
© 2012 Baileigh Industrial, Inc.
REPRODUCTION OF THIS MANUAL IN ANY FORM WITHOUT WRITTEN APPROVAL OF BAILEIGH INDUSTRIAL, INC.
IS PROHIBITED. Baileigh Industrial, Inc. does not assume and hereby disclaims any liability for any damage or loss
caused by an omission or error in this Operator’s Manual, resulting from accident, negligence, or other occurence.
Rev. 11/2012
Baileigh Industrial, Inc.
P.O. Box 531
Manitowoc, WI 54221-0531
Phone: 920.684.4990
Fax: 920.684.3944
sales@baileighindustrial.com
OPERATOR’S
MANUAL
TABLE SAW
MODEL: TS-1044H

Table of Contents
THANK YOU & WARRANTY .......................................................................................... 1
INTRODUCTION ............................................................................................................ 3
GENERAL NOTES.......................................................................................................... 3
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS .............................................................................................. 4
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS ............................................................................................... 6
SPECIFICATIONS ........................................................................................................ 10
INTENDED USE ........................................................................................................... 11
Tools: ......................................................................................................................... 11
TECHNICAL SUPPORT ............................................................................................... 11
UNPACKING ................................................................................................................. 12
Cleaning .................................................................................................................... 12
GETING TO KNOW YOUR MACHINE ......................................................................... 13
TRANSPORTING AND LIFTING .................................................................................. 15
INSTALLATION ............................................................................................................ 16
ASSEMBLY ................................................................................................................... 18
INSTALL TABLE EXTENSION WINGS ..................................................................... 18
MOUNT FENCE STORAGE BRACKETS ................................................................. 18
FRONT RAIL INSTALLATION ................................................................................... 19
REAR RAIL INSTALLED ........................................................................................... 20
INSTALL BLADE GUARD ............................................................................................. 21
LOOSEN LOCK KNOB .............................................................................................. 21
ANTI-KICK BACK PAWL ........................................................................................... 22
RIVING KNIFE ........................................................................................................... 23
TABLE INSERT ......................................................................................................... 24
SAW BLADE ................................................................ ................................................. 25
FENCE ASSEMBLY...................................................................................................... 26
Align the Fence Parallel to the Blade ......................................................................... 26
Align the Rip Fence Perpendicular (90°) to the Table ................................................ 26
LEVEL THE FENCE .................................................................................................. 27
ADJUST & ALIGN RIP FENCE POINTER ................................................................ 27
DUST COLLECTOR ..................................................................................................... 28
PUSH STICK ................................................................................................................ 29
MITER GAUGE ............................................................................................................. 29
ELECTRICAL ................................................................................................................ 30
Extension Cord Safety ................................ ................................ ............................... 31
ADJUSTMENT .............................................................................................................. 32
ADJUSTING THE 45° & 90° BEVEL STOPS ............................................................ 32
ADJUSTING THE BEVEL ANGLE POINTER ............................................................ 33
BLADE TILT /BEVEL ADJUSTMENT ................................................................ ........ 33
BLADE HEIGHT ADJUSTMENT ............................................................................... 34
OPERATION ................................ ................................ ................................................. 35
Safety Precautions Before Operations ...................................................................... 35
Electrical Operation ................................................................................................... 35
Operation ................................................................................................................... 35
Non-Through & Through Cuts ................................................................................... 36
Workpiece Inspection ................................................................................................ 36
BLADE REQUIREMENTS ............................................................................................ 37
BLADE SELECTION ..................................................................................................... 37
DADO BLADES ............................................................................................................ 38
Ripping ...................................................................................................................... 39
Miter Ripping ............................................................................................................. 41
Ripping Small Work Pieces ....................................................................................... 41
Crosscutting............................................................................................................... 41
MAINTENANCE ............................................................................................................ 50
Cleaning .................................................................................................................... 51
Lubrication ................................................................................................................. 51
Changing Belt ............................................................................................................ 52
TROUBLESHOOTING .................................................................................................. 53
TABLE SAW PARTS DIAGRAMS................................................................................. 55
Table Saw Parts List .................................................................................................. 59
1
1
THANK YOU & WARRANTY
Thank you for your purchase of a machine from Baileigh Industrial. We hope that you find it
productive and useful to you for a long time to come.
Inspection & Acceptance. Buyer shall inspect all Goods within ten (10) days after receipt thereof. Buyer’s
payment shall constitute final acceptance of the Goods and shall act as a waiver of the Buyer’s rights to inspect or
reject the goods unless otherwise agreed. If Buyer rejects any merchandise, Buyer must first obtain a Returned
Goods Authorization (“RGA”) number before returning any goods to Seller. Goods returned without a RGA will be
refused. Seller will not be responsible for any freight costs, damages to goods, or any other costs or liabilities
pertaining to goods returned without a RGA. Seller shall have the right to substitute a conforming tender. Buyer will
be responsible for all freight costs to and from Buyer and repackaging costs, if any, if Buyer refuses to accept
shipment. If Goods are returned in unsalable condition, Buyer shall be responsible for full value of the Goods.
Buyer may not return any special order Goods. Any Goods returned hereunder shall be subject to a restocking fee
equal to 30% of the invoice price.
Specifications. Seller may, at its option, make changes in the designs, specifications or components of the Goods
to improve the safety of such Goods, or if in Seller’s judgment, such changes will be beneficial to their operation or
use. Buyer may not make any changes in the specifications for the Goods unless Seller approves of such changes
in writing, in which event Seller may impose additional charges to implement such changes.
Limited Warranty. Seller warrants to the original end-user that the Goods manufactured or provided by Seller
under this Agreement shall be free of defects in material or workmanship for a period of twelve (12) months from
the date of purchase, provided that the Goods are installed, used, and maintained in accordance with any
instruction manual or technical guidelines provided by the Seller or supplied with the Goods, if applicable. The
original end-user must give written notice to Seller of any suspected defect in the Goods prior to the expiration of
the warranty period. The original end-user must also obtain a RGA from Seller prior to returning any Goods to
Seller for warranty service under this paragraph. Seller will not accept any responsibility for Goods returned without
a RGA. The original end-user shall be responsible for all costs and expenses associated with returning the Goods
to Seller for warranty service. In the event of a defect, Seller, at its sole option, shall repair or replace the defective
Goods or refund to the original end-user the purchase price for such defective Goods. Goods are not eligible for
replacement or return after a period of 30 days from date of receipt. The foregoing warranty is Seller’s sole
obligation, and the original end-user’s exclusive remedy, with regard to any defective Goods. This limited warranty
does not apply to: (a) die sets, tooling, and saw blades; (b) periodic or routine maintenance and setup, (c) repair or
replacement of the Goods due to normal wear and tear, (d) defects or damage to the Goods resulting from misuse,
abuse, neglect, or accidents, (f) defects or damage to the Goods resulting from improper or unauthorized
alterations, modifications, or changes; and (f) any Goods that has not been installed and/or maintained in
accordance with the instruction manual or technical guidelines provided by Seller.
EXCLUSION OF OTHER WARRANTIES. THE FOREGOING LIMITED WARRANTY IS IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER
WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. ANY AND ALL OTHER EXPRESS, STATUTORY OR IMPLIED
WARRANTIES, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO, ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS
FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMED. NO WARRANTY IS MADE WHICH
EXTENDS BEYOND THAT WHICH IS EXPRESSLY CONTAINED HEREIN.
Limitation of Liability. IN NO EVENT SHALL SELLER BE LIABLE TO BUYER OR ANY OTHER PARTY FOR
ANY INCIDENTIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL OR SPECIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST
PROFITS OR DOWN TIME) ARISING FROM OR IN MANNER CONNECTED WITH THE GOODS, ANY BREACH
BY SELLER OR ITS AGENTS OF THIS AGREEMENT, OR ANY OTHER CAUSE WHATSOEVER, WHETHER
BASED ON CONTRACT, TORT OR ANY OTHER THEORY OF LIABILITY. BUYER’S REMEDY WITH RESPECT
TO ANY CLAIM ARISING UNDER THIS AGREEMENT IS STRICTLY LIMITED TO NO MORE THAN THE
AMOUNT PAID BY THE BUYER FOR THE GOODS.

2
2
Force Majuere. Seller shall not be responsible for any delay in the delivery of, or failure to deliver, Goods due to
causes beyond Seller’s reasonable control including, without limitation, acts of God, acts of war or
terrorism, enemy actions, hostilities, strikes, labor difficulties, embargoes, non-delivery or late delivery of materials,
parts and equipment or transportation delays not caused by the fault of Seller, delays caused by civil authorities,
governmental regulations or orders, fire, lightening, natural disasters or any other cause beyond Seller's reasonable
control. In the event of any such delay, performance will be postponed by such length of time as may be reasonably
necessary to compensate for the delay.
Installation. If Buyer purchases any Goods that require installation, Buyer shall, at its expense, make all
arrangements and connections necessary to install and operate the Goods. Buyer shall install the Goods in
accordance with any Seller instructions and shall indemnify Seller against any and all damages, demands, suits,
causes of action, claims and expenses (including actual attorneys’ fees and costs) arising directly or indirectly out
of Buyer’s failure to properly install the Goods.
Work By Others; Safety Devices. Unless agreed to in writing by Seller, Seller has no responsibility for labor or
work performed by Buyer or others, of any nature, relating to design, manufacture, fabrication, use, installation or
provision of Goods. Buyer is solely responsible for furnishing, and requiring its employees and customers to use all
safety devices, guards and safe operating procedures required by law and/or as set forth in manuals and instruction
sheets furnished by Seller. Buyer is responsible for consulting all operator’s manuals, ANSI or comparable safety
standards, OSHA regulations and other sources of safety standards and regulations applicable to the use and
operation of the Goods.
Remedies. Each of the rights and remedies of Seller under this Agreement is cumulative and in addition to any
other or further remedies provided under this Agreement or at law or equity.
Attorney’s Fees. In the event legal action is necessary to recover monies due from Buyer or to enforce any
provision of this Agreement, Buyer shall be liable to Seller for all costs and expenses associated therewith,
including Seller’s actual attorneys' fees and costs.
Governing Law/Venue. This Agreement shall be construed and governed under the laws of the State of
Wisconsin, without application of conflict of law principles. Each party agrees that all actions or proceedings arising
out of or in connection with this Agreement shall be commenced, tried, and litigated only in the state courts sitting in
Manitowoc County, Wisconsin or the u.s. Federal Court for the Eastern District of Wisconsin. Each party waives
any right it may have to assert the doctrine of “forum non conveniens” or to object to venue to the extent that any
proceeding is brought in accordance with this section. Each party consents to and waives any objection to the
exercise of personal jurisdiction over it by courts described in this section. Each party waives to the fullest extent
permitted by applicable law the right to a trial by jury.
Summary of Return Policy.
10 Day acceptance period from date of delivery. Damage claims and order discrepancies will not be accepted
after this time.
You must obtain a Baileigh issued RGA number PRIOR to returning any materials.
Returned materials must be received at Baileigh in new condition and in original packaging.
Altered items are not eligible for return.
Buyer is responsible for all shipping charges.
A 30% re-stocking fee applies to all returns.
Baileigh Industrial makes every effort to ensure that our posted specifications, images, pricing and product
availability are as correct and timely as possible. We apologize for any discrepancies that may occur. Baileigh
Industrial reserves the right to make any and all changes deemed necessary in the course of business including but
not limited to pricing, product specifications, quantities, and product availability.
For Customer Service & Technical Support:
Please contact one of our knowledgeable Sales and Service team members at:
(920) 684-4990 or e-mail us at sales@baileighindustrial.com
3
3
INTRODUCTION
The quality and reliability of the components assembled on a Baileigh Industrial machine
guarantee near perfect functioning, free from problems, even under the most demanding
working conditions. However if a situation arises, refer to the manual first. If a solution cannot be
found, contact the distributor where you purchased our product. Make sure you have the serial
number and production year of the machine (stamped on the nameplate). For replacement parts
refer to the assembly numbers on the parts list drawings.
Our technical staff will do their best to help you get your machine back in working order.
In this manual you will find: (when applicable)
Safety procedures
Correct installation guidelines
Description of the functional parts of the machine
Capacity charts
Set-up and start-up instructions
Machine operation
Scheduled maintenance
Parts lists
GENERAL NOTES
After receiving your equipment remove the protective container. Do a complete visual
inspection, and if damage is noted, photograph it for insurance claims and contact your
carrier at once, requesting inspection. Also contact Baileigh Industrial and inform them of the
unexpected occurrence. Temporarily suspend installation.
Take necessary precautions while loading / unloading or moving the machine to avoid any
injuries.
Your machine is designed and manufactured to work smoothly and efficiently. Following proper
maintenance instructions will help ensure this. Try and use original spare parts, whenever
possible, and most importantly; DO NOT overload the machine or make any unauthorized
modifications.
Note: This symbol refers to useful information throughout the manual.

4
4
IMPORTANT
PLEASE READ THIS OPERATORS MANUAL CAREFULLY
It contains important safety information, instructions, and necessary operating procedures.
The continual observance of these procedures will help increase your production and
extend the life of the equipment.
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
LEARN TO RECOGNIZE SAFETY INFORMATION
This is the safety alert symbol. When you see this symbol
on your machine or in this manual, BE ALERT TO THE
POTENTIAL FOR PERSONAL INJURY!
Follow recommended precautions and safe operating
practices.
UNDERSTAND SIGNAL WORDS
A signal word – DANGER, WARNING, or CAUTION is
used with the safety alert symbol. DANGER identifies a
hazard or unsafe practice that will result in severe Injury
or Death.
Safety signs with signal word DANGER or WARNING are
typically near specific hazards.
General precautions are listed on CAUTION safety signs.
CAUTION also calls attention to safety messages in this
manual.

