Page 1

Barracuda Web Filter Administrator’s Guide
Version 4.0
Barracuda Networks Inc.
3175 S. WInchester Blvd
Campbell, CA 95008
http://www.barracuda.com
1
Page 2

Copyright Notice
Copyright 2004-2008, Barracuda Networks
www.barracuda.com
v40-081113-01-1113
All rights reserved. Use of this product and this manual is subject to license. Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Trademarks
Barracuda Web Filter is a trademark of Barracuda Networks, Inc. All other brand and product names mentioned in this document are
registered trademarks or trademarks of their respective holders.
2 Barracuda Web Filter Administrator’s Guide
Page 3

Administrator’s Guide
Contents
Chapter 1 – Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Spyware-blocking techniques . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Content-filtering techniques . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
User and group-based policy control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Application-blocking techniques. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Energize Updates minimize administration and maximize protection . . . . . . 10
Deploying the Barracuda Web Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Inline pass-through (transparent) mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Forward proxy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Chapter 2 – Getting Started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Network considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Routers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
External DNS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Internal DNS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Enterprise class Layer 3 switch, VLANS, VPN concentrators . . . . . . . 16
Firewall DMZ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Internal servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Cache . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
QoS/packet reconfiguration (Quality of Service, packet shapers) . . . . . 17
Mounting and cabling considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Installing the Barracuda Web Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Step 1. Verify that you have the necessary equipment . . . . . . . . . . 18
Step 2. Install the Barracuda Web Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Step 3. Configure the Barracuda Web Filter IP and network settings . . . 19
Step 4. Configure your corporate firewall . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Step 5. Configure the Barracuda Web Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Step 6. Update the Barracuda Web Filter firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Step 7. Verify your subscription status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Step 8. Update the definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Step 9. Integrate the Barracuda Web Filter into your network . . . . . . . 23
Step 10. Test and adjust the Barracuda Web Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Connecting the Barracuda Web Filter to your network . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Advanced Deployments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Web Cache Control Protocol (WCCP) deployment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Inline pass-through with pre-existing proxy deployment . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Connecting inline to your network with a pre-existing proxy server . . . . . . . 29
Chapter 3 – Configuring, Monitoring, and Managing the
Barracuda Web Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Configuring the Barracuda Web Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Configuring system IP information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
3
Page 4

Barracuda Web Filter Release 3.3
Controlling access to the Web interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Customizing the appearance of the Web interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Changing the language of the Web interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Setting the time zone of the system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Enabling and disabling virus protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Enabling and disabling Web caching . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Setting up a syslog server to centrally monitor system logs . . . . . . . . . . 35
Advanced Configuration Topics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Setting up linked management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Data propagated to the linked systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Switching a system to standby mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Monitoring the Barracuda Web Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Viewing performance statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Understanding the indicator lights. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Viewing the traffic log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Viewing the application log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Viewing the warned activity list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Automating the delivery of system alerts and notifications . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Viewing a list of infected clients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Viewing system tasks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Managing the Barracuda Web Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Backing up and restoring system configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Updating the Barracuda Web Filter firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Updating the spyware, virus, and category definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Replacing a failed system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Reloading, restarting, and shutting down the system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Using the built-in troubleshooting tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Rebooting the system in recovery mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Reboot options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Generating System Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Chapter 4 – Managing Users and Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
About local users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
About domain users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Creating local users and groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Creating local user accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Creating local groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Creating IP address groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Integrating with a user authentication service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Enabling LDAP domain user authentication. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
To enable LDAP user authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
About the optional Barracuda DC Agent software . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Installing the Barracuda DC Agent on your domain controllers . . . . . . 54
Exempting selected LDAP domain users from filtering . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Enabling NTLM domain user authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
About NTLM authentication in Windows 2000 or 2003 AD domains . . . . 55
Reasons for using an NTLM authentication server . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Requirements for using an NTLM authentication server . . . . . . . . . . 55
Limitations when using an NTLM authentication server . . . . . . . . . . 55
Viewing and managing accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
4:
Page 5

Administrator’s Guide
Chapter 5 – Managing Policies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Creating block and accept filters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Best practices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Filtering and blocking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Content filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Application filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Domain filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
URL pattern filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Custom categories filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
MIME type blocking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
IP-based exemption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
IP-based blocking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Exception policies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Block messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
HTTPS filtering option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Scope of HTTPS traffic filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Limitations for HTTPS traffic filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
To enable the HTTPS traffic-filtering option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Testing Web site access. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
About the Barracuda Spyware Removal Tool. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Enabling the Barracuda Spyware Removal Tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Chapter 6 – Reporting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Generating system reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Appendix A – About the Barracuda Web Filter Hardware . . 69
Front panel of the Barracuda Web Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Barracuda Web Filter 210, 310, and 410 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Barracuda Web Filter 610 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Barracuda Web Filter 810 and 910 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Back panel of the Barracuda Web Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Barracuda Web Filter 210, 310, and 410 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Barracuda Web Filter 610 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Barracuda Web Filter 810 and 910 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Hardware compliance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Notice for the USA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Notice for Canada . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Notice for Europe (CE Mark) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Appendix B – Regular Expressions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Using special characters in expressions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Appendix C – Limited Warranty and License . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Limited warranty. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
5
Page 6

Barracuda Web Filter Release 3.3
Exclusive remedy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Exclusions and restrictions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Software license. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Energize Update Software license . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Open Source Licensing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
6:
Page 7

Administrator’s Guide
Chapter 1
Introduction
This chapter provides an overview of the Barracuda Web Filter and includes the following topics:
• Overview on page 8
• Deploying the Barracuda Web Filter on page 11
7
Page 8
Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
Overview
The Barracuda Web Filter is an integrated anti-spyware and content filtering solution that eliminates
spyware and other forms of malware from your organization.
The Barracuda Web Filter combines preventative, reactive, and proactive measures to form a
complete anti-spyware solution. The Barracuda Web Filter:
• Provides user and group-based policy control
• Stops spyware downloads (including drive-by downloads)
• Uses content filters to block access to Web site categories like gaming or online shopping sites
• Blocks access to applications like instant messaging and music streaming
• Blocks access to spyware Web sites
• Detects spyware access to the Internet
• Identifies infected machines
• Facilitates spyware removal by providing access to the Barracuda Spyware Removal Tool
The sections in this guide will detail the typical tasks that are performed by Web Filter administrators:
1. Installation
2. Configuring, Monitoring and Managing
3. Managing Users and Groups
4. Managing Policies
5. Reporting
Spyware-blocking techniques
The Barracuda Web Filter prevents spyware programs from being installed on your users’ systems
and also secures your organization against existing spyware by detecting spyware access to the
Internet and notifying you of infected systems. You can also configure the Barracuda Web Filter to
prompt infected users to run the Barracuda Spyware Removal Tool.
Table 1.1: Spyware Functions
Function Description
Spyware Web site Blocking Barracuda Networks continuously updates a list
containing thousands of known spyware download sites.
The Barracuda Web Filter blocks spyware at the source
by preventing browser and application access to these
locations.
Spyware Download Blocking Spyware is everywhere, even in apparently harmless
8 Chapter 1: Introduction
downloads from legitimate sites. The Barracuda Web
Filter unpacks and examines every individual file within
17 different types of archives. It also uses techniques to
examine password-protected archives.
Page 9

Administrator’s Guide
Table 1.1: Spyware Functions
Function Description
Spyware Detection The Barracuda Web Filter not only identifies infected
machines on the network, but also blocks the spyware
communication from those infected systems to the
spyware servers on the Internet.
Spyware Removal The Barracuda Web Filter can be configured to
automatically prompt users to run the Barracuda Spyware
Removal Tool when spyware is detected on their system.
This feature allows users to proactively remove spyware
so they do not have to rely on network administrators to
perform this task.
The Barracuda Web Filter scans inbound traffic for the following malware over HTTP port 80 and
FTP port 21: spyware (such as keyloggers, Browser Helper Objects [BHOs], and data miners),
adware, trojans, and viruses. The Barracuda Web Filter also scans outbound traffic on all ports and
protocols to prevent spyware from communicating outside of your network.
Content-filtering techniques
In addition to protecting your network from spyware infections, the Barracuda Web Filter also uses
filters to protect your users from visiting offensive Web sites and to help enforce your organization’s
Internet usage policies.
To block access to offensive sites, the Barracuda Web Filter includes a URL list containing millions
of URLs classified into 58 categories for easy and efficient content filtering. This list is continuously
updated by engineers at Barracuda Central and delivered hourly via the Energize Updates
subscription service sold with the Barracuda Web Filter.
In addition, the Barracuda Web Filter allows you to create custom classification and specify domains
for filtering.
These content filters can help organizations comply with new security initiatives and standards.
User and group-based policy control
The Barracuda Web Filter allows you to create Content, Application, Domain, URL and MIME Type
based policies to control user access to online content. The policies can be created by users, groups
or in some cases by IP addresses. These filtering policies can be used to allow, block, warn or monitor
user requests to online content.
The Barracuda Web Filter also enables you to create exception policies for specific users and groups
to override general policies that prevent access to content or applications. These policies are useful in
providing executives and departments with additional control over the content they can access.You
can also use exception policies to allow users to bypass blocking filters during specific hours of the
day. For example, you can configure the Barracuda Web Filter to allow users to access shopping or
gaming sites only during non-business hours.
Overview 9
Page 10
Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
Application-blocking techniques
Many organizations choose to block access to certain applications so they can minimize the amount
of non-essential traffic on their network and to prevent users from running applications that can
spread viruses or other malware. For this reason, the Barracuda Web Filter enables you to control
access to a variety of commonly used applications like Instant Messaging and Media. In addition,
application traffic can also be blocked based on MIME type or port number. For example, you can
use the MIME type blocking feature to prevent users from running executable files (.exe) or from
streaming music and video files over your network.
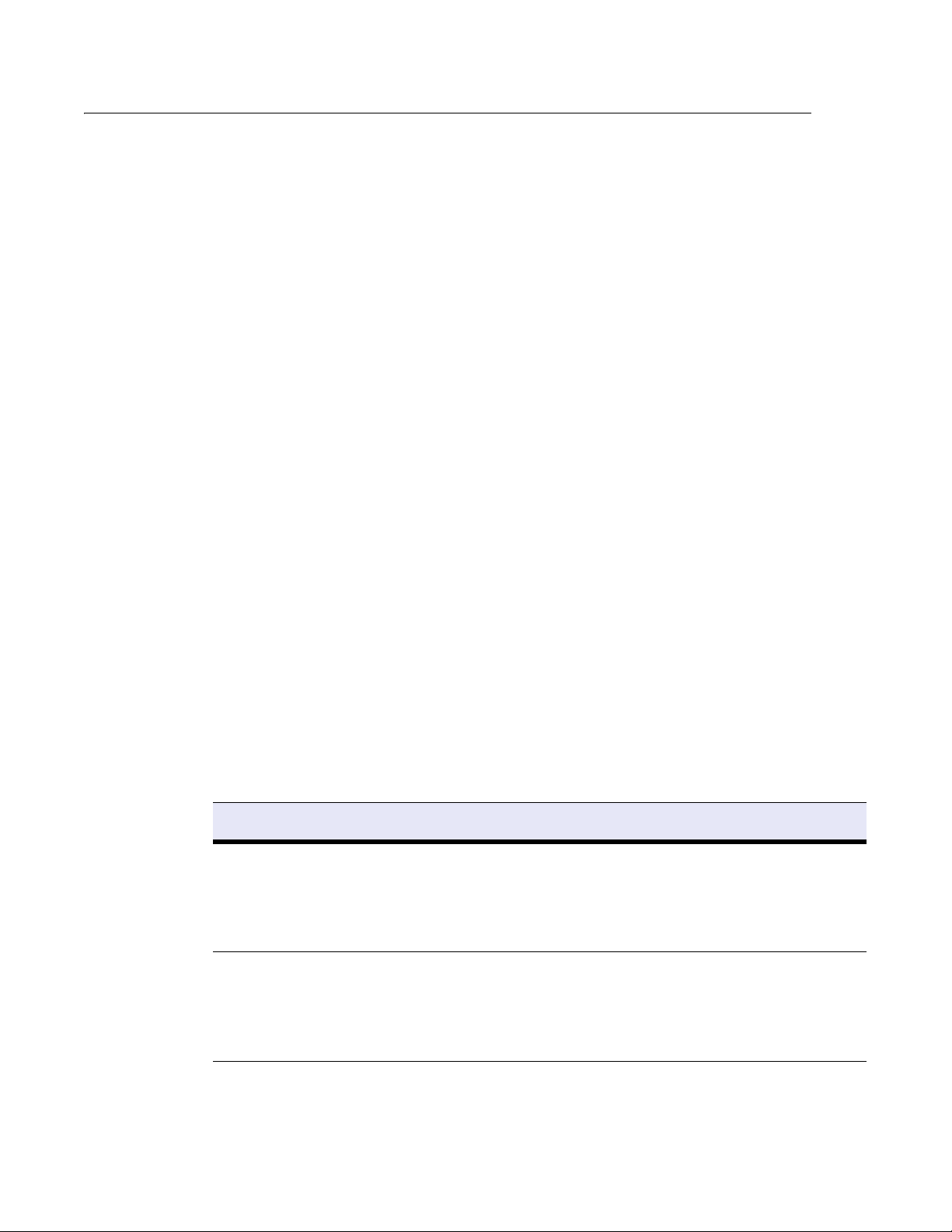
Energize Updates minimize administration and maximize
protection
To provide you with maximum protection against the latest types of spyware, Barracuda Networks
maintains Barracuda Central, a powerful operations center. From this center, engineers monitor the
Internet for trends in spyware and automatically deploy updates and definitions via Barracuda
Energize Updates.
By identifying spyware trends early on, the team at Barracuda Central can quickly develop new and
improved blocking techniques that are quickly made available to your Barracuda Web Filter.
Barracuda Central has identified over 2,000 spyware applications that are actively blocked and is
continuously adding to this list.
The following figure shows how Barracuda Central provides the latest rules and definitions through
the Energize Update feature.
Figure 1.1: Barracuda Energize Updates
10 Chapter 1: Introduction
Page 11
Deploying the Barracuda Web Filter
You can deploy your Barracuda Web Filter so it is either inline with your core network components,
or you can deploy the system as a forward proxy. The following sections provide a brief overview of
each deployment type.
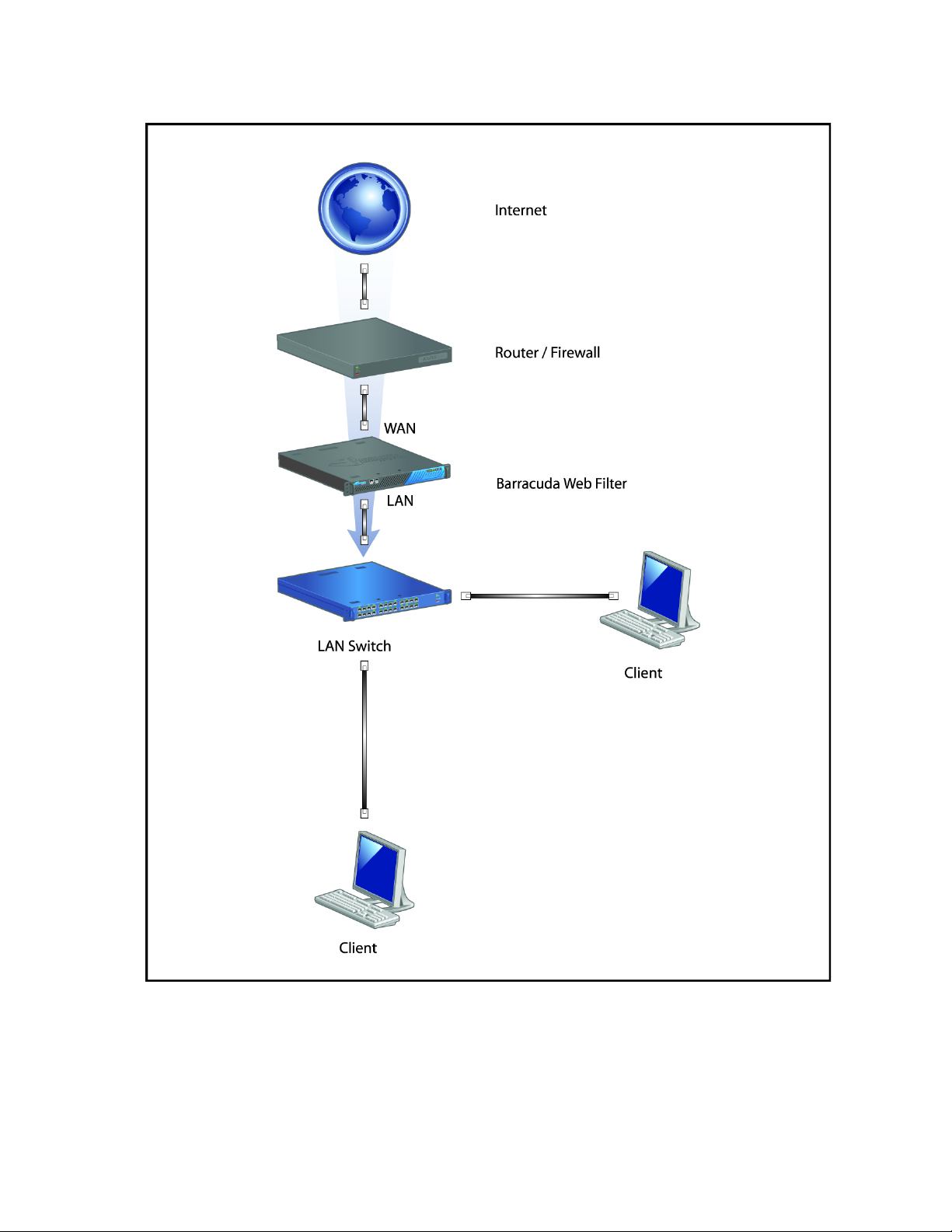
Inline pass-through (transparent) mode
Inline pass-through is the recommended type of deployment because it provides the strongest level of
protection against spyware. In this deployment, the Barracuda Web Filter is directly inline with your
core Internet network components, and all network traffic to the Internet passes through the Barracuda
Web Filter. In this mode, your Barracuda Web Filter is able to:
• Filter and scan all Internet traffic requests.
• Perform content filtering and scan downloads for spyware and viruses.
• Detect and block outbound spyware protocol requests.
• Scan all outbound traffic for spyware activity on all ports to detect infected clients.
Inline pass-through deployment requires you to have an understanding of your network topology
because even though the Barracuda Web Filter acts as a proxy, it does not participate in routing
protocols. As a result, you may need to set up static routes in your Barracuda Web Filter so it knows
how to properly route traffic.
Administrator’s Guide
The following table describes the advantages and disadvantages of deploying your Barracuda Web
Filter in inline pass-through mode.
Advantages Disadvantages
Supports application blocking May require setting up static routes in your Barracuda
Web Filter.
Supports automatic pass-through mode in
the event of a system failure (model 310
and above)
Does not require users to configure proxy
server settings in their Web browser
Uses perimeter transparency mode that
exposes client IP addresses (supports
corporate firewall rules)
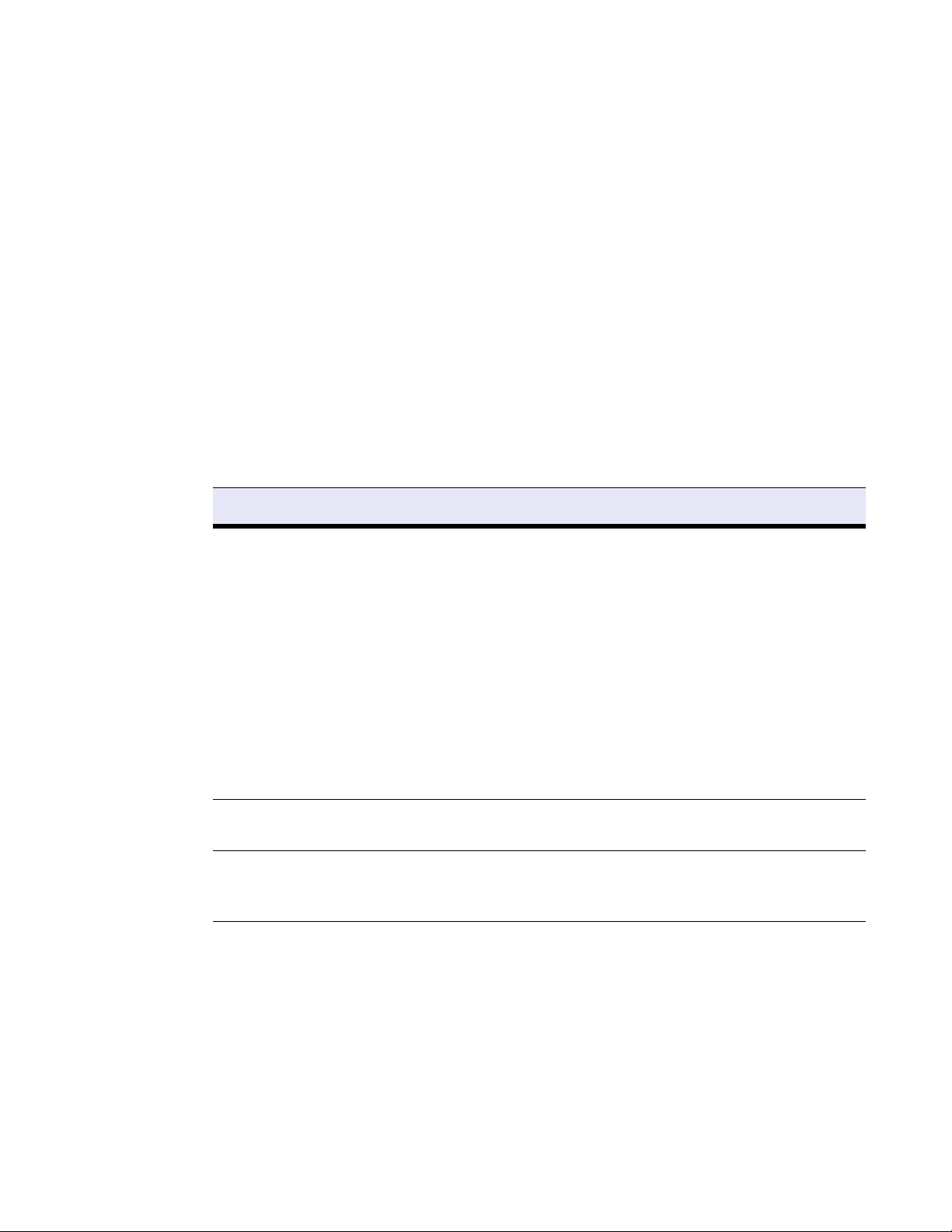
Figure 1.2 illustrates a basic installation using the Inline Pass-Through deployment.
Initial setup requires an interruption to network traffic
while you make necessary cabling changes.
Deploying the Barracuda Web Filter 11
Page 12
Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
Figure 1.2: Inline Pass-through Deployment
12 Chapter 1: Introduction
Page 13
Forward proxy
The forward proxy deployment uses a proxy as an intermediary between a client and the Internet to
protect the client from being visible from the Internet. In a forward proxy deployment, only HTTP
Internet traffic passes through the Barracuda Web Filter. After the Barracuda Web Filter processes
clients’ requests, it sends the requests out directly to the Internet.
When deployed as a forward proxy, the Barracuda Web Filter shows all HTTP traffic as coming from
its own IP address instead of from the individual client IP addresses as is done in the inline passthrough deployment.
We recommend deploying the Barracuda Web Filter in forward proxy mode in the following
situations:
• You need to replace an existing forward proxy (such as Microsoft ISA Server) with the
Barracuda Web Filter.
• You do not want the Barracuda Web Filter to reside inline with all your network traffic and are
satisfied with the system only scanning HTTP traffic for viruses and spyware.
The following table describes the advantages and disadvantages of deploying your Barracuda Web
Filter in forward proxy mode.
Administrator’s Guide
Advantages Disadvantages
The initial setup of forward proxy mode
does not require any interruptions to your
network traffic.
Because the Barracuda Web Filter only scans
outbound HTTP traffic, the system cannot perform
the following functions in forward proxy mode:
• Block access to applications listed on the
BLOCK/ACCEPT > Applications page.
• Block access to applications that use the
destination IP address specified on the
BLOCK/ACCEPT > IP Block/Exempt page.
• Block access to applications that use the
destination port specified on the
> IP Block/Exempt
page.
• Inspect outbound traffic for spyware infection
activity.
Does not require the configuration of static
routes.
The Barracuda Web Filter does not scan non-HTTP
traffic for viruses and spyware.
Requires clients’ Web browsers to be configured with
the IP information of the forward proxy server
(Barracuda Web Filter).
Figure 1.3 illustrates a basic installation using the Forward Proxy Deployment.
BLOCK/ACCEPT
To set up the Barracuda Web Filter as a forward proxy without placing it inline, you must manually
direct all outgoing web traffic through the Barracuda. The initial setup of forward proxy mode does
not require any interruptions to your network traffic. This configuration is also known as "proxy on a
stick." For this to work, the Barracuda Web Filter will need to be connected to the same switch as the
network gateway (just one network hop away).
Once the Barracuda has been installed in this fashion, the following options must be configured on
BASIC > IP Configuration page:
the
Deploying the Barracuda Web Filter 13
Page 14
Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
Set the Operating Mode to Active.
Set the Transparency, Client IP Visibility, or Pass Client IP addresses through WAN port option to
No.
In order to forward outgoing web traffic to the Barracuda Web Filter, it is required that all clients’
web browsers are configured with the IP of the Barracuda Web Filter as their forward proxy server,
on port 8080.
Figure 1.3: Forward Proxy Deployment
14 Chapter 1: Introduction
Page 15

