Page 1

Not Recommended for New Installations.
Please contact Technical Support for more information.
RS-422/RS-485 Line Tester
Documentation Number 485T1995
Designed and Manufactured
B&B Electronics Mfg. Co. Inc.
707 Dayton Road -- P.O. Box 1040 -- Ottawa, IL 61350
PH (815) 433-5100 -- FAX (815) 433-5105
1992 B&B Electronics -- Revised August 1992
Model 485T
This product
In Ottawa, Illinois
USA
of domestic and imported parts by
Internet:
http://www.bb-elec.com
orders@bb-elec.com
support@bb.elec.com
Documentation Number 485T1995 Manual Cover Page
B&B Electronics -- PO Box 1040 -- Ottawa, IL 61350
PH (815) 433-5100 -- FAX (815) 433-5105
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION ...............................................................................1
RS-422 AND RS-485 STANDARDS .................................................1
CONTROLS AND CONNECTIONS ON THE 485T ..........................6
A
AND B TERMINALS ........................................................................6
ROUND TERMINAL..........................................................................6
G
HRESHOLD POT..............................................................................7
T
OSITIVE THRESHOLD EXCEEDED LED.............................................7
P
EGATIVE THRESHOLD EXCEEDED LED............................................7
N
RS-422/RS-485 S
ERMINATION SWITCH ......................................................................8
T
OWER............................................................................................8
P
RS-232 D
ATA OUT CONNECTOR ......................................................8
RS-422/485 TEST .............................................................................9
WITCH.................................................................8
Documentation Number 485T1995 Manual Table of Contents i
B&B Electronics -- PO Box 1040 -- Ottawa, IL 61350
PH (815) 433-5100 -- FAX (815) 433-5105
Page 3

INTRODUCTION
The Model 485T Tester can be used to check the condition of
signals at any node on an RS-422 or RS-485 network. The tester
determines if the maximum permissible negative or positive voltages
are being exceeded. If these voltage levels are exceeded it is
possible to damage the RS-422/485 receivers and drivers. The
tester also checks to see if minimum required differential voltages
exist on the lines. The tester uses the normal data that is
transmitted on the line to check the value of the minimum differential
voltage. There is an RS-232 output that can be used to view the
network data.
RS-422 AND RS-485 STANDARDS
The RS-232 Standard (Interface Between Data Terminal
Equipment and Data Circuit-Terminating Equipment Employing
Serial Binary Data Interchange) was developed many years ago by
the Electronic Industries Association (EIA). It was used to connect
modems to terminals for dial-up computer systems. Since the
modem and terminal were usually located close to each other, wire
length was not much of a factor in the standard. RS-232 maximum
wire lengths were set at 50 feet. RS-232 lines can run farther with
special (low capacitance) wire but there is a practical limit of 300 or
so feet.
The EIA then developed two newer standards to allow serial
data communications to go past the 50 foot barrier. The first is RS422, Electrical Characteristics of Balanced Voltage Digital Interface
Circuits. The second is RS-485, Standard for Electrical
Characteristics of Generators and Receivers for use in Balanced
Digital Multipoint Systems. Using these standards, wire lengths of
about 4000 feet are attainable. This is possible by using two wires
for each signal instead of the one wire used in RS-232.
A typical RS-232 system can have eight wires, seven signals
and one ground, not all of which are used in every system. As each
signal goes high or low (typically +12 and -12 volts) it uses the one
ground wire as a reference. Ground currents can cause confusion.
Also, the RS-232 drivers are not capable of driving much more than
2500 picofarads before the signal on the line is badly distorted.
Both RS-422 and RS-485 use two wires for each signal. These
two wires are driven differentially. When one wire is low the other is
Documentation Number 485T1995 Manual 1
B&B Electronics -- PO Box 1040 -- Ottawa, IL 61350
PH (815) 433-5100 -- FAX (815) 433-5105
Page 4

