Page 1

FRITZ!Box
Installation,
configuration
and operation
Fon WLAN 7170
English Edition
Page 2

Legal Notice
Legal Notice
FRITZ!Box Fon WLAN 7170
This documentation and the software it describes are protected by copyright. AVM grants the nonexclusive right to use the software, which is supplied exclusively in what is known as object code
format. The licensee may create only one copy of the software, which may be used exclusively for
backup use.
AVM reserves all rights that are not expressly granted to the licensee. Without previous approval in
writing, and except for in cases permitted by law, it is particularly prohibited to
copy, propagate or in any other manner make this documentation or this software publicly
accessible, or
process, disassemble, reverse engineer, translate, decompile or in any other manner open the
software and subsequently copy, propagate or make the software publicly accessible in any
other manner.
Please consult the “License.txt” file on the product CD included in the package for specifics about
the licensing conditions.
This documentation and software have been produced with all due care and checked for
correctness in accordance with the best available technology. AVM GmbH disclaims all liability and
warranties, whether express or implied, relating to the AVM product’s quality, performance or
suitability for any given purpose which deviates from the performance specifications contained in
the product description. The licensee bears all risk in regard to hazards and impairments of quality
which may arise in connection with the use of this product.
AVM will not be liable for damages arising directly or indirectly from the use of the manual or the
software, nor for incidental or consequential damages, except in case of intent or gross negligence.
AVM expressly disclaims all liability for the loss of or damage to hardware or software or data as a
result of direct or indirect errors or destruction and for any costs (including connection charges)
related to the documentation and the software and due to incorrect installations not performed by
AVM itself.
The information in this manual and the software are subject to change without notice for the
purpose of technical improvement.
We offer a manufacturer’s warranty for this original product. The conditions of this warranty are
contained in the “Warranty.pdf” file in the “Software/Info” folder on the product CD included with
delivery.
© AVM GmbH 2007. All rights reserved. Documentation release 11/2007
AVM Audiovisuelles Marketing
und Computersysteme GmbH
Alt-Moabit 95
D 10559 Berlin D 10559 Berlin
AVM in the Internet: www.avm.de/en
AVM Computersysteme
Vertriebs GmbH
Alt-Moabit 95
FRITZ!Box 2
Page 3

Legal Notice
Trademarks: Unless otherwise indicated, all trademarks mentioned are legally protected trademarks
owned by AVM GmbH, especially product names and logos. Microsoft, Windows and the Windows
logo are trademarks owned by Microsoft Corporation in the USA and/or other countries. Bluetooth is
a trademark of Bluetooth SIG Inc. licensed to AVM GmbH. All other products and company names are
trademarks of their respective owners
FRITZ!Box 3
Page 4

Contents
Contents
1 This Is FRITZ!Box Fon WLAN 7170 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
1.1 Package Contents. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
1.2 Operation Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2 FRITZ!Box: Connecting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.1 Launching FRITZ!Box Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
2.2 Mounting FRITZ!Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
2.3 Connecting to the Power Supply. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2.4 Connecting the Computer(s) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
2.5 Connecting Computer(s) to a LAN Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
2.6 Connecting to a Computer Wirelessly via WLAN. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
2.7 Connecting to the DSL Line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
2.8 Connecting to the ISDN Line. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
2.9 Connecting with the Analog Telephone Line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
2.10 Connecting Telephone, Fax, Answering Machine. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
2.11 Connecting ISDN Telephones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
2.12 Connecting an ISDN PBX . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
3 Opening the User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
4 Configuring Internet Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
4.1 Configuring Internet Access for a Direct DSL Connection . . . . . . . . . . .32
4.2 Configuring Internet Access for a Connection to an
Existing Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
5 Configuring FRITZ!Box for Telephone Connections . . . . . . 35
5.1 Entering Account Information and Internet Numbers for
Internet Telephony . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
5.2 Entering Numbers for Calls over Fixed Lines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
5.3 Configuring Analog Equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
5.4 Configuring ISDN Telephones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
5.5 ISDN PBXs on FRITZ!Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
5.6 Dialing Rules for Internet and Fixed-Line Telephony . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
FRITZ!Box 4
Page 5

Contents
5.7 Selecting the Type of Connection Manually . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
5.8 How Does Internet Telephony Work? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
6 USB Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
6.1 Connecting USB Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
6.2 Accessing USB Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
6.3 USB Mass Storage Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
6.4 USB Printers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
6.5 AVM FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
6.6 USB Hub . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
7 FRITZ!DSL: The Software Suite . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
7.1 Installing FRITZ!DSL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
7.2 FRITZ!DSL Internet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
7.3 FRITZ!DSL Protect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
7.4 FRITZ!Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
7.5 Update . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
7.6 FRITZ!DSL Diagnosis. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .56
7.7 Web Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .56
8 More about WLAN. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
8.1 Standards. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
8.2 Security. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
8.3 Frequency Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
8.4 Increasing the WLAN Range Using WDS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
9 Network Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
9.1 Basics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
9.2 IP Address. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
9.3 DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
9.4 Subnetwork . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .78
FRITZ!Box 5
Page 6

Contents
10 Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
10.1 Errors Opening the User Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
10.2 The WLAN Adapter Cannot Find FRITZ!Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
10.3 WLAN Connection Is Not Established . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
10.4 Connection via Microsoft WLAN Service Fails with WPA2 . . . . . . . . . . .87
10.5 IP Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87
11 Removing the FRITZ!Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
11.1 Disconnecting the FRITZ!Box from the Computer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .92
11.2 Removing the FRITZ!DSL Software. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .92
11.3 Removing the Printer Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .93
11.4 Removing the Program Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
12 Configuration and Operation by Telephone . . . . . . . . . . . 95
12.1 Operation by Telephone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
12.2 Configuring by Telephone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .104
12.3 Advanced Features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .108
13 Customer Service Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
13.1 Product Documentation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .129
13.2 Information in the Internet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .129
13.3 Updates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .130
13.4 Support from the AVM Service Team. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .130
14 Product Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .133
14.1 FRITZ!Box Fon WLAN LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
14.2 Audible Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
14.3 WLAN Switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .136
14.4 Technical Specifications of FRITZ!Box Fon WLAN 7170. . . . . . . . . . . . .136
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
Declaration of CE Conformity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
FRITZ!Box 6
Page 7
Symbols and Highlighting
Symbols and Highlighting
This manual uses the following symbols for warnings and tips:
This symbol indicates important instructions that must be
observed to avoid malfunctions.
This symbol marks useful hints to assist you in working
with the FRITZ!Box.
The table below explains the highlighting used in this manual.
Highlighting Function Examples
Quotation marks Keys
Buttons
Settings Pages
Menus
Commands
File paths
File names
Blue lettering Internet address www.avm.de/en
Pointed brackets Variables <CD-ROM drive>
Typewriter font Information to be
typed in using the
keyboard
Gray italics Tips, instructions and
warnings
“F1” key
“Help”
“hardware”
“Start / Programs”
“Refresh”
“Documentation\
Manual.pdf”
“Readme.html”
a:\setup
...for more information, see...
FRITZ!Box 7
Page 8
Symbols and Highlighting
The Telephone Keypad
0...9 Numeric keys
s
R
r
Instructions for Operation at the Telephone
Asterisk key
Hold or Flash key
Pound sign key
M
N
O
P
D
Q
K
Ext. Enter an extension number (Ext.). In the place
MSN Enter an ISDN number (MSN). In place of the
XNo./Ext. Enter the external number (XNo.) or extension
XNo. Dial a number.
Dial a number.
Pick up the handset.
Hang up the handset.
Tal k.
Three-party Conference Call
Wait for the acknowledgement tone.
You hear the ring tone.
of the abbreviation “Ext.” used here, enter the
number “1”, “2”, or a higher number, corresponding to the extension you would like to
configure.
abbreviation “MSN” used here, enter the
complete MSN desired, without any dialing
prefix.
number (Ext.) to which your calls are to be
diverted. In the place of the abbreviation
“XNo.”, enter the complete number of the
external line.
FRITZ!Box 8
Page 9
Symbols and Highlighting
Icons Designating the Functions and Features
Safety Instructions
When working with FRITZ!Box, follow the instructions below
to protect yourself and the FRITZ!Box from injury.
Do not install the FRITZ!Box during an electrical storm.
Disconnect FRITZ!Box from the power supply during
The functions and features can be used for analog and
ISDN fixed-line connections as well as for Internet telephony (VoIP).
The functions and features can be used for analog and
ISDN fixed-line connections.
The functions and features can be used only for ISDN
fixed-line connections.
The functions and features can be used only for analog
fixed-line connections.
electrical storms.
Never let liquids get inside the FRITZ!Box. Otherwise,
electric shocks or short circuits may result.
The FRITZ!Box is intended for indoor use only.
Do not open the FRITZ!Box housing. The device con-
tains hazardous components and should only be
opened by authorized repair technicians.
Disposal Instructions
In accordance with the Electrical and Electronic Equipment
Act, the FRITZ!Box Fon WLAN 7170, power supply plug,
adapter, and cable may not be disposed with household
waste. Please bring these to your local collection points for
disposal.
FRITZ!Box 9
Page 10
This Is FRITZ!Box Fon WLAN 7170
s
1 This Is FRITZ!Box Fon WLAN 7170
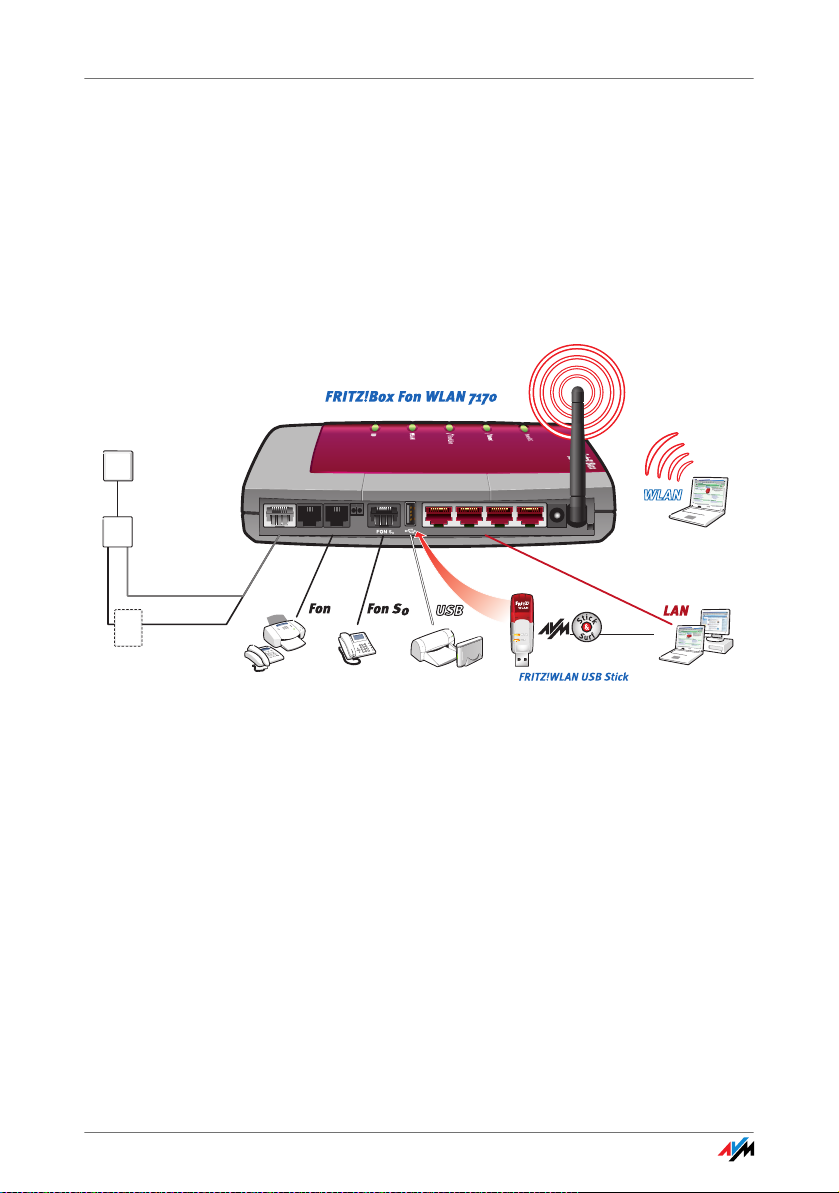
An Overview
FRITZ!Box Fon WLAN 7170 is a Private Branch Exchange (PBX) for making
telephone calls via the Internet and the fixed-line network. FRITZ!Box Fon
WLAN connects one or more computers directly with your DSL line. Each
connected computer can establish an Internet connection over the
FRITZ!Box. As a WLAN access point, FRITZ!Box offers you the possibility of
connecting your computer to the DSL line wirelessly.
Incomming
line jack
Power
ADSL splitter
ADSL
ISDN *
or analog
NT
* ISDN users: connect
FRITZ!Box Fon WLAN to NT
LAN1 LAN2 LAN 3 LAN4
USB printers,
USB mass storage
devices
3x analog
phones, fax
FON 1 FON 2 FON 3 DSL/TEL
ISDN phone,
PBX system
Possibilities for connecting FRITZ!Box
PBX FRITZ!Box is a PBX for the connection of analog and ISDN
terminal devices. You can connect two analog telephones
directly, and connect any existing cabling at your location,
for instance, an additional telephone jack installed in the
attic story, to the FRITZ!Box. Up to eight ISDN telephony devices can be connected to the integrated ISDN S
can make telephone calls using the Internet, ISDN, or the
analog fixed-line network using all of the connected telephones.
WLAN
automatic security
for wireless surng
Notebooks, computer
or PDAs
Computer, game
consoles, network
port. You
0
Connecting
Computers
Four computers can be connected directly to the FRITZ!Box
using the four LAN ports. Using WLAN you can connect multiple computers with FRITZ!Box wirelessly.
FRITZ!Box 10
Page 11

This Is FRITZ!Box Fon WLAN 7170
You can also connect a network hub or switch to the LAN
ports so that even more computers can be connected to
FRITZ!Box.
All computers connected to FRITZ!Box are networked together and can access shared files and printers.
Internet
Connection
All of the computers connected to FRITZ!Box can access the
Internet. There are two different ways of establishing an Internet connection. Both cases require Internet account information from an Internet Service Provider:
The Internet connection is established by FRITZ!Box.
For this the Internet account information must be registered in FRITZ!Box. In this case FRITZ!Box works as a
DSL router and all computers can use the Internet connection at the same time.
The computers connected establish the Internet con-
nections themselves. For this, Internet access software must be installed and the Internet account information entered on the given computer. In this case
FRITZ!Box works as a DSL modem.
Integrated Firewall When FRITZ!Box is operated as a DSL router, the integrated
firewall protects your network from attacks from the Internet.
USB Port The FRITZ!Box is equipped with a USB host controller to
which you can connect a USB storage device (hard drive,
stick), a printer, a AVM FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick or a USB hub.
AVM Stick & Surf technology is provided by the AVM
FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick. This technology allows security settings to be read from the FRITZ!Box automatically. For connecting a printer, FRITZ!Box has a printer server.
Port for Network
Devices
Network devices can be connected to the FRITZ!Box LAN
port along with network hubs or switches, including game
consoles.
WLAN Access
Point
The FRITZ!Box is a WLAN access point. Computers equipped
with a WLAN adapter can be wirelessly connected to
FRITZ!Box.
Operating
Systems
Supported
FRITZ!Box 11
FRITZ!Box can be connected to computers with Windows
operating systems, the Linux operating system or Apple
computers with the Mac OS X operating system.
Page 12

Package Contents
1.1 Package Contents
The following is included in the FRITZ!Box Fon WLAN 7170
package:
FRITZ!Box Fon WLAN 7170
one AC power adapter with cable for connection to the
one 4.25-m combined DSL-telephone cable (gray/black)
one network cable (red) for connecting FRITZ!Box to a
one RJ45-RJ11 adapter (gray) for the DSL line (required
one RJ45-RJ11 adapter (black) for connecting FRITZ!Box
one FRITZ!Box CD with
power mains
for connecting FRITZ!Box to the DSL splitter and the ISDN network terminator (NT) or the analog telephone
line
computer or network hub
in some countries)
Fon WLAN 7170 to the analog telephone network
– Installation Help
– DSL software FRITZ!DSL
– software for the printer port
– documentation for all enclosed AVM components
printed quick guide
FRITZ!Box 12
Page 13

Operation Requirements
1.2 Operation Requirements
In order to operate FRITZ!Box, you must have the following:
a web browser that supports Java Script (for instance,
Internet Explorer from version 6.0 or Netscape 4.0)
a DSL line: Standard ITU G.992.1 Annex A or B (de-
pending on the FRITZ!Box Fon WLAN 7170 model)
for fixed-line telephony: an ISDN point-to-multipoint
line in accordance with the Euro ISDN protocol DSS1,
or an analog telephone line
If you would like to connect the FRITZ!Box via the LAN
port of the computer, you need a computer with a network adapter (standard Ethernet 10/100 Base-T).
If you would like to connect FRITZ!Box wirelessly using
WLAN, you will need a computer equipped with a
WLAN adapter (in accordance with IEEE8 02.11b or
IEEE 802.11g), for instance, a AVM FRITZ!WLAN USB
Stick.
To install the DSL software FRITZ!DSL, the minimum
computer requirements are:
– 300 MHz Pentium II processor with Windows XP or
Windows 2000 and CD drive
– 32 MB RAM
– 20 MB free memory on the hard drive
FRITZ!Box 13
Page 14

