155Mbps-capable fiber optic line
operating at an effective rate of 150Mbps. One serial link (RS-232) and one Ethernet
(10/100BaseT) connection are also multiplexed onto the fiber link(s). Each of these
communication channels is transported end-to-end at full wire speed with very low
latencies.
NOTE
Unless otherwise noted, all references to the iMcV-E1-Mux/4 in this manual are applicable
to the SFP model and the 1x9 fixed fiber transceiver model.
The serial link can be used for extending an independent RS-232 interface to the
remote
POP
location for use in managing or controlling other devices at the
POP
and
supports any data rate up to 250K baud. In addition, each unit also supports an RS232 console port for local configuration by technical support personnel. Both of
these serial links are used for end-to-end system management, fault
detection/isolation and system diagnostics.
The iMcV-E1-Mux/4 provides fault indications on the E1 and fiber links resulting from
real-time active faults. The equipment detects both E1 and fiber
as degraded E1 or fiber lines. The unit will automatically forward
LOS
remote unit after detecting an
(Loss Of Signal) condition on any incoming E1
line. Severe receive optical link failures will result in the automatic generation of
LOS
events as well
AIS
signaling to the
AIS
signaling onto the E1 lines connected to the unit receiving the corrupted optical
signal.
In addition,
CV
(Code Violation) errors are detected on all incoming E1 lines and
BER
calculations for the optical line are constantly being performed by circuitry within the
unit's optical receiver. Error conditions are displayed on the unit’s front panel
LED
indicators and reported to system management software (if equipped) where more
detailed error information can be displayed on the user’s
Systems equipped with
1+1
fiber redundancy can benefit from the enhanced
GUI
.
reliability of a protected fiber link and the system’s ability to automatically switch to
the “best” fiber line should one line become impaired or fail. This automatic
switchover capability is designed to occur rapidly (<50 milliseconds), minimizing data
loss and system down time. In addition, automatic switchover can be overridden;
this allows the end-user to force the unit to receive on a specific optical line if desired
to support periodic maintenance.
1
Page 6
The iMcV-E1-Mux/4 offers the following features:
• Four E1 ports on RJ-48 connectors with surge protection
•
One full bandwidth Ethernet 10/100BaseT port
•
1+1
protection switching via two
DDMI
•
•
One end-to-end serial RS-232 port on an RJ-48 connector
Local
•
•
Remote management capability through iMediaChassis series
AIS
•
•
SNMP
MDI/MDIX automatic Ethernet port switching
•
supported on
CLI
management console port on a Mini Jack connector
SFP
ports
generation on signal loss on all E1 interfaces
Alarm TRAP reporting in managed chassis
SFP
-based optical ports
