Page 1

NextMove ESB
Motion Controller
MOTION CONTROL
Installation Manual
1/04 MN1924
Page 2

Page 3

Contents i
MN1924
Contents
1 General Information 1-1.................................
2 Introduction 2-1........................................
2.1 NextMove ESB features 2-1.................................
2.2 Receiving and inspection 2-3................................
2.2.1 Identifying the catalog number 2-3....................................
2.3 Units and abbreviations 2-4..................................
3 Basic Installation 3-1....................................
3.1 Introduction 3-1............................................
3.1.1 Location requirements 3-1..........................................
3.1.2 Mounting the NextMove ESB 3-2.....................................
3.1.3 Other requirements for installation 3-3................................
4 Input / Output 4-1......................................
4.1 Introduction 4-1............................................
4.1.1 Connector locations 4-2............................................
4.2 Analog I/O 4-3.............................................
4.2.1 Analog inputs 4-3..................................................
4.2.2 Analog outputs 4-5.................................................
4.3 Digital I/O 4-7..............................................
4.3.1 Digital inputs 4-7..................................................
4.3.2 Digital outputs 4-12.................................................
4.4 Other I/O 4-13..............................................
4.4.1 Stepper control outputs 4-13..........................................
4.4.2 Encoder inputs 0-2 4-14.............................................
4.4.3 USB port 4-15.....................................................
4.4.4 Serial port 4-16.....................................................
4.4.5 Using RS232 4-16..................................................
4.4.6 Multidrop using RS485 / RS422 4-17..................................
4.4.7 Connecting serial Baldor HMI Operator Panels 4-18......................
4.5 CAN 4-19..................................................
4.5.1 CAN connector 4-19................................................
4.5.2 CAN wiring 4-20....................................................
4.5.3 CANopen 4-21.....................................................
4.5.4 Baldor CAN 4-22...................................................
4.6 Connection summary - minimum system wiring 4-24.............
Page 4

ii Contents
MN1924
5 Operation 5-1..........................................
5.1 Introduction 5-1............................................
5.1.1 Connecting the NextMove ESB to the PC 5-1..........................
5.1.2 Installing WorkBench v5 5-1.........................................
5.1.3 Starting the NextMove ESB 5-1......................................
5.1.4 Preliminary checks 5-2.............................................
5.1.5 Power on checks 5-2...............................................
5.2 WorkBench v5 5-3..........................................
5.2.1 Help file 5-3......................................................
5.2.2 Starting WorkBench v5 5-4..........................................
5.3 Configuring an axis 5-6.....................................
5.3.1 Selecting a scale 5-6...............................................
5.3.2 Setting the drive enable output 5-7...................................
5.3.3 Testing the drive enable output 5-9...................................
5.4 Stepper axis - testing 5-10....................................
5.4.1 Testing the output 5-10..............................................
5.5 Servo axis - testing and tuning 5-11............................
5.5.1 Testing the demand output 5-11.......................................
5.5.2 An introduction to closed loop control 5-13..............................
5.6 Servo axis - tuning for current control 5-16......................
5.6.1 Selecting servo loop gains 5-16.......................................
5.6.2 Underdamped response 5-18.........................................
5.6.3 Overdamped response 5-19..........................................
5.6.4 Critically damped response 5-20......................................
5.7 Servo axis - eliminating steady-state errors 5-21.................
5.8 Servo axis - tuning for velocity control 5-22.....................
5.8.1 Calculating KVELFF 5-22............................................
5.8.2 Adjusting KPROP 5-25..............................................
5.9 Digital input/output configuration 5-27..........................
5.9.1 Digital input configuration 5-27........................................
5.9.2 Digital output configuration 5-28.......................................
5.10 Saving setup information 5-29.................................
5.10.1 Loading saved information 5-30.......................................
6 Troubleshooting 6-1....................................
6.1 Introduction 6-1............................................
6.1.1 Problem diagnosis 6-1..............................................
6.1.2 SupportMe feature 6-1.............................................
6.2 NextMove ESB indicators 6-2................................
6.2.1 Status display 6-2.................................................
6.2.2 Communication 6-3................................................
6.2.3 Motor control 6-4..................................................
Page 5

Contents iii
MN1924
6.2.4 WorkBench v5 6-5.................................................
6.2.5 CANopen 6-6.....................................................
6.2.6 Baldor CAN 6-8...................................................
7 Specifications 7-1......................................
7.1 Introduction 7-1............................................
7.1.1 Input power 7-1...................................................
7.1.2 Analog inputs 7-1..................................................
7.1.3 Analog outputs 7-1.................................................
7.1.4 Digital inputs 7-2..................................................
7.1.5 Digital outputs - general purpose 7-2..................................
7.1.6 Relay output 7-2...................................................
7.1.7 Encoder inputs 7-2................................................
7.1.8 Stepper control outputs 7-3..........................................
7.1.9 Serial RS232/RS485 port 7-3........................................
7.1.10 CAN interface 7-3.................................................
7.1.11 Environmental 7-3.................................................
7.1.12 Weights and dimensions 7-4........................................
Appendices
A General A-1............................................
A.1 Axis renumbering A-1.......................................
A.2 Feedback cables A-3.......................................
B CE Guidelines B-1......................................
B.1 Outline B-1................................................
B.1.1 EMC Conformity and CE marking B-1.................................
B.1.2 NextMove ESB compliance B-1......................................
B.1.3 Use of CE compliant components B-2.................................
B.1.4 EMC installation suggestions B-2.....................................
B.1.5 Wiring of shielded (screened) encoder cables B-2.......................
Page 6

iv Contents
MN1924
Page 7

www.supportme.net
General Information 1-1MN1924
LT0189A02 Copyright Baldor (c) 2004. All rights reserved.
This manual is copyrighted and all rights are reserved. This document or attached software may not,
in whole or in part, be copied or reproduced in any form without the prior written consent of BALDOR.
BALDOR makes no representations or warranties with respect to the contents hereof and specifically
disclaims any implied warranties of fitness for any particular purpose. The information in this
document is subject to change without notice.
BALDOR assumes no responsibility for any errors that may appear in this document.
Mintt is a registered trademark of Baldor.
Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows ME, Windows NT, Windows 2000 and Windows XP are
registered trademarks of the Microsoft Corporation.
Limited Warranty:
For a period of two (2) years from the date of original purchase, BALDOR will repair or replace without
charge controls and accessories which our examination proves to be defective in material or
workmanship. This warranty is valid if the unit has not been tampered with by unauthorized persons,
misused, abused, or improperly installed and has been used in accordance with the instructions and/or
ratings supplied. This warranty is in lieu of any other warranty or guarantee expressed or implied.
BALDOR shall not be held responsible for any expense (including installation and removal),
inconvenience, or consequential damage, including injury to any person or property caused by items of
our manufacture or sale. (Some countries and U.S. states do not allow exclusion or limitation of
incidental or consequential damages, so the above exclusion may not apply.) In any event,
BALDOR’s total liability, under all circumstances, shall not exceed the full purchase price of the
control. Claims for purchase price refunds, repairs, or replacements must be referred to BALDOR with
all pertinent data as to the defect, the date purchased, the task performed by the control, and the
problem encountered. No liability is assumed for expendable items such as fuses. Goods may be
returned only with written notification including a BALDOR Return Authorization Number and any
return shipments must be prepaid.
Baldor UK Ltd
Mint Motion Centre
6 Bristol Distribution Park
Hawkley Drive
Bristol, BS32 0BF
Telephone: +44 (0) 1454 850000
Fax: +44 (0) 1454 850001
Email: technical.support@baldor.co.uk
Web site: www.baldor.co.uk
Baldor ASR GmbH
Telephone: +49 (0) 89 90508-0
Fax: +49 (0) 89 90508-492
Baldor ASR AG
Telephone: +41 (0) 52 647 4700
Fax: +41 (0) 52 659 2394
Email: technical.support@baldor.ch
Australian Baldor Pty Ltd
Baldor Electric Company
Telephone: +1 479 646 4711
Fax: +1 479 648 5792
Email: sales@baldor.com
Web site: www.baldor.com
AustralianBaldorPtyLt
d
Telephone: +61 2 9674 5455
Fax: +61 2 9674 2495
Baldor Electric (F.E.) Pte Ltd
Telephone: +65 744 2572
Fax: +65 747 1708
Baldor Italia S.R.L
Telephone: +39 (0) 11 56 24 440
Fax: +39 (0) 11 56 25 660
1 General Information
1
Page 8

www.supportme.net
1-2 General Information MN1924
Safety Notice
Only qualified personnel should attempt to start-up, program or troubleshoot this equipment.
This equipment may be connected to other machines that have rotating parts or parts that are
controlled by this equipment. Improper use can cause serious or fatal injury.
Precautions
WARNING: Do not touch any circuit board, power device or electrical connection before you
first ensure that no high voltage is present at this equipment or other equipment to
which it is connected. Electrical shock can cause serious or fatal injury.
WARNING: Be sure that you are completely familiar with the safe operation and programming
of this equipment. This equipment may be connected to other machines that have
rotating parts or parts that are controlled by this equipment. Improper use can
cause serious or fatal injury.
WARNING: The stop input to this equipment should not be used as the single means of
achieving a safety critical stop. Drive disable, motor disconnect, motor brake and
other means should be used as appropriate.
WARNING: Improper operation or programming may cause violent motion of the motor shaft
and driven equipment. Be certain that unexpected motor shaft movement will not
cause injury to personnel or damage to equipment. Peak torque of several times
the rated motor torque can occur during control failure.
CAUTION: The safe integration of this equipment into a machine system is the responsibility
of the machine designer. Be sure to comply with the local safety requirements at
the place where the machine is to be used. In Europe these are the Machinery
Directive, the Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive and the Low Voltage
Directive. In the United States this is the National Electrical code and local codes.
CAUTION: Electrical components can be damaged by static electricity. Use ESD
(electrostatic discharge) procedures when handling this drive.
Page 9

www.supportme.net
Introduction 2-1MN1924
2.1 NextMove ESB features
NextMove ESB is a high performance multi-axis intelligent controller for servo and stepper
motors.
NextMove ESB features the MintMT motion control language. MintMT is a structured form of
Basic, custom designed for stepper or servo motion control applications. It allows you to get
started very quickly with simple motion control programs. In addition, MintMT includes a wide
range of powerful commands for complex applications.
Standard features include:
H Control of 4 stepper and 3 servo axes.
H Point to point moves, software cams and gearing.
H 20 general purpose digital inputs, software configurable as level or edge triggered.
H 11 general purpose digital outputs.
H 2 differential analog inputs with 12-bit resolution.
H 4 single-ended analog outputs with 12-bit resolution.
H USB serial port.
H RS232 or RS485 serial port (model dependent).
H CANopen or proprietary Baldor CAN protocol for communication with MintMT controllers
and other third party devices.
H Programmable in MintMT.
2 Introduction
2
Page 10

www.supportme.net
2-2 Introduction MN1924
Included with NextMove ESB is the Baldor Motion Toolkit CD. This contains a number of
utilities and useful resources to get the most from your MintMT controller . These include:
H Mint WorkBench v5
This is the user interface for communicating with the NextMove ESB. Installing Mint
WorkBench v5 will also install firmware for NextMove ESB.
H PC Developer Libraries
Installing Mint WorkBench v5 will install ActiveX interfaces that allow PC applications to be
written that communi cate with the NextMove ESB.
This manual is intended to guide you through the installation of NextMove ESB.
The chapters should be read in sequence.
The Basic Installation section describes the mechanical installation of the NextMove ESB.
The following sections require knowledge of the low level input/output requirements of the
installation and an understanding of computer software installation. If you are not qualified in
these areas you should seek assistance before proceeding.
Note: You can check that you have the latest firmware and WorkBench v5 releases by
visiting the website www.supportme.net.
Page 11
www.supportme.net
Introduction 2-3MN1924
2.2 Receiving and inspection
When you receive your NextMove ESB, there are several things you should do immediately:
1. Check the condition of the packaging and report any damage immediately to the carrier
that delivered your NextMove ESB.
2. Remove the NextMove ESB from the shipping container and remove all packing material. The
container and packing materials may be retained for future shipment.
3. Verify that the catalog number of the NextMove ESB you received is the same as the
catalog number listed on your purchase order. The catalog/part number is described in
the next section.
4. Inspect the NextMove ESB for external damage during shipment and report any damage
to the carrier that delivered it.
5. If the NextMove ESB is to be stored for several weeks before use, be sure that it is stored
in a location that conforms to the storage humidity and temperature specifications shown
in section 3.1.1.
2.2.1 Identifying the catalog number
Different models of NextMove ESB are available. As a reminder of which product has been
installed, it is a good idea to write the catalog number in the space provided below.
NextMove ESB catalog number:
NSB002-501 or NSB002-502
Installed in: ________________________
Date: ______
A description of the catalog numbers are shown in the following table:
Catalog
number
Description
NSB002-501 NextMove ESB controller with USB and RS232 serial connections
NSB002-502 NextMove ESB controller with USB and RS485 serial connections
Page 12

www.supportme.net
2-4 Introduction MN1924
2.3 Units and abbreviations
The following units and abbreviations may appear in this manual:
V Volt (also V AC and VDC)...............
WWatt..............
A Ampere...............
Ω Ohm...............
mΩ milliohm.............
µF microfarad..............
pF picofarad..............
mH millihenry.............
Φ phase...............
ms millisecond..............
µs microsecond..............
ns nanosecond..............
mm millimeter.............
m meter...............
in inch...............
ft feet...............
lbf-in pound force inch (torque)............
Nm Newton meter (torque).............
ADC Analog to Digital Converter............
ASCII American Standard Code for Information Interchange...........
AWG American Wire Gauge............
CAL CAN Application Layer............
CAN Controller Area Network............
CDROM Compact Disc Read Only Memory.........
CiA CAN in Automation International Users and Manufacturers Group e.V..............
CTRL+E on the PC keyboard, press Ctrl then E at the same time..........
DAC Digital to Analog Converter............
DS301 CiA CANopen Application Layer and Communication Profile..........
DS401 CiA Device Profile for Generic I/O Devices..........
DS403 CiA Device Profile for HMIs..........
EDS Electronic Data Sheet............
EMC Electromagnetic Compatibility............
HMI Human Machine Interface.............
ISO International Standards Organization.............
Kbaud kilobaud (the same as Kbit/s in most applications)...........
LCD Liquid Crystal Display............
MB megabytes.............
Mbps megabits/s...........
(NC) Not Connected............
RF Radio Frequency..............
Page 13

www.supportme.net
Basic Installation 3-1MN1924
3.1 Introduction
You should read all the sections in Basic Installation.
It is important that the correct steps are followed when installing the NextMove ESB.
This section describes the mechanical installation of the NextMove ESB.
3.1.1 Location requirements
You must read and understand this section before beginning the installation.
CAUTION: To prevent equipment damage, be certain that input and output signals
are powered and referenced correctly.
CAUTION: To ensure reliable performance of this equipment be certain that all
signals to/from the NextMove ESB are shielded correctly.
CAUTION: Avoid locating the NextMove ESB immediately above or beside heat
generating equipment, or directly below water steam pipes.
CAUTION: Avoid locating the NextMove ESB in the vicinity of corrosive substances
or vapors, metal particles and dust.
The safe operation of this equipment depends upon its use in the appropriate environment.
The following points must be considered:
H The NextMove ESB is designed to be mounted indoors, permanently fixed and located.
H The NextMove ESB must be secured by the slots in the metal case.
H The NextMove ESB must be installed in an ambient temperature of 0°C to 45°C (32°F to
113°F).
H The NextMove ESB must be installed in relative humidity levels of less than 80% for
temperatures up to 31°C (87°F) decreasing linearly to 50% relative humidity at 45°C
(113°F), non-condensing.
H The NextMove ESB must be installed where the pollution degree according to IEC664
shall not exceed 2.
H There shall not be abnormal levels of nuclear radiation or X-rays.
3 Basic Installation
3
Page 14
www.supportme.net
3-2 Basic Installation MN1924
3.1.2 Mounting the NextMove ESB
CAUTION: Before touching the unit be sure to discharge static electricity from your
body and clothing by touching a grounded metal surface. Alternatively,
wear an earth strap while handling the unit.
Ensure you have read and understood the location requirements in section 3.1.1. Mount the
NextMove ESB using the supplied M4 screws. For effective cooling, the NextMove ESB must
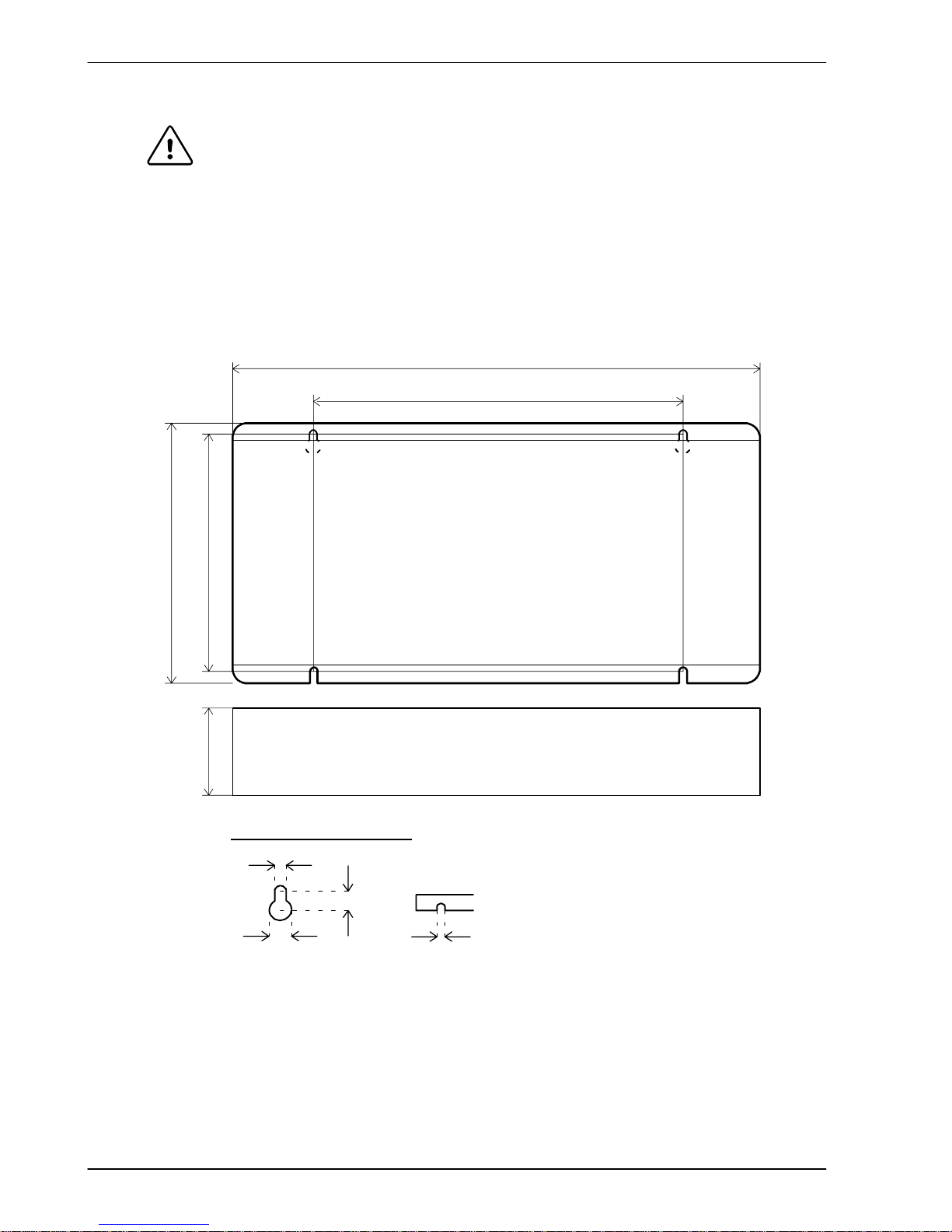
be mounted on a smooth non-flammable vertical surface. Orientation must be as shown in
Figure 1, with the two slots in the metal carrier / heat sink assembly at the bottom.
135 (5.3)
124 (4.9)
170 (6.7)
245 (9.65)
All dimensions shown as
mm (inches)
43 (1.7)
Mounting keyhole and slot detail
A
B
C
A 4.5mm
B 10mm
C 11m m
A
Drawings not to scale
Figure 1 - Package dimensions
There must be at least 20mm (0.8 in) clearance between the NextMove ESB and neighboring
equipment to allow sufficient cooling by natural convection. Remember to allow additional
space around the edges to accommodate the mating connectors and associated wiring. For
example, 70mm (2.8 in) clearance will be required for connection of the serial port cable.
Page 15
www.supportme.net
Basic Installation 3-3MN1924
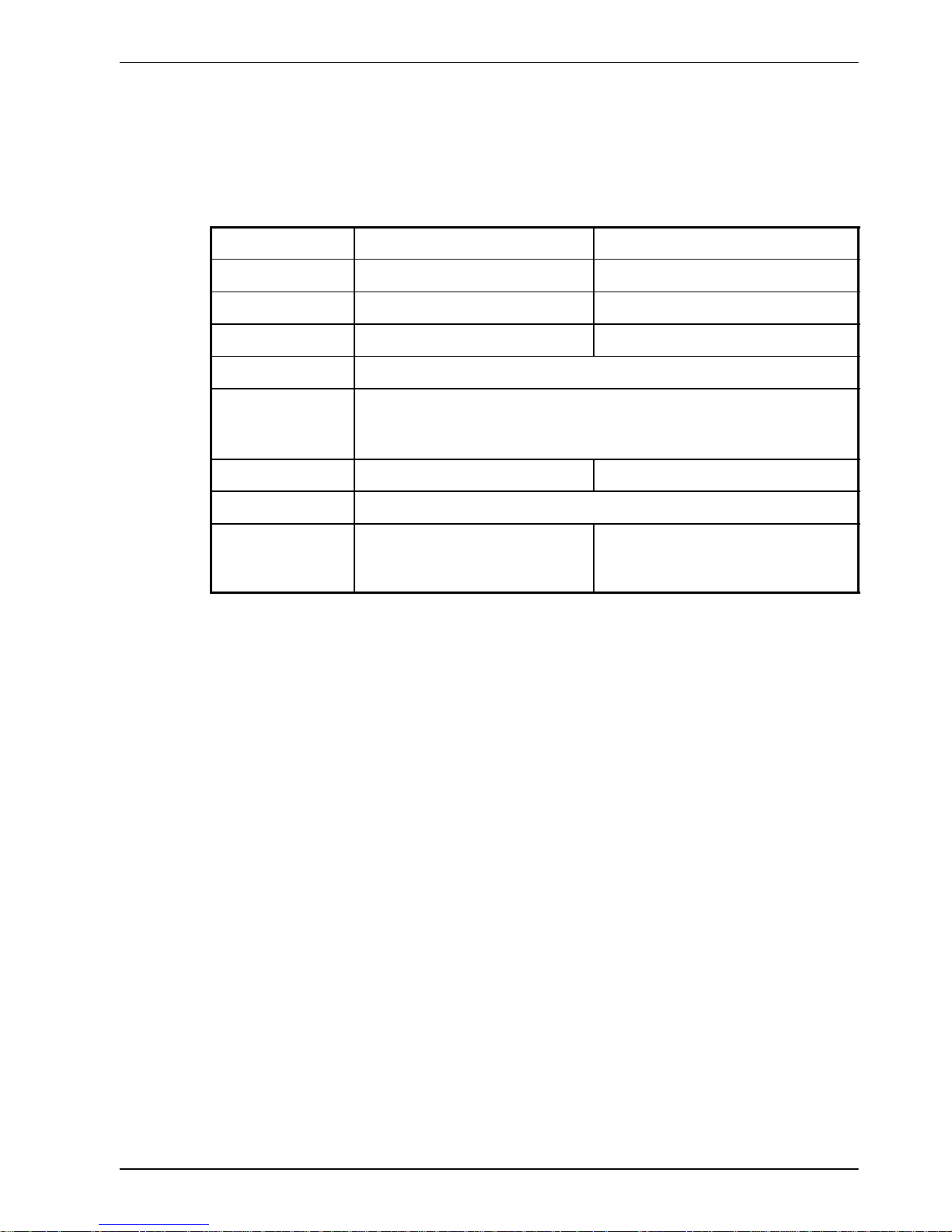
3.1.3 Other requirements for installation
H The NextMove ESB requires +24V power supply capable of supplying 2A continuously.
If digital outputs are to be used, a supply will be required to drive them - see section 4.3.2.
H A PC that fulfills the following specification:
Minimum specification Recommended specification
Processor Intel Pentium 133MHz Intel PentiumII 400MHz or faster
RAM 32MB 128MB
Hard disk space 40MB 60MB
CD-ROM ACD-ROMdrive
Serial port USB port
or
RS232 or RS485 serial port (depending on NextMove ESB model)
Screen 800 x 600, 256 colors 1024 x 768, 16-bit color
Mouse A mouse or similar pointing device
Operating
system
Windows 95, Windows NT Windows 98*, Windows ME*,
Windows NT*, Windows 2000 or
Windows XP
* For USB support, Windows 2000 or Windows XP is required. Software installation will be
described later, in section 5.
H A serial cable (connected as shown in section 4.4.4) or USB cable.
H Your PC operating system user manual might be useful if you are not familiar with Windows.
Page 16