high and vice-versa. Also, the drivers are capable of driving a wire
with as much as 25 times more capacitance before the signal is
badly distorted. Most system designers try to minimize the number
of signals used because these standards take two wires per signal.
This is one reason most RS-422 and RS-485 systems are either
two-wire with ground or four-wire with ground.
There are two major differences between RS-422 and RS-485.
The first is that with RS-422, one driver can only drive 10 receivers.
With RS-485, one driver can drive 32 receivers. Secondly, RS-485
drivers can be “tri-stated” or turned off. This allows you to put all 32
drivers and receivers on one two-wire line. When a device needs to
output data, it first turns on its driver to seize the line and then sends
its data. The other 31 devices will be listening. RS-422 requires at
least two pairs of wires, one pair to send data in one direction and
the other for return data.
Typically, the RS-422 or RS-485 driver will switch between +5
volts and ground. Since devices can be long distances apart, they
can be powered on different power lines or transformers that can
force their “reference grounds” to be at different voltages. The RS422 Standard allows the signal lines to go as high as +7 volts and as
low as -7 volts. The RS-485 Standard allows +12 volts and -7 volts.
Another requirement is that the differential input voltage at the
receiver must be more than 0.2 volts. The differential voltage starts
out from the driver at about 2 volts but the resistance, inductance,
and capacitance of the wire combine to attenuate this signal. As the
wire gets longer, this voltage will get smaller until it falls below the
0.2 volt level and then communications can no longer be
guaranteed.
Both specifications discuss termination of the two-wire line. A
typical two-wire twisted-pair line looks like a 100 ohm transmission
line. In general, the line does not need to be terminated for slow
data rates or for short-wire lengths.
More information and the RS-232, RS-422, and RS-485 Standards
are available from:
ELECTRONICS INDUSTRIES ASSOCIATION
Engineering Department
2001 Eye Street N. W.
Washington, DC 20006
Phone: (202) 457-4900 --- FAX: (202) 457-4985
2 Documentation Number 485T1995 Manual
B&B Electronics -- PO Box 1040 -- Ottawa, IL 61350
PH (815) 433-5100 -- FAX (815) 433-5105
Page 5
Documentation Number 485T1995 Manual 3
B&B Electronics -- PO Box 1040 -- Ottawa, IL 61350
PH (815) 433-5100 -- FAX (815) 433-5105
Page 6

4 Documentation Number 485T1995 Manual
B&B Electronics -- PO Box 1040 -- Ottawa, IL 61350
PH (815) 433-5100 -- FAX (815) 433-5105
Page 7

Documentation Number 485T1995 Manual 5
B&B Electronics -- PO Box 1040 -- Ottawa, IL 61350
PH (815) 433-5100 -- FAX (815) 433-5105
Page 8

