
Original
instructions

OPERATION & SERVICE
MANUAL
8-10t Internal Combustion
Counterbalanced Forklift Truck
KION Baoli (Jiangsu) Forklift Co., Ltd.

PREFACE
Thank you for selecting BAOLI forklift truck! Your trust is a great honor to us!
8-10 ton internal combustion counterbalanced forklift trucks adopt hydraulic
transmission with advanced TCM continuous speed control and integral drive axle with
wheel reducer, so they have a lot of advantages such as good traction and travel
performance, easy operation, reliable brake, wide visibility and safe performance.
These trucks are all suit for handling and stacking packed goods in stations, ports,
goods yards and warehouses and used widely in food processing, light and textile,
mining industries and other factories, with some of attachments fitted, the trucks can be
applied more and more.
This manual states the trucks’ specifications, operation, maintenance, service,
main assemblies’ constructions and working principles so as to be completely familiar
with the truck to get the most of it, and to help the operators to use the trucks correctly
and attain the highest functions. It is necessary to read over the manual before they
operate the trucks or service personnel serve these trucks.
Besides this Operation and Service Manual, there is Operator’s Manual, which
includes important information of safety driving and periodic maintenance. And, the
manual of some important parts is provided.
We suggest you to give the manual a proper storage. If there is something in the
manual you do not understand, ask the distributor to explain it to you. Suggestion and
criticisms are welcome.
This manual content might not correspond with the actual condition because of the
improving of our products. Our products are subject to improvements and changes
without notice.
We heartily wish you keep everything running smoothly during operation of BAOLI
forklift truck!

CONTENTS
Ⅰ. About the forklift truck..........…….………………………................................1
1. External view and specification……………………………………………………1
2. Characteristic of forklift truck………………………………………………………3
Ⅱ. Safety instruction and operation of forklift truck………………………5
1. Handling a new forklift truck………………………………………………………5
2. Inspection before operation………………………………………………………5
3. Start and stop of the engine………………………………...................................6
4. Shipping, loading and unloading, slinging and towing of forklift truck…………7
5. Parking and storing…. . ……………………………………………………………8
6. Information of safety operation…. …………………………...... ………………10
7. Operation device and meter………………………………………………………16
8. Caution plate……………………………………………………..........................18
Ⅲ. Periodic inspection and servicing…………………………………………23
1. General rules on inspection and maintenance…………………………………23
2. Essentials of servicing..............…………………………..............................24
3. Recommended oil...........................……………………............................25
4. Lubrication system..................................………………………..................25
5. Routine check before daily operation...........……………............................27
6. Precautions of cooling system……………………………………………………27
7. Notes during brake-in...........................…………………….............................27
Ⅳ. Construction, principle, adjustment and maintenance of forklift truck…28
1. Power system………………………………………………………………………..28
1.1 General description…………………………………………………………….28
1.2 Engine disposition………………………………………………………………..29
1.3 Inspection and adjustment of engine…………………………………………..31
1.4 Fuel system……………………………………………………………………..31
1.5 Coolant system…………………………………………………………………..33
1.6 Check and adjustment………………………………………………………….33
1.7 Precautions of cooling system…………………………………………………..38
2. Drive unit……………………………………………………………………………39
2.1 General description…………………………………………………………….39

2.2 Torque converter…………………………………………………………………41
2.3 Charging pump……………………………………………………………………42
2.4 Hydraulic clutch…………………………………………………………………..43
2.5 Control valve and inching valve…………………………………………………43
2.6 Hydraulic circulation system…………………………………………………….45
2.7 Principle……………………………………………………………………………46
2.8 Caution when the trouble occurs………………………………………………46
2.9 Trouble shooting…………………………………………………………………47
3. Front axle……………………………………………………………………………50
3.1 General description…………………………………………………………….50
3.2 Main reduction gear & differential……………………………………………….50
3.3 Final reduction gear………………………………………………………………50
3.4 Troubleshooting…………………………………………………………………53
3.5 Service data……………………………………………………………………….53
4. Brake system……………………………………………………………………...54
4.1 General description…………………………………………………………….54
4.2 Power brake……………………………………………………………………..54
4.3 Parking brake……………………………………………………………………58
4.4 Wheel brake……………………………………………………………………..58
4.5 Troubleshooting………………………………………………………………….60
5. Steering system…………………………………………………………………….61
5.1 General description…………………………………………………………….61
5.2 Hand wheel……………………………………………………………………….60
5.3 Cycloid gear type powered steering unit……………………………………..62
5.4 Steering system troubleshooting……………………………………………...70
5.5 Rear axle…………………………………………………………………………..71
6. Hydraulic system…………………………………………………………………..73
6.1 General description………………………………………………………………73
6.2 Main pump……………………………………………………………………….73
6.3 Control valve…………………………………………………………………….73
6.4 Control valve operation………………………………………………………….74

6.5 Main safety valve operation……………………………………………………..76
6.6 Tilt lock valve operation…………………………………………………………77
6.7 Hydraulic circulation system (Main circuit)……………………………………..78
6.8 Troubleshooting………………………………………………………………….79
6.9 Maintenance……………………………………………………………………...80
7. Lift Cylinder & tilt Cylinder……………………………………………………….81
7.1 Lift cylinder……………………………………………………………………….81
7.2 Flow regulator…………………………………………………………………….83
7.3 Tilt cylinder……………………………………………………………………….84
8. Lifting system……………………………………………………………………….85
8.1 General description…………………………………………………………….85
8.2 Inner & outer mast………………………………………………………………..85
8.3 Lift bracket………………………………………………………………………..85
8.4 Roller position…………………………………………………………………..86
8.5 Adjustment of lifting system………………………………………………...88
8.6 Maintenance and adjustment…………………………………………………...88
9. Electric system………………………………………………………………………91
9.1 General description……………………………………………………………. 91
9.2 Brief explanation for operation…………………………………………………..95
9.3 Precautions when using the battery……………………………………………97
9.4 Harness…………………………………………………………………………...97
Product improve suggestion sheet…………………………………………………102
NOTE……………………………………………………………………………………10 3
EC DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY………………………………………………104

1
Ⅰ. About the forklift truck
1. External view and specification
External view of internal forklift truck

2
Main specification
General
Model
CPCD80
-C
CPCD80-W
CPCD100
-C
CPCD100-W
CPCD80-CU1
CPCD100-CU1
Power type
Diesel
Operating way
Sitting
Rated capacity
kg
8000
10000
Load center
mm
600
Dimensions
Lift height
H
mm
3000
Free lift height
H4
mm
205
210
Fork size L×W×T
mm
1500×160×75
1500×160×80
Fork outside spread (Min./Max.)
mm
320/2015
420/2144
Mast tilt angle
α/β
deg
6/12
6/12
Front overhang
X
mm
700
733
Overall
dimensions
Length to fork face
L1
mm
3940
4258
Overall width
B1
mm
2245
Mast lowered height
H1
mm
2695
2845
Mast extended height
H3
mm
4445
4307
Overhead guard height
H2
mm
2565
Turning radius
R
mm
3700
3900
Performance
No load/full load
Travel speed
km/h
28 / 24
28 / 22
Lift speed
mm/sec
480/350
410/350
390/280
390/300
Max. gradeability
%
20
Self weight
kg
11080
12860
Chassis
Tyre
Front
9.00-20-14PR
Rear
9.00-20-14PR
Tread
Front
B2
mm
1600
Rear
B3
mm
1700
Wheelbase
Y
mm
2500
2800
Min. mast ground
clearance
(no load/full load)
Mast
M
mm
245/205
Frame
F
343/323
Drive units &
control
Battery
V/AH
2×12/100

3
2. Characteristic of forklift truck
The forklift truck has advantages as follows:
1. The hydraulic steering device makes steering flexible and the double ladder like
steering bridge makes the turning radius minor.
2. The braking system employs oil brake, makes it possible to manipulate
conveniently and brake reliably.
3. Employed wide-vision extension type mast, the truck is high intensity.
4. Hydraulic transmission type forklift trucks are provided with a drive unit including
a torque converter and a hydraulic transmission. They feature the following:
a. Hydraulic torque converter can change the speed automatically with no limitation
and output torque makes the forklift truck have good performance of drawing.
b. The slight travel device makes it easy for the drivers to aim the truck to the
position of cargo.
c. At work, for the forklift truck that need starting and shifting frequently,
achievement of smooth gear shifting control can raise working efficiency, simplify
operation, reduce the driver’s labor intensity and reduce requirement of the driver’s
operation skill.
5. The trucks’ braking system employs oil brake, make it possible to manipulate
conveniently and brake reliably.
6. Employed wide-vision type mast, and it’s frame is two stage CJ extension type
mast. The truck is high intensity and has wide vision. The mast adopts series design,
having different lifting height according to the needs of the client.
7. Specific outline adopts streamline design, it has advantages such as low noise,
small libration, comfortable operation, safety and reliability.

4
Main parts of forklift truck:
No.
Name
Contents
1
Power system
engine mounting, system of fuel, exhaust and
coolant etc.
2
Transmission
torque converter, transmission, transmission shaft,
etc.
3
Drive axle
housing, half shaft, differential, wheel reducer,
brake, front wheel etc.
4
Brake system
wheel brake and parking brake
5
Steering system
steering wheel, steering shaft, cycloid gear type
powered steering unit and steering axle assy etc.
6
Hydraulic system
pump, valve, HP oil pipe, LP oil pipe, connectors
etc.
7
Electric system
lamps and lanterns, battery, meter, harness etc.
8
Load system
mast, fork, carriage, load backrest, tilt cylinder, lift
cylinder, lift chain, mast roller etc.
Weight of the main parts that can be disassembled
Model
Specification
8T
10T
Balance
weight
Slinging capacity
(kg)
>4500
>5000
Overhead
guard
Slinging capacity
(kg)
>150
Mast
Slinging capacity
(kg)
>2000
>2100
Carriage
Slinging capacity
(kg)
>1000
>1200
Fork
Slinging capacity
(kg)
>220
>250

5
Ⅱ. Safety instruction and operation of forklift truck
It is important for drivers and managers to remember the principle of “first safety”
and ensure the safety operation as the description of Operation & Service Manual.
Please read this manual thoroughly. This will give you a complete understanding of
Baoli forklift truck and you will operate them correctly and safely.
1. Handling a new forklift truck
The performance and service life of the forklift truck depends heavily upon the way
you handle it during the break-in period. Drive with special caution while becoming
familiar with a new forklift truck.
(1) Always warm up your vehicle before putting it to work irrespective of season.
Don’t run engine at high rpm without load needlessly. Operate the vehicle under the
light load, avoid sudden speeding and braking.
(2) Replace gear oil in the differential and reducer after the new forklift truck
working for 100 hours.
(3) Renew the oil in engine oil pan, transmission, driving axle and hydraulic oil tank;
check and readjust the clearance of the driving and driven gear in the reducer after the
new forklift truck working for 200 hours.
2. Inspection before operation
Please pay attention to the following items in order to make the vehicle working
with high efficiency and lengthen its service life.
(1) The forklift truck adopts the home or imported engine, please read the manual
accompanied with the engine carefully when using and maintenance.
(2) Check the tyre inflation pressure, if doesn’t enough, charge air in time. Check
the bolts of all wheels for tightness.
(3) Check the amount of oil in the working oil tank for sufficiency, the position of
lubrication should be lubricated. The oil level should be at the middle position between
the upper and lower scale marks of oil level meter. The contamination level of the
hydraulic oil should be lower than Grade 12.
(4) Check the radiator, and add antifreeze if necessary.
(5) Check hydraulic oil and brake fluid for leakage. Check if any leak or damage
found on the oil pipes, water hoses, vent-pipes and the piping joints, pumps and valves

6
etc.
(6) Check for all the terminals and plugs in normal state. Check the meters, lamps,
switches and electric circuit if they are running properly.
(7) Check every pedal for free stroke and the levers for looseness and smooth
operation. Check lifting system, actuate the lifting and tilting levers to be certain that the
lift bracket moves up and down properly and the mast can be tilted smoothly. Check
brake system and steering system for flexibility and reliability.
(8) Check the wheel brake: the free stroke of brake pedal is 4-8 mm, when
achieving effective brake, the clearance between the front floor and the pedal should be
more than 20mm.
(9) Check the parking brake: the unload forklift truck can park on 20% slope, when
the parking brake is locked.
(10) Check all connectors and fasteners for looseness.
3. Start and stop of the engine
(1) Start of the engine
(a) First set the shift lever at the neutral position and the parking brake at the
braking position.
(b) When starting, put the key into the start switch, turn it in the counter clockwise,
preheat 15-20 seconds, and then turn it in the clockwise to “START” so the starting
motor works. When your hand is away from the key, it automatically returns to “ON” by
spring force. Every starting time shouldn’t morn than 15 seconds. Restarting should be
after 30 seconds. As the engine doesn’t work after some times starting, should check
and remove the trouble, do not keep the starting motor engaged for a long time.
(c) Following the start of the engine, it’s necessary to set the engine on idle running
for five minutes. Full load operation can’t be started until water temperature of the
engine rises above 60℃.
When the engine is on idle running, you must check water thermometer, oil
manometer, ammeter, fuel measurer, and so on for the data, whether to meet the
specification, and check each pedal for free stoke, braking performance for its reliability,
steering operation for its flexibility, tyre pressure for its conformance to the standard. If
there is no trouble, operation may be allowed.

7
(2) Stop the engine
First set the engine on idle running for five minutes, so as to cool the engine
gradually, and then turn off the ignition switch, so the engine is stopped to work.
Notice:
.While the engine running, does not turn the start switch to “START” position, or it
will damage the starting motor.
.Do not keep the start switch at the “ON” position while the engine is shut down.
This will result in battery discharge.
4. Shipping, loading and unloading, slinging and towing of forklift truck
(1) Ship the forklift truck
(a) Apply the parking brake when shipping the forklift trucks by container or freight
car.
(b) Fix the mast and the balance weight with steel wire and use jacks to prevent the
forklift trucks from moving in the cabin.
(c) Pay attention to the overall length, width, height when loading, unloading and
shipping and conforming the regulations is necessary.
(d) Single transporting if necessary after disassembling the mast and balance
weight.
Model
Mast
Balance weight
Dimension(mm)
Weight(kg)
Dimension(mm)
Weight(kg)
8T
2450×2175×850
2423
1980×1166×1325
4193
10T
Mast
2600×1201×695
1864
1980×1610×1169
4826
Carriage
2238×1330×435
1330
Notice:
Dismantling and slinging the component shall not be performed without the
approval of our company. Under special circumstances, the appointed sling position
should be used. The balance weight, fork and mast of the forklift truck all have their
appointed sling position. The above-mentioned data is only for a reference, which
may be adjusted because of configuration or technology optimization.