www.supportme.net
3-4 Basic Installation MN1924
Page 17

www.supportme.net
Input / Output 4-1MN1924
4.1 Introduction
This section describes the input and output capabilities of the NextMove ESB.
The following conventions will be used to refer to the inputs and outputs:
I/O Input / Output..............
DIN Digital Input.............
DOUT Digital Output...........
AIN Analog Input.............
AOUT Analog Output...........
4 Input / Output
4
Page 18
www.supportme.net
4-2 Input / Output MN1924
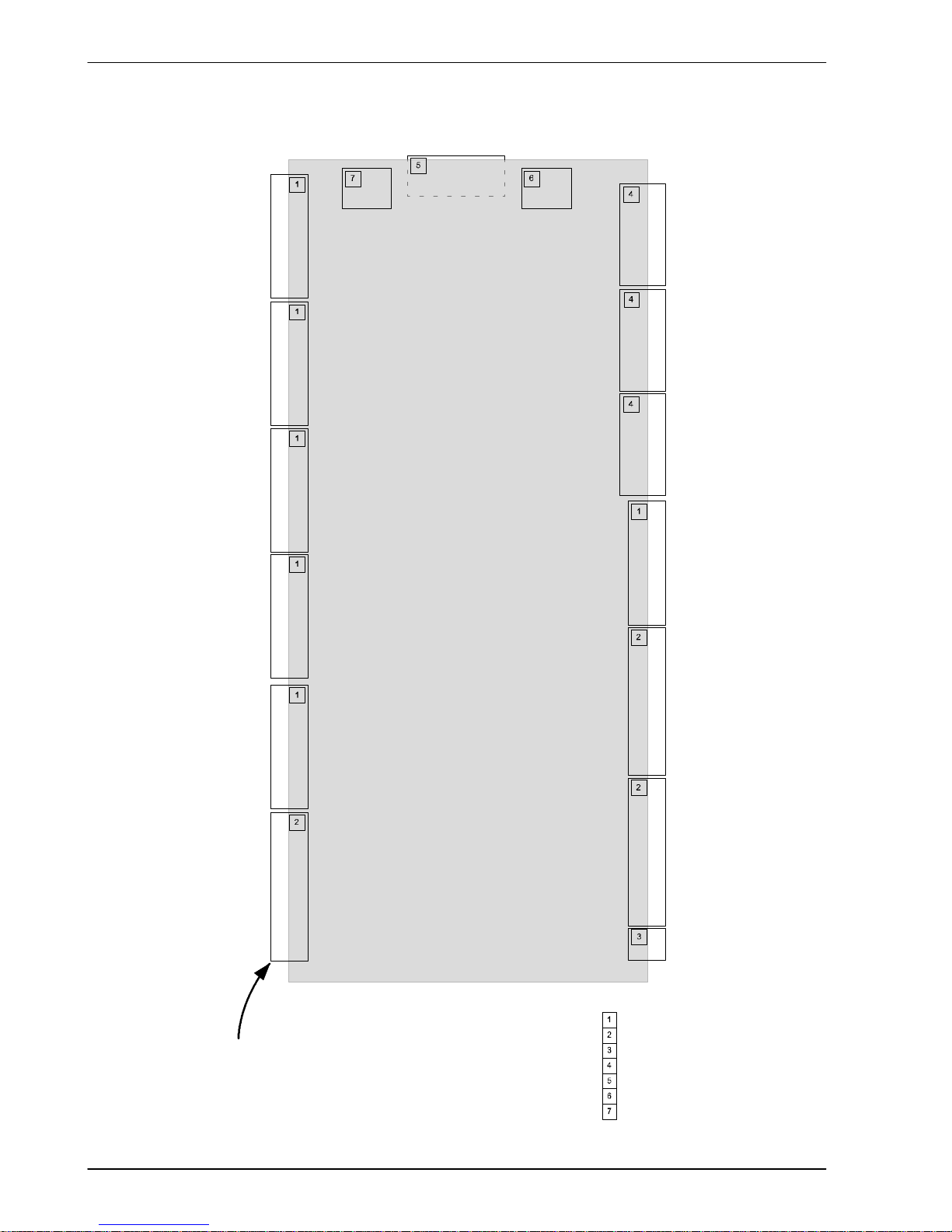
4.1.1 Connector locations
Tightening torque for terminal block
connections is 0.3Nm (2.65 lbf-in)
X12 AIN 0-1
& relay
X7 Encoder2
X6 Encoder1
X4 DOUT 8-10
X2 STEP 0-1
AIN0+
AIN0AGND
AIN1+
AIN1Shield
REL COM
REL NC
REL NO
REL COM
CREF2
CREF1
CREF0
!RSTIN
USR GND
USR V+
USR V+
DOUT10
DOUT9
DOUT8
Shield
DIR1+
DIR1STEP1+
STEP1DGND
Shield
DIR0+
DIR0STEP0+
STEP0DGND
Serial
Required mating connectors:
Sauro CTF10008
Sauro CTF12008
Sauro CTF02008
9-pin D-type plug (male)
9-pin D-type sock et (female)
RJ45 plug
USB type B plug
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
X11 DOUT 0-7
DOUT0
DOUT1
DOUT2
DOUT3
DOUT4
DOUT5
DOUT6
DOUT7
USR V+
USR GND
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
X10 DIN 0-3
(fast interrupts)
DIN3
Shield
CREF0
DIN2
Shield
CREF0
DIN1
Shield
CREF0
DIN0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
X9 DIN 4-11
DIN11
DIN10
DIN9
DIN8
DIN7
DIN6
DIN5
DIN4
CREF1
Shield
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
X8 DIN 12-19
DIN19
DIN18
DIN17
DIN16
DIN15
DIN14
DIN13
DIN12
CREF2
Shield
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
X13 AOUT 0-3
(demands)
DEMAND0
AGND
Shield
DEMAND1
AGND
Shield
DEMAND2
AGND
Shield
DEMAND3
AGND
Shield
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
X3 STEP 2-3
Shield
DIR3+
DIR3STEP3+
STEP3DGND
Shield
DIR2+
DIR2STEP2+
STEP2DGND
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
X5 Encoder0
X1 +24V in
+24V
0V
2
1
CANUSB
Page 19
www.supportme.net
Input / Output 4-3MN1924
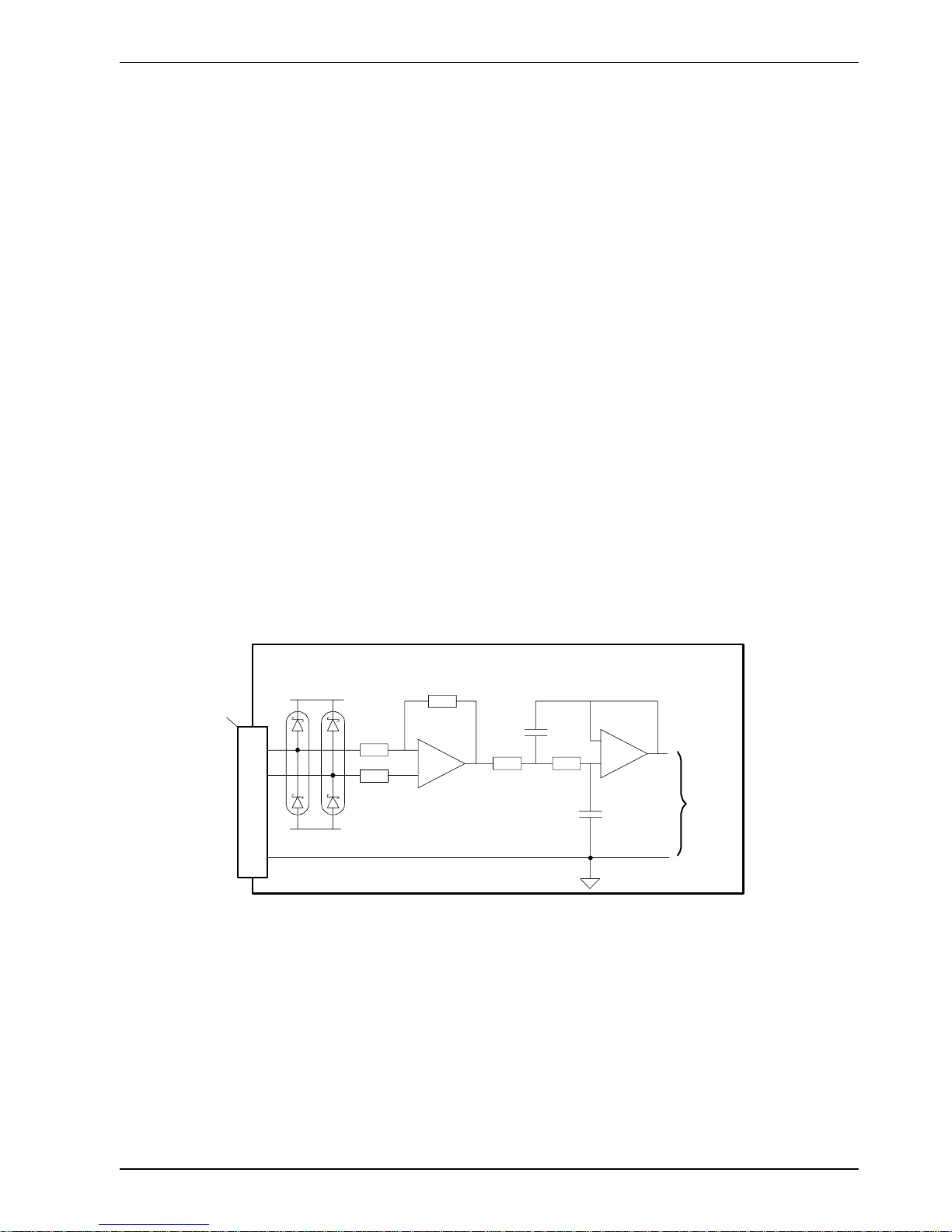
4.2 Analo g I/O
The NextMove ESB provides:
H Two 12-bit resolution analog inputs.
H Four 12-bit resolution analog outputs.
4.2.1 Analog inputs
The analog inputs are available on connector X12, pins 1 & 2 (AIN0) and 4 & 5 (AIN1).
H Differential inputs.
H Voltage range: ±10V.
H Resolution: 12-bit with sign (accuracy ±4.9mV @ ±10V input).
H Input impedance: 120kΩ.
H Sampling frequency: 4kHz maximum, 2kHz if both inputs are enabled.
The analog inputs pass through a differential buffer and second order low-pass filter with a
cut-off frequency of approximately 1kHz.
Both inputs are normally sampled at 2kHz. However, an input can be disabled by setting
ADCMODE to4(_acOFF). With one input disabled, the remaining input will be sampled at 4kHz.
In MintMT , analog inputs can be read using the ADC keyword. See the MintMT help file for full
details of ADC, ADCMODE and other related ADC... keywords.
NextMove ESB
-
+
AIN0+
AIN0-
AGND
MintMT
ADC.0
-
+
120k
120k
15k
10k 10k
22nF
10nF
2
3
1
+12V
-12V
‘X12’
Figure 2 - Analog input, AIN0 shown
For differential inputs connect input lines to AIN+ and AIN-. Leave AGND unconnected.
Page 20
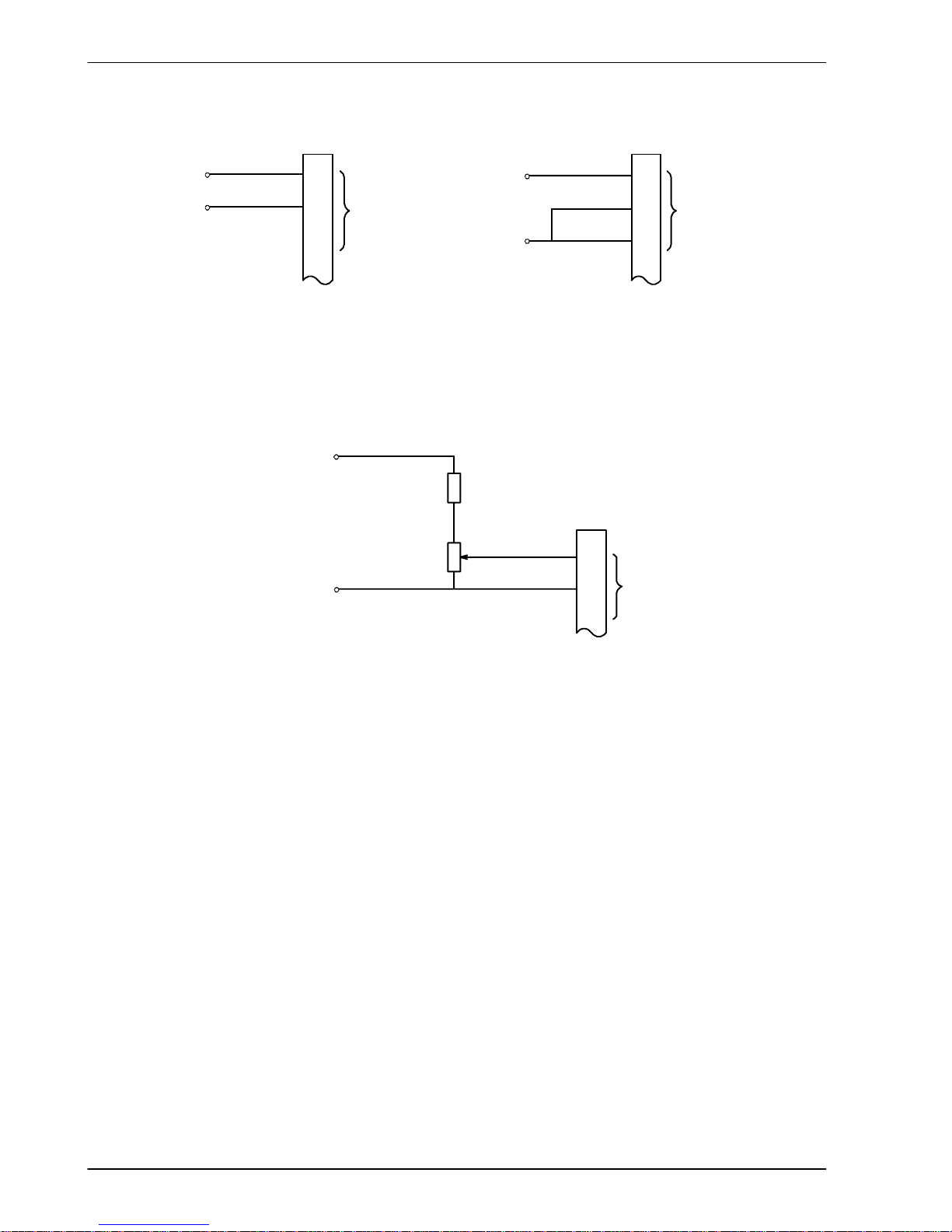
www.supportme.net
4-4 Input / Output MN1924
AIN0
(ADC.0)
X12
AIN0
(ADC.0)
1
2
3
X12
AIN0-
Differential connection Single ended connection
AIN0+
1
2
3
AIN0+
GND
Figure 3 - AIN0 analog input wiring
AIN0
1kΩ,0.25W
potentiometer
(ADC.0)2
1
X12
1.5kΩ, 0.25W
0V
+24VDC
3
Figure 4 - Typical input circuit to provide 0-10V (approx.) input from a 24V source
Page 21

