Page 1

PeriProducer for the Business
Communications Manager
(BCM) Platform
Publication#:
Document Release:
Release Date:
N0059775
1.0
July 14, 2006
Page 2

Important Notice
Nortel reserves the right to make changes in the contents of this publication including
functions and specifications identified herein without notice.
The material contained in this document is intended for Nortel personnel and licensed
customers with a non-disclosure agreement or standard contract.
In the absence of a written agreement to the contrary, Nortel assumes no liability for
applications assistance, customer's product/application/concepts, or infringements of
patents or copyrights of third parties arising from the use of systems and architectures
described herein. Nor does Nortel warrant or represent that any license, either
expressed or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, or other
combination of technology, architecture, or software as might be or is already in use.
This document should not be reproduced, disseminated, or otherwise disclosed
without prior written consent from a Nortel officer.
This document has been copyrighted by Nortel and may not be duplicated.
Copyright © 2006 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved
Page 3

Revision History
July 2006 Standard 1.0
Revision History
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 3
Page 4

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
Page 4 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 5

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Preface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Scope . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Intended Audience . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
How to Get Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Finding the latest updates on the Nortel Web site . . . . . . . . . 8
Getting Help from the Nortel Web site. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Getting Help over the phone from a Nortel Solutions Center 9
Getting Help from a specialist by using an Express Routing
Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Getting Help through a Nortel distributor or reseller . . . . . . . 9
How to Use This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Organization of This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Conventions Used in This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Solaris and Windows Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Two-Button (Windows) vs. Three-Button (Solaris) Mouse . 13
Trademark Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Introduction to the BCM - IVR Integration . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
The Business Communications Manager (BCM) - Interactive Voice
Response (IVR) Integration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
What functionality does IVR integration add to the BCM? . 16
Accessing complete documentation for BCM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Documentation Issues . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
BCM and the Voice File System (VFS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
The BCM Voice File System (VFS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Convert MMF Files to VFS Phrase Files using the MMF2VFS
command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
MMF2VFS Command Line Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Removing VFS Files from the VFS Files System . . . . . . . . 23
VFSRM Command Line Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Correlating Data in mmfxref.dat to the Voice File System . 24
VFSLS Command Line Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Deleting Cabinets from the Voice File System . . . . . . . . . . 26
VFSLS Command Line Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Working with PeriProducer Blocks for BCM . . . . . . . . . . . 27
PeriProducer Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
PeriProducer Blocks Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Variations in Block Functionality. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 5
Page 6

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
New Blocks for PeriProducer 3.00 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
PeriProducer Blocks for the BCM Environment . . . . . . . . . 29
BCM-IVR 2.1 PeriProducer Toolkit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
BCM-IVR 2.1 PeriProducer Toolkit Feature Extensions . . . 29
BCM-IVR 2.1 PeriProducer Toolkit Blocks. . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Set Call Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Get Call Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Park Call . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Check Park Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Begin Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
End Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Variations in Functionality of Standard PeriProducer Blocks . . . 41
Answer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Disconnect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Phone Op . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Transferring calls internally . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Read . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Receive Fax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Record . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Resource . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Select . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Send Fax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Speak . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Environments Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Environments Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Application and System Environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Host Environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Generic Environment Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
VENGINE Environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Resources Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
About Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Supported Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Page 6 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 7

Preface
Page 8
PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
Scope
Business Communications Manager (BCM) is a communications platform that
delivers voice processing, business telephony applications, and data networking
services. To extend these capabilities, Nortel integrated existing Interactive Voice
Recognition (IVR) software to run on the BCM platform.
The PeriProducer for the Business Communications Manager Platform manual
explains variances in PeriProducer functionality when it is integrated with BCM. It is
not meant to replace the PeriProducer User’s Guide; it is meant only to be used as a
supplement to it.
For further information on BCM, see the BCM documentation.
Intended Audience
To use this guide effectively, users should complete an on-site system familiarization
training program conducted as part of the initial system installation. In addition, they
should be familiar with other site-specific operating procedures relating to the
Business Communication Manager (BCM) due to specific BCM application functions
or any other equipment to which the BCM may be connected. Basic knowledge of
operating systems software is also assumed.
How to Get Help
This section explains how to get help for Nortel products and services.
Finding the latest updates on the Nortel Web site
The content of this documentation was current at the time the product was released. To
check for updates to the latest documentation for the MPS 500 and 1000, click one of
the following links:
MPS 500 Takes you directly to the Nortel page for MPS 500 documentation at
www130.nortelnetworks.com/cgi-bin/eserv/cs/main.jsp?cscat=DOCUMENTATION&resetFilter=1&tranProduct=12605
MPS 1000 Takes you directly to the Nortel page for MPS 1000 documentation at
www130.nortelnetworks.com/cgi-bin/eserv/cs/main.jsp?cscat=DOCUMENTATION&resetFilter=1&tranProduct=11721
Getting Help from the Nortel Web site
The best way to get technical support for Nortel products is from the Nortel Technical
Support web site:
www.nortel.com/support
This site provides quick access to software, documentation, bulletins, and tools to
address issues with Nortel products.
Page 8 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 9

Preface
• download software, documentation, and product bulletins
• search the Technical Support web site and the Nortel Knowledge Base for
answers to technical issues
• sign up for automatic notification of new software and documentation for
Nortel equipment
• open and manage technical support cases
Getting Help over the phone from a Nortel Solutions Center
If you do not find the information you require on the Nortel Technical Support web
site, and have a Nortel support contract, you can also get help over the phone from a
Nortel Solutions Center.
In North America, call 1-800-4NORTEL (1-800-466-7835).
Outside North America, go to the following web site to obtain the phone number for
your region:
www.nortel.com/callus
Getting Help from a specialist by using an Express Routing Code
To access some Nortel Technical Solutions Centers, you can use an Express Routing
Code (ERC) to quickly route your call to a specialist in your Nortel product or service.
To locate the ERC for your product or service, go to:
www.nortel.com/erc
Getting Help through a Nortel distributor or reseller
If you purchased a service contract for your Nortel product from a distributor or
authorized reseller, contact the technical support staff for that distributor or reseller.
How to Use This Manual
This manual uses many standard terms relating to computer systems, software
application functions, and the Internet. However, it contains some terminology that
can be explained only in the context of the MPS Series. Refer to the Glossary of
Nortel’s Media Processing Server Series Terminology for definitions of MPS Series
specific terms.
Read this manual from start to finish at least once. When you are familiar with the
document, you can use the Table of Contents to locate topics of interest for reference
and review.
If you are reading this document online, use the cross-reference links (shown in blue)
to quickly locate related topics. Position your cursor over the cross-reference link and
click once. Click any point in a Table of Contents entry to move to that topic. Click the
page number of any Index entry to access that topic page.
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 9
Page 10

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
Familiarize yourself with various specialized textual references within the manualsee
Conventions Used in This Manual on page 11.
Periphonics is now part of Nortel. The name Periphonics, and variations thereof,
appear in this manual only in reference to a product (for example, the PERImps
package, the perirev command, and so on).
Organization of This Manual
This manual is organized in the following way:
Chapter 1 — Introduction to the BCM - IVR Integration
Overviews the Business Communication Manager (BCM) and what functionality the
IVR integration brings to BCM. Explains how to access documentation on Helmsman.
Chapter 2 — Working with the BCM Voice File System
Describes the Voice File System (VFS), and explains how to work with file
conversion utilities.
Chapter 3 — Working with PeriProducer blocks for BCM
Describes exceptions to and variances in PeriProducer block functionality for BCM.
Chapter 4 — Environments support
Overviews environments and notes exceptions to and variances in environments
support for BCM.
Chapter 5 — Resources support
Overviews resources and notes exceptions to and variances in resources support for
BCM.
Page 10 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 11
Conventions Used in This Manual
This manual uses different fonts and symbols to differentiate between document
elements and types of information. These conventions are summarized in the
following table.
Conventions Used in This Manual (Sheet 1 of 2)
Notation Description
Preface
Normal text
important term
system
command
command,
condition
and alarm
file name /
directory
on-screen field
<KEY NAME>
Book Reference
Normal text font is used for most of the document.
The Italics font introduces new terms, highlights meaningful words
or phrases, or distinguishes specific terms from nearby text.
This font indicates a system command or its arguments. Enter
such keywords exactly as shown (that is, do not fill in your own
values).
Command, Condition and Alarm references appear on the screen
in magenta text and reference the Command Reference Manual,
the MPS Developer User’s Guide, or the Alarm Reference Manual,
respectively. Refer to these documents for detailed information
Commands, Conditions, and Alarms.
about
This font highlights the names of disk directories, files, and
extensions for file names. It also shows what is displayed on a
text-based screen (for example, to show the contents of a file.)
This font indicates field labels, on-screen menu buttons, and action
buttons.
A term that appears within angled brackets denotes a terminal
keyboard key, a telephone keypad button, or a system mouse
button.
This font indicates the names of other publications referenced
within the document.
cross-reference
!
A cross-reference appears on the screen in blue. Click the crossreference to access the referenced location. A cross-reference that
refers to a section name accesses the first page of that section.
The Note icon identifies notes, important facts, and other keys to
understanding.
The Caution icon identifies procedures or events that require
special attention. The icon indicates a warning that serious
problems may arise if the stated instructions are not followed
implicitly.
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 11
Page 12

