Page 1

AW-GU700 802.11b/g USB 2.0 Mini-Card WLAN Module
User Guide
Page 2

COPYRIGHT
AzureWave Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced,
transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language in any
form or by any means without the written permission of AzureWave Technologies, Inc.
DISCLAIMER
AzureWave provides this document “as is”, without warranty of any kind, neither expressed nor
implied, including, but not limited to, the particular purpose. AzureWave may make
improvements and/or changes in this document or in the product described in this document at
any time. This document could include technical inaccuracies or typographical errors.
TRADEMARKS
AzureWave is a trademark of AzureWave Technologies, Inc. Other names mentioned in this
document are trademarks/registered trademarks of their respective owners.
USING THIS DOCUMENT
This document provides detailed user guidelines to provide AzureWave 802.11 b/g USB 2.0
Mini-Card WLAN Module operation and setting-up. Though every effort has been made to
assure that this document is current and accurate, more information may have become
available subsequent to the production of this guide. In that event, please contact your
AzureWave representative for additional information that may help in the development process.
ii
Page 3

iii
Contents
Safety statements ........................................................................................................... 2-1
About this guide.............................................................................................................. 2-1
AW-GU700 802.11 b/g USB2.0 Mini-Card WLAN Module specification summary .................. 2-1
Chapter 1 Product Information....................................................................................... 2-2
1.1 Product overview................................................................................................ 2-2
1.2 Features............................................................................................................. 2-2
1.3 LED and antenna port ..............................................................錯誤
錯誤! 尚未定義書籤
尚未定義書籤。
錯誤錯誤
尚未定義書籤尚未定義書籤
。
。。
1.4 Supported network setup .................................................................................... 2-4
1.4.1 Ad-Hoc mode............................................................................................ 2-4
1.4.2 Infrastructure mode .................................................................................. 2-4
1.4.3 Software access point (Soft AP) ................................................................. 2-5
Chapter 2 Installation.................................................................................................... 2-1
2.1 System requirements .......................................................................................... 2-1
2.2 Hardware Installation.......................................................................................... 2-1
Chapter 3 Wi-Set Wizard ............................................................................................... 3-2
3.1 Launch Wi-Set Wizard......................................................................................... 3-2
3.2 Wi-Setup Wizard Steps........................................................................................ 3-4
3.3 Station Mode Configuration ................................................................................. 3-4
3.3.1 Configure Infrastructure type network........................................................ 3-5
3.3.2 Build Ad-Hoc networking mode network ..................................................... 3-6
3.4 Build Soft AP network ......................................................................................... 3-7
3.4.1 Normal User.............................................................................................. 3-8
3.4.2 Advanced User.........................................................................................3-11
Chapter 4 RtWLAN: Wireless LAN Management GUI........................................................ 4-1
4.1 How to Launch RtWLAN ...................................................................................... 4-2
4.2 Introduction of Main Window............................................................................... 4-2
4.3 Station mode...................................................................................................... 4-6
4.3.1 Infrastructure and Ad-Hoc ......................................................................... 4-6
4.4 AP mode ...........................................................................................................4-11
4.5 Windows Zero Configuration...............................................................................4-14
4.5.1 Swap from RtWLAN to Windows Zero Configuration ...................................4-14
4.5.2 Rollback from Windows Zero Configuration to RtWLAN...............................4-15
Appendix A: Mapping of country and channel plan........................................................ 4-1
Appendix B: Q&A........................................................................................................ 4-2
Appendix C: Release History........................................................................................ 4-3
Page 4

Safety statementsFCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter.
About this guide
The user guide contains the information you need to install and configure your AzureWave
802.11 b/g USB WLAN Module.
Guide organization
This guide contains the following chapters:
Chapter 1: Product Information
This chapter describes the general functionality, features and configuration modes of
AzureWave 802.11 b/g USB WLAN Module.
Chapter 2: Installation
It is recommended that users should read thischapter before installing both 802.11b/g
USB 2.0 Mini-Card WLAN Module hardware and software. This chapter presents the
systematic installation of AzureWave 802.11 b/g USB 2.0 Mini-Card WLAN Module and
antenna, utilities and driver on the support CD.
Chapter 3: W-Set Wizard
This chapter shows you the setup of wireless network in your office or home. Follow The
step-by-step directionprovided by Wi-Set wizard, you can have your own wireless local area
network up and running very quickly.
Chapter 4: Management GUI
This chapter teaches you the proper operations of selected mode from W-Set Wizard. The
GUI display network status, connection profiles and network traffic to help you monitor and
manage the network configuration.
802.11b/g USB 2.0 Mini-Card WLAN Module specification
2-1
Page 5

