Page 1

SBC81206 Series
Intel
Pentium
®
Core™ 2 Duo/ Pentium® D/
®
4/ Celeron® Processor
All-In-One
PICMG 1.0 Full-Size Single Board Computer
User’s Manual
Page 2

Disclaimers
This manual has been carefully checked and believed to contain
accurate information. AXIOMTEK Co., Ltd. assumes no responsibility
for any infringements of patents or any third party’s rights, and any
liability arising from such use.
AXIOMTEK does not warrant or assume any legal liability or
responsibility for the accuracy, completeness or usefulness of any
information in this document. AXIOMTEK does not make any
commitment to update the information in this manual.
AXIOMTEK reserves the right to change or revise this document
and/or product at any time without notice.
No part of this document may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval
system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic,
mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior
written permission of AXIOMTEK Co., Ltd.
Caution
If you replace wrong batteries, it causes the danger of explosion. It is
recommended by the manufacturer that you follow the manufacturer’s
instructions to only replace the same or equivalent type of battery,
and dispose of used ones.
©Copyright 2009 AXIOMTEK Co., Ltd.
All Rights Reserved
February 2009, Version A1
Printed in Taiwan
ii
Page 3

ESD Precautions
Computer boards have integrated circuits sensitive to static electricity.
To prevent chipsets from electrostatic discharge damage, please take
care of the following jobs with precautions:
Do not remove boards or integrated circuits from their anti-static
packaging until you are ready to install them.
Before holding the board or integrated circuit, touch an unpainted
portion of the system unit chassis for a few seconds. It
discharges static electricity from your body.
Wear a wrist-grounding strap, available from most electronic
component stores, when handling boards and components.
Trademarks Acknowledgments
AXIOMTEK is a trademark of AXIOMTEK Co., Ltd.
Windows
Phoenix & AWARD are trademarks of Phoenix Technology Ltd.
IBM, PC/AT, PS/2, VGA are trademarks of International Business
Machines Corporation.
Intel
Winbond is a trademark of Winbond Electronics Corp.
Other brand names and trademarks are the properties and registered
brands of their respective owners.
®
is a trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
®
and Pentium® are trademarks of Intel Corporation.
iii
Page 4

Table of Contents
Disclaimers........................................................................................................... ii
ESD Precautions ................................................................................................. iii
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION ....................................................................................1
1.1 Specifications.......................................................................................... 2
1.2 Utilities Supported................................................................................... 4
1.3 I/O Bracket .............................................................................................. 4
CHAPTER 2 JUMPERS AND CONNECTORS............................................................ 5
2.1 Board Dimensions and Fixing Holes....................................................... 5
2.2 Board Layout........................................................................................... 6
2.3 Jumper Settings ...................................................................................... 7
2.3.1 COM2 Mode Select for Type Jumpers (JP1, JP2, JP3)...................8
2.3.2 ATX Auto Power On/Off (JP6).......................................................... 9
2.3.3 CMOS Clear Jumper (JP7) .............................................................. 9
2.4 Connectors............................................................................................ 10
2.4.1 COM1, COM2 Port Connectors...................................................... 11
2.4.2 VGA Connector (VGA1)................................................................. 12
2.4.3 Ethernet RJ-45 Connectors with LED (LAN1, LAN2)..................... 13
2.4.4 SATA Connectors (SATA1~4)........................................................ 13
2.4.5 USB Connectors (USB1, USB2) .................................................... 14
2.4.6 USB Port Connector (USB3/USB4)................................................ 14
2.4.7 Flat Panel Bezel Connector (CN3).................................................15
2.4.8 ATX 12V Power Connector (CN2).................................................. 16
2.4.9 Internal PS/2 Keyboard and Mouse Connector (KB1, MS1).......... 16
2.4.10 3 Pin Fan Connectors (FAN1, FAN3)............................................. 17
2.4.11 4 Pin CPU Fan Connector (FAN2)................................................. 17
2.4.12 Parallel IDE Connector (IDE1)........................................................17
2.4.13 Floppy Disk Port Connector (FDD1)............................................... 18
2.4.14 Parallel Port Connector (PRINT1).................................................. 19
2.4.15 AXIOMTEK ACPI Connector (CN4)............................................... 20
2.4.16 Intel
2.4.17 SMBUS Connector (CN1) .............................................................. 21
2.4.18 LAN1/LAN2 Link/Active & Speed LED Connectors (CN6, CN7)....21
CHAPTER 3 HARDWARE INSTALLATION.............................................................. 23
3.1 Installing the Processor......................................................................... 23
3.2 Installing the Memory............................................................................ 28
CHAPTER 4 HARDWARE DESCRIPTION................................................................ 29
4.1 Microprocessors.................................................................................... 29
4.2 BIOS......................................................................................................29
4.3 System Memory..................................................................................... 29
4.4 I/O Port Address Map............................................................................30
4.4 I/O Port Address Map............................................................................30
4.5 Interrupt Controller ................................................................................ 31
®
HD Audio Digital Header (HDA1)......................................... 20
iv
Page 5

CHAPTER 5 PHOENIX-AWARD BIOS UTILITY....................................................... 33
5.1 Entering Setup....................................................................................... 33
5.2 Control Keys..........................................................................................34
5.3 Getting Help .......................................................................................... 34
5.4 The Main Menu ..................................................................................... 35
5.5 Standard CMOS Setup Menu................................................................ 36
5.6 Advanced BIOS Features...................................................................... 38
5.7 Advanced Chipset Features.................................................................. 43
5.8 Integrated Peripherals........................................................................... 44
5.9 Power Management Setup.................................................................... 49
5.10 PnP/PCI Configuration Setup................................................................ 53
5.11 PC Health Status................................................................................... 55
5.12 Frequency/Voltage Control................................................................... 56
5.13 Load Optimized Defaults ....................................................................... 57
5.14 Set Supervisor/User Password ............................................................. 58
5.15 Save & Exit Setup ................................................................................. 59
5.16 Exit Without Saving ............................................................................... 60
APPENDIX A WATCHDOG TIMER ........................................................................... 61
APPENDIX B CONFIGURING SATA FOR RAID FUNCTION................................... 63
v
Page 6

MEMO
vi
Page 7

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
The SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 full-size Single Board Computer supports
®
Intel
Core™ 2 Duo, Intel® Celeron® 400 Series, Intel® Pentium® 4
processor in the LGA775 Land Grid Array package or Intel
D processor (supports 775-Land package) at FSB 533/800 MT/s
(133/200 MHz). The board integrates chipsets Intel
ICH7/7R (Optional) that deliver outstanding system performance
through high-bandwidth interfaces, multiple I/O functions for
interactive applications and various embedded computing solutions.
There are two 240-pin unbuffered DIMM sockets for dual channel
DDR2-400/533/667 MHz memory, maximum memory capacity up to
2GB. It also features Gigabit/Fast Ethernet, four serial ATA channels
for total four Serial ATA hard drives at maximum transfer rate up to
300MB/sec, and six USB 2.0 high speed compliant.
®
®
Pentium®
945GC and
Introduction
1
Page 8
SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
1.1 Specifications
z CPU
Intel
z System Chipset
Intel
z CPU Socket
LGA775
z Front-Side Bus
533/800 MT/s (133/200 MHz)
z BIOS
Phoenix-Award BIOS, Y2K compliant
8Mbit FWH Flash, DMI, Plug and Play
“Load Optimized Default” to backup customized Setting in
®
CoreTM 2 Duo, Celeron® 400 series , Pentium® 4
processor in the LGA775 Land Grid Array package
and Pentium
®
D processor (supports 775-Land
package)
®
945GC & ICH7/7R(Optional)
the BIOS flash chip to prevent from CMOS battery fail
z System Memory
Two 240-pin unbuffered DDR2 DIMM sockets
Maximum to 2GB DDR2 400/533/667 MHz memory
z Onboard Multi I/O
Controller: Winbond W83627HG
Parallel Port: one bi-directional with ECP/EPP/SPP support
Serial Ports: One ports for RS-232(COM1) and one port for
RS-232/422/485(COM2)
Floppy controller: supports two drives (1.44MB for each)
z USB Interface
Six USB ports with fuse protection and complies with USB
Spec. Rev. 2.0
z Display
Chipset Integrated VGA Controller and Supports up to
2048x1536 at 75 Hz resolution on non-interlaced CRT
2
Introduction
Page 9

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
monitors via 15-pin D-Sub connector on the edge
z Watchdog Timer
1~255 seconds; up to 255 levels
z Ethernet
The LAN1/LAN2: Dual port with RTL8111B for Gigabit/Fast
Ethernet
Via PCI Express x1 bus
Wake-on-LAN support
z Serial ATA
Built-in four SATA/SATA II ports onboard support the
maximum transfer rate up to 3.0 Gb/sec and SATA RAID
0/1/5/10 by ICH7R
z Hardware Monitoring
Monitoring temperatures, voltages, and cooling fan status
z Dimensions: 338 x 122 mm (6 layers)
NOTE All specifications and images are subject to change
without notice.
Introduction
3
Page 10
SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
1.2 Utilities Supported
z Chipset Driver
z Ethernet Driver
z Graphic Driver
z Intel Matrix Storage manager
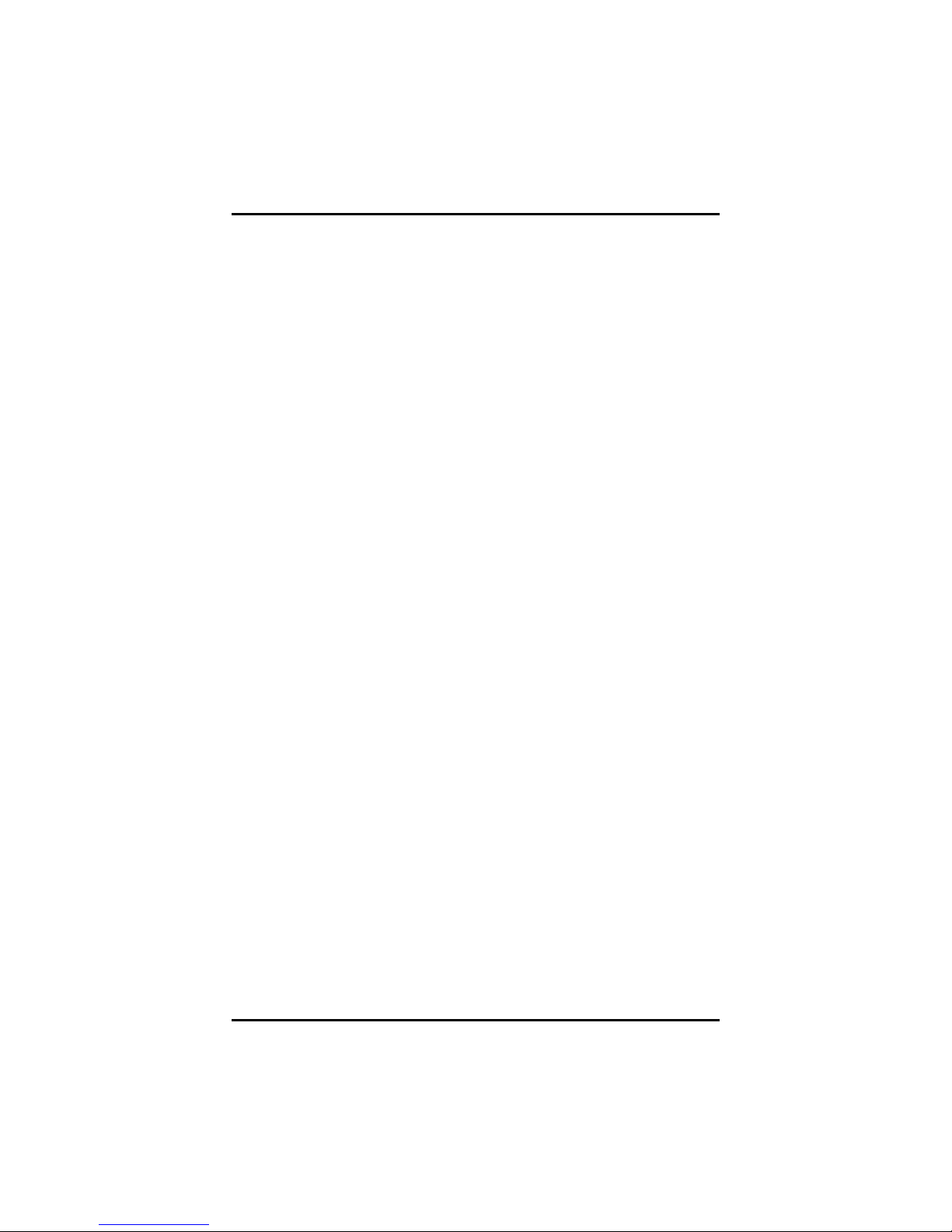
1.3 I/O Bracket
4
Introduction
Page 11