The iMcV-E1-Mux/4 module is a dual-wide iMcV module.
Compatible chassis include the following:
• iMediaChassis series
• MediaChassis series
• IE-MediaChassis series
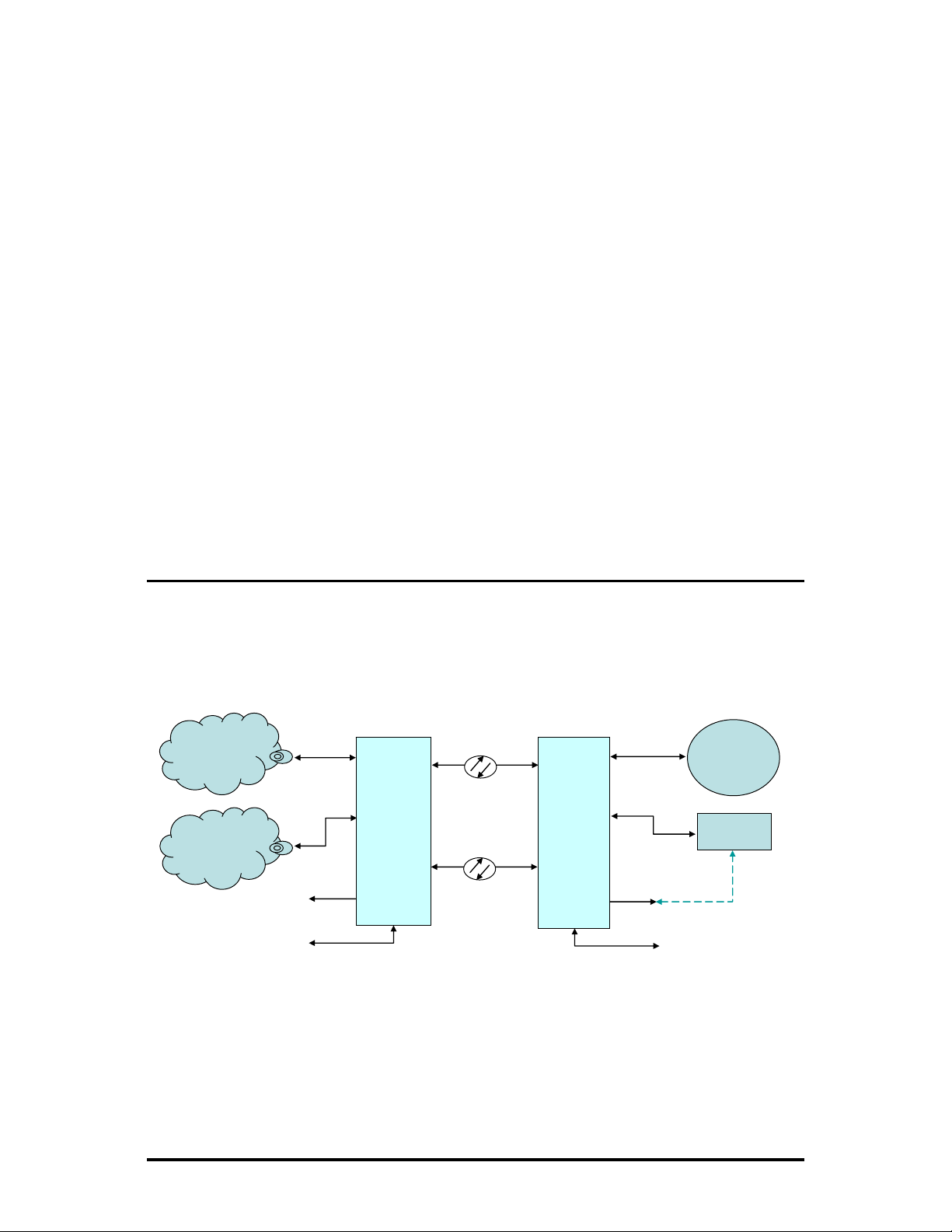
Product Application
The
iMcV-E1-Mux/4 delivers 4 E1 lines to a customer's site over a protected,
dedicated fiber line. In addition, one serial RS-232 line and one 10/100BaseT
Ethernet line can be carried at the same time. All circuits run at full line rates with no
interaction.
ISP Internet
TDM Network
PSTN
Local Far End
10/100BaseT
(1 Port)
E1
(4 port)
Console
E1-Mux
(Network)
Host
Dedicated
Fiber
Dedicated
Fiber
Protection
(1+1)
E1-Mux
(Subscriber)
Remote
10/100BaseT
(1 Port)
E1
(4 Port)
Serial PortSerial Port
Console
Customer
LAN
Customer
PABX
Console RS232
Remote Far End
Managed Modules
The
iMcV-E1-Mux/4 modules are installed as a Host/Remote pair. Host or Remote
configuration is selected by an onboard DIP Switch setting. The Host/Remote pair
can be remotely managed when the HOST is installed in an iMediaChassis with an
SNMP
Management Module.
2
Page 7
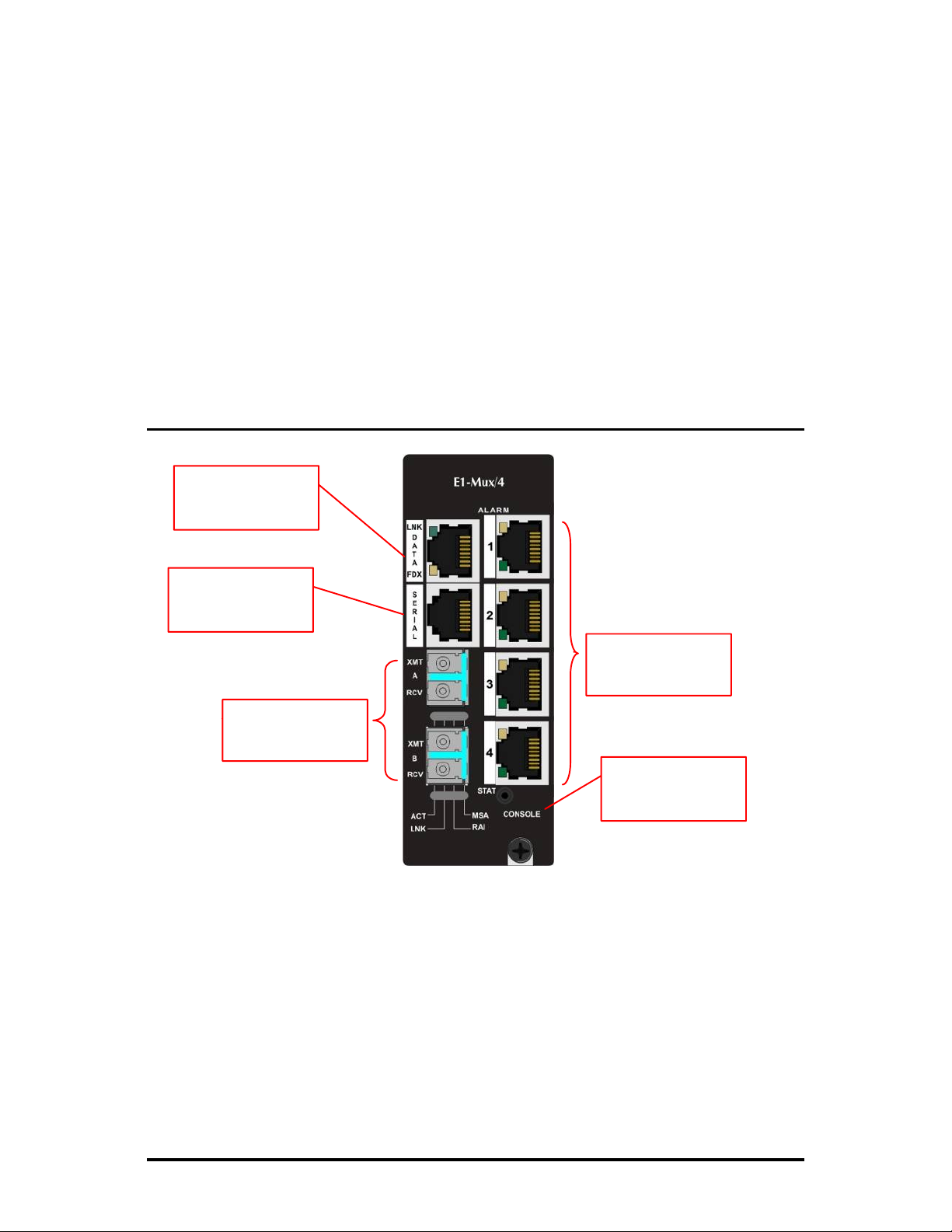
Port Interfaces
A fully-configured iMcV-E1-Mux/4 includes the following ports:
• Four E1 ports on RJ-48 connectors short haul
• One 10/100BaseT twisted pair Ethernet port (optional)
• One fiber
• Optional
SFP
port (requires
SFP
port for optical
SFP
/155-ED module for each port)
1+1
protection.
• One Mini Jack serial RS-232 serial console port
• One user serial RS-232 data port (RJ-45)
The iMcV-E1-Mux/4 is easily configured by using the serial console port connection
or through an
SNMP
management application such as iView².
Console Serial Port Connection
10/100BaseT
Connector
RS-232
Connector
E1 RJ-48
Connectors
SFP
Ports
Console
The iMcV-E1-Mux/4 includes a console serial port. To establish a link between a
module's console port and a local PC, connect the Mini Jack to DB9 adapter that is
included with this module. This RS-232 serial connection provides access to the
iMcV-E1-Mux/4 module
100 emulation
,
38.4K baud, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, no parity
configuration screens. Set the computer/terminal for
and
no flow control
VT-
CLI
Under the VT-100 emulation, set the backspace key to send delete.
.
3
Page 8
iView² Management Software
iView² is the IMC Networks management software designed specifically for the IMC
GUI
Networks “iMcV” family of modules. It features a
and gives network managers
the ability to monitor and control the manageable IMC Networks products.
iView² is available in several versions, including WebServer version 3.0, and can also
function as a snap-in module for HP OpenView Network Node Manager and other
third party SNMP Management software. For assistance in selecting the right version
of iView² for your operating system, please visit:
http://www.imcnetworks.com/products/iview2.cfm
2
iView
supports the following platforms:
• Windows 2000
• Windows XP
• Windows Vista
