Page 1

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
1 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
These Application Notes describe the procedures for configuring the Multi-Tech FaxFinder®
IP Fax Server with Avaya Aura® Communication Manager and Avaya Aura® Session Manager
using a SIP trunk interface.
FaxFinder is an appliance-based fax server that sends and receives fax calls over an IP
network. In the tested configuration, FaxFinder interoperated with Avaya Aura® Session
Manager to send/receive faxes using SIP trunk facilities.
Information in these Application Notes has been obtained through DevConnect compliance
testing and additional technical discussions. Testing was conducted via the DevConnect
Program at the Avaya Solution and Interoperability Test Lab.
Avaya Solution & Interoperability Test Lab
Application Notes for Configuring Multi-Tech FaxFinder® IP
Fax Server with Avaya Aura® Communication Manager and
Avaya Aura® Session Manager via SIP Trunk Interface
- Issue 1.0
Abstract
Page 2

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
2 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
1. Introduction
These Application Notes describe the procedures for configuring Multi-Tech FaxFinder® IP Fax
Server with Avaya Aura® Communication Manager and Avaya Aura® Session Manager.
FaxFinder is an appliance-based fax server solution that sends and receives faxes over an IP
network. FaxFinder utilizes T.38 Fax over Internet Protocol (FoIP) for sending media. In the tested
configuration, FaxFinder interoperated directly with Avaya Aura® Session Manager to send/receive
faxes using SIP signaling.
2. General Test Approach and Test Results
This section describes the compliance test approach used to verify interoperability of Multi-Tech
FaxFinder® IP Fax Server.
2.1. General Test Approach
The general test approach was to make intra-site and inter-site fax calls to and from FaxFinder. The
inter-site calls were made using SIP or ISDN-PRI trunks between the sites. Faxes were sent with
various page lengths, resolutions, and at various fax data speeds. For capacity, a large number of
multi-page faxes were continuously sent between the two FaxFinder servers simultaneously.
Serviceability testing included verifying proper operation/recovery from failed cables, unavailable
resources, and Session Manager and FaxFinder restarts. Fax calls were also tested with different
Avaya Media Gateway media resources used to process the fax data between sites. This included the
TN2302 MedPro circuit pack, the TN2602 MedPro circuit pack in the Avaya G650 Media Gateway;
the integrated VoIP engine of the Avaya G450 Media Gateway and the Avaya MM760 Media
Module installed in the Avaya G450 Media Gateway.
2.2. Test Results
Multi-Tech FaxFinder® IP Fax Server successfully passed compliance testing.
2.3. General Observations
Fax calls consume DSP (Digital Signal Processing) resources for processing fax data on the
TN2302AP IP Media Processor (MedPro) circuit pack and the TN2602AP IP Media Processor
circuit pack in the Avaya G650 Media Gateway, and the integrated Voice over Internet Protocol
(VoIP) engine of the Avaya G450 Media Gateway. To increase the capacity to support simultaneous
fax calls, additional TN2302AP and/or TN2602AP MedPro circuit packs need to be installed in the
Avaya G650 Gateway, and additional Avaya MM760 Media Module or Modules need to be installed
in the Avaya G450 Media Gateway. The information contained in the table below indicates DSP
capacities/usage in the Avaya media processors. Customers should work with their Avaya sales
representatives to ensure that their fax solutions have adequate licenses and DSP resources to match
the intended Fax capacity/usage.
Page 3

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
3 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Platform
Device
DSP Resources
per Platform Device
DSP Resources
per FoIP Call
TN2302, G450, MM760
64
4
TN2602
64
1
Note that the SIP trunk group on Communication Manager for connecting to Session Manager at
each site, as well as the SIP or ISDN-PRI trunk group for connecting the 2 sites must be configured
with adequate number of trunk group members to support the number of simultaneous fax calls
intended.
2.4. Support
Technical support for FaxFinder can be obtained by contacting Multi-Tech Systems at:
Phone: (800) 972-2439 or (763) 717-5863
Email: support@multitech.com
Web: https://support.multitech.com
Page 4
RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
4 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
3. Configuration
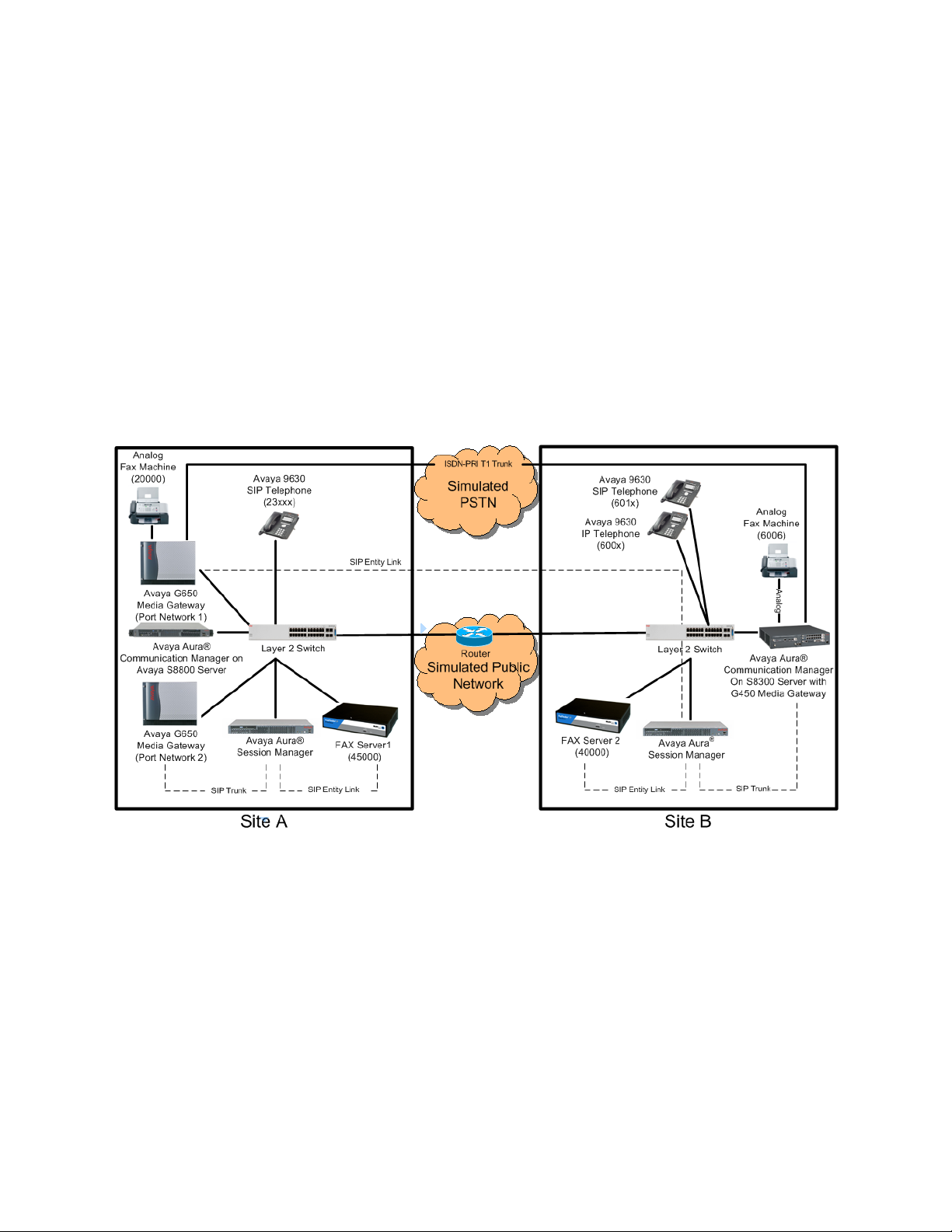
The test configuration was designed to emulate two separate sites with multiple Port Networks at
one site, and modular Gateway resources at the other site. Each site was configured with Multi-Tech
FaxFinder® IP Fax Server, Avaya Aura® Communication Manager and Avaya Aura® Session
Manager. Figure 1 illustrates the configuration used in the tested configuration.
3.1. Configuration Details
In the tested configuration, Communication Manager Servers and Gateways at the two sites were
connected via SIP and ISDN-PRI trunks. Faxes were alternately sent between the two sites using
these two facilities. Connections to Session Manager were via SIP trunk facilities, and the FaxFinder
servers communicated directly with Session Manager via SIP.
Two separate Session Manager Servers were used to connect to the FaxFinder Servers at each site.
Figure 1: Multi-Tech FaxFinder® IP Fax Server sample configuration
Site A had an Avaya S8800 Communication Manager Server with two Avaya G650 Media
Gateways. Each Media Gateway was configured in a separate port networks with separate IP
network regions. The FaxFinder server at this site communicated with Session Manager via SIP. In
turn, Communication Manager used a SIP Trunk which terminated on a CLAN circuit pack in port
network 2 to communicate with Session Manager. IP media resources were provided by Media
Processor (MedPro) circuit packs. Two versions of the MedPro circuit pack were tested in this
configuration: TN2302AP and TN2602AP. Endpoints at this site included an Avaya 9600 Series IP
Telephone (with H.323 firmware), and an analog fax machine.
Page 5