8
(2) Load and unload the forklift truck
(a) Use the plate with enough length, width and strength.
(b) Pull the parking brake and use jacks to stop the wheel.
(c) Fasten the plate on the center of the cabin, there must be no grease on the
plate.
(d) The left and right height of the plate must be equal to make the loading and
unloading smooth.
(e) Don’t change the direction on the plate to prevent the danger.
(f) Reverse the forklift truck slowly when loading it on the freight car.
(3) Sling the forklift truck
(a) Only the specially trained personnel can sling the truck.
(b) Sling points should be always at the positions specified in sling nameplate.
(c) The slinging cable must be enough to hang the forklift truck.
(d) Disassembled parts of forklift truck must be slung in the appointed position.
(4) Towing of forklift truck
(a) The towing pin is installed below the counter weight. When towing the forklift
truck, first extract the pin and fasten a steel wire, then install the pin back.
(b) When towing the forklift truck, release the hand brake lever.
(c) The towing pin only used for following situation, while the forklift truck can’t
move or while transporting the forklift truck.
(d) Fasten the towing steel wire at the appointed position.
(e) Don’t apply capacity abruptly when towing the forklift truck.
(5) Repair the broken-down forklift truck
If the forklift truck broken-down suddenly during using, drag it away and repair in
time to avoid hindering other vehicles or workers.
5. Parking and storing
(1) Safe parking
(a) Park your forklift truck on a level ground preferably in a wide area. If parking on
a slope is unavoidable, pull the parking brake device and block the wheels to prevent

9
accidental roll. The forklift truck is forbidden parking on a steep slope.
(b) Park your forklift truck in the area where designated or traffic conditions permit.
If necessary, put a signpost or signal lights around the truck.
(c) Park your forklift truck on the solid ground. Avoid soft ground, deep mud or
slippery surfaces.
(d) If you can not lower the forks on the ground due to break-down of the lifting
system, put a warning flag to the fork end and park in the traffic conditions permitting.
(2) Storing
·Before storing
Before storing your forklift truck, clean it thoroughly and perform inspection using
the following procedures.
(a) Wipe away grease, oil, etc. adhering to the body of the truck with waste cloth
and water, if needed.
(b) While washing the body of the truck, check general condition of the truck.
Especially check the truck’s body for recess or damage and tyres for wear and nails or
stones in the tread.
(c) Fill the oil tank up with the appointed fuel.
(d) Check for leakage of hydraulic oil, engine oil, fuel or coolant.
(e) Apply grease where needed.
(f) Check for looseness of hub nuts and cylinder piston rod joints. Check the
surface of piston rod for damage.
(g) Check mast rollers to see that they rotate smoothly.
(h) Full oil into the lift cylinders by lifting the lift cylinders at the full stroke.
(i) In cold weather, don’t draw off long antifreeze, if there is cooling water, run it
away.
·Daily storage
(a) Park the forklift truck at a specified place and block the wheels.
(b) Place the shift lever in the neutral position and pull the parking brake lever.
(c) Put the key switch in “OFF” position and turn off the engine, operate the lever of
the control valve several times and release the residual pressure of the cylinder or
pipes.
(d) Remove the key and keep it in a secure place.
·Long time storage

10
Perform the following service and checks in addition to the “Daily storage” service:
(a) Taking the rainy season into consideration, park the truck at a higher and hard
ground.
(b) Apply antirust oil to the exposed parts such as piston rods and shafts which
tends to rust.
(c) Cover components which may be caught with humidity.
(d) The truck should be operated at least once a week. Fill the cooling system, if
cooling water is discharged. Remove grease from the piston rods and shafts. Start the
engine and warm up thoroughly. Move the truck slowly forwards and backwards.
Operate the hydraulic controls several times.
(e) Avoid parking on soft grounds such as asphalted road in summer.
·Operate the forklift truck after long time storage
(a) Remove antirust oil from the exposed parts.
(b) Discharge the engine oil in crankshaft case of the engine, discharge the gear oil
or hydraulic transmission oil in differential and gear box, after cleaning up then renew
oil.
(c) Discharge foreign matter and water from the hydraulic reservoir and fuel tank.
(d) Remove the cylinder cap, the valves and the rocker shafts, check for the
clearance in normal data.
(e) Add cooling fluid to specified level.
(f) Perform pre-operation checks carefully.
(g) Warm up the engine before operation.
Warning:
If at any time your forklift truck is found to be in need of repair, defective, or in any
way unsafe, the condition should be reported to the supervisor, and the truck should be
taken out of service until it has been restored to safe operating condition.
6. Information of safety operation
(1) The forklift truck belongs to special equipment. Only trained and authorized
operator shall be permitted to operate and service the truck.
(2) Wear the safety guards, such as clothing, shoes, helmet and gloves while
operating the truck.

11
(3) When operating the truck, observe and follow all nameplates stuck on the truck.
The nameplates must be replaced if lost or damaged.
(4) Daily maintenance should be done before or after using the truck. Anytime you
find that the truck is not functioning normally, operation of the truck should be halted and
check or repair at once.
(5) When the distance between the gravity center of loads and the fork arms is
600mm, the max. capacity is the rated capacity. When the distance exceeds 600mm,
the capacity shall be reduced according to the load chart. Overloading is strictly
prohibited.
(6) Operate your forklift truck on a hard ground. Operate on other ground, the lift
capacity and travel speed must be decreased. Wipe off the oil and grease from the floor.
(7) If the forklift truck is equipped with attachment, its usage sphere will be wider,
but its allowable load and stability is reduced. The attachment and special device is not
to be diverted to any other purpose. It’s very dangerous to rebuild the attachment.
Please read the additional instruction we supplied and operate the truck following it
strictly.
(8) Users select “Lengthening fork” in order to carry widening loads. Pay much
attention not to overload and observe the allowable load and the capacity chart stuck on
the truck. Careful driving should be taken when traveling and turning.
(9) The unloaded forklift truck with attachment should be operated as a loaded
truck.
(10) Connect the power and turn on the key switch, select the position of direction
switch, check the truck for normal operation by turning steering wheel, depress the
speed-adjusting pedal softly to keep proper acceleration.
(11) During operation, pay attention to the performance and condition of the system
of machinery, hydraulic, electric and speed-adjuster etc.
(12) When operate one lever, pay attention not to shift another lever. Don’t operate
the lever at any position out of the driver’s seat.
(13) The shift distance of control valve lever can control the speed of the lifting or
descending of the goods. When the goods are lifted or descended, the initial speed
shouldn’t be too fast in either case.
(14) When tilting the mast forward or backward to the limit or lifting the fork to the
maximum height, return the directional lever to neutral.

12
(15) The starting, turning, driving, braking and stopping of the truck should be done
smoothly. When turning on the humid or slippery road, the truck should be decelerated.
(16) Because the forklift truck turns by the rear wheels, the end counterweight may
swing widely when turning. Use care in narrow aisles and other workplaces.
(17) Operate the forklift truck smoothly, don’t jerk the steering wheel. Avoid sudden
stop, acceleration, stop or turn. In the case of improper operation, the truck will turn over.
In case of this, the driver must keep calm, don’t jump off the truck. The driver must hold
tightly the control wheel with two hands; meanwhile, his body must incline in opposite
direction of truck’s turning over.
(18) Turning, lateral or deflective traveling shall not be taken on a slope. It could
cause overturning of the truck, it is very dangerous. On a slope, drive the truck with load
forward to ascend and backward to descend. When the truck goes down on a slope,
drive slowly with the brakes on. Make sure that the engine should not be shut down
when traveling on a slope.
(19) The stability of the truck is influenced by the wind-force during outside
operation, you must notice specially.
(20) Be careful and slow driving over a dock or temporary paving slab.
(21) Insert forks deeply under goods. Adjust fork’s distance according to the
dimension of goods. Make the loads distribute on the forks evenly to avoid tilt and slide
of goods.
(22) Don’t pick the loads with single fork. Fork can not be used to pull out any
embedded goods, if necessary, the pulling force should be estimated.
(23) Don’t handle unfixed or loose goods. Be careful to handle bulky goods. To
prevent the collapse of stacked goods, tighten them. Forbid loading loose or little
volume goods without pallet.
(24) When loading the goods, lower the forks to the floor. After the fork inserting
stacked goods, the fork arms should be in contact with the goods. Drive the truck with
mast tilting back for stabilizing the load. Before traveling, raise the forks for
200mm-300mm from the floor.
(25) When handling bulky loads which block your view, operate the forklift truck in
reverse or have a guide.
(26) While mast’s lifting and lowering, anyone is absolutely prohibited from standing
under the lift bracket or being lifted with forks. Never permit anyone to stand or walk

13
under upraised forks.
(27) When lifting the load, according to the weight of the load, accelerate properly
and then pull the lifting lever.
(28) The load descends for the gravity, at this time, the engine must be in idle
position, and the lever must be pulled slowly to prevent the load from sudden falling.
(29) When loading and unloading goods, keep the mast vertical and the truck is in
braking state.
(30) Load should cling to the load backrest. Do not handle the load which exceeds
height of the backrest, or else there is a danger of load’s falling against operator.
(31) When travel with load, don’t tilt mast forward, don’t do handling. Don’t brake
abruptly to prevent goods from slipping off the forks.
(32) It is necessary to brake before tilting the mast forward or backward. It’s also
necessary to decelerate and tilt forward slowly so as to prevent the goods from slipping
off the forks.
(33) Don’t make a sudden braking when the truck traveling with loads.
(34) Drive the forklift truck to the stacked goods at a low speed, at the same time,
pay much attention to sharp and hard objects near the goods, otherwise, the tyres will
be pricked.
(35) Pay attention to pedestrian, obstacle and bumpy road when driving. Pay
attention to the clearance over the forklift truck.
(36) Keep your head, hands, arms, feet and legs within the confines of the cab.
Never allow other persons on the forklift truck.
(37) Tilt the mast of the high lift forklift truck as backward as possible when
operating the truck. Use minimum forward and backward tilt when loading and
unloading. It is dangerous to travel or turn when lifting the goods at high levels.
(38) It is noted that the goods will fall down when the forks of the truck with lifting
height more than 3m lift, take the protection measures if necessary.
(39) Before the truck decelerating and stopping, don’t change gear to reverse shift,
so as to ensure the safe loading.
(40) When the truck stops and the engine is on idle position, the mast must be tilted
backward. You shouldn’t leave the truck with idling engine or hanged goods unattended.
(41) When adding fuel, make the driver leave the truck and the engine flameout.
Don’t ignite when checking the level of fuel tank.

14
(42) Don’t open the radiator cap when the engine is very hot.
(43) After one day’s working, the fuel tank should be added oil to prevent the
humidity in the fuel tank from becoming the blob and then interfusing the fluid.
(44) When leaving, engage the hand brake, lower the forks on the ground and let
the shift lever to neutral, make the engine flameout or cut down the electric supply. If
parking on a slope with smaller gradient, apply the parking brake and block the wheels.
The truck is forbidden parking on a slope with bigger gradient.
(45) Don’t adjust the control valve and relief valve at will to prevent the damage of
hydraulic system and its components because of excessive pressure passing them.
(46) Tyres should be inflated according to the pressure value specified in the
nameplate of “Tyre Pressure”.
(47) Check the chains periodically to make sure that good lubrication condition
exists between the chain elements, the degree of tightness between left and right chain
is identical. If the variation value of the chain pitch exceeds 2% standard value, it
indicates that the chains have been worn excessively, replace it immediately.
(48) The overhead guard is main part which is strong enough to meet safety
standard, and protect the operator from falling materials. It’s very dangerous to
dismantle or rebuild the overhead guard, because these conditions could lead to an
accident.
(49) A load backrest shall be used as protection against back falling objects on the
fork. It’s very dangerous to dismantle or rebuild the load backrest, because these
conditions could lead to an accident.
(50) You can’t change or add other working equipments on the truck without our
company’s permission, or the rated capacity and safety operation will be affected.
(51) Keep safety when serving on high position.
(52) The forklift truck must be operated under the following environment: below an
elevation of 1000 meters and temperature between -20℃and 40℃, relative humidity is
95%. Careful operation must observe under other adverse circumstances.
(53) Because of the danger for the people, the forklift is forbidden operating in
airtight space, or you may be choked by the tail gas. The tail gas’s exhausting standard
shouldn’t be lower than the no-load mechanical vehicle exhaust standard ruled by the
nation that users are in. If in Europe nation, the adopted tail gas’s exhausting index
should be applied Europe StageⅢA standard.

