Page 1

SERIES 22H
Line Regen
AC Flux Vector Control
Installation & Operating Manual
8/03 MN722
Page 2

Table of Contents
Section 1
Quick Start Guide 1-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Overview 1-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Quick Start Checklist 1-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Quick Start Procedure 1-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Section 2
General Information 2-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Overview 2-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Limited W arranty 2-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Safety Notice 2-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Section 3
Receiving & Installation 3-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Receiving & Inspection 3-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Physical Location 3-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Control Installation 3-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Through the Wall Mounting 3-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Optional Remote Keypad Installation 3-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electrical Installation 3-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Load Reactors 3-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
System Grounding 3-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Protection Devices 3-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Internal Fuses 3-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Wire Size and Protection Devices 3-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Three Phase Input Power Connections 3-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Hardware Changes for Reduced Voltage Input 3-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Motor Connections 3-15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
M-Contactor 3-15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Encoder Installation 3-16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Buffered Encoder Output 3-16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Home (Orient) Switch Input 3-17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Control Board Jumpers 3-18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Analog Inputs 3-19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Analog Outputs 3-20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Continued on next page.
Table of Contents iMN722
Page 3

Control Circuit Connections 3-21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Converting Control Board Connections 3-21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inverter Control Board Connections 3-22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Serial Mode 3-22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Keypad Mode Connections 3-23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Standard Run 3 Wire Mode Connections 3-24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
15 Speed 2-Wire Mode Connections 3-25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 Speed Analog 2 Wire Operating Mode 3-26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 Speed Analog 3 Wire Operating Mode 3-27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Bipolar Speed and Torque Mode Connections 3-28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Multiple Parameter Sets 3-29. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Process Mode Connections 3-30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electronic Pot 2 Wire Operating Mode 3-31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electronic Pot 3 Wire Control Mode 3-32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
External Trip Input 3-33. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Opto-Isolated Inputs 3-33. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Opto-Isolated Outputs 3-34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Pre-Operation Checklist 3-35. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power-Up Procedure 3-36. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Section 4
Programming and Operation 4-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Overview 4-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Baldor Keypad 4-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Display Mode 4-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Adjusting Display Contrast 4-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Display Mode Screens 4-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Display Screens & Diagnostic Information Access 4-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fault Log Access 4-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Program Mode 4-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Parameter Blocks Access for Programming 4-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Changing Parameter Values when Security Code Not Used 4-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reset Parameters to Factory Settings 4-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Initialize New Firmware 4-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Parameter Definitions 4-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Converter Control Board Parameters 4-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Inverter Control Board Parameters 4-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Continued on next page.
ii Table of Contents MN722
Page 4

Section 5
Troubleshooting 5-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
No Keypad Display - Display Contrast Adjustment 5-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
When a Fault is Displayed 5-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
How to Access the Fault Log 5-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
How to Clear the Fault Log 5-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
How to Access Diagnostic Information 5-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electrical Noise Considerations 5-15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Special Drive Situations 5-16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Control Enclosures 5-16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Special Motor Considerations 5-16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Section 6
Manual Tuning the Series 22H Control 6-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manually Tuning the Control 6-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Motor Mag Amps Parameter 6-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Slip Frequency Parameter 6-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Current Prop Gain Parameter 6-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Current Int Gain Parameter 6-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Speed Prop Gain Parameter 6-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Speed Int Gain Parameter 6-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PI Controller 6-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Continued on next page.
Table of Contents iiiMN722
Page 5

Section 7
Specifications, Ratings & Dimensions 7-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Specifications 7-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating Conditions 7-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Keypad Display 7-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Control Specifications 7-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Differential Analog Input 7-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Analog Outputs 7-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Digital Inputs 7-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Digital Outputs 7-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Indications 7-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Series 22H Vector Control Ratings 7-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Terminal Tightening Torque Specifications 7-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Dimensions 7-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Size C+ Control 7-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Size D+ Control 7-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Size D Control 7-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Size E Control 7-10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Size E Control – Through–Wall Mounting 7-11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Size F Control 7-13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Size F Control – Through–Wall Mounting 7-14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Size G+ Control 7-16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Size H Control 7-17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EK Controls - Filter Assembly 7-18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EK Controls - Boost Regulators 7-19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Appendix A A-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Converter Section Parameter Values A-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Output Section Parameter Values A-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Appendix B B-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Remote Keypad Mounting Template B-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
iv Table of Contents MN722
Page 6

Section 1
Quick Start Guide
Overview If you are an experienced user of Baldor controls, you are probably already familiar with
the keypad programming and keypad operation methods. If so, this quick start guide has
been prepared for you. This procedure will help get your system up and running in the
keypad mode quickly. This will allow motor and control operation to be verified. This
procedure assumes that the control and motor are correctly installed (see Section 3 for
procedures) and that you have an understanding of the keypad programming & operation
procedures. It is not necessary to wire the terminal strip to operate in the keypad mode, if
Level 2 Protection block parameters “External Trip” and “Local Enable INP” are set to off.
The quick start procedure is as follows:
1. Read the Safety Notice and Precautions in section 2 of this manual.
2. Mount the control. Refer to Section 3, “Physical Location” procedure.
3. Connect AC power. Refer to Section 3, “AC Input Power Connections”.
4. Connect the motor. Refer to Section 3, “Motor Connections”.
5. Connect the encoder. Refer to Section 3, “Encoder Installation ”.
Quick Start Checklist Check of electrical items.
CAUTION: After completing the installation but before you apply power, be
sure to check the following items.
1. Verify AC line voltage at source matches control rating.
2. Inspect all power connections for accuracy, workmanship and torques as well
as compliance to codes.
3. Verify control and motor are grounded to each other and the control is
connected to earth ground.
4. Check all signal wiring for accuracy.
5. Be certain all brake coils, contactors and relay coils have noise suppression.
This should be an R-C filter for AC coils and reverse polarity diodes for DC
coils. MOV type transient suppression is not adequate.
WARNING: Make sure that unexpected operation of the motor shaft during start
up will not cause injury to personnel or damage to equipment.
Check of Motor and Coupling
1. Verify freedom of motion of motor shaft.
2. Verify that motor coupling is tight without backlash.
2. Verify the holding brakes if any, are properly adjusted to fully release and set to
the desired torque value.
Quick Start Guide 1-1MN722
Page 7

Section 1
General Information
Quick Start Procedure
Initial Conditions
Be sure the 22H control and motor are installed and wired according to the procedures in
Section 3 of this manual.
Become familiar with the keypad programming and keypad operation of the control as
described in Section 4 of this manual.
1. Disconnect the load (including coupling or inertia wheels) from the motor shaft if
possible.
2. Verify that all enable inputs to J1-8 are open.
3. Turn power on. Be sure no errors are displayed.
4. Set the Level 1 Input block, Operating Mode parameter to “KEYPAD”.
5. Set the Level 2 Output Limits block, “OPERATING ZONE” parameter as
desired.
6. Enter the following motor data in the Level 2 Motor Data block parameters:
Motor Voltage (Nameplate, VOLTS)
Motor Rated Amps (Nameplate, FLA)
Motor Rated Speed (Nameplate, RPM)
Motor Rated Frequency (Nameplate, HZ)
Motor Mag Amps (Nameplate, NLA)
Encoder Counts
7. At the Level 2 Motor Data, go to CALC Presets and select YES (using the up
arrow key). Press ENTER and let the control calculate the preset values for the
parameters that are required for control operation.
8. Disconnect the motor from the load (including coupling or inertia wheels). If the
load can not be disconnected, refer to Section 6 and manually tune the control.
After manual tuning, perform steps 10, 11, 15, 16 and 17.
WARNING: The motor shaft will rotate during this procedure. Be certain that
unexpected motor shaft movement will not cause injury to
personnel or damage to equipment.
9. At the Level 2 Autotune block, perform the following tests:
CMD OFFSET TRIM
CUR LOOP COMP
STATOR R1
FLUX CUR SETTING
FEEDBACK TESTS
SLIP FREQ TEST
10. Set the Level 2 Output Limits block, “MIN OUTPUT SPEED” parameter.
11 Set the Level 2 Output Limits block, “MAX OUTPUT SPEED” parameter.
12. Remove all power from the control.
13. Couple the motor to its load.
14. Turn power on. Be sure no errors are displayed.
15. Go to Level 2 Autotune block, and perform the SPD CNTRLR CALC test.
16. Run the drive from the keypad using one of the following: the arrow keys for
direct speed control, keypad entered speed or the JOG mode.
17. Select and program additional parameters to suit your application.
The control is now ready for use the in keypad mode. If a different operating mode is
desired, refer to Section 3 for control connection diagrams and Section 4 Programming
and Operation.
1-2 Quick Start Guide MN722
Page 8

Section 2
General Information
Overview The Baldor Series 22H Line Regen Vector Control provides full motoring and line
regeneration to the AC power mains with a near unity power factor. The control uses
PWM controlled by IGBT power transistors in both the converter and inverter sections of
the control to provide 3 phase power to the motor and Regen power to the line. Flux
vector technology (sometimes referred to as Field Oriented Control) is a closed loop
control scheme that adjusts the frequency and phase of voltage and current applied to a
three phase induction motor. The vector control separates the motor current into it’s flux
and torque producing components. These components are independently adjusted and
vectorially added to maintain a 90 degree relationship between them. This produces
maximum torque from base speed down to and including zero speed. Above base
speed, the flux component is reduced for constant horsepower operation. In addition to
the current, the electrical frequency must also be controlled. The frequency of the
voltage applied to the motor is calculated from the slip frequency and the mechanical
speed of the rotor. This provides instantaneous adjustment of the voltage and current
phasing in response to speed and position feedback from an encoder mounted on the
motors’ shaft.
The Line Regen vector control provides several advantages over non-regenerative
drives:
Regenerated energy from the motor is returned to the power source. The
control can provide regenerated energy absorption up to it’s full rating on a
continuous basis.
Input current is controlled to be a near unity power factor at rated load.
Line harmonic distortion is reduced.
DC Bus voltage is always controlled. Therefore, line voltage transients do not
affect the output voltage to the motor.
The Baldor Series 22H control may be used in many different applications. It may be
programmed by the user to operate in different operating zones. It can also be
configured to operate in a number of modes depending upon the application
requirements and user preference.
It is the responsibility of the user to determine the optimum operating zone and mode to
interface the control to the application. These choices are made with the keypad as
explained in the programming section of this manual.
General Information 2-1MN722
Page 9

Limited Warranty
For a period of two (2) years from the date of original purchase, BALDOR will
repair or replace without charge controls and accessories which our
examination proves to be defective in material or workmanship. This
warranty is valid if the unit has not been tampered with by unauthorized
persons, misused, abused, or improperly installed and has been used in
accordance with the instructions and/or ratings supplied. This warranty is in
lieu of any other warranty or guarantee expressed or implied. BALDOR
shall not be held responsible for any expense (including installation and
removal), inconvenience, or consequential damage, including injury to any
person or property caused by items of our manufacture or sale. (Some
states do not allow exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential
damages, so the above exclusion may not apply.) In any event, BALDOR’s
total liability, under all circumstances, shall not exceed the full purchase
price of the control. Claims for purchase price refunds, repairs, or
replacements must be referred to BALDOR with all pertinent data as to the
defect, the date purchased, the task performed by the control, and the
problem encountered. No liability is assumed for expendable items such as
fuses.
Goods may be returned only with written notification including a BALDOR
Return Authorization Number and any return shipments must be prepaid.
2-2 General Information MN722
Page 10

Safety Notice This equipment contains voltages that may be as high as 1000 volts! Electrical shock
can cause serious or fatal injury. Only qualified personnel should attempt the start–up
procedure or troubleshoot this equipment.
This equipment may be connected to other machines that have rotating parts or parts
that are driven by this equipment. Improper use can cause serious or fatal injury. Only
qualified personnel should attempt the start–up procedure or troubleshoot this equipment.
PRECAUTIONS
WARNING: Do not touch any circuit board, power device or electrical
connection before you first ensure that power has been
disconnected and there is no high voltage present from this
equipment or other equipment to which it is connected. Electrical
shock can cause serious or fatal injury. Only qualified personnel
should attempt the start–up procedure or troubleshoot this
equipment.
WARNING: Be sure that you are completely familiar with the safe operation of
this equipment. This equipment may be connected to other
machines that have rotating parts or parts that are controlled by
this equipment. Improper use can cause serious or fatal injury.
Only qualified personnel should attempt the start–up procedure or
troubleshoot this equipment.
WARNING: This unit has an automatic restart feature that will start the motor
whenever input power is applied and a RUN (FWD or REV)
command is issued. If an automatic restart of the motor could
cause injury to personnel, the automatic restart feature should be
disabled by changing the Level 2 Miscellaneous block, Restart
Auto/Man parameter to Manual.
WARNING: Be sure the system is properly grounded before applying power.
Do not apply AC power before you ensure that all grounding
instructions have been followed. Electrical shock can cause
serious or fatal injury.
WARNING: Do not remove cover for at least five (5) minutes after AC power is
disconnected to allow capacitors to discharge. Dangerous voltages
are present inside the equipment. Electrical shock can cause
serious or fatal injury.
WARNING: Improper operation of control may cause violent motion of the
motor shaft and driven equipment. Be certain that unexpected
motor shaft movement will not cause injury to personnel or damage
to equipment. Certain failure modes of the control can produce
peak torque of several times the rated motor torque.
WARNING: Motor circuit may have high voltage present whenever AC power is
applied, even when motor is not rotating. Electrical shock can
cause serious or fatal injury.
WARNING: The motor shaft will rotate during the autotune procedure. Be
certain that unexpected motor shaft movement will not cause injury
to personnel or damage to equipment.
Continued on next page
General Information 2-3MN722
Page 11

Section 1
General Information
Caution: Suitable for use on a circuit capable of delivering not more than the
RMS symmetrical short circuit amperes listed here at rated voltage.
Horsepower RMS Symmetrical Amperes
1–50 5,000
51–200 10,000
201–400 18,000
401–600 30,000
601–900 42,000
Caution: Disconnect motor leads (T1, T2 and T3) from control before you
perform a “Megger” test on the motor. Failure to disconnect motor
from the control will result in extensive damage to the control. The
control is tested at the factory for high voltage / leakage resistance
as part of Underwriter Laboratory requirements.
Caution: Do not supply any power to the External Trip (motor thermostat)
leads at J1-16 and 17. Power on these leads can damage the
control. Use a dry contact type that requires no external power to
operate.
Caution: Do not connect AC power to the Motor terminals T1, T2 and T3.
Connecting AC power to these terminals may result in damage to
the control.
Caution: Baldor recommends not using “Grounded Leg Delta” transformer
power leads that may create ground loops and degrade system
performance. Instead, we recommend using a four wire Wye.
Caution: Do not use power factor correction capacitors at the input power
lines to the 22H Line Regen control. Installing power factor
correction capacitors may damage the control.
2-4 General Information MN722
Page 12

Section 3
Receiving & Installation
Receiving & Inspection The Series 22H Vector Control is thoroughly tested at the factory and carefully packaged
for shipment. When you receive your control, there are several things you should do
immediately.
1. Observe the condition of the shipping container and report any damage
immediately to the commercial carrier that delivered your control.
2. Verify that the part number of the control you received is the same as the part
number listed on your purchase order.
3. If the control is to be stored for several weeks before use, be sure that it is
stored in a location that conforms to published storage specifications. (Refer to
Section 7 of this manual).
Physical Location The location of the 22H is important. It should be installed in an area that is protected
from direct sunlight, corrosives, harmful gases or liquids, dust, metallic particles, and
vibration. Exposure to these elements can reduce the operating life and degrade
performance of the control.
Several other factors should be carefully evaluated when selecting a location for
installation:
1. For effective cooling and maintenance, the control should be mounted vertically
on a flat, smooth, non-flammable vertical surface. Size G+ are floor standing
NEMA 1 enclosures.
2. At least two inches clearance must be provided on all sides for air flow.
3. Front access must be provided to allow the control cover to be opened or
removed for service and to allow viewing of the Keypad Display. (The keypad
may optionally be remote mounted up to 100 feet from the control.)
Controls installed in a floor mounted enclosure must be positioned with
clearance to open the enclosure door. This clearance will also provide
sufficient air space for cooling.
4. Altitude derating. Up to 3300 feet (1000 meters) no derating required. Above
3300 ft, derate the continuous and peak output current by 2% for each 1000 ft.
5. Temperature derating. Up to 40°C no derating required. Above 40°C, derate
the continuous and peak output current by 2% per °C. Maximum ambient is
55°C.
6. 50Hz Operation derating. For operation on 50Hz input power, derate the
continuous and peak output current by 15%.
7. Shock Mounting. The control is designed to withstand 0.5G at 10 to 60 Hz
shock during normal operation.
Shock Mounting
If the control will be subjected to levels of shock greater than 1G or vibration greater than
0.5G at 10 to 60Hz, the control should be shock mounted. Excessive vibration within the
control could cause internal connections to loosen and cause component failure or
electrical shock hazard.
Receiving & Installation 3-1MN722
Page 13
Section 1
CONTROL
CONTROL
NOT
NOT
General Information
,
Table 3-1 lists the Watts Loss ratings for Series 22H controls.
Table 3-1 Series 22H Watts Loss Ratings.
STD PWM
CONTROL
MODEL No. SIZE INPUT VAC
ZD22H210-EL C+ 230 268 315 102 80 LRAC03501 49 499 546
ZD22H215-EL C+ 230 397 311 102 109 LRAC04501 54 662 576
ZD22H220-EL C+ 230 527 458 102 136 LRAC05501 64 829 760
ZD22H225-EL C+ 230 690 611 102 137 LRAC08001 82 1011 932
ZD22H230-EL D+ 230 571 768 170 164 LRAC08001 82 987 1184
ZD22H240-EL D+ 230 1095 942 170 187 LRAC10001 94 1546 1393
ZD22H250-EL D+ 230 1437 1286 170 225 LRAC13001 108 1940 1789
ZD22H410-EL C+ 460 240 326 102 80 LRAC01802 43 465 551
ZD22H415-EL C+ 460 336 259 102 86 LRAC02502 52 576 499
ZD22H420-EL C+ 460 432 379 102 11 0 LRAC03502 54 698 645
ZD22H425-EL D+ 460 544 504 102 134 LRAC03502 54 834 794
ZD22H430-EL D+ 460 640 740 170 158 LRAC04502 62 1030 1130
ZD22H440-EL D+ 460 880 738 170 228 LRAC05502 67 1345 1203
ZD22H450-EL D+ 460 1040 1023 170 217 LRAC08002 86 1513 1496
ZD22H460-EK D+ 460 1280 1236 100 299 LRAC08002 86 1765 1721
ZD22H475-EK E 460 2400 2322 153 395 LRAC10002 84 3032 2954
ZD22H4100-EK E 460 3000 2928 153 420 LRAC13002 180 3753 3681
ZD22H4150-EK F 460 3610 191 750 LRAC20002 168 4719
ZD22H4200-EK F 460 4750 191 850 LRAC25002 231 6022
ZD22H4250-EL G+ 460 6200
ZD22H4300-EL G+ 460 8140
ZD22H4450-EL G+ 460 8400
ZD22H4400-EL G+ 460 10560 1000 1750 LRAC50002 340 13650
ZD22H4450-EL G+ 460 11880 1000 1850 LRAC60002 414 15144
CONV &
INV
Losses
(Watts) (Watts) (Watts) (Watts) Cat. No. (Watts) (Watts) (Watts)
QUIET PWM
CONV & INV
Losses
CONTROL
RATINGS
AVAILABLE
CONTROL
FIXED
Losses
1000 900 LRAC32002 264 8364
1000 1620 LRAC40002 333 11093
1000 1650 LRAC50002 340 11390
BOOST
REG Loss
At Full
Load
Line Reactor Loss At Full
Load
STD PWM
Total
Losses
QUIET PWM
Total Losses
CONTROL
RATINGS
AVAILABLE
3-2 Receiving & Installation MN722
Page 14

Section 1
General Information
Control Installation The control must be securely fastened to the mounting surface. Use the four (4)
mounting holes to fasten the control to the mounting surface or enclosure.
Through the Wall MountingControl sizes E and F are designed for panel or through the wall installation. To mount a
control through the wall, an optional Through the Wall mounting kit must be purchased.
These kits are:
Kit No. Description
V0083991 Size E control Through the Wall mounting kit.
V0084001 Size F control Through the Wall mounting kit.
Procedure:
1. Refer to Section 7 of this manual for drawings and dimensions of the Through
the Wall mounting kits. Use the information contained in these drawings to
layout the appropriate size hole on your enclosure and wall.
2. Cut the holes in your enclosure and wall.
3. Locate and drill holes for mounting hardware as shown in the drawings.
4. Cut foam tape and apply to perimeter of opening as shown.
5. Secure the four (4) brackets to the exterior of the panel with the hardware
provided.
6. Secure the control to the panel using the hardware provided.
Receiving & Installation 3-3MN722
Page 15

Section 1
General Information
Optional Remote Keypad Installation The keypad may be remotely mounted using the optional Baldor keypad
extension cable. The keypad assembly (white - DC00005A-01; grey - DC00005A-02)
comes complete with the screws and gasket required to mount it to an enclosure. When
the keypad is properly mounted to a NEMA Type 4X indoor enclosure, it retains the Type
4X indoor rating.
Tools Required:
• Center punch, tap handle, screwdrivers (Phillips and straight) and crescent
wrench.
• 8-32 tap and #29 drill bit (for tapped mounting holes) or #19 drill (for clearance
mounting holes).
1
• 1-
• RTV sealant.
• (4) 8-32 nuts and lock washers.
• Extended 8-32 screws (socket fillister) are required if the mounting surface is
• Remote keypad mounting template. A tear out copy is provided at the end of
Mounting Instructions: For tapped mounting holes
1. Locate a flat 4″ wide x 5.5″ minimum high mounting surface. Material should
2. Place the template on the mounting surface or mark the holes as shown.
3. Accurately center punch the 4 mounting holes (marked A) and the large
4. Drill four #29 mounting holes (A). Thread each hole using an 8-32 tap.
5. Locate the 1-1/4″ knockout center (B) and punch using the manufacturers
6. Debur knockout and mounting holes making sure the panel stays clean and flat.
7. Apply RTV to the 4 holes marked (A).
8. Assemble the keypad to the panel. Use 8–32 screws, nuts and lock washers.
9. From the inside of the panel, apply RTV over each of the four mounting screws
Mounting Instructions: For clearance mounting holes
1. Locate a flat 4″ wide x 5.5″ minimum high mounting surface. Material should
2. Place the template on the mounting surface or mark the holes as shown on the
3. Accurately center punch the 4 mounting holes (marked A) and the large
4. Drill four #19 clearance holes (A).
5. Locate the 1-1/4″ knockout center (B) and punch using the manufacturers
6. Debur knockout and mounting holes making sure the panel stays clean and flat.
7. Apply RTV to the 4 holes marked (A).
8. Assemble the keypad to the panel. Use 8–32 screws, nuts and lock washers.
9. From the inside of the panel, apply RTV over each of the four mounting screws
/4″ standard knockout punch (1-11/16″ nominal diameter).
thicker than 12 gauge and is not tapped (clearance mounting holes).
this manual for your convenience.
be sufficient thickness (14 gauge minimum).
knockout (marked B).
instructions.
and nuts. Cover a 3/4″ area around each screw while making sure to completely
encapsulate the nut and washer.
be sufficient thickness (14 gauge minimum).
template.
knockout (marked B).
instructions.
and nuts. Cover a 3/4″ area around each screw while making sure to completely
encapsulate the nut and washer.
3-4 Receiving & Installation MN722
Page 16

Section 1
General Information
Electrical Installation Interconnection wiring is required between the motor control, AC power source, motor,
host control and any operator interface stations. Use only UL (cUL) listed closed loop
connectors that are of appropriate size for wire gauge being used. Connectors are to be
installed using crimp tool specified by the manufacturer of the connector. Only Class 1
wiring should be used.
Baldor Series 22H controls feature UL approved adjustable motor overload protection
suitable for motors rated at no less than 50% of the output rating of the control. Other
governing agencies such as NEC may require separate over–current protection. The
installer of this equipment is responsible for complying with the National Electric Code
and any applicable local codes which govern such practices as wiring protection,
grounding, disconnects and other current protection.
Load Reactors Line reactors may be used at the control output to the motor . When used this way, they are
called Load Reactors. Load reactors serve several functions that include:
Protect the control from a short circuit at the motor.
Limit the rate of rise of motor surge currents.
Slowing the rate of change of power the control delivers to the motor.
Load reactors should be installed as close to the control as possible. Select the load
reactor that matches the full load amperes (FLA) stated on the nameplate of the motor
you are using.
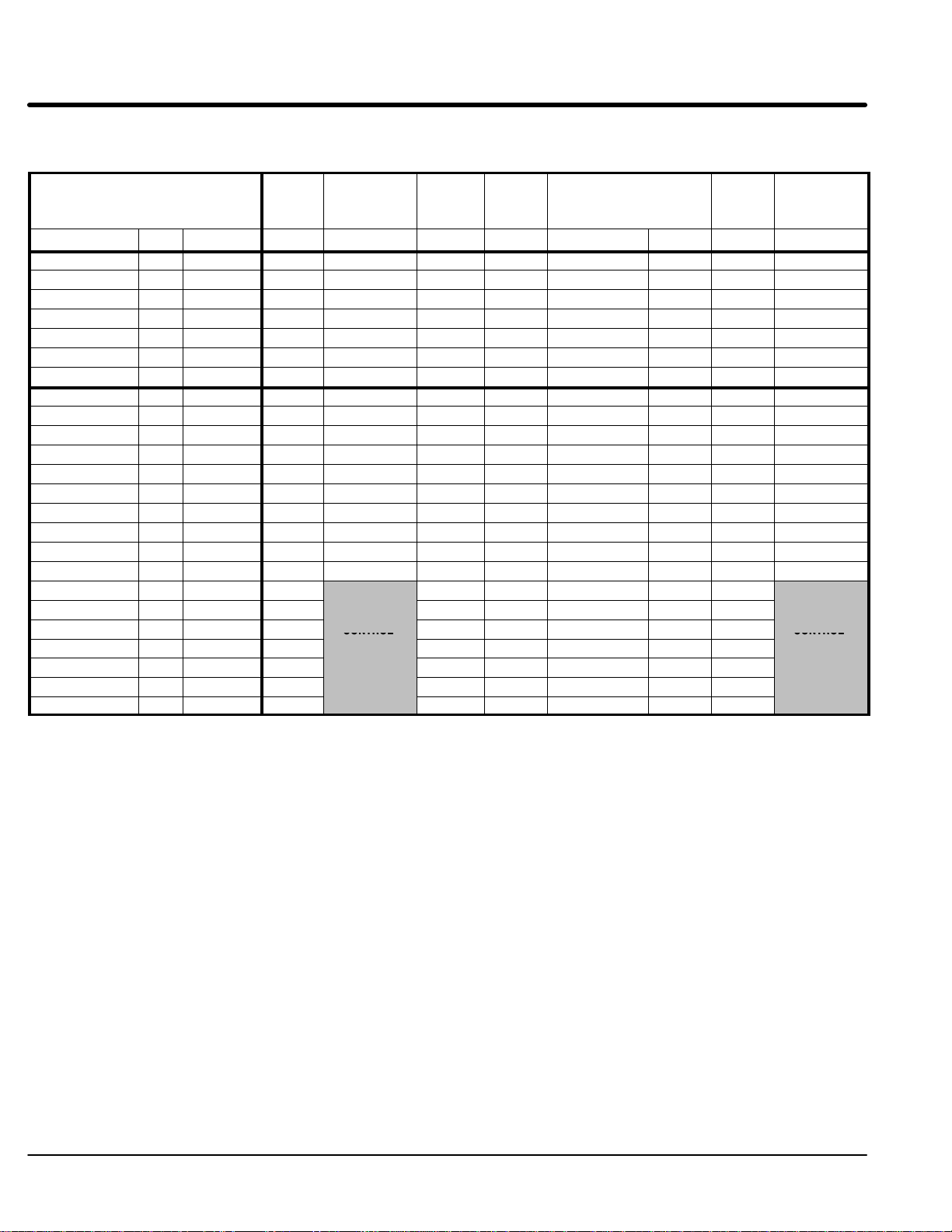
System Grounding Baldor Controls are designed to be powered from standard three phase lines that are
electrically symmetrical with respect to ground. System grounding is an important step in
the overall installation to prevent problems. The recommended grounding method is
shown in Figures 3-1 and 3-2.
Figure 3-1 Recommended System Grounding – EL
Safety
Ground
AC Main
Supply
Driven Earth
Ground Rod
(Plant Ground)
Note: A line reactor is required and
must be ordered separately.
L1
Line
Reactor
Four Wire
“Wye”
L2
L3
Earth
Route all 4 wires L1, L2, L3 and Earth
(Ground) together in conduit or cable.
Route all 4 wires T1, T2, T3 and Motor
Ground together in conduit or cable.
Connect all wires (including motor ground)
inside the motor terminal box.
LOCAL
JOG
DISP
FWD
SHIFT
REV
RESET
STOP
Series H
L1
L2 L3 T1 T2 T3
PROG
ENTER
Note: Wiring shown for clarity of grounding
method only. Not representative of
actual terminal block location.
Note: A load reactor is highly recommended
and must be ordered separately.
Optional
Load
Reactor
Ground per NEC and
Local codes.
Receiving & Installation 3-5MN722
Page 17
Section 1
General Information
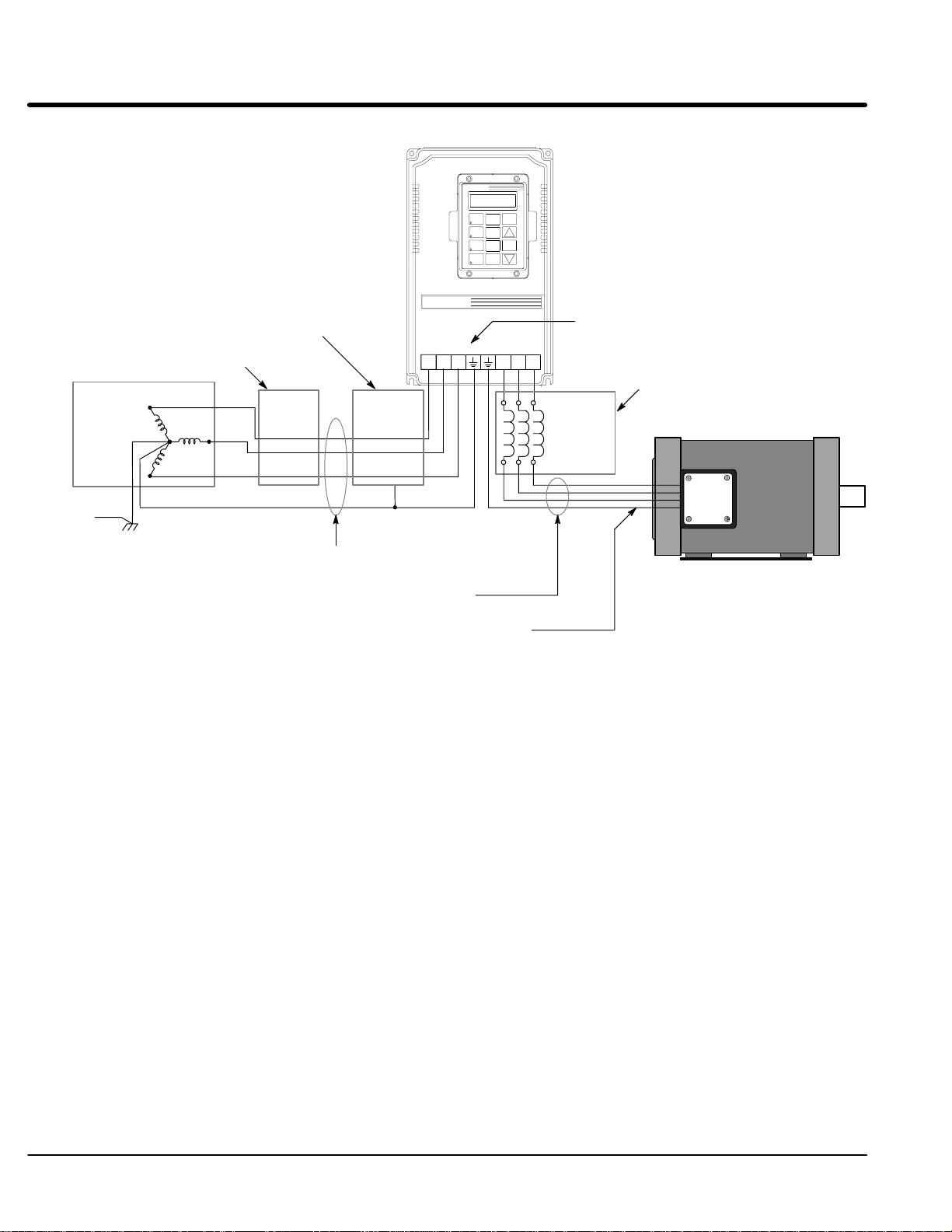
Figure 3-2 Recommended System Grounding – EK
LOCAL
PROG
JOG
DISP
FWD
SHIFT
ENTER
REV
RESET
STOP
Note: A boost regulator is required and
provided with each model EK control.
Note: A line reactor is required and
must be ordered separately.
AC Main
Supply
Safety
Ground
Driven Earth
Ground Rod
(Plant Ground)
Earth
Four Wire
“Wye”
Series H
Note: Wiring shown for clarity of grounding
method only. Not representative of
actual terminal block location.
Note: A load reactor is highly recommended
and must be ordered separately.
Load
Ground per NEC and
Local codes.
L1
L2
L3
Line
Reactor
Route all 4 wires L1, L2, L3 and Earth
(Ground) together in conduit or cable.
Route all 4 wires T1, T2, T3 and Motor
Ground together in conduit or cable.
Connect all wires (including motor ground)
inside the motor terminal box.
Boost
Regulator
L1
L2 L3 T1 T2 T3
Optional
Reactor
Ungrounded Distribution System
With an ungrounded power distribution system it is possible to have a continuous current
path to ground through the MOV devices. To avoid equipment damage, an Isolation
transformer with a grounded secondary is recommended. This provides three phase AC
power that is symmetrical with respect ground.
Input Power Conditioning
Baldor controls are designed for direct connection to standard three phase lines that are
electrically symmetrical with respect to ground. Certain power line conditions must be
avoided. An AC line reactor or an isolation transformer may be required for some power
conditions.
Baldor Series H controls require a minimum line impedance of 3%. Refer to
“Line Impedance” for additional information.
If the feeder or branch circuit that provides power to the control has
permanently connected power factor correction capacitors, an input AC line
reactor or an isolation transformer must be connected between the power factor
correction capacitors and the control.
If the feeder or branch circuit that provides power to the control has power
factor correction capacitors that are switched on line and off line, the capacitors
must not be switched while the control is connected to the AC power line. If the
capacitors are switched on line while the control is still connected to the AC
power line, additional protection is required. TVSS (Transient Voltage Surge
Suppressor) of the proper rating must be installed between the AC line reactor
or an isolation transformer and the AC input to the control.
3-6 Receiving & Installation MN722
Page 18