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
Notation Description
Conventions Used in This Manual (Sheet 2 of 2)
(1): Windows and the flying Window logo are either trademarks or registered
trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
(2): Solaris® is a registered trademark of The Open Group in the U.S. and other
countries.
Solaris and Windows Conventions
This manual depicts examples (command line syntax, configuration files, and screen
shots) in Solaris format. Windows-specific commands, procedures, or screen shots are
shown when required. The following table lists general operating system conventions
used with either the Solaris or Windows operating system.
The flying Window icon identifies procedures or events that apply
to the Windows operating system only.
The Solaris icon identifies procedures or events that apply to the
Solaris operating system only.
(2)
(1)
Solaris Windows
Environment $PPROHOME %PPROHOME%
Paths $PPROHOME/bin %PPROHOME%\bin
Command <command> & start /b <command>
Page 12 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 13
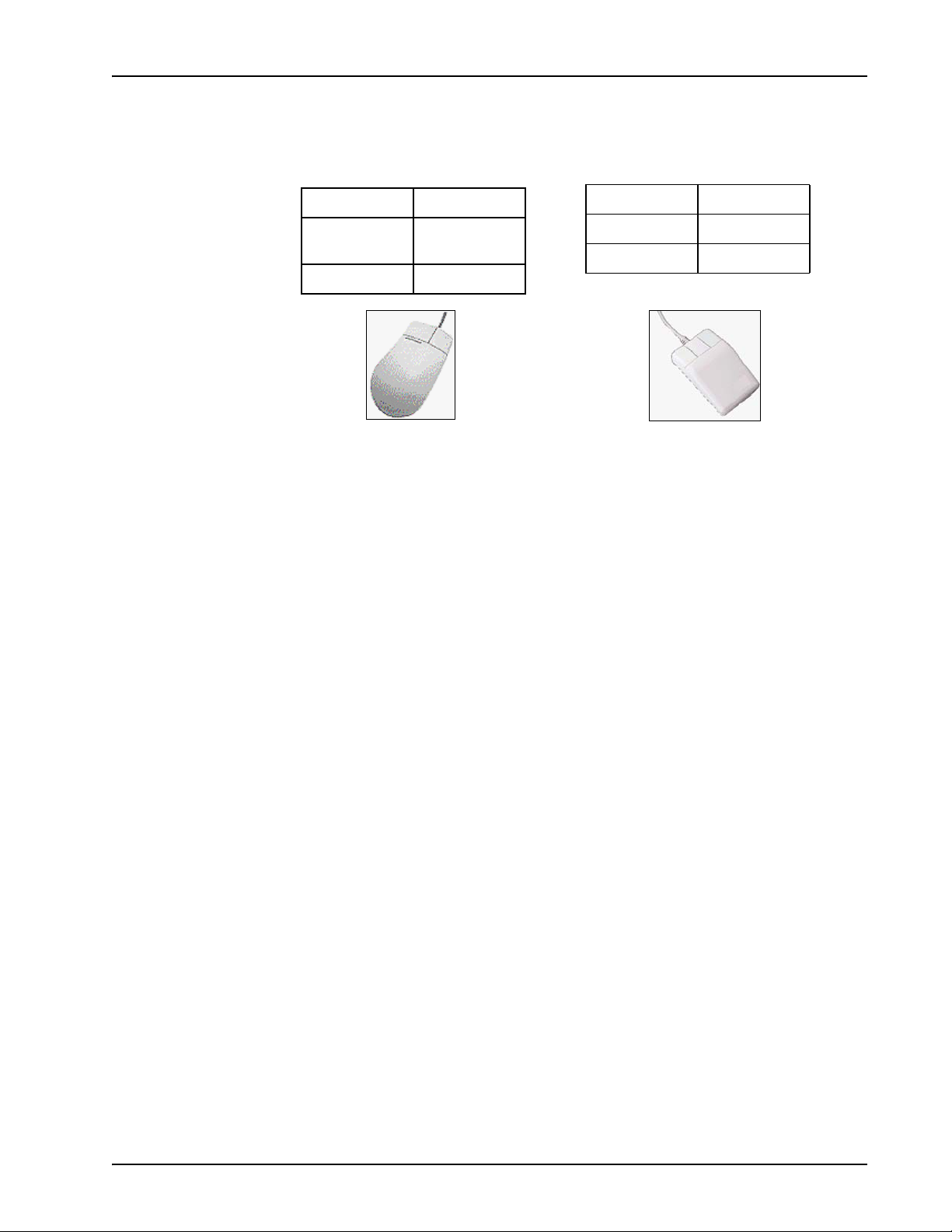
Preface
Two-Button (Windows) vs. Three-Button (Solaris) Mouse
<SELECT> Left button
<ADJUST> Left and Right
<MENU> Right button
Trademark Conventions
The following trademark information is presented here and applies throughout for
third party products discussed within this manual. Trademarking information is not
repeated hereafter.
Solaris
other countries.
Solaris, SunOS, OpenWindows, SPARC, and UltraSPARC are trademarks or
registered trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the United States and other
countries.
®
<SELECT> Left button
<ADJUST> Middle button
together
<MENU> Right button
and Motif® are registered trademarks of The Open Group in the U.S. and
Microsoft, MSSQL, Windows, Internet Explorer, and the Flying Windows logo are
either trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
®
Oracle
Sybase
Informix
is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation.
™
and SYBASE™ are trademarks of Sybase, Inc. or its subsidiaries.
®
and INFORMIX® are registered trademarks of Informix Corporation or its
affiliates.
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 13
Page 14

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
Page 14 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 15
Introduction to the
BCM - IVR
Integration
This chapter covers:
1. The BCM - IVR integration
2. What functionality does the
IVR integration add to the
BCM?
3. Accessing complete
documentation for BCM
Page 16

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
The Business Communications Manager (BCM) - Interactive Voice Response (IVR) Integration
Business Communication Manager 4.0 (BCM) is a fully-integrated communication
system for small businesses, government and retail networks, and enterprise branch
offices.
Interactive Voice Response is a telecommunications system that uses a prerecorded
database of voice messages to present options to a user, typically over telephone lines.
Users can input information using the keys on their touchtone phones.
The BCM 4.0 release leverages IVR functionality by integrating existing Nortel
Media Processing Server (MPS) Series IVR solution with BCM hardware.
What functionality does IVR integration add to the BCM?
The BCM 4.0 offers interactive voice response capabilities through Interactive Voice
Response 2.1 (IVR 2.1). IVR 2.1 is a suite of products that lets businesses create
applications callers can use to access information by responding to a series of prompts
through their touchtone phones.
The IVR applications are developed for the specific customer’s needs and in many
cases are integrated with databases to enable real-time queries and updates. Some
examples of IVR applications are:
• A pharmacy’s application that lets customers access their accounts,
receive real-time status on their prescription refills, and request
prescription refills.
• A bus station’s IVR application that lets customers book seats on a trip or
review projected departure times.
• A bookstore’s application that lets customers hear store hours, purchase
books, and check the delivery of an existing order.
The collection of hardware and software on which the IVR applications are created
and administered on BCMs is collectively referred to as the BCM-IVR 2.1 system.
For information on variations in PeriView, PeriReporter, and COMMGR functionality
for the BCM - IVR integration, see the BCM - IVR Integration Supplement manual.
Page 16 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 17