FRITZ!Box: Connecting
2 FRITZ!Box: Connecting
This chapter contains instructions on the following topics:
launching FRITZ!Box operation: recommended procedure
mounting the FRITZ!Box and connecting it to the power supply
connecting one or several computers to FRITZ!Box
connecting FRITZ!Box to DSL and ISDN or the analog telephone line
connecting analog terminal devices to the FRITZ!Box
connecting ISDN terminal devices to the FRITZ!Box
2.1 Launching FRITZ!Box Operation
We recommend using the Installation Help on the FRITZ!Box
CD when launching operation of the FRITZ!Box for the first
time.
Using the Installation Help on the CD
On computers with Windows operating systems you can
use the Installation Help on the FRITZ!Box CD. The Installation Help presents instructions on the screen, guiding you
through the steps required to launch operation of the
FRITZ!Box.
Insert the FRITZ!Box CD in the CD-ROM drive of your
computer.
The Installation Help starts automatically.
Follow the instructions in the Installation Help to pre-
pare the FRITZ!Box for operation.
FRITZ!Box 14
Page 15

Launching Operation without the Installation Help CD
Launching Operation without the Installation Help CD
If you do not want to use the Installation Help on the CD,
then work through the instructions below in the recommended order:
1. Mounting FRITZ!Box; see the section “Mounting
FRITZ!Box” from page 16.
2. Connecting FRITZ!Box to the power supply; see the
section “Connecting to the Power Supply” on page 16.
3. Connecting FRITZ!Box to the computer(s); see the sec-
tion “Connecting the Computer(s)” on page 17.
4. Connecting FRITZ!Box to DSL; see the section “Con-
necting to the DSL Line” on page 23.
5. If you want to make telephone calls with the fixed-line
network using the FRITZ!Box: connect the FRITZ!Box to
the fixed-line network
– If you want to use the ISDN fixed-line network, con-
nect the FRITZ!Box to the ISDN NT. See the section
“Connecting to the ISDN Line” on page 24.
– If you want to use the analog fixed-line network,
then connect the FRITZ!Box Fon WLAN to the analog telephone jack. See the section “Connecting
with the Analog Telephone Line” on page 25.
6. If you want to make telephone calls via the Internet
and/or the fixed-line network using the FRITZ!Box:
connect your analog equipment to the FRITZ!Box; see
the section “Connecting Telephone, Fax, Answering
Machine” from page 26.
7. If you want to connect an ISDN telephone or an ISDN
PBX to the FRITZ!Box: connect your ISDN equipment;
see the sections “Connecting ISDN Telephones” on
page 28 and “Connecting an ISDN PBX” on page 28.
FRITZ!Box 15
Page 16

Mounting FRITZ!Box
2.2 Mounting FRITZ!Box
You can either place FRITZ!Box on a horizontal surface or
mount it on a wall. Please note the following:
Place or hang the FRITZ!Box in a dry location that is
free of dust and protected from direct sunlight.
Do not place FRITZ!Box on excessively heat-sensitive
surfaces, as the base of the device can heat up during
normal operation.
When connecting FRITZ!Box to your computer using
the network or USB cable, remember to take the
length of the cable into account.
If you would like to establish wireless connections be-
tween FRITZ!Box and the computer, position the device at a central location.
Make sure to keep sufficient distance from potential
interference sources like microwave devices or electric
devices with large metal housings.
2.3 Connecting to the Power Supply
Connecting to the power supply
FRITZ!Box 16
Page 17

Connecting the Computer(s)
Connect the FRITZ!Box to the power supply as described below:
Power Supply Unit Remove the power supply unit from the FRITZ!Box package.
Connecting 1. Connect the power mains adapter to the socket la-
beled “Power”, located at the far right of the back panel of FRITZ!Box.
2. Plug the other end into an AC power outlet.
The green “Power/DSL” LED will begin flashing after a few
seconds to indicate that the FRITZ!Box is ready for operation.
2.4 Connecting the Computer(s)
If you would like to surf the web using the FRITZ!Box or to
open the FRITZ!Box user interface, then you must connect a
computer with the FRITZ!Box.
A computer can be connected with the FRITZ!Box Fon WLAN
in two different ways:
using a LAN port of the FRITZ!Box
wirelessly via WLAN
One computer can be connected to FRITZ!Box by only one of
these means.
One computer can be connected to each of the four LAN
ports of FRITZ!Box, and several computers can be connected with FRITZ!Box at the same time via WLAN.
The way a computer is connected to the FRITZ!Box is the
same regardless of the operating system on the computer.
All of the computers connected with the FRITZ!Box constitute a network.
FRITZ!Box 17
Page 18

Connecting Computer(s) to a LAN Port
2.5 Connecting Computer(s) to a LAN Port
If you want to connect a computer to one of the four LAN
ports on the FRITZ!Box, make sure that your computer is
equipped with a network adapter. A LAN port is usually designated by the icon at left or labeled “LAN”.
Connecting a computer to a LAN port on the FRITZ!Box
Cable A red network cable for connecting a computer is included
in the FRITZ!Box package.
Connecting 1. Remove the network cable from the package.
2. Switch on your computer.
If you work with a Linux operating system, use YaST to
configure your network card with the setting “DHCP”,
if this setting is not already configured.
3. Insert one end of the LAN cable to the computer’s net-
work adapter.
4. Connect the other end of the LAN cable to a socket on
the FRITZ!Box labeled “LAN 1”, “LAN 2”, “LAN 3” or
“LAN 4”.
FRITZ!Box 18
Page 19
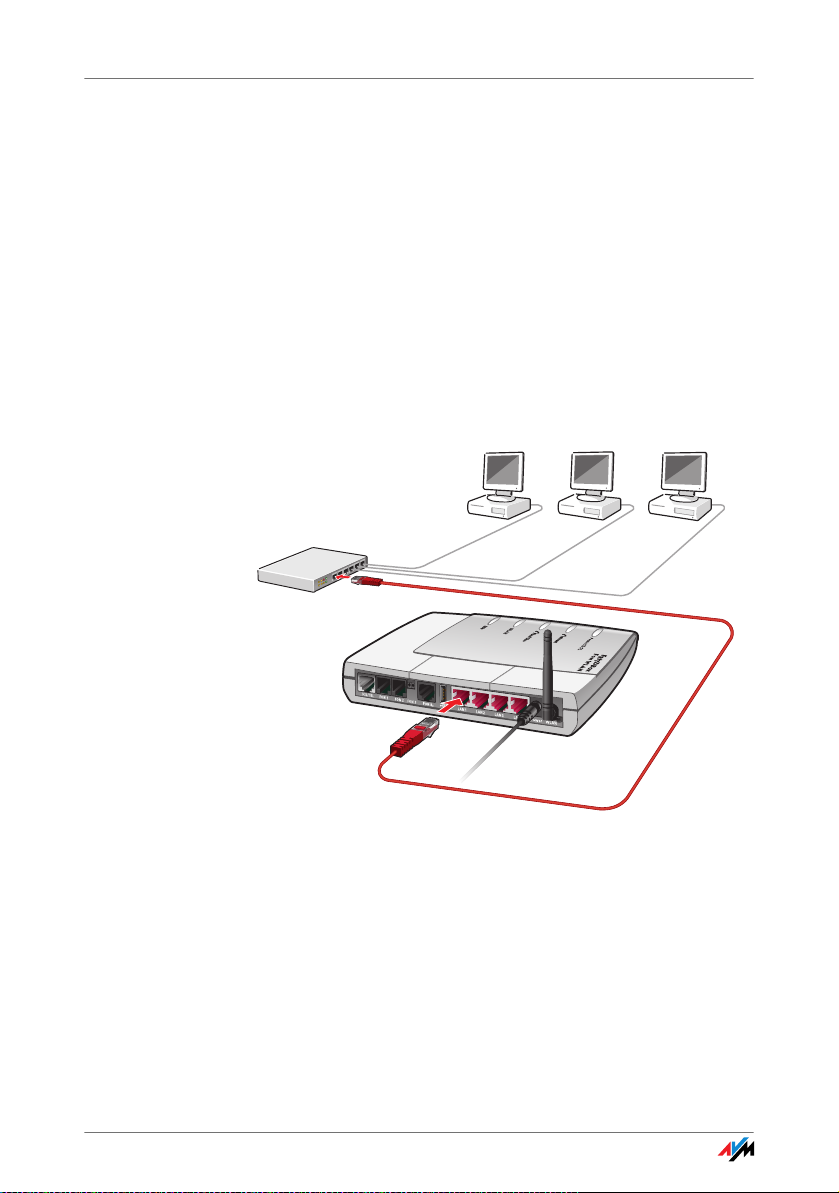
Connecting More Computers to the LAN Ports
Connecting More Computers to the LAN Ports
Additional cables are required to connect further computers. In purchasing a LAN cable, note the instructions in the
section “Cables and Sockets” from page 134.
You can connect a computer to any of the four LAN ports of
the FRITZ!Box at any time.
Connecting to a Network Hub or Network Switch to the LAN Port
You can connect a network hub or switch to the LAN port if
you would like to connect multiple computers to the
FRITZ!Box via LAN.
Connecting FRITZ!Box to a network hub
1. Connect one end of the red LAN cable to the uplink
port of the network hub or switch.
2. Connect the other end of the network cable to one of
the sockets on FRITZ!Box labeled “LAN”.
FRITZ!Box 19
Page 20

Connecting to a Computer Wirelessly via WLAN
2.6 Connecting to a Computer Wirelessly via WLAN
The FRITZ!Box can be connected to a computer wirelessly
using WLAN.
The wireless WLAN connection is identical for all operating
systems. Each computer to be connected to FRITZ!Box via
WLAN must support WLAN, by means of a compatible WLAN
adapter, for instance the AVM FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick.
For more information on WLAN, see the section “More
about WLAN” from page 57.
Presettings in FRITZ!Box
The FRITZ!Box is delivered with preset values for WLAN security. These values must also be entered on the computer
with the WLAN adapter in order to be able to establish a
successful WLAN connection.
The following values are configured in the FRITZ!Box factory
settings:
Setting Preset Value
SSID
(name of the WLAN radio network)
Encryption methods TKIP (WPA)
Encryption WPA PSK
Key The key is printed on the stick-
Network Mode Infrastructure
Channel 6
FRITZ!Box Fon WLAN 7170
ers on the base of the device
and on the cover of the
FRITZ!Box CD.
FRITZ!Box 20
Page 21

Connecting to the AVM FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick
Connecting to the AVM FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick
If your are using a AVM FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick as a WLAN
adapter, you can transmit the security settings conveniently with Stick & Surf. Proceed as follows:
1. Insert the AVM FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick in the USB port
on the FRITZ!Box. The “INFO” LED on the FRITZ!Box begins flashing rapidly. The WLAN security settings are
being transferred to the AVM FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick.
2. As soon as the “INFO” LED stops flashing, transmis-
sion of the settings has been concluded. Remove the
stick.
3. Now insert the AVM FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick in the USB
port of the computer.
The security settings saved on the stick are applied to the
computer. A WLAN connection between the computer and
the FRITZ!Box is established automatically.
See the AVM FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick manual for details.
Connecting Using a WLAN Adapter from Another Manufacturer
1. Switch on your computer.
2. Install the WLAN adapter in your computer along with
the appropriate software. Please take note of the instructions in the documentation of the adapter.
Once installation has been completed, you generally have a
user interface available to control your WLAN connections.
In the Windows operating systems you can open the user
interface by clicking an icon in the taskbar (specific to each
manufacturer) or from the start menu.
In order to establish a WLAN connection to the FRITZ!Box,
you must either use the WLAN software supplied with the
operating system or the manufacturer’s WLAN software included in the WLAN adapter package.
FRITZ!Box 21
Page 22