summary
Host system connections
Interface Fully complies with USB 2.0 or 1.1
USB date transfer rate USB high speed (480Mbps), and full speed (12Mbps)
Chapter 1
1.1
Product overview
Thank you for choosing AzureWave 802.11 b/g USB WLAN Module.
The 802.11b/g USB 2.0 Mini-Card WLAN Moduleis an easy-to-use wireless local area
network (WLAN) adapter which is designed for home or office use. Direct Sequence Spread
Spectrum (DSSS), Complementary Code Keying (CCK), and Orthogonal Frequency Division
Multiplexing (OFDM) base band processing are implemented to support all IEEE 802.11b, and
802.11g data rates. Differential phase shift keying modulation schemes, DBPSK and DQPSK
with data scrambling capability, are available, along with complementary code keying to provide
data rates of 1, 2, 5.5, and 11Mbps, with long or short preamble. A high-speed Fast Fourier
Transform (FFT)/Inverse Fast Fourier Transform (IFFT) combined with BPSK, QPSK, 16QAM
and 64QAM modulation of the individual sub-carriers provides data rates of 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36,
48 and 54Mbps, with rate-compatible punctured convolution coding with a coding rate of 1/2,
2/3, and 3/4.
The 802.11b/g USB 2.0 Mini-Card WLAN Module also supports Wake-On-LAN (WOL)
function and remote wake-up giving you the convenience to remote log in from other places to
this system.
Product Information
To provide efficient security to your wireless communication, the hardware-based IEEE 802.11i
encryption/decryption engine, including 64-bit/128-bit WEP, TKIP, and AES, supports Wi-Fi
alliance WPA and WPA2 security.
With these features and many more, 802.11b/g USB 2.0 Mini-Card WLAN Moduleis ready to
connect you to the world of wireless communication.
1.2
Features
System requirements
2-2
Page 6

The 802.11b/g USB 2.0 Mini-Card WLAN Module is an on-board component on ASUS
motherboard requiring manual installation. Make sure that your system meets the following
requirements.
ASUS motherboard with 802.11b/g USB 2.0 Mini-Card WLAN Module on-board solution
Minimum 64MB system memory
Operating system
Station mode : Windows® 2000/XP/Server 2003, Windows XP/Server 2003 x64
AP/wireless bridge mode : Windows® 2000/XP/Server 2003
Optical drive for utilities and driver installation
Easy hardware installation
Because the 802.11b/g USB 2.0 Mini-Card WLAN Module comes embedded in motherboard,
no hardware installation is necessary. Just connect the antenna, install the driver and utilities
from the motherboard support CD and start wireless communication immediately.
54Mbps speed wireless travel
The 802.11b/g USB 2.0 Mini-Card WLAN Module provides up to five times more data
transmission than IEEE 802.11b standards, and breaks the wireless transmission barrier to
speed up the internet connection.
Wi-Set Wizard
Easy-use wireless LAN setup wizard helps you to connect with present wireless network. The
step-by-step wizard provides a convenient way to facilitate the complex wireless LAN setup
process.
Automatic wireless establishment
The utility application of AzureWaveRTL8187 Wireless LAN USB 2.0 Adapter automatically
searches and reports the hot spots around it and the wireless signal quality and WEP capability
associated with each hot spot.Then you could connect to the most suitable wireless node
2-3
Page 7

1.3
Supported network setup
You can use 802.11b/g USB 2.0 Mini-Card WLAN Module in various wireless network
configurations. We recommend you to select the most appropriate configuration for your home
or office network before setting it up.
1.3.1 Ad-Hoc mode
Ad-Hoc wireless networks bring together
workstations and computers to act as
Mobil station 2
servers to all other users on the network
without complex infrastructure, setup or
administration. Users on the network can
ADSL Modem
share files, printers. When in ad hoc mode,
the 802.11b/g USB 2.0 Mini-Card
WLAN Module connects to another
wireless device within its effective range
and communicates with each other in the
same LAN workgroup. Select this
Mobil station 1
RealTek RTL8187L
configuration when no access point is
present in your wireless network.
1.3.2 Infrastructure mode
Mobil station 1
The biggest difference between
infrastructure mode and ad-hoc mode is
ADSL Modem
that it includes an access point. In
infrastructure mode, an access point
establishes the network that provides
wireless links in the validating range for
clients to communicate with each other or
with a wired network to the internet. On an
Access Point
RealTek RTL8187L
infrastructure network, the access point
may manage the bandwidth to maximize utilization. Infrastructure networking has the following
advantages over ad-hoc networking:
Range Extension
2-4
Page 8

Each wireless LAN enabled computer within the range of the access point can communicate
with other wireless LAN enabled computers within the valid range of signal from the access
point.
Roaming
A wireless LAN enabled computer can physically move from the operating range of one
access point to another without losing connection to the LAN. A quick association
“hand-shake” is made between the new access point and the wireless device as the
computer traverses from the coverage of one access point to another.
Wired to wireless LAN connectivity
Access point establishes the bridge between wireless LAN and other wired counterparts.
1.3.3 Software access point (Soft AP)
You could configure 802.11b/g USB 2.0
ADSL Modem
Mini-Card WLAN Module as a software
access point (soft AP). In this mode, the
RealTek RTL8187L
802.11b/g USB 2.0 Mini-Card WLAN
Module acts as the access point that
provides wireless links in the validating
range to client stations to the internet.
Your system should satisfy the following
two requirements to apply this mode:
The system you use already connects
Mobil station 1
Mobil station 2Access Point
to the internet or intranet through another one Ethernet adapter.
You are using Windows® 2000, XP or Server2003 operation system
Notice: Windows XP/Server2003 x64 platforms are not supported to have software access point
capability.
2-5
Page 9

2-1
Chapter 2 Installation
2.1
System requirements
Before installing the AzureWave 802.11 b/g USB WLAN Module, driver and utilities, make sure
your system satisfy the following requirements
ASUS motherboard with 802.11b/g USB 2.0 Mini-Card WLAN Module specific slot
Intel® Pentium™ 4
Minimum 64MB system memory
Windows® Operation System
Ad-Hoc and infrastructure mode: Windows® 2000, XP and Server 2003
Software AP and Wireless Bridge: Windows® XP and Server 2003
Optical drive for driver and utilities installation
2.2
Hardware Installation
To complete the hardware installation of AzureWave 802.11 b/g USB WLAN Module, you only
need to install the moveable dipolar antenna at the rear of motherboard.
Installing the antenna:
Locate the wireless LAN antenna port on the motherboard rear panel.
Connect the antenna twist-on connector (female) to the wireless LAN antenna port (male)
Place the antenna at an elevated location to enhance your wireless LAN valid coverage.
Page 10