5
5
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS.
Refer to them often and use them to instruct others.
PROTECT EYES
Wear safety glasses or suitable eye
protection when working on or around
machinery.
DUST HAZARD
Wear appropriate dust mask. Dust created while using machinery can
cause cancer, birth defects, and long term respiratory damage. Be aware
of the dust hazards associated with all types of materials.
DUST PARTICLES AND IGNITION SOURCES
DO NOT operate the table saw in areas where explosion risks are
high. Such areas include locations near pilot lights, open flames, or
other ignition sources.
ROTATING BLADE HAZARD
Moving saw blade may result in loss of fingers or limb. DO NOT
operate with guard removed. Follow lockout/tagout procedures
before servicing.

6
6
WARNING: FAILURE TO FOLLOW THESE RULES MAY RESULT IN
SERIOUS PERSONAL INJURY
PROTECT AGAINST NOISE
Prolonged exposure to loud noise can cause impairment or loss of
hearing. Wear suitable hearing protective devices such as ear muffs or
earplugs to protect against objectionable or uncomfortable loud noises.
HIGH VOLTAGE
USE CAUTION IN HIGH VOLTAGE AREAS. DO NOT assume the
power to be off.
(FOLLOW PROPER LOCKOUT PROCEDURES)
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Wood working can be dangerous if safe and proper operating procedures are not followed. As
with all machinery, there are certain hazards involved with the operation of the product. Using
the machine with respect and caution will considerably lessen the possibility of personal injury.
However, if normal safety precautions are overlooked or ignored, personal injury to the operator
may result.
Safety equipment such as guards, push sticks, hold-downs, feather boards, goggles, dust
masks and hearing protection can reduce your potential for injury. But even the best guard won’t
make up for poor judgment, carelessness or inattention. Always use common sense and
exercise caution in the workshop. If a procedure feels dangerous, don’t try it.
REMEMBER: Your personal safety is your responsibility.
1. FOR YOUR OWN SAFETY, READ INSTRUCTION MANUAL BEFORE OPERATING THE
MACHINE. Learn the machine’s application and limitations as well as the specific hazards.
2. Only trained and qualified personnel should operate this machine.
3. Make sure guards are in place and in proper working order before operating
machinery.

7
7
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS (cont.)
4. Kickback. Kickback happens when the piece part is thrown back toward the operator at a
high rate of speed. Before operating this saw, understand how kickback occurs, and how to
prevent it.
5. Reaching Over Saw Blade. NEVER reach behind or over the blade with either hand while
the saw is operating. If kickback of a piece part were to occur, you could amputate your
hands, arms, or fingers.
6. Blade Height. Adjust the blade to the correct height above the piece part so it does not
kickback toward the operator causing injury.
7. Remove any adjusting tools. Before operating the machine, make sure any adjusting tools
have been removed.
8. Blade Guard / Riving Knife. To reduce the risk of kickback, always use the riving knife and
blade guard. Make sure they are properly installed during cutting operations.
9. Dado and Rabbet Operations. Dado and Rabbeting operations require that the blade guard
be removed. Be aware of your personal safety while the guard is off, and replace the blade
guard after these operations are completed.
10. Keep work area clean. Cluttered areas invite injuries.
11. Push Sticks and Push Blocks. When ripping narrow stock, there is a risk of your hands
and fingers contacting the rotating blade, resulting in serious personal injury.
12. Overloading machine. By overloading the machine you may cause injury from flying parts.
DO NOT exceed the specified machine capacities.
13. Crosscutting Operations. Remove the rip fence whenever using the miter gauge to
crosscut a piece part.
14. Operator Position. If kickback occurs, the blade will eject the piece part into the path of the
operator. NEVER stand in- line with the cutting path of the blade during operation.
15. Dress appropriate. DO NOT wear loose fitting clothing or jewelry as they can be caught in
moving machine parts. Protective clothing and steel toe shoes are recommended when
using machinery. Wear a restrictive hair covering to contain long hair.
16. Awkward Positions. Avoid awkward hand and body positions where a sudden slip could
cause your hands or body to contact the spinning blade.
17. Use eye and ear protection. Always wear ISO approved impact safety goggles
18. Do not overreach. Maintain proper footing and balance at all times. DO NOT reach over or
across a running machine.
19. Damaged Saw Blades. A damaged saw blade can cause kickback. If in doubt as to the
condition of the blade, DO NOT use it.

8
8
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS (cont.)
20. Stay alert. Watch what you are doing and use common sense. DO NOT operate any tool or
machine when you are tired.
21. Check for damaged parts. Before using any tool or machine, carefully check any part that
appears damaged. Check for binding of moving parts that may affect proper machine
operation.
22. Observe work area conditions. DO NOT use machines or power tools in damp or wet
locations. Do not expose to rain. Keep work area well lighted. DO NOT use electrically
powered tools in the presence of flammable gases or liquids.
23. DO NOT bypass or defeat any safety interlock systems.
24. Know the location of the ON - OFF switch and the “E”- STOP button.
25. Removing Piece Parts. Before removing cut-offs, always turn the saw OFF, and wait for the
blade to stop turning, to avoid contact with a moving blade.
26. Control of the Piece Part. If the piece part should unexpectedly move or bind the blade,
kickback could occur. Make sure the piece part is supported by either the rip fence or the
crosscut fence. NEVER back a piece part out of a cut.
27. Supporting Piece Part. Provide adequate support to the sides and rear of the saw table for
material that is extra wide and long.
28. Keep visitors a safe distance from the work area.
29. Keep children away. Children must never be allowed in the work area. DO NOT let them
handle machines, tools, or extension cords.
30. DO NOT operate machine if under the influence of alcohol or drugs. Read warning
labels on prescriptions. If there is any doubt, DO NOT operate the machine.
31. DO NOT touch live electrical components or parts.
32. Be Sure all equipment is properly installed and grounded according to national, state, and
local codes. If machine is equipped with a three-prong plug, it should be plugged into a
three-hole electrical receptacle. If an adapter is used to accommodate a two-prong
receptacle, the adapter plug must be attached to a known ground. Never remove the third
prong.
33. Inspect power and control cables periodically. Replace if damaged or bare wires are
exposed. Bare wiring can kill!
34. Maintain machine in top condition. Keep clean for best and safest performance. Follow
instructions for lubricating and changing accessories.
35. Reduce the risk of unintentional starting. Make sure switch is in “OFF” position before
plugging in power cord.
9
9
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS (cont.)
36. Never leave machine running unattended. TURN POWER OFF. Don’t leave machine until
it comes to a complete stop.
37. Make sure machine is disconnected from power supply while motor is being mounted,
connected or reconnected.
38. Saw Appropriate Material. Only use this saw for natural wood stock and wood stock
products such as particle board, plastics, laminates, and medium-density fibre board (MDF).
DO NOT try and cut metal, glass, ceramics, or products containing asbestos or lead paint.
Some of these materials contain hazardous dust and can cause severe respiratory
problems.
39. Warning: The dust generated by certain woods and wood products can be injurious to your
health. Always operate machinery in well ventilated areas and provide for proper dust
removal. Use a wood dust collection system whenever possible.
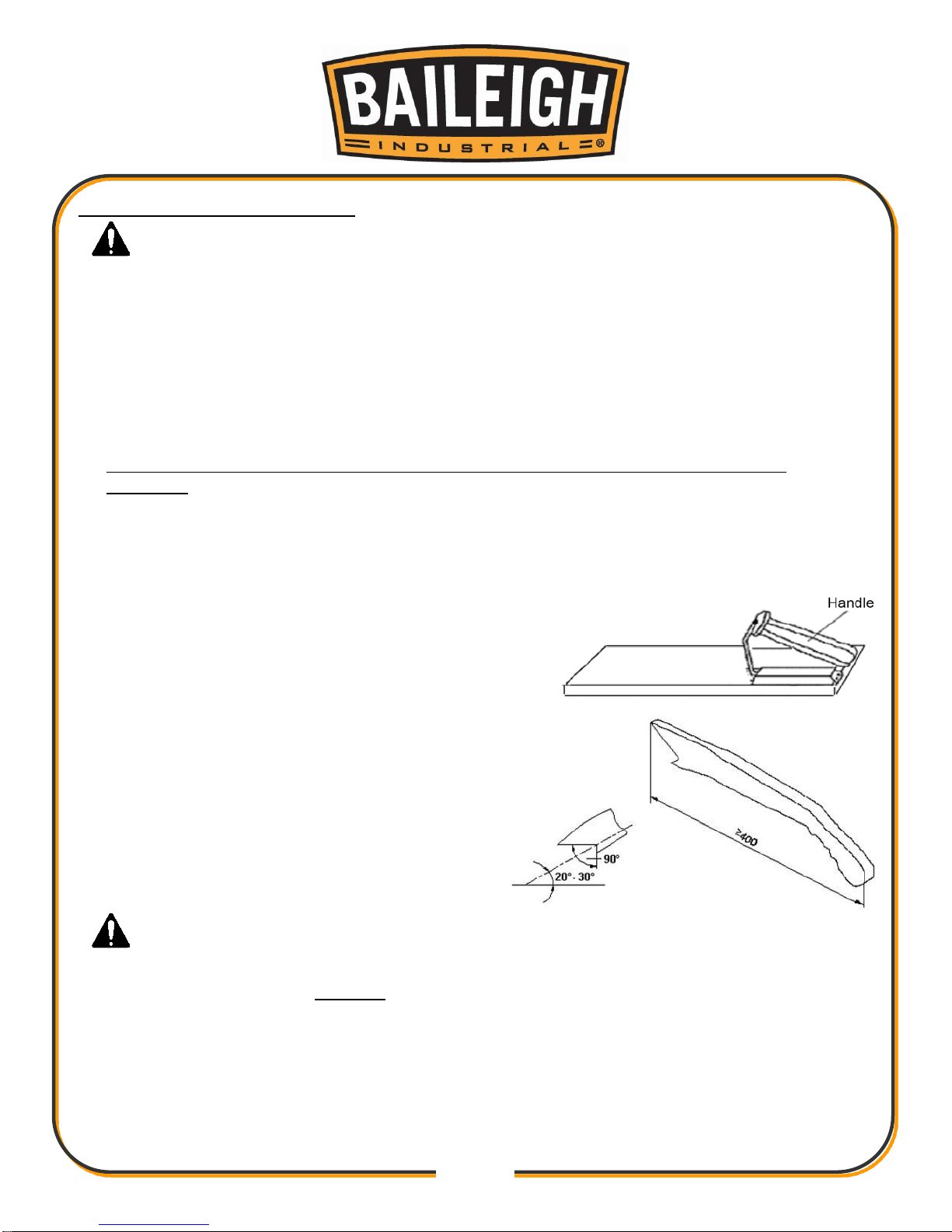
40. A push block and/or a push stick must be used if
the workpieces is less than 5” (127mm) to prevent
your hands from getting too close to the saw blade.
Push block must be used to cut narrow workpieces
and, when necessary, to push the workpiece
against the fence, a push block can be easily made
by the operator.
EMERGENCY STOP
In the event of incorrect operation or dangerous conditions, the machine can be stopped
immediately by pressing the ON/OFF switch.
10
10
Item
TS-1044H
Product Dimensions
Weight
347Ibs
L x W x H
66.4" x 40" x 41"
Foot Print (L x W)
19.1" x 19.5"
Electrical
Switch
Magnetic with Thermal Overload
Protection
Motor
Type
TEFC Capacitor Start Induction
Horsepower, Voltage, Cycle,
Phase, Amps
1.75HP, 110V/220V, 60Hz, 1PH,
14A/7A (pre-wired 110V)
Speed
3450 RPM
Power Transfer
V-Belt Drive
Blade Information
Maximum Blade Diameter
10"
Riving Knife/Spreader Thickness
0.09" (2.3mm)
Required Blade Body Thickness
0.078" (2mm)
Required Blade Kerf Thickness
0.118" (3mm)
Maximum Width of Dado
13/16"
Blade Tilt
Left 0-45°
Arbor Size
5/8“
Arbor Speed
4000 RPM
Arbor Bearings
Sealed and Permanently Lubricated
Cutting Capacities
Maximum Depth of Cut At 90°
3-1/8"
Maximum Depth of Cut At 45°
2-3/16"
Maximum Rip To Right of BladeStandard
36"
Maximum Rip To Left Of Blade
12"
Table
Floor To Table Height
34.5"
Main Table (L x W x T)
44" x 27" x 1-1/2"
Miter Gauge
Miter Gauge Slot Type
T-Slot
Miter Gauge Slot Type (W x H)
3/4" x 3/8"
Other
Dust Port Size
4"
SPECIFICATIONS

11
11
INTENDED USE
Table saw and the workpiece guide equipment supplied with it are intended to be used
exclusively for the following purposes:
Laminated and unlaminated board materials (e.g. chipboard, coreboard, MDF board, ...)
Solid wood
Gypsum plasterboard, Cardboard, Veneer with a suitable clamping device.
Dimensionally stable plastics (thermoset plastics, thermoplastics). Sawing these materials
does not normally involve any risks in respect of dust, chips, and thermal degradation
products.
Tools:
The chosen saw blade must be suitable both for the specific work cycle and for the specific
material.
Only circular blades which are solid chrome vanadium (CV) or tungsten carbide tipped (TCT)
and have a diameter of 10” (255mm), arbor size 5/8” (16mm), as well as a maximum width of
13/16” (20mm) are allowed for the main saw.
Saw blades made of high-alloy high-speed steel (HSS) are not allowed to be used.
Saw blades and their fixing devices shall conform to EN 847-1:2005.
Note:The photos illustrations in this manual are representative only and may not
depict the actual color, labeling or accessories and may be intended to illustrate technique only.
Note: The specifications and dimensions presented here are subject to change
without prior notice due to improvements of our products.
TECHNICAL SUPPORT
Our technical support department can be reached at 920.684.4990, and asking for the support
desk for purchased machines. Tech Support handles questions on machine setup, schematics,
warranty issues, and individual parts needs: (other than die sets and blades).
For specific application needs or future machine purchases contact the Sales Department at:
sales@baileighindustrial.com, Phone: 920.684.4990, or Fax: 920.684.3944.

