Page 1

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
CHAPTER▼ ONE
GETTING TO KNOW THE BASICS
This chapter introduces the features and components of the computer.
1-1
Page 2

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
Performance Features
Hig
Ad
Large LCD Display
Expandability
Swapp le Device Bay
Built-in Multifunction Card Reader
Communication Features
Fir ire (IEEE1394 / 1394a) and USB2.0 ports
h Performance Processor
The noteb
technologi
An on-boa
graphic pe
engine, wh
The co arge 15.4-inch (wide aspect ratio) TFT high-resolution display panel for clear text
and brillian
The sy able hard disk drive and 2 DDR SDRAM sockets for expansion, allowing the user to
easily incr
The sw er to add an additional hard disk drive module for increased storage capacity.
Some system comes with a multiple card reader, which supports SD, MS, MMC Card formats. This allows user to
acces able today.
The sy tem provides built-in Ethernet network adapter for local network and 56K modem.
In addition to a full array of built-in I/O por
bandw peripheral devices.
ook PC is equipped with a powerful Intel processor of the latest sub-micron process, processor
es, and high bus bandwidths.
vanced Graphic Engine
rd ATI Mobility Radeon 9600 Pro video processor with dedicated 64MB frame buffer gives excellent
rformance. The advanced graphic chip also incorporates a hardware-based motion-compensation
ich gives you smooth MPEG video playback. 3D graphics capability also adds realism to PC games.
mputer is equipped with a l
t colors.
stem offers upgrade
ease the storage and system capacities as the need arises.
ab
appable device bay allows us
s a wide array of portable memory devices avail
s
ew
ts, the computer offers IEEE1394 for ultra high-speed connection to high
idth digital video devices and USB2.0 ports to connect to any USB-based
Wireless LAN
The internal Wireless LAN module allows your notebook to connect wirelessly to other 802.11-enabled
systems, devices, or network.
1-2
Page 3
■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
System At A Glance
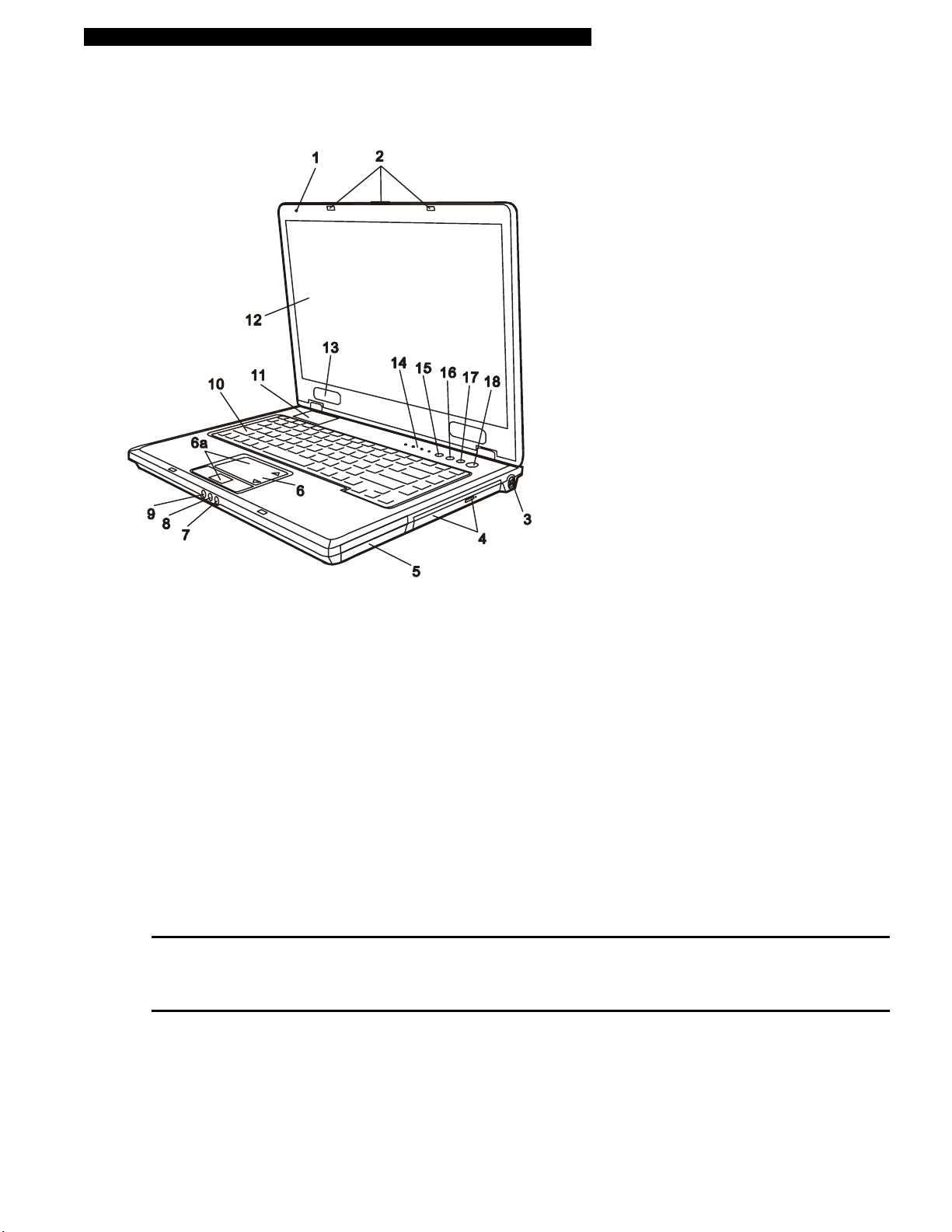
Front View
1. Built-in Microphone
The built-in microphone records sound.
2. LCD Latch
The LCD latches lock / unlock the LCD panel.
3. Power Jack (DC-in)
The DC-out jack of the AC Adapter connects here and powers the computer.
4. Optical Drive and Disk Eject Button and Manual Eject Key Hole
If your computer comes with the Combo drive, DVD-RW, DVD+RW, or DVD-Dual drive, you may save data
onto a CD-R / CD-RW or DVD RW disc. Press the eject button to eject the disk tray. The manual eject
keyhole allows you to manually eject a jammed disk.
Note:
The optical drive resides in the Swappable Device Bay. Additionally, you may also purchase an optional hard drive module to
be used in this bay.
5. Battery Pack
The battery pack is a built-in power source for the notebook.
1-3
Page 4
■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
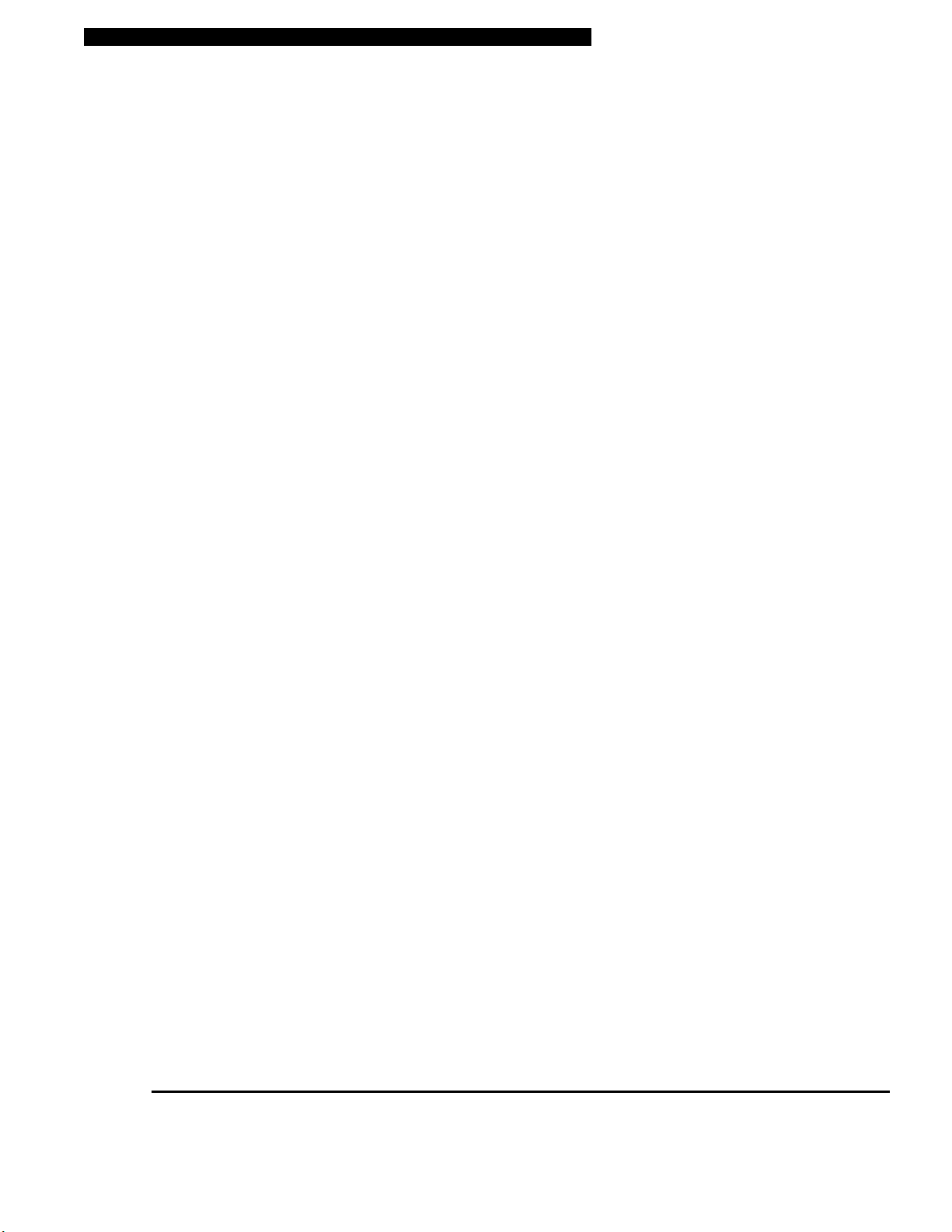
6. Touch Pad with Page Up / Down Function
The touch pad is a built-in pointing device with functions similar to a mouse. Use the Page Up or Down key
to move one page up or down in Windows.
6a. Touch Pad Scroll Bar
The scroll bar works similar to the scroll wheel in the mouse. Use the bar to maneuver long documents in
Windows.
7. Microphone Jack
The microphone jack (3.5-mm diameter) is where you connect a microphone.
8. Audio Line-in Jack
The Audio Line-in jack (3.5-mm diameter) is where you connect an external audio input source such as a
CD Player.
9. Stereo Headphone / SPDIF-out Jack
The stereo headphone jack (3.5-mm diameter) is where you connect the headphones or external speakers.
Alternatively, you may connect the SPDIF output to an external DTS, AC3, or PCM sound processor /
decoder in your home stereo system.
10. Keyboard
The keyboard is used to enter data. It has an embedded numeric keypad and cursor control keys. (See
Keyboard Section for details.)
11. Ventilation Grill
The fan grill is where air is exchanged to dissipate the internal heat. Do not block this airway completely.
12. LCD Display
The panel is where the system content is displayed.
13. Built-in Stereo Speakers
The built-in speakers output the sound in stereo.
14. LED Status Indicator
The LED Status indicators reveal the locking/unlocking of certain key functions - numeric keypad
enable/disable, cap lock, and scroll lock - and HDD and optical drive status. (See the LED Status Indicator
Section for details.)
15. Email Quick Key
The Email Quick Key launches the MS Outlook Express in Windows XP or 2000.
16. Internet Quick Key
The Internet Quick Key launches the Internet Explore automatically in Windows XP or 2000.
1-4
Page 5

