
RTA04N
150M Wireless 11N ADSL2+ Router
- User Manual –

CONTENT TABLE
1. INTRODUCTION ................................................................................................................. 4
1.1. PRODUCT OVERVIEW ............................................................................................................... 4
1.2. MAIN FEATURES ...................................................................................................................... 4
1.3. CONVENTIONS ........................................................................................................................ 5
2. HARDWARE INSTALLATION .................................................................................................. 6
2.1. THE FRONT PANEL ................................................................................................................... 6
2.2. THE BACK PANEL ..................................................................................................................... 7
2.3. INSTALLATION ENVIRONMENT ................................................................................................... 7
2.4. CONNECTING THE ROUTER ........................................................................................................ 8
3. QUICK INSTALLATION GUIDE ................................................................................................ 9
3.1. CONFIGURE PC ....................................................................................................................... 9
3.2. LOGIN .................................................................................................................................. 12
4. SOFTWARE CONFIGURATION ............................................................................................... 16
4.1. STATUS ................................................................................................................................ 16
4.1.1. Device Info ....................................................................................................................... 16
4.1.2. ADSL ................................................................................................................................. 18
4.1.3. Statistics ........................................................................................................................... 19
4.1.4. Wizard .............................................................................................................................. 19
4.2. SETUP .................................................................................................................................. 20
4.2.1. WAN ................................................................................................................................. 20
4.2.2. LAN................................................................................................................................... 24
4.2.3. WLAN ............................................................................................................................... 30
4.3. ADVANCED ........................................................................................................................... 42
4.3.1. Route ............................................................................................................................... 42
4.3.2. NAT .................................................................................................................................. 44
4.3.3. QoS .................................................................................................................................. 49
4.3.4. CWMP .............................................................................................................................. 54
4.3.5. Port mapping ................................................................................................................... 55
4.3.6. Others .............................................................................................................................. 57
4.4. SERVICE ............................................................................................................................... 58
4.4.1. IGMP Proxy ...................................................................................................................... 58
4.4.2. UPnP ................................................................................................................................ 58
4.4.3. SNMP ............................................................................................................................... 59

4.4.4. DNS .................................................................................................................................. 60
4.4.5. DDNS ................................................................................................................................ 61
4.5. FIREWALL ............................................................................................................................. 62
4.5.1. MAC Filter ........................................................................................................................ 62
4.5.2. URL Filter ......................................................................................................................... 65
4.5.3. ACL ................................................................................................................................... 66
4.6. MAINTENANCE ...................................................................................................................... 68
4.6.1. Update ............................................................................................................................. 68
4.6.2. Password .......................................................................................................................... 71
4.6.3. System Restart ................................................................................................................. 71
4.6.4. Time ................................................................................................................................. 72
4.6.5. Log ................................................................................................................................... 74
4.6.6. Diagnostic ........................................................................................................................ 74
APPENDIX A: SPECIFICATIONS .......................................................................................................... 78

RRTTAA0044WW UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 4 out of 78
1. Introduction
Thank you for choosing the RTA04N 150M Wireless 11N ADSL2+ Router.
1.1. Product Overview
The device is designed to provide a simple and cost-effective ADSL Internet connection for a private
Ethernet or IEEE 802.11n/ IEEE 802.11g/ IEEE 802.11b wireless network.
The RTA04N connects to an Ethernet LAN or computers via standard Ethernet ports. The ADSL
connection is made using ordinary telephone line with standard connectors. Multiple workstations
can be networked and connected to the Internet using a single Wide Area Network (WAN) interface
and single global IP address. The advanced security enhancements, MAC Filter, IP/Port Filter,
URL Filter and ACL can help to protect your network from potentially devastating intrusions by
malicious agents from the outside of your network.
Wizard of the Web-based Utility is supplied and friendly help messages are provided for the
configuration. Network and Router management is done through the Web-based Utility which can be
accessed through local Ethernet using any web browser.
ADSL
The RTA04N supports full-rate ADSL2+ connectivity conforming to the ITU and ANSI specifications.
In addition to the basic DMT physical layer functions, the ADSL2+ PHY supports dual latency
ADSL2+ framing (fast and interleaved) and the I.432 ATM Physical Layer.
Wireless
In the most attentive wireless security, the Router provides multiple protection measures. It can be
set to turn off the wireless network name (SSID) broadcast so that only stations that have the SSID
can be connected. The Router provides wireless LAN 64/128-bit WEP encryption security, WPAPSK/WPA2-PSK authentication, as well as TKIP/AES encryption security.
1.2. Main Features
Wireless AP, Router, 4 Port Switch and Firewall
Support ITU-T G.992.1 (G.dmt), ANSI T1.413, G.992.2 (G.Lite), ADSL2 and ADSL2+
Support 802.11n, compatible with 802.11b and 802.11g
Up to 54 Mbps wireless operation rate
64/128 bits WEP for security
WPA and WPA2 support
Four 10/100MBase-T Ethernet interface (LAN)
RFC-1483/2684 LLC/VC-Mux bridge/route mode
RFC-1577 Classical IP over ATM
RFC-2516 PPPoE
RFC-2364 PPPoA
ITU-T 1.610 F4/F5 OAM send and receive loop-back
802.1d Spanning-Tree Protocol
DHCP Client/Server/Relay
NAT