CONTROLS AND CONNECTIONS ON THE 485T
A and B Terminals
The two signal lines used in an RS-422 or RS-485 network
should be labeled A and B. These lines should be connected to the
A and B terminals of the 485T Tester. If your lines are not marked
(or are marked using another method) you can use a DC voltmeter
to determine which is which. With no data being sent, the A line will
be negative with respect to the B line. On an RS-485 network, if all
of the drivers are off, the voltmeter will read zero volts. Under these
conditions, it is not possible to use a voltmeter to determine which
line is A and which is B. Having them connected backwards will only
be a problem when using the RS-232 Data Out Connector.
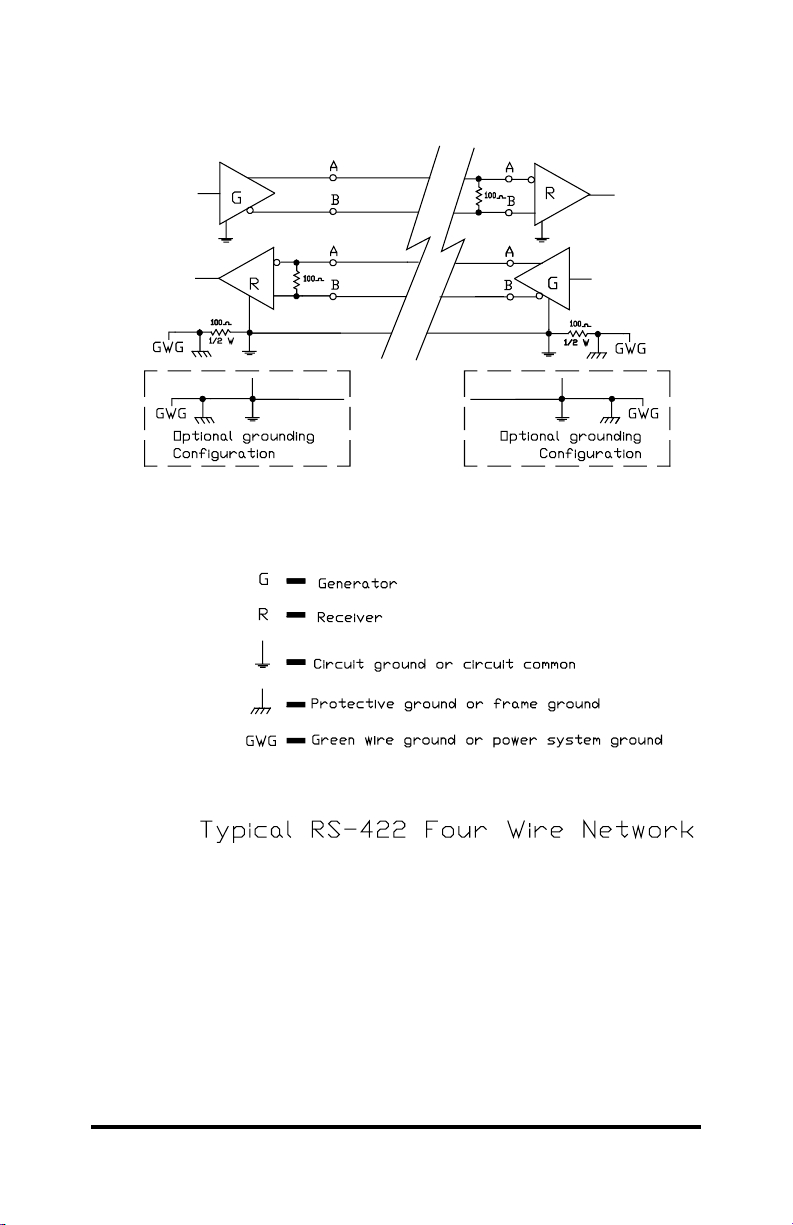
Some networks will use four wires instead of two. In these
networks, one pair will be used to send data out from a master
device. The other pair will send data back from one or a multitude of
other devices. These networks can be tested using the 485T by
treating them as two separate networks. You would first run your
tests on one pair of signal lines and then run them again on the
other pair.
NOTE: Make sure that you are connected to the correct two
lines when using the tester. It is possible for the tester to look
like it is working properly when one line is connected and the
other is floating or connected to a wire in another pair.
Ground Terminal
The GND terminal on the 485T Tester should be connected to
Signal Ground for the device under test. The Signal Ground is
usually the same as the power supply ground for your unit. Some
systems will also have a Frame Ground that is usually connected to
the “Green Wire Ground” of your power supply AC plug. Frame
Ground can also be connected to the wire shield if your pair of wires
is shielded. You want Signal Ground not Frame Ground. In some
systems, Frame Ground will be connected to Signal Ground, usually
through a 100 ohm one-half watt resistor. You still want to be
connected to Signal Ground to make proper measurements, since
they may be at different voltages. There is a 100 ohm one-half watt
resistor connected internally between the GND terminal and the
internal Signal Ground (power supply ground) of the 485T. This is
the optional grounding method from both the RS-422 and the RS485 Standard.
6 Documentation Number 485T1995 Manual
B&B Electronics -- PO Box 1040 -- Ottawa, IL 61350
PH (815) 433-5100 -- FAX (815) 433-5105
Page 9

Threshold Pot
The large pot in the center of the 485T is the threshold pot. In
order for RS-422/485 to work properly, you should have a differential
input voltage of more than .2 volts across the two lines at the RS422/485 receiver. By adjusting this pot you can determine the
amplitude of the RS-422/485 signals. Start with the knob turned
down to zero volts (full clockwise) with data being sent on your
network. The Data LED should be blinking with the data providing
that the network is not running at too high of a baud rate. At higher
baud rates the LED may be on. Turn the threshold pot up
(counterclockwise) until the Data LED stops blinking or turns off.
The reading of the pot at that point is the differential input voltage.
This reading should be .2 volt or more. If the LED does not stop
blinking or turn off with the pot all the way up (full counterclockwise)
the reading is above 1 volt. Readings above 1 volt are not available
since it would make the lower voltage readings difficult to read.
Readings above 1 volt indicate that differential voltage is more than
adequate.
Positive Threshold Exceeded LED
The RS-422 Standard states that a network should not have a
positive common mode voltage of more than 7 volts. This means
that the difference between Signal Ground and either the A or B
input should not be more than positive 7 volts. For RS-485 the
maximum is 12 volts. The Positive Threshold Exceeded LED will
light if these limits are exceeded. This reading is taken with respect
to Signal Ground so the GND terminal must be connected properly
for the reading to be correct.
NOTE: The RS-422/RS-485 switch is used to control this
threshold. It must be in the proper position for these readings to
be correct.
Negative Threshold Exceeded LED
Both the RS-422 and the RS-485 Standards state that the
network should not have a negative common mode voltage of more
than 7 volts. This means that the difference between Signal Ground
and either the A or B input should not be more than minus 7 volts.
The Negative Threshold Exceeded LED will light if this limit is
exceeded. Again this reading is taken with respect to Signal Ground
so the GND terminal must be connected properly for the reading to
be correct.
Documentation Number 485T1995 Manual 7
B&B Electronics -- PO Box 1040 -- Ottawa, IL 61350
PH (815) 433-5100 -- FAX (815) 433-5105
Page 10