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
CHAPTER 2
JUMPERS AND CONNECTORS
2.1 Board Dimensions and Fixing Holes
Jumpers and Connectors
5
Page 12
SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
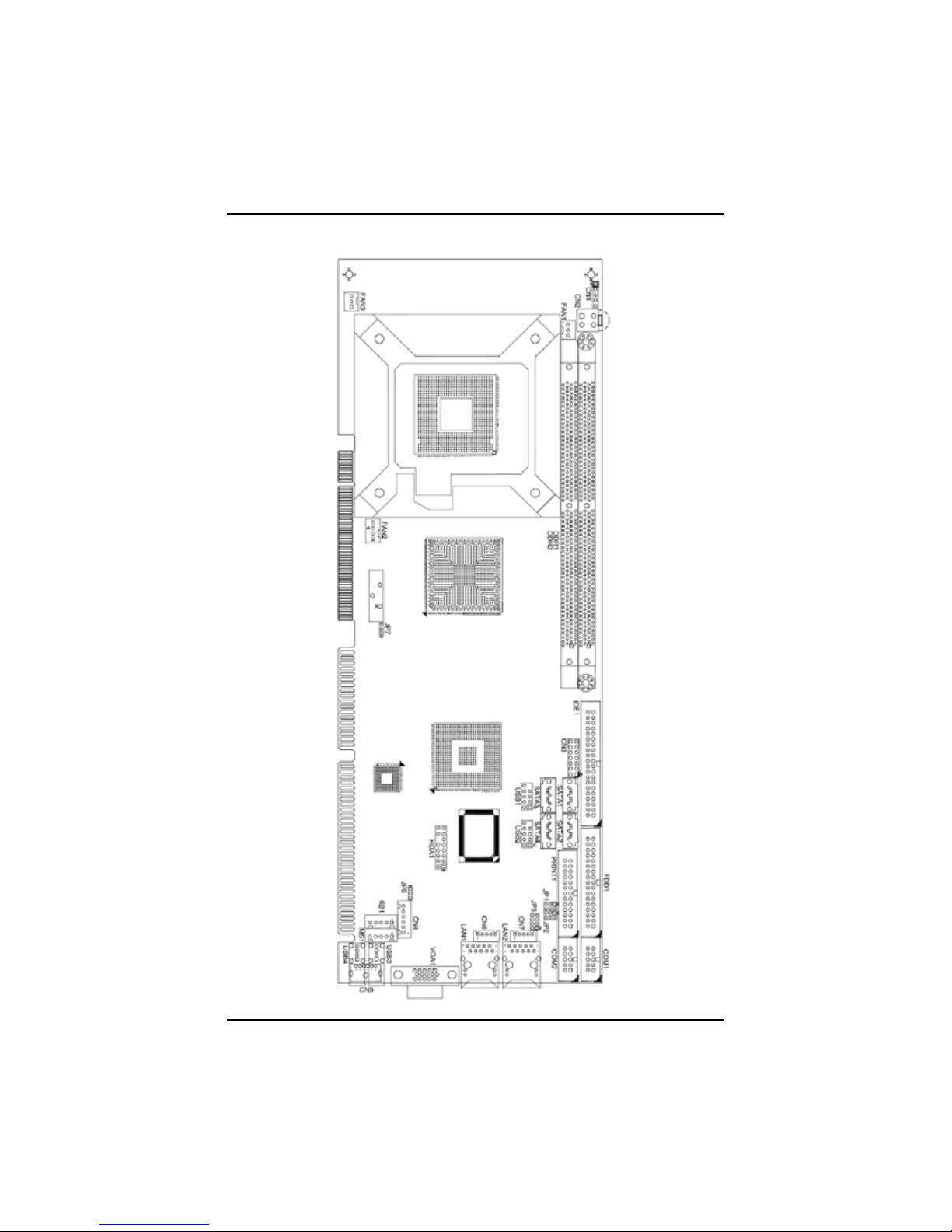
2.2 Board Layout
6
Jumpers and Connectors
Page 13
SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
2.3 Jumper Settings
Proper jumer settings configure the SBC81206 to meet your
application purpose. We are herewith listing a summary table of all
jumpers and default settings for onboard devices, respectively.
Jumper Default Setting
COM2 Pin 1: DCD JP1 COM2 Mode Select
COM2 Pin 8: RI
COM2 Pin 1: DCD JP2 COM2 Mode Select
COM2 Pin 8: RI
JP3 COM2 Mode Select : RS-232 Short 1-2
JP6 ATX Auto Power On/Off : Disable Short 1-2
JP7 Clear CMOS Setting : Normal Short 1-2
Short 3-5
Short 4-6
Short 3-5
Short 4-6
Jumpers and Connectors
7
Page 14

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
2.3.1 COM2 Mode Select for Type Jumpers (JP1, JP2,
JP3)
These jumpers select the COM2 port’s communication mode to
operate RS-232 or RS-422/485.
Description Function Jumper Setting
COM2 Mode
Select
RS-232
(Default)
JP3
JP2
JP1
RS-422
RS-485
JP3 JP2
JP3
JP2
JP1
JP1
8
Jumpers and Connectors
Page 15

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
2.3.2 ATX Auto Power On/Off (JP6)
When Jumper JP6 is set 2-3 short for AC power input, the system will
be automatically power ON without pressing soft power button; when
JP6 is 1-2 short for AC power input, it is necessary to manually press
soft power button to make the system power ON.
Description Function Jumper Setting
ATX Auto Power
On/Off
Disable
(Default)
Enable
Note This function is similar to the feature of Power on after
Power Failed, which is controlled by hardware circuitry
instead of BIOS.
2.3.3 CMOS Clear Jumper (JP7)
You may need to use this jumper is to clear the CMOS memory if
incorrect settings in the Setup Utility.
Description Function Jumper Setting
CMOS Clear
Normal (Default)
Clear CMOS
Jumpers and Connectors
9
Page 16

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
2.4 Connectors
Connectors connect the board with other parts of the system. Loose or
improper connection might cause problems. Make sure all connectors
are properly and firmly connected. Here is a summary table shows you
all connectors on the SBC81206 Series.
Connector Label Connector Label
SM BUS Connector CN1
LAN2 Link/Active &
Speed LED Connector
ATX 4 Pin 12V In CN2 LAN1 Connector LAN1
Front Panel Connector CN3 LAN2 Connector LAN2
AXIOMTEK ACPI
Connector
PS/2 KB/MS Connector
(Optional)
Parallel IDE Connector IDE1 System FAN Connector 1 FAN1
LAN1 Link/Active & Speed
LED Connector
CN7 USB Port2 Connector USB4
CN4 VGA Connector VGA1
DDRII Long-DIMM
CN5
Sockets
CN6
DDR1~2
Floppy Connector FDD1 CPU FAN Connector FAN2
Printer Port Connector PRINT1 System FAN Connector 2 FAN3
Serial Port1 Connector COM1
Serial Port2 Connector COM2
USB Port4/5 Connector USB1
USB Port2/3 Connector USB2
USB Port1 Connector USB3
Internal PS/2 Keyboard
Connector
Internal PS/2 Mouse
Connector
Intel® HD Audio Digital
Header (Optional)
Serial ATA Port
Connectors
10
Jumpers and Connectors
KB1
MS1
HDA1
SATA1~4
Page 17

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
2.4.1 COM1, COM2 Port Connectors
The serial interface for the board consists of COM1 port (COM1)
support for RS-232 and COM2 (COM2) for RS-232/RS422/RS485.
Please refer to the RS-232 pin assignment as listed below:
Pin Signal Pin Signal
Data Carrier Detect
1
(DCD)
3 Receive Data (RXD) 4
5 Transmit Data (TXD) 6 Clear to Send (CTS)
Data Terminal Ready
7
(DTR)
9 Ground (GND) 10 Ground (GND)
COM2 Serial Port 10-pin (Box-header) Connector Pin Assignment list
Pin #
1 TX- DATA2 No connector No connector
3 TX+ DATA+
4 No connector No connector
5 RX+ No connector
6 No connector No connector
7 RX- No connector
8 No connector No connector
9 GND GND
10 GND GND
Data Set Ready
2
(DSR)
Request to Send
(RTS)
8 Ring Indicator (RI)
Signal Name
RS-422 RS-485
Jumpers and Connectors
11
Page 18

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
2.4.2 VGA Connector (VGA1)
The VGA connector VGA1 is a standard 15-pin connector commonly
used for the CRT VGA display.
Pin
1 Red
2 Green
3 Blue
4 N.C
5 Ground
6 Ground
7 Ground
8 Ground(GND)
9 +5V
10 Ground (GND)
11 N.C
12 DDC DATA
13 Horizontal Sync
14 Vertical Sync
15 DDC CLK
Signal
12
Jumpers and Connectors
Page 19