www.supportme.net
Input / Output 4-5MN1924
4.2.2 Analog outputs
The four analog outputs are available on connector X13, as shown in section 4.1.1.
H Four independent bipolar analog outputs.
H Output range: ±10VDC (±0.1%).
H Resolution: 12-bit (accuracy ±4.9mV).
H Output current: 10mA maximum.
H Update frequency: 10kHz maximum (adjustable using the LOOPTIME keyword, factory
default 1kHz).
MintMT and the Mint Motion Library use analog outputs Demand0 to Demand2 to control servo
axes 0 to 2 respectively. The Demand3 output may be used as general purpose analog
output. See the DAC keyword in the MintMT help file.
The analog outputs may be used to drive loads of 1kΩ or greater. Shielded twisted pair cable
should be used. The shield connection should be made at one end only.
NextMove ESB
Demand0
Demand
±100%
120k
30k
-
+
AGND
100pF
TL084
47R
1
2
+12V
-12V
‘X13’
Figure 5 - Analog output - Demand0 shown
NextMove ESB
Demand0
AGND
1
2
13
12
MicroFlex / servo amplifier
AIN0+
AIN0-
Connect overall shield at
one end only
3Shield
Servo
amplifier
±10VDC
demand
input
-
+
‘X3’‘X13’
Figure 6 - Analog output - typical connection to a Baldor MicroFlex
Page 22
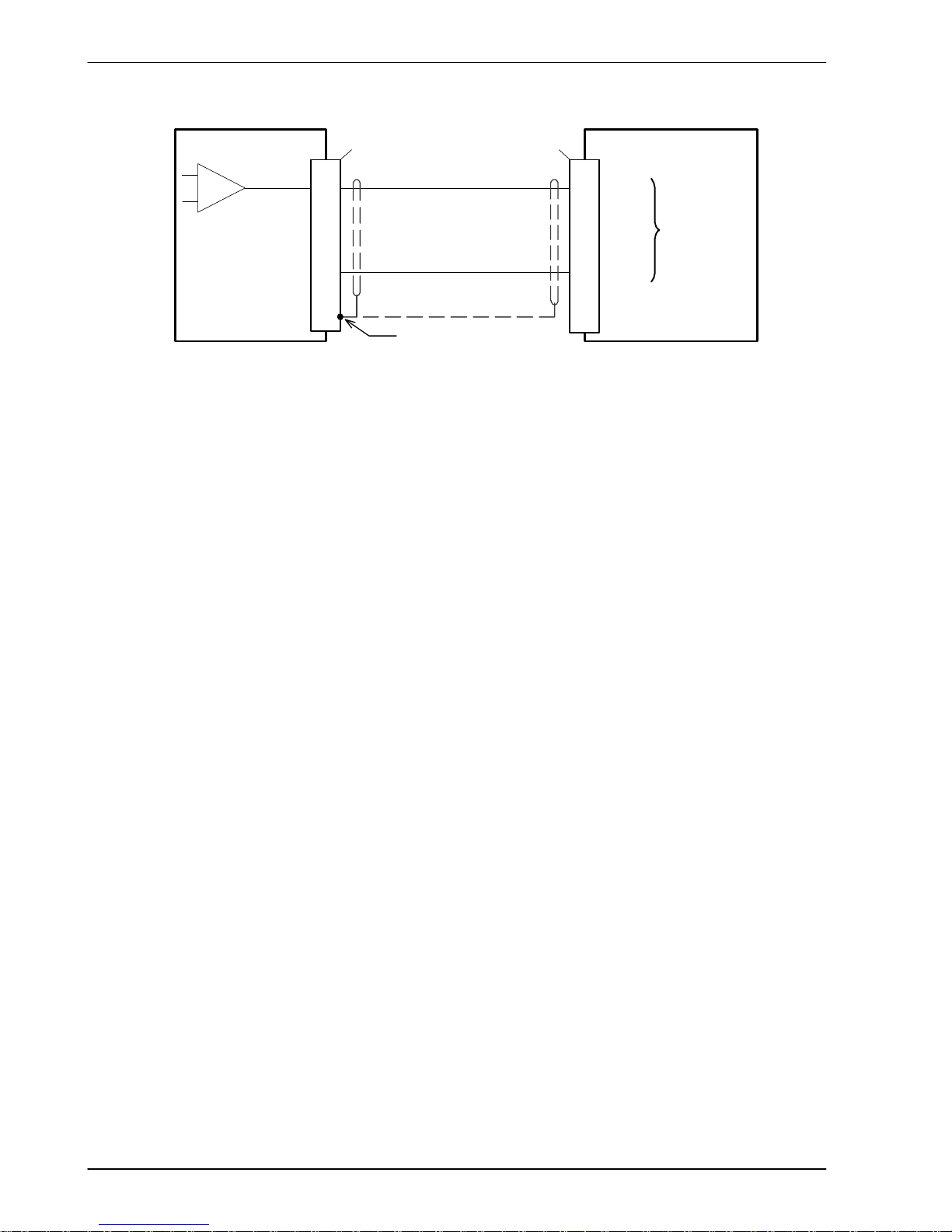
www.supportme.net
4-6 Input / Output MN1924
NextMove ESB
Demand0
AGND
2
FlexDriveII/ servo ampli fier
AIN0+
AIN0-
Connect overall shield at
one end only
3Shield
Servo
amplifier
±10VDC
demand
input
-
+
1
2
1
‘X1’
‘X13’
Figure 7 - Analog output - typical connection to a Baldor FlexDriveII, Flex+DriveIIor MintDrive
II
Page 23
www.supportme.net
Input / Output 4-7MN1924
4.3 Digital I/O
The NextMove ESB provides:
H 20 general purpose digital inputs.
H 11 general purpose digital outputs.
4.3.1 Digital inputs
Digital inputs are available on connectors X8, X9 and X10, as shown in section 4.1.1.
The digital inputs are arranged in three groups, each with their own common connection. This
allows each group to be configured independently for ‘active high’ or ‘active low’ operation.
The general purpose digital inputs DIN0 - DIN19 can be shared between axes, and are
programmable in Mint (using a range of keywords beginning with the letters INPUT... ) to
determine their active level and if they should be edge triggered. The state of individual inputs
can be read directly using the INX keyword. See the MintMT help file.
A general purpose digital input can be assigned to a special purpose function such as a home,
limit, stop or error input. See the keywords HOMEINPUT, LIMITFORWARDINPUT,
LIMITREVERSEINPUT, STOPINPUT and ERRORINPUT in the MintMT help file.
4.3.1.1 DIN0 - DIN3
Digital inputs DIN0 to DIN3 can be assigned as fast interrupts. These are used as high speed
position latches, allowing any combination of axes to be captured by the hardware. The
latency between input triggering and capture is 1µs. Special Mint keywords (beginning with the
letters FAST...) allow specific functions to be performed as a result of fast position inputs
becoming active. See the Mint help file for details.
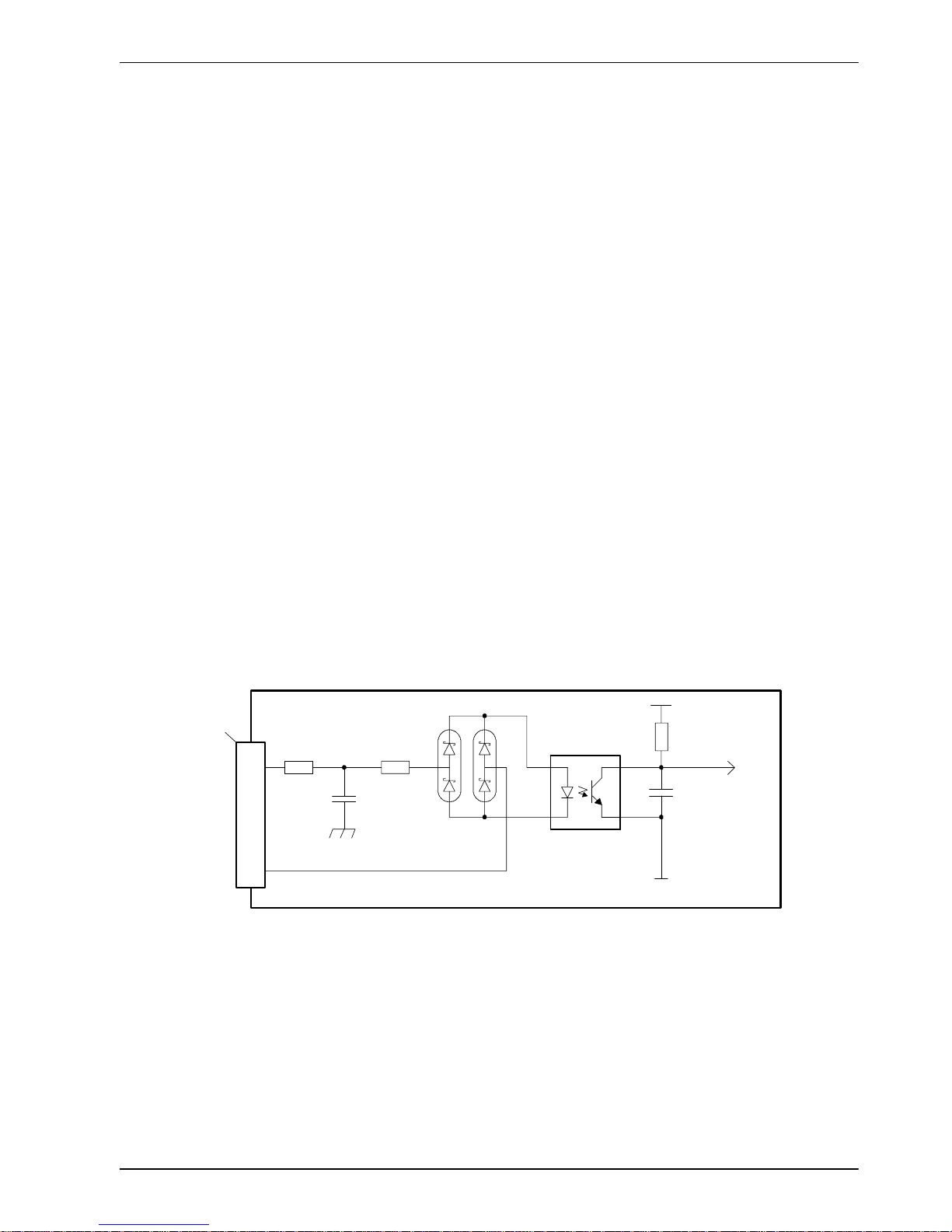
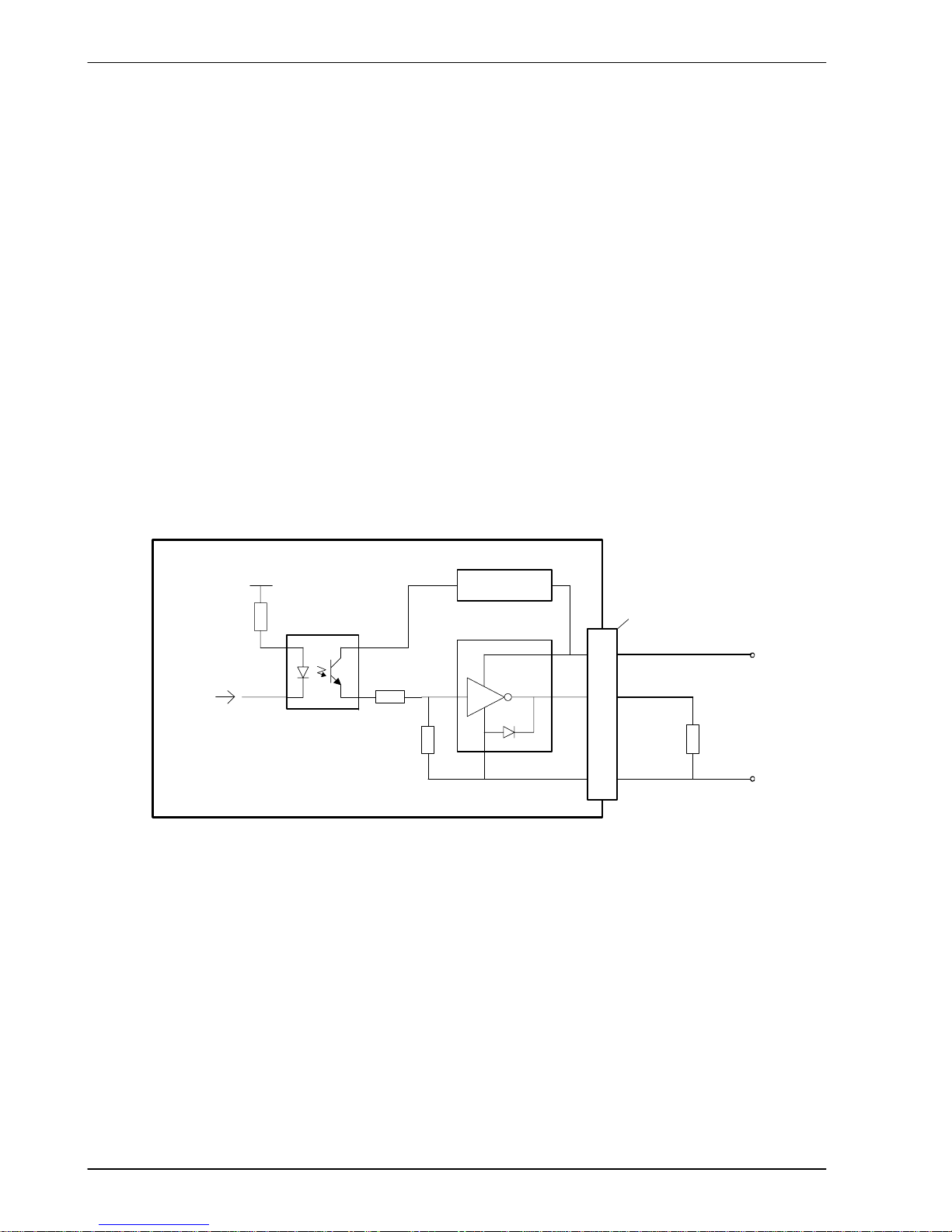
DIN3
3k3
TLP115A
DGND
Mint
1k
Vcc
NextMove ESB
CREF0
4n7
100R
100pF
1
3
Shield 2
‘X10’
Figure 8 - Fast interrupt digital input - DIN3 shown
Digital inputs DIN0 to DIN3 use CREF0 as their common connection.
Note: The fast inputs are particularly sensitive to noise, so inputs must use shielded
twisted pair cable. Do not connect mechanical switches, relay contacts or other
sources liable to signal ‘bounce’ directly to the fast inputs. This could cause
unwanted multiple triggering.
Page 24
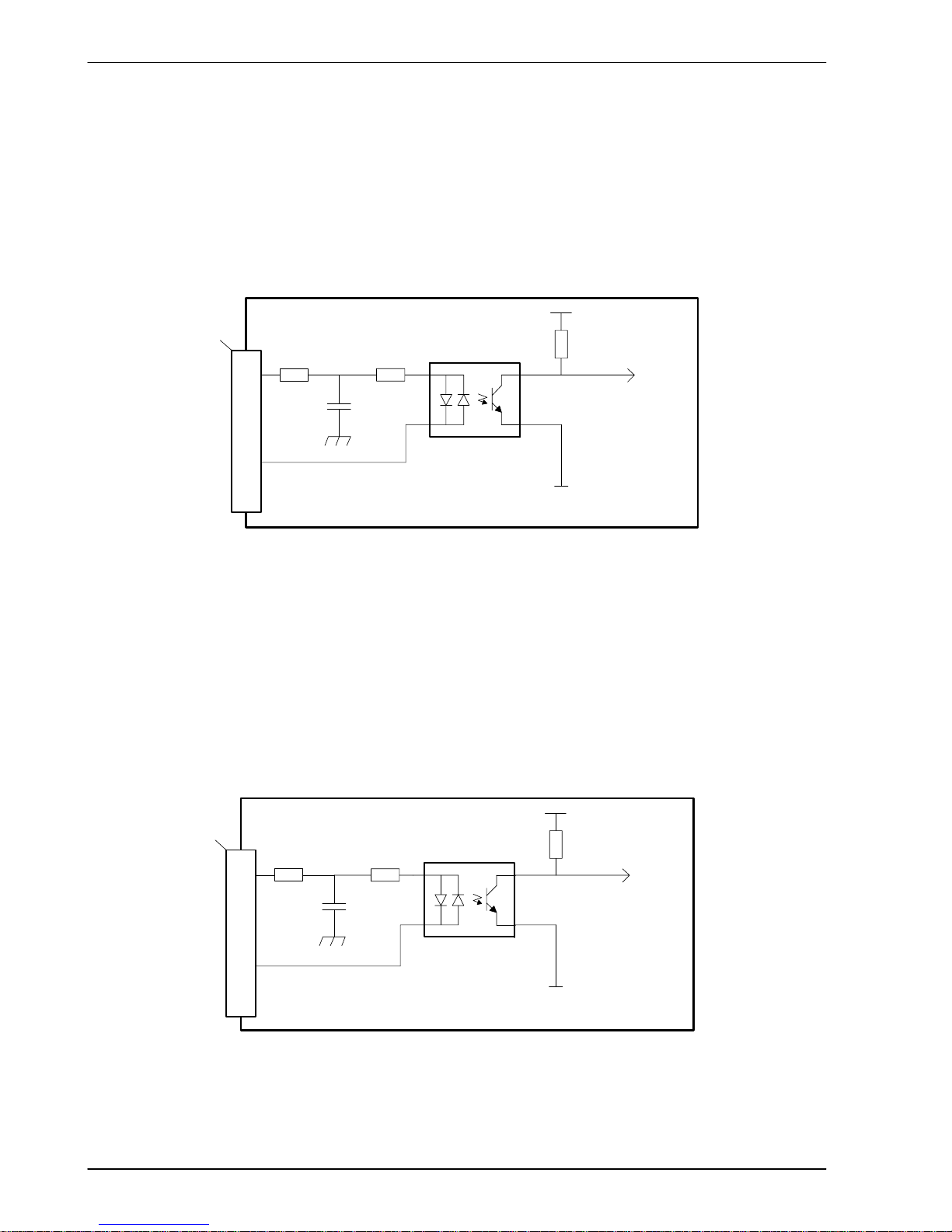
www.supportme.net
4-8 Input / Output MN1924
4.3.1.2 DIN4 - DIN11
Digital inputs DIN4 to DIN11 have a common specification:
H Opto-isolated digital inputs.
H Sampling frequency: 1kHz.
Digital inputs DIN4 to DIN11 use CREF1 as their common connection.
DIN11
3k3
TLP280
DGND
Mint
INX.11
4k7
Vcc
NextMove ESB
CREF1
4n7
100R
1
9
Shield 10
‘X9’
Figure 9 - General purpose digital input - DIN11 shown
If an input is configured as edge triggered, the triggering pulse must have a duration of at least
1ms (one software scan) to guarantee acceptance by MintMT. The use of shielded cable for
inputs is recommended.
4.3.1.3 DIN12 - DIN19
Digital inputs DIN12 to DIN19 have the same electrical specification as DIN4-11, except that
they use CREF2 as their common connection.
DIN19
3k3
TLP280
DGND
Mint
INX.19
4k7
Vcc
NextMove ESB
CREF2
4n7
100R
1
9
Shield 10
‘X8’
Figure 10 - General purpose digital input - DIN19 shown
Page 25
www.supportme.net
Input / Output 4-9MN1924
4.3.1.4 Auxiliary encoder inputs - DIN17 (STEP), DIN18 (DIR), DIN19 (Z)
DIN17-DIN19 may also be used as an auxiliary encoder input. DIN17 accepts step (pulse)
signals and DIN18 accepts direction signals, allowing an external source to provide the
reference for the speed and direction of an axis. The step frequency (20MHz maximum)
determines the speed, and the direction input determines the direction of motion. Both the
rising and falling edges of the signal on DIN17 cause an internal counter to be changed. If 5V
is applied to DIN18 (or it is left unconnected) the counter will increment. If DIN18 is grounded
the counter will be decremented.
Typically, one channel of an encoder signal (either A or B) would be used to provide the step
signal on DIN17, allowing the input to be used as an auxiliary (master) encoder input. The
input can be used as a master position reference for cam, fly and follow move types. For this,
the MASTERSOURCE keyword must be used to configure the step input as a master (auxiliary)
encoder input. The master position reference can then be read using the AUXENCODER
keyword.
Since a secondary encoder channel is not used, DIN18 allows the direction of motion to be
determined. The Z signal on DIN19 can be supplied from the encoder’s index signal, and may
be read using the AUXENCODERZLATCH keyword.
See the MintMT help file for details of each keyword.
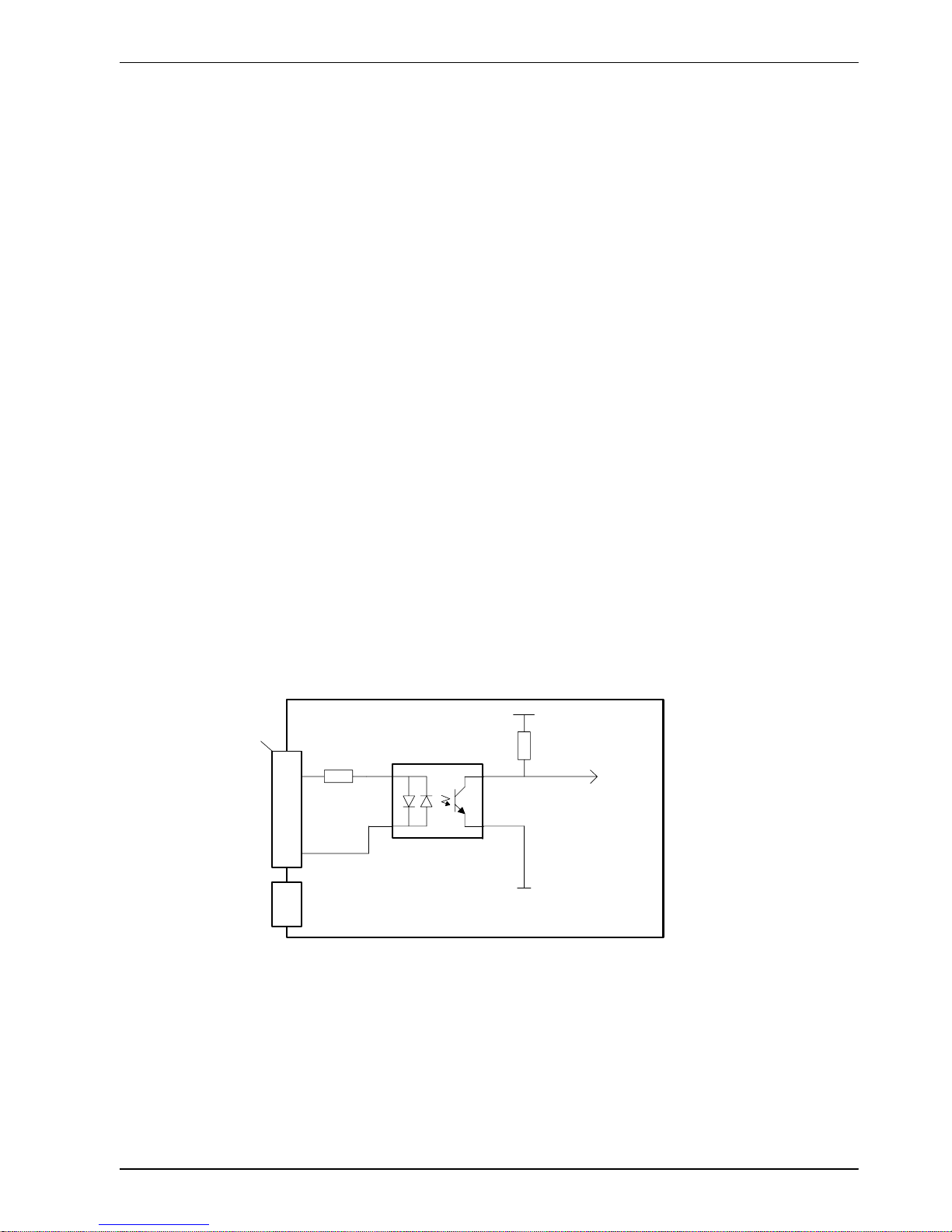
4.3.1.5 Digital inputs - reset
The reset input !RSTIN is available on connector X4, and uses CREF1 as its common
connection. When the reset input is activated it will cause a hardware reset of the NextMove
ESB. This is equivalent to power-cycling the NextMove ESB. Due to the internal pull-up
resistor, the reset input may be left floating.
!RSTIN
3k3
TLP280
DGND
Reset
4k7
Vcc
NextMove ESB
CREF1
7
9
Shield
12
X3
‘X4’
Figure 11 - Reset input
Page 26
www.supportme.net
4-10 Input / Output MN1924
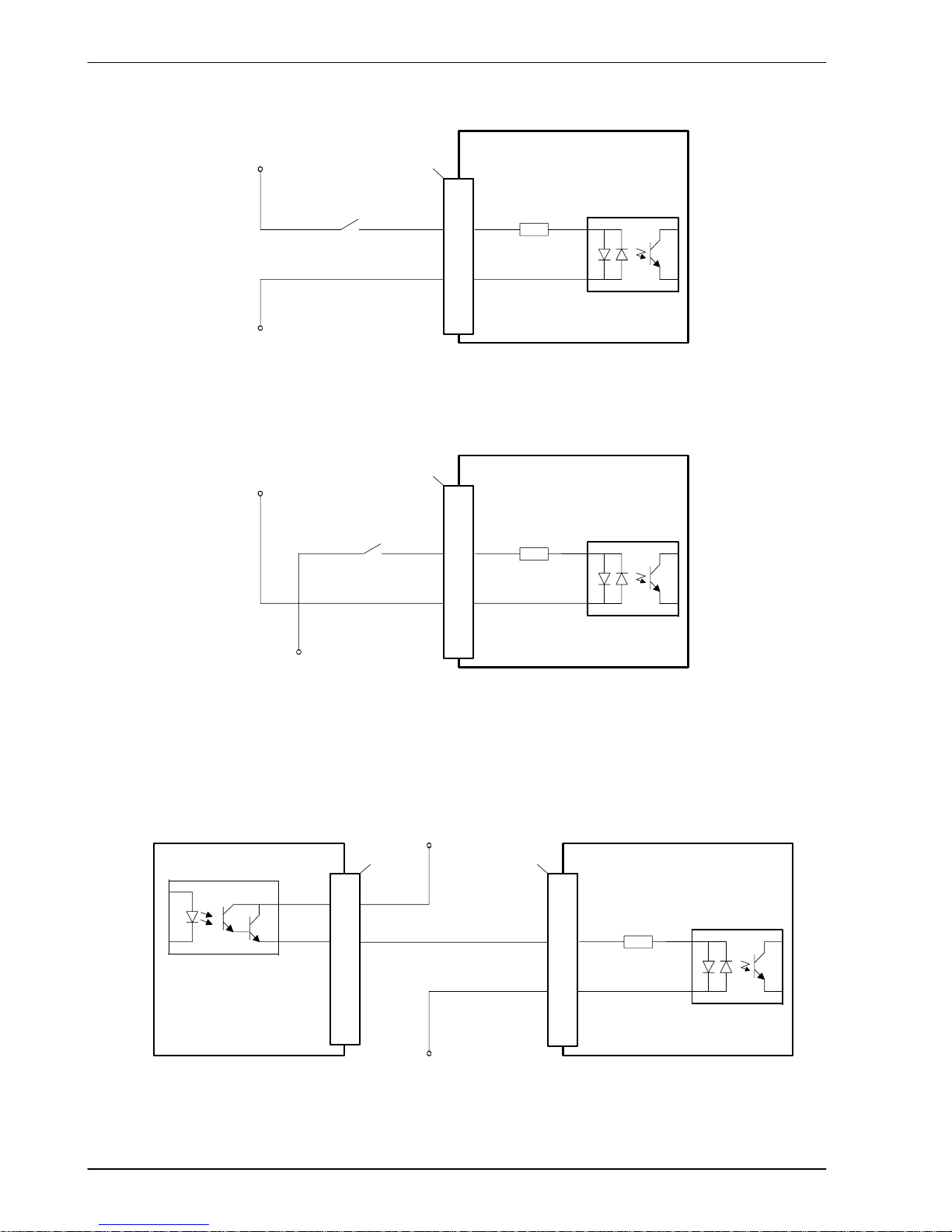
4.3.1.6 Typical digital input wiring
NextMove ESB
8
9
DIN4
CREF1
3k3
TLP280
User
supply
GND
User
supply
24V
‘X9’
Figure 12 - Digital input - typical ‘active high’ input connection using a switch
NextMove ESB
8
9
DIN4
CREF1
3k3
TLP280
User
supply
GND
User
supply
24V
‘X9’
Figure 13 - Digital input - typical ‘active low’ input connection using a switch
Note: The circuits shown in Figures 12 and 13 are not suitable for use with fast inputs
DIN0 to DIN3. Using a mechanical switch, relay contacts or other source liable to
signal ‘bounce’ could cause unwanted multiple triggering.
NextMove ESB
Status+
Status-
8
9
MicroFlex / equi pment output
DIN4
CREF1
NEC P S2562L-1
3k3
TLP280
User
supply
GND
User
supply
24V
3
2
‘X3’
‘X9’
Figure 14 - Digital input - typical connections from a Baldor MicroFlex
Page 27
www.supportme.net
Input / Output 4-11MN1924
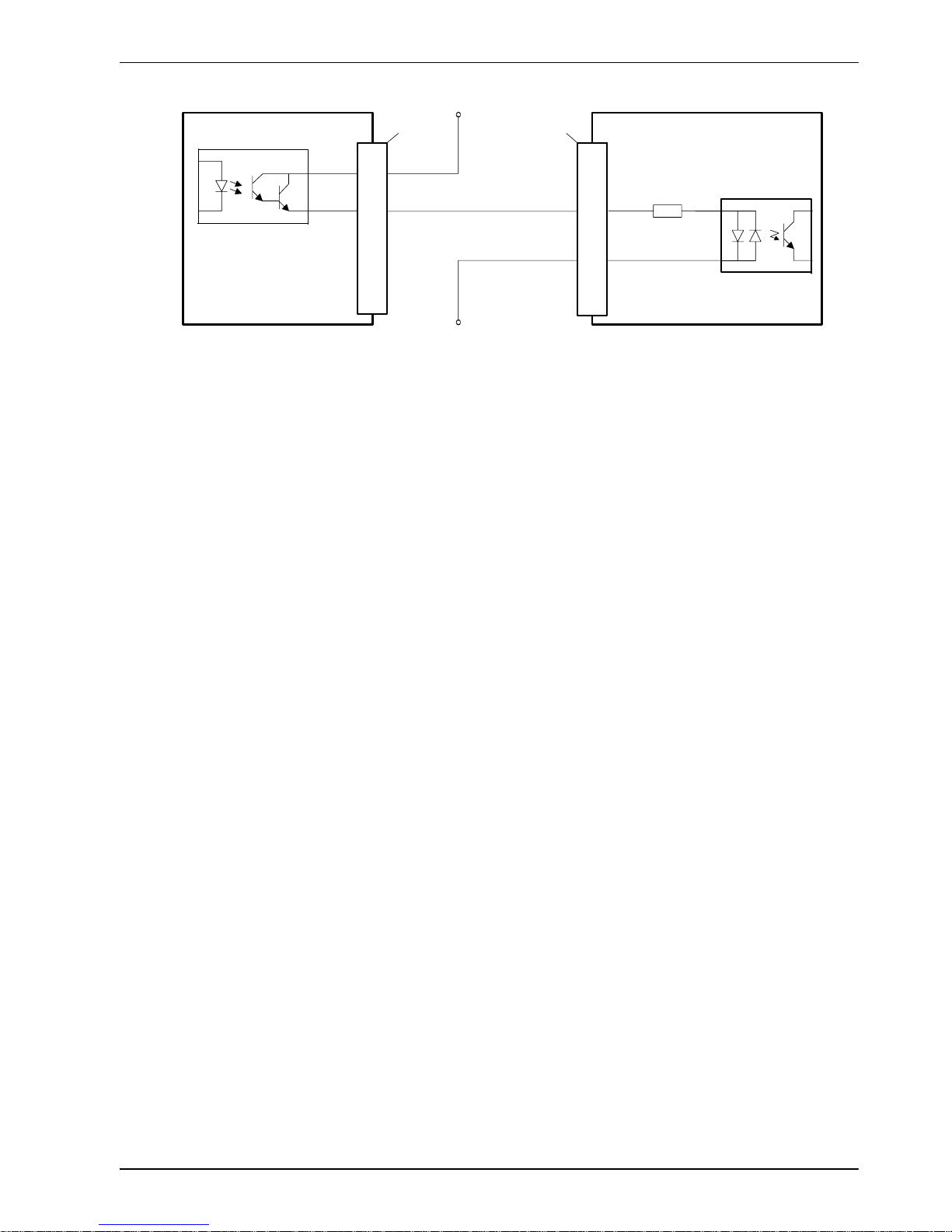
NextMove ESB
USRV+
DOUT0
8
9
FlexDriveII/ equipment output
NEC P S2562L-1
3k3
TLP280
‘X1’
User
supply
GND
User
supply
24V
6
18
DIN4
CREF1
‘X9’
Figure 15 - Digital input - typical connections from a Baldor FlexDriveII,
Flex+Drive
II
or MintDrive
II
Page 28
www.supportme.net
4-12 Input / Output MN1924
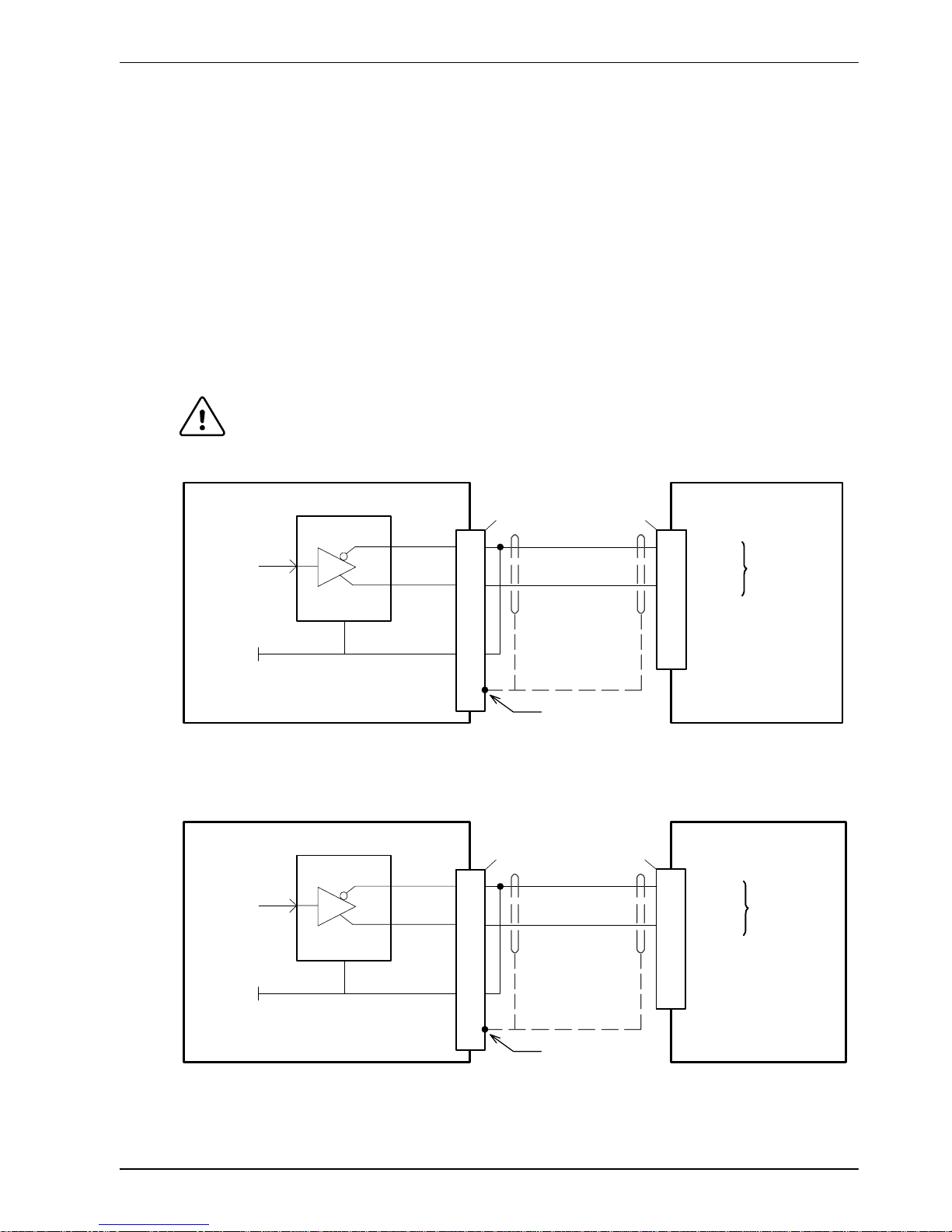
4.3.2 Digital outputs
The digital outputs are available on connectors X4 and X11, as shown in section 4.1.1.
A digital output can be configured in MintMT as a general purpose output, a drive enable
output or a global error output. Outputs can be shared between axes and can be configured
using WorkBench v5 (or the OUTPUTACTIVELEVEL keyword) to determine their active level.
4.3.2.1 DOUT0 - DOUT7
An external supply (typically 24VDC) is used to power the UDN2982 output devices, as shown
in Figure 16. When an output is activated, current is sourced from the user supply through a
UDN2982 output driver.
H A total of 500mA may be sourced by DOUT0 - DOUT7, providing an average 62.5mA per
output when all outputs are on (100% duty cycle, 24V supply).
H A maximum continuous current of 350mA may be sourced on any single output.
H The maximum allowable power dissipation for the UDN2982 driver is 1.5W.
If an output is used to drive an inductive load such as a relay, a suitably rated diode must be
fitted across the relay coil, observing the correct polarity. The use of shielded cable is
recommended.
TLP281
470R
NextMove ESB
MintMT
OUTX.0
10k
10k
DOUT0
USR GND
1
10
UDN2982
User
supply
24V
User
supply
GND
Output
Load
USR V+
9
+5V
Voltage
regulator
‘X11’
Figure 16 - Digital outputs (DOUT0-7) - DOUT0 shown
4.3.2.2 DOUT8 - DOUT10
DOUT8 - DOUT10 use the same type of output circuitry as DOUT0 - DOUT7, with their own
UDN2982 output driver. Because only three of the UDN2982’s eight outputs are being used,
the average current available on DOUT8 - DOUT10 is increased:
H A total of 500mA may be sourced by DOUT8 - DOUT10, providing an average 166mA per
output when all outputs are on (100% duty cycle, 24V supply).
H A maximum continuous current of 350mA may be sourced on any single output.
H The maximum allowable power dissipation for the UDN2982 driver is 1.5W.
Page 29
www.supportme.net
Input / Output 4-13MN1924
4.4 Other I/O
4.4.1 Stepper control outputs
The stepper control outputs are available on connectors X2 and X3, as shown in section 4.1.1.
There are four sets of stepper motor control outputs, operating in the range 0Hz to 500kHz.
Each of the step (pulse) and direction signals from the NextMove ESB is driven by DS26LS31
line drivers, providing RS422 differential outputs.
It is recommended to use separate shielded cables for the step outputs. The shield should be
connected at one end only.
The FREQ keyword can be used to directly control the output frequency, between 60Hz and
500kHz - see the MintMT help file.
CAUTION: The DS26LS31 drivers are static sensitive devices. Take appropriate ESD
precautions when handling the NextMove ESB.
STEP0-
DGND
1
2
DS26LS31
STEP0+
3
NextMove ESB
Step
Output
GND
MicroFlex / servo amplifier
DGND
Step
Connect overall
shield at one end only
6Shield
Step / pulse
input
‘X3’
‘X2’
11
10
Figure 17 - Stepper output - typical connection to a Baldor MicroFlex
6
1
FlexDriveII/ servo amplifier
Pulse+
Pulse
GND
Step / pulse
input
‘X9’
STEP0-
DGND
1
2
DS26LS31
STEP0+
3
NextMove ESB
Step
Output
GND
Connect overall
shield at one end only
6Shield
‘X2’
Figure 18 - Stepper output - typical connection to a Baldor FlexDriveII,
Flex+Drive
II
or MintDrive
II
Page 30
www.supportme.net
4-14 Input / Output MN1924
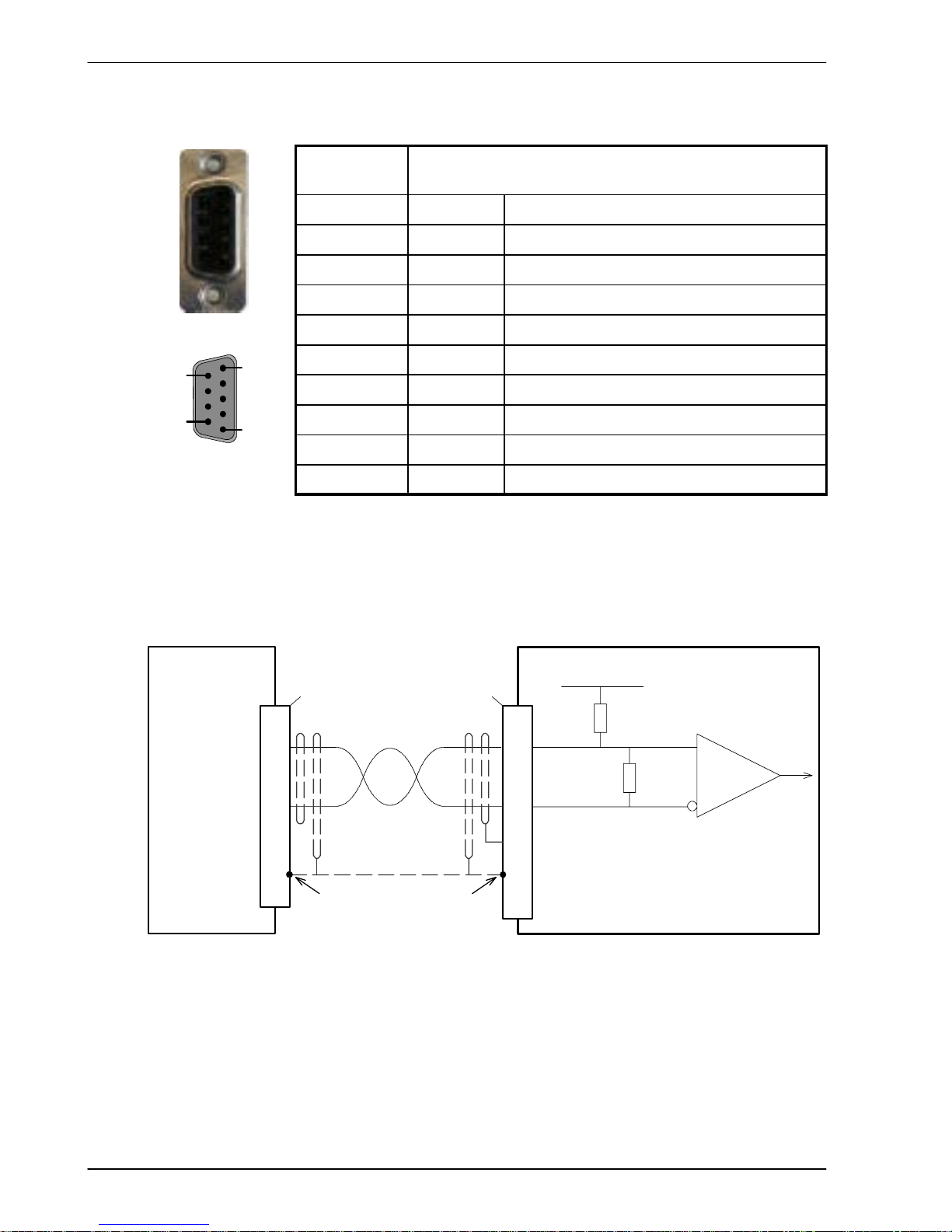
4.4.2 Encoder inputs 0-2
Location X5, X6, X7
Mating connectors: 9-pin male D-type
Pin Name Description
1 CHA+ Channel A signal
2 CHB+ Channel B signal
3 CHZ+ Index channel signal
4 Shield Shield connection
5 GND Digital ground
6 CHA- Channel A signal complement
7 CHB- Channel B signal complement
8 CHZ- Index channel signal complement
9 +5V out Power supply to encoder
Three incremental encoders may be connected to NextMove ESB, each with complementary
A, B and Z channel inputs. Each input channel uses a MAX3095 differential line receiver with
pull up resistors and terminators. Encoders must provide RS422 differential signals. The use
of individually shielded twisted pair cable is recommended. See section 7.1.7 for details of the
encoder power supply.
CHA-
CHA+
to CPU
Vcc
NextMove ESB
MAX3095
120R
10k
1
6
Shield4
Connect overall shield to
connector backshells /
shield connections.
Twisted pair
MicroFlex
FlexDrive
II
Flex+Drive
II
MintDrive
II
encoder output
5 DGND
Connect internal s hield to DGND.
Do not connect other end.
CHA-
CHA+ 1
6
‘X7’ ‘X5’
Figure 19 - Encoder channel input - typical connection from a servo amplifier
(e.g. Baldor MicroFlex, FlexDrive
II
, Flex+DriveIIor MintDriveII)
1
5
6
9
Page 31