12
12
WARNING: DO NOT USE gasoline or other petroleum products to clean
the machine. They have low flash points and can explode or cause fire.
CAUTION: When using cleaning solvents work in a well ventilated area.
Many cleaning solvents are toxic if inhaled.
GAS
UNPACKING
Remove saw from the shipping cartons. Check for damage and ensure all parts are intact. Any
damage should be reported immediately to your distributor and shipping agent. Before
assembling, read the manual thoroughly, familiarizing yourself with correct assembly and
maintenance procedures and proper safety precautions.
If you can't find an item on this list, check the mounting location on the machine or examine the
packaging materials carefully. Occasionally we pre-install certain components for shipping
purposes.
Cleaning
Your machine may be shipped with a rustproof waxy oil coating and grease on the exposed
unpainted metal surfaces. To remove this protective coating, use a degreaser or solvent
cleaner. For a more thorough cleaning, some parts will occasionally have to be removed. DO
NOT USE acetone or brake cleaner as they may damage painted surfaces.
Follow manufacturer’s label instructions when using any type of cleaning product. After cleaning,
wipe unpainted metal surfaces with a light coating of quality oil or grease for protection.
With a screw driver, push a solvent-saturated rag into the T-slots to remove the grease.

13
13
GETING TO KNOW YOUR MACHINE
Thank you for choosing this table saw. This unit is carefully
tested and inspected before shipment and if properly used
and maintained, will provide you with years of reliable
service. To ensure optimum performance and trouble free
operation a reasonable amount of care and attention is
required.
To get the most from your new table saw, please take the
time to read this manual before assembling, installing and
operating the unit.
The table saw features a circular blade underneath that
can be raised and lowered to control the depth of cut.
The rail-mounted fence, which slides freely toward or
away from the blade, is used as the main cutting guide
for the workpiece.
The miter gauge is used to guide and support the
workpiece during the cut when the workpiece cannot slide against the
fence in a stable manner that miter gauge body can be rotated to
allow a wide range of cutting angles.
The blade guard assembly is equipped with a spreader, anti-kickback
pawls and riving knife, which work to prevent kickback and stop or slow
kickback if it happens. The riving knife is used when the guard is
removed for certain non through cuts.
The push stick is used to support the workpiece during the cut and
reduces the risk of injury by keeping hands away from the blade while
cutting.
36” Rail and Extension Table (optional)
14
14
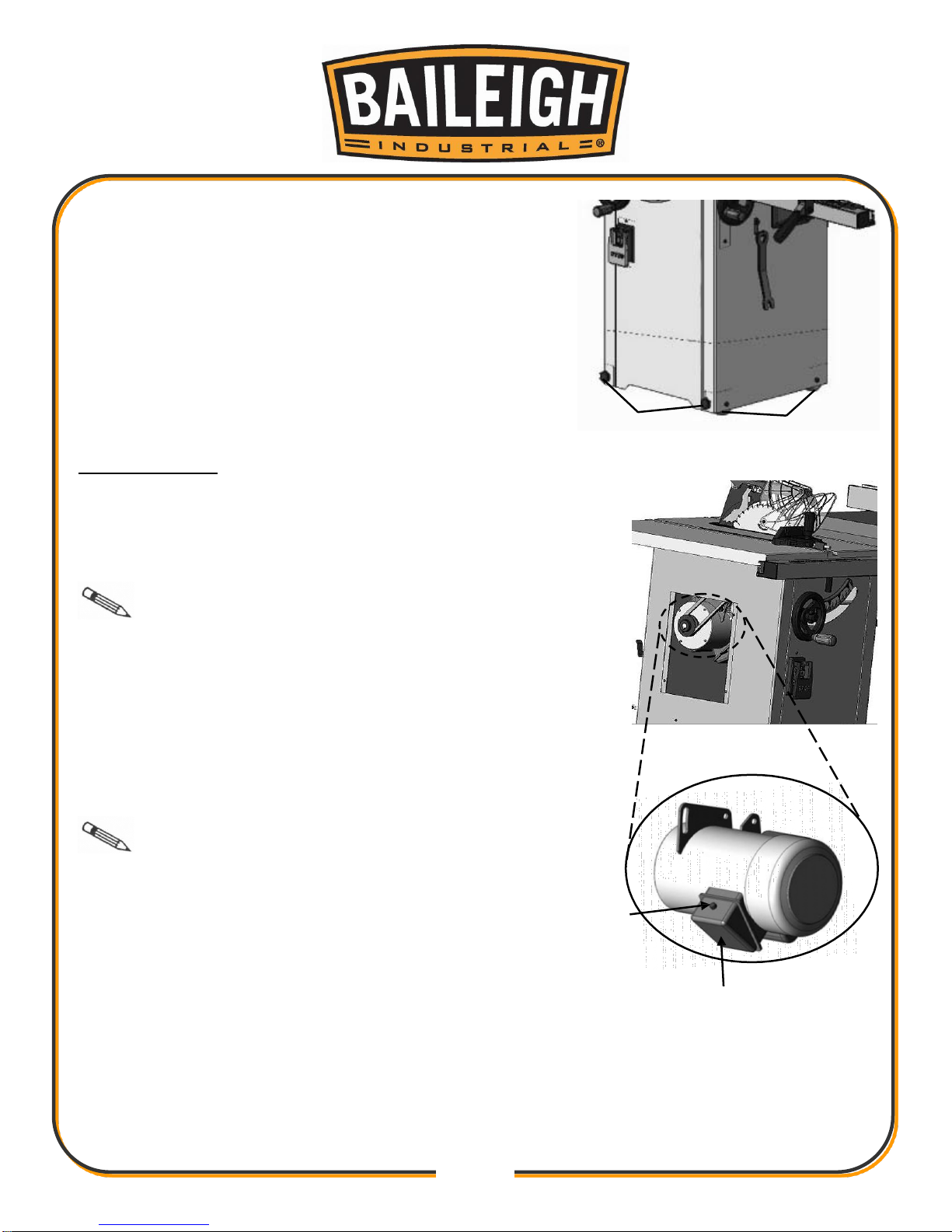
Reset
Switch
Junction
Box
Leveling
Caster
The moveable caster on this saw with (2) casters (2)
leveling screws front caster and front pedal that will
easier to move this saw and to place this saw as you
want.
Before performing machine leveling adjustment, shift the
foot pedal upward to allow the leveling screws to rest on
the floor. Turn the (2) leveling screws located at the
front bottom of the stand using a open wrench.
Reset Protector
Your saw comes equipped with a manual-reset thermaloverload protector designed to open the power line
circuit when the motor temperature exceeds a safe
level, when motor is overloaded, or when a low voltage
condition exists.
Note: This motor should be blown out or
vacuumed frequently to prevent sawdust buildup which
can interfere with normal motor ventilation.
Once the motor is cooled to a safe operating
temperature, reset the thermal overload protector by
pushing the red button on the front of the junction box.
An audible click will indicate the thermal overload
protector is reset. Once the switch button is reset, the
saw may be started and operated as normal.
Note: If the reset button won't click into
place immediately, the motor is still too hot and must be
allowed to cool.
Frequent “blowing” of fuses or tripping of circuit
breakers may result if:
Motor is overloaded. Overloading can occur if a
workpiece is fed too rapidly or if the saw is
misaligned.
Motor circuit is fused differently from recommendations. Always follow instructions for the
proper fuse/breaker. Do not use a fuse/breaker of greater capacity without consulting a
qualified electrician.
15
15
CAUTION: Lifting and carrying operations should be carried out by skilled
workers, such as a truck operator, crane operator, etc. If a crane is used to lift the
machine, attach the lifting chain carefully, making sure the machine is well balanced.
Choose a location that will keep the machine free from vibration and dust from other
machinery. Keep in mind that having a large clearance area around the machine is
important for safe and efficient working conditions.
Low voltage. Although the motor is designed for operation on the voltage and frequency
specified on the motor, normal loads will be handled safely on voltage no more than ten
percent above or below that figure. Heavy loads, however, require that voltage at motor
terminals equal the voltage specified on the motor.
motor fails to perform satisfactorily.
The table saw is equipped with a push-button switch
that will accept a safety padlock (not included). To
safeguard your machine from unauthorized operation
and accidental starting by young children, the use of a
padlock is required.
Note: Always check the connections, the load and the supply circuit whenever the
TRANSPORTING AND LIFTING
While transporting or handling the machine, be careful and let the
activity be done by qualified personnel especially trained for this
kind of activity!
While the machine is being loaded or unloaded, make sure that no
person or object gets crushed by the machine!
Select proper transportation device according to the weight of the machine.
Make sure the lifting capacity of transportation device is competent for the weight of the
machine.

16
16
INSTALLATION
IMPORTANT:
Consider the following when looking for a suitable location to place the machine:
Overall weight of the machine.
Weight of material being processed.
Sizes of material to be processed through the machine.
Space needed for auxiliary stands, work tables, or other machinery.
Clearance from walls and other obstacles.
Maintain an adequate working area around the machine for safety.
Have the work area well illuminated with proper lighting.
Keep the floor free of oil and make sure it is not slippery.
Remove scrap and waste materials regularly, and make sure the work area is free from
obstructing objects.
This machine should be installed and operated only on a solid, flat and stable floor that is able to
support the weight of the saw (312 lbs-142 kgs) and the operator.
Using the dimensions shown as a guideline, plan for placement within your shop that will allow
the operator to work unencumbered and unobstructed by foot traffic or other tools or machinery.
It is important to maintain free area of 36” (914mm) around the machine, which is required for
the working place. If any long material is machined, it is necessary to have a sufficient room in
front of the machine as well behind it in the places of material input and output.
Before beginning assembly, take note of the following precautions and suggestions
The machine is bolted to the pallet. Before attempting any of the assembly procedures
remove all of the loose parts and hardware from the inside of the machine and unbolt the
machine from the pallet.
FLOOR: This tool distributes a large amount of weight over a small area. Make certain that
the floor is capable of supporting both the weight of the machine and the operator. The floor
should also be a level surface. If the unit wobbles or rocks once in place, be sure to eliminate
by using shims.
WORKING CLEARANCES: Take into consideration the size of the material to be processed.
Make sure that you allow enough space for you to operate the machine freely.
OUTLET PLACEMENT: Outlets should be located close enough to the machine so that the
power cord or extension cord is not in an area where it would cause a tripping hazard. Be
sure to observe all electrical codes if installing new circuits and/or outlets.

17
17
WARNING: Before operating; make sure it is positioned firmly on a solid
work surface. If it tips over on you, it could cause severe injury or death.

18
18
WARNING: For your own safety, DO NOT connect the machine to the
power source until the machine is completely assembled and you read and
understand the entire instruction manual.
ASSEMBLY
INSTALL TABLE EXTENSION WINGS
1. Attach the table extension wings to the main table
using 8 x 12mm hex head bolts (4 per wing), and
8 lock washers.
2. Align the table extensions with the table and
loosely attach the bolts.
3. Place a straightedge on the table and extension
to align the extension table and then tighten the
bolts.
MOUNT FENCE STORAGE BRACKETS
The miter gauge and arbor wrench storage brackets are already
installed on the saw.
Install the fence storage brackets on the right side of the saw as
shown in using two Phillips head screws and flat washers.
Note: Be sure that the table extension wings are flush with front edge.

19
19
FRONT RAIL INSTALLATION
The 36” front rail consists of 2 pieces of tubes and
joining pins.
1. Loosely thread the six square head bolts to
the front of the table.
2. Do not tighten down the nuts; leave the square heads of the bolt protruding
from the table
3. From the left side of the saw, slide the upper slot of the left
(shorter) front rail onto the square head bolts
4. Set the left end of the rail flush to the outside edge of the
extension wing.

20
20
5. From the right side of the saw, slide the upper slot of
the right front rail onto the square head bolts.
6. Fit the 2 rails together.
7. Tighten down the nuts to firmly secure the front rails to
the table.
REAR RAIL INSTALLED
36” rear rail with 2 pieces of rail.
1. Use 6 cap screws with lock washers and nuts to
assemble the rear rails to the rear of the saw as
shown.
2. Make sure that the intersection between the two rear
rails is leveled (for 36” rail only).