• Windows 7
SNMP
Please see the
Management Module for software configuration options.
About iView2 (iConfig view)
iView2 (iConfig view) is an in-band utility created by IMC Networks, used for SNMP
configuration for IMC Networks’ SNMP-manageable devices.
2
The iView
(iConfig view) feature allows the following to be performed:
• Set an IP address, subnet mask and default gateway
• Define community strings and SNMP traps
2
iView
(iConfig view) also includes an authorized IP address system and restricted
access to MIB groups which are supported by IMC Networks’ manageable devices.
2
These extra layers of security do not affect SNMP compatibility. iView
(iConfig view)
can upload new versions of the system software and new MIB information. It also
includes diagnostic capabilities for faster resolution of technical support issues.
4
Page 9
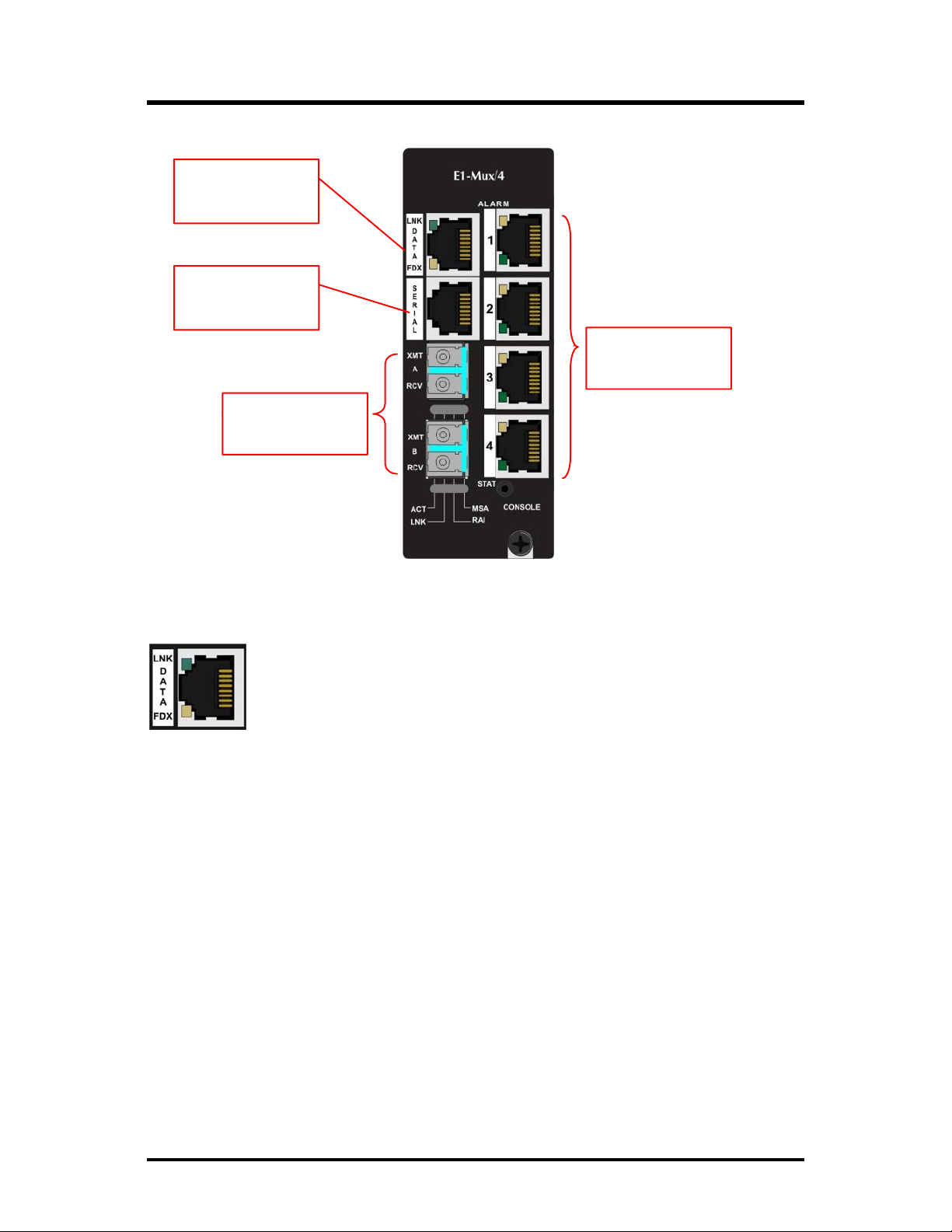
LED
Operation
10/100BaseT
Connector
Connector
RS-232
E1 RJ-48
Connectors
SFP
Ports
The iMcV-E1-Mux/4 features diagnostic
10/100BaseT Connector
LNK:
• OFF when port is not linked/connected
FDX:
• Glows green when link is established
• Blinks green during data activity
• OFF when port is not connected or when running at half-
duplex
• Glows yellow when port is running at full duplex
• Blinks yellow when collisions occur
LED
s as explained below.
5
Page 10
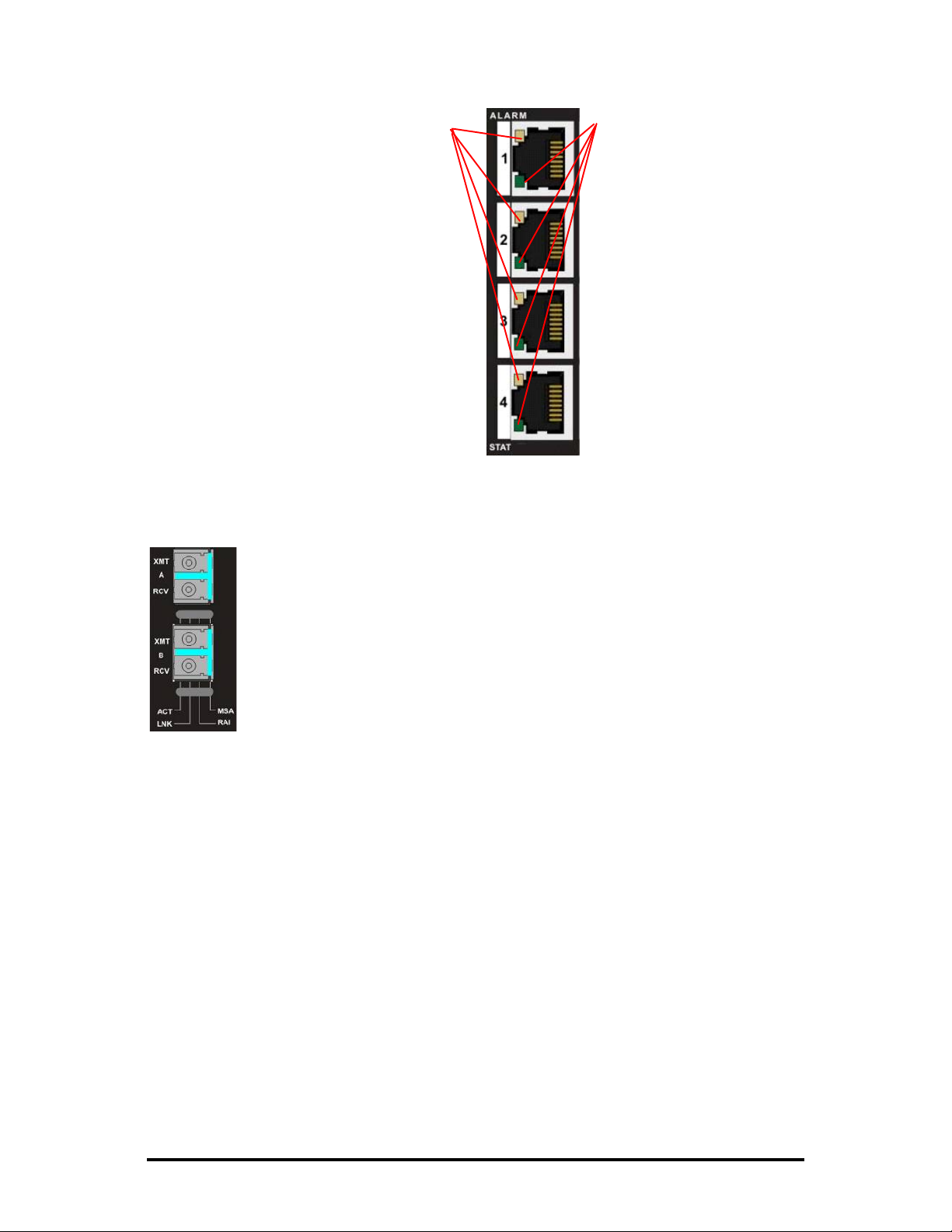
E1 RJ-48 Connectors
ALARM:
• OFF during normal operation
• Blinks red+green simultaneously
when
CV
errors detected on the E1
line at far end of the optical line
• Glows red+green when loss of
service (
continuous bit errors are detected
on the E1 line at far end of the
optical line
• Blinks red when local CV errors
detected on E1 line.
• Glows red when
the local E1 line, OR
when continuous errors are
detected on the local E1 line
SFP
Ports
LOS
) is detected, OR
LOS
detected on
One model offers two
second model offers one
ACT:
• Glows green when the
• OFF when the
• Glows red+green when the
be the active receive line
LNK:
• Glows green when there is a valid link
• Glows red when a loss of optical signal occur,
continuous optical bit errors
RAI
:
• Off when no remote defects are detected
• Glows red+green when remote
MSA
:
• Off when
• Glows green when no
• Glows red+green when
at remote end
• Glows red when
detected locally, i.e., when the
speed is not at 155Mbps
SFP
STAT:
SFP
(A and B) ports for
SFP
without protection.
SFP
port is the active receive line.
SFP
is not the receive line
SFP
is not an IMC Networks
SFP
alarms are detected
SFP
alarms or defects are detected
SFP
alarms or misconfigurations are
1+1
port is manually forced to
LOS
SFP
is missing, or when
• Glows green
during normal
operation
• Glows
red+green when
out-of-service or
when the port is
in a loopback or
test state
• Glows red when
the Host to
Remote fiber
link(s) is down or
badly corrupted
protection; a
LOF
, or with
or
BER
detected
SFP
SFP
6
Page 11