Section 1
General Information
Catalog Numbers Input
ZD22H210–EL 24 ZD22H410–EL 13
ZD22H215–EL 36 ZD22H415–EK 18
ZD22H220–EL 47 ZD22H420–EL 23
ZD22H225–EL 58 ZD22H425–EL 29
ZD22H230–EL 68 ZD22H430–EL 34
ZD22H240–EL 90 ZD22H440–EL 47
ZD22H250–EL 111 ZD22H450–EL 56
Current Requirements
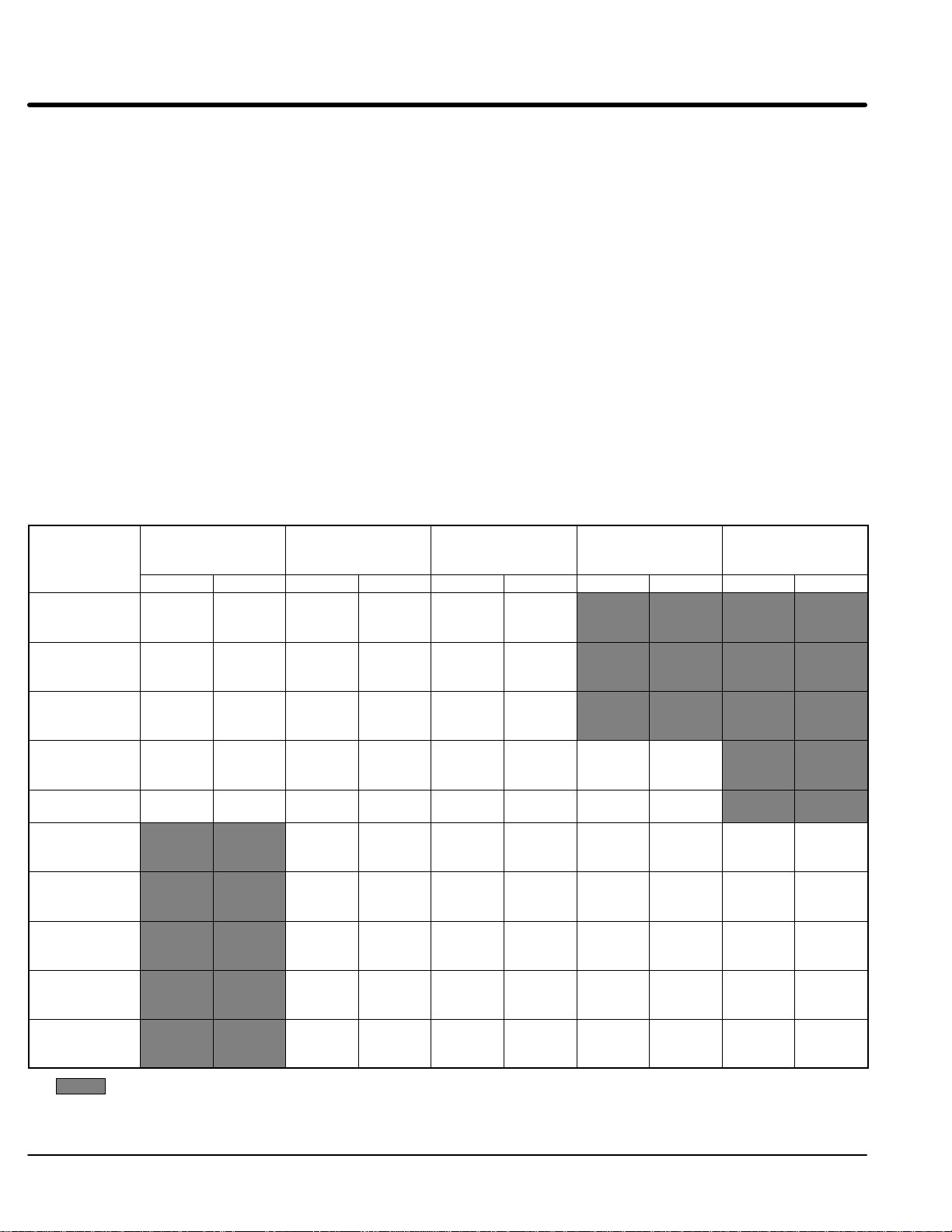
The input current for each control is given in Table 3-2 and the short circuit requirements
are given in Table 3-3. The control may be damaged if input current exceeds ratings.
Table 3-2 Input Current Requirements
230VAC 460VAC
Amps
Catalog Numbers Input
Amps
ZD22H460–EK 68
ZD22H475–EK 85
ZD22H4100–EK 107
ZD22H4150–EK 162
ZD22H4200–EK 213
ZD22H4250–EL 264
ZD22H4300–EL 315
ZD22H4350–EL 357
ZD22H4400–EL 408
ZD22H4450–EL 459
Table 3-3 Short Circuit Current Ratings
230VAC 460VAC
Catalog Numbers Short Circuit
Amps
ZD22H210–EL 240 ZD22H410–EL 130
ZD22H215–EL 360 ZD22H415–EK 180
ZD22H220–EL 470 ZD22H420–EL 230
ZD22H225–EL 580 ZD22H425–EL 290
ZD22H230–EL 680 ZD22H430–EL 340
ZD22H240–EL 890 ZD22H440–EL 470
ZD22H250–EL 1110 ZD22H450–EL 550
Catalog Numbers Short Circuit
Amps
ZD22H460–EK 680
ZD22H475–EK 850
ZD22H4100–EK 1060
ZD22H4150–EK 1620
ZD22H4200–EK 2130
ZD22H4250–EL 2640
ZD22H4300–EL 3150
ZD22H4350–EL 3570
ZD22H4400–EL 4080
ZD22H4450–EL 4590
Receiving & Installation 3-7MN722
Page 19
Section 1
General Information
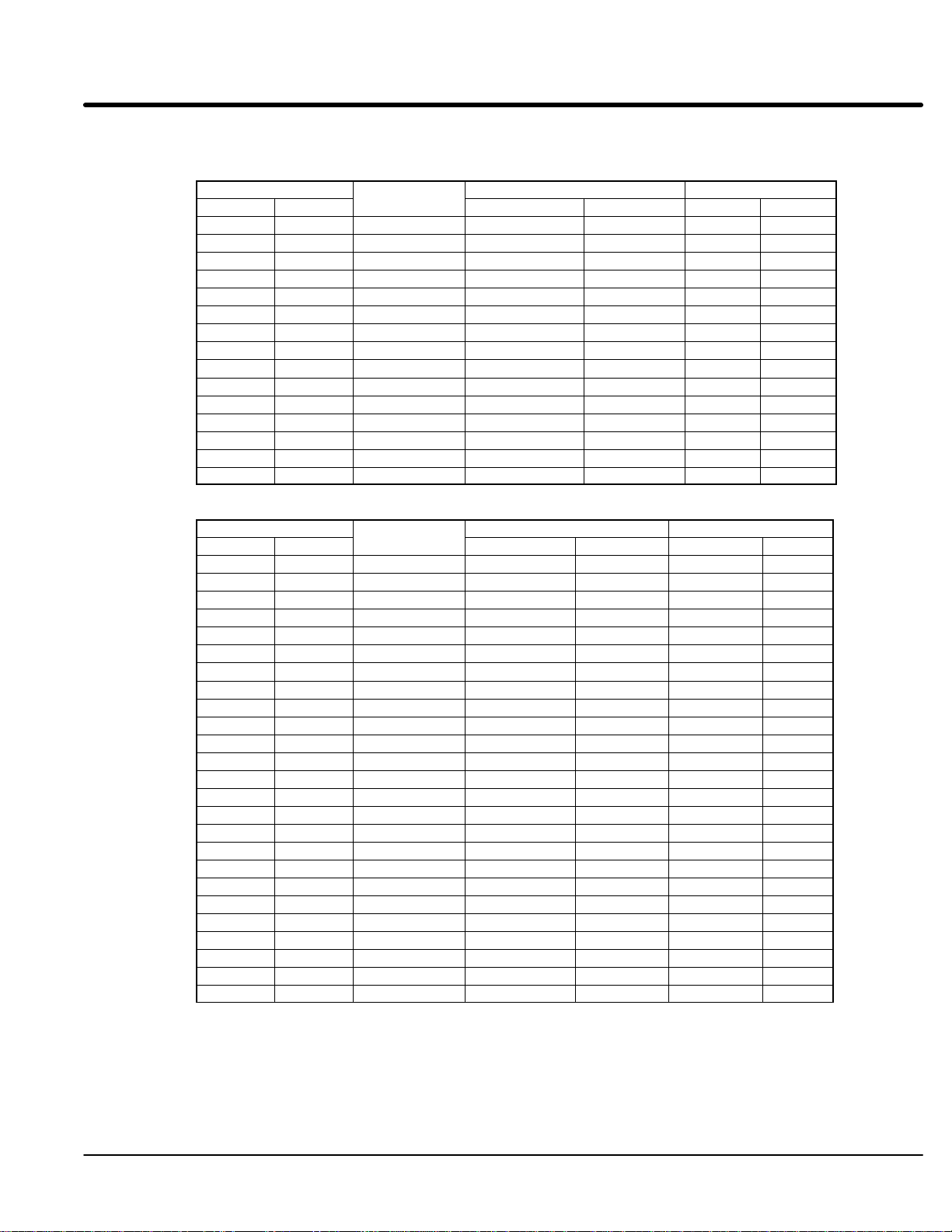
Protection Devices Be sure a suitable input power protection device is installed. Use the recommended
circuit breaker or fuses listed in Table 3-5 and 3-6. Input and output wire size is based on
the use of copper conductor wire rated at 75 °C. The table is specified for NEMA B
motors.
Circuit Breaker: 3 phase, thermal magnetic.
Equal to GE type THQ or TEB for 230 VAC or
GE type TED for 460 VAC
Fast Action Fuses: 230 VAC, Buss KTN
460 VAC, Buss KTS to 600A (KTU 601 - 1200A)
Very Fast Action: 230 VAC, Buss JJN
460 VAC, Buss JJS
Time Delay Fuses: 230 VAC, Buss FRN
460 VAC, Buss FRS to 600A (KLU 601 - 1200A)
Power Disconnect
A power disconnect should be installed between the input power service and the control
for a fail safe method to disconnect power. The control will remain in a powered-up
condition until all input power is removed from the control and the internal bus voltage is
depleted.
Internal Fuses
Table 3-4 Internal Fuses
Control
Size
Size
C+
D+
D
E
F
G+ 250HP
G+300HP
G+350HP
G+400HP
G+450HP
Zero Crossing
(Input Interface
Board)
Filter Fuses
(Filter Board)
Control
Transformer
Soft Start
Transformer
Fan Control
Transformer
Rating Type Rating Type Rating Type Rating Type Rating Type
3
/
A
10
500VAC
3
/
A
10
500VAC
3
/
A
10
500VAC
3
/
A
10
500VAC
3A
600VAC
FLQ-
3
/
10
Equiv.
FLQ-
3
/
10
Equiv.
FLQ-
3
/
10
Equiv.
FLQ-
3
/
10
Equiv.
or
or
or
or
5A
500VAC
5A
500VAC
10A
600VAC
10A
600VAC
ATM-3
or Equiv.3A500VAC
50A
600VAC
50A
600VAC
60A
600VAC
70A
600VAC
70A
600VAC
FNQ-5 or
Equiv.
FNQ-5 or
Equiv.
KTK-10
or Equiv.
KTK-10
or Equiv.
3.2A
250VAC
3.2A
250VAC
3.2A
250VAC
3.2A
250VAC
KTK-3 or
Equiv.3A600VAC
JJS or
Equiv.
JJS or
Equiv.
JJS or
Equiv.
JJS or
Equiv.
JJS or
Equiv.
31/
500VAC
31/
500VAC
31/
500VAC
31/
500VAC
31/
500VAC
2
2
2
2
2
MDA-
2
/
3
Equiv.
MDA-
2
/
3
Equiv.
MDA-
2
/
3
Equiv.
MDA-
2
/
3
Equiv.
KTK-3 or
Equiv.3A600VAC
FNQ-
A
1
/
3
Equiv.
FNQ-
A
1
/
3
Equiv.
FNQ-
A
1
/
3
Equiv.
FNQ-
A
1
/
3
Equiv.
FNQ-
A
1
/
3
Equiv.
or
10
or
10
or
10
1
/
A
or
10
2
250VAC
ABC 1/
or Equiv.
2
KTK-3 or
Equiv.
or
2
or
2
or
2
or
2
or
2
4A
500VAC
4A
500VAC
4A
500VAC
4A
500VAC
4A
500VAC
FNQ-4 or
Equiv.3A500VAC
FNQ-4 or
Equiv.3A500VAC
FNQ-4 or
Equiv.3A500VAC
FNQ-4 or
Equiv.3A500VAC
FNQ-4 or
Equiv.3A500VAC
FNQ-3 or
Equiv.
FNQ-3 or
Equiv.
FNQ-3 or
Equiv.
FNQ-3 or
Equiv.
FNQ-3 or
Equiv.
Not applicable.
3-8 Receiving & Installation MN722
Page 20
Section 1
General Information
Wire Size and Protection Devices
Table 3-5 230VAC Controls (3 Phase) Wire Size and Protection Devices
Control Rating
Amps HP
3 0.75 7 5 4 14 2.5
4 1 7 6 5 14 2.5
7 2 15 12 9 14 2.5
10 3 15 15 12 14 2.5
16 5 20 25 20 12 3.31
22 7.5 30 35 30 10 5.26
28 10 40 45 35 8 8.37
42 15 60 70 60 6 13.3
54 20 70 80 70 6 13.3
68 25 90 100 90 4 21.2
80 30 100 125 110 3 26.7
104 40 150 175 150 1 42.4
130 50 175 200 175 1/0 53.5
145 60 200 225 200 2/0 67.4
192 75 250 300 250 4/0 107.0
Input Breaker
Input Breaker
(Amps)
Input Fuse (Amps) Wire Gauge
Fast Acting Time Delay AWG mm
2
Table 3-6 460VAC Controls (3 Phase) Wire Size and Protection Devices
Control Rating Input Breaker Input Fuse (Amps) Wire Gauge
Amps HP
2 0.75 3 2 2 14 2.5
2 1 3 3 2.5 14 2.5
4 2 7 5 4.5 14 2.5
5 3 7 8 6.3 14 2.5
8 5 15 12 10 14 2.5
11 7.5 15 17.5 15 14 2.5
14 10 20 20 17.5 12 3.31
21 15 30 30 25 10 5.26
27 20 40 40 35 10 5.26
34 25 50 50 45 8 8.37
40 30 50 60 50 8 8.37
52 40 70 80 70 6 13.3
65 50 90 100 90 4 21.2
77 60 100 125 100 3 26.7
96 75 125 150 125 2 33.6
124 100 175 200 175 1/0 53.5
156 125 200 250 200 2/0 67.4
180 150 225 300 250 3/0 85.0
240 200 300 350 300 (2) 2/0 (2) 67.4
302 250 400 450 400 (2) 4/0 (2) 107.0
361 300 450 600 450 (3) 2/0 (3) 67.4
414 350 500 650 500 (3) 3/0 (3) 85.0
477 400 600 750 600 (3) 4/0 (3) 107.0
515 450 650 800 700 (3) 250MCM (3) 127.0
590 500 750 900 800 (3) 300MCM (3) 152.0
Note: All wire sizes are based on 75°C copper wire. Higher temperature smaller gauge wire may be used per NEC
and local codes. Recommended fuses/breakers are based on 40°C ambient, maximum continuous control
output current and no harmonic current.
(Amps)
Fast Acting Time Delay AWG mm
2
Receiving & Installation 3-9MN722
Page 21
Section 1
General Information
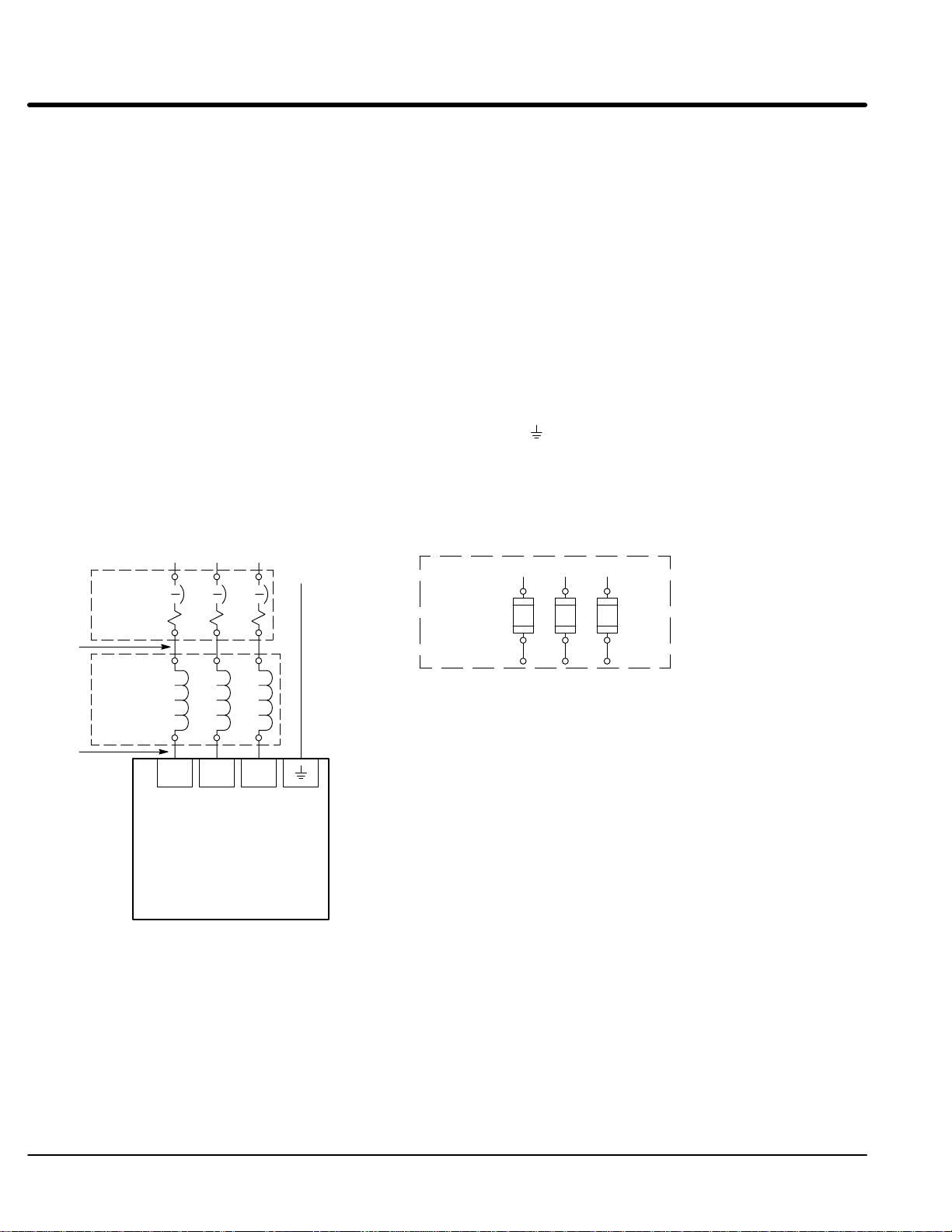
Three Phase Input Power Connections
AC power and motor connections are different for controls that have a model number
suffix of “EL” and “EK”. Be sure to use the correct procedure for your control.
Note: “EK” Controls are input phase sensitive. Be sure all connections are correct.
“EL” suffix
The AC power and motor connections are shown in Figure 3-3. Overloads are not
required. The 22H control has an electronic I2t motor overload protection. If motor
overloads are desired, they should be sized according to the manufacturers specifications
and installed between the motor and the T1, T2 and T3 terminals of the control.
1. Connect the incoming AC power wires from the protection devices to terminals
2. Connect A2, B2 and C2 3% line reactor terminals to the L1, L2 and L3 power
3. * Connect earth ground to the “ ” of the control. Be sure to comply with local
* Grounding by using conduit or panel connection is not adequate. A separate
A1, B1 and C1 at the 3% line reactor.
input terminals of the control.
codes.
conductor of the proper size must be used as a ground conductor.
Note 1
Note 2
Note 3
Note 2
* Circuit
Breaker
Line
Reactor
Figure 3-3 “EL” Control 3 Phase AC Power and Motor Connections
L1 L2 L3
A1 B1 C1
A2 B2 C2
L1 L2 L3
Baldor
Series 22HXXX-EL
Control
Earth
Alternate *
Fuse
Connection
* Optional components not provided with 22H Control.
Notes:
1. See “Protective Devices” described previously in this section.
2. Shield wires inside a metal conduit.
3. 3% Line Reactor is required at input.
L1 L2 L3
Note 1
A1 B1 C1
See Recommended Tightening Torques in Section 7.
3-10 Receiving & Installation MN722
Page 22
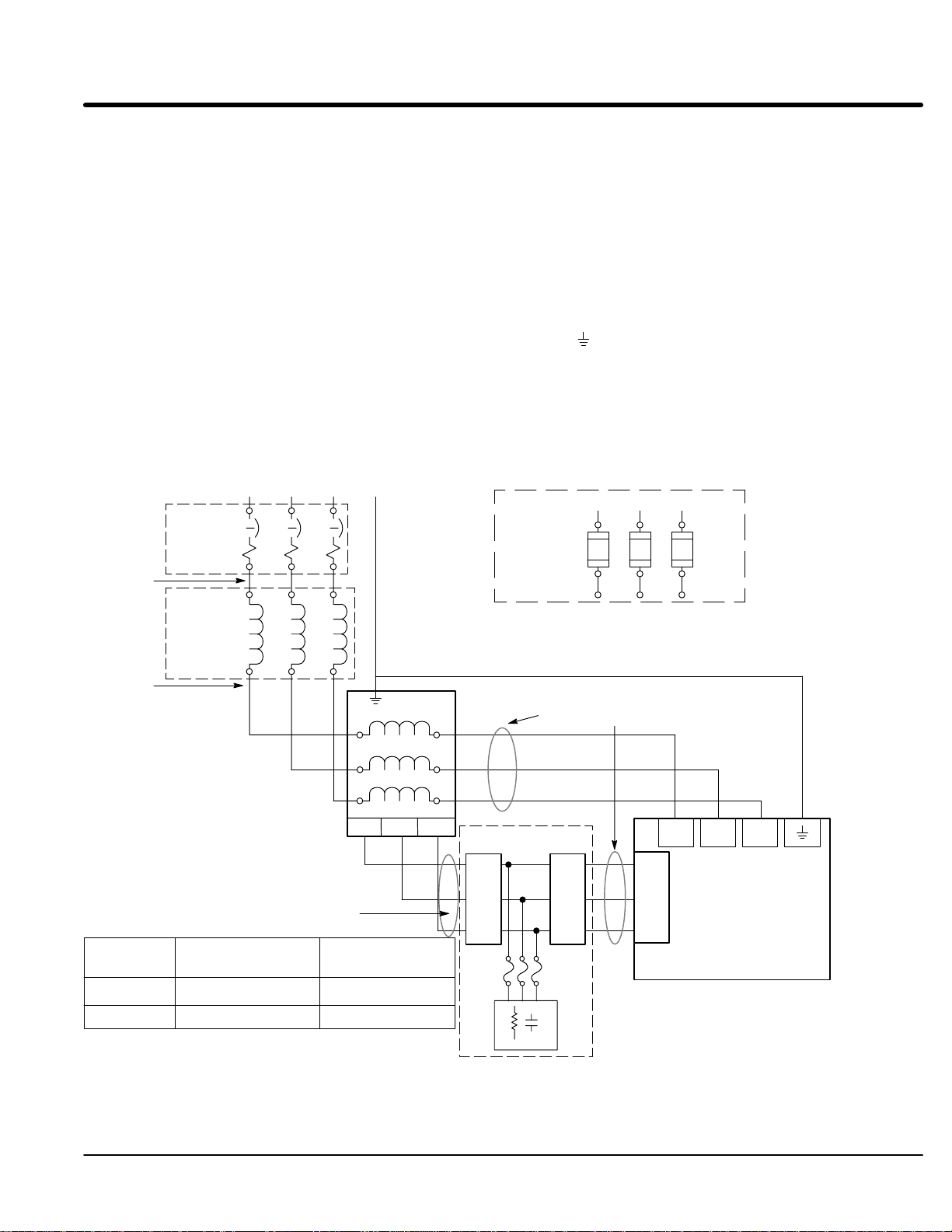
Section 1
General Information
Figure 3-4 “EK” Control 3 Phase AC Power and Motor Connections (Size D, E & F)
L1 L2 L3
Note 1
Note 2
* Circuit
Breaker
A1 B1 C1
“EK” suffix (“EK” Controls are input phase sensitive. Check all connections).
The AC power and motor connections are shown in Figure 3-4. Overloads are not
required. The 22H control has an electronic I2t motor overload protection. If motor
overloads are desired, they should be sized according to the manufacturers specifications
and installed between the motor and the T1, T2 and T3 terminals of the control.
1. Connect the incoming AC power wires from the protection devices to terminals
A1, B1 and C1 of the 3% line reactor.
2. Connect A2, B2 and C2 3% line reactor terminals to the L1, L2 and L3 of the
boost regulator.
3. Connect X1, X2 and X3 boost regulator terminals to X1, X2 and X3 of the control.
4. * Connect earth ground to the “ ” of the control. Be sure to comply with local codes.
5. Connect boost regulator terminals L1A, L2A and L3A to Filter terminals J1-1,
J1-2 and J1-3.
6. Connect filter terminals J2-1, J2-2 and J2-3 to control terminals L1A, L2A and L3A.
* Grounding by using conduit or panel connection is not adequate. A separate
conductor of the proper size must be used as a ground conductor.
Earth
Alternate *
Fuse
Connection
L1 L2 L3
Note 1
A1 B1 C1
Note 3
Note 2
Notes:
1. See “Protective Devices” described
previously in this section.
2. Shield wires inside a metal conduit.
3. 3% Line Reactor is required at input.
Control Size
D & E
F
See Recommended Tightening Torques in Section 7.
3% Line
Reactor
A2 B2
Boost
Regulator
Phase Sensitive Inputs
Boost Regulator to
Filter (5 ft. max.)
14AWG (2.08 mm2)
10AWG (5.26 mm
C2
L1
L2
L3
L1A L2A L3A
Filter to Control
(10 ft. max.)
14AWG (2.08 mm
2
)
10AWG (5.26 mm
X1
X2
X3
J1 J2
1
2
3
2
)
2
)
* Optional components not provided with 22H Control.
Phase Sensitive Inputs
Filter
1
2
3
X1 X2 X3
L1A
L2A
Series 22HXXX-EK
L3A
Baldor
Control
Receiving & Installation 3-11MN722
Page 23
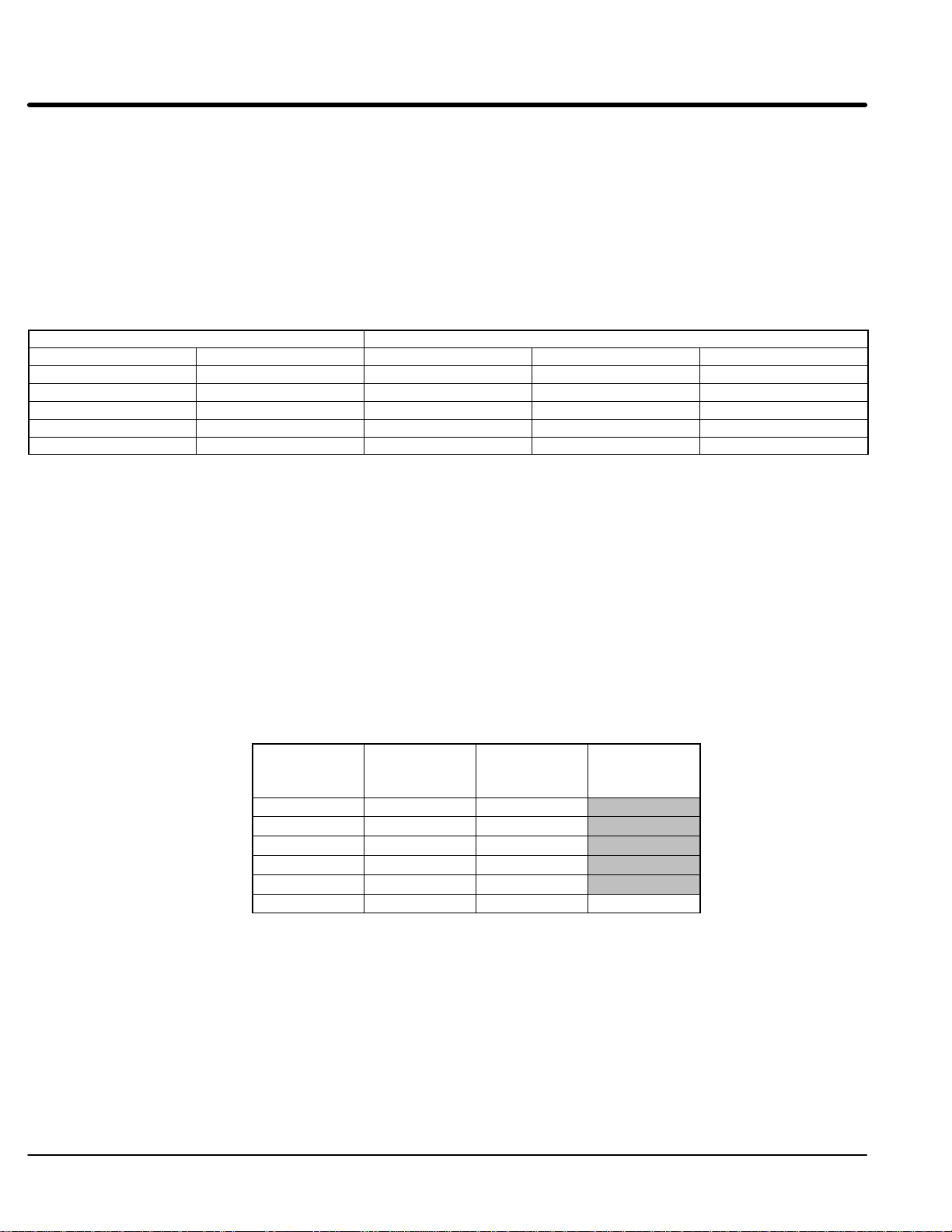
Section 1
General Information
Single Phase Operation
Single phase operation is not possible for Series 22H Line Regen Vector Controls.
Operating the Control at a Reduced Input Voltage
Series 22H Controls use a DC Bus regulation technique that provides full output voltage
(240VAC for 230VAC Controls; or 480VAC for 460VAC controls) for the full input voltage
range. However, at reduced input voltages the output current of the control may have to
be derated. Table 3-7 lists the % derating of the output current for various motor voltage
ratings and input power voltage levels to the control.
Table 3-7 Output Current Derating at Reduced Input Voltages (2.5KHz PWM)
Input Voltage % of Output Current after Derating
230VAC Control 460VAC Control 240/480VAC Motor 230/440VAC Motor 208/400VAC Motor
180VAC 340VAC 77% 84% 93%
190VAC 360VAC 82% 89% 98%
208VAC 400VAC 90% 99% 100%
230VAC 440VAC 100% 100% 100%
240VAC 480VAC 100% 100% 100%
For example:
A 460VAC Control that has a 400VAC input line can provide 90% of the rated current to a
480VAC motor. In the Section 6 specifications we find our example 10HP control is
ZD22H410-EL has a continuous current rating of 15 Amps. The derated current can be
calculated as follows: 15A x 90% = 13.5A derated value.
Hardware Changes for Reduced Voltage Input
Size C+, D+,D, E, F and G+ controls all require modification for operation at a reduced
line voltage (less than rated nominal). Table 3-8 defines the modifications for each
enclosure size. Figure 3-1 shows the locations of the transformer locations for each
enclosure size.
Table 3-8 Hardware changes for 380-400VAC operation
Enclosure
Size
C+ Yes No
D+ Yes No
D Yes No
E Yes Yes
F Yes Yes
G+ No Yes Yes
Transformer
Tap Change
Control
Contactor
Transformer
Tap Change
Fuse Block
Connection
Change
3-12 Receiving & Installation MN722
Page 24
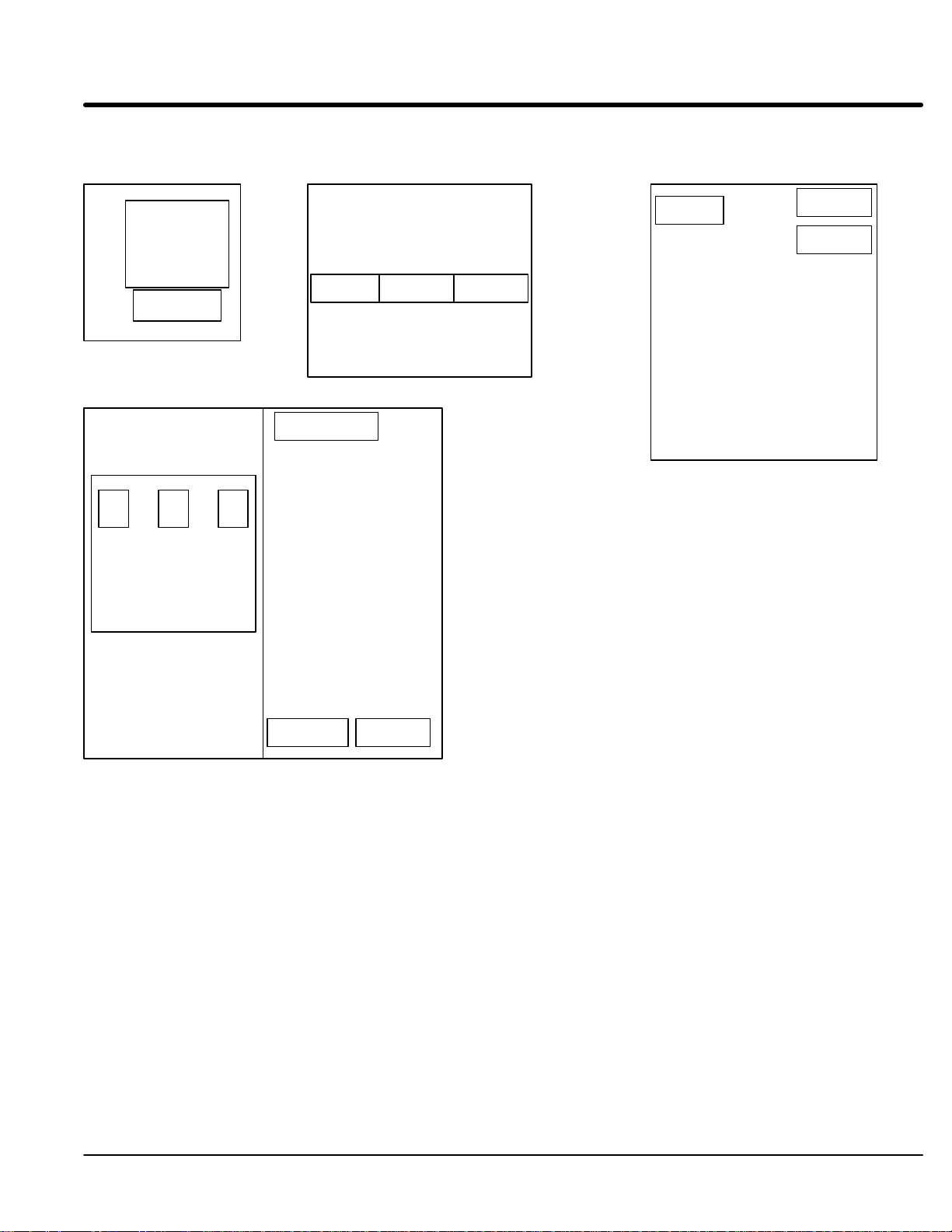
Section 1
General Information
Figure 3-1 Control and Contactor Transformer Locations
Control Sizes
C+, D, D+
Logic Control
Board
Control Size
E
Input
Contactor
Control Size
F
Contactor
Transformer
Transformer
Control
Control
Transformer
Control Size
G+
Fuse
Block
Swing out panel
xfmr xfmr
Contactor
Fan
Transformers
Contactor
Transformer
Input
Contactor
Transformer
Input
Contactor
Control
Transformer
Not drawn to scale or proportion
Size C+, D, D+ E, and F size control procedure:
Control Transformer
1. Terminate drive operation and disable the control.
2. Remove all power sources from the control. If power has been applied, wait at
least 5 minutes for bus capacitors to discharge.
3. Remove or open the front cover and locate the control transformer (Figure 3-2).
4. Remove the wire from terminal 5 of the control transformer.
5. Place the wire that was removed from terminal 5 onto terminal 4.
6. Install or close the front cover.
Receiving & Installation 3-13MN722
Page 25
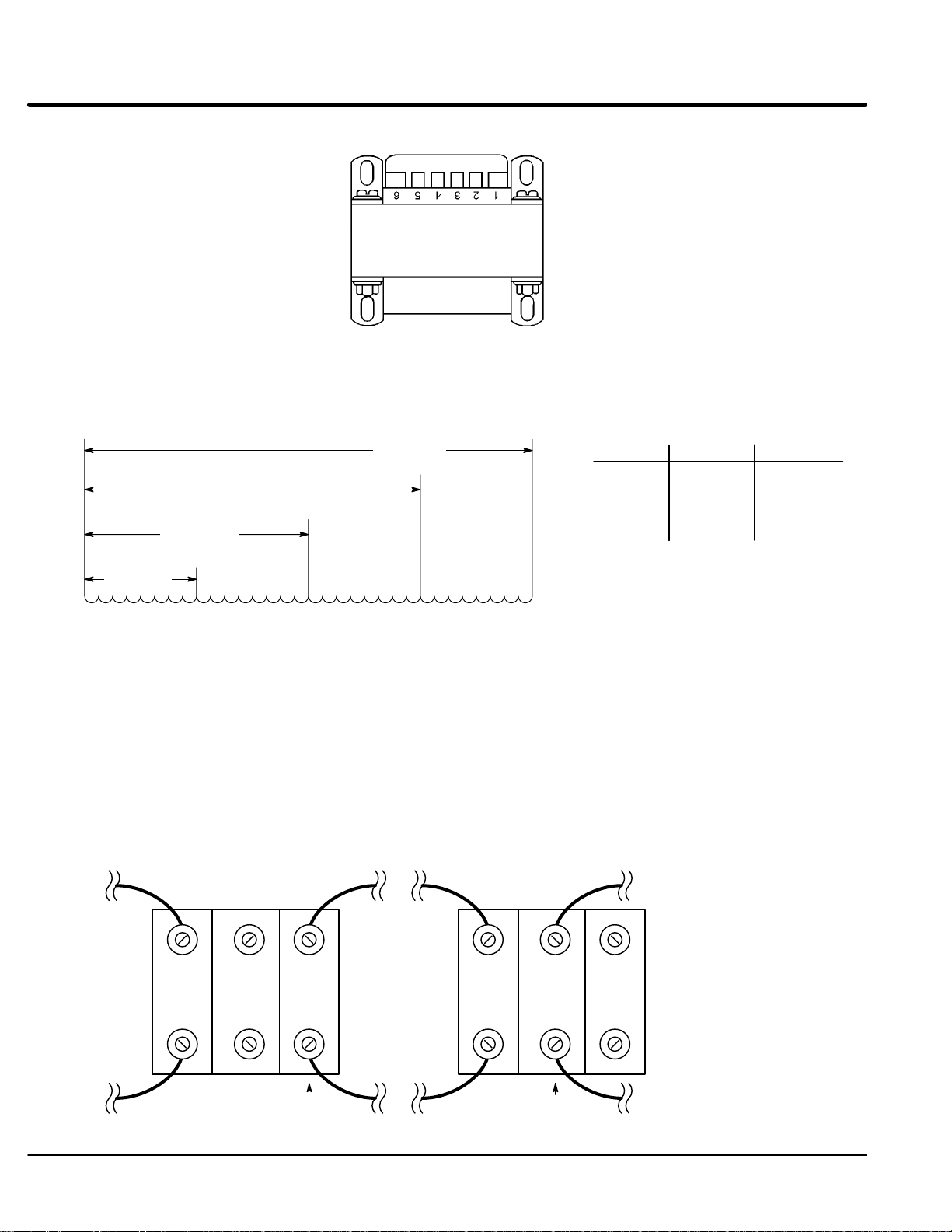
Figure 3-2 Configuring the Control Transformer for 380 - 400 VAC Installation
Contactor Transformer
Only size E and F controls require a change of the contactor transformer tap.
See Figure 3-3. Use the taps (H1 to H5) that are correct for the input voltage.
Figure 3-3 Contactor Transformer Tap Change (380 -400VAC Input)
H1
380VAC
440VAC
H2
550VAC
H3
600VAC
H4
H5
Frequency
50 / 60
Hz
Voltage Taps
380
440-460
550
600
H1 – H2
H1 – H3
H1 – H4
H1 – H5
Size G+and H control procedure: (Refer to Figure 3-4.)
Control Transformer
1. Be sure drive operation is terminated and control is disabled.
2. Remove all power sources from the control. If power has been applied, wait at
least 5 minutes for bus capacitors to discharge.
3. Remove or open the front cover. Locate the control transformer fuse block
(see Figure 3-1).
4. Remove the wires from the two right side terminals (460VAC connection).
5. Place the wires on the center terminals as shown (380VAC connection).
6. Install or close the front cover.
Figure 3-4 Configuring the Control Transformer Fuse Block for 380 - 400 VAC Installation
For Fuse Block, location
refer to Figure 3-1.
460VAC
Connection
380-400VAC
Connection
3-14 Receiving & Installation MN722
Page 26
Section 1
General Information
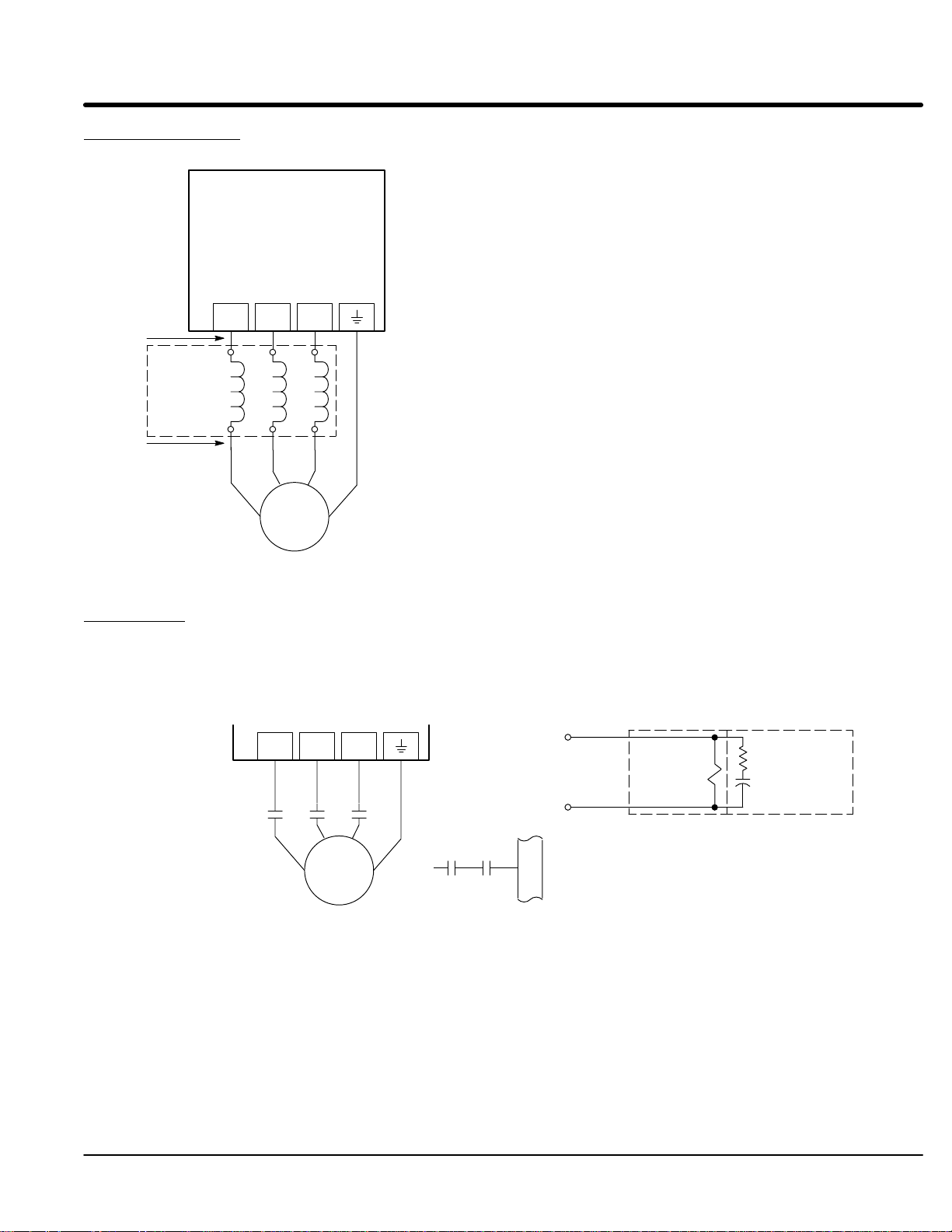
Motor Connections Motor connections are shown in Figure 3-5.
Figure 3-5 Motor Connections
Notes:
1. Metal conduit should be used. Connect conduits so the use of Load
Baldor
Series 22H
Control
T1 T2 T3
Note 1
A1 B1 C1
Reactor or RC Device does not interrupt EMI/RFI shielding.
2. See Line/Load Reactors described previously in this section.
3. Use same gauge wire for Earth ground as for L1, L2 and L3.
Note 2
Note 1
*Optional
Load
Reactor
A2 B2 C2
T2 T3
T1
* AC Motor
G
* Optional components not provided with 22H Control.
Note 3
See recommended terminal tightening torques in Section 7.
M-Contactor If required by local codes or for safety reasons, an M-Contactor (motor circuit contactor)
may be installed. However, incorrect installation or failure of the M-contactor or wiring
may damage the control. If an M-Contactor is installed, the control must be disabled for
at least 20msec before the M-Contactor is opened or the control may be damaged.
M-Contactor connections are shown in Figure 3-6.
Figure 3-6 Optional M-Contactor Connections
T1 T2 T3
MMM
M=Contacts of optional M-Contactor
T2 T3
T1
* Motor
To Power Source
(Rated Coil Voltage)
J1
*
M Enable
G
7
Note: Close “Enable”
8
after “M” contact closure.
9
* M-Contactor
See recommended terminal
tightening torques in Section 7.
* Optional
RC Device
Electrocube
RG1781-3
Receiving & Installation 3-15MN722
Page 27

