Page 1

Configuration of an SQL server
as an index data base
for quarantines in
Avira AntiVir Exchange
Support
August 2009
www.avira.com
Errors in design and contents cannot be excluded
© Avira GmbH
Page 2

Content
INTRODUCTION................................................................................................................................................. 2
ADVANTAGE OF THE JET-DB USED BY DEFAULT ................................................................................................ 2
DISADVANTAGE OF USING AN SQL SERVER ........................................................................................................ 2
EXAMPLES .......................................................................................................................................................... 2
ERROR TREATMENT IN QUARANTINES.................................................................................................... 3
TYPICAL ERROR IN CASE OF SQL SERVERS ......................................................................................................... 3
SUPPORT OF SQL SERVERS ................................................................................................................................. 3
CONSEQUENCES .................................................................................................................................................. 4
CONFIGURATION OF AN SQL SERVER QUARANTINE .......................................................................... 4
CONFIGURATION OF THE SQL-SERVERS ............................................................................................................. 4
CREATION OF THE SQL DATA BASE .................................................................................................................... 5
CREATION OF THE SQL USER .............................................................................................................................. 7
CREATION OF THE TABLES WITH SCRIPT.............................................................................................................. 7
HOW TO CHECK PERMISSIONS OF THE SQL-BASED USER ..................................................................................... 9
DISPLAY OF THE PERMISSIONS .......................................................................................................................... 10
CONFIGURATION OF THE QUARANTINE IN ANTIVIR EXCHANGE ................................................ 11
CONFIGURATION OF THE DATABASE CONNECTION ............................................................................................ 11
THE QUARANTINES ........................................................................................................................................... 13
SELECTION OF THE QUARANTINE IN THE JOB ADVANCED SPAM FILTERING ....................................................... 14
A TIP FOR THE DISPLAY OF VERY LARGE QUARANTINES............................................................... 17
1
Page 3

Introduction
A locally installed SQL server can be used as an index data base for the quarantine
in AntiVir Exchange 7.
The usually used Jet-DB sends warnings in case 80 % of 1 GB data size is reached
because problems are caused by MDB files which are larger than 1 GB. A larger
amount of index data can be kept with an SQL server: either more index data per
email (body extraction, job reports) or more emails (that means a longer period).
Advantage of the JET-DB used by default
The Jet-DBs are really easy to administer and very stable.
Usually the administrator has nearly no work with it. AntiVir Exchange creates this
data base if required, cleans it and can extend the DB schema automatically in case
of a version change.
Disadvantage of using an SQL server
In case of the SQL server the administrator has to do a lot manually. This can be
difficult to users without a special knowledge about the SQL server. Therefore we
recommend our customers to try a solution on the basis of the Jet DB first.
Examples
• 800.000 emails fit into the index on a gateway in case of a simple report of
incoming emails from the outside (address filter job, which writes everything into a
quarantine report without body extraction and job report). That means you can
save the emails for months (about 10.000 emails per day).
• Frequently SPAM-HIGH quarantines cause problems as the spam reports are
quite long and only a few emails fit into the index. Therefore the emails are
already deleted after one week. In case a recipient should miss an email you can
send it again out of the report (view the previous point).
• SPAM-MEDIUM Emails (also with a long spam report) have to be saved for more
time. They are more likely to be required. It is also possible that summaries with
links for the access to these emails are configured. But there are very few emails
in the SPAM-MEDIUM sector: usually a thousand times less than in SPAM-HIGH,
so that the problem of large index DBs does not occur.
• But there are also customers who already use SQL servers and have a profound
knowledge about them. These customers are also able to handle SQL
quarantines as usually everything works properly.
2
Page 4

Error Treatment in quarantines
As a matter of principle there is a setting in every quarantine of AntiVir Exchange
which is called "Mission Critical".
This setting influences the reaction of the jobs in case of errors which occur when an
email is moved to quarantine.
This is not specific to SQL server quarantines. In case of SQL server quarantines this
could cause unwanted effects as errors might occur more frequently.
Typical error in case of SQL servers
• The SQL server service is not active or another administrative problem prevents
the access to the data base (authorizations, firewall, locks, timeout).
• The customer uses SQL express and the limit for the file size of the data base is
reached. The data base does not work anymore without warning.
• The SQL server doesn’t run locally on the email server but on another machine
and there are network problems.
Support of SQL Servers
AntiVir Exchange does only support SQL servers which are locally installed on the
Exchange Server concerning the quarantines. Therefore the third error case is
avoided.
It is technically possible to run the SQL server on another computer. This can be
accepted in very special cases.
Without the "Mission Critical" settings in the quarantine (this is the default setting)
the job will ignore the error of the quarantine.
A distress call is sent via email to the administrator and an entry is written into the
event log. That is all.
The email is not in the quarantine later. This means that the email is lost in the worst
case (e.g. the job action is “move to quarantine, than delete email”).
In case of an infected email that wouldn’t be of any harm.
A “Mission Critical” quarantine will activate an error in the job in case of quarantine
errors. The job is cancelled after that. You find also in the job a setting "Mission
Critical" which defines the following procedure.
In case the job is not "Mission Critical" (most jobs are not "Mission Critical" by
default, except for the virus scanner job), the job deactivates itself when such errors
occur frequently.
Distress calls are sent via email to the administrator and event log entries are written.
(The job will activate itself again. But the admin has to live without it for a certain
time.)
A quarantine which cannot be reached deactivates the job. In case of a virus job this
can be dangerous.
3
Page 5