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
5 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Site B had an Avaya S8300 Communication Manager Server in an Avaya G450 Media Gateway.
The FaxFinder server at this site communicated with Session Manager via SIP. On the Avaya G450
Media Gateway, the signaling and media resources supporting a SIP trunk connected to Session
Manager were integrated directly on the media gateway processor. Endpoints at this site included
Avaya 9600 Series IP Telephones (with H.323 and SIP firmware), and an analog fax machine.
The IP telephones were not involved in the faxing operations, they were present in the configuration
to verify that VoIP telephone calls did not interfere with FoIP faxing operations.
Outbound fax calls originating from FaxFinder were sent to Session Manager first, then to
Communication Manager, via the configured SIP trunks. Based on the dialed digits, Communication
Manager directed the calls to the local fax machine, or the inter-site trunks (ISDN-PRI or SIP) to
reach the remote site. Inbound fax calls to FaxFinder were first received by Communication
Manager from the local fax machine or from across either ISDN-PRI or SIP trunks connected to the
remote Site. Communication Manager then directed the calls to FaxFinder via the configured
Session Manager SIP trunks.
Page 6

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
6 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Equipment
Software/Firmware
Avaya S8800 Servers (at both sites)
Avaya Aura® Session Manager
6.0 (6.0.2.0.602004)
6.1 (6.1.2.0.612004)
Avaya Aura® System Manager 6.0, 6.1
Avaya S8800 Server (at Site A)
Avaya Aura® Communication Manager 6.0 SP1
R016x.00.0.345.0 with patch 18567
Avaya G650 Media Gateway (at Site A)
- 2 CLANs
- 2 MedPros – TN2302
- 2 MedPros – TN2602
TN799DP - HW01 FW38 & HW13 FW 38
TN2302AP - HW20 FW120
TN2602AP - HW02 FW057
Avaya S8300D Server (at Site B)
Avaya Aura® Communication Manager 6.0 SP2
R016x.00.1.510.1 with patch 18734
Avaya G450 Media Gateway (at Site B)
30.14.0/1
Avaya 9620 IP Telephone (SIP)
Avaya 9630 IP Telephone (H.323)
Avaya one-X® Deskphone Edition SIP 2.5
H.323 3.11
Analog Fax Machines
-
Multi-Tech FaxFinder® IP Fax Server
1.0.14
Multi-Tech FaxFinder® Client software
2.2.2
4. Equipment and Software Validated
The following equipment and software/firmware were used for the sample configuration provided:
The Multi-Tech FaxFinder® IP Fax Server is shipped as an all-in-one appliance. The physical
dimensions are 9.1” W x 6.1” L x 1.7” H, roughly the size of a modem.
Page 7

