Bama TM 11-6625-2837-14 technical manual

TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7
TECHNICAL MANUAL
OPERATOR’S, ORGANIZATIONAL, DIRECT SUPPORT,AND GENERAL SUPPORT
MAINTENANCE MANUAL
INCLUDING REPAIR PARTS AND
SPECIAL TOOLS LIST
(INCLUDING DEPOT MAINTENANCE REPAIR
PARTS AND SPECIAL TOOLS)
FOR
RF SECTION HP-86602B (NSN 6625-01-031-8853)
HEADQUARTERS, DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY
OCTOBER 1981


TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7
WARNING
SAFETY
Although this instrument has been designed in accordance with international safety standards, this manual contains information, cautions, and warnings which must be followed to retain the instrument in safe condition. Be sure to read and follow the safety information in Sections 11, III, V, an VIII.
BEFORE CONNECTING THIS SYSTEM TO LINE (MAINS) VOLTAGE, the safety and installation instructions found in Sections II and III of the mainframe manual should be followed.
HIGH VOLTAGE
Adjustments and troubleshooting are often performed with power supplied to the instrument while protective covers are removed. Energy available at many points may constitute a shock hazard
The multi-pin plug connector which provides inter connection from mainframe to RF Section, will be exposed with the RF Section removed from the righthand mainframe cavity. With the Line (Mains Voltage off and power cord disconnected, power supply voltages may still remain and may constitute a shock hazard.
COMPATIBILITY
Damage to the synthesized signal generator system may result if an option 002 RF Section is used with unmodified Model 8660A or 8660B main-frames with serial prefixes 1349A and below.
PERFORMANCE TESTING
To avoid the possibility of damage to the instrument or test equipment, read completely through each test before starting it. Then make any preliminary control settings necessary before continuing with the procedure.
PLUG-IN REMOVAL
Before removing the RF Section plug-in from the mainframe, remove the line (Mains) voltage by disconnecting the power cable from the power outlet.
SEMI-RIGID COAX
Slight but repeated bending of the semi-rigid coaxial cable will damage them very quickly. Bend the cables as little as possible. If necessary, loosen the assembly to release the cable.
WARNING
Voltages are present in this instrument, when energized, which can cause death on contact.
The multi-pin plug connector which provides interconnection from mainframe to RF Section, will be exposed with the RF Section removed from the righthand mainframe cavity. With the line voltage off and power cord disconnected, power supply voltage may still remain and may constitute a shock hazard.
A

TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7
This manual contains copyrighted material reproduced by permission of the Hewlett-Packard Company. All rights reserved.
|
|
TM 11-6625-2825-14&p-7 |
TECHNICAL MANUAL |
) |
HEADQUARTERS |
|
) |
DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY |
No. 11-6625-2825-14&p-7 |
) |
Washington, D.C., 18 October 1981 |
OPERATOR’S, ORGANIZATIONAL, DIRECT SUPPORT
AND GENERAL SUPPORT MAINTENANCE MANUAL
INCLUDING REPAIR PARTS AND SPECIAL TOOLS LISTS
FOR
RF SECTION PLUG-IN, HEWLETT-PACKARD MODEL 86602B (NSN 6625-01-031-8853)
CURRENT AS OF 30 JANUARY 1981
REPORTING ERRORS AND RECOMMENDING IMPROVEMENTS
You can help improve this manual. If you find any mistakes or if you know of a way to improve the procedures, please let us know. Mail your letter or DA Form 2028 (Recommended Changes to Publications and Blank Forms), direct to: Commander, US Army Communications and Electronics Materiel Readiness Command, ATTN: DRSEL-ME-MQ, Fort Monmouth, New Jersey 07703. In either case, a reply will be furnished direct to you.
This manual is an authentication of the manufacturer’s commercial literature which, through usage, has been found to cover the data required to operate and maintain this equipment. The manual was not prepared in accordance with military specifications; therefore, the format has not been structured to consider categories of maintenance. Section IX contains improvements made after the printing of the manufacturer’s manual.
|
CONTENTS |
|
SECTION 0 |
INTRODUCTION |
PAGE |
0-1. |
Scope |
0-1 |
0-2. |
Indexes of Publications |
0-1 |
0-3. |
Maintenance Forms, Records and Reports |
0-1 |
0-4. |
Reporting Equipment Improvement Recommendations (EIR) |
0-1 |
0-5. |
Administrative Storage |
0-2 |
0-6. |
Destruction of Army Electronics Materiel |
0-2 |
i
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7 |
|
|
|
|
|
CONTENTS |
|
|
|
|
Section |
|
|
Page |
Section |
|
Page |
||
I |
GENERAL INFORMATION ......................... |
1-1 |
|
4-16. |
Pulse Modulation Risetime............... |
4-17 |
||
|
1-1. |
Introduction....................................... |
1-1 |
|
4-17. |
Pulse Modulation On/Off Ratio......... |
4-19 |
|
|
1-7. |
Specifications .... .......................... .... |
1-1 |
|
4-18. |
Amplitude Modulation Depth and |
|
|
|
1-9. |
Instruments Covered by Manual....... |
1-1 |
|
|
3 dB Bandwidth............................. |
4-19 |
|
|
1-12. |
|
Manual Change Supplements .......... |
1-1 |
|
4-19. |
Frequency Modulation Rate and |
|
|
1-15. |
|
Description........................................ |
1-5 |
|
|
Deviation ....................................... |
4-23 |
|
1-20. |
|
Options ... .................................. ....... |
1-5 |
|
4-20. |
Output Impedance and VSWR......... |
4-23 |
|
1-24. |
|
Compatibility .............................. ....... |
1-5 |
|
4-21. |
Signal-to-Phase Noise Ratio ............ |
4-25 |
|
1-27. |
Equipment Required but not |
|
|
4-22. |
Signal-to-AM Noise Ratio................. |
4-27 |
|
|
|
|
Supplied ........................................ |
1-5 |
|
4-23. |
Residual FM ..................................... |
4-29 |
|
1-28. |
System Mainframe ....................... .... |
1-5 |
|
4-24. |
Amplitude Modulation Distortion ...... |
4-31 |
|
|
1-31. |
Frequency Extension Module........... |
1-6 |
|
4-25. |
Incidental Phase Modulation .. ......... |
4-33 |
|
|
1-33. |
Auxiliary Section ............................... |
1-6 |
|
4-26. |
Frequency Modulation Distortion...... |
4-35 |
|
|
1-35. |
Modulation Section Plug-ins............. |
1-6 |
|
4-27. |
Incidental AM ................................... |
4-38 |
|
|
1-37. |
Equipment Available......................... |
1-6 |
|
4-28. |
Spurious Signals, Narrowband......... |
4-40 |
|
|
1-40. |
Safety Considerations ...................... |
1-6 |
|
4-29. |
Spurious Signals, Wideband ........... . |
4-41 |
|
|
1-43. |
Recommended Test Equipment....... |
1-6 |
|
4-30. |
Phase Modulation Peak Deviation ... |
4-43 |
|
II |
INSTALLATION |
2-1 |
|
4-31A. |
Phase Modulation Distortion ........... |
4-43 |
||
|
4-31B. |
Phase Modulation Distortion - |
|
|||||
|
2-1. |
Introduction.................................... ... |
2-1 |
|
|
Alternate Procedure...................... |
4-45 |
|
|
2-3. |
Initial Inspection ........................ ....... |
2-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2-5. |
Preparation For Use ................... ...... |
2-1 |
V |
ADJUSTMENTS .......................................... |
5-1 |
||
|
2-6. |
Power Requirements ........................ |
2-1 |
|
5-1. |
Introduction ...................................... |
5-1 |
|
|
2-8. |
Interconnections ............................... |
2-1 |
|
5-4. |
Equipment Required ........................ |
5-1 |
|
|
2-10. |
Modifications..................................... |
2-1 |
|
5-8. |
Safety Considerations ...................... |
5-1 |
|
|
2-13. |
Operating Environment..................... |
2-1 |
|
5-12. |
Factory Selected Components......... |
5-1 |
|
|
2-15. |
Installation Instructions..................... |
2-1 |
|
5-14. |
Related Adjustments ........................ |
5-1 |
|
|
2-17. |
Storage and Shipment................. ..... |
2-2 |
|
5-18. |
Adjustment Locations....................... |
5-2 |
|
|
2-18. |
Environment ..................................... |
2-2 |
|
5-20. |
Adjustments ........................... .......... |
5-2 |
|
|
2-20. |
Packaging.................................. ....... |
2-2 |
|
5-22. |
Post Adjustment Tests . .............. ..... |
5-2 |
|
III |
OPERATION |
3-1 |
|
5-24. |
RF Output Level Adjustment ............ |
5-3 |
||
|
5-25. |
1 dB Step Attenuator Adjustment..... |
5-4 |
|||||
|
3-1. |
Introduction ........................ .............. |
3-1 |
|
5-26. |
Amplitude Modulation Input Circuit |
|
|
|
3-3. |
Panel Features ................................. |
3-1 |
|
|
Adjustment .................................... |
5-5 |
|
|
3-5. |
Operator’s Check.............................. |
3-1 |
|
5-27. |
Phase Modulator Driver Frequency |
|
|
|
3-8. |
Operating Instructions . .................... |
3-1 |
|
|
Response Adjustments................. |
5-7 |
|
IV |
PERFORMANCE TESTS |
4-1 |
|
5-28A. Phase Modulation Level and |
|
|||
|
|
Distortion Adjustments.................. |
5-8 |
|||||
|
4-1. |
Introduction....................................... |
4-1 |
|
5-28B. |
Phase Modulation Level and Distortion |
||
|
4-3. |
Equipment Required......................... |
4-1 |
|
|
Adjustments - Alternate Procedure5-11 |
||
|
4-5. |
Test Record ...................................... |
4-1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4-7. |
Performance Tests ........................... |
4-1 |
VI |
REPLACEABLE PARTS.......................... |
6-1 |
||
|
4-9. |
Frequency Range ............................. |
4-2 |
|
6-1. |
Introduction ...................................... |