Introduction to the BCM - IVR Integration
Accessing complete documentation for BCM
For further information on all these products, download current technical
documentation from Helmsman Express, the Nortel online documentation resource.
To access documentation:
1. Go to www.nortel.com
2. Highlight the Support & Training dropdown list on the upper half of
the browser window.
3. Click Technical Documentation.
4. Under the heading Other Resources at the bottom right of the browser,
click the Helmsman Express link.
5. If you are a registered user of Helmsman, log on. If you are not already a
registered user of Helmsman, register now by following the instructions
online.
6. In the list of Products, click the Business Communications
Manager and Norstar link, then choose the Business
Communications Manager 4.0 link.
.
Documentation Issues
Issue
Documentation currently refers to hardware as the MPS Series.
Wherever the documentation uses MPS Series, assume that this refers to the BCM,
unless otherwise noted.
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 17
Page 18

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
Page 18 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 19
BCM and the
Voice File
System (VFS)
This chapter covers:
1. Elements of the Voice File
System (VFS)
2. Convert MMF files to VFS
phrase files
3. Convert VFS phrase files to
MMF files
Page 20
PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
The BCM Voice File System (VFS)
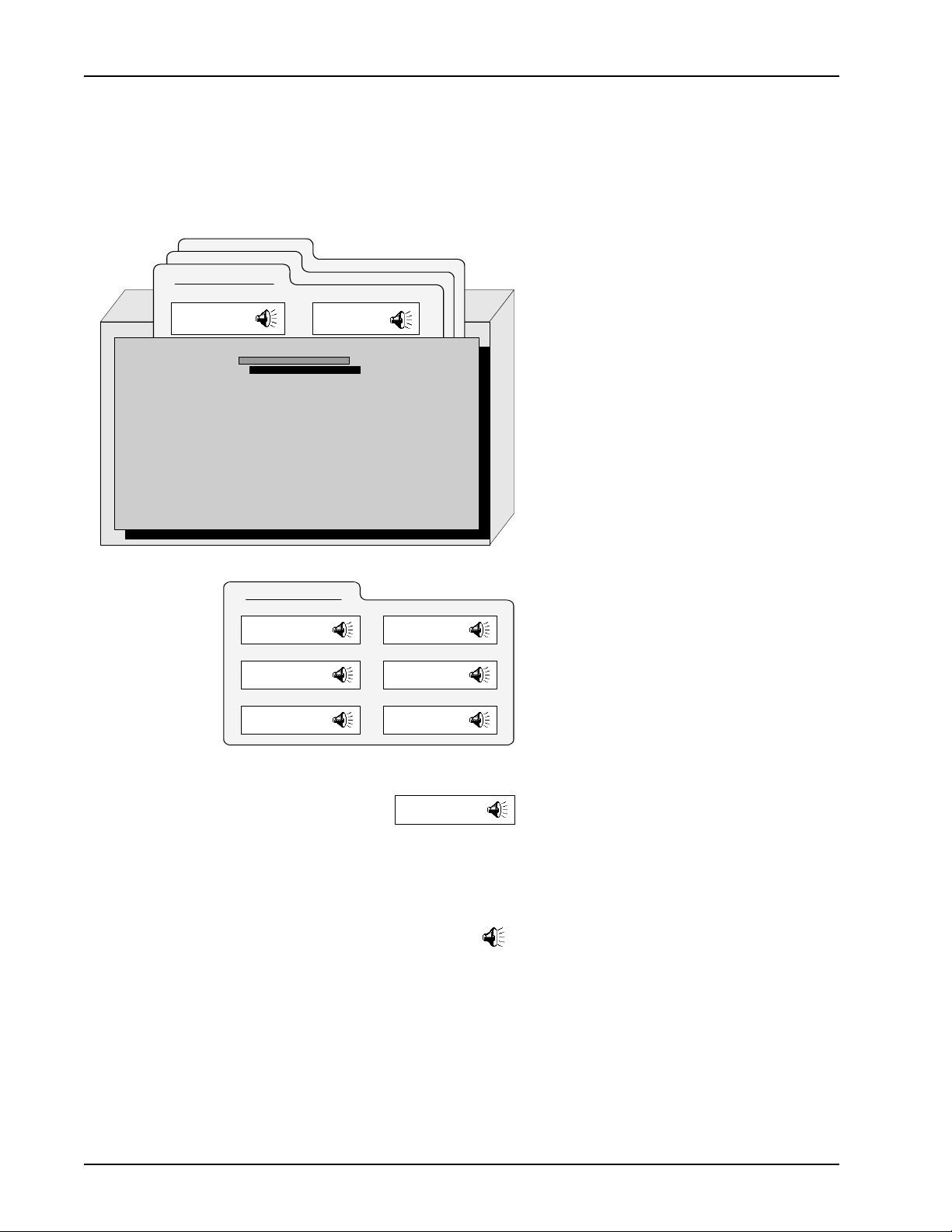
Business Communication Manager (BCM) stores application voice prompts and caller
message recordings in the Voice File System (VFS). Elements of the Voice File
System are:
AcctBalPhrase
1
EnterYou rAc ctN um.mmd
YouEnteredAcctNum.mmd
IVR Cabinet
AcctBalPhrase
2
1
3
5 6
Cabinets. A cabinet acts as a directory. It
contains any number of voice files. All
prerecorded voice prompts are stored in a
cabinet called IVR. All caller message
recordings (CMRs) are stored in a cabinet
called IVR_CMR.
Phrase files. A phrase file contains any
2
number of phrases. For each multimedia
format (MMF) file, a file is created in the
IVR cabinet.
4
1
Phrases. A phrase (.ph) is a prerecorded
element that is spoken to the caller.
PhraseNumbers identify a phrase within a
file. Phrases correspond to .mmi files in
an MMF file.
Segment files. Segment files (.seg)
contain raw audio data and are used for
caller message recordings (CMRs).
Page 20 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 21

BCM and the Voice File System (VFS)
Convert MMF Files to VFS Phrase Files using the MMF2VFS command
Existing MMF files must be converted in order for them to work with BCM.
You can convert existing MMF files with BCM’s Element Manager. MMF files are
converted automatically when IVR prompts are loaded in the Element Manager (see
BCM’s Interactive Voice Response Installation and Configuration Guide for
details).
The mmf2vfs command converts MMF files to VFS phrase files. Use the following
format when issuing the mmf2vfs command:
mmf2vfs [-m <mmf filename> [-f <filetype> [-c <cabinetname>] [-v
<vfsfilename>] [-e <start:end>] [-h] [-d] [-l] [-r <vfs_filename>] [-o]
These options are available with the mmf2vfs command:
Option Description Required?
-m The full pathname to the MMF file. You do not need to specify an .mmi or .mmd
extension.
-f The output file type. Use s for a .seg (segment) file or p for a .ph (phrase) file.
Omitting this option sets the file type to p.
-c The full pathname to the cabinet where you want to store the vfs file. If the
cabinet does not exist, mmf2vfs creates one. Cabinets are stored in
/var/nn/voicecti/cabinets as <cabinetname>.CAB. Omitting this
option stores the file in the IVR cabinet.
-v The full pathname to the vfs file. The vfs file takes the same name as the .mmf
file specified in the -m option. If a vfs file already exists, it is overwritten.
mmf2vfs attaches a .ph extension for phrase files and a .seg extension for
segment files.
-e The Element Access Pointer (EAP) number, or range of EAP numbers, to
convert. A single EAP can be converted to a voice segment file or to a phrase
in a phrase file. An EAP, or range of EAPs, can be converted to a vfs phrase ID
in a phrase file with phrase IDs corresponding to EAP numbers. A range of
EAPs can not be converted to individual voice segment files. Omitting this
option converts all EAPs in the MMF file to a .ph (phrase) file.
-h Displays help for all options. No
-d Turns on debug logging. No
-l Displays a report of the current contents of the mmfxref.dat file. No
Ye s
No
No
No
No
-r Removes the vfs file from the Voice File System and all references to it from
the mmfxref.dat file.
-o Enables error log output. It is used for non-interactive mode. No
No
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 21
Page 22