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
7 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
5. Configure Avaya Aura® Communication Manager
This section describes the Communication Manager configuration necessary to interoperate with
Session Manager and Multi-Tech FaxFinder® IP Fax Server. Connectivity via SIP and PRI trunks
between the two sites used existing configurations which follow standard practices. Therefore, it
focuses on the configuration of the SIP trunks connecting Communication Manager to the Avaya
SIP infrastructure with the following assumption:
The examples shown in this section refer to Site A. Unless specified otherwise, these same
steps also apply to Site B using values appropriate for that location.
The configuration of Communication Manager was performed using the System Access Terminal
(SAT). After the completion of the configuration, the save translation command was used to make
the changes permanent.
5.1. Steps to Configure Communication Manager
The configuration on Communication Manager include the following areas:
Verify Communication Manager License (Step 1)
Identify IP Interfaces (Step 2)
Administer IP Network Regions (Steps 3 – 6)
Administer IP Node Name (Step 7)
Administer IP Network Map (Step 8)
Administer IP Codec Set (Steps 9 – 10)
Administer SIP Signaling Group (Step 11)
Administer SIP Trunk Group (Steps 12 – 13)
Administer Public Unknown Numbering (Step 14)
Administer Route Pattern (Step 15)
Administer AAR Analysis (Steps 16 – 17)
Page 8
RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
8 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Step
Description
1.
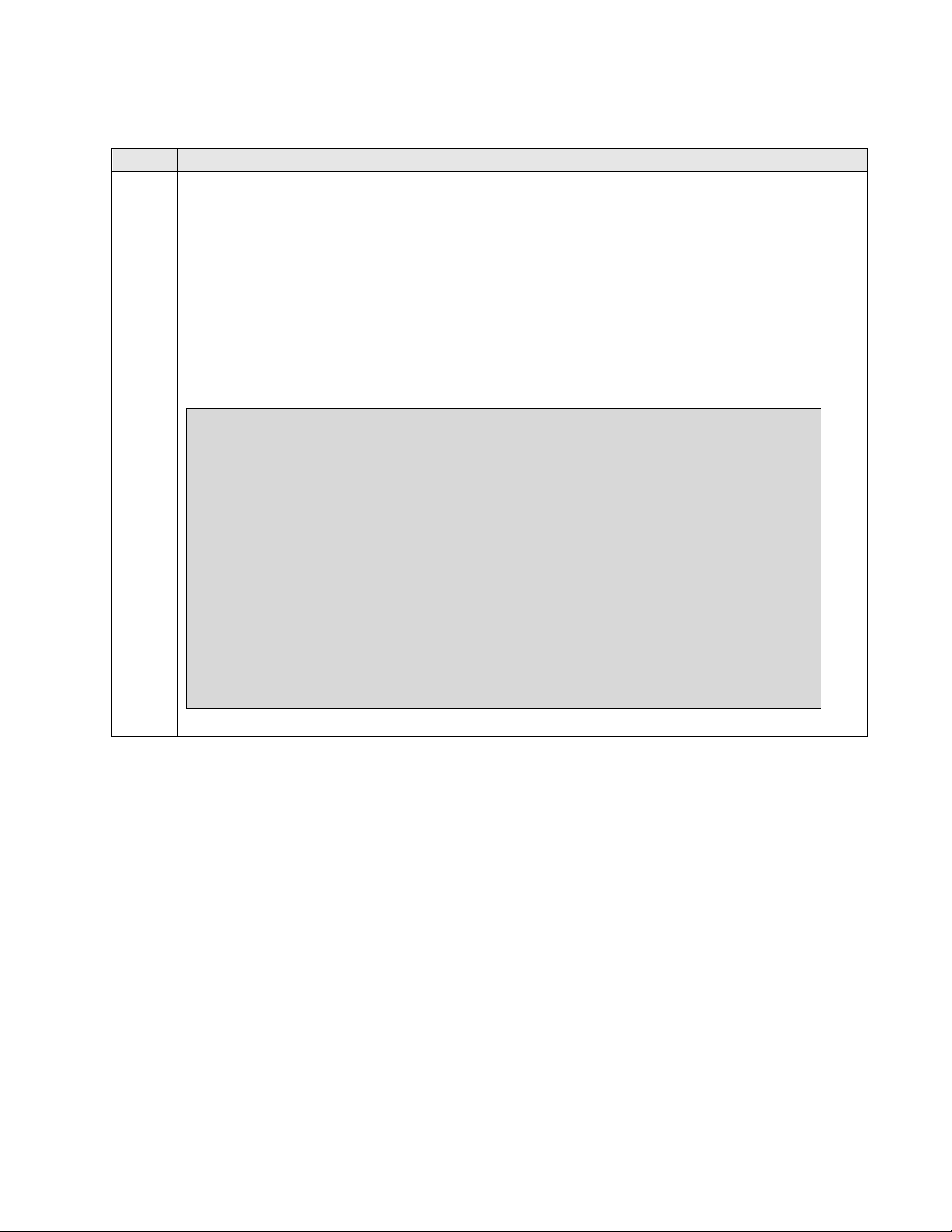
Verify Communication Manager License
Use the display system-parameters customer-options command to verify that the
Communication Manager license has proper permissions for features illustrated in these
Application Notes. Navigate to Page 2, and verify that there is sufficient remaining
capacity for SIP trunks by comparing the Maximum Administered SIP Trunks field
value with the corresponding value in the USED column.
The license file installed on the system controls the maximum permitted. If there is
insufficient capacity, contact an authorized Avaya sales representative to make the
appropriate changes
display system-parameters customer-options Page 2 of 11
OPTIONAL FEATURES
IP PORT CAPACITIES USED
Maximum Administered H.323 Trunks: 12000 96
Maximum Concurrently Registered IP Stations: 18000 1
Maximum Administered Remote Office Trunks: 12000 0
Maximum Concurrently Registered Remote Office Stations: 18000 0
Maximum Concurrently Registered IP eCons: 414 0
Max Concur Registered Unauthenticated H.323 Stations: 100 0
Maximum Video Capable Stations: 18000 0
Maximum Video Capable IP Softphones: 18000 0
Maximum Administered SIP Trunks: 24000 298
Maximum Administered Ad-hoc Video Conferencing Ports: 24000 0
Maximum Number of DS1 Boards with Echo Cancellation: 522 0
Maximum TN2501 VAL Boards: 128 2
Maximum Media Gateway VAL Sources: 250 0
Maximum TN2602 Boards with 80 VoIP Channels: 128 0
Maximum TN2602 Boards with 320 VoIP Channels: 128 2
Maximum Number of Expanded Meet-me Conference Ports: 300 0
Page 9
RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
9 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Step
Description
2.
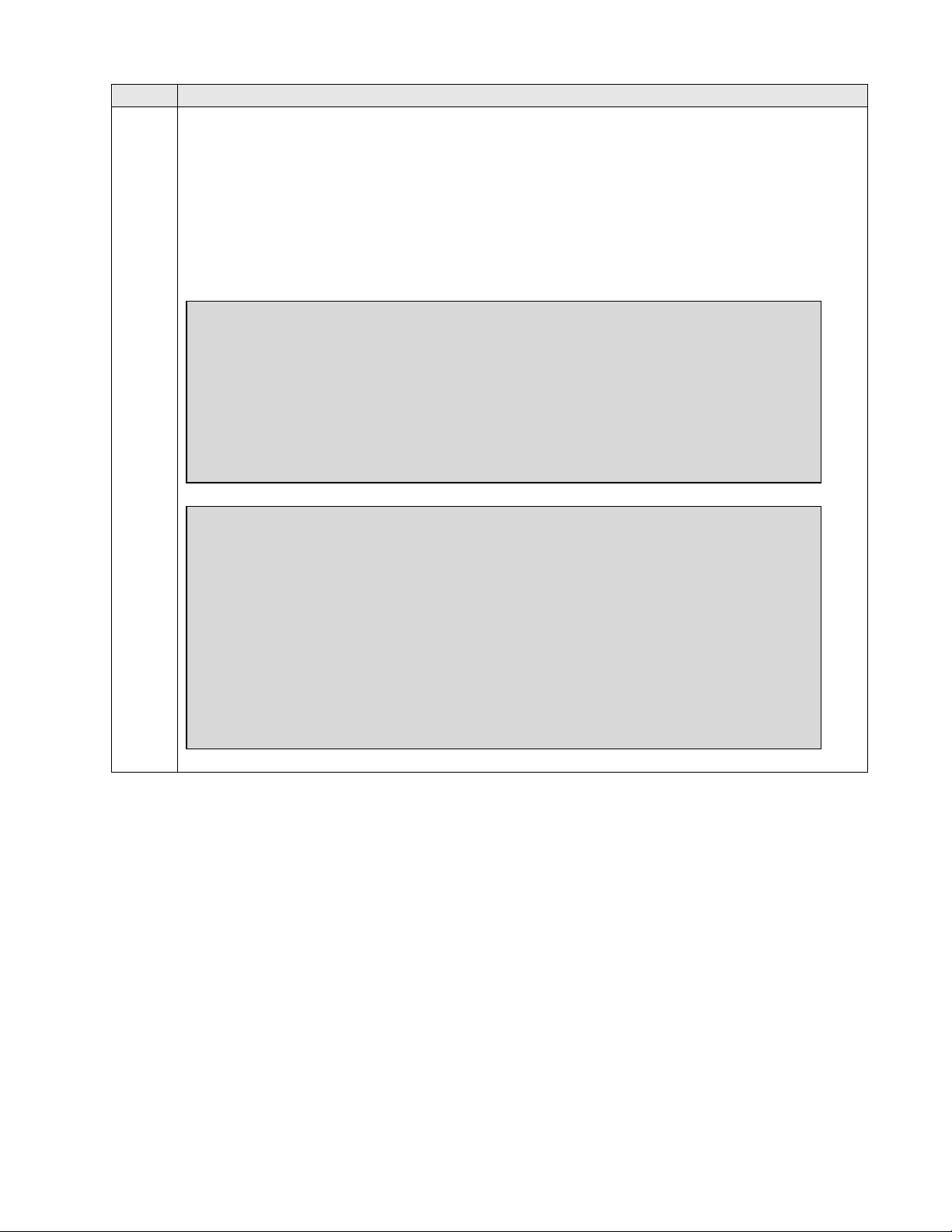
Identify IP Interfaces
Use the list ip-interface clan and list ip-interface medpro commands to identify IP
interfaces in each network region. Interfaces in cabinet 01 (port network 1) as indicated in
the Slot field are in IP network region 1 as indicated in the Net Rgn field.
Testing with the TN2302 and TN2602 circuit packs were done separately. When testing
with the TN2302, the TN2602 was disabled (turned off) and vice versa as indicated in the
ON field.
list ip-interface medpro
IP INTERFACES
Net
ON Slot Code/Sfx Node Name/ Mask Gateway Node Rgn VLAN Virtual Node
IP-Address
-- ----- -------- --------------- ---- --------------- --- ---- -------------- n 01A02 TN2302 MEDPRO1A /24 Gateway001 1 n
10.64.22.15
n 02A02 TN2302 MEDPRO2A /24 Gateway001 2 n
10.64.22.18
y 01A04 TN2602 MEDPRO1A-2 /24 Gateway001 1 n
10.64.22.17
y 02A04 TN2602 MEDPRO2A-2 /24 Gateway001 2 n
10.64.22.20
list ip-interface clan
IP INTERFACES
S kts Net Eth
ON Slot Code/Sfx Node Name/ Mask Gateway Node Warn Rgn VLAN Link
IP-Address
-- ---- -------- --------------- ---- --------------- - --- --- ---- --- y 01A03 TN799 D CLAN1A /24 Gateway001 400 1 n 1
10.64.22.16
y 02A03 TN799 D CLAN2A /24 Gateway001 400 2 n 2
10.64.22.19
Page 10
RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
10 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Step
Description
3.
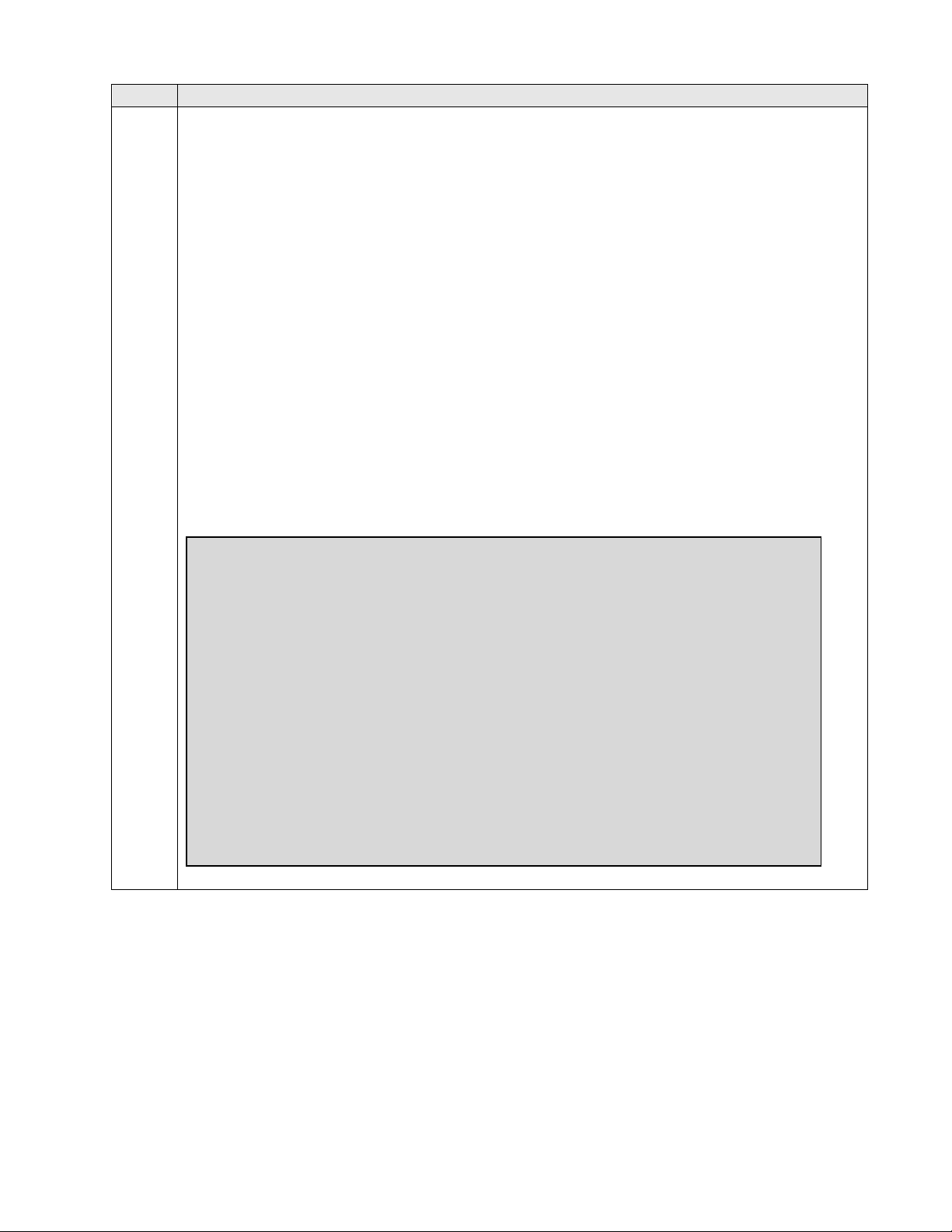
Administer IP Network Region 1
The configuration of the IP network regions (Steps 3 – 6) was already in place and is
included here for clarity. At Site A, the Avaya G650 Media Gateway comprising port
network 1 and all IP endpoints were located in IP network region 1.
Use the display ip-network-region command to view these settings.
A descriptive name was entered for the Name field.
IP-IP Direct Audio (Media Shuffling) was enabled to allow audio traffic to be sent
directly between IP endpoints without using media resources in the Avaya Media
Gateway. This was done for both intra-region and inter-region IP-IP Direct Audio.
This is the default setting. Media Shuffling can be further restricted at the trunk level
on the Signaling Group form.
The Codec Set field was set to the IP codec set to be used for calls within this IP
network region. In this case, IP codec set 1 was selected.
The default values were used for all other fields.
At Site B, all IP components were located in IP network region 1 and the IP network
region was configured in the same manner as shown below.
display ip-network-region 1 Page 1 of 20
IP NETWORK REGION
Region: 1
Location: Authoritative Domain: avaya.com
Name: PN1
MEDIA PARAMETERS Intra-region IP-IP Direct Audio: yes
Codec Set: 1 Inter-region IP-IP Direct Audio: yes
UDP Port Min: 2048 IP Audio Hairpinning? n
UDP Port Max: 3329
DIFFSERV/TOS PARAMETERS RTCP Reporting Enabled? y
Call Control PHB Value: 46 RTCP MONITOR SERVER PARAMETERS
Audio PHB Value: 46 Use Default Server Parameters? y
Video PHB Value: 26
802.1P/Q PARAMETERS
Call Control 802.1p Priority: 6
Audio 802.1p Priority: 6
Video 802.1p Priority: 5 AUDIO RESOURCE RESERVATION PARAMETERS
H.323 IP ENDPOINTS RSVP Enabled? n
H.323 Link Bounce Recovery? y
Idle Traffic Interval (sec): 20
Keep-Alive Interval (sec): 5
Keep-Alive Count: 5
Page 11