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 5 of 78
RIP v1/v2
DNS Relay Agent
Support DMZ, virtual server, ALG
IGMP Proxy/Snooping
Protection against Denial of Service attack
IP Packet filtering
MAC filtering
URL filtering
IP QoS
Dynamic DNS
UPnP support
System log support, can record the state of the router
Remote management
SNMP v1/v2/Trap
Firmware upgrade through FTP, TFTP and HTTP
Configuration backup/restore
Diagnostic tolos
1.3. Conventions
The Router or device mentioned in this User Guide stands for RTA04N without any explanations.
Parameters provided in the pictures are just references for setting up the product, which may differ
from the actual situation.
RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 6 of 78
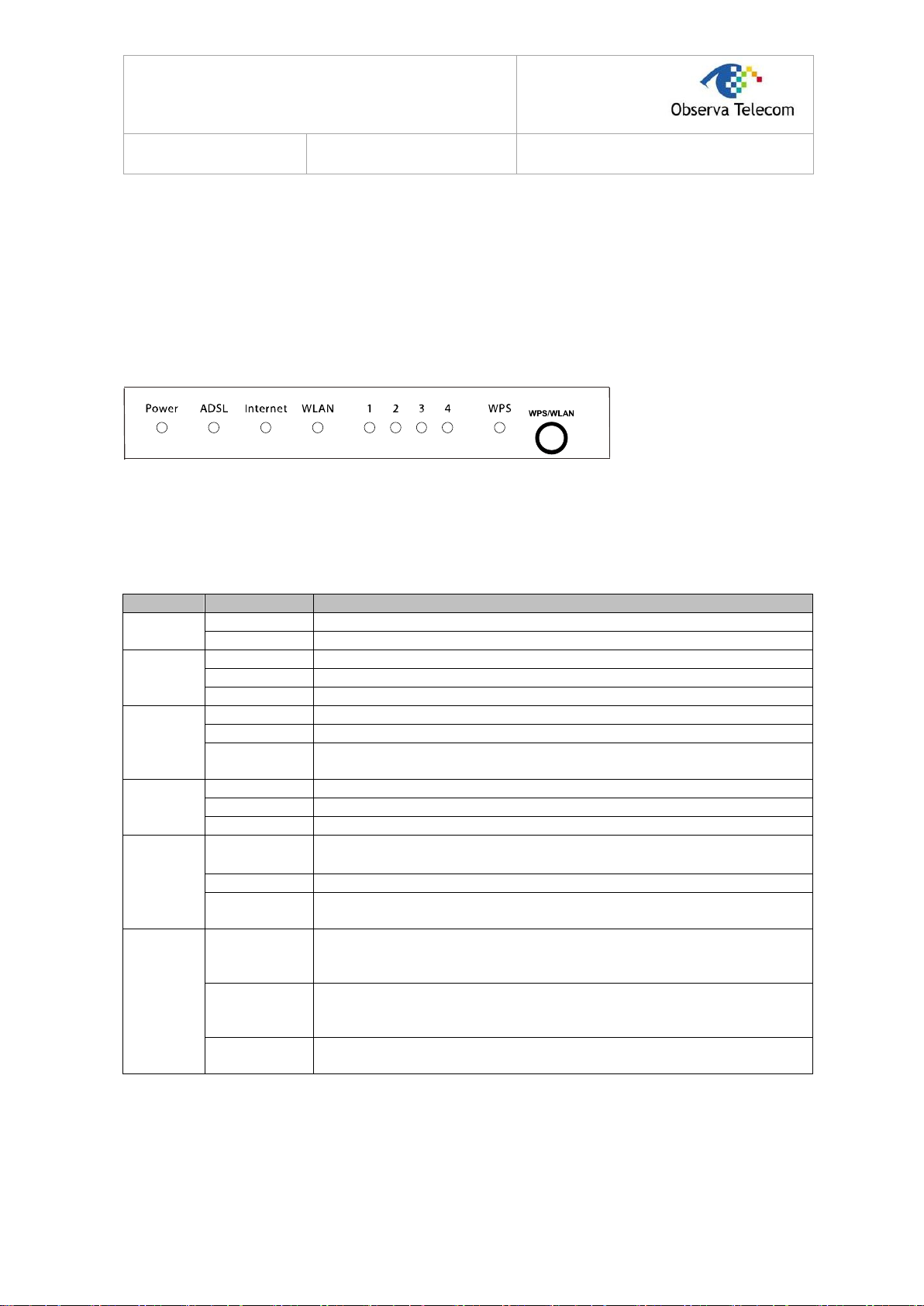
Name
Status
Indication
PWR
On
Power is on.
Off
Power is off.
ADSL
On
The LINE port is linked up.
Flash
The ADSL negotiation is in progress.
Off
The LINE port is linked down.
Internet
On
A successful PPP connection has been built.
Flash
Data is being transferred over the Internet.
Off
There is no successful PPP connection or the Router works on Bridge
mode.
WLAN
On
The wireless function is enabled but no data is being transmitted.
Flash
There is wireless data being transmitted.
Off
The wireless function is disabled.
LAN(1-4)
On
There is a successful connection on the corresponding 1-4 (LAN)
port but no activity.
Flash
Data is being transferred over the 1-4 (LAN) port.
Off
There is no connection on the corresponding 1-4 (LAN) port or the
connection is abnormal.
WPS
On
A wireless device has been successfully added to the network by
WPS function. The LED will keep on for about 5 minutes and then turn
off.
Flash
The WPS function is enabled but no wireless device has been
successfully added to the network by WPS function. The LED will
keep flash for about 2 minutes and then turn off.
Off
The WPS function is disabled or a wireless device failed to be added
to the network by WPS function.
2. Hardware Installation
2.1. The Front Panel
Figure 2-1
The LEDs locate on the front panel. They indicate the device’s working status. For details, please
refer to LED Explanation.
LED Explanation
RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 7 of 78
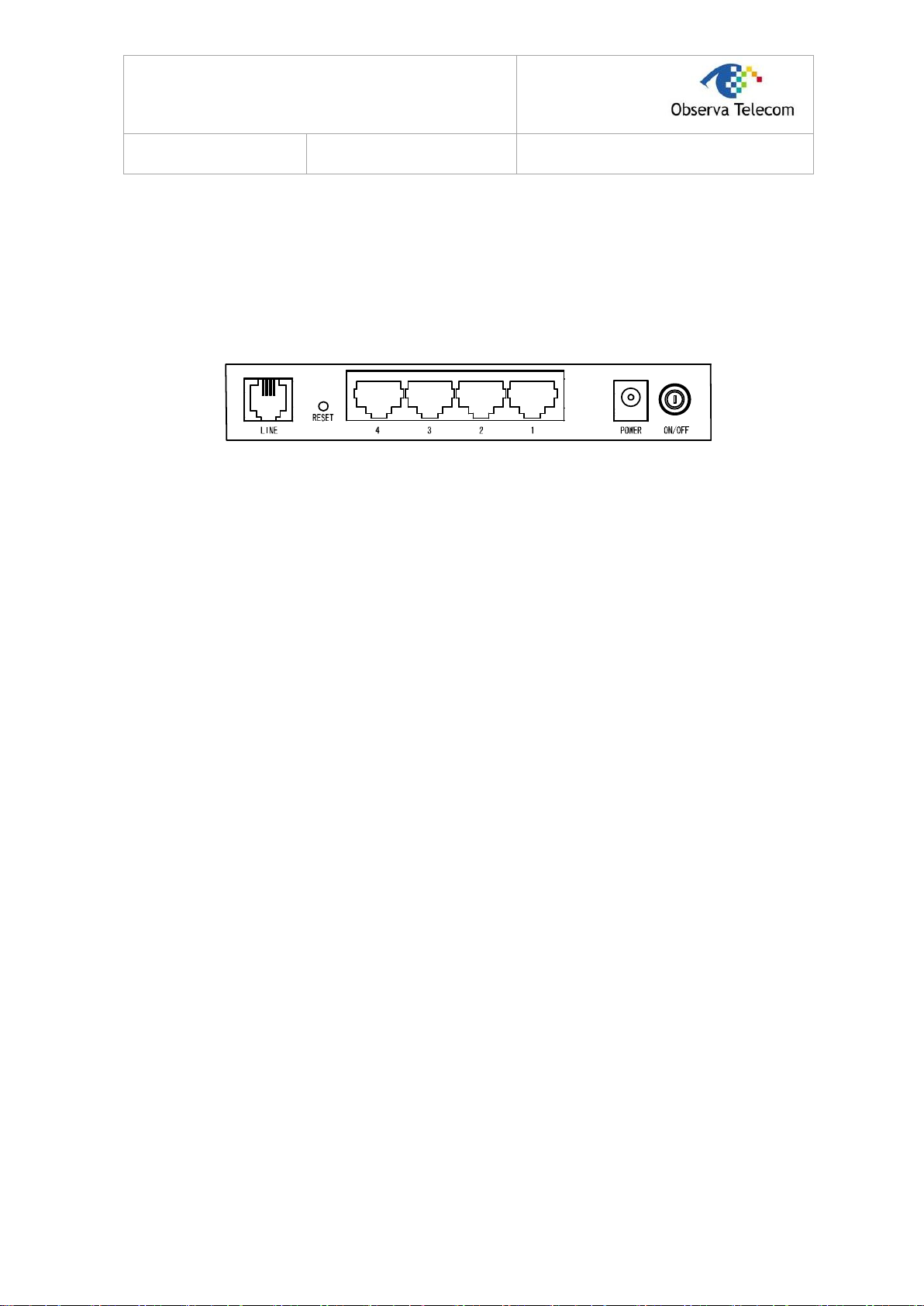
2.2. The Back Panel
Figure 2-2
LINE: Through the port, you can connect the router with the telephone. Or you can connect
them by an external separate splitter. For details, please refer to 2.4.
RESET: There are two ways to reset the Router's factory defaults.
Method one: With the Router powered on, use a pin to press and hold the Reset button for at
least 5 seconds. And the Router will reboot to its factory default settings.
Method two: Restore the default setting from “Maintenance-Rebbot” of the Router's Web-
based Utility.
1, 2, 3, 4 (LAN): Through the port, you can connect the Router to your PC or the other Ethernet
network devices.
POWER: The Power plug is where you will connect the power adapter.
ON/OFF: The switch for the power.
2.3. Installation Environment
The Product should not be located where it will be exposed to moisture or excessive heat.
Place the Router in a location where it can be connected to the various devices as well as to a
power source.
Make sure the cables and power cord are safely placed out of the way so they do not create a
tripping hazard.
The Router can be placed on a shelf or desktop.
Keep away from the strong electromagnetic radiation and the device of electromagnetic
sensitive.
RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 8 of 78
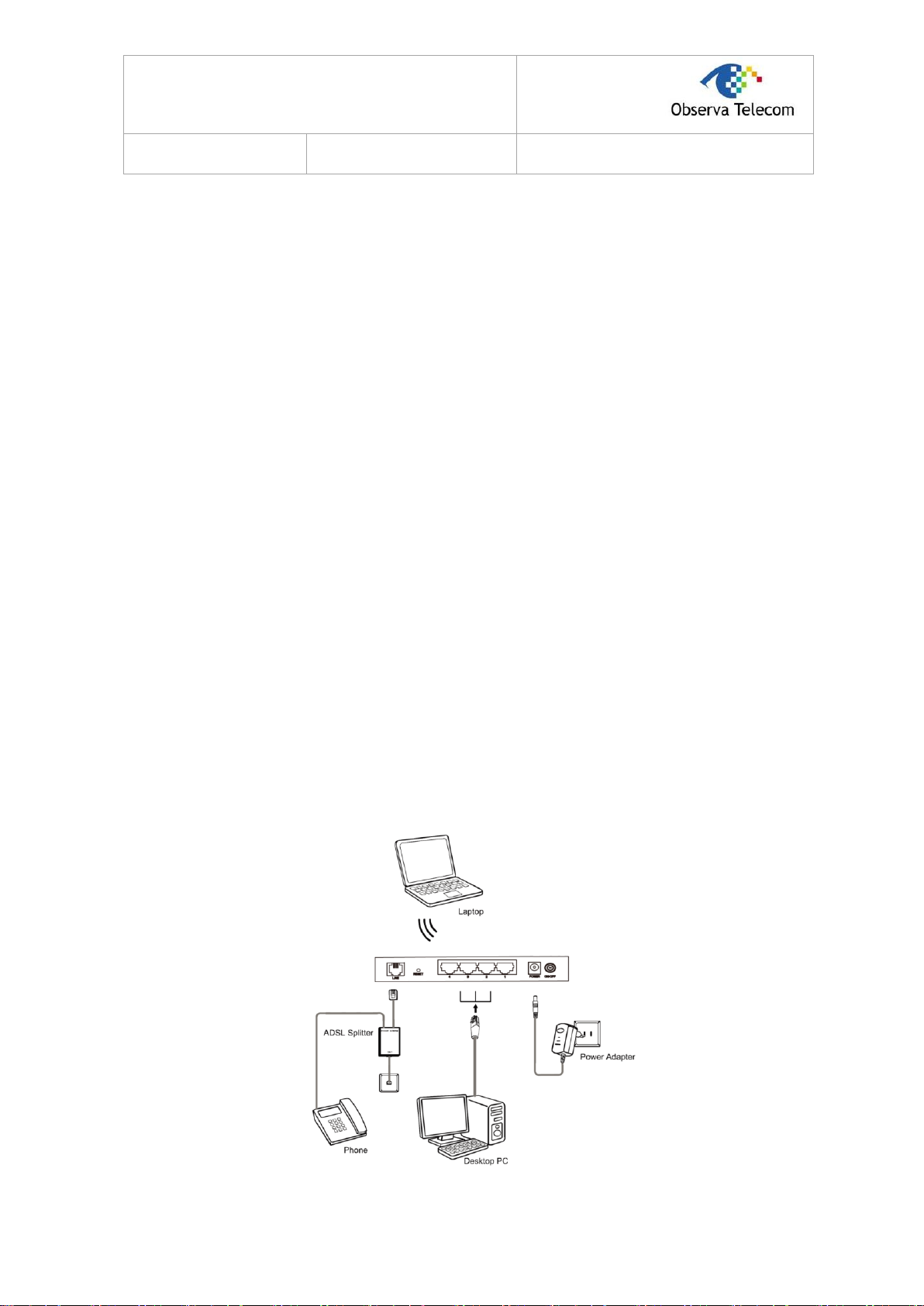
2.4. Connecting the Router
Before installing the device, please make sure your broadband service provided by your ISP is
available. If there is any problem, please contact your ISP. Before cable connection, cut off the
power supply and keep your hands dry. You can follow the steps below to install it.
Step 1: Connect the ADSL Line.
Method one: Plug one end of the twisted-pair ADSL cable into the ADSL LINE port on the
rear panel of RTA04N, and insert the other end into the wall socket.
Method two:You can use a separate splitter. External splitter can divide the data and
voice, and then you can access the Internet and make calls at the same time. The external
splitter has three ports:
• LINE: Connect to the wall jack
• PHONE: Connect to the phone sets
• MODEM: Connect to the ADSL LINE port of RTA04N
Plug one end of the twisted-pair ADSL cable into the ADSL LINE port on the rear panel of
RTA04N. Connect the other end to the MODEM port of the external splitter.
Step 2: Connect the Ethernet cable. Attach one end of a network cable to your computer’s
Ethernet port or a regular hub/switch port, and the other end to the LAN port on the
RTA04N.
Step 3: Power on the computers and LAN devices.
Step 4: Attach the power adapter. Connect the power adapter to the power connector on the rear
of the device and plug in the adapter to a electrical outlet or power extension. The
electrical outlet shall be installed near the device and shall be easily accessible.
Figure 2-3
RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 9 of 78
3. Quick Installation Guide
3.1. Configure PC
After you directly connect your PC to the RTA04N or connect your adapter to a Hub/Switch which
has connected to the Router, you need to configure your PC’s IP address. Follow the steps below to
configure it.
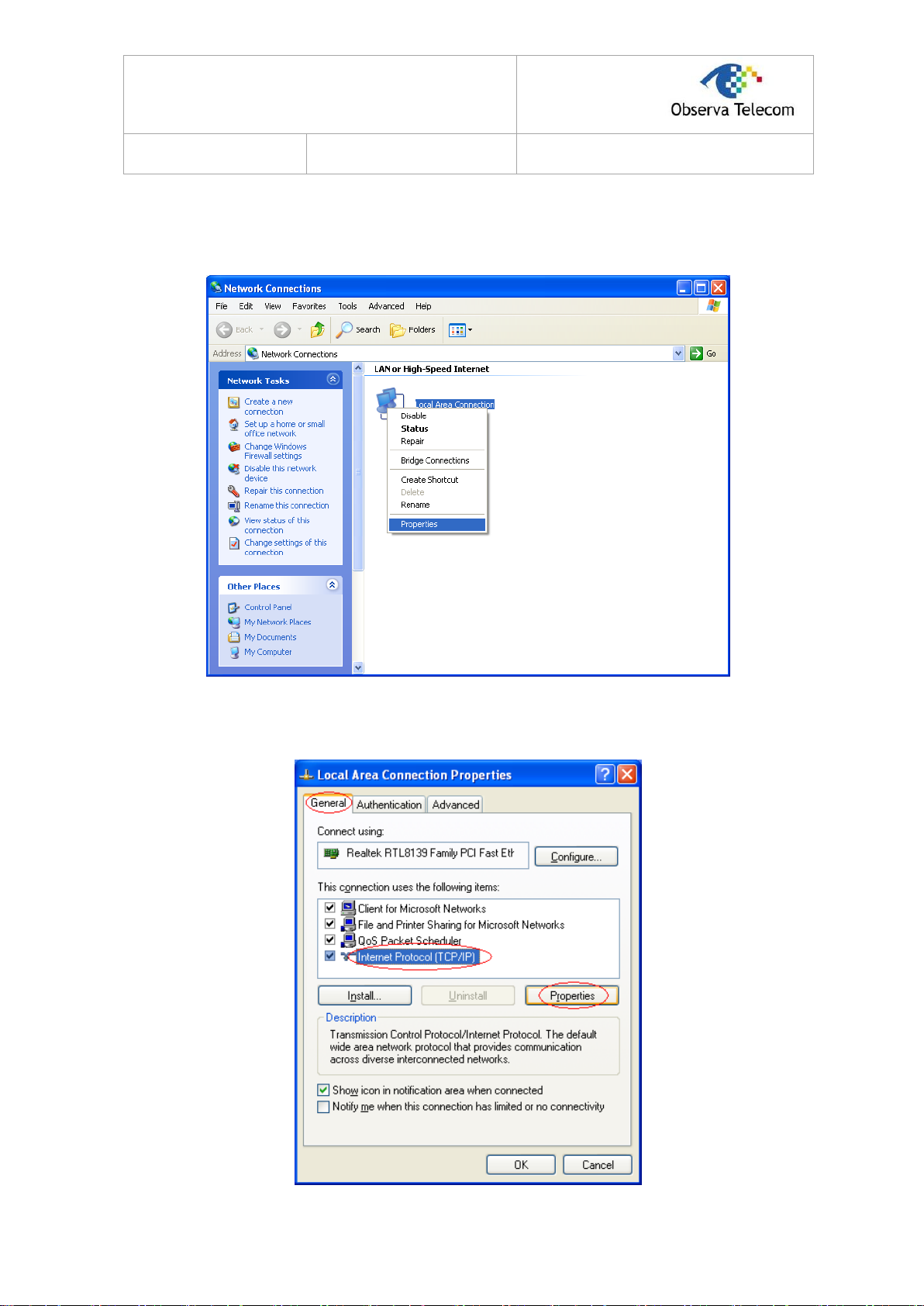
Step 1: Click the Start menu on your desktop, right click My Network Places, and then select
Properties (shown in Figure 3-1).
Figure 3-1
RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 10 of 78
Step 2: Right click Local Area Connection (LAN), and then select Properties.
Figure 3-2
Step 3: Select General tab, highlight Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click the Properties
button.
Figure 3-3
RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 11 of 78
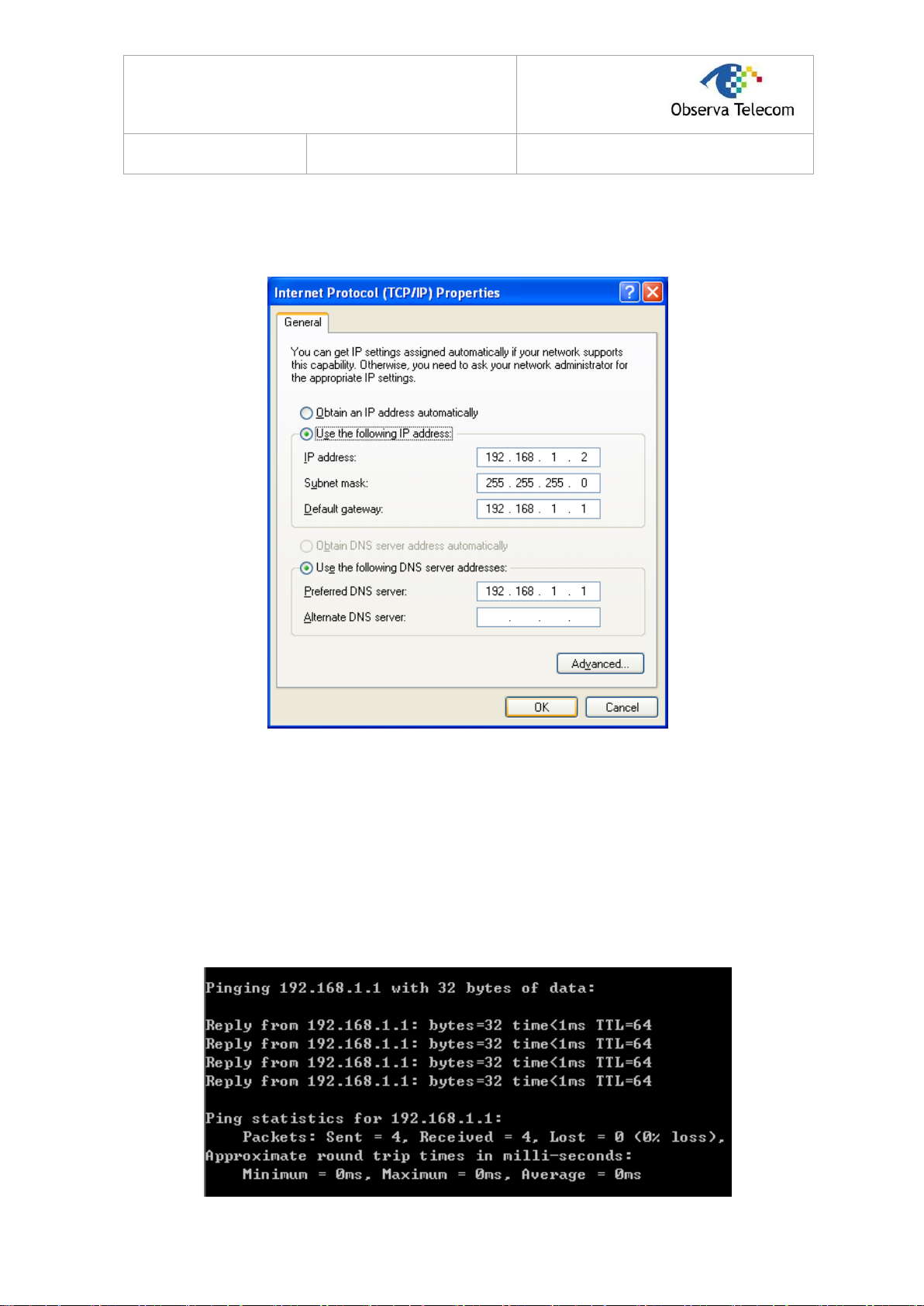
Step 4: Configure the IP address as Figure 3-4 shows. After that, click OK.
Figure 3-4
Note:
You can configure the PC to get an IP address automatically, select “Obtain an IP address
automatically” and “Obtain DNS server address automatically” in the screen above.
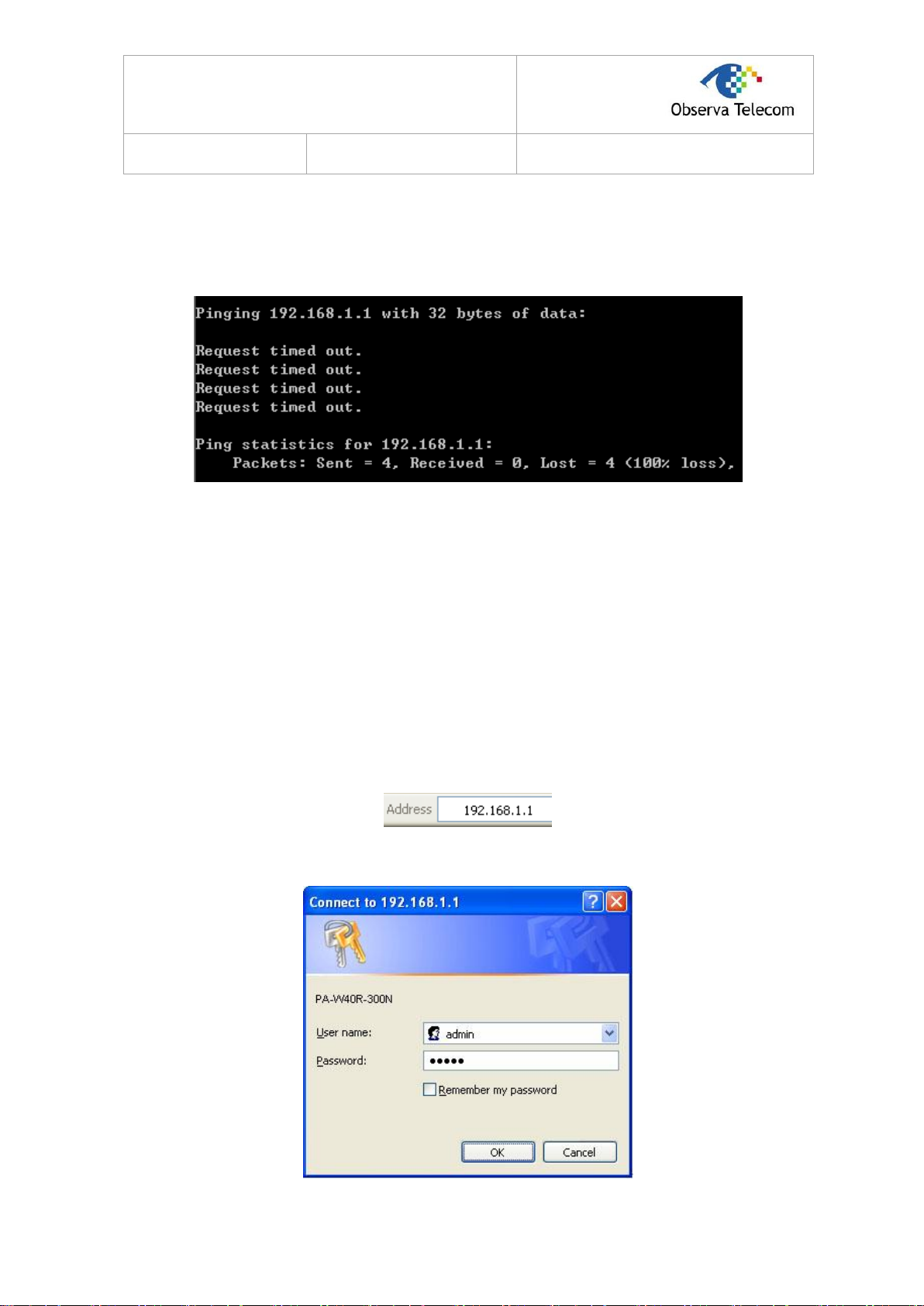
Now, you can run the Ping command in the command prompt to verify the network connection.
Please click the Start menu on your desktop, select run tab, type cmd or command in the field and
press Enter. Type ping 192.168.1.1 on the next screen, and then press Enter.
If the result displayed is similar to the screen below, the connection between your PC and the Router
has been established.
Figure 3-5
RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 12 of 78
If the result displayed is similar to the screen shown below, it means that your PC has not connected
to the Router.
Figure 3-6
You can check it following the steps below:
1) Is the connection between your PC and the Router correct?
The LEDs of LAN port which you link to the device and the LEDs on your PC's adapter should
be lit.
2) Is the TCP/IP configuration for your PC correct?
If the Router's IP address is 192.168.1.1, your PC's IP address must be within the range of
192.168.1.2 ~ 192.168.1.254.
3.2. Login
Once your host PC is properly configured, please proceed as follows to use the Web-based Utility:
Start your web browser and type the private IP address of the Router in the URL field: 192.168.1.1.
After that, you will see the screen shown below, enter the default User name (admin) and the
default Password (gvt12345), and then click OK to access to the Web-based Utility of the Router.
Figure 3-7