RS-422/RS-485 Switch
This switch controls the positive threshold voltage for the
Positive Threshold LED only. When the switch is in the RS-422
position, the positive threshold is +7 volts. When it is in the RS-485
position, the positive threshold is +12 volts. This switch has no
effect on the Data LED, the Threshold Pot, or on the Negative
Threshold LED.
Termination Switch
In some cases RS-422 and RS-485 pairs are terminated. This
termination is usually needed only for long or high speed networks.
Terminations usually consist of a 100 ohm one-half watt resistor
located at each end of the network. In some complicated multi-drop
networks it may be hard to determine exactly were the “ends” are. A
100 ohm one-half watt termination resistor is included in the 485T. It
may be helpful if you are testing an existing network with no
terminations and want to see what happens if you terminate it at one
point. Normally, you should leave this switch OFF (down).
Power
The 485T will work from a nine-volt battery or from 12 VDC
through the 2.5 mm jack marked DC Power 12VDC IN. When you
plug in the external power supply (available from B&B Electronics as
the Model 485PS) the battery is automatically disconnected.
RS-232 Data Out Connector
This is a standard DB-25S RS-232 connector. When the DATA
LED is blinking, any RS-422/485 data on the A & B inputs is
converted to the RS-232 format and output on pin 2. You can
connect this to a device that has an RS-232 port and can read your
data. Be sure you turn the threshold pot all the way down
(clockwise) to zero. For use on standard ASCII data B&B
Electronics sells a program called BreakOut II that will turn a PC into
a serial data monitor. With it and a PC you can monitor data on your
RS-422/485 network.
NOTE: If your data is garbled you may have the A and B lines
connected backwards or the threshold pot may not be all the
way down to zero. It is also possible that the RS-422/485 signal
may be too weak.
8 Documentation Number 485T1995 Manual
B&B Electronics -- PO Box 1040 -- Ottawa, IL 61350
PH (815) 433-5100 -- FAX (815) 433-5105
Page 11

RS-422/485 TEST
A typical test on an RS-422/485 network might go like this: First
start by locating the two wires used for the RS-422/485 network and
try to determine which is A and which is B. Also, locate the Signal
Ground. This may be the same as the ground on the DC power
supply that powers the RS-422/485 device.
Connect the Signal Ground to the GND terminal. Connect the A
and B terminals to what you think are the A and B wires. Turn the
Threshold Pot to zero (full clockwise), the TERMINATION off, the
RS-422 and RS-485 switch to the proper position, and the POWER
switch ON. If you are not sure which is A and which is B, test them
with a DC voltmeter. With no data being sent, the A line should be
negative with respect to the B line. Getting the A and B lines correct
is only important for the RS-232 DATA OUT CONNECTOR. It will
have no affect on the other tests.
The POSITIVE and NEGATIVE THRESHOLD EXCEEDED
LEDs should both be off, both when data is being sent and when the
network is idle. If either of these LEDs is on or blinking, you may
have a grounding problem. You should first check that the RS422/RS-485 switch is in the proper position and that the Signal
Ground is connected correctly to the 485T. Refer to B&B
Electronics' free RS-422/485 Application Note for information on
proper grounding of your network.
NOTE: If the positive or negative thresholds are exceeded, you
may damage your RS-422 or RS-485 line receivers. If either of
the LEDs is on or blinking you should find out why and fix the
problem as soon as possible.
For example, if you have a network with two nodes located in
two different buildings about 4000 feet apart. An RS-422 driver in
building A can be switching between +5 volts and ground and be
powered from building A’s power lines. An RS-422 receiver can be
located in building B with a ground potential that is 3 volts DC lower
than building A. That receiver will see +8 volts for a high (5+3 volts)
and +3 volts for a low (0+3 volts). This is allowed under both
standards and should work fine. However, if the difference in
ground potential is 10 VDC lower, the high (5+10 volts) will be +15
volts and is NOT allowed. The ground difference voltage can also
be an AC voltage which could confuse things even more.
Documentation Number 485T1995 Manual 9
B&B Electronics -- PO Box 1040 -- Ottawa, IL 61350
PH (815) 433-5100 -- FAX (815) 433-5105
Page 12