www.supportme.net
Input / Output 4-15MN1924
4.4.2.1 Encoder input frequency
The maximum encoder input frequency is affected by the length of the encoder cables.
The theoretical maximum frequency is 20 million quadrature counts per second. This is
equivalent to a maximum frequency for the A and B signals of 5MHz. However, the effect of
cable length is shown in Table 1:
A and B signal
Maximum cable length
AandBsignal
frequency
meters feet
1.3MHz 2 6.56
500kHz 10 32.8
250kHz 20 65.6
100kHz 50 164.0
50kHz 100 328.1
20kHz 300 984.2
10kHz 700 2296.6
7kHz 1000 3280.8
Table 1 - Effect of cable length on maximum encoder frequency
The maximum recommended cable length is 30.5m (100ft).
4.4.3 USB port
Location USB
Mating connector: USB T ype B (downstream) plug
Pin Name Description
1 VBUS USB +5V
2 D- Data-
3 D+ Data+
4 GND Ground
The USB connector can be used as an alternative method for connecting the NextMove ESB to
a PC running WorkBench v5. The NextMove ESB is a self-powered, USB 1.1 (12Mbps)
compatible device. If it is connected to a slower USB1.0 host PC or hub, communication speed
will be limited to the USB1.0 specification (1.5Mbps). If it is connected to a faster USB2.0
(480Mbps) host PC or hub, communication speed will remain at the USB1.1 specification of the
NextMove ESB.
Ideally, the NextMove ESB should be connected directly to a USB port on the host PC. If it is
connected to a hub shared by other USB devices, communication could be affected by the activity
of the other devices. A 2m (6.5 ft) standard USB cable is supplied. The maximum recommended
cable length is 5m (16.4 ft).
142
3
Page 32