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
11 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Step
Description
4.
Administer IP Network Region 1 – Continued
On Page 4, codec sets are defined for inter-region calls. In the case of the compliance test
at Site A, calls from IP network Source Region 1 to IP network region 2 (dst rgn 2) used
codec set 1. The default values were used for all other fields. At Site B, only one IP
network region was used, so no inter-region settings were required.
5.
Administer IP Network Region 2
At Site A, IP network region 2 was created for Port Network 2 in a similar manner as IP
network region 1 shown in Step 3 but with a different name. This was the network region
used for SIP Trunk connections to Session Manager.
6.
Administer IP Network Region 2 – Continued
The inter-region codec setting was created similarly to Step 4.
display ip-network-region 2 Page 3 of 19
Source Region: 2 Inter Network Region Connection Management I M
G A e
dst codec direct WAN-BW-limits Video Intervening Dyn A G a
rgn set WAN Units Total Norm Prio Shr Regions CAC R L s
1 1 y NoLimit n all
2 1 all
3 3 y NoLimit n all
display ip-network-region 2 Page 1 of 20
IP NETWORK REGION
Region: 2
Location: Authoritative Domain: avaya.com
Name: PN2
MEDIA PARAMETERS Intra-region IP-IP Direct Audio: yes
Codec Set: 1 Inter-region IP-IP Direct Audio: yes
UDP Port Min: 2048 IP Audio Hairpinning? n
UDP Port Max: 3329
DIFFSERV/TOS PARAMETERS
Call Control PHB Value: 46
Audio PHB Value: 46
Video PHB Value: 26
802.1P/Q PARAMETERS
Call Control 802.1p Priority: 6
Audio 802.1p Priority: 6
Video 802.1p Priority: 5 AUDIO RESOURCE RESERVATION PARAMETERS
H.323 IP ENDPOINTS RSVP Enabled? n
H.323 Link Bounce Recovery? y
Idle Traffic Interval (sec): 20
Keep-Alive Interval (sec): 5
Keep-Alive Count: 5
display ip-network-region 1 Page 4 of 20
Source Region: 1 Inter Network Region Connection Management I M
G A t
dst codec direct WAN-BW-limits Video Intervening Dyn A G c
rgn set WAN Units Total Norm Prio Shr Regions CAC R L e
1 1 all
2 1 y NoLimit n t
3
Page 12