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
MMF2VFS Command Line Examples
mmf2vfs -m numdemo
Converts the entire contents of /var/nn/ivr/mmf/numdemo to its equivalent vfs phrase file
/var/nn/ivr/vfs/numdemo.ph and adds the file to the IVR cabinet.
mmf2vfs -m numdemo -f p -c bcmivr -v vfsnumdemo -e 1:10
Converts EAPs 1 through 10 in the mmf file /var/nn/ivr/mmf/numdemo to phrase IDs 1 through 10
of the vfs phrase file /var/nn/ivr/vfs/numdemo.ph. The phrase files are stored in the cabinet
/var/nn/voicecti/cabinets/bcmivr.CAB.
mmf2vfs -m numdemo -f p -c bcmivr -v vfsnumdemo
Converts the entire contents of the mmf file /var/nn/ivr/mmf/numdemo to the vfs phrase file
/var/nn/ivr/vfs/numdemo.ph. The phrase file is stored in the cabinet
/var/nn/voicecti/cabinets/bcmivr.CAB.
mmf2vfs -m numdemo -f s -c bcmivr -v voicesegment1 -e 1
Converts EAP 1 in the mmf file /var/nn/ivr/numdemo to a voice segment file in the vfs file
/var/nn/ivr/vfs/voicesegment1.seg. The segment file is stored in cabinet
/var/nn/voicecti/cabinets/bcmivr.CAB.
mmf2vfs -l
Displays the contents of /opt/vps/common/etc/mmfxref.dat file. Output shows cabinets created
using mmf2vfs, the phrase and segment files in each cabinet, and the EAP numbers and phrase IDs for each
phrase in the cabinet. The following is an abbreviated mmf2vfs -l sample output:
Page 22 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 23

BCM and the Voice File System (VFS)
Removing VFS Files from the VFS Files System
Use the vfsrm command to remove VFS files from the VFS files system. Use the
following format when issuing the vfsrm command:
vfsrm [-v <vfs filename>] [-f <filetype>] [-c <cabinetname>] [-h] [-d] [o]
These options are available with the vfsrm command:
Option Description Required?
-f The output file type. Use s for a .seg (segment) file or p for a .ph (phrase) file.
Omitting this option sets the file type to p.
-c The full pathname to the cabinet where the vfs file is stored. Omitting this
option sets the pathname to the IVR cabinet. Cabinets are stored in
/var/nn/voicecti/cabinets as <cabinetname>.CAB. No other
extensions are accepted.
-v The vfs file name, without extension or path. The vfs file to be removed must
already exist in /var/nn/ivr/vfs/. This option is required.
-h Displays help for all options. No
-d Turns on debug logging. No
-o Enables error log output. It is used for non-interactive mode. No
No
No
Ye s
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 23
Page 24

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
VFSRM Command Line Examples
vfsrm -v numdemo
Removes the vfs phrase file/var/nn/ivr/vfs/numdemo.ph from the IVR cabinet in the VFS file
system. References to phrases contained in this phrase file and cabinet are removed from the
mmfxref.dat file.
vfsrm -v numdemo -c bcmivr
Removes the vfs phrase file/var/nn/ivr/vfs/numdemo.ph from the bcmivr cabinet in the VFS file
system. References to phrases contained in this phrase file and cabinet are removed from the
mmfxref.dat file.
vfsrm -v vfsnumdemo -f s
Removes the vfs segment file /var/nn/ivr/vfs/numdemo.seg from the IVR cabinet in the VFS file
system. The reference to the phrase contained in this segment file and cabinet are removed from the
mmfxref.dat file.
Correlating Data in mmfxref.dat to the Voice File System
Use the vfsls command to display a summary of the Voice CTI mbQueryCabinet()
data and mbQueryFile() data for the contents of a VFS cabinet. This is used to
correlate data in the mmfxref.dat file (‘mmf2vfs -1) to the actual contents of the Voice
File System.
The file sizes and dates for all phrase and segment files in the IVR cabinet are
displayed first, followed by the storage statistics for the entire cabinet. In the output,
the following symbols are used:
D = Drive Letter (BMC3.X=C-Z, BCM4.0=D)
P/S/F = File type (phrase, segment, fax, and so on)
Number = Number of files in the cabinet
Max = Maximum space allowed (Kilobytes)
Used = Actual space used (Kilobytes)
These options are available with the vfsls command:
Option Description Required?
cabinet The name of a VFS cabinet in /var/nn/voicecti/cabinets. This displays the
mbQueryCabinet() data. This option is required.
Ye s
filespec Optional filenames within the cabinet for which the mbQueryCabinet() data is
displayed. Wildcards (filenames containing an asterisk) are accepted. If
omitted, the default setting is
*.
No
Page 24 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 25

BCM and the Voice File System (VFS)
VFSLS Command Line Examples
vfsls IVR
Displays the file information for all files in the IVR cabinet, followed by the cabinet information:
vfsls IVR dtmf.ph
Displays file information for all files in the cabinet, followed by cabinet information:
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 25
Page 26

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
Deleting Cabinets from the Voice File System
Use the vfsrmcab command to remove cabinets from the VFS file system. To be
deleted, the cabinet must exit and be empty.
These options are available with the vfsrmcab command:
Option Description Required?
cabinet The name of a VFS cabinet in /var/nn/voicecti/cabinets. This option is required. Yes
VFSLS Command Line Examples
vfsrmcab IVR_CMR
Deletes the cabinet file IVR_CMR.CAB from VFS, removing the empty cabinet file from
/var/nn/voicecti/cabinets/.
Page 26 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 27

Working with
PeriProducer Blocks
for BCM
This chapter covers:
1. PeriProducer Configuration
2. PeriProducer Blocks
Overview
3. BCM-IVR 2.1 PeriProducer
Toolkit
4. Block Functionality
Page 28

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
PeriProducer Configuration
Before creating BCM applications with PeriProducer, check the following
configuration prerequisite:
• If your application needs to access ANI digits, DNIS digits, or both, configure the
switch to send ANI/DNIS to the application for all lines. Refer to the BCM
Programming Operations Guide to use Element Manager to configure the switch
to send ANI/DNIS.
PeriProducer Blocks Overview
PeriProducer uses a set of blocks to build applications. Each block represents a
function the application can perform. Some PeriProducer blocks have variations in
functionality when used in the BCM-IVR context. Some PeriProducer blocks, such as
those in the BCM-IVR 2.1 Toolkit, are unique to the BCM-IVR context see BCM-IVR
2.1 PeriProducer Toolkit on page 29.
Variations in Block Functionality
The following blocks are either not supported for BCM or have only partial
functionality:
• Answer (For additional information, see Answer on page 41.)
• Disconnect (For additional information, see Disconnect on page 42.)
• Environment (For additional information, see Environment on page 43.)
• Phone Op (For additional information, see Phone Op on page 44.)
• Read (For additional information, see Read on page 47.)
• Receive Fax (For additional information, see Receive Fax on page 48.)
• Record (For additional information, see Record on page 49.)
• Resource (For additional information, see Resource on page 50.)
• Select (For additional information, see Select on page 51.)
• Send Fax (For additional information, see Send Fax on page 52.)
• Speak (For additional information, see Speak on page 53.)
• System (For additional information, see System on page 54.)
Blocks not listed here maintain their full functionality. For more information about all
PeriProducer blocks, see the PeriProducer 3.00 User’s Guide.
New Blocks for PeriProducer 3.00
The following blocks are new to PeriProducer 3.00:
•Abort
• Call Control
• Call Progress Detection
• Edit Sequence
• Line Operations
For more information about all PeriProducer blocks, see the PeriProducer 3.00
User’s Guide.
Page 28 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 29

PeriProducer Blocks for the BCM Environment
The following PeriProducer blocks, found in the BCM-IVR 2.1 PeriProducer Toolkit,
are unique to the BCM environment:
• Set Call Data
• Get Call Data
• Park Call
• Check Park Status
• Begin Page
• End Page
For more information on the BCM-IVR 2.1 Toolkit, see below.
Running applications that use options not supported by BCM may result in an
!
error. For best results, always test applications before making them available to
users.
BCM-IVR 2.1 PeriProducer Toolkit
Working with PeriProducer Blocks for BCM
The BCM-IVR PeriProducer Toolkit is a group of six blocks that enable applications
to perform BCM platform-specific operations. The six BCM-IVR 2.1 Toolkit blocks
are:
• Set Call Data
• Get Call Data
• Park Call
• Check Park Status
• Begin Page
• End Page
BCM-IVR 2.1 PeriProducer Toolkit Feature Extensions
The following feature extensions, unique to the BCM-IVR system, are enabled by the
BCM-IVR Toolkit blocks:
Set Call Data/Get Call Data
With this feature, data associated with a call can be passed between BCM
applications. For example, with the Set Call Data/Get Call Data feature, a PIN number
or Credit Card number entered by a caller can be passed along to different BCM
applications.
The Set Call Data block associates up to five strings of data per call. Each string of
data is identified by a label. The BCM-IVR Toolkit includes a folder of constant
values for labels to let BCM applications written in PeriProducer share data with other
BCM applications.
The Get Call Data block retrieves data previously associated with the call.
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 29
Page 30