21
21
CAUTION: After changing a saw blade, always check that the Riving
knife or Blade Guard is correctly set!
INSTALL BLADE GUARD
The blade guard assembly that consists of the clear shield, the spreader and the anti-kickback
pawls on each side. Each has important safety functions during the operation of the saw.
1. Disconnect and lockout power to the saw!
2. Remover the table blade insert.
3. Insert the spreader into the bracket slot and
tighten the lock knob shown to secure the
spreader.
4. Tug the spreader up to verify it is locked.
5. Lift the blade guard cover just enough to slide the
table insert into the table slot over the blade, and
then secure the insert with the knob on the front
of the insert. It should swing up high enough to
accommodate the workpiece.
6. Lifting up the right spreader pawl.
7. Place a straightedge against the blade and the
spreader. When properly aligned the
spreader/riving knife will be in the "alignment
zone," shown and will be parallel with the blade.
LOOSEN LOCK KNOB
If you could not loosen the knob by hand, used the
arbor wrench on the knob inside then turn the arbor
wrench counter-clockwise to loosen the knob.

22
22
ANTI-KICK BACK PAWL
The anti-kickback pawls allow the workpiece to travel in only one direction. If the workpiece
moves backwards, the pawls will dig into the workpiece to slow or stop it.
The pawls must return to their bottom-most position
after pivoting.
Note: The right pawl is designed to tilt
slightly away from the blade guard assembly to
prevent the pawl from catching in the table insert.
If the pawls fail to return to the bottom position, the
pivot spring may have been dislodged or broken and
will need to be fixed/replaced.

23
23
RIVING KNIFE
Use the riving knife for all non-through cuts made with
a standard table saw blade or dado blade. Use the
riving knife for those special operations where the
blade guard or its components get in the way of safe
operation, such as with very narrow cuts.
The key difference between the spreader and the
riving knife is that the riving knife mounts below the
blade's highest point of rotation
The riving knife must be kept within the range shown.
A 10" blade is required for operations that use a riving
knife. Do not use the riving knife with a dado blade
that has a diameter smaller than 10". If a smaller
diameter blade is used, the riving knife height will
exceed the blade height and the workpiece will hit the
riving knife during use. This will create a dangerous
situation of trying to turn the saw off with the
workpiece stuck halfway through the cut.
e Riving Knife Thickness
b Saw Blade Thickness
B Blade Kerf (width of saw blade cut)
Note: In order to work properly, the riving knife cannot be bent or misaligned with
the blade. If the riving knife gets accidentally bent, take the time to straighten it or just replace it.
Using a bent or misaligned riving knife will increase the risk of kickback!

24
24
TABLE INSERT
To install the zero clearance insert:
1. Disconnect and lockout power to the saw!
2. Lower the blade to the lowest position below the
table surface.
3. Verify that the blade is properly installed and
secure.
4. Install the table insert.
5. Adjust the table insert set screws with a 2.5mm
hex wrench to make sure the insert is flush with
the table then turn the lock knob to secure the
insert.
6. Connect power to the saw and turn the saw ON.
7. Set the blade angle at 90° then slowly raise the
blade to the maximum height that will be used
during normal operations.
8. Stop the saw and disconnect and lockout power
to the saw.
9. Use a straightedge to determine whether the insert is level with the table top.
10. Turn each of the 5 adjusting screws with the allen wrench until level at all positions.

25
25
WARNING: Blades are dangerously sharp. Use extreme caution when
working with or around the blade. Wear proper safety protection such as heavy
gloves.
WARNING: Turn the power switch “OFF” and unplug the power cord
from its power source when changing the saw blade.
When replacing blades, check the thickness stamped onto the riving knife. You must
select a blade with a kerf width larger than the thickness of the riving knife. Thinner
blades may cause the workpiece to bind during cutting.
USE ONLY 10″diameter blades with 5⁄8″arbor holes, rated at or higher than 3800 rpm.
SAW BLADE
1. Disconnect and lockout power to the
saw!
2. Set the blade to 90º and raise it to its
highest position.
3. Loosen the knob on the table insert and
remove the table insert and blade
guard/riving knife, depending on what is
installed.
4. Use the arbor wrenches to loosen and
remove the arbor nut, flange, and blade.
Note: Loosen the arbor nut by turning
counterclockwise.
5. Reinstall the arbor flange and arbor nut then tighten
them against the blade. Do not over tighten.
6. Slide the blade over the arbor with the teeth facing
the front of the saw.
7. Install the arbor flange and arbor nut, and tighten
them against the blade. Do not overtighten.
8. Install the blade guard/riving knife and table insert.

26
26
WARNING: The rip fence must be parallel to the blade during operation.
Failure to set the rip fence parallel to the blade can result in kickback and possible
serious injury.
FENCE ASSEMBLY
Align the Fence Parallel to the Blade
1. Disconnect and lockout power to the saw!
2. Slide the fence over to the right T-slot on the saw table
top.
3. Lock down the fence handle and make a visual check
that the fence is parallel with the T-slot along the entire
length. Also, you can place a small 3/4” thick block of
wood, upright into the T-slot and slide it from the front to
the back checking its distance from the left edge of the
fence.
4. If the fence is not parallel, it can be adjusted by using an
Allen wrench to turn one or both of the screws (C) or (D).
Do this slowly, just an eighth to a quarter turn at a time, or
you will quickly overshoot the desired adjustment.
recheck the alignment of your fence to the blade.
Align the Rip Fence Perpendicular (90°) to the Table
1. Disconnect and lockout power to the saw!
2. Place a machinist square on the table against the
fence and look for a gap between the square and the
fence (bottom and top) or the table.
3. If needed, adjust either of the two plastic set screws to
tilt the fence slightly and square it to the table.
Note: It is always good practice to periodically

27
27
E
LEVEL THE FENCE
The fence should be parallel to the table and sit
approximately 2mm above the table’s surface (so the
fence will not scratch the table and a thin work piece
will not get stuck or jammed under the fence).
1. Disconnect and lockout power to the saw!
2. Loosen the hex nut (F) on the leveling foot (G)
located under the rear end of the fence.
3. Raise or lower the leveling foot until there is a
spacing of approximately 5/64” (2mm) between
the bottom of the fence and the table.
4. Hold the leveling foot in position and tighten the
hex nut to lock the setting of the leveling foot.
5. If needed, to level the fence, adjust the plastic set
screws (E) equally, thereby raising or lowering the
front of the fence an equal amount on either side
so as not to undo the previous perpendicular
adjustment.
ADJUST & ALIGN RIP FENCE POINTER
1. Disconnect and lockout power to the saw!
2. Set blade to 90° and raise it to the maximum
height.
3. Move the fence until it lightly touches the right
side of the blade and push down the locking lever
to lock the fence in place.
4. With the fence locked in place against the blade,
loosen the pointer screws (B).
5. Line up the reference line on the pointer with the zero point on the tape and tighten the
pointer screws.
Note: When changing blades, re-align the pointer with the zero points on the tapes
to account for thinner or thicker blades.

28
28
DUST COLLECTOR
It is recommended that you use a dust collector (not included) when using this saw. The saw
comes with a 4” dust port located on the lower left side of the machine.
The minimum air flow requirement for this machine are listed below.
Air current speed is 20m/s for vacuum suction dust emission index.
When air current speed of dust collector device (in accordance with EN12779:2004) is not lower
than 20m/s, ensure machine can be normal exhausted. User must wear dustproof mask.
1. Required air flow: 1500 m3/h.
2. Ensure pressure drop of each dust collector outlet carrying air current speed: 1100Pa.
3. Wind speed of dust collector tube m/s:
Dry Chips: 20m/s,
Wet chips: 28m/s (water content is equal to18%)
1. Fit the 4" dust hose over the dust port (not
included), and secure in place with a hose clamp.
2. Make sure the hose does not come off. A tight fit is
necessary for proper performance.
Important: Always turn on the dust
collector before starting the saw and stop the saw
before turning off the dust collector.

29
29
PUSH STICK
The proper use of a push stick will reduce the risk
of injury by keeping your hands away from the
blade while cutting.
Whenever your hands will get within 12" of the
blade a push stick should be used.
To maintain control when cutting large workpieces,
start the cut by feeding with your hands then use
push sticks to finish the cut, so your hands are not
on the end of the workpiece as it passes through
the blade.
Plan and Practice.
With the power to the saw OFF, place the push stick(s) in a position where they will be easy to
reach without reaching over the saw blade or losing control of the workpiece.
MITER GAUGE
The miter gauge is equipped with stop screws that
allow you to easily adjust the miter gauge from 45° to
the left, 90° (centered) and 45° to the right.
The stop screws contact the stop shaft to stop the
gauge at the three most common positions.
The stop shaft moves in to contact the stop screws or
out to allow the gauge to swing past the stop.
For adjustments slide the miter gauge into the T-slot on
the table, and then push the sliding shaft all the way
into the miter gauge.
To use a setting other than 90°, loosen the lock knob (A) by turning it
counter-clockwise, pull the stop-lock pin (B) and rotate the miter head
to 45°, or any angle shown on the numerical guide.
Turn the lock knob (A) clockwise to tighten and secure the miter head.
To check the accuracy of the miter gauge’s settings, set it at 90° and
check it with an L-square or T-square. To verify the setting, make a
test cut in scrap stock and then use a square to check the cut piece.
Repeat adjustment if necessary.
If the miter gauge needs adjusting, manually turn the head so the
pointer is where you think it ought to be, tighten the lock knob and
loosen the nut.

30
30
CAUTION: HAVE ELECTRICAL UTILITIES CONNECTED TO MACHINE BY
A CERTIFIED ELECTRICIAN!
Check if the available power supply is the same as listed on the machine nameplate.
WARNING: Make sure the grounding wire (green) is properly connected
to avoid electric shock. DO NOT switch the position of the green grounding wire if
any electrical plug wires are switched during hookup.
WARNING: In all cases, make certain the receptacle in question is
properly grounded. if you are not sure, have a qualified electrician check the
receptacle.
ELECTRICAL
Connections
A separate electrical circuit should be used for your tools. If an extension cord is used, use
only 3-wire extension cords, which have grounding type plugs and receptacles, which accept
the tool’s plug. Before connecting the motor to the power line, make sure the switch is in the
“OFF” position and be sure that the electric current is of the same characteristics as
indicated on the tool.
All line connections shall make good contact. Running on low voltage will damage the motor.
In the event of a malfunction or breakdown, grounding provides a path of least resistance for
electric current to reduce the risk of electric shock. This tool is equipped with an electric cord
having an equipment-grounding conductor and a grounding plug. The plug must be plugged
into a matching outlet that is properly installed and grounded in accordance with all local
codes and ordinances.
Do not modify the plug provided - if it will not fit the outlet, have the proper outlet installed by
a qualified electrician.
Improper connection of the equipment-grounding conductor can result in risk of electric
shock. The conductor with insulation having an outer surface that is green with or without
yellow stripes is the equipment-grounding conductor. If repair or replacement of the electric
cord or plug is necessary, do not connect the equipment-grounding conductor to a live
terminal.
Check with a qualified electrician or service personnel if the grounding instructions are not
completely understood, or if in doubt as to whether the tool is properly grounded.
Use only 3-wire extension cords that have grounding type plugs and receptacles that accept
the tool’s plug.

31
31
LENGTH
AMP RATING
25ft
50ft
100ft
0-6
16
16
16
7-10
16
16
14
11-12
16
16
14
13-16
14
12
12
17-20
12
12
10
21-30
10
10
No
WIRE GAUGE
Repair or replace damaged or worn cord immediately.
Extension Cord Safety
Extension cord should be in good condition and meet the minimum wire gauge requirements
listed below:
An undersized cord decreases line voltage, causing loss of power and overheating. All cords
should use a ground wire and plug pin. Replace any damaged cords immediately.

32
32
WARNING: Make sure the electrical disconnect is OFF before working on
the machine.
Always follow proper safety precautions when working on or around any machinery.
ADJUSTMENT
Before operation, the machine should be carefully adjusted for best performance.
ADJUSTING THE 45° & 90° BEVEL STOPS
1. Disconnect and lockout power to the saw!
2. Raise the blade to its highest position and lift the blade
guard.
3. Loosen the bevel lock knob and turn the blade tilting
handwheel clockwise until it stops.
4. Verify the angle of the blade with a combination square
from the left side of the blade; keep the square flat against
the table and against the flat part of the blade. Do not
touch the teeth or the table insert.
5. If the blade angle is incorrect, turn the 90° A stop screw
located on the table top to the left of the blade one full
counter-clockwise turn using the supplied 6 mm allen key.
6. Turn the hand wheel until the blade is at 90° to the table
surface. Then re-tighten the 90° stop screw clockwise until
slight resistance is felt. Do not over tighten stop screw.
7. Verify the 45° setting by tilting the blade as far as possible
to the left and using the square, check the angle and if
needed adjust as for the 90° stop, this time using the right
stop screw B.

33
33
ADJUSTING THE BEVEL ANGLE POINTER
The bevel pointer should read “0” when the blade is
at 90° to the table. If not, with the blade set 90°
vertical to the table, proceed as follows:
1. Disconnect and lockout power to the saw!
2. Remove the handwheel by loosening the
handwheel lock knob.
3. Once the hand wheel has been removed, loosen
the cap screw on the pointer mounting bracket
with screw driver, and manually align the pointer
with the zero on the bevel scale, then re-tighten the
screw and re-attach the hand wheel.
BLADE TILT /BEVEL ADJUSTMENT
The blade tilt (bevel) adjustment handwheel (C) is located on the side of the saw. The bevel
locking lever (D) is located under the table at the front of the saw and allows the user to lock the
tilting mechanism and secure the blade at the desired angle.
To change the angle of the blade:
1. Loosen the bevel locking handle (D) by turning it
counter-clockwise.
2. Turn the handwheel (C) left or right as required to
set the blade to the desired angle. The blade can
be tilted to the left anywhere from 0° (90° to the
table) to 45°.
3. With the blade tilted to the desired angle, tighten
the bevel locking handle by turning it clockwise to
lock the tilting mechanism and secure the blade.