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
2.4.3 Ethernet RJ-45 Connectors with LED (LAN1,
LAN2)
The board is equipped with two high performance Plug and Play
Ethernet interface fully compliant with the IEEE 802.3 standard. To
connect the board to 10-Base-T, 100-Base-T or 1000 Base-T hub, just
plug one end of cable to the Ethernet connector and connect the other
end (phone jack) to a 10-Base-T, 100-Base-T or 1000 Base-T hub.
Pin Signal
RJ-1(For 1000 base T-Only)
1
RJ-1(For 1000 base T-Only)
2
Rx- (Data reception negative)
3
4 RJ-1(For 1000 base T-Only)
5 RJ-1(For 1000 base T-Only)
Rx+(Data reception positive)
6
Tx- (Data transmission negative)
7
8 Tx+ (Data transmission positive)
A Active LED
B 100 LAN LED(Green)/
1000 LAN LED(Orange)
2.4.4 SATA Connectors (SATA1~4)
These SATA connectors are for high-speed SATA interface ports and
they can be connected to hard disk devices.
Pin Signal
1 GND
2 SATA_TX+
3 SATA_TX4 GND
5 SATA_RX6 SATA_RX+
7 GND
Jumpers and Connectors
13
Page 20

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
2.4.5 USB Connectors (USB1, USB2)
These Universal Serial Bus (USB) connectors on this board are for
installing versatile USB interface peripherals. These are 10-pin
standard USB connectors.
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 +5V 2 +5V
3 USB D4- 4 USB D5-
5 USB D4+ 6 USB D5+
7 Ground (GND) 8 Ground (GND)
9 NC 10 Ground (GND)
USB1
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 +5V 2 +5V
3 USB D2- 4 USB D3-
5 USB D2+ 6 USB D3+
7 Ground (GND) 8 Ground (GND)
9 NC 10 Ground (GND)
USB2
2.4.6 USB Port Connector (USB3/USB4)
The 4-pin standard Universal Serial Bus (USB) port connector on the
board is for the installation of peripherals supporting the USB interface.
Pin Signal
1 USB POWER
2 USB 3 USB +
4 GND
USB3/4
1234
14
Jumpers and Connectors
Page 21

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
2.4.7 Flat Panel Bezel Connector (CN3)
Power LED
This 3-pin connector named as Pin 1, 3 and Pin 5 connect the
system power LED indicator to such a switch on the case. Pin 1 is
assigned as +, and Pin 3, Pin 5 as -. The Power LED lights up
when the system is powered ON.
External Speaker and Internal Buzzer Connector
Pin 2, 4, 6 and 8 can be connected to the case-mounted speaker
unit or internal buzzer. While connecting the CPU card to an
internal buzzer, please short pins 2-4; while connecting to an
external speaker, you need to set pins 2-4 to Open and connect the
speaker cable to pin 8 (+) and pin 6 (-).
ATX Power On/Off Button
This 2-pin connector named as Pin 9 and 10 connect the front
panel’s ATX power button to the CPU card, which allows users to
control ATX power supply to be power on/off.
System Reset Switch
Pin 11 and 12 can be connected to the case-mounted reset switch
that reboots your computer, not turns OFF the power switch. It is a
better way to reboot your system for a longer life of the system’s
power supply.
HDD Activity LED
This connection is linked to hard drive activity LED on the control
panel. LED flashes when HDD is being accessed. Pin 13 and 14
connect the hard disk drive to the front panel HDD LED, Pin 13
assigned as -, and Pin 14 as +.
Jumpers and Connectors
15
Page 22

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
2.4.8 ATX 12V Pow er Connector (CN2)
Connect the power cable to CN2 for +12V ATX power supply.
Pin Signal
1 GND
2 GND
3 +12V
4 +12V
2.4.9 Internal PS/2 Keyboard and Mouse Connector
(KB1, MS1)
The board provides the Keyboard (KB1)/ Mouse (MS1) interface with a
5-pin connector
1
Clock
2
Data
GND
Power
3
4
5
No Connection
16
Jumpers and Connectors
Page 23

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
2.4.10 3 Pin Fan Connectors (FAN1, FAN3)
You can connect the system cooling fan cable to FAN1, FAN3.
Pin Signal
1 Ground
2 +12V
3 Sensor
2.4.11 4 Pin CPU Fan Connector (FAN2)
You can connect the CPU cooling fan cable to FAN2. It is for CPU
cooling fan power.
Pin Signal
1 GND
2 +12V
3 Sensor
4 NC
2.4.12 Parallel IDE Connector (IDE1)
IDE1 is a 40-pin IDE interface connector for standard 3.5” IDE device.
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 Reset # 2 GND 3 Data 7
4 Data 8 5 Data 6 6 Data 9
7 Data 5 8 Data 10 9 Data 4
10 Data 11 11 Data 3 12 Data 12
13 Data 2 14 Data 13 15 Data 1
16 Data 14 17 Data 0 18 Data 15
19 GND 20 NC 21 DREG#
22 GND 23 IOW # 24 GND
25 IOR # 26 GND 27 IOCHRDY
28 CSEL 29 DACK# 30 GND
Jumpers and Connectors
17
Page 24

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
31 Interrupt 32 NC 33 SA1
34 PDIAG# 35 SA0 36 SA2
37 HDC CS0 # 38 HDC CSI # 39 HDD Active #
40 GND
2.4.13 Floppy Disk Port Connector (FDD1)
The board provides a 34-pin header type connector, FDD1, supporting
up to two floppy drives. The floppy drives may be any one of the
following types: 5.25" 360KB/1.2MB and 3.5" 720KB/1.44MB/2.88MB.
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 GND 2
4 No connector 5 GND 6 No connector
7 GND 8 Index# 9 GND
10 Motor enable A# 11 GND 12 No connector
13 GND 14 Drive select A# 15 GND
16 No connector 17 GND 18 Direction#
19 GND 20 STEP# 21 GND
22 Write data# 23 GND 24 Write gate#
25 GND 26 Track 0 # 27 GND
28 Write protect# 29 No connector 30 Read data#
31 GND 32 Head selection# 33 No connector
34 Disk change#
Drive Density Select
3 GND
18
Jumpers and Connectors
Page 25

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
2.4.14 Parallel Port Connector (PRINT1)
Print Port Connector [Default]
This board has a multi-mode parallel port to support:
1. Standard Mode:
IBM PC/XT, PC/AT and PS/2™ are compatible with bi-directional
parallel port.
2. Enhanced Mode:
Enhance parallel port (EPP) is compatible with EPP 1.7 and EPP 1.9
(IEEE 1284 compliant).
3. High Speed Mode:
Microsoft and Hewlett Packard extended capabilities port (ECP) is
IEEE 1284 compliant.
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 Strobe# 2 Auto Form Feed#
3 Data 0 4 Error#
5 Data 1 6 Initialize#
7 Data 2 8 Printer Select In#
9 Data 3 10 GND
11 Data 4 12 GND
13 Data 5 14 GND
15 Data 6 16 GND
17 Data 7 18 GND
19 Acknowledge# 20 GND
21 Busy 22 GND
23 Paper Empty# 24 GND
25 Printer Select 26 GND
1
3
5
78
9
11
13
15
17
19
21
23
25
2
4
6
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
Jumpers and Connectors
19
Page 26
SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
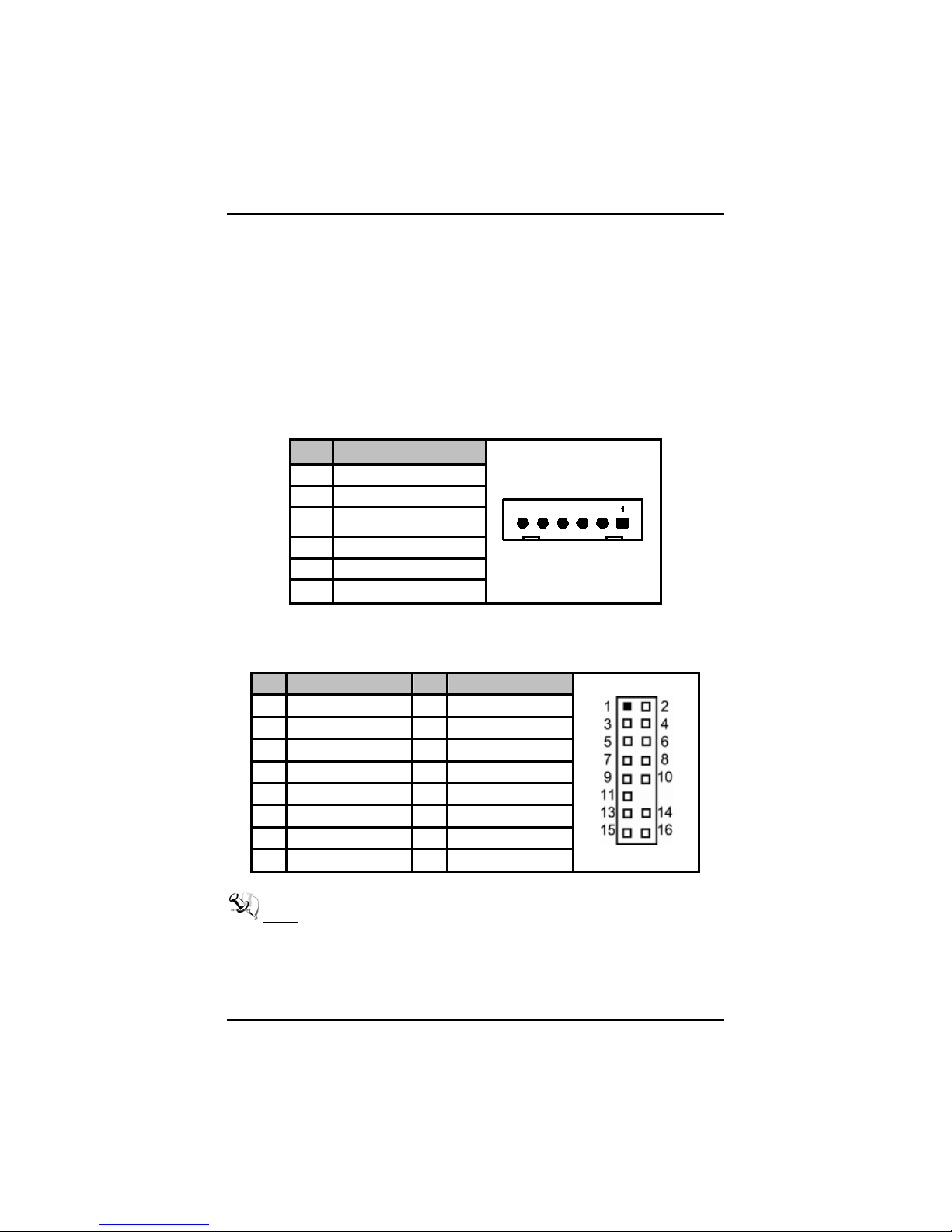
2.4.15 AXIOMTEK ACPI Connector (CN4)
Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) defines a flexible
and extensible interface that allows system designers to select
appropriate cost/feature trade-offs for power management. The
interface enables and supports reliable power management through
improved hardware and operating system coordination. The
specification enables new power management technology to evolve
independently in operating systems and hardware while ensuring that
they continue to work together.
CN4 is a 6-pin header connector that provides ACPI interface.
Pin Signal
1 EXTSMI
2 GND
3 Power Button
4 GND
5 PSON
6 +5VSB
2.4.16 Intel® HD Audio Digital Header (HDA1)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 BCLK 2 GND
3 RST# 4 VCC3
5 SYNC 6 GND
7 SDOUT 8 VCC3
9 SDI0 10 +12V
11 No connector
13 No connector 14 3VDUAL
15 No connector 16 GND
Note It is an optional function by request.
20
Jumpers and Connectors
Page 27