Administrator’s Guide
Chapter 2
Getting Started
This chapter provides general instructions for installing the Barracuda Web Filter.
This chapter covers the following topics:
Network considerations ...................................................................... 16
Installing the Barracuda Web Filter ....................................................18
Advanced Deployments ......................................................................26
15
Page 16

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
Network considerations
The Barracuda Web Filter appliance is designed for low-risk deployment because it is intended to be
a bridge within your network. The appliance can view Internet traffic that passes through the network
but does not affect its routing. To reduce the risk of interfering with important network traffic, initially
set the Barracuda Web Filter to monitor and log the spyware activity only. Determine which internal
servers and clients to exclude from spyware and virus scans.
These pre-installation considerations may help you understand some of the issues that may occur.
Routers
Make sure the default gateway is properly set to reach the Internet. Also, if you are testing the
Barracuda Web Filter in one portion of your network and move to another portion of the network for
deployment, make sure that you check the default gateway and make changes as necessary.
External DNS
Some of the considerations regarding DNS include the following issues:
Optimal DNS query response time—When the Barracuda Web Filter is in Active mode, it proxies all
Internet requests for the clients. As a result, the Barracuda Web Filter needs to resolve website
hostnames to IP addresses while proxying the HTTP requests made by the users. The response for
DNS queries needs to be optimal to allow the Barracuda Web Filter to look up and quickly process
these requests. A slow DNS server will cause the Barracuda Web Filter to respond slowly to clients,
which adds latency to their Internet access.
Requests for fully qualified Web application server names—If a user attempts to browse to a Web
site by specifying a Web server name is not a fully qualified name that includes the domain name, the
Barracuda Web Filter automatically appends the string
order to resolve the request. For example, if the user enters the server name
myserver.mydomain.com, the Barracuda Web Filter resolves the request using the hostname
myserver.barracuda.com.
barracuda.com to the unqualified name in
myserver instead of
Internal DNS
If you have an internal server that is only resolvable via an internal DNS, make sure that this DNS
server is used by the Barracuda Web Filter as a secondary DNS.
Enterprise class Layer 3 switch, VLANS, VPN concentrators
These device types are normally capable of handling multiple subnets and providing default routes to
clients. However, they may affect the Barracuda Web Filter deployment in the following ways:
• A Layer 3 switch can also be set up to have multiple VLANs (Virtual Local Networks) using
port assignments. There is no side effect by having VLAN tags in the traffic that is visible to the
Barracuda Web Filter. However, when the Barracuda Web Filter is set up to a single subnet, it
needs to have routes to process requests for other subnets.
• A standard solution is to add static routes to these foreign subnets. All Layer 3 switch subnets
should use its IP address as the gateway. In the case of a VPN concentrator, use the IP of the
concentrator as the default gateway for all the networks aggregated by that VPN concentrator.
16 Chapter 2: Getting Started
Page 17

Administrator’s Guide
Firewall DMZ
A demilitarized zone (DMZ) is an area where any servers that access the Internet are placed. Servers
inside this zone may be configured to access certain servers within an internal network with their own
security rules set up. Normally these servers need to be accessible from the Internet, such as email
servers. The Barracuda Web Filter should not be deployed to protect these machines. The Barracuda
Web Filter is not designed to protect servers but to protect end user machines.
Internal servers
In most organizations, internal servers are protected by corporate firewalls that use port forwarding
rules to limit access to the servers. Port forwarding rules define the ports that can be used to access
the servers (such as HTTP, FTP, and mail servers). These servers should have optimal response time.
As a result, the server traffic must not be interrupted. Barracuda Networks recommends that you
exempt or bypass these servers from the Barracuda Web Filter. To reduce Layer 2 bridging overhead,
place a switch between the firewall and the Barracuda Web Filter and connect your server farm on a
different port on the switch. In this case, set up the servers parallel to the Barracuda Web Filter instead
of behind it, and the configure exempt IP addressing feature to exclude these IP addresses from server
exemption.
Cache
Caching provides faster access to repeatedly requested content by storing content locally on the
Barracuda Web Filter.The Barracuda Web Filter handles the data by using an LRU (Least Recently
Used) algorithm. The Barracuda Web Filter must be configured with the accurate time since it uses
the current time to ensure accurate cache updates.
QoS/packet reconfiguration (Quality of Service, packet shapers)
There are many products available that can control traffic in a LAN environment, specify priorities,
and size these different traffic types. Normally, this is done using a Layer 7 device on different types
of applications. The Barracuda Web Filter deployment is affected when the Barracuda Web Filter is
placed in front of these devices to benefit from the shaped data. Place the Barracuda Web Filter close
to the Internet to help reduce noise and overhead on both the Layer 2 bridging and HTTP proxy.
Mounting and cabling considerations
To install the Barracuda Web Filter you need to:
• Mount it on a rack or shelf
• Cable it to other network devices
The Barracuda Web Filter is designed to be installed in a data center with other networking devices
and servers. Its dimensions are suitable for a 19-inch rack. You must position it within cabling
distance of any switches or other devices that access the network segments that you want to protect.
The appliance can be mounted facing either direction in your rack, so consider which side will have
access to the ports and which will have access to the LED lights.
You may need access to the ports during installation, and you may need to use the back panel during
initial configuration.
Network considerations 17
Page 18

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
Installing the Barracuda Web Filter
These are the general steps to set up your Barracuda Web Filter. For more detailed instructions for
each step, see the following reference pages.
Step 1. Verify that you have the necessary equipment on page 18
Step 2. Install the Barracuda Web Filter on page 18
Step 3. Configure the Barracuda Web Filter IP and network settings on page 19
Step 4. Configure your corporate firewall on page 20
Step 5. Configure the Barracuda Web Filter on page 20
Step 6. Update the Barracuda Web Filter firmware on page 21
Step 7. Verify your subscription status on page 22
Step 8. Update the definitions on page 23
Step 9. Integrate the Barracuda Web Filter into your network on page 23
Step 10. Test and adjust the Barracuda Web Filter on page 24
Step 1. Verify that you have the necessary equipment
Before installing your Barracuda Web Filter, make sure you have the following equipment:
• Barracuda Web Filter (check that you have received the correct model)
• AC power cord
• Ethernet cables
• Mounting rails and screws (available for models 610, 810, and 910 only)
• VGA monitor (recommended)
• PS2 keyboard (recommended)
Step 2. Install the Barracuda Web Filter
To physically install the Barracuda Web Filter:
1. Fasten the Barracuda Web Filter to a standard 19-inch rack or other stable location.
CAUTION! Do not block the cooling vents located on the front and rear of the unit.
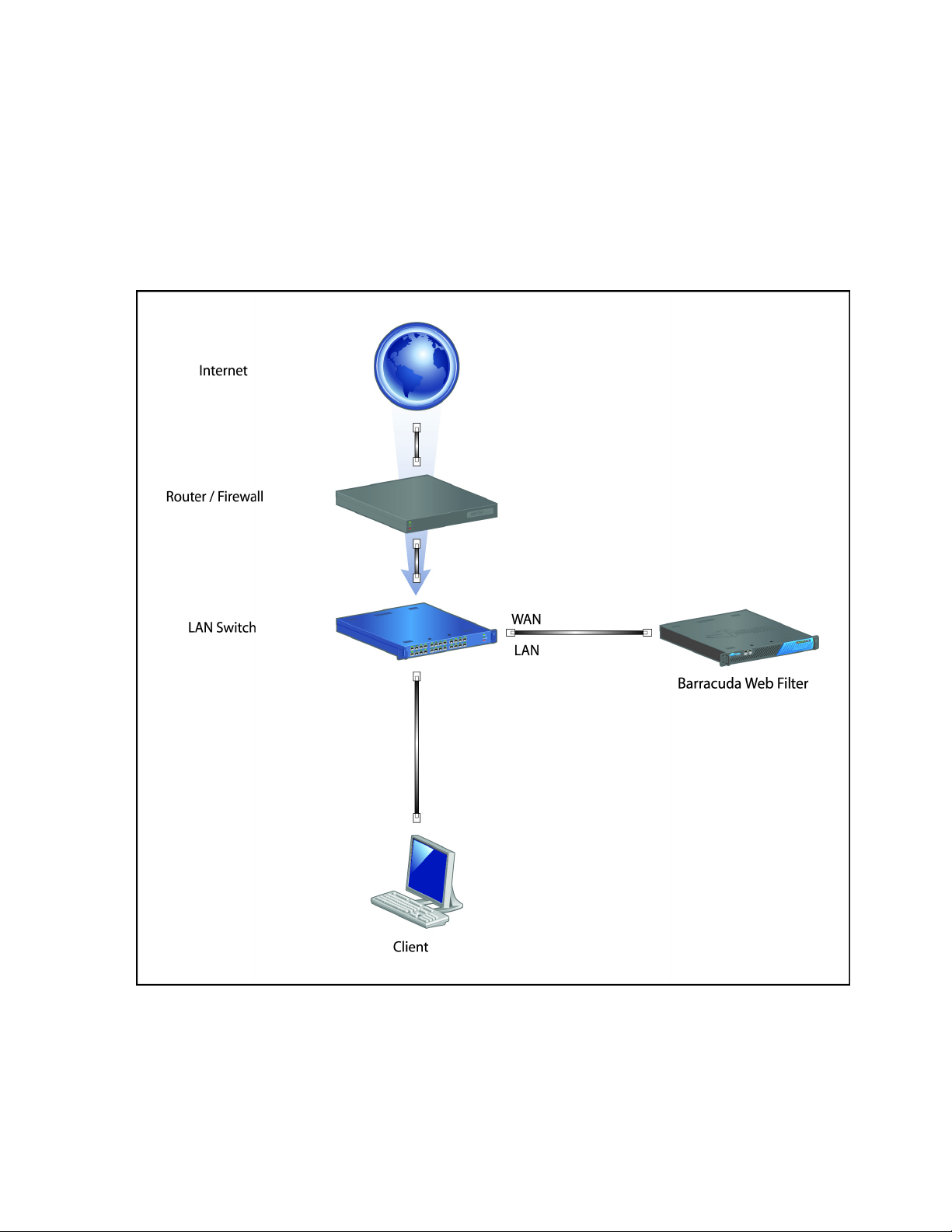
2. Connect a CAT5 Ethernet cable from your network switch to the LAN port on the front of your
Barracuda Web Filter, as shown in the following figure.
18 Chapter 2: Getting Started
Page 19
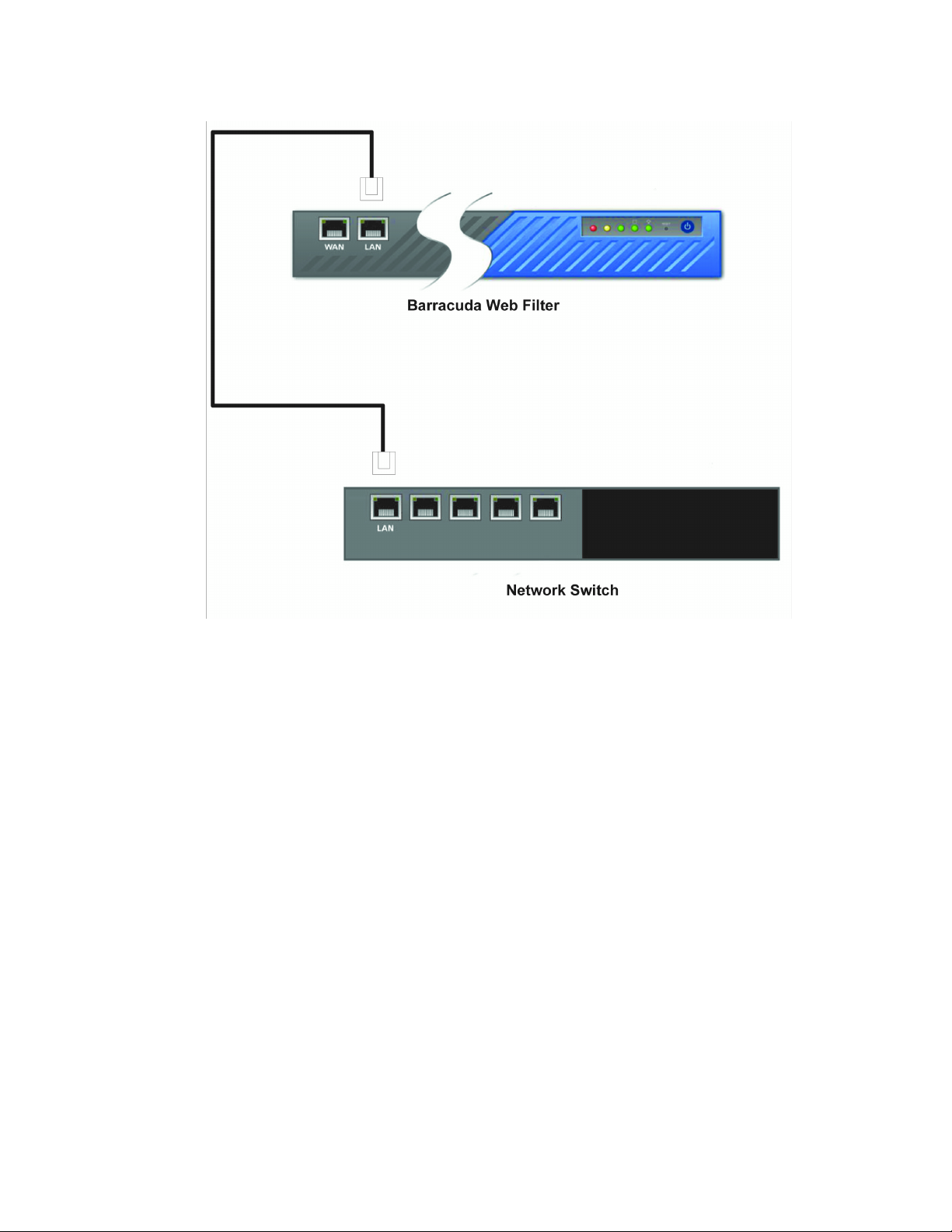
Figure 2.1: Connecting the Barracuda Web Filter to your Network
Administrator’s Guide
The Barracuda Web Filter supports 10BaseT, 100BaseT, and Gigabit Ethernet (higher end models
only).
Do not connect any other cables to the unit. The connectors on the back panel are for diagnostic
purposes.
3. Connect the following hardware to your Barracuda Web Filter:
•Power cord
•VGA monitor
• PS2 keyboard
After you connect the AC power cord, the Barracuda Web Filter may power on for a few
seconds and then power off. This behavior is normal.
4. Press the Power button located on the front of the unit.
The login prompt for the administrative console displays on the monitor and the power light on
the front of the Barracuda Web Filter turns on. For a description of each indicator light, refer to
Understanding the indicator lights on page 39.
Step 3. Configure the Barracuda Web Filter IP and network settings
The Barracuda Web Filter is assigned a default IP address of 192.168.200.200. You can change the
address using the administrative console or by pressing and holding the RESET button on the front
panel.
Holding RESET for eight seconds changes the default IP address to 192.168.1.200. Holding the
button for 12 seconds changes the IP address to 10.1.1.200.
Installing the Barracuda Web Filter 19
Page 20

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
To set a new IP address from the administrative console:
1. Connect your keyboard and monitor directly to the Barracuda Web Filter.
2. At the barracuda login prompt, enter admin for the login and admin for the password.
The User Confirmation Requested window displays the current IP configuration of the
Barracuda Web Filter.
3. Using your Tab key, select Change and click Enter to change the IP configuration.
4. Enter the new IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway IP address for your Barracuda Web
Filter. Select Save
optional. Select
The new IP address and network settings are applied to your Barracuda Web Filter.
Step 4. Configure your corporate firewall
If your Barracuda Web Filter is located behind a corporate firewall, refer to Table 2.1 for the ports
that need to be opened on your corporate firewall to allow communication between the Barracuda
Web Filter and remote servers.
Table 2.1: Ports to Open on Your Corporate Firewall
to enter your changes. The Primary DNS and Secondary DNS files are
Exit.
Port Direction Protocol Description
22 In/Out TCP Remote diagnostics and technical
support services
25 Out TCP Email and email bounces
53 Out TCP/UDP DNS (Domain Name Server)
80 Out TCP Virus, spyware, category definition
updates, and firmware updates
123 In/Out UDP NTP (Network Time Protocol)
8000 Out TCP See Step 5. Configure the Barracuda
Web Filter
8001, 8002 In/Out TCP Synchronization between linked
systems. For more information, see
on page 20.
Controlling access to the Web
interface
on page 34.
In addition to the ports listed above, you may have to configure your corporate firewall to allow the
Barracuda Web Filter to email system alerts and reports. Some organizations create firewall rules that
only allow emails to be sent from the IP address of their email server. In this case, you should
configure your corporate firewall to allow emails to be sent from the Barracuda Web Filter as well.
If your Barracuda Web Filter is located in a DMZ, you may need to configure your corporate firewall
to allow the Barracuda Web Filter to send notifications to your internal email server.
Step 5. Configure the Barracuda Web Filter
After specifying the IP address of the Barracuda Web Filter and opening the necessary ports on your
corporate firewall, configure the Barracuda Web Filter from the administration interface. Make sure
the client’s computer that you configured the Barracuda Web Filter for is connected to the same
network and that the appropriate routing is in place to allow connection to the Barracuda Web Filter’s
IP address via a Web browser.
20 Chapter 2: Getting Started
Page 21