Establishing a WLAN Connection with the WLAN Software Provided by the Manufacturer
Establishing a WLAN Connection with the WLAN Software
Provided by the Manufacturer
The FRITZ!Box is delivered with preset values for WLAN security. You must enter these values during the configuration
of the WLAN adapter.
If you would like to establish a WLAN connection using
these preset values, then your WLAN adapter must support
the WPA encryption procedure.
1. Start the WLAN software.
2. Enter the followign values for the connection between
the FRITZ!Box and the WLAN adpater:
SSID
(name of the WLAN radio
network)
Encryption methods TKIP (WPA)
Encryption WPA PSK
Key The key is printed on the stick-
Network mode Infrastructure
Channel 6
FRITZ!Box Fon WLAN 7170
er on the base of the device
and on the cover of the
FRITZ!Box CD.
3. Confirm your entries using the relevant button in the
user interface (for instance, “OK”, “Send”, “Submit”
or “Connect”).
4. Now read the information in section “Opening the Us-
er Interface” from page 30 and follow the security instructions in the section “Security” from page 59.
If the WLAN Adapter Does Not Support the WPA Mechanism
If your WLAN adapter does not support WPA, you must
change the WLAN settings in the FRITZ!Box. To do so, proceed as follows:
1. Connect the FRITZ!Box and the computer using the
network cable (see the section “Connecting Computer(s) to a LAN Port” on page 18).
FRITZ!Box 22
Page 23
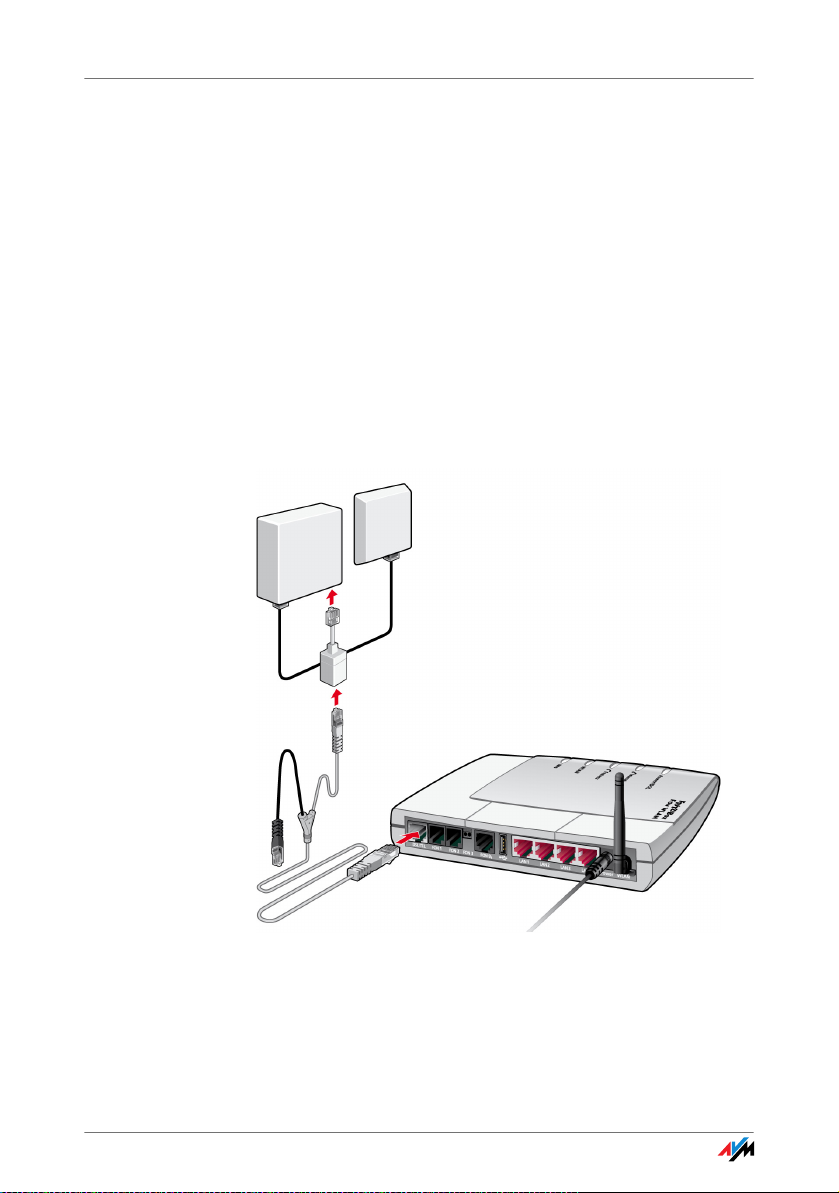
Connecting to the DSL Line
2. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see the section
“Opening the User Interface” from page 30).
3. In the “WLAN / WLAN Security” menu, select WEP en-
cryption and enter a network key.
4. Click the “Apply” button.
5. A window is displayed with the WLAN security set-
tings. Print out the page by clicking “Print Page”.
6. Close the user interface and clear the connection be-
tween the FRITZ!Box and the computer. Remove the
network cable.
2.7 Connecting to the DSL Line
Connecting to the DSL splitter
Cable The gray and black Y-shaped cable is for connecting to the
DSL splitter. This cable is a combination of a DSL cable and
a telephone cable.
FRITZ!Box 23
Page 24
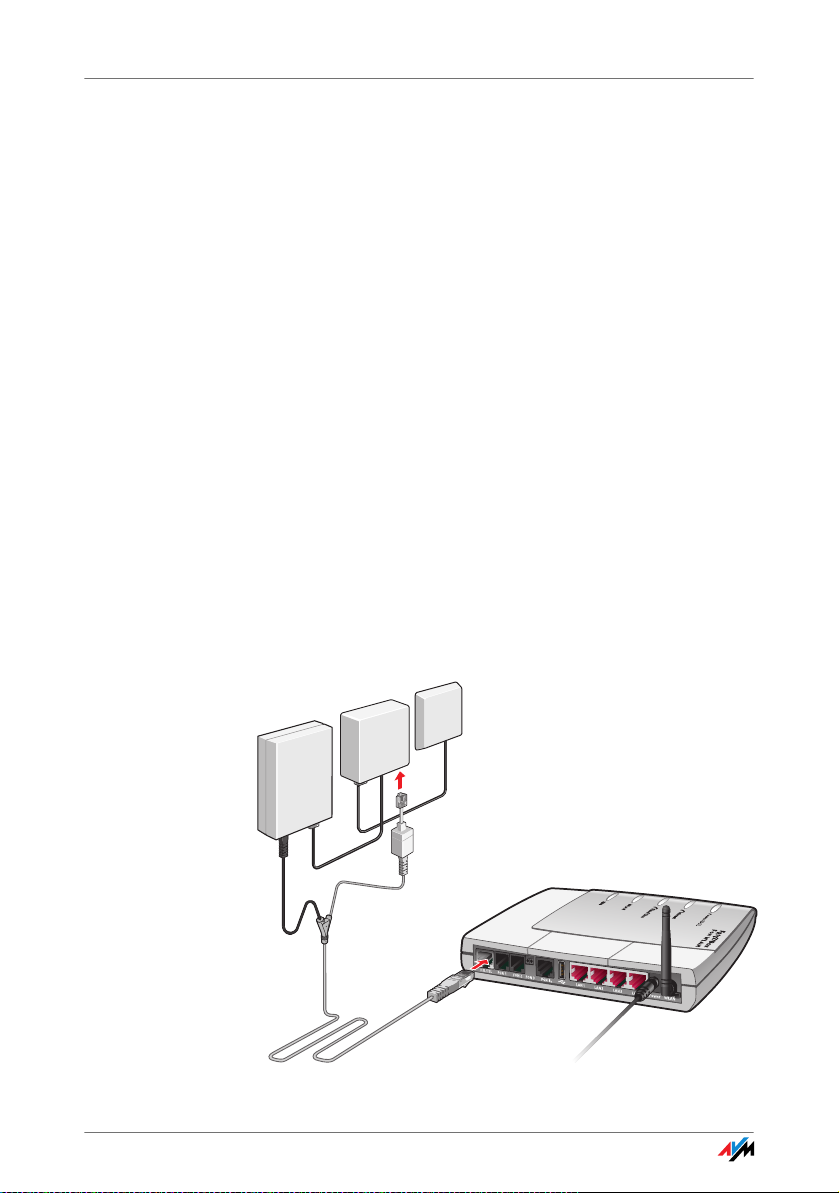
Connecting to the ISDN Line
Connecting 1. Connect the longer of the two gray branches of the ca-
ble to the socket labeled “DSL/TEL”, located at the far
left of the back panel of the FRITZ!Box.
2. Then connect the other end of the cable to the socket
on the DSL splitter labeled “DSL”. If the end of the cable does not fit into the socket on the splitter, insert
the end of the cable into the gray RJ45-RJ11 adapter included in the package and then insert the adapter into
the socket on the DSL splitter.
The black branch of the cable is for the fixed-network
telephone line (see the section “Connecting to the
ISDN Line” on page 24 or the section “Connecting with
the Analog Telephone Line” on page 25).
The green “Power” LED stops flashing after a short time and
remains lit to signalize that FRITZ!Box is ready for Internet
connections over DSL.
2.8 Connecting to the ISDN Line
You only have to connect the FRITZ!Box with the ISDN line if
you have an ISDN line and want to use the FRITZ!Box for ISDN
fixed-line telephony.
Connecting to the ISDN NT
FRITZ!Box 24
Page 25
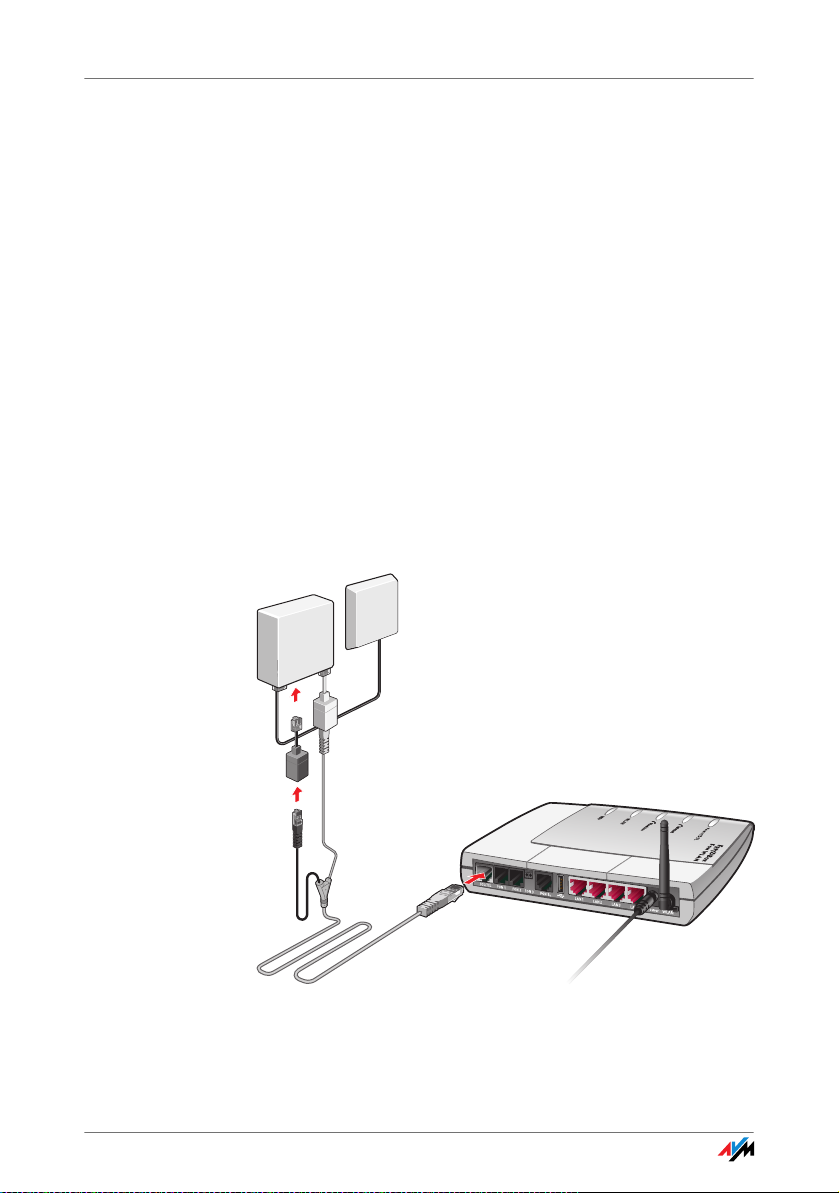
Connecting with the Analog Telephone Line
Cable The gray and black Y-shaped cable is for connecting to the
ISDN line. This cable is a combination of a DSL cable and a
telephone cable.
Connecting 1. Connect the longer, gray end of the cable to the socket
labeled “DSL/TEL”, located at the far left of the back
panel of the FRITZ!Box.
2. Insert the black end of the Y-branch of the cable into
the socket of your ISDN NT. If the end of the cable does
not fit into the socket on the splitter, insert the end of
the cable into the gray RJ45-RJ11 adapter included in
the package and then insert the adapter into the socket of the ISDN-NTBA.
2.9 Connecting with the Analog Telephone Line
You only have to connect the FRITZ!Box with the analog line
if you have an analog line and want to use the FRITZ!Box for
analog fixed-line telephony.
Connecting to the analog telephone line via the DSL splitter
Cable The gray and black Y-shaped cable is for connecting to the
ISDN line. This cable is a combination of a DSL cable and a
telephone cable.
FRITZ!Box 25
Page 26

Connecting Telephone, Fax, Answering Machine
Connecting 1. Connect the longer, gray end of the cable to the socket
labeled “DSL/TEL”, located at the far left of the back
panel of the FRITZ!Box.
2. Then insert the black plug into the appropriate jack of
your DSL splitter. If the plug does not fit into the splitter, connect the end of the cable to the black RJ45-RJ11
adapter included in the package and then insert the
adapter into the socket on the DSL splitter.
2.10 Connecting Telephone, Fax, Answering Machine
Connect your analog equipment to the FRITZ!Box so that
you can make telephone calls and fax using the Internet or
the fixed-line network.
Prerequisites: If you would like to use your fixed line to make telephone
calls or fax, note the following requirements:
For fixed-line telephony via ISDN you must connect the FRITZ!Box
with the ISDN NT (see the section “Connecting to the ISDN Line”
on page 24).
In order to use the analog fixed-line network, the FRITZ!Box must
be connected with the analog fixed line (see the section “Connecting to the ISDN Line” on page 24).
Connecting to an Analog Telephone
The ports “FON 1”, “FON 2” and “FON 3” on the FRITZ!Box
are available for connecting your analog terminal equipment.
Use “FON 1” and “FON 2” to connect your analog
equipment directly to the FRITZ!Box.
“FON 3” serves to connect analog terminal equipment
that is located further away to the FRITZ!Box, for instance an additional telephone jack on a higher floor,
using the wiring at your location.
FRITZ!Box 26
Page 27
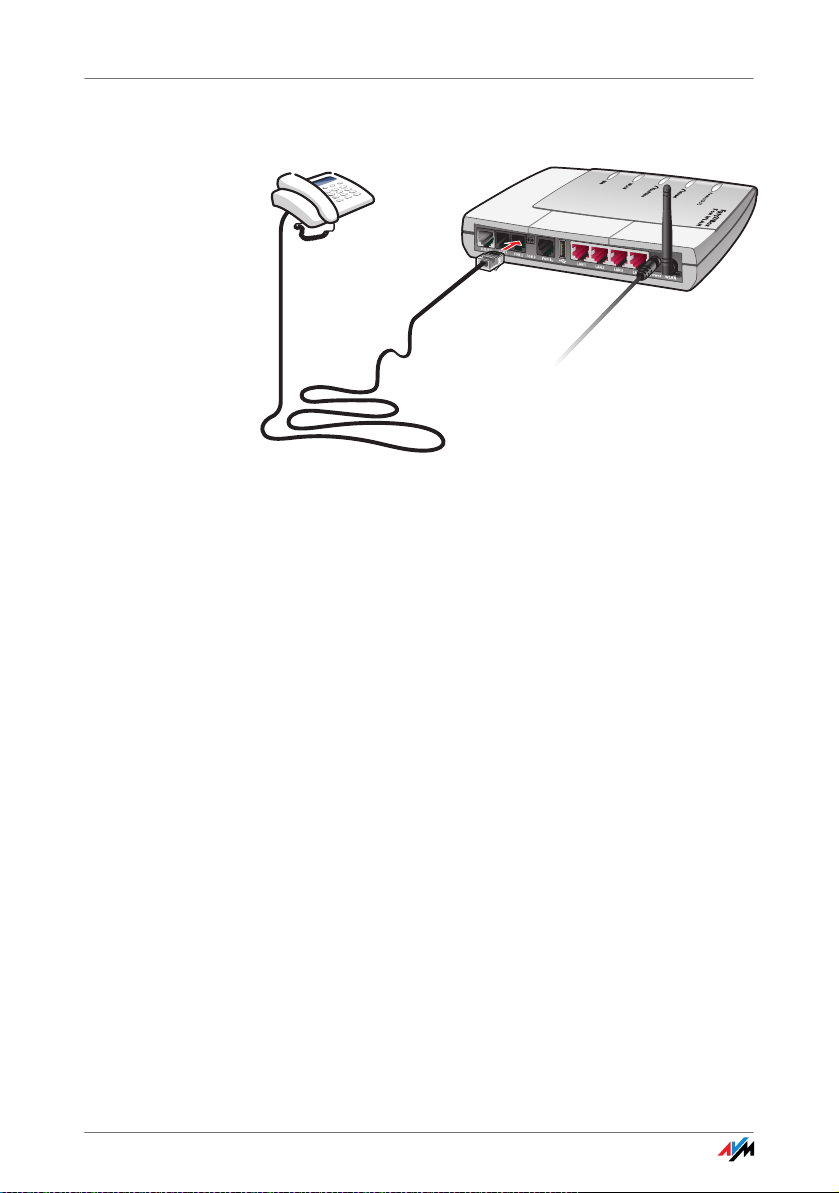
Connecting to “FON 1” or “FON 2”
Connecting an analog telephone to FRITZ!Box
Connecting to “FON 1” or “FON 2”
To connect analog terminal devices like a telephone, fax
device or answering machine, insert the plugs of your analog devices into the “FON1” or “FON2” socket on FRITZ!Box.
Connecting to “FON 3”
To connect analog devices located further away to the
FRITZ!Box, connect the cables of the telephone jack that
has been led through (the wiring at your location) to the cable clips. Please note the following:
The wire must be 0.5 to 1 mm in diameter.
Strip the insulation from the wire to expose a length of
10 mm.
To connect a cable, press back the orange lever, insert a
wire and release the lever. Repeat the procedure with the
second wire of the cable.
FRITZ!Box 27
Page 28