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
17. Wireless On/Off Quick Key
When Wireless icon (key top) appears green, the wireless LAN function is enabled. Press the quick key to
disenable this function.
18. Power / Suspend Button
The power/suspend button turns the notebook on and off and it also acts as a system suspend key. Press
momentarily to turn on the system. Press and hold for at least 3~4 seconds to turn off the system. How this
key behaves can be defined in [Start > Settings > Control Panel > Power Options > Advanced] menu. Press
the power / suspend button again to return from the suspend mode. (See Chapter 3 for more details on
system suspend function.)
1-5
Page 6
■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
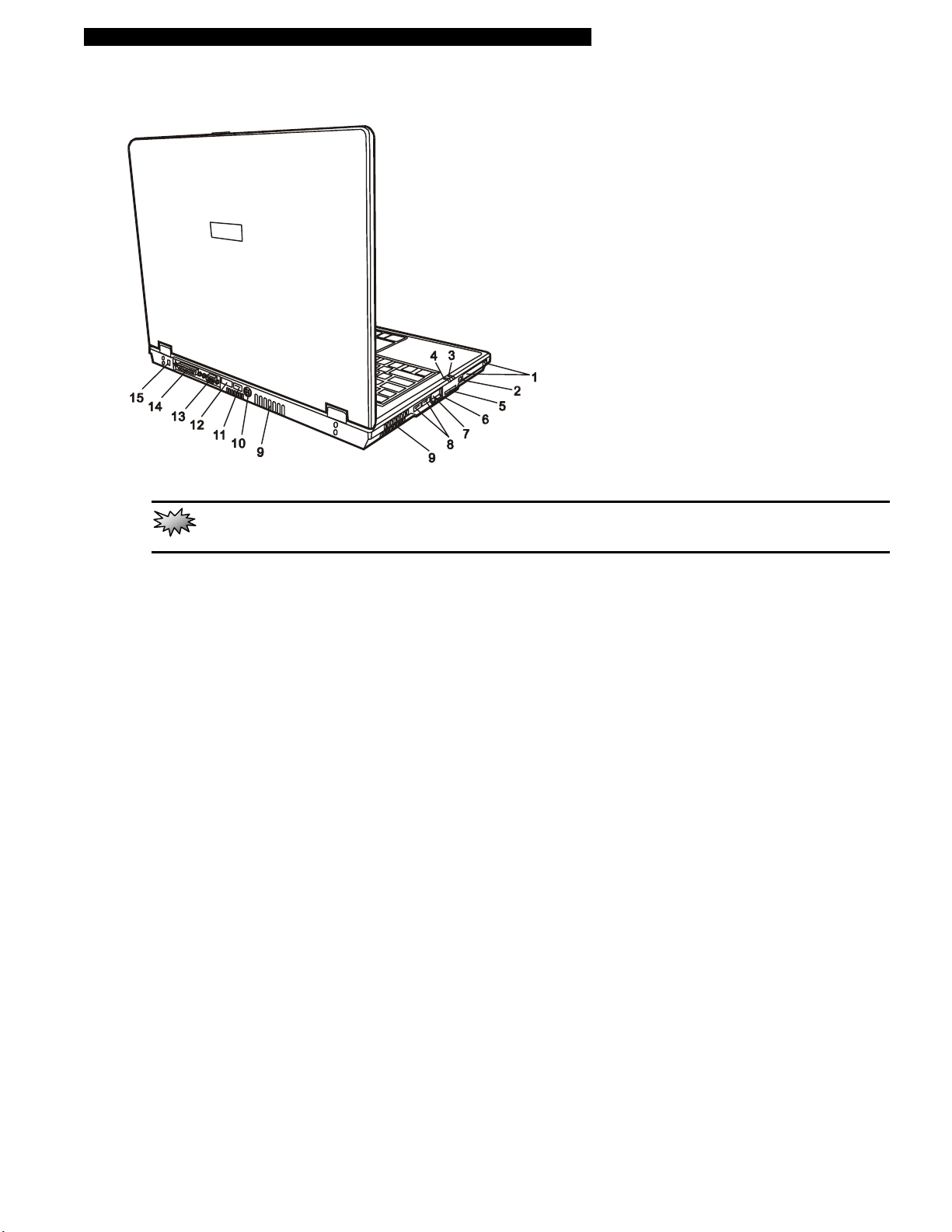
Rear View
Warning:
Do not place any heavy objects on the top of notebook. This may damage the display
1. PC Card Slot (Type II PCMCIA) and Card Eject Button
The slot is where PC Card (Type II PCMCIA) is inserted. Press the eject button to release the PC Card.
2. Firewire / IEEE1394 / 1394a Port
This is a high-speed serial data port. You may connect any Fire-wire-ready device to this port.
3. Suspend Status LED
Flashing green light indicates the notebook is in suspend mode. (See the LED Status Indicator Section for
details.)
4. Battery Status LED
The multi-color LED indicates the battery status of the notebook. (See the LED Status Indicator Section for
details.)
5. Multifunction Card Reader
The built-in multifunction card reader allows you to access portable memory devices such as SD, MS, and
MMC Cards.
6. Ethernet / LAN Port
The port connects to a network hub via the RJ-45 cable and also conforms to 10/100Base-TX transmission
protocol.
7. Modem Port
This is where you plug the phone jack (RJ-11) for fax/modem functions.
1-6
Page 7
■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
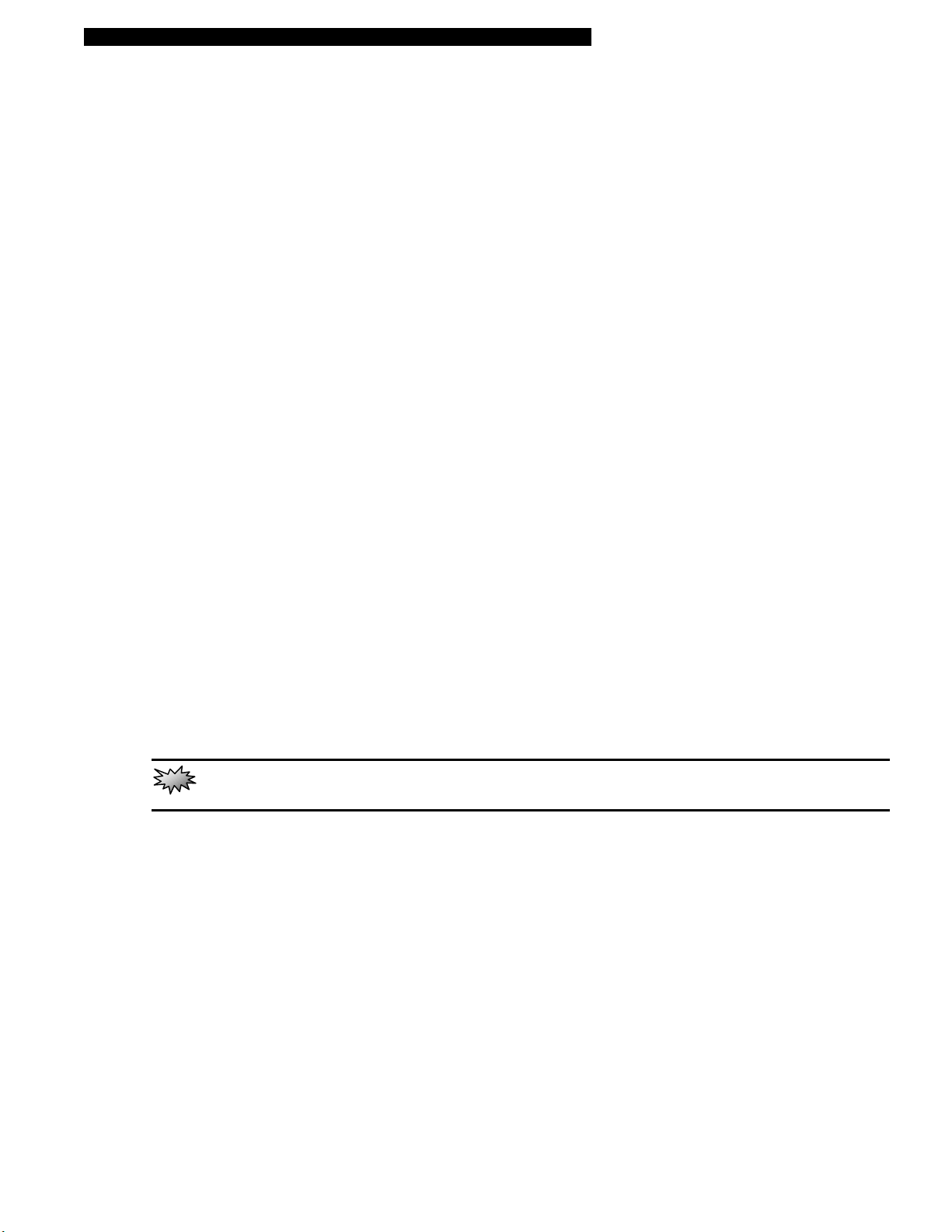
8. USB2.0 Port (x2)
The Universal Serial Bus (USB2.0-compliant) port allows you to connect a wide variety of devices to your
computer at a rate of up to 480 Mbps. This port conforms to the latest USB2.0 plug-and-play standards.
9. Ventilation Grill
The fan grill is where air is exchanged to dissipate the internal heat. Do not block this airway completely.
10. TV (S-Video) Port
The S-Video port permits you to redirect the screen output to a television set or any analog video playback
device. This TV Port is Macrovision-compliant; when DVD movie is played, the output is scrambled to
prevent analog recording.
11. USB2.0 Port (x1)
The Universal Serial Bus (USB2.0-compliant) port allows you to connect a wide variety of devices to your
computer at a rate of up to 480 Mbps. This port conforms to the latest USB2.0 plug-and-play standards.
12. Infrared Port
Infrared Data Association (IrDA) compliant serial infrared port enables 4Mbps (FIR mode) wireless data
transfer with IrDA 1.1-compatible external devices.
13. External VGA Port
The 15-pin VGA analog port is for connecting the external CRT monitor or projector.
14. Parallel Port
The 25-pin parallel port connects to any parallel-port devices such as a printer.
15. Kensington Lock Key Hole
A Kensington-type security lock latches to this keyhole for anti-theft purpose.
Warning:
Do not block the Fan Grill outlet. Place the machine on hard surface only. The bottom case may get very hot.
1-7
Page 8
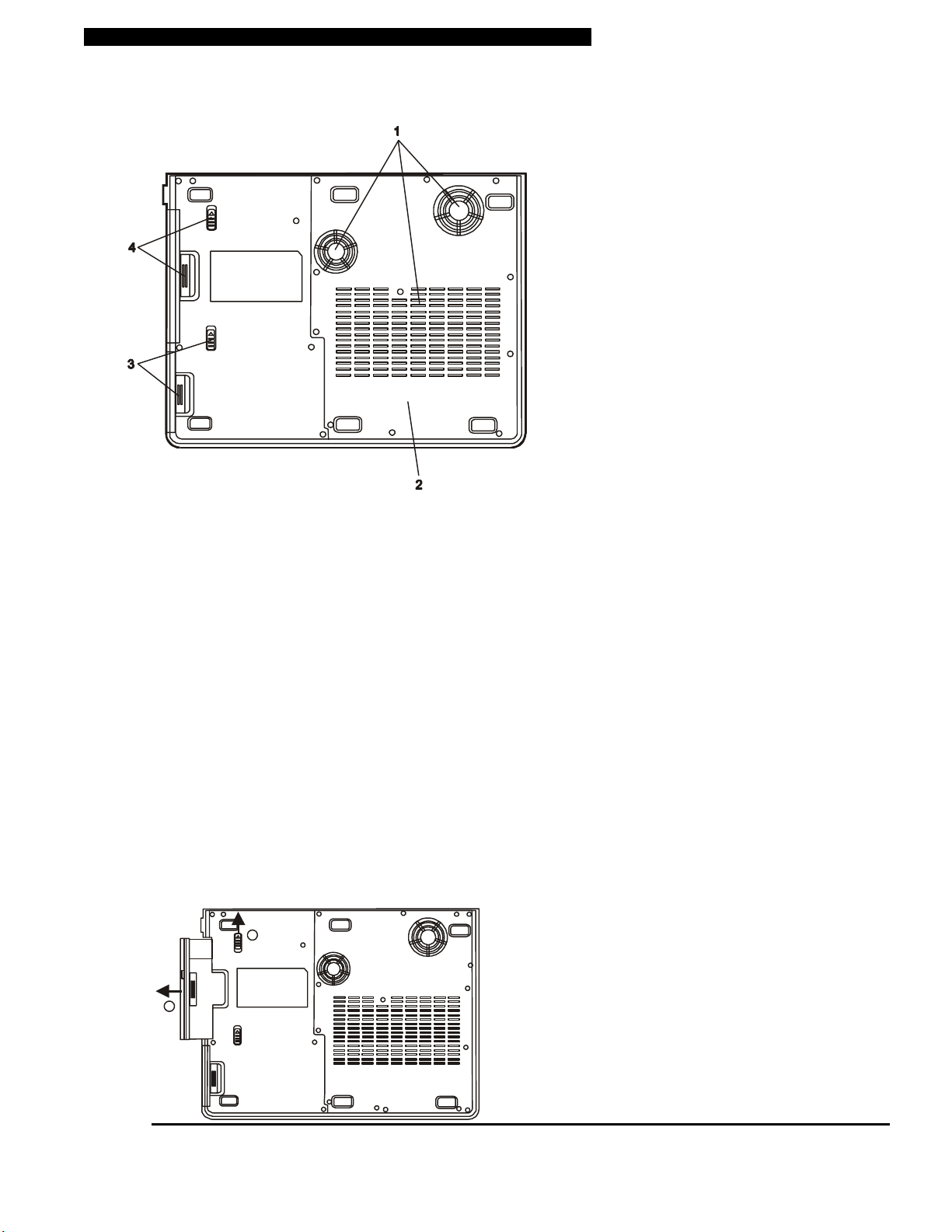
■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
Bottom View
1. Ventilation Grill
The fan grill is where air is exchanged to dissipate the internal heat. Do not block this airway completely.
2. System Device Cover
The system’s processor with cooler assembly, hard drive, wireless LAN card, and DDR memory module are
located under the case cover. The hard disk drive and system memory can be upgraded to a larger capacity.
(See Chapter 4 for instructions on a hard drive upgrade.)
3. Battery Pack and Battery Latch
The battery pack is a built-in power source for the notebook. Slide the battery latch to release the battery
pack.
4. Swappable Device Bay and Latch
Push the latch and pull on the drive hard case to remove the swappable device.
1
1-8
2
Page 9