In case the job is also "Mission Critical" the quarantine error will completely cancel
the processing of the email. (The reason is: a "Mission Critical" job has to be finished.
Otherwise the email cannot go on.)
The email is moved to the badmail quarantine (By the way: this badmail
quarantine cannot be moved to the SQL server). As long as the SQL server is not
reachable all emails are blocked and moved to badmail (and can be proceeded from
there afterwards).
Such a setting is quiet strict.
Consequences
Thus the consequences of a non reachable quarantine data base are between the
extremes “emails get lost” and “no emails arrive”. Therefore it is essential that the
quarantines are working properly and the local Jet DBs are here really important.
Configuration of an SQL server quarantine
The configuration of the quarantine data base is proceeded as follows:
1. Configuration of the necessary SQL user and the quarantine data base
2. Configuration of the quarantine in AntiVir Exchange
Configuration of the SQL-Servers
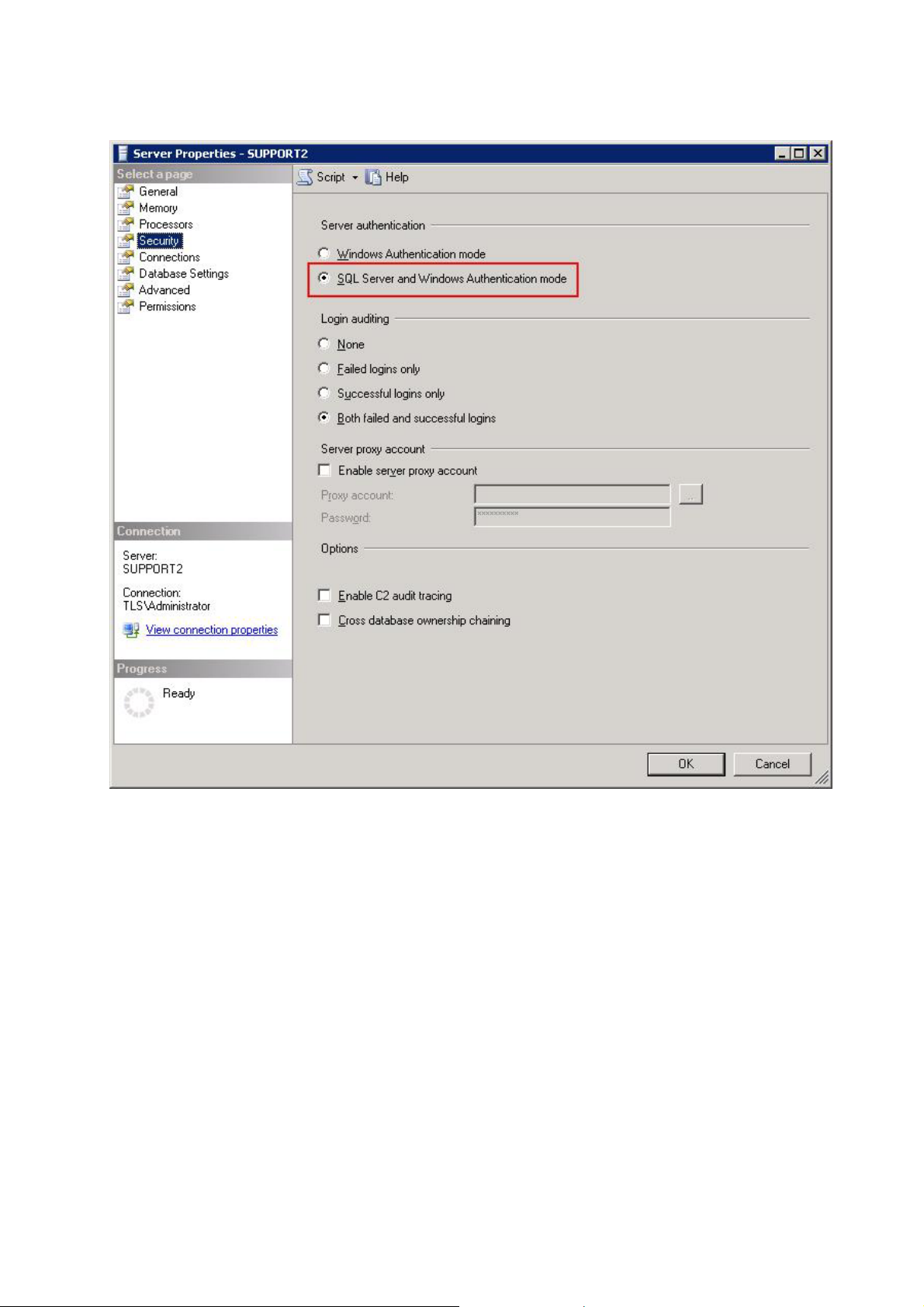
We need a user and a data base with the tables in the SQL server.
The user cannot be a Windows user. It has to be an SQL user. (The SQL server calls
that "Mixed Mode"), as the AntiVir Exchange service runs as a local system and
doesn’t work under a user context. User name and password are handed over in
case of activation.
4
Page 6
Creation of the SQL data base
The SQL administrator creates the data base. The data base name should be an
easy short string without blanks or something like that. This is important as the
quarantine is created accordingly and the same string is used there as folder name
for the saving of the quarantine emails. (view underneath)
5
Page 7