Section 1
General Information
Encoder Installation Electrical isolation of the encoder shaft and housing from the motor is required. Electrical
isolation prevents capacitive coupling of motor noise that will corrupt the encoder signals.
Baldor provides shielded wire for encoder connection. Figure 3-7 shows the electrical
connections between the encoder and the encoder connector. Figure 3-8 shows the
connections between the encoder connector and J1 of the control.
Figure 3-7 Encoder Connections
J1
23
A
24
Electrically
Isolated
Encoder
Figure 3-8 Control Connections
Encoder End Control End
A J1-23
A J1-24
B J1-25
B J1-26
Index(C) J1-27
Index(C) J1-28
+5VDC J1-29
Common J1-30
Shield J1-30
25
26
27
28
29
30
A
B
B
C
C
+5V
COMMON
See recommended terminal
tightening torques in Section 7.
Single Ended Connections
Differential inputs are recommended for best noise immunity. If only single ended
encoder signals are available, connect them to A, B, and INDEX (C) (J1-23, J1-25 and
J1-27 respectively).
Buffered Encoder Output The control provides a buffered encoder output on pins J1-31 to J1-38. This output may
be used by external hardware to monitor the encoder signals. It is recommended that this
output only drive one output circuit load (a 26LS31 type device drives this output).
3-16 Receiving & Installation MN722
Page 28
Section 1
General Information
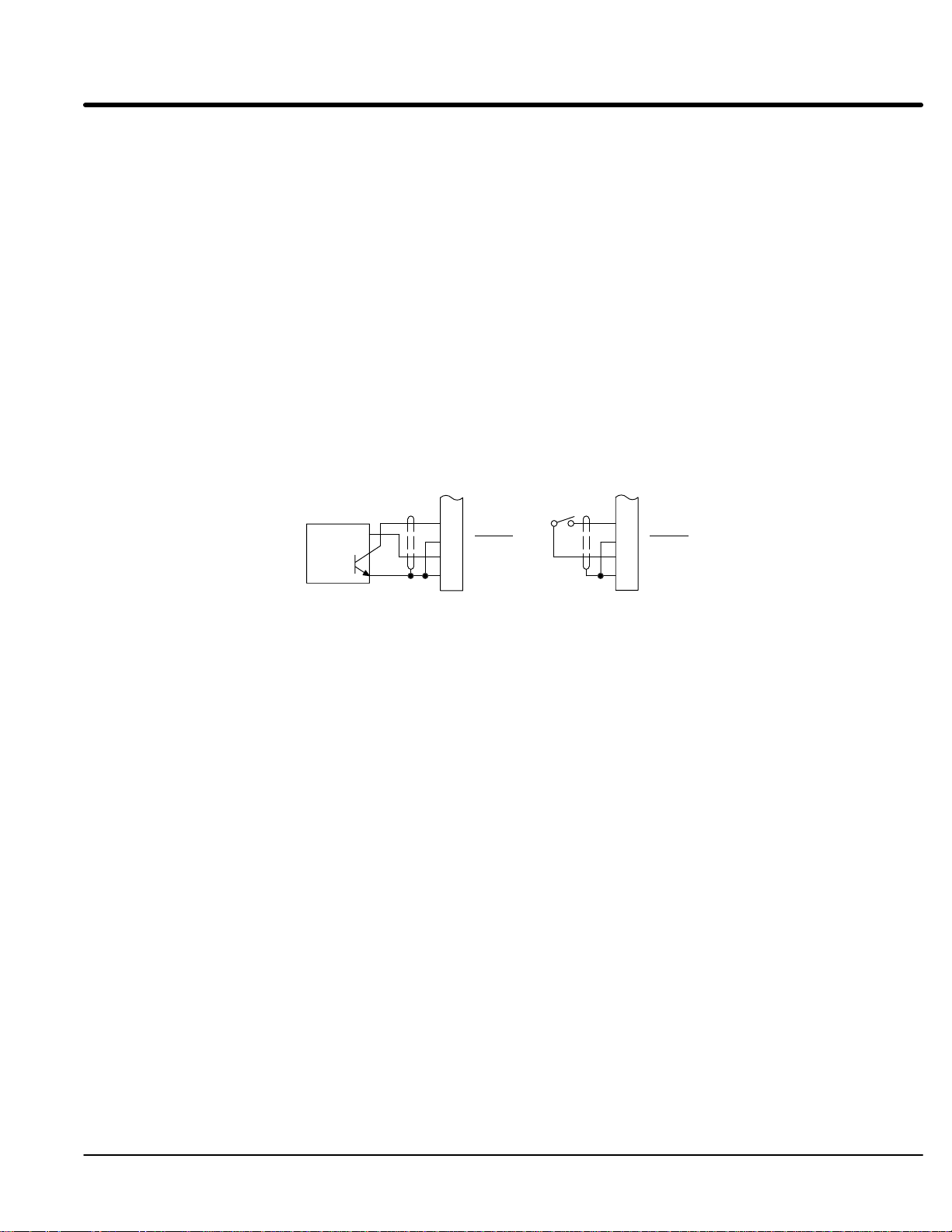
Home (Orient) Switch Input The Home or Orient function is active in the Bipolar and Serial modes and causes the
motor shaft to rotate to a predefined home position. The homing function allows shaft
rotation in the drive forward direction only. The home position is located when a machine
mounted switch or the encoder “Index” pulse is activated (closed). Home is defined by a
rising signal edge at terminal J1-27. The shaft will continue to rotate only in a “Drive
Forward” direction for a user defined offset value. The offset is programmed in the Level
2 Miscellaneous Homing Offset parameter. The speed at which the motor will “Home” or
orient is set with the Level 2 Miscellaneous Homing Speed parameter.
A machine mounted switch may be used to define the Home position in place of the
encoder index channel. A differential line driver output from a solid state switch is
preferred for best noise immunity. Connect this differential output to terminals J1-27 and
J1-28.
A single ended solid-state switch or limit switch should be wired as shown in Figure 3-9.
Regardless of the type of switch used, clean rising and falling edges at J1-27 are required
for accurate positioning.
Note: A control may require dynamic brake hardware for Orient (Homing) function to
work. The control may trip without dynamic brake hardware installed.
Figure 3-9 Typical Home or Orient Switch Connections
J1
J1
27
+5V Input
Output
Common
See recommended terminal tightening torques in Section 7.
28
29
30
INDEX
INDEX
+5V
Common
Limit Switch (Closed at HOME).5VDC Proximity Switch
27
28
29
30
INDEX
INDEX
+5V
Common
Example:
If the drive is operating in the forward direction when the “Orient” J1-11 input is closed,
the drive will decel at “DECEL #1” speed. Then continue in the forward direction at the
“Homing Speed” until the index pulse is received. The drive will continue past the int
index in the forward direction by the amount of the “Homing Offset”. The drive will then
stop and maintain position.
Receiving & Installation 3-17MN722
Page 29
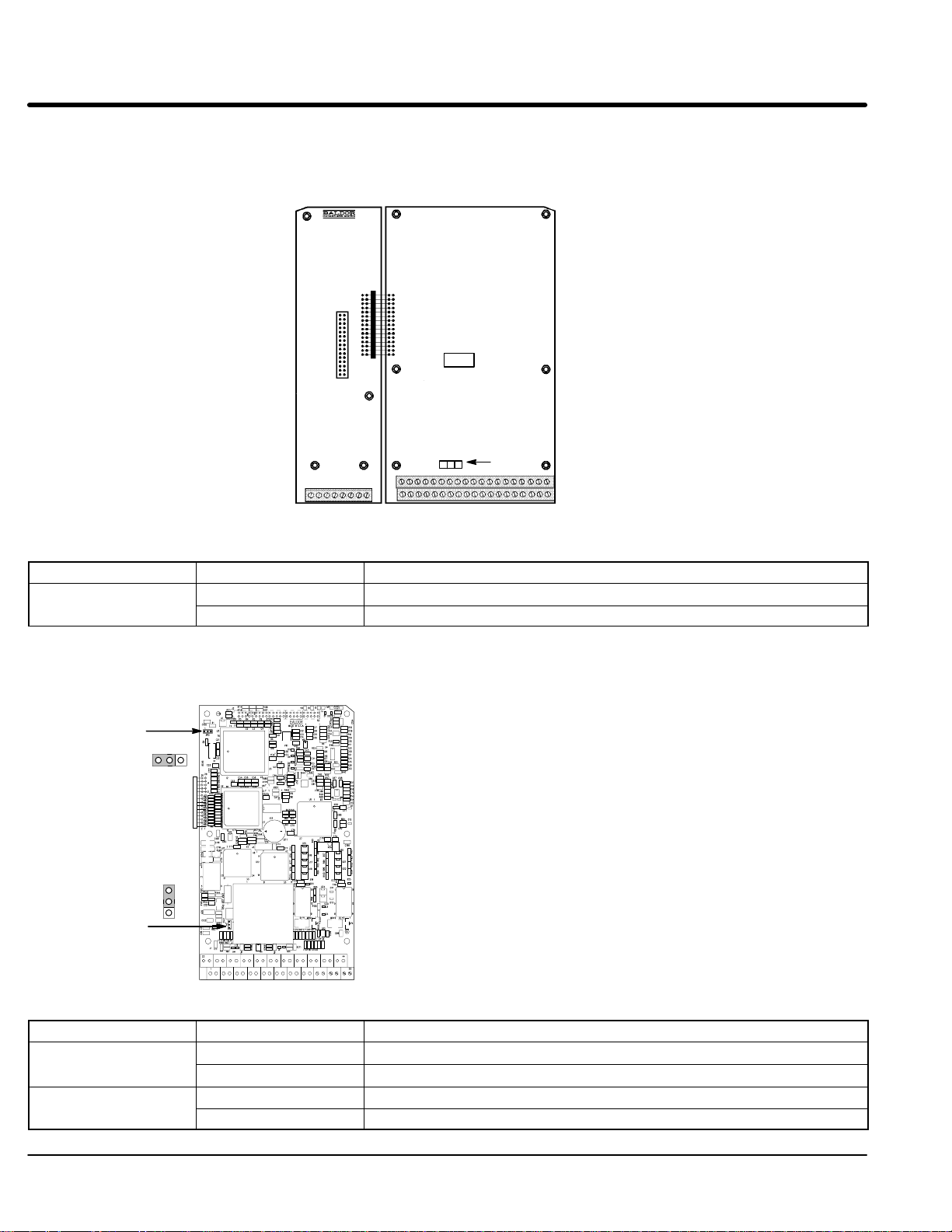
Control Board Jumpers
Converter Section Control Board
Figure 3-10 Converter Control Board Jumper JP1 Location
Expansion Board Motor Control Board
Keypad
Connector
321
JP1
See recommended terminal tightening
torques in Section 7.
Table 3-9 Converter Control Board Jumper
Jumper Jumper Position Description of Jumper Position Setting
JP1
1–2 Voltage Speed Command Signal. (Factory Setting)
2–3 4–20mA Speed Command Signal.
Inverter Section Control Board
Figure 3-11 Inverter Control Board Jumper Locations
JP2
123
Refer to Table 3-10
for jumper placement information.
123
JP1
See recommended terminal tightening torques in Section 7.
Table 3-10 Inverter Control Board Jumper
Jumper Jumper Position Description of Jumper Position Setting
JP1
JP2
3-18 Receiving & Installation MN722
1-2 Voltage Speed Command Signal. (Factory Setting)
2-3 4-20mA input at Analog #2
1-2 Factory Setting
2-3 Not used.
Page 30