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
2.4.17 SMBUS Connector (CN1)
This connector CN1 is for SMBUS interface support.
Pin Signal
1 SMBUS_CLOCK
2 NC
3 GND
4 SMBUS_DATA
5 +5V
2.4.18 LAN1/LAN2 Link/Active & Speed LED
Connectors (CN6, CN7)
Pin Signal
1 Link/Active LED (+)
2 Link/Active LED (-)
3 Speed LED-10/100, Low Active
4 + 3.3V
5 Speed LED-1000, Low Active
Jumpers and Connectors
21
Page 28
SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
MEMO
22
Jumpers and Connectors
Page 29

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
CHAPTER 3
HARDWARE INSTALLATION
Before installing the processor, please access Intel® website for more
detailed information http://www.intel.com
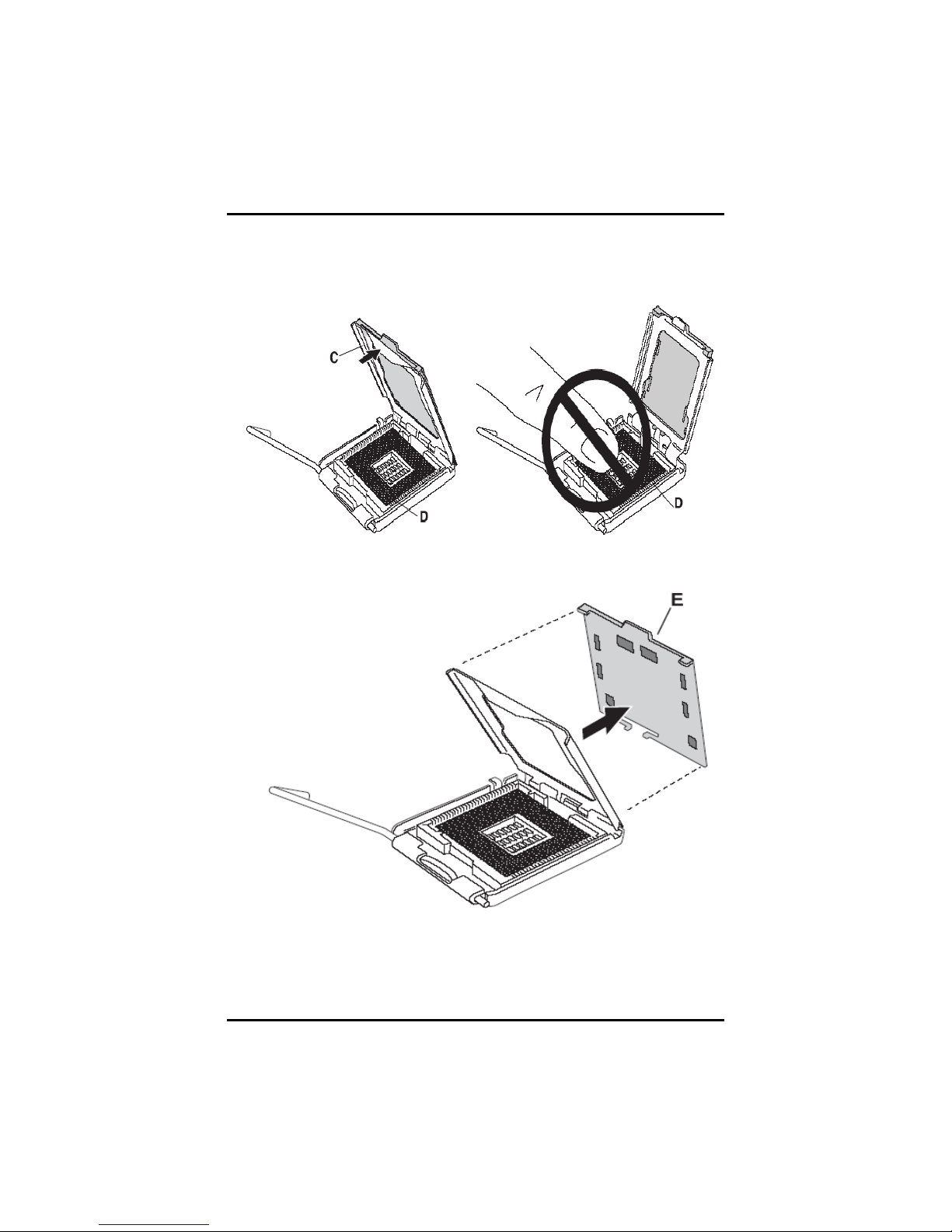
3.1 Installing the Processor
The LGA775 processor socket comes with a cover to protect the
processor. Please install the processor into the CPU socket step by
step as below:
1. Hold the hook (A) of the lever and push it down. Pull the lever (B)
aside to unlock the cover.
.
Hardware Installation
23
Page 30
SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
2. Open the cover (C), you can
see the contact.
3. Be careful not to touch the
contact (D).
4. Remove the plastic cap (E) from the cover.
24
Hardware Insatllation
Page 31

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
5. Place the CPU down into the socket. Be careful not to touch the
contact.
6. Hold the edges of the CPU, and orientate it as the marked direction
(G) down into the socket to match the (H) and (F) locations.
Hardware Installation
25
Page 32

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
7. Slightly push down the cover and hook the lever (I~J). The CPU is
completely locked.
8. Orientate the CPU cooling fan to fixing holes on the board.
26
Hardware Insatllation
Page 33

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
9. Screw the CPU cooling fan onto the board.
10. Make sure the CPU fan is plugged to the CPU fan connector.
Hardware Installation
27
Page 34

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
3.2 Installing the Memory
The board supports four 240-pin DDR2 DIMM memory sockets with
maximum memory capacity up to 2GB.
Please follow steps below to install the memory modules:
1 Push down latches on each side of the DIMM socket.
2 Align the memory module with the socket that notches of
memory module must match the socket keys for a correct
intallation.
3 Install the memory module into the socket and push it firmly
down until it is fully seated. The socket latches are levered
upwards and clipped on to the edges of the DIMM.
4 Install any remaining DIMM modules.
28
Hardware Insatllation
Page 35

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
HARDWARE DESCRIPTION
4.1 Microprocessors
CHAPTER 4
The SBC81206 Series supports Intel® Core™ 2 Duo, Intel® Celeron®
400 Series, Intel
Array package or Intel
package), which make your system operated under Windows 2000/XP
and Windows VISTA environments.The system performance depends
on the microprocessor. Make sure all correct settings are arranged for
your installed microprocessor to prevent the CPU from damages.
®
Pentium® 4 processor in the LGA775 Land Grid
®
Pentium® D processor (supports 775-Land
4.2 BIOS
The SBC81206 Series uses Award Plug and Play BIOS with a single
8Mbit FWH Flash, DMI, Plug and Play.
4.3 System Memory
The SBC81206 Series industrial CPU card supports two 240-pin
unbuffered DDR2 DIMM sockets for a maximum memory of 2GB DDR2
SDRAMs. The memory module can come in sizes of 128MB, 256MB,
512MB, 1GB and 2GB.
Hardware Description
29
Page 36

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
4.4 I/O Port Address Map
The Intel® Core™ 2 Duo Processor, Intel® Pentium® D Processor,
®
Celeron® Processor can communicate via I/O ports. There are
Intel
total 1KB port addresses available for assignment to other devices via
I/O expansion cards.
30
Hardware Description
Page 37

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
4.5 Interrupt Controller
The SBC81206 Series is a 100% PC compatible control board. It
consists of 16 interrupt request lines, and four out of them can be
programmable. The mapping list of the 16 interrupt request lines is
shown as the following table.
IRQ Parity check error
IRQ0 System timer
IRQ1 Standard 101/102-Key or Microsoft Natural PS/2
Keyboard
IRQ2 Interrupt rerouting from IRQ8 through IRQ15
IRQ3 Serial port #2
IRQ4 Serial port #1
IRQ6 Standard floppy disk controller
IRQ7 Parallel port
IRQ8 System CMOS/real time clock
IRQ9 Microsoft ACPI-Conpliant System
IRQ12 PS/2 Compatible Mouse
IRQ13 Numeric data processor
IRQ14 Primary IDE channel
IRQ15 Secondary IDE channel
Hardware Description
31
Page 38
SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
MEMO
32
Hardware Description
Page 39

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
CHAPTER 5
PHOENIX-AWARD BIOS UTILITY
The Phoenix-Award BIOS provides users with a built-in Setup program
to modify basic system configuration. All configured parameters are
stored in a battery-backed-up RAM (CMOS RAM) to save the Setup
information whenever the power is turned off.
5.1 Entering Setup
There are two ways to enter the Setup program. You may either turn
ON the computer and press <Del> immediately, or press the <Del>
and/or <Ctrl>, <Alt>, and <Esc> keys simultaneously when the
following message appears at the bottom of the screen during POST
(Power on Self Test).
TO ENTER SETUP PRESS DEL KEY
If the message disappears before you respond and you still want to
enter Setup, please restart the system to try it again. Turning the
system power OFF and ON, pressing the “RESET” button on the
system case or simultaneously pressing <Ctrl>, <Alt>, and <Del> keys
can restart the system. If you do not press keys at the right time and
the system doesn’t boot, an error message will pop out to prompt you
the following information:
PRESS <F1> TO CONTINUE, <CTRL-ALT-ESC> OR <DEL> TO ENTER SETUP
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
33
Page 40