3-2
Chapter 3 Wi-Set Wizard
3.1
Launch Wi-Set Wizard
In this section, youwill obtain detail instruction in setting wireless configuration by following
Wi-Set Wizard. Please refer to Chapter 1.4 to understand the network types the 802.11b/g
USB 2.0 Mini-Card WLAN Module supports.
In the first time installation, Wi-Set Wizard is executed immediately after installation to help you
set the proper wireless configuration.
In addition, you could launch it from either program menu
or Wireless LAN Management GUI.
In the following sections, we represent the steps, the convenient and easy wireless set up, in
Page 11

3-3
Wi-Set Wizard.
Page 12

3-4
3.2
Wi-Setup Wizard Steps
Whatever which wireless configuration
you would set up, the first scene of
Wi-Set Wizard is “Select Operation
Mode” dialog that shows as right picture.
You could select either station or AP
mode from the first step.
For Ad-hoc and infrastructure type
configuration, you should select Station
mode. The software access point
configuration could be archived by select
AP mode.
Station
Set the operation mode to be “Station”. Follow steps in section 4.3.
AP
Set the operation mode to be “Access Point”. Follow steps in section 4.4.
Next
Go to next step of selected mode.
Cancel
Give up Wi-Set Wizard. The default wireless configuration will be automatically applied as
“Infrastructure” type of Station mode if user won’t set it up here.
3.3
Station Mode Configuration
Two types, infrastructure and ad-hoc types,
of station mode are provided here.
Infrastructure
Configure the wireless as infrastructure
type network. Follow steps in 4.3.1
Build Infrastructure type network.
Ad-Hoc
Page 13

3-5
Configure the wireless as Ad-Hoc type network. Follow steps in 4.3.2 Build Ad-Hoc
networking mode network
Back
Go back to previous step – Select Operation Mode.
Next
Go to next steps of selected type.
Cancel
Give up Wi-Set Wizard and keep the last configuration.
3.3.1 Configure Infrastructure type network
It is easy to build up infrastructure type network with Wi-Set Wizard. The next step after select
infrastructure type network is to select the desired connection.
Select the BSS connection list
Select valid wireless BSS, Infrastructure
Basic Service Set, connection nearby
your system for connecting. The listed
BSS are touchable access point around
you. You have to pick one from the list
and go to next.
SSID list box
Four fields are shown in the list box
to provide access point status.
SSID: the name of access point
Security: the security status of access point. None means security/password is not necessary. WEP
means the access point acquire security/password to log in.
Channel: the channel this access point applies.
Signal: The signal strength; higher mean better.
Refresh
Rescan the IBSS list.
Back
Go back to previous step ~ Select Station Type.
Page 14

3-6
Next
Go to next step of infrastructure type configuration. It is relative the security status of
selected access point.
None: Setup TCP/IP.
WEP: A WEP dialog is pope dup before Setup TCP/IP as below picture. You have to input the
password/network key to join this access point before setup TCP/IP. The password/network key is
defined by the administrator of access point. The invalid network key will stop going to next step.
Cancel
Give up Wi-Set Wizard and keep the last configuration.
Setup TCP/IP
You have to setup the TCP/IP by
following the configuration of connect
access point. The following setting
should match the configuration of access
point you join. Please check the setting
of it.
Back
Go back to previous step ~ Select the
IBSS connection list
Finish
All settings of infrastructure are
finished.
3.3.2 Build Ad-Hoc networking mode network
It is easy to build up Ad-Hoc type network with Wi-Set Wizard. The next step after select
Ad-Hoc type network is to select the
desired connection.
Select The IBSS Connection List
In this step, you could select the present
Page 15

3-7
Ad-Hoc station to join. In addition, you could create another Ad-Hoc station by press “New
IBSS” button.
SSID list box
Display all present Ad-Hoc station around this system.
New IBSS
Create a new Ad-Hoc station by the shown-up
dialog instead of joining with a present Ad-Hoc
node. In this dialog, you could configure network
name, applied channel, authentication and
encryption rule on this Ad-Hoc node. After
creating a new Ad-Hoc node, the steps of build
Ad-Hoc network connection is finished.
Refresh
Rescan the Ad-Hoc stations nearby this system.
Back
Go back to previous step ~ Select Station Type.
Next
The wizard will show up the contents of profile. You should set it up to match the security
configuration with selected Ad-Hoc station. Then the steps are finished.
Cancel
Give up Wi-Set Wizard and keep the last configuration.
3.4
Build Soft AP
network
Setup a Wireless Network
The setting of Soft AP could settle done
Page 16