Section 1
General Information
Analog Inputs Two analog inputs are available: analog input #1 (J1-1 and J1-2) and analog input #2
(J1-4 and J1-5) as shown in Figure 3-12. Either analog input may be selected in the
Level 1 INPUT block, Command Select parameter value. Analog input #1 is selected if
the parameter value is “Potentiometer”. Analog input #2 is selected if the parameter
value is “+/-10Volts, +/-5 Volts or 4-20mA”. Figure 3-13 shows the equivalent circuits of
the Analog Inputs.
Figure 3-12 Analog Inputs and Outputs
J1
Analog GND
Command Pot or
0-10VDC
±5VDC, ±10VDC or 4-20 mA Input
5KW
See recommended terminal tightening torques in Section 7.
Analog Input 1
Pot Reference
Analog Input +2
Analog Input -2
Analog Input #1 When using a potentiometer as the speed command, process feedback or setpoint
(Single Ended) source, the Level 1 Input block COMMAND SELECT parameter must be set to
“POTENTIOMETER”.
Note: A potentiometer value of 5kW to 10kW, 0.5 watt may be used.
Parameter Selection
The single ended analog input #1 can be used in one of three ways:
1. Speed or Torque command (Level 1 Input block, Command Select=Potentiometer).
2. Process Feedback (Level 2 Process Control block, Process Feedback=Potentiometer).
3. Setpoint Source (Level 2 Process Control block, Setpoint Source=Potentiometer).
When using Analog Input #1, the respective parameter must be set to
“POTENTIOMETER”.
1
2
3
4
5
Analog Input 1
Analog Input 2
Analog Input #2 Analog input #2 accepts a differential command 0-5VDC, 0-10VDC, ±5VDC, ±10VDC or
(Differential) 4-20 mA. If pin J1-4 is positive with respect to pin 5, the motor will rotate in the forward
direction. If pin J1-4 is negative with respect to pin 5, the motor will rotate in the reverse
direction. JP1 must be set for voltage or current operation as required. Analog Input #2
can be connected for single ended operation by grounding either of the inputs, provided
the common mode voltage range is not exceeded.
Note: The common mode voltage can be measured with a voltmeter. Apply the
maximum command voltage to analog input 2 (J1-4, 5). Measure the AC and
DC voltage across J1-1 to J1-4. Add the AC and DC readings together.
Measure the AC and DC voltage from J1-1 to J1-5. Add the AC and DC
readings together.
If either of these measurement totals exceeds a total of ±15 volts, then the
common mode voltage range has been exceeded. To correct this condition,
either change the command source or isolate the command signal with a
signal isolator.
Receiving & Installation 3-19MN722
Page 31

Section 1
General Information
J1
1
-15VDC
Figure 3-13 Analog Inputs Equivalent Circuits
30KW
.033 mF
5.1V Zener
Notes:
+
–
All OP Amps are TL082 or TL084
5KW
20KW
2
1.96KW
3
10KW 10KW
4
JP1
4-20mA
500W
X N/C
10KW
–
+
+15VDC
+
–
To Microprocessor
See recommended terminal tightening
torques in Section 7.
To Microprocessor
10KW
Analog Ground is separated from
Chassis Ground. Electrically they
are separated by an RC network.
5
Analog Outputs Two programmable analog outputs are provided on J1-6 and J1-7. See Figure 3-14.
These outputs are scaled 0 - 5 VDC (1mA maximum output current) and can be used to
provide real-time status of various control conditions. The output conditions are defined
in Table 4-4 of Section 4 of this manual.
The return for these outputs is J1-1 analog ground. Each output is programmed in the
Level 1 Output block.
Figure 3-14 Analog Outputs Equivalent Circuits
J1
1
Notes:
+
–
All OP Amps are TL082 or TL084
Analog Ground is separated from
Chassis Ground. Electrically they
are separated by an RC network.
See recommended terminal tightening
torques in Section 7.
From Microprocessor
From Microprocessor
10KW
.033 mf
10KW
.033 mf
+
–
10KW
+
–
10KW
50W
6
50W
7
3-20 Receiving & Installation MN722
Page 32

Section 1
General Information
Control Circuit Connections
There are two control boards in a Series 22H Vector Control. The Converter Control
Board is used to rectify and process the incoming power. The Inverter Control Board
provides the inverting and power output functions. The keypad is normally connected to
the Inverter Control Board. Each converter board has its own J1 terminal strip. The
Inverter Control Board provides the user interface for most external connections.
Converter Control Board Connections
All necessary connections for the Converter Control Board have been made at the factory
prior to shipment.
The jumper between J1-8 and J1-17 provides the enable signal to allow converter
operation. The jumper between J1-39 and J1-40 provides +24VDC from the internal
supply to allow the opto isolated input at J1-8 to operate. These jumpers should remain
installed at all times.
Sometimes it is necessary to troubleshoot the converter section using the isolated opto
outputs. Figure 3-15 shows how to connect external relays to the board to “Sink” or
“Source” the relay current.
The function of each opto output is as follows: (these functions cannot be changed)
J1-19 Ready
J1-20 At Voltage
J1-21 Fault
J1-22 Overtemperature Warning
24Com
Optional
Customer
Supplied
Relays &
Diodes
Using Internal Supply
(Sinking the Relay Current)
Note: Add appropriately rated
protective device for AC relay
(snubber) or DC relay (diode).
17
18
19
20
21
22
Figure 3-15 Converter Control Board Opto Output Wiring
39
41
42
43
44
+24VDC
24Com
See recommended terminal tightening torques in Section 7.
17
18
19
20
21
22
Using Internal Supply
(Sourcing the Relay Current)
39
41
42
43
44
+24VDC
Optional
Customer
Supplied
Relays &
Diodes
Receiving & Installation 3-21MN722
Page 33

Section 1
General Information
Inverter Control Board Connections
Ten operating modes are available in the Series 22H vector control. These operating
modes define the basic motor control setup and the operation of the input and output
terminals. After the circuit connections are completed, the operating mode is selected by
programming the Level 1 Input block, Operating Mode parameter.
Available operating modes include:
Each mode requires connections to the J1 terminal strip (except keypad and serial
modes, all connections are optional). The J1 terminal strip is shown in Figure 3-16. The
connection of each input or output signal is described in the following pages.
Refer to Analog Inputs
Refer to Analog Outputs
Refer to opto isolated Inputs
Refer to opto isolated Outputs
• Keypad Control
• Standard Run, 3 Wire Control
• 15 Speed, 2 Wire Control
• Three Speed, 2 Wire Control
• Three Speed, 3 Wire Control
• Serial
• Bipolar Speed or Torque
• Process Control
• EPOT, 2 Wire Control
• EPOT, 3 Wire Control
Figure 3-16 Control Signal Connections
J1
Analog GND
Analog Input 1
Pot Reference
Analog Input +2
Analog Input -2
Analog Out 1
Analog Out 2
Input #1
Input #2
Input #3
Input #4
Input #5
Input #6
Input #7
Input #8
Input #9
Opto In Common
Opto Out #1
Opto Out #2
Opto Out #3
Opto Out #4
See recommended terminal tightening torques in Section 7.
1
23
A
2
24
A
3
25
B
4
26
B
5
27
INDEX
6
28
INDEX
7
29
+5VDC
8
30
Common
9
31
A
10
32
A
11
33
B
12
34
B
13
35
INDEX
14
36
INDEX
15
37
Not Used
16
38
Common
17
39
18
40
19
41
Opto Out #1 Return
20
42
Opto Out #2 Return
21
43
Opto Out #3 Return
22
44
Opto Out #4 Return
Refer to Encoder Installation
Refer to Buffered Encoder Output
+24VDC
Opto In Power
J1-39 & 40 Jumper as shown to power
the opto inputs from the
internal +24VDC supply.
Note: J1-18 and J1-41 are connected
together on the control circuit
board.
Serial Mode The Serial operating mode requires one of the optional Serial Interface expansion boards
(RS232 or 422/485). Installation and operation information for these serial expansion
boards is provided in Serial Communications expansion board manual MN1310. This
manual is shipped with the serial expansion board.
3-22 Receiving & Installation MN722
Page 34

Section 1
General Information
Keypad Mode Connections The Keypad operating mode allows the control to be operated from the keypad. This
mode requires no connections to J1. However, the Enable, Stop and External Trip inputs
may optionally be used. All other opto inputs remain inactive. The analog outputs and
opto-outputs remain active at all times. See Figure 3-17.
Parameter Selection
For operation in Keypad mode, set the Level 1 Input block, Operating Mode parameter to
Keypad. The STOP key can operate in two ways:
Press STOP key one time to brake or coast to stop.
Press STOP key two times to disable control.
To use the Enable input, J1-8 must be connected and the Local Enable INP parameter in
the Level 2 Protection block must be set to ON. The Enable line is normally closed.
When opened, the motor will COAST to a stop. When the enable line is again closed, the
motor will not start until a new direction command is received from the keypad.
To use the Stop input, J1-11 must be connected and the Level 1 Keypad Setup block,
LOC. Hot Start parameter must be set to ON. The Stop line is normally closed. When
opened, the motor will COAST or REGEN to a stop depending upon the setting of Level 1
Keypad Setup block Keypad Stop Mode parameter value. Closing the input will
immediately start the motor.
The External Trip input causes a fault condition during a motor over temperature
condition (when normally closed input opens). The External Trip input (J1-16) must be
connected and the External Trip parameter in the Level 2 Protection block must be set to
“ON”. When J1-16 is opened, an external trip fault occurs. The control will disable and
the motor coasts to a stop. An external trip fault is displayed on the keypad display (also
logged into the fault log).
Figure 3-17 Keypad Control Connection Diagram
J1-8 If J1-8 is connected, you must set Level 2 Protection block, Local Enable INP
parameter to “ON” to activate the opto input.
CLOSED allows normal operation.
OPEN disables the control and motor coasts to a stop.
J1-11 If J1-11 is connected, you must set Level 1 Keypad Setup block,
Loc. Hot Start parameter to to “ON” to activate the opto input.
CLOSED allows normal operation.
OPEN motor decels to stop (depending on Keypad Stop mode). The motor
will restart when J1-11 closes after open (if the keypad FWD or REV key is
still pressed).
J1-16 If J1-16 is connected, you must set Level 2 Protection block, External Trip to
“ON” to activate the opto input.
CLOSED allows normal operation.
OPEN causes an external trip to be received by the control. The control will
disable and display external trip. When this occurs, the motor stop command
is issued, drive operation is terminated and an external trip fault is displayed
on the keypad display (also logged into the fault log).
Refer to Figure 3-26.
See recommended terminal tightening torques in Section 7.
No Connection
Enable
Stop
External Trip
Analog GND
Analog Input 1
Pot Reference
Analog Input +2
Analog Input -2
Analog Out 1
Analog Out 2
Input #1
Input #2
Input #3
Input #4
Input #5
Input #6
Input #7
Input #8
Input #9
Opto In Common
J1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
Receiving & Installation 3-23MN722
Page 35

Section 1
General Information
Standard Run 3 Wire Mode Connections
In Standard Run mode, the control is operated by the opto isolated inputs at J1-8 through
J1-16 and the analog command input. The opto inputs can be switches as shown in
Figure 3-18 or logic signals from another device. The external trip opto input at J1-16 is
active if connected as shown and the Level 2 Protection block, External Trip parameter is
set to ON.
For 4–20mA operation, refer to Table 3-10. Analog input 2 can then be used for 4–20mA
operation.
Figure 3-18 Standard Run 3-Wire Connection Diagram
J1-8 CLOSED allows normal control operation.
OPEN disables the control and motor coasts to a stop.
J1-9 MOMENTARY CLOSED starts motor operation in the Forward direction.
In JOG mode (J1-12 CLOSED), continuous CLOSED jogs motor in the
Forward direction.
J1-10 MOMENTARY CLOSED starts motor operation in the Reverse direction.
In JOG mode (J1-12 CLOSED), CONTINUOUS closed JOGS motor in the
Reverse direction.
J1-11 MOMENTARY OPEN causes motor to decel to stop (depending on Keypad
Stop Mode parameter setting). Motor current continues to be applied to the
motor.
J1-12 CLOSED places control in JOG mode, Forward and Reverse run are used
to jog the motor.
J1-13 CLOSED selects group 2.
OPEN selects ACC / DEC / S-CURVE group 1.
J1-14 CLOSED selects preset speed #1, (J1-12, will override this preset speed).
OPEN allows speed command from Analog input #1 or #2 or Jog.
J1-15 CLOSED to reset fault condition.
OPEN to run.
J1-16 If J1-16 is connected, you must set Level 2 Protection block, External Trip
to “ON” to activate the opto input.
CLOSED allows normal control operation.
OPEN causes an external trip to be received by the control. The control
will disable and display external trip. When this occurs, the motor stop
command is issued, drive operation is terminated and an external trip fault
is displayed on the keypad display (also logged into the fault log).
Command Pot or
0-10VDC
5KW
Programmable Output
Programmable Output
Refer to Figure 3-26.
See recommended terminal
tightening torques in Section 7.
Analog GND
Analog Input 1
Pot Reference
Analog Input +2
Analog Input -2
Analog Out 1
Analog Out 2
Enable
Forward Run
Reverse Run
Stop
Jog
Accel/Decel
Preset Speed #1
Fault Reset
External Trip
Opto In Common
J1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
3-24 Receiving & Installation MN722
Page 36

Section 1
General Information
15 Speed 2-Wire Mode Connections Switch Truth Table is defined in Table 3-11.
Operation in the 15 Speed 2-Wire mode is controlled by the Opto Isolated inputs at J1-8
through J1-16. The Opto inputs can be switches as shown in Figure 3-19 or logic signals
from another device.
Switched inputs at J1-11 through J1-14 allow selection of 15 preset speeds and provide
Fault Reset as defined in Table 3-11.
Figure 3-19 15 Speed 2-Wire Control Connection Diagram
J1-8 CLOSED allows normal control operation.
J1-9 CLOSED operates the motor in the Forward direction (with J1-10 open).
J1-10 CLOSED operates motor in the Reverse direction (with J1-9 open).
J1-11 to 14 Selects programmed preset speeds as defined in Table 3-11.
J1-15 Selects ACC/DEC group. OPEN selects group 1. CLOSED selects
J1-16 If J1-16 is connected, you must set Level 2 Protection block, External
OPEN disables the control and motor coasts to a stop.
OPEN motor decels to stop (depending on Keypad Stop mode parameter
setting).
OPEN motor decels to stop depending on Keypad Stop mode parameter
setting.
group 2.
Trip to “ON” to activate the opto input.
CLOSED allows normal control operation.
OPEN causes an external trip to be received by the control. The control
will disable and display external trip. When this occurs, the motor stop
command is issued, drive operation is terminated and an external trip
fault is displayed on the keypad display (also logged into the fault log).
See recommended terminal tightening torques in Section 7.
Programmable Output
Programmable Output
No Connection
Refer to Figure 3-26.
Analog Input +2
Analog Input -2
Accel/Decel/S Select 1
Opto In Common
Analog GND
Analog Input 1
Pot Reference
Analog Out 1
Analog Out 2
Enable
Forward Run
Reverse Run
Switch 1
Switch 2
Switch 3
Switch 4
External Trip
J1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
Table 3-11 Switch Truth Table for 15 Speed, 2 Wire Control Mode
Function J1-11 J1-12 J1-13 J1-14
Preset 1 Open Open Open Open
Preset 2 Closed Open Open Open
Preset 3 Open Closed Open Open
Preset 4 Closed Closed Open Open
Preset 5 Open Open Closed Open
Preset 6 Closed Open Closed Open
Preset 7 Open Closed Closed Open
Preset 8 Closed Closed Closed Open
Preset 9 Open Open Open Closed
Preset 10 Closed Open Open Closed
Preset 11 Open Closed Open Closed
Preset 12 Closed Closed Open Closed
Preset 13 Open Open Closed Closed
Preset 14 Closed Open Closed Closed
Preset 15 Open Closed Closed Closed
Fault Reset Closed Closed Closed Closed
Receiving & Installation 3-25MN722
Page 37

Section 1
General Information
3 Speed Analog 2 Wire Operating Mode
Allows selection of 3 preset speeds with 2 wire inputs. The opto inputs can be switches
as shown in Figure 3-20 or logic signals from another device.
The values of the preset speeds are set in the Level 1 Preset Speeds block, Preset
Speed #1, Preset Speed #2 and Preset Speed #3.
Figure 3-20 3 SPD ANA 2 Wire Control Connection Diagram
J1-8 CLOSED allows normal operation.
OPEN disables the control and the motor coasts to a stop.
J1-9 CLOSED operates the motor in the Forward direction (with J1-10 open).
OPEN motor decels to stop (depending on Keypad Stop mode).
J1-10 CLOSED operates the motor in the Reverse direction (with J1-9 open).
OPEN motor decels to stop (depending on Keypad Stop mode).
Note: Closing both J1-9 and J1-10 at the same time will reset a fault condition.
J1-11 CLOSED selects Analog Input #1.
OPEN selects Level 1 Input block, Command Select parameter.
Note: If Command Select (Level 1 Input block) is set to Potentiometer, then Analog
Input #1 is always selected regardless of this switch position.
J1-12 CLOSED selects STOP/START and Reset commands from terminal strip.
OPEN selects STOP/START and Reset commands from Keypad.
J1-13 CLOSED selects Level 1 Input block, Command Select parameter.
OPEN selects speed commanded from Keypad.
Note: When changing from Terminal Strip to Keypad (J1-12 or J1-13) the motor speed
and direction will remain the same after the change.
J1-14 Selects preset speeds as defined in the Speed Select Table (Table 3-12).
J1-15 Selects preset speeds as defined in the Speed Select Table (Table 3-12).
J1-16 If J1-16 is connected, you must set Level 2 Protection block, External Trip to “ON”
to activate the opto input.
CLOSED allows normal operation.
OPEN causes an external trip to be received by the control. The control will disable
and display external trip. When this occurs, the motor stop command is issued,
drive operation is terminated and an external trip fault is displayed on the keypad
display (also logged into the fault log).
Command Pot or
0-10VDC
5KW
Refer to Figure 3-26.
See recommended terminal
tightening torques in Section 7.
Analog GND
Analog Input 1
Pot Reference
Analog Input +2
Analog Input -2
Analog Out 1
Analog Out 2
Enable
Forward Run
Reverse Run
Analog Input Select
Run Command
Speed Command
Switch 1
Switch 2
External Trip
Opto In Common
J1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
Table 3-12 Speed Select Table
J1-14 J1-15 Command
OPEN
CLOSED
OPEN
CLOSED
OPEN
OPEN
CLOSED
CLOSED
3-26 Receiving & Installation MN722
Analog Input
(Command Select)
Preset #1
Preset #2
Preset #3
Page 38

Section 1
General Information
3 Speed Analog 3 Wire Operating Mode
Allows selection of 3 preset speeds with 3 wire inputs. The opto inputs can be switches
as shown in Figure 3-21 or logic signals from another device.
The values of the preset speeds are set in the Level 1 Preset Speeds block, Preset
Speed #1, Preset Speed #2 and Preset Speed #3.
Figure 3-21 3 SPD ANA 3 Wire Control Connection Diagram
J1-8 CLOSED allows normal operation.
OPEN disables the control and the motor coasts to a stop.
J1-9 MOMENTARY CLOSED starts motor operation in the Forward direction.
J1-10 MOMENTARY CLOSED starts motor operation in the Reverse direction.
Note: Closing both J1-9 and J1-10 at the same time will reset a fault condition.
J1-11 Momentary OPEN motor decels to stop (depending on Keypad Stop mode).
J1-12 CLOSED selects STOP/START and Reset commands from terminal strip.
OPEN selects STOP/START and Reset commands from Keypad.
J1-13 CLOSED selects Level 1 Input block, Command Select parameter.
OPEN selects speed commanded from Keypad.
Note: When changing from Terminal Strip to Keypad (J1-12 or J1-13) the motor
speed and direction will remain the same after the change.
J1-14 Selects preset speeds as defined in the Speed Select Table (Table 3-13).
J1-15 Selects preset speeds as defined in the Speed Select Table (Table 3-13).
J1-16 If J1-16 is connected, you must set Level 2 Protection block, External Trip to
“ON” to activate the opto input.
CLOSED allows normal operation.
OPEN causes an external trip to be received by the control. The control will
disable and display external trip. When this occurs, the motor stop command
is issued, drive operation is terminated and an external trip fault is displayed on
the keypad display (also logged into the fault log).
Command Pot or
0-10VDC
5KW
Refer to Figure 3-26.
See recommended terminal
tightening torques in Section 7.
Analog GND
Analog Input 1
Pot Reference
Analog Input +2
Analog Input -2
Analog Out 1
Analog Out 2
Enable
Forward Run
Reverse Run
Stop
Run Command
Speed Command
Switch 1
Switch 2
External Trip
Opto In Common
J1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
Table 3-13 Speed Select Table
J1-14 J1-15 Command
OPEN
CLOSED
OPEN
CLOSED
OPEN
OPEN
CLOSED
CLOSED
Analog Input
(Command Select)
Preset #1
Preset #2
Preset #3
Receiving & Installation 3-27MN722
Page 39

Section 1
General Information
Bipolar Speed and Torque Mode Connections
Provides bipolar speed or torque control. Also, you may store up to four (4) complete
sets of operating parameters. This is important if you wish to store and use different
acceleration rates, speed commands, jog speeds or to store tuning parameter values for
different motors etc. The opto inputs can be switches as shown in Figure 3-22 or logic
signals from another device.
Figure 3-22 Bipolar Speed or Torque Connection Diagram
J1-8 CLOSED allows normal operation.
OPEN disables the control & motor coasts to a stop.
J1-9 CLOSED to enable operation in the Forward direction.
OPEN TO DISABLE Forward operation (drive will brake to a stop if a Forward
command is still present).
Reverse operation is still possible if J1-10 is closed.
J1-10 CLOSED to enable operation in the Reverse direction.
OPEN to disable Reverse operation (drive will brake to a stop if a Reverse
command is still present).
Forward operation is still possible if J1-9 is closed.
Note: If J1-9 and J1-10 are both opened, the drive will brake to a stop.
J1-11 CLOSED causes the motor to rotate in the forward direction until the load
reaches a marker or external switch location.
OPEN allows normal operation.
J1-12 CLOSED puts the control in torque command mode.
OPEN puts the control in speed (velocity) command mode.
Note: If a stop command is issued while in the torque (current) mode, the
control will stop but will not maintain position (zero current). This is
different than zero speed operation for the velocity mode.
J1-13 & 14 Select from four parameter tables as defined in Table 3-14.
J1-15 Momentary CLOSED to reset fault condition.
OPEN allows normal operation.
J1-16 If J1-16 is connected, you must set Level 2 Protection block, External Trip to
“ON” to activate the opto input.
CLOSED allows normal operation.
OPEN causes an external trip to be received by the control. The control will
disable and display external trip. When this occurs, the motor stop command
is issued, drive operation is terminated and an external trip fault is displayed
on the keypad display (also logged into the fault log).
Command Pot or
0-10VDC
5KW
Refer to Figure 3-26.
See recommended terminal
tightening torques in Section 7.
Analog GND
Analog Input 1
Pot Reference
Analog Input +2
Analog Input -2
Analog Out 1
Analog Out 2
Enable
Forward Enable
Reverse Enable
Homing
Speed/Torque
Switch 1
Switch 2
Fault Reset
External Trip
Opto In Common
J1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
Table 3-14 Bipolar Mode Table Select Truth Table
Function J1-13 J1-14
Parameter Table #0 Open Open
Parameter Table #1 Closed Open
Parameter Table #2 Open Closed
Parameter Table #3 Closed Closed
Note: See multiple parameter sets.
3-28 Receiving & Installation MN722
Page 40

Section 1
General Information
Multiple Parameter Sets
The following procedure allows you to program up to four complete sets of parameter
values and to use these multiple parameter sets. When programming each parameter
set, use the ENTER key to accept and automatically save parameter values.
Note: The control can be programmed in the REMOTE mode with the drive enabled.
The control must be disabled to change the operating mode parameter and
the operating mode can not be stored in a parameter table.
1. If this is a new installation, do this procedure after the Pre-Operation Checklist
and Power-Up Procedures at the end of this section.
2. Set the Level 1 INPUT block, Operating Mode parameter value to BIPOLAR in
each of the parameter sets.
3. Set switches J1-13 and J1-14 to Parameter Table #0 (both switches open). Be
sure switches J1-9 and J1-10 are OPEN, J1-8 is CLOSED. Enter all parameter
values, and autotune as instructed in Section 3 of this manual. This creates
and saves the first parameter set which is numbered Table#0.
4. Set switches J1-13 and J1-14 to Parameter Table #1. Be sure switches J1-9
and J1-10 are OPEN, J1-8 is CLOSED. Enter all parameter values, and
autotune as instructed in Section 3 of this manual. This creates and saves the
second parameter set which is numbered Table#1.
5. Set switches J1-13 and J1-14 to Parameter Table #2. Be sure switches J1-9
and J1-10 are OPEN, J1-8 is CLOSED. Enter all parameter values, and
autotune as instructed in Section 3 of this manual. This creates and saves the
third parameter set which is numbered Table#2.
6. Set switches J1-13 and J1-14 to Parameter Table #3. Be sure switches J1-9
and J1-10 are OPEN, J1-8 is CLOSED. Enter all parameter values, and
autotune as instructed in Section 3 of this manual. This creates and saves the
final parameter set which is numbered Table#3.
7. Remember that to change the value of a parameter in one of the parameter
tables, you must first select the table using the switches. You cannot change a
value in a table until you have first selected that table.
Note: Preset speed does not apply to table select.
Receiving & Installation 3-29MN722
Page 41

Section 1
ËËËË
General Information
Process Mode Connections The process control mode provides an auxiliary closed loop general purpose PID set point
control. The process control loop may be configured in various ways and detailed
descriptions of the process mode are given in MN707 “Introduction to Process Control”.
The opto inputs can be switches as shown in Figure 3-23 or logic signals from another device.
Figure 3-23 Process Mode Connection Diagram
J1-8 CLOSED allows normal operation.
J1-9 CLOSED to enable operation in the Forward direction.
J1-10 CLOSED to enable operation in the Reverse direction.
J1-11 CLOSED = TABLE 1, OPEN = TABLE 0. (See multiple parameter sets.)
J1-12 CLOSED, the control is in torque command mode.
J1-13 CLOSED to enable the Process Mode.
J1-14 CLOSED places control in JOG mode. The control will only JOG in the forward
J1-15 CLOSED to reset a fault condition.
J1-16 If J1-16 is connected, you must set Level 2 Protection block, External Trip to “ON”
See recommended terminal tightening torques in Section 7.
OPEN disables the control & motor coasts to a stop.
OPEN TO DISABLE Forward operation (drive will brake to a stop if a Forward
command is still present). Reverse operation is still possible if J1-10 is closed.
OPEN to disable Reverse operation (drive will brake to a stop if a Reverse
command is still present). Forward operation is still possible if J1-9 is closed.
Note: If J1-9 and J1-10 are both opened, the drive will brake to a stop.
OPEN, the control is in speed (velocity) command mode.
Note: If a stop command is issued while in the torque (current) mode, the control
will stop but will not maintain position (zero current). This is different than
zero speed operation for the velocity mode.
direction.
OPEN to run.
to activate the opto input.
CLOSED allows normal operation.
OPEN causes an external trip to be received by the control. The control will
disable and display external trip. When this occurs, the motor stop command is
issued, drive operation is terminated and an external trip fault is displayed on the
keypad display (also logged into the fault log).
Command Pot or
0-10VDC
5KW
Analog Input +2
Analog Input -2
Forward Enable
Reverse Enable
Process Mode Enable
Opto In Common
Refer to Figure 3-26.
Table 3-15 Process Mode Input Signal Compatibility
Setpoint or
Feedforward
J1-1 & 2
J1-4 & 5
5V EXB
10V EXB
4-20mA EXB
3-15 PSI EXB
DC Tach EXB
EXB PULSE FOL
Serial EXB
J1-1 & 2 J1-4 & 5
5V EXB 10V EXB
Requires expansion board EXB007A01 (High Resolution Analog I/O EXB).
Requires expansion board EXB004A01 (4 Output Relays/3-15 PSI Pneumatic Interface EXB).
Requires expansion board EXB006A01 (DC Tachometer Interface EXB).
Requires expansion board EXB005A01 (Master Pulse Reference/Isolated Pulse Follower EXB).
Used for Feedforward only. Must not be used for Setpoint Source or Feedback.
Requires expansion board EXB001A01 (RS232 Serial Communication EXB). or
Requires expansion board EXB002A01 (RS422/RS485 High Speed Serial Communication EXB). or
Requires expansion board EXB012A01 (RS232/RS485 Serial Communication EXB).
Conflicting inputs. Do not use same input signal multiple times.
Conflicting level 1 or 2 expansion boards. Do not use!
Feedback
4-20mA
EXB
3-15 PSI
EXB
Analog GND
Analog Input 1
Pot Reference
Analog Out 1
Analog Out 2
Enable
Table Select
Speed/Torque
Fault Reset
External Trip
Tach EXB
Jog
DC
J1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
3-30 Receiving & Installation MN722
Page 42