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
5.2 Control Keys
Up arrow
Down arrow
Left arrow
Right arrow
Esc key
PgUp/“+” key
PgDn/“−“ key
F1 key
(Shift) F2 key
F3 key
F4 key
F5 key
F6 key
F7 key
F8 key
F9 key
F10 key
Move cursor to the previous item
Move cursor to the next item
Move cursor to the item on the left hand
Move to the item in the right hand
Main Menu -- Quit and delete changes into CMOS
Status Page Setup Menu and Option Page Setup
Menu -- Exit current page and return to Main Menu
Increase the numeric value or make changes
Decrease the numeric value or make changes
General help, only for Status Page Setup Menu and
Option Page Setup Menu
Change color from total 16 colors. F2 to select color
forward, (Shift) F2 to select color backward
Reserved
Reserved
Restore the previous CMOS value from CMOS, only
for Option Page Setup Menu
Load the default CMOS value from BIOS default table,
only for Option Page Setup Menu
Load the Setup default, only for Option Page Setup
Menu
Reserved
Reserved
Save all the CMOS changes, only for Main Menu
5.3 Getting Help
z Main Menu
The online description of the highlighted setup function is displayed
at the bottom of the screen.
z Status Page Setup Menu/Option Page Setup Menu
Press <F1> to pop out a small Help window that provides the
description of using appropriate keys and possible selections for
highlighted items. Press <F1> or <Esc> to exit the Help Window.
34
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
Page 41

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
5.4 The Main Menu
Once you enter the Award BIOS CMOS Setup Utility, the Main Menu
appears on the screen. In the Main Menu, there are several Setup
functions and a couple of Exit options for your selection. Use arrow
keys to select the Setup Page you intend to configure then press
<Enter> to accept or enter its sub-menu.
NOTE If your computer can not boot after making and saving
system changes with Setup, the Award BIOS will reset
your system to the CMOS default settings via its built-in
override feature.
It is strongly recommended that you should avoid changing the
chipset’s defaults. Both Award and your system manufacturer have
carefully set up these defaults that provide the best performance and
reliability.
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
35
Page 42

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
5.5 Standard CMOS Setup Menu
The Standard CMOS Setup Menu displays basic information about
your system. Use arrow keys to highlight each item, and use <PgUp>
or <PgDn> key to select the value you want in each item.
z Date
The date format is <day>, <date> <month> <year>. Press <F3> to
show the calendar.
day
date
month
year
z Time
It is determined by the BIOS and read only, from Sunday
to Saturday.
It can be keyed with the numerical/ function key, from 1
to 31.
It is from January to December.
It shows the current year of BIOS.
This item shows current time of your system with the format <hour>
<minute> <second>. The time is calculated based on the 24-hour
military-time clock. For example, 1 p.m. is 13:00:00.
36
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
Page 43

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
z IDE Channel 0/1 Master/Slave
These items identify the types of each IDE channel installed in the
computer. There are 45 predefined types (Type 1 to Type 45) and
2 user’s definable types (Type User) for Enhanced IDE BIOS.
Press <PgUp>/<+> or <PgDn>/<−> to select a numbered hard disk
type, or directly type the number and press <Enter>. Please be
noted your drive’s specifications must match the drive table. The
hard disk will not work properly if you enter improper information. If
your hard disk drive type does not match or is not listed, you can
use Type User to manually define your own drive type.
If selecting Type User, you will be asked to enter related
information in the following items. Directly key in the information
and press <Enter>. This information should be provided in the
documentation from your hard disk vendor or the system
manufacturer.
If the HDD interface controller supports ESDI, select “Type 1”.
If the HDD interface controller supports SCSI, select “None”.
If the HDD interface controller supports CD-ROM, select “None”.
CYLS.
HEADS
PRECOMP
number of cylinders
number of heads
write precom
LANDZONE
SECTORS
MODE
landing zone
number of sectors
HDD access mode
If there is no hard disk drive installed, select NONE and press
<Enter>.
z Drive A
Select the type of floppy drive installed in your system, and the
default is “None”.
z Halt On
This item determines whether the system will halt or not, if an error
is detected while powering up.
No errors
All errors
All, But
Keyboard
All, But
Diskette
The system booting will halt on any errors detected.
(default)
Whenever BIOS detects a non-fatal error, the
system will stop and you will be prompted.
The system booting will not stop for a keyboard
error; it will stop for other errors.
The system booting will not stop for a disk error; it
will stop for other errors.
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
37
Page 44

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
All, But
Disk/Key
Press <Esc> to return to the Main Menu page.
The system booting will not stop for a keyboard or
disk error; it will stop for other errors.
5.6 Advanced BIOS Features
This section allows you to configure and improve your system, to set
up some system features according to your preference.
38
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
Page 45

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
z CPU Feature
Scroll to this item and press <Enter> to view the CPU Feature sub
menu.
¾ Delay prior to Thermal
This filed is used to select the time that would force the CPU
to a 50% duty cycle when it exceeds its maximum operating
temperature therefore protecting the CPU and the system
board from overheating to ensure a safe computing
environment.
¾ Thermal Management
Thermal Monitor 1 On-die throttling
Thermal Monitor 2 Ratio and VID transition
¾ Limit CPUID MaxVal
The CPUID instruction if some newer CPUs will return a
value greater than 3. The default is “Disabled“, because this
problem does not exist in the Windows series operating
systems. If you are using an operating system other than
Windows, this problem may occur. To avoid this problem,
you can enable this field to limit the return value to 3 or
lesser than 3.
¾ C1E Function
The Intel
®
CPU Enhanced Halt (C1E) function is a CPU
power-saving function in system halt state. When enabled,
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
39
Page 46

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
the CPU core frequency and voltage will be reduced during
system halt state to decrease power consumption.
¾ Execute Disable Bit
Use this item to enable the hardware-based security feature
that reduces exposure to viruses and malicious-code attacks.
¾ Virtualization Technology
Wnen this feature is enabled, the computer system can
operate as multiple "virtual" systems.
Press <Esc> to return to the Advanced BIOS Features page.
z Hard Disk Boot Priority
Scroll to this item and press <Enter> to view the sub menu to
decide the disk boot priority.
Press <Esc> to return to the Advanced BIOS Features page.
z CPU L1 & L2 Cache
These two options speed up memory access. However, it depends
on the CPU/chipset design. The default setting is “Enabled”.
without built-in internal cache will not provide the “CPU Internal
Cache” item on the menu.
40
Enabled
Disabled
CPUs
Enable cache
Disable cache
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
Page 47
SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
z Quick Power On Self Test
This option speeds up Power on Self Test (POST) after you turn on
the system power. If set as Enabled, BIOS will shorten or skip some
check items during POST. The default setting is “Enabled”.
Enabled
Disabled
z First/Second/Third Boot Device
Enable Quick POST
Normal POST
These items let you select the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd devices that the
system will search for during its boot-up sequence. There is a wide
range of options for your selection.
z Boot Other Device
This item allows the user to enable/disable the boot device not
listed on the First/Second/Third boot devices option above. The
default setting is “Enabled”.
z Boot Up Floppy Seek
During POST, BIOS will determine the floppy disk drive type, 40 or
80 tracks. The 360Kb type is 40 tracks while 720Kb, 1.2MB and
1.44MB are all 80 tracks. The default value is “Enabled”.
BIOS searches for floppy disk drive to determine if it is
Enabled
Disabled
40 or 80 tracks. Please be noted BIOS can not
differentiate 720K, 1.2M or 1.44M drive types as they all
are 80 tracks.
BIOS will not search for the type of floppy disk drive by
track number. There will be no warning message
displayed if the installed drive is 360K.
z Boot Up NumLock Status
Set the the Num Lock status when the system is powered on.
The default value is “On”.
z Security Option
This item allows you to limit access to the system and Setup, or
just to Setup. The default value is “Setup”.
System
Setup
If a wrong password is entered at the prompt, the system
will not boot, the access to Setup will be denied, either.
If a wrong password is entered at the prompt, the system
will boot, but the access to Setup will be denied.
NOTE To disable the security, select PASSWORD
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
41
Page 48

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
SETTING at Main Menu and then you will be
asked to enter a password. Do not type anything,
just press <Enter> and it will disable the security.
Once the security is disabled, the system will boot
and you can enter Setup freely.
z APIC Mode
Use this item to enable or disable APIC (Advanced Programmable
Interrupt Controller) mode that provides symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) for systems.
z MPS Version Control For OS
This item specifies the version of the Multiprocessor Specification
(MPS). Version 1.4 has extended configuration tables to improve
support for multiple PCI bus configurations and provide future
expandability.
z OS Select for DRAM >64MB
This item allows you to access the memory over 64MB in OS/2.
z Report No FDD For WIN 95
Select Yes to release an IRQ when the system doesn’t have any
floppy drive, for compatibility with Windows 95 logo certification. In
the Integrated Peripherals screen, select Disabled for the Onboard
FDC Controller field.
Press <Esc> to return to the Main Menu page.
42
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
Page 49

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
5.7 Advanced Chipset Features
This section contains completely optimized chipset’s features on the
board that you are strongly recommended to leave all items on this
page at their default values unless you are very familiar with the
technical specifications of your system hardware.
z PCI-E Compliancy Mode
This item allows users to set the version of the PCI Express based
on the specification by which the motherboard has to comply.
*** VGA Setting ***
z On-Chip Frame Buffer Size
Use this item to set the VGA frame buffer size.
z DVMT Mode
DVMT (Dynamic Video Memory Technology) helps you select the
video mode.
z DVMT/Fixed Memory Size
DVMT (Dynamic Video Memory Technology) allows you to select a
maximum size of dynamic amount usage of the video memory. The
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
43
Page 50
SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
system would configure the video memory dependent on your
application.
Press <Esc> to return to the Main Menu page.
5.8 Integrated Peripherals
This section allows you to configure your OnChip IDE Device, Onboard
Device and SuperIO Device.
44
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
Page 51

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
z OnChip IDE Device
Scroll to this item and press <Enter> to view the sub menu OnChip
IDE Device.
¾ IDE HDD Block Mode
Block mode is also called block transfer, multiple commands,
or multiple sector read/write. If your IDE hard drive supports
block mode (most new drives do), select
detection of the optimal number of block read/writes per sector the
drive can support.
¾ IDE DMA transfer access
Automatic data transfer between system memory and IDE
device with minimum CPU intervention. This improves data
throughput and frees CPU to perform other tasks.
¾ On-Chip Primary/Secondary PCI IDE
The integrated peripheral controller contains an IDE
interface with support for two IDE channels. Select Enabled
to activate each channel separately. The default value is
“Enabled”.
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
Enabled for automatic
45
Page 52

