Page 1

Avaya P120 SMON
User Guide
April 2002
Page 2

Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Copyright 2002 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved
The products, specifications, and other technical information regarding the products contained
in this document are subject to change without notice. All information in this document is
believed to be accurate and reliable, but is presented without warranty of any kind, express or
implied, and users must take full responsibility for their application of any products specified in
this document. Avaya disclaims responsibility for errors which may appear in this document,
and it reserves the right, in its sole discretion and without notice, to make substitutions and
modifications in the products and practices described in this document.
Avaya™, Cajun™, P550™, LANstack™, CajunView™, and SMON™ are trademarks of
Avaya Inc.
ALL OTHER TRADEMARKS MENTIONED IN THIS DOCUMENT ARE PROPERTY OF THEIR
RESPECTIVE OWNERS.
Release 1.002
Page 3

Table of Contents
Preface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .vi
The Purpose of this Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vi
Who Should Use this Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .vii
Organization of this Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .vii
Chapter 1 — SMON Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
What is RMON . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
What is SMON . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Overview of SMON . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
SMON Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Filtering Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Device SMON Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Switch Statistics Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Port Statistics Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
VLAN Statistics Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Alarms and Events Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Chapter 2 — Device SMON . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Accessing Device SMON . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
The Device SMON User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Application Tabs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Device SMON Toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Dialog Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Desktop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Status Bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Status Line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Working with Device SMON Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Mouse Actions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Using Dialog Box Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Generating Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Chapter 3 — Switch Statistics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Using Switch Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Gauges and Pie Charts in the Switch Statistics Window . . . . . .17
Traffic Graph in the Switch Statistics Window . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide iii
Page 4

Table of Contents
Chapter 4 — Port Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Using Port Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Selecting Ports to Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Port Statistics Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
The Port Statistics Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Chapter 5 — VLAN Statistics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Using VLAN Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Selecting VLANs to Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
VLAN Statistics Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
VLAN Statistics Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Chapter 6 — Alarms and Events. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Using Alarms and Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Alarms Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Alarms Table Fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Tooltips . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Editing Alarms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Alarm Wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Overview of the Alarm Wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Activating the Alarm Wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Alarm Wizard Screens . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Device Event Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
iv Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Page 5

Table of Contents
Appendix A — SMON Dialog Boxes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Using the General Options Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Polling Interval . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Display Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Report Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
Using the Report Now Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
Using the Auto Report Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
Using the Switch Options Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Samples Per Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Samples To Store . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Logarithmic Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Level Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Using the Port/VLAN Options Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
Items Per Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
Using the Find Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
Finding a VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Finding a Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Finding a LAG . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Using the Define Port Filter Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
Using the Define VLAN Filter Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Using the Define TopN Filter Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Using the Find Top5 Peaks Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Using the Sort Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
Appendix B — Setting Up the SMON License . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
SMON Embedded License . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
Index. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide v
Page 6
Preface
Welcome to A vaya P120 SMON. This chapter provides an introduction to
the structure and assumptions of the guide. It includes the following
sections:
• The Purpose of this Guide - A description of the intended
purpose of this guide.
• Who Should Use this Guide - A description of the intended
audience of this guide.
• Organization of the Guide - A brief description of the subjects
covered in each chapter of this guide.
The Purpose of this Guide
This guide contains the information needed to operate Avaya P120
SMON switch monitoring application efficiently and effectively.
The following table provides information about where to find
documentation about Enterprise SMON and Device SMON for other
devices.
Table 1. SMON Documentation
Application Document
Enterprise SMON Avaya MultiService SMON User Guide
SMON for Avaya M770 Devices Avaya M770 and M-MLS SMON User
Guide
SMON for Avaya P130 Devices
SMON for Avaya P330 Devices
SMON for Avaya P580/P882
Devices
Avaya P130 SMON User Guide
Avaya P330 SMON User Guide
Avaya P580/P882 SMON User Guide
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide vi
Page 7

Who Should Use this Guide
This guide is intended for use by network managers familiar with network
management and its fundamental concepts. It is assumed that the user
has the basic responsibility for monitoring A v aya Technologies’ intelligent
switching devices and the network traffic.
Organization of this Guide
This guide is structured to reflect the following conceptual divisions:
• Preface - This chapter describes the guide’s purpose, intended
audience, and organization.
• Overview - This chapter provides an overview of the RMON
standard and Avaya Inc’s SMON concepts and an introduction to
the SMON tools.
Preface
• Device SMON - This chapter describes how to launch
Avaya P120 SMON and the Device SMON tools. It also describes the
Device SMON user interface.
• Switch Statistics - This chapter describes the Switch Statistics
tool in detail, including sample screens and filtering options.
• Port Statistics - This chapter describes the Port Statistics tool in
detail, including sample screens and filtering options.
• VLAN Statistics - This chapter describes the VLAN Statistics tool
in detail, including sample screens and filtering options.
• Alarms and Events - This chapter describes the Alarms Table,
Alarms Wizard, and Device Event Log in detail, with instructions
on how to define and activate alarms.
The following Appendices are included at the end of this guide:
• Appendix A - Dialog boxes that appear in SMON tools.
• Appendix B - How to set up the SMON license so that SMON will
work with Avaya P120 Devices.
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide vii
Page 8