3-8
by either convenient “Normal User” or complex “Advanced User” operation.
Normal User
Only basic settings are included in following steps. Less-experience users could apply this
kind setup to archive access point setup. Fundamental security setting is included.
Advanced User
You need more security knowledge on wireless network to help you go through following
steps. Experienced user could select this kind setup. Advanced security settings are
included.
Back
Go back to previous step ~ Select Operation Mode
Next
The next step is dependant on the option user select:
Normal User: Please follow steps in 4.4.1 Normal User
Advanced User: Please follow steps in 4.4.2 Advanced User
Cancel
Give up current Wi-Set Wizard setup and roll back to previous configuration.
3.4.1 Normal User
For normal user mode, the basic security function only request two types network/password key
to provide WEP encryption.
Wireless Network Properties
Network Name (SSID)
The service serve identify of this
access point. The length of the
self-naming does not exceed 32
characters.
WEP Encryption
Enable: The joined wireless station
should have same
Page 17

3-9
network/password key with this access point.
Disable: no network/password key is required for joined wireless station.
Back
Back to previous step ~ Setup a Wireless Network
Next
The next step is dependant on the decision of WEP to be either Enable or Disable.
WEP Enable: You should prepare network/password key for WEP. Go to Wireless Network Security.
WEP Disable: The access point is set as an opened hot-spot. Anyone could join this access point
and connect to internet.
Cancel
Give up current Wi-Set Wizard setup and roll back to previous configuration.
Wireless Network Security
Two types pass key, ASCII and
Passphrase, perform security with different
level.
ASCII
You should provide either 5 or 8 ASCII
characters on Network key edit box.
PASSPHRASE
You could input words on Network Key
edit box.
64 bits: The generated pass key is 64-bits to be company with data packets.
128 bits: The generated pass key is 128-bits to be company with data packets.
Back
Go back to previous step ~ Wireless Network Properties
Next
Go to next step ~ Show Setting Information
Cancel
Give up current Wi-Set Wizard setup and roll back to previous configuration.
Page 18

3-10
Show Setting Information
Back
If you do not satisfy with current
setting, you could go back to previous
step ~ Wireless Network Security
Next
Confirm the current setting and go to
next step ~ Finish.
Cancel
Give up current Wi-Set Wizard setup and roll back to previous configuration.
Select the Internet Connection List
This step only shows with multiple network
connection system. If there is only one
internet connection available, this step is
discarded. In this step, you have to select
one network connection from the list box.
This network connection should be
configured to connect internet.
Network List Box
In the list box, you could see all
network connection this system
provides. You have to pick one from
the list.
Back
Go back to previous step ~ Show Setting Information.
Next
Go to next step, Finish, while the internet connection is selected.
If the status of selected network connection is disconnected, a warning dialog will pop up
to inform you that.
Cancel
Page 19

3-11
Give up current Wi-Set Wizard setup and roll back to previous configuration.
Finish
Finish
Press finish button to close Wi-Set
wizard. The wireless configuration is
going to be applied within few seconds.
3.4.2 Advanced User
The steps of advanced user provide more detail configuration including channel and
authentication
Wireless Network Properties
In this step, you could assign the
channel number and authentication
mode for the access point.
If the setting of WEP to be “Disable” and
Authentication to be “Open system”,
then this access point is opened for free
join.
Network Name (SSID)
The service serve identify of this access point. The length of the self-naming does not
exceed 32 characters.
Channel select
You could pick one channel from 1 to 11.
Page 20

3-12
WEP Encryption
An encryption system prevents eavesdropping on wireless network traffic.
Enable: The joined wireless station should have same network/password key with this access
point.
Disable: no network/password key is required for joined wireless station.
Authentication
The next generation of Wi-Fi security, Wi-Fi Protected Access, or WPA, will use
authentication to verify whether users have access to a particular wireless network.
Open system: This access point is without authentication protection with user.
Share key: Any station would join this access point should pass with key same as the setting on
access point.
Back
Go back to previous step ~ Setup a Wireless Network.
Next
Go to next step. It depends on the setting of WEP and Authentication.
Authentication
Encryption
Open system Shared key WPA-PSK
WEP WLAN Security
EP(Disable) Show Network Setting
Cancel
Give up current Wi-Set Wizard setup and roll back to previous configuration.
Wireless Network Security
Two types pass key, ASCII and
Passphrase, perform security with
different level.
ASCII
You should provide either 5 or 8 ASCII
characters on Network key edit box.
PASSPHRASE
You could input words on Network
Key edit box.
n/a
格格格格式化
式化:::: 本文縮排1.1, 置中
式化式化
格格格格式化
式化:::: 本文, 行距: 最小行
式化式化
高 0 pt
格格格格式化
式化:::: 置中, 間距 套用後:
式化式化
0 pt, 在段落中分頁
格格格格式化
式化:::: 置中, 間距 套用後:
式化式化
0 pt, 在段落中分頁
格格格格式化
式化:::: 本文縮排1.1, 置中
式化式化
Page 21

3-13
64 bits: The generated pass key is 64-bits to be company with data packets.
128 bits: The generated pass key is 128-bits to be company with data packets.
Back
Go back to previous step ~ Wireless Network Properties
Next
Go to next step ~ Show Setting Information
Cancel
Give up current Wi-Set Wizard setup and roll back to previous configuration.
Show Setting Information
Back
If you do not satisfy with current
setting, you could go back to previous
step ~ Wireless Network Security
Next
Confirm the current setting and go to
next step ~ Finish.
Cancel
Give up current Wi-Set Wizard setup
and roll back to previous configuration.
Select the Internet Connection List
This step only shows with multiple network
connection system. If there is only one
internet connection available, this step is
discarded. In this step, you have to select
one network connection from the list box.
This network connection should be
configured to connect internet.
Network List Box
In the list box, you could see all
network connection this system
provides. You have to pick one from
the list.
Page 22