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
Park ‘n Page
The Park ‘n Page feature, enabled when the Park block is used in combination with the
Page block, lets the BCM system to put an external call on hold while the system
pages the appropriate personnel to retrieve the call. A caller on hold is treated to either
a silent audio stream, a period tone audio stream or Music on Hold input. When a call
is parked, a retrieval code is passed back to the application. This retrieval code is
relayed in the page and lets other devices take control of the call.
If a page is initiated when a call is not parked, the call is implicitly put on hold and
cannot be retrieved by personnel responding to the page. When the page function is
complete, the call is taken off hold and returned to the IVR application’s call flow.
The following figure shows a sample Park ‘n Page application flow:
Page 30 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 31

Working with PeriProducer Blocks for BCM
Park/Page Statistics
Application statistics for the Park’n Page functionality are maintained within the
BCM-IVR 2.1 PeriProducer Toolkit. These statistics are viewable using PeriReporter
and can be consolidated and archived like any other statistics collected by
PeriReporter (for more information, see the PeriReporter User’s Guide).
Park ‘n Page application statistics are collected at 15-minute intervals and then
consolidated on hourly, daily, weekly, monthly and yearly bases. With
PeriConsolidator, you can configure the granularity of statistic file consolidation,
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 31
Page 32

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
including the duration that statistics files are retained.
User-defined reports are generated using PeriDefiner. By default, no predefined
reports are provided for Park ‘n Page. Only the raw statistics are viewable. These
statistics can be displayed by hour, day, week, month, and so on.
The raw statistics provided by the BCM-IVR Toolkit include:
• PageAttemptCnt: number of attempted pages
• PageCnt: number of successful pages
• PageFailureCnt: number of failed pages (paging system in use)
• ParkAttemptCnt: number of attempted park calls
• ParkCallCnt: number of the parked call that failed
• ParkFailureCnt: number of failed parked calls that failed
• ParkDuration: total number of seconds calls have been parked
• ParkTransferSuccessCnt: number of times parked calls were retrieved
• ParkAbandonedCnt: Number of times parked callers hung up
• ParkReturnedCnt: Number of times parked calls were returned to the
application
• ParkInternalCnt: Number of internally parked calls
From the above-noted statistics, any custom reports can be created, including:
• Average duration of parked calls (ParkDuration/ParkCallCnt)
• Average number of pages per call (PageCnt/ParkCallCnt)
• Average number of pages for a user-definable period (PageCnt/ x)
BCM-IVR 2.1 PeriProducer Toolkit Blocks
The BCM-IVR 2.1 PeriProducer Toolkit has six blocks:
Page 32 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 33

Set Call Data
Working with PeriProducer Blocks for BCM
Set Call Data associates data with a call. Multiple (up to five) strings
of data can be stored per call. Each string of data is identified by a
Label. Constant values for Labels are included as part of the BCM
Toolkit (BCM-Constants); however, system developers can also
custom-define Labels. Predefined Constant Labels are used if BCM
applications developed in PeriProducer share data with other BCM
applications.
When Set Call Data block is selected, the Set Call Data window appears:
Set Call Data Options
Option Description
Label to Set Specify the label used in setting call data in the Label to Set
field. The number value can be any number greater than 0
and less than 65536 and may be either a static expression
or a datacard. Use predefined Label values from the
BCM/Constants folder when sharing call data between
different types of BCM applications.
There are several predefined labels in the BCM/Constants
folder:
CallDataLabels.CallAnsweringMailboxNumber
CallDataLabels.VoiceMailLogin
CallDataLabels.IdentificationNumber
Data String of characters under a particular Label that is
associated with a call. This string of characters is later
retrieved by the Get Call Data function. The string used can
be up to 42 characters long and can be either a static
expression or the contents of a datacard.
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 33
Page 34

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
Get Call Data
Get Call Data retrieves call data (a string of text) from a call using the
specified Label.
When Get Call Data block is selected, the Get Call Data window appears:
Get Call Data Options
Option Description
Label to Get Specifies the Label for which call data is retrieved. The Label
specified must match a previously set Label, such as a Label
from the BCM Constants folder or a custom-defined Label.
The number value used can be either a static expression or
a datacard.
Data Specifies the character datacard that holds the retrieved
data upon completion.
Status Specifies the character datacard that contains information
on the status of the operation upon completion.
There are several predefined Status labels in the
BCM/Constants folder:
Statuses.GetCallData.Ok
Statuses.GetCallData.CallDataNotFound
Statuses.GetCallData.NoCall
Statuses.GetCallData.BadParam
Page 34 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 35

Park Call
Working with PeriProducer Blocks for BCM
Park Call puts a call on hold so that it may be retrieved by another
device in the BCM system. While parked, the caller is connected to
one of three on-hold streams:
•a silence audio stream;
•a periodic tone audio stream; or
• the Music On Hold input of the BCM.
When a call is parked, a “Park Code” is returned to the application. When Park Call is
used in combination with the Page and Speak blocks, a page is sent to personnel
advising that a call is on hold and relaying the code needed to retrieve the call. The
Page block is described in more detail below. See PeriProducer User’s Guide for
more information on PeriProducer blocks.
A call is returned to the application if it is not retrieved within a specified amount of
time.
On-hold treatment is configured in the BCM and applies only to external callers.
Internal callers receive a silent audio stream when on hold.
An parked internal call is not be returned to the application after the specified time
period has expired. As such, there is no need to execute the Check Park Status
command. For additional information, see Check Park Status on page 37.
If a page is initiated when a caller is not parked, the caller is put on hold and receives
the configured on-hold treatment described above. The call cannot be retrieved at this
time by personnel responding to the page. Rather, personnel must wait for the page
function to finish. The caller is then taken off hold and put back in the IVR
application’s call flow.
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 35
Page 36

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
Park Call Options
Option Description
Park Code Character datacard containing the Park Code. The Park
Status Character datacard containing the status of the operation
Abort Page on Completion Boolean value indicating how paging behaves when a
Code is a unique code in the system that is used by
personnel to retrieve the parked call from another device.
upon completion.
There are several predefined Park Call Status Constants:
Statuses.ParkCall.Ok
Statuses.ParkCall.NoParkPrefix (no Park prefix has been
configured)
Statuses.ParkCall.NoParkRetrievalCodes (no retrieval
codes were available)
Statuses.ParkCall.NoCall
Statuses.ParkCall.BadParam
parked call is completed (abandoned, retrieved, or timeout).
When true, speak commands to the paging system are
aborted when the parked call completes.
Page 36 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 37

Check Park Status
Working with PeriProducer Blocks for BCM
Check Park Status checks the status of call parked in the system. If a
Timeout value is specified (in seconds), the application blocks in this
toolkit block for the specified number seconds. If the Timeout value is
O, the block immediately completes.
The status of a parked call indicates either that a specified timeout has
occurred and the call is still parked or the call has been automatically unparked by the
system as a result of being parked too long.
The disc condition indicates that a call has been retrieved by another device in the
system or that the caller disconnected while parked.
Check Park Status Options
Option Description
Timeout The maximum amount of time in seconds to wait for the call
to be retrieved before returning control to the application.
Status Character datacard containing the status of the operation
upon completion.
There are two predefined Status labels in the Constants
folder:
Statuses.CheckParkStatus.Timeout (Timeout occurred, call
still parked)
Statuses.CheckParkStatus.NotParked (No call is parked)
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 37
Page 38

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
Begin Page
The Begin Page block attaches the voice port to a paging system. Once
attached, the application’s speech function are heard over the paging
system.
There are three Page types available:
• Internal zone
• External speaker
• Both
The Application Developer can specify page zones. Page zone values only apply if the
Page type is Internal Zone or Both.
Page 38 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 39