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 13 of 78
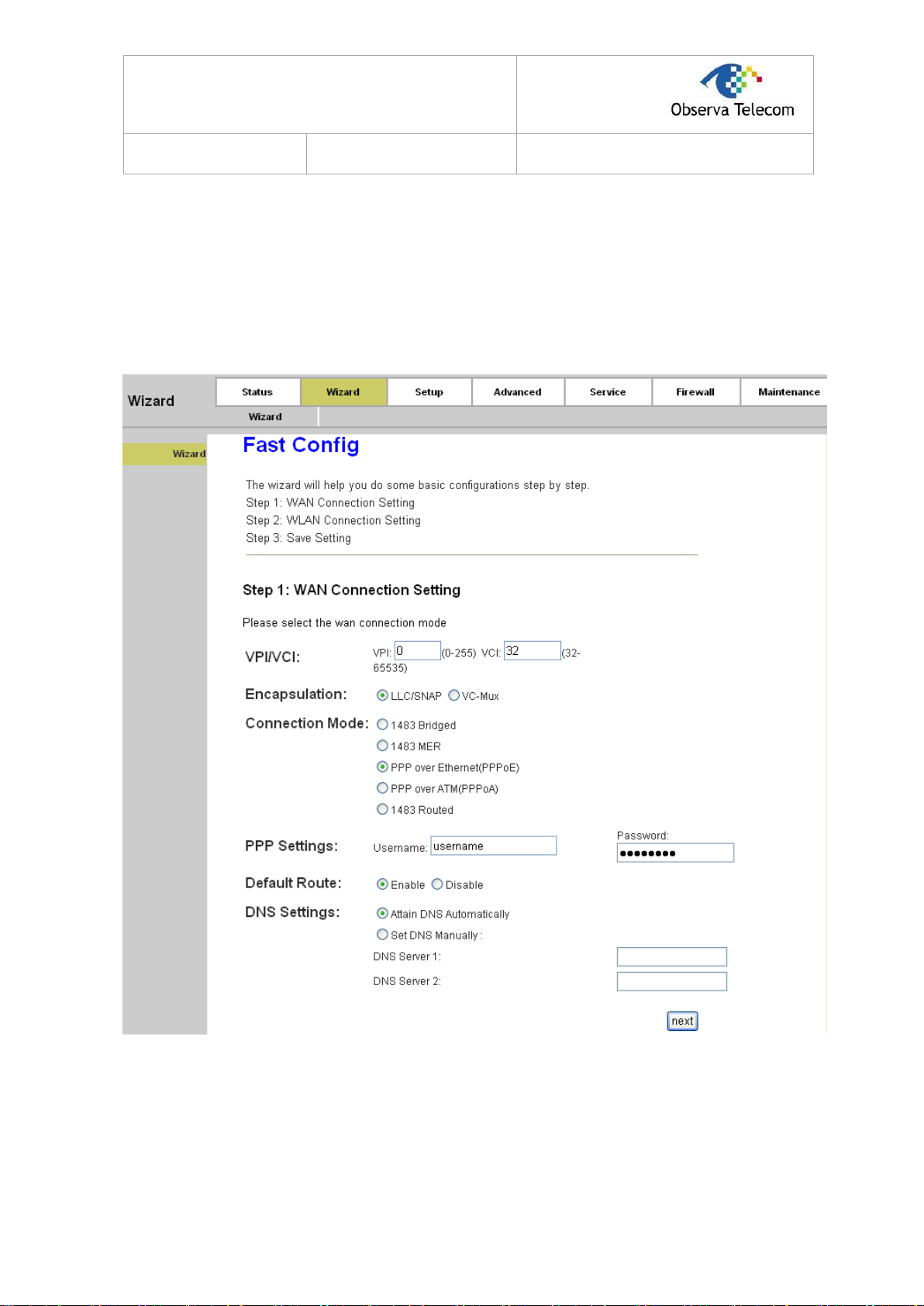
Step 1: Select the Wizard tab and you will see the next screen.
Figure 3-8
RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 14 of 78
Step 2: Configure the Router with the information provided by your ISP, including VPI/VCI,
Connection Mode and the following parameters. Take PPPoE for example, you need to
enter Username, Password and DNS parameters. All these information are provided by
your ISP. After that, click the next button to continue.
Figure 3-9
RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 15 of 78
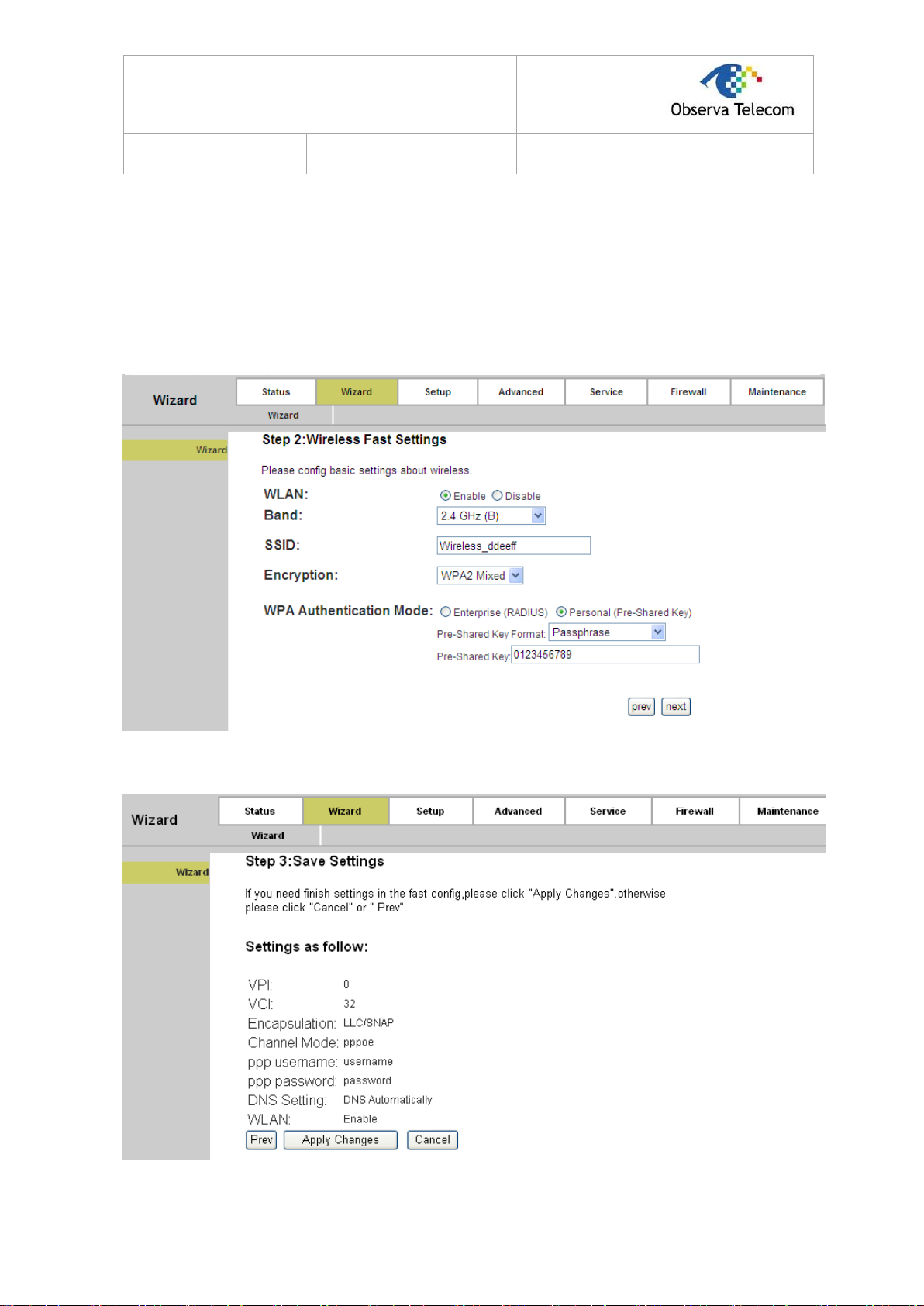
Step 3: Choose to enable your wireless network or not. If it’s enabled, you need to create a name
for your wireless network. It’s recommended that the name be unique and easy to
remember. You can also keep default without the device being affected. Select an
Encryption and Authentication Mode for the security of your wireless network, and then
enter the key in the corresponding field. After that, click the next button to continue.
Figure 3-10
Step 4: Click the Apply Changes button to finish the wizard.
Figure 3-11