Connector Pinout and DIP Switch Assignments
DIP Switch Assignments
A single 10-position DIP Switch is located on the unit to set the configuration. The
switch positions are defined as follows:
Switch # Function Settings Factory Default
1 Host/Remote OFF = Host,
OFF
ON = Remote
2 Reserved OFF OFF
3 Reserved OFF OFF
4 Reserved OFF OFF
5 Reserved OFF OFF
6 Reserved OFF OFF
7 Reserved OFF OFF
8 Reserved OFF OFF
9 Reserved OFF OFF
10 Reserved OFF OFF
NOTE
Switch #1 must be set to ON at the Remote location.
Switches #2 through #10 are reserved for factory use only and must be OFF for proper
operation.
7
Page 12

10/100BaseT Ethernet Mating Connector Pinout
The following table lists the pin configuration for the standard RJ-45 Ethernet
connector.
Pin Signal
1 Transmit +
2 Transmit -
3 Receive +
4 None
5 None
6 Receive -
7 None
8 None
Pin 1
NOTE
MDI/MDIX AutoCross function will automatically transpose the Transmit and Receive lines if
required.
E1 Port Mating Connector Pinout
The following table lists the pin configuration for the standard RJ-48 E1 port mating
connectors.
Pin Signal
1 Receive 1 (Tip in to unit)
2 Receive 2 (Ring in to unit)
3 None
4 Transmit 1 (Tip from unit)
5 Transmit 2 (Ring from unit)
6 None
7 None
8 None
Pin 1
NOTE
The pin configuration is consistent with a DTE interface.
RS-232 Port Mating Connector Pinout
The following table lists the pin configuration for the RS-232 port mating connector.
8
Page 13