3-14
Back
Go back to previous step ~ Show Setting Information.
Next
Go to next step, Finish, while the internet connection is selected.
Cancel
Give up current Wi-Set Wizard setup and roll back to previous configuration.
Finish
Finish
Press finish button to close Wi-Set
wizard. The wireless configuration
is going to be applied within few
seconds.
Page 23

4-1
Chapter 4 RtWLAN: Wireless LAN Management GUI
Page 24

4-2
4.1
How to Launch RtWLAN
You could launch RtWLAN from either Windows® Program Menu or tray icon. The tray icon is
an optional quick launch to be enabled by user.
Windows® Program Menu
It is the absolute way to launch RtWLAN from program folder.
Tray Icon
The tray icon will not be
show until you enable the
“Show Tray Icon” from
RtWLAN as the right picture.
As the RtWLAN icon shown
on system tray, you could
double click the icon with
mouse button to launch it.
格格格格式化
式化:::: 本文縮排1.1
式化式化
格格格格式化
式化:::: 本文縮排1.1
式化式化
4.2
Introduction of Main Window
The main window is assembled with five parts, main menu, adapter list area, properties area,
global control bar and status bar. Please read the explanations below before operating the
RtWLAN.
格格格格式化
式化:::: 項目符號及編號
式化式化
Page 25

4-3
Main Menu
The main menu includes five submenus.
Refresh
As clicking the refresh menu, the contents of adapter list area are re-enumerated and
updated.
Wi-Set
Quickly launching the Wi-Set Wizard. The
convenient quick launching helps you to
reprogram the wireless configuration as need.
Mode
Quickly switching wireless configuration to be either
[Station] or [Access Point]. The item with check mark
in front is the current wireless configuration.
格格格格式化
式化:::: 本文縮排1.1+項目
式化式化
+內文
Page 26

4-4
View
Enable/disable the present of status bar. With
check mark in front will make the status bar
showing up. Otherwise the status bar is hidden.
Help
Click the menu item
“About RtWLan” to
show the about dialog.
The about dialog shows
you the application
version and license
information.
Adapter List Area
This area displays all connected adapters on this system for mutiple
adatper installations. The easy switch helps user to change the
selected adapter by one click. The contents of properties area are
dependant on wireless configuration that the selected adapter was
set up. For single adatper installed system, the only one adapter is
always selected.
格格格格式化
式化:::: 本文縮排1.1+項目
式化式化
+內文
Page 27