Section 1
General Information
Electronic Pot 2 Wire Operating Mode
Provides speed Increase and Decrease inputs to allow EPOT operation with 2 wire
inputs. The opto inputs can be switches as shown in Figure 3-24 or logic signals from
another device. The values of the preset speeds are set in the Level 1 Preset Speeds
block, Preset Speed #1 or Preset Speed #2.
Figure 3-24 EPOT, 2 Wire Control Connection Diagram
J1-8 CLOSED allows normal operation.
OPEN disables the control and motor coasts to a stop.
J1-9 CLOSED starts motor operation in the Forward direction.
OPEN motor decels to stop (depending on Keypad Stop mode).
J1-10 CLOSED starts motor operation in the Reverse direction.
OPEN motor decels to stop (depending on Keypad Stop mode).
Note: Closing both J1-9 and J1-10 at the same time will reset a fault condition.
J1-11 Selects preset speeds as defined in the Speed Select Table (Table 3-16).
J1-12 Selects preset speeds as defined in the Speed Select Table (Table 3-16).
J1-13 CLOSED selects ACC / DEC / S-CURVE group 2.
OPEN selects ACC / DEC / S-CURVE group 1.
J1-14 Momentary CLOSED increases motor speed while contact is closed.
J1-15 Momentary CLOSED decreases motor speed while contact is closed.
J1-16 If J1-16 is connected, you must set Level 2 Protection block, External Trip
to “ON” to activate the opto input.
CLOSED allows normal operation.
OPEN causes an external trip to be received by the control. The control will
disable and display external trip. When this occurs, the motor stop
command is issued, drive operation is terminated and an external trip fault
is displayed on the keypad display (also logged into the fault log).
Command Pot or
0-10VDC
5KW
Refer to Figure 3-26.
Analog GND
Analog Input 1
Pot Reference
Analog Input +2
Analog Input -2
Analog Out 1
Analog Out 2
Enable
Forward Run
Reverse Run
Switch 1
Switch 2
Accel/Decel
Increase
Decrease
External Trip
Opto In Common
J1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
Table 3-16 Speed Select Table
J1-11 J1-12 Function
OPEN
CLOSED
OPEN
CLOSED
* Command Select refers to the Level 1 Command Select parameter.
OPEN
OPEN
CLOSED
CLOSED
Electronic Pot
Command Select *
Preset #1
Preset #2
See recommended terminal
tightening torques in Section 7.
Receiving & Installation 3-31MN722
Page 43

Section 1
General Information
Electronic Pot 3 Wire Control Mode
Provides speed Increase and Decrease inputs to allow EPOT operation with 3 wire
inputs. The opto inputs can be switches as shown in Figure 3-25 or logic signals from
another device.
Figure 3-25 EPOT, 3 Wire Control Connection Diagram
J1-8 CLOSED allows normal operation.
OPEN disables the control and motor coasts to a stop.
J1-9 Momentary CLOSED starts motor operation in the Forward direction.
J1-10 Momentary CLOSED starts motor operation in the Reverse direction.
Note: Closing both J1-9 and J1-10 at the same time will reset a fault condition.
J1-11 Momentary OPEN motor decels to stop (depending on Keypad Stop mode).
J1-12 CLOSED selects Level 1 Command Select parameter value.
OPEN selects EPOT.
J1-13 CLOSED selects ACC / DEC / S-CURVE group 2.
OPEN selects ACC / DEC / S-CURVE group 1.
J1-14 Momentary CLOSED increases motor speed while contact is closed.
J1-15 Momentary CLOSED decreases motor speed while contact is closed.
J1-16 If J1-16 is connected, you must set Level 2 Protection block, External Trip to
“ON” to activate the opto input.
CLOSED allows normal operation.
OPEN causes an external trip to be received by the control. The control will
disable and display external trip. When this occurs, the motor stop command
is issued, drive operation is terminated and an external trip fault is displayed
on the keypad display (also logged into the fault log).
Command Pot or
0-10VDC
Refer to Figure 3-26.
5KW
EPOT/Command Select
See recommended terminal
tightening torques in Section 7.
Analog GND
Analog Input 1
Pot Reference
Analog Input +2
Analog Input -2
Analog Out 1
Analog Out 2
Enable
Forward Run
Reverse Run
Stop
Accel/Decel
Increase
Decrease
External Trip
Opto In Common
J1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
3-32 Receiving & Installation MN722
Page 44

Section 1
General Information
External Trip Input To activate the External Trip input, the External Trip parameter in the programming
Protection Block must be set to “ON”.
Terminal J1-16 is available for connection to a normally closed thermostat or overload
relay in all operating modes as shown in Figure 3-26. The thermostat or overload relay
should be a dry contact type with no power available from the contact. If the motor
thermostat or overload relay activates the control will automatically shut down and give
an External Trip fault.
Connect the External Trip Input wires to J1-16 and J1-17. Do not place these wires in the
same conduit as the motor power leads.
Figure 3-26 Motor Temperature Relay
T1 T2 T3
Customer Provided
Source Voltage
Note: Add appropriately rated
protective device for AC relay
(snubber) or DC relay (diode).
External or remote motor
overload protection may
be required by National
Electrical Code or equivalent
MMM
See recommended terminal
tightening torques in Section 7.
T2
T1
* Motor
T3
G
Motor Thermostat Leads
*
CR1
Do not run these wires in
same conduit as motor
leads or AC power wiring.
Optional hardware. Must be ordered separately.
*
J1
16
17
External Trip
Opto-Isolated Inputs The equivalent circuit for the nine Opto inputs is shown in Figure 3-27. The function of
each input depends on the operating mode selected and are described previously in this
section. This Figure also shows the connections using the internal opto input Supply.
Figure 3-27 Opto-Input Equivalent Circuit (Using Internal Supply)
J1
Opto In #1
Opto In #2
Opto In #3
Opto In #4
Opto In #5
Opto In #6
Opto In #7
Opto In #8
Opto In #9
Opto In Common
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
+24VDC @ 200mA
(supply terminal 39).
Jumper terminals 39 to 40
(Factory Installed)
39
40
6.8K 6.8K 6.8K 6.8K 6.8K 6.8K 6.8K 6.8K 6.8K
See recommended terminal tightening torques in Section 7.
Receiving & Installation 3-33MN722
Page 45

Section 1
General Information
Figure 3-28 Opto-Input Equivalent Circuit (Using External Supply)
Opto In #1
Opto In #2
Opto In #3
Opto In #4
Opto In #5
Opto In #6
Opto In #7
Opto In #8
Opto In #9
* User VCC (-)
* User VCC (+)
J1
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
39
40
8
9
Opto In #1
Opto In #2
Opto In #3
Opto In #4
Opto In #5
Opto In #6
Opto In #7
Opto In #8
Opto In #9
* User VCC (+)
* User VCC (-)
Opto Inputs Closing to Ground Opto Inputs Closing to +VCC
J1
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
39
40
8
9
See recommended terminal
tightening torques in Section 7.
* User VCC = 10 - 30VDC
External Power Source
Opto-Isolated Outputs Four programmable Opto-isolated outputs are available at terminals J1-19 through J1-22.
See Figure 3-29. Each output may be programmed to represent one output condition.
The output conditions are defined in Table 4-4 of Section 4 of this manual.
The Opto-isolated outputs may be configured for sinking or sourcing 50 mA each.
However, all must be configured the same. The maximum voltage from opto output to
common when active is 1.0 VDC (TTL compatible). The Opto-isolated outputs may be
connected in different ways as shown in Figure 3-29. The equivalent circuit for the
Opto-isolated outputs is shown in Figure 3-30.
If the opto outputs are used to directly drive a relay, a flyback diode rated at 1A, 100 V
(IN4002) minimum should be connected across the relay coil. See Electrical Noise
Considerations in Section 5 of this manual.
Each Opto Output is programmed in the Output programming block.
Figure 3-29 Opto-isolated Output Configurations
Optional
Customer
Supplied
Relays &
Diodes
-
Optional Customer Supplied
10VDC to 30VDC Source
+
Optional
Customer
Supplied
Relays &
Diodes
(Sinking the Relay Current)
(Sinking the Relay Current)
24Com
17
18
19
20
21
22
Using Internal Supply
17
18
19
20
21
22
Using External Supply
See recommended terminal tightening torques in Section 7.
39
41
42
43
44
39
41
42
43
44
+24VDC
Optional Customer Supplied
10VDC to 30VDC Source
-
+
24Com
17
39
18
19
20
21
22
Using Internal Supply
(Sourcing the Relay Current)
17
41
42
43
44
39
18
19
20
21
22
Using External Supply
(Sourcing the Relay Current)
41
42
43
44
+24VDC
Optional
Customer
Supplied
Relays &
Diodes
Optional
Customer
Supplied
Relays &
Diodes
3-34 Receiving & Installation MN722
Page 46

Section 1
General Information
Figure 3-30 Opto-Output Equivalent Circuit
PC865
50mA max
See recommended terminal tightening torques in Section 7.
PC865
50mA max
PC865
50mA max
PC865
50mA max
J1
18
Opto Output 1
19
Opto Output 2
20
Opto Output 3
21
Opto Output 4
22
Opto Out 1 Return
41
Opto Out 2 Return
42
Opto Out 3 Return
43
Opto Out 4 Return
44
10 – 30VDC
Opto Outputs
Pre-Operation Checklist Check of Electrical Items
CAUTION: After completing the installation but before you apply power, be
sure to check the following items.
1. Verify AC line voltage at source matches control rating.
2. Inspect all power connections for accuracy, workmanship and tightness and
compliance to codes.
3. Verify control and motor are grounded to each other and the control is
connected to earth ground.
4. Check all signal wiring for accuracy.
5. Be certain all brake coils, contactors and relay coils have noise suppression.
This should be an R-C filter for AC coils and reverse polarity diodes for DC
coils. MOV type transient suppression is not adequate.
WARNING: Make sure that unexpected operation of the motor shaft during start
up will not cause injury to personnel or damage to equipment.
Check of Motor and Coupling
1. Verify freedom of motion of motor shaft.
2. Verify that motor coupling is tight without backlash.
3. Verify the holding brakes if any, are properly adjusted to fully release and set to
the desired torque value.
Receiving & Installation 3-35MN722
Page 47

Section 1
General Information
Power-Up Procedure This procedure will help get your system up and running in the Keypad mode quickly.
This will allow you to prove the motor and control operation. This procedure assumes
that the control and motor are correctly installed (see Section 3 for procedures) and that
you have an understanding of the keypad programming & operation procedures. It is not
necessary to wire the terminal strip to operate the motor in the Keypad mode.
Initial Conditions
Be sure the control and motor are wired according to the procedures described previously
in this manual. Become familiar with the keypad programming and keypad operation of
the control as described in Section 4 of this manual.
1. Disconnect the load (including coupling or inertia wheels) from the motor shaft if
possible.
2. Verify that all enable inputs to J1-8 are open.
3. Turn power on. Be sure no errors are displayed.
4. Set the Level 1 Input block, Operating Mode parameter to “KEYPAD”.
5. Set the Level 2 Output Limits block, “OPERATING ZONE” parameter as desired
(STD CONST TQ, STD VAR TQ, QUIET CONST TQ or QUIET VAR TQ).
6. Enter the following motor data in the Level 2 Motor Data block parameters:
Motor Voltage (Nameplate, VOLTS)
Motor Rated Amps (Nameplate, FLA)
Motor Rated Speed (Nameplate, RPM)
Motor Rated Frequency (Nameplate, HZ)
Motor Mag Amps (Nameplate, NLA)
Encoder Counts
7. At the Level 2 Motor Data, go to CALC Presets and select YES (using the up
arrow key). Press ENTER and let the control calculate the preset values for the
parameters that are required for control operation.
8. Disconnect the motor from the load (including coupling or inertia wheels). If the
load can not be disconnected, refer to Section 6 and manually tune the control.
After manual tuning, perform steps 10, 11, 15, 16 and 17.
WARNING: The motor shaft will rotate during this procedure. Be certain that
unexpected motor shaft movement will not cause injury to
personnel or damage to equipment.
9. At the Level 2 Autotune block, perform the following tests:
CMD OFFSET TRIM
CUR LOOP COMP
STATOR R1
FLUX CUR SETTING
ENCODER TESTS
SLIP FREQ TEST
10. Set the Level 2 Output Limits block, “MIN OUTPUT SPEED” parameter.
11. Set the Level 2 Output Limits block, “MAX OUTPUT SPEED” parameter.
12. Remove all power from the control.
13. Couple the motor to its load.
14. Turn power on. Be sure no errors are displayed.
15. Go to Level 2 Autotune block, and perform the SPD CNTRLR CALC test.
16. Run the drive from the keypad using one of the following: the arrow keys for
direct speed control, keypad entered speed or the JOG mode.
17. Select and program additional parameters to suit your application.
The control is now ready for use the in keypad mode. If a different operating mode is
desired, refer to Section 3 for control connection diagrams and Section 4 Programming
and Operation.
3-36 Receiving & Installation MN722
Page 48

Section 4
Programming and Operation
Overview The Series 22H Vector Line Regen Control has two control boards installed. The
“Converter Control Board” is used to rectify and process the incoming power. The
“Inverter Control Board” provides the inverting and power output functions. Each control
board has its own J1 terminal strip.
The Inverter Control Board normally has the keypad connected to it. The J1 terminal strip
of the Inverter Board provides the user interface for most external connections and
software parameters. The Inverter Control board is mounted above the Converter
Control Board.
The Converter Control Board is programmed at the factory and should not require
program changes. However, you can change the values of several parameters within the
firmware (refer to parameters in Appendix B). The J1 terminal strip of the Converter
Control Board is factory wired for normal operation.
The keypad must be plugged into the Converter Control Board to change parameter
values, or access the fault log or the diagnostic information of the Converter Control
Board. A sheet metal panel separates the two control boards and there is a small access
hole the the sheet metal panel to attach the keypad to the Converter Control Board. To
attach the keypad to the Converter control board, use the following procedure:
Keypad Installation in the Converter Control Board
1. Be sure all power is disconnected from the Series 22H Control. Wait at least 5
minutes for the bus capacitors to discharge before you proceed.
2. Open the Series 22H cover.
3. Remove the keypad from the Inverter Control Board (secured by 4 screws).
4. Remove the extension ribbon cable from its retaining strap (secured to the
sheet metal panel).
5. Connect one end of the ribbon cable into the keypad connector in the Converter
Control Board (through the access hole in the sheet metal panel).
6. Connect the other end of the ribbon cable to the keypad.
The control can now be powered up and the Converter Control Board can be
programmed or the fault log may be examined. To restore the keypad as factory
installed, use the following procedure:
Keypad Installation in the Inverter Control Board
1. Be sure all power is disconnected from the Series 22H Control. Wait at least 5
minutes for the bus capacitors to discharge before you proceed.
2. Remove the keypad from the ribbon cable and remove the ribbon cable from
the keypad connector in the Converter Control Board.
3. Store the extension ribbon cable in its retaining strap (secured to the sheet
metal panel).
4. Install the keypad on Inverter Control Board (secured by 4 screws).
5. Close and secure the Series 22H cover.
Programming & Operation 4-1MN722
Page 49

Section 1
General Information
Baldor Keypad The keypad is used to program the control parameters, operate the motor and monitor
the status and outputs of the control by accessing the display options, diagnostic menus
and the fault log.
Figure 4-1 Keypad
JOG - (Green) lights when Jog is active.
FWD - (Green) lights when FWD direction is commanded.
REV - (Green) lights when REV direction is commanded.
STOP - (Red) lights when motor STOP is commanded.
Indicator Lights
Keypad Display - Displays status
information during Local or Remote
operation. It also displays information
during parameter setup and fault or
Diagnostic Information.
PROG - Press PROG to enter the
program mode. While in the Program
mode the PROG key is used to edit a
JOG - Press JOG to select the
preprogrammed jog speed. After the
JOG key has been pressed, use the
FWD or REV keys to run the motor in the
direction that is needed. The JOG key is
only active in the Local mode.
FWD - Press FWD to initiate forward
rotation of the motor. This key is only
active in the Keypad or Local mode.
REV - Press REV to initiate reverse
rotation of the motor. This key is active
only in the Keypad or Local mode.
STOP - Press STOP one time to initiate
a stop sequence. Depending on the
setup of the control, the motor will either
ramp or coast to a stop. This key is
operational in all modes of operation
unless it has been disabled by the
Keypad Stop parameter in the Keypad
(programming) Setup Block. Press STOP
twice to disable control (coast to stop).
LOCAL - Press LOCAL to change
between the local (keypad) and remote
operation. When the control is in the
local mode all other external commands
to the J1 terminal strip will be ignored
with the exception of the external trip
input.
DISP - Press DISP to return to Display
mode from Programming mode. Provides
operational status and advances to the
next display menu item including the
diagnostic screens.
SHIFT - Press SHIFT in the program
mode to control cursor movement.
Pressing the SHIFT key once moves the
blinking cursor one character position to
the right. While in Program mode, a
parameter value may be reset to the
factory preset value by pressing the
SHIFT key until the arrow symbols at the
far left of the keypad display are flashing,
then press an arrow key. In the Display
mode the SHIFT key is used to adjust
the keypad contrast.
RESET - Press RESET to clear all fault
messages (in local mode). Can also be
used to return to the top of the block
programming menu without saving any
parameter value changes.
parameter setting.
- (UP Arrow).
Press to change the value of the
parameter being displayed. Pressing
increments the value to the next greater
value. Also, when the fault log or
parameter list is displayed, the key will
scroll upward through the list. In the
local mode pressing the key will
increase motor speed to the next greater
value.
ENTER - Press ENTER to save
parameter value changes and move
back to the previous level in the
programming menu. In the Display
mode the ENTER key is used to directly
set the local speed reference. It is also
used to select other operations when
prompted by the keypad display.
- (Down Arrow)
Press to change the value of the
parameter being displayed. Pressing
decrements the value to the next lesser
value. Also, when the fault log or
parameter list is displayed, the key will
scroll downward through the list. In the
local mode pressing the key will
decrease motor speed to the next lower
value.
4-2 Programming & Operation MN722
Page 50

Section 1
General Information
Display Mode The control is in the DISPLAY MODE at all times except when parameter values are
changed (Programming mode). The Keypad Display shows the status of the control as in
the following example.
Motor Status
Control Operation
Output Condition
Value and Units
The DISPLAY MODE is used to view operating status, Diagnostic INFO and the Fault
Log. The description of how to do these tasks are described on the following pages.
Adjusting Display Contrast When AC power is applied to the control, the keypad should display the status of the
control. If there is no visible display, use the following procedure to adjust the contrast of
the display.
(Contrast may be adjusted in display mode when motor is stopped or running)
Action Description Display Comments
Apply Power No visible display
Press DISP Key Places control in display mode
Press SHIFT SHIFT Allows display contrast
Press or Key
Press ENTER Saves level of contrast and exits
adjustment
Adjusts display intensity
Typical display
to display mode
Display Mode Screens
Action Description Display Comments
Apply Power Logo display for 5 seconds.
Display mode showing motor
speed.
Press DISP key Display mode showing custom
unit output rate.
Press DISP key Display Frequency
Press DISP key DIsplay Current
Press DISP key DIsplay Voltage
Press DISP key Combined DIsplay
Press DISP key Screen to enter Fault Log
Press DISP key Screen to enter Diagnostic Menu
Press DISP key Exit Display mode and return to
Motor Speed display
No faults present. Local keypad
mode. If in remote/serial mode,
press local for this display.
Output rate display will only
appear if Value At Speed
parameter is entered.
Programming & Operation 4-3MN722
Page 51

Section 1
General Information
Display Mode Continued
Display Screens & Diagnostic Information Access
Action Description Display Comments
Apply Power Logo display for 5 seconds.
Display mode showing motor
speed.
Press DISP key 6 times Scroll to Diagnostic Information
Press ENTER key Access diagnostic information. First Diagnostic Information
Press DISP key Display mode showing control
Press DISP key Display mode showing bus
Press DISP key Display mode showing %
Press DISP key Display mode showing opto
Press DISP key Display mode showing actual
Press DISP key Display mode showing operating
Press DISP key Display mode showing continuous
Press DISP key Display mode showing which
Press DISP key Display mode showing motor
Press DISP key Display mode showing parameter
screen
temperature.
voltage.
overload current remaining.
inputs & outputs states.
0=OPEN, 1=CLOSED.
drive running time.
zone, voltage and control type.
amps; PK amps rating; amps/volt
scale of feedback, power base ID.
Group1 or 2 expansion boards
are installed and recognized.
shaft revolutions from the REV
home set point.
table selected.
XXXV
No faults present. Local keypad
mode. If in remote/serial mode,
press local for this display.
Diagnostic Access screen.
screen.
Opto Inputs states (Left);
Opto Outputs states (Right).
HR.MIN.SEC format.
Typical display.
ID is displayed as a hexadecimal
value.
Press DISP key Display mode showing software
Press DISP key Displays exit choice. Press ENTER to exit diagnostic
version and revision installed in
the control.
information.
4-4 Programming & Operation MN722
Page 52

Section 1
General Information
Display Mode Continued
Fault Log Access When a fault condition occurs, motor operation stops and a fault code is displayed on the
Keypad display. The control keeps a log of up to the last 31 faults. If more than 31 faults
have occurred the oldest fault will be deleted from the fault log to make room for the
newest fault. To access the fault log perform the following procedure:
Action Description Display Comments
Apply Power Logo display for 5 seconds.
Display mode showing motor
speed.
Press DISP key 5 times Scroll to the Fault Log screen Fault Log access screen.
Press ENTER key Display first fault type and time
Press key
Press ENTER key Return to display mode. Display mode stop key LED is on.
fault occurred.
Scroll through fault messages.
Display mode.
1=Most recent fault displayed.
2=Second most recent fault, etc.
If no messages, the fault log exit
choice is displayed.
Programming & Operation 4-5MN722
Page 53

Section 1
General Information
Program Mode The Program Mode is used to:
1. Enter motor data.
2. CALC Presets and Autotune the drive.
3. Customize the drive (Control and Motor) parameters to your application.
From the Display Mode press the PROG key to access the Program Mode.
Note: When a parameter is selected, alternately pressing the Disp and Prog keys
will toggle between the Display Mode and the selected parameter. When a
parameter is selected for programming, the keypad display gives you the
following information:
Parameter
Parameter Status
Parameter Status. All programmable parameters are displayed with a “P:” in the lower
left corner of the keypad display. If a parameter is displayed with a “V:”, the parameter
value may be viewed but not changed while the control is enabled. If the parameter is
displayed with an “L:”, the value is locked and the security access code must be entered
before its’ value can be changed.
Parameter Blocks Access for Programming
Use the following procedure to access parameter blocks to program the control.
Value and Units
Action Description Display Comments
Apply Power Keypad Display shows this
Press PROG key Press ENTER to access Preset
Press or key
Press or key
Press ENTER key First Level 2 block display.
Press or key
Press ENTER key Return to display mode.
opening message.
If no faults and programmed for
LOCAL operation.
If no faults and programmed for
REMOTE operation.
Scroll to the ACCEL/DECEL
block.
Scroll to the Level 2 Block.
Scroll to Programming Exit menu.
Logo display for 5 seconds.
Display mode.
If fault is displayed, refer to the
Troubleshooting section of this
manual.
Speed parameters.
Press ENTER to access Accel
and Decel rate parameters.
Press ENTER to access Level 2
Blocks.
Press ENTER to return to Display
mode.
4-6 Programming & Operation MN722
Page 54

Section 1
General Information
Program Mode Continued
Changing Parameter Values when Security Code Not Used
Use the following procedure to program or change a parameter already programmed into
the control when a security code is not being used.
The example shown changes the operating mode from Keypad to Bipolar.
Action Description Display Comments
Apply Power Keypad Display shows this
opening message.
Logo display for 5 seconds.
If no faults and programmed for
LOCAL operation.
Press PROG key Access programming mode.
Press or key
Press ENTER key Access Input Block. Keypad mode shown is the
Press ENTER key Access Operating Mode
Press key
Press ENTER Save selection to memory. Press ENTER to save selection.
Press key
Press ENTER key Return to Input Block.
Press DISP key Return to Display Mode. Typical display mode.
Scroll to Level 1 Input Block.
parameter.
Scroll to change selection.
Scroll to menu exit.
Display mode. Stop LED on.
Press ENTER to access INPUT
block parameter.
factory setting.
Keypad mode shown is the
factory setting.
At flashing cursor, select desired
mode, BIPOLAR in this case.
Programming & Operation 4-7MN722
Page 55

Section 1
General Information
Program Mode Continued
Reset Parameters to Factory Settings
Sometimes it is necessary to restore the parameter values to the factory settings. Follow
this procedure to do so. Be sure to change the Level 2 Motor Data block “Motor Rated
Amps” to the correct value after this procedure (restored factory setting is 999).
Note: All specific application parameters already programmed will be lost when
resetting the control to factory settings.
Note: After factory settings are restored, the drive must be re-tuned.
Action Description Display Comments
Apply Power Keypad Display shows this
opening message.
Logo display for 5 seconds.
If no faults and programmed for
LOCAL operation.
Press PROG key Enter program mode.
Press or key
Press ENTER key Select Level 2 Blocks.
Press or key
Press ENTER key Select Miscellaneous block.
Press key
Press ENTER key Access Factory Settings
Press key
Press ENTER key Restores factory settings. “Loading Presets” is first message
Press key
Scroll to Level 2 Blocks.
Scroll to the Miscellaneous block.
Scroll to Factory Settings
parameter.
parameter.
Scroll to YES, to choose original
factory settings.
Scroll to menu exit.
Display mode. Stop LED on.
represents blinking cursor.
“Operation Done” is next
“No” is displayed last.
Press ENTER key Return to Level 1 blocks. Exit Level 2 blocks.
Press or key
Press ENTER key Return to display mode. Display mode. Stop LED on.
Scroll to Programming exit.
Exit Programming mode and
return to Display mode.
4-8 Programming & Operation MN722
Page 56

Section 1
General Information
Program Mode Continued
Initialize New Firmware
After new firmware is installed, the control must be initialized to the new firmware version
and memory locations. Use the following procedure to Initialize the firmware.
Action Description Display Comments
Apply Power Keypad Display shows this
opening message.
Logo display for 5 seconds.
If no faults and programmed for
LOCAL operation.
Press PROG key Enter program mode.
Press or key
Press ENTER key Select Level 2 Blocks.
Press or key
Press ENTER key Select Miscellaneous block.
Press key
Press ENTER key Access Factory Settings
Press key
Press ENTER key Restores factory settings. “Loading Presets” is first message
Press key
Scroll to Level 2 Blocks.
Scroll to the Miscellaneous block.
Scroll to Factory Settings
parameter.
parameter.
Scroll to YES, to choose original
factory settings.
Scroll to menu exit.
Display mode. Stop LED on.
represents blinking cursor.
“Operation Done” is next
“No” is displayed last.
Press ENTER key Return to display mode. Display mode. Stop LED on.
Press DISP key several
times
Press ENTER key Access diagnostic information. Displays commanded speed,
Press DISP key Display mode showing software
Press DISP key Displays exit choice. Press ENTER to exit diagnostic
Scroll to diagnostic information
screen.
version and revision installed in
the control.
If you wish to verify the software
version, enter diagnostic info.
direction of rotation, Local/
Remote and motor speed.
Verify new firmware version.
information.
Programming & Operation 4-9MN722
Page 57

Section 1
General Information
Parameter Definitions
Converter Control Board Parameters
Converter section parameters are programmed at the factory. Table 4-1 is a list of the
parameters that can be changed. However, to make any parameter adjustments the
keypad must be installed in the Converter Control Board as described previously in this
section. Each Converter section parameter is defined in Table 4-2.
Table 4-1 Converter Section Parameter List
LEVEL 1 BLOCKS
Miscellaneous
Factory Settings
Line Inductor
Bus Capacitance
DAC Selection
Security Control
Security State
Access Timeout
Access Code
4-10 Programming & Operation MN722
Page 58

Section 1
General Information
Table 4-2 Converter Control Board Parameter Definitions
Block Title Parameter Description
MISC Factory Settings Restores factory settings for converter section parameters. Select YES and press
Line Inductor
(Boost
Regulator)
Bus Capacitance Sets the nominal DC Bus capacitance. This parameter sets the voltage loop gain for the
DAC Selection This parameter configures both Analog Outputs #1 (J1-6) and #2 (J1-7) at the same time
SECURITY
CONTROL
Security State Off - No security Access Code required to change parameter values.
Access Timeout The time in seconds the security access remains enabled after leaving the programming
Access Code A 4 digit number code. Only persons that know the code can change secured Level 1
ENTER to restore factory parameter values. The Keypad Display will show
“Operation Done” then return to “NO” when complete.
The value of the internal or external boost regulator inductor in “mH”. This parameter
sets the current loop gain of the converter section. This value is factory set and
should not require adjustment.
converter section. This value is factory set and should not require adjustment unless
more capacitance or more controls are added across the DC Bus.
for troubleshooting purposes.
AB BC Cross- This selection provides a scaled 0-5VDC signals at Outputs #1 and #2.
Analog Output #1 represents the Line-Line voltage (L1–L2).
Analog Output #2 represents the Line-Line voltage (L2–L3).
DQ CONTRLR- This selection provides a scaled 0-5VDC signals at Outputs #1 and #2.
Analog Output #1 represents the Direct Control voltage.
Analog Output #2 represents the Quadrature Control voltage.
DQ Currents- This selection provides a scaled 0-5VDC signals at Outputs #1 and #2.
Analog Output #1 represents the Direct Control current.
Analog Output #2 represents the Quadrature Control current.
IQ Command-This selection provides a scaled 0-5VDC signals at Outputs #1 and #2.
Analog Output #1 represents the Quadrature Command signal.
Analog Output #2 represents the Quadrature Feedback signal.
IB and IC- This selection provides a scaled 0-5VDC signals at Outputs #1 and #2.
Analog Output #1 represents the Phase B current feedback.
Analog Output #2 represents the Phase C current feedback.
Va and Vb- This selection provides a scaled 0-5VDC signals at Outputs #1 and #2.
Analog Output #1 represents the PWM voltage for Phase A.
Analog Output #2 represents the PWM voltage for Phase B.
Ia and Ib- This selection provides a scaled 0-5VDC signals at Outputs #1 and #2.
Analog Output #1 represents Phase A current.
Analog Output #2 represents Phase B current.
Local - Requires security Access Code to be entered (using the keypad) before
parameter changes can be made using the Keypad.
Serial - Requires security Access Code to be entered (over the Serial Link) before
parameter changes can be made using the Serial Link.
Total - Requires security Access Code to be entered (using Keypad or Serial Link)
before parameter changes can be made using the Keypad or serial link.
Note: If security is set to Local, Serial or Total you can press PROG and scroll
through the parameter values and view their values but you are not allowed
to change their values unless you enter the correct access code.
mode. If you exit and go back into the program Mode within this time limit, the
security Access Code does not have to be re-entered. This timer starts when leaving
the Program Mode (by pressing DISP).
Note: This feature is not available when using the Serial operating mode or if
power is cycled.
and Level 2 parameter values.
Note: Please record your access code and store it in a safe place. If you cannot
gain entry into parameter values to change a protected parameter, please
contact Baldor. Be prepared to give the 5 digit code shown on the lower
right side of the Keypad Display at the Security Control Access Code
parameter prompt.
Programming & Operation 4-11MN722
Page 59