Connecting ISDN Telephones
2.11 Connecting ISDN Telephones
If you have an ISDN telephone, you can connect this telephone to the FRITZ!Box and use it to make calls via the Internet and the fixed-line network. With appropriate cabling,
up to eight ISDN telephones can be connected.
Connecting an ISDN telephone to the FRITZ!Box
Cable Connect an ISDN telephone using an ISDN cable.
Connecting 1. Connect one end of the ISDN cable with the ISDN tele-
phone.
2. Connect the other end of the ISDN cable with the “FON
S
” port of the FRITZ!Box.
0
2.12 Connecting an ISDN PBX
If you have an ISDN PBX, you can connect this PBX to the
FRITZ!Box Fon WLAN. With the telephones connected to the
PBX you can make calls both via the Internet and via the
fixed-line network.
The ISDN PBX must support a point-to-multipoint line.
FRITZ!Box 28
Page 29
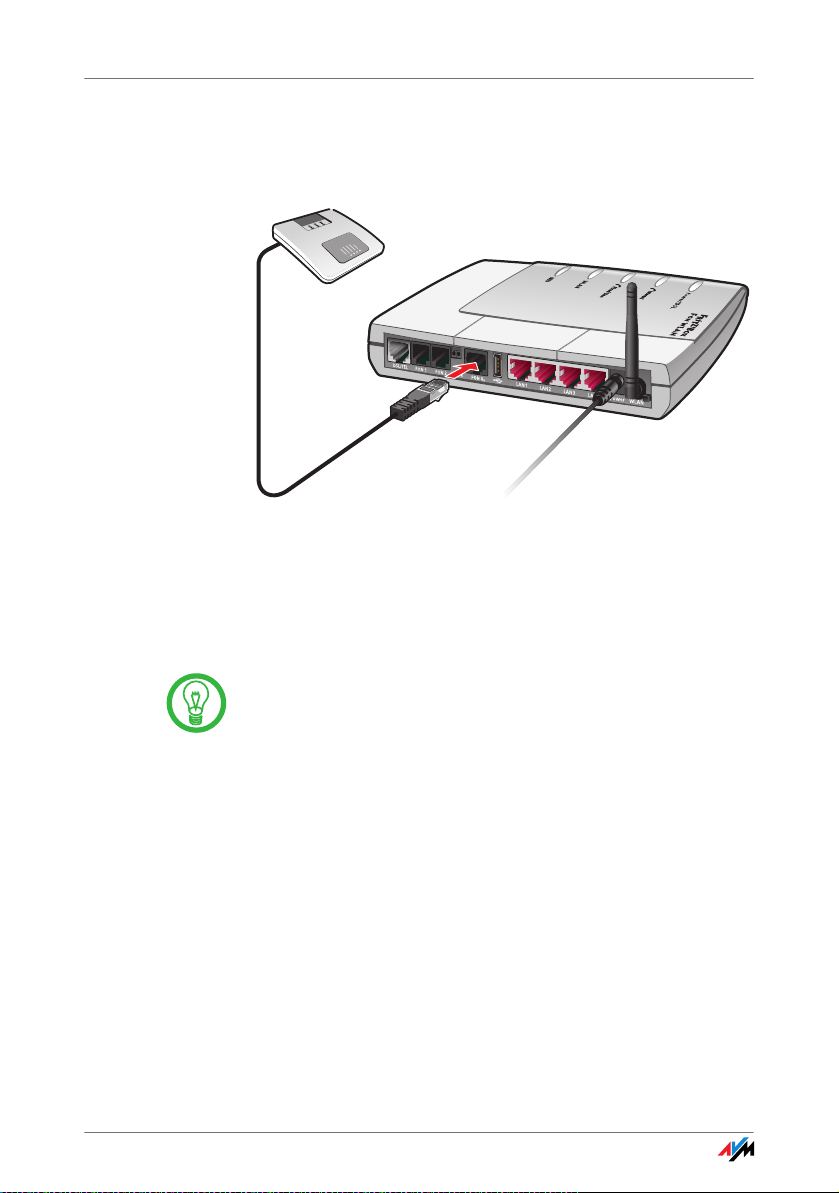
Connecting an ISDN PBX
Connecting an ISDN PBX to the FRITZ!Box
Cable Connect ISDN PBXs using an ISDN cable.
Connecting 1. Connect one end of the ISDN cable with the ISDN PBX.
2. Insert the other end of the ISDN cable into the socket
on FRITZ!Box labeled “FON S
”.
0
If you have no more than three analog devices connected to
the PBX, you can connect them directly to the FRITZ!Box
and do without the PBX.
FRITZ!Box 29
Page 30
Opening the User Interface
3 Opening the User Interface
The FRITZ!Box is equipped with a web-based interface. This is where you
configure the settings for operating the FRITZ!Box. This interface can be
accessed from any of the computers connected with FRITZ!Box. The settings are saved in FRITZ!Box.
There are two ways to open the FRITZ!Box user interface:
with the FRITZ!DSL software
Install the FRITZ!DSL software included in the
FRITZ!Box package on your computer, and open the
FRITZ!Box user interface from the FRITZ!DSL Start Center. For more information about FRITZ!DSL, see the
chapter “FRITZ!DSL: The Software Suite” from page 53.
with a web browser
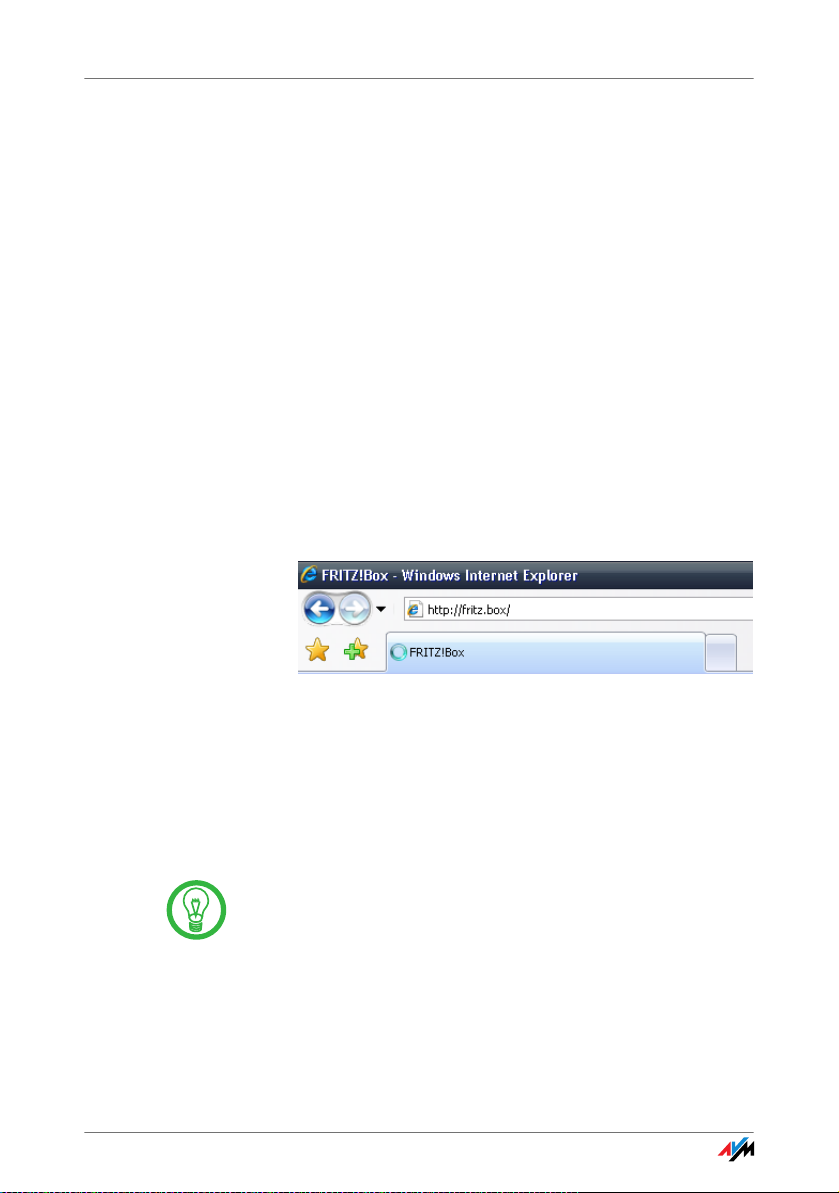
Open your Internet browser on the computer and enter
fritz.box.
The “fritz.box” address entry in the address field of an Internet
browser
When the FRITZ!Box user interface is started, FRITZ!Box is
ready for operation.
The FRITZ!Box user interface has several pages, each of
which can be accessed directly by clicking the menu command on the left edge.
If the user interface does not open, see the instructions in
the section “Errors Opening the User Interface” from
page 80.
See the section “Configuring Internet Connections” from
page 31 for instructions on configuring Internet connections
for the FRITZ!Box.
FRITZ!Box 30
Page 31

Configuring Internet Connections
4 Configuring Internet Connections
The Internet access is set up in the FRITZ!Box user interface.
Internet access for the FRITZ!Box can be made available via two different
connection types:
Internet connection via DSL
With this kind of connection the FRITZ!Box can be operated as a DSL
router. In this case the DSL connection is established by the
FRITZ!Box, and registration at the Internet Service Provider is also
taken care of by the FRITZ!Box.
Internet connection via LAN 1 / WAN
The FRITZ!Box must be connected to an existing system via a network, as a cable modem, or as a DSL router (see the connection instructions).
For this connection type the FRITZ!Box can be connected with an already existing Internet connection via the local network, an existing
DSL router or a similar means. In this case the FRITZ!Box is operated
either as an NAT router for the connected computers, or as an IP client in the network that shares the existing Internet connection.
Then the LAN 1 port functions as an uplink or WAN port.
The following section presents instructions for configuring Internet access for both types of connection.
The Internet access is configured by setting up the FRITZ!Box for the selected connection type and operation mode and defining the connection
settings. If necessary, enter the account information provided by your Internet Service Provider.
FRITZ!Box 31
Page 32

Configuring Internet Access for a Direct DSL Connection
4.1 Configuring Internet Access for a Direct DSL Connection
See also the Help available in the user interface for assistance in configuring the Internet access.
Using the
Configuration
Wizard
Manual
Configuration
If you have connected the FRITZ!Box directly at the DSL port
and have account data from an Internet Service Provider at
your disposal, you can use the Configuration Wizard available in the user interface. With the Configuration Wizard all
of the necessary basic settings are performed in just a few
steps.
If you would like to configure the Internet access without
the assistance of the Configuration Wizard, proceed as follows:
Keep the Internet access information you received from
your Internet Service Provider handy.
1. Start a web browser.
2. Enter fritz.box in the address field.
3. Select the “Settings” menu.
4. Select the the “Account Information” command from
the “Internet” menu.
5. Select the connection type “Internet connection via
DSL” in the “Connection” area.
6. In the “Operating Mode” area, select the “Use one In-
ternet connection for all computers (router)” setting.
7. Your Internet access is defined either by means of ac-
count data (user name and password) or in accordance with RFC 1483/RFC 2684.
– If you require a user name and password for Inter-
net access, select the setting “Account information
required (PPPoE/PPPoA connection)”.
– If your DSL Internet access does not require any ac-
count information, because the connection is established via DHCP or static IP address (transparent bridging/bridged ethernet in accordance with
FRITZ!Box 32
Page 33

Configuring Internet Access for a Connection to an Existing Network
RFC 1483/RFC 2684), select the setting “No account information required (in accordance with
RFC 1483/RFC 2684)”.
8. Enter the Internet account information you received
from your Internet Service Provider in the “Connection
Settings” area.
9. Click the “Apply” button to transmit your entries to the
FRITZ!Box.
Now your Internet access is configured and all connected
computers can use this Internet connection at the same
time.
4.2 Configuring Internet Access for a Connection to an Existing Network
If you connected the FRITZ!Box to an already existing network (LAN), a cable modem or a DSL router, proceed as follows to configure Internet access:
1. Start a web browser.
2. Enter fritz.box in the address field.
3. Select the “Settings” menu.
4. Select the the “Account Information” command from
the “Internet” menu.
5. Select the connection type “Internet Connection via
LAN 1” in the “Connection” area.
Two different operating modes are possible for this kind of
connection. The following section presents separate instructions on how to proceed for each of these operating
modes.
Operating Mode “Establish own Internet connection (NAT router with PPPoE or IP)”
In this operating mode the Internet connection is established by the FRITZ!Box and made available to all connected network devices.
FRITZ!Box 33
Page 34

Operating Mode “Share existing Internet connection in the network (IP Client)”
1. In the “Operating Mode” area, select the setting “Es-
tablish own Internet connection (NAT router with PPPoE or IP)”.
2. You access the Internet either via account data (user
name and password) or via the IP address.
– If your Internet access requires account informa-
tion, select the setting “Account information required (PPPoE/PPPoA connection)”.
– If your Internet access takes place via the IP ad-
dress, select the “No account information required
(IP)” setting.
3. Enter the Internet account information you received
from your Internet Service Provider in the “Connection
Settings” area.
4. Click the “Apply” button to transmit your entries to the
FRITZ!Box.
Operating Mode “Share existing Internet connection in the
network (IP Client)”
1. In the “Operating Mode” area, select the setting
“Share existing Internet connection in the network (IP
Client)”.
2. Configure the IP settings.
3. Configure the speed of your DSL line.
4. Click the “Apply” button to transmit your entries to the
FRITZ!Box.
FRITZ!Box 34
Page 35

Configuring FRITZ!Box for Telephone Connections
5 Configuring FRITZ!Box for Telephone Connections
This chapter describes how to set up FRITZ!Box for fixed-line and Internet
telephony. The following steps are necessary:
Entering account information and Internet numbers for Internet tele-
phony
Entering numbers for calls over fixed lines
Configuring connected analog terminal devices, ISDN telephones or
ISDN PBXs at FRITZ!Box
Information on the following topics is also presented here:
Dialing rules for Internet and fixed-line telephony
How does Internet telephony work with FRITZ!Box?
5.1 Entering Account Information and Internet Numbers for Internet Telephony
If you configured the Internet connection and Internet telephony using the FRITZ!Box Configuration Wizard, the required data are already entered.
If you would like calls from the Internet to be able to reach
you at all times, then disable the option “Hang up after...
seconds” on the “Internet / Account Information” page.
Configuring Additional Internet Numbers
You can set up additional Internet numbers in FRITZ!Box
Fon WLAN. To do this you will need the corresponding account information from your Internet telephony provider.
Proceed as follows to set up an additional Internet number:
1. Start a web browser.
2. Enter fritz.box in the address field.
3. Select the “Settings” menu.
4. Click the “Internet Telephony” command in the “Tele-
phony” menu.
5. Click the “New Internet Number” button.
FRITZ!Box 35
Page 36

Entering Numbers for Calls over Fixed Lines
6. Enter the account information you received from your
Internet telephony provider in the appropriate fields.
7. Click the “Apply” button.
The new number is added to the list of Internet numbers.
5.2 Entering Numbers for Calls over Fixed Lines
For fixed-line telephony your fixed-line numbers must be
configured in the FRITZ!Box. Proceed as follows:
1. Start a web browser.
2. Enter fritz.box in the address field.
3. Select the “Settings” menu.
4. Click the “Extensions” command in the “Telephony”
menu.
5. Select the “Fixed-line Numbers” page.
6. Specify whether your fixed line is an ISDN line or an
analog line.
7. Enter the ISDN numbers (MSNs) or the analog number
in the corresponding fields.
8. Click the “Apply” button.
5.3 Configuring Analog Equipment
FRITZ!Box is configured so that you can make calls to the
analog network immediately after connecting analog terminal devices, without any additional settings required.
The following settings are preconfigured at the analog lines
“FON 1”, “FON 2” and “FON 3”:
calls can be accepted on all three lines: connected ter-
minal devices will ring at the same time
outgoing calls can be conducted on all three lines
FRITZ!Box 36
Page 37

Configuring Analog Equipment
If the connected terminal devices are to react only to certain
numbers, numbers must be assigned to the extensions.
The number defined as “Number of the extension” also defines whether calls from this extension will be conducted
using the fixed-line network or the Internet.
To do this, perform the following steps:
1. Start a web browser.
2. Enter fritz.box in the address field.
3. Select the “Settings” menu.
4. Click the “Extensions” command in the “Telephony”
menu.
5. On the “Overview” page, click the button next to the
number of the extension to change its properties.
6. If the terminal equipment is to react only to the speci-
fied number, remove the checkmark from the checkbox “React to all numbers”.
7. Select the desired number from the “Number of the
extension drop-down menu”.
The device connected to the “FON 1” extension reacts
to incoming calls placed to this number and uses the
kind of connection specified for outgoing connections
with this number.
8. If you would like to assign additional numbers to the
extension, select from the “Additional numbers” dropdown menus any other numbers the device at the
“FON 1” line should react to for incoming calls.
9. Click the “Apply” button.
10. If desired, set up the “Extension FON 2” and the “Ex-
tension FON 3” in the same manner.
FRITZ!Box 37
Page 38

Configuring ISDN Telephones
5.4 Configuring ISDN Telephones
Up to eight ISDN phones can be connected to the
FRITZ!Box. Connect the ISDN telephones to the ISDN S
“FON S
The following ISDN services are supported for Internet telephony:
voice, telephony, audio 3.1 and fax G2/G3.
All other ISDN features are supported on the ISDN line. Outgoing connections with these ISDN service indicators are
automatically routed via the ISDN line.
Assigning Internet and Fixed-Line Numbers to ISDN Tel eph one s
If the connected ISDN telephones should only react to certain numbers, MSNs must be configured in the ISDN telephones.
Proceed as follows to specify whether calls are conducted
on the fixed-line network or over the Internet:
No MSNs Are Configured in the ISDN Telephone
”.
0
port
0
If no MSNs are configured in the ISDN telephone, the main
phone number is used for outgoing calls. The main number
is listed in the “Telephony / ISDN Terminal Devices” menu.
If the main number is a fixed line, all calls will be con-
ducted on the fixed-line network.
If the main number is an Internet number, all calls will
be conducted over the Internet.
MSNs Are Configured in the ISDN Telephone
If you specify an Internet number as the outgoing MSN
in the ISDN telephone, outgoing calls will be conducted over the Internet.
Internet numbers can be set up in the ISDN phone just
like MSNs.
FRITZ!Box 38
Page 39

ISDN PBXs on FRITZ!Box
If you have entered only fixed-line numbers as MSNs
in the ISDN telephone, all calls will be conducted on
the fixed-line network. If you want to use Internet telephony, you must replace an MSN with an Internet
number.
See the documentation for your ISDN telephone for instructions on setting up MSNs.
In FRITZ!Box you can enter additional Internet or fixed-line
numbers, which can then be assigned to the ISDN telephones. A list of all registered numbers is displayed after
selecting “Telephony / ISDN Terminal Devices” in the
menu.
All of the MSNs set up in the ISDN terminal devices must also be entered in FRITZ!Box.
5.5 ISDN PBXs on FRITZ!Box
ISDN PBXs can be connected to the ISDN S0 port “FON S0”
of the FRITZ!Box.
The following ISDN services are supported for Internet telephony:
voice, telephony, audio 3.1 and fax G2/G3.
All other ISDN features are supported on the ISDN line. Outgoing connections with these ISDN service indicators are
automatically routed via the ISDN line.
When PBXs are connected, only the ISDN BRI (basic rate interface) is supported.
1. If not all of your MSNs have been configured in the
PBX, enter your MSNs now. The MSNs must match the
numbers registered in the FRITZ!Box. In the “Telephony / ISDN Devices” menu, all of the numbers registered in the FRITZ!Box are displayed in the “Existing
Numbers” list.
FRITZ!Box 39
Page 40

Dialing Rules for Internet and Fixed-Line Telephony
2. If you want to use Internet telephony, the Internet
numbers must be set up in the ISDN PBX. The Internet
numbers are then assigned to the extensions of the
PBX as outgoing numbers.
See the documentation for your ISDN PBX for instructions
on setting up MSNs.
5.6 Dialing Rules for Internet and Fixed-Line Telephony
Dialing rules specify when calls are conducted on the fixedline network, and when they take place over the Internet.
1. Start a web browser.
2. Enter fritz.box in the address field.
3. Select the “Settings” menu.
4. Click the “Dialing Rules” command in the “Telephony”
menu.
5. On the “Dialing Rules” page you can define the kind of
connection for ranges of numbers.
All connections to number ranges for which a dialing
rule has been defined are established using the specified connection type.
6. Click the “New Dialing Rule” button to define as many
dialing rules as desired.
7. Click the “Apply” button.
FRITZ!Box 40
Page 41