4-5
Properties Area
The contents of this area are dependent
on current wireless configuration. You
could know the current configuration
through previous explanation of submenu
“Mode”. The detail contents are described
in following wireless configuration sections
for both Station and AP mode.
Global Control Bar
Each control items on this
bar affects the adapter or management GUI directly.
Show Tray Icon
Making this item to be checked, the management GUI will minimize and stay on the
tray icon located at the right down corner of Windows while pressing “Close” button. In
other word, management GUI will shut down while pressing “Close” button with
unchecked condition.
格格格格式化
式化:::: 本文縮排1.1+項目
式化式化
+內文
Windows Zero Config
Help switching to Microsoft Windows ® XP Wireless network configure service if you do
not prefer applying RtWLAN as your wireless LAN manager. The detail steps you
should follow are described in section 4.5.
Radio Off
Turn off the radio for saving power. While the radio being off, the links with other
wireless network nodes are disconnected. User should be care of it while the wireless
configuration is in AP mode. The radio off will cause the sub network belong to the AP
to disconnect with internet/intranet.
Disable Adapter
Make this wireless LAN adapter being functionless for increasing better system
resource management on performance and CPU utilization.
Close
Shutdown or hide the management GUI. The behavior depends on the check box of
“Show Tray Icon”.
Status Bar
The status bar presents the hints or status of the management GUI.
格格格格式化
式化:::: 本文縮排1.2+項目
式化式化
+內文
格格格格式化
式化:::: 字型: 粗體
式化式化
格格格格式化
式化:::: 本文縮排1.1+項目
式化式化
+內文
Page 28
4-6
4.3
Station mode
Two types, Ad-Hoc and infrastructure in station mode could be configured through Wi-Set
Wizard. The following two sections explain the operation of management GUI for each type.
The following explanations focus on the properties area.
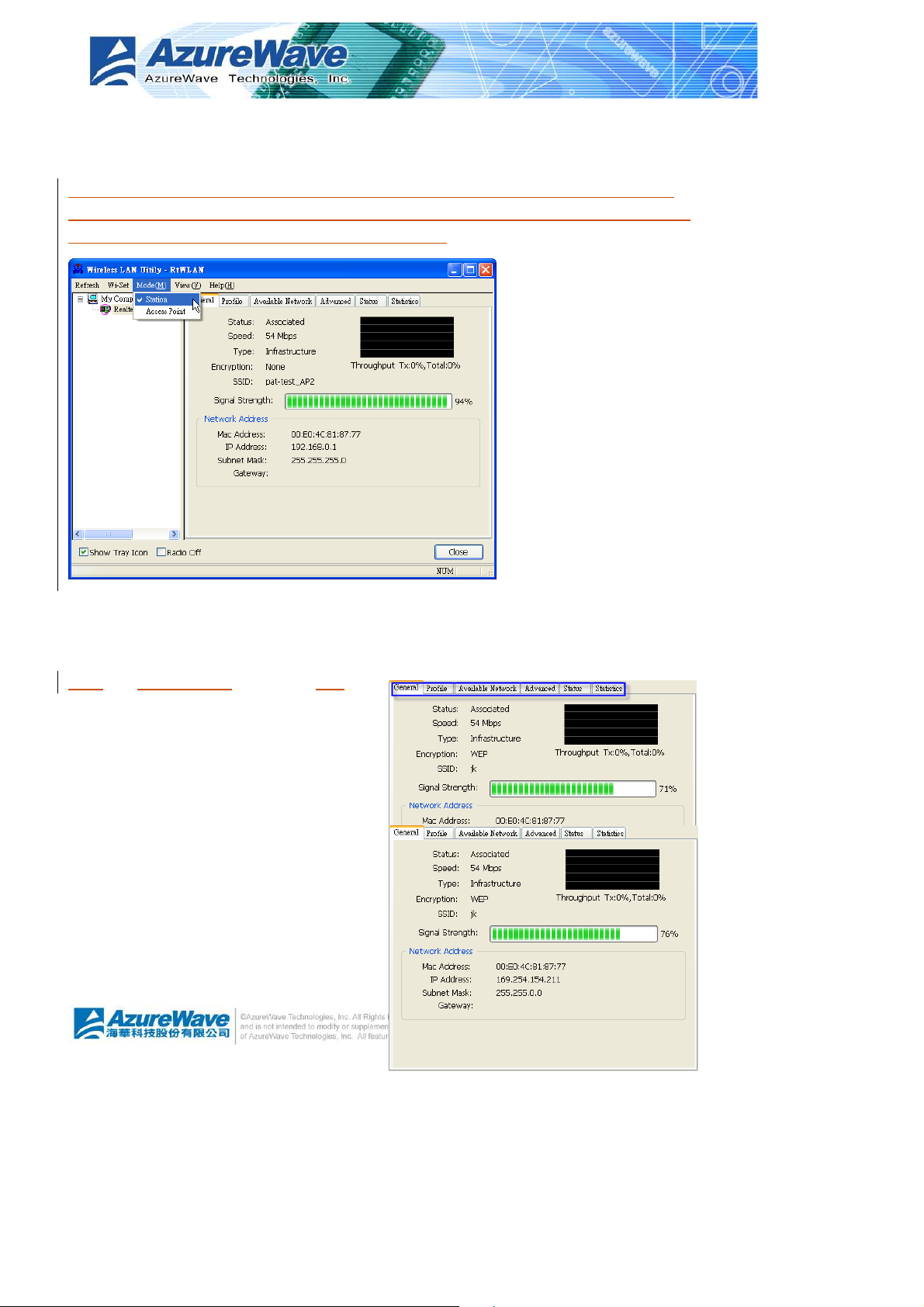
4.3.1 Infrastructure and Ad-Hoc
With both Infrastructure and Ad-Hoc types,
the properties should looks like the picture
beside. Six property pages present different
information of current wireless network
status.
Reading the following explanations before
you reviewing these pages, it could help you
to well know the wireless environment
around the system.
It is easy use to switch property pages just by
left button clicking of mouse the title of each
page The following six sections describes
detail information of the opposite page.
Page 29

4-7
General page
This page represents the general information of this adapter.
Status
The connection status with access point this station has.
Speed
Current transition speed in Mbps.(Mega-Bits-Per-Second)
Type
Current wireless LAN configuration type
Encryption
Current encryption mode used
SSID
Name of wireless network
Signal Strength
The average quality of signal pf packets received from wireless network. We recommend
connecting access point with over 70% signal strength.
Throughput diagram
Transition (Tx) performance
Network Address group
Mac Address: six two-digital number of this adapter
IP Address: assigned network address by DHCP server or self-definition in four three-digital
number format
Subnet Mask: the only valid value is 2555.255.255.0
Gateway: It comes from connected access point. Your system can not connect internet with this
field empty.
Profile page
This page provides profiles management like
add, remove, edit and duplicate just by
pressing the button.
Available Profile(s)
The list box shows all the created profiles.
Add
Add a new access point profile by manual
input.
Page 30

4-8
Remove
Remove the selected profile
Edit
Edit contents of selected profile
Duplicate
Make copy of selected profile.
Set Default
Set the selected profile as default selection.
Available Network page
This page presents all access points around
this system. And you could pick one of these
network connections.
Available Network(s)
Present network connection around this
system
Refresh
Rescan network connection around this
system
Add to Profile
Create profile for selected network connection in profile list and add it in to profile list.
Advanced page
Power Save
None: without power save mode
Min: wake up every two time interval to
receive packets
Max: wake up every ten time interval to
receive packets
Wireless Mode
802.11b
802.11g/b
802.11b Preamble Mode
Long: higher quality but with lower
performance than preamble short mode
Short: Normal quality but with higher
Page 31

4-9
performance then preamble long mode.
Auto: select the proper preamble mode by current signal frame information.
Fragment Threshold
The threshold of fragment length. Higher threshold increase data transition performance
with good signal quality. Pool signal quality results more worst data throughput on high
fragment threshold.
RTS Threshold
Request to send threshold. The request will not send out until the accumulated data over
threshold.
WOL (Wake On LAN)
The wake-on-LAN is applied for remote control purpose. You could wake up a system
through network packets. For AzureWave 802.11 b/g USB WLAN Module, only the same
adapter on another system could wake it up.
Input MAC Address: the six two-digit numbers of AzureWave 802.11 b/g USB WLAN Module on
target system.
Wake Up: press this button to wake it up
Set Defaults
Restore the default value to be current setting
Apply
Apply the current setting to GUI
Page 32