Working with PeriProducer Blocks for BCM
Begin Page Options
Option Description
Begin Page Character datacard indicating the Page type.
There are three predefined Page Type Constants:
PageTypes.InternalZone
PageTypes.ExternalSpeaker
PageTypes.Combined
Page Zone Character datacard indicating the Page zone. Page zones
are customized for the Application Developer and defined as
Constants.
Up to six different Page zones can be defined:
PageZones.AllZones
PageZones.Zone1
PageZones.Zone2
PageZones.Zone3
PageZones.Zone4
PageZones.Zone5
PageZones.Zone6
Status Character datacard containing the status of the operation
upon completion.
There are two predefined Begin Page Status constants:
Statuses.BeginPage.Ok
Statuses.BeginPage.BadParam
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 39
Page 40

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
End Page
The End Page block detaches the voice port from the paging system.
An application must perform this operation whenever it is not actively
paging since the paging system can only be connected to one device at
a time. If an application issues a page and then waits to try again at a
later time, it must end the page before it waits.
An application can be connected to the paging system for a maximum
of 3 minutes. After that time, the voice port automatically disconnects from the paging
system.
Page 40 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 41

Working with PeriProducer Blocks for BCM
Variations in Functionality of Standard PeriProducer Blocks
Answer
The Answer block determines the manner in which an application
handles an incoming call. An Answer block is generally used to cause
the application to receive a call (that is, answer the phone) and provide
a specified message (for example,“Welcome to the automated
system.”) to the caller.
For complete information on the Answer block, see the PeriProducer
User’s Guide.
Function Variation
Answer After ... Ring to Ring
Count
Send/Receive Protocol Data Not supported
Detect: Fax, Touch-Tones Not supported
Not supported. To set this on the BCM, start
the Element Manager, start the CallPilot
Manager, and go to Lines Administration. Set
the Line Properties to the number of rings
after which to answer calls.
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 41
Page 42

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
For applications that receive faxes, you may want to dedicate a specific line to
receive them. Depending on your supported protocols, you can then obtain the
dialed phone number (DNIS) to learn whether a fax should be received.
Disconnect
The Disconnect block causes the application to hang up its phone line.
Once this happens, the application can no longer perform phone line
functions except to outdial. Generally, when the caller is disconnected,
the system invokes certain low-level functions to perform clean-up
procedures on the phone line and its data buffers. This prepares the
line for the next incoming call.
For complete information on the Disconnect block, see the
PeriProducer User’s Guide.
Function Variation
Send/Receive Protocol Data Not supported.
Page 42 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 43

Environment
Working with PeriProducer Blocks for BCM
Environment options control functions and application behavior. They
can be set or changed in an Environment block.
When you make changes to environment options, the changes are
specific only to the current application phone line and remain in effect
for that phone line until explicitly changed.
For a list of supported environments, see Environments Support on
page 55. For complete information on the Environment block, see the
PeriProducer User’s Guide.
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 43
Page 44

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
Phone Op
Use the Phone Op (originate) block in applications that originate a call
to an outside party. A Phone Op (originate) block causes the
application to outdial a specific number and connect with the outside
party.
For example, use Phone Op block in an application for a mortgage
company that calls local residents to inform them about current home
equity loan rates.
For complete information on the Phone Op block, see the
PeriProducer User’s Guide.
Page 44 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 45

Working with PeriProducer Blocks for BCM
Function Variation
Originate Supervised transfer not supported.
Transfer – Supported.
– Internal transfers require a special format.
Send/Receive
Protocol Data
Event
Notification
Not supported.
Not supported.
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 45
Page 46

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
Transferring calls internally
Specify the following Dial Number string to transfer calls internally:
@<dn>[[:<label>,<data>]...]
where dn is the dial number of the BCM application to which you are transferring the
call, label is the label of the call data to set, and data is the new value of the label.
Currently, only the following labels are available:
label value description
1 <mailbox#> Transfers to voicemail for caller to leave
2 <mailbox#> Transfers to voicemail for caller to log into
Terminate the string with a the PeriProducer system constant, LowValues.
message in mailbox.
mailbox.
Page 46 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 47

Read
Working with PeriProducer Blocks for BCM
Use the Read block to obtain caller input through touchtones. Input
data can either be a number or a string of characters. Prompts can be
spoken before the caller enters the data.
For complete information on the Read block, see the PeriProducer
User’s Guide.
Function Variation
Speech Recognition Not supported.
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 47
Page 48

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
Receive Fax
Use the Receive Fax block to receive a fax from an external fax
machine.
For complete information on the Receive Fax block, see the
PeriProducer User’s Guide.
Function Variation
Receive In Faxes are stored in /var/nn/ivr/fax.
BIM assigns a unique file name to
received faxes.
Maximum Pages Not supported.
Options Not supported.
For applications that receive faxes, you may want to dedicate a specific line to
receive them. Depending on your supported protocols, you can then obtain the
dialed phone number (DNIS) to learn whether a fax should be received.
Page 48 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 49

Record
Working with PeriProducer Blocks for BCM
Use the Record block to acquire either a single message recording
from the caller or a group of related recordings.
For complete information on the Record block, see the PeriProducer
User’s Guide.
Function Variation
Data Card Name Specifying a CMR token or a
named element to record into not
supported.
Append Not supported.
Asynchronous Recording Not supported.
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 49
Page 50

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
Resource
External resources are essentially software daemons that control the
function of some other device or software process.
For a list of supported resources, see Resources Support on page 65.
for a list of supported resources. For complete information on the
Resources block, see the PeriProducer User’s Guide.
Page 50 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 51

Select
Working with PeriProducer Blocks for BCM
The Select block accepts a single touchtone key from the caller and
then determines the execution path based on that selection. The block
is usually used to receive a caller’s choice in response to a voice menu.
For complete information on the Select block, see the PeriProducer
User’s Guide.
Function Variation
Speech Recognition Not supported.
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 51
Page 52

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
Send Fax
Use the Send Fax block to send a fax that has already been composed
and stored as a TIFF file or a .txt file.
For complete information on the Send Fax block, see the
PeriProducer User’s Guide.
Function Variation
Send from – To send a fax, define a composite folder with an
MSToken card and a character data card (len=41).
Set the initial value of the character data card to the
fax file name.
– MSToken must contain the filename of the fax to
send. Send Fax assumes that files not listed with a
full path are stored in the default directory of
/var/nn/ivr/fax.
– File names must be shorter than 255 characters.
Page 52 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 53

Speak
Working with PeriProducer Blocks for BCM
The Speak block provides voice output to the caller, either to present
the caller with requested information or to prompt the caller to enter
data. Click the Prompt... button to open a window where you can add
vocabulary phrases.
For complete information on the Speak block, see the PeriProducer
User’s Guide.
Function Variation
Prompt... – Only Element Name and Direct Element
name are supported as speak options.
– TTS Literal is not supported.
Accept
Speech/Input
Not supported.
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 53
Page 54

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
System
PeriProducer applications use many predefined system functions
known as call functions. Call functions may use internal system
variables and sometimes perform tasks that are not readily accessible
using the supplied building blocks. You can access these functions
with the System block.
For complete information on the System block, see the PeriProducer
User’s Guide.
Function Variation
Function Delete Vocabulary Item function (part of Delete
MSToken or Vocabulary Item function) not supported.
Page 54 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 55

Environments
Support
This chapter covers:
1. Environments Overview
2. Environments
Page 56