34
34
CAUTION: To limit your exposure to the blade and maximise the
effectiveness of the anti-kickback pawls (when using the riving style splitter & blade
guard), never take more blade height than is required to complete the cut. When
setting the blade height for through-cuts (cuts all the way through the thickness of a
board) set the height of the blade to roughly 1/4" higher than the thickness of the
board.
BLADE HEIGHT ADJUSTMENT
The blade height adjustment handwheel is located on
the front of the saw and there is a lock knob on the
handwheel that allows you to lock the wheel and
secure the blade at the desired height.
To raise or lower the blade:
1. Loosen the blade height lock knob by turning
counter clockwise.
2. To raise the blade: Turn the handwheel clockwise.
To lower the blade: Turn the handwheel counter
clockwise.
3. With the blade set to the desired height, tighten the lock knob by turning clockwise to lock
the blade.

35
35
WARNING: Never operate the saw with any gaurds or covers removed
missing or damaged. It could cause severe injury or death.
CAUTION: Always wear proper eye protection with side shields or a face
shield, safety footwear, dust mask, and possibly heavy gloves to protect from, chips,
dust, burrs, and slivers.
WARNING: Check that saw blade clamping system is tight before
operating the machine.
B
A
OPERATION
Safety Precautions Before Operations
The operation of power tools involves a certain amount of hazard for the operator. Before
attempting regular work we recommend you get the feel of operations using scrap lumber to
check settings. Read entire instructions before you start to cut workpiece.
Always pay attention to safety precautions to avoid personal injury.
Electrical Operation
Become familiar with the location and operation of the Start and
Stop buttons. Practice reaching for the buttons, espesially the Stop
button, with power disconnected from the saw.
A Start button
B Stop button
DO NOT stand directly inline with the saw blade when starting.
Operation
Plain sawing includes ripping and crosscutting, plus a few other standard operations of a
fundamental nature. The following methods feature safety. As with all power tools there is a
certain amount of hazard involved with the operation and use of the tool. Using the tool with the
respect and caution demanded as far as safety precautions are concerned will considerably
lessen the possibility of personal injury. However, if normal safety precautions are overlooked or
completely ignored, personal injury to the operator can develop. It is good practice to make trial
cuts using scrap material when setting up you saw for operation.
36
36
Non-Through & Through Cuts
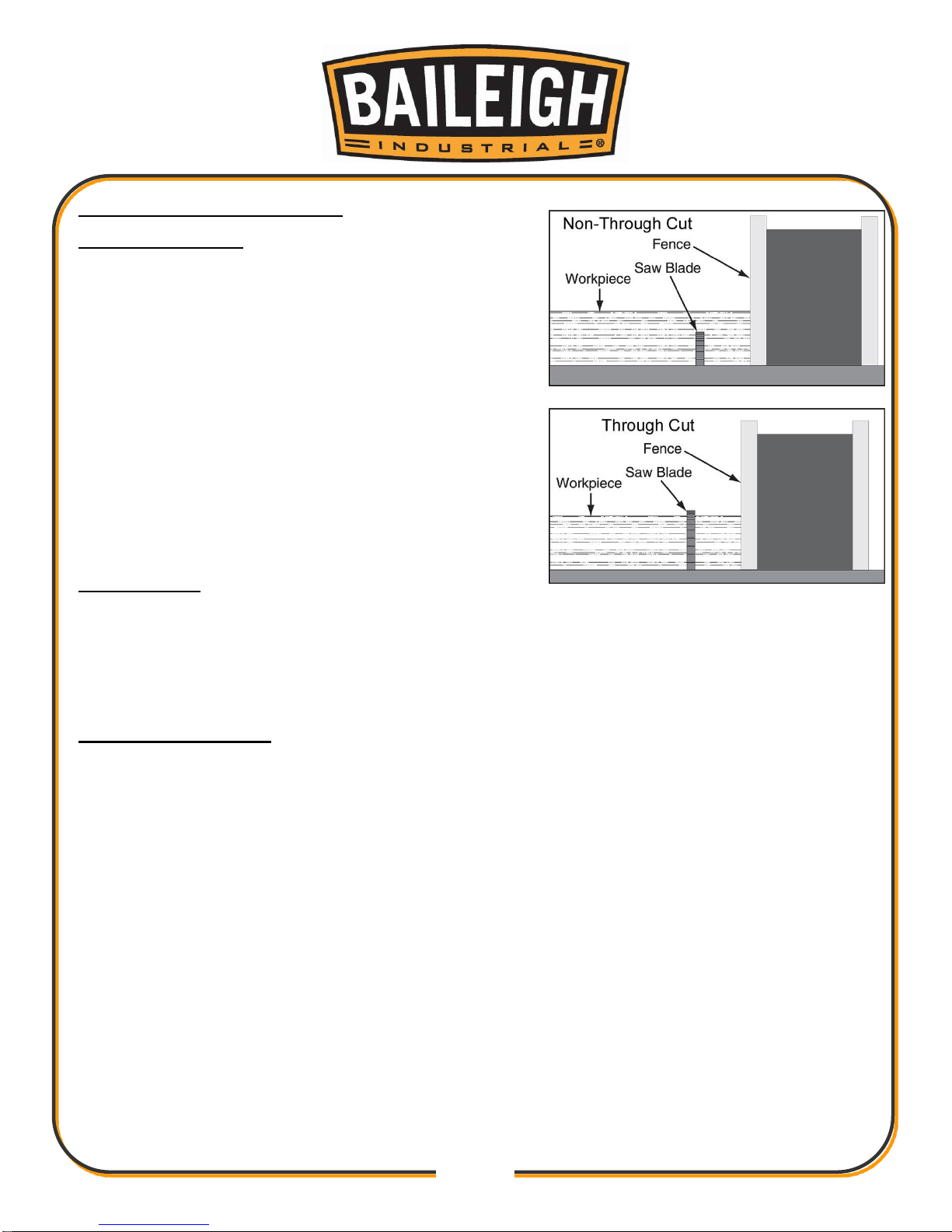
Non-Through Cuts
A non-through cut is a sawing operation where the
blade does not extend above the top face of the wood
stock.
Examples of non-through cuts include dadoes and
rabbets. Non-through cuts have a higher risk of injury
from kickback because the blade guard must be
removed. However, the riving knife MUST be installed
because it still provides some protection. When making
non-through cuts with a dado blade, do not attempt to
cut the full depth in one pass. Instead, take multiple
light passes to reduce the load on the blade. A dado
blade smaller than 10" will require removal of the riving
knife, because the riving knife will be higher than the
blade.
Through Cuts
A through cut is a sawing operation in which the blade does extend through the workpiece and
the result is a workpiece which is completely sawn through. Examples of through cuts are rip
cuts, cross cuts, miter cuts, and beveled cuts. The blade guard assembly MUST be used when
performing through cuts.
Workpiece Inspection
Some workpieces are not safe to cut on this machine or may need to be modified before they
can be safely cut. Before cutting, inspect all workpieces for the following:
Material Type: This machine is intended for cutting natural and man-made wood products,
laminate covered wood products, and some plastics. Cutting drywall or cement based backer
board creates extremely fine dust and may reduce the life of the motor bearings. This
machine is NOT designed to cut metal, glass, stone, tile, etc.; cutting these materials with a
table saw greatly increases the risk of injury and damage to the saw or blade.
Foreign Objects: Nails, staples, dirt, rocks and other foreign objects are often embedded in
wood. While cutting, these objects can become dislodged and hit the operator, cause
kickback, or break the blade, which might then fly apart. Always visually inspect your
workpiece for these items. If they can't be removed, DO NOT cut the workpiece.
Large/Loose Knots: Loose knots can become dislodged during the cutting operation. Large
knots can cause kickback and machine damage. Choose workpieces that do not have
large/loose knots or plan ahead to avoid cutting through them.
Wet or "Green" Stock: Cutting wood with a moisture content over 20% causes
unnecessary wear on the blades, increases the risk of kickback, and yields poor results.
Excessive Warping: Workpieces with excessive cupping, bowing, or twisting are dangerous
to cut because they are unstable and may move unpredictably when being cut.

37
37
Minor Warping: Slightly cupped workpieces can be safely supported with cupped side
facing the table or fence; however, work-pieces supported on the bowed side will rock during
the cut, which could cause kickback.
BLADE REQUIREMENTS
To ensure that the spreader or riving knife works safely, the following requirements MUST be
met when installing new blades.
Blade Diameter: 10"
Required Blade Body Thickness (excluding teeth): 0.078" (2mm)
Required Blade Kerf Thickness: 0.118"- (3mm)
The spreader or riving knife MUST be aligned/adjusted to blade.
These requirements DO NOT apply to dado blades.
BLADE SELECTION
This section on blade selection is by no means comprehensive. Always follow the saw blade
manufacturer's recommendations to ensure safe and efficient operation of your table saw.
Ripping Blade Features
Best for cutting with the grain
20-40 teeth
Flat-top ground tooth profile
Large gullets for large chip removal
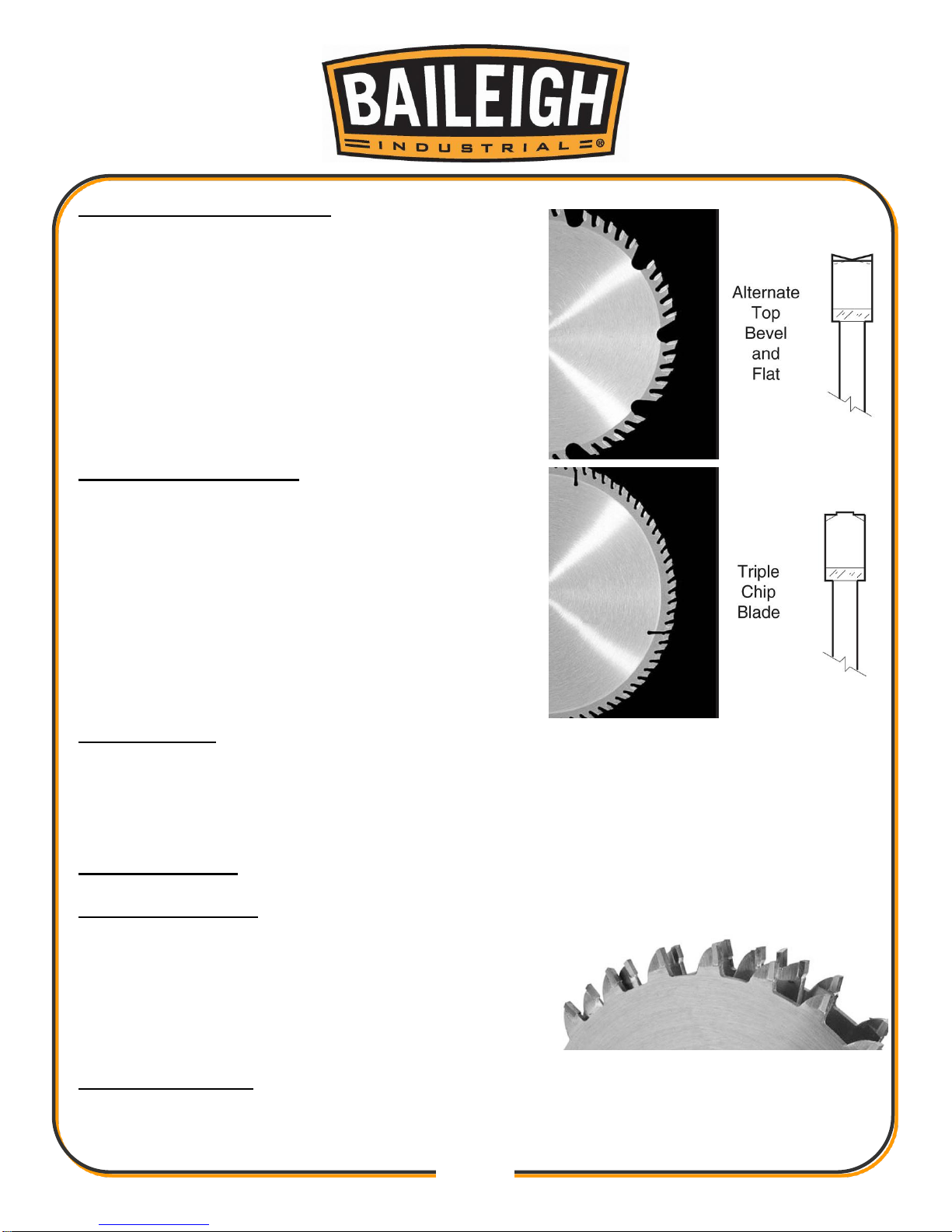
Crosscut Blade Features
Best for cutting across the grain
60-80 teeth
Alternate top bevel tooth profile
Small hook angle and a shallow gullet
38
38
Combination Blade Features
Designed to cut both with and across grain
40-50 teeth
Alternate top bevel and flat, or alternate top bevel
and raker tooth profile
Teeth are arranged in groups
Gullets are small and shallow (similar to a cross-cut
blade), then large and deep (similar to a ripping
blade
Laminate Blade Features
Best for cutting plywood or veneer
40-80 teeth
Triple chip tooth profile
Very shallow gullet
Thin Kerf Blade
A blade with thinner kerf than a standard blade. Since the spreader/riving knife included with this
table saw is sized for standard blades, thin kerf blades cannot be used on this saw unless they
meet the Blade Requirements specified in this manual; otherwise, they will increase the risk of
kickback.
DADO BLADES
Stacked Dado Blade
Multiple blades are stacked together to control the
cutting width. Stacked dado blades are more expensive
than wobble blades, but typically produce higher quality
results.
Wobble Dado Blade
A single blade mounted at a slight angle on an arbor hub. The blade angle is adjustable on the
hub, and the width of the dado cut is controlled by the angle setting of the blade.