Section 1
General Information
Inverter Control Board Parameters (Version 3.20)
To make programming easier, parameters have been arranged into the two level structure shown in
Table 4-3. Press the PROG key to enter the programming mode and the “Preset Speeds”
programming block will be displayed. Use the Up () and Down () arrows to scroll through the
parameter blocks. Press ENTER to access parameters within a programing block.
Tables 4-4 and 4-5 provide an explanation of each parameter. A complete Parameter Block Values
list is located at the end of this manual. This list defines the programmable range and factory preset
value for each parameter. The list has a space to record your settings for future reference.
Table 4-3 Inverter Section Parameter List
LEVEL 1 BLOCKS
Preset Speeds Input Output Limits Motor Data – Continued
Preset Speed #1 Operating Mode Operating Zone Resolver Speeds
Preset Speed #2 Command Select Min Output Speed CALC Presets
Preset Speed #3 ANA CMD Inverse Max Output Speed
Preset Speed #4 ANA CMD Offset PK Current Limit Brake Adjust
Preset Speed #5 ANA 2 Deadband PWM Frequency Resistor Ohms
Preset Speed #6 ANA1 CUR Limit CUR Rate Limit Resistor Watts
Preset Speed #7 DC Brake Current
Preset Speed #8 Output Custom Units
Preset Speed #9 Opto Output #1 Decimal Places Process Control
Preset Speed #10 Opto Output #2 Value at Speed Process Feedback
Preset Speed #11 Opto Output #3 Units of Measure Process Inverse
Preset Speed #12 Opto Output #4 Setpoint Source
Preset Speed #13 Zero SPD Set PT Protection Setpoint Command
Preset Speed #14 At Speed Band Overload Set PT ADJ Limit
Preset Speed #15 Set Speed External Trip Process ERR TOL
Analog Out #1 Local Enable INP Process PROP Gain
Accel / Decel Rate Analog Out #2 Following Error Process INT Gain
Accel Time #1 Analog #1 Scale Torque Proving Process DIFF Gain
Decel Time #1 Analog #2 Scale Follow I:O Ratio
S-Curve #1 Position Band Miscellaneous Follow I:O OUT
Accel Time #2 Restart Auto/Man Master Encoder
Decel Time #2 Vector Control Restart Fault/Hr
S-Curve #2 Ctrl Base Speed Restart Delay Communications Protocol
Feedback Filter Factory Settings Protocol
Jog Settings Feedback Align Homing Speed Baud Rate
Jog Speed Current PROP Gain Homing Offset Drive Address
Jog Accel Time Current INT Gain
Jog Decel Time Speed PROP Gain Security Control Auto-Tuning
Jog S-Curve Time Speed INT Gain Security State CALC Presets
Speed DIFF Gain Access Timeout CMD Offset Trim
Keypad Setup Position Gain Access Code CUR Loop Comp
Keypad Stop Key Slip Frequency Flux CUR Setting
Keypad Stop Mode Stator R1 Motor Data Feedback Test
Keypad Run Fwd Stator X1 Motor Voltage Slip Freq Test
Keypad Run Rev Prop Gain #1 Motor Rated Amps SPD CNTRLR CALC
Keypad Jog Fwd Int Gain #1 Motor Rated SPD
Keypad Jog Rev Motor Rated Freq
Local Hot Start Motor Mag Amps
Encoder Counts
LEVEL 2 BLOCKS
4-12 Programming & Operation MN722
Page 60

Section 1
General Information
Table 4-4 Inverter Control Board Level 1 Parameter Definitions
Block Title Parameter Description
PRESET
SPEEDS
ACCEL/DECEL
RATE
JOG SETTINGS Jog Speed Jog Speed is the programmed speed used during for jog. Jog can be initiated from the
Preset Speeds
#1 – #15
Allows selection of 15 predefined motor operating speeds.
Each speed may be selected using external switches connected to J1-11, J1-12,
J1-13 and J1-14 when Operating Mode is set to 15 Speed.
For motor operation, a motor direction command must be given along with a preset
speed command.
Accel Time #1,2 Accel time is the number of seconds required for the motor to increase at a linear rate
from 0 RPM to the RPM specified in the “Max Output Speed” parameter in the Level 2
Output Limits block.
Output Limits block.
Decel Time #1,2
Decel time is the number of seconds required for the motor to decrease at a linear rate
from the speed specified in the “Max Output Speed” parameter to 0 RPM.
S-Curve #1,2 S-Curve is a percentage of the total Accel and Decel time and provides smooth starts
and stops. Half of programmed S-Curve % applies to Accel and half to Decel ramps.
0% represents no “S” and 100% represents full “S” with no linear segment.
Note: Accel #1, Decel #1 and S-Curve #1 are associated together. Likewise,
Accel #2, Decel #2 and S-Curve #2 are associated together. These
associations can be used to condition any Preset Speed or External Speed
command.
Note: If drive faults occur during rapid Accel or Decel, selecting an S-curve may
eliminate the faults.
keypad or terminal strip. At the Keypad, press the JOG key then press and hold the
FWD or REV. For Standard Run, close the JOG input (J1-12) then close and maintain
the direction input (J1-9 or J1-10).
Jog Accel Time
Jog Decel Time
Jog S-Curve
0%
Curve
20
%
Output Speed
0
Accel Time
Accel S-Curves
40%
Curve
Process Control mode operation is different. If the terminal strip Process Mode
Enable input (J1-13) is closed, pressing the Keypad JOG key (or closing J1-14) will
cause the drive to move in the direction of the error (without pressing FWD or REV).
Jog Accel Time changes the slope of the jog accel ramp. It is the time from zero speed
to maximum speed programmed in seconds.
Jog Decel Time changes the slope of the jog decel ramp. It is the time from maximum
speed to zero speed programmed in seconds.
Jog S-Curve changes the S-Curve to a preset value for jog mode.
Figure 4-2 40% S-Curve Example
40%
Curve
20
%
20
%
Output Speed
0
Decel S-Curves
0%
Curve
Decel Time
20
%
Programming & Operation 4-13MN722
Page 61

Section 1
General Information
Table 4-4 Inverter Control Board Level 1 Parameter Definitions - Continued
Block Title Parameter Description
KEYPAD SETUP Keypad Stop Key
Keypad Stop Mode
Keypad Run FWD
Keypad Run REV
Keypad Jog FWD
Keypad Jog REV
Loc. Hot Start
INPUT Operating Mode
Command Select
ANA CMD Inverse “OFF” will cause a low input voltage (e.g. 0VDC) to be a low motor speed command and
ANA CMD Offset Provides an offset to the Analog Input to minimize signal drift. For example, if the
ANA 2 Deadband
ANA 1 CUR Limit
Stop Key - Allows keypad “STOP” key to initiate motor stop during remote or serial
Stop Mode - Selects if the Stop command causes the motor to “COAST” to a stop or
Run FWD - ON makes the keypad “FWD” key active in Local mode.
Run REV - ON makes the keypad “REV” key active in Local mode.
Jog FWD - ON makes the keypad “FWD” key active in Local Jog mode.
Jog REV - ON makes the keypad “REV” key active in Local Jog mode.
Loc. Hot Start OFF disables the Stop input at J1-11 in the keypad operating mode.
Ten “Operating Modes” are available. Choices are: Keypad, Standard Run, 15SPD, 3
SPD ANA 2 Wire, 3 SPD ANA 3 Wire, Serial, Bipolar, Process, EPOT 2 Wire and
EPOT 3 Wire. External connections to the control are made at the J1 terminal strip
(wiring diagrams are shown in Section 3 “Operating Modes”).
Selects the external speed reference to be used. The easiest method of speed control is
to select POTENTIOMETER and connect a 5KW pot to J1-1, J1-2, and J1-3. ±5, ±10VDC
or 4-20mA input command can be applied to J1-4 and J1-5.
If long distance is required between the external speed control and the control, the 4-20mA
selections at J1-4 and J1-5 should be considered. Current loop allows long cable lengths
without attenuation of the command signal.
10 VOLT W/T ORQ FF - when a differential command is present at J1-4 and 5, allows addi-
tional 5V torque feedforward input at J1-1, 2 and 3 to set a predetermined amount of
torque inside the rate loop with high gain settings.
EXB PULSE FOL - selects optional Master Pulse Reference/Isolated Pulse Follower ex-
pansion board if installed.
5VOLT EXB - selects optional High Resolution I/O expansion board if installed.
10VOLT EXB - selects optional High Resolution I/O expansion board if installed.
4–20mA EXB – selects the 4–20mA input of the optional High Resolution I/O expansion
board if installed.
3-15 PSI EXB selects optional 3-15 PSI expansion board if installed.
Tachometer EXB- selects optional DC Tachometer expansion board if installed.
Serial -selects optional Serial Communications expansion board if installed.
None - Used in Process Control mode, two input configuration with no Feedforward input.
Note: When using the 4-20mA input, the JP1 jumper on the main control board
a maximum input voltage (e.g. 10VDC) to be a maximum motor speed command.
“ON” will cause a low input voltage (e.g. 0VDC) to be a maximum motor speed command
and a maximum input voltage (e.g. 10VDC) to be a low motor speed command.
minimum speed signal is 1VDC (instead of 0VDC) the ANA CMD Offset can be set to
-10% so the minimum voltage input is seen by control as 0VDC.
Allows a defined range of voltage to be a deadband. A command signal within this
range will not affect the control output. The deadband value is the voltage above and
below the zero command signal level.
“OFF” Allows normal control operation.
“ON” Allows the 5V input at J1-2 (referenced to J1-1) to be used for reduction of the
programmed current limit parameter for torque trimming during operation.
operation (if Stop key is set to Remote ON). If active, pressing “STOP”
automatically selects Local mode and initiates the stop command.
“REGEN” to a stop. In COAST, the motor is turned off and allowed to
coast to a stop. In REGEN, the voltage and frequency to the motor is
reduced at a rate set by “Decel Time”.
ON enables the Stop input at J1-11 in the keypad operating mode.
must be moved to pins 2 and 3.
4-14 Programming & Operation MN722
Page 62

Section 1
General Information
Table 4-4 Inverter Control Board Level 1 Parameter Definitions - Continued
Block Title Parameter Description
OUTPUT OPTO OUTPUT
#1 – #4
Zero SPD Set PT Sets the speed at which the Zero Speed opto output becomes active (turns on). When the
At Speed Band The At Speed Band serves two Opto Output Conditions and the Level 2 Protection block
Set Speed Sets the speed that the AT Set Speed opto output becomes active (turns on). When the
Four optically isolated digital outputs that have two operating states, logical High or Low.
Each output may be configured to any of the following conditions:
Condition Description
Ready - Active when power is applied and no faults are present.
Zero Speed - Active when motor RPM is below the value of the Level 1 Output
At Speed - Active when output speed is within the speed range defined by
At Set Speed - Active when output speed is at or above the Level 1 Output
Overload - Active during an Overload fault caused by a time out when
Keypad Control - Active when control is in Local keypad control.
Fault - Active when a fault condition is present.
Following ERR - Active when the motor speed is outside the user specified
Motor Direction - Active High when REV direction feedback is sensed. Active Low
Drive On - Active when control is “Ready” (has reached excitation level and
CMD Direction - Active when Forward or Reverse is selected or enabled. Logical
AT Position - Active during an internal positioning command when control is
Over Temp Warn - Active when control heat sink is within 3°C of Int Overtemp.
Process Error - Active when process feedback signal is outside the Level 2
Drive Run - Active when drive is Ready, Enabled, Speed or Torque command
Serial – Active when in Serial mode.
speed is less than the ZERO SPD SET PT, the Opto Output becomes active. This is useful when a motor brake is to interlock operation with a motor.
Following Error:
Sets the speed range in RPM at which the At Speed opto output turns on and remains
active within the range.
Sets the Following Error Tolerance Band for the Level 1 OUTPUT, Opto Output condition
Following ERR. The opto output is active if the motor speed is outside this band.
Sets the allowable following error speed band. This value is used by the Level 2
Protection block, Following Error parameter (if it is set to ON). If the drive speed falls
out of this band, the Level 2 Protection block, Following Error parameter will shut
down the drive (if it is set to ON).
speed is greater than the Level 1 Output SET SPEED parameter, the Opto Output
becomes active. This is useful when another machine must not start or stop until the
motor exceeds a predetermined speed.
“Zero SPD Set Pt” parameter.
the Level 1 Output “At Speed Band” parameter.
“Set Speed” parameter.
output current is greater than Rated Current.
tolerance band defined by the At Speed Band parameter.
when FWD direction feedback is sensed.
capable of producing torque).
output state indicates Forward or Reverse direction. High=FWD,
Low=REV.
within the position band parameter tolerance.
Process Control block, PROC ERR TOL parameter value. Turns
off when process feedback error is within tolerance.
received with FWD/REV direction issued.
Programming & Operation 4-15MN722
Page 63

Section 1
General Information
Table 4-4 Inverter Control Board Level 1 Parameter Definitions - Continued
Block Title Parameter Description
OUTPUT
(Continued)
Analog Output
#1 and #2
Analog #1 Scale &
Analog #2 Scale
Position Band Sets the acceptable range in digital counts (pulses) at which the AT Position Opto
Two Analog 0-5VDC linear outputs may be configured to represent any of 19 conditions
Condition Description
ABS Speed - Represents the absolute motor speed where 0VDC = 0 RPM and
ABS Torque - Represents the absolute value of torque where
Speed Command - Represents the absolute value of commanded speed where
PWM Voltage - Represents the amplitude of PWM voltage where
Flux Current - Represents the actual portion of total current used for excitation.
CMD Flux CUR - Represents the calculated value for flux current.
Load Current - Represents the actual portion of total current used to produce torque
CMD Load Current - Represents the calculated value of load current.
Motor Current - Amplitude of continuous current including motor excitation current.
Load Component - Amplitude of load current not including the motor excitation
Quad Voltage - Load controller output. Used to diagnose control problems.
Direct Voltage - Flux controller output. Used to diagnose control problems.
AC Voltage - A scaled AC waveform that represents the AC line to line motor
Bus Voltage - Bus voltage scaled to 0-5VDC. 5V = 1000VDC.
Torque - Bipolar torque output. 2.5V centered, 5V = Max Positive Torque,
Power - Bipolar power output. 2.5V = Zero Power, 0V = negative rated peak
Velocity - Represents motor speed scaled to 0V = negative max RPM,
Overload - (Accumulated current)
PH 2 Current - Sampled AC phase 2 motor current. 2.5V = zero amps,
PH 3 Current - Sampled AC phase 1 motor current. 2.5V = zero amps,
Process Feedback - Represents the selected Process Feedback signal.
Setpoint Command - Represents the selected Setpoint Command signal.
Position - Position within a single revolution. +5V = 1 complete revolution.
Serial – 0–5VDC level that indicates a value programmed by a serial
Scale factor for the Analog Output voltage. Useful to set the zero value or full scale
range for external meters.
becomes active (turns on).
as follows:
+5VDC = MAX RPM.
+5VDC = Torque at CURRENT LIMIT.
+5VDC = MAX RPM.
+5VDC = MAX AC Voltage.
5VDC= MAX flux current.
5VDC= MAX commanded flux current.
(CW and CCW torque).
5V = Max. CW torque, 0V = Max. CCW torque.
5V = Max. commanded load current.
5VDC = Rated Current.
current. 5VDC = Rated Current.
terminal voltage. 0V = Neg Peak PWM voltage. 2.5V centered.
5V = Pos Peak PWM voltage. At rated motor voltage, a full 0 to 5V
sinusoidal waveform should be present. This waveform should be at
or greater than the motor base frequency. (At half the motor base
frequency, a 1.25V to 3.75 sine wave is present.)
0V = Max negative torque.
power, +5V = Positive rated peak power.
+2.5V = Zero Speed, +5V = positive max RPM.
0V = negative rated peak amps, +5V = positive rated peak amps.
0V = negative rated peak amps, +5V = positive rated peak amps.
2.5V centered, 5V = 100%, 0V = –100%.
2.5V centered, 5V = 100%, 0V = –100%.
The counter will reset to 0 every revolution.
command.
2
x (time), Overload occurs at +5V.
4-16 Programming & Operation MN722
Page 64

Section 1
General Information
Table 4-4 Inverter Control Board Level 1 Parameter Definitions - Continued
Block Title Parameter Description
VECTOR CONTROL CTRL BASE Speed
Sets the speed in RPM at which the saturation voltage of the control is reached. Above
this RPM value the control will output constant voltage and variable frequency.
Feedback Filter
Feedback Align
Current PROP
Gain
Current INT Gain
Speed PROP Gain
Speed INT Gain
Speed DIFF Gain
Position Gain
Slip Frequency
Stator R1 Stator resistance in ohms. If set too high, the motor will tend to stall at zero speed when
Stator X1 Stator leakage reactance, in ohms at 60Hz. This parameter has most impact when
Prop Gain #1 The anti–saturation controller’s proportional gain. Leave the gain at the factory setting.
INT Gain #1 The anti–saturation controller’s integral gain. Leave the gain at the factory setting.
LEVEL 2 BLOCK ENTERS LEVEL 2 MENU
A larger value provides a more filtered signal but at the cost of reduced bandwidth.
Sets the encoder’s electrical direction of rotation to match that of the motor.
Sets the current loop proportional gain.
Sets the current loop integral gain.
Sets the speed (velocity) loop proportional gain.
Sets the speed (velocity) loop integral gain.
Sets the speed (velocity) loop differential gain.
Sets the position loop proportional gain.
Sets the rated slip frequency of the motor.
reversing or accelerating from low speed. Reducing this value may eliminate the
problem. When too low, speed regulation may suffer.
reversing motor rotation at full current limit. If set too low, the decel time will tend to
increase.
Do not change this gain unless authorized by Baldor.
Do not change this gain unless authorized by Baldor.
Programming & Operation 4-17MN722
Page 65

Section 1
General Information
Table 4-5 Inverter Control Board Level 2 Parameter Definitions
Block Title Parameter Description
OUTPUT LIMITS Operating Zone Sets the PWM operating zone to Standard 2.5KHz or Quiet 8.0KHz output carrier
MIN Output Speed Sets the minimum motor speed in RPM. During operation, the motor speed will not be
MAX Output Speed Sets the maximum motor speed in RPM.
PK Current Limit The maximum output peak current to the motor. Values above 100% of the rated current
PWM Frequency The frequency that the output transistors are switched. PWM frequency is also referred
CUR Rate Limit Limits the rate of torque change in response to a torque command.
CUSTOM UNITS Decimal Places
Value At Speed
Units of Measure
PROTECTION Overload Sets the protection mode to Fault (trip off during overload condition) or to Foldback
External Trip OFF - External Trip is Disabled.
Local Enable INP OFF - Ignores J1-8 input when in the “LOCAL” mode.
Following Error This parameter determines if the control is to monitor the amount of following error that
Torque Proving When this parameter is set to ON the control measures output current in all three
frequency. Two operating modes are also selectable: Constant Torque and Variable
Torque.
Constant Torque allows 170 - 200% for 3 seconds overload or 150% for 60 seconds
overload.
Variable Torque allows 115% peak overload for 60 seconds.
allowed to go below this value except for motor starts from 0 RPM or during dynamic
braking to a stop.
are available depending upon the operating zone selected.
to as “Carrier” frequency. PWM should be as low as possible to minimize stress on
the output transistors and motor windings. It is recommended that the PWM
frequency be set to approximately 15 times the maximum output frequency of the
control. Ratios less than 15 will result in non-Sinusoidal current waveforms. See
Figure 4-3.
The number of decimal places of the Output Rate display on the Keypad display. This
value will be automatically reduced for large values. The output rate display is only
available if the Value At Speed parameter value is non zero.
Sets the desired output rate per RPM of motor speed. Two numbers are displayed on
the keypad display (separated by a slash “/”). The first number (left most) is the value
you want the keypad to display at a specific motor speed. The second number (right
most) is the motor RPM corresponding to the units in the first number. A decimal may
be inserted into the left numbers by placing the flashing cursor over the up/down
arrow and use the arrow keys.
Allows user specified units of measure to be displayed on the Output Rate display. Use
the shift and arrow keys to scroll to the first and successive characters. If the
character you want is not displayed, move the flashing cursor over the special
up/down character arrow on the left side of the display. Use the up/down arrows and
the shift key to scroll through all 9 character sets. Use the ENTER key to save your
selection.
(automatically reduce the output current below the continuous output level) during an
overload. Foldback is the choice if continuous operation is desired. Fault will require
the control be “Reset” manually or automatically after an overload.
Note: The “Foldback” selection may not be available on some early versions of
the software.
ON - External Trip is enabled. If a normally closed contact at J1-16 is opened, an
External Trip fault will occur and cause the drive to shut down.
ON - Requires J1-8 input to be closed to enable the control when in the “LOCAL” mode.
occurs in an application. Following Error is the programmable tolerance for the AT
Speed Opto output as defined by the Level 1 Output block, AT Speed Band
parameter. Operation outside the speed range will cause a fault and the drive will
shut down.
phases to the motor. If output current is unbalanced, the control will trip off generating
a torque proving fault. In a hoist application, for example, this is useful to ensure that
motor torque exists before the fail safe brake is released. “Drive On” output, if
programmed, will not occur if torque proving fails.
4-18 Programming & Operation MN722
Page 66

Section 1
General Information
Figure 4-3 Maximum Output Frequency vs PWM Frequency
It is recommended that the PWM frequency parameter be set
to approximately16 times the maximum output frequency of
the control. The greater the ratio, the more sinusoidal the
output current waveform will be.
500
400
OUTPUT FREQUENCY
300
200
100
HZ
50
1.00KHz 8.00KHz 16.00KHz
Note: The output current rating of the control must be derated for high PWM
frequency operation as follows:
Standard Constant Torque and Standard Variable Torque: Linearly
derate to 10% between 2.5 and 5.0KHz (10% derating at 5.0KHz).
Quiet Constant Torque and Quiet Variable Torque: Linearly derate to
30% between 8.0 and 16KHz (30% derating at 16KHz).
PWM FREQUENCY
Table 4-5 Inverter Control Board Level 2 Parameter Definitions - Continued
Block Title Parameter Description
MISCELLANEOUS Restart Auto/Man Manual - If a fault or power loss occurs, the control must be manually reset to resume
Restart Fault/Hr The maximum number of automatic restart attempts before requiring a manual restart.
Restart Delay The amount of time allowed after a fault condition for an automatic restart to occur.
Factory Settings Restores factory settings for all parameter values. Select YES and press “ENTER” key
Homing Speed In Bipolar and Serial modes, this parameter sets the speed that the motor shaft will
Homing Offset In Bipolar and Serial modes, this parameter sets the number of digital encoder counts
operation.
Automatic - If a fault or power loss occurs, the control will automatically reset to
resume operation.
After one hour without reaching the maximum number of faults or if power is turned
off and on again, the fault count is rest to zero.
Useful to allow sufficient time to clear a fault before restart is attempted.
to restore factory parameter values. The keypad Display will show “Operation Done”
then return to “NO” when completed.
Note: When factory settings are reset, the Motor Rated Amps value is reset to
999.9 amps. This Level 2 Motor Data block parameter value must be
changed to the correct value (located on the motor rating plate) before
attempting to start the drive.
rotate to a “Home” position when the orient command is issued.
past home at which the motor zero speed command is issued. Quadrature encoder
pulses are 4 times the number of encoder lines per revolution. The recommended
minimum number is 100 encoder counts to allow for deceleration distance to allow the
motor to stop smoothly.
Note: Homing direction is always in the forward direction.
Programming & Operation 4-19MN722
Page 67

Section 1
General Information
Table 4-5 Inverter Control Board Level 2 Parameter Definitions - Continued
Block Title Parameter Description
SECURITY
CONTROL
MOTOR DATA Motor Voltage The rated voltage of the motor (listed on the motor nameplate).
Security State Off - No security Access Code required to change parameter values.
Local - Requires security Access Code to be entered (using the keypad) before
parameter changes can be made using the Keypad.
Serial - Requires security Access Code to be entered (over the Serial Link) before
parameter changes can be made using the Serial Link.
Total - Requires security Access Code to be entered (using Keypad or Serial Link)
before parameter changes can be made using the Keypad or serial link.
Note: If security is set to Local, Serial or Total you can press PROG and scroll
through the parameter values and view their values but you are not allowed
to change their values unless you enter the correct access code.
Access Timeout The time in seconds the security access remains enabled after leaving the programming
mode. If you exit and go back into the program Mode within this time limit, the
security Access Code does not have to be re-entered. This timer starts when leaving
the Program Mode (by pressing DISP).
Note: This feature is not available when using the Serial operating mode or if
power is cycled.
Access Code A 4 digit number code. Only persons that know the code can change secured Level 1
and Level 2 parameter values.
Note: Please record your access code and store it in a safe place. If you cannot
gain entry into parameter values to change a protected parameter, please
contact Baldor. Be prepared to give the 5 digit code shown on the lower
right side of the Keypad Display at the Security Control Access Code
parameter prompt.
Motor Rated Amps The full load current of the motor (listed on the motor nameplate). If the motor current
exceeds this value for a period of time, an Overload fault will occur.
Motor Rated SPD The rated speed of the motor (listed on the motor nameplate). If Motor Rated SPD =
1750 RPM and Motor Rated Freq = 60 Hz, the Keypad Display will show 1750 RPM
at 60 Hz and 875 RPM at 30Hz.
Motor Rated Freq The rated frequency of the motor (listed on the motor nameplate).
Motor Mag Amps The motor magnetizing current value (listed on the motor nameplate). Also called no
load current. Measure using a clamp on amp meter at the AC power line while the
motor is running at line frequency with no load connected to the motor shaft.
Encoder Counts The number of encoder feedback counts (lines per revolution).
Resolver Speed The speed of the resolver, if a resolver is used for feedback.
CALC Presets This procedure loads preset values into memory that are required to perform Auto Tune.
Always run CALC Presets as the first step of Auto Tune.
4-20 Programming & Operation MN722
Page 68

Section 1
General Information
Table 4-5 Inverter Control Board Level 2 Parameter Definitions - Continued
Block Title Parameter Description
BRAKE ADJUST Resistor Ohms The dynamic braking resistor value in ohms. Refer to dynamic braking manual or call
Resistor Watts
DC Brake Current
PROCESS
CONTROL
COMMUNICATIONS Protocol Sets the type of communication the control is to use, RS-232 ASCII, RS-485 ASCII,
Process Feedback
Process Inverse
Setpoint Source
Setpoint Command
Set PT ADJ Limit
Process ERR TOL
Process PROP
Gain
Process INT Gain
Process DIFF Gain
Follow I:O Ratio
Follow I:O Out
Master Encoder
Baud Rate Sets the speed at which communication is to occur.
Drive Address Sets the address of the control for communication.
Baldor for additional information.
The dynamic braking resistor watts rating. Refer to dynamic braking manual or call
Baldor for additional information.
The amount of DC injection brake current. 0% = Flux current, 100% = Motor rated
current. (Used during encoderless operation).
Sets the type of signal used for the process feedback signal.
Causes the process feedback signal to be inverted. Used with reverse acting processes
that use a unipolar signal such as 4-20mA. If “ON”, 20mA will decrease motor speed
and 4mA will increase motor speed.
Sets the source input signal to which the process feedback will be compared.
If “Setpoint CMD” is selected, the fixed value of the set point is entered in the Setpoint
Command parameter value.
Sets the value of the setpoint the control will try to maintain by adjusting motor speed.
This is only used when the Setpoint Source is a fixed value “Setpoint CMD” under
Setpoint Source.
Sets the maximum speed correction value to be applied to the motor (in response to the
maximum feedback setpoint error). For example, if the max motor speed is 1750
RPM, the setpoint feedback error is 100% and the setpoint adjustment limit is 10%,
the maximum speed the motor will run in response to the setpoint feedback error is
±175 RPM. If at the process setpoint, the motor speed is 1500 RPM, the maximum
speed adj limits is then 1325 to 1675 RPM.
Sets the width of the comparison band (% of setpoint) with which the process input is
compared. The result is that if the process input is within the comparison band the
corresponding Opto Output will become active.
Sets the PID loop proportional gain. This determines how much adjustment to motor
speed or torque (within the Set PT ADJ Limit) is made to reduce process error.
Sets the PID loop Integral gain. This determines how quickly the motor speed or torque
is adjusted to correct long term error.
Sets the PID loop differential gain. This determines how much adjustment to motor
speed (within the Set PT ADJ Limit) is made for transient error.
Sets the ratio of the Master to the Follower in Master/Follower configurations. Requires
the Master Pulse Reference/ Isolated Pulse Follower expansion board. For example,
the master encoder you want to follow is a 1024 count encoder. The follower motor
you wish to control also has a 1024 count encoder on it. If you wish the follower to
run twice the speed of the master, a 1:2 ratio is entered. Fractional ratios such as
0.5:1 are entered as 1:2. Ratio limits are (1-65,535) : (1-20).
Note: The Master Encoder parameter must be defined if a value is entered in the
Follow I:O Ratio parameter.
Note: When using Serial Communications to operate the control, this parameter
value is the MASTER portion of the ratio. The FOLLOWER portion of the
ratio is set in the Follow I:O Out parameter.
This parameter is used only when Serial Communications is used to operate the control.
A Master Pulse Reference/ Isolated Pulse Follower expansion board is required. This
parameter represents the FOLLOWER portion of the ratio. The MASTER portion of
the ratio is set in the Follow I:O Ratio parameter when using Serial operating mode.
Only used if an optional Master Pulse Reference/Isolated Pulse Follower expansion
board is installed. Defines the number of pulses per revolution of the master encoder.
Programmed into follower drives only.
RS-232 BBP or RS-485 BBP protocol.
Programming & Operation 4-21MN722
Page 69

Section 1
General Information
Table 4-5 Inverter Control Board Level 2 Parameter Definitions - Continued
Block Title Parameter Description
AUTO TUNING
CALC Presets
CMD Offset Trim
CUR Loop COMP
Flux CUR Setting
Feedback Tests
Slip FREQ Test
SPD CNTRLR
CALC
LEVEL 1 BLOCK ENTERS LEVEL 1 MENU
The Auto Tune procedure is used to automatically measure and calculate certain
parameter values. Dynamic Brake Hardware is required to perform “Slip Freq Test”
and “Spd Cntrlr Calc” autotuning test. Occasionally, the Auto Tune procedure cannot
be run due to various circumstances such as the load cannot be uncoupled from the
motor. The control can be manually tuned by entering the parameter values based on
calculations you have made. Refer to “Manually Tuning the Control” in the
Troubleshooting section of this manual.
Loads operating values into memory. These values are based on information
programmed into the Level 2 Output Limits and Motor Data parameter values.
CALC Presets must be run before Autotuning or manually tuning the drive.
This procedure trims out voltage offsets for the differential analog input at J1-4 and J1-5.
Measures current response to pulses of one half the rated motor current.
Sets motor magnetizing current by running motor at near rated speed.
Checks the values for Encoder Lines per revolution and encoder alignment parameters
while the motor is running at near full rated speed. Test will automatically switch
encoder phasing to match motor rotational direction.
Calculates motor Slip Frequency during repeated motor accelerations.
Should be performed with the load coupled to the motor shaft. Sets the motor current to
acceleration ratio, Speed INT gain and Speed PROP gain values. If done under no
load, the Integral gain will be too large for high inertia loads if the PK Current Limit is
set too low. If the control is too responsive when the drive is loaded, adjust the PK
Current Limit parameter to a greater value and repeat this test.
4-22 Programming & Operation MN722
Page 70