SMON Overview
1
This chapter describes SMON, A vaya Inc.’ s switched network monitoring
system. This chapter includes the following s:
• What is RMON - A brief description of the RMON standard.
• What is SMON - A general description of SMON switch
• Overview of SMON - An introduction to SMON.
• Device SMON Tools - The Device SMON tools and how they
What is RMON
monitoring technology.
function.
RMON is the internationally recognized and approved standard for
detailed analysis of shared Ethernet and Token Ring media. It ensures
consistency in the monitoring and display of statistics between different
vendors.
RMON’s advanced remote networking capabilities provide the tools
needed to monitor and analyze the behavior of segments on a network.
In conjunction with an RMON agent, RMON gathers details and logical
information about network status, performance, and users running
applications on the network.
An RMON agent is a probe that collects information about segments,
hosts, and traffic, and sends it to a management station.
The network administrator uses software tools to view the information
collected by the RMON agent on the management station.
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 1
Page 9

RMON has two levels:
• RMON I analyzes the MAC layer (Layer 2 in the OSI seven-layer
• RMON II analyzes the upper layers (Layers 3 and above).
RMON is an industry standard that Avaya Inc. and other companies have
adopted in their network management applications. SMON takes the
RMON standard and extends it to the switching environment.
What is SMON
SMON is an extension of the RMON standard. SMON adds to the
monitoring capabilities of RMON in the following ways:
• It provides additional tools and features for monitoring in the
SMON Overview
model).
switch environment.
• It provides a global view of traffic flow in a network with multiple
switches.
Device SMON extends RMON I for the MAC layer, and AnyLayer SMON
extends RMON II for the network layer and above. SMON monitoring
collects and displays data in real-time.
Using SMON monitoring, you can get:
• A global view of traffic for all switches on the network.
• An overall view of traffic passing through a specific switch.
• Detailed data about the hosts transmitting packets through a
switch.
• An analysis of traffic passing through each port connected to a
switch.
• A view of traffic between various hosts connected to a switch.
Overview of SMON
SMON is an RMON-compliant network management suite that
implements the SMON extensions to RMON. SMON works with the other
components of Avaya MultiService Network Manager to provide a full
spectrum of in-depth monitoring of switch traffic and network
performance.
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 2
Page 10

Chapter 1
SMON consists of a software console application on a workstation and
remote monitoring probes in network devices that support SMON.
The SMON console communicates constantly with the SMON devices on
your network. The console uses the SNMP protocol to gather information
from the devices. SMON provides a suite of powerful graphic display tools
to view this information.
SMON gives you detailed analysis of the traffic flow on your switched
network, from a global view down to a specific host, and from total MAC
layer traffic down to a specific application protocol - all in real-time.
In addition, SMON allows you to set alarms based on traffic thresholds.
When an alarm is triggered, a trap can be sent to the device’s manager
and the event that triggered the alarm can be entered in SMON’s Event
Log.
SMON Devices
SMON provides monitoring capabilities for Avaya Inc’s network devices
that support the SMON extensions of the RMON standard.
Filtering Options
SMON tools provide different methods of filtering the information
displayed on the screen. These method include:
• Specific filtering
• TopN filtering
For information on how to use filters, refer to Appendix A, SMON Dialog
Boxes.
Specific
Filtering
TopN
Filtering
Specific filtering options provide the ability to specify the switches,
VLANs, or ports for which you want to view SMON information.
TopN filtering provides the ability to filter information based on the
amount of a particular type of traffic being monitored. When using TopN
filtering, specify the number of switches, VLANs, or ports for which you
want to view SMON information. Then select a statistic which will be
used as the basis for the filtering.
Using TopN filtering you can, for example, view information on only the
top 5 most active ports, or on the 8 switches generating the most error
traffic.
3 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Page 11