Selecting the Type of Connection Manually
5.7 Selecting the Type of Connection Manually
If you would like to use a certain kind of connection (Internet or fixed-line) for one call, dial the following keys on the
telephone keypad before the number:
Fixed-line Connections
s111r
establishes a fixed-line connection
Internet Connections
s12r
establishes an Internet connection. The Internet number used is the Internet number set for
line 1
s12 P r establishes an Internet connection for a select-
ed Internet number. For “P”, enter the position
of the Internet number in the “List of Internet
Numbers”.
5.8 How Does Internet Telephony Work?
All kinds of data transmission in the Internet use the Internet Protocol (IP). IP is packet-oriented. This means that the
data are broken down into data packets for transmission
and IP takes care of the transport of the individual data
packets through the Internet. Language is also transmitted
in the Internet in this manner.
In opposition to this, fixed-line telephony transmits data in
a line-oriented manner. In this case data are transmitted in
a coherent data stream.
For packet-oriented transmission in the Internet, the loss of
packets cannot be ruled out completely. Under unfavorable
conditions this can lead to speech quality in Internet telephony that is inferior to that in fixed-line telephony.
FRITZ!Box 41
Page 42

Telephony Scenarios
Telephony Scenarios
If you have configured both a fixed-line number and an Internet number in FRITZ!Box, you can make calls in all directions:
from the fixed-line network into the fixed-line network
from the Internet into the fixed-line network
from the Internet into the Internet
and receive calls from all directions as well.
Bandwidth Management with FRITZ!Box
FRITZ!Box is equipped with integrated bandwidth management. This function ensures that the speech quality during
telephone calls over the Internet is not reduced by surfing
activity. FRITZ!Box adjusts all uploads and downloads to
the currently available bandwidth. Because FRITZ!Box also
places a higher priority on Internet telephony connections
over Internet data connections, unwelcome interference is
largely avoided. Just as for any other analog call, once Internet telephony transmission capacity has been reached, remote partners receive a busy sign.
FRITZ!Box 42
Page 43

USB Devices
6USB Devices
The FRITZ!Box is equipped with a USB port (also known as a USB host
controller). Various USB devices can be connected to the host controller:
a AVM FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick
a USB mass storage device (hard drive, memory stick)
a printer
a USB hub
At the USB hub you can connect two USB mass storage devices and one
USB printer, or three USB mass storage devices.
6.1 Connecting USB Devices
Some of the USB devices, such as memory sticks or the
AVM FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick, are inserted directly into the
USB port of the USB host controller. Other devices like USB
printers are connected to the USB host controller by means
of a USB cable.
Connecting a USB cable to the USB Port
FRITZ!Box 43
Page 44

Accessing USB Devices
1. Insert the end of the cable with the flat plug into the
USB port.
2. Insert the end of the cable with the square plug into
the USB port on your USB device.
6.2 Accessing USB Devices
Network Access As soon as a USB device is connected to the FRITZ!Box, all
of its functions are available in the entire network:
The files in the USB mass storage can be accessed
from the network via FTP (File Transfer Protocol), or you
can make the USB mass storage device available as a
network storage device.
USB printers are available as network printers.
6.3 USB Mass Storage Devices
USB mass storage devices include hard drives and memory
sticks.
File Systems Supported
For access via FTP (File Transfer Protocol), USB mass storage
devices are supported using the file systems FAT and
FAT32.
Connecting USB Mass Storage Devices
A USB mass storage device can be connected either directly
to the USB port or via the USB hub (see the section “USB
Hub” on page 52).
Access Rights and Password Protection
On the FRITZ!Box user interface you can configure access
rights and a password to protect USB mass storage.
1. Start a web browser.
2. Enter fritz.box in the address field.
FRITZ!Box 44
Page 45

Accessing the Data in the USB Mass Storage
3. Select the “Settings” menu.
4. Select the “USB Devices / Mass Storage Device”
menu.
5. Configure the access rights and password protection
for the USB mass storage devices.
The access rights and password are valid for all USB mass
storage devices. It is not possible to assign a different password for each individual mass storage device.
Accessing the Data in the USB Mass Storage
USB mass storage devices connected to the FRITZ!Box directly or via a USB hub are displayed with their device name
in the “USB Devices / Mass Storage Device” menu on the
user interface.
Access via FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
All of the computers in the network can access the data in
the USB mass storage simultaneously via FTP.
Click the name of the mass storage device in the “USB Devices / Mass Storage Device” menu or open a web browser
and enter FTP://fritz.box in the address field. The
folder structure of the USB storage device is displayed in
the web browser.
The data in USB mass storage can be accessed via FTP using any FTP client.
Files from the USB storage device cannot be executed or
opened in a suitable program until they have been copied
to your computer or your local network.
Access to USB Network Storage
The FRITZ!Box offers you the possibility of making USB
mass storage devices available in the Windows network as
network drives (Samba). Files in the USB memory then can
be opened and processed directly on the USB mass storage
device.
Files are supported up to a size of 2 GB.
FRITZ!Box 45
Page 46

USB Printers
6.4 USB Printers
A USB printer can be connected to the USB port for use as a
network printer. The printer is then available to all computers connected with the FRITZ!Box.
If you would like to connect a USB printer, please note the
following:
Only printers that can be addressed with the device
class “Printer” are supported as network printers. This
is not the case for some multi-function devices, for instance combined fax-scanner-printers.
Host-based printers, like those that work according to
the GDI system, are not supported for operation as
network printers with the FRITZ!Box.
For multi-function devices (printers with additional
functions like fax or scanning) operated as network
printers, only the printing function is supported.
If the printer you are using as a network printer is
equipped with a status monitor, you may not be able
to use this.
For computers with Linux:
The printer must be supported by CUPS (Common UNIX Printing System) software and be detected correctly
at the USB port of the FRITZ!Box.
For Apple computers:
The only printers that can be used are the ones whose
drivers can be selected in the Printer utility or for
which a compatible driver is available there.
If you want to use the printer as a network printer, the printer connection must be configured, and the suitable printer
drivers installed, on every computer. Print jobs are forwarded to the IP address of the printer server in the local network via the printer port.
FRITZ!Box 46
Page 47

Configuring the Printer Port in the Windows Operating Systems
Configuring the Printer Port in the Windows Operating
Systems
If the “FRITZ!Box” entry is already listed in the “Programs”
group of the start menu of the computer, this means that
the printer port is already configured on this computer.
Otherwise, work through the following steps to create the
entry in the start menu and thus configure the printer port:
1. Insert the FRITZ!Box CD in your CD-ROM drive.
The Installation Help for starting operation of the
FRITZ!Box is started.
2. Click the “View CD Contents” button.
3. Click the “Start Menu Entry” button.
The printer port designated “AVM: (FRITZ!Box USB
Printer Port)” will be configured.
Now you can install the printer drivers of the printer connected to FRITZ!Box for this printer port.
Installing Print Drivers in Windows Vista
1. Click the “Start” button in the task bar and select the
“Control Panel”.
2. Select “Printers”.
3. Click “Add Printer”.
4. Select “Add a local printer”.
You must make this selection because the printer port
on the computer functions as a local port.
5. Select the setting “Use an existing port” and then
choose the entry “AVM: (FRITZ!Box USB Printer Port)”
from the list. Click “Next”.
6. Select the manufacturer for the USB printer connected
to the FRITZ!Box from the “Manufacturers” list and
then select the exact model from the “Printers” list.
If the manufacturer or the model is not included in the
lists, use an installation disk or CD with the required
files and click “Have Disk...”.
FRITZ!Box 47
Page 48

Installing Print Drivers in Windows XP/2000
7. You can enter a name for the printer in the “Printer
Name” field. The operating system will use this name
to administer the printer.
8. Conclude the installation by clicking “Finish”.
Installing Print Drivers in Windows XP/2000
1. Open the start menu of the computer and click the
“Printers and Faxes” entry (Windows XP) or click
“Start / Settings / Printer” (Windows 2000).
2. In the “Printers and Faxes” window, click “Add a print-
er” in the “Printer Tasks” area on the left hand side.
The “Add Printer Wizard” will be started.
3. Click “Next”.
4. Select the option “Local printer attached to this com-
puter (Windows XP)” or “Local Printer” (Windows 2000)
and make sure that the setting “Automatically detect
and install my Plug and Play printer” is disabled.
You must make this selection because the printer port
on the computer functions as a local port.
5. Click “Next”.
6. In the “Select a Printer Port” window, select the option
“Use the following port” and select “AVM: (FRITZ!Box
USB Printer Port)” from the list field. Click “Next”.
7. Select the manufacturer for the USB printer connected
to the FRITZ!Box from the “Manufacturers” list and
then select the exact model from the “Printers” list.
If the manufacturer or the model is not included in the
lists, use an installation disk or CD with the required
files and click “Have Disk...”.
8. In the “Name Your Printer” window, answer the ques-
tion “Do you want to use this printer as the default
printer?” (Windows XP) or “Do you want your Windows-based programs to use this printer as the default printer?” with “No”.
FRITZ!Box 48
Page 49

Setting Up Printers in SUSE Linux Systems
Setting Up Printers in SUSE Linux Systems
You can connect a USB printer to the USB port of the
FRITZ!Box for use as a network printer. The printer is then
available to all computers connected with the FRITZ!Box.
Installing a Printer
You install the printer as “superuser”.
1. Open a console and enter the following command:
lpadmin -p <printer_name> -E -v
socket://<IP_address_of_FRITZ!Box> -m
<printer_description_file.ppd>
2. For information about the necessary settings, please
refer to:
http://www.cups.org/man/lpadmin.html
Example
For a laser jet printer with the example name of “Laserjet4”
and the PPD file “laserjet.ppd” at a FRITZ!Box with the default address 192.168.178.1, on the console you must enter:
lpadmin -p LaserJet4 -E -v
socket://192.168.178.1 -m laserjet.ppd
You can view the PPD files installed in the system with the
following command:
lpinfo -m
Please direct any questions about PPD files for your printer
to the manufacturer of the printer or system used. More detailed information on the CUPS printing software is included in the following documentation:
http://www.cups.org/documentation.php
Configuration questions should also be directed to the
manufacturer of the distribution or to an Internet-based or
usenet forum that deals with CUPS or the distribution used.
FRITZ!Box 49
Page 50

Setting Up USB Printers on Apple Computers
Setting Up USB Printers on Apple Computers
A USB printer can be connected to the USB port of the
FRITZ!Box for use as a network printer. The printer is then
available to all computers connected with the FRITZ!Box.
Installing a Printer
1. Under “Go / Utilities”, open the “Printer Setup Utility”.
2. Click “Add”.
3. Select “IP Printer”.
4. In the “Protocol” field, select the entry “HP Jet Direct –
Socket”.
If the printer cannot be selected, it may be possible to
select a compatible printer or printer driver.
5. Enter in the “Address” field the IP address of the
FRITZ!Box:
192.168.178.1:
6. Leave the “Queue” field empty.
7. Enter the desired values in the “Name” and “Loca-
tion” fields.
8. Enter a driver compatible with your printer in the “Print
Using” field.
9. Click the “Add” button to save your settings.
FRITZ!Box 50
Page 51

AVM FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick
Information about compatible printers or printer drivers is
available in the Internet, for instance on the page:
http://gimp-print.sourceforge.net/p_Supported_Printers.php3
or from the printer manufacturer.
6.5 AVM FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick
The AVM FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick is a WLAN adapter for connection to a computer. Using this WLAN adapter you can
connect the computer wirelessly with any FRITZ!Box.
AVM Stick & Surf Technology
With this technology it is easy to establish a secure WLAN
connection.
1. Insert the Stick in the port on your FRITZ!Box for the
USB host controller.
2. The “INFO” LED on the FRITZ!Box begins flashing rap-
idly. The WLAN security settings are being transferred
to the AVM FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick.
3. As soon as the “INFO” LED stops flashing, transmis-
sion of the settings has been concluded. You can now
remove the stick.
After the security settings have been transmitted automatically, you can insert the AVM FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick in a
computer and establish a connection to the FRITZ!Box. No
manual settings are necessary.
FRITZ!Box 51
Page 52

USB Hub
6.6 USB Hub
A USB hub can be connected to the USB host controller. A
USB hub is a device to extend existing USB ports.
You can connect two USB mass storage devices and one
USB printer, or three USB mass storage devices (like a hard
drive or memory stick) to the USB hub.
If more than one USB device without its own power supply
is connected to the FRITZ!Box, please note that, in accordance with the USB specification, the total current consumption may not exceed a value of 500 mA. Otherwise unspecified malfunctions with the USB devices or even damage to the FRITZ!Box may occur.
FRITZ!Box 52
Page 53

FRITZ!DSL: The Software Suite
7 FRITZ!DSL: The Software Suite
The FRITZ!DSL software suite is included in your FRITZ!Box package. The
software includes a number of programs and tools we will introduce
briefly in this chapter.
Once you have installed FRITZ!DSL, the “Start Center” icon
appears on your desktop. All of the programs in the software package are integrated in the FRITZ!DSL Start Center,
from where they can be started directly.
The Start Center contains the following buttons:
Click the “Internet” button to start the FRITZ!DSL Internet
program. FRITZ!DSL Internet is the Internet monitoring software for your FRITZ!Box, with which you receive more detailed information about your current Internet connection.
The “Protect” button starts the FRITZ!DSL Protect program,
which checks the Internet connections and supplements
the firewall functions of your FRITZ!Box.
Click the “FRITZ!Box” button to open the user interface of
FRITZ!Box in your web browser.
Click the “Update” button to check whether a firmware update for your FRITZ!Box is available on the AVM web site.
The “Diagnosis” button starts the FRITZ!DSL Diagnosis. It
displays all data relevant to your DSL connection, and
checks the installation and connection of FRITZ!Box.
Click the “Web Test” button to start the WebWatch program.
WebWatch can measure the quality of your Internet connection to any remote site.
For detailed information on configuring and using
FRITZ!DSL programs, see the corresponding Online Help
programs.
FRITZ!Box 53
Page 54

Installing FRITZ!DSL
7.1 Installing FRITZ!DSL
Proceed as follows:
1. Insert the FRITZ!Box CD and double-click the “Set-
up.exe” file.
2. Select “View CD contents / Install FRITZDSL”.
3. The “File Download” window opens. Select the
“Open” button in this window.
4. The FRITZ!DSL welcome screen appears. Confirm with
“Continue”.
5. Specify the folder in which you want to install
FRITZ!DSL on your computer. Confirm with “Continue”.
6. Next, specify the program group for FRITZ!DSL in the
Start menu. Confirm with “Continue”.
7. Confirm with “Finish”.
This concludes the installation.
7.2 F RI TZ !DS L I nte rn et
FRITZ!DSL Internet is the Internet monitoring software for
your FRITZ!Box. For instructions on how to configure the
program and use it to connect to the Internet, see the corresponding Online Help.
As soon as an Internet connection has been established,
FRITZ!DSL Internet presents you with information about the
current Internet connection. If is used in combination with
a router, the program displays the connection status, provides information about the course of data transmissions,
and allows the Internet connection of FRITZ!Box to be established or cleared from the computer.
FRITZ!Box takes care of dialing into the Internet, firewall
protection from unauthorized incoming connections, and
keeps track of transmission volume and online time. In addition you can also use the FRITZ!DSL program to check the
outgoing Internet connections.
FRITZ!Box 54
Page 55

FRITZ!DSL Protect
7.3 FRIT Z! DSL Pro te ct
FRITZ!DSL Protect protects your computer from unwanted
Internet connections, supplementing the firewall functions
of your FRITZ!Box. With FRITZ!DSL Protect you can check all
Internet connections that are established or accepted by local programs on your computer. You can permit or prohibit
individual programs from accepting connections. If an unknown program attempts to establish an Internet connection, you will be asked whether you wish to allow such a
connection.
An overview shows the programs already set up in
FRITZ!DSL Protect along with their access rights. A Journal
grants you an overview of all successful and rejected attempts to access the Internet.
One of the most convenient functions offered by FRITZ!DSL
Protect works in combination with the UPnP capability of
the FRITZ!Box. If enable the option “Allow changes to security settings over UPnP” in the FRITZBox, FRITZ!DSL Protect
can foward ports for incoming connections on the
FRITZ!Box whenever they are needed by programs. For this
capability you must activate the “Use port forwarding“ option in the “Settings” of FRITZ!DSL Protect. In this manner
you can participate in online activities like gaming without
having to reconfigure the FRITZ!Box firewall functions manually.
7. 4 F R IT Z ! Bo x
Click the “FRITZ!Box” button to open the user interface of
FRITZ!Box in your web browser. In the FRITZ!Box user interface you can set up a shared Internet access for all connected computers and change the FRITZ!Box settings.
7.5 Update
New firmware updates for FRITZ!Box are provided by AVM at
regular intervals, free of charge. The updates can add new
functions to your FRITZ!Box.
Click the “Update” button to check whether there is a new
update available for the FRITZ!Box firmware.
FRITZ!Box 55
Page 56