15
(54) According to the Directive 2000/14/EC and based on EN12053 standard,the
noise pressure level at the operator’s position and the measured sound power level and
the guaranteed sound power level is referred to the following table. But the noise of the
forklift truck may fluctuate due to different operation and the influence of the external
environment.
(55) The driver feels the vibration of the forklift truck when operating and traveling
the forklift truck.. According to ISO3691 and based on EN13059 standard. The vibration
of the forklift truck fluctuates according to environment condition. In normal working
condition, the vertical direction acceleration mean value from the seat to the operator by
testing is in the following table. But the vibration frequency felt by the driver depends on
the working condition (etc. road, operation method), so the actual vibration frequency
must be determined according to environment condition when necessary.
(56) To prevent the fire, accident or other unpredictable event, prepare the fire
extinguishers in advance and operate them according to the instructions.
(57) Preventive maintenance services should be done before or after using the
truck. Anytime you find that the truck is not functioning properly, operation of the truck
should be halted and check or repair the trouble.
(58) When operating the machine, observe and follow all markings on the machine.
If the marking is lost, please stick it in time.
Model
The noise pressure
level at the
operator’s position
The measured
sound power level
The
guaranteed
sound power
level
The vertical
direction
acceleration
mean value from
the seat to the
operator
EN12053
EN12053
2000/14/EC
CPCD80
87 dB(A)
110 dB(A)
111 dB(A)
0.92 (m/s2)
CPCD100
86 dB(A)
109 dB(A)
111 dB(A)
1.06 (m/s2)

16
7. Operation device and meter
1.
Inching pedal
11.
Air filter indicator (option)
2.
Button for stopping engine
12.
Water temp. gauge
3.
Brake pedal
13.
Sedimentor indicator (option)
4.
Parking brake lever
14.
Hour meter
5.
Hand wheel adjusting lever
15.
Horn button
6.
Shift lever
16.
Turn signal lever
7.
Oil pressure indicator
17.
Accelerator pedal
8.
Fuel gauge
18.
Lift lever
9.
Charge signal
19.
Tilt lever
10.
Neutral signal

17
The function and use method of operation device and meter is listed as follows:
No.
Name
Function
Use method
1
Inching pedal
Couple or uncouple the
transmission.
When the pedal is pressed,
the transmission is
uncoupled.
2
Button for
stopping engine
Stop the engine.
Pull the button to stop the
engine.
3
Brake pedal
Brake the truck.
Depress the pedal to brake
the truck.
4
Parking brake lever
Park the truck.
Pull the lever backward fully.
5
Hand wheel
adjusting lever
Adjust the angle of
steering wheel.
6
Shift lever
Change the travel
direction.
Pull the lever forward, the
truck travels forward.
7
Oil pressure
indicator
Indicate the pressure of
engine oil.
Pressure is insufficient, it
lights up.
8
Fuel gauge
Indicate the fuel capacity.
Ignition switch is set at on.
9
Charge signal
Indicate the battery
condition of charge.
Lamp comes on when the
ignition switch is set at on.
10
Neutral signal
Indicate the neutral
position.
Shift lever is in neutral
position, it lights up.
11
Air filter indicator
(option)
It will warn when the air
filter is blocked.
Exceed standard resistance,
it flashes.
12
Water temp. gauge
Indicate the temperature
of engine coolant.
Ignition switch is set at on.
13
Sedimentor
indicator (option)
Indicate water amount in
sedimentor.
Water reaches to a certain
level, it lights up
14
Hour meter
Shift lever is in neutral
position.
Ignition switch is set at on.
15
Horn button
Control the horn.
Press it to sound horn.
16
Turn signal lever
Indicate the turning
direction.
Pull the lever, the turn signal
light blinks.
17
Accelerator pedal
Increase the engine speed
Depress the pedal to
increase the speed.
18
Lift lever
Control lift cylinder.
Pull backward to lift, pull
forward to decline.
19
Tilt lever
Control tilt cylinder.
Pull the lever backward to tilt
the mast backward.

18
8. Caution plate
The caution plates attached on the vehicle indicates the operating method and
instructions. Before driving it, please be sure to read them thoroughly. If the caution
plate drops, stick it again. When maintaining, check if the caution plate is complete and
the writing is legible, if necessary, please replace them.
(1) Safety mark (People are forbidden to stand on or down the fork.)
(2) General information when operating
(3) Nameplate of forklift truck

19
(4) Lubrication system
(5) Capacity chart
(6) Inspections before starting
20
(7) Adjust parking brake
(8) Add hydraulic oil
(9) Add fuel
(10) Add antifreeze
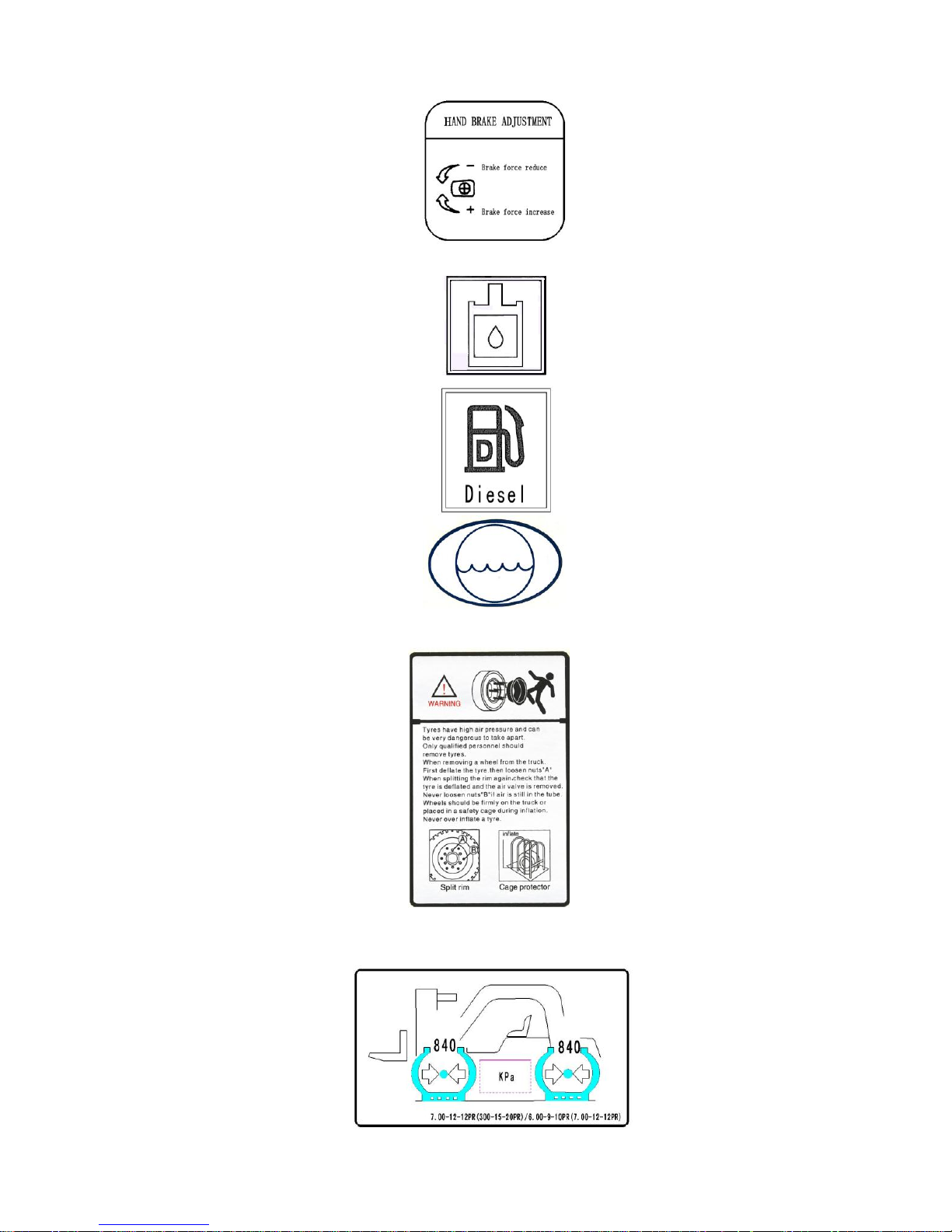
(11) Tyre safety decal (charging tyre)
(12) Tyre pressure decal (charging tyre)

21
(13) Cautions for high voltage
(14) Sling point indication
(15) Sling decal
(16) Forbid entering into the space behind the mast
(17) Forbid conveying person

22
(18) Hand caution decal
(19) Fan hurting hands
(20) Hood crushing hands
Energy accumulator decal
Belt pulley thumb hand decal

23
Ⅲ. Periodic inspection and servicing
During operating the forklift truck, it is necessary to operate carefully, service and
maintain periodically to make the forklift truck keep in good condition.
1. General rules on inspection and maintenance
(1) Only use genuine parts provided by our company.
(2) Only use genuine or recommended oil when replacing or adding.
(3) Clean oil fillers and grease fittings with a brush or waste cloth before adding oil
or grease.
(4) Checking oil level and adding oil should be made with the truck parked on a
level ground.
(5) Preventive maintenance should be done in an orderly manner and due care
taken not to injure yourself.
(6) If any damage or fault is found, stop the truck and report the condition to the
manager. Do not operate the truck until it has been repaired completely.
.Regular inspection
(1) Check the seal and the reliability of the hydraulic system.
(2) Check the reliability of the steering and braking system.
(3) Check the reliability of mast, driving axle and steering axle connecting with the
frame.
(4) Check all wheels for tightness.
.Irregular inspection
(1) Check the reliability of each welding joints of the mast, frame and so on.
(2) Check the reliability of connecting joints of steering cylinder, joint plate and
gimbals etc.
(3) Check all pipes and hoses for any leakage and breakage.
(4) Check the performance of the traveling brake and the parking brake.
Caution:
.Only trained and authorized serviceman shall be permitted to service and
repair the truck.
.When checking and maintaining the forklift truck, do not use the mast or the
load backrest instead of a ladder, these actions will lead to a dangerous condition
unexpectedly.

24
2. Essentials of servicing
(1) Some critical components must be replaced according to demands periodically.
Use genuine parts only.
(2) Use the same model oil only when replacing or adding.
(3) If any damage or fault is found, stop the truck and report the condition to the
manager. Do not operate the truck until it has been repaired completely.
Periodic service and maintenance must be done according to the following list after
using the forklift truck.
No.
Item
Contents
Period (hrs.)
Remark
1
Bearing, steering wheel
Replace grease
1000
2
Bearing, drive wheel
Replace grease
1000
3
Steering link lever
Replace grease
1000
4
Parking brake lever
Add grease
200
5
Pin, foot brake
Add grease
200
6
Drive axle body
Replace gear oil
2400
7
Braking oil
Add
Whenever
necessary
8
Pin, tilting cylinder
Add lubricating grease
400
9
King pin, knuckle
Replace grease
1000
10
Hydraulic tank and filter
Clean
1000
11
Hydraulic oil
Replace
1000
12
Lift chain
Replace
3000
If damaged,
replace it.
13
H. P. hose
Replace
3000
14
Switch, hydraulic motor
Clean photoelectric
coupler
200
15
Brush, traction motor
Check
1000
16
Brush, hydraulic motor
Check
1000
17
Brush, steering motor
Check
1000
Notice:
When serving and checking the truck, do not use the mast or the load
backrest instead of a ladder, these actions will lead to a dangerous condition
unexpectedly.9. Periodic servicing

25
3. Recommended oil
Name
Brand or code
Quantity
Domestic
Overseas
Diesel
Refer to diesel engine manual
or
select GB252-81 light
diesel:
Winter―10~―35#
Summer0#
JISK2204/2#
(general region)
JISK2204/3# (cold region)
140L
Lubricant oil
Select refer to engine manual
or working condition
diesel:GB5323-85
SAE10W (Winter)
SAE30 (Summer)
Hydraulic oil
N32# or N46#
ISOVG30
90L
Torque
converter oil
6# Torque converter oil
SAE10W
20L
Gear oil
85W/90
SAE85W/90
18L
Brake fluid
DOT3 Compound brake fluid
1.5L
Lubricant
grease
3# Lithium base grease
(drop point 170)
JISK2220/2#
Coolant
Water or―35℃ Long Life Coolant (FD-2)
Filled
Adding oil, grease and coolant should follow relevant automobile standard. The
waster of the forklift truck must be reclaimed obeying the relevant laws and regulations.
Incorrect treatment will pollute water, soil and atmosphere etc.
Wear a helmet, safety shoes and working clothes to avoid contacting with body
when adding oil, grease and coolant.
4. Lubrication system
NO.
Position
Grease
point
Type
Time(hours)
50
100
500
1000
1
Support of steering
2
Lime grease
+
2
The two end joints of
steering cylinder
2
Lime grease
+
3
Bearing of knuckle
4
Lime grease
+ 4
Bracket of foot control
1
Lime grease
+ 5
Pin of tilt cylinder
2
Lime grease
+ 6
Lever head of tilt cylinder
2
Lime grease
+
7
Support bushing of mast
2
Lime grease
+
8
Lift roller of fork bracket
8
Lime grease
+
Note: About lubrication of the engine, refer to the ENGINE OPERATION MANUAL.

26
Lubrication diagram

27
5. Routine check before daily operation
(1) Check the storage of fuel.
(2) Check if any leak or damage found on the oil pipe, water hose, vent-pipe and
hydraulic parts.
(3) Check whether the hydraulic hose storage attain to the regular capacity, the oil
level should be at the middle position between the upper and lower scale marks of oil
level meter.
(4) Check if fix or loose found on the wheel bolt and transmission bolt.
(5) Check tires air pressure.
(6) Check steering and transmission for flexibility and reliability.
(7) Check the traveling brakes: The free travel of brake pedal is 40mm, the
clearance between the front floor and the pedal should be bigger than 20mm.
(8) Check the parking brake: The unload truck can park on the 20% grade ramp,
when the parking level is pulled to the bottom.
(9) Check the electric system to see whether connect, the connector whether loose,
the lights, meter whether work normally.
6. Precautions of cooling system
(1) Use extreme care when removing the radiator pressure cap. In pressure system,
the sudden release of pressure can cause a steam flash which would cause a serious
personal injury. Loosen cap slowly to allow steam to escape. After that, tighten cap
securely.
(2) Check the radiator coolant reservoir fluid level. It should between FULL and
LOW mark. Add the same type coolant to specified level if necessary. The coolant can
be used all the year round.
(3) Put the coolant on a safe place and mark “Dangerous Matter” for its poisonous.
If swallowed by accident, take the emergency first aid and consult a physician
immediately.
(4) According to variety working condition, periodic wiping away the dirt adhering to
the surface of the radiator is necessary.
7. Notes during brake-in
Operating the machine under the light load, low speed condition for the first stage
of operation of 100 hours. Avoid suddenly speeding and brake. Renew the oil in engine
oil pan, transmission, driving axle and hydraulic oil tank after 200 operation hours.