Administrator’s Guide
To configure the Barracuda Web Filter:
1. From a Web browser, enter the IP address of the Barracuda Web Filter followed by port 8000.
For example: http://192.168.200.200:8000.
2. To log into the administration interface, enter admin for the username and admin for the
password.
3. Select BASIC > IP Configuration, and perform the following steps:
3a. Enter the IP address of your primary and secondary DNS servers (if these have not yet
been set up).
3b. Set Operating Mode to Audit.
3c. Set Enable Perimeter Transparency to one of the following depending your type of
deployment:
• For Inline Pass-Through deployment, select Yes to expose the IP addresses of your
clients instead of allowing all HTTP traffic coming from the Barracuda Web Filter.
• For Forward Proxy deployment, select No.
3d. (Optional) Configure any static routes.
3e. Click Save Changes.
Note: If the IP address of your Barracuda Web Filter on the IP Configuration page is changed,
you are disconnected from the Web interface. If this occurs, log in again using the new IP
address.
4. Select BASIC > Administration, and perform the following steps:
4a. Assign a new administration password to the Barracuda Web Filter (optional). This step
is highly recommended.
4b. Make sure the local time zone is set correctly.
Time on the Barracuda Web Filter is automatically updated via NTP (Network Time
Protocol). It requires that port 123 is opened for inbound and outbound UDP (User
Datagram Protocol) traffic on your firewall (if the Barracuda Web Filter is located
behind one).
It is important that the time zone is set correctly because this information is used to
determine the delivery times for messages and is displayed in certain mail reading
programs.
4c. If desired, change the port number used to access the Barracuda Web Filter
administration interface. The default port is 8000.
4d. Enter the amount of time for the session expiration length (in minutes) of your
administration interface session.
At expiration, you are required to log back into the administration interface.
4e. (Optional) Specify your local SMTP server. Enter the email address for your
Administrator to receive system and threat email alerts and notifications.
4f. Click Save Changes.
Step 6. Update the Barracuda Web Filter firmware
To update the firmware on the Barracuda Web Filter:
1. Select ADVANCED > Firmware Update.
2. Read the release notes to learn about the latest features and fixes provided in the new firmware
version.
3. Click Download Now next to Latest General Release. Click OK on the download duration
window.
Installing the Barracuda Web Filter 21
Page 22
Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
Verify your subscriptions are current
Updating the firmware may take several minutes. Do not turn off the unit during this process.
Download Now is disabled if the Barracuda Web Filter is already up-to-date with the latest
firmware version.
The Barracuda Web Filter begins downloading the latest firmware version. You can view the
download status by clicking
4. Click Apply Now when the download completes.
5. Click OK when prompted to reboot the Barracuda Web Filter.
A Status page displays the progress of the reboot. Once the reboot is complete, the login page
appears.
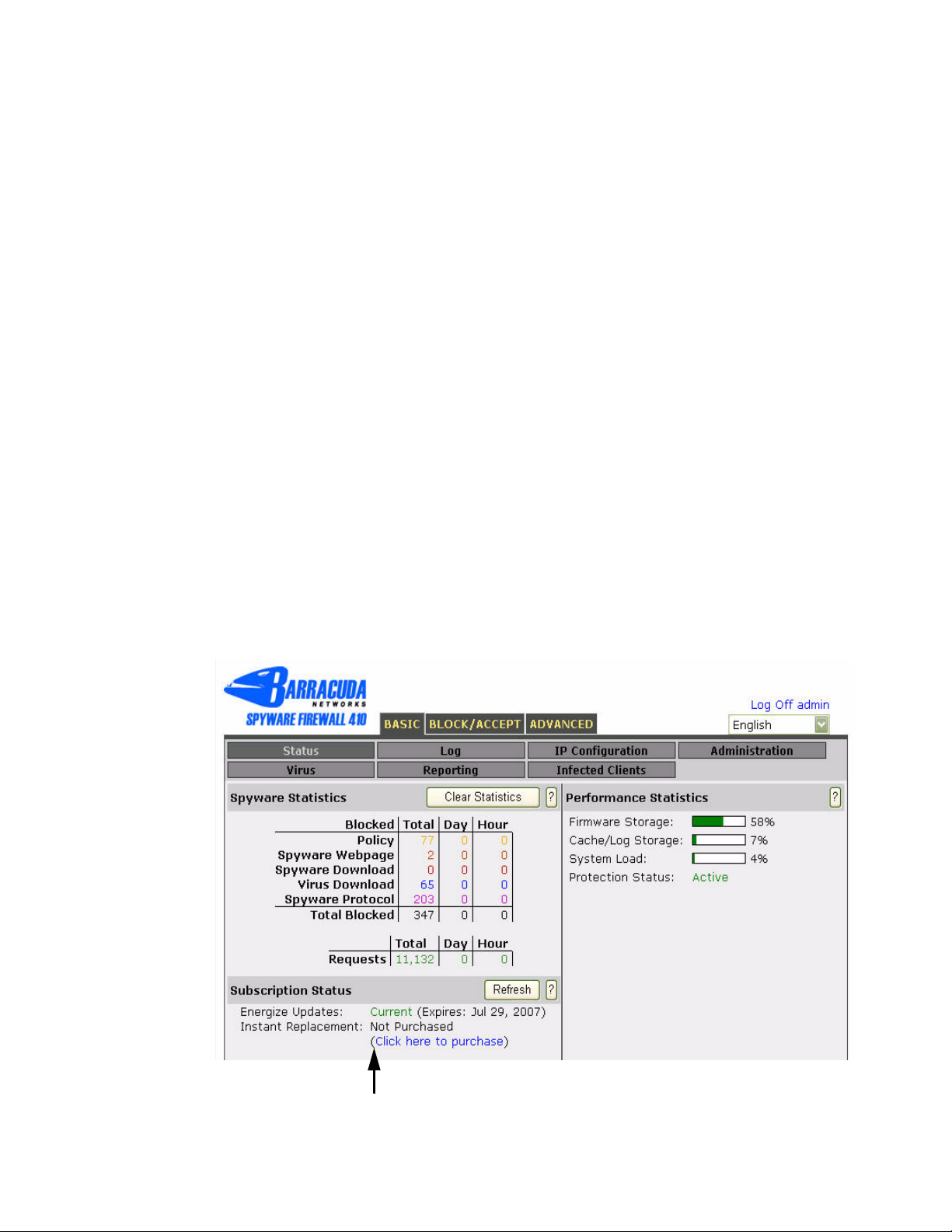
Step 7. Verify your subscription status
After you install the Barracuda Web Filter, your Energize Update and Instant Replacement
subscriptions are most likely active. However, it is important you verify the subscription status so
your Barracuda Web Filter can continue to receive the latest virus and spyware updates from
Barracuda Central. The Energize Update service is responsible for downloading these virus and
spyware definitions to your Barracuda Web Filter.
To check your subscription status:
Refresh. A message displays once the download is complete.
1. Select BASIC > Status.
2. From the Subscription Status section, verify that the word Current appears next to Energize
Updates
and Instant Replacement Service (if purchased).
Figure 2.2 shows the location of the Subscription Status section.
Figure 2.2: Subscription Status
22 Chapter 2: Getting Started
Page 23

Administrator’s Guide
Click to activate your
subscription
3. Enable your subscription:
3a. Click the Activate link as shown in Figure 2.3. The product activation displays in a
new browser window.
Figure 2.3: Location of the Activate Link
3b. In the Product Activation window, fill in the required fields and click Activate. A
confirmation page opens to display the terms of your subscription.
3c. After a few minutes, from the Barracuda Web Filter administration interface, click
Refresh in the Subscription Status section of the BASIC > Status page. The status of
your subscriptions displays as Current.
Note: If your subscription status does not change to Current, or if you have trouble filling out
Product Activation window, call your Barracuda Networks sales representative.
the
Step 8. Update the definitions
To update the spyware, virus, and category definitions:
1. Select ADVANCED > Energize Updates.
2. Check to see if the current version is the same as the latest version available for spyware, virus,
and category definitions. If the definitions are up-to-date, proceed to Step 9.
3. Click Update for each of these sections.
4. In the spyware, virus, and category definition sections, select Hourly or Daily for Automatically
Update. The recommended setting is Hourly for both spyware and virus definitions, and Daily
for category definition.
5. Click Save Changes.
Step 9. Integrate the Barracuda Web Filter into your network
Table 2.2 describes how to integrate the Barracuda Web Filter into your network depending on your
deployment type.
Table 2.2: Integrating your Barrauda System into your Network
Deployment Type Next Step
Inline pass-through Connect your Barracuda Web Filter to your network. For more
information, see Connecting the Barracuda Web Filter to your
network on page 24.
Forward proxy Configure your clients’ HTTP proxy settings from their browser to
access the Internet. See your Web browser’s technical
documentation for further information.
Installing the Barracuda Web Filter 23
Page 24

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
Step 10. Test and adjust the Barracuda Web Filter
After connecting your Barracuda Web Filter to the network, verify connectivity. Open your Web
browser from a machine on your network. If you cannot browse the Web, review the installation steps
to make sure your Barracuda Web Filter is properly configured and connected to your corporate
firewall and network switch.
If you can browse the Web without any issues, you are ready to adjust the settings on the Barracuda
Web Filter. The most common adjustment to make is to create filters that determine what traffic and
applications the Barracuda Web Filter blocks and accepts. For more information about the available
filters, refer to Monitoring the Barracuda Web Filter on page 38.
Go to the
BLOCK/ACCEPT > IP Block/Exempt page, and use the IP and Port Exemption section to
bypass scanning or filtering for clients or targeted servers. To avoid accidentally specifying a broader
than intended exemption range, be sure to apply the proper subnet mask.
Connecting the Barracuda Web Filter to your network
To connect the Barracuda Web Filter to your network:
1. Connect the Ethernet cable from your corporate firewall to the WAN port on the front panel of
the Barracuda Web Filter. This step may require disconnecting your internal network switch
from the corporate firewall.
Note: A crossover cable may be needed if your corporate firewall does not have a switchable
port and therefore cannot switch between RX and TX. Another solution is to place a switch
between the corporate firewall and the Barracuda Web Filter.
Note:
Ethernet bridge between the WAN and LAN ports.
You do not need to configure the WAN port. The Barracuda Web Filter creates an
24 Chapter 2: Getting Started
Page 25
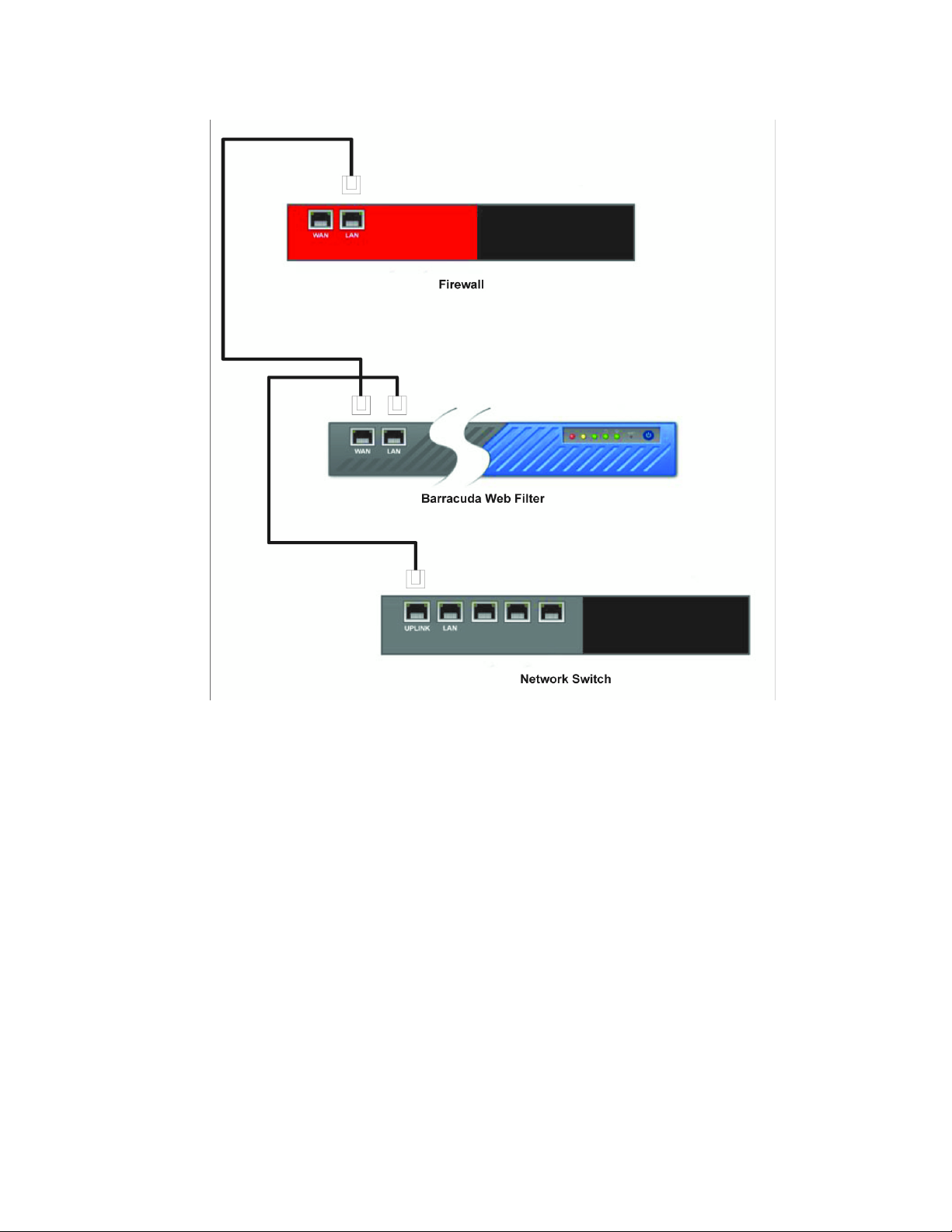
Figure 2.4: Connecting the Barracuda Web Filter to your Network
Administrator’s Guide
2. Connect an Ethernet cable from the LAN port on the Barracuda Web Filter to your internal
network switch Uplink port (if one is available).
Note: If your switch records the MAC address of an external device, make sure you delete all
pre-existing MAC address records from your switch.
3. Select BASIC > IP Configuration page in the administration interface, and set the Operating
Mode setting to Active.
Note: A hard bypass feature is available on the Barracuda Web Filter 310 and higher models.
4. If necessary, set up static routes on the BASIC > IP Configuration page. Setting up static routes is
often necessary in complex networks so the Barracuda Web Filter knows the proper way to
route traffic on your network.
Static routes are generally necessary to enable the Barracuda Web Filters to protect any client
machines that are at IP addressed outside of the native subnet of the Barracuda Web Filter.
For example, if the Barracuda Web Filter is assigned an IP address of 172.20.0.6 and a subnet mask
of 255.255.255.0 and uses the default gateway at 172.20.0.9, you will need to create a static route to
reach client machines in the 192.168.2.x range with a Netmask value of 255.255.255.0. The Gateway
Address should be inside 172.20.0.x.
Installing the Barracuda Web Filter 25
Page 26

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
Advanced Deployments
This section describes advanced installation topics that may apply to your Barracuda Web Filter
deployment.
Web Cache Control Protocol (WCCP) deployment
All Barracuda Web Filter models 410 and above can be deployed as WCCP cache engines on a
network with a WCCP capable core routing platform.
Because the WCCP control router or switch transparently redirects content requests, end users need
not configure browsers to use the Barracuda Web Filter as an HTTP proxy. This deployment means
that the Barracuda Web Filter is not inline and is not configured as a forward proxy.
In addition to compatibility with other WCCP capable routers, the Barracuda Web Filter supports
Cisco v1 and v2 routers. Enabling WCCP on your Barracuda Web Filter allows you to take full
advantage of your WCCP capable Cisco router’s ability to provide for failover and load balancing for
multiple Barracuda Web Filters connected to the router in a proxy configuration. For large
installations requiring high availability and fault tolerance, this is an attactive deployment option.
Note: WCCP allows Cisco routers/switches to forward non-http traffic to web cache servers, but the
Barracuda Web Filter only accepts http traffic (port 80) in this configuration. WCCP also allows
multiple Cisco routers to be connected to the same web cache server. The Barracuda Web Filter does
not support this feature and can only be connected to one WCCP router/switch. However, as always,
multiple Barracuda Web Filters can be connected to a single router/switch.
Note that NTLM and Kerberos authentication mechanisms will not work when the Barracuda Web
Filter is deployed using WCCP because they both require that the Barracuda Web Filter be a trusted
host in the Windows Domain and that it receive traffic directly from the users (as a proxy). In WCCP
deployments, the Barracuda Web Filter receives outgoing traffic via the Cisco Router.
Figure 2.5 shows this deployment method with two Barracuda Web Filters configured as WCCP
cache engines.
26 Chapter 2: Getting Started
Page 27
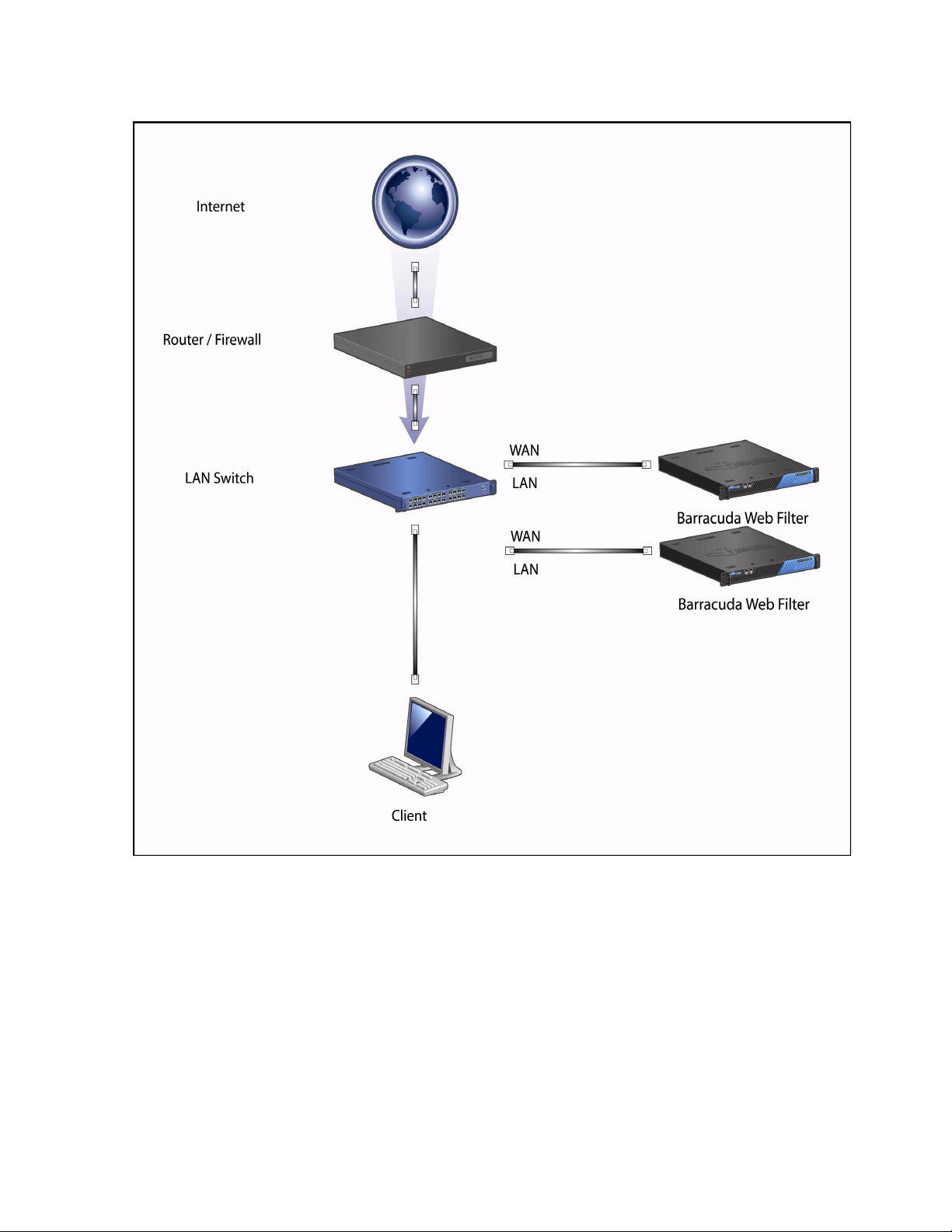
Figure 2.5: WCCP Deployment
Administrator’s Guide
Inline pass-through with pre-existing proxy deployment
Another deployment type that is much less common than either Inline mode or Forward Proxy mode
is using the Barracuda Web Filter as an inline device that uses a pre-existing proxy server on your
network. This type of deployment is not recommended because it breaks the following features of the
Barracuda Web Filter:
• Infection reports do not display the IP addresses of infected clients.
• Infected clients cannot be automatically redirected to the Barracuda Spyware Removal Tool.
Advanced Deployments 27
Page 28