Section 5
Troubleshooting
Baldor Series 22H Controls require very little maintenance and should provide years of
trouble free operation when installed and applied correctly. Occasional visual inspection
should be considered to ensure tight wiring connections and to avoid the build up of any
dust, dirt, or foreign debris which can reduce heat dissipation. The control should be
mounted in a location that protects the internal circuits and external wiring from moisture
or liquid contaminants.
When a fault condition occurs, motor operation stops and the fault is displayed on the
Keypad Display. If a REGEN FLT is displayed, this indicates a fault in the converter
section of the control. To determine the specific converter section fault, the keypad must
be moved to the Converter Control Board keypad connector. The fault log can be
examined and the specific faults will help to further isolate the failure. A list of possible
Converter Control Board Fault Messages is given in Table 5-1. Other fault messages that
pertain to the Inverter Control Board are given in Table 5-2.
When a fault has been identified, all input power must be removed from the control to
avoid the possibility of electrical shock. The servicing of this equipment should be
handled by a qualified electrical service technician experienced in the area of high power
electronics.
It is important to familiarize yourself with the following information before attempting any
troubleshooting or service of the control. Most troubleshooting can be performed using
only a digital voltmeter having an input impedance exceeding 1 megOhm. In some
cases, an oscilloscope with 5 MHZ minimum bandwidth may be useful. Before consulting
the factory, check that all power and control wiring is correct and installed per the
recommendations given in this manual.
No Keypad Display - Display Contrast Adjustment
If there is no visible display, use the following procedure to adjust the contrast of the
display.
Action Description Display Comments
Apply Power No visible display.
Press DISP key Puts control in Display mode. Display mode with nothing visible.
Press SHIFT key 2 times Accesses display contrast
Press or key
Press ENTER key Saves display contrast
adjustment.
Adjusts display contrast
(intensity).
adjustment level and exits to
display mode.
When a Fault is Displayed When a fault is displayed, press “DISP” so that you can view the menu items (to go to
Diagnostic or Fault Log menus etc.). When you exit these menus, the fault message will
again be displayed. The control must be reset to clear the fault message from the
display.
Troubleshooting 5-1MN722
Page 71

Section 1
General Information
Table 5-1 Converter Control Board Fault Messages
FAULT MESSAGE DESCRIPTION
Current Sens FLT Defective phase current sensor or open circuit detected between control board and current
sensor.
DC Bus High Bus over voltage condition occurred.
DC Bus Low Bus under voltage condition occurred.
GND FLT Low impedance path detected between an output phase and ground.
High INIT CUR Phasing between main power connections, zero crossing detectors, line reactor and
control does not match.
ID:No Feedback Control board installed in power base that does not have current feedback and current
feedback is required.
INT Over-Temp Temperature of control heatsink exceeded safe level.
Invalid Base ID Control does not recognize power base ID.
Logic Supply FLT Logic power supply not working properly.
Lost AB Phase
Lost BC Phase
Lost User Data Battery backed RAM parameters have been lost or corrupted.
Low INIT Bus V Insufficient bus voltage on startup.
Memory Error EEPROM error occurred. Contact Baldor.
mP Reset
New Base ID Control board sensed a different power base since last time it was powered up.
No Faults Fault log is empty.
Overcurrent FLT Instantaneous over current condition detected by bus current sensor.
Overload Output current exceeded allowable rating.
PWR Base FLT Desaturation of power device occurred or bus current threshold exceeded.
Sync To Line Incorrect line phasing or frequency detected on startup.
Missing phase detected by mP.
Missing phase detected by mP.
When fault cleared (Reset), the control should reset to factory preset values.
Watchdog timer detected error.
5-2 Troubleshooting MN722
Page 72

Section 1
General Information
Table 5-2 Inverter Control Board Fault Messages
FAULT MESSAGE DESCRIPTION
Current Sens FLT Defective phase current sensor or open circuit detected between control board and current
sensor.
DC Bus High Bus over voltage condition occurred.
DC Bus Low Bus under voltage condition occurred.
Encoder Loss Encoder coupling slipping or broken; noise on encoder lines, encoder power supply loss or
defective encoder.
External Trip An open circuit on J1-16 typically indicating an external over temperature condition.
Following Error Excessive following error detected between command and feedback signals.
GND FLT Low impedance path detected between an output phase and ground.
INT Over-Temp Temperature of control heatsink exceeded safe level.
Invalid Base ID Control does not recognize power base ID.
Inverter Base ID Control board installed on power base without current feedback.
Line Regen FLT Indicates a converter section fault.
Logic Supply FLT Logic power supply not working properly.
Lost User Data Battery backed RAM parameters have been lost or corrupted.
When fault cleared (Reset), the control should reset to factory preset values.
Low INIT Bus V Insufficient bus voltage on startup.
Memory Error EEPROM error occurred. Contact Baldor.
New Base ID Control board sensed a different power base since last time it was powered up.
No Faults Fault log is empty.
No EXB Installed Programmed parameter requires an expansion board.
Over Current FLT Instantaneous over current condition detected by bus current sensor.
Overload - 1 min Output current exceeded 1 minute rating.
Overload - 3 sec Output current exceeded 3 second rating.
Over speed Motor RPM exceeded 110% of programmed MAX Motor Speed.
mP Reset
PWR Base FLT Desaturation of power device occurred or bus current threshold exceeded.
Resolver Loss Resolver feedback problem is indicated (if resolver used).
Torque Prove FLT Unbalanced current between all 3 motor phases.
User Fault Text Custom software operating fault occurred.
Power cycled before the residual Bus voltage reached 0VDC.
Troubleshooting 5-3MN722
Page 73

Section 1
General Information
How to Access the Fault Log When a fault condition occurs, motor operation stops and a fault code is displayed on
the keypad display. The control keeps a log of up to the last 31 faults. If more than 31
faults have occurred the oldest fault will be deleted from the fault log to make room for the
newest fault. To access the fault log use the following procedure:
Action
Apply Power Logo display for 5 seconds.
Display mode showing output
frequency
Press DISP key 5 times Use DISP key to scroll to the
Press ENTER key Display first fault type and time
Press key
Press ENTER key Return to display mode. Display mode stop key LED is on.
Fault Log entry point.
fault occurred.
Scroll through fault messages.
Description Display Comments
Display mode.
Typical display.
If no messages, the fault log exit
choice is displayed.
5-4 Troubleshooting MN722
Page 74

Section 1
General Information
How to Clear the Fault Log Use the following procedure to clear the fault log and reset the internal clock.
Action
Apply Power Logo display for 5 seconds.
Display mode showing output
frequency.
Press DISP key Press DISP to scroll to the Fault
Press ENTER key Displays most recent message. 1=Most recent fault.
Press SHIFT key
Press RESET key
Press SHIFT key
Press ENTER key Fault log is cleared. No faults in fault log. Also resets
Press or key
Log entry point.
Scroll Fault Log Exit.
Description Display Comments
Display mode.
2=Second most recent fault, etc.
the internal clock.
Press ENTER key Return to display mode.
Troubleshooting 5-5MN722
Page 75
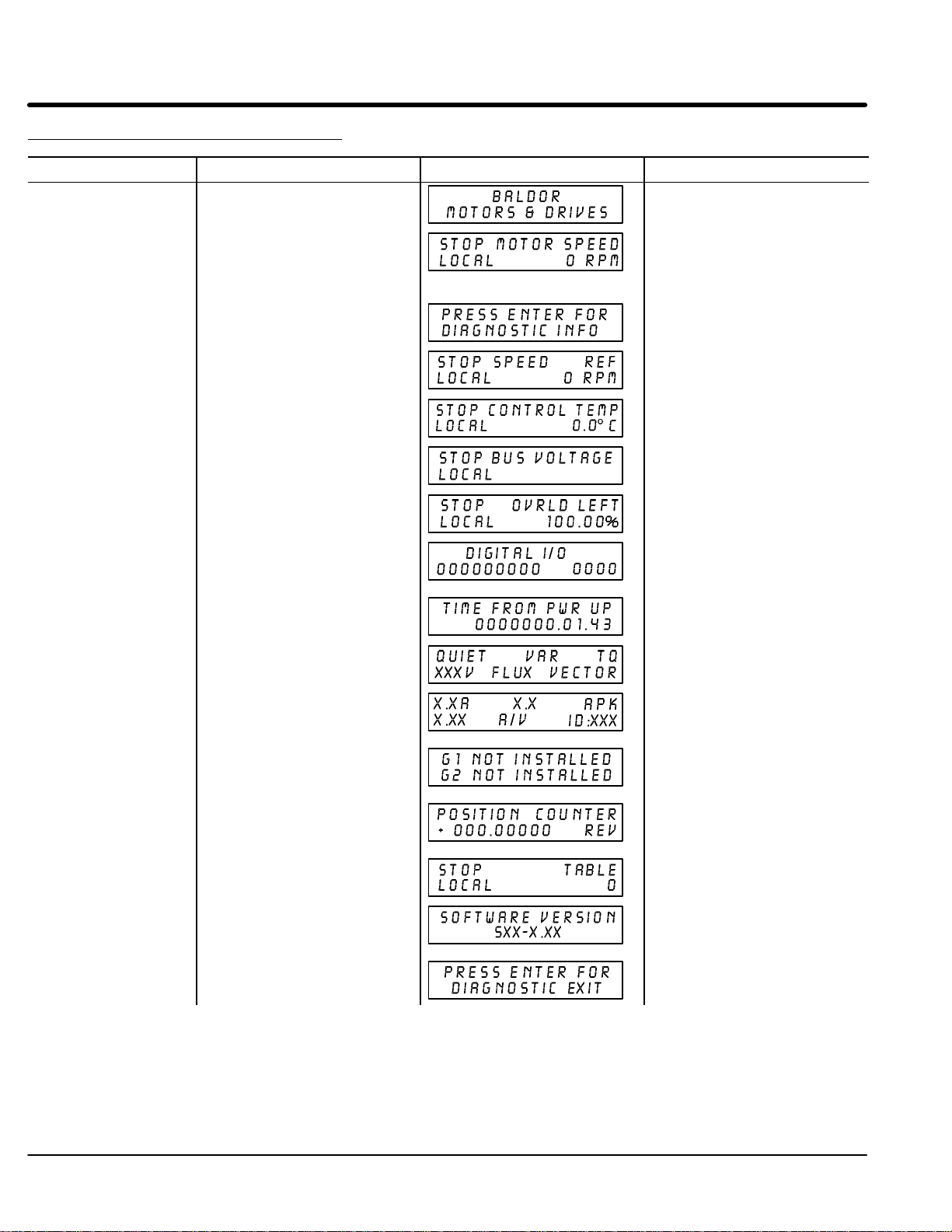
Section 1
General Information
How to Access Diagnostic Information
Action Description Display Comments
Apply Power Logo display for 5 seconds.
Display mode showing motor
speed.
Press DISP key 6 times Scroll to Diagnostic Information
screen
Press ENTER key Access diagnostic information. First Diagnostic Information
Press DISP key Display showing control
temperature.
Press DISP key Display showing bus voltage.
No faults present. Local keypad
mode. In remote/serial mode,
disable drive then press local for
this display.
Diagnostic Access screen.
screen.
XXXV
Press DISP key Display showing % overload
Press DISP key Display showing opto inputs &
Press DISP key Display showing actual drive
Press DISP key Display showing operating zone,
current remaining.
outputs states.
0=OPEN, 1=CLOSED.
running time.
voltage and control type.
Opto Inputs states (Left);
Opto Outputs states (Right).
HR.MIN.SEC format.
Press DISP key Display showing continuous
amps; PK amps rating; amps/volt
scale of feedback, power base ID.
Press DISP key Display showing which Group1 or
2 expansion boards are installed
and recognized.
Press DISP key Display showing motor shaft
revolutions from the REV home
set point.
Press DISP key Display mode showing parameter
table selected.
Press DISP key Display showing software version
and revision installed in the
control.
Press DISP key Displays exit choice. Press ENTER to exit diagnostic
ID is displayed as a hexadecimal
value.
information.
5-6 Troubleshooting MN722
Page 76

Section 1
General Information
Table 5-3 Converter Section Troubleshooting
INDICATION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTIVE ACTION
Current Sense FLT Open circuit between control board
DC Bus High Incorrect setting of converter bridge
DC Bus Low Input voltage too low. Monitor power line fluctuations with date and time imprint
GND FLT Improper wiring. Disconnect wiring between control and motor. Retry test.
High INIT CUR Incorrect phasing between input
ID:No Feedback Control board is installed on wrong
INT Over-Temp Ambient temperature too high. Relocate control to a cooler area. Add cooling fans or air condition the
Invalid Base ID Control does not recognize
Logic Supply FLT Power supply malfunctioned. Replace logic power supply.
Lost AB Phase Wire disconnected or phase lost. Check for input power on all 3 phases.
Lost BC Phase Wire disconnected or phase lost. Check for input power on all 3 phases.
Lost User Data Battery backed memory failure. Parameter data was erased. Disconnect power to control and
Low INIT Bus V Improper AC line voltage. Check input AC voltage level.
Memory Error EEPROM memory fault occurred. Press “RESET” key on keypad. If fault remains, call Baldor.
mP Reset
New Base ID Software parameters are not
and current sensor or defective
current sensor.
parameter.
Decel rate too fast. Increase Decel time parameter setting.
power, filter assembly and line
reactors.
power base.
Drive overloaded. Verify proper sizing of control and motor. Correct loading of motor.
Cooling fans or air path is clogged. Clean fans and air path.
converter power base.
Power was cycled before Bus
voltage reached 0VDC.
initialized on newly installed
control board.
Check control wires between control board and current feedback sensor.
Check Bus Capacitance value of converter section parameters.
to isolate power problem.
Check power line disturbances (sags caused by start up of
other equipment).
Use step up isolation transformer if needed.
If GND FLT is cleared, reconnect motor leads and retry the test.
Rewire as necessary.
Repair motor.
If GND FLT remains, contact Baldor.
Check connections for proper phasing as detailed in Section 3 of this
manual.
Change power base to one that has current feedback sensors.
cabinet.
Ensure fans are operating.
Press “RESET” key on keypad. If fault remains, call Baldor.
Check wiring and correct errors in all output wiring and wiring between
individual components on EK type controls. Press “RESET” key on
keypad. If fault remains, call Baldor.
Check wiring and correct errors in all output wiring and wiring between
individual components on EK type controls. Press “RESET” key on
keypad. If fault remains, call Baldor.
apply power (cycle power). Enter all parameters.
Cycle power. If problem persists, contact Baldor.
Press “RESET” key on keypad.
Disconnect power and allow at least 5 minutes for
Bus capacitors to discharge before applying power.
If fault remains, call Baldor.
Press “RESET” key on keypad to clear the fault condition. Cycle power
(turn power OFF then ON). Refer to Section 4 and initialize new software.
Access diagnostics and compare power base ID number to list in Table
5-5 to ensure a match. Re-enter the Parameter Block Values you
recorded in the User Settings at the end of this manual. Autotune the
control. If fault remains, call Baldor.
Continued on next page.
Troubleshooting 5-7MN722
Page 77

Section 1
General Information
Table 5-3 Converter Section Troubleshooting Continued
INDICATION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTIVE ACTION
Over Current FLT Possible converter transistor failure. Check transistors for shorted junctions.
Incorrect inductance set in Line
Inductor parameter.
Overload FLT Drive overloaded. Verify proper sizing of control and motor.
PWR Base FLT Incorrect phase connections. Check connections for proper phasing of EK drive components as
Excessive current draw.
Power device saturated.
Electrical noise from DC coils. Install flyback diodes (reverse biased 1N4002 or equivalent)across all
Electrical noise from AC coils. Install RC snubbers on all external AC coils.
Sync To Line Incorrect phase connections. Check connections for proper phasing as detailed in Section 3 of this
Incorrect frequency detected at
startup.
Check inductance parameter value.
detailed in Section 3 of this manual.
Disconnect motor wiring and retry test. If fault remains, call Baldor.
external DC relay coils..
manual.
Check incoming line voltage and frequency.
5-8 Troubleshooting MN722
Page 78

Section 1
General Information
Table 5-4 Inverter Section Troubleshooting
INDICATION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTIVE ACTION
No Display Lack of input voltage. Check input power for proper voltage.
Loose connections. Check input power termination.
Bent pins in keypad to control
connector.
Adjust display contrast. See Adjust Display Contrast in Sec. 4.
Auto Tune Encoder miswired. Correct wiring problems.
Encoder Test failed
Current Sense FLT Open circuit between control board
DC Bus High Excessive regenerated power. Increase the DECEL time.
DC Bus Low Input voltage too low. Disconnect dynamic brake hardware and repeat operation.
Encoder Loss Encoder power supply failure. Check 5VDC at J1-29 and J1-30.
Encoder coupling slipping, broken
or misaligned.
Excessive noise on encoder lines. Check the position counter in the Diagnostic Information for
Wrong parameter values for “Motor
Base Speed”, “Frequency” or
“Encoder Counts”.
Motor coupled to load. Disconnect load then autotune.
and current sensor.
Defective current sensor. Replace current sensor.
Input voltage too high. Verify proper AC line voltage.
Encoder coupling slipping, broken
or misaligned
Excessive noise on encoder lines. Check the position counter in the Diagnostic Information for
Verify fuses are good (or breaker is not tripped).
Verify connection of operator keypad.
Check connector pins and straighten as required.
Correct encoder to motor coupling.
jittering which will confirm an encoder problem.
Use recommended encoder cable.
Check encoder connections including shields.
Separate encoder leads from power wiring.
Cross encoder wires and power leads at 90°.
Electrically isolate encoder from motor.
Install optional Isolated Encoder Feedback expansion board.
Enter correct parameter values.
Check connections between control board and current sensor.
Use step down isolation transformer if needed.
Use line reactor to minimize spikes.
Verify proper AC line voltage.
Use step up isolation transformer if needed.
Check power line disturbances (sags caused by start up of
other equipment).
Monitor power line fluctuations with date and time imprint
to isolate power problem.
Also check at encoder end pins D and F.
Check encoder cable continuity.
Correct or replace encoder to motor coupling.
jittering which will confirm an encoder problem.
Check encoder connections.
Separate encoder leads from power wiring.
Use Baldor encoder cable.
Cross encoder wires and power leads at 90°.
Electrically isolate encoder from motor.
Install optional Isolated Encoder Feedback expansion board.
Continued on next page.
Troubleshooting 5-9MN722
Page 79

Section 1
General Information
Table 5-4 Inverter Section Troubleshooting Continued
INDICATION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTIVE ACTION
External Trip Motor ventilation insufficient. Clean motor air intake and exhaust.
Motor draws excessive current. Check motor for overloading.
No thermostat connected. Connect thermostat.
Poor thermostat connections. Check thermostat connections.
External trip parameter incorrect. Verify connection of external trip circuit at J1-16.
Following ERR Speed proportional gain set too low. Following error tolerance band set too narrow.
Current limit set too low. Increase Current Limit parameter value.
ACCEL/DECEL time too short. Increase ACCEL/DECEL parameter time
Excessive load. Verify proper sizing of control and motor.
GND FLT Improper wiring.
Wiring shorted in conduit.
Motor winding shorted.
INT Over-Temp Motor Overloaded. Correct motor loading.
Ambient temperature too high. Check that air flow path is clean and free of debris.
Invalid Base ID Control does not recognize HP and
Inverter Base ID Power base with no output phase
Logic Supply FLT Power supply malfunctioned. Replace logic power supply.
Lost User Data Battery backed memory failure. Parameter data was erased. Disconnect power to control and
Low INIT Bus V Improper AC line voltage. Check input AC voltage level.
Memory Error EEPROM memory fault occurred. Press “RESET” key on keypad. If fault remains, call Baldor.
mP Reset
Voltage configuration.
current sensors being used.
Power was cycled before Bus
voltage reached 0VDC.
Check external blower for operation.
Verify motor’s internal fan is coupled securely.
Verify correct line power to external blower.
Verify proper sizing of control and motor.
Verify connection of all external trip circuits used with thermostat.
Disable thermostat input at J1-16 (External Trip Input).
Set external trip
at J1-16.
Increase Speed PROP Gain parameter value.
Disconnect wiring between control and motor. Retry test.
If GND FLT is cleared, reconnect motor leads and retry the test.
Rewire as necessary.
Repair motor.
If GND FLT remains, contact Baldor.
Verify proper sizing of control and motor.
Relocate control to cooler operating area.
Add cooling fans or air conditioner to control cabinet.
Press “RESET” key on keypad. If fault remains, access diagnostic info
and compare power output section Power Base ID # with Table 5-5. If
different, contact Baldor.
Replace power base with one that has output leg current
feedback. Contact Baldor.
apply power (cycle power). Enter all parameters.
Cycle power. If problem persists, contact Baldor.
Press “RESET” key on keypad.
Disconnect power and allow at least 5 minutes for
Bus capacitors to discharge before applying power.
If fault remains, call Baldor.
parameter to “OFF” if no connection made
Continued on next page.
5-10 Troubleshooting MN722
Page 80

Section 1
General Information
Table 5-4 Inverter Section Troubleshooting Continued
INDICATION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTIVE ACTION
Motor has wrong
response to
Speed Command
Motor Shaft
Oscillates back
and forth
Motor Shaft
rotates at low
speed regardless
of commanded
speed
Motor Shaft
rotates in wrong
direction
Motor Will Not Not enough starting torque. Increase Current Limit setting.
Start
Motor Will Not Max Output Speed set too low. Adjust Level 2 Output Limits block, MAX Output Speed parameter value.
Reach Maximum
Speed
Motor Will Not
Stop Rotation
Analog input common mode voltage
may be excessive.
Incorrect MIN or MAX speed
settings.
Analog offset trim is incorrectly set. Re-run “Offset Trim” autotune test.
Speed gain value is too large. Reduce the Level 1 Vector Control block, Speed PROP Gain and
Incorrect encoder alignment
direction.
Incorrect encoder alignment
direction.
Incorrect encoder wiring. Reverse the A and A or B and B encoder wires at the J1 input to control
Motor overloaded. Check for proper motor loading.
Motor may be commanded to run
below minimum speed setting.
Incorrect Command Select
parameter.
Incorrect speed command. Verify control is receiving proper command signal at J1.
Motor overloaded. Check for mechanical overload. If unloaded motor shaft does not rotate
Improper speed command. Verify control is set to proper operating mode to receive speed command.
Speed potentiometer failure. Replace potentiometer.
MIN Output Speed parameter set
too high.
Improper speed command. Verify control is receiving proper command signal at input terminals.
Speed potentiometer failure. Replace potentiometer.
Analog input common mode voltage
may be excessive.
Analog offset trim set incorrectly. Re-run “Offset Trim” autotune test.
Connect control input source common to control common to minimize
common mode voltage. Maximum common mode voltage at terminals
J1-4 and J1-5 is ±15VDC referenced to chassis common.
Check Level 2 Output Limits block, MIN Output Speed and MAX Output
Speed parameter values and adjust as needed.
Speed INT Gain parameter values.
Change the Feedback Align parameter in the Level 1 Vector Control block.
If Reverse, set to Forward. If Forward, set to Reverse.
Check encoder connections.
Change the Feedback Align parameter in the Level 1 Vector Control block.
If Reverse, set to Forward. If Forward, set to Reverse.
and change encoder direction in the Feedback Align parameter in the
Level 1 Vector Control block.
Check couplings for binding.
Verify proper sizing of control and motor.
Increase speed command or reduce minimum speed setting.
Change Command Select parameter to match wiring at J1.
freely, check motor bearings.
Verify control is receiving proper command signal at input terminals.
Check velocity loop gains.
Adjust MIN Output Speed parameter value.
Verify control is set to receive speed command.
Connect control input source common to control common (J1-1) to
minimize common mode voltage. Maximum common mode voltage at
terminals J1-4 and J1-5 is ±15VDC referenced to chassis common.
Adjust the Level 1 Input block, ANA CMD Offset parameter to obtain zero
speed.
Continued on next page.
Troubleshooting 5-11MN722
Page 81

Section 1
General Information
Table 5-4 Inverter Section Troubleshooting Continued
INDICATION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTIVE ACTION
New Base ID Software parameters are not
No EXB Installed Incorrect programmed parameter. Change the Level 1 Input block, Command Select parameter and the Level
Over Current FLT Current Limit parameter set lower
Overload - 3 Sec
FLT
Overload - 1 Min
FLT
Over Speed Motor exceeded 110% of MAX
initialized on newly installed
control board.
Need expansion board. Install the correct expansion board for selected operating mode.
than drive rating.
ACCEL/DECEL time too short. Increase the Level 1 ACCEL/DECEL Rate block ACCEL/DEC parameters.
Encoder coupling slipping, broken
or misaligned.
Encoder bearing failure. Replace encoder.
Excessive noise on encoder lines. Check the position counter in the Diagnostic Information for
Electrical noise from external DC
coils.
Electrical noise from external AC
coils.
Excessive load. Reduce the motor load.
Peak output current exceeded 3
second rating.
Encoder coupling slipping, broken
or misaligned.
Encoder bearing failure. Replace encoder.
Peak output current exceeded 1
minute rating.
Encoder coupling slipping, broken
or misaligned.
Encoder bearing failure. Replace encoder.
Speed parameter value.
Press “RESET” key on keypad to clear the fault condition. Reset
parameter values to factory settings. Access diagnostics and compare
power base ID number to list in Table 5-5 to ensure a match. Re-enter the
Parameter Block Values you recorded in the User Settings at the end of
this manual. Autotune the control.
2 Process Control block, Process Feedback and Setpoint Source
parameters to a value that does not require an expansion board.
Increase the Level 2 Output Limits block, PK Current Limit parameter.
Do not exceed drive rating.
Correct or replace encoder to motor coupling.
jittering which will confirm an encoder problem.
Check encoder connections.
Separate encoder leads from power wiring.
Use Baldor encoder cable.
Cross encoder wires and power leads at 90°.
Electrically isolate encoder from motor.
Install optional Isolated Encoder Feedback expansion board.
Install reverse biased diodes across all external DC relay coils as shown in
the Opto Output circuit examples of this manual. See Electrical Noise
Considerations in Section 5 of this manual.
Install RC snubbers on all external AC coils. See Electrical Noise
Considerations in Section 5 of this manual.
Verify proper sizing of control and motor.
Check the Level 2 Output Limits block PK Current Limit parameter.
Change the Level 2 Protection block Overload parameter from Trip to
Foldback.
Check motor for overloading.
Increase Level 1 ACCEL/DECEL Rate block ACCEL/DEC parameters.
Reduce motor load.
Verify proper sizing of control and motor.
Correct or replace encoder to motor coupling.
Verify proper motor data has been entered.
Check the Level 2 Output Limits block PK Current Limit parameter.
Change the Level 2 Protection block Overload parameter from Trip to
Foldback.
Check motor for overloading.
Increase Level 1 ACCEL/DECEL Rate block ACCEL/DEC parameters.
Reduce motor load.
Verify proper sizing of control and motor.
Correct or replace encoder to motor coupling.
Check the Level 2 Output Limits block Max Output Speed.
Increase the Level 1 Vector Control block Speed PROP Gain.
Continued on next page.
5-12 Troubleshooting MN722
Page 82
Section 1
General Information
Table 5-4 Inverter Section Troubleshooting Continued
INDICATION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTIVE ACTION
Power Module Power supply failure. Press “RESET” key on keypad. If fault remains, call Baldor.
PWR Base FLT Improper ground
Excessive current usage.
Encoder coupling slipping, broken
or misaligned.
Encoder bearing failure. Replace encoder.
Excessive noise on encoder lines. Check encoder connections.
Electrical noise from external DC
coils.
Electrical noise from external AC
coils.
Excessive load. Correct motor load.
Excessive power in dynamic brake
circuit.
Regen PWR FLT Excessive input voltage. Verify proper AC Line voltage.
Resolver Loss Resolver defect. Check resolver to motor coupling (align or replace if needed).
Torque Prove FLT Unbalanced current in 3 motor
phases.
Unknown Fault Fault occurred but cleared before its
source could be identified.
User Fault Text Fault detected by custom software. Refer to custom software fault list.
Be sure control has separate ground wire to earth ground.
Panel grounding or conduit connections is not sufficient.
Disconnect motor leads from control and retry test. If fault remains, call
Baldor.
Correct or replace encoder to motor coupling.
Separate encoder leads from power wiring.
Use Baldor encoder cable.
Cross encoder wires and power leads at 90°.
Electrically isolate encoder from motor.
Install optional Isolated Encoder Feedback expansion board.
Install reverse biased diodes across all external DC relay coils as shown in
the Opto Output circuit examples of this manual. See Electrical Noise
Considerations in Section 5 of this manual.
Install RC snubbers on all external AC coils. See Electrical Noise
Considerations in Section 5 of this manual.
Verify proper sizing of control and motor.
Verify proper Ohm and Watt parameters of Brake Adjust block.
Increase decel time.
Use step down transformer if needed.
Use line reactor to minimize spikes.
Verify correct wiring. Refer to the Resolver to Digital
expansion board manual.
Electrically isolate resolver from motor.
Use Baldor Resolver cable.
Check continuity from control to motor windings and verify motor
connections.
Check AC line for high frequency noise.
Check input switch connections and switching noise.
Troubleshooting 5-13MN722
Page 83

Section 1
General Information
Catalog Numbers Power
ZD22H210–EL 919 ZD22H410–EL B2D
ZD22H215–EL 910 ZD22H415–EK B10
ZD22H220–EL 911 ZD22H420–EL B11
ZD22H225–EL 91D ZD22H425–EL B12
ZD22H230–EL 913 ZD22H430–EL B13
ZD22H240–EL 914 ZD22H440–EL B14
ZD22H250–EL 915 ZD22H450–EL B15
Table 5-5 Power Base ID - Series 22H
230VAC 460VAC
Catalog Numbers Power
Base
ID No.
ZD22H460–EK B16
ZD22H475–EK BAB
ZD22H4100–EK B18
ZD22H4150–EK B9A
ZD22H4200–EK B9B
ZD22H4250–EL BC3
ZD22H4300–EL BAE
ZD22H4350–EL BA6
ZD22H4400–EL BA7
ZD22H4450–EL BA9
Base
ID No.
Note: The Power Base ID number of a control is displayed in a Diagnostic
Information screen as a hexadecimal value.
Note: The power Base ID number is the same for both the converter and the
Inverter sections of the control.
5-14 Troubleshooting MN722
Page 84