28
Ⅳ. Construction, principle, adjustment and maintenance
of forklift truck
In order to keep good condition of your truck, you must have an intimate
understanding of the construction, principle, adjustment and maintenance of the forklift
truck. When find damage or a fault at the truck, stop operating the truck and inform a
professional serviceman. Use genuine parts of our company for replacement.
1. Power system
1.1 General description
Power system consists of the engine, fuel system, cooling system and exhaust
system. The engine is connected with the frame by rubber cushion to avoid vibration
(Fig.1.1).
For the construction and adjustment of engine, please refer to the operation and
maintenance manual of engine.
Fig. 1.1 Installation of engine

29
1.2 Engine disposition
The engine used for 8-10t forklift truck includes the import engine 6BG1 (ISUZU),
the home engine 6102BG6 (Zhaoyang).
Engine model
6102BG6A
A-6BG1QC
QSB4.5
Place of production
Zhaocai
Japan(ISUZU)
Cummins,Inc.
Rated output / Speed kw/rpm
80.9/2500
82.3/2000
82/2200
Rated torque / Speed N.m/rpm
353/1600
416/1400-1600
488/1500
Cylinder number
6 6 4
Bore×Stroke mm
102×118
105×125
102×137
Total displacement L
5.785
6.494
4.5
Appropriate truck model
CPCD80-CY
CPCD100-CY
CPCD80
CPCD100
CPCD80-CU1
CPCD100-CU1
Parallel table for engine and forklift model which is coincidence and stuck with
CE label:
Engine model
The guaranteed
sound power level
LwA(dB)
2000/14/EC
Exhausting
2004/26/EC
CE
CONFORMITY
2006/42/EC
Truck model
Diesel
engine
Cummins,Inc.
QSB4.5
111
StageⅢA
yes
CPCD80-CU1
CPCD100-CU1
Note: The sound power level L
WA
according to 2000/14/EC standard, the
exhausting according to 2004/26/EC standard.
Here we give a brief description of the construction, parameter and disposition
about model 6BG1 imported engine. For the construction and specifications of other
engines, see their respective operation instruction. Refer to Fig 1.2 and attached list
about the construction and specifications of 6BG1.

30
Fig.1.2 A-6BG1QC diesel engine
Main performance and disposition of A-6BG1QC
Model
A-6BG1QC
Type
4-cycle,water-cooled,overhead valve
No. of cylinder—bore×stroke
6-105mm×125mm
Total displacement (L)
6.494
Compression ratio
17
Performance
Rated speed
rpm
2000
Rated output
kw
82.3
Max. torque (N.m/rpm)
416/1400-1600
Full-load fuel consumption
g/kwh
233
No-load Min. speed
rpm
700
Weight
kg
450
Dimension
mm
1129.5×672.0×860.0
Injection start pressure
kg/cm2
kg/cm2
Compress pressure
kg/cm2
kg/cm2

31
1.3 Inspection and adjustment of engine
In order to keep good condition of your truck, you must carry out periodic inspection
and adjustment of power system.
(1) Regularly clear the dust of air cleaner.
(2) Regularly replace oil filter and fuel filter.
(3) Check and apply the coolant periodically.
(4) Periodic inspection of throttle valve and injection pump.
(5) Check fan belt for tension and all fasteners.
Note:
Always check the exhaust gas of the engine during using the forklift truck. Especially
after maintaining the engine, it’s necessary to verify the discharge indicator ensure that
discharge value is fit for the national standard, so as to minimum damage to the person
and environment.
1.4 Fuel system
The fuel system composed with the fuel tank, filter, fuel sensor.
1.4.1 Fuel tank
The fuel tank is a welded construction integrated with the truck frame. It is located
on the left side of the truck frame. The tank cover with a fuel sensor is located on the top
surface of the tank. Once every 600 hours operation, it is required to clean the fuel tank.
Fig.1.3 Fuel tank

32
1.4.2 Fuel sensor
The function of the fuel sensor is to change the oil in the oil tank to the electric
through the bobber up and down sport, in the end transfer to the fuel chart in the
dashboard, let others to know the oil quantity directly. See Fig.1.4.
(a) Once every 600 hours operation, it is required to replace the filter assembly.
(b) Apply several drops of fuel to the around of the new filter’s seal before
installation, it should be screwed 2/3 circles again when the filter’s seal touches the
body of engine.
(c) When the warning lamp is on, drain all the water by loosing the draining switch.
Note: Turn off the draining switch after draining water.
Fig.1.4 Fuel filter
1.4.3 Fuel filter
The fuel filter was installed in the engine enters hose, used to filtrate the fuel supply
to the engine. There also have other through valve inside of the filter, when the filter
jammed, it also can supply the oil to the engine. See Fig.1.5.
Fig.1.5 Fuel sensor

33
1.5 Coolant system
The coolant system composed with water pump, fan, radiator and the ancillary
radiator, the water pump installed in the engine, the crank through the V-series tape to
drive the water pump work.
1.6 Check and adjustment
To have a good work state, it needs to check and research on the engine termly.
The main point is as following:
1.6.1 Cleaning of the air condition (Fig.1.6)
(1) Take out the filter.
(2) Check the dust and the damage of the filter, fist puff away from inside to outside
to clean with low pressure air, if it’s jammed and can’t clean or has been damage,
change a new one.
(3) Clean the dust in the cover.
Fig.1.6 Air condition
1.6.2 Replacement of fuel filter (Fig.1.7)
(1) Use the filter specially spanner disassemble, if damage or
block, need to change.
(2) Along with the around of the new filter seal O-ring, add little
lube then install, when it contact the filter, screw 2/3 circle.
Fig.1.7

34
1.6.3 Replacement of oil filter (Fig.1.8)
(1) Use the filter specially spanner disassemble
and change.
(2) Along with the around of the new oil filter seal
o-ring, add little lube then install, when it contact the
filter, screw 2/3 circle.
Fig.1.8
1.6.4 Vice radiator (Fig.1.9)
(1) Check the coolant in the vice radiator
The ancillary radiator as Fig.1.8, when the antifreeze under the “LOW” scale, it
means need to add coolant, add to the 2/3 scale of the up and down scale.
(2) Change the coolant
a. Stop working more than half an hour, wait it cooling, then open the radiator cover,
and loose the water outlet valve under the radiator.
b. Loose the engine water outlet valve, release all the coolant.
c. After releasing, screw down those two valve which mentioned in the above.
d. Add the regular coolant, after idle work few time, check the ancillary radiator, it
should be in the 2/3 scale.
Fig.1.9 Fig.1.10

35
1.6.5 Adjust the fan belt
If the fan belt is loose, tighten it. See Fig.1.10.
Step: loosen the fixed bolt B and C of generator, move the generator out. Press
the A section of belt with the force of 10kg strength, the flexible degree is about 10mm,
then tighten the bolt B,C orderly.
1.6.6 Tighten the bolt of the engine cylinder end
(1) Tighten the bolt with 68Nm twisting moment by the order of Fig 1.11.
(2) Tighten the twisting moment to 93Nm, then tighten the bolt orderly.
(3) Turn the bolt 90 degree and tighten them.
Fig.1.11
1.6.7 Valve clearance adjustment
(1) Turn the crank shaft clockwise, make the "TC" mark on shock absorber of belt
coincide with the pointer.
(2) Inspect the hole cover, affirm the position of soleplate mark and pointer.
If the soleplate mark coincide with hand position, show the 1st cylinder. TDC, adjust
the valve clearance with "△" mark. And adjust the valve clearance with "※"mark.
Valve clearance value: 0.4mm. (the same to absorb and exhaust, cooling state)
Refer to Fig1.12, 1.13, 1.14.
Fig.1.12

36
Fig.1.13 Fig.1.14
The material adjustment see Table 3.2.
Cylinder NO.
1 2 3 4 5
6
I:inspiration valve
E: exhaust valve
I E I E I E I E I E I
E
1st cyl. in TDC
△ △ △ △ △ △
6th cyl. in TDC
※ ※ ※ ※ ※
※
1.6.8 Fuel injection ignition time affirmation
(1) Affirm if the "assemble countermark" is in conformity with the place of injection
pump flange. See Fig1.15.
(2) Put the 1st cylinder to the TDC position, turn the crank shaft about 30°
counterclockwise, See Fig1.16.
Fig.1.15 Fig.1.16

37
(3) Loosen the 1st cylinder injection pipe,
dismantle the spring on drain valve bracket and drain
valve, then install the drain valve bracket on injection
pump. See Fig1.17.
Fig.1.17
4) While charging pump transmit fuel, it turn the
crank shaft clockwise , when the fuel lever of drain valve
bracket up to the stop position, stop turning the crank
shaft. Affirm the hand sign. See Fig 1.18.
Fig.1.18
1.6.9 Fuel injection ignition time adjustment
(1) Dismantle pipe installed on injection pump.
(2) Loosen installed bolt of injection pump.
(3) While affirm the ignition time according 1.5.7 gist, turn it over engine under
advance condition , turn it to engine under "delay" condition.
(4) After adjustment, tighten all the bolt of injection pump, affirm the ignition time
again.
(5) Assemble the drain valve used in the 1st cylinder, and install each bolt on each
position.
1.6.10 Measurement of compression pressure (Fig 1.19)
Fig.1.19
(1) Dismantle heat spark plug and fuel injection pipe.
(2) Install manometer on the heat spark plug of 1st cylinder, the demarcate value of

38
the manometer is 500N/ cm2.
(3) Running the starting device by plenty battery, meter the pressure at this time.
(4) Measure the other 5 cylinder by the same way, and measure 2 times, then
figure out each average value; compression pressure: 304N/cm2 (limit value 255N/cm2)
1.6.11 Exhaust of injection pump ( Fig 1.20)
(1) Loosen core vent of injection pump.
(2) Operate hand pump slowly till the core vent doesn't bubbling.
(3) Tighten the core vent.
Fig.1.20
1.7 Precautions of cooling system
(1) During using the forklift truck, if the temperature of the radiator or coolant is too
high, don’t open the cap of the radiator immediately. To find the reason for boiling, use
extreme care when removing the cap, the sudden release of pressure can cause a
steam flash which would cause a serious personal injury. Lower the running speed of
the engine to moderate speed, after the cooling system cooled then turn to idle speed,
loosen cap slowly to allow steam to escape, the cap can be removed. After that, make
sure the cap is tightened securely.
(2) Check the radiator coolant reservoir fluid level. It should between FULL and
LOW mark. Add the same type coolant to specified level if necessary. The coolant can
be used all the year round.
(3) Put the coolant on a safe place and mark “Dangerous Matter” for its toxicity. If
swallowed by accident, take the emergency first aid and consult a physician
immediately.
(4) According to variety working condition, periodic wiping away the dirt adhering to
the surface of the radiator with detergent, compressed air or high pressure water
(pressure less than 4kg/cm2) is necessary.

39
2. Drive unit
Drive unit consists of torque converter and a hydraulic transmission. The structure
of the hydraulic transmission refers to Fig.2-1, the structure of the torque converter
refers to Fig.2-2.
Main technical parameter
Item
Parameter
Torque
converter
Type
3-element,1-stage,2-phase type
Torque converter ratio
12.5″(Φ315) ratio 3.1
Pressure setting
Mpa
0.5~0.7
Charging
pump
Type
Inner-mesh gear type
Flow rate (l/min)
40 (2000rpm, 2Mpa)
Transmission
Type
Power-shift constant mesh
Shift NO.
Apiece 2 Fwd/Bwd
Gear ration
Ⅰ:1.621 / Ⅱ:0.526
Clutch
Friction piece
mm
O.D.Φ134 / I.D.Φ90 / T.2.8
Surface area
cm2
77.4
Pressure
Mpa
1.2~1.5
Weight (kg)
295
Oil amount (l)
20
Oil type
NO.6 torque converter oil/ SAE10W
2.1 General description
The power-shift transmission mounted on the forklift truck has excellent features as
follows:
(1) An inching valve provides the machine with improved inching performance. Due
to this valve, the lift truck is allowed to perform inching operation regardless of whether
the engine is at low RPM or at high RPM, and when the truck is started up.
(2) As clutch plates, seven steel plates and the same number of composite plates
subjected to special treatment are provided so that improved durability can be ensured.
(3) Both one-way overrun clutches in the torque converter are used to increase the
efficiency for power transmission.
(4) High quality of oil filters is helpful to increasing the life of the torque converter.

40
Fig.2.1 Torque converter transmission
1.
Control valve
9.
Parking brake
17.
Oil seal
2.
Charging pump
10.
Strainer
18.
Ball bearing
3.
Ball bearing
11.
Oil seal
19.
Gear
4.
Drive shaft
12.
Gear
20.
Reverse clutch pack
5.
Ball bearing
13.
Ball bearing
21.
Forward clutch pack
6.
Torque converter
14.
Shaft
22.
Input plate
7.
Ball bearing
15.
Bearing cover
23.
Transmission output shaft
8.
Gear
16.
Output shaft

41
2.2 Torque converter
The torque converter consists of pump wheel installed on input shaft, a turbine
wheel installed on output shaft and stator wheel fixed on torque converter body.
Pump rotor is driven by elastic plate, the elastic plate is connected with flywheel,
the pump rotor start turning while the engine is running. The liquid in pump rotor eject
along blade lattice. The mechanical energy changes to kinetic energy.
So the liquid feed into vane of turbo, and transfer the moment to output shaft, the
direction that the liquid leave turbo change under the action of idler pulley, and the liquid
flow into pump rotor with the best angle, it produce counterforce moment to push the
idler pulley and the output shaft add a moment which is equal to the counterforce
moment
When the turbo rotate speed increase and near to input rotate speed, the change of
liquid angle reduce, the moment of output reduce to it, finally, the liquid flow into idler
pulley in the reverse direction, and then the above counterforce moment act backward.
Under the circumstance, the torque from output shaft is less than the input shaft's. To
prevent the phenomenal, there is a unilateralism clutch installed in idler pulley, when the
counterforce moment act backward, the idler pulley running freely, under the
circumstance, the input torque is equal to output torque, and ensure work efficiently.
The torque converter changes the transfer of moment by mechanic method, and
has coupling mechanism and torque converter function, so it' is two phase, operate
swiftly and raise efficiency.
There are unilateralism clutch, turbo, pump rotor and idler pulley installed in torque
converter. The torque converter is full of oil.
On pump wheel end, there is a gear engaged with the drive gear of charging pump
to drive changing pump.
The turbine wheel is connected with input shaft by spine, transfer power to
hydraulic clutch.
The structure of the torque converter refers to Fig.2-2.