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
Note:
The optical drive resides in the Swappable Device Bay. Additionally, you may also purchase an optional hard drive module to
be used in this bay.
1-9
Page 10
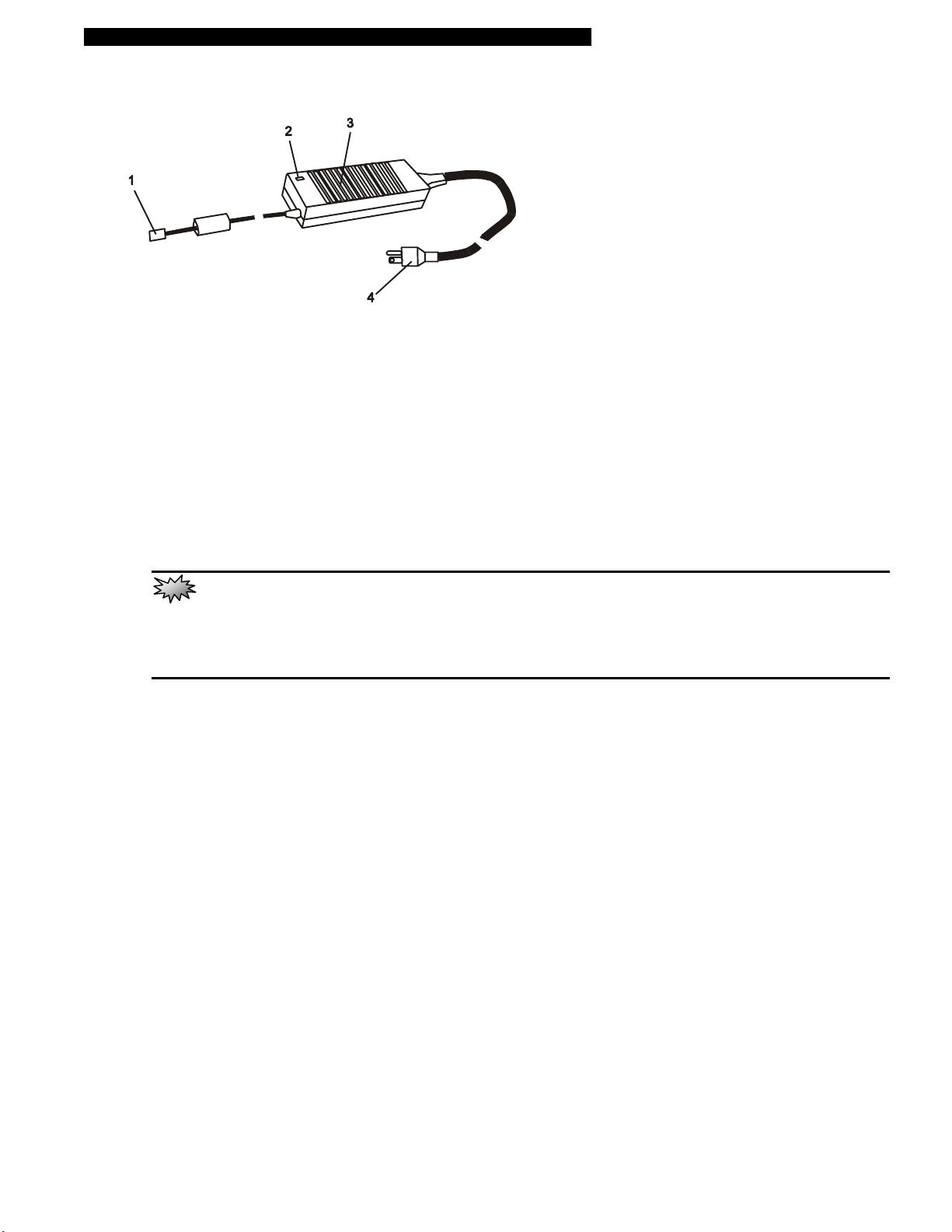
■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
AC Adapter
1. DC-out Connector
The DC-out connector docks to the power jack (DC-in) on the computer.
2. LED Lamp
The LED lamp appears green when the unit is plugged into a valid AC source.
3. Adapter
The adapter converts alternating current into constant DC voltage for the computer.
4. AC Plug
The AC plug plugs to the AC wall outlet.
Warning:
sensation on any of the computer’s metal parts such as the I/O ports. This is caused by leakage current when the AC adapter is not
properly grounded (via the ground pin). However, the amount of leakage current is within the safety regulation and is not harmful to
human body.
Make sure you are using a standard 3-prong AC wall socket with a ground pin. If not, you may feel a slight tingling
1-10
Page 11
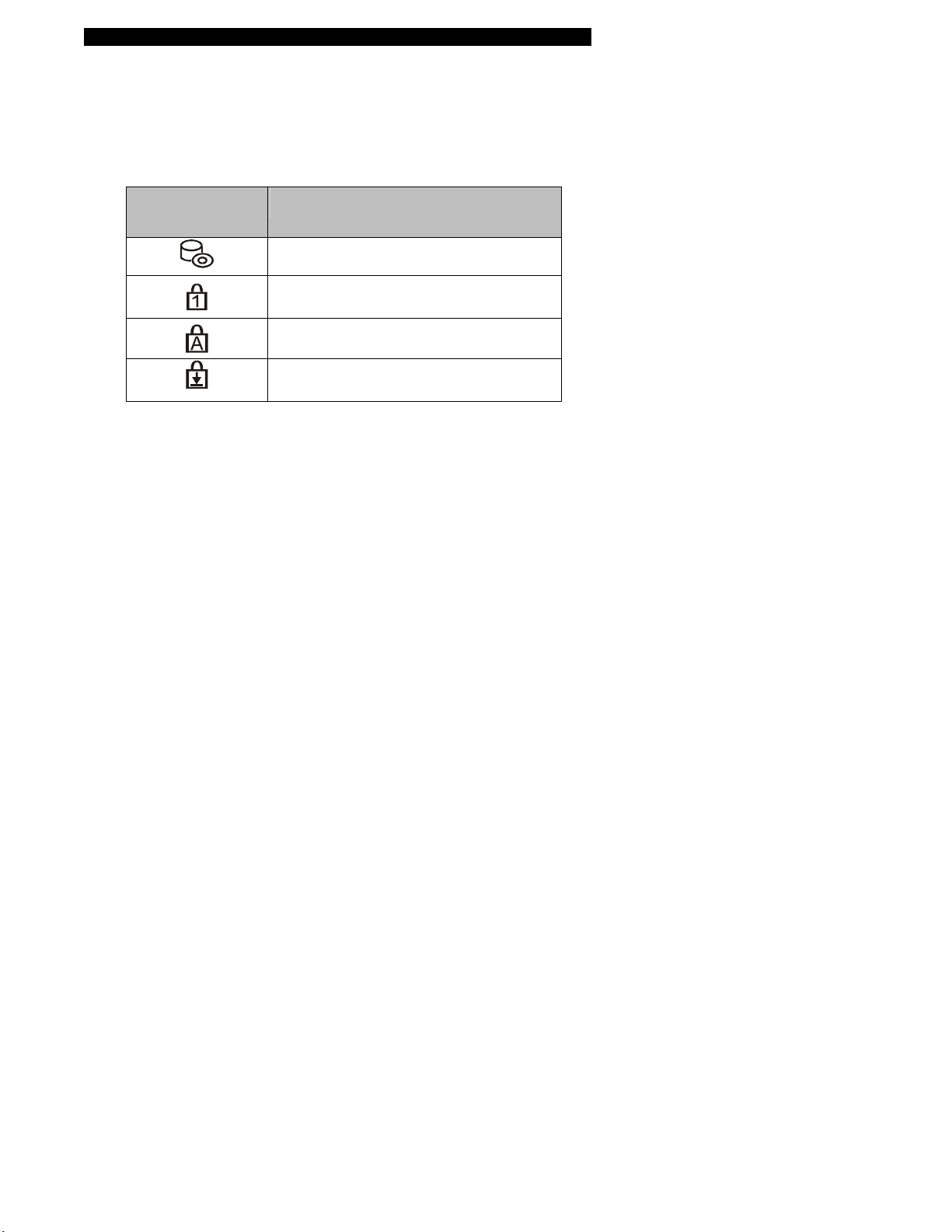
■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
LED Status Indicator
The LED Status Indicator displays the operating status of your notebook. When a certain function is
enabled, an LED will light up. The following section describes its indication.
System Status Indicator
LED Graphic
Symbol
Indication
Green light indicates the hard drive
and/or optical drive is being accessed.
Green light indicates the numeric keypad
is activated.
Green light indicates the cap-lock is
activated.
Green light indicates the scroll-lock is
activated.
1-11
Page 12