www.supportme.net
4-16 Input / Output MN1924
4.4.4 Serial port
Location Serial
Mating connector: 9-pin female D-type
Pin RS232 name RS485 / RS422 name
1 Shield (NC)
2 RXD RX- (input)
3 TXD TX- (output)
4 (NC) (NC)
5 DGND 0V DGND
6 (NC) (NC)
7 RTS TX+ (output)
8 CTS RX+ (input)
9 DGND (NC)
NextMove ESB is available with either an RS232 or RS485 serial port (see section 2.2.1). The
port is fully ESD protected to IEC 1000-4-2 (15kV). When the NextMove ESB is connected to
WorkBench v5, the Tools, Options menu item can be used to configure the serial port. The
configuration can also be changed using the Mint keyword SERIALBAUD (see the Mint help
file for details). It is stored in EEPROM and restored at power up. The port is capable of
operation at up to 115.2 Kbaud on RS232.
4.4.5 Using RS232
The NextMove ESB has a full-duplex RS232 serial port with the following preset configuration:
H 57.6 Kbaud
H 1startbit
H 8 data bits
H 1stopbit
H No parity
H Hardware handshaking lines RTS and CTS must be connected.
NextMove ESB
(DTE)
9-pin
Computer
COM Port
(DTE)
Serial
RXD 2
TXD 3
GND 5
2RXD
3TXD
5GND
RTS 7
CTS 8
7RTS
8CTS
COM
Connect overall shield
to connector bac kshell.
Figure 20 - RS232 serial port connections
1
5
6
9
Page 33

www.supportme.net
Input / Output 4-17MN1924
The RS232 port is configured as a DCE (Data Communications Equipment) unit so it is
possible to operate the controller with any DCE or DTE (Data T erminal Equipment). Full duplex
transmission with hardware handshaking is supported. Only the TXD, RXD and 0V GND
connections are required for communication. Pins 4 and 6 are linked on the NextMove ESB.
The maximum recommended cable length is 3m (10ft) at 57.6 Kbaud (the factory preset rate).
When using lower baud rates, longer cable lengths may be used up to maximum of 15m (49ft)
at 9600 baud.
4.4.6 Multidrop using RS485 / RS422
Multidrop systems allow one device to act as a ‘network master’, controlling and interacting
with the other (slave) devices on the network. The network master can be a controller such as
NextMove ESB, a host application such as WorkBench v5 (or other custom application), or a
programmable logic controller (PLC). RS422 may be used for multi-drop applications as
shown in Figure 21. Four-wire RS485 may be used for single point-to-point applications
involving only one Baldor controller. If firmware is updated over RS485/RS422, it can only be
downloaded to the controller that was chosen in the Select Controller dialog in WorkBench v5.
Master and final slav e are shown
with terminating resistors, TR,
typical value 120Ω.
Network slave
T
R
RX-
DGND
RX+
TX+
TX- RX-
DGND
RX+
TX+
TX-
RX-
DGND
RX+
TX+
TX-
Twisted pairs
T
R
Connect overall shield
to connector backshell.
Network slave
Network
master
Figure 21 - 4-wire RS422 multi-drop connections
Each transmit/receive (TX/RX) network requires a termination resistor at the final RX
connection, but intermediate devices must not be fitted with termination resistors. An exception
is where repeaters are being used which may correctly contain termination resistors.
Termination resistors are used to match the impedance of the load to the impedance of the
transmission line (cable) being used. Unmatched impedance causes the transmitted signal to
not be fully absorbed by the load. This causes a portion of the signal to be reflected back into
the transmission line as noise. If the source impedance, transmission line impedance, and
load impedance are all equal, the reflections (noise) are eliminated. Termination resistors
increase the load current and sometimes change the bias requirements and increase the
complexity of the system.
Page 34

www.supportme.net
4-18 Input / Output MN1924
4.4.7 Connecting serial Baldor HMI Operator Panels
Serial Baldor HMI Operator Panels use a 15-pin male D-type connector (marked PLC PORT),
but the NextMove ESB Serial connector uses a 9-pin male D-type connector. The NextMove
ESB may be connected with or without hardware handshaking, as shown in Figure 22:
7RTS
8CTS
3TXD
2RXD
5GND
1
RXD 2
TXD 3
GND 5
Baldor HMI
PLC PORT
NextMove ESB
Serial Port
Twisted pair
7RTS
8CTS
3TXD
2RXD
5GND
1
RXD 2
TXD 3
GND 5
Baldor HMI
PLC PORT
CTS 11
RTS 10
Twi st ed pair
NextMove ESB
Serial Port
Without hardware handshaking With hardware handshaking
Figure 22 - RS232 cable wiring
Alternatively, the Baldor HMI panel may be connected using RS485/422, as shown in Figure 23:
8RX+
2RX-
7TX+
3TX-
5GND
1
RX+ 15
RX- 7
GND 5
Baldor HMI
PLC PORT
TX+ 14
TX- 6
Twisted pair
NextMove ESB
Serial Port
Figure 23 - RS485/422 cable wiring
Page 35

www.supportme.net
Input / Output 4-19MN1924
4.5 CAN
The CAN bus is a serial based network originally developed for automotive applications, but
now used for a wide range of industrial applications. It offers low-cost serial communications
with very high reliability in an industrial environment; the probability of an undetected error is
4.7x10
-11
. It is optimized for the transmission of small data packets and therefore offers fast
update of I/O devices (peripheral devices) connected to the bus.
The CAN protocol only defines the physical attributes of the network, i.e. the electrical,
mechanical, functional and procedural parameters of the physical connection between
devices. The higher level network functionality is defined by a number of standards and
proprietary protocols; CANopen is one of the most used standards for machine control within
industries such as printing and packaging machines.
In addition to supporting CANopen, Baldor have developed a proprietary protocol called Baldor
CAN. Both protocols are supported by NextMove ESB, but unlike other Baldor devices both
cannot be supported at the same time. This is because NextMove ESB only has a single
hardware CAN channel. Separate firmware builds are available to support each of the
protocols.
To determine which firmware is currently installed, start WorkBench v5 and connect to the
NextMove ESB (see section 5). At the bottom of the WorkBench v5 window, the status bar
will show the name of the controller, followed by ‘CANopen’ or ‘Baldor CAN’. If the correct
option is not shown, it will be necessary to download alternative firmware by using the Install
System File and/or Download Firmware menu items in WorkBench v5. The firmware file can
be found on the Baldor Motion Toolkit CD supplied with your product, or downloaded from
www.supportme.net
. See the MintMT help file for details about downloading firmware.
4.5.1 CAN connector
The CAN connection is made using the RJ45 connector on the NextMove ESB.
Location
NextMove ESB
Pin Name Description
1 CAN+ CAN channel positive
2 CAN- CAN channel negative
3 - (NC)
4 CAN 0V Ground/earth reference for CAN signals
5 CAN V+ CAN power V+ (12-24V)
6 - (NC)
7 - (NC)
8 - (NC)
Description
Opto-isolated CAN interface using a RJ45 connector.
The maximum (default) transmission rate on NextMove ESB is 500Kbit/s.
1
8
Page 36

www.supportme.net
4-20 Input / Output MN1924
4.5.2 CAN wiring
A very low error bit rate over CAN can only be achieved with a suitable wiring scheme, so the
following points should be observed:
H The two-wire data bus line may be routed parallel, twisted and/or shielded, depending on
EMC requirements. Baldor recommend a twisted pair cable with the shield/screen
connected to the connector backshell, in order to reduce RF emissions and provide
immunity to conducted interference.
H The bus must be terminated at both ends only (not at intermediate
points) with resistors of a nominal value of 120Ω. This is to reduce
reflections of the electrical signals on the bus, which helps a node to
interpret the bus voltage levels correctly. If the NextMove ESB is at
the end of the network then ensure that jumper JP1, located just
behind the status display, is in position. This will connect an internal
terminating resistor. To access the jumper it will be necessary to
remove the top cover from the NextMove ESB. Before removing the
top cover be sure to discharge static electricity from your body and
clothing by touching a grounded metal surface. Alternatively, wear an
earth strap while handling the unit.
H All cables and connectors should have a nominal impedance of 120Ω. Cables should have
a length related resistance of 70mΩ/m and a nominal line delay of 5ns/m. A range of suitable
CAN cables are available from Baldor, with catalog numbers beginning CBL004-5... .
H The maximum bus length depends on the bit-timing
configuration (baud rate). The table opposite shows
the approximate maximum bus length (worst-case),
assuming 5ns/m propagation delay and a total
effective device internal in-out delay of 210ns at
1Mbit/s, 300ns at 500 - 250Kbit/s, 450ns at 125Kbit/s
and 1.5ms at 50 - 10Kbit/s.
(1)
CAN baud rate not supported on Baldor CAN.
(2)
For bus lengths greater than about 1000m,
bridge or repeater devices may be needed.
H The compromise between bus length and CAN baud rate must be determined for each
application. The CAN baud rate can be set using the BUSBAUD keyword. It is essential
that all nodes on the network are configured to run at the same baud rate.
H The wiring topology of a CAN network should be as close as possible to a single line/bus
structure. However , stub lines are allowed provided they are kept to a minimum (<0.3m at
1Mbit/s).
H The 0V connection of all of the nodes on the network must be tied together through the
CAN cabling. This ensures that the CAN signal levels transmitted by NextMove ESB or
CAN peripheral devices are within the common mode range of the receiver circuitry of
other nodes on the network.
4.5.2.1 Opto-isolation
On the NextMove ESB, the CAN channel is opto-isolated. A voltage in the range 12-24V must
be applied to pin 5 of the CAN connector. From this supply, an internal voltage regulator
provides the 5V at 100mA required for the isolated CAN circuit. CAN cables supplied by
Baldor are ‘category 5’ and have a maximum current rating of 1A, so the maximum number of
NextMove ESB units that may be used on one network is limited to ten. Practical operation of
the CAN channel is limited to 500Kbit/s owing to the propagation delay of the opto-isolators.
JP1
CAN Maximum
Baud Rate Bus Length
1Mbit/s 25m
500Kbit/s 100m
250Kbit/s 250m
125Kbit/s 500m
100Kbit/s
(1)
600m
50Kbit/s 1000m
20Kbit/s 2500m
(2)
10Kbit/s 5000m
(2)
Page 37

www.supportme.net
Input / Output 4-21MN1924
4.5.3 CANopen
The NextMove ESB must have the CANopen firmware loaded to use this protocol.
Baldor have implemented a CANopen protocol in MintMT (based on the ‘Communication
Profile’ CiA DS-301) which supports both direct access to device parameters and time-critical
process data communication. The NextMove ESB design does not comply with a specific
CANopen device profile (DS4xx), although it is able to support and communicate with the
following devices:
H Any third party digital and analog I/O device that is compliant with the ‘Device Profile for
Generic I/O Modules’ (CiA DS-401).
H Baldor HMI (Human Machine Interface) operator panels, which are based on the ‘Device
Profile for Human Machine Interfaces’ (DS403).
H Other Baldor controllers with CANopen support for peer-to-peer access using extensions
to the CiA specifications (DS301 and DS302).
The functionality and characteristics of all Baldor CANopen devices are defined in individual
standardized (ASCII format) Electronic Data Sheets (EDS) which can be found on the Baldor
Motion T oolkit CD supplied with your product, or downloaded from www.supportme.net
.
Figure 24 shows a typical CANopen network with two NextMove ESB units and a Baldor HMI
operator panel:
1
2
4
5
NextMove ESB
RJ45
7
2
Baldor HMI
Operator Panel
Twi st ed pairs Twis te d pairs
T
R
T
R
End
node
1
2
4
5
1
2
4
5
24V
0V
NextMove ESB
RJ45
6
5
CANopen
D-type
1
2
Power
supply
terminal
block
24V
0V
CAN+
CAN-
Figure 24 - Typical CANopen network connections
Note: The NextMove ESB CAN channel is opto-isolated, so a voltage in the range
12-24V must be applied to pin 5 of the CAN connector.
The configuration and management of a CANopen network must be carried out by a single
node acting as the network master. This role can be performed by the NextMove ESB when it
is configured to be the Network Manager node (node ID 1), or by a third party CANopen
master device.
Up to 126 CANopen nodes (node IDs 2 to 127) can be added to the network by a NextMove
ESB Manager node using the MintMT NODESCAN keyword. If successful, the nodes can then
be connected to using the MintMT CONNECT keyword. Any network and node related events
can then be monitored using the MintMT BUS1 event.
Page 38

www.supportme.net
4-22 Input / Output MN1924
Note: All CAN related MintMT keywords are referenced to either CANopen or Baldor
CAN using the ‘bus’ dot parameter. Although the NextMove ESB has a single
physical CAN bus channel that may be used to carry either protocol, MintMT
distinguishes between the protocols with the ‘bus’ dot parameter. For CANopen
the ‘bus’ dot parameter must be set to 1.
Please refer to the MintMT help file for further details on CANopen, MintMT keywords and dot
parameters.
4.5.4 Baldor CAN
The NextMove ESB must have the Baldor CAN firmware loaded to use this protocol.
Baldor CAN is a proprietary CAN protocol based on CAL. It supports only the following range
of Baldor CAN specific I/O nodes and operator panels:
H InputNode 8 (Baldor part ION001-503) - an 8 x digital input CAN node.
H OutputNode 8 (Baldor part ION003-503) - an 8 x digital output CAN node.
H RelayNode 8 (Baldor part ION002-503) - an 8 x relay CAN node.
H IoNode 24/24 (Baldor part ION004-503) - a 24 x digital input and 24 x digital output CAN
node.
H KeypadNode (Baldor part KPD002-501) - an operator panel CAN node with 4 x 20 LCD
display and 27 key membrane labeled for control of 3 axes (X, Y , Z).
H KeypadNode 4 (Baldor part KPD002-505 ) - an operator panel CAN node with 4 x 20 LCD
display and 41 key membrane labeled for control of 4 axes (1, 2, 3, 4).
A typical Baldor CAN network with a NextMove ESB and a Baldor CAN operator panel is
shown in Figure 18.
RJ45J1 / J2
Twisted pair
24V
0V
T
R
24V
0V
J3
Baldor CAN Operator Panel
Operator
Panel
supply
CAN-
CAN+
1
2
4
5
4
3
2
1
NextMove ESB
1
2
4
5
JP3 T
R
Figure 25 - Baldor CAN operator panel connections
The NextMove ESB CAN channel is opto-isolated, so a voltage in the range 12-24V must be
applied to pin 5 of the CAN connector. From this supply, an internal voltage regulator provides
the 5V required for the isolated CAN circuit. The required 12-24V can be sourced from the
Baldor CAN I/O node or operator panel’s supply, which is internally connected to the CAN
connector as shown in Figure 25.
On Baldor CAN I/O nodes and operator panels, jumpers JP1 and JP2 must be set to position
‘1’ (the lower position) for the network to operate correctly. This configures the node’s CAN
Page 39

www.supportme.net
Input / Output 4-23MN1924
channel to operate on pins 1 and 2 of the RJ45 connectors. On the Baldor CAN node, jumper
JP3 can be used to connect an internal 120Ω terminating resistor, provided the node is at the
end of the network. Jumpers JP4 and JP5 can be used to configure the node ID and baud
rate.
Up to 63 Baldor I/O nodes (including no more than 4 operator panels) can be added to the
network by the NextMove ESB using the MintMT NODETYPE keyword. Any network and node
related events can then be monitored using the MintMT BUS2 event.
Note: All CAN related MintMT keywords are referenced to either CANopen or Baldor
CAN using the ‘bus’ dot parameter. Although the NextMove ESB has a single
physical CAN bus channel that may be used to carry either protocol, MintMT
distinguishes between the protocols with the ‘bus’ dot parameter. For Baldor CAN
the ‘bus’ dot parameter must be set to 2.
Please refer to the MintMT help file for further details on Baldor CAN, MintMT keywords and
dot parameters.
Page 40