42
Fig.2.2 Torque conv
Fig 2.2 Torque converter
2.3 Charging pump
Fig 2.3 shows the structure of charging pump.
The charging pump consists of drive gear, driven gear, case and cover. They are
fixed on the head of torque converter housing. The drive gear is driven by pump wheel,
driven gear and drive gear, the charging pump feeds oil in the under part of
transmission to each part of it.
Fig.2.3 Charging pump

43
2.4 Hydraulic clutch
Fwd clutch see Fig 2.4, reverse clutch see Fig.2.5.
There is a hydraulic clutch fixed on transmission, the drive gear on the side of
clutch is engaged with the corresponding driven gear, the drive gear on the side of
reverse clutch is engaged with the opposite gear.
The clutch is consists of 6 clutch disks and 7 steel plates. They are installed
alternately and assembled with piston.
The piston is provided with sliding type oil seal on its inner and outer
circumferences to insure oil sealing during operation. When out the action, the
dish-shaped return spring comes away the hydraulic clutch, the surface of clutch is
lubricated by the oil from oil condenser, to prevent conglutination and abrasion on clutch
surface.
When pressure oil acts to piston, the clutch and steel plate which fitted together are
pressed, so the clutch transfer the power to drive gear from torque converter.
The transfer flow of power from torque to transmission is as follows:
Turbine wheel-input shaft-clutch drum-steel plate-clutch disk-forward or reverse
gear-output shaft.
2.5 Control valve and inching valve
The control valve see Fig.2.6.
The control valve is installed on the top of transmission housing, reverse valve and
inching valve are installed in it.
Hydraulic clutch relief valve adjusts the oil pressure of clutch in transmission, the
torque converter relief valve adjusts the pressure of oil feed into torque converter.
The inching valve pole is connected with inching pedal, when press inching pedal,
the inching pedal press in , the oil pressure of clutch depress for a while, the clutch
loosen.

44
Fig.2.4 Forward shift clutch
Fig.2.5 Reverse shift clutch
Fig.2.6 Control valve

45
2.6 Hydraulic circulation system (see Fig. 2.7)
When the engine is started and the charging pump is put into operation, the torque
converter fluid in the oil tank (transmission case) is forcibly sent to the control valve from
the pump through the strainer.
The fluid sent from the charging pump is divided to two directions in the torque
converter case, one for torque converter and the other for transmission.
Pressure of the fluid for clutch is adjusted to 1.2 to 1.5 MPa with the relief valve.
And then it is supplied to the control valve. Pressure of the fluid divided for the converter
is adjusted to 0.5 to 0.7 MPa with the converter relief valve. After that this fluid reaches
the wheel of torque converter. After it is cooled by the oil cooler, it lubricates the clutch
group and then returns to the oil tank through the filter.
When the selector valve is in neutral position, the circuit from the selector valve to
the clutch is closed. Therefore the fluid is joined with the torque converter filling fluid.
When the selector spool is set to the forward or reverse position, fluid flows into the
accumulator due to action of modulate valve, so that pressure rises gradually. During
this time the clutch starts to engage.
When the accumulator is filled with fluid, hydraulic pressure rises intensively so that
the hydraulic clutch is completely engage. While the forward or reverse clutch is
operating, another clutch is rotating between the sintered plates and the steel plates.
Therefore this part is lubricated with oil sent from the oil cooler to prevent seizure of
plates.
When the brake pedal is depressed and the inching valve is actuated, most of
hydraulic oil supplied to the clutch is drained from the inching valve and returns to the
transmission case. The fluid for the torque converter circulates in the same manner as
in neutral state.

46
Fig. 2.7 Hydraulic circulation system
2.7 Principle
The torque converter consists primarily of a pump wheel connected to the input
shaft, a turbine wheel connected to the output shaft, and a stator wheel fixed to the
housing.
The transmission consists of charging pump, hydraulic clutch, the forward gear and
reverse gear.
Power transmission route from the torque converter to the transmission is as
follows: Turbine wheel — main shaft — clutch drum — steel plate — clutch
plate—forward or reverse gear—output shaft.
2.8 Caution when the trouble occurs
When the truck cannot run by itself due to trouble and it must be dragged with
another machine, be sure to observe the following requirements.
(1) Remove the propeller shaft between the transmission and the differential.
(2) Set the shift lever in neutral position.
When the charging pump does not operate, normal lubrication is not performed.
Therefore, if rotation is transmitted from the front wheel to the transmission gear and
clutch disk, seizure may occur.

47
2.9 Trouble shooting
(1) Insufficient power
Parts
Problem
Possible cause and remedy
Torque
converter
A. Too low oil pressure
1. Lower oil level
Check oil level and add oil.
2. Air entering in resulting from
loose connectors.
Check connectors or oil pipes.
Retighten
each connectors or replace seals.
3. Blocked oil filter
Check, clean or replace
4. Oil can not be pumped out.
Check and replace.
5. Deformed spring of relief
valve.
Check tension of spring
6. Seal ring or O-ring seal
damaged
Check and replace.
B. Fly wheel damaged
Check oil, if have dirt, replace it.
Gear
box
A .Unsuitable oil or air bubble
Check oil
1. Air entering in resulting
from loose connections.
Check connectors or oil pipes.
Retighten each connector or replace
seals.
2. Too lower oil pressure or air
bubble in oil
Measure and adjust pressure.
B. Slipped clutch
1. Oil pressure lower
Measure and adjust pressure.
2. Seal ring damaged
Check and replace
3. Piston ring of the clutch
damaged
Check and replace
4. Worn friction piece or
deformed steel piece
Replace
C. Incorrect position between
inching rod and shift rod.
Check and adjust.
Engine
Insufficient engine power
Adjust or repair engine

48
(2) Too higher oil temperature
Parts
Problem
Possible cause and remedy
Torque
converter
1. Lower oil level
Check oil level and add oil.
2. Blocked oil filter
Check, clean or replace.
3. Fly wheel bump against other
parts.
Check oil, if have dirt, replace it.
4. Air entering in resulting
from loose connectors.
Check connectors or oil pipes.
Retighten each connector or
replace seals.
5. Water mixed into oil
Check and replace oil.
6. Low oil flow
Check pipes and replace.
7. Worn bearing
Check and replace.
Gear
box
1. Slipped clutch
Replace friction piece of clutch.
2. Worn bearing
Check and replace.
(3) Noisy gear box
Parts
Problem
Possible cause and remedy
Torque
converter
1. Elasticity plate is broken.
Check noise and replace elasticity plate.
2. Damaged or worn bearing.
Check or replace
3. Gear is broken.
Check or replace
4. Spline is worn
Check or replace
5. Noisy main pump
Check or replace
6. Loosen bolt
Check, tighten or replace
Gear
box
1. Bearing is worn
Check or replace
2. Gear is broken
Check or replace
3. Spline is worn
Check or replace
4. Loosen bolt
Check, tighten or replace

49
(4) Too lower transmission efficiency
Parts
Problem
Possible cause and remedy
Torque
converter
1. Elasticity plate is broken.
Check turn noise and replace.
2. Lower oil amount.
Check oil level and add oil.
3. Driving system of oil pump
is ineffective.
Check and replace.
4. Shaft is broken.
Check and replace.
5. Too lower oil pressure.
Check oil pump for suction pipe.
Gear
box
1. Lower oil amount.
Check oil level and add oil.
2. Seal ring is worn.
Check and replace.
3. Slipped clutch.
Check oil pressure of the clutch.
4. Shaft is broken.
Check and replace.
5. Clutch cap is broken.
Check and replace.
6. Retainer ring of clutch cap
is broken.
Check and replace.
7. Foreign matters mixed in oil
tank of clutch.
Check, clean or replace.
8. Spline of shaft is worn.
Check and replace.
(5) Oil leakage
Parts
Problem
Possible cause and remedy
Torque
Converter
or Gear
Box
1. Worn seal ring
Check and replace seal ring.
2. Incorrect connection of case.
Check, tighten or replace.
3. Loose connector and oil pipe.
Check, tighten or replace.
4. Loose drain plug.
Check, tighten or replace.
5. Oil spray from air hole.
Check connectors, air holes or
replace pipes.
6. Much oil.
Check oil level and drain surplus
oil.

50
3. Front axle
The main specifications of the front axle:
Type
Full-floating type, integral shaped
Main reduction gear
Type
Spiral bevel pinion type
Reduction ratio
6.33
Final reduction gear
Type
Planetary gear type
Reduction ratio
3.58
Total reduction ratio
22.66
Amount of oil
Main reduction gear
10 L
Final reduction gear
8 L (left and right)
Driving wheel
Tire
9.00-20-14PR
Rim
7.00-20
Air pressure
760
3.1 General description
The front axle consists of the main reduction gear, the differential, the final reduction
gear and brakes. (see Fig. 3.1) The front axle is bolted to the front side of the frame.
The mast is installed on the axle housing.
3.2 Main reduction gear & differential
The main reduction gear & differential consists primarily of a cross case, ring gear
(spiral bevel pinion) and drive pinions, which are all assembled on the main reduction
gear carrier as shown in Fig. 3.2, and is fitted to the axle housing through packing.
3.3 Final reduction gear
The final reduction gear is of the planet gear type consisting of a sun gear, planetary
gears and an internal gear. Two final reduction gears are installed on each end of the
axle housing. The sun gear is splined to the axle shaft and locked with snap ring. The
planetary gears are installed onto the shafts in the planet carrier which is fixed to the
wheel hub. The internal gear is splined to the axle spindle through hub.
The principle of power transmission is as follows (see Fig. 3.3).
When the sun gear turns, the rotation is transmitted to the pinion gears and ring gear.
However, since the ring gear is fixed to the spindle, the pinion gears revolve around the
sun gear while spinning themselves. The pinion gears are installed to the carrier which
is fixed to the wheel hub, therefore, power of the drive shaft causes the wheel to turn.

51
Fig.3.1 Front axle
1.
Breaking dial
8.
Lock nut(in)
15.
Roller bearing
2.
Wheel assembly
9.
Prevent-loosen gasket
16.
Steel ball
3.
Tyre
10.
Lock nut(out)
17.
Pinion gear shaft
4.
Oil seal
11.
Inner-gear seat
18.
Thrust washer
5.
Taper roller bearing
12.
Braking plate and shell
assembly
19.
Half-bearing cover
6.
Wheel assembly
13.
Inner gear ring
20.
Pinion gear bracket
7.
Taper roller bearing
14.
Pinion gear
21.
Clamp brake

52
Fig. 3.2 Reducer & differential
1.
Adjust nut
11.
Flange half
21.
O-ring
2.
Cap
12.
Side gear
22.
Spacer
3.
Lock plate
13.
Thrust washer
23.
Shim
4.
Taper roller bearing
14.
Roller bearing
24.
Taper roller bearing
5.
Plain half
15.
Carrier
25.
Seal retainer
6.
Side gear
16.
Lock nut
26.
Oil seal
7.
Pinion gear
17.
Adjust bolt
27.
Flange
8.
Spiral bevel pinion
18.
Drive pinion
28.
O-ring
9.
Spider
19.
Taper roller bearing
29.
Washer
10.
Thrust washer
20.
Bearing cage
30.
Lock nut

53
Fig. 3.3 Final reduction gear
3.4 Troubleshooting
Trouble
Cause
Correction
Oil leaks from
differential carrier.
Loose bolt or broken gasket of
differential carrier.
Retighten or replace.
Breather is clogged.
Clean or replace.
Oil seal is worn or damaged.
Replace.
Noisy differential
Gear is worn, damaged or broken.
Replace.
Bearing is worn, damaged or broken.
Replace.
Improper backlash.
Adjust
Loose spline fitness of side gear to
propeller shaft.
Replace parts.
Insufficient gear oil.
Add as necessary.
3.5 Service data
Parts
Item
Standard value
(mm)
Differential
Tightening torque of ring gear set bolt
140-160(N.m)
Tightening torque of cross case set bolt
140-160(N.m)
Thickness of pinion washers
1.562-1.613
Axle housing
Tightening torque of the set bolt for axle
housing and differential carrier.
150-175(N.m)
Tightening torque set bolt securing axle
housing to frame.
630-946(N.m)
Tightening torque set bolt brake board
to axle housing.
280-330(N.m)
Hub
I.D. of hub oil seal fitting part
164.6-165
Tightening torque of set bolt securing brake
drum to hub.
280-330(N.m)
Tightening torque of set bolt securing planet
carrier to hub.
98-113(N.m)
Tightening torque of hub nut.
480-560(N.m)

54
4. Brake system
4.1 General description
The brake system consists of two wheel brakes installed on the front axle and
parking brake on the propeller shaft.
4.2 Power brake (see Fig.4.1)
The wheel brake system consists of brake pedal, brake valve, power accumulator
and brake.
The power brake works by making use of pressure oil provided by gear pump of
hydraulic system, the pressure oil is divided to two directions, one for the brake valve,
and the other for the energy reservoir. They are controlled by the stroke of the brake
pedal.
4.2.1 Position of brake pedal (Fig. 4.2)
The brake pedal and the inching pedal are mounted on the left side of the frame by a
bracket. The piston of the brake valve is actuated through the push rod by the operation
of the brake pedal. The inching pedal also can control the brake valve by linkage with
the brake pedal, in the meantime, can control the inching valve in the transmission.
Fig. 4.1 Brake system

55
Fig. 4.2 Position of brake pedal

56
4.2.2 Brake valve (Fig. 4.3)
(1) Non-brake state
Since the brake valve A port is open, the nozzle of the pump and powered steering
is interlinked, the operation of steering is normal in the state of non-brake. When the
brake pedal isn’t been pressed, the oil pressure in the chamber D won’t go up in that the
port B is close.
(2) Brake state
A. When pressing the brake pedal, the piston 10 shifts to the left, valve sleeve 7 and
recoil piston 5 are pressed to the left by the spring group 8, in the meantime, the return
spring 6 is compressed to the left.
B. A port is closed owing to the shift of the part 7, and chamber D disconnects with
the port of the return oil tank, and the chamber D connects with the port of pump in that
the port B is closed.
C. Now the valve sleeve 7 shifts to the left, the oil pressure of the pump port and the
chamber D rises in that the C is compressed, in the meantime, the recoil piston 5 is
pushed by higher oil pressure in the chamber D .
D. When the max. pedal force acts on the right end of the piston, the bolt and the
pedal bracket can limit the position in order to make the oil pressure in the chamber D
lower the max. adjusting oil pressure.
E. When your foot releases the pedal, the valve sleeve 7 returning to the original
position relies on the opposite force, the process of the brake ends.
(3) Reservoir working performance
When the oil pump stops working (engine flameout) or damage, the reservoir is on
working performance.
A. Press the brake pedal, valve sleeve 7, backswing piston 5, check valve pin 3 will
be shifted left, the pin tips the ball over, at the same time, chamber D is connected with
reservoir connector, acts on the brake cylinder with reservoir pressure.
B. Leaves the pedal, valve sleeve, backswing piston and pin moves left, the ball of
check valve is connected with valve seat (check valve closed) acting by spring force,
the pin stops in the corresponding position.
C. Backswing moves right, chamber C opens, the oil of brake cylinder goes back to
the oil tank through chamber D.
4.2.3 Energy reservoir (Fig.4.4)
The energy reservoir can supply energy when the engine stops working or the oil
pump is in trouble. The type of the energy storage is spring type.
The buzzer of the warning switch sounds continuously when the reservoir doesn’t
storage energy.
When pressing the brake pedal, the oil pressure exceeds 3.9MPa, the check valve