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
Power Indicator
LED Graphic
Symbol
Indication
Persistent green light indicates Power On.
Light-off indicates the notebook is in
Power Off mode.
Blinking green light indicates the battery
power is currently low.
Blinking orange light indicates the battery
is being charged.
Persistent green light indicates the
notebook is neither in Power Saving mode
nor in suspend mode.
Blinking green light indicates the notebook
is in suspend mode.
Light-off indicates the notebook is in
Power Saving mode.
1-12
Page 13
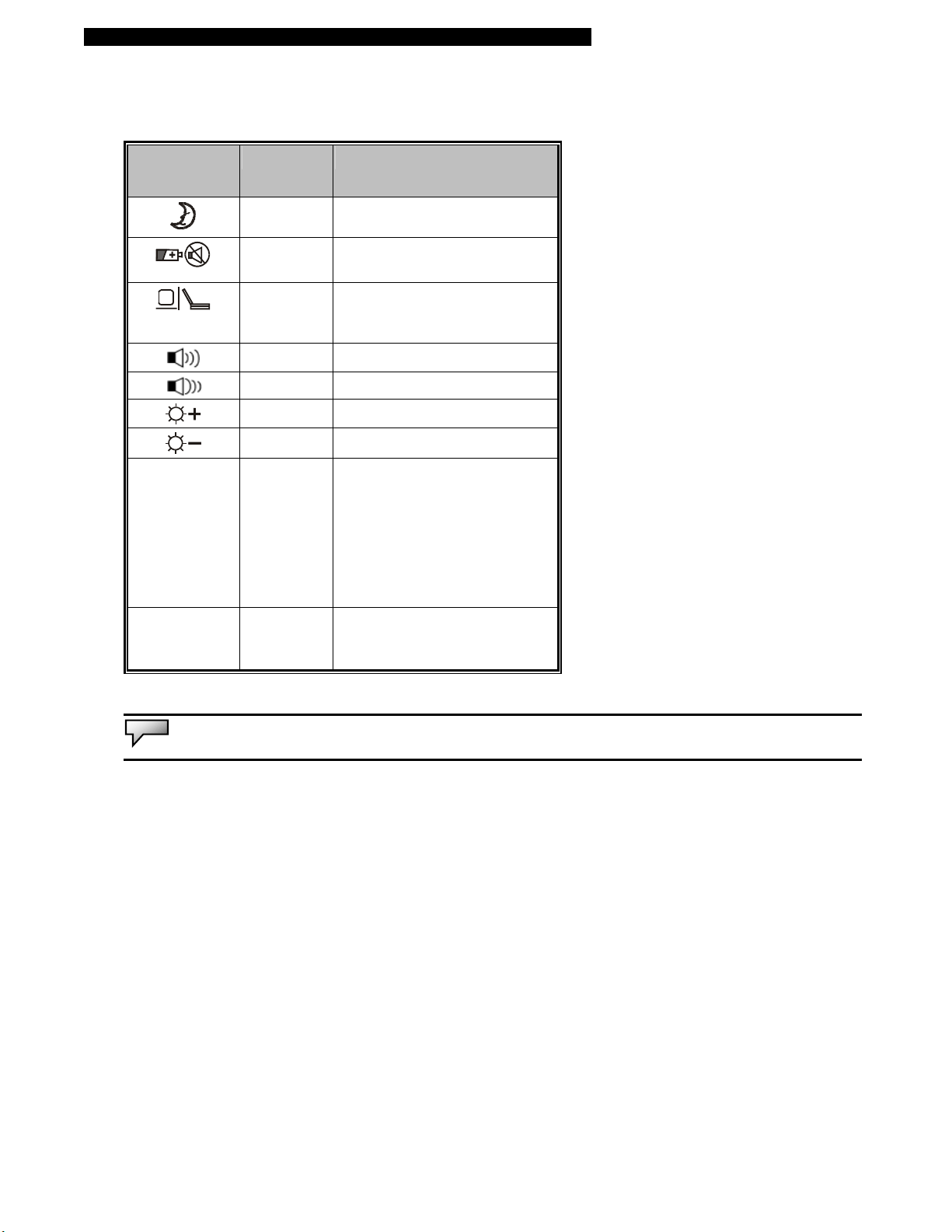
■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
Keyboard Features
Function Keys (Quick Keys)
Graphic
Symbol
Scroll Lock
Action System Control
Fn + F1 Enters Suspend Mode.
Fn + F3 Turns Battery Warning Beep on
Fn + F4 Changes Display Mode:
Fn + F5 Turns Speaker Volume up.
Fn + F6 Turns Speaker Volume down.
Fn + F7 Increases Display Brightness.
Fn + F8 Decreases Display Brightness.
Num Lock
or off.
LCD-only, CRT-only and
LCD&CRT.
Enables the embedded keypad
to work in numeric mode. The
keys act like numeric keypads
in a calculator. Use this mode
when you need to do a lot of
numeric data entry. An
alternative would be to connect
an external numeric keypad.
Press the Scroll Lock key and
then press ↑or ↓to move one
line up or down.
Note:
For various system controls, press the Fn (Function) key and the Fx key simultaneously.
1-13
Page 14

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
/
Windows Keys
Your keyboard also has two Windows keys:
1. Start Key
This key allows you to pull up the Windows Start Menu at the bottom of the taskbar.
2. Application Menu Key
This key brings up the popup menu for the application, similar to a click of the right mouse button.
Embedded Numeric Keypad
Press Num Lock to enable the embedded numeric keypad. The numbers are printed in upper right corner of
a key, in a color different from the alphabets. This key pad is complete with arithmetic operators (+, -, * , /).
Press Num Lock to revert to normal character keys.
Num
Lock
789
456
123
0
*
-
+
.
Enter
1-14
Page 15
■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
Touch Pad with Page Up / Page Down Function
The built-in touch pad, which is a PS/2-compatible pointing device, senses movement on its surface. As you
move your fingertip on the surface of the pad, the cursor responds accordingly.
The following items teach you how to use the touch pad:
1. Move your finger across the touch pad to move the cursor.
2. Press buttons to select or execute functions. These two buttons are similar to the left and right buttons on a
mouse. Tapping on the touch pad twice produces is similar to clicking the left button of a mouse.
3. Press Page Up / Down button to move up or down a page.
Function Left Button Right
Execution Click twice
quickly
Selection Click once Tap once
Drag Click and hold
Access
Context
Menu
Move One
Page Up or
Down
to drag the
cursor
Click
Click upper portion
Button
Tap twice (at the same
Tap twice quickly and on
once
Tips on Using the Touch Pad:
1. The double-click speed is timed. If you double-click too slowly, your notebook responds as if you
single-clicked twice.
2. Keep your fingers dry and clean when using the touch pad. Also keep the surface of touch pad clean and
dry to prolong its life.
3. The touch pad is sensitive to finger movements. Hence, the lighter the touch, the better the response.
Heavy touch does not produce better response.
Page Up /
Down Button
to move up a page
Click lower portion
to move down
Equivalent Tapping
Action
speed as double-clicking
the mouse button)
the second tap hold
finger to the touch pad
to drag the cursor
1-15
Page 16
■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
Graphic Subsystem
Your computer uses a high performance 15.4-inch (wide aspect ratio) active matrix TFT panel with high
resolution and multi-million colors for comfortable viewing. The ATI Mobility Radeon 9600 Pro video graphics
accelerator, which is Microsoft DirectX 9 compatible, performs graphic rendering at a lighting-fast speed.
Adjusting the Display Brightness
The notebook uses special key combinations, called hot keys, to control brightness.
Press Fn+F7 to increase the brightness.
Press Fn+F8 to decrease the brightness.
Note:
To maximize your battery operating time, set the brightness to the lowest comfortable setting, so that the internal backlight
uses less power.
Extending the Life of the TFT Display Device
Observe the following guidelines to maximize the life of the backlight in the display.
1. Set the brightness to the lowest comfortable setting (Fn+F8).
2. When working at your desk, connect your notebook to an external monitor and disable the internal
display Fn+ F4.
3. Do not disable the suspend time-outs.
4. If you are using AC power and have no external monitor attached, change to suspend mode when not
in use.
Opening and Closing the Display Panel
To open the display, slide the LCD latch to the right and lift up the lid. Then tilt it to a comfortable viewing
position.
To close the display cover, fold it down gently until the LCD latches click into place.
Warning:
display is closed
To avoid damaging the display, do not slam it when closing. Do not place any object on top of the computer when the
1-16
Page 17

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
Audio Subsystem
Your computer’s audio subsystem is Sound Blaster Pro-compatible.
Adjusting the Volume Manually
To increase the volume, press Fn+ F5.
To decrease the volume, press Fn+F6.
Adjusting the Audio Volume in Windows
1. Click the speaker symbol in the task tray in Windows.
2. Drag the volume control bar up or down to adjust the volume.
3. To temporarily silence the speaker without changing the volume setting, click Mute.
Voice Recording
A built-in microphone allows you to record sound. You will need to use audio processing software to enable
the built-in microphone. For example, you may use Microsoft Sound Recorder.
1-17
Page 18
■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
Modem
Your computer comes with a 56K V.90 internal fax/modem and a phone jack (RJ-11), which is located on the left side of
your computer.
Use a telephone cable to connect the computer to the telephone wall outlet.
Connecting the Modem
1. Plug one end of the phone line into the modem port located on the rear side of the computer. (For EMI
compliance, you need to clip the included EMI CORE to the phone line.)
2. Plug the other end of the line into the analog phone wall outlet.
Depending on where your computer is used, you may need to change settings in the modem. Correct setting will allow
you to maintain a stable connection in a country where its telecommunication system may be different to others.
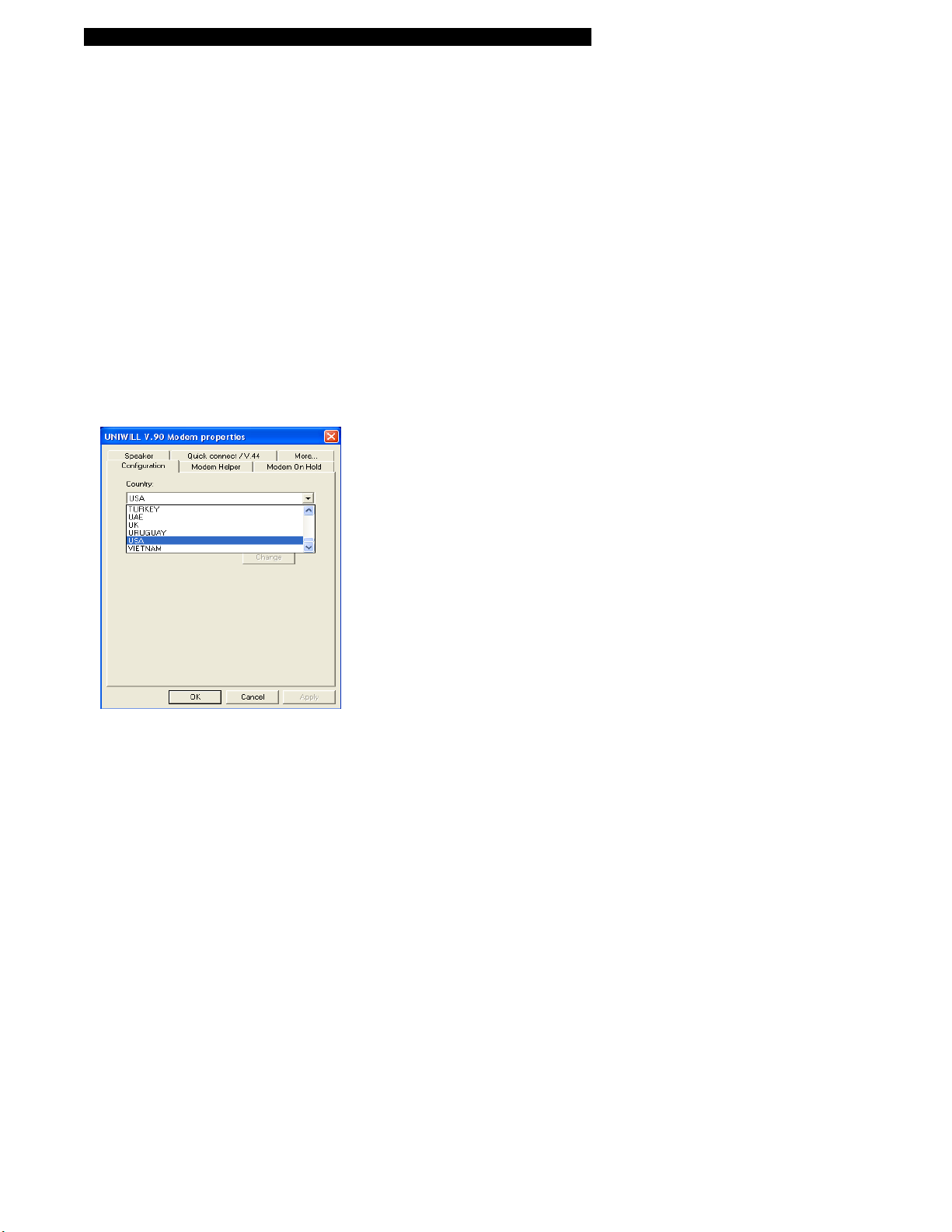
To change the modem setting, do the following:
1. Go to [Start > Settings > Control Panel] and double-click on Modem Settings icon. You will see a similar dialog
box.
2. Click on the pull-down menu and select the country where it is applicable. Click on OK to exit.
1-18
Page 19

■ chapter 1 getting to know the basics
Ethernet
Your
computer is equipped with a 10/100Base-TX Fast Ethernet network adapter. Connect the active LAN cable to
the R l
J-45 LAN port located on the left side of the computer. This allows you to access and transmit data in the loca
area
network.
Con
necting to the Network
Use Un
1.
recepta
2.
concen
Cab
The fol
shielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Ethernet cable only.
Insert one end of the UTP cable into the network connector until the connector snaps securely into the
cle.
Either connect the other end of the cable to an RJ-45 jack wall outlet or to an RJ-45 port on a UTP
trator or hub in the network.
ling Restriction for Networks
lowing restrictions should be observed for 100BASE-TX networks:
The maximum cable run length is 100 meters(m) (328 feet[ft]).
For 100/1000-Mbps operations, use Category 5 wiring and connections.
Consult Windows manual and / or Novell Netware user’s guide for the software installation, configuration, operation of the network.
Note:
1-19
Page 20

■ chapter 2 bios setup and security feature
CHAPTER▼ TWO
BIOS SETUP AND SECURITY FEATURE
In this chapter, you will le
settings. You will also lea
arn how to enter the BIOS Setup Menu and manipulate various hardware control
rn how to use the built-in security features.
2-1
Page 21