FRITZ!DSL Diagnosis
When the FRITZ!DSL Start Center is started, the AVM web
site is automatically checked for new updates every 30
days. You will be informed when a new update is available.
7.6 FRITZ!DSL Diagnosis
FRITZ!DSL Diagnosis reports comprehensively about all of
the details of the DSL connection, including data transmission and the activated fast-path mode. The integrated comprehensive DSL diagnosis makes it possible to monitor the
FRITZ!Box connection and installation.
7.7 Web Tes t
Click the “Web Test” button in the FRITZ!DSL Start Center to
start the WebWatch program. WebWatch tests the quality
of your Internet connection, and displays the results of
these tets graphically.
Once any URL is entered, WebWatch sends a signal to the
destination address.
The response times measured and the path of the data
packets through the Internet are displayed in a diagram
and in an overview.
FRITZ!Box 56
Page 57

More about WLAN
8More about WLAN
WLAN is a radio technology that allows Ethernet networks and access to
the Internet to be provided without cable connections. This allows multiple users to share one wireless Internet connection.
8.1 Standards
The WLAN standards IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g and
IEEE 802.11i were developed by the Institute of Electrical
and Electronic Engineers (IEEE).
Standards for the Throughput Rate
Data Throughput The standards IEEE 802.11b and IEEE 802.11g define the
transmission rate within a wireless LAN. These standards
differentiate between gross and net transmission rates. The
net speed describes the transmission rate of the user data.
The standards are intended for different frequency bands.
Standard Frequency Band /
Frequency Bands
802.11b 2.4 GHz 11 Mbit/s 5 Mbit/s
802.11g 2.4 GHz 54 Mbit/s 25 Mbit/s
Gross Data Throughput Net Data Throughput
The FRITZ!Box supports both standards. WLAN adapters
based on one or more of the standards listed can be used
for WLAN connections with the FRITZ!Box.
Range The range within a WLAN is highly dependent on the follow-
ing three factors:
the WLAN adapter used,
the structural conditions
the amount of radio traffic on the same frequency
band. Other WLAN networks, microwave ovens or
Bluetooth transmitters (mobile telephones) may be
active.
FRITZ!Box 57
Page 58

Setting the Right Standard in the FRITZ!Box
IEEE 802.11b With a maximum throughput rate of 11 Mbit/s, this is the
oldest standard for radio networks. Older WLAN adapters of
the first generation can communicate with the FRITZ!Box
using 802.11b. However, if the WLAN adapter supports
newer standards such as 802.11g, the latest standard
should be used.
IEEE 802.11g This is currently the most common WLAN standard. It com-
municates with a maximum of 54 Mbit/s in the 2.4-GHz frequency range (ISM) and guarantees broad compatibility
with many WLAN devices. However, due to heavy use of the
2.4-GHz range, interference is more common than in the
less-used 5-GHz range.
Setting the Right Standard in the FRITZ!Box
In order to be able to set the right standard for throughput,
you must first switch to the Expert Mode on the user interface:
1. Select the menu “Settings / Advanced Settings / Sys-
tem / Expert Mode”.
2. Select “Show expert settings” and then click “Apply”.
You must configure the standard you want to use for the
transmission rate in the FRITZ!Box. The settings is configured in the “Settings / WLAN / Radio Settings” menu, in the
“Mode” field.
Note the following for the configuration of this setting:
In order to communicate with each other, the
FRITZ!Box and all WLAN adapters must work in the
same frequency band.
The standard you configure in the FRITZ!Box must be
compatible with the standards of all WLAN adapters
used in the WLAN.
Make a note of which standards the WLAN adapters in your
network are compatible with and then set the correct mode
based on this information.
FRITZ!Box 58
Page 59

The Standard for Security
The Standard for Security
IEEE 802.11i The WPA security mechanism is defined in the IEEE 802.11i
standard. WPA2 is an extension of the familiar security
mechanism WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access).
The main feature of the extension of WPA to WPA2 is the
AES-CCM encryption process.
Mechanism Encryption
WPA TKIP (Temporary Key Integrity Protocol)
WPA2 TKIP
AES-CCM
based on the extremely secure AES (Advanced
Encryption Standard) procedure. CCM
(Counter with CBC-MAC) defines how the AES
procedure is applied to WLAN packets.
FRITZ!Box supports the AES encryption procedure as part of
the WPA2 mechanism, and the TKIP encryption procedure as
part of the WPA mechanism. This means that the FRITZ!Box
can be used in combination with any WLAN adapters that also support WPA2 with AES or WPA with TKIP.
8.2 Security
Security is of utmost importance within radio networks. Radio signals can also be received outside of office or residential spaces and abused for criminal purposes.
Therefore it is important that no unauthorized users can
register in a WLAN to use its Internet access or shared network resources.
FRITZ!Box includes settings on various levels that contribute to the security of your WLAN and thus to the security of
your computers.
FRITZ!Box 59
Page 60

Encryption
Encryption
The most important security setting is encryption.
FRITZ!Box supports the security mechanisms WEP (Wired
Equivalent Privacy), WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) and
WPA2 as follows:
As part of the WEP mechanism a static key is deter-
mined to serve for the encryption of the user data. The
key must also be entered in the WLAN settings of the
WLAN clients.
The WPA and WPA2 mechanisms provide for authenti-
cation while the connection is being established. For
this a WPA password must be defined.
When WPA is selected, the TKIP encryption method is used
to encrypt the user data. In WPA2 the AES-CCMP encryption
method is used.
The security mechanis selected must also be supported by
your WLAN adapter.
The user data are encrypted using an automatically generated key. This key is regenerated at regular intervals.
The WPA password used may be 8 to 63 characters in
length. For increased security, however, the password
should be at least 20 characters long. Use numerals, letters
and special characters and combine capitals and lowercase letters.
Encryption Configured in the Factory Settings
In the FRITZ!Box a combined encryption “WPA + WPA2” with
the TKIP/AES-CCMP encryption method is preconfigured.
This setting allows you to use WLAN adapters that support
WPA (TKIP) or WPA2 (AES-CCMP) or both methods.
It is advisable to change the preconfigured WLAN key as
soon as possible. Changes to the settings can be configured on the FRITZ!Box user interface.
FRITZ!Box 60
Page 61

Encryption
Changing the Encryption Method: Recommendations
If your WLAN adapter supports an encryption method that
is more secure than the one preconfigured in your
FRITZ!Box, you should select the more secure encryption
method in your FRITZ!Box.
To configure the best security settings possible with
FRITZ!Box and your WLAN adapter, please note the following recommendations:
If your WLAN adapter supports WPA2 in accordance
with the 802.11i standard:
– Enable WPA encryption.
– Select the WPA mode “WPA2 (CCMP)” or
“WPA+WPA2”.
– Replace the WPA key with a new, unique value.
If your WLAN adapter supports the WPA mechanism,
but not the WPA2 mechanism:
– Enable WPA encryption.
– Select the WPA mode “WPA (TKIP)” or “WPA+WPA2”.
– Replace the WLAN network key with a new, unique
value.
If your WLAN adapter supports neither the WPA nor the
WPA2 mechanism:
– Enable WEP encryption.
– Replace the WLAN key with a new, unique value.
We strongly recommend the use of a WLAN adapter that
supports WPA or WPA2 (for instance, the AVM FRITZ!WLAN
USB Stick). WEP is out of date and data encrypted with WEP
can be deciphered within a few hours.
FRITZ!Box 61
Page 62

WLAN Radio Network Name (SSID)
WLAN Radio Network Name (SSID)
The factory settings of FRITZ!Box include a value of
“FRITZ!Box Fon WLAN 7170” preset for the SSID (Service Set
Identifier).
If an additional device with the same network name is located in the vicinity, it can occur that the WLAN adapter attempts to register there. Therefore you should change the
SSID as soon as possible.
8.3 Frequency Range
WLAN uses the frequency range around 2.4 GHz in the ISM
band, or, alternatively, the area around 5 GHz.
2.4-GHz Range WLAN in the 2.4-GHz frequency band works in the same ar-
ea as Bluetooth, microwave devices and many cordless
telephones. This means that interference may occur within
WLANs operated in the vicinity of such devices. Generally
the only adverse effects are to the transmission rate; aborted connections and data losses are rare.
In Europe, 13 channels are provided for WLAN in the 2.4GHz
range. One channel has a bandwidth of 22 MHz. A 5-MHz interval is left empty between adjacent channels. That means
that channels located directly next to each other may overlap
and result in mutual interference. If several WLANs are operated within a small space, a distance of at least five channels
should be left empty between each two channels used. For
instance, if channel 1 is selected for one WLAN, the channels
7 through 13 can be selected for a second WLAN. This maintains the minimum distance between channels.
WLAN
Autochannel
With the WLAN Autochannel function, the FRITZ!Box automatically searches for the channel subject to the least interference. Should problems with interference persist despite
this function, try to identify the source of interference and
switch it off manually.
Additional tips on interference in the WLAN radio network
are presented in the section “Eliminating Disturbances
Caused by Another WLAN Radio Network” from page 85.
FRITZ!Box 62
Page 63

Allocation of the WLAN Channels in the 2.4-GHz Range
Allocation of the WLAN Channels in the 2.4-GHz Range
Channel Frequency (GHz) Channel Frequency (GHz)
1 2.412 8 2.447
2 2.417 9 2.452
3 2.422 10 2.457
4 2.427 11 2.462
52.432 122.467
6 2.437 13 2.472
7 2.442
8.4 Increasing the WLAN Range Using WDS
You can extend the range in your wireless network using
WDS (Wireless Distributed System). For this you need another WLAN access point in addition to the FRITZ!Box. One
of the two WLAN access points works as the base station,
the other as a repeater. The base station and repeater are
connected to each other via WLAN. The base station then
can use the repeater to reach even computers that would
be located beyond its range without the repeater.
WDS: Expanding the WLAN range using a repeater
Please note:
In order to expand the range of your wireless network,
you need at least one additional WLAN access point.
The wireless network of your FRITZ!Box can be expanded to a WDS (Wireless Distributed System) with up to
four WLAN access points.
FRITZ!Box 63
Page 64

Increasing the WLAN Range Using WDS
All WLAN access points implemented in the WDS must
support WDS and be configured for this technology.
All WLAN access points implemented as repeaters in
the WDS must be located within the range of the base
station.
When WDS in the FRITZ!Box is enabled, it can function
as a base station to establish the Internet connection
for other repeaters, or as a repeater to expand the
range of a base station.
Make sure that the WLAN connections in the wireless
network are encrypted for security.
Make sure that all WLAN access points in the WDS use
the same radio channel.
Every access point participating in the WDS fulfills the
tasks of a WLAN access point for its given WLAN clients. This means that the WLAN clients see each
WLAN access point with an individual name (SSID)
and individual encryption settings.
If you use the WLAN control software provided by the
Windows XP Service Pack 2 on your WLAN clients, you
can assign the same SSID and the same encryption
settings to different WLAN access points. Each client
can then automatically register at the WLAN access
point with the best availability.
Make sure that each IP address is assigned only once
in the wireless network.
FRITZ!Box 64
Page 65

Enabling WLAN in the FRITZ!Box
Enabling WLAN in the FRITZ!Box
Make sure that the “Show expert settings” option is enabled in the “System / Expert Mode” menu.
Perform the following steps:
1. Start your computer and open a web browser.
2. Enter fritz.box or 192.168.178.1 in the ad-
dress line of your web browser and confirm by hitting
the enter key. The FRITZ!Box user interface opens.
3. Click the “Settings” menu entry.
4. Click the “WLAN” menu entry.
5. Make sure that the wireless radio network (WLAN) is
enabled.
If necessary, enable the setting “Enable WLAN” in the
“WLAN / Radio Settings” menu and click the “Apply”
button.
6. Click the “Repeater” menu command.
7. Enable the “Enable support for WLAN repeater (WDS)”
setting.
Now WDS support is enabled in your FRITZ!Box.
The next step is to specify whether the FRITZ!Box is to work
as a base station or as a repeater. Continue with the following section for instructions.
FRITZ!Box 65
Page 66

Specifying the WDS Mode for the FRITZ!Box
Specifying the WDS Mode for the FRITZ!Box
The FRITZ!Box can be configured as a base station or as a
repeater:
As a base station, the FRITZ!Box establishes Internet
connections for other WLAN repeaters and WLAN clients.
As a repeater, the FRITZ!Box extends the range of a
base station in the wireless network.
Configuring FRITZ!Box as a Base Station
The MAC address of the repeater must be determined before you can configure the FRITZ!Box as a base station.
1. Connect the device you want to use as a repeater to
your computer. Proceed as described in the corresponding documentation.
2. Make note of the MAC address of the repeater or print
it out.
The MAC address is generally printed on a sticker on
the base of the device. If the other repeater is a
FRITZ!Box, the MAC address will be listed as “Local
MAC Address of this FRITZ!Box” in the “WLAN / Monitor”. You can also print out this information using the
print command in your browser.
Once you have determined the MAC address of the repeater, you must register its address in the settings of the base
station.
1. To do this, reconnect the FRITZ!Box to your computer
and open a web browser.
2. Enter fritz.box in the address line of your web
browser and confirm your entry by pressing Enter. The
FRITZ!Box user interface opens.
3. Open the “Operating Mode” settings page by clicking
through the “Settings / WLAN / Repeater” menus and
select the “Base station” option.
FRITZ!Box 66
Page 67

Configuring FRITZ!Box as a Repeater
4. Enter the MAC address of the repeater(s) with which
you would like to extend your wireless network.
5. Select on the “Security” settings page.
6. Specify the type of encryption for the connection.
WPA2 encryption can be used only if the repeater is also a FRITZ!Box. With other repeaters, WDS can only be
used non-encrypted or with WEP encryption, since the
WLAN standard is not stipulated for any other encryption with WDS.
7. Enter a password.
8. Click “Apply”.
9. The “Repeater Settings” window appears. It displays
the repeater settings of the FRITZ!Box. We recommend
printing out these settings by clicking the “Print Page”
button.
This concludes the configuration of the FRITZ!Box as a base
station.
Register the FRITZ!Box settings you printed out in each repeater operating in your wireless network. If you are using a
FRITZ!Boxas a repeater, please read the next section.
Configuring FRITZ!Box as a Repeater
First enable your base station for WDS operation and make
sure that the WLAN function has been enabled.
1. Open the “Operating Mode” settings page by clicking
through “Settings / WLAN / Repeater” and select the
“Repeater” option.
2. Enter the MAC address of the base station here.
The MAC address is generally printed on a sticker on
the base of the device. If the base station is a
FRITZ!Box, enter the address you printed out as described in the section “Configuring FRITZ!Box as a
Base Station” on page 66.
FRITZ!Box 67
Page 68

Configuring FRITZ!Box as a Repeater
3. Make sure that the FRITZ!Box and your base station
are located in the same IP range and that both devices
have been assigned an unique IP address.
Please note that the repeater subsequently can only
be reached via this new IP address!
4. Select on the “Security” settings page.
5. Set the kind of encryption used on your base station
and use the same password as you did for the base
station.
6. Click “Apply”.
7. The “Repeater Settings” window appears. It displays
the repeater settings of the FRITZ!Box. All settings
must correspond to the settings in the base station.
This concludes the configuration of the FRITZ!Box as a repeater.
FRITZ!Box 68
Page 69

Network Settings
9 Network Settings
Upon delivery, the network settings of the FRITZ!Box are preconfigured as
follows:
Factory Settings
All computers are located in the same IP network enabled
IP address 192.168.178.1
Subnet mask 255.255.255.0
DHCP server enabled
According to these settings, all computers connected with the FRITZ!Box
are located in the same subnetwork.
You can change any of these settings, but should only do so if you are
well versed in network settings. If you do not have much experience in
setting up networks, please read this chapter in full.
The “Basics” section explains terms and concepts having to do with
IP networks.
The sections “IP Address”, “DHCP Server” and “Subnetwork” ex-
plain when it may make sense to change the preconfigured network
settings, what the effects of these changes are, and how to make
the changes.
9.1 Basics
What Is IP?
IP is the abbreviation for Internet Protocol.
The IP Internet Protocol is the most important basic proto-
col for the control of data exchange in local networks and in
the Internet. The Internet protocol works without a connection; in other words, data packets are transmitted from the
sender to the recipient without previous consultation. The
addresses of the recipient and the sender in the data packets are given as IP addresses.
IP Network A network in which data exchange takes place on the basis
of the Internet Protocol is called an IP network.
FRITZ!Box 69
Page 70

What Is an IP Address?
What Is an IP Address?
The term IP address is the abbreviation for Internet Protocol
address.
The IP address corresponds to the “postal” address of a device located in the Internet or in a local IP network. So that
data packets are sure to be delivered to the right address,
each IP address may be assigned only once within the Internet or a local IP network.
The IP address consists of four three-digit groups of numbers (e.g. 192.168.178.154). Each group of numbers can assume values between 000 and 255.
IP addresses can be public or private, and also fixed or assigned dynamically.
Public IP Address A public IP address is an IP address valid in the Internet. Ev-
ery computer or router participating in the Internet must
have a uniquely assigned public IP address. This address is
usually negotiated dynamically with the Internet Service
Provider when a connection to the Internet is dialed. The Internet Service Provider assigns the negotiated IP address to
the computer or router for the duration of an Internet session.
Private IP Address Private IP addresses are used for computers and other net-
work devices within local IP networks.
Since many local IP networks are not connected to the In-
ternet except via single computers or routers (gateway), certain address ranges are excluded from the publicly available IP addresses so that they are available for assignment
in local IP networks. An IP address may only be assigned
once within the local network. A private IP address may exist in any number of other local networks.
Fixed IP Address Fixed IP addresses are IP addresses which are permanently
assigned to a computer or another device like a network
printer.
FRITZ!Box 70
Page 71