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
To resolve these issues, we recommend that you remove your pre-existing proxy server and deploy
the Barracuda Web Filter inline as described in
The Barracuda Web Filter can be placed on the client or the server side of the existing proxy server.
If the existing proxy server is performing user authentication, then the Barracuda Web Filter must be
placed on the server side of the proxy. In this deployment, the Barracuda Web Filter detects all
network traffic. The proxy server connects directly to the Barracuda Web Filter LAN port. This
connection may require a crossover cable. No special port or IP address is required. The Barracuda
Web Filter scans for all inbound and outbound HTTP traffic from the proxy server. All outbound
traffic on other ports is scanned for normal spyware communication. However, since the proxy server
will most likely hide user identity, the Barracuda Web Filter cannot apply any user, group or IP based
policies.
Figure 2.6 illustrates this deployment type.
Alternately, the Barracuda Web Filter can be placed inline on the client side of the existing proxy
server. The LAN Switch can be connected to the LAN port of the Barracuda Web Filter and the WAN
port of the Barracuda Web Filter can be connected to the Proxy Server. This will ensure that the
Barracuda Web Fitler can identify users before the requests are proxied. In this configuration, you
may have to ensure that the Barracuda Web Filter passes client IP addresses through to the proxy
server or that the proxy server can handle requests coming from the Barracuda Web Filter’s IP
address. However, this configuration may not work when the proxy server is performing strong user
authentication.
Inline pass-through (transparent) mode on page 11.
The placement of your pre-existing proxy server and its functionality will have an impact on the
Barracuda Web Filter deployment. Some configurations may require technical assistance from
Barracuda Technical Support.
28 Chapter 2: Getting Started
Page 29
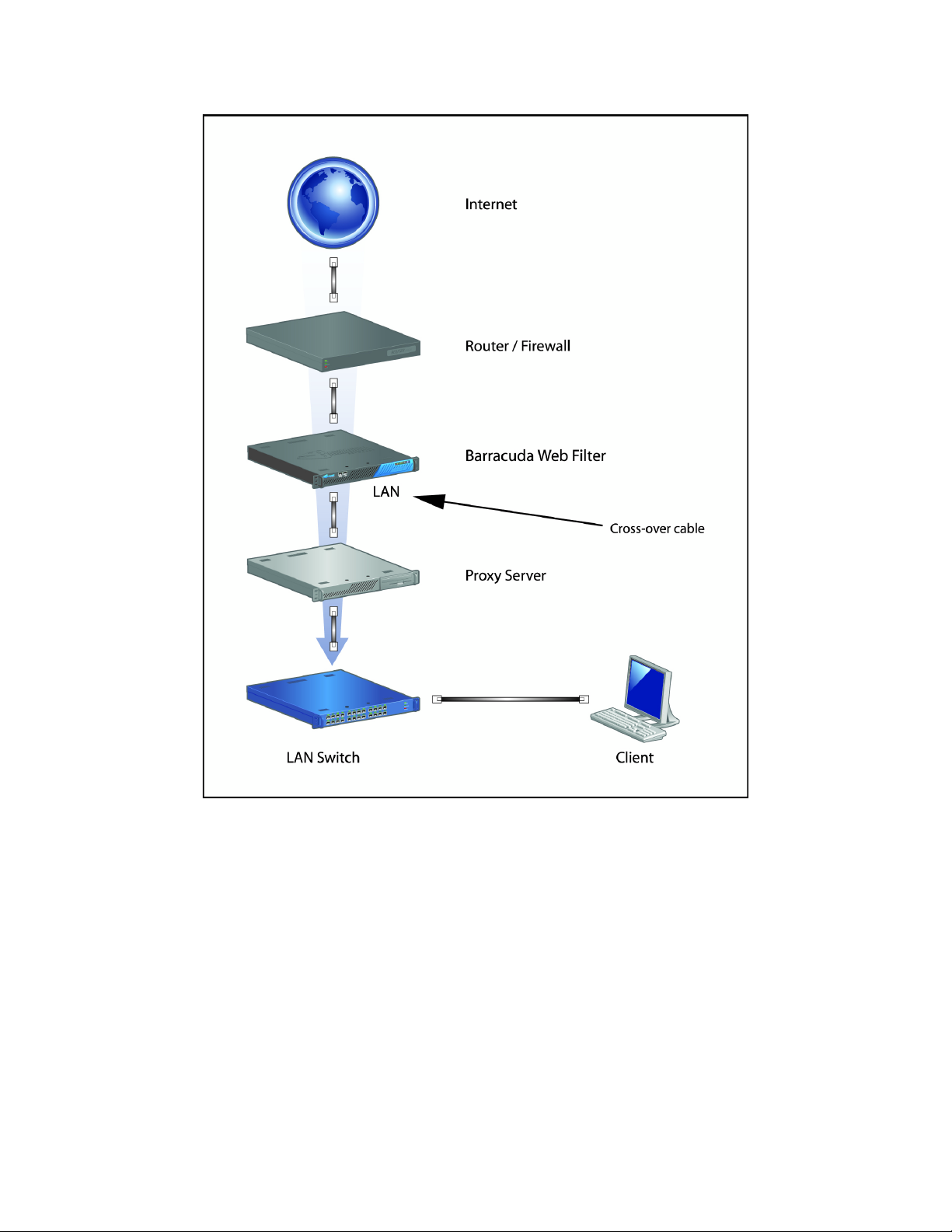
Figure 2.6: Inline Passthrough with Pre-existing Proxy Server Deployment
Administrator’s Guide
Connecting inline to your network with a pre-existing proxy
server
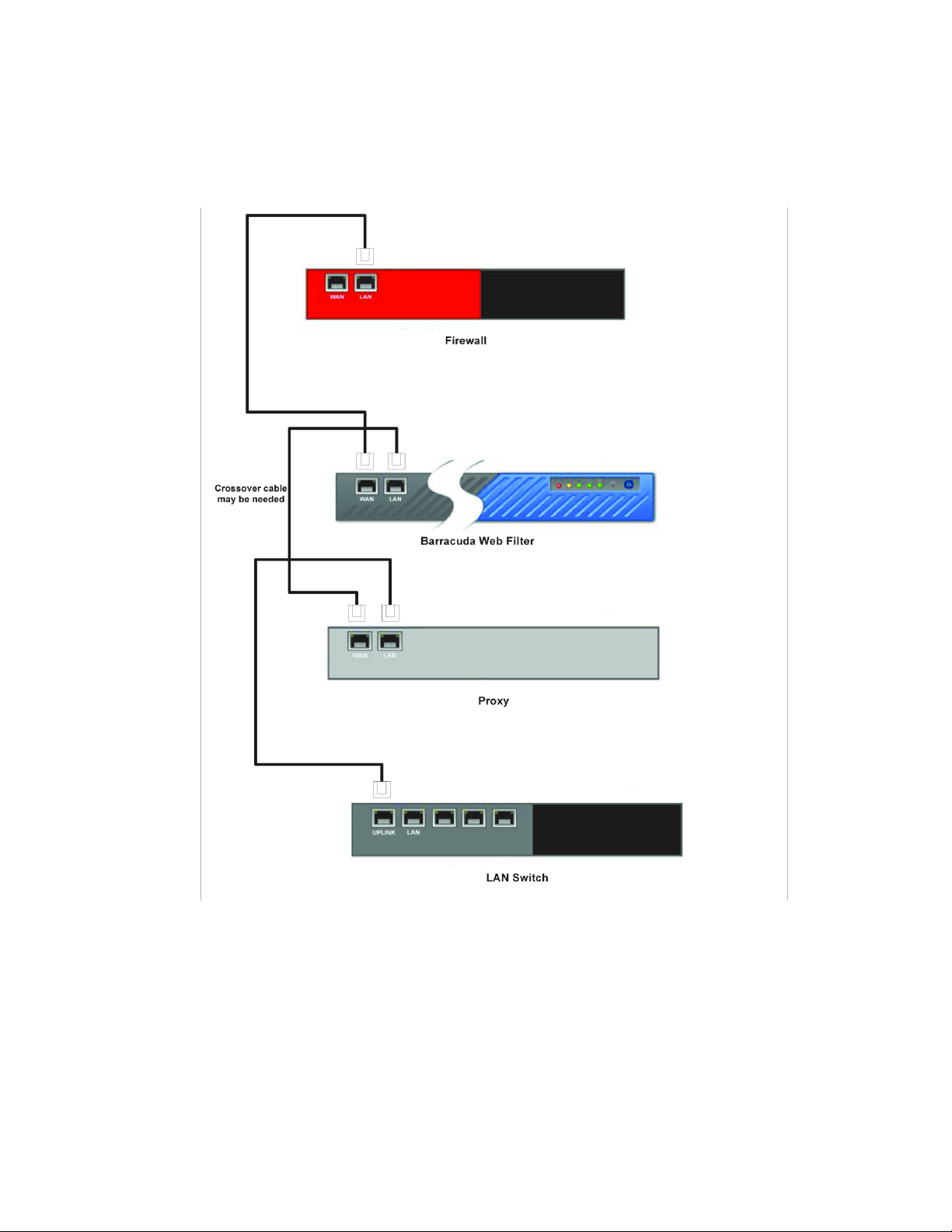
To set up the Barracuda Web Filter inline with your existing proxy server, place the proxy server
between the Barracuda Web Filter and your internal network switch.
If you have a proxy server, most HTTP requests are routed from your internal network through the
proxy server to the Barracuda Web Filter. When a Web site responds, the responding traffic goes
through the Barracuda Web Filter, which filters any spyware and viruses before allowing the traffic
to go through the proxy server and back to the clients.
The Barracuda Web Filter has been tested with Microsoft ISA and Squid proxy servers.
Advanced Deployments 29
Page 30
Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
To connect your Barracuda Web Filter and existing proxy server to your network:
1. Connect your LAN port from your proxy server to the Uplink port of your internal network
switch.
Figure 2.7: Proxy Behind the Barracuda Web Filter
2. Connect the Ethernet cable from your WAN port of your proxy server to the LAN port on the
front panel of the Barracuda Web Filter.
Note: A crossover cable may be needed if your corporate firewall does not have a switchable
port and therefore cannot switch between RX and TX. Another solution is to place a switch
between the corporate firewall and the Barracuda Web Filter.
Note:
Ethernet bridge between the WAN and LAN ports.
3. Connect an Ethernet cable from the WAN port on the Barracuda Web Filter to the LAN port on
You do not need to configure the WAN port. The Barracuda Web Filter creates an
your firewall.
30 Chapter 2: Getting Started
Page 31

Administrator’s Guide
4. Select BASIC > IP Configuration page in the administration interface, and set the Operating
Mode setting to Active
Advanced Deployments 31
Page 32

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
32 Chapter 2: Getting Started
Page 33

Administrator’s Guide
Chapter 3
Configuring, Monitoring, and Managing the
Barracuda Web Filter
This chapter describes the configuration, monitoring, and management tasks you can perform from
the administration interface. The following topics are covered:
Configuring the Barracuda Web Filter................................................ 34
Monitoring the Barracuda Web Filter .................................................38
Managing the Barracuda Web Filter ...................................................43
Generating System Reports ................................................................ 47
For more detailed information about a specific page in the Web interface, view the online help by
clicking the question mark icon on the right side of the interface.
33
Page 34

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
Configuring the Barracuda Web Filter
This section describes the configuration tasks you can perform from the administration interface. This
section covers the following topics:
Configuring system IP information..................................................... 34
Controlling access to the Web interface.............................................. 34
Controlling access to the Web interface.............................................. 34
Customizing the appearance of the Web interface .............................. 34
Changing the language of the Web interface ......................................35
Setting the time zone of the system....................................................35
Enabling and disabling virus protection.............................................. 35
Enabling and disabling Web caching ..................................................35
Setting up a syslog server to centrally monitor system logs ............... 35
Configuring system IP information
The BASIC > IP Configuration page contains the network configuration for your Barracuda Web
Filter. Use this page to specify the following settings:
• System IP address, Subnet Mask and Default Gateway. The default gateway is the IP address of
the next outbound hop from the device. The Barracuda Web Filter sends all egress traffic to the
default gateway via the WAN port. For forward proxy deployment, use the same default
gateway that is used by hosts on the network.
• Primary and Secondary DNS servers
• Operating Mode (Active/Audit/Hard Bypass)
• Client IP Visibility for HTTP—Specifies whether the Barracuda Web Filter is to expose client
IP Addresses in egress HTTP traffic. If you change this setting to No, all HTTP traffic passing
through the system will have the IP address of the Barracuda Web Filter.
• Enable proxy on WAN. Setting to “No” protects against WAN-side proxy requests if the
Barracuda Web Filter is deployed outside of the corporate firewall.
• Cisco Web Cache Control Protocol (WCCP), supporting WCCP v1 and v2.
• Static routes
• Domain Configuration for alerts, notifications, messages and reports.
Controlling access to the Web interface
Use the BASIC > Administration page to perform the following tasks:
• Specify the IP addresses or subnet mask for the systems that you want to access the
administration interface. All other systems will be denied access.
• Change the password of the administration account.
• Change the port used to access the administration interface.
• Change the length of time users can be logged into the administration interface (default is 60
minutes).
Customizing the appearance of the Web interface
Use the ADVANCED > Appearance page to customize the default images used on the administration
interface and in the email quarantine messages sent to users. This tab is only displayed on the
Barracuda Web Filter 410 and above.
34 Chapter 3: Configuring, Monitoring, and Managing the Barracuda Web Filter
Page 35

Changing the language of the Web interface
You can change the language of the administration interface by selecting a language from the dropdown menu in the upper right corner of the window. Supported languages include Chinese, Japanese,
Spanish, French, and others.
The language you select is only applied to your individual administration interface. No other user’s
administration interface is affected.
Setting the time zone of the system
Use the BASIC > Administration page to set the time zone of your Barracuda Web Filter.
Enabling and disabling virus protection
Use the BASIC > Virus Checking page to turn off virus scanning, which is not recommended. By
default, virus scanning is automatically enabled, and the virus definitions are updated on a regular
basis (hourly by default) using Energize Updates.
When virus scanning is enabled, all traffic processed by the Barracuda Web Filter is scanned for
viruses and any traffic that contains a virus is blocked.
Administrator’s Guide
Enabling and disabling Web caching
Use the ADVANCED > Caching page to enable or disable Web caching. Web caching can accelerate
Web page downloads and also reduce the traffic on the external network connections. For these
reasons, we recommend you keep Web caching enabled.
Setting up a syslog server to centrally monitor system logs
Use the ADVANCED > Syslog page to specify a server to which the Barracuda Web Filter sends syslog
data. Syslog is a standard UNIX/Linux tool for sending remote system logs and is available on all
UNIX/Linux systems.
Syslog servers are also available for Windows platforms from a number of free and premium vendors.
Barracuda Networks has tested with a Windows freeware syslog server from Kiwi Enterprises
(www.kiwisyslog.com). Barracuda Networks makes no guarantees that your Barracuda Web Filter
will be completely compatible with this syslog server.
Syslog support is not available on the Barracuda Web Filter 210.
Configuring the Barracuda Web Filter 35
Page 36

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
Advanced Configuration Topics
This section details advanced configuration settings. It is recommended that you contact Barracuda
Networks Technical Support before implementing.
Setting up linked management
Use the ADVANCED > Linked Management page to link (“cluster”) multiple Barracuda Web Filters
together so they can synchronize configuration settings. Clustered systems can be geographically
dispersed and do not need to be co-located on the same network. Linked management does not
provide load-balancing functionality. The Barracuda Web Filter uses ports 8001 and 8002 to
synchronize configuration between linked systems.
Linked Management is available on the Barracuda Web Filter 410 and above.
Note:
systems together. For example, if you have multiple network segments that each require different
policies, it may be better to provide a dedicated, unlinked Barracuda Web Filter for each segment. This
way you can configure each Barracuda Web Filter without the configuration settings propagating to
the other systems.
Some network environments may not be suitable to linking multiple Barracuda Web Filter
To link two or more Barracuda Web Filter devices, see the online help on the ADVANCED > Linked
Management
page.
Data propagated to the linked systems
Linking systems together not only makes it easier to manage multiple Barracuda Web Filters, but it
also provides 100 percent redundant coverage of the propagated data. Table 3.1 identifies the data that
is propagated to the other clustered systems when a new system joins.
Table 3.1: Data Propagated Between Linked Systems
Propagated Data Data Not Propagated
System settings (global and domain)
configured through the Administration
interface. This includes the block/accept
filters.
• System IP configuration (IP address, subnet mask, default
gateway, and DNS server) configured on the BASIC > IP
Configuration page.
• System password and time zone as configured on the
BASIC > Administration page.
• Cluster hostname and cluster local host map configured on
the ADVANCED > Linked Management page.
Switching a system to standby mode
You can also use the ADVANCED > Linked Management page to switch a clustered system from
Active to Standby mode. When a system is in standby mode, it does not synchronize its configuration
with the other active systems in the cluster.
We recommend switching a system to Standby mode when you need to:
• Upgrade the firmware of all systems in a cluster. If a system is part of a cluster, we recommend
changing the system’s mode to Standby before you upgrade its firmware, and then repeat this
36 Chapter 3: Configuring, Monitoring, and Managing the Barracuda Web Filter
Page 37

Administrator’s Guide
process on each system in the cluster. Once the firmware on each system has been upgraded, you
can then change the mode on each system back to Active.
Changing a linked systems to standby mode before upgrading prevents a system on a more
recent firmware version from trying to synchronize its configuration with a system on an earlier
firmware version.
• Perform maintenance that requires a system to be powered down or disconnected from your
network. For example, if you need to physically move a Barracuda Web Filter you should
change its mode to Standby so the other systems in the cluster do not try to synchronize their
configuration while the system is down.
Advanced Configuration Topics 37
Page 38

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
Monitoring the Barracuda Web Filter
This section describes the monitoring tasks you can perform from the administration interface and
from the front panel of the Barracuda Web Filter. This section covers the following topics:
Viewing performance statistics ...........................................................38
Understanding the indicator lights ......................................................39
Viewing the traffic log........................................................................40
Viewing the application log................................................................40
Viewing the warned activity list ......................................................... 41
Automating the delivery of system alerts and notifications ................41
Viewing a list of infected clients ........................................................ 41
Viewing system tasks ......................................................................... 41
Viewing performance statistics
The BASIC > Status page provides an overview of the health and performance of your Barracuda Web
Filter:
• Filtering statistics (such as threats blocked by the filtering rules, blocked visits to known
spyware Web sites, blocked downloads of spyware or viruses) for the past day and hour, as well
as total statistics since installation (or last reset) of the Barracuda Web Filter.
• Performance statistics, such as CPU temperature, throughput, system load and TCP connections.
Statistics displayed in red signify that the value exceeds the normal threshold.
• System Load represents an estimate of CPU and disk load on the system. It is not unusual
for the load to reach 100%, especially when the incoming queue is large. 100% load for long
periods of time indicates trouble in the system, especially if the incoming queue continues
to increase in size. If the System Load exceeds 50% for more than 5 minutes, the
Operating Mode will automatically shift to “Safe Mode” (unless the Barracuda Web Filter
is deployed in WCCP configuration) and will pass traffic without filtering or logging until
normal operation can be resumed. See the online help for the
information.
• Throughput gauges the total volume of traffic that is passing through the Web Filter and is
measured in Mb/s.
• TCP Connections indicates number of concurrent TCP connections used by the Barracuda
Web Filter to service Internet traffic, reported as a percentage of the maximum number of
connections that can be handled by the system. A single user typically requires 1 to 1.5
active TCP connections; however, the peak number of TCP connections can significantly
increase with heavy Web browsing or with bandwidth-intensive Internet applications such
as voice, instant messaging (IM) or other streaming media applications.
• Subscription status for Energize Updates, Instant Replacement, and Premium Support.
• Lists of infected clients blocked Web requests.
• A set of bar graphs that illustrate an hourly breakdown of requests made by your users in the last
24 hours, and a set of bar graphs that illustrate a daily breakdown of requests made by your users
in the last 30 days. Both sets of graphs illustrate the following data:
• Number of requests blocked
• Number of requests received
• Number of kilobytes per second used by the requests allowed
Each bar graph is accompanied by two Top Ten lists: domains represented in the graph and Web
content categories represented in the graph.
BASIC > Status page for more
38 Chapter 3: Configuring, Monitoring, and Managing the Barracuda Web Filter
Page 39

Understanding the indicator lights
The Barracuda Web Filter has five indicator lights on the front panel that blink when the system
processes HTTP traffic.
Figure 3.1 displays the location of each of the lights.
Figure 3.1: Indicator Lights
Table 3.2 describes each indicator light.
Administrator’s Guide
Table 3.2: Description of the Indicator Lights
Light Color Description
Spyware Access Red Blinks when the Barracuda Web Filter blocks
installed spyware from accessing external sites.
Spyware Download Yellow Blinks when the Barracuda Web Filter blocks a
spyware application from being downloaded.
Traffic Green Blinks when the Barracuda Web Filter processes
traffic.
Disk Green Blinks during disk activity.
Power Green Displays a solid green light when the system is
powered on.
Monitoring the Barracuda Web Filter 39
Page 40

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
Viewing the traffic log
The BASIC > Web Log page displays a list of system logs for your Barracuda Web Filter. On a regular
basis you should view the Log page to monitor the Web and spyware traffic (both HTTP and nonHTTP) passing through your Barracuda Web Filter. Use this page to view the following information
about each entry in this log:
• Date and time the Barracuda Web Filter processed the request.
• IP address of the client that originated the request.
• IP address of the requested Web site or application
• Type of file contained in the request, as designated by the HTTP header. For a list of common
MIME types, see the help page for the MIME Type Blocking feature.
• The user name or group that sent the request.
• The action taken by the Barracuda Web Filter.
• The reason the Barracuda Web Filter performed the action.
• Detailed information about the actions.
• Number of bytes of data processed for this request.
You can perform the following operations on the
• Apply filters to locate specific log entries
• Refresh to update the log. The most recent entry is at the top of the list.
• Clear the log to purge all the current entries.
Viewing the application log
The BASIC > Application Log page displays the log of all the Web application traffic processed by the
Barracuda Web Filter. Use this page to view the following information about each entry in this log:
• Date and time the Barracuda Web Filter blocked the request.
• IP address of the client that initiated the request.
• Action taken by the Barracuda Web Filter
• Reason the Barracuda Web Filter performed the action.
• Name of the application that was blocked.
• Number of bytes of data processed for the request.
You can perform the following operations in the
• Customize the appearance of the display
• Update the contents displayed in this page
• Clear the contents of the traffic log itself
• Filter the entries displayed
• Export the displayed entries to a CSV file
Log page:
Application Log page:
40 Chapter 3: Configuring, Monitoring, and Managing the Barracuda Web Filter
Page 41

Viewing the warned activity list
The BASIC > Warned Activity page displays the list of all warned activity that is in effect for the client
machines protected by the Barracuda Web Filter system. Use this page to view the following
information about each entry in this log:
• Date and time that the warned activity was triggered.
• IP address of the client machine that triggered the warned activity.
• Username that triggered the warned activity. This field indicates whether the user account is
from the local, LDAP or NTLM realm.
• The URL that the user was attempting to access when the warned activity triggered.
• The domain names that triggered the warned activity.
• The Web content category that triggered the warned activity.
Administrator’s Guide
You can perform the following operations in the
• View details about a warned activity
• Clear all warned activity
A warned activity remains in effect until it times out (as configured in the
Configuration
Activity
deleted, the user must click the Proceed button to re-acknowledge the warning and then access the
Web site again.
page) or until it is explicitly removed by the Administrator (using the BASIC > Warned
page). If the user attempts to access the same Web site after a warned activity times out or is
Warned Activity page:
BLOCK/ACCEPT >
Automating the delivery of system alerts and notifications
Use the BASIC > Administration page to configure the Barracuda Web Filter to automatically email
system alerts to the email addresses you specify.
System alerts notify you when:
• Your Energize Update subscription is about to expire
• New virus definitions are available
• New firmware updates are available
• Your system is low on disk space
Viewing a list of infected clients
Use the BASIC > Infection Activity page to view a list of clients that are infected with a virus or
spyware.
You can use this list to determine if any of your clients have been prompted to use the Barracuda
Spyware Removal Tool. By default, this tool is disabled but you can enable the tool on the
BLOCK/ACCEPT > Block Messages page.
Viewing system tasks
The ADVANCED > Task Manager page provides a list of tasks that are in the process of being
performed and also displays any errors encountered when performing these tasks.
Monitoring the Barracuda Web Filter 41
Page 42

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
Some of the tasks that the Barracuda Web Filter tracks include:
• Linked management setup
• Configuration restoration
If a task takes a long time to complete, you can click
Cancel next to the task name and then run the
task at a later time when the system is less busy.
The Task Errors section will list an error until you manually remove it from the list. The errors are not
phased out over time.
42 Chapter 3: Configuring, Monitoring, and Managing the Barracuda Web Filter
Page 43

Managing the Barracuda Web Filter
This section describes how to manage and maintain your Barracuda Web Filter using the
administration interface.This section covers the following topics:
Backing up and restoring system configuration ..................................43
Updating the Barracuda Web Filter firmware ..................................... 43
Updating the spyware, virus, and category definitions ....................... 43
Replacing a failed system................................................................... 44
Reloading, restarting, and shutting down the system..........................44
Using the built-in troubleshooting tools.............................................. 44
Rebooting the system in recovery mode ............................................. 45
Backing up and restoring system configuration
The ADVANCED > Backup page lets you back up and restore the configuration of your Barracuda Web
Filter. You should back up your system on a regular basis in case you need to restore this information
on a replacement Barracuda Web Filter or in the event your current system data becomes corrupt.
If you are restoring a backup file on a new Barracuda Web Filter that is not configured, you need to
assign your new system an IP address and DNS information on the
Administrator’s Guide
BASIC > IP Configuration page
Note the following about the backup file:
• Do not edit backup files. Any configuration changes you want to make need to be done through
the administration interface. The configuration backup file contains a checksum that prevents
the file from being uploaded to the system if any changes are made.
• You can safely view a backup file in Windows WordPad or Microsoft Word. You should avoid
viewing backup files in Windows Notepad because the file can become corrupted if you save the
file from this application.
• The following information is not included in the backup file:
• System password
• System IP information
•DNS information
Updating the Barracuda Web Filter firmware
Use the ADVANCED > Firmware Update page to manually update the firmware version of the system
or revert to a previous version. The only time you should revert back to an old firmware version is if
you recently downloaded a new version that is causing unexpected problems. In this case, call
Barracuda Networks Technical Support before reverting back to a previous firmware version.
If you have the latest firmware version already installed, the Download Now button is disabled.
Note:
should apply new firmware versions during non-business hours.
Applying a new firmware version results in a temporary loss of service. For this reason, you
Updating the spyware, virus, and category definitions
Use the ADVANCED > Energize Updates page to manually update the current spyware, virus, and
category definitions, as well as change the interval at which the Barracuda Web Filter checks for
updates. Energize Updates provide the Barracuda Web Filter with the latest definitions.
Managing the Barracuda Web Filter 43
Page 44