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
12 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Step
Description
7.
Administer IP Node Name
Use the change node-names ip command to create a node name that maps to the Session
Manager IP address. This node name is used in the configuration of the SIP trunk
signaling group in Step 11.
8.
Administer IP Network Map
Session Manager and the FaxFinder server were configured to be located in an IP
network region different than the default region 1. The region was assigned using the
change ip-network-map command. In the case of the compliance test, the IP addresses
for these resources at the Main Site were assigned to IP network region 2 as shown in the
example below. At the Remote Site, Session Manager and the FaxFinder server were
located in the default IP network region 1, so it did not require an IP address map entry.
9.
Administer IP Codec set
Use the change ip-codec-set 1 command to verify that G.711MU or G.711A is contained
in the codec list. The example below shows the value used in the compliance test.
display ip-codec-set 1 Page 1 of 2
IP Codec Set
Codec Set: 1
Audio Silence Frames Packet
Codec Suppression Per Pkt Size(ms)
1: G.711MU n 2 20
change ip-network-map Page 1 of 63
IP ADDRESS MAPPING
Subnet Network Emergency
IP Address Bits Region VLAN Location Ext
--------------------------------------------- ------ ------ ---- ------------ FROM: 10.64.20.31 / 2 n
TO: 10.64.20.31
FROM: 10.64.22.170 / 2 n
TO: 10.64.22.170
change node-names ip Page 1 of 2
IP NODE NAMES
Name IP Address
CLAN1A 10.64.22.16
CLAN2A 10.64.22.19
CM-Remote 10.64.21.111
DemoSM 10.64.20.31
Gateway001 10.64.22.1
MEDPRO1A 10.64.22.15
MEDPRO1A-2 10.64.22.17
MEDPRO2A 10.64.22.18
MEDPRO2A-2 10.64.22.20
TR18300 10.64.10.67
Page 13