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 16 of 78
4. Software Configuration
This User Guide recommends using the “Quick Installation Guide” for first-time installation. For
advanced users, if you want to know more about this device and make use of its functions
adequately, maybe you will get help from this chapter to configure the advanced settings through the
Web-based Utility.
After your successful login, you can configure and manage the device. There are main menus
on the top of the Web-based Utility; submenus will be available after you click one of the main
menus. On the center of the Web-based Utility, there are the detailed configurations or status
information. To apply any settings you have altered on the page, please click the SAVE button.
4.1. Status
Choose “Status”, you can see the next submenus: Device Info and Statistics. Click any of them,
and you will be able to configure the corresponding function.
Click any of them, and you will be able to view the corresponding information.
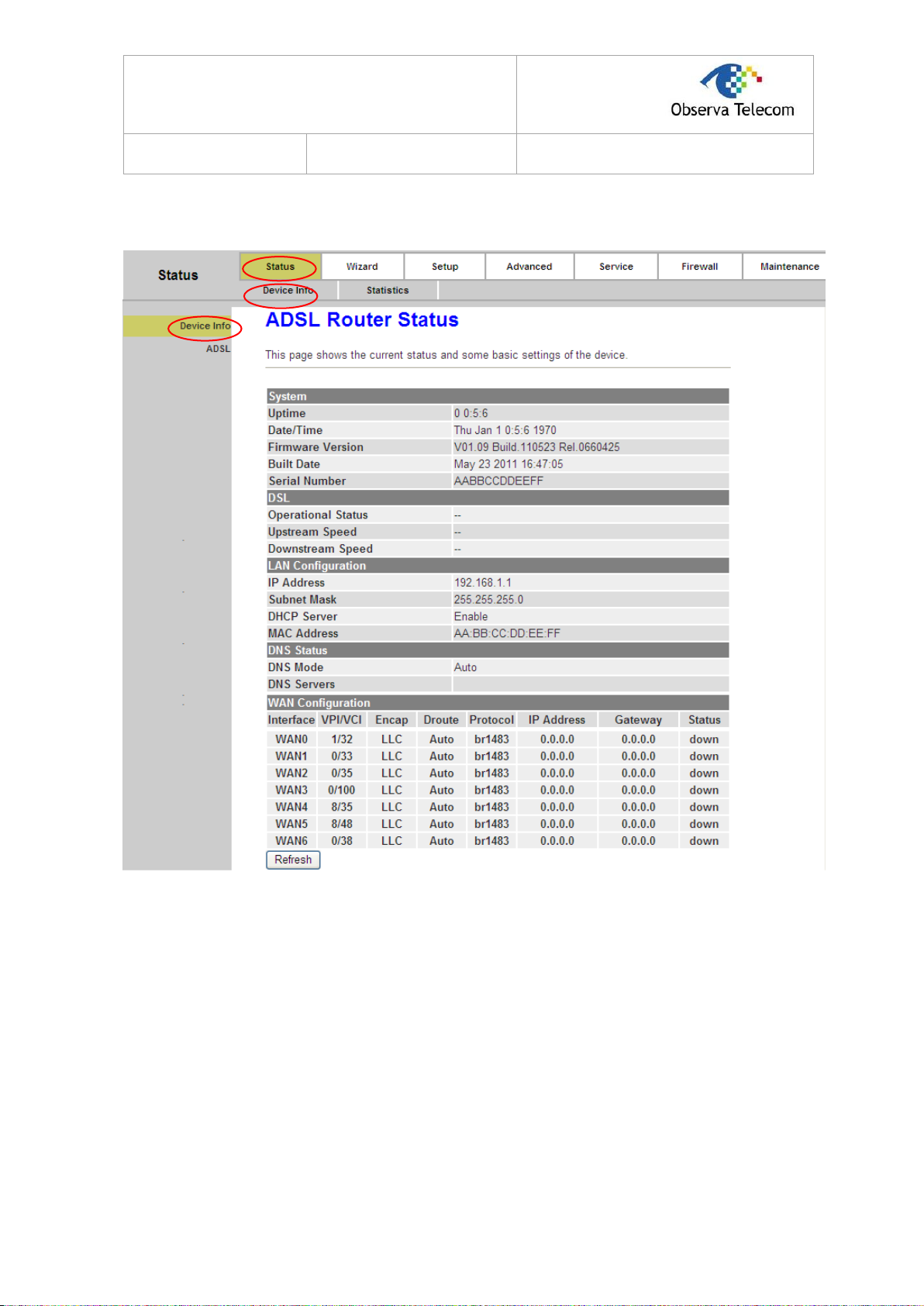
4.1.1. Device Info
Choose “Status→Device Info→Device Info” menu, and you will be able to view the
device information, including System, DSL, LAN, DNS, and WAN. The information will vary
depending on the settings of the Router.
RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 17 of 78
Figure 4-1
Click the Refresh button to refresh immediately.
RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 18 of 78
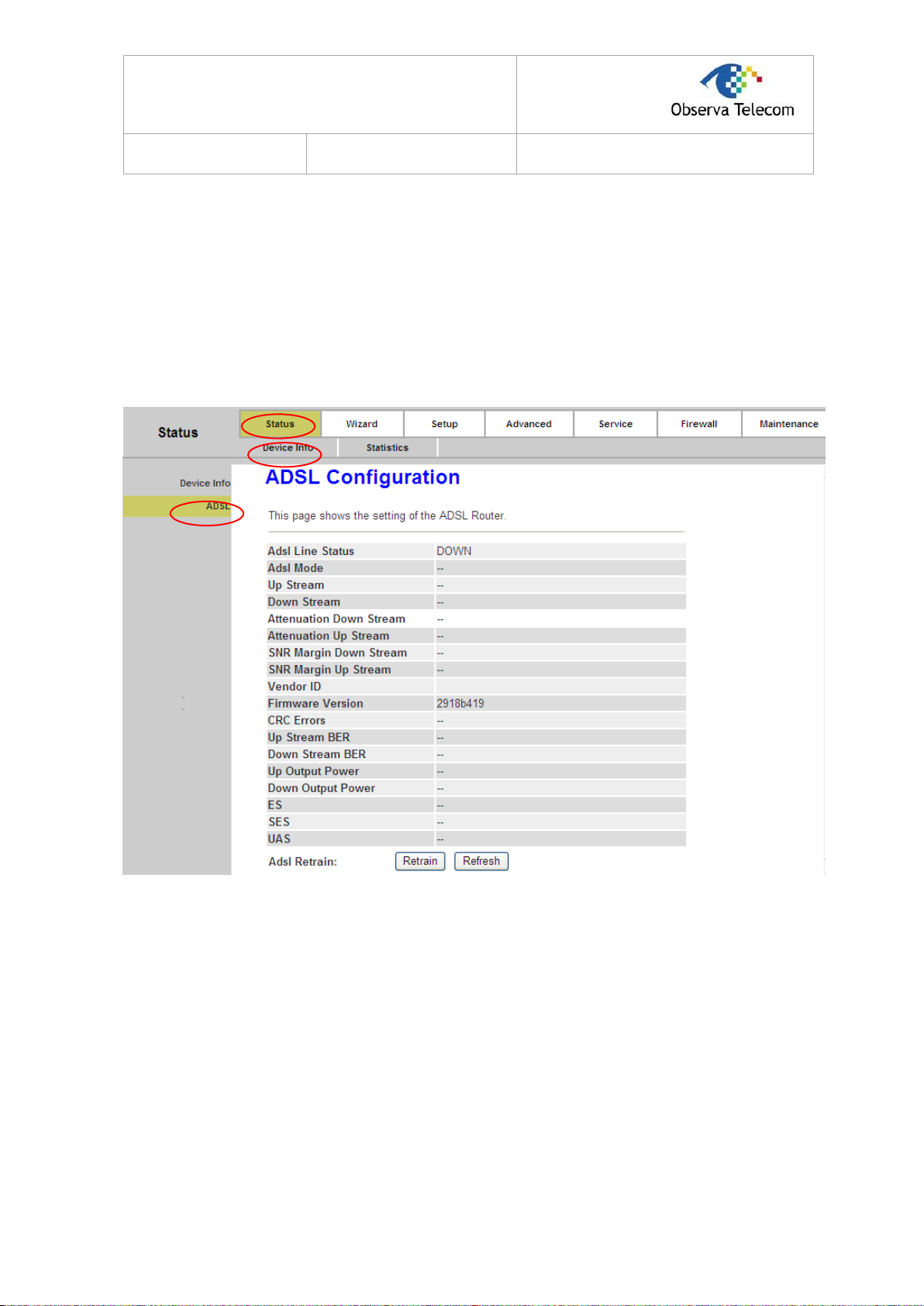
4.1.2. ADSL
Choose “Status→Device Info→ADSL” menu, and you will be able to view the ADSL configuration.
Figure 4-2
Click the Retrain button to retrain the information again.
Click the Refresh button to refresh immediately.
RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 19 of 78
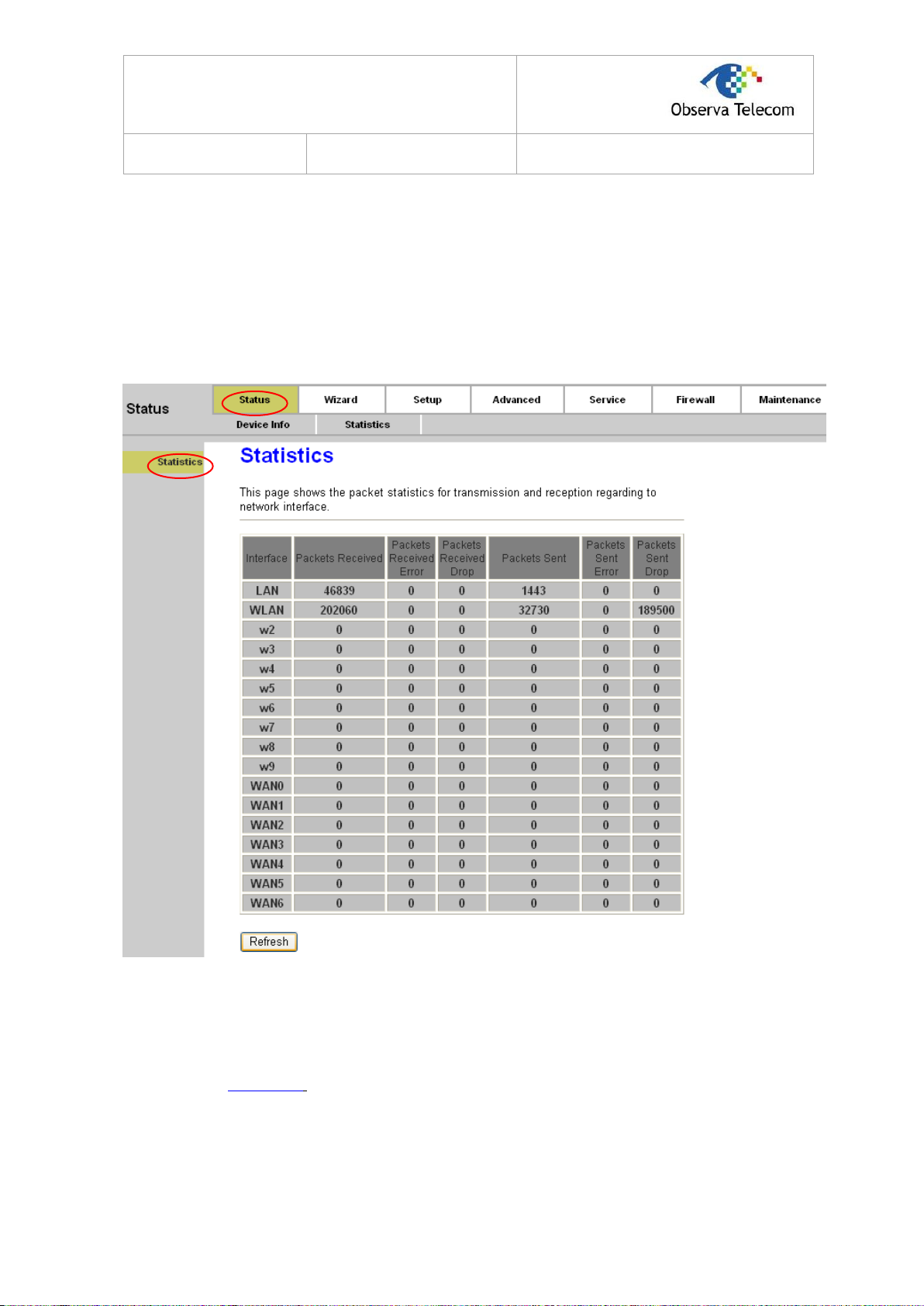
4.1.3. Statistics
Choose “Status→Statistics” menu, and you will be able to view the network traffic.
Figure 4-3
Click the Refresh button to refresh immediately.
4.1.4. Wizard
Please refer to “3.2 Login".
RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 20 of 78
4.2. Setup
Choose “Setup”, you can see the next submenus: WAN, LAN and WLAN.
Click any of them, and you will be able to configure the corresponding function.
4.2.1. WAN
Choose “Setup→WAN→WAN” menu, you can configure the parameters for WAN in the next screen
(shown in Figure 4-4).
Figure 4-4