■ chapter 2 bios setup and security feature
The m).
Setup Utility is a hardware configuration program built into your computer’s BIOS (Basic Input/Output Syste
It run
s and maintains a variety of hardware functions. It is a menu-driven software, which allows you to easily
conf
igure and change the settings.
The
BIOS contains manufacture’s default settings for the computer’s standard operations. However, there are
occa
sions when you may be required to modify the default settings in the BIOS. For example, you may need to
conf m.
igure the BIOS power management (APM) settings if you are using DOS, or non-Windows operating syste
The BIOS allows you to set up passwords to limit access to users. This is an important feature because a great deal
of vit
al information is carried within the computer nowadays. Unauthorized access can be prevented. Later in this
chap
ter, you will learn how to use this security feature.
2-2
Page 22
■ chapter 2 bios setup and security feature
Entering the BIOS Setup Screen
First te
turn on the power. When the BIOS performs the POST (Power-On Self Test), press F2 key quickly to activa
the A
MI BIOS Setup Utility.
You may need to press F2 key fairly quickly. Once the system begins to load Windows, you may have to retry by cycle-power on again
Note:
eaving the BIOS Setup Screen
L
When you have finished modifying the BIOS
CMO
S.
IOS Action Keys
B
Function Key Command Description
Leaves a sub
ESC Exit
previous menu OR exits the BIOS se
while saving changes.
settings, exit the BIOS. It takes a few seconds to record changes in the
-menu to return to the
tup
F1 General Help
F10
<Tab> next field. Select a field Selects the
↑ Select an item item. Selects the next upper
↓ Select an item Selects the next lower item.
- Lower value Selects the next value within a field.
+ Higher value Selects the next value within a field.
Save and Exit
Shows the Help Screen
Saves changes and reboo
computer.
ts the
2-3
Page 23
■ chapter 2 bios setup and security feature
Modifying the BIOS Settings
The
AMIBIOS setup main menu is subdivided into sub-menus. Each menu item is described in this section.
Mai
n Setup
Und
er this menu, you may change time/date and view basic processor and system memory information.
Item Selections /
Sub-menu
Date N/A Type in the current date, in MM/DD/YY
Time N/A Type in the current date, in HH:MM:SS
Description
format.
format.
Advanced Setup
►IDE Configuration
Item Selections /
Sub-menu
Primary
IDE
Master
Secondary
IDE
Master
►Super IO Configuration (Port Address)
Item Selections /
IR Mode Disable
On Board
Parallel
Port
Parallel
Port Mode
Auto
ARMD
ATAPI CDROM
Not Installed
Sub-menu
Enable
Disabled
Enable
Normal
ECP+EPP
EPP
ECP
Description
Primary Master is where BIOS tries to
boot from first. The primary master
controls the hard drive. Normally, Auto
is selected.
The secondary master controls the
ATAPI CD-ROM drive. Normally, Auto is
selected.
Description
Select the I/O address and IRQ for IR
[Disabled]:
The port is disabled.
Or you may choose a value for the
parallel port.
You may choose any one of these
settings. ECP offers the best
performance.
Item Selections /
Sub-menu
2-4
Description
Page 24

■ chapter 2 bios setup and security feature
Touch
Pad
Disabled
Enabled
Enable or disable the built-in touchpad.
Support
About Hard Disk Drive Setting
Select Auto to let BIOS configure the drive parameters automatically. Only for certain old types of hard disk
drive will you need to modify the settings. After pressing Enter on [Hard Disk], BIOS display the drive
parameters. If the detected drive parameters are not correct or if you’re trying to enable the enhanced IDE
feature, you may still change the value manually.
32 Bit Mode:
Select On to allow data transmission in 32-bit format.
PIO Mode:
Normally use Auto To let BIOS decide the PIO mode setting. If the selected PIO mode is not supported by
the IDE drive, the hard disk drive may not work properly.
S.M.A.R.T. Mode:
Self-diagnostic and self-monitoring features are built into newer type hard drive. Select Auto to enable
S.M.A.R.T.
DMA Mode:
The hard drive in your computer support Ultra DMA mode.
Block Multi-Sector Transfer:
The hard drive in your computer support Multi-sector data Transfer.
Note: AMIBIOS automatically sets IDE drive parameters. Select Auto whenever possible. An incorrect setting make cause the computer to
malfunction.
Boot Setup
►Boot Settings Configuration
Item Selections /
Sub-menu
Boot-up
NumLock
Off
On
►Boot Device Priority
Description
[On]: NumLock (numeric keyboard) is
enabled on boot.
[Off]: The keyboard functions normally;
embedded numeric keyboard is disabled.
2-5
Page 25

■ chapter 2 bios setup and security feature
Item Selections /
Description
Sub-menu
1st Boot
Device
Removable Dev.
ATAPI CDROM
Hard Drive
Intel UNDI, PXE-2
Set the type of device for the 1st drive
BIOS attempts to boot from. If Intel UNDI,
PXE-2 is selected, system will attempt to
load boot sector from the Ethernet port.
Disabled
2nd Boot
Device
3rd Boot
Device
4th Boot
Device
Set the type of device for the 2nd drive
BIOS attempts to boot from.
Set the type of device for the 3rd drive
BIOS attempts to boot from.
Set the type of device for the 4th drive
BIOS attempts to boot from.
Note:
If you select Intel UNDI, PXE-2, the system will attempt to boot from the network.
Note: When the BIOS performs POST, you may also press F12 Key to enable the Boot Device selection menu. You may choose ATAPI
CDROM, Hard Drive, or Intel UNDI PXE-2 as the first storage device to boot from. If you have already connected a USB Floppy Disk Drive
before powering up, it will appear as a Removable Device in the Boot Device selection menu.
Security Setup
►Boot Settings Configuration
Item Selections /
Sub-menu
Change
N/A Install or Change the Password
Supervisor
Password
Change
N/A Install or Change the Password
User
Password
Clear User
N/A Install or Change the Password
Password
Boot
Sector
Disabled
Enabled
Virus
Protection
Description
To enable or disable the boot sector
protection.
When Enabled, BIOS gives a warning
when any program attempts to rewrite
or delete the boot sector.
Note:
About Boot Sector Virus Protection:
If enabled, the following warning message appears when a program attempts to alter the boot sector. You may have to enter “N” several
times to prevent the boot sector write.
2-6
Page 26

■ chapter 2 bios setup and security feature
Boot Sector Write!!!
Possible VIRUS: Continue (Y/N)? _
The following warning message appears when a program attempts to format the hard disk drive.
Format!!!
Possible VIRUS: Continue (Y/N)? _
Using Password Protection
Two Levels of Password Protection are available. The BIOS provides both a Supervisor and a User password. If
you try to activate both passwords, the Supervisor password must be set first.
The passwords activate two different levels of protection:
1. System always asks for password every time it is powered on.
2. System asks for password only when you attempt to enter BIOS utility.
The passwords are encrypted and stored in NVRAM. Make sure you write them down or memorize them. If you
lost the passwords, the computer may need to be sent back to the factory or to an authorized service dealer to
reset the passwords.
2-7
Page 27

■ chapter 2 bios setup and security feature
Power Setup
Item Selections /
Sub-menu
Description
Exit Setup
Item Selections /
Sub-menu
Saves
Changes and
Exit
Discard
Changes
Load Optimal
Defaults
N/A After you have completed the BIOS
N/A Discards changes done so far to any of
N/A Load Optimal Default value for all the
Description
settings, select this item to save all
settings, exit BIOS Setup utility, and
reboot. New system settings will take
effect on next power-up.
the setup questions.
setup questions. F9 key can be used for
this operation.
2-8
Page 28

■ chapter 3 battery power & power management
CHAPTER▼ THREE
BATTERY POWER & POWER MANAGEMENT
In this chapter, you will learn the fundamentals of power management and how to
use it to achieve longer battery life.
3-1
Page 29

■ chapter 3 battery power & power management
In this chapter, you will learn how to operate your notebook on battery power, how to handle and maintain the
battery pack, and learn about the system’s power saving features.
TFT display, central processor, hard disk drive are the major hardware subsystems that consume the most
power. Power management deals how these key components should behave to conserve power. For example,
you can have the system turn off its display after 2 minutes of inactivity to save power. Efficient power
management can help you work longer sessions before having to recharge the battery.
The Battery Pack
Lithium-Ion Battery
Your notebook uses an eight-cell Lithium-Ion battery pack that provides power when you don’t have
access to an AC outlet.
Note:
It is necessary that you charge the battery pack for at least 6 hours before using it for the first time.
Note: In the Standby Suspend mode, a fully charged battery loses its power in roughly 1/2 day or less. When not being used,
the battery’s power will deplete in 1-2 month.
3-2
Page 30

■ chapter 3 battery power & power management
Battery Low-Power Warning
1. Low Battery Warning
Low battery condition occurs when battery power is reduced to 6%. The green power LED indicator
blinks and the system beeps once every 16 seconds or so.
2. Very Low Battery Warning
Very Low battery condition occurs at 3 % power remaining. The power LED indicator blinks and the
system beeps at 4-second interval.
When the notebook warns you of its low battery condition, you will have about 3-5 minutes to save
your current work.
Warning:
This may adversely affect the battery pack.
Note: You may use Fn+F3 function keys to disable battery-warning (low power) beeps.
Do not expose battery packs to temperatures below 0 degree Celsius (32 degree F) or above 60 degree C (140F).
3-3
Page 31

■ chapter 3 battery power & power management
Installing and Removing the Battery Pack
Note:
The system is not designed for frequent battery pack removal. When you need to remove the battery pack, please observe the
following steps.
To Remove the Battery Pack:
1. Place the notebook bottom-side up on a flat and secured surface.
2. Push the latch and pull the battery’s hard case away from the notebook.
1
2
3-4
Page 32

■ chapter 3 battery power & power management
To Install the Battery Pack:
1. Place the notebook bottom-side up on a flat and secured surface.
2. Carefully insert the battery pack into the battery compartment of the notebook.
Charging the Battery and Charging Time
To charge the battery, while the battery pack is in the notebook, plug the AC adapter into the notebook and
an electrical outlet.
The charging time is approximately 4-5.5 hours when the notebook is turned off and approximately 4.5-6
hours when the notebook is turned on.
When the battery is fully charged, the battery charge indicator becomes dark (off).
If system runs at heavy loading or in a high temperature environment, the battery may not be fully charged. You need to
Note:
continue to charge it with the AC adapter plugged in until the charging LED turns off.
3-5
Page 33

■ chapter 3 battery power & power management
Checking the Battery Level
You can check the remaining battery power in the Windows battery status indicator, which is located at the
lower right-hand corner of the task bar. (If you do not see a battery or AC-in icon on the task tray, go to
Power Options Properties box and click on the Advanced tab. Check off ``Always show icon on the task
bar``.)
Alternatively, you can access the power meter by clicking the Power Options icon in the Windows Control
Panel.
Prolonging the Battery’s Life and Usage Cycles
There are ways you can do to prolong the use of battery.
Use the AC adapter wherever AC wall outlet is available. This will ensure uninterrupted computing.
Purchase additional battery pack.
Store the battery pack in room temperature. Higher temperature tends to deplete the battery’s power
faster.
Make good use of the power management function. Save To Disk (Hibernate) saves the most energy
by storing current system contents in a hard disk space reserved for this function.
The life expectancy of the battery is approximately 300 recharges.
See the notices section in the beginning of the user manual on how to care for the battery pack.
Note: Read Section Protecting Your Notebook in the beginning of this manual for tips about how to maintain the battery pack.
Note: To achieve optimal battery performance, you may need to do a battery calibration at a 3-month interval. To do this:
1. Fully charge the battery.
2. Then discharge the battery by entering the BIOS setup screen. (Press F2 key as soon as you turn on the computer. And let it
remain at the setup screen until the battery runs out.
3. Fully charge the battery again.
3-6
Page 34