Subnetwork
Assigning fixed IP addresses makes sense in cases where a
local network has a sufficiently large pool of IP addresses
available, or when a computer is always supposed to be accessible at a certain address (such as a web server or email server).
Dynamic IP
Address
A dynamic IP address is an IP address valid only for the duration of one Internet or network session.
Every computer participating in the Internet must have a
uniquely assigned public IP address. Since only a limited
number of such IP addresses is available, they must be
used sparingly. That is why most of the Internet participants who dial in to the Internet receive a dynamic IP address. They are called dynamic because every participant
receives a new public address that has not been assigned
yet each time he or she dials in to the Internet.
By contrast, dynamic addresses are usually used in local IP
networks because they are easy to handle, and because using them avoids incorrect IP address entries or unintentional double assignments. The DHCP service is responsible for
assigning unique dynamic IP addresses.
Subnetwork
A local IP network can consist of one subnetwork or be divided into multiple subnetworks. The division into subnetworks is performed when the local IP network is configured.
The subnetworks of a local IP network are also IP networks.
Subnet Mask The subnet mask indicates which part of an IP address is
the network address and which the address of the computer. The network address defines what is called the subnet.
Example 1
IP address: 192.168.178.247
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
The assignment of the first three groups of numerals in the sub-
net mask indicates that the first three groups of numerals in the
IP address define the network. The following addresses result:
FRITZ!Box 71
Page 72

Subnetwork
Example 1
Network address of the
subnet:
Address of the computer
in the subnet:
IP address pool in the
subnet:
Example 2
IP address: 192.168.178.247
Subnet mask: 255.255.0.0
The assignment of the first two groups of numerals in the subnet
mask indicates that the first two groups of numerals in the IP address define the network. The following addresses result:
Network address (subnet): 192.168.0.0
Address of the computer
in the subnet:
IP address pool in the
subnet:
192.168.178.0
192.168.178.247
192.168.178.0 - 192.168.178.255
The IP addresses 192.168.178.0 and
192.168.178.255 are reserved. This
means that the addresses from
192.168.178.1 to 192.168.178.254 are
available for assignment to the computers.
192.168.178.247
192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255
The IP addresses 192.168.0.0 and
192.168.255.255 are reserved. This
means that the addresses from
192.168.0.1 to 192.168.255.254 are
available for assignment to the computers.
FRITZ!Box 72
Page 73

What Is DHCP?
9.2 IP Address
What Is DHCP?
DHCP is the abbreviation for Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol.
DHCP is a protocol for the dynamic negotiation of the operating parameters for the TCP/IP protocol (TCP is a transport
protocol based on the Internet protocol). The computers of
a local IP network (DHCP clients) access the DHCP server as
part of their operating systems’ start procedure.
The DHCP server assigns each client an IP address that has
not yet been assigned at the present time. The DHCP server
also informs the client of the IP addresses of the DNS server to be used and of the default gateway. In assigning the IP
addresses the DHCP server selects from a prescribed pool
of IP addresses.
The central administration of the TCP/IP operation parameters makes it possible to avoid address conflicts due to IP
addresses accidentally assigned more than once.
The FRITZ!Box is delivered with an IP address preset.
Factory Settings
All computers are located in the same IP network
IP address 192.168.178.1
Subnet mask 255.255.255.0
DHCP server enabled
The IP address and the corresponding subnet mask automatically yield the following values:
Network address of the subnet 192.168.178.0
Entire IP address pool for the
computers
You can change the preset IP address.
FRITZ!Box 73
enabled
192.168.178.2 - 192.168.178.253
Page 74

When Does It Make Sense to Change the IP Address?
When Does It Make Sense to Change the IP Address?
You should change the IP address of the FRITZ!Box if the following apply to your network:
You have an existing local IP network, one subnet with
several computers.
Fixed IP addresses are registered in the network set-
tings of the computer, and you do not want to or are
not permitted to change these addresses.
You want to connect the FRITZ!Box to the subnet in or-
der to make the FRITZ!Box features available to all of
the computers in the subnet.
What IP Address Must You Assign for the FRITZ!Box and What Else Must Be Taken into Consideration?
The IP address must come from the address range of
your existing subnet.
The subnet mask must correspond with that of the
connected subnet.
When the DHCP server of the FRITZ!Box is enabled, the
addresses 20 through 200 in the fourth group of numerals of the IP address are reserved for the DHCP
server. If none of the computers in your network has
an address from this pool, the DHCP server can remain
switched on. If one of the computers has a fixed address assigned from this pool, you should switch off
the DHCP server.
If you can no longer open the FRITZ!Box user interface
after entering the IP address, see the information in
the section “Errors Opening the User Interface” from
page 80.
FRITZ!Box 74
Page 75

Reserved IP Addresses
Reserved IP Addresses
The following address range is reserved in FRITZ!Box for internal purposes.
192.168.180.1 - 192.168.180.254
IP addresses from this range may not be assigned to
FRITZ!Box.
How Can the IP Address Be Changed?
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see the section
“Opening the User Interface” from page 30).
2. Click “Expert Mode” in the “System” menu, enable the
setting “Show expert settings” and confirm this setting by clicking “Apply”.
3. Open the “System / Network Settings” menu.
4. Click the “IP Addresses” button.
5. Make the changes on the “IP Settings” page and then
click “Apply”.
9.3 DHCP Server
FRITZ!Box is equipped with its own DHCP server. The DHCP
server is enabled by default in the factory settings. Every
time the operating system on a computer connected with
FRITZ!Box is started, it is assigned an IP address by the
DHCP server.
Only one DHCP server may be active within any network.
Factory Settings
All computers are located in the same IP network
IP address 192.168.178.1
Subnet mask 255.255.255.0
DHCP server enabled
FRITZ!Box 75
enabled
Page 76

Fixed IP Addresses when the DHCP Server Is Enabled
The IP address, the corresponding subnet mask and the activated DHCP server automatically yield the following values:
Network address of the subnet 192.168.178.0
Entire IP address pool for the
computers
Address pool of the DHCP server 192.168.178.20 - 200
In every subnet of the FRITZ!Box, the addresses 20 through
200 in the fourth group of numerals of the IP address are
reserved for the DHCP server.
Assigning the IP addresses via the DHCP server ensures
that all of the computers connected with the FRITZ!Box are
located in a single subnet.
The computers can receive their IP addresses from the
DHCP server only if the setting “Obtain an IP address automatically” is enabled in the their IP settings. For more information, see the section “IP Settings” from page 87.
Fixed IP Addresses when the DHCP Server Is Enabled
If you would like to give fixed IP addresses to individual computers connected with the FRITZ!Box, despite the fact that the
DHCP server is enabled, then you must disable the option
“Obtain an IP address automatically” in this computer’s network settings and enter the fixed IP address manually.
192.168.178.2 - 192.168.178.253
Which IP Addresses Can You Assign to the Computers?
The IP addresses must be from the same subnet as
FRITZ!Box.
The IP addresses may not come from the address pool
of the DHCP server.
If the factory settings are not changed, that means the following IP addresses are available:
192.168.178.2 - 192.168.178.19
192.168.178.201 - 192.168.178.253
Each IP address can be assigned only once.
FRITZ!Box 76
Page 77

Disabling the DHCP Server
Disabling the DHCP Server
You can switch off the DHCP server.
To make sure that all computers remain in the same subnet
as the FRITZ!Box even when the DHCP server is disabled,
you must enter the IP addresses manually in the computers’ network settings. First disable the option “Obtain an IP
address automatically” and then enter the IP address manually in the appropriate field.
In the case of the preset IP address of the FRITZ!Box, the following IP addresses are available for assignment to the
computers:
192.168.178.2 - 192.168.178.253
Each IP address can be assigned only once.
Changing the DHCP Server Settings
Proceed as follows to open the DHCP server settings:
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see the section
“Opening the User Interface” from page 30).
2. Click “Expert Mode” in the “System” menu, enable the
setting “Show expert settings” and confirm this setting by clicking “Apply”.
3. Open the “System / Network Settings” menu.
4. Click the “IP Addresses” button.
The “IP Settings” page is opened. Here you can make
the settings for the DHCP server.
FRITZ!Box 77
Page 78

Subnetwork
9.4 Subnetwork
By default the option “All computers are located in the
same IP network” is enabled in the FRITZ!Box.
Factory Settings
All computers are located in the same IP network
IP address 192.168.178.1
Subnet mask 255.255.255.0
DHCP server enabled
enabled
If the factory settings were not changed, this setting has the
following effect:
The DHCP server of the FRITZ!Box assigns all of the computers connected with the FRITZ!Box an IP address from the address pool of the DHCP server:
Address pool of the DHCP server: 192.168.178.20 - 200
This means that all of the computers connected with the
FRITZ!Box are located in the same subnet.
Disabling “All computers are located in the same IP network”
If you switch off the setting “All computers are located in
the same IP network”, the interfaces of the FRITZ!Box will
receive their own IP addresses. The following settings are
configured by default:
Interface IP Address Subnet Mask DHCP Server
LAN 1 192.168.178.1 The subnet
LAN 2 like LAN 1
LAN 3 like LAN 1
LAN 4 like LAN 1
WLAN 192.168.182.1
FRITZ!Box 78
mask
255.255.255.0
is set at every
interface.
The DHCP
server is enabled at every
interface.
Page 79

Disabling the Setting “All computers are located in the same IP network”
This the following address pools are available to the DHCP
server:
Interface Address Pool of the DHCP Server at the Interface
LAN 1 192.168.178.20 - 200
LAN 2 like LAN 1
LAN 3 like LAN 1
LAN 4 like LAN 1
WLAN 192.168.182.20 - 200
Computers connected with the FRITZ!Box via different interfaces are located in different subnets.
Interface Address Pool of the DHCP Server at the Interface
LAN 1 192.168.178.0
LAN 2 like LAN 1
LAN 3 like LAN 1
LAN 4 like LAN 1
WLAN 192.168.182.0
Disabling the Setting “All computers are located in the
same IP network”
Proceed as follows to open the DHCP server settings:
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see the section
“Opening the User Interface” from page 30).
2. Click “Expert Mode” in the “System” menu, enable the
setting “Show expert settings” and confirm this setting by clicking “Apply”.
3. Open the “System / Network Settings” menu.
4. Click the “IP Addresses” button.
The “IP Settings” page is opened. Here you can
change the setting “All computers are located in the
same IP network”.
FRITZ!Box 79
Page 80

Troubleshooting
10 Troubleshooting
This chapter provides advice if you are not able to open the user interface
of your FRITZ!Box, if you are having problems with the WLAN connection,
or if you want to change the IP settings on your computer.
10.1 Errors Opening the User Interface
If you see an error message when you open the user interface, work through the following steps to find the source of
the error and resolve the error.
Checking the
Cable Connections
Entering an IP
Address
Obtaining an
IP Address
Automatically
Make sure that all cable connections are plugged in securely.
In the Internet browser, enter the following IP address in
place of “fritz.box”:
192.168.178.1
The IP addresses of the connected computers must be assigned automatically (see “IP Settings” from page 87).
Checking the Internet Browser Settings
Check the settings of the Internet browser:
1. The browser must use the network connection be-
tween the computer and FRITZ!Box when the user interface is opened.
2. The Internet browser must be in online operation.
3. If the Internet browser uses a proxy server, the DNS
name and the IP address of the FRITZ!Box must be entered as exceptions in the proxy settings of the web
browser.
4. The user interface must be allowed to execute CGI
scripts.
The following example explains how to check the settings
of Internet Explorer 6:
FRITZ!Box 80
Page 81

Checking the Internet Browser Settings
Disabling Automatic Dial-up Connections
1. Select the “Connections” settings page under “Tools /
Internet Options...”.
2. In the “Dial-up and Virtual Private Network settings”
section, enable the option “Never dial a connection”.
3. As a final step, click “Apply” and then “OK”.
Configuring Internet Explorer 6 for Online Operation
1. Open the “File” menu.
2. If a checkmark is displayed in front of “Work Offline”,
click this line. The checkmark will be removed and Internet Explorer will switch to online operation.
Entering the DNS Name and IP Address of the FRITZ!Box as Exceptions in the Proxy Settings of the Web Browser
1. Select the “Connections” settings page under “Tools /
Internet Options...”.
2. Click the “LAN Settings...” button in the “Local Area Net-
work (LAN) settings” area, and in the next window, click
the “Advanced...” button in the “Proxy server” area.
3. Under “Exceptions” enter:
fritz.box; 192.168.178.1; 169.254.1.1;
192.168.178.254
and click “OK”.
Allowing Execution of CGI Scripts in the Internet Browser
1. Select “Tools / Internet Options... / Security”.
2. If the “Default Level” button is not available for selec-
tion, the “Medium” security level is already configured, which means that CGI scripts can be executed in
the Internet browser.
Proceed as follows if the “Default Level” button is
available for selection:
3. Select the “Local Intranet” icon and click the “Sites...”
button.
FRITZ!Box 81
Page 82

Checking the Protection Software
4. In the next window, click the “Advanced...” button and
enter in the “Add this Web site to the zone:” field:
fritz.box
5. Disable the option “Require server verification (https:)
for all sites in this zone”.
Checking the Protection Software
Protection software like firewalls and security software can
block access to the FRITZ!Box user interface. Set exceptions
for the FRITZ!Box in all active protection software.
If you would like to exit protection software to test access to
the FRITZ!Box, remove the DSL cable first! After testing, first
start the protection software before reinserting the DSL cable and connecting to the Internet!
Restarting the FRITZ!Box
Restart the FRITZ!Box. Remove the power cable from the
socket. Wait five seconds before reconnecting to the power
supply.
If these points are all in order but you still have no access
to the user interface, work through the following instructions:
Opening the FRITZ!Box User Interface via a LAN Connection
The FRITZ!Box is equipped with a fixed IP address that cannot be changed. FRITZ!Box always can be reached at this IP
address.
The fixed IP address at which the FRITZ!Box can always be
reached depends on the firmware version.
The new fixed IP address is: 169.254.1.1
The older fixed IP address is: 192.168.178.254
The following section describes how to open the user interface in both the new and the old firmware versions. If you
cannot open the user interface using the new fixed IP address, try again using the old fixed IP address.
FRITZ!Box 82
Page 83

Opening the FRITZ!Box User Interface via a LAN Connection
Opening the User Interface Using the New Fixed IP Address
1. Connect the FRITZ!Box and the computer using the red
LAN cable (see the section “Connecting Computer(s)
to a LAN Port” from page 18).
2. Make sure that the computer obtains its IP address auto-
matically. You can check this setting in the computer’s IP
settings (see section “IP Settings” from page 87).
3. Restart your computer.
4. Start your Internet browser and enter FRITZ!Box’s fixed
IP address:
169.254.1.1
The FRITZ!Box user interface opens.
5. Once you have reached the FRITZ!Box user interface
again, you should check the FRITZ!Box settings and
correct them if necessary.
Opening the User Interface Using the Older Fixed IP Address
1. Connect the FRITZ!Box and the computer using the red
LAN cable (see the section “Connecting Computer(s)
to a LAN Port” from page 18).
2. Take note of the computer’s current IP settings.
3. Change the IP settings by entering the following fixed
IP address:
192.168.178.250
4. Start your Internet browser and enter FRITZ!Box’s fixed
IP address:
192.168.178.254
The FRITZ!Box user interface opens.
5. Once you have reached the FRITZ!Box user interface
again, you should check the FRITZ!Box settings and
correct them if necessary.
6. Enter the settings you noted in the computer’s IP set-
tings dialog.
FRITZ!Box 83
Page 84

The WLAN Adapter Cannot Find FRITZ!Box
10.2 The WLAN Adapter Cannot Find FRITZ!Box
If the “FRITZ!Box Fon WLAN 7170” radio network is not
found by the WLAN adapter of a computer, work through
the following steps to find the source of the error and resolve it.
Making Sure that the WLAN Adapter is Ready for Operation
Make sure that the WLAN adapter is ready for operation.
Some of the WLAN adapters installed in notebooks must be
activated by flipping a switch on the notebook.
For questions on the WLAN adapter of your computer,
please contact the manufacturer.
Enabling WLAN in the FRITZ!Box Fon WLAN
If the “WLAN” LED on the FRITZ!Box is not lit up or is flashing, this means that WLAN is not enabled.
Press the WLAN switch on the back panel of the FRITZ!Box.
The “WLAN” LED begins flashing and then lights constantly.
This means that the WLAN function is enabled.
Announcing the Name of the Radio Network
Make sure that the setting “Announce name of the radio
network (SSID)” is enabled in the WLAN settings of the
FRITZ!Box.
1. Connect the FRITZ!Box to a computer using a network
cable. Proceed as described in the sections “Connecting Computer(s) to a LAN Port” from page 18.
2. Start a web browser.
3. Enter fritz.box in the address field.
4. Select the “Settings” menu.
5. Select the “WLAN / Radio Settings” menu and enable
the setting “Announce name of the radio network
(SSID)”.
6. Click the “Apply” button.
FRITZ!Box 84
Page 85