39
39
WARNING: Keep the blade guard installed and in the down position.
Failure to do this could result in serious personal injury or death.
Never reach in towards the blade while the blade is still spinning!
Whenever a rip cut is completed, turn off the saw and wait for the blade to come to a
complete stop before reaching in to remove the workpiece or the waste material.
Failure to follow this warning could result in accidental contact with rotating blade,
causing lacerations or amputation.
Ripping
Ripping is the operation of making a lengthwise cut through a board. The rip fence is used to
position and guide the workstock. One edge of the workstock rides against the rip fence while
the flat side of the board rest on the table.
Since the workstock is pushed along the fence, it must have a straight edge and make solid
contact with the table.
The saw guard must be used. The guard has antikickback fingers and a splitter to prevent the saw kerf
from closing.
• Never rip or cut wood without using the fence or
miter gauge to guide it because the stock could
kickback.
• Always use the blade guard and splitter assembly
when cutting wood. It has anti-kickback fingers
and a splitter to prevent the saw “kerf” (the slit cut
by the blade) from closing and binding the blade, which can overload and/or stall the motor
or cause the blade to lift and eject the workpiece towards the front of the saw at very high
speeds. The blade guard keeps your fingers away from the blade and also reduces the
amount of sawdust flying free.
• While certain operations require the removal of the blade guard and splitter assembly, it
should always be replaced for regular cutting.
• If the work to be ripped is narrow, it is safer to use
a push stick, rather than the hands, to feed it into
the blade. Push sticks with non-slip grippers can
be purchased, but shop-made push sticks works
just as well. When ripping extremely narrow stock
that may not clear the width of the blade guard, or
very thin material such as paneling, which may
slip between the underside of the fence and the
table surface, a strip of wood as an auxiliary guide
can be attached to the fence.

40
40
WARNING: Serious injury can be caused by kickback. Kickback is a
high-speed ejection of stock from the table saw toward an operator. The operator or
bystanders may be struck by flying stock, or the operator's hands can be pulled into
the blade during the kickback.
1. Take the necessary precautions to reduce the likelihood of kickback.
2. If using natural wood, joint one long edge of the workpiece on a jointer. This provides a flat,
consistent surface that can slide along the fence, which minimizes chances of the workpiece
moving during the cut, and reduces the risk of kickback.
3. Disconnect and lockout power to the saw!
4. Verify that the blade guard and spreader are
installed.
5. Set the fence to the desired width of cut on the
scale.
6. Adjust the blade height so the highest saw tooth
extends no more than 1/4" above the
workpiece.
7. Set up safety devices such as featherboards or
other anti-kickback devices.
8. Rotate the blade to make sure it does not come
into contact with any of the safety devices.
9. Connect the saw to the power source, turn it ON, and allow it to reach full speed.
Note: The jointed edge of the workpiece must slide against the fence during the
cutting operation.
10. Advance the workstock using push sticks as needed, through the saw blade holding it down
and against the fence until the workpiece is completely beyond the saw blade. Never, stand
in the line of the saw cut when ripping.
11. When the cut is complete, the workstock will either stay on the table, tilt up slightly and be
caught by the rear end of the guard or slide off the table to the floor. Alternately, the feed can
continue to the end of the table, after which the workstock is lifted and brought back along
the outside edge of the fence. The waste stock remains on the table and is not touched with
the hands until the saw is stopped and the blade comes to a complete stop. This will allow
for safe removal.

41
41
WARNING: Keep the blade guard installed and in the down position.
Failure to do this could result in serious personal injury or death.
Never reach in towards the blade while the blade is still spinning!
Whenever a cut is completed, turn off the saw and wait for the blade to come to a
complete stop before reaching in to remove the workpiece or the waste material.
Failure to follow this warning could result in accidental contact with rotating blade,
causing lacerations or amputation.
Miter Ripping
Miter ripping is performed the same as ripping but with the saw blade set to an angle not
perpendicular with the table surface. To tilt the blade to the left, anywhere between 0° and 45°.
This is used most often when cutting bevels, compound miters or chamfers.
After changing the bevel angle verify the alignment of the guard and splitter; make sure there is
clearance with the saw blade.
Ripping Small Work Pieces
Do not attempt rip cuts if the work piece is too small, as this will oblige you to place your hands
too close to the blade and put you at serious risk of injury. When ripping narrower widths; use a
push block or a push stick in order to avoid placing hands near the blade.
Crosscutting
Cutting against the grain, to shorten the length of a
board is crosscutting. With some smaller sized and
rectangular pieces, you often have the choice of
ripping or crosscutting. Always use the miter gauge,
when crosscutting; never cut a piece unsupported. The
miter gauge may be used in either slot, but most
operators prefer the left groove for typical work. When
the blade is tilted for bevel cutting, use the table slot
that does not cause interference with your hand or the
saw blade guard.
Place the workstock against the miter gauge and
advance both the miter gauge and workstock toward the saw blade.
Start the cut slowly and hold the workstock firmly against the miter gauge and the table.
42
42
WARNING: Serious injury can be caused by kickback. Kickback is a
high-speed ejection of stock from the table saw toward an operator. The operator or
bystanders may be struck by flying stock, or the operator's hands can be pulled into
the blade during the kickback.
• One of the rules in running a saw is that you never hang onto or touch a free piece of
workstock. Hold the supported piece, not the free piece that is cut off. The feed in
crosscutting continues until the workstock is cut in two, The workstock is then slid sideways
slightly away from the blade and then the miter gauge and workstock are pulled back to the
starting point.
• Never pick up any short length of free workstock from the table while the saw is running. A
smart operator never touches a cut-off piece unless it is at least a foot long.
• Never use the fence as a cut-off gauge when crosscutting.
• Never use the miter gauge in combination with the rip fence.
To make a crosscut using the miter gauge:
1. Disconnect and lockout power to the saw!
2. Verify that blade guard and spreader is installed.
3. Move or remove the rip fence so that it will not
interfere with the cut.
4. Position the miter gauge in either the left or right
miter slot, and adjust it to 90°
5. Adjust the saw blade to not more than 1/4" higher
than the workpiece to be cut.
6. Slide the miter gauge near the blade, and adjust
the workpiece so the blade will cut on the waste
side of the line.
7. Place the work on the miter gauge and slide it
up close to the blade to align the outer edges of
the teeth with your cut mark.
8. Keep a firm grip as you pull the miter gauge and
the workstock back away from the blade.
9. Lower the blade guard.
10. Start the saw and make the cut. When the work
is cut through, move one or both cut pieces. If
long enough to handle without danger immediately off to the side, away from the turning
blade.
11. Turn off the motor.

43
43
WARNING: Turn OFF the saw and allow the blade to come to a complete
stop before removing the cut-off piece. Failure to follow this warning could result in
serious personal injury.
Miter Cross Cutting
This operation is the same as cross cutting, except
the miter gauge is set to an angle other than 0.
After changing the blade angle, verify the alignment
of the guard and splitter and verify that there is
clearance with the saw blade.
Hold the work piece firmly against the miter gauge
and feed the workpiece slowly into the blade to
prevent it from moving during the cut.
Blade Tilt/Bevel Cuts
When the blade tilt stop bolts are properly
adjusted, the blade tilt handwheel allows the
operator to tilt the blade to the left, between 0°
and 45°. This is used most often when cutting
bevels, compound miters or chamfers.
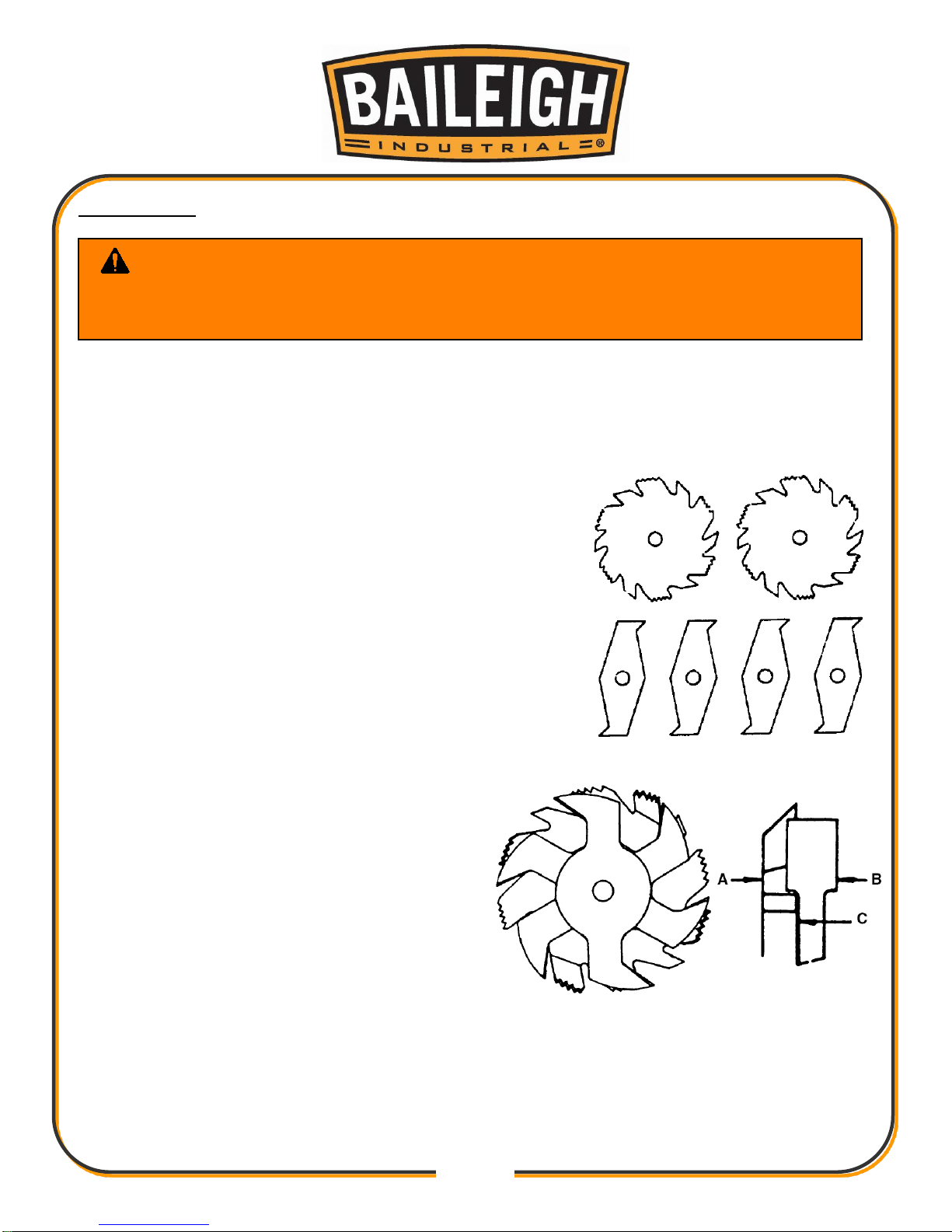
44
44
WARNING: Blades are dangerously sharp. Use extreme caution when
working with or around the blade. Wear proper safety protection such as heavy
gloves.
Dado Cutting
Dadoing is cutting a rabbet or a wide groove into the workpiece that does not cut all the way
through the material. Most dado head sets are made up of two outside blades and four or five
inside cutters. Dadoing may also be performed using a standard blade and making multipule
passes across the blade.
This saw can accommodate dado blades up to 10" in
diameter. The riving knife MUST be installed while using
a 10" diameter dado blade. This will reduce the risk of
hands being pulled into the blade if kickback occurs.
DO NOT use the riving knife if you install a dado blade
smaller than 10" in diameter. If the riving knife height
exceeds the blade height, workpiece will hit the riving
knife during the cut. This will force the operator into a
dangerous situation of trying to turn the saw off with the
workpiece stuck halfway through the cut.
Various combination of saws and cutters are used to cut
grooves from 1/8” to 13/16” for use in shelving, making
joints, tenoning, grooving, ect.
The cutters are heavily swaged and must be
arranged so that this heavy portion falls in the
gullet of the outside blades. The saw and cutter
overlap (A) being the outside blade, (B) and
inside cutter, and (C) a paper washer which can
be used as needed to control the exact width of
groove. A 1/4” groove is cut by using the two
outside blades. The teeth of the blades should
be positioned so that the raker on one saw is
beside the cutting teeth on the other saw.
The dado head set is assembled to the saw arbor in the same manner as the standard saw
blade.
The guard splitter and anti-kickback finger assembly can not be used when dadoing operations
and must be removed from the saw. A dado head table insert (not included) must be used in
place of the standard table insert.