4-10
Status page
Manufacturer: It always is RealTek.
NDIS Driver Version:
Short Radio Header
Encryption: Current encryption mode.
Authenticate: authentication state
Channel Set: selected channel plan
currently. Please reference Appendix-A
with the detail comparisons.
MAC Address: MAC address of this
adapter.
Data Rate: wireless LAN transition speed
Channel(Frequency): current channel number
Status: wireless network status
SSID: name of connecting access point
Network Type: indicate current network configuration type
Power Save Mode: current setting power save mode
Associated AP MAC: MAC address of connecting access point
Associated AP IP: IP address of connecting access point
Up Time: total connection time
格格格格式化
式化:::: 本文縮排1.1+項目
式化式化
Statistics page
You could watch the Tx/Rx status of current
wireless connection. It provides a statistic
analysis of packet transition.
格格格格式化
式化:::: 本文縮排1.1
式化式化
Page 33

4-11
4.4
AP mode
General Page
In this page, it provides general information of
this access point including name, MAC address
and list of joined stations.
SSID
The name of this access point is.
BSSID
Six two-digital numbers configure the MAC
address of this access point.
Association Table
It is the list of joined station on this access point.
AID (Association ID)
The AID field is a value assigned by an AP during association that represents 16-bit ID of
a station. It is a unique value assigned by AP.
MAC address
It is the six two-digit numbers that assemble the MAC address of joined station.
Life Time
It is timer and counts down from 10 minutes whenever the access point connects the
station successfully.
Config
A dialog of this access point is shown up for
configuration modification except by Wi-Set
wizard.
Network Name (SSID)
Name of the access point searched by other
wireless nodes. The length of SSID should
be shorter than 32 characters.
Channel
Select the wireless channel within current
channel plan.
Network Authentication & Data Encryption
Page 34

4-12
Three types authentication:
Open System
It is combined with data encryption type to be WEP or disable.
Encryption ~ disabled: you decide to open this access point to every one without network
authentication.
Encryption ~ WEP: you decide to setup the basic data encryption with a defined network key.
Shared Key + WEP
You decide to apply both authentication and data encryption to prevent illegal login.
WPA-PSK + TKIP
The most advance authentication and data encryption could provide best security protection.
ASCII
You should provide either 5 or 13 ASCII characters on Network key edit box.
PASSPHRASE
You could input words on Network Key edit box.
64 bits: The generated pass key is 64-bits to be company with data packets.
128 bits: The generated pass key is 128-bits to be company with data packets.
Hexadecimal
While both ASCII and PASSPHRASE are not checked, you should input hexadecimal
number in the network key box.
Key index (1 ~4)
At most four key index to represent the opposite network key.
Advanced Page
In this page, expert could setup the advance
characteristics of network packet on
transmission.
Beacon Interval
Page 35

4-13
This filed represents the interval between each beacon that this AP sends out. Longer
interval may increase the competition of wireless nodes. The maximum value of it is
DTIM Period
The DTIM Period field indicates the number of Beacon intervals between successive DTIMs.
Preamble Mode
Long: higher quality but with lower performance than preamble short mode
Short: Normal quality but with higher performance then preamble long mode.
Auto: select the proper preamble mode by current signal frame information.
Statistics Page
You could watch the Tx/Rx status of current
wireless connection. It provides a statistic
analysis of packet transition.
SoftAP Page
ConnName list box
List all network connections on this
system. You should pick up one from the
listed item(s) if you would connect the
network domain, created by Soft AP, to
internet/intranet network.
Select
Pick up the desired network connection to
public network.
Apply
Execute the current setting.
Page 36

4-14
4.5
Windows Zero Configuration
The Windows Zero Configuration is a wireless LAN service that does not provided by Microsoft
Windows® until Windows XP. It provides basic and easy on connecting the wireless network. In
this chapter, we introduce you the steps to swap between Windows Zero Configuration and
RtWLAN. If you prefer Windows Zero Configuration instead through RtWLAN, then you should
follow the steps in 4.5.1 to switch to Windows Zero Configuration. In addition, you could rollback
to RtWLAN by following the steps in 4.5.2.
4.5.1 Swap from RtWLAN to Windows Zero Configuration
Five steps are required to archive this operation as following:
Windows Zero Configuration is disabled after installing RtWLAN. You should enable it by
making the “Windows Zero Config” item being checked on global control bar. And then a Zero
Config dialog is shown up to inform you. Then you have to press OK to confirm the translation.
After opening the page of present wireless network, if you see the scene similar to the following
figure, then you had been swapped to Windows Zero Configuration successfully. Otherwise,
you should check and repeat the previous steps again.
Page 37

4-15
4.5.2 Rollback from Windows Zero Configuration to RtWLAN
If you prefer the RtWLAN instead of Microsoft® Windows Zero Config, please follow the steps
to rollback. Open RtWLAN, make the “Windows Zero Config” item on global control bar to be
unchecked. After a while, the property area starts to display network connection.
Page 38