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 21 of 78
Current ATM VC Table: ATM settings are used to connect to your ISP. Your ISP provides VPI
(Virtual Path Identifier), VCI (Virtual Channel Identifier) settings to you. In this Device, there is
one VC configured by default. You can totally setup 8 VCs on different encapsulations, if you
apply 8 different virtual circuits from your ISP. You need to activate the VC to take effect.
: Click this icon to enter the VC modification page. Besides, some advanced settings can
be configured there.
: Click this icon to delete the corresponding VC.
VPI: Identifies the virtual path between endpoints in an ATM network. The valid range is
from 0 to 255. Please input the value provided by your ISP.
VCI: Identifies the virtual channel endpoints in an ATM network. The valid range is from 32
to 65535 (1 to 31 is reserved for well-known protocols). Please input the value provided by
your ISP.
Encapsulation: Specifies the type of Multiplexing, either LLC or VC-Mux. Please note that
VC-Mux is not available for IPoA channel mode.
Channel Mode: There are six channel modes, 1483 Bridged, 1483 MER, PPPoE, PPPoA,
1483 Routed and IPoA. Please choose the mode that you want to use.
Enable NAPT: Choose to enable the NAPT function or not.
Enable IGMP: Choose to enable the IGMP function or not.
PPP Settings: These parameters are only available for PPPoE and PPPoA channel mode.
User Name: Enter your user name for your PPPoE/PPPoA connection.
Password: Enter your password for your PPPoE/PPPoA connection.
Type: Select Continuous, Connect on Demand or Manually for the network connection.
Continuous means the Internet connection will always keep on. Connect on demand is
dependent on the traffic. If it’s idle (there is no traffic) for a pre-specified period of time), the
connection will tear down automatically. And once there is traffic send or receive, the
connection will be automatically on. Manually means you have to manually connect or
disconnect your Internet by clicking the Connect or Disconnect button at the bottom of
this page.
Idle Time (min): Specifies the idle time for Connect on Demand type.
WAN IP Settings: These parameters are only available for 1483 MER and 1483 Routed
channel mode. Please note that for1483 Routed mode, DHCP is not available.
Type: Selects to use Fixed IP or DHCP. If Fixed IP is selected, then you have to fill the
following parameters, including Local IP Address, Remote IP Address, and Netmask.
Otherwise, these parameters will not be available.
Local IP Address: The IP address of the router on the PVC channel.
Remote IP Address: The gateway’s IP address of the router on the PVC channel.
Netmask: The subnet mask of the router on the PVC channel.
Connect/Disconnect: When there is a VC using PPPoE/PPPoA channel and Manually type,
you need to click this button to connect/disconnect the network.
RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 22 of 78
Add: Click this button to add a VC. First fill the parameters above and then click this button,
thus your new VC will be added to the Current ATM VC Table.
Modify: Click this button to modify your existed VC. First choose the desired VC and modify the
parameters, and then click this button, thus your existed VC will be modified.
Delete: Click this button to delete your existed VC. First choose the desired VC, and then click
this button, thus your existed VC will be deleted.
Undo: Click this button to abandon your operation.
Refresh: Click this button to refresh the ATM VC table.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
4.2.1.1. ATM
Choose “Setup→WAN→ATM” menu, you can configure the parameters for the ATM of your ADSL
Router in the next screen (shown in Figure 4-4). Here you may change the setting for QoS, PCR,
CDVT, SCR and MBS.
Figure 4-5
VPI/VCI: Choose a desired ATM VC, and the VPI/VCI value will be displayed. The values can
not be changed.
RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 23 of 78
QoS: Select the Quality of Service types for the Virtual Circuit, including UBR (Unspecified Bit
Rate), CBR (Constant Bit Rate), and nrt-VBR (Variable Bit Rate) and rt-VBR. Please note that
the selection of QoS type will lead to the availability of the following parameters, including PCR
(Peak Cell Rate), CDVT (Cell Delay Variation Tolerance), SCR (Sustained Cell Rate) and MBS
(Maximum Burst Size). Please configure them according to your needs.
Click Apply Changes to save your configuration.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
4.2.1.2. ADSL
Choose “Setup→WAN→ADSL” menu, you can configure some advanced parameters for your
ADSL Router in the next screen (shown in Figure 4-4).
Figure 4-6
After configuration, click Apply Changes button to save your changes.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 24 of 78
4.2.2. LAN
4.2.2.1. LAN
Choose “Setup→LAN→LAN” menu, and you will see the LAN Interface Setup screen (shown
in Figure 4-7). Here you can change IP address, subnet mask and other parameters for LAN
interface.
Figure 4-7
Interface Name: Displays the name of the LAN interface for the device.
IP Address: The Router’s local IP Address. You can access to the Web-based Utility via
the IP Address, the default value is 192.168.1.1. You can change the IP address if needed.
The LAN IP address is private to your internal network and cannot be seen on the Internet.
Subnet Mask: The subnet mask of the ADSL Router’s LAN interface. The default value is
255.255.255.0.
Secondary IP: If you enable the “Secondary IP”, you should configure another IP address and
subnet mask for the LAN interface.
IGMP Snooping: You can enable or disable the IGMP Snooping function according to your
needs.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 25 of 78
MAC Address Control: The router supports the MAC address control on Ethernet port. Select
the LAN interface on which you want to run MAC Address Control. Click the Apply Changes
button to make the configuration take effect. For example, if you enable the MAC address
control on “LAN1”, then the traffic from interface “LAN1” will be flowed only when its MAC
address matches the Current Allowed MAC Address Table, otherwise the traffic will be
dropped by the router.
New MAC Address: This field allows you to add a new MAC address to the Current Allowed
MAC Address Table. To add a new MAC address, enter the MAC address and then click Add
button.
Current Allowed MAC Address Table: Displays the current allowed MAC address. Click the
Delete button and then the corresponding MAC address will be deleted.
After configuration, click Apply Changes button to save your changes.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
4.2.2.2. DHCP
Choose “Setup→LAN→DHCP” menu, and then you will see the DHCP Mode screen (shown in
Figure 4-7). Here you can configure the DHCP mode of your ADSL Router as None, DHCP Relay or
DHCP Server. DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Control Protocol. The DHCP Server gives out IP
addresses when a device is booting up and request an IP address to be logged on to the network.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 26 of 78
Figure 4-8
LAN IP Address: Displays the LAN IP address of the Modem Router
Subnet Mask: Displays the subnet mask of the Modem Router.
DHCP Mode: Options available are None, DHCP Relay and DHCP Server.
1) None: In this mode, the Modem Router will do nothing when the host requests an IP address
by DHCP protocol. The screen will be shown as in Figure 4-9.
Figure 4-9

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 27 of 78
2) DHCP Relay: In this mode, the Router will work as a DHCP Relay. A DHCP relay is a device
that forwards DHCP data between computers that request IP addresses and the DHCP server
that assigns the addresses. Each of the device's interfaces can be configured as a DHCP relay.
In this mode, the DHCP requests from local PCs will be forwarded to the DHCP server running
on WAN side.
Figure 4-10
Relay Server: Enter the IP Address of the DHCP server running on WAN side.
3) DHCP Server: Select this mode, then the screen will be shown as in Figure 4-11. The Router
will work as a DHCP Server; it becomes the default gateway for DHCP client connected to it.
That device on your local network must be set as a DHCP client to obtain the IP address
automatically. By default, the DHCP Server is enabled.
Figure 4-11

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 28 of 78
IP Pool Range: Specify the start and end IP address for the DHCP server's IP
assignment. The default start and end IP Address are 192.168.1.100 and 192.168.1.200
separately. Please note that both addresses should be smaller than 192.168.1.254.
Default Gateway: The default gateway address.
Max Lease Time: The time that the DHCP client is allowed to maintain the assigned
dynamic IP. After the dynamic IP address has expired, the user will be automatically
assigned a new one. The default is 1440 minutes.
Domain Name: Specify a user-friendly name to refer to the group of hosts (subnet) that
will be assigned addresses from this pool.
DNS Servers: The IP address of DNS server used in option filed of DHCP message.
Apply Changes: Click this button to save your configuration.
Undo: Click this button to cancel your configuration.
Set VendorClass IP Range: Click this button and then you will enter the screen as shown in
Figure 4-12. This page allows you to configure the IP address range depending on device’s
option60.
Figure 4-12
Device name: Give a name for the class of your device, such as PC, Phone, TV, etc.
Start address: Specify the start address.
End address: Specify the end address.
Default gateway: Enter the IP address of the Modem Router.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 29 of 78
Option60: A string of n octets, interpreted by DHCP servers, used by DHCP client to
optionally identify the vendor type and configuration of a DHCP client. In Figure 4-12, we
suppose 11 as PC’s option60.
After configuration, click Apply Changes button to save your changes.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
4.2.2.3. DHCP Static
Choose “Setup→LAN→DHCP Static” menu, you can view and add a static address for client via
the next screen (shown in Figure 4-13). When you specify a static IP address for a PC on the LAN,
that PC will always receive the same IP address each time when it accesses the DHCP server.
Static IP address is recommended to be assigned to the client that requires permanent IP settings.
Figure 4-13
IP Address: Enter the IP address desired to be assigned to the client.
Mac Address: Enter the MAC address of the client.
Add: Click this button to add a new static IP entry.
Delete Selected: Click this button to delete the selected entry in the DHCP Static IP Table.
Undo: Click this button to delete your entering.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 30 of 78
4.2.3. WLAN
There are six submenus under the WLAN menu, Basic, Security, Access Control, Advanced, WPS,
and WDS. Click any of them, and you will be able to configure the corresponding function.
4.2.3.1. Basic
Choose “Setup→WLAN→Basic” menu, and you will see the Wireless Basic Settings screen (shown
in Figure 4-14). Please configure the parameters for wireless according to the descriptions below.
Disable Wireless LAN Interface: Choose to disable the Wireless function of the ADSL Router.
Band: Options available are 2.4 GHz (B), 2.4 GHz (G), 2.4 GHz (B+G), 2.4 GHz (N), 2.4 GHz
(G+N), and 2.4 GHz (B+G+N).
Mode: Options are AP and AP+WDS. If AP+WDS is selected, then the Router can bridge two
or more WLANs.
SSID: Wireless network name shared among all points in a wireless network. The SSID must
be identical for all devices in the wireless network. It is case-sensitive and must not exceed 32
characters (use any of the characters on the keyboard). Make sure this setting is the same for
all stations in your wireless network. Type the desired SSID in the space provided.
Channel Width: Select the width you want to use from the drop-down List. There are three
options, 20MHz, 40MHZ and 20/40MHz. If bigger bandwidth is selected, device could transmit
and receive data with higher speed.
Control Sideband: Options are Upper and Lower.
Figure 4-14