Pin Signal
1 None
2 None
3 None
4 Signal Ground
5 Receive Data (in to unit)
6 Transmit Data (out of unit)
7 None
8 None
Pin 1
This port provides an end-to-end RS-232 line that can support up to 250K Baud and
is transparent to all RS-232 protocols.
RS-232 Serial Console Port
The following table lists the pin configuration for the RS-232 3-pin Mini Jack mating
connector for the console serial port.
Pin DB9-F Pin# Signal Name Direction
Tip 2 Transmit Out of Unit
Ring 3 Receive In to Unit
Sleeve 5 Return Return
Sleeve
Ring
Tip
9
Page 14

Installation Instructions
Each iMcV-E1-Mux/4 module requires two adjacent slots in an iMediaChassis or
MediaChassis. To install the module in a chassis, remove the blank faceplates
covering the slots where the module is to be installed. Then slide the module into
the chassis card guides until the module is seated securely in the slots. Secure the
module to the chassis by tightening the captive screw.
Host
All iMcV-E1-Mux/4 units are shipped from the factory configured as
units. The
iMcV-E1-Mux/4 modules must be installed in pairs. For two iMcV-E1-Mux/4 units to
properly operate together one unit needs to be configured as a
Remote
.
Configuration as a Host or Remote is controlled via a DIP switch setting (S1-1).
Small Form-Factor Pluggable Ports (
The fiber link on the iMcV-E1-Mux/4 module is supported through one or two
depending on the model
(
) running at 155Mbps. Many
SFP
)
SFP
s, including those from
SFP
s
IMC Networks, feature enhanced diagnostics capabilities DDMI (Data and Diagnostic
Management Information).
DDMI
statistics provide real-time access to transceiver
operating parameters such as voltage, temperature, laser bias current, and both
DDMI
transmitted and received optical power.
2
iView
. Models with fixed 1x9 fiber transceivers cannot support the SFP table.
information can be accessed in
AutoCross Feature
The 10/100BaseT Ethernet port on the iMcV-E1-Mux/4 includes an AutoCross feature
that automatically selects between a crossover workstation and a straight-through
connection depending on the connected device.
10
Page 15