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
13 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Step
Description
10.
Administer IP Codec set – Fax settings
On Page 2, set the FAX Mode field to t.38-standard. This is necessary to support the
FaxFinder server assigned to IP network region 2. The Modem Mode field should be set
to off.
Leave the FAX Redundancy setting at its default value of 0. A packet redundancy level
can be assigned to improve packet delivery and robustness of FAX transport over the
network (with increased bandwidth as trade-off). Avaya uses IETF RFC-2198 and ITU-T
T.38 specifications as redundancy standard. With this standard, each Fax over IP packet
is sent with additional (redundant) 0 to 3 previous fax packets based on the redundancy
setting. A setting of 0 (no redundancy) is suited for networks where packet loss is not a
problem.
change ip-codec-set 1 Page 2 of 2
IP Codec Set
Allow Direct-IP Multimedia? n
Mode Redundancy
FAX t.38-standard 0
Modem off 0
TDD/TTY US 3
Clear-channel n 0
Page 14

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
14 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Step
Description
11.
Administer SIP Signaling Group
For the compliance test, a signaling group with the associated SIP trunk group was used
for routing fax calls to/from the FaxFinder server via Session Manager. For the
compliance test at Site A, signaling group 12 was configured using the parameters
highlighted below. All other fields were set as described in [3].
The Group Type was set to sip.
The Transport Method was set to the recommended default value of tls (Transport
Layer Security). As a result, the Near-end Listen Port and Far-end Listen Port are
automatically set to 5061.
The Near-end Node Name was set to CLAN2A, the node name that maps to the IP
address of the CLAN circuit pack used to connect to Session Manager. Node names
are defined using the change node-names ip command (see Step 7 above).
The Far-end Node Name was set to demoSM. This node name maps to the IP
address of the Session Manager server as defined using the change node-names ip
command.
The Far-end Network Region was set to 2. This is the IP network region which
contains Session Manager and FaxFinder.
The Far-end Domain was set to avaya.com. This domain is sent in the headers of SIP
INVITE messages for calls originating from and terminating to Session Manager
using this signaling group.
Direct IP-IP Audio Connections was set to y. This field must be set to y to enable
Media Shuffling on the trunk level (see Step 3 on IP-IP Direct Audio).
The DTMF over IP field was set to the default value of in-band.
The default values were used for all other fields.
change signaling-group 12 Page 1 of 1
SIGNALING GROUP
Group Number: 12 Group Type: sip
IMS Enabled? n Transport Method: tls
Q-SIP? n SIP Enabled LSP? n
IP Video? n Enforce SIPS URI for SRTP? y
Peer Detection Enabled? y Peer Server: SM
Near-end Node Name: CLAN2A Far-end Node Name: demoSM
Near-end Listen Port: 5061 Far-end Listen Port: 5061
Far-end Network Region: 2
Far-end Domain: avaya.com
Bypass If IP Threshold Exceeded? n
Incoming Dialog Loopbacks: eliminate RFC 3389 Comfort Noise? n
DTMF over IP: in-band Direct IP-IP Audio Connections? y
Session Establishment Timer(min): 3 IP Audio Hairpinning? n
Enable Layer 3 Test? y Initial IP-IP Direct Media? n
H.323 Station Outgoing Direct Media? n Alternate Route Timer(sec): 6
Page 15

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
15 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Step
Description
12.
Administer SIP Trunk Group
For the compliance test, trunk group 12 with the associated signaling group was used for
routing fax calls to/from Session Manager. Trunk group 12 was configured using the
parameters highlighted below. All other fields were set as described in [3].
On Page 1:
The Group Type field was set to sip.
A descriptive name was entered for the Group Name.
An available trunk access code (TAC) that was consistent with the existing dial plan
was entered in the TAC field.
The Service Type field was set to tie.
The Signaling Group was set to the signaling group shown in the previous step.
The Number of Members field contained the number of trunks in the SIP trunk
group. It determines how many simultaneous SIP calls can be supported by the
configuration. Each SIP call between two SIP endpoints (whether internal or
external) requires two SIP trunks for the duration of the call.
The default values were used for all other fields.
change trunk-group 12 Page 1 of 21
TRUNK GROUP
Group Number: 12 Group Type: sip CDR Reports: y
Group Name: PN2 to demoSM COR: 1 TN: 1 TAC: *012
Direction: two-way Outgoing Display? n
Dial Access? n Night Service:
Queue Length: 0
Service Type: tie Auth Code? n
Member Assignment Method: auto
Signaling Group: 12
Number of Members: 50
Page 16

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
16 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Step
Description
13.
Administer SIP Trunk Group – continued
On Page 3:
Set the Numbering Format field to public. This field specifies the format of the
calling party number sent to the far-end.
Default values may be used for all other fields.
change trunk-group 12 Page 3 of 21
TRUNK FEATURES
ACA Assignment? n Measured: none
Maintenance Tests? y
Numbering Format: public
UUI Treatment: service-provider
Replace Restricted Numbers? n
Replace Unavailable Numbers? n
Modify Tandem Calling Number: no
Show ANSWERED BY on Display? y
14.
Administer Public Unknown Numbering
Public unknown numbering defines the calling party number to be sent to the far-end.
Use the change public-unknown-numbering command to create an entry that will be
used by the trunk groups defined in Steps 12-13. In the example shown below, all calls
originating from a 5-digit extension beginning with 2 or 4 and routed across any trunk
group (Trk Grp column is blank) were sent as a 5-digit calling party number.
change public-unknown-numbering 0 Page 1 of 2
NUMBERING - PUBLIC/UNKNOWN FORMAT
Total
Ext Ext Trk CPN CPN
Len Code Grp(s) Prefix Len
Total Administered: 6
5 1 5 Maximum Entries: 9999
5 2 5
5 4 5 Note: If an entry applies to
5 5 5 a SIP connection to Avaya
4 6 4 Aura(tm) Session Manager,
5 7 5 the resulting number must
be a complete E.164 number.
Page 17