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
We recommend that the Automatically Update setting for your spyware and virus definitions be set
to Hourly so your Barracuda Web Filter receives the latest definitions as soon as new threats are
identified by Barracuda Central.
Replacing a failed system
Before you replace your Barracuda Web Filter, use the tools provided on the ADVANCED >
Troubleshooting
In the event that a Barracuda Web Filter system fails and you cannot resolve the issue, customers that
have purchased the Instant Replacement service can call technical support and receive a new unit
within 24 hours.
After receiving the new system, ship the failed Barracuda Web Filter back to Barracuda Networks at
the address below. Barracuda Networks Technical Support can provide details on the best way to
return the unit.
page to try to resolve the problem.
Barracuda Networks
3175 S. Winchester Blvd
Campbell, CA 95008
Note:
system, restore the backup file from the old system onto the new system, and then manually configure
the new system’s IP information on the
data, refer to
To set up the new Barracuda Web Filter so it has the same configuration as your old failed
BASIC > IP Configuration page. For information on restoring
Backing up and restoring system configuration on page 43.
Reloading, restarting, and shutting down the system
Use the System Reset/Shutdown section on the BASIC > Administration page to shutdown, reset, and
reload the Barracuda Web Filter.
Shutting down the system powers off the unit. Restarting the system reboots the unit. Reloading the
system re-applies the system configuration.
You can also reset the system by pressing the RESET button on the front panel of the system. The
following actions occur:
• Reboots the system
• Resets the firmware version to the factory setting
Do not press and hold the RESET button for longer than a few seconds. Doing so changes the IP
address of the system. Pushing and holding the RESET button for 5 seconds changes the default IP
address to
10.1.1.200.
192.168.1.200. Holding the button for 12 seconds changes the IP address to
Using the built-in troubleshooting tools
The ADVANCED > Troubleshooting page provides various tools that help troubleshoot network
connectivity issues that may be impacting the performance of your Barracuda Web Filter.
For example, you can test the connection between the Barracuda Web Filter to Barracuda Central to
make sure it can successfully download the latest virus and spyware definitions. You can also ping
devices from the Barracuda system, perform a traceroute from the Barracuda system to a destination
server, and other tasks.
44 Chapter 3: Configuring, Monitoring, and Managing the Barracuda Web Filter
Page 45

Rebooting the system in recovery mode
If your Barracuda Web Filter experiences a serious issue that impacts its core functionality, you can
use diagnostic and recovery tools that are available at the reboot menu to return your system to an
operational state.
Before you use the diagnostic and recovery tools, do the following:
Administrator’s Guide
• Use the built-in troubleshooting tools on the
ADVANCED > Troubleshooting page to help
diagnose the problem.
• Perform a system restore from the last known good backup file.
• Contact Barracuda Networks Technical Support for additional troubleshooting tips.
As a last resort, you can reboot your Barracuda Web Filter and run a memory test or perform a
complete system recovery, as described in this section.
To perform a system recovery or hardware test:
1. Connect a monitor and keyboard directly to your Barracuda Web Filter.
2. Reboot the system by doing one of the following:
• In the Web interface: Go to the BASIC > Administration page, navigate to the System
Reload/Shutdown section, and click
Restart.
• At the front panel of the Barracuda Web Filter: Press the Power button on the front panel to
turn off the system, and then press the Power button again to turn the system on.
The Barracuda splash screen displays with the following three boot options:
Barracuda
Recovery
Hardware_Test
3. Use your keyboard to select the desired boot option, and press the Enter key.
You must select the boot option within three seconds after the splash screen appears. If you do
not select an option within three seconds, the Barracuda Web Filter starts up in Normal mode
(first option).
For a description of each boot option, refer to Reboot options on page 46.
Note:
keys.
To stop a hardware test, reboot your Barracuda Web Filter by pressing the Ctrl-Alt-Del
Managing the Barracuda Web Filter 45
Page 46

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
Reboot options
Table 3.3 describes the options available at the reboot menu.
Table 3.3: Reboot Options
Reboot Options Description
Barracuda Starts the Barracuda Web Filter in the normal (default) mode. This
Recovery Displays the Recovery Console, where you can select the following
option is automatically selected if no other option is specified within the
first three seconds of the splash screen appearing.
options:
• Perform filesystem repair—Repairs the file system on XFS-based
Barracuda Web Filter. Select this option only if the serial number on
your Barracuda Web Filter is below 24364; otherwise select the
Perform Full System Re-image option.
• Perform full system re-image—Restores the factory settings on
your Barracuda Web Filter and clears out the configuration
information. Select this option if the serial number on your Barracuda
Web Filter is 24364 or above.
• Enable remote administration—Turns on reverse tunnel that
allows Barracuda Networks Technical Support to access the system.
Another method for enabling remote administration is to click
Establish Connection to Barracuda Central on the ADVANCED
>Troubleshooting page.
• Run diagnostic memory test—Runs a diagnostic memory test from
the operating system. If problems are reported when running this
option, we recommend running the Hardware_Test option next.
Hardware_Test Performs a thorough memory test that shows most memory related
errors within a two-hour time period. The memory test is performed
outside of the operating system and can take a long time to complete.
Reboot your Barracuda Web Filter to stop the hardware test.
46 Chapter 3: Configuring, Monitoring, and Managing the Barracuda Web Filter
Page 47

Generating System Reports
Use the BASIC > Reports page to choose from 40 different system reports that can help you keep track
of activity performed by the Barracuda Web Filter. You can either generate a system report ondemand or configure the Barracuda Web Filter to automatically generate the system reports on a daily,
weekly or monthly basis and email the reports to specific email addresses. Reports can be anchored
on user-activity, content or actions. For detailed descriptions of the system reports, see the online help
for the
BASIC > Reports page.
Administrator’s Guide
Generating System Reports 47
Page 48

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
48 Chapter 3: Configuring, Monitoring, and Managing the Barracuda Web Filter
Page 49

Administrator’s Guide
Chapter 4
Managing Users and Groups
This chapter explains how to manage users and groups on your Barracuda Web Filter. This chapter
covers the following topics:
Overview ............................................................................................ 50
Creating local users and groups .......................................................... 51
Integrating with a user authentication service.....................................52
Viewing and managing accounts ........................................................56
49
Page 50

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
Overview
The Barracuda Web Filter distinguishes between two basic classes of the users who access Web sites
and Web applications from client machines that it has been configured to protect: local users and
domain users.
You can apply filtering and blocking policies as well as exception rules to both classes of users.
You can also view the following information about both classes of users:
• Account View
•Traffic Log
• Applications Log
• Warned Activity
• Reports output
Local users are shown as anonymous until they authenticate in the Barracuda Web Filter system by
providing login information in order to proceed to a blocked or warned Web page or application.
Domain users are shown as anonymous until they become authenticated in the Barracuda Web Filter
system by providing credentials to their respective authentication service that has been integrated with
the Barracuda Web Filter. Authenticated domain users are shown by username, client IP address, and
group membership.
In some cases, you may need to create local accounts as well as enable your Barracuda Web Filter to
look up domain accounts. For example, if your regular employees have LDAP accounts but contract
employees do not, then you might need to create local accounts for the contractor employees.
About local users
Local users that you define by listing their existing usernames in the USERS/GROUPS > New Users
page. The Barracuda Web Filter authenticates these users from its local database. To apply Web
filtering policies (and exception rules to your filtering policies) to multiple local users, you can assign
local users to local groups that you define in
You can also create IP subnet-based groups, locally define groups of users who access
Web sites and Web applications from client machines within specific ranges of IP
addresses. Define IP subnet-based groups of local users in the
page.
For more information, see Creating local users and groups on page 51.
About domain users
The Barracuda Web Filter can authenticate domain users using your existing authentication service.
You can integrate the Barracuda Web Filter with any of the following types authentication servers:
the USERS/GROUPS > Local Groups page.
USERS/GROUPS > IP Groups
• LDAP
• NTLM
Doing so enables you to apply Web filtering policies and policy exceptions to your domain users
without having to re-create local accounts for these users.
For more information, see Integrating with a user authentication service on page 52.
50 Chapter 4: Managing Users and Groups
Page 51

Creating local users and groups
This section describes how to create local accounts that you can assign to exception policies. This
section contains the following topics:
Creating local user accounts ............................................................... 51
Creating local groups..........................................................................51
Creating IP address groups................................................................. 51
Creating local user accounts
Use the USERS/GROUPS > New Users page to create new users that the Barracuda Web Filter will
authenticate locally from its database. If you want users to be authenticated using your existing user
authentication service instead, go to the
your authentication server.
Authentication Services page and enter the information for
Administrator’s Guide
Note:
the default admin account to log into the administration interface.
If you want a new user account to be a member of a group, be sure the group already exists. If you
need to create a group, go to the
Local user accounts cannot be used to log into the administration interface. You can only use
USERS/GROUPS > Local Groups page.
Creating local groups
Use the USERS/GROUPS > Local Groups page to create groups for your local users. The most
common reason to create a group is so you can apply an exception policy to multiple users at the same
time instead of to individual users.
To create a group, enter the group name in the provided field and click Add.
To assign an existing user to this group, go to the
account that you want to join the group. A user can belong to multiple groups.
Creating IP address groups
The USERS/GROUPS > IP page lets you create a group for a single or range of IP addresses. The most
common reasons to create an IP group is to apply an exception policy to:
• Multiple users on the same subnet. In this case, enter the subnet mask for the subnet in the
provided field.
• A static IP address. In this case, enter the static IP address in the provided field.
Accounts View page and click Edit next to the
After you enter the IP address or subnet mask and click
the IP group on the
BLOCK/ACCEPT > Exceptions page.
Add, you can assign an exception policy to
Creating local users and groups 51
Page 52

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
Integrating with a user authentication service
You can integrate the Barracuda Web Filter with your existing authentication server to gain the
following benefits:
Web filtering policy exceptions can be applied to domain users—If you do not integrate with your
LDAP or NTLM authentication server, you can apply filtering policy exceptions only to local users
and groups that you create in the
Domain users can be authenticated in the Barracuda Web Filter—LDAP users are authenticated
when credentials are provided in order to proceed to a blocked or warned Web page or application.
NTLM users are authenticated by single sign-on access against the NTLM authentication service.
Authenticated domain users are known by username, client IP address, and group membership:
USERS/GROUPS tab.
• Usernames and client IP addresses of authenticated domain users are visible in the
page (with the exception of NTLM users), the Log page, the Applications Log page, and in
View
Reports output.
• Group membership information about authenticated domain users is available by opening the
Lookup facility (accessed by clicking Lookup in the
using the Active Directory User/Group section of that window.
USERS/GROUPS > Exceptions page) and
Domain users that are unauthenticated in the Barracuda Web Filter appear as anonymous
users.
Use the USERS/GROUPS > Authentication Services page to integrate the Barracuda Web Filter with
your existing authentication server:
Enabling LDAP domain user authentication.......................................52
Enabling NTLM domain user authentication...................................... 55
Enabling LDAP domain user authentication
If your network uses a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) or Active Directory
authentication (AD) server, your LDAP domain users can use the LDAP or AD authentication service
to become authenticated in the Barracuda Web Filter system.
To enable LDAP user authentication
Account
To enable LDAP domain user authentication against your LDAP or AD server, go to the
USERS/GROUPS > Authentication page. In the LDAP tab, provide information about connecting to
the LDAP server, binding to the LDAP server, and the encryption type.
About the optional Barracuda DC Agent software
If your LDAP directory authenticates against a domain controller running Windows Server 2003
with Service Pack 1 (SP1) or Windows Server 2008, you can enable the Barracuda Web Filter to
recognize your LDAP domain users whenever those users authenticate against the LDAP domain
controller server. To enable the Barracuda Web Filter to transparently track user login activity in your
Windows domains, install the Barracuda DC Agent software on each relevant LDAP domain
controller server, and configure each relevant Barracuda Web Filter to communicate with each DC
agent.
52 Chapter 4: Managing Users and Groups
Page 53

Administrator’s Guide
If the Session Manager, which communicates with the DC Agent, is not enabled on the Barracuda
Web Filter (or cannot be supported by your domain controller), LDAP domain users will surf
anonymously until providing credentials for a second time in order to proceed past a blocked or
warned Web activity page.
Communication between the LDAP domain controller servers and the Barracuda Web Filters in your
network enable each Barracuda Web Filter to transparently track user login activity in your LDAP
domains. This communication is managed by the following software components:
Domain controller audit policies—The local audit policies are configured so that the domain
controller audits user log-on and log-off activity and generates an “account log-on event” when a
domain user account is authenticated on this domain controller.
Barracuda DC Agent—The DC Agent is a Windows service that you install and configure on each
LDAP domain controller server that runs Windows Server 2003 with SP1 or Windows Server 2008.
Configuration of the service consists of specifying the Barracuda Web Filter devices with which the
DC Agent is to communicate. Each instance of this service maintains a record of all the users that have
been authenticated by the LDAP server.
The DC Agent service appears in the Windows
Control Panel > Services window. You can manually
stop and start the DC Agent like all other Windows services. You should configure this service to start
automatically. The DC Agent service does not impact the performance of your domain controller.
Session Manager—This is the process that you enable and configure on the USERS/GROUPS >
Authentication
page of each Barracuda Web Filter that is to communicate with the DC Agent running
on the domain controller. This process has the capability to communicate with multiple DC Agents.
Note:
Moreover, no additional authentication services can be configured in the Barracuda Web Filter system
if NTLM authentication is enabled.
The Barracuda DC Agent software should not be installed on your NTLM domain controller.
The DC Agent performs the following functions:
• Enables the Barracuda Web Filter to track authenticated accounts in your LDAP directory.
• Keeps a record of all the users that have been authenticated by the domain controller, and then
provides this information to the Session Manager on the Barracuda Web Filter. The Session
Manager polls the DC Agent every 15 seconds to obtain the list of authenticated users. You can
change the polling frequency (“Synchronization Interval”) for each domain controller on the
USERS/GROUPS > Configuration page.
• All logging information for the DC Agent is stored in the
C:\Program Files\Barracuda directory. The DC Agent creates a new log file daily
in the
DCDebug.txt log, which is located
or when the size of existing log file exceeds 100 KB, whichever comes first. For example,
DCDebug.txt_2 is automatically created when the size of DCDebug.txt_1 reaches 100 KB or
passes the daily marker. Only the last ten log files are kept on the system. After the tenth log is
created, the first log file is overwritten with new data. For this reason, it is important to view the
time stamp on the log file to determine which file contains the latest data. Logging information
is also shown on the Logs tab of the Barracuda DC Agent management interface. To open this
interface, go to your domain controller and select
Start > Programs > Barracuda > DCAgent.
The following figure illustrates this process.
Integrating with a user authentication service 53
Page 54

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
Barracuda Web Filter
Session
Manager
DC Agent
End User
Primary Domain Controller
⌦
Restricted Content
1. A user logs into their domain and is authenticated by the domain controller.
2. The DC Agent keeps a record of the newly authenticated user.
3. The Session Manager polls the DC Agent (every 15 seconds by default) and retrieves the latest
list of authenticated users.
4. The user attempts to access a Web site that is blocked by the Barracuda Web Filter. The
Barracuda Web Filter prompts the user to enter account information that will allow them to
override the filter.
5. The user enters account information, and the Barracuda Web Filter determines if an exception
policy exists that allows the account to override the filter. If an exception policy does exist, the
user is allowed to access the previously blocked content.
Installing the Barracuda DC Agent on your domain controllers
To download, install, and configure the Barracuda DC Agent software, go to the USERS/GROUPS >
Configuration
Agent.
page and navigate to the DC Agent Configuration section for the link to install the DC
Exempting selected LDAP domain users from filtering
To exempt LDAP domain users from policy engine processing, go to the USERS/GROUPS >
Configuration
be entered. One use for this feature is to prevent traffic caused by script logic or other background
users from appearing in the traffic log.
page and navigate to the DC Agent Configuration section where exempt user names can
54 Chapter 4: Managing Users and Groups
Page 55

Enabling NTLM domain user authentication
If your network uses an NT LAN Manager (NTLM) authentication server, your NTLM domain users
transparently become authenticated in the Barracuda Web Filter using their Microsoft Windows
credentials. This single sign-on (SSO) method of access control is provided by transparent proxy
authentication against the your NTLM server.
To enable transparent proxy authentication against your NTLM server, you must join the Barracuda
Web Filter to the NTLM domain as an authorized host. The process of joining the domain also
synchronizes NTLM group information from your domain controller to the Barracuda Web Filter.
Configure NTLM authentication on the
About NTLM authentication in Windows 2000 or 2003 AD domains
Windows Server 2000 with Active Directory runs the NTLM authentication protocol by default.
With Windows Server 2003, NTLM authentication is available only in a mixed mode Active
Directory domain. In a native mode Active Directory domain, Windows Server 2003 runs the
Kerberos authentication protocol.
Reasons for using an NTLM authentication server
Typical reasons for using an NTLM authentication server are listed below:
USERS/GROUPS > Authentication page NTLM tab.
Administrator’s Guide
• If you are replacing an existing forward proxy server that uses NTLM authentication with the
Barracuda Web Filter.
• If your network cannot rely on all users presenting a unique IP address.
For detailed descriptions of these scenarios, see the online help for the
Authentication
page.
USERS/GROUPS >
Requirements for using an NTLM authentication server
Before you integrate with an NTLM authentication server, verify the following requirements:
• The Barracuda Web Filter must be deployed as a forward proxy.
• No other authentication services (LDAP, Kerberos, etc.) may be configured.
• No Barracuda DC Agents may be in use on any of your domain controllers.
• You must enable the Forced Proxy Authentication option in the
Configuration
page.
USERS/GROUPS >
• Web browsers must use the Barracuda Web Filter as the HTTP proxy.
For detailed descriptions of these requirements, see the online help for the
Authentication page.
USERS/GROUPS >
Limitations when using an NTLM authentication server
The following limitations apply when using an NTLM authentication server with the Barracuda Web
Filter:
• No login override of blocked pages for NTLM domain users who encounter a block message.
• No logout option for NTLM domain users who proceed to a blocked Web page.
• NTLM domain users are not listed in the
Account View page.
• NTLM realm is not listed for users listed in the syslog output.
For detailed descriptions of these restrictions, see the online help for the
Authentication
page.
Integrating with a user authentication service 55
USERS/GROUPS >
Page 56

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
Viewing and managing accounts
The USERS/GROUPS > Account View page displays all the user accounts that have either been created
locally on your Barracuda Web Filter or which reside in your LDAP database. This page lets you view
details about each account and make the following changes to any locally created accounts:
• Edit a local account by assigning it to a group or enabling/disabling the account
• Change the password of a local account
• Delete a local account
To quickly locate a specific account, use the filter feature at the top of the page to search for specific
patterns in the account details.
56 Chapter 4: Managing Users and Groups
Page 57

Administrator’s Guide
Chapter 5
Managing Policies
This chapter explains how to manage user and group policies on your Barracuda Web Filter. This
chapter covers the following topics:
Creating block and accept filters ........................................................ 58
About the Barracuda Spyware Removal Tool ..................................... 65
57
Page 58

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
Creating block and accept filters
This section describes the BLOCK/ACCEPT tab, which provides a wide range of filters that enhance
the default spyware and virus detection capabilities of the Barracuda Web Filter.
This section contains the following topics:
Best practices .....................................................................................58
Filtering and blocking.........................................................................59
Content filtering........................................................................... 59
Application filtering ..................................................................... 60
Domain filtering........................................................................... 60
URL pattern filtering ................................................................... 60
Custom categories filtering .......................................................... 61
MIME type blocking.................................................................... 61
IP-based exemption...................................................................... 61
IP-based blocking ........................................................................ 61
Exception policies .............................................................................. 62
Block messages .................................................................................. 62
HTTPS filtering option....................................................................... 63
Testing Web site access ...................................................................... 63
Best practices
When creating block or accept filters, keep the following best practices in mind:
• You can apply domain, pattern, content, application, and MIME type blocking filters to
authenticated and unauthenticated users. Before you create or modify a filter, make sure to use
the drop-down menu on the right side of the interface to select which type of user you want the
filter applied to.
• Use exception policies (
group basis. For example, if you configure your content filters to block access to auction sites
for both authenticated and unauthenticated users but a member of your Purchasing department
requires access to these sites, you can create an exception policy that allows access to only this
individual. Exception policies are applied in the order in which they are created.
• When a user tries to access content that is blocked by one of the Barracuda Web Filter filters, the
user receives a block message that contains login fields (shown in Figure ). If you want to hide
the login fields because you have not created any exception policies that allow users to bypass
the block filter, go to the
override of block pages setting to No.
• The Barracuda Web Filter will recognize specific types of block and accept rules in the order
they are listed (from top to bottom). If conflicting rules are created, the rule listed first will be
honored. Whitelist or “allow” rules take precedence over block rules of the same type.The
different rules, configured under the
1.IP Block/Exempt
BLOCK/ACCEPT > Exceptions page) to override a filter on per-user or
BLOCK/ACCEPT > Configuration page and change the Enable login
BLOCK/ACCEPT tab, are applied in this order:
2.Applications
3.Exceptions
4.Domains
5.URL Patterns
6.Content Filter
7.MIME Type Blocking
58 Chapter 5: Managing Policies
Page 59

Block Message with Login Fields
Administrator’s Guide
Filtering and blocking
This section describes the filtering and blocking features of the Barracuda Web Filter:
• Content filtering
• Application filtering
• Domain filtering
• URL pattern filtering
• Custom categories filtering
• MIME type blocking
• IP-based exemption and blocking
Filtering and blocking policies can be applied separately to Authenticated and Unauthenticated
users. Be sure to specify this before applying the policy.
Content filtering
Use the BLOCK/ACCEPT > Content Filter page to control access to categories of Web sites that should
be blocked, warned, monitored, or allowed. When you block a category, you block all HTTP traffic
to the associated URLs in that category.
For example, http://mail.yahoo.com is categorized as a Web-based Email site. If you want to block
users from accessing their Web-based email accounts, block the Web-based Email category.
You can also use this page to turn on Safe Search mode for common Web search engines. Safe Search
prevents a Web search engine from displaying objectionable thumbnail images in search results.
Google, Yahoo, MSN, and Dogpile all allow users to control whether Safe Search mode is applied to
Creating block and accept filters 59
Page 60

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
their image searches. However, when you enable Safe Search mode through the Barracuda Web
Filter, users cannot override the setting when conducting image searches, and only filtered thumbnails
are displayed in their search results.
Application filtering
Use the BLOCK/ACCEPT > Applications page to block or allow specific Instant Messenger services
and other types of applications. For a user to download or use an application, the user’s application
needs to communicate with an external server. When you select to block an application, the Barracuda
Web Filter searches for traffic that contains data associated with an application server and then blocks
that traffic.
You can use the Applications filter as a pre-emptive measure to protect your network against
malware.
For example, you may want to block the IRC application because this type of application often
introduces BOTS into networks. BOTS are automated programs that repeatedly run specific tasks,
and malicious BOTS activity is common in IRC communications.
You can also use the application blocking feature when you hear about a virus spreading over a
specific IM service or tool. In this case, you can proactively protect your network from the infection
by blocking that particular service until the threat has been resolved.
Domain filtering
Use the BLOCK/ACCEPT > Domains page to blacklist (block), warn, monitor) or whitelist (allow)
traffic to specific domains and subdomains. Use domain whitelists to allow access to domains that
belong to categories that are generally blocked. Use domain blacklists to restrict access to domains in
addition to those specified in other filtering categories.
Tip: To control access to a domain and all its associated URLs, make sure you enter the domain
identifier. For example, www.example.com will control access only to the specific URL but
example.com will control access to all URLs under the domain.
URL pattern filtering
Use the BLOCK/ACCEPT > URL Patterns page to enter regular expressions or keyword that, if
matched to a URL, will block (blacklist), warn, monitor, or allow (whitelist) that URL. For more
information about using regular expressions, refer to Appendix B, Regular Expressions on page 79.
Examples:
• If you want to block all Web sites that contain porn in the URL, then enter porn as a blocked
pattern.
• Sometimes spyware applications use different hostnames but the same domain name so the
URLs appear to be from different hosts. In this case you can enter the domain name as a pattern
to block all URLs on that domain.
• Another example is if you want to allow access to example.com but want to block
maps.example.com. In this case, specify example.com as an allowed pattern and specify
maps.example.com as a blocked URL (see Domain filtering on page 60).
Tip: Run a test on your regular expressions with special characters before you encode them in a
pattern filter.
60 Chapter 5: Managing Policies
Page 61