■ chapter 3 battery power & power management
Using Windows Power Options
Windows Power Management provides basic power saving features. In the Windows Power Options
Properties [Start > Settings > Control Panel > Power Options] dialogue box, you may enter time-out values
for display and hard disk drive. Windows power manager saves power by turning off hard drive after 1
minute of inactivity, for example.
Windows’ Power Schemes
The power management control panel in Windows XP, known as Power Schemes, is designed to
provide the user with an easy-to-use interface. The Power Schemes tab can be found in the Power
Options Properties panel that is accessible via the control panel window.
Schemes are easy to understand, based on notebook usage scenarios, and control not only
processor power usage but other system peripherals as well.
Go to [Start > Settings > Control Panel] and double-click the Power Options icon.
Always on mode puts the processor into maximum performance mode, which provides no power
saving. The other schemes control processor performance based on demand. For example, Max
Battery mode lowers the processor’s speed and voltage to conserve power as much as possible.
In this dialog box, you can manually set the LCD and hard drive’s time-out values in the Plugged in
column and in the Running on batteries column. Lower time-out values will save more battery power.
Note: Also consult Windows user guide for more information on how to use Windows power management functions.
Note: Actual dialogue box shown above may appear slightly different.
3-7
Page 35

■ chapter 3 battery power & power management
3-8
Page 36

■ chapter 3 battery power & power management
Suspend Mode
Standby Suspend
The system automatically enters this mode after a period of inactivity, which is set in the Power
Schemes dialog box. In Standby mode, hardware devices, such as display panel and hard disk, are
turned off to conserve energy.
Hibernate Suspend
In this mode, all system data are saved in the hard disk before powering down. When this mode is
activated, all system state and contents are saved to the hard disk drive after a period of inactivity
defined by the user. No power or very little power is drawn from the battery module under this mode.
However, depending on how much RAM that have been installed on your computer, the amount of
time the system requires to restore all its previous contents can range from 5 to 20 seconds.
For Windows 2000 / XP users, hibernation is handled by the operating system; therefore, no special
disk partition or disk file is necessary.
If you wish to activate Hibernate mode, you need enable Hibernate Support in the Hibernate tab of
the Power Options menu.
Note:
Do not install or remove the memory module when the system is in the suspend mode.
Note: Actual dialogue box shown above may appear slightly different.
3-9
Page 37

■ chapter 3 battery power & power management
Power Button Action
The notebook PC’s power button can be set to turn off the system or activate the suspend mode.
Go to [Start > Settings > Control Panel > Power Options] and click on the Advanced tab. In the
pull-down menu, select how you wish the power button to work as.
Actual dialogue box shown above may appear slightly different.
Note:
Warning:
system will still run at high speed while the processor’s fan grill is fully blocked by the closed LCD panel. The heat will damage
the LCD panel.
In the When I close the lid of my portable computer pull-down menu, DO NOT select Do nothing – otherwise the
3-10
Page 38

■ chapter 3 battery power & power management
Low Battery Warning
You can define when and how the system warns you of its battery-low condition.
Go to the Alarms tab in the Power Options Properties box. If you wish to hear audible beeps, click on
the Alarm Action button and put a check on Sound Alarm.
Note: Consult Windows user guide for more information on how to use Windows power management functions.
Note: Actual dialogue box shown above may appear slightly different.
3-11
Page 39

■ chapter 3 battery power & power management
Power Manu Quick Access
Instead of making specific selections in the Power Options Properties box, you can quickly and easily
specify which pre-set power saving function you desire by clicking on the Battery icon at the lower
right-hand corner of the task bar. (If you do not see a battery or AC-in icon, go to Power Options
Properties box and click on the Advanced tab. Check off ``Always show icon on the task bar``.) Select
Max Battery if you want the system to enter suspend mode more often. Or, select Always On if your
notebook PC is plugged into an AC power source.
Note: Actual dialogue box shown above may appear slightly different.
3-12
Page 40

■ chapter 4 upgrading your computer
CHAPTER▼ FOUR
UPGRADING YOUR COMPUTER
In this c
optional
hapter, you will learn how to upgrade the DRAM, hard disk drive, and to install the
wireless LAN mini PCI card.
4-1
Page 41

■ chapter 4 upgrading your computer
Upgrading the Hard Disk Drive
R
eplacing the original drive with one of larger capacity can increase the hard drive capacity of your computer.
T
he computer uses a 9.5 mm (height), 2.5-inch Ultra ATA-66 / 100 / 133 type hard disk.
B
e sure to make a backup copy of all your data before attempting this operation.
Warning:
install it for you. Damages due to mishandling of this procedure are NOT covered by the manufacture’s warranty.
Warning:
Do not drop or apply any shock.
Do not press on the cover.
Do not touch the connector with your fingertips.
Mishandling of the hard drive can result in permanent loss of data. Make a backup copy of the drive s content before you remove it.
Note:
Hard drive upgrade is a delicate process. Please observe the following instructions carefully or have a qualified technician
Apply care when handling the hard disk.
Certain models that come with the IBM-brand hard drive emit a clattering sound when it is being rattled. This is a normal condition.
4-2
Page 42

■ chapter 4 upgrading your computer
Upgrading the Hard Disk Drive
To replace the hard disk drive, do the following:
1. Turn OFF the computer. Unhook the AC cord and all cables/devices attached to the notebook.
2. Place your hand on a large metal object momentarily to discharge any static electricity.
3. Locate and remove 11 Screw A’s on the Metal Cover.
4. Remove the Metal Cover.
5. Locate and remove 1 Screw B. Gently push the HDD module to the right to disengage from the HDD
connector.
6. Locate and remove 4 Screw C’s from the HDD module. Remove the metal case.
4-3
Page 43

■ chapter 4 upgrading your computer
7. Re-attach the metal cover to the new hard drive and tighten 4 Screw C’s. Note the green PC board of
the hard disk drive is facing against the metal case.
8. Re-insert the HDD module to the HDD connector.
9. Re-attach and tighten 1 Screw B. (If the HDD assembly is not fully inserted into the bay, the screw
and its hole will not line up.)
10. Replace the System Device Cover and 11 Screw A’s.
Congratulations! You have now completed the hard drive upgrade. When you boot up the PC, you may
need to create a primary HDD partition and reformat the new drive and re-install O/S, drivers, and all the
necessary applications.
4-4
Page 44

■ chapter 4 upgrading your computer
Upgrading the System Memory
Many applications will generally run faster when the computer’s dynamic memory capacity is increased. The
computer provides one DDR memory socket, located underneath the System Device Cover. You can increase
the amount of memory by replacing the existing one with a dual inline memory module (commonly known as
DIMM) of a higher capacity. The DIMM can be 128MB, 256MB, 512MB, or 1024MB in capacity. The DIMM is of
type DDR SDRAM, has 200 pins and runs on 2.5V. The DIMM should be PC2100 or PC2700 compliant.
Note: If your computer comes with Intel P4 FSB800 CPU, you must choose PC2700 compliant DIMM module.
Warning:
it for you. Damages due to mishandling of this procedure are NOT covered by the manufacture’s warranty.
Warning:
Make sure you turn off the power and unplug the AC cord before proceeding with a memory upgrade.
Memory upgrade is a delicate process. Please observe the following instructions carefully or have a qualified technician install
Changing memory while your computer is in suspend or power-saving mode may cause permanent damage to the hardware.
Warning:
unstable.
You should only use the DIMM module that is approved by the reseller or the manufacturer; otherwise the system may become
4-5
Page 45

■ chapter 4 upgrading your computer
Installing a memory module (DIMM) into the system
To install the DIMM, do the following:
1. Power OFF the notebook. Unplug the AC cord and all cables/devices attached to the notebook.
2. Place your hand on a large metal object momentarily to discharge any static electricity. Place the
notebook on a flat surface and fully open the LCD lid.
3. Locate and remove 11 Screw A’s on the Metal Cover.
4. Remove the Metal Cover. The DIMM socket is now seen as shown below.
Dual DDR
DIMM Sockets
5. If you need to remove an old DIMM from the socket, press out on the latches located on both edges
of the socket at the same time. The DIMM should pop up to an angle of 30 degree (see diagram below.).
Pull the DIMM module out of the memory socket. Store away the DIMM for the future use.
4-6
6. Install the new DIMM module into the memory socket. The DIMM will only fit in one orientation.
Insert the DIMM at an angle of approximately 30 degrees into the empty memory socket. Then press it
firmly so that the contact edge is driven into the receiving socket.
Page 46

■ chapter 4 upgrading your computer
Notch
7. Pivot the DIMM until the latches on both sides of the socket snap into place.
Notice the notch on the DIMM. The notches should fit nicely with the socket.
Note:
8. Replace the System Device Cover and 11 Screw A’s.
Congratulations! You have just completed the memory upgrade. When you boot up the computer, you
should expect to see an increase in DRAM capacity.
Note: Your computer has been tested with a wide range of DIMM on the market. However, not all memory modules are compatible.
Check with your system vendor for a list of compatible DIMM for your computer.
4-7
Page 47

■ chapter 4 upgrading your computer
4-8
Page 48

■ chapter 4 upgrading your computer
4-9
Page 49

■ chapter 5 trouble shooting
CHAPTER▼ FIVE
TROUBLE SHOOTING
In this chapter, you will learn how to solve common hardware and software problems.
5-1
Page 50

■ chapter 5 trouble shooting
Your computer has been fully tested and complies with the system specifications before shipping. However,
incorrect operations and/or mishandling may cause problems.
This chapter provides a reference for identifying and correcting common hardware and software problems that
you may encounter.
When you encounter a problem, you should first try to go through the recommendations in this chapter. Instead
of returning the computer and waiting for repair, you may easily solve the problems by considering the following
scenarios and possible solutions. If the error continues, contact your reseller for service information.
Before taking further actions, consider the following suggestions:
Check to see if the problem persists when all the external devices are removed.
Check to see that the green light indicator on the AC adapter is lit.
Check to see the power cord is properly plugged to the wall outlet and to the computer.
Check to see the power indicator of the computer is on.
Check to see if your keyboard is operational by pressing and holding any key.
Check for any incorrect or loose cable connections. Make sure the latches on the connectors latch
securely on to the receptor end.
Be sure you have not performed an incorrect setting on the hardware devices in the BIOS Setup utility. A
faulty setting may cause the system to misbehave. If you are not sure of the changes you made, try to restore
all the settings to factory defaults.
Be sure all the device drivers are installed properly. For example, without the audio driver properly
installed, the speakers and microphone will not work.
If external devices such as USB camera, scanner, printer do not function correctly when connected to the
system, it is usually the device’s own problem. Consult the device’s manufacturer first.
Some software programs, which have not gone through rigorous coding and testing, may cause problems
during your routine use. Consult the software vendor for problem solving.
Legacy peripheral are not plug-and-play capable. You need to restart the system with these devices
powered up and connected first.
Be sure to go to BIOS SETUP and load DEFAULT SETTING after BIOS re-flash.
Be sure the Quick Key Lockout Switch on the bottom of the computer is not engaged; otherwise the quick
keys will not work.
5-2
Page 51

■ chapter 5 trouble shooting
Audio Problems
No speaker output -
Turn up the volume dial located at the right edge of the computer. See Chapter 1 for its location.
Software volume control is turned down in Microsoft Sound System or is muted. Double-click the
speaker icon on the lower right corner of the taskbar to see if the speaker has been muted or turned down
all the way.
Most audio problems are software-related. If your computer worked before, chances are software
may have been set incorrectly.
Go to [Start > Settings > Control Panel] and double-click the Sounds and Audio Devices icon. In the
Audio page, make sure that Realtek AC97 Audio is the default playback device.
Sound cannot be recorded -
Double-click the speaker icon on the lower right corner of the taskbar to see if the microphone has
been muted.
1. Click Options and select Properties.
2. Select Recording and click the OK button.
3. After Click OK button, the recording volume control panel will appear.
Go to [Start > Settings > Control Panel] and double-click the Multimedia icon (or Sounds and Audio
Devices icon). In the Volume or Audio page, make sure that Realtek AC97 Audio is the default recording
device.
5-3
Page 52