Configuration Options
The following sections describe the configurable features.
Use the "default" command to restore the unit's default settings. This restores the
card's default configuration and resets the default username and password.
User: admin / Password: admin
Ethernet Line Setup
If the Ethernet port is not used, it can be set to disabled via a console session or via
iView², to effectively block all traffic on this port.
Packet Size
The Ethernet transport can accommodate packets up to 1916 bytes.
Auto Negotiation
The iMcV-E1-Mux/4 ships from the factory with Auto Negotiation enabled on the
Ethernet port. In this mode, the port negotiates for speed, duplex and flow control.
Forcing the Speed, Duplex Mode, and Flow Control
The Ethernet port on the iMcV-E1-Mux/4 can be selectively advertised or manually
forced for 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps operation at Half- or Full-Duplex (i.e., 10 Mbps
Full-Duplex, 10 Mbps Half-Duplex, 100 Mbps Full-Duplex, etc.). Flow control can
also be enabled on the Ethernet port when the connecting equipment supports this.
These features can be enabled through iView².
FX LinkLoss and
LFPT
During normal operation, link integrity pulses are transmitted by all point-to-point
Ethernet devices. When an iMcV-E1-Mux/4 receives valid link pulses, it knows that
the device to which it is connected is up, and that the cable coming from that device
is intact. The appropriate “LNK” (link)
LED
is lit to indicate this. However, these
signals are not normally transmitted across a normal store and forward Ethernet
bridge function. A failed Ethernet line on one end of the fiber link is not forwarded
to the Ethernet port at the other end of the optical transport. A failed optical line is
also not normally forwarded to the Ethernet port. The FX LinkLoss and LFPT
functions are used to enable these features.
For troubleshooting information utilizing the FX LinkLoss and
iMcV-E1-Mux/4 modules, refer to
LFPT
Both the LinkLoss and
features are set to "Disabled" by default.
Troubleshooting
at the end of this manual.
LFPT
features of the
11
Page 16

FX LinkLoss (FXLL)
FX LinkLoss is a link integrity monitoring feature that forwards fiber link faults to the
RJ-45 DATA port to indicate that a fiber link fault has occurred. FX LinkLoss can be
enabled in iView².
Link Fault Pass-Through (
Link Fault Pass-Through (
the Ethernet port on one module through to the Ethernet port on the other module.
LFPT
can be enabled via iView² or through the console port.
The link fault is passed through the media conversion and is observed at each end. It
acts just as it would if the end devices were directly connected without a fiber link.
E1 Ports Setup
Alarm Level
E1 lines are defined as LOST when no signal is received as defined by ITU G.775
LOS
specifications
these conditions lasts for more than 2.5 seconds, an ALARM state is declared. This
error condition must be absent for 10 seconds for the alarm state to clear.
The starting and ending event of all alarm conditions will generate an
when the unit is installed in a managed chassis and set to the IS state. During initial
installation or normal maintenance, the end-user can place the unit in the
Of-Service) state to inhibit unwanted
Loopback
, and are considered in error with a
LFPT
)
LFPT
) is a troubleshooting feature that passes a link fault from
BER
of 10^-6. If either of
SNMP
TRAP
OOS
SNMP
TRAP alarms.
(Out-
Each E1 port can be tested in loopback mode by enabling either a Host loopback or
Remote loopback test path. This capability allows the end-user to help troubleshoot
and isolate system problems such as improper/broken line terminations, cables or
malfunctioning equipment.
With Host loopback, the E1 copper port, connected to the Host unit, is looped back
to that port within the local unit. E1 data coming from the remote unit to that port
over the optical link is also looped back to the remote unit at the same point within
the local unit.
With remote loopback, an E1 line connected to the Host unit is transported onto the
optical link and looped back within the remote unit back onto the optical link
without passing onto the copper E1 line of the remote unit. The remote’s incoming
E1 copper line is also looped-back to the copper line within the remote unit.
The default value for loopback is "none."
12
Page 17

Console Screens
Configuration Using the Console Port
The following section describes configuration using the console screens. The Remote
module is only configured through the Host.
Login Screen
After running through an initial self test, the log-in screen is displayed (the diagnostic
information displayed below is for illustration purposes only and may differ from the
actual screen display):
The username is case sensitive with a maximum length of 16 characters. After a
username is entered, the system prompts the end-user for a password.
Password is case sensitive with a maximum length of 16 characters. After the system
validates the username and password, the Main Menu is displayed.
13
Page 18

Main Menu
From the main menu, the end-user can view essential unit configuration data,
including active alarms in order of importance, and a clock indicating when the
displayed information was last refreshed.
Menu Options
1
= Refer to the
2
= Refer to the
3
= Refer to the
4
= Refer to the
= Refer to the
5
6
= Refer to the
7
= Refer to the
Unit Configuration Screen
Port Alarm Status
SFP
Line Status
screen
screen;
SFP DDMI
Ethernet Port Configuration
Ethernet Port Status
E1 Port Configuration
E1 Port Status
screen
screen
screen
alarms are also displayed
screen
NOTE
On all configuration screens, the title is the same as the "option" selected from the previous
screen.
Unit Configuration Screen
The unit configuration screen displays the names of the Host and Remote units as
well as the service state, whether fiber protection is enabled and the SFP
BER
alarm
level. In addition, the unit time can be set from this screen and the username and
password can be set/reset.
14
Page 19