Eliminating Disturbances Caused by Another WLAN Radio Network
7. Remove the network cable and try again to establish a
connection.
Eliminating Disturbances Caused by Another WLAN Radio
Network
If there is another WLAN radio network in the direct vicinity
of your FRITZ!Box, you must ensure that there are at least
five channels between the radio channels used by the two
networks. Otherwise the frequency bands of the two radio
networks will overlap and mutual interference may occur. A
total of thirteen radio channels are reserved for WLAN.
If there is another WLAN radio network in the direct vicinity
of your FRITZ!Box, test a different radio channel for your
FRITZ!Box.
1. Connect the FRITZ!Box to a computer using a network
cable. Proceed as described in the section “Connecting Computer(s) to a LAN Port” from page 18.
2. Start a web browser.
3. Enter fritz.box in the address field.
4. Select the “Settings” menu.
5. Open the “WLAN / Radio Settings” menu.
6. Select a different radio channel from the “Select radio
channel” list.
7. Click the “Apply” button.
8. Remove the network cable and try again to establish a
connection.
FRITZ!Box 85
Page 86

WLAN Connection Is Not Established
10.3 WLAN Connection Is Not Established
Comparing the Security Settings for WLAN
Make sure that the WLAN security settings registered in the
FRITZ!Box agree with the security settings of the WLAN
adapter.
Here is how to view the WLAN security settings of the
FRITZ!Box and print them out.
1. Connect the FRITZ!Box to a computer using a network
cable. Proceed as described in the section “Connecting Computer(s) to a LAN Port” from page 18.
2. Start a web browser.
3. Enter fritz.box in the address field.
4. Select the “Settings” menu.
5. Select the “WLAN / Security” menu.
6. Click the “Apply” button.
A window is displayed with the WLAN security settings. Print out this page by clicking the “Print Page”
button at the upper left of the page.
7. Remove the network cable and try again to establish a
connection.
Testing the WLAN Connection Without Security Settings
Disable the WLAN security settings to test whether a WLAN
connection between the FRITZ!Box and the WLAN adapter is
possible at all.
1. Connect the FRITZ!Box to a computer using a network
cable. Proceed as described in the section “Connecting Computer(s) to a LAN Port” from page 18.
2. Open the “WLAN / Security” menu and select “En-
able Access without Encryption”. As a final step, click
“Apply”.
FRITZ!Box 86
Page 87

Connection via Microsoft WLAN Service Fails with WPA2
This non-secured condition should be used only for
testing, to find out whether a WLAN connection is possible at all.
3. Remove the network cable and try again to establish a
connection.
If the attempt to connect to the WLAN using the non-encrypted connection is not successful either, check the installation of the WLAN adapter and contact the manufacturer of the WLAN adapter if necessary.
10.4 Connection via Microsoft WLAN Service Fails with WPA2
The WLAN connection to FRITZ!Box cannot be established
using the Microsoft WLAN Service (WZC) in Windows XP Service Pack 2.
The required Microsoft patch for WPA2 (IEEE 802.11i) may
not be not installed.
Support for WPA2 in Microsoft WLAN service was not available until the current patch for Microsoft Windows XP Service Pack 2. Install the current patch from Microsoft:
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/893357/EN-US
10.5 IP Settings
The FRITZ!Box is equipped with its own DHCP server. This
means that FRITZ!Box assigns the connected computers
their IP addresses. The connected computers must be configured such that they can receive their IP addresses automatically. The steps for checking and adjusting this option
differ among the operating systems. See the relevant section for your operating system.
If FRITZ!Box is operated in a network, no other DHCP server
may be activated in this network. If you need to operate a
DHCP server, please disable the DHCP feature in the “Advanced System Settings”.
FRITZ!Box 87
Page 88

IP Settings
Obtaining an IP Address Automatically in Windows Vista
Proceed as follows in Windows Vista:
1. Click the “Start” button in the task bar and select
“Control Panel / Network and Sharing Center”.
2. From the “Tasks”, select “Manage network connec-
tions”.
3. In the “LAN or High-Speed Internet” area, select the
LAN connection between your computer and the
FRITZ!Box. Click the right mouse button and select
“Properties”.
4. If the “User Account Control” window is displayed,
click “Continue” in this window.
5. Under “This connection uses the following items”, se-
lect the “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” entry
and click “Properties”.
6. Enable the options “Obtain an IP address automatically”
and “Obtain DNS server address automatically”.
Properties of the Internet protocol (TCP/IP)
7. Confirm your selection by clicking “OK”.
If necessary, repeat steps 5 through 7 for the “Internet
Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6)” as well.
The computer now receives an IP address from the
FRITZ!Box.
FRITZ!Box 88
Page 89

IP Settings
Obtaining an IP Address Automatically in Windows XP
Proceed as follows in Windows XP:
1. Go to “start / Control Panel / Network and Internet
Connections / Network Connections” and double-click
the LAN connection icon of the network adapter connected to FRITZ!Box.
2. Click the “Properties” button.
3. Select “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)” in the list of items
used in this network connection and click “Properties”.
4. Enable the options “Obtain an IP address automatical-
ly” and “Obtain DNS server address automatically”.
Properties of the Internet protocol (TCP/IP)
5. Confirm your selection by clicking “OK”.
The computer now receives an IP address from the
FRITZ!Box.
FRITZ!Box 89
Page 90

IP Settings
Obtaining an IP Address Automatically in Windows 2000
Proceed as follows in Windows 2000:
1. Select “Start / Settings / Control Panel / Network and
Dial-up Connections”.
2. Click to select the LAN connection with the network
adapter bound to FRITZ!Box.
3. Click the “Properties” button.
4. Double-click to select “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)” in
the list of network components.
Properties of the LAN connection of a network adapter
5. Enable the options “Obtain an IP address automatically”
and “Obtain DNS server address automatically”.
The “Obtain an IP address automatically” option
FRITZ!Box 90
Page 91

IP Settings
6. Confirm your selection by clicking “OK”.
The computer now receives an IP address from the
FRITZ!Box.
Obtaining an IP Address Automatically in Mac OS X
In the Mac OS X operating system, proceed as follows to set
the TCP/IP properties:
1. Select the “System Preferences” in the Apple menu.
2. In the “System Preferences” window, click the “Net-
work” icon.
3. In the “Network” window, select the “Built-in Ether-
net” entry from the “Show:” drop-down menu.
4. Switch to the “TCP/IP” settings page and select the
“Using DHCP:” option from the “Configure IPv4” dropdown menu.
5. Click “Apply Now”.
The computer now receives an IP address from the
FRITZ!Box.
Linux
For comprehensive information on the basics of network
configuration in Linux, see, e.g.:
http://
www.tldp.org/HOWTO/NET3-4-HOWTO-5.html
FRITZ!Box 91
Page 92

Removing the FRITZ!Box
11 Removing the FRITZ!Box
This chapter describes how to:
disconnect the FRITZ!Box from the computer
uninstall the FRITZ!DSL software package
remove the printer port
remove the “FRITZ!Box” program group.
11.1 Disconnecting the FRITZ!Box from the Computer
LAN Ports If the computer is connected to one of the LAN ports on the
FRITZ!Box, simply remove the network cable.
If the computer is connected to the FRITZ!Box via a network
hub or switch, remove the network cable between the computer and the network hub or switch.
WLAN If the computer is connected to the FRITZ!Box wirelessly via
WLAN, deactivate the WLAN connection to FRITZ!Box in the
WLAN adapter of the computer.
11.2 Removing the FRITZ!DSL Software
You can remove the FRITZ!DSL software using the Control
Panel of the Windows operating system.
Removing FRITZ!DSL in Windows XP
Proceed as follows:
1. Open “start / Control Panel / Add or Remove Pro-
grams”. Make sure that the “Change or Remove Programs” button is selected in the column at left.
2. Select the “AVM ” entry from the list of “Currently in-
stalled programs”.
3. Click the “Change/Remove” button.
This concludes the removal of FRITZ!DSL.
FRITZ!Box 92
Page 93

Removing the Printer Port
11.3 Removing the Printer Port
The AVM FRITZ!Box printer port is removed using the Control Panel of the Windows operating system.
Removing the Printer Port in Windows Vista
Proceed as follows:
1. Open “Start / Settings / Control Panel / Programs and
Functions”.
2. Select the “AVM FRITZ!Box Printer Port” entry from the
list.
3. Click the “Uninstall/Change” button.
4. Confirm the next query by clicking “Continue”.
This concludes the uninstallation of the printer port.
Removing the Printer Port in Windows XP
Proceed as follows:
1. Open “start / Control Panel / Add or Remove Pro-
grams”. Make sure that the “Change or Remove Programs” button is selected in the column at left.
2. Select the “AVM FRITZ!Box Printer Port” entry from the
list of “Currently installed programs”.
3. Click the “Change/Remove” button.
This concludes the uninstallation of the printer port.
Removing the Printer Port in Windows 2000
Proceed as follows:
1. Open “Start / Settings / Control Panel / Add/Remove
Programs”. Make sure that the “Change or Remove
Programs” button is selected in the column at left.
2. Select the “AVM FRITZ!Box Printer Port” entry from the
list of “Currently installed programs”.
3. Click the “Change/Remove” button.
This concludes the uninstallation of the printer port.
FRITZ!Box 93
Page 94

Removing the Program Group
11.4 Removing the Program Group
Remove the “FRITZ!Box” program group using the Control
Panel of the Windows operating system.
Removing the Program Group in Windows Vista
Proceed as follows:
1. Open “Start / Settings / Control Panel / Programs and
Functions”.
2. Select the “AVM FRITZ!Box” entry from the list of cur-
rently installed programs.
3. Click the “Uninstall/Change” button.
4. Confirm the next query by clicking “Continue”.
This completes uninstallation of the program group.
Removing the Program Group in Windows XP
Proceed as follows:
1. Open “start / Control Panel / Add or Remove Pro-
grams”. Make sure that the “Change or Remove Programs” button is selected in the column at left.
2. Select the “AVM FRITZ!Box” entry from the list of “Cur-
rently installed programs”.
3. Click the “Change/Remove” button.
This completes uninstallation of the program group.
Removing the Program Group in Windows 2000
Proceed as follows:
1. Open “Start / Settings / Control Panel / Add/Remove
Programs”. Make sure that the “Change or Remove
Programs” button is selected in the column at left.
2. Select the “AVM FRITZ!Box” entry from the list of “Cur-
rently installed programs”.
3. Click the “Change/Remove” button.
This completes uninstallation of the program group.
FRITZ!Box 94
Page 95

Configuration and Operation by Telephone
12 Configuration and Operation by Telephone
Many of the FRITZ!Box functions and features can be configured and used over a telephone connected to a FRITZ!Box
extension. Only tone-dialing (dual-tone multifrequency =
DTMF) telephones can be used in configuration and operation. Pulse dialing telephones are not suitable.
The telephone network features can be used only if they are
supported by your telephone network carrier and enabled
on your telephone line.
Entries input on the telephone are confirmed with an acknowledgement tone. Entries made correctly are confirmed
with a positive acknowledgement tone (a single tone of one
second in length). An error, such as an incorrect key sequence, is indicated by a failure tone, an intermittent tone
at intervals of about 0.25 seconds.
For more information on the audio signals, see the section
“Audible Signals” on page 134.
Designation of the Functions and Features
Functions and features whose application has direct effects
on the connection are marked with icons. The icons indicate the connection types with which the function or feature can be used or applied.
Functions and features that have no effect on the connection are not marked.
An overview of all of the icons used in this chapter is presented in the section “Symbols and Highlighting” from
page 7 of this manual.
FRITZ!Box 95
Page 96

Operation by Telephone
12.1 Operation by Telephone
This section describes how you can use the FRITZ!Box features via your telephone keypad.
Shortening the Dialing Procedure
FRITZ!Box automatically recognizes when a number has
been entered, but not until a few seconds after the final
digits are entered.
To shorten the dialing procedure, enter the “#” character after the last digit of a number.
<number>r indicates to FRITZ!Box that the number can be
Enabling/Disabling WLAN
The WLAN function of FRITZ!Box can be switched on and off
using the telephone keypad. This is especially comfortable
when the WLAN function has been switched off. Simply use
your telephone to turn it back on. This means that the
WLAN function can be enabled without having use a wired
connection to open the FRITZ!Box user interface.
dialed immediately, thus shortening the dialing procedure
r96s1s
r96s0s
enables the WLAN function of FRITZ!Box
disables the WLAN function of FRITZ!Box
Do Not Disturb
You can enable the Do Not Disturb function for any telephone connected to FRITZ!Box in the user interface. When
Do Not Disturb is enabled, the telephone will not ring.
Enabling Do Not Disturb Effective Immediately
Use the following combination of keys to enable Do Not Disturb on an extension immediately. Do Not Disturb will remain enabled until you disable it.
r81 <Ext.> s0s immediately enables Do Not Disturb for
FRITZ!Box 96
extension entered as Ext.
Page 97

Do Not Disturb
Enabling Do Not Disturb for a Prescribed Period
On any extension you can enter a Do Not Disturb period
during which the telephone will not ring.
At the extension for which a Do Not Disturb period is to be
configured, define the period during which the phone
should not ring and save your entries. Then enable Do Not
Disturb. Do Not Disturb will be switched on daily at the time
entered in the “Start” field and switched off again at the
time defined in the “End” field.
Example: Do Not Disturb should be configured from 20:00
p.m. until 07:00 a.m. daily. Enter the value 2000 for <Start>
and 0700 for End.
r80<Ext.>s
<Start>s<End>s
r91ss
defines the period for Do Not Disturb at
extension Ext.
saves the settings in the FRITZ!Box
r81<Ext.>s1s enables Do Not Disturb for the defined
period
Disabling Do Not Disturb
r81 <Ext.> s6s disables Do Not Disturb for extension
Ext.
FRITZ!Box 97
Page 98

Alarm
Alarm
The FRITZ!Box includes an alarm clock function. The alarm
clock can be configured individually for each connected
telephone.
Configuring the Alarm for a Telephone
First enter on the telephone the time at which you would
like to be awoken and save this entry. Then enable the
alarm function.
Example: The telephone should ring to wake you at 07:00
a.m. Enter the value 0700 as <Time>.
r881s<Time>s<Ext.>
s
r91ss
defines for the extension Ext. the
time at which the telephone
should ring
saves the settings in the
FRITZ!Box
Enabling/Disabling the Alarm Function
r881ss
r881r
enables the alarm function for all extensions
on which a time was configured
disables the alarm function for all extensions
Selecting the Outgoing Number and the Type of Connection
For outgoing connections you can specify the kind of connection that should be used. For this entry you can use settings already made in FRITZ!Box or circumvent the settings
currently configured in FRITZ!Box.
Defining the Connection Type
You have the option of specifying the type of outgoing connection, independent of the settings configured in the
FRITZ!Box. In this case the dialing rules are suspended for
FRITZ!Box 98
Page 99

Selecting the Outgoing Number and the Type of Connection
the given dialing procedure. To do this, enter one of the following keypad codes before dialing a number on your telephone:
s111r
<number>
s12r
<number>
dials up this connection using the fixed line
dials up this connection using the Internet (Internet number for access 1
s12 P r establishes an Internet connection for a select-
ed Internet number. For “P”, enter the position
of the Internet number in the “List of Internet
Numbers”
Establishing a Connection Using a Selected Internet Number
By placing an Internet Number ID before the number you
can specify which of your Internet numbers should be used
to conduct a telephone call.
If you enter an Internet number in the FRITZ!Box user interface, an ID for the Internet number is created automatically.
The Internet Number ID is displayed in the “Telephony / Internet Telephony” menu of the user interface, in the “Internet Number ID” column of the list of Internet numbers.
<Internet Number ID> <number>
establishes a connection for this call using the
Internet number specified by the <Internet Number ID>
FRITZ!Box 99
Page 100

Making Internal Calls
Making Internal Calls
All calls conducted between telephones connected to the
FRITZ!Box Fon WLAN 7170, be they analog or ISDN/DECT
phones, are internal telephone calls. These calls are free of
charge.
Dialing Internal Calls with Automatic Outside Dialing
N
Pick up the handset. You hear the external dial
tone immediately, since the extension is set for
automatic outside dialing.
R or ss Press the Hold button, or press the asterisk key
twice. You now hear the internal dial tone.
M1 or 2
or
M50
or
M5 MSN r
Dial “1” or “2” to call the connected analog
telephones.
Dial “50” to call all of the ISDN telephones
for which no number is configured.
Dial an MSN to call the ISDN telephones
whose numbers are configured as this MSN.
Dialing Internal Calls without Automatic Outside Dialing
N
M1 or 2
or
M50
or
M5 MSN r
Pick up the handset. You hear the internal dial
tone.
Dial “1” or “2” to call the connected analog
telephones.
Dial “50” to call all of the ISDN telephones
for which no number is configured.
Dial an MSN to call the ISDN telephones
whose numbers are configured as this MSN.
FRITZ!Box 100
 Loading...
Loading...