See B&B Electronics' free RS-422/485 Application Note for
information on proper wiring and grounding of an RS-422/485
network.
If the POSITIVE and NEGATIVE THRESHOLD LEDs are both
off, you can then test for proper signal amplitude. With the
THRESHOLD pot turned to zero (full clockwise), the DATA LED
should blink or stay on when data is sent. When data is being sent
on the network, turn the THRESHOLD pot counterclockwise until the
LED goes out.
If, for instance, the LED goes out when the pot is pointing at .5,
then you have a differential input voltage of plus or minus .5 volts.
Both RS-422 and RS-485 require at least plus or minus .2 volts to
work properly. If your network node is below this level, you may
need a line booster, a repeater, or you may need to change your
wiring layout. Refer to B&B Electronics' free RS-422/485 Application
Note for information on network wiring. If the LED does not go out
with the THRESHOLD pot turned up to 1.0 (full counterclockwise),
then your differential input voltage is more than 1 volt. Most RS422/485 drivers start out with a differential of about 2 volts but the
resistance, inductance, and capacitance in the line can reduce it
considerably.
NOTE: The differential voltage you are trying to measure is the
RECEIVED voltage. You should only make the threshold
measurement when the node you are testing is RECEIVING
data, not when it is transmitting. If you have a multiple node
system with each node at a different location, you may have to
have each node transmit separately while you take a reading.
You may get a different differential voltage reading from each
node.
For example, if you have an RS-485 network with five nodes
each located 1000 feet apart for a total of 4000 feet. Node 1 is at
one end, node 2 next, etc., and node 5 is at the far end. If you
connect the 485T Tester to node 1 and watch while data is sent from
node 2, there will only be 1000 feet of wire and the signal should be
fairly strong.
However, when node 5 sends data, there will be 4000 feet of
wire and the signal will be weaker. If you have the different nodes
sending randomly it will be impossible to take a reading. You have
to have only one node sending to take a proper reading. You may
be able to turn the power off unwanted nodes to stop them from
transmitting. However, this may change the loading on the line, so
be careful using this method.
10 Documentation Number 485T1995 Manual
B&B Electronics -- PO Box 1040 -- Ottawa, IL 61350
PH (815) 433-5100 -- FAX (815) 433-5105
Page 13

You can then use the 485T Tester to monitor the data that is
being sent or received on your network. If you have a datascope or
a computer running a datascope-like program you can connect it to
the RS-232 DATA OUT connector on the 485T. A typical program
would be BreakOut II which is available from B & B Electronics. The
RS-232 DATA OUT connector is wired as a DTE with data output on
pin 2. Pin 4 is connected to pin 5 and pin 6 is connected to pins 8
and 20 for handshake loopback. Pin 7 is ground and there is no
connection to pin 3.
NOTE: If the data you receive is garbled, you may have the A &
B connectors backwards. Try reversing them.
With the 485T connected and the THRESHOLD pot turned to
zero (full clockwise), any RS-422/485 data on the network will
appear as RS-232 data at pin 2 of the RS-232 DATA OUT jack. If
you have a four-wire network you can only view one pair of lines at a
time. This means that you can only see data transmitted from that
node or data received by that node, not both at the same time. On a
two-wire node (RS-485) you can see both received and transmitted
data at the same time.
NOTE: Your datascope must be able to receive data at the
same baud rate, etc. as the data that is transmitted on the RS422/485 network.
Documentation Number 485T1995 Manual 11
B&B Electronics -- PO Box 1040 -- Ottawa, IL 61350
PH (815) 433-5100 -- FAX (815) 433-5105
Page 14

12 Documentation Number 485T1995 Manual
B&B Electronics -- PO Box 1040 -- Ottawa, IL 61350
PH (815) 433-5100 -- FAX (815) 433-5105
 Loading...
Loading...