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 31 of 78
Channel Number: This field determines which operating frequency will be used. Select the
channel to use from the drop-down list. It is not necessary to change the default channel unless
you notice interference problems with another nearby access point.
Radio Power (Percent): Here you can specify the Radio Power of Router. You can select
High, Middle or Low which you would like. High is the default setting and is recommended.
Associated Clients: Click the Show Active Clients button to view the information of wireless
clients that connects to the ADSL Router.
Click Apply Changes button to save your changes.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
4.2.3.2. Security
Choose “Setup→WLAN→Security” menu, and you will see the Wireless Security Setup screen
(shown in Figure 4-15). Here you can configure the security settings of your wireless network. There
are six encryptions supported by the Router: WEP, WPA (TKIP), WPA (AES), WPA2 (AES), WPA2
(TKIP) and WPA2 Mixed.
Encryption: There are six encryptions supported by the Router: WEP, WPA (TKIP), WPA
(AES), WPA2 (AES), WPA2 (TKIP) and WPA2 Mixed.
Use 802.1x Authentication: If you want to use the authentication, check this box and then set
the port, IP address and password for the Authentication RADIUS Server.
Figure 4-15

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 32 of 78
1. WEP
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is a data privacy mechanism based on a 64-bit and 128-bit shared
key algorithm, as described in the IEEE 802.11g standard.
To configure WEP settings, select follow the steps below.
Step 1. Select “WEP” from the Encryption drop-down list. The following available options will change
to offer the appropriate settings.
Figure 4-16
Step 2. Click Set WEP Key button to enter the Wireless WEP Key Setup screen as shown in Figure
4-17.
Figure 4-17

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 33 of 78
Step 3. Fill in the above parameters according to the guides below.
Key Length: Select the desired length. Options available are 64-bit and 128-bit.
Key Format: Select the desired format. Options available are ASCII (5 characters)
and Hex (10 characters).
Default Tx Key: Select the desired key for the configuration.
Encryption Key 1/2/3/4: Create a key for your wireless network.
Step 4. Click Apply Changes to save your configuration. Click Close to close the screen and return
to Wireless Security Setup screen.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
2. WPA/WPA2
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) and WPA2 (WPA version 2) are based on Radius Server. There are
two WPA encryption rules, AES and TKIP. There are also two WPA Authentication Mode, Enterprise
(RADUIS) or Personal (Pre-Shared Key).
To configure WEP settings, select follow the steps below.
Step 1. Select “WPA (TKIP), WPA (AES), WPA2 (TKIP), WPA2 (AES) or WPA2 (Mixed)” encryption
from the Encryption drop-down list. Then the following available options will change to offer
the appropriate settings.
TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) - a wireless encryption protocol that provides
dynamic encryption keys for each packet transmitted.
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) - A security method that uses symmetric 128-
bit block data encryption.
Figure 4-18

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 34 of 78
Step 2. Select the desired WPA Authentication Mode, Enterprise (RADIUS) or Personal (Pre-
Shared key). After the selection, the following available options will change to offer the
appropriate configuration.
Enterprise (RADIUS): If this mode is selected, parameters including Port, IP address
and Password are required in Authentication RADIUS Server filed.
Personal (Pre-Shared Key): If this mode is selected, parameters in Pre-Shared Key
Format and Pre-Shared Key filed are required. For Pre-Shared Key Format,
Passphrase and Hex (64 characters) are provided. You then need to create a key for
your Router in Pre-Shared Key filed. The least length of the key will change
according to the format selected in Pre-Shared Key Format field.
Step 3. Click Apply Changes to save your configuration.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
4.2.3.3. Access control
Choose “Setup→WLAN→Access Control” menu, and you will see the Wireless Access Control
screen (shown in Figure 4-19). Wireless access control function is used to allow or deny the wireless
client’s access to the wireless network by MAC address.
Wireless Access Control Mode: Options are “Disable”, “Allow Listed” and “Deny Listed”. If the
mode is “Disable”, it means the wireless access control function is closed; if the mode is “Allow
Listed”, only the client on the list will be able to connect to you access point; if the mode is
Figure 4-19

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 35 of 78
“Deny Listed”, these wireless clients on the list will not be able to connect to you access point.
Click Apply Changes to save your configuration.
MAC Address: Enter the MAC address of the client you want to allow or deny.
Current Access Control List: Shows the MAC address table you configured, you can delete it
as you need.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
4.2.3.4. Advanced
Choose “Setup→WLAN→Advanced” menu, and you will see the Wireless Advanced Settings
screen (shown in Figure 4-20). You can configure the advanced parameters for your WLAN.
Fragment Threshold: This value specifies the maximum size for a packet before data is
fragmented into multiple packets. If you experience a high packet error rate, you may slightly
increase the Fragmentation Threshold. Setting the Fragmentation Threshold too low may result
in poor network performance. Only minor reduction of the default value is recommended. In
most cases, it should remain at its default value of 2346.
RTS Threshold: Should you encounter inconsistent data flow, only minor reduction of the
default value 2347 is recommended. If a network packet is smaller than the preset RTS
threshold size, the RTS/CTS mechanism will not be enabled. The Router sends Request to
Send (RTS) frames to a particular receiving station and negotiates the sending of a data frame.
After receiving an RTS, the wireless station responds with a Clear to Send (CTS) frame to
acknowledge the right to begin transmission. In most cases, keep its default value of 2347.
Figure 4-20

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 36 of 78
Beacon Interval: Enter a value between 20-1000 milliseconds. The Beacon Interval value
indicates the frequency interval of the beacon. A beacon is a packet broadcast by the Router to
synchronize the wireless network. The default value is 100.
DTIM Interval: This value, between 1 and 255, indicates the interval of the Delivery Traffic
Indication Message (DTIM). A DTIM field is a countdown field informing clients of the next
window for listening to broadcast and multicast messages. When the Router has buffered
broadcast or multicast messages for associated clients, it sends the next DTIM with a DTIM
Interval value. Its clients hear the beacons and awaken to receive the broadcast and multicast
messages. The default value is 1.
Broadcast SSID: When wireless clients survey the local area for wireless networks to
associate with, they will detect the SSID broadcast by the Router. To broadcast the Router’s
SSID, select “Enable”. If you don’t want to broadcast the Router’s SSID, select “Disable”.
After configuration, click Apply Changes button to save your changes.
Note:
1. These settings are only for more technically advanced users who have a sufficient knowledge
about wireless LAN. They should not be changed unless you know exactly what will happen for
the changes on your Access Point.
2. After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
4.2.3.5. WPS
Choose “Setup→WLAN→WPS” menu, and you will see the Quick Secure Setup screen (shown in
Figure 4-21). Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) is a simple way to establish the connection between the
wireless client and access point. You don’t need to select the encryption method and encryption key.
You just need to input the correct PIN or start PBC and press the WPS button on the router to set
the WPS.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 37 of 78
Figure 4-21
Disable WPS: Select to disable WPS function.
WPS state: Display the current WPS state.
Self PIN Number: Displays the PIN number of the Router. You can click the Regenerate PIN
button to generate a new PIN number.
Push Button Configuration: Click Start PBC button when using PBC method for WPS
configuration.
1) PBC
If the wireless adapter supports WPS and the Push Button Configuration (PBC) method, you can
add it to the network by PBC with the following two methods.
Method One:
Step 1: Press the WPS button on the front panel of the Router or click Start PBC button in Figure
4-21.
Step 2: Press and hold the WPS button of the adapter directly for 2 or 3 seconds.
Step 3: Wait for a while until the next screen appears. Click Finish to complete the WPS
configuration.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 38 of 78
The WPS Configuration Screen of Wireless Adapter
Method Two:
Step 1: Press the WPS button on the front panel of the Router or click Start PBC button in Figure
4-21.
Step 2: For the configuration of the wireless adapter, please choose “Push the button on my
access point” in the configuration utility of the WPS as below, and click Next.
Step 3: Wait for a while until the next screen appears. Click Finish to complete the WPS
configuration.
The WPS Configuration Screen of Wireless Adapter

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 39 of 78
The WPS Configuration Screen of Wireless Adapter
2) PIN code
If the wireless adapter supports WPS and the PIN method, you can add it to the network by PIN with
the following two methods.
Method One: Enter the PIN into my Router
Step 1: For the configuration of the wireless adapter, please choose “Enter a PIN into my access
point or a registrar” in the configuration utility of the WPS, and get the PIN code on the
screen as below, then click Next.
Step 2: For the Router, enter the PIN code of the wireless adapter in the Client PIN Number field
as shown below. Then click Start PIN.
The WPS Configuration Screen of Wireless Adapter

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 40 of 78
Figure 4-22
Method Two: Enter the PIN from my Router
Step 1: Get the Current PIN code of the Router from Self-PIN Number in Figure 4-22 (each Router
has its unique PIN code. Here takes the PIN code 12345670 of this Router for example).
Step 2: For the configuration of the wireless adapter, please choose “Enter a PIN from my access
point” in the configuration utility of the WPS as below, and enter the PIN code of the
Router into the Access Point PIN field. Then click Next.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 41 of 78
The WPS Configuration Screen of Wireless Adapter
Note:
1. The default PIN code of the Router can be found in its label or the WPS configuration screen as
shown in Figure 4-22.
2. After saving your configuration, you need to click the Save button on the left panel to make your
configuration take effect.
4.2.3.6. WDS
Choose “Setup→WLAN→WDS” menu, and you will see the WDS settings screen (shown in Figure
4-23). WDS, short for Wireless Distribution System, uses wireless media to communicate with other
Access Points, like the Ethernet does. With this function enabled, the Router can communicate with
two or more WLANs.
To do this, you must set these Access Points in the same channel and add MAC addresses of other
Access Points to communicate with to the Current WDS AP List.
Note:
If you want to enable the WDS, please go to the page WLAN->Basic, and select the "Mode" to be
AP+WDS.
Enable WDS: Select to enable WDS.
Add WDS AP: To add MAC addresses of other Access Point, follow the steps below.
Step 1. Enter MAC Address of the Access Point to communicate with in “MAC Address” field.
Step 2. Give a description for that Access Point in “Comment” field.
Step 3. Click Apply Changes button to save the MAC address to “Current WDS AP List”.
Figure 4-23