6-1 |
|
|
4-10. |
Frequency Accuracy and Stability .... |
4-3 |
|
6-3. |
Exchange Assemblies...................... |
6-1 |
|
|
4-11. |
Frequency Switching Time ............... |
4-3 |
|
6-5. |
Abbreviations ............................. ...... |
6-1 |
|
|
4-12. Output Level Switching Time ............. |
4-5 |
|
6-7. |
Replaceable Parts List ..................... |
6-1 |
||
|
4-13A |
. |
Output Accuracy ................... ....... |
4-7 |
|
|
|
|
|
4-13B |
. |
Output AccuracyAlternate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Procedure.............................. ........ |
4-12 |
|
|
|
|
|
4-14. |
Output Flatness ............................ .... |
4-15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4-15. |
Harmonic Signals. ............................ |
4-16 |
|
|
|
|
|
ii
|
|
|
|
|
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7 |
|
|
|
|
CONTENTS (Cont’d) |
|
|
|
Section |
|
Page |
Section |
|
Page |
|
VII |
MANUAL CHANGES . .............................. |
7-1 |
8-17. |
System Troubleshooting.. ................ |
8-2 |
|
|
7-1. |
Introduction ...................................... |
7-1 |
8-19. |
RF Section Troubleshooting............. |
8-2 |
|
7-3. |
Manual Changes. ............................. |
7-1 |
8-21. |
Troubleshooting Aids ....................... |
8-2 |
|
7-6. |
Manual Change Instructions............. |
7-2 |
8-28. |
Recommended Test Equipment ...... |
8-2 |
VIII |
SERVICE |
8-1 |
8-30. |
Repair............................................... |
8-2 |
|
8-31. |
General Disassembly Procedures.... |
8-2 |
||||
|
8-1. |
Introduction....................................... |
8-1 |
8-34. |
Non-Repairable Assemblies............. |
8-2 |
|
8-8. |
Safety Considerations ...................... |
8-1 |
8-36. |
Module Exchange Program.............. |
8-3 |
|
8-12. |
Principles of Operation ..................... |
8-1 |
8-38. |
Repair Procedures ........................... |
8-3 |
|
8-16. |
Troubleshooting................................ |
8-1 |
8-42. |
Post Repair Adjustments ................. |
8-3 |
|
|
|
|
IX |
ERRATA |
|
|
|
ILLUSTRATIONS |
|
|
|
Figure |
|
Page |
Figure |
|
Page |
1-1. |
HP Model 86602B RF Section (Opt. 002 |
|
4-17A. |
Phase Modulation Distortion Test Setup |
4-44 |
|
Shown) |
|
4-17B. Phase Modulation Distortion Test Setup |
|
|
1-2. |
40 dB Test Amplifier................................ |
1-0 |
|
(Alternate Procedure)....................... |
4-46 |
1-3. |
15 kHz Low Pass Filter .......................... |
1-11 |
5-1. |
RF Output Level Adjustment Test Setup 5-3 |
|
1-4. |
Low Pass Filters...................................... |
1-11 |
5-2. |
1 dB Step Attenuator Adjustment Test |
|
2-1. |
RF Section Partially Inserted into |
|
|
Setup................................................ |
5-4 |
|
5-3. Amplitude Modulation Input Circuit |
|
|||
|
Mainframe ........................................ |
2-2 |
|
Adjustment Test Setup..................... |
5-5 |
3-1. |
Front Panel Controls, Connectors, and |
|
5-4. Phase Modulator Driver Frequency |
|
|
|
Indicators .......................................... |
3-2 |
|
Response Adjustment Test Setup ... |
5-7 |
3-2. |
Rear Panel Connectors and Indicators ... |
3-3 |
5-5A. |
Phase Modulation Level and Distortion |
|
3-3. |
Operator’s Check .................................... |
3-4 |
|
Adjustment Test Setup..................... |
5-9 |
4-1. |
Frequency Range Test Setup |
4-2 |
5-5B. Phase Modulation Level and Distortion |
|
|
|
Adjustment Test Setup (Alternate |
|
|||
4-2. |
Frequency Switching Time Test Setup ... |
4-4 |
|
Procedure) ....................................... |
5-12 |
4-3. |
Output Level Switching Time Test Setup |
4-6 |
|
|
|
4-4A. |
Output Accuracy Test Setup .................. |
4-8 |
7-1. |
Phase Modulator Driver Frequency Response |
|
4-4B. |
Output Accuracy Test Setup (Alternate |
|
|
Adjustment Test Setup (Change B) . |
7-2 |
|
Procedure ......................................... |
4-13 |
7-2. |
A16 Phase Modulator Driver Assembly |
|
4-5. |
Pulse Modulation Risetime Test Setup . . |
4-18 |
|
Component and Test Point Locations |
|
4-6. |
Amplitude Modulation, Depth and 3 dB |
|
|
(Change B)....................................... |
7-6 |
|
Bandwidth Test Setup ...................... |
4-20 |
7-3. |
Phase Modulation Section Schematic |
|
4-7. |
Output Impedance Test Setup ................ |
4-24 |
|
Diagram (Option 002) (Change B) .. . |
7-8 |
4-8. |
Signal-to-Phase Noise Ratio Test Setup . |
4-26 |
7-4. |
A17 Phase Modulator Assembly |
|
4-9. |
Signal-to-AM Noise Ratio Test Setup ..... |
4-28 |
|
Component Locations (Change C) .. |
7-9 |
4-10. |
Residual FM Test Setup ......................... |
4-29 |
7-5. |
P/O Phase Modulation Section Schematic |
|
4-11. |
Amplitude Modulation Distortion Test |
|
|
Diagram (Change C) ........................ |
7-11 |
|
Setup ................................................ |
4-30 |
7-6. |
P/O Attenuator Section Schematic |
|
4-12. |
Incidental Phase Modulation Test Setup |
4-32 |
|
Diagram (Change D) ........................ |
7-11 |
4-13. |
Frequency Modulation Distortion Test |
|
7-7. P/O All Logic Assembly Schematic |
|
|
|
Setup ................................................ |
4-35 |
|
Diagram (Change E) ........................ |
7-12 |
4-14. |
Incidental AM Test Setup ................. ...... |
4-38 |
|
|
|
4-15. |
Narrowband Spurious Signal Test Setup. |
4-39 |
8-1. |
LO Signal Circuits Repair ....................... |
8-4 |
4-16. |
Wideband Spurious Signal Test Setup .. . |
4-41 |
|
|
|
iii
|
|
|
|
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7 |
|
|
ILLUSTRATIONS (Cont’d) |
|
|||
Figure |
|
Page |
Figure |
|
Page |
8-2. |
Rear Panel Disassembly......................... |
8-8 |
8-16. |
.Amplifier/Detector Section |
|
8-3. |
Schematic Diagram Notes. ..................... |
8-9 |
|
Schematic Diagram.......................... |
8-27 |
8-4. |
System Test Point Locations .................. |
8-17 |
8-17. |
A3 ALC Amplifier Assembly Component |
|
8-5. |
Mainframe Interconnect Jack.................. |
8-17 |
|
and Test Point Locations.................. |
8-28 |
8-6. |
System Troubleshooting Block |
|
8-18. |
A10 Reference Assembly |
|
|
Diagram ............................................ |
8-17 |
|
Component Locations . .................... |
8-29 |
8-7. |
RF Section Simplified Block Diagram ..... |
8-19 |
8-19. |
A2 ALC Mother Board Assembly |
|
8-8. |
Main Troubleshooting Block Diagram .... |
8-19 |
|
Component Locations ...................... |
8-29 |
8-9. |
Logic Troubleshooting Block Diagram . .. |
8-21 |
8-20. |
ALC Section |
|
8-10. |
A7 Mixer Assembly’s Subassembly and |
|
|
Schematic Diagram.......................... |
8-29 |
|
Component Location ........................ |
8-22 |
8-21. |
A9 Attenuator Driver Assembly |
|
8-11. |
Mixer Section Schematic Diagram.......... |
8-23 |
|
Component Locations . .................... |
8-31 |
8-12. |
A16 Phase Modulator Driver Assembly |
|
8-22. |
Attenuator Section |
|
|
Component and Test Point Locations |
8-25 |
|
Schematic Diagram.......................... |
8-31 |
8-13. |
A17 Phase Modulator Assembly |
|
8-23. |
All Logic Assembly |
|
|
Component Locations . .................... |
8-25 |
|
Component Locations. ..................... |
8-33 |
8-14. |
Phase Modulation Section Schematic |
|
8-24. |
All Logic Assembly |
|
|
Diagram (Option 002) ....................... |
8-25 |
|
Schematic Diagram.......................... |
8-33 |
8-15. |
A4 Detector Amplifier Assembly |
|
8-25. Assemblies, Chassis Parts, and Adjustable |
||
|
Component and Test Point Locations |
8-27 |
|
Component Locations . .............. ...... |
8-35 |
|
|
|
|
|
TABLES |
|
|
Table |
|
|
|
Page |
Table |
|
Page |
1-1. |
Models 86602B/11661 Specifications..... |
1-2 |
6-1. Reference Designations & Abbreviations6-3 |
||||
1-2. |
Recommended Test Equipment ............. |
1-7 |
6-2. |
Replaceable Parts .................................. |
6-5 |
||
3-1. |
Operating Instructions |
|
3-6 |
6-3. Code Lists of Manufacturers................... |
6-15 |
||
............................ |
6-4. Parts to NSN Cross Refererence ........... |
6-16 |
|||||
4-1. |
dB to Power Ratio Conversion |
4-37 |
7-1. Manual Changes by Serial Prefix ........... |
7-1 |
|||
7-2. Summary of Changes by Component .... |
7-1 |
||||||
4-2. |
Narrowband Spurious .....Signal Checks |
4-40 |
7-3. Replaceable Parts (P/O Change B)........ |
7-7 |
|||
4-3. |
Wideband Spurious Signal ........Checks |
4-41 |
|
|
|
||
4-4. |
Performance Test Record ...................... |
4-47 |
8-1. Front Panel Housing Repair ................... |
8-7 |
|||
5-1. |
Factory Selected Components |
5-2 |
8-2. |
Adjustable Components Locations .. |
8-34 |
||
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
APPENDICES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Page |
|
APPENDIX |
A. ............................................................................................. |
References |
|
|
|
A-1 |
|
APPENDIX |
B. |
Maintenance Allocation |
|
|
|
|
|
Section |
I. ............................................................................................. |
Introduction |
|
|
|
B-1 |
|
|
II. |
Maintenance Allocation |
.......................................................................... |
|
B-5 |
|
|
|
III. |
Tool and Test Equipment Requirements ............................................ |
B-6 |
|||
NOTE
Users of this manual are advised to consult SECTION IX, ERRATA. SECTION IX contains errors and changes in text and illustrations. The user should correct the errors and perform the changes indicated, as needed.