45
45
WARNING: NEVER use the dado head in a bevel position unless you
make your own dado insert!
ALWAYS install blade guard after operation is complete!
IMPORTANT: Dado blades have a higher risk of kickback than normal
blades because their larger size applies stronger forces to the workpiece. This risk
increases relative to the depth and width of the cut. To minimize your risk of serious
personal injury, ensure that stock is flat and straight, and make multiple light cuts
(rather than one deep cut) to achieve the desired cutting depth.
DO NOT make through cuts with a dado blade. Dado blades are only intended for non-
through cuts. Failure to heed this warning could result in serious injury.
Never try to dado a warped board by holding it down against the table. If kickback occurs,
your hand could be pulled into the blade, resulting in accidental contact with the rotating
blade, causing lacerations or amputation.
Cutting Dadoes with a Dado Blade
Use a sequential process of making multiple, light cuts that get progressively deeper. The actual
number of cuts used should be determined by workpiece hardness, total dado depth, and feed
rate. In general, if you hear the motor slow down during the cut, you are cutting too deep or
feeding too fast.
1. Disconnect and lockout power to the saw!
2. Install the dado blade set to the desired width of cut and a dado insert.
3. Adjust the dado blade to the desired depth of cut, keeping in mind that you may need to
make several passes to complete the cut.
4. Align the workpiece to the dado blade to remove the waste material.
Use either the fence or the miter gauge to guide the material through the cut. NEVER use
both.
Adjust the distance between the fence and the inside edge of the blade to dado the length of
a workpiece.
Use the miter gauge and carefully line up the desired cut with the dado blade when dadoing
across the workpiece.
DO NOT use the fence in combination with the miter gauge, to prevent binding with the
workpiece.

46
46
5. Reconnect the saw to the power source.
6. Turn the saw ON. The blade should run smoothly, with no vibrations.
7. When the blade has reached full speed, perform a test cut with a scrap piece of wood.
8. If the cut is satisfactory, repeat the cut with the actual workpiece.
Cutting Dadoes with a Standard Blade
A ripping blade is typically the best blade to use when cutting dadoes with a standard blade
because it removes sawdust very efficiently.
1. Disconnect and lockout power to the saw!
2. Ensure that the riving knife and included table insert are installed and properly adjusted. Do
not use the included insert if it has lost the zero clearance feature by modification; if so, you
must install a new standard zero clearance insert.
3. Mark the width of the dado cut on the workpiece. Include marks on the edge of the
workpiece so the cut path can be aligned when the workpiece is positioned on the table.
4. Raise the blade up to the desired depth of cut (depth of dado channel desired).
5. Set the saw up for the type of cut you need to make, depending on if it is a rip cut or
crosscut.
6. Align the blade to cut one of the dado sides.
7. Reconnect the saw to the power source and turn the saw ON. Allow the blade to reach full
speed, and then make the cut.
8. Repeat the cut on the other side of the dado channel.
9. Make additional cuts in the center of the dado to clear out the necessary material. The dado
is complete when the channel is completely cleared out.

47
47
IMPORTANT: Dado blades have a higher risk of kickback than normal
blades because their larger size applies stronger forces to the workpiece. This risk
increases relative to the depth and width of the cut. To minimize your risk of serious
personal injury, ensure that stock is flat and straight, and make multiple light cuts
(rather than one deep cut) to achieve the desired cutting depth.
CAUTION: Always use push sticks, featherboards, push paddles and
other safety accessories whenever possible to increase safety and control during
operations which require that the blade guard be removed from the saw. ALWAYS
replace the blade guard after dadoing is complete.
Rabbet Cutting
A rabbet is an L-shaped groove cut in the edge of the workpiece. Rabbets can be cut with either
a dado blade or a standard saw blade.
Rabbet cutting on the edge of the workpiece with a dado blade requires a sacrificial fence. Make
the sacrificial fence the same length as the fence and 3/4" thick. Attach it to the fence with
screws or clamps, making sure they are all secure and tight. Raise the blade into the sacrificial
fence to the height needed.
When using a dado blade, a dado insert (not included), must be installed and used during
rabbeting operations.
Cutting Rabbets with a Dado Blade
1. Disconnect and lockout power to the saw!
2. Adjust the dado blade to the height needed for the rabbeting operation. When cutting deep
rabbets, take more than one pass to reduce the risk of kickback.
3. Adjust the fence and align the workpiece to perform the cutting operation.
4. Reconnect the saw to the power source and turn the saw ON. When the blade has reached
full speed, perform a test cut with a scrap piece of wood.
If the cut is satisfactory, repeat the cut with the final workpiece.

48
48
WARNING: DO NOT place a tall board on edge to perform a rabbet cut
with a standard blade. Workpieces that are too tall to properly support with the fence
can easily shift during operation and cause kickback. Instead, place the stock flat on
the saw and perform the rabbet cut with a dado blade.
Cutting Rabbets with a Standard Blade
A ripping blade is typically the best blade to use for cutting rabbets when using a standard blade
because it removes sawdust very efficiently. Also, a sacrificial fence is not required when cutting
rabbets with a stan- dard blade.
To cut rabbets with the standard blade:
1. Disconnect and lockout power to the saw!
2. Ensure that the riving knife and included table insert are installed and properly adjusted. Do
not use the included insert if it has lost the zero clearance feature by modification; if so, you
must install a new standard zero clearance insert.
3. Mark the width of the rabbet cut on the edge of the workpiece, so you can clearly identify the
intended cut while it is laying flat on the saw table.
4. Raise the blade up to the desired depth of cut (depth of rabbet channel desired).
5. Stand the workpiece on edge, and then adjust the fence so the blade is aligned with the
inside of your rabbet channel.
If the workpiece is very tall, or is unstable when placed against the fence, lay it flat on the
table and use a dado blade to perform the rabbet cut.
6. Reconnect the saw to the power source, and then perform the cut.
7. Lay the workpiece flat on the table, and adjust the saw blade height to intersect with the first
cut, and then perform the second cut to complete the rabbet.
49
49
CUTTING TOOLS (OPTIONAL)
Cutting tools such as pushsticks (one included with the saw), push blocks, featherboard,
crosscut sleds, etc.. are extremely useful in provideing additional safety as well as added
accuracy to your cut.
While these types of tools may be purchased, they are often the first projects to be completed
when setting up shop. Plans for these tools are easily available with a little research through
libiraies, trade magazines, lumber supply locations and the internet.
We recommend useing these sources to obtain information and plans for these tool not only to
build them but to allow you to be exposed to a wider veriety of options, uses, and additional
safety precautions that may be more specific to your particular saw usage.
Outfeed & Support Tables
One of the best accessories for improving the safety and ease of using a table saw is simply
placing a large table (outfeed table) behind the saw to catch the workpiece. Additionally, another
table to the left of the saw (support table) can also help support large workpieces so they can be
cut safely and accurately.

50
50
WARNING: Make sure the electrical disconnect is OFF before working on
the machine.
Maintenance should be performed on a regular basis following proper safety
precautions.
MAINTENANCE
This table saw requires very little maintenance other than minor lubrication and cleaning. The
following sections detail what will need to be done in order to assure continued operation of your
saw.
Check daily for any unsafe conditions and fix immediately.
Check that all nuts and bolts are properly tightened.
On a weekly basis clean the machine and the area around it.
Apply rust inhibitive lubricant to all non-painted surfaces.
Inspect/test the ON/OFF switch before each use. Do not operate the saw with a damaged
switch - replace a damaged switch immediately.
Inspect the saw blade for damage or chipped teeth before each use. Replace a damaged or
chipped blade immediately. Never operate the saw with a damaged or chipped blade.
Keep the saw table clean and free of dust, pitch or glue. An occasional light coating of paste
wax can be use to protect the cast-iron surface.
Occasionally open the cabinet door and brush off and vacuum out accumulated dust from
inside the cabinet and on the blade tilting gears and on or around the motor.
Periodically inspect the power cord and plug for damage. To minimize the risk of electric
shock or fire, never operate the saw with a damaged power cord or plug. Replace a
damaged power cord or plug at the first sign of damage.
To minimize airborne dust particles periodically inspect all dust collection fittings – re-tighten
as needed.
Check the drive belt for tightness. It should be snug but not overly tight.
Use a mill file to remove any nicks or dings from the infeed or outfeed tables.
Note: Proper maintenance can increase the life expectancy of your machine.

51
51
Cleaning
Cleaning the saw is relatively easy. Vacuum excess wood chips and sawdust, and wipe off the
remaining dust with a dry cloth. If any resin has built up, use a resin dissolving cleaner to
remove it.
After cleaning, treat all unpainted cast iron and steel with a non-staining lubricant.
Occasionally it will become necessary to clean the internal parts with more than a vacuum. To
do this, remove the table top and clean the internal parts with resin/pitch dissolver or mineral
spirits and a stiff wire brush or steel wool.
Make sure the internal workings are dry before using the saw again, so that wood dust will not
accumulate. If any essential lubrication is removed during cleaning, re-lubricate those areas.
Lubrication
The table saw has sealed lubricated bearings in the motor housing and the arbor assembly, they
will not require any additional lubrication. Use a wire brush to clean off the worm gears and
trunnions and apply a white lithium grease to keep them lubricated.
Keep the blade height screw A (under the table on
the left side) as well as the blade tilt screw B (under
the table on the right side) well lubricated and free of
dust or debris.
Clean and remove dust, debris, and old lubricant as
needed depending on frequency of use.
After cleaning, reapply lubricant as needed.
Note: Use any all-purpose grease,
available at any hardware store.
No other part of this table saw needs lubrication.
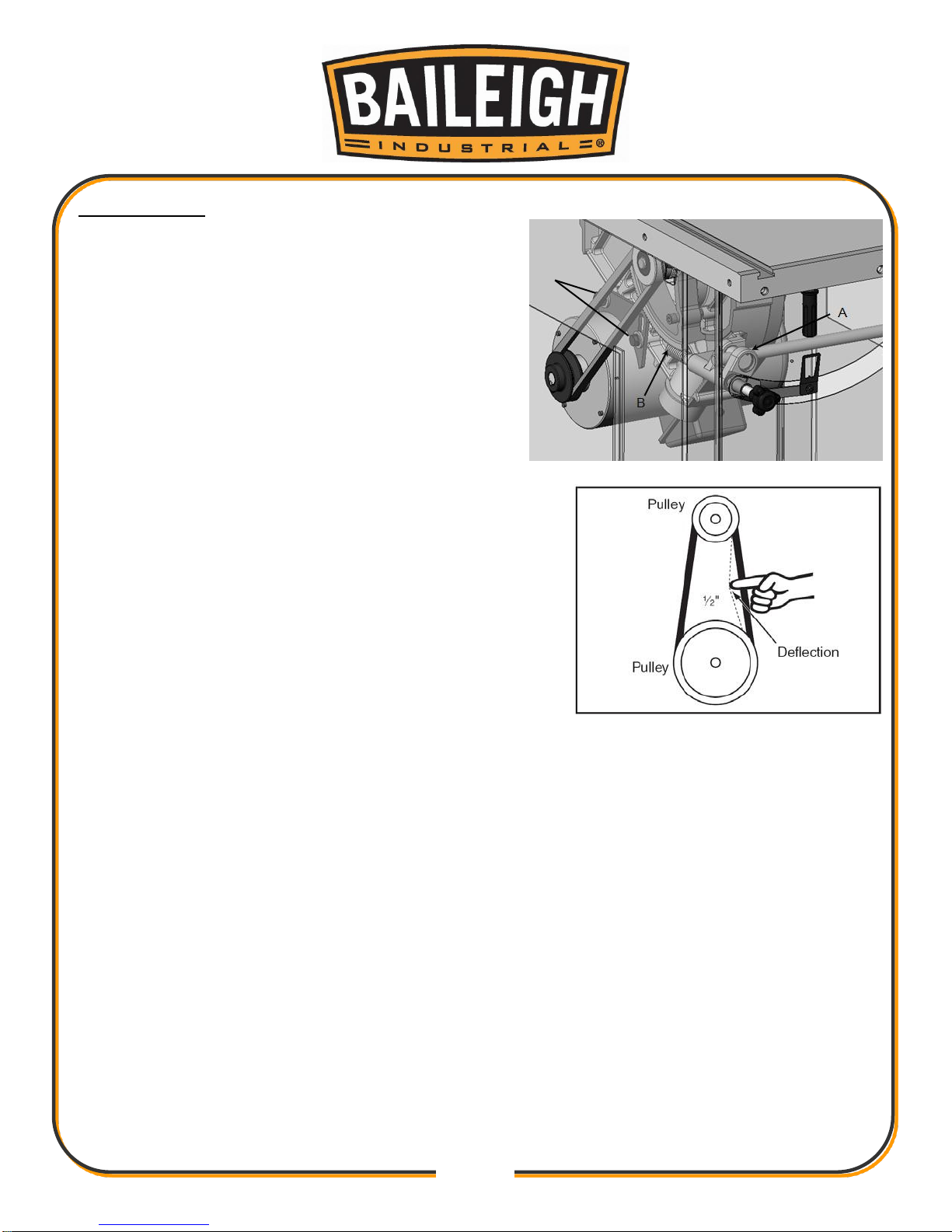
52
52
C
Changing Belt
1. Disconnect and lockout power to the saw!
2. Lower the blade completely, and then open the
side access cover.
3. Loosen the hex nuts (C) that secure the motor
and raise the motor fully to remove tension on
the V-belt.
4. Roll the V-belt off of the arbor and motor pulleys.
5. While continuing to raise the motor, install a new
V-belt onto the pulleys.
6. Lower the motor to tension the V-belt, and then tighten
the hex nuts.
7. Check V-belt tension.
8. Close the motor access cover.