www.supportme.net
4-24 Input / Output MN1924
4.6 Connection summary - minimum system wiring
As a guide, Figure 26 shows an example of the typical minimum wiring required to allow the
NextMove ESB and a single axis servo amplifier to work together. Details of the connector
pins are shown in Table 2.
Servo amplifier
(axis 0)
Encoder output from
drive (or motor)
Gnd
Enable
Demand -
Demand +
Host PC
+24V
control
supply
+24V
0V
X13
X5
X1
NextMove ESB
1
2
3
9
10
X12
Common
earth/ground
Serial or USB
connection
USB
Figure 26 - Example minimum system wiring
Page 41

www.supportme.net
Input / Output 4-25MN1924
NextMove ESB
connector
Pin Name of
signal
Function Connection on amplifier
(Note: connections may
be labeled differently)
X1 1 0V Control supply ground
2 +24V Control supply +24V input
X5 Encoder0 Encoder0 feedback input Encoder output
X12 9 REL NO Normally open relay contact
(closed to enable drive)
Enable +24V
10 REL COM Common relay connection Enable GND
X13 1 Demand0 Demand output 0 Demand+
2 AGND Analog GND Demand-
3 Shield Shield connection (Do not connect)
Table 2 - Connector details for minimum system wiring shown in Figure 26
Page 42

www.supportme.net
4-26 Input / Output MN1924
Page 43

www.supportme.net
Operation 5-1MN1924
5.1 Introduction
The software provided includes a number of applications and utilities to allow you to configure,
tune and program the NextMove ESB. The Baldor Motion Toolkit CD containing the software
can be found separately within the packaging.
5.1.1 Connecting the NextMove ESB to the PC
The NextMove ESB can be connected to the PC using either RS232 or RS485 (model
dependent), or USB (all models).
To use RS232 or RS485, connect an appropriate serial cable between a PC serial port (often
labeled as “COM”) and the NextMove ESB Serial connector. If you are using an intermediate
RS232 to RS485 converter, connect this as specified by the manufacturer. WorkBench v5 can
scan all the PC’s COM ports, so you can use any port. If you are not using the Baldor serial
cable CBL001-501, your cable must be wired in accordance with Figure 20 in section 4.4.5.
To use USB, connect a USB cable between a PC USB port and the NextMove ESB USB
connector. Your PC must be using Windows 2000 or Windows XP.
5.1.2 Installing WorkBench v5
You will need to install WorkBench v5 to configure and tune the NextMove ESB.
1. Insert the CD into the drive.
2. After a few seconds the setup wizard should start automatically. If the setup wizard does not
appear, select Run... from the Windows Start menu and type
d:\start
where d represents the drive letter of the CD device.
Follow the on-screen instructions to install WorkBench v5. The setup Wizard will copy the files
to appropriate folders on the hard drive. The preset folder is C:\Program Files\Baldor\MintMT,
although this can be changed during setup.
5.1.3 Starting the NextMove ESB
If you have followed the instructions in the previous sections, you should have now connected
the power sources, your choice of inputs and outputs, and a serial or USB cable linking the PC
with the NextMove ESB.
5 Operation
5
Page 44

www.supportme.net
5-2 Operation MN1924
5.1.4 Preliminary checks
Before you apply power for the first time, it is very important to verify the following:
H Disconnect the load from the motor until instructed to apply a load.
H Inspect all power connections for accuracy, workmanship and tightness.
H Verify that all wiring conforms to applicable codes.
H Verify that the NextMove ESB is properly earthed/grounded.
H Check all signal wiring for accuracy.
5.1.5 Power on checks
If the status display shows one of the digits 0 - 7 with a flashing decimal point during startup,
this indicates that the NextMove ESB has detected a fault - see section 6.
1. Turn on the 24V control supply.
2. After a brief test sequence (
followed by ), the Status display should show the node
number, for example
, the factory default. If the display is not lit then re-check the power
supply connections.
5.1.5.1 Installing the USB driver
If you have connected the NextMove ESB to the PC using the USB connection, it will be
necessary to install the USB driver. When the NextMove ESB is powered, Windows (2000 or
XP only) will automatically detect the controller and request the driver. The driver consists of
two files, baldorusb.inf and baldorusb.sys. Both files must be present for installation.
1. Follow the on-screen instructions to select and install the driver. The driver files are available
on the supplied Baldor Motion Toolkit CD. If you are using a copy of the driver located on the
hard disk, a floppy disk or another CD, the two driver files must be in the same folder.
2. During installation, Windows XP may report that the driver is ‘unsigned’. This is normal for the
NextMove ESB driver, so click the Continue Anyway button to continue with the installation.
When installation is complete, a new Baldor USB device will be listed in the Universal Serial
Bus controllers section of Windows Device Manager.
The NextMove ESB is now ready to be configured using WorkBench v5.
Note: If the NextMove ESB is later connected to a different USB port on the host
computer, Windows may report that it has found new hardware. Either install the
driver files again for the new USB port, or connect the NextMove ESB to the
original USB port where it will be recognized in the usual way.
Page 45

www.supportme.net
Operation 5-3MN1924
5.2 WorkBench v5
WorkBench v5 is a fully featured application for programming and controlling the NextMove ESB.
The main WorkBench window contains a menu system, the Toolbox and other toolbars. Many
functions can be accessed from the menu or by clicking a button - use whichever you prefer . Most
buttons include a ‘tool-tip’; hold the mouse pointer over the button (don’t click) and its description
will appear.
5.2.1 Help file
WorkBench v5 includes a comprehensive help file that contains information about every MintMT
keyword, how to use WorkBench and background information on motion control topics. The help
file can be displayed at any time by pressing F1. On the left of the help window, the Contents tab
shows the tree structure of the help file; each book
contains a number of topics . The Index
tab provides an alphabetic list of all topics in the file, and allows you to search for them by name.
The Search tab allows you to search for words or phrases appearing anywhere in the help file.
Many words and phrases are underlined and highlighted with a color (normally blue) to show that
they are links. Just click on the link to go to an associated keyword. Most keyword topics begin
with a list of relevant See Also links.
Figure 27 - The WorkBench help file
For help on using WorkBench v5, click the Contents tab, then click the small plus sign
beside the WorkBench v5 book icon. Double click a topic name to display it.
Page 46

www.supportme.net
5-4 Operation MN1924
5.2.2 Starting WorkBench v5
1. On the Windows Start menu, select Programs, WorkBench v5, WorkBench v5.
WorkBench v5 will start, and the Tip of the Day dialog will be displayed.
You can prevent the Tip of the Day dialog appearing next time by removing the check
mark next to Show tips at startup.
Click Close to continue.
2. In the opening dialog box, click Start New Project...
Page 47

www.supportme.net
Operation 5-5MN1924
3. In the Select Controller dialog, go to the drop down box near the top and select the PC
serial port to which the NextMove ESB is connected. If you are unsure which PC serial
port is connected to the drive, select Scan all serial ports. If the NextMove ESB is
connected using USB, it will be scanned automatically.
Click Scan to search for the NextMove ESB.
When the search is complete, click ‘NextMove ESB’ in the list to select it, and then click
Select.
Note: If the NextMove ESB is not listed, check the serial or USB cable between the
NextMove ESB and the PC. Check that the NextMove ESB is powered correctly.
Click Scan to re-scan the ports.
4. A dialog box may be displayed to tell you that WorkBench v5 has detected new firmware.
Click OK to continue. WorkBench v5 reads back data from the NextMove ESB. When this
is complete, Edit & Debug mode is displayed. This completes the software installation.
Page 48

www.supportme.net
5-6 Operation MN1924
5.3 Configuring an axis
The NextMove ESB is capable of controlling 4 stepper and 3 servo axes. This section
describes the basic setup for both types of axis. Commands typed in the Command window
have immediate effect - they do not need to be separately downloaded to the NextMove ESB.
5.3.1 Selecting a scale
MintMT defines all positional and speed related motion keywords in terms of encoder
quadrature counts (for servo motors) or steps for stepper motors. The number of quadrature
counts (or steps) is divided by the SCALEFACTOR allowing you to use units more suitable for
your application. The unit defined by setting a value for scale is called the user unit (uu).
Consider a servo motor with a 1000 line encoder . This provides 4000 quadrature counts for
each revolution. If SCALEFACTOR is not set, a MintMT command that involves distance,
speed, or acceleration may need to use a large number to specify a significant move. For
example MOVER=16000 (Move Relative) would rotate the motor by 16000 quadrature counts only four revolutions. By setting a SCALEFACTOR of 4000, the user unit becomes revolutions.
The more understandable command MOVER=4 could now be used to move the motor four
revolutions.
The same concept applies to stepper motors, where the scale can be set according to the
number of steps per revolution. Typically, this would be 200 for a motor with a 1.8° step angle,
or 400 if driven in half step mode. By setting a SCALEFACTOR of 200 (or 400 if driven in half
step mode), the user unit becomes revolutions.
In applications involving linear motion a suitable value for SCALEFACTOR would allow
commands to express values in linear distance, for example inches, feet or millimeters.
1. In the Toolbox, click Setup, then click
the Parameters icon.
2. Click the Scale tab.
3. Click in the Axis drop down box to select the
axis. Each axis can have a different scale if
required.
4. Click in the Scale box and type a value.
Page 49

www.supportme.net
Operation 5-7MN1924
5. Click Apply.
This immediately sets the scaling factor for
the selected axis, which will remain in the
NextMove ESB until another scale is defined
or power is removed from the
NextMove ESB. See section 5.10 for details
about saving configuration parameters.
5.3.2 Setting the drive enable output
A drive enable output allows NextMove ESB to enable the external amplifier to allow motion, or
disable it in the event of an error. Each axis can be configured with its own drive enable output,
or can share an output with other axes. If an output is shared, an error on any of the axes
sharing the output will cause all of them to be disabled.
The drive enable output can either be the relay or a digital output.
1. In the Toolbox, click the Digital I/O icon.
2. At the bottom of the Digital I/O screen, click
the Digital Outputs tab.
The left of the screen shows yellow High and
Low icons. These describe how the output
should behave when activated (to enable the
axis).
3. If you are going to use the relay, ignore this
step and go straight to step 4.
If you are going to use a digital output, drag
the appropriate yellow icon to the grey OUT
icon that will be used as the drive enable
output. In this example, OUT1 is being used.
The icon’s color will change to bright blue.
Page 50

www.supportme.net
5-8 Operation MN1924
4. If you are going to use
the relay, drag the
Relay0 icon to the grey
Drive Enable OP icon
on the right of the
screen.
To configure multiple axes to use the error output, repeat this step for the other axes.
If you are using a digital
output, drag the bright
blue OUT icon to the
grey Drive Enable OP
axis icon on the right of
the screen.
To configure multiple
axes with the same drive enable output, repeat this step for the other axes.
5. Click Apply at the bottom of the screen. This
sends the output configuration to the
NextMove ESB.
See section 5.10 for details about saving
configuration parameters.
Page 51

www.supportme.net
Operation 5-9MN1924
5.3.3 Testing the drive enable output
1. On the main WorkBench v5 toolbar , click the
Axis 0-7 button. In the Select Default Axes
dialog, select the axes to be controlled. Click
OK to close the dialog.
2. On the main WorkBench v5 toolbar , click the
Drive enable button. Click the button again.
Each time you click the button, the drive
enable output(s) for the selected axes are
toggled.
When the button is in the pressed (down)
position the amplifier should be enabled.
When the button is in the raised (up) position
the amplifier should be disabled.
If this is not working, or the action of the button is reversed, check the electrical
connections between the NextMove ESB and amplifier. If you are using the relay, check
that you are using the correct normally open (REL NO) or normally closed (REL NC)
connections.
If you are using a digital output, check that it is using the correct high or low triggering
method expected by the amplifier.
Page 52

www.supportme.net
5-10 Operation MN1924
5.4 Stepper axis - testing
This section describes the method for testing a stepper axis. The stepper control is an open
loop system so no tuning is necessary.
5.4.1 Testing the output
This section tests the operation and direction of the output. It is recommended that the system
is initially tested with the motor shaft disconnected from other machinery.
1. Check that the Drive enable button is
pressed (down).
2. In the Toolbox, click the Edit & Debug icon.
3. Click in the Command window.
4. Type:
JOG.0=2
where 0 is the axis (s tepper output ) to be
tested and 2 is the speed.
The JOG command s pec ifies the speed in
user units per second, so the speed is
affected by SCALEFACTOR(sec t ion 5.3.1). If you hav e not selec ted a sc ale, thecommand
JOG.0=2 will caus e rotation at only 2 half steps per second, s o it may be neces s ary to
increase this figure s ignif ic antly, to 200 f or example. If y ou have selected a s c ale t hat
provides us er units of revolut ions ( as described in sect ion 5.3.1) JOG.0=2 will c aus e
rotation at 2 r ev olutions per second. If t here appears to be no step or direction output,
check the electric al connections to connector X2, pins 2 and 3 (for axis 0).
5. To repeat the tests for reverse moves, type:
JOG.0 = -2
6. To remove the demand and stop the test, type:
STOP.0
Page 53

www.supportme.net
Operation 5-11MN1924
5.5 Servo axis - testing and tuning
This section describes the method for testing and tuning a servo axis. The amplifier must
already have been tuned for basic current or velocity control of the motor.
5.5.1 Testing the demand output
This section tests the operation and direction of the demand output for axis 4. By default, axis
4 is a servo axis (although it can be reassigned as a stepper - see section A.1). It is
recommended that the motor is disconnected from the load for this test.
1. Check that the Drive enable button is
pressed (down).
2. In the Toolbox, click Application then click
the Edit & Debug icon.
3. Click in the Command window.
4. Type:
TORQUE.4=5
where 4 is the axis to be tested. In this
example, this should cause a demand of +5%
of maximum output (0.5V) to be produced at
the DEMAND0 output (connector X13, pin 1).
In WorkBench v5, look at the Spy window
located on the right of the screen. In the Axis selection box at the top, select Axis 4.
The S py window’s Command display should show 5 percent (approximately). If there seems
to be no command output, check the electrical connections to X13.
The Spy window’s V elocity display should show a positive value. If the value is negative check
that the DEMAND0 output, and the Encoder0 A and B channels, have been wired correctly.
If necessary, the ENCODERMODE keyword can be used to swap the encoder A and B channels,
thus reversing the encoder count - see the MintMT help file.
By default, axis 4 uses demand output 0 and encoder 0, axis 5 uses demand output 1 and
encoder 1, and axis 6 uses demand output 2 and encoder 2. See section 4.2.2 for details of
the demand outputs.
Page 54

www.supportme.net
5-12 Operation MN1924
5. To repeat the tests for negative (reverse) demands, type:
TORQUE.4=-5
This should cause a demand of -5% of maximum output (-0.5V) to be produced at the
DEMAND0 output. Correspondingly, the Spy window’s Velocity display should show a
negative value.
6. To remove the demand and stop the test, type:
STOP.4
This should cause the demand produced at
the DEMAND0 output to become 0V.
If it is necessary for the motor to turn in the opposite direction for a positive demand, then the
DACMODE and ENCODERMODE keywords should be used. The DACMODE keyword is used to
invert the demand output voltage. The ENCODERMODE keyword must then also be used to
reverse the incoming feedback signal, to correspond with the inverted demand output. Note
that if ENCODERMODE had already been used to compensate for a reversed encoder count (as
described in step 4. above), it will be necessary to change it back to its original setting to
correspond with the inverted demand output set using DACMODE. See the MintMT help file for
details of each keyword.
Page 55

www.supportme.net
Operation 5-13MN1924
5.5.2 An introduction to closed loop control
This section describes the basic principles of closed loop control. If you are familiar with
closed loop control go straight to section 5.6.1.
When there is a requirement to move an axis, the NextMove ESB control software translates
this into a demand output voltage. This is used to control the drive (servo amplifier) which
powers the motor. An encoder or resolver on the motor is used to measure the motor’s
position. Every 1ms* (adjustable using the LOOPTIME keyword) the NextMove ESB compares
the demanded and measured positions. It then calculates the demand needed to minimize the
difference between them, known as the following error.
This system of constant measurement and correction is known as closed loop control.
[ For the analogy, imagine you are in your car waiting at an intersection. You are going to go
straight on when the lights change, just like the car standing next to you which is called
Demand. You’re not going to race Demand though - your job as the controller (NextMove ESB)
is to stay exactly level with Demand, looking out of the window to measure your position ].
The main term that the NextMove ESB uses to correct the error is called Proportional gain
(KPROP). A very simple proportional controller would simply multiply the amount of error by
the Proportional gain and apply the result to the motor [ the further Demand gets ahead or
behind you, the more you press or release the gas pedal ].
If the Proportional gain is set too high overshoot will occur, resulting in the motor vibrating back
and forth around the desired position before it settles [ you press the gas pedal so hard you go
right past Demand. T o try and stay level you ease off the gas, but end up falling behind a little.
You keep repeating this and after a few tries you end up level with Demand, traveling at a
steady speed. This is what you wanted to do but it has taken you a long time ].
If the Proportional gain is increased still further, the system becomes unstable [ you keep
pressing and then letting off the gas pedal so hard you never travel at a steady speed ].
To reduce the onset of instability, a term called V elocity Feedback gain (KVEL) is used. This
resists rapid movement of the motor and allows the Proportional gain to be set higher before
vibration starts. Another term called Derivative gain (KDERIV) can also be used to give a
similar effect.
With Proportional gain and Velocity Feedback gain (or Derivative gain) it is possible for a
motortocometoastopwithasmallfollowingerror[Demandstopped so you stopped too, but
not quite level ]. The NextMove ESB tries to correct the error, but because the error is so
small the amount of torque demanded might not be enough to overcome friction.
This problem is overcome by using a term called Integral gain (KINT). This sums the error
over time, so that the motor torque is gradually increased until the positional error is reduced to
zero [ like a person gradually pushing harder and harder on your car until they’ve pushed it
level with Demand].
However, if there is large load on the motor (it is supporting a heavy suspended weight for
example), it is possible for the output to increase to 100% demand. This effect can be limited
using the KINTLIMIT keyword which limits the effect of KINT to a given percentage of the
demand output. Another keyword called KINTMODE can even turn off integral action when it’s
not needed.
* The 1ms sampling interval can be changed using the LOOPTIME keyword to either 2ms,
500µs, 200µs or 100µs.
Page 56

www.supportme.net
5-14 Operation MN1924
The remaining gain terms are Velocity Feed forward (KVELFF) and Acceleration Feed
forward (KACCEL) described below.
In summary, the following rules can be used as a guide:
H KPROP: Increasing KPROP will speed up the response and reduce the effect of
disturbances and load variations. The side effect of increasing KPROP is that it also
increases the overshoot, and if set too high it will cause the system to become unstable.
The aim is to set the Proportional gain as high as possible without getting overshoot,
instability or hunting on an encoder edge when stationary (the motor will buzz).
H KVEL: This gain has a damping effect on the whole response, and can be increased to
reduce any overshoot. If KVEL becomes too large it will amplify any noise on the velocity
measurement and introduce oscillations.
H KINT: This gain has a de-stabilizing effect, but a small amount can be used to reduce any
steady state errors. By default, KINTMODE is always on (mode 1).
H KINTLIMIT: The integration limit determines the maximum value of the effect of integral
action. This is specified as a percentage of the full scale demand.
H KDERIV: This gain has a damping effect dependent on the rate of change of error, and so
is particularly useful for removing overshoot.
H KVELFF: This is a feed forward term and as such has a different effe ct on the servo
system than the previous gains. KVELFF is outside the closed loop and therefore does
not have an effect on system stability. This gain allows a faster response to demand
speed changes with lower following errors, for example you would increase KVELFF to
reduce the following error during the slew section of a trapezoidal move. The trapezoidal
test move can be used to fine-tune this gain. This term is especially useful with velocity
controlled servos
H KACCEL: This term is designed to reduce velocity overshoots on high acceleration
moves.
Page 57

www.supportme.net
Operation 5-15MN1924
Figure 28 - The NextMove ESB servo loop
Page 58

www.supportme.net
5-16 Operation MN1924
5.6 Servo axis - tuning for current control
5.6.1 Selecting servo loop gains
All servo loop parameters default to zero, meaning that the demand output will be zero at
power up. Most servo amplifiers can be set to current (torque) control mode or velocity control
mode; check that the servo amplifier will operate in the correct mode. The procedure for
setting system gains differs slightly for each. To tune an axis for velocity control, go straight to
section 5.8. It is recommended that the system is initially tested and tuned with the motor shaft
disconnected from other machinery. Confirm that the encoder feedback signals from the motor
or servo amplifier have been connected, and that a positive demand causes a positive
feedback signal.
Note: The method explained in this section should allow you to gain good control of the
motor, but will not necessarily provide the optimum response without further
fine-tuning. Unavoidably, this requires a good understanding of the effect of the
gain terms.
1. In the Toolbox, click the Fine-tuning icon.
The Fine-tuning window is displayed at the
right of the screen. The main area of the
WorkBench v5 window displays the Capture
window. When tuning tests are performed,
this will display a graph representing the
response.
2. In the Fine-tuning window, click in the Axis
selection box at the top and select Axis 4.
By default, axis 4 is a servo axis (although it
can be reassigned as a stepper - see section
A.1).
Click in the KDERIV box and enter a starting
value of 1.
Click Apply and then turn the motor shaft by
hand. Repeat this process, slowly increasing
the value of KDERIV until you begin to feel
some resistance in the motor shaft. The
exact value of KDERIV is not critical at this
stage.
Page 59