iv

TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7
SECTION 0
INTRODUCTION
0-1. Scope
This manual describes RF Section Hewlett-Packard Model 86602B, hereinafter referred to as the RF Section, and provides instructions for its operation and maintenance.
This manual applies directly to instruments with serial numbers prefixed 1638A. It is also applicable to instruments with other serial number prefixes for which manual changes are given in SECTION VII.
SECTION VI includes Table 6-4, a cross reference between the Hewlett-Packard part numbers and the equivalent NATO/NATIONAL Stock Numbers (NSN).
Appendix A provides a reference of pertinent Department of the Army publications.
Appendix B contains the Maintenance Allocation Chart (MAC) which defines the levels and scope of maintenance functions for the equipment in the Army system and a list of the tools and test equipment required.
0-2. Indexes of Publications
a. DA Pam 310-4. Refer to the latest issue of the DA Pam 310-4 to determine whether there are new editions, changes or additional publications pertaining to the equipment.
b. DA Pam 310-7. Refer to DA Pam 310-7 to determine whether there are Modification Work Orders (MWOs) pertaining to the equipment.
0-3. Maintenance Forms, Records and Reports
a. Reports of Maintenance and Unsatisfactory Equipment. Department of the Army forms and procedures used for equipment maintenance will be those prescribed by TM 38-750, the Army Maintenance Management System.
b. Report of Item and Packaging Discrepancies. Fill out and forward SF 364 (Report of Discrepancy (ROD) as prescribed in AR 735-11-2/DLAR 4140.55/NAVSUPINST 4440.127E/AFR 400.54/MCO 4430.E.
c. Discrepancy in Shipment Report (DISREP) (SF 361). Fill out and forward Discrepancy in Shipment Report (DISREP) (SF 361) as prescribed in AR 55-38/NAVSUPINST 4610.33B/AFR 75-18/MCO P4610.19C and DLAR 4500.15.
0-4. Reporting Equipment Improvement Recommendations (EIR)
If your HP 86602B RF Section needs improvement, let us know. Send us an EIR. You, the user, are the only one who can tell us what you don’t like about your equipment. Let us know why you don’t like the design. Tell us why a procedure is hard to perform. Put it on an SF 368 (Quality Deficiency Report). Mail it to: Commander, US Army Communications - Electronics Command, ATTN: DRSEL-ME-MQ, Fort Monmouth, New Jersey 07703. We’ll send you a reply.
0-1
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7
0-5. Administrative Storage.
Store in accordance with Paragraphs 2-17 through 2-22.
0-6. Destruction of Army Electronics Materiel
Destruction of Army electronics materiel to prevent enemy use shall be in accordance with TM 750-244-2.
0-2

Section 1 |
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7 |
||
|
|
|
|
Figure 1-1. HP Model 86602B RF Section (Option 002 Shown)
1-0
Section 1 |
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7 |
SECTION I
GENERAL INFORMATION
1-1. INTRODUCTION
1-2. This manual contains all information required to install, operate, test, adjust and service the HewlettPackard Model 86602B RF Section plug-in, hereinafter referred to as the RF Section. For information concerning related equipment, such as the HewlettPackard Model 8660-series mainframes or the Model 11661 Frequency Extension Module, refer to the appropriate manual or manuals.
1-3. This manual is divided into eight sections which provide information as follows:
a. SECTION I, GENERAL INFORMATION, contains the instrument description and specifications as well as the accessory and recommended test equipment list.
1-4. Figure 1-1 shows the Option 002 RF Section.
1-5. DELETED
1-6. On the title page of this manual, below the manual part number, is a “Microfiche” part number. This number may be used to order 4 x 6-inch microfilm transparencies of the manual. Each microfiche contains up to 60 photoduplicates of the manual pages. The microfiche package also includes the latest Manual Changes supplement as well as all pertinent Service Notes.
b.SECTION II, INSTALLATION, contains information relative to receiving inspection, preparation for use, mounting, packing, and shipping.
c.SECTION III, OPERATION, contains operating instructions for the instrument.
d.SECTION IV, PERFORMANCE TESTS, contains information required to verify that instrument performance is in accordance with published specifications.
e.SECTION V, ADJUSTMENTS, contains information required to properly adjust and align the instrument after repair.
f.SECTION VI, REPLACEABLE PARTS, contains information required to order all replacement parts and assemblies.
1-7. SPECIFICATIONS
1-8. Instrument specifications are listed in Table 1-1. These specifications are the performance standards, or limits against which the instrument may be tested.
1-9. INSTRUMENTS COVERED BY MANUAL 1-10. This instrument has a two-part serial number. The first four digits and the letter comprise the serial number prefix. The last five digits form the sequential suffix that is unique to each instrument. The contents of this manual apply directly to instruments having the same serial number prefix(es) as listed under SERIAL NUMBERS on the title page.
1-11. For information concerning a serial number prefix not listed on the title page or in the Manual Changes supplement, contact your nearest Hewlett-Packard office.
g.SECTION VII, MANUAL CHANGES, provides information to document all serial number prefixes listed on the title page.
h.SECTION VIII, SERVICE, contains descriptions of the circuits, schematic diagrams, parts location diagrams, and troubleshooting procedures to aid the user in maintaining the instrument.
1-12. MANUAL CHANGE SUPPLEMENTS
1-13. An instrument manufactured after the printing of this manual may have a serial prefix that is not listed on the title page. This unlisted serial
1-1
Section 1 |
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7 |
Table 1-1. Models 86602B/11661 Specifications (1 of 3)
SPECIFICATIONS
Spurious Signals (CW, AM, and OM only):
80 dB down from carrier at frequencies <700 MHz
80 dB down from carrier within 45 MHz of the carrier at frequencies >700 MHz
70 dB down from carrier >45 MHz from carrier at frequencies >700 MHz
50 dB down from carrier on the +10 dBm range.
All Power Line Related spurious signals are 70 dB down from carrier.
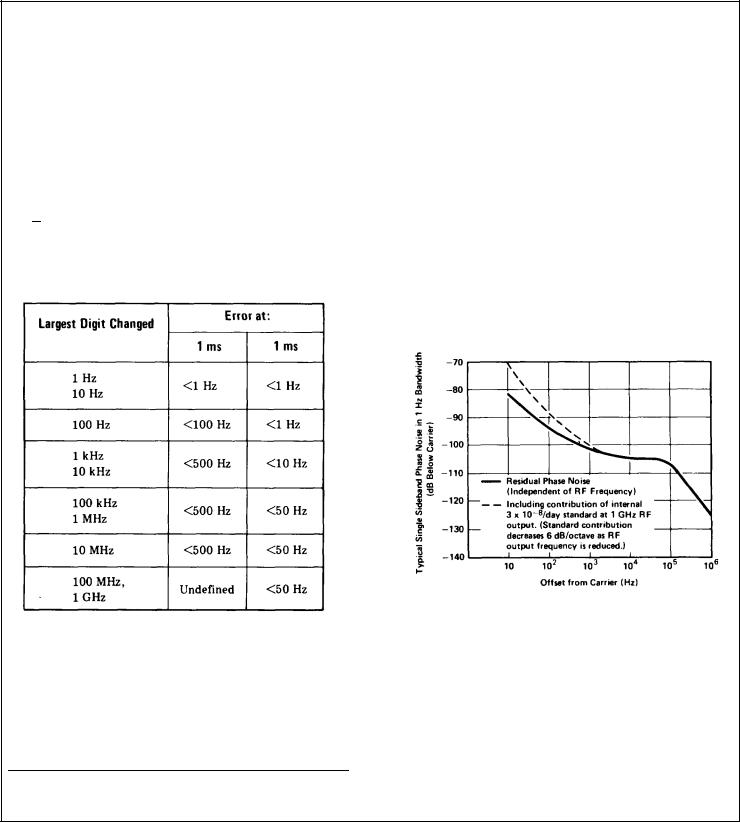
Signal-to-Phase Noise Ratio (CW, AM, and OM only): Greater than 45 dB in a 30 kHz band centered on the carrier and excluding a 1 Hz band centered on the carrier.