Administrator’s Guide
Custom categories filtering
Use the BLOCK/ACCEPT > Custom Categories page to create a custom filter, which can consist of
the domain names or built-in Web content categories you select.
Note:
You can select a maximum of three built-in categories per custom category.
Custom categories are used in the same way as the built-in filters:
• You can apply a custom category to either authenticated or unauthenticated users.
• You can define a user- or group- specific exception rule to a custom category policy.
After you define a custom category, allow between five and ten minutes for the Barracuda Web Filter
to compile and then fully activate the new category. To verify that a newly created custom category
is active, you can use the Content Filter Lookup
facility in the Content Filter page, as described in
the online help for the Custom Categories page.
MIME type blocking
Use the BLOCK/ACCEPT > MIME Blocking page to specify standard MIME types that you want to
block.
Note:
Many organizations choose to block Internet radio and streaming media because they add load to the
internal network, as well as executable files because they can install viruses and various other
malware. To block Internet radio, which uses MPEG (.mpg, mpega, or .abs) or Microsoft audio (.wav)
files, enter audio/x-mpeg or audio/x-wav as blocked MIME types.
To block streaming media, which uses MPEG video, enter video/mpeg or video/x-msvideo as blocked
MIME types.
Web sites that are whitelisted are not subject to the MIME type blocking rules you create.
To block access to executables (.exe), enter application/octet-streamapplications as a blocked MIME
type.
IP-based exemption
If you want to exempt certain clients or sub-networks from all filtering (including spyware filtering),
you can use the
BLOCK/ACCEPT > IP Block/Exempt page and specify the source IP address for those
clients under IP and Port Exemptions. For example, if you want to exempt an executive’s client
machine from all filtering, you can do so using the IP address of the client. Similarly, if you want to
exempt certain external devices (such as trusted servers outside the protected network), from all
filtering, you can specify the destination IP address and specific port under IP and Port Exemptions.
Exempted IP addresses will bypass the following block filters:
• Content filtering
• IM blocking
• All types of download blocking
Note:
Barracuda Web Filter will still detect spyware activity on these clients.
The IP addresses you add to the exempted list will not be protected against spyware, but the
IP-based blocking
If you want to block certain clients or sub-networks from all access, you can use the BLOCK/ACCEPT
> IP Block/Exempt
Exemptions. For example, if you want to block traffic from a suspicious client machine or email
page and specify the source IP address for those clients under IP and Port
Creating block and accept filters 61
Page 62

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
servers or internal web servers, you can do so using the IP address of the client. Similarly, if you want
to block certain external devices, y can specify the destination IP address and specific port under IP
and Port Exemptions.
Note:
on request destination are not applied.
When the Barracuda Web Filter is deployed as a forward proxy, IP block/exempt rules based
Exception policies
Use the BLOCK/ACCEPT > Exceptions page to create exception policies for specific users or groups
so they can override the filters that block access to applications and Web sites.
For example, by default the Barracuda Web Filter uses a content filter to block access to game playing
sites. If you want to allow users to access gaming sites during non-business hours, create an allow
exception policy between the hours of 18:00 (6pm) and 8:00 (8am) for the Content Filter category and
Game Playing subcategory.
Or you may want to create an exception policy that allows a subset of your users to access content
that is blocked for other users. For example, some organizations configure their content filters to
block access to Job Search and Career Development sites like Monster.com. However, your Human
Resources department may require access to such sites. In this case, you can create an allow exception
for the Job Search and Career Development subcategory and assign the policy to your Human
Resources group.
You can create exception policies for the following types of filters:
• Domains
•URL Patterns
• MIME type blocking
• Content
• Applications
• All Web traffic
When a user tries to access content that is blocked by one of the Barracuda Web Filter filters, the user
receives a block message containing login fields (shown in Figure ). If an exception policy exists for
the blocked content, the user can enter the username and password for the account that was assigned
to the exception policy. After the user enters the correct account information, the Barracuda Web
Filter applies the effective policy for that authenticated user.
Note:
access to all Web Traffic for Unauthenticated users but allow access to selected web-sites, first create
the block exception and then create the allow exception. You can also reorder exception rules once
they are created.
Exceptions are applied in the order in which they are created. For example, if you want to block
Block messages
When the Barracuda Web Filter blocks access to a Web site, it displays a message that informs the
user why that site is being blocked. The Barracuda Web Filter blocks a Web site if it contains spyware,
a virus, content that has been blocked, or a blacklisted URL. Use the
Messages
• Select the language that the block message is displayed in for all users.
• Customize the message in case the default text is insufficient.
page to perform the following tasks:
BLOCK/ACCEPT > Block
62 Chapter 5: Managing Policies
Page 63

HTTPS filtering option
By default, the Barracuda Web Filter does not block or scan SSL (https://) traffic because most Web
traffic is non-encrypted. However, you do have the option to enable HTTPS traffic filtering.
Scope of HTTPS traffic filtering
When the HTTPS traffic-filtering option is enabled, filters created using the following mechanisms
will block HTTPS traffic:
Content filters (both built-in and custom)—When HTTPS filtering is enabled, content filters
specified in the
Domain-based filters—When HTTPS filtering is enabled, filters specified in the Domains page will
also filter HTTPS traffic.
URL pattern filters—When HTTPS filtering is enabled, filters specified in the URL Patterns page will
also filter HTTPS traffic for which the hostname portion of the URL matches.
Blocking exceptions—When HTTPS filtering is enabled, HTTPS traffic is included in any exceptions
to the following types of blocking-exception rules that are in effect:
• All Web traffic
• Content category filters (both built-in and custom)
• Domain-based filters
• URL pattern filters
Content Filters page and the Custom Categories page will also filter HTTPS traffic.
Administrator’s Guide
Limitations for HTTPS traffic filtering
When the HTTPS traffic-filtering option is enabled, the following limitations apply:
• If HTTPS access is denied, the user is not presented with a block page because the traffic is
blocked at Layer 3.
• If HTTPS access to a particular domain name is denied, HTTPS access to any subdomain of
that same domain will also be denied for the same users.
• For any filtering policy that is set to Warn, the HTTPS request is Blocked instead.
• For URL pattern filters, only the unencrypted portion of the requested HTTPS URL can be
checked for a match with the specified pattern.
To enable the HTTPS traffic-filtering option
To expand your HTTP filtering policies to include HTTPS filtering, enable the HTTPS Filtering
option in the
Note:
an HTTPS session are communicating with an IP address and will not be blocked. In this situation, the
HTTPS Web site IP address remains in the DNS client resolver cache (as well as in the DNS table on
the core router or domain controller) until the DNS request time-to-live (TTL) expires. This can take up
to a day or two, depending upon how the HTTPS sites configure TTL.
BLOCK/ACCEPT > Configuration page.
Immediately after you enable this option, any client machines that had previously established
Testing Web site access
To determine if a specific Web site is allowed or blocked, based on the filters you set up, go to the
BLOCK/ACCEPT > Browse Test page to perform a URL test.
Creating block and accept filters 63
Page 64

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
Enter the URL in the field provided, and click Go. If the Web site appears in the display area on that
page, then your users will be able to access the site. If you receive a message that the Web site has
been blocked, then your users will not be able to access the site.
It is recommended that you make a list of the sites you want to block and allow, and then use the
Browse Test page to test each URL and verify the filters have been set up correctly.
The
Browse Test feature only works for http:// sites.
64 Chapter 5: Managing Policies
Page 65

About the Barracuda Spyware Removal Tool
The Barracuda Spyware Removal Tool performs a comprehensive scan of your computer for any
traces of spyware or other malware. This scan is very thorough and takes several minutes to complete.
After the analysis is complete, you can remove all the malware and traces of malware that have been
found.
The Barracuda Spyware Removal Tool detects and removes many small traces, cookies, potential
spyware files, and temporary files from your computer. Although these files are normally harmless,
removing them can cause some Web sites to malfunction, and it is generally not appropriate that the
Barracuda Web Filter block them at the network level. As such, the Barracuda Spyware Removal
Tool may identify potential files for removal from your computer that are not blocked at the network
level by the Barracuda Web Filter.
For maximum security, complete removal of these files from your computer is recommended.
Administrator’s Guide
Use the Infection Warning Threshold
field to configure whether your users are prompted to run the
Barracuda Spyware Removal Tool when spyware is detected on their system. By default, the
Barracuda Spyware Removal Tool is disabled.
Note:
Address Translation (NAT) environments because the Barracuda Web Filter uses the IP address to
identify an infected system. As a result, if one system becomes infected with spyware, then all systems
in the NAT environment are prompted to use the Barracuda Spyware Removal Tool regardless of their
infection status. This issue can occur when you deploy the Barracuda Web Filter with a pre-existing
proxy server.
We recommend that you keep the Infection Warning Threshold field set to 0 in Network
Enabling the Barracuda Spyware Removal Tool
To enable users to run the Barracuda Spyware Removal Tool:
1. Clear the Infection Activity log so users are not prompted to run the Barracuda Spyware
Removal Tool based on old infection activity data or false positives. To clear the log, go to the
BASIC > Infection Activity page and click Clear.
2. On the BLOCK/ACCEPT > Configuration page, and enter a value greater than 0 in the Infection
War ning Threshold
the value of this field, the user is prompted to run the Barracuda Spyware Removal Tool. The
user can then select to run the tool immediately or postpone running the tool until the following
day.
3. (Optional) Create a dedicated fully qualified hostname for the Barracuda Spyware Removal
Tool:
field. When the number of infection activities on a user’s system exceeds
3a. In the Dedicated Removal Tool Hostname field, enter a custom fully qualified
hostname for the tool.
3b. Add the custom hostname to your DNS server with the following resolving IP address:
172.27.72.27.
4. Click Save Changes.
About the Barracuda Spyware Removal Tool 65
Page 66

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
66 Chapter 5: Managing Policies
Page 67

Generating system reports
Use the BASIC > Reports page to choose from 40 different system reports that can help you keep track
of activity performed by the Barracuda Web Filter. You can either generate a system report ondemand or configure the Barracuda Web Filter to automatically generate the system reports on a daily,
weekly or monthly basis and email the reports to specific email addresses. Reports can be anchored
on user-activity, content or actions. For detailed descriptions of the system reports, see the online help
for the
BASIC > Reports page.
Administrator’s Guide
Chapter 6
Reporting
67
Page 68

Barracuda Web Filter Release 3.3
68 Chapter 6: Reporting
Page 69

Administrator’s Guide
Appendix A
About the Barracuda Web Filter Hardware
This appendix provides hardware information for the Barracuda Web Filter. The following topics are
covered:
Front panel of the Barracuda Web Filter............................................. 70
Back panel of the Barracuda Web Filter............................................. 74
Hardware compliance ......................................................................... 77
69
Page 70

Barracuda Web Filter Release 3.3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Front panel of the Barracuda Web Filter
Figure A.1, Figure A.2, and Figure A.3 illustrate the front panels for each model.
Barracuda Web Filter 210, 310, and 410
Figure A.1: Barracuda Web Filter 210, 310, and 410 Front Panel
Table A.1: Front Panel Descriptions for the Barracuda Web Filter models 210, 310 and 410
Diagram Location Component Name Description
1 WAN port Port for WAN connection
2 LAN port Port for LAN connection
3 Spyware Activity Displays spyware activity
4 Spyware or Virus Downloads Displays download activity
5 Web Activity Displays normal Web traffic
6 Hard Disk Displays hard disk activity
7 System Power Displays system power
8 Reset Button Resets the Barracuda Web Filter
9 Power Button Powers the Barracuda Web Filter
on or off
70 Appendix A: About the Barracuda Web Filter Hardware
Page 71

Barracuda Web Filter 610
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
15
11
12
13
14
10
Figure A.2: Barracuda Web Filter 610 Front Panel
Table A.2: Barracuda Web Filter 610 Front Panel Descriptions
Administrator’s Guide
Diagram Location Component Name Description
1 Hard Disk Drive #1 Location of #1 hard disk drive
2 Hard Disk Drive Inactivity Displays the hard disk is inactive
3 Hard Disk Drive Activity Displays the hard disk drive is
active
4 Hard Disk Drive #2 Location of #2 hard disk drive
5 Hard Disk Drive Inactivity Displays the hard disk is inactive
6 Hard Disk Drive Activity Displays the hard disk drive is
active
7 Spyware Activity Displays spyware activity
8 Spyware or Virus Downloads Displays spyware or virus
downloads
9 Internet Activity Displays normal Internet activity
10 WAN port Port for WAN connection
11 Hard Disk Displays hard disk activity
12 System Power Displays system power
13 LAN Port Port for LAN connection
14 Reset Button Resets the Barracuda Web Filter
15 Power Button Powers the Barracuda Web Filter
on or off
Front panel of the Barracuda Web Filter 71
Page 72

Barracuda Web Filter Release 3.3
3
2
1
4
5
6
7
9
8
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
Barracuda Web Filter 810 and 910
.
Figure A.3: Barracuda Web Filter 810 and 910 Front Panel
Table A.3: Barracuda Web Filter 810 and 910 Front Panel Descriptions
Diagram Location Component Name Description
1 Hard Disk Drive Locks Location of #1 hard disk drive
2 Hard Disk Drive #2 Location of #2 hard disk drive
3 Hard Disk Drive #3 Location of #3 hard disk drive
4 Hard Disk Drive #4 Location of #4 hard disk drive
5 Hard Disk Drive #5 Location of #5 hard disk drive
6 Hard Disk Drive #6 Location of #6 hard disk drive
7 Hard Disk Drive #7 Location of #7 hard disk drive
8 Hard Disk Drive #8 Location of #8 hard disk drive
9 Reset Button Resets the Barracuda Web Filter
10 WAN port Port for WAN connection
11 LAN port Port for LAN connection
12 Spyware Activity
Displays spyware activity
indicator
13 Spyware or Virus
14 Web Activity Displays normal web traffic
15 Hard Disk Activity Displays hard disk activity
72 Appendix A: About the Barracuda Web Filter Hardware
download indicator
Displays virus/spyware
download activity
Page 73

Table A.3: Barracuda Web Filter 810 and 910 Front Panel Descriptions
Diagram Location Component Name Description
16 System power Displays system power
17 Power Button Powers the Barracuda Web Filter
on or off
Administrator’s Guide
Front panel of the Barracuda Web Filter 73
Page 74

Barracuda Web Filter Release 3.3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Back panel of the Barracuda Web Filter
Figure A.4, Figure A.5, and Figure A.6 illustrate the back panels for each model.
Barracuda Web Filter 210, 310, and 410
Figure A.4: Barracuda Web Filter 210, 310, and 410 Back Panel
Table A.4: Barracuda Web Filter 210, 310, and 410 Back Component Descriptions
Diagram Location Component Name Description
1 Power Supply Connection for the AC power cord; standard
power supply
2 Fan Location of the fan
3 Mouse Port Connection for the mouse
4 Keyboard Port Connection for the keyboard
5 Serial Port Connection for the serial console cable
6 Parallel Port Connection for the parallel cable
7 Monitor Port Connection for the monitor
8 USB Ports (4) Connection for USB devices
9 LAN Port Connection for the LAN
74 Appendix A: About the Barracuda Web Filter Hardware
Page 75

Barracuda Web Filter 610
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Figure A.5 shows the back components as described in Table A.5.
Figure A.5: Barracuda Web Filter 610 Back Panel
Table A.5: Barracuda Web Filter 610 Back Component Descriptions
Diagram Location Component Name Description
1 Fan Location of the fan
Administrator’s Guide
2 Power Supply Connection for the AC power
3 Mouse Port Connection for the mouse
4 Keyboard Port Connection for the keyboard
5 USB Ports (2) Connection for USB devices
6 Serial Port Connection for the serial console
7 Monitor Port Connection for the monitor
8 LAN Port Connection for the LAN
Barracuda Web Filter 810 and 910
Figure A.6 shows the back panel components as described in Table A.6.
Figure A.6: Barracuda Web Filter 810 Back Panel
cord; standard power supply
cable
Back panel of the Barracuda Web Filter 75
Page 76

Barracuda Web Filter Release 3.3
Table A.6: Barracuda Web Filter 810 and 910 Back Component Descriptions
Diagram Location Component Name Description
1 Power Supplies (2) Connection for the AC power
cord; standard power supply
2 Mouse Port Connection for the mouse
3 Keyboard Port Connection for the keyboard
4 Not Used Not Used
5 USB ports (2) Connections for USB devices
6 Serial Port Connection for the serial
console cable
7 Monitor Port Connection for the monitor
8 Not Used Not Used
9 Not Used Not Used
10 Not Used Not Used
76 Appendix A: About the Barracuda Web Filter Hardware
Page 77

Hardware compliance
This section contains compliance information for the Barracuda Web Filter hardware.
Notice for the USA
Compliance Information Statement (Declaration of Conformity Procedure) DoC FCC Part 15: This
device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules.
Operation is subject to the following conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference received including interference that may cause
undesired operation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television
reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user in encouraged
to try one or more of the following measures:
Administrator’s Guide
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
• Plug the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that of the receiver.
• Consult the dealer on an experienced radio/ television technician for help.
Notice for Canada
This apparatus compiles with the Class B limits for radio interference as specified in the Canadian
Department of Communication Radio Interference Regulations.
Notice for Europe (CE Mark)
This product is in conformity with the Council Directive 89/336/EEC, 92/31/EEC (EMC).
Hardware compliance 77
Page 78

Barracuda Web Filter Release 3.3
78 Appendix A: About the Barracuda Web Filter Hardware
Page 79

Administrator’s Guide
Appendix B
Regular Expressions
You can use regular expressions in many of the Barracuda Web Filter features. Regular Expressions
allow you to flexibly describe text so that a wide range of possibilities can be matched.
The following caveats apply when using regular expressions:
• Be careful when using special characters such as |, *, '.' in your text. For more information, refer
to Using special characters in expressions on page 80.
• All matches are NOT case sensitive.
Table B.1 describes the most common regular expressions supported by the Barracuda Web Filter.
Table B.1: Common Regular Expressions
Expression Matches...
Operators
* Zero or more occurrences of the character immediately preceding
+ One or more occurrences of the character immediately preceding
? Zero or one occurrence of the character immediately preceding
| Either of the characters on each side of the pipe
( ) Characters between the parenthesis as a group
Character Classes
. Any character except new line
[ac] Letter 'a' or letter 'c'
[^ac] Anything but letter 'a' or letter 'c'
[a-z] Letters 'a' through 'z'
[a-zA-Z.] Letters 'a' through 'z' or 'A' through 'Z' or a dot
[a-z\-] Letters 'a' through 'z' or a dash
\d Digit, shortcut for [0-9]
\D Non-digit, shortcut for [^0-9]
\a Digit, shortcut for [0-9]
\w Part of word: shortcut for [A-Za-z0-9_]
\W Non-word character: shortcut for [^\w]
\s Space character: shortcut for [ \n\r\t]
\S Non-space character: shortcut for [^\s]
Miscellaneous
^ Beginning of line
79
Page 80

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
Table B.1: Common Regular Expressions
Expression Matches...
$ End of line
\b Word boundary
\t Tab character
Using special characters in expressions
The following characters have a special meaning in regular expressions and should be prepended by
a backward slash ( \ ) when you want them interpreted literally:
Table B.2: Special Characters
. $
[(
] )
\|
*^
?@
Examples
Table B.3 provides some examples to help you understand how regular expressions can be used.
Table B.3: Regular Expressions
Example Matches...
viagra viagra, VIAGRA or vIaGRa
d+ One or more digits: 0, 42, 007
(bad|good) letters 'bad' or matches the letters 'good'
^free letters 'free' at the beginning of a line
v[i1]agra viagra or v1agra
v(ia|1a)gra viagra or v1agra
v\|agra v|agra
v(i|1|\|)?agra vagra, viagra, v1agra or v|agra
\*FREE\* *FREE*
\*FREE\* V.*GRA *FREE* VIAGRA, *FREE* VEHICLEGRA, etc
80 Appendix B: Regular Expressions
Page 81

Limited warranty
Barracuda Networks, Inc., or the Barracuda Networks, Inc. subsidiary or authorized Distributor
selling the Barracuda Networks product, if sale is not directly by Barracuda Networks, Inc.,
("Barracuda Networks") warrants that commencing from the date of delivery to Customer (but in case
of resale by a Barracuda Networks reseller, commencing not more than sixty (60) days after original
shipment by Barracuda Networks, Inc.), and continuing for a period of one (1) year: (a) its products
(excluding any software) will be free from material defects in materials and workmanship under
normal use; and (b) the software provided in connection with its products, including any software
contained or embedded in such products will substantially conform to Barracuda Networks published
specifications in effect as of the date of manufacture. Except for the foregoing, the software is
provided as is. In no event does Barracuda Networks warrant that the software is error free or that
Customer will be able to operate the software without problems or interruptions. In addition, due to
the continual development of new techniques for intruding upon and attacking networks, Barracuda
Networks does not warrant that the software or any equipment, system or network on which the
software is used will be free of vulnerability to intrusion or attack. The limited warranty extends only
to you the original buyer of the Barracuda Networks product and is non-transferable.
Administrator’s Guide
Appendix C
Limited Warranty and License
Exclusive remedy
Your sole and exclusive remedy and the entire liability of Barracuda Networks under this limited
warranty shall be, at Barracuda Networks or its service centers option and expense, the repair,
replacement or refund of the purchase price of any products sold which do not comply with this
warranty. Hardware replaced under the terms of this limited warranty may be refurbished or new
equipment substituted at Barracuda Networks option. Barracuda Networks obligations hereunder are
conditioned upon the return of affected articles in accordance with Barracuda Networks then-current
Return Material Authorization ("RMA") procedures. All parts will be new or refurbished, at
Barracuda Networks discretion, and shall be furnished on an exchange basis. All parts removed for
replacement will become the property of the Barracuda Networks. In connection with warranty
services hereunder, Barracuda Networks may at its discretion modify the hardware of the product at
no cost to you to improve its reliability or performance. The warranty period is not extended if
Barracuda Networks repairs or replaces a warranted product or any parts. Barracuda Networks may
change the availability of limited warranties, at its discretion, but any changes will not be retroactive.
IN NO EVENT SHALL BARRACUDA NETWORKS LIABILITY EXCEED THE PRICE PAID
FOR THE PRODUCT FROM DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RESULTING FROM THE USE OF THE PRODUCT, ITS
ACCOMPANYING SOFTWARE, OR ITS DOCUMENTATION.
Exclusions and restrictions
This limited warranty does not apply to Barracuda Networks products that are or have been (a)
marked or identified as "sample" or "beta," (b) loaned or provided to you at no cost, (c) sold "as is,"
(d) repaired, altered or modified except by Barracuda Networks, (e) not installed, operated or
maintained in accordance with instructions supplied by Barracuda Networks, or (f) subjected to
abnormal physical or electrical stress, misuse, negligence or to an accident.
81
Page 82