57
opens and oil flows to the energy reservoir. Now the piston shifts to the left, the warning
switch doesn’t ring.
The reservoir storages the maximum energy along with the oil pressure rises
constantly, the oil pressure is 13 MPa, this value is controlled by the safety valve.
The energy reservoir storages the pressure energy, there are safety valve and
pressure alarm switch inside it. Preventive maintenance should be done by authorized
serviceman. Failure to use will cause crack. Depressurization treatment should be done
when the truck parking or preventive maintenance.
The method to decrease the pressure: After the engine is flameout, press the brake
pedal for 5 to 8 times, then the pressure of reservoir in brake system can be decreased.
Fig. 4.3 Brake valve
1
Plug
5
Recoil piston
9
Oil seal
2
One-way valve base
6
Return spring
10
Piston assy
3
One-way valve pin
7
Valve sleeve
4
Piston guide base
8
Spring group
Fig. 4.4 Energy reservoir

58
4.3 Parking brake
The parking brake is of internal expansion and lining type, and built in the output
shaft of the torque converter transmission.
The operation of the parking brake is shown in Fig.4.5.
When the forklift truck parks on a slope with standard capacity, the hand operation
force should below 300N. Adjust the pull force by diagrammatic direction.
4.4 Wheel brake (Fig. 4.6)
Wheel brake is clamp brake, installing symmetry around. Clamp brake consists of
clamp body, operating cylinder (four by one couple), rub pieces (two by one couple),
brake plate. The structure is seen in the picture. The wheel brake is consisting of a pair
of brake shoes, operating cylinder, a adjuster, 3-4 return springs and backing plates.
Two wheel brakes are provided on each end of the front axle. The adjuster adjusts the
clearance between the brake shoes and the inner surface of brake drum.
Fig. 4.5 Parking brake device

59
Fig.4.6 clamp brake
1
clamp body
6
dustproof cover
11
deflate spile
2
rectangle ring seal
7
O-ring seal
12
deflate seat
3
rub piece assy
8
bolt
13
nut
4
below crock cover
9
above crock cover
14
bolt
5
pump plunger
10
pin shaft

60
4.5 Troubleshooting
Problem
Possible cause
Remedy
Poor
braking
force
Fluid leakage from brake system
Repair
Maladjustment of brake shoe clearance
Adjust
Brake overheating
Check for dragging
Poor contact between brake drum and friction
piece
Adjust
Foreign matter adhered on friction piece
Repair or replace
Foreign matter mixed in brake fluid
Replace
Maladjustment of brake pedal
Adjust
Noisy
brake
Hardened friction piece surface or
foreign matter adhered thereto
Repair or replace
Deformed backing plate or loose bolts
Repair or replace
Deformed shoe or incorrect installation
Repair or replace
Worn friction piece
Replace
Loose wheel bearing
Replace
Uneven
braking
Oil-contaminated friction piece
Repair or replace
Malfunction operating cylinder
Repair or replace
Eccentric brake drum
Repair or replace
Maladjustment clearance of friction piece
Adjust
Improper tire pressure
Adjust
Soft or
spongy
brake
Brake fluid leaks from system
Repair
Maladjustment clearance of friction piece
Adjust and repair
Air mixed in brake system
Exhaust air
Maladjustment of brake pedal
Readjust

61
5. Steering system
5.1 General description
Steering system contains mainly a steering hand wheel, a steering column, a
cardan joint, a powered steering unit, a steering axle and a steering cylinder.
The steering shaft is connected with the steering unit and steering hand wheel by
the joint. The steering column may be tilted properly forward or backward. Turn the
hand wheel clockwise, the forklift truck will turn to the right, on the contrary, the truck will
turn to the left.
Main parameter and structure of the steering system sees below:
Item
Parameter & structure
Type
Rear wheel steering powered
Diameter of steering hand wheel
mm
360
Steering
unit
Type
BZZ powered steering unit
Displacement
min
280
Rated pressure
MPa
16
Steering
cylinder
Type
Double-action type
Cylinder dia. / Rod dia.
mm
Φ115/Φ85
Stroke
mm
2×216
Divider
Setting pressure
MPa
12.5
Rated displacement
27
Steering
axle
Type
Transverse cylinder type
Steering angle(outside/inside)
76°/54°
Rear tread
mm
1700
Interval of knuckle spindle
mm
1500
Diameter of cardan joint
mm
Φ42
Wheel
Tire
9.00-20-14PR
Rim
7.00-20
Pressure
KPa
760
5.2 Hand wheel
Hand wheel is operated in normal way, that is to say,
when turning the hand wheel right, the truck will turn right.
When turning the hand wheel left, the truck will turn left. The
rear wheels of the forklift truck are steering wheels, which
make the tail section of the truck swing out when turning. The
turning method can be mastered easily through practice.

62
5.3 Cycloid gear type powered steering unit
The steering unit can transmit the pressure oil from the flow divider by pipes to the
steering cylinder in terms of the rotating angle of the hand wheel. When the engine stop
running, the charging pump will not work, in this case a man-powered steering should
be adopted. The sketch map of powered steering system is shown as Fig.5.1. The
structure of the steering unit is shown as Fig.5.2.
Fig. 5.1 Hydraulic steering system
1.
Hand wheel and steer shaft
5.
Steering cylinder
2.
Oil pump
6.
Steering axle
3.
Flow control valve
7.
Hose
4.
Hydraulic steering unit

63
5.3.1 Steering unit assy
Fig.5.2 Cycloid gear type powered steering unit
1.
Spacing sleeve
6.
Joint sleeve
2.
Valve body
7.
Rotor
3.
Valve core
8.
Stator
4.
Interlock shaft
9.
Valve sleeve
5.
Spring piece

64
5.3.2 Work principle
Valve bore, valve sleeve, valve body in the redirector makes up of along valve,
having an effect of controlling the direction of the oil flow. Rotor and stator makes up of
cycloid mesh, having an effect of measure element when turning, to make sure that the
oil quantity in oil crock and corner of steering wheel makes direct ratio; having an effect
of hand moving oil pump when turning by manpower; and linkage shaft having an effect
of transferring wrest rules.
Middle position (steering wheel isn’t running), in the opening ring system, the oil
from oil pump passes through the lumen of valve bore to oil box.(Fig.5.2 a)
When turning by power, oil from oil pump pass through the along valve to cycloid
pin wheel mesh, force rotor running following steering wheel, and press the ration oil to
the left or the right of crock, force turning wheel to turn by power, and oil in the other
cylinder flows back to oil box.(Fig.5.2 b, c)
When engine comes out flameout, the steering wheel will be operated by
manpower, with valve bore, melt, interlock shaft, driving rotor to press oil in one cylinder
to the other one, then force turning wheel, to carry out turning by manpower (Fig.5.2 d).
Filling oil by oil box when passing through filling unilateralism valve.
Fig5.3 Oil circuit of steering unit

65
5.3.3 Usage of the steering unit
(1) Install the steering unit
When installing the steering unit, it must ensure concentric with the connecting
shaft, axial clearance can avoid propping by valve core, checking the hand wheel if it
can return to the neutral position flexibly after installing.
The allowable flow rate of the inlet oil pipe is 1-1.5m/s, the allowable flow rate of the
outlet oil pipe is 4-5m/s. The experimental pressure of the high pressure tube must high
than 1.5 times as much as the maximum working pressure.
For the safety and convenient repair, it is suggested that a connector should be
installed at the inlet port of the steering unit for a pressure gauge.
(2) Oil temperature range:-20℃~+80℃
Normal oil temperature:+30℃~+60℃
(3) Choose oil: N46 or N32 hydraulic oil
(4) Filter oil: The accuracy of oil inputted into the steering unit is 30 micron.
0.2-0.3MPa Back pressure of outlet oil of the steering unit can prevent the oil from
flowing into the oil for the manpower turning.
(5) Cleaning pipes of the system and closed oil tank can reduce the oil pollution.
(6) Trial run: Clean the oil tank and add oil to the top level before trial run. Loose the
bolt connector of the steering cylinder and bleed air at the low speed of the oil pump.
Disassemble the piston rod and steering wheel, turn the hand wheel, make the
piston at the limit left or right position, then add oil into the oil tank to the top level.
Tighten all bolt connectors and connect the piston rod, check the steering system
for the good condition. If the hand wheel can’t be operated flexibly, it’s necessary to find
possible cause and remedy it.
Check the system pressure when the piston of the steering cylinder reaches the
limit position.
(7) Maintenance: Check the condition of the leakage, oil level of the oil tank
everyday. Regularly replace the oil filter and oil. During operation abnormal condition is
found, it’s necessary to find possible cause and remedy it. Don’t turn the hand wheel by
two men at the same time.

66
5.3.4 Check and maintenance of the steering unit
In order to keep the steering system in good working condition and avoid
accidents, it is necessary to check the steering system regularly. The structure of
steering unit is referred to Fig5.4.
(1) Regularly check water, foreign matter and acid number of the working oil, if
necessary, replace it with new oil.
(2) When checking the steering system, don’t disassembly the steering unit readily,
if the steering unit is in trouble, please ask professional service men to repair it.
(3) Dismounting tool used and repair site must be clean. It would be the best
adopting indoor operations.
(4) Notes of assembling
a. Wash all parties clearly with gasoline or kerosene before assembling, for there is
paint on the connection surface, it must be washed with acetone. You can’t wash the
parties with cotton yarn or cloth, but with brush, even clear away with compress air if
possible. Shouldn’t immerse the rubber in the gasoline for a long time. After assembling
the steering, join 50-100ml pressure oil in the orifice, turn the valve bore to right and left,
then install and practice the truck if they are not abnormal.
b. Valve body, block plate, stator, rotor and the connection surface of the back
cover must be kept clean, and they can’t be hurt.
c. Notice that the whorl cover most be lower than the surface of the valve body.
d. Block ring and slip ring have an inverse surface, the surface of block ring should
face the front cover, while the slip ring faces the valve bore.
e. There is mark on the surface of the rotor and interlock shaft, the mark must be
face to face when assembling.
f. The gasket of the bolt (with pin) must be cuprum or aluminum.
g. The method of riveting the seven bolt in the back cover: screw one by two in
order, not in turn but gradually, with the power of 30-40N.m.
h. When assembling the oil pipe, notice the mark “in”, “back”, “left”, “right” on the
valve body, they must be connected with the right oil pipe.
(5) Disassembly and assembly
a. Order of disassembly: front cover-block ring-slip ring-valve sleeve- (shim- shift
arm-valve core-spring piece)-back cover-spacing sleeve- stator-rotor- interlock
shaft-block plate-pin cover-steel ball-valve body.

67
b. Order of assembly
valve core-spring piece-valve sleeve-shift arm-shim-valve body-slip ring-block ringfront cover-steel ball-screw cover-block plate-interlock shaft -rotor-stator
-spacing sleeve-back cover.
Fig5.4 Structure of steering unit
5.3.5 Inspection on reassembly of steering system
(1) Check the arrangement of the hydraulic pipeline and the turning direction for
correctness.
(2) Check the force necessary to turn the steering handwheel to right and left until it
can’t be turned any more to see if they are identical each other and check the operation
if the steering handwheel for smoothness during above operation.
(3) After assembling a steering system, put up the turning wheel, make the engine
to run at a slack speed, then turn the steering wheel slowly, and do it times and times, to
exhaust the air in the hydraulic pipeline and cylinder. Check whether voice for it to turns
is normal or not. If abnormal voice can’t be heard, it says that the air has been
exhausted absolutely. Then make the engine run at a slack speed, to go up the oil
temperature.
(4) Measure the operation of steering
Place the truck on the dry and flat road. Attach the spring equilibrator to the verge

68
of the steering wheel with the parking detent, to measure the operation of steering,
which must be under 150N.
(5) Measure the pressure with pressure meter (15-20MPa), cutoff valve and soft
tube in Fig. 5.4.
Remove the split-flow valve to the line of the turning implement, engage a line with
pressure meter on the side of diffluent valve, engage a line with breaking valve on the
side of turning implement, then make the engine run at a slack speed.
When the steering wheel is at a free state, the oil pressure is about 0.5-2MPa. If the
pressure is higher than it, check whether the diffluent valve and line is stopped or not. If
there is no abnormal thing, speed up the engine to about 1500r/min. Then close the
parking valve slowly and notice that the temperature of pressure is improved.
Move the highest pressure of the diffluent valve to 12MPa, so, when the parking
valve is closed, the pressure meter will show its pressure.
If the pressure is over 12MPa, it shows that the diffluent valve has malfunction. But if the
pressure is too low, it shows that the oil pump has malfunction or the spring of the
diffluent valve has rupture. In this circumstance, the time of the closed of the parking
valve can’t be over 15 seconds.
Notice: The oil pump provides pressure oil to make the cylinder run, so its task
must be thought in two ways, demarcate pressure and rating flux.
The pressure is to force the cylinder while the flux is relation to the speed of the
cylinder. It says that, even though the pressure is normal, to 12MPa, if the flux is lack,
the cylinder can’t run normally, resulting in that the steering is too heavy to operate. So
when the diffluent valve needs to be disassembled and be assembled again, adjust the
flux valve and safety valve properly according to the capacity and the operation of the
cylinder, then mark in the proper position to assemble again or measure the distance of
the bolt.
Fig5.5 Measure the pressure

69
5.3.6 Steering unit troubleshooting
Problem
Possible cause
Remedy
Oil
leakage
Oil leaks from the connection surface of
valve body, stator and rear cap due to
the dirty.
Clean.
The rubber ring is worn.
Replace rubber ring.
The washer of limit bolt is uneven.
Grind or replace washer.
Hard
steering
operation
Oil pump can’t supply insufficient fuel.
Select appropriate oil pump or
check the divider.
Air mixed in steering system.
Vent air and check oil pipes.
Oil tank isn’t full.
Add oil to specified level.
Oil is too sticky.
Use recommended viscosity
oil.
The ball check valve inside the valve
body malfunctioning.
If the ball is lost, fit a Φ8 ball. If
the ball is blocked by the dirty,
clean it.
Oil pressure of the divider is lower than
the working pressure or the divider is
blocked by the dirty.
Adjust the pressure of the
divider or clean it.
Steering
malfunction
Spring piece is broken off. The hand
wheel can’t return to neutral position
automatically.
Replace the spring piece.
Shift arm is broken off or deformed.
Replace the shift arm.
Drive shaft is broken off or deformed
Replace the drive shaft.
Mutual position between the rotor and
the drive shaft is disorder.
Reassemble the rotor and the
drive shaft.
Bilateral overload valve is out of order.
(the steel ball is seized up by the dirty )
Clean the valve.
Handwheel
can’t return
to neutral
position.
1. Valve core and the column is
decentraction.
2. Valve core is propped by the column.
3. Hard to steer the column.
4. Broken spring piece
Readjust or replace.
No hand
steering
device
Radial and axial clearance between the
rotor and stator is improper.
Replace rotor and stator.