Typical SSB Phase Noise Curve:
Typical 86602B Phase Noise
Signal-to-AM Noise Ratio: Greater than 65 dB down in a 30 kHz bandwidth centered on the carrier and excluding a 1 Hz band centered on the carrier
1-2
Section 1 |
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7 |
Table 1-1. Models 86602B/11661 Specifications (2 of 3)
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Level: Continuously adjustable from +10 to -146 dBm (0.7 Vrms to 0.01 /Vrms) into a 50Q resistive load. Output attenuator calibrated in 10 dB steps from 1.OV full scale (+10 dBm range) to 0.03 pVrms full scale (-140 dBm range). Vernier provides continuous adjustment between attenuator ranges. Output level indicated on output level meter calibrated in volts and dBm into 50 ohms.
Accuracy: (Local and remote modes)
+ 1.5 dB to -76 dBm; + 2.0 dB to -146 dBm at meter readings between +3 and -6 dB.
Flatness: Output level variation with frequency is less than ±1.0 dB from 1-1300 MHz at meter readings between +3 and --6 dB.
Level Switching Time: In the remote mode any level change can be accomplished in less than 50 ms. Any change to another level on the same attenuator range can be accomplished in less than 5 ms.
Impedance: 50Q.
VSWR: <2.0 on +10 and O dBm range; <1.3 on -10 dBm range and below.
MODULATION CHARACTERISTICS (With compatible Modulation Sections)
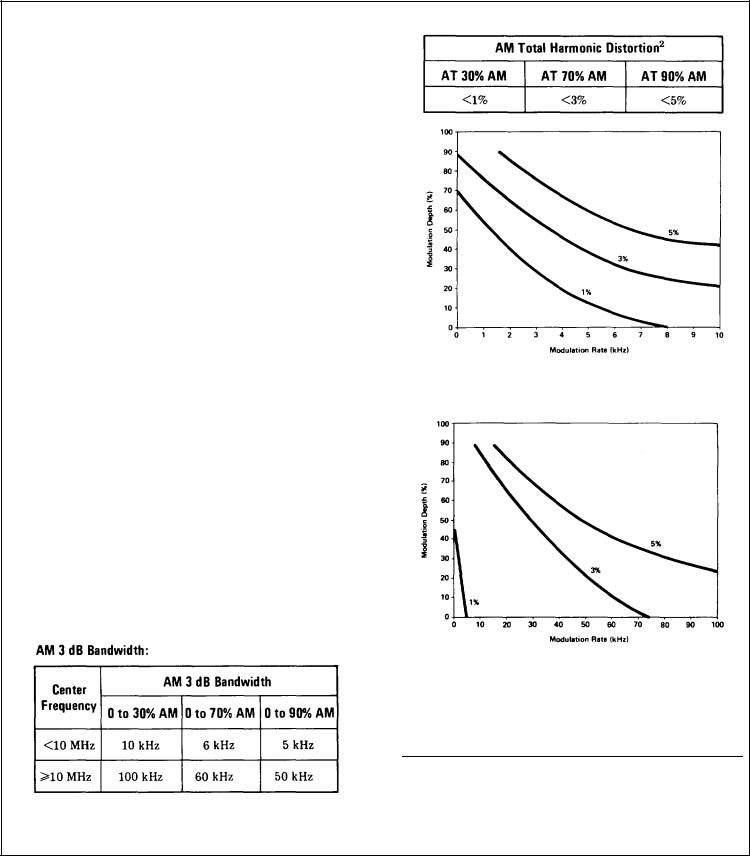
Amplitude Modulation:
Depth: 0 - 90% for RF output level meter readings from +3 to -6 dB and only at +3 dBm and below.
AM 3 db Bandwidth:
Typical AM Distortion (Center Frequency <10 MHz)
Typical AM Distortion (Center Frequency > 10 MHz)
Incidental PM: Less than 0.2 radians peak at 30% AM.
Incidental FM: Less than 0.2 times the frequency of modulation (Hz) at 30% AM.
2 Applies only at 400 Hz and 1 kHz rates with the RF Section front panel meter indicating from O to +3 dBm. At a meter indication of 6 dB the distortion approximately doubles. The modulating signal distortion must be <0.3% for the system performance to meet these specifications.
1-3
Section 1 |
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7 |
Table 1-1. Models 86602B/1 1661 Specifications (3 of 3)
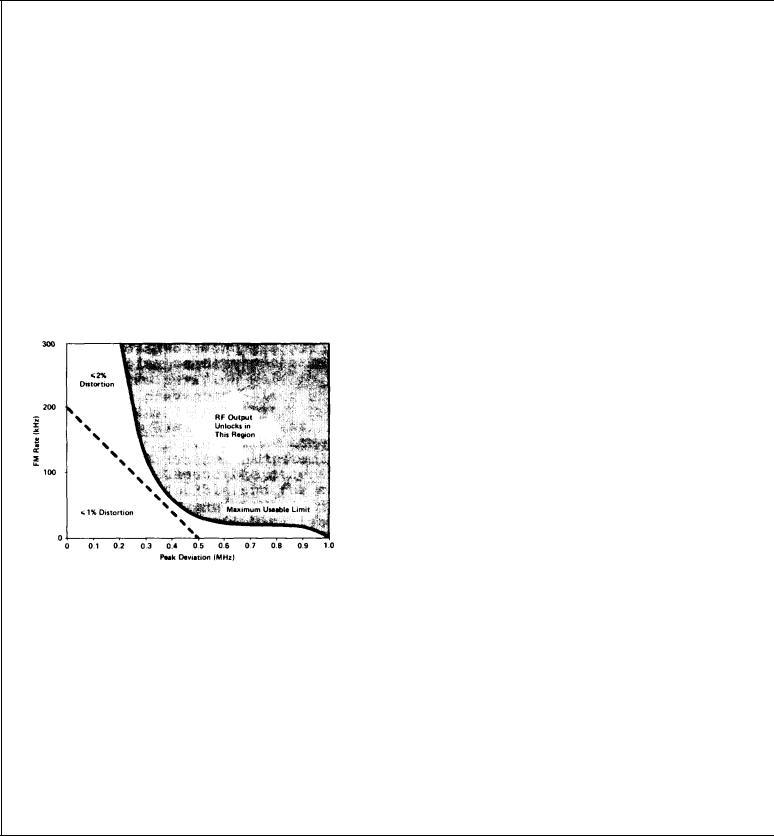
FREQUENCY MODULATION
Rate: DC to 200 kHz with the 86632B and 86635A. 20 Hz to 100 kHz with the 86633B.
Maximum Deviation (peak):
200 kHz with the 86632B and 86635A
100 kHz with the 86633B
Incidental AM: AM sidebands are greater than 60 dB down from the carrier with 75 kHz peak deviation at a 1 kHz rate.
FM Total Harmonic Distortion (at rates up to 20 kHz);
<1% up to 200 kHz deviation. (External modulating signal distortion must be less than 0.3%.)
Residual FM: less than 10 Hz rms average in 300 kHz, Post-detection bandwidth, FM x 0.1 mode.
Typical FM Distortion Curve
PULSE MODULATION
(With the 86631B Auxiliary Section only) Source: External
Rise/Fall Time: 50 ns.
ON/OFF Ratio: At least 40 dB.
Input Level Required: -10-+ 0.5 Vdc turns RF on.
PHASE MODULATION (Option 002 Instruments only)
Rate:
with 86635A dc to 1 MHz with 86634A
dc to 1 MHz at center frequencies less than 100 MHz dc to 10 MHz at center frequencies greater or equal to 100 MHz.
Maximum Peak Deviation:
0 to 100 degrees peak. May be overdriven to 2 radians (1150) in the Modulation Section’s external dc mode.
M Distortion:
<5% up to 1 MHz rates <7% up to 5 MHz rates <15% up to 10 MHz rates
(External modulation signal distortion must be less than 0.3% to meet this specification.)
REMOTE PROGRAMMING (Through the 8660-series mainframes)
Frequency: Programmable in 1 Hz steps.
Output Level: Programmable in 1 dB steps from +10 to -146 dBm.
Modulation: See specifications for modulation section installed.
GENERAL
Leakage: Meets radiated and conducted limits of MIL-I- 6181D.
Size: Plug-in to fit 8660-series mainframe.
Weight: Net 9 lb (3.9 kg).
1-4

Section 1 |
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7 |
prefix indicates that the instrument is different from those documented in this manual. The manual for this instrument is supplied with a yellow Manual Changes supplement that contains “change information” that documents the differences.
1-14. In addition to change information, the supplement may contain information for correcting errors in the manual. To keep this manual as current and accurate as possible, Hewlett-Packard recommends that you periodically request the latest Manual Changes supplement. The supplement for this manual is keyed to this manual’s print date and part number, both of which appear on the title page. Complimentary copies of the supplement are available from Hewlett-Packard.
1-15. DESCRIPTION
1-16. The HP Model 86602B RF Section is one of several RF Sections available for use in an 8660-series Synthesized Signal Generator System. This RF Section plug-in is used with an option 100 8660-series mainframe (Frequency Extension Module installed). The RF Section provides precisely tuned RF output frequencies over the 1 to 1300 MHz range with 1 Hz frequency resolution (8660-series option 004 instruments have resolutions of 100 Hz.) Frequencies from 200 kHz to 1 MHz can also be generated with some degradation in the amplitude leveling and other related specifications.