T opN filtering is powerful in that it allows you to focus on the information
that is important to you.
Device SMON Tools
The Device SMON tools for Avaya P120 Devices include:
• Switch Statistics - Detailed information on traffic passing
through the switch fabric.
• VLAN Statistics - Detailed information on switch traffic
associated with a VLAN.
• Port Statistics - Detailed information on port traffic to help
determine the precise cause of a problem.
• Alarms and Events - Notification of user defined Events that
help monitor a rise or fall of the rate of specified packets on
selected ports.
SMON Overview
Switch Statistics Overview
The Switch Statistics tool provides details of the traffic passing through
the switch fabric and allows you to detect problems on the switch. Once a
problem has been detected, you can use VLAN or Port Statistics to
determine more precisely the cause of the problem.
The display includes two sections:
• Pie charts and gauges showing traffic breakdown.
• A traffic graph that describes the characteristics of the traffic
passing through the device.
You can use the Switch Statistics tool for the following purposes:
• Gaining an overall view of the switched traffic over a specific time
period. This can help in discovering problems and analyzing traffic
trends.
• Discovering whether the device is being utilized efficiently or not.
• Monitoring the load distribution among VLANs.
• Detecting a large number of broadcast messages sent. This indicates
there may be a problem with a station on the network.
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 4
Page 12

Chapter 1
• Treating any variable with abnormal behavior as an issue that
should be investigated further using other SMON tools.
In general, the Switch Statistics tool can help you spot problems that only
become apparent from a high-level view over time. By periodically
viewing Switch Statistics, you can detect normal and abnormal behavior
of the specific switch configuration.
SMON collects and displays all information in real-time. In addition,
information collected during a session can be saved in a report.
Port Statistics Overview
The Port Statistics tool measures the traffic travelling through each port
on the selected device. For each port, SMON summarizes the traffic, such
as packets into the device and packets from the device. You can sort by
port name or by any of the packet types. You can see, for example, the
ports generating the most errors.
If you notice that a particular port displays a disproportionate amount of
errors, this may suggest that a device connected to the port is responsible
for the problem.
You select the most active ports by using a rate base. SMON measures the
rate base for all the ports to find the most active ports and then displays
these ports and their statistics. This process is called Port TopN.
Using the Port Statistics tool in conjunction with VLAN Statistics and
Switch Statistics makes it straightforward to discover the cause of a
problem. For example, using Switch Statistics you may discover that there
are too many errors on a specific switch. Y ou could then use Port Statistics
to help indicate the port from which the problem originates.
VLAN Statistics Overview
The VLAN Statistics tool measures the switched traffic travelling through
VLANs on the selected switch. A VLAN consists of stations connected
logically rather than physically. A VLAN can be used, for example, to
distribute network resources by department, even if the department’s
stations are not all located in the same area. Therefore, a VLAN can
incorporate stations from different devices.
By comparing the load of each VLAN you can discover which VLANs are:
• Utilizing their full capacity.
• Under capacity.
5 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Page 13
• Over-extended and probably causing a degradation in performance
to the users.
VLAN Statistics represents the information as a horizontal bar chart. Using
this tool in conjunction with Port Statistics and Switch Statistics makes it
straightforward to discover the cause of a problem. For example, using
VLAN Statistics you may discover that there are too many broadcast
errors on a specific VLAN. You could then use Port Statistics to help
indicate from which port the problem originates.
Alarms and Events Overview
The Alarms and Events tool reports when a specified counter on selected
ports, or on a device, cross user defined thresholds. The Alarm Wizard
provides a simple method for defining upper and lower thresholds of a
counter on selected ports or on the device. This definition of the
thresholds is an Alarm.
An Event is the crossing of a defined threshold in the direction it was
defined. For example, a Rising Event is when the rate of a specified
counter on a selected port rises above the defined Rising (upper)
Threshold. A Falling Event is when the rate of a specified counter on a
selected port falls below the defined Falling (lower) Threshold.
SMON Overview
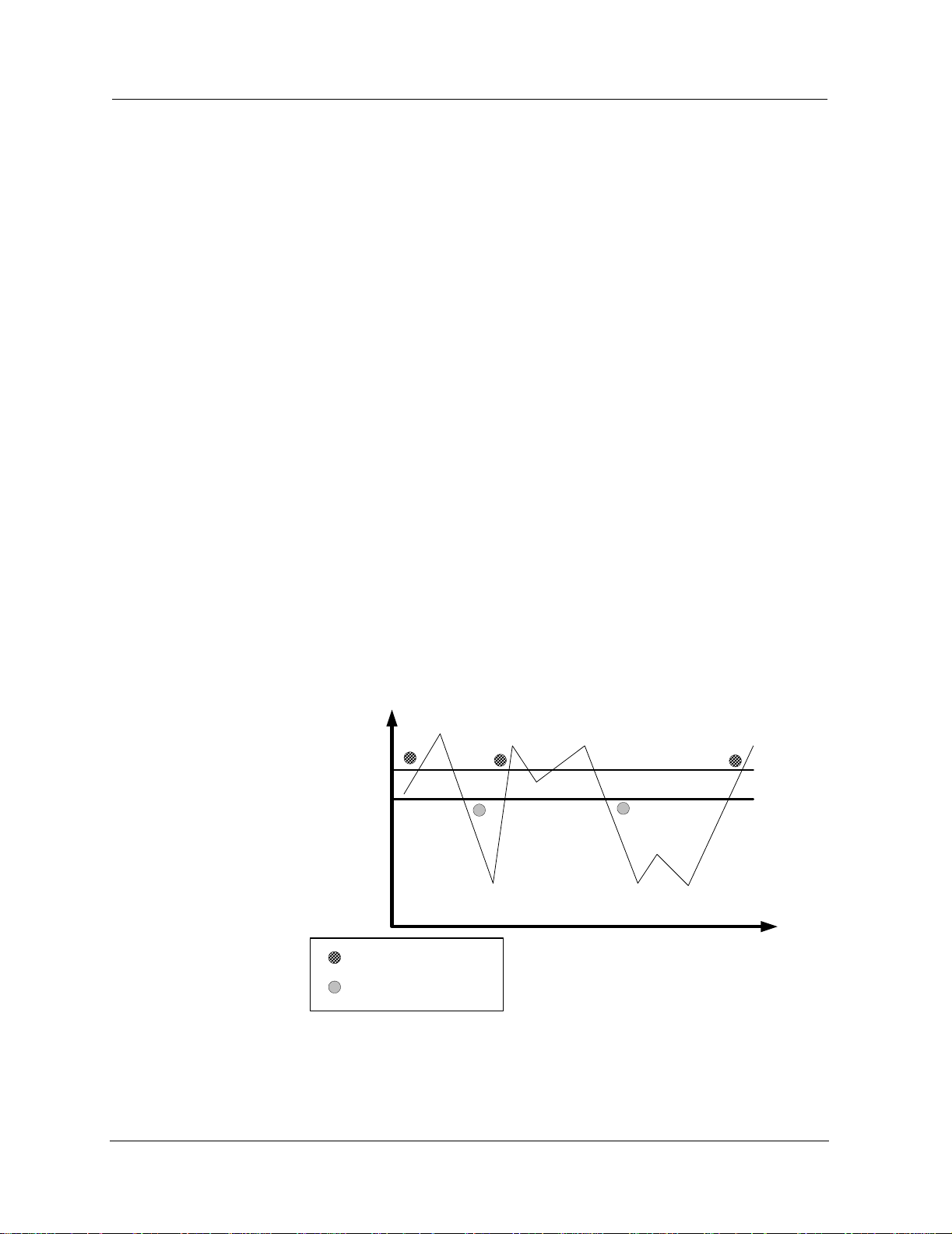
The following figure shows the scheme used to generate Events.
Figure 1-1. Events Overview
Counter
Rate
Rising Threshold
Falling Threshold
u
- Rising Event
- Falling Event
Time
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 6
Page 14