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
EXCEPT FOR THE ABOVE WARRANTY, BARRACUDA NETWORKS MAKES NO OTHER
WARRANTY, EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR STATUTORY, WITH RESPECT TO BARRACUDA
NETWORKS PRODUCTS, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION ANY IMPLIED
WARRANTY OF TITLE, AVAILABILITY, RELIABILITY, USEFULNESS,
MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, NONINFRINGEMENT, OR
ARISING FROM COURSE OF PERFORMANCE, DEALING, USAGE OR TRADE. EXCEPT
FOR THE ABOVE WARRANTY, BARRACUDA NETWORKS PRODUCTS AND THE
SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS" AND BARRACUDA NETWORKS DOES NOT WARRANT
THAT ITS PRODUCTS WILL MEET YOUR REQUIREMENTS OR BE UNINTERRUPTED,
TIMELY, AVAILABLE, SECURE OR ERROR-FREE, OR THAT ANY ERRORS IN ITS
PRODUCTS OR THE SOFTWARE WILL BE CORRECTED. FURTHERMORE, BARRACUDA
NETWORKS DOES NOT WARRANT THAT BARRACUDA NETWORKS PRODUCTS, THE
SOFTWARE OR ANY EQUIPMENT, SYSTEM OR NETWORK ON WHICH BARRACUDA
NETWORKS PRODUCTS WILL BE USED WILL BE FREE OF VULNERABILITY TO
INTRUSION OR ATTACK.
Software license
PLEASE READ THIS SOFTWARE LICENSE AGREEMENT ("AGREEMENT") CAREFULLY
BEFORE USING THE BARRACUDA SOFTWARE. BY USING THE BARRACUDA
SOFTWARE YOU ARE AGREEING TO BE BOUND BY THE TERMS OF THIS LICENSE. IF
YOU DO NOT AGREE TO THE TERMS OF THIS LICENSE DO NOT USE THE SOFTWARE.
IF YOU DO NOT AGREE TO THE TERMS OF THIS LICENSE YOU MAY RETURN THE
SOFTWARE OR HARDWARE CONTAINING THE SOFTWARE FOR A FULL REFUND TO
YOUR PLACE OF PURCHASE.
1. The software, documentation, whether on disk, in read only memory, or on any other media or in
any other form (collectively "Barracuda Software") is licensed, not sold, to you by Barracuda
Networks, Inc. ("Barracuda") for use only under the terms of this License and Barracuda reserves all
rights not expressly granted to you. The rights granted are limited to Barracuda's intellectual property
rights in the Barracuda Software and do not include any other patent or intellectual property rights.
You own the media on which the Barracuda Software is recorded but Barracuda retains ownership of
the Barracuda Software itself.
2. Permitted License Uses and Restrictions. This License allows you to use the Software only on the
single Barracuda labeled hardware device on which the software was delivered. You may not make
copies of the Software and you may not make the Software available over a network where it could
be utilized by multiple devices or copied. You may not make a backup copy of the Software. You
may not modify or create derivative works of the Software except as provided by the Open Source
Licenses included below. The BARRACUDA SOFTWARE IS NOT INTENDED FOR USE IN
THE OPERATION OF NUCLEAR FACILITIES, AIRCRAFT NAVIGATION OR
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS, LIFE SUPPORT MACHINES, OR OTHER EQUIPEMENT IN
WHICH FAILURE COULD LEAD TO DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR ENVIRONMENTAL
DAMAGE.
3. You may not transfer, rent, lease, lend, or sublicense the Barracuda Software.
4. This License is effective until terminated. This License is automatically terminated without notice
if you fail to comply with any term of the License. Upon termination you must destroy or return all
copies of the Barracuda Software.
5. YOU EXPRESSLY ACKNOWLEDGE AND AGREE THAT THE USE OF THE BARRACUDA
SOFTWARE IS AT YOUR OWN RISK AND THAT THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO
SATISFACTION, QUALITY, PERFORMANCE, AND ACCURACY IS WITH YOU. THE
82 Appendix C: Limited Warranty and License
Page 83

Administrator’s Guide
BARRACUDA SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS" WITH ALL FAULTS AND WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, AND BARRACUDA HEREBY DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES
AND CONDITIONS WITH RESPECT TO THE BARRACUDA SOFTWARE, EITHER
EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED OR STATUTORY, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
IMPLIED WARRANTIES AND/OR CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTIBILITY, OF
SATISFACTORY QUALITY, OF FITNESS FOR ANY APPLICATION, OF ACCURACY, AND
OF NON-INFRINGEMENT OF THIRD PARTY RIGHTS. BARRACUDA DOES NOT
WARRANT THE CONTINUED OPERATION OF THE SOFTWARE, THAT THE
PERFORMANCE WILL MEET YOUR EXPECTATIONS, THAT THE FUNCTIONS WILL
MEET YOUR REQUIREMENTS, THAT THE OPERATION WILL BE ERROR FREE OR
CONTINUOUS, OR THAT DEFECTS WILL BE CORRECTED. NO ORAL OR WRITTEN
INFORMATION GIVEN BY BARRACUDA OR AUTHORIZED BARRACUDA
REPRESENTATIVE SHALL CREATE A WARRANTY. SHOULD THE BARRACUDA
SOFTWARE PROVE DEFECTIVE, YOU ASSUME THE ENTIRE COST OF ALL NECESSARY
SERVICING, REPAIR, OR CORRECTION.
6. License. YOU EXPRESSLY ACKNOWLEDGE AND AGREE THAT YOU WILL PROVIDE
AN UNLIMITED ZERO COST LICENSE TO BARRACUDA FOR ANY PATENTS OR OTHER
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS UTILIZED IN THE BARRACUDA SOFTWARE
WHICH YOU EITHER OWN OR CONTROL.
7. Limitation of Liability. TO THE EXTENT NOT PROHIBITED BY LAW, IN NO EVENT
SHALL BARRACUDA BE LIABLE FOR PERSONAL INJURY OR ANY INCIDENTAL
SPECIAL, INDIRECT, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES WHATSOEVER, INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF PROFITS, LOSS OF DATA, BUSINESS
INTERRUPTION, OR ANY OTHER COMMERCIAL DAMAGES OR LOSSES, ARISING OUT
OF OR RELATED TO YOUR ABILITY TO USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE BARRACUDA
SOFTWARE HOWEVER CAUSED, REGARDLESS OF THE THEORY OF LIABILITY AND
EVEN IF BARRACUDA HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF DAMAGES. In no
event shall Barracuda's total liability to you for all damages exceed the amount of one hundred dollars.
8. Export Control. You may not use or otherwise export or re-export Barracuda Software except as
authorized by the United States law and the laws of the jurisdiction where the Barracuda Software
was obtained.
Energize Update Software license
PLEASE READ THIS ENERGIZE UPDATE SOFTWARE LICENSE CAREFULLY BEFORE
DOWNLOADING, INSTALLING OR USING BARRACUDA NETWORKS OR BARRACUDA
NETWORKS-SUPPLIED ENERGIZE UPDATE SOFTWARE.
BY DOWNLOADING OR INSTALLING THE ENERGIZE UPDATE SOFTWARE, OR USING
THE EQUIPMENT THAT CONTAINS THIS SOFTWARE, YOU ARE CONSENTING TO BE
BOUND BY THIS LICENSE. IF YOU DO NOT AGREE TO ALL OF THE TERMS OF THIS
LICENSE, THEN (A) DO NOT DOWNLOAD, INSTALL OR USE THE SOFTWARE, AND (B)
YOU MAY RETURN THE SOFTWARE FOR A FULL REFUND, OR, IF THE SOFTWARE IS
SUPPLIED AS PART OF ANOTHER PRODUCT, YOU MAY RETURN THE ENTIRE
PRODUCT FOR A FULL REFUND. YOUR RIGHT TO RETURN AND REFUND EXPIRES 30
DAYS AFTER PURCHASE FROM BARRACUDA NETWORKS OR AN AUTHORIZED
BARRACUDA NETWORKS RESELLER, AND APPLIES ONLY IF YOU ARE THE ORIGINAL
PURCHASER.
83
Page 84

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
The following terms govern your use of the Energize Update Software except to the extent a particular
program (a) is the subject of a separate written agreement with Barracuda Networks or (b) includes a
separate "click-on" license agreement as part of the installation and/or download process. To the
extent of a conflict between the provisions of the foregoing documents, the order of precedence shall
be (1) the written agreement, (2) the click-on agreement, and (3) this Energize Update Software
License.
License. Subject to the terms and conditions of and except as otherwise provided in this Agreement,
Barracuda Networks, Inc., or a Barracuda Networks, Inc. subsidiary (collectively "Barracuda
Networks"), grants to the end-user ("Customer") a nonexclusive and nontransferable license to use
the Barracuda Networks Energize Update program modules and data files for which Customer has
paid the required license fees (the "Energize Update Software"). In addition, the foregoing license
shall also be subject to the following limitations, as applicable:
Unless otherwise expressly provided in the documentation, Customer shall use the Energize Update
Software solely as embedded in, for execution on, or (where the applicable documentation permits
installation on non-Barracuda Networks equipment) for communication with Barracuda Networks
equipment owned or leased by Customer; Customer's use of the Energize Update Software shall be
limited to use on a single hardware chassis, on a single central processing unit, as applicable, or use
on such greater number of chassis or central processing units as Customer may have paid Barracuda
Networks the required license fee; and Customer's use of the Energize Update Software shall also be
limited, as applicable and set forth in Customer's purchase order or in Barracuda Networks' product
catalog, user documentation, or web site, to a maximum number of (a) seats (i.e. users with access to
the installed Energize Update Software), (b) concurrent users, sessions, ports, and/or issued and
outstanding IP addresses, and/or (c) central processing unit cycles or instructions per second.
Customer's use of the Energize Update Software shall also be limited by any other restrictions set
forth in Customer's purchase order or in Barracuda Networks' product catalog, user documentation or
web site for the Energize Update Software.
General Limitations. Except as otherwise expressly provided under this Agreement, Customer shall
have no right, and Customer specifically agrees not to:
i. transfer, assign or sublicense its license rights to any other person, or use the Energize
Update Software on unauthorized or secondhand Barracuda Networks equipment, and any
such attempted transfer, assignment or sublicense shall be void;
ii. make error corrections to or otherwise modify or adapt the Energize Update Software or
create derivative works based upon the Energize Update Software, or to permit third parties
to do the same; or
iii. decompile, decrypt, reverse engineer, disassemble or otherwise reduce the Energize Update
Software to human-readable form to gain access to trade secrets or confidential
information in the Energize Update Software.
Upgrades and Additional Copies. For purposes of this Agreement, "Energize Update Software" shall
include (and the terms and conditions of this Agreement shall apply to) any Energize Update
upgrades, updates, bug fixes or modified versions (collectively, "Upgrades") or backup copies of the
Energize Update Software licensed or provided to Customer by Barracuda Networks or an authorized
distributor/reseller for which Customer has paid the applicable license fees. NOTWITHSTANDING
ANY OTHER PROVISION OF THIS AGREEMENT: (1) CUSTOMER HAS NO LICENSE OR
RIGHT TO USE ANY SUCH ADDITIONAL COPIES OR UPGRADES UNLESS CUSTOMER,
AT THE TIME OF ACQUIRING SUCH COPY OR UPGRADE, ALREADY HOLDS A VALID
LICENSE TO THE ORIGINAL ENERGIZE UPDATE SOFTWARE AND HAS PAID THE
APPLICABLE FEE FOR THE UPGRADE; (2) USE OF UPGRADES IS LIMITED TO
BARRACUDA NETWORKS EQUIPMENT FOR WHICH CUSTOMER IS THE ORIGINAL END
USER PURCHASER OR LESSEE OR WHO OTHERWISE HOLDS A VALID LICENSE TO USE
THE ENERGIZE UPDATE SOFTWARE WHICH IS BEING UPGRADED; AND (3) USE OF
ADDITIONAL COPIES IS LIMITED TO BACKUP PURPOSES ONLY.
84 Appendix C: Limited Warranty and License
Page 85

Administrator’s Guide
Energize Update Changes. Barracuda Networks reserves the right at any time not to release or to
discontinue release of any Energize Update Software and to alter prices, features, specifications,
capabilities, functions, licensing terms, release dates, general availability or other characteristics of
any future releases of the Energize Update Software.
Proprietary Notices. Customer agrees to maintain and reproduce all copyright and other proprietary
notices on all copies, in any form, of the Energize Update Software in the same form and manner that
such copyright and other proprietary notices are included on the Energize Update Software. Except
as expressly authorized in this Agreement, Customer shall not make any copies or duplicates of any
Energize Update Software without the prior written permission of Barracuda Networks. Customer
may make such backup copies of the Energize Update Software as may be necessary for Customer's
lawful use, provided Customer affixes to such copies all copyright, confidentiality, and proprietary
notices that appear on the original.
Protection of Information. Customer agrees that aspects of the Energize Update Software and
associated documentation, including the specific design and structure of individual programs,
constitute trade secrets and/or copyrighted material of Barracuda Networks. Customer shall not
disclose, provide, or otherwise make available such trade secrets or copyrighted material in any form
to any third party without the prior written consent of Barracuda Networks. Customer shall implement
reasonable security measures to protect and maintain the confidentiality of such trade secrets and
copyrighted material. Title to Energize Update Software and documentation shall remain solely with
Barracuda Networks.
Indemnity. Customer agrees to indemnify, hold harmless and defend Barracuda Networks and its
affiliates, subsidiaries, officers, directors, employees and agents at Customers expense, against any
and all third-party claims, actions, proceedings, and suits and all related liabilities, damages,
settlements, penalties, fines, costs and expenses (including, without limitation, reasonable attorneys
fees and other dispute resolution expenses) incurred by Barracuda Networks arising out of or relating
to Customers (a) violation or breach of any term of this Agreement or any policy or guidelines
referenced herein, or (b) use or misuse of the Barracuda Networks Energize Update Software.
Term and Termination. This License is effective upon date of delivery to Customer of the initial
Energize Update Software (but in case of resale by a Barracuda Networks distributor or reseller,
commencing not more than sixty (60) days after original Energize Update Software purchase from
Barracuda Networks) and continues for the period for which Customer has paid the required license
fees. Customer may terminate this License at any time by notifying Barracuda Networks and ceasing
all use of the Energize Update Software. By terminating this License, Customer forfeits any refund
of license fees paid and is responsible for paying any and all outstanding invoices. Customer's rights
under this License will terminate immediately without notice from Barracuda Networks if Customer
fails to comply with any provision of this License. Upon termination, Customer must cease use of all
copies of Energize Update Software in its possession or control.
Export. Software, including technical data, may be subject to U.S. export control laws, including the
U.S. Export Administration Act and its associated regulations, and may be subject to export or import
regulations in other countries. Customer agrees to comply strictly with all such regulations and
acknowledges that it has the responsibility to obtain licenses to export, re-export, or import Energize
Update Software.
Restricted Rights. Barracuda Networks' commercial software and commercial computer software
documentation is provided to United States Government agencies in accordance with the terms of this
Agreement, and per subparagraph "(c)" of the "Commercial Computer Software - Restricted Rights"
clause at FAR 52.227-19 (June 1987). For DOD agencies, the restrictions set forth in the "Technical
Data-Commercial Items" clause at DFARS 252.227-7015 (Nov 1995) shall also apply.
85
Page 86

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
No Warranty. The Energize Update Software is provided AS IS. Customer's sole and exclusive
remedy and the entire liability of Barracuda Networks under this Energize Update Software License
Agreement will be, at Barracuda Networks option, repair, replacement, or refund of the Energize
Update Software.
Renewal. At the end of the Energize Update Service Period, Customer may have the option to renew
the Energize Update Service at the current list price, provided such Energize Update Service is
available. All initial subscriptions commence at the time of sale of the unit and all renewals
commence at the expiration of the previous valid subscription.
In no event does Barracuda Networks warrant that the Energize Update Software is error free or that
Customer will be able to operate the Energize Update Software without problems or interruptions. In
addition, due to the continual development of new techniques for intruding upon and attacking
networks, Barracuda Networks does not warrant that the Energize Update Software or any equipment,
system or network on which the Energize Update Software is used will be free of vulnerability to
intrusion or attack.
DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTY. ALL EXPRESS OR IMPLIED CONDITIONS,
REPRESENTATIONS, AND WARRANTIES INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY
IMPLIED WARRANTY OR CONDITION OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE, NONINFRINGEMENT, SATISFACTORY QUALITY OR ARISING
FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, LAW, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE, ARE HEREBY
EXCLUDED TO THE EXTENT ALLOWED BY APPLICABLE LAW. TO THE EXTENT AN
IMPLIED WARRANTY CANNOT BE EXCLUDED, SUCH WARRANTY IS LIMITED IN
DURATION TO THE WARRANTY PERIOD. BECAUSE SOME STATES OR JURISDICTIONS
DO NOT ALLOW LIMITATIONS ON HOW LONG AN IMPLIED WARRANTY LASTS, THE
ABOVE LIMITATION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU. THIS WARRANTY GIVES YOU SPECIFIC
LEGAL RIGHTS, AND YOU MAY ALSO HAVE OTHER RIGHTS WHICH VARY FROM
JURISDICTION TO JURISDICTION.
General Terms Applicable to the Energize Update Software License Disclaimer of Liabilities. IN NO
EVENT WILL BARRACUDA NETWORKS BE LIABLE FOR ANY LOST REVENUE, PROFIT,
OR DATA, OR FOR SPECIAL, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR PUNITIVE
DAMAGES HOWEVER CAUSED AND REGARDLESS OF THE THEORY OF LIABILITY
ARISING OUT OF THE USE OF OR INABILITY TO USE THE ENERGIZE UPDATE
SOFTWARE EVEN IF BARRACUDA NETWORKS OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN
ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. In no event shall Barracuda Networks'
liability to Customer, whether in contract, tort (including negligence), or otherwise, exceed the price
paid by Customer. BECAUSE SOME STATES OR JURISDICTIONS DO NOT ALLOW
LIMITATION OR EXCLUSION OF CONSEQUENTIAL OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, THE
ABOVE LIMITATION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
This Energize Update Software License shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the
laws of the State of California, without reference to principles of conflict of laws, provided that for
Customers located in a member state of the European Union, Norway or Switzerland, English law
shall apply. The United Nations Convention on the International Sale of Goods shall not apply. If any
portion hereof is found to be void or unenforceable, the remaining provisions of the Energize Update
Software License shall remain in full force and effect. Except as expressly provided herein, the
Energize Update Software License constitutes the entire agreement between the parties with respect
to the license of the Energize Update Software and supersedes any conflicting or additional terms
contained in the purchase order.
86 Appendix C: Limited Warranty and License
Page 87

Open Source Licensing
Barracuda products may include programs that are covered by the GNU General Public License
(GPL) or other "open source" license agreements. The GNU license is re-printed below for you
reference. These programs are copyrighted by their authors or other parties, and the authors and
copyright holders disclaim any warranty for such programs. Other programs are copyright by
Barracuda Networks.
GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE, (GPL) Version 2, June 1991
Copyright (C) 1989, 1991 Free Software Foundation, Inc. 51
Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA
Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies of this license document, but changing
it is not allowed.
Preamble
The licenses for most software are designed to take away your freedom to share and change it. By
contrast, the GNU General Public
License is intended to guarantee your freedom to share and change free software--to make sure the
software is free for all its users. This General Public License applies to most of the Free Software
Foundation's software and to any other program whose authors commit to using it. (Some other Free
Software Foundation software is covered by the GNU Library General Public License instead.) You
can apply it to your programs, too.
Administrator’s Guide
When we speak of free software, we are referring to freedom, not price. Our General Public Licenses
are designed to make sure that you have the freedom to distribute copies of free software (and charge
for this service if you wish), that you receive source code or can get it if you want it, that you can
change the software or use pieces of it in new free programs; and that you know you can do these
things.
To protect your rights, we need to make restrictions that forbid anyone to deny you these rights or to
ask you to surrender the rights. These restrictions translate to certain responsibilities for you if you
distribute copies of the software, or if you modify it.
For example, if you distribute copies of such a program, whethergratis or for a fee, you must give the
recipients all the rights that you have. You must make sure that they, too, receive or can get the source
code. And you must show them these terms so they know their rights.
We protect your rights with two steps: (1) copyright the software, and (2) offer you this license which
gives you legal permission to copy, distribute and/or modify the software.
Also, for each author's protection and ours, we want to make certain that everyone understands that
there is no warranty for this free software. If the software is modified by someone else and passed
on, we want its recipients to know that what they have is not the original, so that any problems
introduced by others will not reflect on the original authors' reputations.
Finally, any free program is threatened constantly by software patents. We wish to avoid the danger
that redistributors of a free program will individually obtain patent licenses, in effect making the
program proprietary. To prevent this, we have made it clear that any patent must be licensed for
everyone's free use or not licensed at all.
The precise terms and conditions for copying, distribution and modification follow.
GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR COPYING,
DISTRIBUTION AND MODIFICATION
87
Page 88

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
0. This License applies to any program or other work which contains a notice placed by the copyright
holder saying it may be distributed under the terms of this General Public License. The "Program",
below, refers to any such program or work, and a "work based on the Program" means either the
Program or any derivative work under copyright law: that is to say, a work containing the Program or
a portion of it, either verbatim or with modifications and/or translated into another language.
(Hereinafter, translation is included without limitation in the term "modification".) Each licensee is
addressed as "you".
Activities other than copying, distribution and modification are not covered by this License; they are
outside its scope. The act of running the Program is not restricted, and the output from the Program
is covered only if its contents constitute a work based on the Program (independent of having been
made by running the Program). Whether that is true depends on what the Program does.
1. You may copy and distribute verbatim copies of the Program's source code as you receive it, in any
medium, provided that you conspicuously and appropriately publish on each copy an appropriate
copyright notice and disclaimer of warranty; keep intact all the notices that refer to this License and
to the absence of any warranty; and give any other recipients of the Program a copy of this License
along with the Program.
You may charge a fee for the physical act of transferring a copy, and you may at your option offer
warranty protection in exchange for a fee.
2. You may modify your copy or copies of the Program or any portion of it, thus forming a work based
on the Program, and copy and distribute such modifications or work under the terms of Section 1
above, provided that you also meet all of these conditions:
a) You must cause the modified files to carry prominent notices stating that you changed the files
and the date of any change.
b) You must cause any work that you distribute or publish, that in whole or in part contains or is
derived from the Program or any part thereof, to be licensed as a whole at no charge to all third parties
under the terms of this License.
c) If the modified program normally reads commands interactively when run, you must cause it,
when started running for such interactive use in the most ordinary way, to print or display an
announcement including an appropriate copyright notice and a notice that there is no warranty (or
else, saying that you provide a warranty) and that users may redistribute the program under these
conditions, and telling the user how to view a copy of this License. (Exception: if the Program itself
is interactive but does not normally print such an announcement, your work based on the Program is
not required to print an announcement.)
These requirements apply to the modified work as a whole. If identifiable sections of that work are
not derived from the Program, and can be reasonably considered independent and separate works in
themselves, then this License, and its terms, do not apply to those sections when you distribute them
as separate works. But when you distribute the same sections as part of a whole which is a work based
on the Program, the distribution of the whole must be on the terms of this License, whose permissions
for other licensees extend to the entire whole, and thus to each and every part regardless of who wrote
it.
Thus, it is not the intent of this section to claim rights or contest your rights to work written entirely
by you; rather, the intent is to exercise the right to control the distribution of derivative or collective
works based on the Program.
In addition, mere aggregation of another work not based on the Program with the Program (or with a
work based on the Program) on a volume of a storage or distribution medium does not bring the other
work under the scope of this License.
88 Appendix C: Limited Warranty and License
Page 89