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
17 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Step
Description
15.
Administer Route Pattern
Use the change route-pattern command to create a route pattern that will route fax calls
to the SIP trunk that connects to the FaxFinder server.
The example below shows the route pattern used for the compliance test at the Main Site.
A descriptive name was entered for the Pattern Name field. The Grp No field was set to
the trunk group created in Steps 12–13. The Facility Restriction Level (FRL) field was
set to a level that allows access to this trunk for all users that require it. The value of 0 is
the least restrictive level. The default values were used for all other fields.
change route-pattern 12 Page 1 of 3
Pattern Number: 12 Pattern Name: To SM
SCCAN? n Secure SIP? n
Grp FRL NPA Pfx Hop Toll No. Inserted DCS/ IXC
No Mrk Lmt List Del Digits QSIG
Dgts Intw
1: 12 0 n user
16.
Administer AAR Analysis
Automatic Alternate Routing (AAR) was used to route calls to FaxFinder via Session
Manager. Use the change aar analysis command to create an entry in the AAR Digit
Analysis Table for this purpose. The example below shows entries previously created for
the Main Site using the display aar analysis 0 command. The 3rd highlighted entry
specifies that 5 digit dial string 40000 was to use route pattern 12 to route calls to the
FaxFinder server at Site A via Session Manager. The dial string 45000 (the FaxFinder
server at Site B) used Route Pattern 15 to route calls between Communication Managers.
change aar analysis 0 Page 1 of 2
AAR DIGIT ANALYSIS TABLE
Location: all Percent Full: 1
Dialed Total Route Call Node ANI
String Min Max Pattern Type Num Reqd
10 4 4 4 aar n
3 5 5 12 aar n
40000 5 5 12 aar n
45000 5 5 15 aar n
Page 18

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
18 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
6. Configure Avaya Aura® Session Manager - Overview
This section covers the configuration of Session Manager at Site A. Session Manager is configured
via an Internet browser using the administration web interface. It is assumed that the setup screens of
the administration web interface have been used for initial configurations. For additional
information on these installation tasks, refer to [3].
Each SIP endpoint used in the compliance test that registered with Session Manager required that a
user and endpoint profile be created and associated with Session Manager. This configuration is not
directly related to the interoperability of the products being tested, so it is not included here. These
procedures are covered in [3].
This section summarizes the configuration steps that are necessary for interoperating with MultiTech FaxFinder® IP Fax Server. The test environment was previously configured to enable Avaya
Aura® Communication Manager and Session Manager at each site to communicate with each other.
Details of this configuration are not described in this document, and additional information can be
obtained in [3].
The documented configurations were repeated for the Session Manager at Site B using values
appropriate for that site from Figure 1. This includes but is not limited to the IP addresses, SIP
domain and user extensions.
The steps used were:
Create a SIP Entity for the FaxFinder Server
Create a SIP Entity Link for the FaxFinder Server
Create a Routing Policy
Create or modify Dial Patterns
Page 19

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
19 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
6.1. Configure Session Manager - Details
Step
Description
1.
Login
Access the System Manager administration web interface by entering
https://<ip-addr>/SMGR as the URL in an Internet browser, where <ip-addr> is the IP
address (or FQDN) of the System Manager server.
Log in with the appropriate credentials.
2.
Create a SIP Entity for the FaxFinder Server
Navigate to Routing\SIP Entities and click New to create an Entity definition. In the
screenshot below, the Entity RB_FaxServer was previously created using the following
settings.
This section summarizes the applicable user-defined parameters used during the SIP installation
procedures.
Page 20

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
20 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Step
Description
3.
Create a SIP Entity for the FaxFinder Server - Continued
Enter a descriptive Name such as RB_FaxServer and enter the FQDN or IP Address
for the FaxFinder server as shown below. Select Other for the Entity Type. All other
settings were defaults.
4.
Create an Entity Link for the FaxFinder Server
An Entity Link establishes the details of how Entities will communicat e with each other.
Use the Add button to create a new link. In this case, Session Manager at the Main Site,
demoSM, was configured to communicate with RB_FaxServer using UDP protocol
over port 5060 as a Trusted Entity.
Page 21

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
21 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Step
Description
5.
Create a Routing Policy
Navigate to Routing\Routing Policies and click New to create a routing policy for
incoming calls to the FaxFinder server. The illustration below was captured after the
Policy RB_Fax_Server_2 had been created and the following steps will describe how
this policy was created.
A Routing Policy consists of a definition of the SIP Entity as Destination, the Time of
Day the policy applies, and the Dial Patterns that will trigger this particular policy.
Below are the settings used for this test. Use the Select or Add buttons to create or use
existing definitions for each parameter.
Page 22

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
22 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Step
Description
6.
Create or Modify Dial Patterns
Associating a dial pattern with a SIP Routing Policy instructs Session Manager how to
route calls matching the administered Dial Pattern(s). In the test, existing Routing
Policies were modified for routing to endpoints or Entities at the Remote Site, and new
Dial Patterns were created to route to the Main Site and Remote Site Fax Servers using
the existing and new routing policies.
In the snapshot below, the Dial Patterns were previously created. The applicable patterns
were all 5 Digit extension patterns: dialed numbers beginning with 2 (the local analog
fax machine at Site A), dialed numbers beginning with 40 (to route incoming Fax calls
to the FaxFinder server at Site B), dialed numbers beginning with 45 (to route to
Communication Manager at Site A in order to route via the public network interface
between the sites). In addition, an existing 4 digit patterns beginning with 60 was used to
route Fax calls to Communication Manager at the Main Site for routing via the public
network interfaces to the analog machine at the Remote Site.
The ‘40’ and ‘45’ dial patterns were created for this test, all others were in place in the
test environment.
Page 23

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
23 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Step
Description
7.
Create or Modify Dial Patterns – Continued
The entries required to create the new Dial Pattern for routing calls to the FaxFinder
server at the Main Site are illustrated below. The Pattern, Min and Max number of
digits, and SIP Domain entries were used for this Dial Pattern definition. Click Add to
associate the dial pattern with an existing Routing Policy, in this case the
RB_Fax_Server_2 policy created in Step 5 above. The Originating Location Name
All was used in this case to apply this pattern regardless of originating locations.
In the same way, a new Dial Pattern was created (not shown) and associated with the
existing policy to route calls to Communication Manager at the Main Site (for onward
routing to remote site) using the Dial Pattern 45. This was used to route calls from the
Main Site Fax Server to the Remote Site Fax Server.
Page 24

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
24 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
7. Configure Multi-Tech FaxFinder® IP Fax Server
This section describes the configuration of Multi-Tech FaxFinder® IP Fax Server. For further
instructions on configuring FaxFinder, consult the Administrator User Guide [4].
7.1. Configure FaxFinder Details
The configuration procedures covered in this section include tasks in the following sub categories:
1. System Configuration
Launch FaxFinder web configuration tool
Configure Network Settings
Configure SMTP Settings
Configure Time Settings
Configure Printers and Network Shares
2. Fax Configuration
Configure SIP/T.38
Configure Inbound Routing
Configure Outbound rules
3. Configure Users and Contacts
The examples shown in this section refer to Site A. Unless specified otherwise, these same steps also
apply to Site B using values appropriate from Figure 1.
Page 25