■ chapter 5 trouble shooting
Hard Disk Problems
The hard disk drive does not work or is not recognizable -
If you had just performed a hard disk upgrade, make sure the hard drive connector is not loose and
the hard disk drive is also correctly seated. Remove it and reinsert it firmly, and restart your PC. (Refer to
Chapter 4 for details.)
The new HDD may need to be partitioned and reformatted. O/S and drivers will need to be
re-installed as well.
Check the hard disk indicator LED. When you access a file, the LED lamp should light up
momentarily.
The new HDD may be defective or is not compatible.
If your computer has been subjected to static electricity or physical shock, you may have damaged
the disk drive.
The hard drive is making abnormal whining noises -
You should back up your files as soon as possible.
Make sure the source of noise is indeed from the hard drive and not the fan or other devices.
The hard disk drive has reached its capacity -
Run Disk Cleanup utility in Windows. [Start > All Programs > Accessories > System Tools > Disk
Cleanup] The system will prompt you for what to do.
Archive files or programs that you had no longer used by moving them to an alternative storage
medium (floppy disk, optical record-able disk, etc.) or uninstall programs that no longer use.
Many browsers store files in the hard drive as a cache to speed up the performance. Check the
program’s Online Help for instructions on decreasing the cache size or on removing temporary Internet
files.
Empty the Recycle Bin to create more disk space. When you delete files, Windows saves them to the
Recycle Bin.
The hard disk takes longer to read a file -
If you have been using the drive for a period, the files may be fragmented. Go to [Start > Programs >
Accessories > System Tools > Disk Defragmenter] to perform a disk defragmentation. This operation may
take a while.
Interrupt requests or problems with other hardware devices may have occupied the CPU and
therefore slows down the system performance.
The files are corrupted -
Run the Error-checking utility in Windows to check the HDD. Double-click My Computer. Right-click C:
and select Properties. Click Check Now in Error-checking in Tools.
Optical Drive Problems
5-4
Page 53

■ chapter 5 trouble shooting
The optical drive does not work -
Try rebooting the system.
The disk is damaged or files are not readable.
After you have inserted a CD-ROM disk, it may take a moment before you can access its content.
The drive dose not read any disks -
The CD may not be properly seated in the tray. Make sure the disk is firmly seated onto the spindle.
The disk is damaged or not readable.
The disk cannot be ejected -
Normally, it takes a few seconds to eject the disk.
If the disk cannot be ejected, it may be mechanically jammed. Straighten out a paper clip and insert it
to a tiny hole next to the eject button. This should reject the disk tray. If not, return the unit for repair. Do not
forcefully pull on the disk tray.
The Combo or DVD RW drive (optional device) cannot record -
You need to purchase and install a burner utility program to record files to a blank media.
5-5
Page 54

■ chapter 5 trouble shooting
Display Problems
The display panel is blank when the system is turned on -
Make sure the computer is not in the Standby or Hibernate suspend modes. The display is turned off
to conserve energy in these modes.
The screen is difficult to read -
The display resolution should at least be set to at least 1280x800 for optimal viewing.
1. Go to [Start > Settings > Control Panel] and double-click the Display icon.
2. Under the Settings page, set screen resolution to at least 1280x800 and choose at least 16bit color.
The screen flickers -
It is normal if the display flickers a few times during shutting down or powering up.
5-6
Page 55

■ chapter 5 trouble shooting
Keyboard and Mouse Problems
The built-in touch pad performs erratically -
Make sure there is no excess perspiration or humidity on your hand when using the touch pad. Keep
the surface of the touch pad clean and dry.
Do not rest your palm or wrist on the surface of the touch pad while typing or using the touch pad.
The built-in keyboard accepts no input -
If you are connecting an external keyboard to the system, the built-in keyboard may not work.
Try restarting the system.
The characters on the screen repeat while I type.
You may be holding the keys down too long while you’re typing.
Keep the keyboard clean. Dust and dirt under the keys could cause them to stick.
Configure the keyboard to wait longer before the auto repeat feature starts. To adjust this feature, Go
to [Start > Settings > Control Panel], and double-click the Keyboard icon. A dialogue box shows up with the
adjustable settings for the keyboard.
5-7
Page 56

■ chapter 5 trouble shooting
CMOS Battery Problem
A message “CMOS Checksum Failure” displays during the booting process or the time (clock)
resets when booting -
Try to reboot the system.
If the message “CMOS Checksum Failure” appears during the booting procedure even after rebooting, it may indicate
failure of the CMOS battery. If so, you need to replace the battery. This battery normally lasts two to five years. Have
your notebook serviced by a professional
5-8
Page 57

■ chapter 5 trouble shooting
Memory Problems
The POST does not show an increased memory capacity when you have already installed additional
memory -
Certain brands of memory module may not be compatible with your system. You should ask your
vendor for a list of compatible DIMM.
The memory module may not be installed properly. Go back to Chapter 4 to review the details of this
operation.
The memory module may be defective.
The O/S issues an insufficient memory error message during operation -
This is often a software or Windows-related problem. A program is draining the memory resources.
Close the application programs you’re not using and restart the system.
You need to install additional memory module. For instructions, go to Chapter 4 Upgrading Your
Computer.
5-9
Page 58

■ chapter 5 trouble shooting
Modem Problems
The built-in modem does not respond -
Make sure the modem driver is loaded properly.
Go to [Start > Settings > Control Panel > Phone and Modem Options] and go to Modems tab. Make
sure SmartLink 56K Voice Modem or V.90 Modem is listed. Otherwise, click the Add button to add the
modem drive, which is located in the factory CD-ROM (or floppy diskette).
Go to [Start > Settings > Control Panel > System] and click Device Manager button in the Hardware
page to check for possible resource or driver conflict. See Windows on-line help or manual for how to
handle such problems.
Make sure the phone line, which the computer is connected to, is working.
Connection difficulties -
Be sure to disable Call Waiting on the phone line.
Be sure to have the correct country setting where your computer is used. [Start > Settings > Control
Panel > Modem Settings > Configuration] In the Country/Area pull-down menu, select the appropriate
country setting.
Excessive line noise might cause the connection to be dropped. To check this, put the regular phone
handset on the line and placing a phone call. If you do hear abnormal noise, try to make the modem
connection with a different line or contact your local telephony company for service.
Make sure the cable connection is firm.
Try a different receiver number and see if the problem persists.
5-10
Page 59

■ chapter 5 trouble shooting
Network Adapter / Ethernet Problems
The Ethernet adapter does not work -
Go to [Start > Settings > Control Panel > System > Hardware > Device Manager]. Double-click on
Network Adapters and check if SiS 900-Based PCI Fast Ethernet Adapter appears as one of the adapters.
If it does not exist, Windows has not detected the National Semiconductor Fast Ethernet adapter or the
device driver has not been installed properly. If there is a yellow mark or red-cross on the network adapter, it
may be a device or resource conflict. Replace or update the device driver from the factory CD-ROM disk or
consult Windows manual on how to solve the resource conflict problem.
Make sure the physical connections on both ends of the cable are good.
The hub or concentrator may not be working properly. Check to see if other workstations connected
to the same hub or concentrator is working.
The Ethernet adapter does not appear to operate in the 100Mbps transmission mode -
Make sure the hub you are using supports 100Mbps operation.
Make sure that your RJ-45 cable meets the 100Base-TX requirements.
Make sure the Ethernet cable is connected to the hub socket that supports 100Base-TX mode. The
hub may have both 100Base-TX and 100Base-T sockets.
5-11
Page 60

■ chapter 5 trouble shooting
PC Card / PCMCIA Problems
Some system may not have the PC Card Slot option.
Note:
PC Cards do not function-
Make sure you have properly installed the driver for the card.
Consult the card’s manual or contact the vendor for trouble-shooting.
The PC card cannot be recognized -
Windows NT4.0 does not support PCMCIA (PC Card) function. You may need an external program
for this.
Make sure the card is fully inserted; the outer end of the card should be even with the edge of the
computer.
Remove and insert the PC card again.
Make sure there is no IRQ conflict with the card. See Windows on-line help for solving IRQ conflicts.
Reboot the computer and see if the problem persists.
The card may be defective. Try the card on another system, if possible.
Windows crashes or freezes when you remove the PC card-
Make sure you have <Stop> the PC card before removing it. Double-click the Safely Remove
Hardware icon at the lower right corner of the task bar and select the card you wish to stop. When you click
<Close>, in few seconds Windows will prompt you to remove the card.
5-12
Page 61

■ chapter 5 trouble shooting
Performance Problems
The computer becomes hot -
In a 35
degrees.
Make sure the air vents are not blocked.
If the fan does not seem to be working at high temperature (50 degrees Celsius and up), contact the
service center.
Certain programs that are processor-intensive may increase the computer temperature to a degree
where the computer automatically slows down its CPU clock to protect itself from thermal damage.
The program appears stopped or runs very slowly -
Press CTRL+ALT+DEL to see if an application is still responding.
Restart the computer.
This may be normal for Windows when it is processing other CPU-intensive programs in the
background or when the system is accessing slow-speed devices such the floppy disk drive.
You may be running too many applications. Try to close some applications or increase system
memory for higher performance.
The processor may have been overheated due to the system’s inability to regulate its internal heat.
Make sure the computer’s ventilation grills are not blocked.
o
C environment, the certain areas of the computer’s back case are expected to reach 50
5-13
Page 62

■ chapter 5 trouble shooting
Printer Problems
The printer does not print -
Make sure the cable connection is secured and the printer is powered up, if the printer is connected
via the parallel port.
Run the printer self-test to see if it reports any problem.
Check if the printer displays any error messages. A paper jam may have occurred.
Make sure you have already installed the printer driver.
Try rebooting the system with the printer powered up and connected first.
The printer does not print what’s on the screen -
The information displayed on the screen may not exactly be the same as what is printed.
If the printer prints extra and strange symbols, it is the result of the cache (garbage) in the printer
memory buffer. Cancel all the printer tasks and toggle off the printer power switch to clear up the memory
buffer. Then, turn the printer back online and print again.
Make sure you install the correct printer driver.
The printer does not respond to infrared communication -
See Infrared Problems listed elsewhere in this chapter.
5-14
Page 63

■ chapter 5 trouble shooting
Firewire (IEEE1394) and USB2.0 Problems
The USB device does not work -
Windows NT 4.0 does not support USB protocols
Check the settings in the Windows Control Panel.
Make sure you have installed the necessary device drivers.
Contact the device vendor for additional support.
The IEEE1394 port does not work -
Go to [Start > Settings > Control Panel > System > Hardware > Device Manager]. You should see an
entry which reads “IEEE 1394 Bus host controllers”. If it does not exist, Windows has not detected the host
controller or the device driver has not been installed properly. If there is a yellow mark or red-cross on the
1394 host controller, it may be a device or resource conflict. Replace or update the device driver from the
factory CD-ROM disk or consult Windows manual on how to solve the resource conflict problem.
Make sure the cable is fully connected.
Make sure you have installed the necessary device drivers.
Contact the device vendor for additional support.
5-15
Page 64

■ appendix A product specification
A
APPENDIX▼ A
PRODUCT SPECIFICATION
-1
Page 65

■ appendix A product specification
A
▼ Processor and Core Logic
Processor
Core Logic
Intel P4 (2.66 ~ 3.2 GHz or higher), 478 Pins FC-PGA2 Type, 533/800 MHz FSB, 512 KB L2 with
Error Correction Code
SiS 648FX + SiS SB963 chipset with audio, modem LAN, USB2.0, and IEEE1394 controllers
integrated
533/800 MHz Front Side Bus
266/333/400 MHz DDR interface
▼
System Memory
Memory Type
Default
Memory
Expansion
DDR SDRAM, 400/333/266 MHz, PC3200/PC2700 / PC2100 compatible
0 / 128 / 256 / 512 / 1024MB, 2.5-Volt 64-bit bus
Two 200-pin DIMM sockets, Max 2 GB
▼
Display
LCD Panel
Graphic
Accelerator
AGP Bus
Motion
Playback
15.4-inch (1680x1050 WSXGA+ or 1280x800 WXGA) active-matrix TFT display with up to 16M
colors
ATI Mobility Radeon 9600 Pro 256-bit 2D / 3D graphics accelerator
8X AGP architecture graphics capability
Hardware Motion Compensation and IDCT Supported for MPEG1/2 Playback
64MB DDR DRAM
Direct3D compatible, DirectX compatible
Frame Buffer
Other
Features
-2
Page 66

■ appendix A product specification
A
▼ Audio
Chipset
Audio Codec
Sound
Capabilities
SiS SB963 integrated audio controller
ALC655
DirectSound 3D accelerator
SoundBlaster Pro compatible
AC97 V2.2 compatible
2 Stereo Speakers
▼
Modem
Chipset
Transmission
Rate
SiS SB963 integrated Modem Controller with MDC card, AC97 V2.2 Modem support
V.90 / K56flex for download data speed up to 56Kbps.
V.34, V.17, V.29 protocol supported
▼
LAN / Ethernet
Chipset
PnP Function
Flow Control
Speed
Selection
Other
Features
SiS SB963 integrated Ethernet function for 10/100Base-TX network standards or
Windows 2000 / XP Plug and Play compatible
Automatic Jam and auto-negotiation for flow control
Auto Negotiation and Parallel detection for automatic speed selection (IEEE 802.3u)
High performance 32-bit PCI bus master architecture with integrated DMA controller for low CPU
and bus utilization
Remote Wake-up Scheme supported
Hot Insertion supported
-3
Page 67