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 42 of 78
Note:
If changes are made, after clicking Apply Changes button, a Save button will appear on the left
panel. You need to click the Save button to make your changes take effect.
4.3. Advanced
Choose “Advanced”, you can see the next submenus:
Click any of them, and you will be able to configure the corresponding function.
4.3.1. Route
4.3.1.1. Static Route
Choose “Advanced→Route→Static Route” menu, you can configure the routing information in the
next screen (shown in Figure 4-24). Here you can add or delete IP routes.
Figure 4-24
Enable: Check the box to enable this function.
Destination: Enter the IP network address of the final destination. It can be a subnet IP or a
host address. All zeros indicate that the route entry should be used for all destinations for which
no other route is defined.
Subnet Mask: Enter the subnet mask of the destination.
Next Hop: The IP address of the next hop through which traffic will forward the destination.
Interface: Select the interface to which a static route is to be applied.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 43 of 78
Click the Add Route button to add the new route in the Static Route Table.
The Static Route Table shows the current static route entries.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
4.3.1.2. RIP
Choose “Advanced→Route→RIP” menu, you can configure the RIP settings in the next screen
(shown in Figure 4-25). RIP is an internet protocol you can set up to share routing table information
with other routing devices.
Figure 4-25
RIP: Select to enable the RIP function or not. Click the Apply button to save your configuration.
Interface: Select the interface on which you want to enable RIP.
Recv Version: Indicate the RIP version in which information must be passed to the device. It
can be accepted into its routing table.
Send Version: Indicate the RIP version this interface will use when it sends its route
information to the other device.
Click the Add button to add a RIP configuration to the Rip Config List. Click the Delete button to
delete it.
The RIP Config List shows the current RIP setting of the device.
Note:
After adding a new entry, a Save button will appear on the left panel. You need to click the Save
button to make your changes take effect.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 44 of 78
4.3.2. NAT
4.3.2.1. DMZ
Choose “Advanced→NAT→DMZ”, you can configure the DMZ host in the screen as shown in
Figure 4-26.
A DMZ (demilitarized zone) is a host between a private local network and the outside public network.
It allows a single host on your LAN to expose all of its ports to the Internet. Users of the public
network outside the company can access to the DMZ host.
Figure 4-26
Enable DMZ: Check the box to enable DMZ function.
DMZ Host IP Address: Enter the specified IP Address for DMZ host on the LAN side.
Click Apply Changes to save your configuration.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
4.3.2.2. Virtual Server
Choose “Advanced→NAT→Virtual Server”, and then you can configure the Virtual Server in the
screen as shown in Figure 4-27.
The Virtual Server is the server or server(s) behind NAT (on the LAN). It allows a single host on your
LAN to provide the specified service to the Internet, for example Web server or FTP server, which
you can make visible to the outside world even though NAT makes your whole inside network
appear as a single machine to the outside world.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 45 of 78
Figure 4-27
Usual Service Name: The Router provides some common services. Select the one you need.
User-defined Service Name: If the service can not be found in the Usual Service Name drop-
down list, just enter the name manually in this field instead.
Protocol: The protocol used for this virtual server.
WAN Setting: The WAN setting of this virtual server used; it can be interface and IP address.
Select a desired one, and then options available will change to offer the configuration.
WAN Interface: The interface on which the virtual server used on WAN side
WAN IP Address: The IP address which the virtual server used on WAN side. You can access
this IP and WAN port from WAN side to obtain the service.
WAN Port: The open port on WAN side. It can be either a single port or a port range.
LAN Open Port: The open port on LAN host. It can be either a single port or a port range.
LAN IP Address: The IP address of the host which provides the service on LAN side.
Click the Apply Changes button to save your configuration.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 46 of 78
For example: If you want to set up a FTP Server on LAN host 192.168.1.33, you can configure a
virtual server rule as follows:
Step 1: Select “FTP” from Usual Service Name drop-down list. Protocol, WAN Port, and LAN
Open Port will be automatically filled, and you don’t need to change them.
Step 2: Select the WAN Setting for the service.
Step 3: Enter 192.168.1.33 in LAN IP Address field.
Step 4: Click Apply Changes button to save your configuration. And the Virtual Server will be
added to the Current Virtual Server Forwarding Table.
Step 5: Click Save button on the left panel to make sure your configuration can still take effect
after the Router reboots.
4.3.2.3. ALG
Choose “Advanced→NAT→ALG”, and then you can configure the ALG settings in the screen as
shown in Figure 4-28. The router supports several NAT ALG and pass-Through function. Here you
can enable or disable the ALG or pass-through function for each application.
Figure 4-28
Click the Apply Changes button to save your configuration.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
4.3.2.4. Port Trigger
Choose “Advanced→NAT→Port Trigger”, and then you can configure the port trigger rules in the
screen as shown in Figure 4-29.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 47 of 78
Port trigger is used to restrict certain types of data packets from your local network to Internet. Some
applications require multiple connections, like Internet games, video conferencing, Internet calling and
so on. These applications cannot work with a pure NAT Router. Port Trigger is used for some of these
applications that can work with an NAT Router, which can be helpful in securing and restricting your
local network.
Figure 4-29
Nat Port rigger: Enable or disable the port trigger function on the device. After selecting, click
the Apply Changes button to save your configuration.
Application Type: You can select the service from the “Usual Application Name” and then
the following parameters, Match Port, Trigger Protocol, Relate Port and Open Protocol, will be
automatically filled. You can also define the application by yourself in the “User-defined
Application Name” field. But, you need to fill the following related parameters manually.
Start Match Port / End Match port: The start and end port to match.
Trigger Protocol: The protocol to trigger the rule, it can be TCP, UDP or TCP/UDP.
Start Relate Port / End Relate Port: The start and end related port.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 48 of 78
Open Protocol: It can be TCP, UDP or TCP/UDP.
NAT Type: It can be outgoing or incoming.
Click the Apply Changes button to save your configuration. And then the trigger rule will be added
to the Current Portrigger Table.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
4.3.2.5. IP Address Mapping
Choose “Advanced→NAT→IP Address Mapping”, and then you can configure the mapping rules
in the screen as shown in Figure 4-30.
NAT IP mapping allows you to configure one IP pool for specified source IP address from LAN, so a
packet whose source IP is in range of the specified address will select one IP address from pool for
NAT.
Figure 4-30
Type: There are four types of mapping rule, “One-to-One”, “Many-to-One”, “Many-to-Many” and
“One-to-Many”.
One-to-One: One local IP will be mapped to one global IP.
Many-to-One: The IP between “Local Start IP” and “Local End IP” will be mapped to a
global IP.
Many-to-Many: The IP between “Local Start IP” and “Local End IP” will be mapped to the
IP between “Global Start IP” and “Global End IP”.
One-to-Many: One local IP will be mapped to any of the IP between “Global Start IP” and

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 49 of 78
“Global End IP”.
Local Start IP / Local End IP: Enter the local IP Address you plan to map to. Local Start IP is
the starting local IP address and Local End IP is the ending local IP address. If the rule is for all
local IPs, then the Start IP is 0.0.0.0 and the End IP is 255.255.255.255.
Global Start IP / Global End IP: Enter the global IP Address you want to do NAT. Global Start
IP is the starting public IP address and Global End IP is the ending public IP address. If you
have a dynamic IP, enter 0.0.0.0 as the Global Start IP.
Current NAT IP MAPPING Table: This displays the information about the Mapping address.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
4.3.3. QoS
Choose “Advanced→QoS”, you can configure the QoS in the next screen. QoS helps to prioritize
data as it enters your router. By attaching special identification marks or headers to incoming
packets, QoS determines which queue the packets enter, based priority. This is useful when there
are certain types of data you want to give higher priority, such as voice data packets give higher
priority than Web data packets. This option will provide better service of selected network traffic over
various technologies.
Figure 4-31
IP QoS: Choose “enable”, and then you will see the following parameters.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 50 of 78
QoS Policy: Policy of QoS. The traffic will be classified on the base of this policy. It can be
based on stream, 802.1p or DSCP. For detail instruction, please refer to 4.3.3.1 Stream, 4.3.3.2
802.1p and 4.3.3.3 DSCP.
Schedule Mode: The schedule mode of the IP QoS function, it can be “strict prior” or “WFQ
(4:3:2:1)”.
Strict prior: Traffic with different priority will be send by its priority, the higher priority the
traffic is, the higher priority the traffic will be send out.
WFQ (4:3:2:1): Traffic with different priority will be send in proportion of its priority, the four
priority traffic will be send out in proportion to 4:3:2:1.
Apply: Click this button to save your changes.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
4.3.3.1. Stream
If the QoS policy is “stream based”, you should configure the QoS rule. To add a QoS rule, you need
to click the add rule button, and then some corresponding parameters will appear as shown in
Figure 4-32.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 51 of 78
Figure 4-32
Src IP: The source IP address of the rule.
Src Mask: The source mask of the rule.
Dest IP: The destination IP address of the rule.
Dest Mask: The destination mask of the rule.
Src Port: The source port number of the rule. If the “Protocol” filed is not been selected or is
selected as ICMP, the “Src Port” filed can’t be configured.
Dest Port: The destination port number of the rule. If the “Protocol” filed is n ot been selected or
is selected as ICMP, the “Dest Port” filed can’t be configured.
Protocol: The protocol of the rule. It can be TCP, UDP, and ICMP.
Phy port: The incoming port of the rule. It indicates the physical port of the traffic is incoming.
Set Priority: The priority of the rule. It can be p0(highest), p1, p2, p3(lowest). The traffic
matches the rule will be assigned the priority you have configured.
Insert or modify QoS mark: You can insert or modify the DSCP or 802.1p tag. The traffic
matches the rule will be added or modified the mark.
Note:
If you select 802.1p tag, please make sure 802.1q is enabled in specified WAN interface;
otherwise 802.1p tag will not be tagged.
Apply: After filling the parameters, click this button to add a new rule.
QoS Rule List: Shows the current rules on the device.
Delete: Select a rule then press the delete button, the selected rule will be deleted from QoS
rule list.
Delete all: Delete all the rules from QoS rule list.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 52 of 78
4.3.3.2. 802.1p
If the QoS policy is “802.1p based”, you should configure the 802.1p setting.
Figure 4-33
802.1p rule list: Shows the current rules on the device.
802.1p tag: The number of 802.1p tag.
Send priority: The priority to transmit. The traffic matches the 802.1p filed will be assigned this
priority.
Modify: Click this button to save your priority configuration.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 53 of 78
4.3.3.3. DSCP
If the QoS policy is “DSCP based”, you should configure the DSCP setting. Press the “DSCP config”
button to configure the DSCP priority.
Figure 4-34
DSCP tag: The value of the DSCP filed.
Transmit prior: The priority to transmit. The traffic matches the DSCP filed will be assigned
this priority.
Dscp rule list: Shows the current rules on the device.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 54 of 78
4.3.4. CWMP
Choose “Advanced→CWMP”, you can configure the CWMP function in the screen (shown in Figure
4-35). Here you may change the setting for the ACS’s parameters.
CPE WAN Management Protocol (CWMP) is a protocol for communication between a CPE and
Auto-Configuration Server (ACS). The function supports TR-069 protocol which collects information,
diagnoses the devices and configures the devices automatically via ACS (Auto-Configuration
Server).
Figure 4-35
ACS parameters
Enable: Enable or disable the CWMP.
URL: Enter the website of ACS which is provided by your ISP.
User Name/Password: Enter the User Name and password the device should use when
connecting to the ACS.
Periodic Inform Enable: When this field is enabled, the device will send an Inform RPC to the
ACS server at the system startup, and will continue to send it periodically at an interval defined
in “Periodic Inform Interval” field; when this field is disabled, the device will only send Inform
RPC to the ACS server once at the system startup.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 55 of 78
Periodic Inform Interval: The interval to send Inform RPC.
Connection Request parameters
User Name/Password: Enter the User Name and Password the remote ACS should use when
connecting to the device.
Path: The path of the device ConnectionRequestURL.
Port: The port of the device ConnectionRequestURL.
Apply Changes: Click this button to save your configurations.
Reset: Click this button to delete your entering.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
4.3.5. Port mapping
Choose “Advanced→Port Mapping”, you can configure the mapping group in the screen (shown in
Figure 4-36).
The device provides multiple interface groups, up to five interface groups are supported including
one default group. Traffic coming from one interface of a group can only be flowed to the interfaces
in the same interface group. Thus, the device can isolate traffic from group to group for some
application. By default, all the interfaces (LAN and WAN) belong to the default group, and the other
four groups are all empty. It is possible to assign any interface to any group but only one group.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 56 of 78
Figure 4-36
You can enable or disable the port mapping function of the device by the select radio button. If
“Enable” radio is selected, you can configure the mapping group as follow steps.
1. Select a group (Group 1, Group 2, Group3 or Group 4) from the table, then you can see the
available interface (LAN and WAN) and grouped interface list
2. Select interfaces from the “WAN” and “LAN” interface list and add it to the “Interface group”

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 57 of 78
using Add> button or delete it from the “Interface group” using >Del button to manipulate the
required mapping of the ports.
3. Click the Apply button to finish the configuration.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
4.3.6. Others
Choose “Advanced→Others”, you can configure the client limit settings in the screen (shown in
Figure 4-37). Client limit allows you to force how many devices can access to the internet. Here you
can enable or disable the client limit function and the maximum device to access to the internet.
Figure 4-37
Client Limit Capability: Enable or disable the client limit function.
Maximum Devices: limit the maximum number of devices that can access to the Internet.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 58 of 78
4.4. Service
Choose “Service”, you can see the next submenus:
Click any of them, and you will be able to configure the corresponding function.
4.4.1. IGMP Proxy
Choose “Service→IGMP Proxy” menu, you can configure the IGMP proxy in the screen (shown in
Figure 4-38). Here you can enable or disable the IGMP proxy function on all WAN interface, and you
can also set the parameters of the IGMP function.
IP hosts use Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) to report their multicast group
memberships to neighbor routers. Similarly, multicast routers use IGMP to discover which of their
hosts belong to multicast group. The router supports IGMP proxy that handles IGMP message.
When enabled, the router will act as a proxy for a LAN host making request to join and leave
multicast groups, and a multicast router sending multicast packets to multicast groups on WAN side.
Figure 4-38
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
4.4.2. UPnP
Choose “Service→UPnP” menu, you can configure the UPnP in the screen (shown in Figure 4-39).
UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) is a distributed, open networking standard that uses TCP/IP for
simple peer-to-peer network connectivity between devices. An UPnP device can dynamically join a
network, obtain an IP address, convey its capabilities and learn about other devices on the network.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 59 of 78
In turn, a device can leave a network smoothly and automatically when it is no longer in use. UPnP
broadcasts are only allowed on the LAN.
Figure 4-39
UPnP: Choose to enable or disable the UPnP function. Only when the function is enabled, can
the UPnP take effect.
WAN interface: Select to run UPnP function on which interface.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
4.4.3. SNMP
Choose “Service→SNMP”, you can see the SNMP screen (shown in Figure 4-40).
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a troubleshooting and management protocol
which uses the UDP protocol on port 161 to communicate between the clients and servers. The
router can be managed locally or remotely by SNMP protocol.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 60 of 78
Figure 4-40
Enable SNMP: Choose to enable or disable the SNMP support.
System Description: System description of the device.
System Contact: Contact information of the device.
System name: Name of the device.
System Location: The physical location of the device
Trap IP address: Destination IP address of SNMP trap.
Community name (read-only): Name of the read-only community. This read-only community
allows read operation to all objects in the MIB.
Community name (read-write): Name of the read-write community. This read-write community
allows read and write operation to all objects defines as read-writable in the MIB.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
4.4.4. DNS
Choose “Service→DNS”, you can see the DNS screen (shown in Figure 4-41).
Figure 4-41
Attain DNS Automatically: Select this option, so the device will use the DNS servers which
obtained by the WAN interface via the auto-configuration mechanism.
Set DNS Manually: Select this option, and then you need to configure the DNS IP address
manually.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 61 of 78
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
4.4.5. DDNS
Choose “Service→DDNS”, you can configure the DDNS function in the screen (shown in Figure
4-42).
The router offers a Dynamic Domain Name System (DDNS) feature. The feature lets you use a
static host name with a dynamic IP address. User should type the host name, user name and
password assigned to your ADSL Router by your Dynamic DNS provider.
Figure 4-42
DDNS provider: There are two DDNS provider to be selected in order to register your device,
DynDNS.org and TZO.
Hostname: Domain name to be registered with the DDNS server.
Interface: The WAN interface over which your device will be accessed.
Enable: Check to enable the registration account for the DDNS server.
DynDns Settings:

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 62 of 78
Username: Username assigned by the DDNS provider.
Password: Password assigned by the DDNS provider
TZO Settings:
Email: Email address assigned by DDNS provider.
Key: Key assigned by DDNS provider.
Dynamic DDNS Table: Display the DDNS entry of this device.
Click the Add button to add the DDNS entry. Click the Remove button to delete the existed DDNS
entry.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
4.5. Firewall
Choose “Firewall”, you can see the next submenus:
Click any of them, and you will be able to configure the corresponding function.
4.5.1. MAC Filter
Choose “Firewall→MAC Filter” menu, and you will see the next screen (shown in Figure 4-43). In
order to management your local network better, you can use the MAC address filter function to
control the internet access. Here you can set the MAC filtering rules.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 63 of 78
Figure 4-43
Outgoing/Incoming Default Policy: The default action of outgoing/incoming connection. It can
be “Deny” or “Allow”. If the connection doesn’t match any MAC filtering rules, the router will
handle the connection with the default action you have set.
Direction: The direction of the filter entry, it can be “Outgoing” or “Incoming”.
Action: The action of the filter entry, it can be “Deny” or “Allow”. If the action is “Deny”, the
connection matches the filter rule will be denied, if the action is “Allow”, the connection matches
the filter rule will be allowed.
Source MAC: The source MAC address of the filter entry. Empty means matching any source
MAC address.
Destination MAC: The destination MAC address of the filter entry. Empty means matching any
source MAC address.
Add: Click this button to add your rule into “Current MAC Filter Table”.
Current MAC Filter Table: It shows the current MAC filtering rules. You can delete the entry on
the list.
Delete: Check the desired rule and then click this button to delete the corresponding rule.
Delete All: Click this button to delete all the rules in the table.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 64 of 78
IP/Port Filter
Choose “Firewall→IP/Port Filter” menu, and you will see the next screen (shown in Figure 4-44).
Here you can set the IP/Port filter rules to secure or restrict your local network.
Figure 4-44
SPI Firewall: Choose to enable or disable the SPI firewall.
Rule Action: The filter mode of this entry, it can be “Permit” and “Deny”. If the mode is “Permit”,
the IP connection matches the rule will be permitted; if the mode is “Deny”, the IP connection
matches the rule will be denied.
Protocol: The protocol of this entry, it can be “IP”, “ICMP”, “TCP” and “UDP”.
Direction: The direction of this entry, it can be “upstream” and “Downstream”.
Source IP Address / Mask Address: The source IP address and mask address of the entry.
Dest IP Address / Mask Address: The destination IP address and mask address of the entry.
SPort: Tf the protocol is “TCP” or “UDP”, you should set the source port of the entry. It can be a
single port or a port range.
Dport: TI the protocol is “TCP” or “UDP”, you should set the destination port of the entry. It can
be a single port or a port range.
Enable: Choose to enable or disable this filter entry.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 65 of 78
Current Filter table: It shows the current filter rules. You can enable or disable or delete the
filter entry.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.
4.5.2. URL Filter
Choose “Firewall→URL Filter” menu, and you will see the next screen (shown in Figure 4-45). Here
you can specify which site can’t be accessed based on URL to secure or restrict your local network.
Figure 4-45
URL Blocking Capability: Enable or disable the URL filtering function. If it is enabled, the
access to the site which matches the keyword will be blocked by the router; if it is disabled,
nothing will be done.
Keyword: The keyword of the site you want to block.
URL Blocking Table: It shows the current URL filtering entry. You can delete the selected
entry.
For example: If you want to forbid the user to access the website including “yahoo.com”.
Step 1: Select “Enable” (shown in Figure 4-45).
Step 2: Enter “yahoo.com” in the Keyword field.
Step 3: Finally click the AddKeyword to save the entry.
Note:
After configuration, you need to click the Save button appeared on the left panel so that your
configuration can still take effect after the Router reboots.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 66 of 78
4.5.3. ACL
Choose “Firewall→ACL”, you can see the next screen (shown in Figure 4-46). ACL function is used
to specify which services are accessible from LAN or WAN side.
Figure 4-46
Direction Select: The direction of the ACL entry, it can be LAN or WAN.
1) LAN
If “LAN” is selected, you can see the next screen (shown in Figure 4-47)
Figure 4-47

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 67 of 78
LAN ACL Switch: You can enable or disable the ACL function on LAN side. If it is disabled, all
hosts on LAN side can access the services which your router provides. If it is enabled, only the
hosts on the “Current ACL Table” can access the specified services.
IP Address: The IP address of the host, “0.0.0.0” means any IP.
Service Allowed (LAN side): The allowed services which the host can access. It can be “any”,
or any specified service, such as “web”, ”telnet”, ”ftp”, ”tftp”, ”snmp” and “ping”. If select “any”, it
means the host can access all the services the router provides.
2) WAN
If “WAN” is selected, you can see the next screen (shown in Figure 4-48)
Figure 4-48
WAN Setting: The setting of WAN side, it can be “Interface” or “IP Address”.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 68 of 78
If it is “Interface”, you should specify a WAN interface for this ACL entry.
If the WAN setting is “IP Address”, you should specify the IP address of the host on
WAN side.
Service Allowed: You can specify the service and opened port for this service on WAN side.
The host access the specified port can obtain the specified service the router provides.
Current ACL Table: It shows the current ACL setting.
4.6. Maintenance
Choose “Maintenance”, you can see the next submenus:
Click any of them, and you will be able to configure the corresponding function.
4.6.1. Update
4.6.1.1. Firmware Update
Choose “Maintenance→Update→Firmware Update”, you can upgrade the firmware of the Router
in the screen (shown in Figure 4-49). Make sure the firmware you want to use is on the local hard
drive of the computer. Click Browse to find the local hard drive and locate the firmware to be used
for upgrade.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 69 of 78
Figure 4-49
To upgrade the router's firmware, follow these instructions below:
Step 1: Type the exact path of the update file into the “Select File” field. Or click the Browse button
to locate the update file.
Step 2: Click the Upload button.
Note:
1. When you upgrade the router's firmware, you may lose its current configurations, so please
back up the router’s current settings before you upgrade its firmware.
2. Do not turn off the router or press the Reset button while the firmware is being upgraded.
3. The router will reboot after the upgrading has been finished.
4.6.1.2. Backup/Restore
Choose “Maintenance→Update→Backup/Restore”, you can save the current configuration
settings to a file, and you can also restore the settings from a configuration file (shown in Figure
4-50).
Figure 4-50
To backup the Router’s current settings:
Step 1: Click the Save button (shown in Figure 4-50) to proceed.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 70 of 78
Figure 4-51
Step 2: Save the file as the appointed file (shown in Figure 4-52).
Figure 4-52
To restore the Router’s settings:
Step 1: Click the Browse button to locate the file for the device, or enter the exact path in “Load
Settings from File” field.
Step 2: Click the Upload button to complete.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 71 of 78
4.6.2. Password
Choose “Maintenance→Password”, you can configure the user account of the router in the screen
(shown in Figure 4-53). Here you can add user account to access the web server, and modify the
password of the specified user.
Figure 4-53
4.6.3. System Restart
Choose “Maintenance→Reboot”, you can select to restart the device with current settings or
restore to factory default settings in the screen (shown in Figure 4-54).
Figure 4-54

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 72 of 78
4.6.4. Time
Choose “Maintenance→Time”, you can configure the system time in the screen (shown in Figure
4-55).
Simple Network Timing Protocol (SNTP) is a protocol used to synchronize the system time to the
public SNTP server. You can also configure the time manually.
Figure 4-55
1) Manually
You need to set the date and time corresponding to the current time. And then click Apply Changes
button to save your configuration.
Figure 4-56

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 73 of 78
2) NTP
Figure 4-57
State: Indicate the current state of NTP function. Choose to enable the NTP or not.
Server/Server2: Enter the IP address or the host name of the NTP server.
Interval: The interval time of NTP function.
Time Zone: The time zone in which the device resides.
Get GMT Time: After setting the NTP configuration correctly, click this button to start the NTP
function. Then you can see the GMT time obtained from NTP server.
Note:
If changes are made, after clicking Apply Changes button, a Save button will appear on the left
panel. You need to click the Save button to make your changes take effect.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 74 of 78
4.6.5. Log
Choose “Maintenance→Log”, you can view and configure the logs of the Modem Router
(shown in Figure 4-58).
Figure 4-58
Note:
If changes are made, after clicking Apply Changes button, a Save button will appear on the left
panel. You need to click the Save button to make your changes take effect.
4.6.6. Diagnostic
The router provides several useful diagnostic tools.
4.6.6.1. Ping
Choose “Maintenance→Diagnostic→Ping”, you can ping a specified host (shown in Figure 4-59).
Figure 4-59

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 75 of 78
Host: Enter the IP address or host name you want to ping.
After setting the host, click the PING button to start the ping process, then the ping result will be
shown.
4.6.6.2. Tracert
Choose “Maintenance→Diagnostic→Tracert”, you can tracert a host you want (shown in Figure
4-60).
The router provides a tracert command to measure the route path and transit times of packets
across an Internet Protocol (IP) network.
Figure 4-60
Host: Enter the IP address or host name you want to run trace route command.
NumberofTriers: Enter the number of try.
Timeout: The time for the trace route command timeout.
Datasize: Data size of the trace route packet.
MaxHopCount: The maximum hop count.
Interface: The interface to which the trace route is to be applied.
For example, you can set the host to “www.baidu.com”, and then click the traceroute button to start
the trace route process. Several times later, you can see the trace route result.
4.6.6.3. OAM Loopback
Choose “Maintenance→Diagnostic→OAM Loopback”, you can perform the loopback function to
check the connectivity of the VCC (shown in Figure 4-61).

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 76 of 78
OAM Loopback allows you to verify the connectivity between VP/VC endpoints, as well as segment
endpoints within the VP/VC. ATM uses two cell flows: F4 used in VPs and F5 used in VCs.
Figure 4-61
Flow type: The ATM OAM flow type. The selection can be F5 Segment, F5 End-to-End, F4
Segment or F4 End-to-End.
VPI: The VPI number you want to do the loopback diagnostics.
VCI: The VCI number you want to do the loopback diagnostics.
4.6.6.4. ADSL Diagnostic
Choose “Maintenance→Diagnostic→ADSL Diagnostic”, you will see the next screen (shown in
Figure 4-62). ADSL diagnostics allows you to diagnostics the ADSL tone.

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 77 of 78
Figure 4-62
Click the Start button to start the diagnostic, and then wait several minutes later you will see the test
result.
4.6.6.5. Diag-Test
Choose “Maintenance→Diagnostic→Diag-Test”, you can select an interface to run diagnostic in
Figure 4-63.
The Diagnostic Test allows you to test your DSL connection of the physical layer and protocol layer
for both LAN and WAN sides.
Figure 4-63

RRTTAA0044NN UUsseerr’’ss MMaannuuaall
EEdd..00..11
Page 78 of 78
General
Standards and Protocols
ANSI T1.413, ITU G.992.1, ITU G.992.2, ITU G.992.3, ITU G.992.5,
IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g, IEEE 802.11n, IEEE 802.3, IEEE
802.3u, TCP/IP, PPPoA, PPPoE, SNTP, HTTP, DHCP, ICMP, NAT
Safety & Emission
FCC, CE
Ports
Four 10/100M Auto-Negotiation RJ45 ports(Auto MDI/MDIX)
One RJ11 port
LEDs
Power, ADSL, Internet, WLAN, 1,2,3,4(LAN), WPS
Network Medium
10Base-T: UTP category 3, 4, 5 cable
100Base-TX: UTP category-5
Max line length: 6.5Km
Data Rates
Downstream: Up to 24Mbps
Upstream: Up to 3.5Mbps(With Annex M enabled)
System Requirement
Internet Explorer 5.0 or later, Netscape Navigator 6.0 or later
Win 9x/ ME/ 2000/ XP/ Vista/Windows 7
Physical and Environment
Working Temperature
0℃ ~ 40℃
Working Humidity
10% ~ 90% RH (non-condensing)
Storage Temperature
-40℃ ~ 70℃
Storage Humidity
5% ~ 90% RH (non-condensing)
Click the Run Diagnostic Test button to start the test, and then wait several times later you can see
the diagnostic result.
Appendix A: Specifications
 Loading...
Loading...