70
5.4 Steering system troubleshooting
5.4.1 Inspection after reassembling the steering system
(1) Check the force when turning the steering handwheel to right and left until it
can’t be turned any more to see if they are identical each other and check the operation
if the steering handwheel for smoothness during above operation.
(2) Check the arrangement of the hydraulic pipeline and the turning direction for
correctness.
(3) Lift up the rear wheels and slowly turn the handwheel over several times to
exhaust the air in the hydraulic pipelines and the cylinder.
5.4.2 The troubleshooting of the steering system for the distributor valve is the
following table:
Problem
Possible cause
Remedy
Steering wheel is
caught when rapidly
turned.
Flow control valve spool
blocked
Disassemble, repair or
replace
Flow control valve spool worn
Replace as assembly
Oil pressure does not
rise.
Relief valve stuck open
Replace as assembly
Oil pressure higher
than relief set
pressure.
Relief valve stuck closed
Replace as assembly
Noisy relief valve
Relief valve vibrating.
Replace as assembly
Too high oil
temperature.
Relief valve stuck closed
Replace as assembly
Hard steering
operation while idling.
Relief valve stuck open
Replace as assembly
Flow control valve spool
blocked
Disassemble, repair or
replace
Flow control valve spool worn
Replace as assembly
Varying steering
force.
Relief valve vibrating.
Replace as assembly
Flow control valve spool
blocked
Disassemble, repair or
replace
Flow control valve spool worn
Replace as assembly
Hard steering
operation.
Relief valve stuck open
Replace as assembly
Flow control valve spool
blocked
Disassemble, repair or
replace
Flow control valve spool worn
Replace as assembly

71
5.5 Rear axle
The rear axle is primarily composed of an axle body, right and left knuckles, tie rods,
wheels, hubs and steering cylinder. The steering axle is of cranks and slider mechanism.
The cylinder piston rod pushes the knuckle steering through tie rod, causing wheel’s
deflection and truck’s steering. The steering axle is bolted to the rear frame by the
buffer.
(1) Rear axle body
The rear axle body is of the steel plate weld construction type and has boss holes
for knuckles at both ends.
(2) Right and left knuckles
On the knuckle, a hub for installing a wheel thereon is installed by two bearings.
The hub is provided with an oil seal for grease. The knuckle is installed between two
bosses with bearings through which a king pin is inserted. Lubricate all bearings by a
nozzle installed on the top cover, users must add lubricant in time.
(3) Steering cylinder
The steering cylinder is of double-action piston type. The seal unit consists of the
supporting ring and O-ring seal. The construction of the steering cylinder is shown as
Fig. 5.6.
Fig. 5.6 Steering cylinder
1.
Dust ring
5.
Back-up ring
9.
Bushing
2.
Seal ring
6.
O-ring
10.
Piston rod
3.
Snap ring
7.
Back-up ring
11.
Cylinder body
4.
O-ring
8.
Bearing

72
(4) Rear wheel bearing pre-load adjustment
a. As shown in Fig5.7, fill up the chamber formed by wheel hubs, wheel hub
bearing and wheel hub covers with lubricating grease. Coat the lips of the oil seals with
lubricating grease.
b. Press the hub bearing into the hub and fit the hub on the knuckle shaft.
c. Fit a flat washer and tighten a castle nut with torque of 206~235N.m and loosen
it and then tighten it again with torque of 9.8N.m.
d. To ensure firm installation of the hub, slightly knock at it with a wooden hammer
and in the meantime, rotate the hub for 3~4 turns.
e. Tighten the castle nut and align one of its notches with a hole drilled in the
steering knuckle.
f. Again slightly knock at the hub with a wooden hammer and in this time, rotate
manually the hub for 3~4 turns to ensure its smooth rotation with a specified torque of
2.94~7.8N.m.
g. If the torque value necessary to rotate the hub is more than the specified one
above-mentioned, screw out the castle nut for 1/6 turn and measure the torque value
then.
h. When the torque value measured is up to the specified one, lock the castle nut
with a cotter pin.
Fig5.7 Pre-load adjustment

73
6. Hydraulic system
Hydraulic
oil pump
Type
Gear pump
Displacement
32 ml/r 36 ml/r
Control
valve
Type
Two-pool type with relief valve, flow divider
and tilt self-locking valve
Setting
pressure
19 MPa
Dividing
pressure
12 MPa
Flow rate
25 L/min
6.1 General description
The hydraulic system mainly consists of main pump, control valve, high & low
pressure oil pipes and joints. The main pump is a gear type and installed on the side of
the transmission. As the engine runs, the main pump is driven to draw up oil from the
tank and send it to the control valve. The control valve, provided with a relief valve to
keep the circuit pressure within the specified one, controls the cylinders by changing
over the oil passages inside the valve body with the spools.
6.2 Main pump
The main pump consists primarily of a drive gear, driven gear and pump body
which contain the two gears and other components. The drive gear is in mesh with the
driven gear.
6.3 Control valve (See Fig.6.1)
The control valve is a sectional type consisting of the inlet section, plunger section
and outlet section which are assembled with three bolts.
At the inlet section there is a cartridge type relief valve to set the oil pressure in the
circuit. The steering relief valve is used for adjusting the oil pressure in the steering oil
circuit. Twist them clockwise, raise the oil pressure, on the contrary, reduce the oil
pressure. The plunger section controls the hydraulic cylinders by changing over the flow
of oil from the relief valve with plungers. The tilt cylinder plunger section is equipped
with a tilt lock valve. Oil returned from the cylinders is returned to the tank through the

74
outlet section. Each section is sealed with O-ring, and the oil passage at the high
pressure side is given a check valve.
Caution: Don’t adjust the pressure of the main relief valve at will. If the pressure is
too high, the hydraulic system and hydraulic component may be damaged. When
maintaining or using, if oil pressure isn’t the same as the standard value, on the basis of
JB/TT3300 test way, the professional serviceman should adjust the pressure according
to the following procedures:
(a) Screw the plug screw off the inlet port of the control valve, install a 25MPa oil
pressure gauge.
(b) Operate the tilt lever, measure the pressure when the oil pressure stroke to the
end.
(c) When the oil pressure isn’t the same as the standard value, twist the adjusting
nut, twist it clockwise, raise oil pressure, on the contrary, reduce oil pressure.
(d) After adjusting, tighten the nut.
Fig.6.1 Control valve
6.4 Control valve operation
(1) Middle position (See Fig.6.2)
The oil that is expelled from the main pump will pass the middle passage and be
back to fuel tank. This moment, the cylinder port A & B must be off.

75
Fig.6.2 Middle position
(2) Push slide valve (See Fig.6.3)
At that time, the middle passage is off. The oil that is come from the oil enter will
push out the one-way valve, and inflood cylinder port B. The oil that is expelled from the
cylinder port A will pass the low-pressure passage and be back to fuel tank. The slide
valve will replace to the middle position recur to the replacement spring.
(3) Pull slide valve (See Fig.6.4)
This moment, the middle position passage is off. The oil that is come from the oil
enter port will push out the one-way valve, and inflood cylinder port A, the oil that is
expelled from the cylinder port B will pass the low-pressure passage and be back to fuel
tank. The slide valve will replace to the middle position recur to the replacement spring.
Fig.6.3 push slide valve Fig.6.4 pull slide valve

76
6.5 Main safety valve operation
(1)The main safety valve must be installed between the cylinder HP port and LP
passage. The oil that pass through the valve core will be acting on the different diameter
surface A & B, so the core K of the one-way valve and the core D of the main safety
valve will be firmly fall into the valve base. (See Fig.6.5)
(2)When the oil pressure of the cylinder HP port is overrun the spring limit pressure,
the precursor valve core E will be open, and the oil will inflood the hole via the valve
core circumference, then reach the LP passage. (See Fig.6.6)
(3)Once the precursor valve core E is open, the back pressure of the core C will be
reduced, so the core C will be shift to the right direction, then be on the core E. As a
result, the back oil route of the core D will be cut off, the inside pressure will be also
reduced. (See Fig.6.7)
(4)Compared with the cylinder port HP, the inside pressure is imbalance, then the
safety valve core will be open, so the oil of the HP side will reach LP passage directly.
(See Fig.6.8)
Fig.6.5 Fig.6.6
Fig.6.7 Fig.6.8

77
6.6 Tilt lock valve operation
Tilt lock valve is used for preventing the shaking of the mast (because the tilt
cylinder maybe cause the inside negative pressure), at the same time, it can avoid the
danger that the mast will be tilted due to the wrong operation (hit the tilt operation staff)
when the engine is off. In traditional structure, even if the engine is off, the mast will be
pitch if someone hit the tilt operation staff. But using this new-style tilt lock valve, in spite
of the strength that push the tilt operation staff, this complexion will be not occurred. Tilt
lock valve structure, see Fig.6.9. In the picture, the port A is connect with the front of the
tilt cylinder and the port B is with the behind. When pull the tilt operation staff ( pull slide
valve), the oil that is come from the oil pump will be inpour A, and the oil that is come
from B port will be back to Oil tank. As a result, the mast will be retroverted. On the other
hand, push the tilt operation staff (push slide valve), the oil that is come from oil pump
will be inpour B, recur to the HP oil, the lock valve begin to work, then Port A can
connect with LP, the mast will be pitch. But when the engine is off, that is, have no HP oil
make the lock valve work, so Port A cannot connect with LP, and the mast will not be
pitch, at the last, the tilt cylinder will not be cause the negative pressure.
Fig. 6.9 Tilt lock valve
T: to oil tank P: to oil pump A,B: to tilt cylinder

78
6.7 Hydraulic circulation system (Main circuit)
The hydraulic system sketch sees Fig. 6.10.
The hydraulic circulation system of the main circuit is complicated with the
hydraulic for power steering. The hydraulic piping is of O-ring fitting type with excellent
sealing performance, providing secure oil tightness.
The hydraulic oil sent from the rear main pump flows directly to the control valve,
while the hydraulic oil sent from the front main pump is divided by the flow divider valve
in two portions for steering and load handling operation.
The hydraulic oil for load handling flows into the control valve and mingles with the
hydraulic oil from the rear main pump. With the control valve in neutral position, the oil
returns to the oil tank, passing through the valve.
When the lift lever is pulled, the hydraulic oil from the control valve flows through
the flow regulator valve and reaches the lower part of the lift cylinder piston to push up
the piston rod. When the lift lever is pushed, the circuit between the lower part of the lift
cylinder piston and the oil tank is opened, and the piston begins to descend due to the
weight of the piston rod, lift bracket, forks, etc. In this case, the oil returning to the
control valve is regulated by the flow regulator.
When the tilt lever is operated, the hydraulic oil from the main pump reaches one
side of the piston to push it. The oil pushed by the piston returns to the oil tank through
the control valve.
Fig.6.10 Hydraulic system
Ton
t 8 10
Flow of control valve Q1
L/min
160
160
Flow of steering unit Q2
L/min
25
25
Pressure of primary safety valve P1
MPa
20
20
Pressure of steering safety valve P2
MPa
12.3
12.3

79
6.8 Troubleshooting
Problem
Possible cause
Remedies
Gear pump
can not be
pressurized.
Parts worn.
Disassembly, repair or replace
parts.
Blocked oil pipe.
Make the oil pipe through.
Blocked oil tank or filter.
Clean dirty or replace oil.
Too high oil stickiness or oil
temperature.
Use recommended oil.
Noisy or
undulate
pressure.
Blocked oil filter.
Clean dirty.
Lower oil level.
Add oil up to specified oil level.
Air entering in resulting from
loose suction connections.
Retighten each connection.
Gear precision is reduced.
Replace gear or shave.
Control valve
leaks.
O-ring seal (ends of valve body)
broken down.
Replace O- ring seal.
O-ring seal (connections of valve
body) broken down.
Replace O- ring seal.
Spool can not
be reset.
Return spring become deformed.
Replace return spring.
There is dirty between valve body
and spool valve.
Clean.
Valve body deformed with the too
tight coupling bolt.
Retighten coupling bolt.
The pressure
of the relief
valve is not
right.
Pressure regulating spring
deformed.
Replace pressure regulating
spring.
Cone valve is worn.
Replace cone valve.
Lock nut is loosen.
Tighten and lock.
Outlet port is block up.
Clean.
The lower
slippage of
the mast is
too large.
The clearance between valve
body and spool becomes large.
Repair or renew spool.
The spool isn’t in neutral position.
Make the spool in neutral
position.
Cone valve is worn or seized by
dirt.
Replace cone valve or clean
dirty.

80
6.9 Maintenance
6.9.1 Detaching of multi-way valve
Detach the valve from forklift and clean it.
(1) Loose bolts and separate each part ,please note that 1-way valve or spring on
contact surface shall be kept well.
(2) Loose the bolts at a side of slide valve end as well as at cover side, and then
detach them together with valve leather, o-ring and sealing washer.
(3) Place slide valve onto table vice, loose bolts and dismantle spring and its base,
spring and valve rod shall be taken out in the case of tilt slide valve with self-locking tilt
valve.
6.9.2 Reassembly of multi-way valve
Clean all parts with mineral oil and check if there is any burrs or scars, replace it if
necessary. valve body ,slide valve and valve rod shall be in good order, replace
complete part if necessary.
(1) Clamp the slice valve with table vice, and then assemble valve rod and spring in
right direction.
(2) Put O-ring, valve leather, sealing washer, spring and its base in good order into
end of slide valve, and then cover it and tighten the bolts at 25~32N.m.
(3) Insert slide valve (1 piece)assembly into valve body and cover it, tighten the
bolts with hex at hexagon slot (torque9~11N.m).
(4) Fix O-ring and valve leather onto the head of slide valve and screw the bolts
with 4.6~5.8N.m.
(5) After the above assembly, 1-way valve ,spring and o-ring shall be inserted into
every slide valve, tighten it with 3 bolts (torque 103N.m for large bolts, 66N.m for small
ones).