The screen displays the current status for items 1 through 8. For security reasons, the
current username and password are not displayed.
For items 1 through 8, enter the number of the menu item to be changed, and then
enter the new value when prompted. The unit and port names can be assigned by
SNMP
the end-user and are used in
associated TRAP alarm messages.
Port Alarm Status Screen
The Port Alarm Status screen displays the status of the Host and Remote alarms on
each of the unit's ports. This screen can be refreshed as needed to display current
data.
SFP
Line Status Screen
The
SFP
Line Status screen displays the status of the Host and Remote
The detailed
SFP
information may be viewed by entering "1" for
SFP
SFP
links.
A or "2" for
SFP
Displayed data includes the manufacturer name, code, part number and revision
number. These values may not be modified.
SFP
For
modules that support
and optical receive/transmit, levels can be obtained through
DDMI
values for temperature, voltage, diode current
SNMP
Management
Module.
B.
15
Page 20

Ethernet Port Configuration Screen
The screen displays the current values for items 1 through 9 for both the Host and
Remote site.
Enter the number of the menu item to change its configuration, and then enter the
new value(s) when prompted.
Ethernet Port Status Screen
This screen displays the current Ethernet port status for both the Host and Remote
site.
16
Page 21

E1 Port Configuration Screen
Use this screen to access the loopback and name details for each of the four E1 ports.
Enter the number of the menu item to edit, and enter the new value(s) when
prompted.
E1 Port Status Screen
Use this screen to display the current status for each of the four E1 ports for the Host
and Remote units.
Enter the number of the menu item to edit, and enter the new value(s) when
prompted.
17
Page 22

Troubleshooting
• All iMcV-E1-Mux/4 units are shipped configured as Host units via DIP
Switch #1 = OFF. The Remote unit should be set to DIP Switch #1 = ON.
Be sure to confirm that the iMcV-E1-Mux/4 card is set correctly when used.
• The fiber transport is independent of all other ports and should be
established first. If this is not possible, a physical fiber loopback can be used
for fiber port verification. A fiber loopback will cause all connected ports to
loop back their respected data.
• If the fiber is not connected, all E1 ports will send the all-ones,
This can be physically looped back to verify E1 port operation.
AIS
signal.
18
Page 23

Fiber Optic Port Verification
As a troubleshooting aid, the fiber optic ports can be verified by placing a physical
LED
loopback optical line on the ports and verify the
behavior as shown:
The ACT
will arbitrarily be configured to either the A or B fiber line. The
RAI LED
LED
is RED/GREEN indicating that there is something wrong at the far end of the fiber line
(in this case, the remote unit is missing). The ALARM LED is RED because the E1 port
is not connected. The STAT LED is RED when there is no fiber link but turns GREEN
when the fiber link is valid.
NOTE
The E1 ports are all sending
E1 port. Without the fiber looped, it is because of the
AIS
. However, with the fiber looped, it is because of the
LOS
of the fiber port.
LOS
on the
WARNING
An optical loopback will also loop back the Ethernet port. If the network cannot tolerate this,
remove the Ethernet port connection before connecting the fiber loopback.
19
Page 24

E1 Port Verification
By placing a physical loopback connection on the E1 port, a valid signal can be
detected by each individual E1 port to verify its operation. Without the fiber looped,
the ALARM
LED
for the looped E1 port will show RED/GREEN indicating there is a
problem at the far end of the fiber transport (In this case the far end unit is missing)
and the STAT LED is RED because the fiber is in LOS. With the fiber looped, the E1
port will only show a normal GREEN STAT LED.
Normal Operation
Under normal operation the following
10/100BaseT
RS-232
E1
E1
E1
E1
LED
display is given:
GREEN LNK
10/100BaseT
RS-232
GREEN
ACT, LNK, MSA
E1
E1
E1
E1
GREEN STAT
20
Page 25

Fiber Optic Cleaning Guidelines
Fiber Optic transmitters and receivers are extremely susceptible to contamination by
particles of dirt or dust, which can obstruct the optic path and cause performance
degradation. Good system performance requires clean optics and connector ferrules.
Use fiber patch cords (or connectors, as appropriate) only from a reputable
1.
supplier; low-quality components can cause many hard-to-diagnose problems in
an installation.
2. Dust caps are installed at IMC Networks to ensure factory-clean optical devices.
These protective caps should not be removed until the moment of connecting
the fiber cable to the device. Should it be necessary to disconnect the fiber
device, reinstall the protective dust caps.
Store spare caps in a dust-free environment such as a sealed plastic bag or box
3.
so that when reinstalled they do not introduce any contamination to the optics.
If it is suspected that the optics have been contaminated, alternate between
4.
blasting with clean, dry, compressed air and flushing with methanol to remove
particles of dirt.
21
Page 26

Electrostatic Discharge Precautions
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can cause damage to any product, add-in modules or
stand alone units, containing electronic components. Always observe the following
precautions when installing or handling these kinds of products
Do not remove unit from its protective packaging until ready to install.
1.
Wear an ESD wrist grounding strap before handling any module or component.
2.
If the wrist strap is not available, maintain grounded contact with the system unit
throughout any procedure requiring ESD protection.
Hold the units by the edges; do not touch the electronic components or gold
3.
connectors.
After removal, always place the boards on a grounded, static-free surface, ESD
4.
pad or in a proper ESD bag. Do not slide the modules or stand alone units over
any surface.
WARNING!
extremely susceptible to electrostatic discharge damage. Do not
handle these components directly unless you are a qualified service
technician and use tools and techniques that conform to accepted
industry practices.
Integrated circuits and fiber optic components are
22
Page 27