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
25 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Step
Description
1.
System Configuration: Launch FaxFinder web configuration tool
The FaxFinder configuration is performed using a web browser. Access the tool by
pointing your web browser to http://<ip_address>. The home page is displayed below:
System Configuration: Configure Network Settings
FaxFinder ships with a default network address, so initial configuration needs to be
performed from a browser on a host manually configured with an address on the same
network segment. Once connected, navigate to System Configuration > Network to
assign an appropriate Hostname, IP Address, and other relevant network settings as
shown below. Click Save to commit the changes which will reboot the device. To
complete the remaining settings, access the web configuration tool from a host that has
access to the network segment of the newly configured address.
Page 26

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
26 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Step
Description
System Configuration: Configure SMTP Settings
FaxFinder can be configured to generate email alerts for a number of events. Navigate to
System Configuration > SMTP to configure the outgoing mail gateway, click Save to
commit the changes. Below is an example:
System Configuration: Configure Time Settings
Set the current date and time, it is also recommended that an NTP server be configured
to keep the system time in synch with other servers. Click Set and Save when entries are
completed in each section. Below is an example of the settings used in the tested
configuration:
Page 27

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
27 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Step
Description
System Configuration: Configure Printers and Network Shares
FaxFinder can be configured to deliver inbound faxes to an email address, to a printer, or
to a network share. In the tested configuration, all inbound faxes were saved to a network
share. To add a share, click the Add link and provide the path and credentials for the
share. The share was previously configured, however the Edit dialog shown below looks
similar to the Add dialog:
Page 28

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
28 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Step
Description
2.
Fax Configuration: Configure SIP/T.38
Navigate to Fax Configuration > SIP / T.38 and provide the appropriate information
for the Session Manager in the SIP section. Note that at this time, UDP is the only option
for communications with Session Manager. Default T.38 settings were used in the
compliance tests.
Page 29

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
29 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Step
Description
Fax Configuration: Configure Inbound Routing
Navigate to Fax Configuration > Inbound Routing to define Global, Default and
specific Recipient routing rules. For each rule, a network share, email address or printer
can be defined for fax delivery. Click on Edit in each section to define or modify the
respective rules. Below is a view of the rules used in the tested configuration:
Global Routing was configured by clicking the Add link (from the dialog that appears
when the Edit link is clicked in Global Routing), this rule applies to all Faxes received,
in addition to any other routing rules:
A default destination can be defined if no other routing policies apply:
A Recipient Routing rule will automatically be created when users are configured (in the
following Step 3).
Page 30

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
30 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Step
Description
Fax Configuration: Configure Outbound Rules
Configuration is needed only if an archive of outbound faxes is to be used. In the tested
configuration, outbound archiving was configured to save in PDF format to the network
share that was used in the previous step for inbound fax delivery. This was intermittently
enabled and disabled by clicking on the Enable Outbound Archive selection on the Fax
Configuration > Outbound page.
An Outbound approval rule was used to hold outbound faxes for a portion of the testing.
This was not a requirement, but was a useful method for traffic test scenarios. The
approval setup simply requires a check on the Enable Outbound Approval setting, and
selecting a User to approve outbound faxes:
Page 31

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
31 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
Step
Description
3.
Configure Users and Contacts
Two users were configured, an administrator (admin) and a standard user (test).
To create a user, navigate to the Users tab, then click the Add link and enter a
Username, Full Name, Password and Email address for each user. In addition, if a user
has a unique inbound fax extension, a routing rule can be created by providing
information in the lower section of the form.
Global and Personal contacts and Groups can be configured by clicking on the Contacts
tab. In the tested configuration, these were used to simplify sending proceedures. See the
Administration Guide [4] for complete instructions on managing contacts.
Page 32

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
32 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
8. Verification Steps
The following steps may be used to verify the configuration:
From Avaya Aura® Communication Manager SAT, use the status signaling-group
command to verify that the signaling groups are in-service.
From Communication Manager SAT, use the status trunk-group command to verify that
the trunk groups are in-service.
Verify that fax calls can be placed to/from Multi-Tech FaxFinder® IP Fax Server servers at
each site.
From Communication Manager SAT, use the list trace tac command to verify that fax calls
are routed to the expected trunks.
From Avaya Aura® System Manager, confirm that the Entity Link between Avaya Aura®
Session Manager and the FaxFinder server is in service.
From the FaxFinder web interface, navigate to Status & Logs > Fax Status to see the
current status of each port and any inbound or outbound fax activity currently in progress:
Additional System Status information such as the status of connectivity to Session Manager and
network shares can be found on the Status & Logs > System Status page:
Additional status screens showing mail queues and logs, inbound and outbound fax logs etc are
also available (not pictured) from the Status and Logs web pages.
Page 33

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
33 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
9. Conclusion
These Application Notes describe the procedures required to configure Multi-Tech FaxFinder® IP
Fax Server interoperate with Avaya Aura® Communication Manager and Avaya Aura® Session
Manager. Multi-Tech FaxFinder® IP Fax Server successfully passed compliance testing.
10. Additional References
[1] Avaya Aura™ Communication Manager Feature Description and Implementation, Doc # 555-
245-205, Release 6.0, Issue 8.0, June, 2010.
[2] Administering Avaya Aura™ Communication Manager, Doc # 03-300509, Release 6.0, Issue
6.0, June, 2010.
[3] Administering Avaya Aura™ Session Manager, Doc # 03-603324, Release 6.0, Issue 3, August,
2010.
[4] FaxFinder IP® Administrator User Guide, S000493A, Version A Model: FF240-IP
Documentation for:
Avaya products may be found at http://support.avaya.com.
Multi-Tech products may be found at https://support.multitech.com
Page 34

RAB; Reviewed:
SPOC 7/12/2011
Solution & Interoperability Test Lab Application Notes
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
34 of 34
FaxFinder_SM61
©2011 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Avaya and the Avaya Logo are trademarks of Avaya Inc. All trademarks identified by ® and ™
are registered trademarks or trademarks, respectively, of Avaya Inc. All other trademarks are the
property of their respective owners. The information provided in these Application Notes is
subject to change without notice. The configurations, technical data, and recommendations
provided in these Application Notes are believed to be accurate and dependable, but are
presented without express or implied warranty. Users are responsible for their application of any
products specified in these Application Notes.
Please e-mail any questions or comments pertaining to these Application Notes along with the
full title name and filename, located in the lower right corner, directly to the Avaya DevConnect
Program at devconnect@avaya.com.
 Loading...
Loading...