www.supportme.net
Operation 5-17MN1924
3. Click in the KPROP box and enter a value
that is approximately one quarter of the value
of KDERIV. If the motor begins to vibrate,
decrease the value of KPROP or increase
the value of KDERIV until the vibration stops.
Small changes may be all that is necessary.
4. In the Move Type drop down box, check that
the move type is set to Step.
5. Click in the Distance box and enter a distance
for the step move. It is recommended to set
a value that will cause the motor to turn a
short distance, for example one revolution.
Note: The distance depends on the scale set in section 5.3.1.
If you set a scale so that units could be expressed in revolutions (or other unit of
your choice), then those are the units that will be used here. If you did not set a
scale, the amount you enter will be in encoder counts.
6. Click in the Duration box and enter a duration
for the move, in seconds. This should be a
short duration, for example 0.15 seconds.
7. Click Go.
The NextMove ESB will perform the move and the motor will turn. As the soon as the
move is completed, WorkBench v5 will upload captured data from the NextMove ESB. The
data will then be displayed in the Capture window as a graph.
Note: The graphs that you see will not look exactly the same as the graphs shown here!
Remember that each motor has a different response.
8. Using the check boxes below the graph,
select the traces you require, for example
Demand position and Measured position.
Page 60

www.supportme.net
5-18 Operation MN1924
5.6.2 Underdamped response
If the graph shows that the response is underdamped (it overshoots the demand, as shown in
Figure 29) then the value for KDERIV should be increased to add extra damping to the move.
If the overshoot is excessive or oscillation has occurred, it may be necessary to reduce the
value of KPROP.
Measured position
Demand position
Figure 29 - Underdamped response
9. Click in the KDERIV and/or KPROP boxes
and make the required changes. The ideal
response is shown in section 5.6.4.
Page 61

www.supportme.net
Operation 5-19MN1924
5.6.3 Overdamped response
If the graph shows that the response is overdamped (it reaches the demand too slowly, as
shown in Figure 30) then the value for KDERIV should be decreased to reduce the damping of
the move. If the overdamping is excessive, it may be necessary to increase the value of
KPROP.
Measured position
Demand
position
Figure 30 - Overdamped response
10. Click in the KDERIV and/or KPROP boxes
and make the required changes. The ideal
response is shown in section 5.6.4.
Page 62

www.supportme.net
5-20 Operation MN1924
5.6.4 Critically damped response
If the graph shows that the response reaches the demand quickly and only overshoots the
demand by a small amount, this can be considered an ideal response for most systems.
See Figure 31.
Measured position
Demand position
Figure 31 - Critically damped (ideal) response
Page 63

www.supportme.net
Operation 5-21MN1924
5.7 Servo axis - eliminating steady-state errors
In systems where precise positioning accuracy is required, it is often necessary to position
within one encoder count. Proportional gain, KPROP, is not normally able to achieve this
because a very small following error will only produce a small demand for the drive which may
not be enough to overcome mechanical friction (this is particularly true in current controlled
systems). This error can be overcome by applying integral gain. The integral gain, KINT,
works by accumulating following error over time to produce a demand sufficient to move the
motor into the required position with zero following error .
KINT can therefore overcome errors caused by gravitational effects such as vertically moving
linear axes. With current controlled drives a non-zero demand output is required to hold the
load in the correct position, to achieve zero following error.
Care is required when setting KINT since a high value will cause instability during moves.
A typical value for KINT would be 0.1. The effect of KINT should also be limited by setting the
integration limit, KINTLIMIT, to the smallest possible value that is sufficient to overcome friction
or static loads, for example 5. This will limit the contribution of the integral term to 5% of the full
demand output range.
1. Click in the KINT box and enter a small
starting value, for example 0.1.
2. Click in the KINTLIMIT box and enter a value
of 5.
With NextMove ESB, the action of KINT and KINTLIMIT can be set to operate in various
modes:
H Never - the KINT term is never applied
H Always - the KINT term is always applied
H Smart - the KINT term is only applied when the demand speed is zero or constant.
H Steady State - the KINT term is only applied when the demand speed is zero.
This function can be selected using the KINTMODE drop down box.
Page 64

www.supportme.net
5-22 Operation MN1924
5.8 Servo axis - tuning for velocity control
Drives designed for velocity control incorporate their own velocity feedback term to provide
system damping. For this reason, KDERIV (and KVEL) can often be set to zero.
Correct setting of the velocity feed forward gain KVELFF is important to get the optimum
response from the system. The velocity feed forward term takes the instantaneous velocity
demand from the profile generator and adds this to the output block (see Figure 28).
KVELFF is outside the closed loop and therefore does not have an effect on system stability.
This means that the term can be increased to maximum without causing the motor to oscillate,
provided that other terms are setup correctly.
When setup correctly, KVELFF will cause the motor to move at the speed demanded by the
profile generator . This is true without the other terms in the closed loop doing anything except
compensating for small errors in the position of the motor. This gives faster response to
changes in demand speed, with reduced following error.
Before proceeding, confirm that the encoder feedback signals from the motor or servo
amplifier have been connected, and that a positive demand causes a positive feedback signal.
5.8.1 Calculating KVELFF
To calculate the correct value for KVELFF, you will need to know:
H The speed, in revolutions per minute, produced by the motor when a maximum demand
(+10V) is applied to the drive.
H The setting for LOOPTIME. The factory preset setting is 1ms.
H The resolution of the encoder input.
The servo loop formula uses speed values expressed in quadrature counts per servo loop.To
calculate this figure:
1. First, divide the speed of the motor, in revolutions per minute, by 60 to give the number of
revolutions per second. For example, if the motor speed is 3000rpm when a maximum
demand (+10V) is applied to the drive:
Revolutions per second = 3000 / 60
=
50
2. Next, calculate how many revolutions will occur during one servo loop. The factory preset
servo loop time is 1ms (0.001 seconds), so:
Revolutions per servo loop = 50 x 0.001 seconds
=
0.05
3. Now calculate how many quadrature encoder counts there are per revolution. The NextMove
ESB counts both edges of both pulse trains (CHA and CHB) coming from the encoder, so for
every encoder line there are 4 ‘quadrature counts’. With a 1000 line encoder:
Quadrature counts per revolution = 1000 x 4
=
4000
4. Finally, calculate how many quadrature counts there are per servo loop:
Quadrature counts per servo loop = 4000 x 0.05
=
200
Page 65

www.supportme.net
Operation 5-23MN1924
The analog demand output is controlled by a 12-bit DAC, which can create output voltages in
the range -10V to +10V. This means a maximum output of +10V corresponds to a DAC value
of 2048. The value of KVELFF is calculated by dividing 2048 by the number of quadrature
counts per servo loop, so:
KVELFF = 2048 / 200
=
10.24
5. Click in the KVELFF box and enter the value.
The calculated value should give zero
following error at constant velocity. Using
values greater than the calculated value will
cause the controller to have a following
error ahead of the desired position. Using
values less than the calculated value will
cause the controller to have following error
behind the desired position.
6. In the Move Type drop down box, check that
the move type is set to Trapezoid.
7. Click in the Distance box and enter a distance
for the step move. It is recommended to set
a value that will cause the motor to make a
few revolutions, for example 10.
Note: The distance depends on the scale set in section 5.3.1. If you set a scale so that
units could be expressed in revolutions (or other unit of your choice), then those
are the units that will be used here. If you did not set a scale, the amount you
enter will be in encoder counts.
8. Click Go.
The NextMove ESB will perform the move and the motor will turn. As the soon as the
move is completed, WorkBench v5 will upload captured data from the NextMove ESB. The
data will then be displayed in the Capture window as a graph.
Note: The graph that you see will not look exactly the same as the graph shown here!
Remember that each motor has a different response.
Page 66

www.supportme.net
5-24 Operation MN1924
9. Using the check boxes below the graph,
select the Measured velocity and Demand
velocity traces.
Measured velocity
Demand velocity
Figure 32 - Correct value of KVELFF
It may be necessary to make changes to the calculated value of KVELFF. If the trace for
Measured velocity appears above the trace for Demand velocity, reduce the value of KVELFF.
If the trace for Measured velocity appears below the trace for Demand velocity, increase the
value of KVELFF. Repeat the test after each change. When the two traces appear on top of
each other (approximately), the correct value for KVELFF has been found as shown in
Figure 32.
Page 67

www.supportme.net
Operation 5-25MN1924
5.8.2 Adjusting KPROP
The KPROP term can be used to reduce following error. Its value will usually be much smaller
than the value used for an equivalent current controlled system. A fractional value, for example
0.1, will probably be a good starting figure which can then be increased slowly.
1. Click in the KPROP box and enter a starting
value of 0.1.
2. Click Go.
The NextMove ESB will perform the move and the motor will turn. As the soon as the
move is completed, WorkBench v5 will upload captured data from the NextMove ESB. The
data will then be displayed in the Capture window as a graph.
Note: The graph that you see will not look exactly the same as the graph shown here!
Remember that each motor has a different response.
3. Using the check boxes below the graph,
select the Measured position and Demand
position traces.
Page 68

www.supportme.net
5-26 Operation MN1924
Measured position
Demand position
Figure 33 - Correct value of KPROP
The two traces will probably appear with a small offset from each other, which represents the
following error. Adjust KPROP by small amounts until the two traces appear on top of each
other (approximately), as shown in Figure 33.
Note: It may be useful to use the zoom function to magnify the end point of the move.
In the graph area, click and drag a rectangle around the end point of the traces.
To zoom out, right-click in the graph area and choose Undo Zoom.
Page 69

www.supportme.net
Operation 5-27MN1924
5.9 Digital input/output configuration
The Digital I/O window can be used to setup other digital inputs and outputs.
5.9.1 Digital input configuration
The Digital Inputs tab allows you to define how each digital input will be triggered, and if it
should be assigned to a special purpose function such as a Home or Limit input. In the
following example, digital input 1 will be set to trigger on an active low input, and allocated to
the forward limit input of axis 0:
1. In the Toolbox, click the Digital I/O icon.
2. At the bottom of the Digital I/O screen, click
the Digital Inputs tab.
The left of the screen shows a column of
yellow icons - High, Low, Rising, Falling
and Rise/Fall. These describe how the
input will be triggered.
3. Drag the Low icon
onto the IN1 icon . This will setup IN1 to respond to a low input.
Page 70

www.supportme.net
5-28 Operation MN1924
4. Now drag the IN1 icon onto the Fwd Limit icon .
This will setup IN1 as the Forward Limit input of axis 0.
5. Click Apply to send the changes to the NextMove ESB.
Note: If required, multiple inputs can be configured before
clicking Apply.
5.9.2 Digital output configuration
The Digital Outputs tab allows you to define how each digital output will operate and if it is to
be configured as a drive enable output (see section 5.3.2). Remember to click Apply to send
the changes to the NextMove ESB.
Page 71

www.supportme.net
Operation 5-29MN1924
5.10 Saving setup in fo rmation
When power is removed from the NextMove ESB all data, including configuration and tuning
parameters, is lost. You should therefore save this information in a file, which can be loaded
when the unit is next used.
1. In the Toolbox, click the Edit & Debug icon.
2. On the main menu, choose File, New File.
A new program editing window will appear.
3. On the main menu, choose Tools,
Upload Configuration Parameters.
WorkBench v5 will read all the
configuration information from the
NextMove ESB and place it in a Startup
block. For details of the Startup block,
see the MintMT help file.
Page 72

www.supportme.net
5-30 Operation MN1924
4. On the main menu, choose File, Save File. Locate a folder, enter a filename and click Save.
5.10.1 Loading saved information
1. In the Toolbox, click the Edit & Debug icon.
2. On the main menu, choose File, Open File...
Locate the file and click Open.
A Startup block should be included in every Mint program, so that whenever a program is
loaded and run the NextMove ESB will be correctly configured. Remember that every
drive/motor combination has a different response. If the same program is used on a
different NextMove ESB installation, the Startup block will need to be changed.
Page 73

www.supportme.net
Troubleshooting 6-1MN1924
6.1 Introduction
This section explains common problems and their solutions. If you want to know the meaning
of the LED indicators, see section 6.2.
6.1.1 Problem diagnosis
If you have followed all the instructions in this manual in sequence, you should have few
problems installing the NextMove ESB. If you do have a problem, read this section first.
In WorkBench v5, use the Error Log tool to view recent errors and then check the help file.
If you cannot solve the problem or the problem persists, the SupportMe feature can be used.
6.1.2 SupportMe feature
The SupportMe feature is available from the Help menu, or by clicking the buttononthe
motion toolbar. SupportMe can be used to gather information which can then be e-mailed,
saved as a text file, or copied to another application. The PC must have e-mail facilities to use
the e-mail feature. If you prefer to contact Baldor technical support by telephone or fax, contact
details are provided at the front of this manual. Please have the following information ready:
H The serial number of your NextMove ESB (if known).
H Use the Help, SupportMe menu item in WorkBench v5 to view details about your system.
H The type of servo amplifier and motor that you are using.
H A clear description of what you are trying to do, for example performing fine-tuning.
H A clear description of the symptoms that you can observe, for example error messages
displayed in WorkBench v5, or the current value of any of the Mint error keywords
AXISERROR, AXISSTATUS, INITERROR, and MISCERROR.
H The type of motion generated in the motor shaft.
H Give a list of any parameters that you have setup, for example the gain settings you have
entered.
6 Troubleshooting
6
Page 74

www.supportme.net
6-2 Troubleshooting MN1924
6.2 NextMove ESB indicators
6.2.1 Status display
The Status LED normally displays the unit’s node number. To display information
about a specific axis, use the LEDkeyword (see the MintMT help file). When a specific
axis is selected, the following symbols may be displayed by the Status LED. Some
characters will flash to indicate an error.
Spline. A spline move is being performed. See the SPLINE keyword and related
commands.
Axis enabled.
Torque mode. The NextMove ESB is in Torque mode. See the TORQUE keyword and
related commands.
Hold to Analog. The axis is in Hold To Analog mode. See the HTA keyword and related
commands.
Follow and offset. When an axis is following a demand signal it may be necessary to
advance or retard the slave in relation to the master. T o do this an offset move is
performed in parallel with the follow. See the FOLLOW and OFFSET keywords.
Circle. A circle move is being performed. See the CIRCLEA or CIRCLER keywords.
Cam. A Cam profile is being profiled. See the CAM keyword.
General error. See the AXISERROR keyword. The motion toolbar displays the status of
AXISERROR, which is a bit pattern of all latched errors. See also the Error Log topics in
the help file.
Error input. The ERRORINPUT has been activated and generated an error.
Flying shear. A flying shear is being profiled. See the FLY keyword.
Position following error. A following error has occurred. See the AXISERROR keyword
and associated keywords. Following errors could be caused by a badly tuned
drive/motor. At higher acceleration and deceleration rates, the following error will
typically be greater. Ensure that the drive/motor is adequately tuned to cope with these
acceleration rates.
The following error limit can be adjusted to suit your application (see the
FOLERRORFATAL and VELFATAL keywords). Following error could also be the cause
of encoder/resolver loss (see also the FEEDBACKFAULTENABLE keyword).
Follow mode. The axis is in Follow mode. See the FOLLOW keyword.
Homing. The axis is currently homing. See the HOME keyword.
Incremental move. An incremental move is being profiled. See the INCA and INCR
keywords.
Jog. The axis is jogging. In the Mint help file, see the topics JOG, JOGCOMMAND and
Jog mode.
Page 75

www.supportme.net
Troubleshooting 6-3MN1924
Offset move. The axis is performing an offset move.
Positional Move. The axis is performing a linear move. See the MOVEA and MOVER
keywords.
Stop. A STOP command has been issued or the stop input is active.
Axis disabled. The axis/drive must be enabled before operation can continue. See
section 5.3.3. Click the Drive enable button in WorkBench v5.
Suspend. The SUSPEND command has been issued and is active. Motion will be
ramped to zero demand whilst active.
Reverse software or hardware limit. A reverse software limit has been activated.
See AXISERROR and/or AXISSTATUS to determine which applies.
Forward software or hardware limit. A forward software limit has been activated.
See AXISERROR and/or AXISSTATUS to determine which applies.
Firmware being updated (horizontal bars appear sequentially). New firmware is being
downloaded to the NextMove ESB.
Initialization error. An initialization error has occurred at power on. See the Error Log or
INITERROR topics in the help file. Initialization errors should not normally occur.
When a node number between 1 and 15 is displayed, it is shown in hexadecimal format (1 - F).
For node numbers greater than 15, three horizontal bars are displayed. User defined symbols
can be made to appear using the keywords LED and LEDDISPLAY. See the MintMT help file
for details of each keyword.
If the status display shows one of the digits 0 - 7 with a flashing decimal point during startup,
this indicates that the NextMove ESB has detected a fault and cannot be started. In this
unlikely event, please contact Baldor technical support.
6.2.2 Communication
If the problem is not listed below please contact Baldor technical support.
Symptom
Check
Cannot detect NextMove ESB Check that the NextMove ESB is powered.
For serial connections, check that the serial cable is wired
correctly and properly connected. Check that no other
application on the PC is attempting to use the same serial
port.
For USB connections, check that the cable is properly
connected. Check that the USB device driver has been
installed.
Cannot communicate with the
controller.
Verify that WorkBench v5 is loaded and that NextMove
ESB is the currently selected controller.
Page 76

www.supportme.net
6-4 Troubleshooting MN1924
6.2.3 Motor control
Symptom Check
Controller appears to be
working but will not cause
motor to turn.
Check that the connections between motor and drive are
correct. Use WorkBench v5 to perform the basic system
tests (see section 5.5 or 5.4).
Confirm that the drive enable output has been configured
(see section 5.3.2).
Ensure that while the NextMove ESB is not in error the
drive is enabled and working. When the NextMove ESB is
first powered up the drive should be disabled if there is no
program running (there is often an LED on the front of the
drive to indicate status).
(Servo outputs only) Check that the servo loop gains are
setup correctly - check the Fine-tuning window. See
sections 5.5.2 to 5.7.
Motor runs uncontrollably
when controller is switched on.
Verify that the NextMove ESB and drive are correctly
grounded to a common ground.
(Servo outputs only) Check that the correct encoder
feedback signal is connected to the encoder input, the
encoder has power (if required, see sections 4.4.2 and
7.1.7) and is functioning correctly.
Check that the drive is connected correctly to the
NextMove ESB and that with zero demand there is 0V at
the drive’s demand input. See section 5.5.1.
Motor runs uncontrollably
when controller is switched on
and servo loop gains are
applied or when a move is set
in progress. Motor then stops
after a short time.
(Servo outputs only) Check that the encoder feedback
signal(s) are connected to the correct encoder input(s).
Check the demand to the drive is connected with the
correct polarity.
Check that for a positive demand signal, a positive
increase in axis position is seen. The ENCODERMODE
keyword can be used to change encoder input direction.
The DACMODE keyword can be used to reverse DAC
output polarity.
Check that the maximum following error is set to a
reasonable value. For setting up purposes, following error
detection may be disabled by setting FOLERRORMODE=0.
Motor is under control, but
vibrates or overshoots during a
move.
(Servo outputs only) Servo loop gains may be set
incorrectly. See sections 5.5.2 to 5.7.
Page 77

www.supportme.net
Troubleshooting 6-5MN1924
Symptom Check
Motor is under control, but
when moved to a position and
then back to the start it does
not return to the same position.
Verify that the NextMove ESB and drive are correctly
grounded to a common earth point.
(Servo outputs only) Check:
H all encoder channels are free from electrical noise;
H they are correctly wired to the controller;
H when the motor turns, the two square wave signals
are 90 degrees out of phase. Also check the
complement signals.
Ensure that the encoder cable uses shielded twisted pair
cable, with the outer shield connected at both ends and
the inner shields connected only at the NextMove ESB
end.
(Stepper outputs only) The motor is not maintaining
synchronization with the NextMove ESB drive output
signals due to excessive acceleration, speed or load
demands on the motor.
Check that the acceleration, speed and load are within the
capabilities of the motor.
6.2.4 WorkBench v5
Symptom Check
The Spy window does not
update
The system refresh has been disabled. Go to the Tools,
Options menu item, select the System tab and then
choose a System Refresh Rate (500ms is recommended).
Page 78