1-17. The output power can be set to any level between +10 and --146 dBm by means of the front panel VERNIER and calibrated OUTPUT RANGE controls. A front panel-mounted meter and the OUTPUT RANGE switch indicate the output power and voltage levels delivered by the RF Section to any external load having a characteristic impedance of 50 ohms. Output power levels are maintained within + 1 dB of selected values through internal leveling of the output signal over the full frequency range of the instrument.
1-18. Amplitude, frequency, phase, or pulse modulation of the RF OUTPUT signal can be accomplished within the RF Section by using the appropriate Auxiliary or Modulation Section plug-in.
1-19. External programming permits remote selection of the output signal frequency in 1 Hz steps (100 Hz for option 004 mainframes) and the output power in 1 dB steps over the full operating
1-5
range of the instrument. External programming is accomplished via the mainframe computer-compatible interface and digital control unit circuits.
1-20. OPTIONS
1-21. This RF Section has two options available. They affect the instrument’s RF output level, and phase modulation capabilities.
1-22. Option 001. The RF output attenuator is removed. This limits the RF output level range from +10 to -6 dBm.
1-23. Option 002. Circuits are added to provide the phase modulation capability. A compatible modulation section is required.
1-24. COMPATIBILITY
1-25. Except for Option 002 instruments, the Model 86602B is compatible with all 8660-series option 100 mainframes, all AM-FM Modulation Sections and the Auxiliary Section. This RF Section is partially compatible with the FM/OM Modulation Section.
Damage to the signal generator system may result if an option 002 RF Section is used with Model 8660A or 8660B main-frames with serial prefixes 1349A and below.
1-26. Option 002 instruments are compatible with all instruments which are part of the Model 8660-series Synthesized Signal Generator System except early model 8660A and 8660B Mainframes. Refer to the paragraph entitled Modifications in Section II of this manual for further information.
1-27. EQUIPMENT REQUIRED BUT NOT SUPPLIED
1-28. System Mainframe
1-29. The mainframe uses phase-locked loops to accurately generate clock, reference, and tuning signals required for operation of the Synthesized Signal Generator System. Front panel-mounted mainframe controls are used to digitally tune two phase-locked loops in the Frequency Extension Module which, in turn, produce two high-frequency output signals that are applied to the RF Section. The RF Section mixes the two signals
Section 1
and presents their frequency difference at the front panel OUTPUT jack. The output frequency is either the value selected by the mainframe front panel controls or external programming.
1-30. The mainframe power supply provides all dc operating voltages required by the RF Section, Frequency Extension Module, and Modulation Section plug-ins. Remote programming of the plug-ins is accomplished via the mainframe interface and digital control unit circuits.
1-31. Frequency Extension Module
1-32. The Frequency Extension Module plug-in extends the output frequency range of the main-frame to meet the input requirements of the RF Section. The Frequency Extension Module plug-in contains two highfrequency phase-locked loops which receive digital tuning signals, variable synthesized signals, and fixed synthesized signals from the mainframe. The phaselocked loops use the main-frame signals, in conjunction with the output frequency from a 4.43 GHz oscillator that is common to both loops, to produce two high-frequency output signals that are supplied to the RF Section. One output signal is generated by a phase-locked loop using a Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO) that is tuneable in 1 Hz steps (100 Hz steps for option 004 mainframe) over the 3.95 to 4.05 GHz range. The other output signal is generated by a phase-locked loop using a Yittrium-Iron- Garnet (YIG) oscillator that is tunable in 100 MHz steps over the 3.95 to 2.75 GHz range. The two outputs from the Frequency Extension Module plug-in are applied to the RF Section for mixing, amplification of the converted signal, and final output power level control.
1-33. Auxiliary Section
1-34. The Auxiliary Section plug-in provides a means of applying externally generated amplitude or pulse modulation drive signals to modulate the RF Section’s output carrier.
1-6
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7
1-35. Modulation Section Plug-ins
1-36. The Model 86630-series Modulation Section plugins can accept external modulation drive signals or generate internal drive signals to amplitude, frequency, phase or pulse modulate the RF Sections output signal.
1-37. EQUIPMENT AVAILABLE
1-38. Extender cables, coaxial adapters, and an adjustment tool are available for use in performance testing, adjusting, and maintaining the RF Section. Each piece may be ordered separately or as part of the 11672A Service Kit.
1-39. Extender cards for use in servicing the RF Section and a type N to BNC adapter for use on the front panel RF OUTPUT connector are contained in the HP Rack Mount Kit, Part Number 08660-60070, that is supplied with the mainframe.
1-40. SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
1-41. This instrument has been designed in accord-ance with international safety standards and has been supplied in safe condition.
1-42. Although this instrument has been designed in accordance with international safety standards, this manual contains information, cautions, and warnings which must be followed to retain the instrument in safe condition. Be sure to read and follow the safety information in Sections II, III, V, and VIII.
1-43. RECOMMENDED TEST EQUIPMENT 1-44.
Table 1-2 lists the test equipment and accessories recommended for use in testing, adjusting, and servicing the RF Section. If any of the recommended test equipment is unavailable, instruments with equivalent specifications may be used. See Appendix B, Section III.
Section 1
Item
Adapter (Male Type N to GR874 )
Adapter, SMA-to-BNC
Adapter, SMA-to-OSM
Right Angle
Adapter, Type N-to-
SMA
Amplifier, 20 dB
Amplifier, 40 dB
Analyzer, Distortion
Analyzer, Spectrum
Analyzer, Spectrum
Analyzer, Wave
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7
See Appendix B, Section III
Table 1-2. Recommended Test Equipment (1 of 4)
Critical Specifications |
Suggested Model |
Use* |
|
|
|
|
|
Frequency range 100 MHz to 1.3 GHz |
HP 1250-0847 |
P |
|
|
|
|
|
2 required |
OSM 21190 |
P |
|
|
|
|
|
OSM 219 |
|
P |
|
|
|
|
|
OSM 21040 |
P |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
-20 dB gain at 30 MHz |
HP 8447A |
P |
|
Input SWR <1.7 |
|
|
|
Special |
(see Figure 1-2) |
P |
|
|
|
|
|
20 Hz to 20 kHz; must measure <0.1% distortion |
HP 333A |
P |
|
Measurement Accuracy +2.0 dB from 1 kHz |
HP 8553B with HP 8552B |
P.,A |
|
to 110 MHz |
and HP 1-10T |
|
|
Measurement Accuracy +2.0 dB from 10 MHz |
HP 8555A with HP 8552B |
P. A, T |
|
to 8 GHz |
and HP 140T |
|
|
Center frequencies 20 to 40 kHz |
HP 3581A |
P |
|
Resolution bandwidth <3 Hz |
|
|
|
Bandpass shape factor 10:1 |
|
|
|
Analog output 0 to 5V |
|
|
|
Noise level (at 11 kHz center frequency with a |
|
|
|
3 Hz bandwidth) <-150 dBV |
|
|
Attenuator, 3 dB |
3 dB |
HP 8491A Option 003 |
P |
|
Fixed |
|
|
|
|
Attenuator, 10 dB Step |
Calibrated at 30 MHz; refer to calibration curve |
HP 355D-H38 (only) |
P, A |
|
Attenuator, 40 dB |
40 dB |
HP 8491A Option 040 |
P |
|
Fixed |
|
|
|
|
Cables, Double |
Minimum input <300 mVrms (5 required) |
HP 08708-6033 |
P |
|
Shielded |
|
|
|
|
Capacitor, 1500 pF |
|
HP 0160-2222 |
P |
|
|
||||
Capacitor, 100 pF |