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
Environments Overview
Environment options control line-specific functions and application behavior. They
can be set or changed in an Environment block.There are three environment categories
to choose from.
• “Application and System Environment” on page 56)
• “Host Environment” on page 59
• “Generic Environment Options” on page 60
The tables in this chapter specify which options are supported in PeriProducer 3.00
when operating on the BCM platform.
For more information on all environment options, see the PeriProducer User’s Guide.
Application and System Environment
Application and System Environment Options
Environment Option Supported Description, including variations for the BCM
DtmfFirst Supported Maximum time allowed before first tone.
The maximum amount of time allowed for the caller to enter
the first touchtone in an input sequence. The timer starts as
soon as the input prompt finishes speaking. If the timer
expires, the getinputfail condition (with Status ErrFirst)
is generated.
DtmfGuard Not supported Enable TT extended time verification during voice output and
record
If DtmfGuard is on, the system does not consider a
touchtone valid until it lasts for DtmfToneDur time.
DtmfGuard should be used only for testing and diagnostics. If
DtmfGuard is off, any detected touch-tone longer than 40 ms
is considered valid.
DtmfInter Supported Maximum time allowed between tones.
The maximum amount of time allowed for the caller to pause
between entering touchtones in a multiple-key input
sequence. The timer starts as soon as the caller enters the
first touch-tone. If the inter timer expires, and timeout is off,
getinputfail is generated (with Status ErrInter) and no
caller input is returned.
DtmfToneDur Not supported Extended touchtone verification time.
Specifies the amount of time a touchtone must be detected
before it is considered valid. The minimum recommended
value is 40 ms (the default). DtmfToneDur is used only when
DtmfGuard (see above) is enabled.
Page 56 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 57

Environments Support
Application and System Environment Options
LinePickUp Supported Blind or guard timer for completing outbound calls.
In a system without call progress detection or answer
supervision, expiration of the pickup timer results in the
origcmp or transfercmp condition being returned to the
application, following outdial or referral, respectively. The
condition indicates successful completion of the call transfer
function.
Note: In a system containing call progress detection or
answer supervision, the LinePickUp timer should be set to a
value high enough so that it does not preempt any of these
functions. The default is 30 seconds.
LineStandbyMode Not supported Set state between calls.
Specify the tone a caller hears when an incoming call
reaches a line that is between ending a call and ready to
accept another call. The default is the busy tone.
LineTotalCall Supported Total call timeout (including any time in referral).
The maximum duration for a call. The timer starts when the
call is answered. When the total timer expires, calltim is
generated. Note that the total call duration includes any time
spent in referral. If the call is in referral when the total timer
expires, the application does not receive calltim; instead,
the LineTotalCall timer restarts.
LvrFirst Not supported First speech timer.
The maximum amount of time allowed for the caller to begin
speaking input (and having it recognized). This is similar to
the DtmfFirst option, but is specific to speech recognition. If
the timer expires, the getinputfail condition (with Status
ErrFirst) is generated.
LvrTooMuchSpeech Not supported Maximum time for speech to end once it begins.
The amount of time allowed for the caller to finish speaking
requested input once recognition starts. If this timer is
consistently exceeded, either there is background noise
being detected as speech, or callers do not have enough
time to speak the requested input. Timer expiration results in
the getinputfail condition (with Status
ErrTooMuchSpeech).
LvrTooSlowRecogni
zer
Not supported Maximum time for recognizer result after speech ends.
The maximum amount of time the application should wait for
recognition results after recognition stops. If this timer
expires, the recognition attempt is aborted and the
application receives the getinputfail condition (with
Status ErrTooSlowRecognition).
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 57
Page 58

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
Application and System Environment Options
MediaHighWaterMa
rkEvent
MediaLowWaterMar
kEvent
RecFirstSil Not supported Maximum silence allowed before voice response.
RecInterSil Supported Maximum duration of intermediate silence.
RecSilStrip Not supported Do not record silence periods longer than.
Not supported Notify if media high water mark reached.
Enables or disables sending the mmfhigh condition to the
application.
Not supported Notify if media low water mark reached.
Enables or disables sending the mmflow condition to the
application.
The amount of time the caller has to begin speaking at the
beginning of the recording. If the caller does not begin
speaking within this time period, the recording terminates.
The amount of time the caller can remain silent (after
beginning to speak) before the system automatically
terminates the recording. No error condition is returned
because the system assumes that the caller is finished
recording and the message is valid. This should always be
set to higher than RecSilStrip.
To save disk space during recording, silence periods greater
than RecSilStrip and less than RecInterSil are not included in
the recording. RecSilStrip should always be set less than
RecInterSil.
RscConfig Not supported Configuration string for OSCAR resource.
Send configuration parameters directly to the OSCAR
resource. This may be entered multiple times within the
Environment block.
RscLabel Not supported Change label of an OSCAR resource.
Switch the label (grammar) used by an OSCAR resource.
This is typically used while the OSCAR resource is already
allocated. The application can perform recognitions from
different vocabularies without releasing the resource.
Page 58 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 59

Host Environment
Environments Support
Host Environment Options
Environment
Option
er Supported Set the enquiry timeout or response timeout.
headermode Supported Enables or disables translation of 24-byte header/PACE messages.
hostctl Supported Enables or disables host up or down messages to applications.
intime Supported Set the intermediate ("Please hold on.") timeout.
Supported Description, including variations for the BCM
The amount of time the host has to respond to an enquiry. If the host does
not respond within the er interval, hrcvtxtfail or hrcvmapfail is
generated (with Status ErrTimeout). This must be set higher than the intime
timer .
If headermode is enabled, 24-byte header messages are translated. If
headermode is disabled, the header messages are not translated but are
instead passed to the application.
If hostctl is enabled, hctlon (host is up) or hctloff (host is down) is
sent to the application when the host changes state. If hostctl is disabled,
these conditions are not generated.
The enquiry or response intermediate timer can be used to time the playing
of a please hold on message to the caller while waiting for host data . When
intime expires, hostinter is generated. This timer must be set lower than
the er timer and can be disabled by setting it to 0.
refer Supported Set the phone line mode after a 24-byte header referral.
Supported input Wait for touchtone input from the line after establishing the
referral.
Supported output Send a voice prompt to the referral line after establishing the
referral.
Supported hangup Hang up after establishing the referral.
rfno Supported Set the 24-byte header referral phone number.
If a referral number is not specified for rfno, it is assumed that the host
provides the referral number.
session Supported Set the host session number.
Sets the host number that the line uses for host-based I/O. If the application
does not use VT pooling, setting session to 0 effectively disables the host
link. Note that the usepool option automatically sets session to 0 (when
using VT pooling), so there is no need to set session to 0 when using VT
pooling.
setaid Supported Set line-specific AID (override aiddefault for next send only)
Changes the default AID key for the line on which it is running, that is,
specifies the desired AID key and associates it with the next send.
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 59
Page 60

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
unlocks Supported Number of unlocks received before actually unlocking keyboard.
Causes the COMMGR to ignore one less than the specified number of
unlocks following a SEND TEXT/MAP command, before actually unlocking
the keyboard.
usepool Supported Specify name of virtual terminal pool to use
When using VT pooling, set the pool to use for host transactions. If
usepool is not specified, the current pool is used. usepool automatically
sets session to 0.
Generic Environment Options
Generic Environment Option Supported?
Host Environment Options
Application and system options No
Host manager options No
Vengine options Yes
Specifies an environment option (for the COMMGR (Host) or VENGINE), which is
not available in the existing environment classes. The Generic Environment options
permit use of data cards (as well as literals) to specify option values.
Page 60 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 61

VENGINE Environment
Environments Support
VENGINE Environment Options
Environment
Option
alarmdbtask Supported Set the alarm database task name.
apprestart Supported Restart the application when it ends.
centurymark Supported Set the century boundary.
debug Supported Turn Vengine debugging on or off (a/n) [as by AMU command: debug mw
deltimedcall Supported Named CALL Function should no longer be timed.
intermsg Supported Set the host intermediate timeout message item.
Supported Description, including variation for the BCM
Specifies the task name that alarms are associated with. This function is
also available in the Application Configuration window under the Main
Container Properties menu.
Forces the application to restart automatically.
Specifies how PeriProducer speaks a two-digit year.
If the year is greater than or equal to the centurymark, PeriProducer speaks
the 20th century; if the year is less than the centurymark, PeriProducer
speaks 21st century.
a/n].
Dynamically enables (a) or disables (n) VENGINE debugging.
Specifies the vocabulary element to play if the host intermediate enquiry or
response timer expires.
mode Supported Switches dynamically to IVR or World Wide Web mode.
To be able to switch from IVR to Web mode, you must start the VENGINE
running the application in Web mode (that is, vengine -W).
notice Supported Ensure delivery at or after a blocking event.
numset Supported Set voice output conversion types.
Specifies the level of concatenation for producing numeric speech output,
that is, the number of elements used to speak each number. For example,
an application can speak 1000 as "one-thousand" (one element) instead of
"one", "thousand" (two elements).
Supported better Provides maximum concatenation up to 9,999.
Supported best Provides maximum concatenation from 10,000 and up. Up to
10,000, there is no difference between the better and best
options.
Supported dollars Speaks numeric data items as dollars and cents. Dollars
automatically implies the better method of concatenation.
This can be combined with the best option.
Supported off Does not concatenate any numeric speech.
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 61
Page 62