www.supportme.net
6-6 Troubleshooting MN1924
6.2.5 CANopen
Symptom Check
The CANopen bus is ‘passive’ This means that the internal CAN controller in the
NextMove ESB is experiencing a number of Tx and/or Rx
errors, greater than the passive threshold of 127.
Check:
H 12-24V is being applied to pin 5 of the RJ45 CAN
connector, to power the opto-isolators.
H There is at least one other CANopen node in the
network.
H The network is terminated only at the ends, not at
intermediate nodes.
H All nodes on the network are running at the same
baud rate.
H All nodes have been assigned a unique node ID.
H The integrity of the CAN cables.
The NextMove ESB should recover from the ‘passive’
state once the problem has been rectified (this may take
several seconds).
The CANopen bus is ‘off’ This means that the internal CAN controller in the
NextMove ESB has experiencing a fatal number of Tx
and/or Rx errors, greater than the off threshold of 255.
At this point the node will have switched itself to a state
whereby it cannot influence the bus.
Check:
H 12-24V is being applied to pin 5 of the RJ45 CAN
connector, to power the opto-isolators.
H There is at least one other CANopen node in the
network.
H The network is terminated only at the ends, not at
intermediate nodes.
H All nodes on the network are running at the same
baud rate.
H All nodes have been assigned a unique node ID.
H The integrity of the CAN cables.
To recover from the ‘off’ state the bus must be reset. This
can be done using the MintMT BUSRESET keyword, or by
resetting the NextMove ESB.
Page 79

www.supportme.net
Troubleshooting 6-7MN1924
Symptom Check
The Manager node cannot
scan/recognize a node on the
network using the MintMT
NODESCAN keyword.
Assuming that the network is working correctly (see
previous symptoms) and the bus is in an ‘Operational’
state, check the following:
H Only nodes that conform to DS401, DS403 and other
Baldor CANopen nodes are supported by the MintMT
NODESCAN keyword.
H Check that the node in question has been assigned a
unique node ID.
H The node must support the node guarding process.
NextMove ESB does not support the Heartbeat
process.
H Try power-cycling the node in question.
If the node in question does not conform to DS401 or
DS403 and is not a Baldor CANopen node,
communication is still possible using a set of general
purpose MintMT keywords. See the MintMT help file for
further details.
The node has been
successfully scanned /
recognized by the Manager
node, but communication is still
not possible.
For communication to be allowed, a connection must be
made to a node after it has been scanned.
H Baldor controller nodes are automatically connected
to after being scanned.
H Nodes that conform to DS401, DS403 must have the
connections made manually using the MintMT
CONNECT keyword.
If a connection attempt using CONNECT fails then it may be
because the node being connected to does not support an
object which needs to be accessed in order to setup the
connection.
Page 80

www.supportme.net
6-8 Troubleshooting MN1924
6.2.6 Baldor CAN
Symptom Check
The Baldor CAN bus is
‘passive’
This means that the internal CAN controller in the
NextMove ESB is experiencing a number of Tx and/or Rx
errors, greater than the passive threshold of 127.
Check:
H 12-24V is being applied to pin 5 of the RJ45 CAN
connector, to power the opto-isolators.
H There is at least one other Baldor CAN node in the
network, with jumpers JP1 and JP2 in the ‘1’ (lower)
position.
H The network is terminated only at the ends, not at
intermediate nodes.
H All nodes on the network are running at the same
baud rate.
H All nodes have been assigned a unique node ID.
H The integrity of the CAN cables.
The NextMove ESB should recover from the ‘passive’
state once the problem has been rectified.
The Baldor CAN bus is ‘off’ This means that the internal CAN controller in the
NextMove ESB has experiencing a fatal number of Tx
and/or Rx errors, greater than the off threshold of 255.
At this point the node will have switched itself to a state
whereby it cannot influence the bus.
Check:
H 12-24V is being applied to pin 5 of the RJ45 CAN
connector, to power the opto-isolators.
H There is at least one other Baldor CAN node in the
network, with jumpers JP1 and JP2 in the ‘1’ (lower)
position.
H The network is terminated only at the ends, not at
intermediate nodes.
H All nodes on the network are running at the same
baud rate.
H All nodes have been assigned a unique node ID.
H The integrity of the CAN cables.
To recover from the ‘off’ state the bus must be reset. This
can be done using the MintMT BUSRESET keyword, or by
resetting the NextMove ESB.
Page 81

www.supportme.net
Specifications 7-1MN1924
7.1 Introduction
This section provides technical specifications of the NextMove ESB.
7.1.1 Input power
Description Value
Input power
Nominal input voltage
Power consumption
24V (±20%)
50W (2A @24V)
7.1.2 Analog inputs
Description Unit Value
Type Differential
Common mode voltage range VDC ±10
Input impedance kΩ 120
Input ADC resolution bits 12 (includes sign bit)
Equivalent resolution (±10V input) mV ±4.9
Sampling interval µs 500 (both inputs enabled)
250 (one input disabled)
7.1.3 Analog outputs
Description Unit Value
Type Bipolar
Output voltage range VDC ±10
Output current (maximum) mA 10
Output DAC resolution bits 12
Equivalent resolution mV ±4.9
Update interval µs 100 - 2000
(same as LOOPTIME; default = 1000)
7 Specifications
7
Page 82

www.supportme.net
7-2 Specifications MN1924
7.1.4 Digital inputs
Description Unit Value
Type Opto-isolated
USR V+ supply voltage
Nominal
Minimum
Maximum
VDC
24
12
30
Input voltage
Active
Inactive
VDC
> 12V
<2V
Input current
(maximum per input, USR V+ = 24V)
mA 7
7.1.5 Digital outputs - general purpose
Description Unit Value
USR V+ supply voltage
Nominal
Minimum
Maximum
VDC
24V
12V
30V
Output current
Max. source per output, one output on
Max. source per output, all outputs on
Maximum total output current
mA DOUT0-7 DOUT8-10
350 350
62.5 166
500 500
Update interval Immediate
7.1.6 Relay output
All models Unit All models
Contact rating (resistive) 1A @ 24VDC
or
0.25A @ 30VAC
Operating time (max) ms 5
7.1.7 Encoder inputs
Description Unit Value
Encoder input RS422 A/B Differential, Z index
Maximum input frequency
quadrature, encoder inputs 0 and 1
quadrature, encoder input 2
MHz
20
8
Output power supply to encoders 5V, 500mA (maximum total for all axes)
Maximum allowable cable length 30.5m (100ft)
Page 83

www.supportme.net
Specifications 7-3MN1924
7.1.8 Stepper control outputs
Description Unit Value
Output type RS422 step (pulse) and direction
Maximum output frequency kHz 500
Output current
(maximum, per output pair)
mA
20
7.1.9 Serial RS232/RS485 port
Unit All models
Signal RS232 non-isolated CTS/RTS or RS485
non-isolated
(model dependent)
Bit rates baud 9600, 19200, 38400,
57600 (default), 115200 (RS232 only)
7.1.10 CAN interface
Description Unit Value
Signal 2-wire, isolated
Channels 1
Protocols CANopen or Baldor CAN
(selected by choice of firmware)
Bit rates
CANopen
Baldor CAN
Kbit/s
10, 20, 50, 100, 125, 250, 500, 1000
10, 20, 50, 125, 250, 500, 1000
7.1.11 Environmental
Description Unit
Operating temperature range Min Max
°C
°F
0
+32
+45
+113
Maximum humidity
%
80% for temperatures up to 31°C (87°F)
decreasingly linearly to 50% relative
humidity at 45°C (113°F), non-condensing
(according to DIN40 040 / IEC144)
Maximum installation altitude
(above m.s.l.)
m
ft
2000
6560
See also section 3.1.1.
Page 84

www.supportme.net
7-4 Specifications MN1924
7.1.12 Weights and dimensions
Description Value
Weight Approximately 700g (1.5 lb)
Nominal overall dimensions 245mm x 135mm x 43mm
(9.65in x 5.32in x 1.69in)
Page 85

www.supportme.net
General A-1MN1924
A.1 Axis renumbering
The factory preset axis numbering assigns axes 0 - 3 as stepper axes and axes 4 - 6 as servo
axes. However, it is possible to alter the axis numbering scheme. For example, you might wish
axes 0 and 1 to refer to the servo axes, and axes 2 to 5 to refer to the stepper axes. There are
certain hardware limitations that must be considered when altering the axis numbering
scheme:
H A maximum of 3 servo axes and 4 stepper axes may be assigned.
H Axes 0 and 4 share an internal hardware channel. This means they cannot both be servo
or stepper axes. If one is servo, the other must be stepper. The servo demand output for
axis 0 or 4 is always the DEMAND0 output, with Encoder0 as the feedback channel.
The stepper output is always STEP0.
H Axes 1 and 5 share an internal hardware channel. This means they cannot both be servo
or stepper axes. If one is servo, the other must be stepper. The servo demand output for
axis 1 or 5 is always the DEMAND1 output, with Encoder1 as the feedback channel. The
stepper output is always STEP1.
H Axes 2 and 6 share an internal hardware channel. This means they cannot both be servo
or stepper axes. If one is servo, the other must be stepper. The servo demand output for
axis 2 or 6 is always the DEMAND2 output, with Encoder2 as the feedback channel. The
stepper output is always STEP2.
H Axis 3 is always a stepper axis; it cannot be reassigned as a servo axis.
Its output is always STEP3.
Before axes can be reassigned, they must be turned off. This removes their existing servo /
stepper assignments and inhibits their electrical outputs. In the following example, axis 4 will
be reassigned as a stepper axis, and axis 0 as a servo axis:
1. In the Toolbox, click Application, then
click the Edit & Debug icon.
A General
A
Page 86

www.supportme.net
A-2 General MN1924
2. Click in the Command window.
3. Type the command:
CONFIG[0,1,2,3,4,5,6]=_cfOFF;
This will turn off all axes. There will now
be no electrical output for any of the
axes.
4. Now type:
CONFIG.4=_cfSTEPPER
where 4 is the axis to be configured.
Press Enter to enter the value. This
immediately configures axis 4 to be a
stepper axis.
5. To configure axis 0 as a servo axis,
type:
CONFIG.0=_cfSERVO
Other axes can be assigned as required, subject to the limitations described above. It is
recommended that unused axes are always turned off. This provides more processing time
for the axes that are in use. Attempting to assign an axis when there is not an appropriate
hardware channel available, or the axis is already in use, will result in a “Hardware channel
required is in use” or “Hardware not available” error message. See the MintMT help file for
details of the CONFIG and AXISCHANNEL keywords.
Page 87

www.supportme.net
General A-3MN1924
A.2 F eedback cables
The Baldor cables listed in T able 3 connect the ‘Encoder Out’ signal from a servo amplifier (for
example MicroFlex, FlexDrive
II
, Flex+DriveIIor MintDriveII), to the ‘Enc0’, ‘Enc1’ and ‘Enc2’
encoder input connectors on the NextMove ESB. One cable is required for each servo axis.
See section 4.4.2 for the connector pin configuration.
Length
Cab
l
e assem
bly
d
esc
r
ipt
ionBal
dorcatal
og numbe
r
m ft
Servo Amplifier to NextMove ESB
Feedback Cable,
with 9-pin male D-type connectors
at both ends
CBL005MF-A2
CBL010MF-A2
CBL015MF-A2
CBL020MF-A2
0.5
1
1.5
2.0
1.6
3.3
5
6.6
Table 3 - Servo amplifier to NextMove ESB feedback cables
If you are not using a Baldor cable, be sure to obtain a cable that is a shielded twisted pair
0.34mm
2
(22 AWG) wire minimum, with an overall shield. Ideally, the cable should not exceed
30.5m (100ft) in length. Maximum wire-to-wire or wire-to-shield capacitance is 50pF per
300mm (1ft) length, to a maximum of 5000pF for 30.5m (100ft).
Page 88

www.supportme.net
A-4 General MN1924
Page 89

www.supportme.net
CE Guidelines B-1MN1924
B.1 Outline
This section provides general information
regarding recommended methods of installation
for CE compliance. It is not intended as an
exhaustive guide to good practice and wiring
techniques. It is assumed that the installer of the
NextMove ESB is sufficiently qualified to perform
the task, and is aware of local regulations and
requirements. Baldor products that meet the
EMC directive requirements are indicated with a
“CE” mark. A duly signed CE declaration of
conformity is available from Baldor.
B.1.1 EMC Conformity and CE marking
The information contained herein is for your guidance only and does not guarantee that the
installation will meet the requirements of the council directive 89/336/EEC.
The purpose of the EEC directives is to state a minimum technical requirement common to all
the member states within the European Union. In turn, these minimum technical requirements
are intended to enhance the levels of safety both directly and indirectly.
Council directive 89/336/EEC relating to Electro Magnetic Compliance (EMC) indicates that it
is the responsibility of the system integrator to ensure that the entire system complies with all
relative directives at the time of installing into service.
Motors and controls are used as components of a system, per the EMC directive. Hence all
components, installation of the components, interconnection between components, and
shielding and grounding of the system as a whole determines EMC compliance.
The CE mark informs the purchaser that the equipment has been tested and complies with the
appropriate standards. It rests upon the manufacturer or his authorized representative to
ensure the item in question complies fully with all the relative directives in force at the time of
installing into service, in the same way as the system integrator previously mentioned.
Remember that it is the instructions of installation and the product that should comply with the
directive.
B.1.2 NextMove ESB compliance
When installed as directed in this manual, NextMove ESB units meet the emission limits for an
‘industrial’ environment, as defined by the EMC directives (EN50081-2: 1994). To meet the
more stringent emission limits of the ‘residential, commercial and light industrial’ environment
(EN50081-1: 1992), the NextMove ESB must be mounted in a suitable metal cabinet
incorporating 360° screened cable glands.
B CE Guidelines
B
Page 90

www.supportme.net
B-2 CE Guidelines MN1924
B.1.3 Use of CE compliant components
The following points should be considered:
H Using CE approved components will not guarantee a CE compliant system!
H The components used in the controller, installation methods used, materials selected for
interconnection of components are important.
H The installation methods, interconnection materials, shielding, filtering and
earthing/grounding of the system as a whole will determine CE compliance.
H The responsibility of CE mark compliance rests entirely with the party who offers the end
system for sale (such as an OEM or system integrator).
B.1.4 EMC installation suggestions
To ensure electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), the following installation points should be
considered to help reduce interference:
H Earthing/grounding of all system elements to a central earth/ground point (star point).
H Shielding of all cables and signal wires.
B.1.5 Wiring of shielded (screened) encoder cables
1
6
2
7
3
8
9
5
NextMove ESB
X5 / X6 / X7
Encoder Connector
Housing
Cable
Twisted pairs
Connect overall shield
to connector backshell.
Connect overall shield
to connector backshell.
CHA+
CHA-
CHB+
CHB-
CHZ+
CHZ-
+5V
GND
Figure 34 - Encoder signal cable grounding
Page 91

Index
MN1924
A
Abbreviations, 2-4
Analog I/O, 4-3
analog inputs, 4-3
analog outputs, 4-5
Auxiliary encoder inputs, 4-9
B
Basic Installation, 3-1
location requirements, 3-1
mounting, 3-2
C
Calculating KVELFF, 5-22
CAN interface
Baldor CAN, 4-22
CANopen, 4-21
connector, 4-19
introduction, 4-19
opto-isolation, 4-20
specifications, 7-3
terminator, 4-20
wiring, 4-20
Catalog number, identifying, 2-3
CE Guidelines, B-1
Closed loop control, an introduction, 5-13
Command outputs. See Demand outputs
Configuration
axis, 5-6
axis renumbering, A-1
digital inputs, 5-27
digital outputs, 5-28
selecting a scale, 5-6
setting the drive enable output, 5-7
testing a stepper axis, 5-10
testing and tuning a servo axis, 5-11
testing the drive enable output, 5-9
Connectors
CAN, 4-19
locations, 4-2
serial, 4-16
USB, 4-15
Critically damped response, 5-20
D
Demand outputs, 4-5, 5-11
Digital I/O, 4-7
auxiliary encoder inputs, 4-9
configuration, 5-27
digital inputs, 4-7
digital outputs, 4-12
Drive enable output
setting, 5-7
testing, 5-9
E
Encoder
cables, A-3
inputs, 4-14
Environmental, 3-1, 7-3
F
Features, 2-1
Feedback, 4-14, 7-2
cables, A-3
H
Hardware requirements, 3-3
Help file, 5-3
I
Indicators, 6-2
status display, 6-2
Input / Output, 4-1
analog inputs, 4-3, 7-1
analog outputs, 4-5, 7-1
CAN connection, 4-19
connection summary, 4-24
connector locations, 4-2
digital inputs, 4-7, 7-2
Index
Page 92

Index
MN1924
digital outputs, 4-7, 4-12, 7-2
encoder inputs, 4-14, 7-2
serial port, 4-16
multidrop using RS485/RS422, 4-17
using RS232, 4-16
stepper control outputs, 4-13, 7-3
USB port, 4-15
Installation, 3-1
Introduction to closed loop control, 5-13
L
LED indicators, status display, 6-2
Loading saved information, 5-30
O
Operation, 5-1
connecting to the PC, 5-1
installing the USB driver, 5-2
installing WorkBench v5, 5-1
power on checks, 5-2
preliminary checks, 5-2
starting, 5-1
Operator panels, HMI operator panels, 4-18
Overdamped response, 5-19
P
Power sources, 3-3, 7-1
Precautions, 1-2
R
Receiving and Inspection, 2-3
RS232, 4-16
specification, 7-3
RS485, 4-17
multidrop using RS485/RS422, 4-17
specifications, 7-3
S
Safety Notice, 1-2
Saving setup information, 5-29
Scale, selecting, 5-6
Serial port, 4-16
connecting serial Baldor HMI panels, 4-18
Servo axis, 5-11
adjusting KPROP , 5-25
eliminating steady-state errors, 5-21
testing the demand output, 5-11
tuning for current control, 5-16
tuning for velocity control, 5-22
Specifications, 7-1
analog inputs, 7-1
analog outputs (demands), 7-1
CAN interface, 7-3
digital inputs, 7-2
digital outputs, 7-2
encoder inputs, 7-2
environmental, 7-3
power, 7-1
relay, 7-2
serial port, 7-3
stepper outputs, 7-3
weights and dimensions, 7-4
Status display, 6-2
Stepper axis, 5-10
control outputs, 4-13
testing the output, 5-10
T
Tes t i n g
servo axis, 5-11
stepper axis, 5-10
Troubleshooting, 6-1
Baldor CAN, 6-8
CANopen, 6-6
communication, 6-3
help file, 5-3
motor control, 6-4
problem diagnosis, 6-1
status display, 6-2
SupportMe, 6-1
WorkBench v5, 6-5
Tuning
adjusting KPROP , 5-25
axis for velocity control, 5-22
calculating KVELFF, 5-22
critically damped response, 5-20
eliminating steady-state errors, 5-21
overdamped response, 5-19
selecting servo loop gains, 5-16
underdamped response, 5-18
Page 93

Index
MN1924
U
Underdamped response, 5-18
Units and abbreviations, 2-4
USB
installing the driver, 5-2
port, 4-15
W
Weights and dimensions, 7-4
WorkBench v5, 5-3
digital input/output configuration, 5-27
help file, 5-3
loading saved information, 5-30
saving setup information, 5-29
starting, 5-4
Page 94

Index
MN1924
Page 95

CommentsMN1924
If you have any suggestions for improvements to this manual, please let us know. Write your
comments in the space provided below, remove this page from the manual and mail it to:
Manuals
Baldor UK Ltd
Mint Motion Centre
6 Bristol Distribution Park
Hawkley Drive
Bristol
BS32 0BF
United Kingdom.
Alternatively, you can e-mail your comments to:
manuals@baldor.co.uk
Comment:
continued...
Comments
Page 96

Comments MN1924
Thank you for taking the time to help us.
Page 97

Page 98

PrintedinUK
E Baldor UK Ltd
Europe (Southern)
Baldor ASR AG, Switzerland
Tel: +41 52 647 4700
Fax: +41 52 659 2394
Europe
Baldor ASR GmbH, Germany
Tel: +49 (0) 89 905 080
Fax: +49 (0) 89 905 08491
Australia
Australian Baldor PTY Ltd
Tel: +61 2 9674 5455
Fax: +61 2 9674 2495
Mexico
Baldor de Mexico
Tel: +52 477 761 2030
Fax: +52 477 761 2010
U.S.A. (Headquarters)
Baldor Electric Company
Tel: +1 479 646 471 1
Fax: +1 479 648 5792
Singapore
Baldor Electric PTE Ltd
Tel: +65 744 2572
Fax: +65 747 1708
Japan
Baldor Japan Corporation
Tel: +81 45 412 4506
Fax: +81 45 412 4507
United Kingdom
Baldor UK Ltd
Tel: +44 1454 850000
Fax: +44 1454 859001
For additional office locations visit www.baldor.com
Baldor Electric Company
P.O. Box 2400
Ft. Smith, AR 72902-2400
U.S.A.
Visit www.supportme.net for the latest documentation and software releases.
LT0189A02
 Loading...
Loading...