Administrator’s Guide
3. You may copy and distribute the Program (or a work based on it, under Section 2) in object code
or executable form under the terms of Sections 1 and 2 above provided that you also do one of the
following:
a) Accompany it with the complete corresponding machine-readable source code, which must be
distributed under the terms of Sections 1 and 2 above on a medium customarily used for software
interchange; or,
b) Accompany it with a written offer, valid for at least three years, to give any third party, for a
charge no more than your cost of physically performing source distribution, a complete machinereadable copy of the corresponding source code, to be distributed under the terms of Sections 1 and 2
above on a medium customarily used for software interchange; or,
c) Accompany it with the information you received as to the offer to distribute corresponding source
code. (This alternative is allowed only for noncommercial distribution and only if you received the
program in object code or executable form with such an offer, in accord with Subsection b above.)
The source code for a work means the preferred form of the work for making modifications to it. For
an executable work, complete source code means all the source code for all modules it contains, plus
any associated interface definition files, plus the scripts used to control compilation and installation
of the executable. However, as a special exception, the source code distributed need not include
anything that is normally distributed (in either source or binary form) with the major components
(compiler, kernel, and so on) of the operating system on which the executable runs, unless that
component itself accompanies the executable.
If distribution of executable or object code is made by offering access to copy from a designated place,
then offering equivalent access to copy the source code from the same place counts as distribution of
the source code, even though third parties are not compelled to copy the source along with the object
code.
4. You may not copy, modify, sublicense, or distribute the Program except as expressly provided
under this License. Any attempt otherwise to copy, modify, sublicense or distribute the Program is
void, and will automatically terminate your rights under this License. However, parties who have
received copies, or rights, from you under this License will not have their licenses terminated so long
as such parties remain in full compliance.
5. You are not required to accept this License, since you have not signed it. However, nothing else
grants you permission to modify or distribute the Program or its derivative works. These actions are
prohibited by law if you do not accept this License. Therefore, by modifying or distributing the
Program (or any work based on the Program), you indicate your acceptance of this License to do so,
and all its terms and conditions for copying, distributing or modifying the Program or works based on
it.
6. Each time you redistribute the Program (or any work based on the Program), the recipient
automatically receives a license from the original licensor to copy, distribute or modify the Program
subject to these terms and conditions. You may not impose any further restrictions on the recipients'
exercise of the rights granted herein. You are not responsible for enforcing compliance by third parties
to this License.
7. If, as a consequence of a court judgment or allegation of patent infringement or for any other
reason (not limited to patent issues), conditions are imposed on you (whether by court order,
agreement or otherwise) that contradict the conditions of this License, they do not excuse you from
the conditions of this License. If you cannot distribute so as to satisfy simultaneously your obligations
under this License and any other pertinent obligations, then as a consequence you may not distribute
the Program at all. For example, if a patent license would not permit royalty-free redistribution of the
Program by all those who receive copies directly or indirectly through you, then the only way you
could satisfy both it and this License would be to refrain entirely from distribution of the Program.
89
Page 90

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
If any portion of this section is held invalid or unenforceable under any particular circumstance, the
balance of the section is intended to apply and the section as a whole is intended to apply in other
circumstances.
It is not the purpose of this section to induce you to infringe any patents or other property right claims
or to contest validity of any such claims; this section has the sole purpose of protecting the integrity
of the free software distribution system, which is implemented by public license practices. Many
people have made generous contributions to the wide range of software distributed through that
system in reliance on consistent application of that system; it is up to the author/donor to decide if he
or she is willing to distribute software through any other system and a licensee cannot impose that
choice.
This section is intended to make thoroughly clear what is believed to be a consequence of the rest of
this License.
8. If the distribution and/or use of the Program is restricted in certain countries either by patents or by
copyrighted interfaces, the original copyright holder who places the Program under this License may
add an explicit geographical distribution limitation excluding those countries, so that distribution is
permitted only in or among countries not thus excluded. In such case, this License incorporates the
limitation as if written in the body of this License.
9. The Free Software Foundation may publish revised and/or new versions of the General Public
License from time to time. Such new versions will be similar in spirit to the present version, but may
differ in detail to address new problems or concerns.
Each version is given a distinguishing version number. If the Program specifies a version number of
this License which applies to it and "any later version", you have the option of following the terms
and conditions either of that version or of any later version published by the Free Software
Foundation. If the Program does not specify a version number of this License, you may choose any
version ever published by the Free Software Foundation.
10. If you wish to incorporate parts of the Program into other free programs whose distribution
conditions are different, write to the author to ask for permission. For software which is copyrighted
by the Free Software Foundation, write to the Free Software Foundation; we sometimes make
exceptions for this. Our decision will be guided by the two goals of preserving the free status of all
derivatives of our free software and of promoting the sharing and reuse of software generally.
NO WARRANTY
11. BECAUSE THE PROGRAM IS LICENSED FREE OF CHARGE, THERE IS NO WARRANTY
FOR THE PROGRAM, TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW. EXCEPT
WHEN OTHERWISE STATED IN WRITING THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND/OR OTHER
PARTIES PROVIDE THE PROGRAM "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO THE QUALITY AND PERFORMANCE OF THE PROGRAM IS
WITH YOU. SHOULD THE PROGRAM PROVE DEFECTIVE, YOU ASSUME THE COST OF
ALL NECESSARY SERVICING, REPAIR OR CORRECTION.
12. IN NO EVENT UNLESS REQUIRED BY APPLICABLE LAW OR AGREED TO IN
WRITING WILL ANY COPYRIGHT HOLDER, OR ANY OTHER PARTY WHO MAY MODIFY
AND/OR REDISTRIBUTE THE PROGRAM AS PERMITTED ABOVE, BE LIABLE TO YOU
FOR DAMAGES, INCLUDING ANY GENERAL, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE
PROGRAM (INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO LOSS OF DATA OR DATA BEING
RENDERED INACCURATE OR LOSSES SUSTAINED BY YOU OR THIRD PARTIES OR A
90 Appendix C: Limited Warranty and License
Page 91

Administrator’s Guide
FAILURE OF THE PROGRAM TO OPERATE WITH ANY OTHER PROGRAMS), EVEN IF
SUCH HOLDER OR OTHER PARTY HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGES.
END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
How to Apply These Terms to Your New Programs
If you develop a new program, and you want it to be of the greatest possible use to the public, the best
way to achieve this is to make it free software which everyone can redistribute and change under these
terms.
To do so, attach the following notices to the program. It is safest to attach them to the start of each
source file to most effectively convey the exclusion of warranty; and each file should have at least the
"copyright" line and a pointer to where the full notice is found.
one line to give the program's name and an idea of what it does.
Copyright (C) yyyy name of author
This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU
General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License,
or (at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY;
without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with this program; if not,
write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place - Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307,
USA.
Also add information on how to contact you by electronic and paper mail.
If the program is interactive, make it output a short notice like this when it starts in an interactive
mode:
Gnomovision version 69, Copyright (C) 19yy name of author Gnomovision comes with
ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY; for details type `show w'. This is free software, and you are
welcome to redistribute it under certain conditions; type `show c' for details.
The hypothetical commands `show w' and `show c' should show the appropriate parts of the General
Public License. Of course, the commands you use may be called something other than `show w' and
`show c'; they could even be mouse-clicks or menu items--whatever suits your program.
You should also get your employer (if you work as a programmer) or your school, if any, to sign a
"copyright disclaimer" for the program, if necessary. Here is a sample; alter the names:
Yoyodyne, Inc., hereby disclaims all copyright interest in the program `Gnomovision' (which makes
passes at compilers) written by James Hacker.
signature of Ty Coon, 1 April 1989 Ty Coon,
President of Vice
This General Public License does not permit incorporating your program into proprietary programs.
If your program is a subroutine library, you may consider it more useful to permit linking proprietary
applications with the library. If this is what you want to do, use the GNU Library General Public
License instead of this License.
91
Page 92

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
Barracuda Products may contain programs that are copyright (c)1995-2005 International Business
Machines Corporation and others. All rights reserved. These programs are covered by the following
License:
"Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and
associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including
without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, and/or sell copies of the
Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, provided that the above
copyright notice(s) and this permission notice appear in all copies of the Software and that both the
above copyright notice(s) and this permission notice appear in supporting documentation."
Barracuda Products may include programs that are covered by the BSD License: "Redistribution and
use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted provided that the
following conditions are met:
Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the
following disclaimer.
Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and
the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
The names of the authors may not be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software
without specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED ``AS IS'' AND WITHOUT ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE."
Barracuda Products may include the libspf library which is Copyright (c) 2004 James Couzens &
Sean Comeau All rights reserved. It is covered by the following agreement: Redistribution and use in
source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted provided that the following
conditions are met: 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list
of conditions and the following disclaimer. 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the
above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation
and/or other materials provided with the distribution. THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED ``AS IS''
AND ANY EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS
MAKING USE OF THIS LICENSE OR ITS CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT,
INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES
(INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION)
HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT,
STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN
ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
Barracuda Products may contain programs that are Copyright (c) 1998-2003 Carnegie Mellon
University. All rights reserved. Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met: 1. Redistributions of
source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
disclaimer. 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of
conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with
the distribution. The name "Carnegie Mellon University" must not be used to endorse or promote
products derived from this software without prior written permission. For permission or any other
legal details, please contact Office of Technology Transfer Carnegie Mellon University 5000 Forbes
Avenue Pittsburgh, PA 15213-3890 (412) 268-4387, fax: (412) 268-7395 techtransfer@andrew.cmu.edu .Redistributions of any form whatsoever must retain the following
92 Appendix C: Limited Warranty and License
Page 93

Administrator’s Guide
acknowledgment: "This product includes software developed by Computing Services at Carnegie
Mellon University (http://www.cmu.edu/computing/)." CARNEGIE MELLON UNIVERSITY
DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES WITH REGARD TO THIS SOFTWARE, INCLUDING ALL
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS, IN NO EVENT SHALL
CARNEGIE MELLON UNIVERSITY BE LIABLE FOR ANY SPECIAL, INDIRECT OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OR ANY DAMAGES WHATSOEVER RESULTING FROM
LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT,
NEGLIGENCE OR OTHER TORTIOUS ACTION, ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION
WITH THE USE OR PERFORMANCE OF THIS SOFTWARE.
Barracuda products may include programs that are covered by the Apache License or other Open
Source license agreements. The Apache license is re-printed below for you reference. These programs
are copyrighted by their authors or other parties, and the authors and copyright holders disclaim any
warranty for such programs. Other programs are copyright by Barracuda Networks.
Apache License Version 2.0, January
2004 http://www.apache.org/licenses/
TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR USE, REPRODUCTION, AND DISTRIBUTION
1. Definitions.
"License" shall mean the terms and conditions for use, reproduction, and distribution as defined by
Sections 1 through 9 of this document.
"Licensor" shall mean the copyright owner or entity authorized by the copyright owner that is
granting the License.
"Legal Entity" shall mean the union of the acting entity and all other entities that control, are
controlled by, or are under common control with that entity. For the purposes of this definition,
"control" means (i) the power, direct or indirect, to cause the direction or management of such entity,
whether by contract or otherwise, or (ii) ownership of fifty percent (50%) or more of the outstanding
shares, or (iii) beneficial ownership of such entity.
"You" (or "Your") shall mean an individual or Legal Entity exercising permissions granted by this
License.
"Source" form shall mean the preferred form for making modifications, including but not limited to
software source code, documentation source, and configuration files.
"Object" form shall mean any form resulting from mechanical transformation or translation of a
Source form, including but not limited to compiled object code, generated documentation, and
conversions to other media types.
"Work" shall mean the work of authorship, whether in Source or Object form, made available under
the License, as indicated by a copyright notice that is included in or attached to the work (an example
is provided in the Appendix below).
"Derivative Works" shall mean any work, whether in Source or Object form, that is based on (or
derived from) the Work and for which the editorial revisions, annotations, elaborations, or other
modifications represent, as a whole, an original work of authorship. For the purposes of this License,
Derivative Works shall not include works that remain separable from, or merely link (or bind by
name) to the interfaces of, the Work and Derivative Works thereof.
"Contribution" shall mean any work of authorship, including the original version of the Work and any
modifications or additions to that Work or Derivative Works thereof, that is intentionally submitted
to Licensor for inclusion in the Work by the copyright owner or by an individual or Legal Entity
authorized to submit on behalf of the copyright owner. For the purposes of this definition, "submitted"
means any form of electronic, verbal, or written communication sent to the Licensor or its
representatives, including but not limited to communication on electronic mailing lists, source code
93
Page 94

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
control systems, and issue tracking systems that are managed by, or on behalf of, the Licensor for the
purpose of discussing and improving the Work, but excluding communication that is conspicuously
marked or otherwise designated in writing by the copyright owner as "Not a Contribution."
"Contributor" shall mean Licensor and any individual or Legal Entity on behalf of whom a
Contribution has been received by Licensor and subsequently incorporated within the Work.
2. Grant of Copyright License. Subject to the terms and conditions of this License, each Contributor
hereby grants to You a perpetual, worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
copyright license to reproduce, prepare Derivative Works of, publicly display, publicly perform,
sublicense, and distribute the Work and such Derivative Works in Source or Object form.
3. Grant of Patent License. Subject to the terms and conditions of this License, each Contributor
hereby grants to You a perpetual, worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
(except as stated in this section) patent license to make, have made, use, offer to sell, sell, import, and
otherwise transfer the Work, where such license applies only to those patent claims licensable by such
Contributor that are necessarily infringed by their Contribution(s) alone or by combination of their
Contribution(s) with the Work to which such Contribution(s) was submitted. If You institute patent
litigation against any entity (including a cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that the
Work or a Contribution incorporated within the Work constitutes direct or contributory patent
infringement, then any patent licenses granted to You under this License for that Work shall terminate
as of the date such litigation is filed.
4. Redistribution. You may reproduce and distribute copies of the Work or Derivative Works thereof
in any medium, with or without modifications, and in Source or Object form, provided that You meet
the following conditions:
(a) You must give any other recipients of the Work or Derivative Works a copy of this License; and
(b) You must cause any modified files to carry prominent notices stating that You changed the files;
and
(c) You must retain, in the Source form of any Derivative Works that You distribute, all copyright,
patent, trademark, and attribution notices from the Source form of the Work, excluding those notices
that do not pertain to any part of the Derivative Works; and
(d) If the Work includes a "NOTICE" text file as part of its distribution, then any Derivative Works
that You distribute must include a readable copy of the attribution notices contained within such
NOTICE file, excluding those notices that do not pertain to any part of the Derivative Works, in at
least one of the following places: within a NOTICE text file distributed as part of the Derivative
Works; within the Source form or documentation, if provided along with the Derivative Works; or,
within a display generated by the Derivative Works, if and wherever such third-party notices normally
appear. The contents of the NOTICE file are for informational purposes only and do not modify the
License. You may add Your own attribution notices within Derivative Works that You distribute,
alongside or as an addendum to the NOTICE text from the Work, provided that such additional
attribution notices cannot be construed as modifying the License.
You may add Your own copyright statement to Your modifications and may provide additional or
different license terms and conditions for use, reproduction, or distribution of Your modifications, or
for any such Derivative Works as a whole, provided Your use, reproduction, and distribution of the
Work otherwise complies with the conditions stated in this License.
5. Submission of Contributions. Unless You explicitly state otherwise, any Contribution intentionally
submitted for inclusion in the Work by You to the Licensor shall be under the terms and conditions
of this License, without any additional terms or conditions. Notwithstanding the above, nothing
herein shall supersede or modify the terms of any separate license agreement you may have executed
with Licensor regarding such Contributions.
94 Appendix C: Limited Warranty and License
Page 95

Administrator’s Guide
6. Trademarks. This License does not grant permission to use the trade names, trademarks, service
marks, or product names of the Licensor, except as required for reasonable and customary use in
describing the origin of the Work and reproducing the content of the NOTICE file.
7. Disclaimer of Warranty. Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, Licensor
provides the Work (and each Contributor provides its Contributions) on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied,
including, without limitation, any warranties or conditions of TITLE, NON-INFRINGEMENT,
MERCHANTABILITY, or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. You are solely responsible
for determining the appropriateness of using or redistributing the Work and assume any risks
associated with Your exercise of permissions under this License.
8. Limitation of Liability. In no event and under no legal theory, whether in tort (including
negligence), contract, or otherwise, unless required by applicable law (such as deliberate and grossly
negligent acts) or agreed to in writing, shall any Contributor be liable to You for damages, including
any direct, indirect, special, incidental, or consequential damages of any character arising as a result
of this License or out of the use or inability to use the Work (including but not limited to damages for
loss of goodwill, work stoppage, computer failure or malfunction, or any and all other commercial
damages or losses), even if such Contributor has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
9. Accepting Warranty or Additional Liability. While redistributing the Work or Derivative Works
thereof, You may choose to offer, and charge a fee for, acceptance of support, warranty, indemnity,
or other liability obligations and/or rights consistent with this License. However, in accepting such
obligations, You may act only on Your own behalf and on Your sole responsibility, not on behalf of
any other Contributor, and only if You agree to indemnify, defend, and hold each Contributor
harmless for any liability incurred by, or claims asserted against, such Contributor by reason of your
accepting any such warranty or additional liability.
END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
APPENDIX: How to apply the Apache License to your work.
To apply the Apache License to your work, attach the following boilerplate notice, with the fields
enclosed by brackets "[]" replaced with your own identifying information. (Don't include the
brackets!) The text should be enclosed in the appropriate comment syntax for the file format. We also
recommend that a file or class name and description of purpose be included on the same "printed
page" as the copyright notice for easier identification within third-party archives.
Copyright [yyyy] [name of copyright owner]
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in
compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is
distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND,
either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
Source Code Availability
Per the GPL and other "open source" license agreements the complete machine readable source code
for programs covered by the GPL or other "open source" license agreements is available from
Barracuda Networks at no charge. If you would like a copy of the source code or the changes to a
particular program we will gladly provide them, on a CD, for a fee of $100.00. This fee is to pay for
the time for a Barracuda Networks engineer to assemble the changes and source code, create the
95
Page 96

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
media, package the media, and mail the media. Please send a check payable in USA funds and include
the program name. We will mail the packaged source code for any program covered under the GPL
or other "open source" license.
96 Appendix C: Limited Warranty and License
Page 97

Index
A
about 65
accounts, creating 51
Active mode 16, 25
administration interface
logging in
Administration page 34, 41, 44
alerts, email 41
Appearance page 34
Applications page 60
Audit mode 21
authentication server
LDAP
NTLM 55
21
52
B
back panel details 74
backing up configuration 43
Backup page 43
Barracuda reboot option 46
Barracuda Spyware Removal Tool 65
about 65
enabling 65
viewing a list of prompted clients 41
Barracuda Web Filter
configuring
connecting to network 24
installing 18
linking 36
managing 43
monitoring 38
Block Messages page 62
block/accept filters 58
Browse Test page 63
20, 34
creating
local accounts
local groups 51
Custom Categories page 61
51
D
definitions, updating 23, 43
deployment types
forward proxy
inline pass-through 11
diagnostic memory test 46
domain users
LDAP
52
NTLM 55
Domains page 60
13
E
Energize Updates 10, 43
F
failed system, replacing 44
files system repair 46
filters
block messages
blocked IP addresses 61
content 59
custom categories 61
domains and subdomains 60
MIME-type blocking 61
URL patterns 60
Web applications 60
firewall, configuring 20
Firmware Update page 43
forward proxy deployment 13
front panel details 70
62
C
Caching page 35
character tags 81
configuring, Barracuda Web Filter 20
Content Filter page 59
G
groups, creating 51
H
hardware compliance information 77
97
Page 98

Barracuda Web Filter Release 4.0
hardware test 46
Hardware_Test reboot option 46
See also HTTPS filtering option 63
I
indicator lights 39
infected clients list 41
Infection Activity page 41
inline pass-through deployment 11
installing, Barracuda Web Filter 18
IP address, setting 19
IP Block/Exempt page 61
IP Configuration page 34
L
language, changing in administration interface 35
LDAP authentication server 52
LEDs (on front panel) 39
lights (on front panel) 39
Linked Management page 36
local users 51
See also domain users 50
Log page 40
HTTPS filtering option
filtering
P
pre-existing proxy server 27
R
reboot options 45, 46
Recovery Console reboot option 46
recovery mode 45
regular expressions, about 79
re-imaging system 46
reloading the system 44
remote administration 46
repairing, file system 46
replacing failed system 44
Reports page 47, 67
RESET button, using 44
restarting the system 44
restoring configuration 43
S
M
MIME Blocking page 61
monitoring spyware and Web activity
Account View page
Application Log page 40
Infection Activity page 41, 65
Log page 40
Reports page 47, 67
Status page 38
Warned Activity page 41
monitoring system status
Barracuda Web Filter 210, 310, and 410 front panel
Barracuda Web Filter 610 front panel 71
Barracuda Web Filter 810 and 910 front panel 72
Status page 38
Troubleshooting page 44, 45, 46
52, 55, 56
N
network planning 16
network time protocol (NTP) 21
notifications, email 41
NTLM authentication server 55
O
70
shutting down the system 44
standby systems 36
Status page 38
subscription
activating
status 22
Syslog page 35
23
T
Task Manager page 41
TCP ports 20
testing memory 46
testing URLs 63
time zone, setting 35
transparent mode 11
Troubleshooting page 44
U
UDP ports 20
updating
definitions
firmware 43
URL Patterns page 60
23, 43
operating mode, Barracuda Web Filter
Active mode
Audit mode 21
98
16, 25
V
Virus Checking page 35
Page 99

W
Warned Activity page 41
99
 Loading...
Loading...