HP 0180-2207 |
P |
|
|
|
||||
Connector, BNC |
HP 1250-0118 |
T |
|
|
|
||||
Panel Mount |
|
|
|
*Use: P = Performance Tests, A = Adjustments, T = Troubleshooting
1-7

Section 1 |
|
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7 |
||
|
Table 1-2. Recommended Test Equipment (2 of 4) |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Item |
Critical Specifications |
Suggested Model |
Use* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Counter, Computing |
50 kHz to 50 MHz with a 1 ms gate time and |
HP 5360A with HP 5365A |
P |
|
|
external trigger; 1 Hz resolution |
plug-in |
|
|
Counter, Frequency |
Range: 0.2-1300 MHz |
HP 5340A |
P |
|
|
Resolution: 1 Hz |
|
|
|
|
10 MHz external reference output |
|
|
|
|
7.2 Vrms output into 170 ohms |
|
|
|
Coupler, Directional |
Frequency range 100 MHz to 1.3 GHz |
HP 778D Option 12 |
P |
|
Detector, Crystal |
1 to 1200 MHz |
HP 8471A |
P |
|
Detector, Crystal |
10 MHz to 1.3 GHz |
HP 423A |
P, A |
|
FM Discriminator |
Input frequency 100 kHz to 10 MHz |
HP 5210A |
P, A |
|
|
Linear Analog Output 1V full scale |
|
|
|
Filter Kit |
Accessory for HP 5210A |
HP 10513A |
P, A |
|
Filter, Low Pass, |
Special |
(see Figure 1-3) |
P |
|
15 kHz |
|
|
|
|
Filter, Low Pass, |
Cutoff frequency: 4 MHz |
CIR-Q-TEL |
P |
|
4 MHz |
FLT/21B-4-3/50-3A/3B |
|
|
|
Filter, Low Pass, |
Cutoff frequency: 2200 MHz |
HP 360C |
P |
|
2200 MHz |
|
|
|
|
Filters, Low Pass, |
100 kHz at 50 and 600 ohms |
Specials (See Figure 1-4) |
A |
|
100 kHz |
|
|
|
|
Filters, Low Pass, |
1 MHz - 50 and 600 ohms |
Specials (See Figure 1-4) |
P, A |
|
1 MHz |
|
|
|
|
Filters, Low Pass, |
5 and 10 MHz - 50 ohms |
Specials (See Figure 1-4) |
P |
|
5 and 10 MHz |
|
|
|
|
Filter, Band Pass |
Pass band 1-2 GHz |
HP 8430A |
P |
|
Generator, |
Distortion less than 0.3% |
HP 203A |
P |
|
Function |
Range: 0.5 Hz to 20 kHz |
|
|
|
|
Output level: 0.1 to 2.0 Vrms into 600 ohms |
|
|
|
Generator, Pulse |
Output -10 Vpk with <10 ns risetime in 600 |
HP 8013B |
P |
|
|
ohms |
|
|
|
Generator, Sweep |
Sweep Width 0.1 to 100 MHz |
HP 8601A |
A |
|
|
Output Level +20 to -80 dBm |
|
|
|
|
Flatness +0.25 dB |
|
|
|
Generator, Synthe- |
+1 Hz from 1 MHz to 1300 MHz, +7 dBm output |
HP 8660 with HP 86631B |
P, A |
|
sized Signal |
10 MHz Reference output |
|
|
|
|
>0.5V into 170 ohms |
|
|
|
*Use: P = Performance Tests, A = Adjustments, T = Troubleshooting
1-8

Section 1 |
|
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7 |
||
|
Table 1-2. Recommended Test Equipment (3 of 4) |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Item |
Critical Specifications |
Suggested Model |
Use* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mixer, Double |
1 MHz to 110 MHz |
HP 10514A |
A |
|
Balanced |
|
|
|
|
Mixer, Double |
300 to 1300 MHz |
Watkins-Johnson M1J |
P |
|
Balanced |
|
|
|
|
Oscillator, Test |
1 kHz to 10 MHz |
HP 651B |
P, A |
|
1.0 to 2.0 Vrms into 600 |
|
|
|
|
or 50 ohms |
|
|
|
|
Oscilloscope |
Vertical: |
HP 180C with HP 1801A |
P, A, T |
|
|
Bandwidth 50 MHz with sensitivity of |
and HP 1821A plug-ins |
|
|
|
5mV/ division minimum |
|
|
|
|
Horizontal: |
|
|
|
|
Sweep time 10 ns to 1 s |
|
|
|
|
Delayed sweep |
|
|
|
|
External triggering to 100 MHz |
|
|
|
Oscilloscope, |
Input impedance |
HP 10004 |
P, A, T |
|
10:1 divider probes |
10 megohm shunted by 10 pF |
|
|
|
Power MeterISensor |
Range: -10 to +10 dBm from 10 MHz to 1.3 |
HP 435A/8481A |
P, A, T |
|
GHz |
|
|
|
|
Power Supply, DC |
0-10 volts |
HP 721A |
P |
|
Programmer, Marked |
Capable of programming BCD or HP-IB data |
HP 3260A Option 001 |
P, A |
|
Card |
|
|
|
|
Probe, Logic |
TTL Compatible |
HP 10525T |
T |
|
Resistor, 1000 ohm |
+2% |
HP 0757-0280 |
P, A |
|
Resistor, 10K ohm |
+2% |
HP 0757-0442 |
P |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Resistor, 100K ohm |
f2% |
HP 0698-7284 |
P |
|
Service Kit |
Interconnect cables, adaptors, and coaxial |
HP 11672A (See |
A, T |
|
|
cables compatible to 8660-series plus and |
Operating Note or |
|
|
|
jacks |
mainframe manual for |
|
|
|
parts list) |
|
|
|
Stub, Adjustable |
Frequency range 100 MHz to 1.3 GHz |
General Radio 874-D50L |
P |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tee, Coaxial |
2 required |
HP 1250-0781 (BNC) |
P, A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Termination, 50 |
50 ohm |
HP 11048C |
P |
|
ohm Feed Thru |
|
|
|
|
*Use: P = Performance, A = Adjustments, T = Troubleshooting
1-9

Section 1
Item
Termination, 50 ohm
Test Set, Phase
Modulation
|
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7 |
|
Table 1-2. Recommended Test Equipment (4 of 4) |
|
|
|
|
|
Critical Specifications |
Suggested Model |
Use* |
|
|
|
50 ohm, (2 required) |
HP 11593A |
P |
|
|
|
Input Frequency Range 250 to 950 MHz |
HP 8660C-K10 (only) |
P, A |
Distortion |
|
|
<2% up to 2 MHz rates |
|
|
<3.5% up to 5 MHz |
|
|
<5.0% up to 10 MHz |
|
|
Voltmeter, AC |
Accuracy +2% of full scale from |
HP 403B |
P, A, T |
|
|
1 Hz to 1 MHz |
|
|
|
|
1 mVrms to 10 Vrms full scale |
|
|
|
Voltmeter, Digital |
Range 0.00 to 60.00 volts |
HP 34740A/34702A |
P, A, T |
|
|
DC Accuracy +(0.3%, of reading +0.01% of |
|
|
|
|
range) |
|
|
|
|
AC Accuracy +(0.25% of reading +0.05% of |
|
|
|
|
range) |
|
|
|
|
45 Hz to 20 kHz |
|
|
|
Voltmeter, Vector |
Frequency range 5 to 15 MHz |
HP 8405A |
P |
|
Input level 100 mVrms to 1 Vrms
Analog output: +0.5 Vdc for +180°
*Use: P = Performance Tests. A = Adjustments, T = Troubleshooting
1-10
Section 1 |
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7 |
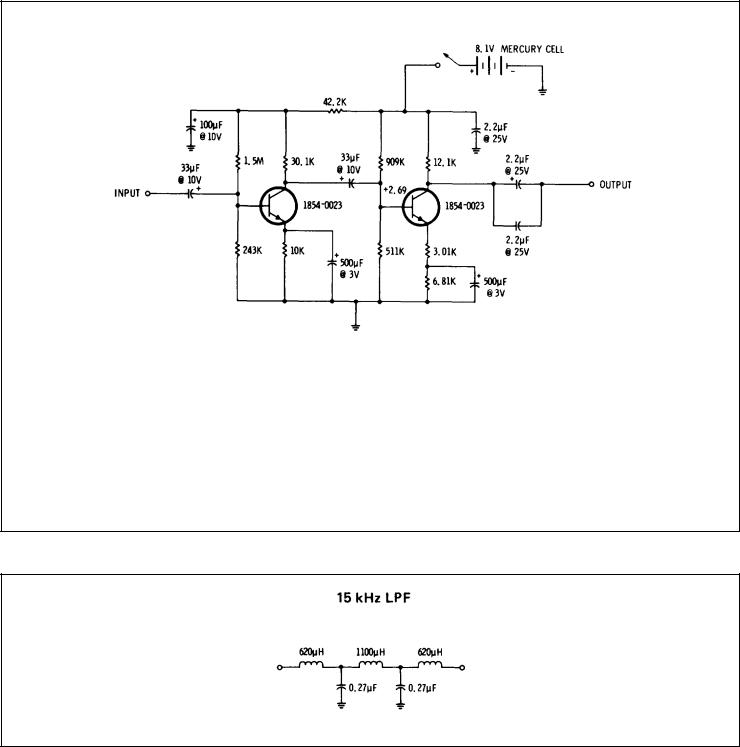
40 dB TEST AMPLIFIER
|
Amplifier Specifications |
Gain |
44 dB at 25°C |
Bandwidth |
100 kHz (3 dB down) |
Noise Bandwidth |
157 kHz |
Input Impedance |
75K Ohms |
Output Impedance |
12K Ohms |
Current Drain |
260 Microamperes |
Output (Maximum) |
1 Volt |
Dynamic Range |
66 dB |
Figure 1-2. 40 dB Test Amlifier
Figure 1-3. 15 kHz Low Pass Filter
1-11
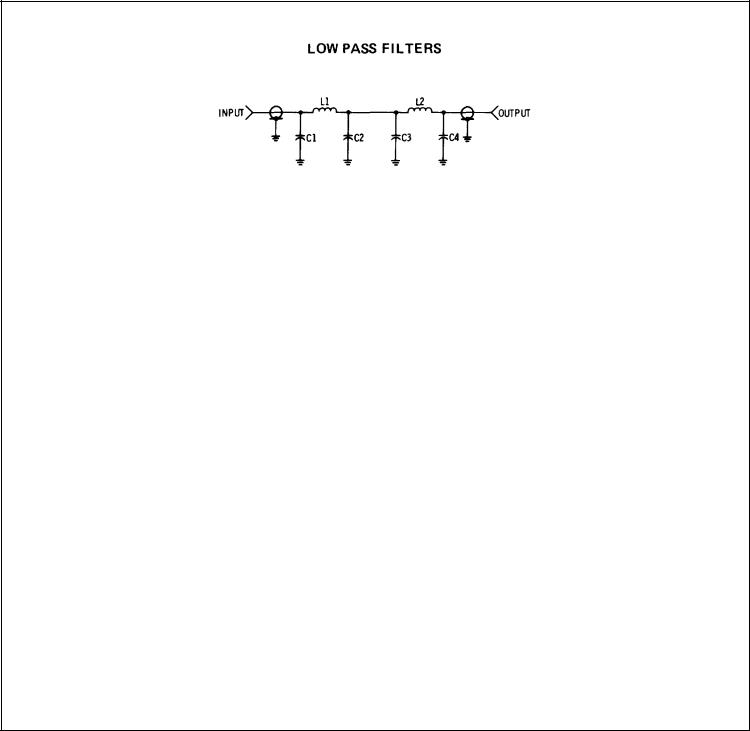
Section 1 |
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7 |
|
100 kHz - 50 ohms |
|
||
C1, C4 |
0.015 |
μF |
Mylar |
0160-0194 |
C2 |
0.027 |
μF |
Mylar |
0170-0066 |
C3 |
0.022 |
μF |
Mylar |
0160-0162 |
L1, L2 |
100 |
μH |
|
9140-0210 |
1 MHz -50 ohms
C1, C4 |
1500 pF |
0160-2222 |
|
C2 |
3300 pF |
0160-2230 |
|
C3 |
1600 pF |
0160-2223 |
|
L1, L2 10H ±10% |
9140-0114 |
||
|
|
5 MHz - 50 ohms |
|
C1, C2, C4 |
300 pF |
0160-2207 |
|
C3 |
|
680 pF |
0160-3537 |
L1, L2 |
2 μH |
9100-3345 |
|
|
100 kHz - 600 ohms |
|
C1, C4 |
1300 pF |
0160-2221 |
C2 |
3000 pF |
0160-2229 |
C3 |
1100 pF |
0160-2219 |
L1, L2 |
1200 μH |
9100-1655 |
|
1 MHz - 600 ohms |
|
C1, C4 |
130 pF |
0140-0195 |
C2 |
300 pF |
0160-2207 |
C3 |
120, μH |
0140-0194 |
L1, L2 |
120 μ |
9100-1637 |
|
10 MHz - 50 ohms |
|
C1, C4 |
150 pF |
0140-0196 |
C2 |
330 pF |
0160-2208 |
C3 |
160 pH |
0160-2206 |
L1, L2 |
1 μH±10% |
9140-0096 |
NOTE
Unless otherwise noted, tolerance of components is + 5% and capacitors are mica. Part numbers are Hewlett-Packard
Figure 1-4. Low Pass Filters
1-12

Section 2 |
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7 |
SECTION II
INSTALLATION
2-1. INTRODUCTION
2-2. This section provides information relative to initial inspection, preparation for use, and storage and shipment of the Model 86602B RF Section plug-in. Initial Inspection provides instructions to be followed when an instrument is received in a damaged condition. Preparation For Use gives all necessary interconnection and installation instructions. Storage and Shipment provides instructions and environmental limitations pertaining to instrument storage. Also provided are packing and packaging instructions which should be followed in preparing the instrument for shipment.