4-1
Appendix A:
Mapping of country and channel plan
Channels
1~11
1~13
10 ~ 13
3~9
1~14
14 only
10~11
Country Channel Set
Argentina ,Brazil ,Canada ,Colombia ,Mexico ,Taiwan ,United States of
America,Yugoslavia
Australia ,Austria ,Bahrain ,Belarus ,Belgium ,Bolivia ,Bulgaria ,Chile ,China ,Co
sta Rica ,Croatia ,Cyprus ,Czech
Republic,Denmark ,Egypt ,Estonia ,Finland ,France2 ,Germany ,Greece ,Hong
Kong,Hungary ,Iceland ,India ,Indonesia ,Ireland ,Italy ,Kuwait ,Latvia ,Lebanon ,
Liechenstein ,Lithuania ,Luxembourg ,Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav
Republic of ,Malaysia ,Morocco ,Netherlands ,New
Zealand,Nigeria ,Norway ,Panama ,Paraguay ,Peru ,Philippines ,Poland ,Portug
al ,Puerto Rico,Romania ,Russia ,Saudi
Arabia,Singapore ,Slovakia ,Slovenia ,South Africa,South
Korea,Sweden ,Switzerland ,Thailand ,Turkey ,United Arab Emirates,United
Kingdom ,Uruguay ,Venezuela
France,Jordan France
Isreal Isreal
Japan1 MKK1+MKK
Japan2 MKK
Spain Spain
FCC,IC
ETSI,MKK1
Page 39

4-2
Appendix B:
Q&A
Q:
After applying security setting, why my computer can not connect to the system that configures
the AzureWave 802.11 b/g USB WLAN Module as AP mode?
A:
There are several condition could result this issue.
Security setting mismatch: please make sure the security and network key are identical to
both AP and station side.
Station utilizes Windows Zero Configuration to join the Access Point: you could change the
WEP to be ASCII or Hexadecimal. The PassPhrase format is not supported by Windows
Zero Configuration.
Q:
My notebook cannot browse internet after connecting the AzureWave 802.11 b/g USB WLAN
Module. I could see the station on the general page of RtWLAN. What’s happened?
A:
It could lose ICS connection. First, you should make sure the access point connect to
intranet/internet through another network connection. And then select the network connection
as ICS. Please reference the “Soft AP Page” segment in section 4.4.
Page 40

4-3
Appendix C:
Version Comments Opposite Package Version
1.2 Update ICS operation of user interface
Add Appendix C for release history
1.1 Update Windows Zero Configuration operations of user interface 10.27 ~
1.0 First formal release 09.27 ~
Release History
10.27 ~
Page 41

4-4
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates,
uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is
no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning
the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one of the
following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that
to which the receiver is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept
any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user's authority to operate this equipment.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC RF radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment. This device was tested for typical lap held operations with the
device contacted directly to the human body to the back side of the notebook computer. To
maintain compliance with FCC RF exposure compliance requirements, avoid direct contact
to the transmitting antenna during transmitting.
This equipment should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm between
the radiator & your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna
or transmitter.
IEEE 802.11b or 802.11g operation of this product in the U.S.A. is firmware-limited to
channels 1 through 11.
Page 42

4-6
This device is intended only for OEM integrators under the following conditions:
The antenna must be installed such that 20 cm is maintained between the antenna and
users, and the transmitter module may not be co-located with any other transmitter or
antenna.
As long as 2 conditions above are met, further transmitter test will not be required. However,
the OEM integrator is still responsible for testing their end-product for any additional
compliance requirements required with this module installed (for example, digital device
emissions, PC peripheral requirements, etc.).
IMPORTANT NOTE: In the event that these conditions can not be met (for example certain
laptop configurations or co-location with another transmitter), then the FCC authorization is no
longer considered valid and the FCC ID can not be used on the final product. In these
circumstances, the OEM integrator will be responsible for re-evaluating the end product
(including the transmitter) and obtaining a separate FCC authorization.
End Product Labeling
This transmitter module is authorized only for use in device where the antenna may be
installed such that 20 cm may be maintained between the antenna and users. The final end
product must be labeled in a visible area with the following: “Contains TX FCC ID:
GU700”. FCC ID:TLZ-BT253
TLZ-
Manual Information That Must be Included
The OEM integrator has to be aware not to provide information to the end user regarding
how to install or remove this RF module in the users manual of the end product which
integrate this module.
The users manual for OEM integrators must include the following information in a prominent
location “ IMPORTANT NOTE: To comply with FCC RF exposure compliance requirements,
Page 43

4-7
the antenna used for this transmitter must be installed to provide a separation distance of at
least 20 cm from all persons and must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with
any other antenna or transmitter.
Industry Canada Statement
Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1) this device may not cause interference and
2) this device must accept any interference, including interference that may cause
undesired operation of the device
Antenna having a higher gain is strictly prohibited per regulations of Industry
Canada. The required antenna
impedance is 50 ohms.
To reduce potential radio interference to other users, the antenna type and its gain
should be so chosen that the EIRP is not more than required for successful
communication.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
IC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with IC radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment. This equipment should be installed and operated
with minimum distance 20cm between the radiator & your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter.
Page 44

4-8
NCC 警語
警語 :
警語警語
經型式認證合格之低功率射頻電機,非經許可,公司、商號或使用者均不得擅自變更頻率、加大
功率或變更原設計之特性及功能。
低功率射頻電機之使用不得影響飛航安全及干擾合法通信;經發現有干擾現象時,應立即停用,
並改善至無干擾時方得繼續使用。前項合法通信,指依電信法規定作業之無線電通信。低功率射
頻電機須忍受合法通信或工業、科學及醫療用電波輻射性電機設備之干擾。
本模組於取得認證後將依規定於模組本體標示審驗合格標籤,並要求平台上標示「本產品內含射
頻模組:ID編號」
 Loading...
Loading...