■ appendix A product specification
A
▼ Firewire IEEE1394(a)
Chipset
PHY Layer
Capabilities
SiS SB963 IEEE1394 OHCI Host Controller and
Up to 400 Mbps
FW802B
Expandable up to 63 devices in chains
▼
Storage
Hard Drive
Combo Drive
DVD±R/±RW
or DVD-Dual or
DVD-Multi
Standards
2.5-inch format hard disk drive
5.25-inch format (12.7mm height) fixed module (Optional Purchase)
5.25-inch format (12.7mm height) fixed module (Optional Purchase)
▼
Keyboard & Touch pad
Keyboard
Touch pad
88/90-key QWERTY keyboard with embedded numeric keypad and Windows keys, 19mm Pitch
Built-in Touch Pad with PageUp / PageDown Buttons and Scroll Bar
19.05mm Pitch
-4
Page 68

■ appendix A product specification
A
▼ Ports and Connectors
Mic-In Port
Audio-in Port
Audio-Out / SPDIF
Firewire
USB2.0 Port
Ethernet
Modem
S-Video
Power-In
Parallel
VGA Port
FIR/SIR
Card Reader
PC Card Slot
One Microphone-in jack
One Line-in jack
One Headphone / SPDIF jack
One Firewire (IEEE1394) host connector
Three USB2.0-compliant connectors
One standard network Ethernet connector (RJ-45)
One modem / phone connector (RJ11)
One S-video (TV-out) output connector
One DC-in connector
One 25-pin parallel port connector
One 15-pin VGA connector
One SIR/FIR Port
One Card Reader slot (MMC/MS/SD supported)
One PC Card Slot (type II)
▼
Battery Pack / AC Adapter
Battery Pack
Options
Feature
Adapter
AC-Input /
DC-Output
Li-ion 8-Cell pack, 14.4V x 4400 mAh, or
Li-ion 8-Cell pack, 14.4V x 4000 mAh
Smart Battery Compliant
Autosensing AC-in 100~240V, DC-out 20V, 160W
-5
Page 69

■ appendix A product specification
A
▼ BIOS
PnP Function
Self Test
Auto
Detection
Power
Management
Security
Other
Features
AMI PnP BIOS
Power On Self Test
DRAM auto-detection, auto-sizing
L2 Cache auto-detection
Hard disk type auto-detection
APM 1.2 (Advanced Power Management) &
ACPI 2.0 (Advanced Configuration Power Interface)
Smart Power ®
Two Level Password Protections
32bit access, Ultra DMA, PIO5 Mode support
Multi-boot capability
O/S
Compatible with Microsoft Windows 2000 / XP / DOS
▼
Physical Specification
Dimension
Weight
Environmental
Limits
358 (W) x 269 (D) x 35.8 (H) mm
7.7 lbs / 3.5 KG (with Combo Drive)
Operating Temperature: 5 to 35oC (41 to 95oF)
Operating Humidity: 20 to 90 percent RH (5 to 35
Storage Temperature: -20 to 50
oC
(-4 to 122oF)
oC
)
-6
Page 70

■ appendix B agency regulatory notices
APPENDIX▼ B
AGENCY REGULATORY NOTICES
B-1
Page 71

■ appendix B agency regulatory notices
Fede
ral Communications Commission Notice
This
equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC
Rule This
s. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation.
equip
ment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instru
ctions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not
occu be
r in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can
deter
mined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the
follow
ing measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio or television technician for help.
Mod
ifications
The ved
FCC requires the user to be notified that any changes or modifications made to this device that are not expressly appro
by th
e Manufacture may void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Conn
ections to Peripheral Devices
Conn iance
ections to this device must be made with shielded cables with metallic RFI/EMI connector hoods to maintain compl
with
FCC Rules and Regulations.
Decl
aration of Conformity
This
device complies with Part 15/68 the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not
caus
e harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
unde
sired operation.
Euro
pean Notice
Prod
ucts with the CE Marking comply with both the EMC Directive (89/336/EEC) and the Low Voltage Directive (73/23/EEC) and
R&T
TE Directive (1999/5/EC) issued by the Commission of the European Community.
Com
pliance with these directives implies conformity to the following European Norms:
EN55022 (CISPR 22) Radio Frquency Interference
EN50082 (IEC801-2, IEC801-3, IEC801-4) Electro-magnetic Immunity
EN 300 328-2 (ETS 300 328) Radio Spectrum Matter.
TBR21 (ETS TBR21) Terminal Equipment.
EN60950 (IEC950) I.T.E. Product Safety
Cana
dian Notice
This
digital apparatus does not exceed the Class B limits for radio noise emissions from digital apparatus as set out in the radio
interf
erence regulations of the Canadian Department of Communications.
Le pr riques
esent appareil numerique nemet pas de bruits radioelectriques depassant les limites applicables aux appareils nume
de Cl
asse B prescrites dans le reglement sur le brouillage radioelectrique edicte par le Ministere des Communications du
Cana
da.
Pow
er Cord Requirement
The y
power cord supplied with the AC adapter should match the plug and voltage requirements for your local area. Regulator
appr
oval for the AC adapter has been obtained using the power cord for the local area. However, if you travel to a different area
and n
eed to connect to a different outlet or voltage, you should use one of the power cords listed below. To purchase a power
cord
(including one for a country not listed below) or a replacement ac adapter, contact your local dealer.
U.S.
and Canada
The cord set must be UL-Listed and CSA-Certified or C-UL Listed.
The minimum specifications for the flexible cord are (1) No. 18 AWG, (2) Type SJ, and (3) 3-conductor.
The cord set must have a rated current capacity of at least 10 A.
The attachment plug must be an earth-grounding type with a NEMA 5-15P (15A, 125V) or NEMA 6-15P (15 A, 250V)
B-2
Page 72

■ appendix B agency regulatory notices
configuration.
Japa
n
All components of the cord set (cord, connector, and plug) must bear a `PSE` mark and registration number in
accordance with the Japanese Dentori Law.
The minimum specification for the flexible cord are: (1) 0.75 mm
2
conductors, (2) Type VCT or VCTF, and (3)
3-conductor.
The cord set must have minimum rated current capacity of 7 A.
The attachment plug must be a two-pole, grounded type with a Japanese Industrial Standard C8303 (15 A, 125 VAC)
configuration.
Othe
r Countries
The cord set fittings must bear the certification mark of the agency responsible for evaluation in a specific country.
Acceptable agencies are:
BSI (UK)
OVE (Austral
CEBEC (Belg
SEMKO (Swe
FIMKO (Finla
DEMKO (Den
NEMKO (Nor
SETI (Finland
EANSW (Aus
SEV (Switzer
ia)
ium)
den)
nd)
mark)
way)
)
tralia)
land)
IMQ (Italy)
UTE (France
)
CCC (China)
PSB (Singap
ore)
PSE (Japan)
BSMI (Taiwan
)
B (Polish)
VDE (Germa
ny)
The flexible cord must be of a HAR (harmonized) type HO5VV-F 3-conductor cord with a minimum conductor size of
0.03 square inches.
The minimum specification for the flexible cord for Class II product are: (1) 2X0.75 mm
2
conductors, (2) 2-conductor
cord.
The cord set must have a current capacity of at least 10 A and a nominal voltage rating of 125 / 250 VAC.
CAUTION: MODEL 258SAx IS DESIGNED TO USE WITH THE FLLOWING AC ADAPTER MODEL ONLY
Manufacture: LITE-ON ELECTRONICS, INC.; LI SHIN INTERNATIONAL ENTERPRISE CORP.
Model: PA-1161-02, PA-1161-01(160W); 0226A20160, 226C20160(160W)
Te
lephone lines requirement
The appropriate utilization of 26AWG telephone line cord on unit.
CAUTION: Always disconnect all telephone lines from the wall outlet before servicing or disassembling this equipment.
CAUTION: To reduce the risk of fire, use only No. 26AWG or larger telecommunication line cord.
Batte
ry Pack Safety
The battery pack is intended to use only with this notebook.
not
Do disassemble the pack.
not
Do dispose of the battery pack in fire or water.
B-3
Page 73

■ appendix B agency regulatory notices
To avoid risk of fire, burns, or damage to your battery pack, do not allow a metal object to touch the battery contacts.
dle area
Han a damaged or leaking battery with extreme care. If you come in contact with the electrolyte, wash the exposed
with soap
Do not battery pack if the ambient temperature exceeds 45℃ (113℉).
bta
not e 60℃, 140℉).
C th same or equivalent type recommended by the
AU xplosion if battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only wi
m
anu
VORSICHT! Explisionsgefahr bei unsachgernazen Austausch der Batterie. Ersatz nur dur
H
ersteller empfohlenem ahnlichen Typ. Entsorgung gebrauchter Batterien navh Angaben des Herstellers.
Laser Safety
The d with this computer is certified as a Class 1 laser device according to the U.S. Department of Health and
Hum
EN60
ER PRODUCT
S
Warning!
Do n o disassemble the cabinet containing the laser. The laser beam used in this product is harmful to the eyes. The
use o
safet
LED (Infrared) Safety
The i he left side of this computer is classified as a Class 1 LED (light-emitting diode) device according to
Inter
recom
DUKT
and water. If it contacts the eye, flush the eye with water for 15 minutes and seek medical attention.
charge the
To o in a replacement battery, contact your local dealer.
Do expose the battery pack to high storage temperatures (abov
When discarding a battery pack, contact your local waste disposal provider regarding
or recycling of batteries.
pter for charging.
Use only supplied AC Ada
TION: Danger of e
facturer. Discard used batteries according to the manufacturer`s instructions or local laws.
optical drive use
an Services (DHHS) Radiation Performance Standard and International Standards IEC 825 / IEC 825-1 (EN60825 /
825-1). The device is not considered harmful, but the following precautions are recommended:
Do not open the unit.
Avoid direct exposure
If the unit requires service, contact an auth
Ensure proper use by reading and following the instructions caref
Do not attempt to make any adjustment of the unit.
CLASS 1 LAS
APP REIL A LASER DE CLASSE 1 A
ELA RSCHUTZKLASSE 1 PRODUKT
ot attempt t
f optical instruments, such as magnifying lenses, with this product increase the potential hazard to your eyes. For your
y, have this equipment serviced only by an authorized service provider.
nfrared port located on t
national Standard IEC 825-1 (EN60825-1). This device is not considered harmful, but the following precautions are
mended:
Do not attempt to view the
Do not attempt to make any adjustment of the unit.
If the unit requires service, contact an authorized ser
Avoid direct eye exposure to the infrared LED beam. Be aware th
CLASS 1 LED PRODUCT
to the laser beam.
orized service center.
ully.
infrared LED beam with any type of optical device.
vice center.
at the beam is invisible light and cannot be seen.
local restrictions on the disposal
ch denselben oder einem vom
O LEDSCHUTZKLASSE 1 PR
Lithium battery warning
T thium battery to power the clock and calendar circuitry.
his computer contains a li
B-4
Page 74

■ appendix B agency regulatory notices
CAUTION: Danger of explosion if battery is replaced incorrectly. Replace only with the same or
e
quivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Discard used batteries according to the
m
anufacturer’s instructions.
A TENTION: Il y a danger d’xplosion s’il y a remplacement incorrect de la batterie. Remplacer
T
u
niquement avcc unc batterie du meme type ou d’un type recommande par le constructer. Mettre au
r
ebut les batteries usagees conformement aux instructions du fabricant.
VORSICHT! Explosionsgefahr bei unsachgemBen Austausch der Batterie Ersatz nur durch denselben
o
der einem vom Hersteller empfohlenem ahnlichen Typ. Entsorgung gebrauchter Batterien nach
A
ngaben des Herstellers.
Der Arbeitsplatzbezogene Schalldruckpegel nach DIN 45 635 betragt 70dB (A) oder weniger.
Zum Netzanschlua dieses Gerates ist eine geprufte Leitung zu verwenden. Fur einen Nennstrom bis 6A
u
nd einem Gerategewicht groBer 3kg ist eine Leitung nicht leichter als (1)H05VV-F, 3G, 0.75mm
(
2)2X0.75 mm
2
conductors einzusetzen.
Die Steckdose muB nahe dem Gerat angebracht und leicht zuganglich sein.
2
B-5
 Loading...
Loading...