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
NOTE Choosing Disabled for these options will
automatically remove the IDE Primary Master/
Slave PIO and/or IDE Secondary Master/Slave
PIO items on the menu.
¾ IDE Primary/Secondary Master/Slave PIO
The four IDE PIO (Programmed Input/Output) fields let you
set a PIO mode (0-4) for each of the four IDE devices that
the onboard IDE interface supports. Modes 0 to 4 provide
successively increased performance. In Auto mode, the
system automatically determines the best mode for each
device.
¾ IDE Primary/Secondary Master/Slave UDMA
Select the mode of operation for the IDE drive. Ultra DMA33/66/100/133 implementation is possible only if your IDE
hard drive supports it and the operating environment
includes a DMA driver. If the hard drive and system software
both support Ultra DMA-33/66/100/133, select Auto to
enable UDMA mode by BIOS.
*** On-Chip Serial ATA Setting ***
¾ SATA Mode
There are these options for you to set up SATA mode: IDE
or RAID.
¾ On-Chip Serial ATA
Use this item to enable or disable the built-in on-chip serial
ATA.
¾ SATA PORT Speed Settings
Use this item to select SATA I or SATA II device support
forcedly.
¾ PATA IDE Mode
Use this item to set the PATA IDE mode. When the PATA
IDE mode is set for Primary, P1 and P3 are Secondary; on
the other hand, when set for Secondary, P0 and P2 are
Primary.
¾ SATA Port
When the “PATA IDE Mode“ is Primary, SATA Port will be ”
P1, P3 is Secondary” that means SATA 2 and SATA 4 are
Secondary; when Secondary, it will be “P0, P2 is Primary “,
SATA 1 and SATA 3 are Primary.
46
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
Page 53
SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
Press <Esc> to return to the Integrated Peripherals page.
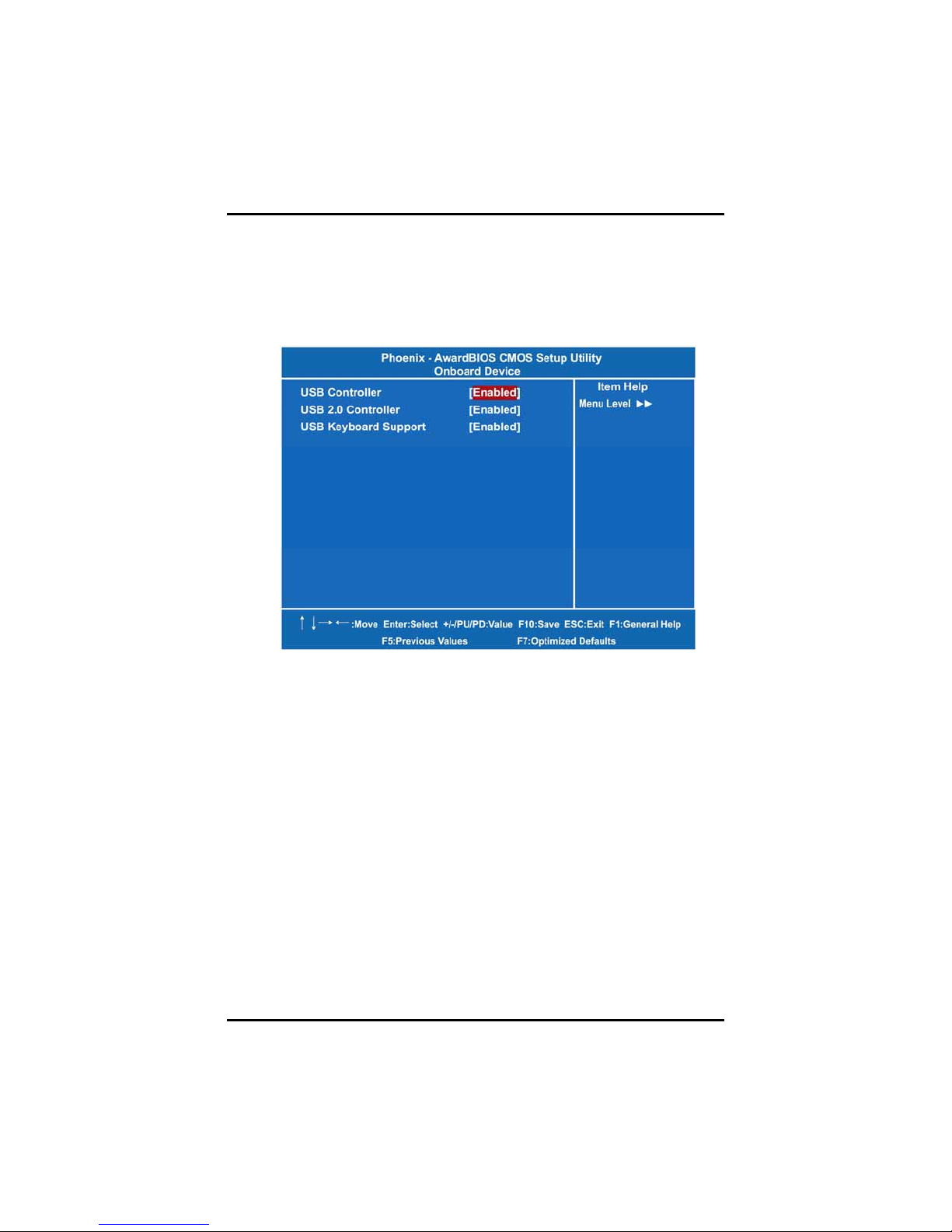
z Onboard Device
Scroll to this item and press <Enter> to view the sub menu
Onboard Device.
¾ USB Controller
Enable this item if you are using the USB in the system. You
should disable this item if a higher-level controller is added.
¾ USB 2.0 Controller
Enable this item if you are using the EHCI (USB2.0)
controller in the system.
¾ USB Keyboard Support
Enable this item if the system has a Universal Serial Bus
(USB) controller, and you have a USB keyboard.
Press <Esc> to return to the Integrated Peripherals page.
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
47
Page 54

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
z Super IO Device
Scroll to this item and press <Enter> to view the sub menu Super
IO Device.
¾ Onboard FDC Controller
Select Enabled, if your system has a floppy disk controller
(FDC) installed on the system board and you want to use it.
If you install and-in FDC or the system has no floppy drive,
select Disabled in this field. Options: “Enabled” and
“Disabled”.
¾ Onboard Serial Port 1/2
Select an address and corresponding interrupt for the serial
port.
¾ Parallel Port Mode
Select an operating mode for the onboard parallel (printer)
port. Select Normal unless your hardware and software
require another mode in this field. There are several options
for your selection, “EPP1.9”, “ECP”, “SPP”, “ECPEPP1.7”,
“EPP1.7”, etc.
¾ EPP Mode Select
Select EPP port type 1.7 or 1.9.
¾ ECP Mode Use DMA
Select a DMA channel for the parallel port while using the
ECP mode.
48
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
Page 55

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
¾ PWRON After PWR-Fail
This item enables your computer to automatically restart or
return to its operating status.
Press <Esc> to return to the Integrated Peripherals page.
z Onboard Lan Boot ROM
Use this item to enable or disable the Boot ROM function of the
onboard LAN chip when the system boots up.
5.9 Power Management Setup
The Power Management Setup allows you to save energy of your
system effectively. It will shut down the hard disk and turn OFF video
display after a period of inactivity.
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
49
Page 56

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
z ACPI Function
This item allows you to enable/disable the Advanced Configuration
and Power Management (ACPI). The function is always “Enabled”.
z ACPI Suspend Type
This item specifies the power saving modes for ACPI function. If
your operating system supports ACPI, such as Windows 98SE,
Windows ME and Windows 2000, you can choose to enter the
Standby mode in S1 (POS) or S3 (STR) fashion through the setting
of this field. Options are:
[S1(POS)] The S1 sleep mode is a low power state. In this
state, no system context is lost (CPU or chipset) and
hardware maintains all system context.
[S3(STR)] The S3 sleep mode is a lower power state where
the information of system configuration and open
applications/files is saved to main memory that remains
powered while most other hardware components turn off to
save energy. The information stored in memory will be used
to restore the system when a “wake up” event occurs.
z Power Management
This option allows you to select the type (or degree) of power saving for
Doze, Standby, and Suspend modes. The table below describes each
power management mode:
Max Saving
User Define
Min Saving
It is maximum power savings, only available for SL
CPUs. The inactivity period is 1 minute in each mode.
It sets each mode. Select time-out periods in the PM
Timers section.
It is minimum power savings. The inactivity period is 1
hour in each mode (except the hard drive).
z Video Off Method
This setting determines the manner in which the monitor is blanked.
V/H
SYNC+Blank
DPMS
50
Turns OFF vertical and horizontal
synchronization ports and writes blanks to the
video buffer
Select this option if your monitor supports the
Display Power Management Signaling (DPMS)
standard of the Video Electronics Standards
Association (VESA). Use the software supplied
for your video subsystem to select video power
management values.
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
Page 57
SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
Blank Screen
z Video Off In Suspend
System only writes blanks to the video buffer.
This item defines if the video is powered down when the system is
put into suspend mode.
z Suspend Type
If this item is set to the default Stop Grant, the CPU will go into Idle
Mode during power saving mode.
z Suspend Mode
After the selected period of system inactivity (1 minute to 1 hour),
all devices except the CPU shut off. The default value is “Disabled”.
Disabled
1/2/4/6/8/10/2
0/30/40
Min/1 Hr
z HDD Power Down
System will never enter SUSPEND mode
Defines the continuous idle time before the system
entering SUSPEND mode.
If any item defined in (J) is enabled & active,
SUSPEND timer will be reloaded
If HDD activity is not detected for the length of time specified in this
field, the hard disk drive will be powered down while all other
devices remain active.
z Soft-Off by PWR-BTTN
This option only works with systems using an ATX power supply. It
also allows the user to define which type of soft power OFF
sequence the system will follow. The default value is “Instant-Off”.
This option follows the conventional manner systems
Instant-Off
Delay 4 Sec.
z Power On by Ring
perform when power is turned OFF. Instant-Off is a soft
power OFF sequence requiring only the switching of the
power supply button to OFF
Upon turning OFF system from the power switch, this
option will delay the complete system power OFF
sequence by approximately 4 seconds. Within this delay
period, system will temporarily enter into Suspend Mode
enabling you to restart the system at once.
This option allows the system to resume or wake up upon detecting
any ring signals coming from an installed modem. The default value
is “Enabled”.
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
51
Page 58

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
z Resume by Alarm
If enable this item, the system can automatically resume after a
fixed time in accordance with the system’s RTC (realtime clock).
z Primary/Secondary IDE 0/1
Use this item to configure the IDE devices monitored by the system.
z FDD, COM, LPT Port
Use this item to configure the FDD, COM and LPT ports monitored
by the system.
Press <Esc> to return to the Main Menu page.
52
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
Page 59