2-3. INITIAL INSPECTION
2-4. Inspect the shipping container for damage. If the shipping container or cushioning material is damaged, it should be kept until the contents of the shipment have been checked for completeness and the instrument has been checked mechanically and electrically. The contents of the shipment should be as shown in Figure 1-1, and procedures for checking electrical performance are given in Section IV. If the contents are incomplete, if there is mechanical damage or defect, or if the instrument does not pass the electrical performance test, notify the nearest Hewlett-Packard office. If the shipping container is damaged, or the cushioning material shows signs of stress, notify the carrier as well as the HewlettPackard office. Keep the shipping materials for carrier’s inspection. The HP office will arrange for repair or replacement without waiting for claim settlement.
2-5. PREPARATION FOR USE
2-6. Power Requirements
2-7. All power required for operation of the RF Section is furnished by the mainframe. This RF Section requires approximately 40 volt-amperes.
2-8. Interconnections
2-10. Modifications
2-11. A power supply modification to older versions of Model 8660A and 8660B mainframes are required if they are to be used with the option 002 RF Section.
Damage to the synthesized signal generator system may result if an option 002 RF Section is used with an older 8660A or 8660B mainframe.
2-12. Due to the increased power consumption of the option 002 instrument, mainframes with serial prefixes 1349A and below must be modified by installing a Field Update Kit. For mainframe configurations other than option 003 (60 Hz line operation), order kit number 08660-60273. For option 003 mainframes (50 - 400 Hz line operation) order kit number 08660-60274.
NOTE
Verify that a new higher current fuse, HP Part Number 2110-0365, 4A Slow Blow, is used in mainframes with the power supply modification.
2-13. Operating Environment
2-14. The RF Section is designed to operate within the following environmental conditions:
Temperature |
........................................ 0° to +55°C |
Humidity ..................................... |
less than 95% relative |
Altitude ....................................... |
less than 15,000 feet |
2-15. Installation Instructions
WARNING
2-9. Prior to installing the RF Section plug-in into the mainframe, verify that the Frequency Extension Module plug-in and interconnecting cable assemblies have been installed in accordance with the instructions contained in the Frequency Extension Module manual.
2-1
The multi-pin plug connector which provides interconnection from mainframe to RF Section, will be exposed with the RF Section removed from the right-hand mainframe cavity. With the Line (Mains) Voltage off and power cord disconnected, power supply voltages may still remain which, if contacted, may constitute a shock hazard.
Section 1
2-16. Insert the plug-in approximately half-way into the right cavity of the mainframe. Rotate the latch (lower right corner) to the left until it protrudes perpendicular to the front panel. Refer to Figure 2-1, which shows the plug-in partially inserted into the mainframe and the latch rotated to a position that is perpendicular to the plug-in front panel. Push the plug-in all the way into the mainframe cavity and then rotate the latch to the right until it snaps into position.
2-17. STORAGE AND SHIPMENT
2-18. Environment
2-19. The storage and shipping environment of the RF Section should not exceed the following limits:
Temperature................................ |
40° to +75°C |
Humidity....................................... |
less than 95% relative |
Altitude......................................... |
less than 25,000 feet |
2-20. Packaging
2-21. Original Type Packaging. Containers and materials identical to those used in factory packaging are available through Hewlett-Packard offices. If the instrument is being returned to Hewlett-Packard for servicing, attach a tag indicating the type of service required, return address, model number, and full serial Figure 2-1. RF Section Partially Inserted into Mainframe
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7
number. Also mark the container FRAGILE to assure careful handling. In any correspondence, refer to the instrument by model number and full serial number.
2-22. Other Packaging. The following general instructions should be used for re-packaging with commercially available materials:
a.Wrap the instrument in heavy paper or plastic. (If shipping to a Hewlett-Packard office or service center, attach a tag indicating the type of service required, return address, model number, and full serial number.)
b.Use a strong shipping container. A doublewall carton made of 350-pound test material is adequate.
c.Use enough shock-absorbing material (3 to 4- inch layer) around all the sides of the instrument to provide firm cushion and prevent movement inside the container. Protect the control panel with cardboard.
d.Seal the shipping container securely.
e.Mark the shipping container FRAGILE to assure careful handling.
Figure 2-1. RF Section Partially Inserted into Mainframe
2-2
Section 3 |
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7 |
SECTION III
OPERATION
3-1. INTRODUCTION
3-2. This section contains information which will enable the operator to learn to operate and quickly check for proper operation of the RF Section plug-in as part of the Synthesized Signal Generator System.
3-3. PANEL FEATURES
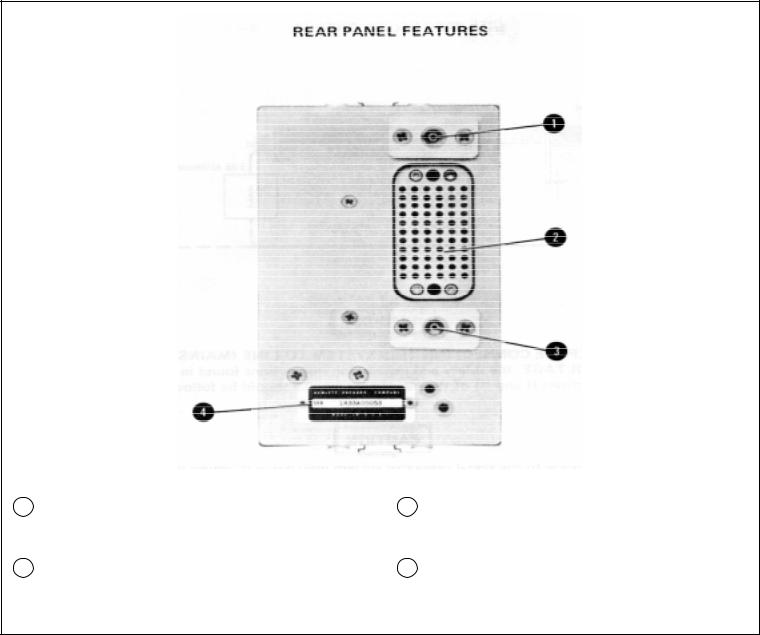
3-4. The front and rear panel controls, connectors, and indicators of the RF Section and its options are described by Figure 3-1 and 3-2.
3-5. OPERATOR’S CHECKS
3-6. The RF Section, as part of the Synthesized Signal Generator System, accepts inputs from the rest of the system but controls only the RF output level. Even though the controlled circuits for most other functions are within the RF Section, the actual checks are found in the manual of the instrument which controls that function.
3-7. The Operator’s Checks in this manual are intended to verify proper operation of the circuits which control and are controlled by the RF output level controls. This includes the meter, the VERNIER control, the OUTPUT RANGE switch, and the Output Range Attenuator when operating in the local mode. When the system is being remotely controlled, the 1 dB and 10 dB remote step attentator switches are checked in place of the VERNIER control and OUTPUT RANGE switch. Refer to Figure 3- 3.