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
rscertime Supported Sets the error timeout for non-OSCAR-based resources. When rscertime
expires, the application receives ertimeout.
rscintime Supported Sets the intermediate timeout for non-OSCAR-based resources. When
rscintime expires, the application receives intertimeout.
setvpsline Supported Uses MPS:line for outgoing messages.
softterm Supported Set the soft termination timeout.
Specifies the maximum amount of time that an application can continue
running after a soft termination (kill) signal is issued. This function is also
available in the Application Configuration window under the Main Container
Properties menu.
Setting the soft termination timeout within the application overrides the
application configuration from PeriView or the VENGINE command line
options.
You must explicitly set the soft termination timeout in linked applications (or
accept the value inherited from the mail application).
speak Supported Set voice output language conventions.
VENGINE Environment Options
Determines which set of language rules the application uses to speak
numbers, dates, time, and money. These rules include the order the
application uses for the tokens, as well as any additional structures unique
to each language. For example, when an application speaks an even dollar
amount (that is, without cents) using British language rules, the application
speaks “exactly” after the dollar amount.
Supported Japanese Select the Japanese method.
Supported Cantonese Select the Cantonese method.
Supported Mandarin Select the Mandarin method.
Supported British Select the UK (British) English method.
Supported Arabic Select the Arabic method.
Supported U.S. Select the American English method.
Supported European Use day-month order for dates (British and U.S. only).
Supported Improved Select the Improved method.
Supported Korean Select the Korean method.
Supported TDD
Literal
Supported TDD
Name
Select TDD (Telecommunications Device for the Deaf) Literal
method. This is not currently supported.
Select TDD Name method. This is not currently supported.
Supported Spanish Select the Spanish method.
strictrsc Supported Postpone delivery of unexpected resource message.
timedcall Supported Named CALL Function should be timed.
unnotice Supported Restore default processing (remove from notice list).
vmstimedcall Supported Named CALL Function should be timed, is interruptible.
Page 62 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 63

VENGINE Environment Options
vpsrcvtime Supported Set the system response timeout
If the system does not respond to a request within the vpsrcvtime
interval, vrto is generated. This function is also available in the Application
Configuration window under the Main Container Properties menu.
Setting the response timeout (vpsrcvtime) within the application overrides
the application configuration from PeriView or the VENGINE command line
options.
By default, linked applications inherit the vpsrcvtime set by the main
application. To change this, the linked application must explicitly set
vpsrcvtime.
Environments Support
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 63
Page 64

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
Page 64 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 65

Resources Support
This chapter covers:
1. About Resources
2. Supported Resources
Page 66

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
About Resources
Resources refer to external resources that PeriProducer applications can access.You
can set applications to get information from a resource, to send information to a
resource, or to receive input from a resource.
Supported Resources
ausvr (Audio Server) No
jsb (Java Services Bridge) No
htmls (HyperText Markup Language) No
lvr-a (Nuance Large Vocabulary Recognition) No
extts-a (TrueTalk) No
screendaemon (screendaemon) No
Resource Supported?
cti (Computerized Telephony Integration) No
gencti (Computerized Telephony Integration, generic method) No
vtcpd (VAS/TCP Daemon) Yes
phone (phone line) Yes
ccss (Common Channel Signaling Server) No
tcap (Transaction Capabilities Application Part, SS7 protocol) No
sip (Session Initiation Protocol) No
generic (a generic method to generate code) No
xgeneric (a generic method to generate code) No
phonePRS (Phone Resource Server) No
DTMF (Dial Tone Multi Frequency) No
Player No
Recorder No
FullDuplexRecorder No
Fax No
Page 66 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 67

Index
Page 68

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
A
alarmdbtask 61
28
ANI
Answer block
apprestart
41
61
B
blocks. See individual block names.
bridge call
44
C
cabinets 20
caller message recordings (CMRs)
calltim
ccss (Common Channel Signaling Server) resource
centurymark
CMRs
Common Channel Signaling Server resource
Computerized Telephony Integration resource
conditions
conventions
Convert MMF files
cti (Computerized Telephony Integration) resource
57
66
20
calltim
hctloff
hctlon
63
vrto
manual
11
66
61
57
59
59
21
20
66
66
D
debug 61
deltimedcall
directory of VFS files
Disconnect block
28
DNIS
DtmfFirst
DtmfGuard
DtmfInter
DtmfToneDur
61
20
42
56
56
56
56
E
end transfer 44
Environment block
environment options
43
??–63
alarmdbtask
apprestart
centurymark
debug
deltimedcall
DtmfFirst
DtmfGuard
DtmfInter
DtmfToneDur
er
generic environment
hangup
headermode
host environment
hostctl
input
intermsg
intime
LineStandbyMode
LineTotalCall
LvrFirst
LvrTooMuchSpeech
LvrTooSlowRecognizer
MediaHighWaterMarkEvent
MediaLowWaterMarkEvent
mode
notice
numset
output
RecFirstSil
RecInterSil
RecSilStrip
refer
rfno
RscConfig
rscertime
rscintime
RscLabel
session
setaid
setvpsline
softterm
speak
strictrsc
timedcall
unlocks
unnotice
usepool
vmstimedcall
vpsrcvtime
61
59
59
59
59
61
61
61
59
59
59
59
62
61
61
61
61
56
56
56
56
60
59
59
59
61
57
57
57
57
57
58
58
58
58
62
62
58
59
62
62
62
62
60
62
60
62
63
58
58
Page 68 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
Page 69

Index
environment options. See individual environment op-
tion names.
er
59
error log
extts-a (TrueTalk) resource
21, 23
66
F
fax 48, 52
G
gencti (Computerized Telephony Integration) re-
source
66
generic environment options
generic resource
66
60
H
hangup 59
hctloff
hctlon
headermode
hkfdisc
hookflash
host environment options
hostctl
59
59
59
45
44
59
59
I
input 59
intermsg
internal transfers
intime
IVR cabinet
IVR_CMR cabinet
61
46
59
20
20
J
Java Services Bridge resource 66
jsb (Java Services Bridge) resource
66
L
LineStandbyMode 57
LineTotalCall
lvr-a (Nuance Large Vocabulary Recognition) re-
source
LvrFirst
LvrTooMuchSpeech
LvrTooSlowRecognizer
57
57
66
57
57
M
manual conventions 8, 10
MediaHighWaterMarkEvent
MediaLowWaterMarkEvent
20
.mmd
MMF files
mmf2vfs
.mmi
mode
multimedia format (MMF) files
20
21
20
61
58
58
20
N
notice 61
Nuance Large Vocabulary Recognition resource
numset
61
O
originate 44
output
59
P
.ph 20
Phone Op block
phone resource
Phone Resource Server resource
phonePRS (Phone Resource Server) resource
phrase files
phrases
20
44
66
66
20
R
Read block 47
Receive Fax block
RecFirstSil
RecInterSil
Record block
RecSilStrip
refer
Resource block
resources. See individual resource names.
rfno
RscConfig
rscertime
rscintime
RscLabel
rtype
59
59
45
48
58
58
49
58
50
58
62
62
58
66
66
# N0059775 Ver: 1.0 Nortel Confidential Page 69
Page 70

PeriProducer for the BCM Platform
S
screendaemon resource 66
20
.seg
segment files
Select block
Send Fax block
session
setaid
setvpsline
sip
66
softterm
speak
Speak block
strictrsc
System block
20
51
52
59
59
62
62
62
53
62
54
T
tcap (Transaction Capabilities Application Part) re-
66
source
timedcall
Transaction Capabilities Application Part resource
transfers
internal
TrueTalk resource
62
66
44
46
66
U
unbridge call 44
unlocks
unnotice
usepool
60
62
60
V
VAS/TCP Daemon resource 66
20
VFS
vmstimedcall
Voice File System (VFS)
vpsrcvtime
vrto
63
vtcpd (VAS/TCP Daemon) resource
62
20
63
X
xgeneric resource 66
66
Page 70 Nortel Confidential # N0059775 Ver: 1.0
 Loading...
Loading...