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
5.10 PnP/PCI Configuration Setup
This section describes the configuration of PCI (Personal Computer
Interconnect) bus system, which allows I/O devices to operate at
speeds close to the CPU speed while communicating with other
important components. This section covers very technical items that
only experienced users could change default settings.
z PNP OS Installed
Select Yes if the system operating environment is Plug-and-Play
aware (e.g., Windows 95). The default value is “No”.
z Init Display First
This item allows you to decide whether PCI Slot or Onboard to be
the first primary display card.
z Reset Configuration Data
Normally, you leave this item Disabled. Select Enabled to reset
Extended System Configuration Data (ESCD) when you exit Setup
or if installing a new add-on cause the system reconfiguration a
serious conflict that the operating system can not boot. Options:
Enabled, Disabled.
z Resources Controlled By
The Award Plug and Play BIOS can automatically configure all
boot and Plug and Play-compatible devices. If you select Auto, all
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
53
Page 60
SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
interrupt request (IRQ), DMA assignment, and Used DMA fields
disappear, as the BIOS automatically assigns them. The default
value is “Auto (ESCD)”.
z IRQ Resources
When resources are controlled manually, assign each system
interrupt to one of the following types in accordance with the type
of devices using the interrupt:
1. Legacy ISA Devices compliant with the original PC AT bus
specification, requiring a specific interrupt (such as IRQ4 for serial port
1).
2. PCI/ISA PnP Devices compliant with the Plug and Play standard,
whether designed for PCI or ISA bus architecture.
The default value is “PCI/ISA PnP”
z DMA Resources
.
When resources are controlled manually, assign each system DMA
channel as one of the following types, depending on the type of
device using the interrupt:
Legacy ISA Devices compliant with the original PC AT bus
specification, requiring a specific DMA channel.
PCI/ISA PnP Devices compliant with the Plug and Play standard,
whether designed for PCI or ISA bus architecture.
The default value is “PCI/ISA PnP”.
z PCI/VGA Palette Snoop
Some non-standard VGA display cards may not show colors
properly. This item allows you to set whether MPEG ISA/VESA
VGA Cards can work with PCI/VGA or not. When enabled, a
PCI/VGA can work with a MPEG ISA/VESA VGA card; when
disabled, a PCI/VGA cannot work with a MPEG ISA/VESA Card.
** PCI Express relative items **
z Maximum Payload Size
When using DDR SDRAM and Buffer size selection, another
consideration in designing a payload memory is the size of the
buffer for data storage. Maximum Payload Size defines the
maximum TLP (Transaction Layer Packet) data payload size for
the device
Press <Esc> to return to the Main Menu page.
54
.
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
Page 61

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
5.11 PC Health Status
This section supports hardware monitering that lets you monitor those
parameters for critical voltages, temperatures and fan speed of the
board.
z Current GMCH Temperature
The current GMCH temperature will be automatically detected by
the system.
z Current CPU Temperature
These read-only fields show the functions of the hardware thermal
sensor by CPU thermal diode that monitors the chip blocks to
ensure a stable system.
z Current SYS Temperature
Show you the current system temperature.
z Current CPU FAN Speed
These optional and read-only items show current speeds in RPM
(Revolution Per Minute) for the CPU fan and chassis fan as
monitored by the hardware monitoring IC.
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
55
Page 62

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
z Current SYSTEM FAN1 Speed
Show you the current system fan1 speed.
z Current SYSTEM FAN2 Speed
Show you the current system fan2 speed.
z Vcore +3.3V/+5V/+12V/VBAT(V)/5VSB
It shows the voltage of +3.3V/+5V/+12V.
Press <Esc> to return to the Main Menu page.
5.12 Frequency/Voltage Control
This section is to control the CPU frequency and Supply Voltage,
DIMM OverVoltage and AGP voltage.
z Auto Detect PCI Clk
The enabled item can automatically disable the clock source for a
PCI slot without a module, to reduce EMI (ElectroMagnetic
Interference).
z Spread Spectrum
If spread spectrum is enabled, EMI (ElectroMagnetic Interference)
generated by the system can be significantly reduced.
56
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
Page 63

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
Press <Esc> to return to the Main Menu page.
5.13 Load Optimized Defaults
This option allows you to load your system configuration with default
values. These default settings are optimized to enable high
performance features.
To load CMOS SRAM with SETUP default values, please enter “Y”. If
not, please enter “N”.
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
57
Page 64

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
5.14 Set Supervisor/User Password
You can set a supervisor or user password, or both of them. The
differences between them are:
1. Supervisor password: You can enter and change the options on
the setup menu.
2. User password: You can just enter, but have no right to change
the options on the setup menu.
When you select this function, the following message will appear at the
center of the screen to assist you in creating a password.
ENTER PASSWORD
Type a maximum eight-character password, and press <Enter>. This
typed password will clear previously entered password from the CMOS
memory. You will be asked to confirm this password. Type this
password again and press <Enter>. You may also press <Esc> to
abort this selection and not enter a password.
To disable the password, just press <Enter> when you are prompted to
enter a password. A message will confirm the password is getting
disabled. Once the password is disabled, the system will boot and you
can enter Setup freely.
PASSWORD DISABLED
When a password is enabled, you have to type it every time you enter
the Setup. It prevents any unauthorized persons from changing your
system configuration.
Additionally, when a password is enabled, you can also require the
BIOS to request a password every time the system reboots. This would
prevent unauthorized use of your computer.
You decide when the password is required for the BIOS Features
Setup Menu and its Security option. If the Security option is set to
“System”, the password is required during booting up and entry into the
Setup; if it is set as “Setup”, a prompt will only appear before entering
the Setup.
58
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
Page 65

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
5.15 Save & Exit Setup
This section allows you to determine whether or not to accept your
modifications. Type “Y” to quit the setup utility and save all changes
into the CMOS memory. Type “N” to bring you back to the Setup utility.
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
59
Page 66

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
5.16 Exit Without Saving
Select this option to exit the Setup utility without saving changes you
have made in this session. Type “Y”, and it will quit the Setup utility
without saving your modifications. Type “N” to return to the Setup utility.
60
Phoenix-Award BIOS Utility
Page 67

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
APPENDIX A
WATCHDOG TIMER
Watchdog Timer Setting
After the system stops working for a while, it can be auto-reset by the
Watchdog Timer. The integrated Watchdog Timer can be set up in the
system reset mode by program.
Using the Watchdog Function
Start
↓
Un-Lock WDT:
O 2E 87 ; Un-lock super I/O
O 2E 87 ; Un-lock super I/O
↓
Select Logic device:
O 2E 07
O 2F 08
↓
Activate WDT:
O 2E 30
O 2F 01
↓
Set Second or Minute:
O 2E F5
O 2F N N=00 or 08 (Note#)
↓
Set base timer:
O 2E F6
O 2F M=00, 01, 02,…FF(Hex) ,Value=0 to 255
↓
WDT counting re-set timer:
O 2E F6
O 2F M; M=00, 01, 02,…FF
Watchdog Timer
61
Page 68

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
; IF to disable WDT:
O 2E 30
O 2F 00; Can be disable at any time
z Timeout Value Range
1 to 255
Minute / Second
z Program Sample
2E, 87
2E, 87
2E, 07
2F, 08
2E, 30
2F, 01
2E, F5
2F, N
2E, F6
2F, M
Note#:
Logical Device 8
Activate
Set Minute or Second
N=08 (Min),00(Sec)
Set Value
M = 00 ~ FF
N=00
M= 00h: Time-out Disable
01h: Time-out occurs after 1 second
02h: Time-out occurs after 2 second
03h: Time-out occurs after 3 second
……………………….......................................
FFh: Time-out occurs after 255 second
N=08
M= 00h: Time-out Disable
01h: Time-out occurs after 1 minute
02h: Time-out occurs after 2 minutes
03h: Time-out occurs after 3 minutes
……………………….......................................
FFh: Time-out occurs after 255 minutes
62
Watchdog Timer
Page 69

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
APPENDIX B
CONFIGURING SATA FOR RAID
FUNCTION
Configuring SATA Hard Drive(s) for RAID
®
Function (Controller: Intel
Please follow up the steps below to configure SATA hard drive(s):
(1) Install SATA hard drive(s) in your system.
(2) Enter the BIOS Setup to configure SATA controller mode and boot
sequence.
(3) Configure RAID by the RAID BIOS.
(4) Create a floppy disk for the SATA controller driver.
(5) Install the SATA controller driver during the OS installation.
Before you begin the SATA configuration, please prepare:
(a) Two SATA hard drives (to ensure optimal performance, it is
recommended that you use two hard drives with identical model
and capacity).
(b) An empty formatted floppy disk
(c) Windows XP setup disk
(1) Installing SATA hard drive(s) in your system
Connect one end of the SATA signal cable to the rear of the SATA
hard drive, and the other end to available SATA port(s) on the
board. Then, connect the power connector of power supply to the
hard drive.
(2) Configuring SATA controller mode and boot sequence by the
BIOS Setup
You have to make sure whether the SATA controller is configured
correctly by system BIOS Setup and set up BIOS boot sequence for
the SATA hard drive(s).
ICH7R only)
Configuring SATA for RAID Function
63
Page 70

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
(2)-1 Turn on your system and press the Del button to enter BIOS
Setup during running POST (Power-On Self Test). If you want
to create RAID, just select RAID for SATA Mode (default IDE)
under the Integrated Peripherals menu.
Figure 1
64
Configuring SATA for RAID Function
Page 71

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
(2)-2 Set CDROM for First Boot Device under the Advanced
BIOS Features menu to boot CD-ROM after system restarts
(Figure 2).
Figure 2
(2)-3 Save and exit the BIOS Setup.
(3) Configuring RAID by the RAID BIOS
Enter the RAID BIOS setup utility to configure a RAID array.
Configuring SATA for RAID Function
65
Page 72