6
Page 8

Creation of the SQL user
Creation of the tables with script
Afterwards there is a script QUARANTINE.sql in the support folder (Avira/AntiVir
Exchange/Support) which creates the necessary tables, links and stored procedures
in the data base. In the QUARANTINE.sql all details are described.
An SQL administrator knows how to handle that. The script can be copied into the
management console of the SQL server and started there.
7
Page 9

8
Page 10

How to check permissions of the SQL-based user
The SQL user needs the authorization to add, change and delete entries in the data
base table. AntiVir Exchange won’t proceed any schema changes of the table. That
is why the user doesn’t need these rights at the moment. In case changes of the
schema should be necessary the SQL admin has to do that manually during the
update of AntiVir Exchange.
9
Page 11

Display of the permissions
10
Page 12

Configuration of the quarantine in AntiVir Exchange
There are two points in AntiVir Exchange where settings concerning the SQL
quarantine have to be done.
- in the data base connection
- and in the quarantine itself
Configuration of the database connection
The data base connection consists of the ADO connection string of the already
created SQL user with its password and of a timeout setting.
The ADO Connection String has to be taken into consideration. It defines the
access to the data source with ADO.
The Default is:
Provider=SQLOLEDB;Initial Catalog=[DBCatalog];Data Source=[Server];User
ID=[ADOUser];Password=[ADOPwd]
and works for locally installed SQL server.
11
Page 13

An example:
Provider=SQLOLEDB;DataSource=SUPPORT2\AVQUAR;Trusted_Connection=No;I
nitial Catalog=[DBCatalog]; UserID=[ADOUser];Password=[ADOPwd];Connect
Timeout=120;
As the server SUPPORT2 is very slow and the default timeout is not enough for the
creation of a connection we increased this value a bit.
In the beginning you can work with default values. In case there should be any
problems about the reachability of the data base this value can be slowly increased.
The variables [ADOUser] and [ADOPwd] refer to the corresponding settings on the
same site. This prevents that the password is saved in clear test. But the user and
the password can also be written directly into the ADO-string. The variable
[DBCatalog] shows the data base which has to be used.
AntiVir Exchange enters here the corresponding value after the quarantine was
created, view underneath.
The variable allows you to use the same data base connection for several
quarantines. The variable [Server] is replaced by the local server name. As you can
see in the second example you can also enter the SQL instance in a more specific
way.
12
Page 14

The Quarantines
In order to create an SQL quarantine you always have to create a “new” quarantine.
You cannot change existing (Jet DB-) quarantines into SQL quarantines afterwards
(but you can create a new SQL quarantine and then copy the saved emails from the
old quarantine in to the new SQL quarantine via drag & drop.)
13
Page 15

There is one “trick” about it – the chosen folder name of the new quarantine is used
at the same time for the variable [DBCatalog] of the SQL quarantines. You enter the
data base name as folder name (here "SQL_SPAM_HIGH") and choose the above
created database connection. The "Name" above this is only a display string and can
be chosen individually.
After having pressed OK, you can’t change the folder name anymore, so pay
attention.
Certainly you can enter the data base name also directly into the ADO connection
string without using the [DBCatalog] variable. But doing so you would have to
configure a data base connection for every quarantine.
Now you can use the new quarantine in a job. Thus you can see on the screen if it
works properly.
Selection of the quarantine in the job Advanced spam filtering
As we only want to use the „SPAM-HIGH“ quarantine via the installed SQL index the
corresponding job has to be configured.
For that purpose we use the job „Advanced spam filtering“ and the „Action“ -> High.
14
Page 16

Now we can choose the “Action” where our „SPAM-HIGH“ quarantine has to be
moved. We select the already created quarantine „avquar“ which is used by our SQL
server.
15
Page 17

At the end we should not forget to save the entered configurations.
Finished.
16
Page 18

A tip for the display of very large quarantines
It is possible that slow systems need a certain time to show the entries after the
double click on a very large quarantine.
It can help to set the filter of the selected quarantine to “Today” with the right mouse
button before you double click on the quarantine.
17
 Loading...
Loading...