81
7. Lift cylinder & tilt cylinder
Lift
cylinder
Type
Single-action piston type, with cut-off valve
Bore diameter
Φ100
Stroke
1495mm (Only for 3m lift height)
Tilt
cylinder
Type
Double-action piston type
Bore diameter
Φ115
Stroke
242mm
7.1 Lift cylinder
The two lift cylinders of single acting type are used and located behind each outer
mast frame. The bottoms of the cylinders are sustained by the mast support of the outer
mast while the tops of cylinders, or the piston rod tops are inserted into the upper beam
of the inner mast.
The lift cylinder assembly consists primarily of a cylinder body, piston, piston rod
and cylinder cap. At the lower part of the cylinder body is arranged an inlet for
high-pressure oil, and at the upper part there is an outlet for low-pressure oil above the
piston packing, to which a return pipe is connected.
The piston is fastened to the piston rod with a steel clamp. A wear ring, packing
and back-up ring are attached to the outside periphery of the piston which is moved
along the inner surface of the cylinder by high-pressure oil. An oil seal and bushing are
installed on the cylinder cap which is screwed into the cylinder body. The bushing
supports the piston rod, and the oil seal prevents dust from entering the cylinder. The
upper end of the piston rod and inner mast upper beam is locked with bolts.
When the lift lever is tilted backward, high oil pressure is sent into the lift cylinders
through their inlets to push up the piston rods and the piston head, causing the forks to
rise through chains. The height from the ground to the fork upper position when the
inner mast channel beam upper ends exceed the outer mast upper ends is called “Free
lift” . Within this range, the mast height does not vary.
With the lift lever tilted forward, the piston rods of the lift cylinders descend by the
weights of the piston rods, inner mast, lift bracket, finger bar and forks, causing oil under
the piston to flow out of the cylinders. The oil discharged from the cylinders is regulated
by the flow regulator and returns through the control valve to the oil tank.
The structure of the lift cylinder is shown in Fig. 7.1.
Note: Please pay more regard to safety when adjusting the lift cylinder.

82
Fig.7.1 Lift cylinder
1. Adjusting pacer
2. Dust ring
3. Yx ring
4. Cylinder cap
5. Bushing
6. O-seal ring
7. Cylinder body
8. Piston rod
9. Snap ring, steel
10. Wear ring
11. Yx ring
12. Piston
13. Lift chain
14. Chain wheel
15. Ball bearing
16. Snap ring
17. Spring
18. Cut-off valve
19. Upper beam

83
7.2 Flow regulator
The flow regulator is located between the control valve and the high pressure ports
of the two lift cylinders, near the left lift cylinder. The structure of the flow regulator valve
is shown in Fig7.2.
When the lift spool valve is placed in the “lift” position, the oil from the control valve
flows through the oil chambers A and B, C, oil holes H, G, D, E, and the chamber I to the
lift cylinder without any regulation. When the control valve is placed in the “down”
position, the oil flows through chamber I, oil holes E, D, G, H, and chambers C, B, A to
the valve. Then there is pressure difference between chamber A and C. Turn on the ball
valve (4), a pressure difference overcomes the force of the spring (9) and moves the
valve core (5) right, thus the oil flow being decreased by narrowing of the hole G and H,
and reduces the oil flow passing through the throttle plate.
The flow regulator valve serving both as a flow regulating valve while forks are
being lowering and a safety device if rubber hoses between the control valve and lift
cylinders are damaged due to any reason.
Fig.7.2 Flow regulator
1. Spring
4. Nylon ball
7. Snap ring
10. Joint
2. Valve sleeve
5. Valve core
8. Valve body
3. Spring
6. Throttle plate
9. Spring

84
7.3 Tilt cylinder
Two tilt cylinders of double acting type are provided at each side of the frame. The
front end of the piston rod is installed on the mast and the cylinder tail is on the frame
with pins. The tilt cylinder assembly consists primarily of a cylinder body, cylinder cap,
piston and piston rod. The structure of the tilt cylinder is shown as Fig7.3.
When the tilt lever in the driver’s room is tilted forward, high pressure oil enters
from the cylinder tail to shift the piston forward, tilting the mast forward 6°. With the tilt
lever tilted, high pressure oil enters from the cylinder cap side. This shifts the piston to
the rear, causing the mast to tilt backward 12°.
Fig7.3 Tilt cylinder
1.
Ear ring
7.
Guide sleeve
13.
Piston
2.
Dust ring
8.
O-ring
14.
Piston rod
3.
Adjusting sleeve
9.
Bearing
15.
Plug
4.
Dust ring
10.
Cylinder body
16.
Screw
5.
Snap ring
11.
Yx-ring
17.
Snap ring
6.
Yx-ring
12.
Retainer ring
18.
Snap ring

85
8. Lifting system
8.1 General description
The lifting system is of two-stage, rolling telescopic mast type. The inner mast
frames have J-shaped section. The outer mast frames have C-shaped section. The
masts of forklift trucks all contain a free lift range. The structure of the mast sees Fig. 8.1
and Fig8.2.
Fig8.1 Mast (8t)
1. Fork
2. Lift bracket
3. Lift chain
4. Inner mast
5. Outer mast
6. Tilt cylinder
7. Lift cylinder
Fig8.2 Mast (10t)
1. Fork
2. Lift bracket
3. Lift chain
4. Inner mast
5. Outer mast
6. Tilt cylinder
7. Lift cylinder

86
8.2 Inner & outer mast
The mast assembly is of the free lift range-contained two stage telescopic type
consisting of the inner and outer mast, and is sustained by mast supports. The mast
supports are welded to the bottom of the outer mast, being extended from the axle
housing. The outer masts are provided with brackets for lock pins of tilt cylinder
connecting hardware. The mast is tilted by operation of the tilt cylinders.
The inner mast is composed of right and left mast frames which are connected with
each other by upper and lower connecting members. At the upper inside of each outer
mast frame an end roller is installed on the end roller shaft welded to the frame, with a
snap ring. In addition, the outer mast frames are fitted with side rollers to sustain the
inner mast frames. At the lower outside of each inner mast frame an end roller is
installed on the end roller shaft with snap ring, which is welded to the inner mast. Under
the end rollers other side rollers are located to sustain transverse load. With the aid of
these rollers, the inner mast can smoothly operate.
Notice: Please pay more regard to safety when maintaining the main rollers and
side rollers on the upper of outer mast.
8.3 Lift bracket
At the lift brackets, end rollers that roll along the inside of the inner mast frames are
installed on the end roller shafts with snap rings. The end roller shafts are welded to the
lift brackets. The side rollers that roll along on the inside of the inner mast frames are
bolt fitted, being shim adjusted. To prevent the rolling of the finger bar, two retaining
rollers are used, which roll along on the outside of inner mast frames. The longitudinal
load is sustained by the end rollers of which the upper ones emerge from the top mast
when the forks reach the maximum lift height.
The transverse load is sustained by upper retaining rollers and lower side rollers. As we
mentioned above, the mast assembly and lift brackets are designed with rigidity, stability
and smooth operation in mind.
Furthermore, the finger bar and lift brackets are made into one body construction
using high tension steel to improve the durability. This meets the ISO Standards.
The two forks installed on the finger bar are made of special alloy steel which has
been subjected to heat treatment.
The fork pin fastens the fork on the definite position. When adjusting the clearance

87
of the fork, pull the fork pin turn 1/4 circle, the fork clearance must be adjusted
according to the loaded goods.
8.4 Roller position
There are three kinds of rollers, main roller, side roller group and side roller. They
are separately mounted on the inner mast, outer mast and lift bracket. The main rollers
sustain the main loads from front, which can’t be adjusted, and rear direction and the
side rollers sustain the side loads with the left and right side clearance adjusted by the
gasket group, this will make the inner mast and lift bracket move freely. See Fig8.3,
Fig8.4.
Fig8.3 Roller mounting (8t forklift)
Fig8.4 Roller mounting (10t forklift)

88
8.5 Adjustment of lifting system
a. The clearance between the inner mast and the guide plate of the outer mast is
0.5-1.0mm, which is adjusted by the spacer of the guide plate. The clearance between
the side roller and the channel beam is 0.3-0.8mm, which is adjusted by the axial bolt
inner the roller.
b. Make the forks descend to the ground, adjust the lifting chain to assure the
distance between the center of lift bracket lower rollers and the bottom of inner mast is
smaller than 25mm.
c. Make the mast assembly tilts backward, adjust the pulling force of lift chains and
let the tightness of lift chains be equal.
d. Make use of the spacer of the lift cylinder to adjust the error occurred between
the right and left cylinders in height.
8.6 Maintenance and adjustment
8.6.1 Adjustment of lift cylinder (Fig8.5)
When replace the lift cylinder, inner mast or
outer mast, we shall readjust the stroke of the lift
cylinder as following:
(1) Install the piston rod in the upper beam of
the inner mast without shims.
(2) Lift the mast slowly to the max. stroke of the
cylinder and check the two cylinders synchronize or
not.
(3) Install shims between the top of the piston
rod of the cylinder which stop first and the upper
beam of the inner mast. The thickness of the shim is
0.2mm or 0.5mm.
(4) Adjust the tightness of lift chains. Fig8.5
Notice: Please pay more regard to safety when adjusting the lift cylinder at an
elevated height.

89
8.6.2 Carriage adjustment
(1) Park forklift on horizontal place and let mast vertical.
(2) Put the bottom of fork onto ground, screw the adjustable nut at the end of joint
and let main idler wheel come out l/4-l/3 of its radius. See Fig8.6.
Fig.8.6
(3) Lift fork to Max. height, and ensure gap B
between limit blocks of fork and of inner mast shall be
5-10mm. See Fig8.7.
Fig.8.7
(4) Put down the fork and tilt to specified position, adjust
the nut at chain upside and tensility of two chains should be
same. See Fug8.8.
Fig.8.8
8.6.3 Replace rollers of the lift bracket
(1) Place a pallet on the forks and let the truck parking on the horizontal ground.
(2) Make the forks and the pallet down to the ground.
(3) Disassemble the end nipple of the upper chain and take the chain down from
the sheave.
(4) Lift the inner mast (See Fig8.9 ①).
(5) Make the truck back-up if the lift bracket is fully separated from the outer mast.
(See Fig8.9 ②)

90
(6) Replace the main rollers.
·Disassemble all the snap rings and take out the main rollers with a drawing tool
except the adjusting shims.
·Ensure the new rollers have the same types as the replaced rollers. Install the new
rollers inside the lift bracket and fasten them with snap rings.
8.6.4 Replace rollers (Fig8.10)
(1) Use the same way as 8.5 to disassemble the lift bracket from the inner mast.
(2) Let the truck parking on the horizontal ground and wedge up the front wheels for
250mm to 300mm.
(3) Apply the parking brake and wedge up the rear wheels.
(4) Disassemble the bolts which fasten the lift cylinder and the inner mast. Hang up
the inner mast not to loose the shims of the piston rod heads.
(5) Disassemble the connecting bolts for the lift cylinder and the bottom of the outer
mast. Disassemble the lift cylinders and the oil pipes between the two cylinders without
loosen the oil pipe joints.
(6) Main rollers on the upper outer mast will be showed on the top of the inner mast
as soon as main rollers were taken apart from bottom of the inner mast after laying
down the inner mast.
(7) Replace the main rollers.
·Disassemble the upper main rollers with a drawing tool, don’t loose the adjust
shims.
·Install the new rollers and the shims disassembled before.
(8) Hang up the inner mast to let all the rollers in the mast.
(9) Reassemble the lift cylinder and the lift bracket.
Fig8.9 Fig8.10

91
9. Electric system
9.1 General description
The electric system for this forklift truck is of the single-pole type. It mainly consists
of the following systems (See the principle diagram in Fig9.1, Fig9.2):
(1) Charge system
This system contains generator, battery, charging indictor, etc. It supplies current
for all the electric appliances.
Voltage: DC24V
Dealing with the waste and worn batteries according to relevant laws and
regulations.
(2) Starting system
This system mainly consists of mid-relay, starting relay (only ISUZU diesel engine),
key switch, starting protection circuit, starting motor, etc. This system is used for starting
the engine.
(3) Parking control system (ISUZU diesel engine)
This system consists of the key switch, relay for stopping engine and automatic
device for stopping engine.
For the truck equipped with a homemade engine, this system is controlled by a
cable for stopping engine.
(4) Instruments
It mainly consists of hour meter, fuel meter, water temperature meter, charge signal,
oil pressure indicator, neutral signal, air filter indicator and sedimentor indicator. They
are all performance checking instruments for the forklift truck.
The instrument panel adopts Curtis internal-combustion engine meter core. The
fuel meter and water temperature meter are ten solid state bars of multicolor LED
display. The hour meter in the BAOLI instrument panel is solid state digital display with
back lamp.
Notice for operation of instrument:
a. Working circumstance: Elevation is lower than 1200 meters, working
temperature -25℃~+40℃, relative humidity is not larger than 95%.

92
b. Forbid wetting the meter. When washing the truck, don’t let water into the meter,
if it happens, clean it with dry cloth.
c. Don’t pull the plug of the meter and harness for the connection.
d. Forbid impacting or scratching the meter strongly.
e. When the meter works abnormally, contact with our company for maintenance.
(5) Lighting and signal device
They include all kinds of illuminating lamps, signal lamps, horn and buzzer, etc.
Headlight:55W
Front combination lamp (turning/front):21W/5W
Rear combination lamp (turning/rear/brake/backing) (up):
21W(yellow)/5W(red)/21W(red)/10W(white)
Rear combination lamp (down): 55W (yellow)
Warning lamp (optional):21W
Rear lamp (optional): 70W
Decal lamp (optional): 10W

93
Fig.9.1 Principle diagram of electric system (domestic) CPCD80-100CY

94
Fig.9.2 Principle diagram of electric system (imported) CPCD80-100W
 Loading...
Loading...