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
(3)-1 After the POST memory testing and before the operating
system booting, a message "Press <Ctrl-I> to enter
Configuration Utility" (as Figure 3) shows up, accordingly,
press <CTRL+ I> to enter the RAID BIOS setup utility.
Figure 3
(3)-2 After you press <CTRL+ I>, the Create RAID Volume screen
will appear (as Figure 4). If you want to create a RAID array,
select the Create RAID Volume option in the Main Menu and
press ENTER.
66
Figure 4
Configuring SATA for RAID Function
Page 73
SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
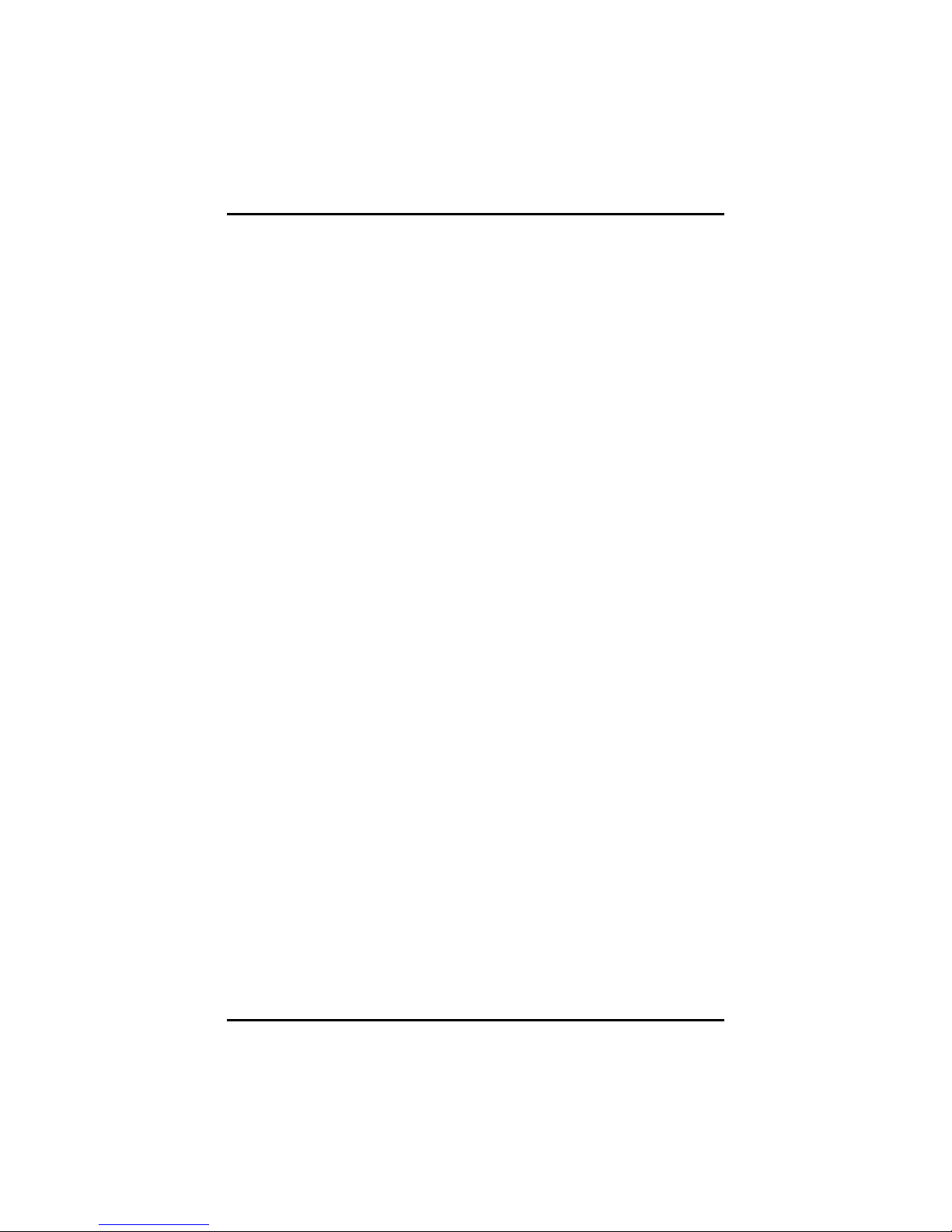
(3)-3 After entering the CREAT VOLUME MENU screen, you can
type the disk array name with 1~16 letters (letters cannot be
special characters) in the item “Name”. When finished, press
ENTER to select a RAID level (as Figure 5). There are two
RAID levels, RAID0 and RAID1. Select a RAID level and
press ENTER.
Figure 5
(3)-4 Set the stripe block size (as Figure 6). The KB is the standard
unit of stripe block size. The stripe block size can be 4KB to
128KB. After the setting, press ENTER for the array capacity.
Configuring SATA for RAID Function
Figure 6
67
Page 74

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
(3)-5 After setting all the items on the menu, select Create Volume
and press ENTER (as Figure 7) to start creating the RAID
array.
Figure 7
(3)-6 When prompting the confirmation, press “Y“ to create this
volume, or “N“ to cancel the creation.
68
Figure 8
Configuring SATA for RAID Function
Page 75

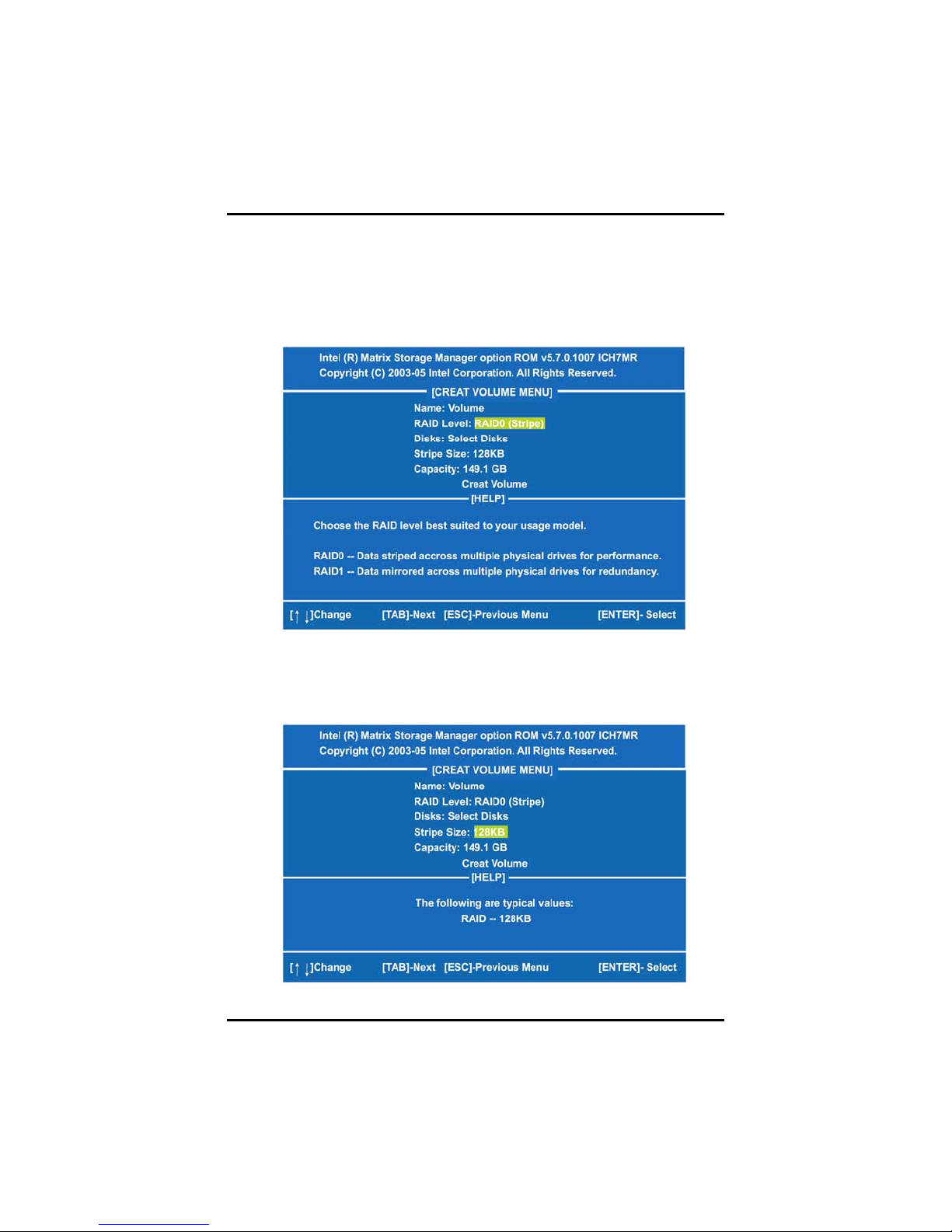
SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
After the creation is completed, you can see detailed information about
the RAID Array in the DISK/VOLUME INFORMATION section,
including RAID mode, disk block size, disk name, and disk capacity,
etc.
Figure 9
Configuring SATA for RAID Function
69
Page 76
SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
Delete RAID Volume
If you want to delete a RAID volume, select the Delete RAID Volume
option in Main Menu. Press ENTER and follow on-screen instructions.
Figure 10
Please press [ESC] to exit the ICH7MR RAID BIOS utility.
Now, you can proceed to install a SATA controller and the operating
system.
(4) Making a SATA Driver Disk
To install the operating system onto a serial ATA hard disk successfully,
you need to install the SATA controller driver during the OS installation.
Without the driver, the hard disk may not be recognized during the
Windows setup process. First of all, please format a blank floppy disk.
Secondly, follow up these steps below to produce a SATA driver disk.
70
Configuring SATA for RAID Function
Page 77
SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
(4)-1 Users can insert the Driver CD and the formatted blank floppy
disk in another system. And then, please execute the
f6flpy32.exe file in the folder of the Driver CD.
Note Please execute the f6flpy64.exe file, if installing 64-
bit Windows Operating System.
(4)-2 When this screen pops out, please click the “CONFIRM” button.
(4)-3 When the Driver is written to the floppy disk, the SATA driver
disk is completed.
Configuring SATA for RAID Function
71
Page 78

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
(5) Installing the SATA controller driver during the OS installation
Now, the SATA driver disk is ready, and BIOS settings configured, you
can proceed to install Windows XP onto your SATA hard drive using
the SATA driver. Here is an example for Windows XP installation.
(5)-1 Restart your system to boot the Windows XP Setup disk, and
press F6 button as soon as you see the message "Press F6 if
you need to install a 3rd party SCSI or RAID driver" (as
Figure 11). After pressing the F6 button, there will be a few
moments for some files being loaded before next screen
appears.
Figure 11
72
Configuring SATA for RAID Function
Page 79

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
(5)-2 When you see the screen below, insert the floppy disk
containing the SATA driver and press “S” (as Figure 12).
Figure 12
(5)-3 If the Setup correctly recognizes the driver of the floppy disk,
a controller menu (as Figure 13) will appear below. Use the
ARROW keys to select Intel(R) 82801GR/GH SATA RAID
Controller (Desktop ICH7R/DH) and press ENTER. Then it
will begin to load the SATA driver from the floppy disk.
Configuring SATA for RAID Function
Figure 13
73
Page 80

SBC81206 PICMG 1.0 SBC User’s Manual
If a message on the screen saying that one or some
Note
file(s) cannot be found, please check the floppy disk or
copy the correct SATA driver again from the driver CD.
(5)-4 When the screen appears as below, press ENTER to
continue installing the SATA driver through the floppy disk. It
will take about one minute to finish the driver installation.
Figure 14
After the SATA controller driver installation is completed, you can
proceed to install the Windows XP.
74
Configuring SATA for RAID Function
 Loading...
Loading...