Specifications
Power Consumption (Typical):
0.96A @ +5 VDC
Operating Temperature:
+32°F to +122°F (0°C to +50° C)
Storage Temperature:
-40°F to +160°F (-40°C to +70° C)
Humidity:
5 to 95% (non-condensing); 0 to 10,000 ft. altitude
Dimensions:
Dual Slot iMcV module
Standards/Compliance
• IEEE 802.3x Flow Control
• IEEE 802.3i 10Base-T twisted pair
• IEEE 802.3u 100Base-TX twisted pair
• IEEE 802.3u 100Base-FX or SX fiber
• ITU G.775
• GR-820-CORE
23
Page 28

IMC Networks Technical Support
Tel:
(949) 465-3000 or (800) 624-1070 (in the U.S. and Canada);
+32-16-550880 (Europe)
Fax:
E-Mail:
Web:
(949) 465-3020
techsupport@imcnetworks.com
www.imcnetworks.com
24
Page 29

Definition of Terms/Acronyms
The following are terms and phrases used within this manual (shown in
which are found in documents associated with this equipment.
1+1
The Term “1+1” refers to line protection where identical
information is transmitted on two redundant lines. The Receiver
BER
of the line.
AIS
chooses the “best” line to use based on the
Alarm Indication Signal: Used in E1 signaling, the AIS is a
predetermined bit stream (all ones) that is transmitted (forwarded)
upon the loss of an incoming E1 signal or when the E1 signal is
disrupted.
AN
Auto Negotiation: A signaling protocol used by an Ethernet PHY to
determine the characteristics (speed, duplex mode) of its “link
BER
partner” and configure itself automatically
Bit Error Rate: The percentage of bits with errors divided by the
total number of bits that have been transmitted, received or
processed over a one second time period.
CLI
Command Line Interface: An interface screen, often DOS-based,
used for system management and diagnostics requiring the user to
GUI
type commands rather than use a
.
italics
), or
CV
DDMI
FFL
GUI
HDB3
IS
Code Violation: An anomaly of a decoded physical-layer signal
stream resulting in coding (signaling) error(s). Noise bursts or
intermittent connections on a link are the usual causes of code
violations; an
HDB3
coding error.
Digital Diagnostic Monitor Interface: A defined serial interface and
data format typically used to access SFP internal information
Fiber Fault Loopback: When the fiber line fails, the Ethernet port
that is being forwarded over the fiber line is forced out of LINK.
Similar to the Fiber Alert function.
Graphical User Interface: Software that provides a visual interface
to enable an end-user to manage and monitor network devices.
High Density Bipolar 3 Coding: A physical-layer signal encoding
scheme defined for E1 transmission which ensures sufficient
signaling transitions for robust clock/data recovery.
In-Service stat is the normal state of an active port with normal
error reporting.
25
Page 30

LED
Light Emitting Diode: A small stack of lights to indicate link,
duplex or other options.
LFPT
LOF
LOS
MDI/MDIX
MIB
MSA
Link Fault Pass-Through: LFPT can be enabled via iView² or
through the console port.
Loss Of Frame: An error condition where the receiver/decoder
misses detection of the framing signal.
Loss Of Signal: An error condition where the receiving line
interface unit does not detect a signal.
Media-Dependent Interface/ Media-Dependent Interface
Crossover. The ability of an Ethernet port to automatically detect
and configure its cabling connections to accommodate crossover
or non-crossover wiring, depending on its link partner and cabling.
Management Information Base: A database of objects that can be
monitored by a network management system. Both SNMP and
RMON use standardized MIB formats that allow any SNMP and
RMON tools to monitor any device defined by a MIB.
Multi-Source Agreement (SFP): The standard an SFP must meet to
be compatible in network devices.
OOS
POP
RAI
SFP
SNMP
Out-Of-Service, OOS is used by the CRAFT personnel to turn OFF
the alarm reporting so they can service the line without causing
alarm TRAPS to be sent to the NOC Center. The LEDs display a
line status but do not report any line related alarms back to the
NOC. A card removal or insertion is still reported, but a PORT
up/down or changes to its configuration are not.
Point(s) Of Presence: The demarcation point where carrier owned
equipment is located at the customer site.
Remote Alarm Indication: Status information received from the
line indicating there is an alarm condition at the far end of the
transport.
Small Form-Factor Pluggable: An industry standard optical
pluggable module.
Simple Network Management Protocol: A set of protocols for
managing complex networks over a standards-based IP network.
26
Page 31

Certifications
CE: The products described herein comply with the Council Directive on
Electromagnetic Compatibility (2004/108/EC).
European Directive 2002/96/EC (WEEE) requires that any equipment that bears this
symbol on product or packaging must not be disposed of with unsorted municipal
waste. This symbol indicates that the equipment should be disposed of separately
from regular household waste. It is the consumer’s responsibility to dispose of this
and all equipment so marked through designated collection facilities appointed by
government or local authorities. Following these steps through proper disposal and
recycling will help prevent potential negative consequences to the environment and
human health. For more detailed information about proper disposal, please contact
local authorities, waste disposal services, or the point of purchase for this equipment.
27
Page 32

19772 Pauling • Foothill Ranch, CA 92610-2611 USA
TEL: (949) 465-3000 • FAX: (949) 465-3020
www.imcnetworks.com
© 2011 IMC Networks. All rights reserved.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. IMC Networks assumes no responsibility for any
errors that may appear in this document. iMcV-E1-Mux/4 is a trademark of IMC Networks. Other brands or product
names may be trademarks and are the property of their respective companies.
Document Number 57-80400-01 A0 November 2011
 Loading...
Loading...