Section 1
General Information
Electrical Noise Considerations All electronic devices are vulnerable to significant electronic interference signals
(commonly called “Electrical Noise”). At the lowest level, noise can cause intermittent
operating errors or faults. From a circuit standpoint, 5 or 10 millivolts of noise may cause
detrimental operation. For example, analog speed and torque inputs are often scaled at 5
to 10 VDC maximum with a typical resolution of one part in 1,000. Thus, noise of only 5
mV represents a substantial error.
At the extreme level, significant noise can cause damage to the drive. Therefore, it is
advisable to prevent noise generation and to follow wiring practices that prevent noise
generated by other devices from reaching sensitive circuits. In a control, such circuits
include inputs for speed, torque, control logic, and speed and position feedback, plus
outputs to some indicators and computers.
Unwanted electrical noise can be produced by many sources. Various methods can be
used to reduce the effects of this noise. All methods are less costly when designed into a
system initially than if added after installation.
Relay and Contactor CoilsAmong the most common sources of noise are the ever–present coils of contactors and
relays. When these highly inductive coil circuits are opened, transient conditions often
generate spikes of several hundred volts in the control circuit. These spikes can induce
several volts of noise in an adjacent wire that runs parallel to a control–circuit wire.
Figure 5-1 illustrates noise suppression for AC and DC operated coils.
Figure 5-1 AC & DC Coil Noise Suppression
AC Coil
Wires between Controls and Motors
Output leads from a typical 460 VAC drive controller contain rapid voltage rises created
by power semiconductors switching 650V in less than a microsecond, 1,000 to 10,000
times a second. These noise signals can couple into sensitive drive circuits. If shielded
pair cable is used, the coupling is reduced by nearly 90% compared to unshielded cable.
Even input AC power lines contain noise and can induce noise in adjacent wires. In
severe cases, line reactors may be required.
To prevent induced transient noise in signal wires, all motor leads and AC power lines
should be contained in rigid metal conduit, or flexible conduit. Do not place line
conductors and load conductors in same conduit. Use one conduit for 3 phase input
wires and another conduit for the motor leads. The conduits should be grounded to form
a shield to contain the electrical noise within the conduit path. Signal wires - even ones in
shielded cable should never be placed in the conduit with motor power wires.
If flexible conduit is required, the wires should be shielded twisted-pair. Although this
practice gives better protection than unshielded wires, it lacks the protection offered by
rigid metal conduit.
RC snubber
0.47 mF
33 W
+
DC Coil
–
Diode
Troubleshooting 5-15MN722
Page 85

Section 1
General Information
Electrical Noise Considerations Continued
Special Drive Situations
For severe noise situations, it may be necessary to reduce transient voltages in the wires
to the motor by adding load reactors. Load reactors are installed between the control and
motor.
Reactors are typically 3% reactance and are designed for the frequencies encountered in
PWM drives. For maximum benefit, the reactors should be mounted in the drive
enclosure with short leads between the control and the reactors. Baldor can deliver line
and load reactors that will reduce ripple current and improve motor life.
Control Enclosures Motor controls mounted in a grounded enclosure should also be connected to earth
ground with a separate conductor to ensure best ground connection. Often grounding
the control to the grounded metallic enclosure is not sufficient. Usually painted surfaces
and seals prevent solid metallic contact between the control and the panel enclosure.
Likewise, conduit should never be used as a ground conductor for motor power wires or
signal conductors.
Special Motor Considerations
Motor frames must also be grounded. As with control enclosures, motors must be
grounded directly to the control and plant ground with as short a ground wire as possible.
Capacitive coupling within the motor windings produces transient voltages between the
motor frame and ground. The severity of these voltages increases with the length of the
ground wire. Installations with the motor and control mounted on a common frame, and
with heavy ground wires less than 10 ft. long, rarely have a problem caused by these
motor–generated transient voltages.
Sometimes motor frame transient voltages are capacitively coupled to feedback devices
mounted on the motor shaft. To prevent this problem, add electrical isolation between
the motor and the feedback device. The most simple isolation method, shown in Figure
5-2, has two parts: 1) A plate of electrical insulating material placed between the motor
mounting surface and the feedback device. 2) An insulating coupling between motor
shaft and the shaft of the feedback device.
Figure 5-2 Isolated Mounting Method
Insulating plate
Insulating Coupling
Encoder or other
feedback device
5-16 Troubleshooting MN722
Mounting bracket
Page 86

Section 6
Manual Tuning the Series 22H Control
Manually Tuning the Control In some applications the drive cannot be accurately auto-tuned in an application. In
these cases it is necessary to calculate the values needed to tune the drive and manually
enter these calculated parameter values.
Motor Mag Amps Parameter This parameter is located in the Level 2, Motor Data Block. This parameter is
normally entered using the nameplate data (motor no load amps) or auto–tuned. If no
other data is available, set Motor Mag Amps parameter to about 40% of the motor rated
current stated on the nameplate.
The following procedure should be used for setting the Motor Mag Amps parameter with
the motor coupled to the load:
1. Adjust the Motor Mag Amps Parameter to 40% of the motor nameplate full load
current rating.
2. Give the controller a speed command input of 80% of the Base Speed on motor
nameplate.
3. Select motor voltage on keypad display by pressing the DISP key until the
motor voltage value is displayed.
4. Observe the motor voltage. Ideally, it should read 80% of motor nameplate
voltage. By raising the Motor Mag Amps parameter value, the motor voltage
will raise proportionally. Continuing to raise the Motor Mag Amps parameter
value will eventually saturate the motor voltage. By lowering the Motor Mag
Amps parameter value, the motor voltage will lower proportionally.
5. While the motor is running adjust the Motor Mag Amps parameter until the
display indicates the proper voltage (80% of motor rated).
Slip Frequency Parameter This parameter is located in the Level 1, Vector Control Block. The slip frequency
may be calculated from nameplate data or auto tuned.
F
+ Rated Freq *
slip
(
Rated RPM x Number of Motor Poles
ƪ
120
)
ƫ
OR
F
+ Rated Freq *
slip
Base Speed
ǒ
Sync Speed
(
Ǔ
Rated Freq
)
Current Prop Gain Parameter This parameter is located in the Level 1, Vector Control Block. The Current Prop
Gain parameter is normally auto–tuned when motor inductance is not known. Where
auto–tuning can’t be used, the proper manual setting for the proportional gain can be
calculated by:
ƪ
Current PROP Gain +
Where:
L = Line to neutral leakage inductance of the motor in mH
VAC = Nominal line Volts
A/V = The Amps/Volt scaling of the current feedback
Motor line to neutral leakage inductance can be obtained either from the motor
manufacturer or by measuring the line–to–line inductance and dividing by two.
The A/V scaling for the controller can be found in the diagnostic information located in the
DISPLAY MODE.
For most applications setting the Current Prop Gain parameter to a value of 20 will yield
adequate performance.
740xLxǒAńV
VAC
Ǔ
ƫ
Manual Tuning the Series 22H Control 6-1MN722
Page 87

Section 1
General Information
Current Int Gain Parameter
Speed Prop Gain Parameter
Speed Int Gain Parameter
The Current Int Gain parameter located in the Level 1 Vector Control Block is factory
preset at 150 Hz. This setting is suitable for essentially all systems. DO NOT CHANGE
WITHOUT FACTORY APPROVAL.
The Speed Prop Gain parameter located in the Level 1 Vector Control Block is factory set
to 10. This gain may be increased or decreased to suit the application. Increasing the
Speed Prop Gain parameter will result in faster response, excessive proportional gain will
cause overshoot and ringing. Decreasing the Speed Prop Gain parameter will cause
slower response and decrease overshoot and ringing caused by excessive proportional
gain.
The Speed Int Gain parameter located in the Level 1 Vector Control Block is set to 1 Hz
and may be set at any value from zero to 9.99 Hz. See also, PI Controller later in this
section.
Setting the Speed Int Gain parameter to 0Hz removes integral compensation that results
in a proportional rate loop. This selection is ideal for systems where overshoot must be
avoided and substantial stiffness (ability of the controller to maintain commanded speed
despite varying torque loads) isn’t required.
Increasing values of the Speed Int Gain parameter increases the low frequency gain and
stiffness of the controller, an excessive integral gain setting will cause overshoot for
transient speed commands and may lead to oscillation. Typical setting is 4 Hz. If the
Speed Prop Gain parameter and the Speed Int Gain parameter are set too high, an
overshoot condition can also occur.
To manually tune the control, the following procedure is used:
1. Set the speed Int Gain parameter = 0 (remove integral gain).
2. Increase the Speed Prop Gain parameter setting until adequate response to
step speed commands is attained.
3. Increase the Speed Int Gain parameter setting to increase the stiffness of the
drive or its’ ability to maintain speed with dynamic load changes.
Note: It is convenient to monitor speed step response with a strip chart recorder or
storage oscilloscope connected to J1–6 or –7 with Level 1, Output Block
Analog Out #1 or #2 set to ABS SPEED, 0 VDC = zero speed. See Section 3
for a discussion of analog outputs.
6-2 Manual Tuning the Series 22H Control MN722
Page 88

Section 1
General Information
PI Controller
Both the current and rate control loops are of the Proportional plus Integral type. If “E” is
defined to be the error signal,
E = Command – Feedback
then the PI controller operated on “E” as
Output = (Kp * E) + (Ki s E dt)
where Kp is the proportional gain of the system and Ki is the integral gain of the system.
The transfer function (output /E) of the controller using 1/s (Laplace Operator) to denote
the integral,
Output/E = Kp + KI / s = Kp (s + Ki/Kp) /s.
The second equation shows that the ratio of Ki/Kp is a frequency in radians/sec. In the
Baldor Series 22H AC Vector Control, the integral gain has been redefined to be,
KI = (Ki / Kp) / (2p) Hz,
and the transfer function is,
Output/E = Kp (s + 2pKI) / s.
This sets the integral gain as a frequency in Hz. As a rule of thumb, set this frequency
about 1/10 of the bandwidth of the control loop.
The proportional gain sets the open loop gain of the system, the bandwidth (speed of
response) of the system. If the system is excessively noisy, it is most likely due to the
proportional gain being set too high.
Manual Tuning the Series 22H Control 6-3MN722
Page 89

Section 1
General Information
6-4 Manual Tuning the Series 22H Control MN722
Page 90

Section 7
Specifications, Ratings & Dimensions
Specifications:
Horsepower 10-50 HP @ 230VAC
10-450 HP @ 460VAC
Input Frequency 50/60 HZ ± 5%
Note: 50Hz operation requires a 15% control
derating.
Output Voltage 0 to Maximum Input VAC
Output Current See Ratings Table
Service Factor 1.0
Duty Continuous
Overload Capacity Constant Torque Mode: 170-200% for 3 secs
150% for 60 secs
Variable Torque Mode: 115% for 60 secs
Speed Command Potentiometer 5k or 10k ohm, 0.5 watt
Operating Conditions:
Voltage Range: 230 VAC Models
460 VAC Models
Input Line Impedance: 3% minimum
Ambient Operating Temperature: 10 to +40 °C
Rated Storage Temperature: – 30 °C to +65 °C
Enclosure: NEMA 1: EL (suffix) Control Module
Humidity: NEMA 1: 10 to 90% RH Non-Condensing
Altitude: Sea level to 3300 Feet (1000 Meters)
Shock: 1G
Vibration: 0.5G at 10Hz to 60Hz
Keypad Display:
Display Backlit LCD Alphanumeric
Keys 12 key membrane with tactile response
Functions Output status monitoring
LED Indicators Forward run command
Remote Mount 100 feet (30.3m) max from control
180-264 VAC 3φ 60 Hz / 180-230 VAC 3φ 50 Hz
340-528 VAC 3φ 60 Hz / 340-460 VAC 3φ 50 Hz
Note: 50Hz operation requires a 15% control
derating.
Derate Output 2% per °C over 40 °C to 55 °C Max
NEMA 1: EK (suffix) Control Module
NEMA 1: EK (suffix) Filter Assembly
Open Chassis: EK 12% Boost Regulator
3% Line Reactor
Derate 2% per 1000 Feet (303 Meters) above 3300 Feet
2 Lines x 16 Characters
Digital speed control
Parameter setting and display
Diagnostic and Fault log display
Motor run and jog
Local/Remote toggle
Reverse run command
Stop command
Jog active
Specifications, Ratings & Dimensions 7-1MN722
Page 91

Control Specifications:
Control Method PWM
Velocity Loop Bandwidth Adjustable to 180 Hz
Current Loop Bandwidth Adjustable to 1200 Hz
Maximum Output Frequency 500 Hz
Standard Frequency Version Full rating 1-2.5 KHz PWM frequency,
Adjustable to 5 KHz with linear derating (between 2.5 - 5KHz)
by 10% at 5 KHz
Quiet Frequency Version Full rating 1-8 KHz PWM frequency,
Adjustable to 16 KHz with linear derating (between 8 - 16KHz)
by 30% at 16 KHz
Selectable Operating Modes Keypad
Standard 3 Wire Control
15 Speed Two Wire Control
3 Speed, 2 Wire Control
3 Speed, 3 Wire Control
Bipolar Speed/Torque Control
Serial
Process Control
EPOT, 2 Wire Control
EPOT, 3 Wire Control
Differential Analog Input:
Common Mode Rejection 40 db
Full Scale Range ±5VDC, ±10VDC, 4-20 mA
Resolution 9 bits + sign
Other Analog Input:
Full Scale Range 0 - 10 VDC
Resolution 9 bits + sign
Analog Outputs:
Analog Outputs 2 Assignable
Full Scale Range 0 - 5 VDC
Source Current 1 mA maximum
Resolution 8 bits
7-2 Specifications, Ratings & Dimensions MN722
Page 92

Digital Inputs:
Opto-isolated Logic Inputs 9 Assignable
Rated Voltage 10 - 30 VDC (closed contacts std)
Input Impedance 6.8 K Ohms
Leakage Current
10 mA maximum
Digital Outputs:
Opto-isolated Logic Outputs 4 Assignable
ON Current Sink 50 mA Max
ON Voltage Drop 2 VDC Max
Maximum Voltage 30 VDC
Diagnostic Indications:
Inverter Section:
Current Sense Fault Over speed New Base ID DC Bus High
Ground Fault Lost User Data Torque Proving DC Bus Low
Over Current FLT Soft Start Fault Following Error External Trip
Overload - 3 sec No EXB Installed Encoder Loss Int. Overtemp
Low INIT Bus Volts Ready Logic Supply Fault Invalid Base ID
Microprocessor Reset Memory Errors Power Base Fault Inverter Base ID
Over temperature (Motor or Control) Overload - 1 min Line REGEN Fault Resolver Loss
User Text Fault
Converter Section:
Current Sense Fault Invalid Base ID DC Bus Low Fault
GND Fault ID No Feedback High Initial Current Fault
Over Current Fault Power Base Fault Lost AB Phase
Overload Fault Lost User Data Lost BC Phase
New Base ID DC Bus High Low Init Bus Volts
Microprocessor Reset Sync to Line Fault Memory Error
Int Over temperature Logic Supply Fault
Specifications, Ratings & Dimensions 7-3MN722
Page 93

Series 22H Vector Control Ratings
CATALOG
NO.
ZD22H210–EL 230 C+ 10 7.4 28 56 10 7.4 28 32 10 7.4 28 48 10 7.4 28 32
ZD22H215–EL 230 C+ 15 11.1 42 84 15 11.1 42 48 10 7.4 30 61 15 11.1 42 48
ZD22H220–EL 230 C+ 20 14.9 55 100 20 14.9 55 62 15 11.1 42 92 20 14.9 54 62
ZD22H225–EL 230 C+ 25 18.6 68 116 25 18.6 68 78 20 14.9 54 92 25 18.6 68 78
ZD22H230–EL 230 D+ 30 22.3 80 140 30 22.3 80 92 25 18.6 70 122 30 22.3 80 92
ZD22H240–EL 230 D+ 40 29.8 105 200 40 29.8 105 120 30 22.3 80 160 40 29.8 104 120
ZD22H250–EL 230 D+ 50 37.2 130 225 50 37.2 130 150 40 29.8 105 183 50 37.2 130 150
ZD22H410–EL 460 C+ 10 7.4 15 30 10 7.4 15 17 7.5 5.5 11 22 10 7.4 15 17
ZD22H415–EL 460 C+ 15 11.1 21 36 15 11.1 21 24 10 7.4 15 30 15 11.1 21 24
ZD22H420–EL 460 C+ 20 14.9 27 54 20 14.9 27 31 15 11.1 21 46 20 14.9 27 31
ZD22H425–EL 460 C+ 25 18.6 34 58 25 18.6 34 39 20 14.9 27 46 25 18.6 34 39
ZD22H430–EL 460 D+ 30 22.3 40 70 30 22.3 40 46 25 18.6 35 61 30 22.3 40 46
ZD22H440–EL 460 D+ 40 29.8 55 100 40 29.8 55 63 30 22.3 40 80 40 29.8 52 60
ZD22H450–EL 460 D+ 50 37.2 65 115 50 37.2 65 75 40 29.8 55 92 50 37.2 65 75
ZD22H460–EK 460 D 60 44.7 80 140 60 44.7 80 92 50 37.2 65 122 60 44.7 80 92
ZD22H475–EK 460 E 75 56 100 170 75 56 100 115 60 44.7 80 140 75 56 100 115
ZD22H4100–EK 460 E 100 75 125 220 100 75 125 144 75 56 100 180 100 75 125 144
ZD22H4150–EK 460 F 150 112 190 380 150 112 190 220 125 93 150 260 150 112 170 200
ZD22H4200–EK 460 F 200 149 250 500 200 149 250 290 150 112 190 380 175 131 210 240
ZD22H4250–EL 460 G+ 250 187 310 620 250 187 310 356
ZD22H4300–EL 460 G+ 300 224 370 630 300 224 370 425
ZD22H4350–EL 460 G+ 350 261 420 720 350 261 420 480
ZD22H4400–EL 460 G+ 400 298 480 820 400 298 480 552
ZD22H4450–EL 460 G+ 450 336 540 920 450 336 540 620
INPUT
VOLT
ENCLO- STANDARD 2.5 kHz PWM QUIET 8.0 kHz PWM
SURE
SIZE
CONSTANT TORQUE VARIABLE TORQUE CONSTANT TORQUE VARIABLE TORQUE
HP KW IC IP HP KW IC IP HP KW IC IP HP KW IC IP
IC = Continuous Output Current (in Amps)
IP= Peak Output Current (in Amps)
EL= NEMA 1 enclosure
EK= Control, filter, and boost regulator shipped separately. Control and filter in NEMA1 enclosure.
Boost regulator and 3% line reactor are open chassis.
PWM Frequency Continuous and Peak Current Derating:
2.5KHz Ratings - Full rating from 1 - 2.5KHz
Adjustable from 1 - 5KHz with linear derating to 90% current rating at 5KHz
8.0KHz Ratings - Full rating from 1 - 8.0KHz
Adjustable from 1 - 16KHz with linear derating to 70% current rating at 16KHz
Custom Order.
Not Available.
7-4 Specifications, Ratings & Dimensions MN722
Page 94
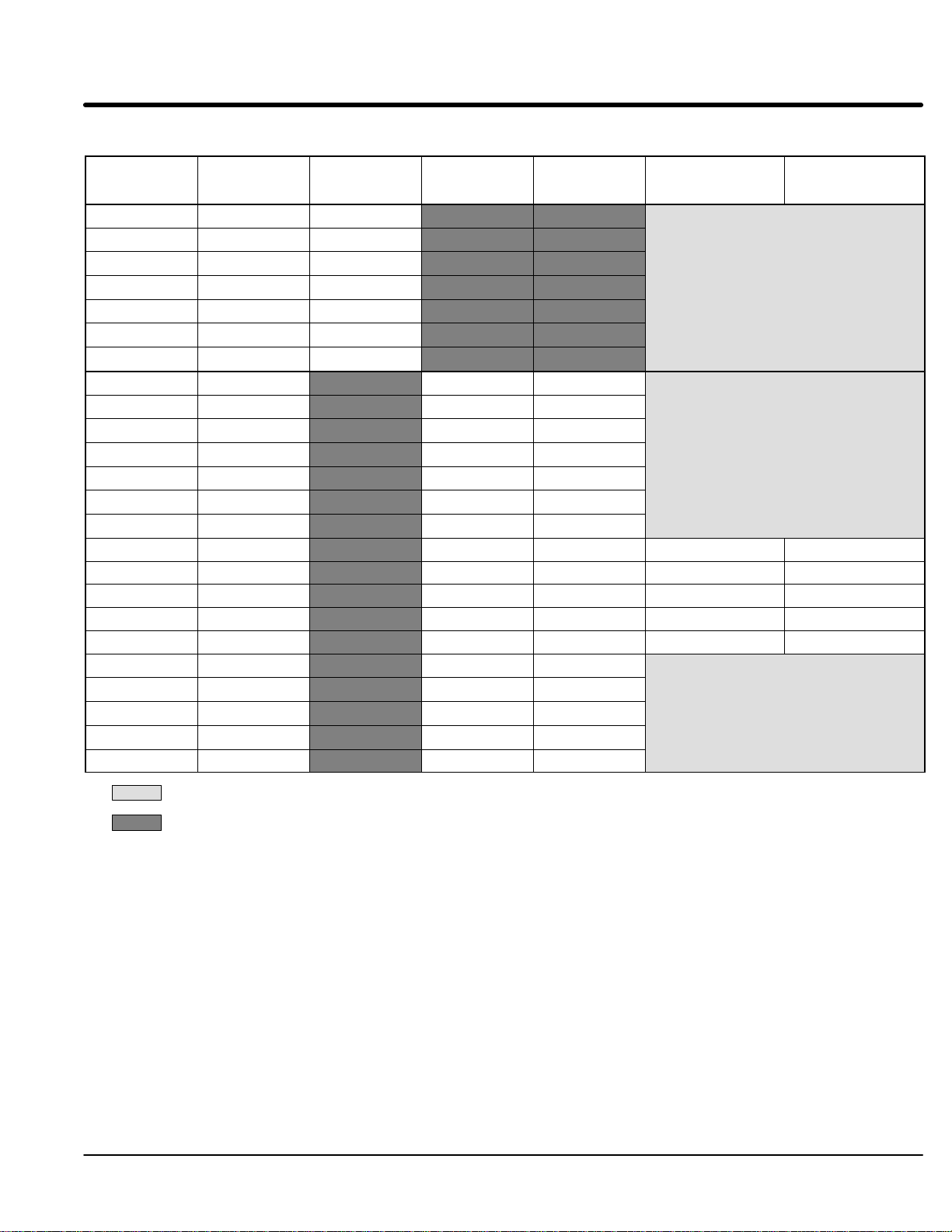
Section 1
General Information
Table 7-6 Matched Component Matrix
Control
Catalog No.
ZD22H210–EL VE0574A00 LRAC03501
ZD22H215–EL VE0575A00 LRAC04501
ZD22H220–EL VE0576A00 LRAC05501
ZD22H225–EL VE0577A00 LRAC08001
ZD22H230–EL VE0568A00 LRAC08001
ZD22H240–EL VE0569A00 LRAC10001
ZD22H250–EL VE0570A00 LRAC13001
ZD22H410–EL VE0565A00 LRAC01802 LRAC01802
ZD22H415–EL VE0082A00 LRAC02502 LRAC02502
ZD22H420–EL VE0088A00 LRAC03502 LRAC03502
ZD22H425–EL VE0090A00 LRAC04502 LRAC03502
ZD22H430–EL VE0092A00 LRAC04502 LRAC04502
ZD22H440–EL VE0094A00 LRAC05502 LRAC05502
ZD22H450–EL VE0096A00 LRAC08002 LRAC08002
ZD22H460–EK VE0097A00 LRAC08002 LRAC08002 V2080709 LF1015
ZD22H475–EK VE0099A00 LRAC10002 LRAC10002 V2080710 LF1015
ZD22H4100–EK VE0077A00 LRAC13002 LRAC13002 V2080711 LF1015
ZD22H4150–EK VE0079A00 LRAC25003 LRAC20002 V2080712 LF2015
ZD22H4200–EK VE0084A00 LRAC32003 LRAC25002 V2080713 LF2015
ZD22H4250–EL VE0671A00 LRAC32002 LRAC32002
ZD22H4300–EL VE0631A00 LRAC40002 LRAC40002
ZD22H4350–EL VE0632A00 LRAC50002 LRAC50002
ZD22H4400–EL VE0633A00 LRAC60002 LRAC50002
ZD22H4450–EL VE0634A00 LRAC75003 LRAC60002
Control
Specification
No.
230 VAC
3% Line Reactor
Catalog No.
380-415 VAC
4% Line Reactor
Catalog No.
460 VAC
3% Line Reactor
Catalog No.
Boost Regulator
Specification No.
Included in “EL” Suffix
Catalog Numbers
Catalog Numbers
Included in “EL” Suffix
Catalog Numbers
Catalog Numbers
Included in “EL” Suffix
Catalog Numbers
Catalog Numbers
FIlter
Specification No.
Included in EL Suffix Control Catalog Number.
Not applicable.
Note: Line reactor, boost regulator, filter assembly and control must be ordered separately.
Specifications, Ratings & Dimensions 7-5MN722
Page 95

Section 1
General Information
Terminal Tightening Torque Specifications
Table 7-7 Tightening Torque Specifications
Tightening Torque
Catalog No.
Power TB1 Ground Control J1 Interface J3 &
L1A, L2A, L3A
Lb-in Nm Lb-in Nm Lb-in Nm Lb-in Nm Lb-in Nm Lb-in Nm
ZD22H210–EL 35 4 50 5.6 7 0.8
ZD22H215–EL 35 4 50 5.6 7 0.8
ZD22H220–EL 35 4 50 5.6 7 0.8
ZD22H225–EL 35 4 50 5.6 7 0.8
ZD22H230–EL 35 4 50 5.6 7 0.8
ZD22H240–EL 35 4 50 5.6 7 0.8
ZD22H250–EL 35 4 50 5.6 7 0.8
ZD22H410–EL 35 4 50 5.6 7 0.8
ZD22H415–EL 35 4 50 5.6 7 0.8
ZD22H420–EL 35 4 50 5.6 7 0.8
ZD22H425–EL 35 4 50 5.6 7 0.8
ZD22H430–EL 35 4 22–26 2.5–3 7 0.8
ZD22H440–EL 22–26 2.5–3 22–26 2.5–3 7 0.8
ZD22H450–EL 22–26 2.5–3 22–26 2.5–3 7 0.8
ZD22H460–EK 22–26 2.5–3 22–26 2.5–3 7 0.8 7 0.8 7 0.8 50 5.6
ZD22H475–EK 22–26 2.5–3 50 5.6 7 0.8 7 0.8 7 0.8 50 5.6
ZD22H4100–EK 140 15 50 5.6 7 0.8 7 0.8 7 0.8 50 5.6
ZD22H4150–EK 275 31 275 31 7 0.8 7 0.8 7 0.8 50 5.6
ZD22H4200–EK 275 31 275 31 7 0.8 7 0.8 7 0.8 50 5.6
ZD22H4250–EL 275 31 275 31 7 0.8
ZD22H4300–EL 375 42 375 42 7 0.8
ZD22H4350–EL 375 42 375 42 7 0.8
ZD22H4400–EL 375 42 375 42 7 0.8
ZD22H4450–EL 375 42 375 42 7 0.8
Filter
J1 & J2
Line Reactor
Not Applicable.
7-6 Specifications, Ratings & Dimensions MN722
Page 96

Section 1
General Information
Dimensions
Size C+ Control
0.40
(10.2)
0.50
(12.7)
28.32
(719.3)
11.50
(292.1)
5.25
(133.3)
5.25
(133.3)
0.31
(7.9)
AIR OUTLET
AIR OUTLET AIR OUTLET
JOG LOCAL PROG
FWD
DISP
REV SHIFT ENTER
RESETSTOP
12.20(309.9mm)
12.00(304.8)
LIFTING
FLANGE
30.00
(762.0)
29.25
(743.0)
AIR INLET (Top)
AIR OUTLET
AIR OUTLET
.31(7.9mm)
AIR INLET (Bottom)
Note:
Allow 2 inches minimum clearance on all sides
for ventilation.
An internal baffle divides the enclosure into two parts.
The upper and lower parts each have separate air
inlets and outlets as shown.
AIR INLET
(Bottom)
Specifications, Ratings & Dimensions 7-7MN722
Page 97

Section 1
General Information
Dimensions Continued
Size D+ Control
0.40(10.2)
36.00
(914.4)
35.25
(895.4)
0.50
(12.7)
34.08
(865.6)
14.50(368.3)
6.75
(171.5)
AIR OUTLET
AIR OUTLET
AIR INLET (Top)
JOG LOCAL PROG
FWD
DISP
REV SHIFT ENTER
RESETSTOP
6.75
(171.5)
0.31
(7.9)
AIR OUTLET
12.20(309.9)
12.00(304.8)
LIFTING FLANGE
AIR INLET
(Bottom)
AIR OUTLET
AIR OUTLET
0.31
(7.9)
WIDE
AIR INLET (Bottom)
Note:
Allow 2 inches minimum clearance on all sides
for ventilation.
An internal baffle divides the enclosure into two parts.
The upper and lower parts each have separate air
inlets and outlets as shown.
7-8 Specifications, Ratings & Dimensions MN722
Page 98

Section 1
General Information
Dimensions Continued
Size D Control
25.00
(635.0mm)
24.25
(616.0mm)
14.50
(368.5mm)
13.50
(343.0mm)
JOG LOCAL PROG
FWD
DISP
REV SHIFT ENTER
RESETSTOP
Air
Outlet
23.12
(587.0mm)
.31
(8.0mm)
CUSTOMER
POWER
CONNECTIONS
10.00
(254.0mm)
10.20
(259.0mm)
AIR INLET
Specifications, Ratings & Dimensions 7-9MN722
Page 99

Section 1
General Information
Dimensions Continued
Size E Control
Air
Outlet
.38
(9.5mm)
2 Places
30.00
(762mm)
Thru–wall
Mounting Flange
R
AM
VO
Hz
JOG LOCAL PROG
FWD
DISP
REV SHIFT ENTER
RESETSTOP
Surface
Mounting
Flange
.38
(9.5mm)
2 Places
17.70
(450mm)
5.75
(146mm)
6.25
(159mm)
Air Inlet
7-10 Specifications, Ratings & Dimensions MN722
Page 100

Section 1
General Information
Dimensions Continued
Size E Control – Through–Wall Mounting
Mounting hole locations for Thru-Wall or
surface mounting. Recommended hardware: 5/16″ or M8. (4 Places)
(716mm)
(711mm)
(686mm)
(672mm)
28.19
28.00
27.00
26.44
Mounting hole locations for Thru-Wall
mounting using kit #0083991. Thru hole
.218″ (5.5mm) DIA. (4 Places)
(552mm)
(343mm)
(133mm)
(14mm)
(25mm)
(30mm)
21.75
13.50
5.25
.56
.00
1.00
1.19
.00
.19
.79
(5mm)
(20mm)
Cutout for thru–wall mounting
1.25
(32mm)
6.00
(152mm)
10.75
(273mm)
16.94
16.75
15.50
(425mm)
(430mm)
(394mm)
17.54
(445mm)
Specifications, Ratings & Dimensions 7-11MN722
 Loading...
Loading...