3-8. OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
3-9. In this system, the mainframe and plug-ins contain the controls for frequency, modulation, and RF level selection. The mainframe controls frequency, the Modulation Section plug-in controls modulation type and level, and the RF Section plug-in controls RF output level. The Operating Instructions for the RF Section plug-in are included in Table 3-1.
3-1
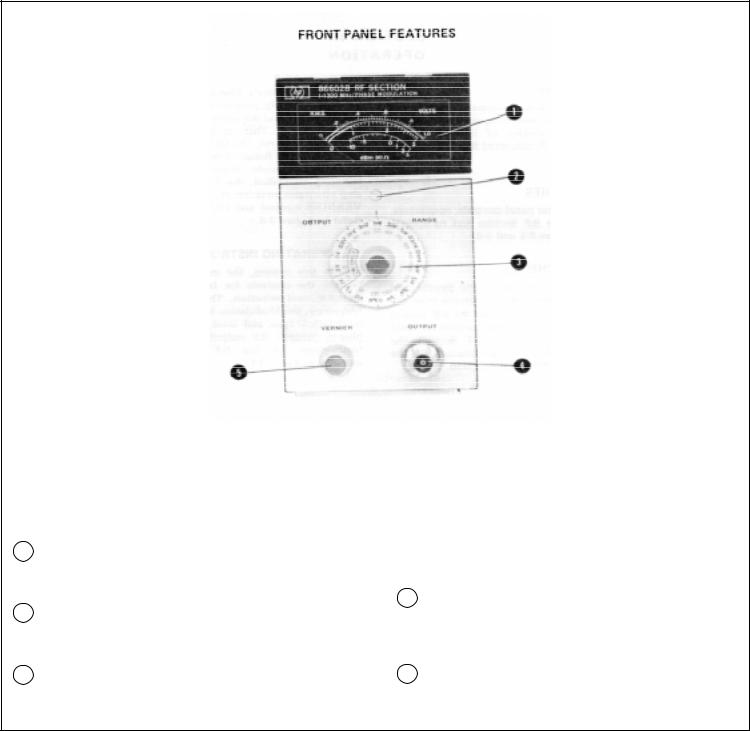
Section 3 |
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7 |
NOTE
The front panel of the option 002 instrument is shown. The standard instrument does not have the term PHASE MODULATION after 1-1300 MHz. The option 001 instrument has an OUTPUT RANGE switch which shows only the +10 and 0 dBm ranges.
1Meter. Indicates the RF Output level in Vrms and dBm (50w) with the scale reference indicated by the OUTPUT RANGE switch.
2Mechanical Meter Zero Control. Sets the Panel Meter indicator to zero when the mainframe LINE Switch is set to STBY.
3OUTPUT RANGE Switch. Sets the output level range of all except option 001 instruments from
+10 to -140 dBm (502) in 10 dB steps. For option 001 instruments, +10 and 0 dBm ranges only.
4OUTPUT Jack. Type-N female coaxial connector. RF Output level +10 to -146 dBm (0.7 Vrms to 0.01 /IVrms) into a 50Q load. Frequency range is 1 to 1299.999 999 MHz in 1 Hz steps.
5VERNIER Control. RF Output continuously var-iable within the useable range (+3 to --6 dB) as indicated by the meter.
Figure 3-1. Front Panel Controls, Connectors, and Indicators
3-2
Section 3 |
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7 |
1Coaxial Plug. Connects the 3.95 to 2.75 GHz RF Input signal to the RF Section from the Frequency Extension Module.
2Interconnect Plug. Provides interconnection of power supply voltages; RF and control signals between the RF Section plug-in and the Main-frame, Frequency Extension Module, and Modulation Section plug-in.
3Coaxial Plug. Connects the 3.95 to 4.05 GHz LO Input signal to the RF Section plug-in from the Frequency Extension Module.
4Serial Number Plate. Metal plate with stamped serial number. Four-digit and letter for prefix. Suffix is unique to an instrument.
Figure 3-2. Rear Panel Connectors and Indicators
3-3
Section 3 |
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7 |
WARNING
BEFORE CONNECTING THIS SYSTEM TO LINE (MAINS) VOLTAGE, the safety and installation instructions found in Sections II and III of the mainframe manual should be followed.
Damage to the signal generator system may occur if option 002 RF Sections are used with unmodified 8660A and 8660B main frames with serial prefixes 1349A and below. See the paragraph entitled Modifications in Section II.
NOTE
Refer to Section HI for RF Section Installation instructions.
1. |
Set the System controls as follows: |
|
|
Mainframe |
|
|
LINE Switch .................................................................................... |
ON |
|
REFERENCESELECTOR .............................................................. |
EXT |
|
CENTER FREQUENCY ................................................................. |
500 MHz |
|
Modulation Section plug-in |
|
|
MODE Switch ................................................................................. |
OFF |
|
RF Section plug-in |
|
|
OUTPUT RANGE Switch ............................................................... |
0 dBm |
|
VERNIER Control ........................................................................... |
+3 dB meter reading |
|
|
|
|
Figure 3-3. |
Operator’s Checks (1 of 2) |
|
|
3-4 |
Section 3 |
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7 |
OPERATOR’S CHECKS
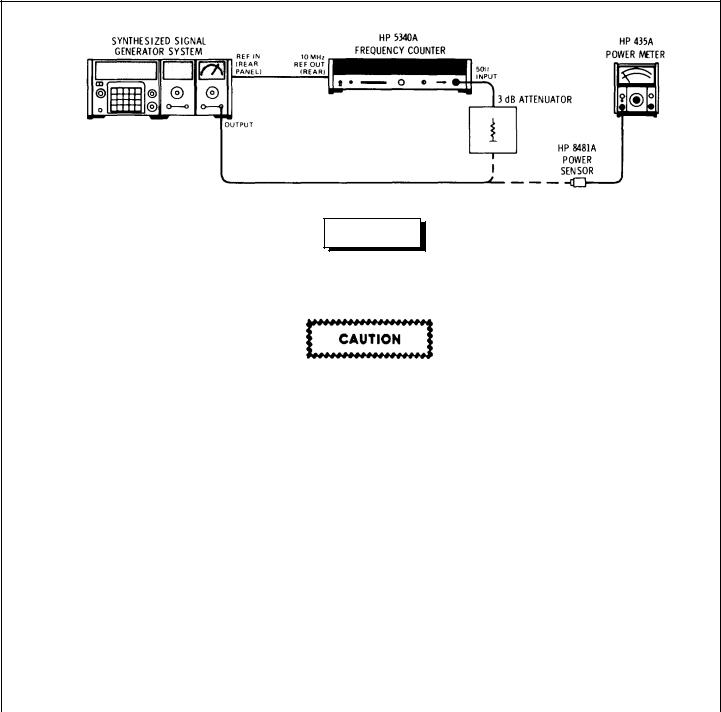
2.Connect the RF Section OUTPUT to the power sensor input. Verify that the amplitude of the 500 MHz signal is approximately +3 dBm.
3.Set the OUTPUT RANGE Switch to +10 dBm and adjust the VERNIER control for a -3 dB meter reading. Verify that the output level is approximately +7 dBm.
4.Connect the RF Section OUTPUT to the frequency counter input through the 3 dB attenuator. Verify that the signal is accurate within +1 Hz.
5.To check the remote control capabilities of the RF Section, connect a control unit to the mainframe. Repeat steps 1 through 4 while the system is remotely programmed from an external source. Application Note 164-1 "Programming the 8660A/B Synthesized Signal Generator" provides the information needed for remote BCD operation of this system. Application Note 164-2 "Calculator Control of the 8660A/B/C Synthesized Signal Generator" provides the information needed for calculator control of the system using the HP-IB (option 005). Section III of the mainframe manual contains the same information in abridged form.
Figure 3-3. Operator’s Checks (2 of 2)
3-5

Section 3 |
TM 11-6625-2837-14&P-7 |
Table 3-1. Operating Instructions (1 of 2)
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
TURN ON
BEFORE CONNECTING THIS SYSTEM TO THE LINE (MAINS)
VOLTAGE, the safety and installation instructions found in Sections
II and III of the mainframe manual should be followed.
Damage to the signal generator system may occur if option 002 RF Sections are used with unmodified 8660A and 8660B mainframes with serial prefixes 1349A and below. See the paragraph entitled Modifications in Section II.
NOTE
Refer to Section II for RF Section Installation Instructions.
1.Set the mainframe’s LINE Switch to ON and the rear panel REFERENCE SELECTOR Switch to INT. Wait for the mainframe "oven" indication to go out.
FREQUENCY SELECTION
2.Refer to Section III of the mainframe operating and service manual for information on system frequency selection.
RF OUTPUT LEVEL
3.dBm. Set the OUTPUT RANGE switch to within +3 and --6 dB of the desired output level. Adjust the VERNIER control for a meter reading which when added to the OUTPUT RANGE switch indication equals the desired output level.
4.VOLTS. To set the RF output level in rms volts, the OUTPUT RANGE switch selected the full scale meter reading and the VERNIER control is adjusted for the correct voltage reading on the meter. The voltage level for meter scale 1.0 should not be set below 0.32 of full scale. The voltage level should not be set below 1 when using the meter scale of 3.
NOTE
In order to achieve the output level accuracy specified, the level selected must be S<+10 dBm and the RF Section front panel meter reading must be as stated above.
5.Connect the RF Output to the Device Under Test. The front panel meter reading of RF Output level will be correct only if the input impedance of the Device Under Test is 50w2.
3-6
 Loading...
Loading...