53
53
PROBLEM
SOLUTION
SAW WILL NOT START
1. Saw not plugged in.
2. Fuse blown or circuit breaker tripped.
3. Cord damaged.
1. Plug in saw.
2. Replace fuse or reset circuit breaker.
3. Have cord replaced by a certified
electrician.
OVERLOAD KICKS OUT FREQUENTLY
1. Extension cord too light or too long.
2. Feeding stock too fast.
3. Blade in poor condition (dull, warped,
gummed).
4. Blade binding due to misaligned rip fence.
5. Blade binding due to warped wood.
6. Low house current.
1. Replace with adequate size cord
2. Feed stock more slowly.
3. Clean or replace blade.
4. Check and adjust the rip fence. See rip
fence instructions.
5. Select another piece of wood.
6. Contact your electrical company.
DOES NOT MAKE ACCURATE 45 AND 90
RIP CUTS
1. Positive stop(s) not adjusted properly.
2. Tilt angle pointer not set properly.
1. Check blade with square and adjust positive
stop.
2. Check blade with square and adjust pointer
to zero.
MATERIAL PINCHES BLADE WHEN
RIPPING
1. Rip fence not aligned with blade.
2. Warped wood.
1. Check and adjust rip fence.
2. Select another piece of wood.
MATERIAL BINDS ON SPLITTER
1. Splitter not aligned correctly with blade kerf.
1. Check and align splitter with blade kerf.
SAW MAKES UNSATISFACTORY CUTS
1. Dull blade.
2. Blade mounted backwards.
3. Gum or pitch on blade.
4. Incorrect blade for work being done.
5. Gum or pitch on table causing erratic feed.
1. Replace blade.
2. Turn blade around.
3. Remove blade and clean with terpentine
and steel wool.
4. Change the blade.
5. Clean the table with turpentine and steel
wool.
WARNING: Disconnect machine from the power source before
attempting any troubleshooting
TROUBLESHOOTING

54
54
BLADE DOES NOT COME UP TO SPEED
1. Extension cord too light or too long.
2. Low house current.
3. Motor not wired for correct voltage.
1. Replace with adequate size extension cord.
2. Contact your electric company.
3. Refer to motor and /or nameplate.
MACHINE VIBRATES EXCESSIVELY
1. Table not mounted securely to cabinet
stand.
2. Stand is on uneven floor.
3. Damaged saw blade.
4. Bad V-belt(s).
5. V-belts not tensioned properly.
6. Bent pulley.
7. Improper motor mounting.
8. Loose hardware.
1. Tighten all mounting hardware.
2. Reposition on flat level surface.
3. Replace blade.
4. Replace V-belt(s).
5. Adjust V-belt tension.
6. Replace pulley.
7. Check and adjust motor mounting.
8. Tighten all nuts, bolts and set screws.
BLADE DOES NOT RAISE OR TILT FREELY
1. Sawdust or dirt in raising or tilting
mechanisms.
1. Brush or blow out loose dust or dirt.

55
55
TABLE SAW PARTS DIAGRAMS

56
56
57
57
58
58

59
59
Item
Descriptions
Specification
Qty.
1
Rip Fence Assembly
36" 1 1.1
End Cap
4
1.2
Adaptor
2
1.3
Hex Screw
M6 x 1.0p x 45
1
1.4
Bracket
1
1.5
Frictional Plate
1
1.6
Square Bolt
M8 x 1.25p x 20
6
1.7
Pointer
2
1.8
Round Head Tapping Screw
M3 x 1.06p x 6
4
1.9
Pan Head Screw
M6 x 1.0p x 6
4
1.10
Fence Body
1
1.11
Hex Nut
M6 x 1.0p (10b x 5h)
1
1.12
Frictional Wheel
1
1.13
Hex Nut
M8 x 1.25p (13b x 6.5h)
6
1.14
Flat Washer
8.5 x 16 x 2.0t
6
1.15
Plastic Set Screw
M12 x 1.75p
2
1.16
Hex Screw
M10 x 1.5p x 50
1
1.17
Handle
1
1.18
Compress Cam Assembly
1
1.19
Frictional Plate
2
1.20
Flat Head Screw
M6 x 1.0p x 8
2
1.21
Bracket For Frictional Plate
1
1.22
Anit-Loose Nut
M10 x 1.5p (17b x 12h)
1
1.23
Anit-Loose Nut
M6 x 1.0p (10b x 7h)
1
1.24
Set Screw
M6 x 1.0p x 6
2
1.25
Bracket For Pointer
2
2
Blade Guard Assembly
1
2.1
Protective Shield-Left
1
2.2
Anit-Loose Nut
M5 x 0.8p (8b x 6h)
4
2.3
Flat Head Screw
M5 x 0.8p x 15
4
2.4
Left Cover
1
2.5
Pin 1 2.6
Pan Head Screw
M5 x 0.8p x 6
4
Table Saw Parts List

60
60
2.7
Bolt 1 2.8
Rod 1 2.9
Rod Bracket-Left
2
2.10
Rod Bracket-Right
2
2.11
Pan Head Screw
M4 x 0.7p x 10
2
2.12
Pin 2 2.13
Right Cover
1
2.14
Protective Shield-Right
1
2.15
Anit-Loose Nut
M5 x 0.8p (8b x 6h)
1
2.16
Anit-Kick Finger-Left
1
2.17
Spring
1
2.18
Block
1
2.19
Pin 1 2.20
Spreader Shaft
1
2.21
Spring
1
2.22
Retaining Ring
ETW-7
1
2.23
Spring
1
2.24
Anti-Kick Finger-Right
1
2.25
Pan Head Screw
M5 x 0.8p x 30
1
2.26
Spreader
1
2.27
O-Ring
P3 4 2.28
Warning Label
1
2.29
Warning Label
1
2.30
Flat Washer
5.3 x 12 x 1.0t
2
3
Miter Gauge Assembly
1
3.1
Miter Gauge Handle Assembly
1
3.2
Flat Washer
8.5 x 16 x 2.0t
1
3.3
Miter Gauge Body
1
3.4
Pan Head Screw
M4 x 0.7p x 20
3
3.5
Hex Nut
M4 x 0.7p (7b x 3.2h)
3
3.6
Pan Head Screw
M5 x 0.8p x 10
3
3.7
Pointer
1
3.8
Spacer
1
3.9
Angle Set Bar
1
3.10
Shoulder Screw
1
3.11
Slot Bar
1

61
61
3.12
Ring
1
3.13
Flat Head Screw
M6 x 1.0p x 8
1
3.14
Miter Scale
1
4
Extension Table
2
6
Table Insert Assembly
1
7
Bolt 1 8
Set Screw
M5 x 0.8p x 12
4
9
Set Screw
M8 x 1.25p x 20
2
10
Table
1
11
Hex Nut
M8 x 1.25p (13b x 6.5h)
4
12
Trunnion Support
2
13
Flat Washer
8.5 x 16 x 2.0t
15
14
Spring Washer
8.2 x 15.4
8
15
Hex Screw
M8 x 1.25p x 25
4
16
Hex Screw
M8 x 1.25p x 20
12
17
Anit-Loose Nut
M10 x 1.5p (17b x 12h)
1
18
Flat Washer
10 x 25 x 3.0t
1
19
Flat Washer
8.2 x 22 x 3.0t
2
20
Hex Screw
M10 x 1.5p x 80
1
21
Motor Assembly
1.75hp, 120V/240V, 60hz, 1ph
1
22
Magnetic Switch Assembly
120V x Csa
1
22.1
Magnetic Switch Assembly
1
22.2
Swtich Box
1
22.3
Switch Plate
1
22.4
Pan Head Screw
M4 x 0.7p x 25
2
22.5
Pan Head Screw
M4 x 0.7p x 6
2
22.6
Tooth Washer
4.3 x 8.5 (BW-4)
2
22.7
Hex Nut
M4 x 0.7p (7b x 3.2h)
2
22.8
Strain Relief
SB8R-3
2
22.9
Connect Wire
SJT14awg x 3C x 1600mm
1
2.10
Power Cord
SJT14awg x 3C x 2600mm
1
23
Belt
17-310
1
24
Poly V-Belt
125J-6
1
25
Set Screw
M6 x 1.0p x 10
2
26
Pulley
1
27
Flat Washer
15.5 x 21 x 0.8
1

62
62
28
Ball Bearing
6202 2 29
Key
5 x 5 x 18
1
30
Arbor
1
31
Hex Screw
M6 x 1.0p x 20
3
32
Fixed Plate
1
33
Flat Washer
6.7 x 16 x 2.0t
3
34
Anit-Loose Nut
M6 x 1.0p (10b x 7h)
3
35
Socket Hex Screw
M6 x 1.0p x 12
4
36
Clamper Support
1
37
Pulley
1
38
Retaining Ring
STW-15
1
39
Ball Bearing
6002 2 40
Long Rod
1
41
Shaft Gear
1
42
Cap Screw
M8 x 1.25p x 50
1
43
Bushing
1
44
Rod
1
45
Packing
1
46
Hex Screw
M5 x 0.8p x 12
1
47
Stretch Out Plate
1
48
Pan Head Screw
3/16"-24nc x 3/8"
2
49
Slide Shelf
2
50
36" Rail Assembly
1
50.1
Cap Screw W/Spring Washer
M8 x 1.25p x 20/8.2 x 15.4
6
50.2
Flat Washer
8.5 x 16 x 2.0t
12
50.3
Hex Nut
M8 x 1.25p (13b x 6.5h)
12
50.4
Square Bolt
M8 x 1.25p x 20
6
50.5
End Cap-Left
1
50.6
End Cap-Right
1
50.7
Self-Tapping Screw
M4 x 1.59p x 12
4
50.8
Rear Rail-Left
1
50.9
Rear Rail-Right
1
50.10
Front Rail-Left
1
50.11
Front Rail-Right
1
50.12
Pin
2
50.13
Length Scale-Left
0"~12"
1

63
63
50.14
Length Scale-Right
0"~36"
1
51
Sawblade
10'' x 40t
1
52
Sawblade Clamp
1
53
Nut
TW5/8"-12 (In)
1
54
Dust Guard
1
55
Pan Head Screw
M5 x 0.8p x 30
4
58
Fix Shaft Bolt
1
59
Handle
1
60
Spring
1
61
Retaining Ring
ETW-8
1
62
Retaining Ring
RTW-24
1
63
Guide Shaft
1
64
Fixing Knob
1
65
Handwheel Assembly
1
66
Spacer
1
67
Cap Screw
M5 x 0.8p x 12
3
68
Fence Blocl
1
69
Retaining Ring
ETW-12
2
70
Worm Shaft
1
71
O-Ring
P12 2 72
Wave Washer
WW-16
1
73
Round Head Screw W/Washer
M4 x 0.7p x 8/4 x 10 x 0.8t
1
74
Pointer
1
75
Bracket
1
76
Flat Washer
6.3 x 13 x 1.0t
2
77
Pan Head Screw
M5 x 0.8p x 12
4
78
Fixing Pin
2
79
Anit-Loose Nut
M5 x 0.8p (8b x 6h)
2
80
Clamper Support
1
81
Fixed Plate
1
82
Pan Head Screw
M4 x 0.7p x 10
10
83
Bracket
1
84
Hex Screw W/Washer
M6 x 1.0p x 40 (12)
1
85
Spring
1
86
Flat Washer
6.4 x 20 x 3.0t
1
87
Turning
1

64
64
88
Hex Screw W/Washer
M8 x 1.25p x 12 (13b x 6.5h)
3
89
Fixed Plate
1
90
Round Head Screw
M4.5 x 1.81p x 9
5
91
Stand
1
92
Strain Relief
SB8R-1
1
93
Side Cover
1
94
Push Sticks
1
96
Hex Screw
M8 x 1.25p x 60
4
97
Wheel
4
98
Anit-Loose Nut
M8 x 1.25p (13b x 9h)
4
99
Knob
5/16"-18nc x 3/4"
2
100
Motor Cover
1
101
Worm Shaft Assembly
1
102
Handwheel Assembly
1
104
Riving Knife
1
105
Set Lock Screw
M6 x 1.0p x 8
4
106
Round Head Screw
M5 x 0.8p x 16
2
107
Handle
1
108
Spring Washer
5.1 x 9.3
2
109
Round Head Socket Lock Screw
M5 x 0.8p x 12
1
110
Bracket For Riving Knife
1
111
Cap Screw
M8 x 1.25p x 10
2
112
Spring
1
113
Knob
1
114
Block
1
115
Hex Wrench
2.5mm
1
116
Hex Wrench
4mm
1
117
Hex Wrench
6mm
1
118
Open Wrench
11 x 13
1
119
Spanner
2
128
Exhaust Pipe Group
1
129
Quick Clamping Hose Clamp
60-80mm
2
130
Duct
2.5" x 800mm
1

65
65
NOTES
BAILEIGH INDUSTRIAL, INC. 1625 DUFEK DRIVE MANITOWOC, WI 54220
PHONE: 920. 684. 4990 FAX: 920. 684. 3944
WWW.BAILEIGHINDUSTRIAL.COM
BAILEIGH INDUSTRIAL, INC. 1455 S. CAMPUS AVENUE ONTARIO, CA 91761
PHONE: 920. 684. 4990 FAX: 920. 684. 3944
BAILEIGH INDUSTRIAL LTD. UNIT 1 FULLWOOD CLOSE
ALDERMANS GREEN INDUSTRIAL ESTATE
COVENTRY, CV2 2SS UNITED KINGDOM
PHONE: +44 (0)24 7661 9267 FAX: +44 (0)24 7661 9276
WWW.BIFABUK.CO.UK
BAILEIGH INDUSTRIAL GMBH HOFENER STRAßE 64
70736 FELLBACH
DEUTCHSLAND
WWW.BAILEIGHINDUSTRIAL.DE
 Loading...
Loading...