Chapter 1
The first Event is a Rising Event, caused by the counter rate rising above
the Rising Threshold. The second Event is a Falling Event, caused by the
counter rate falling below the Falling Threshold. The third Event is a
Rising Event. Note, that although the rate falls below the Rising Threshold
and then rises above it again, no Event is generated. A new Rising Event
can only be generated after the rate falls below the Falling Threshold.
Similarly, after the fourth Event, although the rate rises above the Falling
Threshold and then falls below it again, no Event is generated. A new
Falling Event can only be generated after the rate rises above the Rising
Threshold.
If you want to be informed of the rise or fall of the rate of a particular type
of packet on a port, you could use the Alarm Wizard to define thresholds
for the packet type on the port. You co uld then specify whethe r an Even t
causes a trap to be sent to the device’s manager, or is listed in SMON’s
Device Event Log, or both.
If you suspect a problem on a port, you can use Alarms and Events to
notify you when a problem occurs. You could then use the Port History
tool to identify the duration and frequency of the problem. This can help
you locate the cause of the problem.
7 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Page 15

Device SMON
2
This chapter provides information about SMON for Avaya P120 Devices,
and contains the following sections:
• Accessing Device SMON - Instructions on accessing the Device
SMON window.
• The Device SMON User Interface - A detailed description of
the user interface for Avaya P120 SMON.
• Working with Device SMON Tools - Techniques for using
Device SMON more effectively.
Accessing Device SMON
To access SMON for the Avaya P120 Devices, click the Device SMON tab
in the Avaya P120 Manager.
Or
1. Open Avaya MultiService SMON Manager Enterprise Switch
Statistics.
2. Double-click on the bar corresponding to an Avaya P120 Device.
Or
Right-click on the bar corresponding to an Avaya P120 Device
and select
P120 Device opens.
Execute Device SMON. SMON for the selected Avaya
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 8
Page 16
Chapter 2
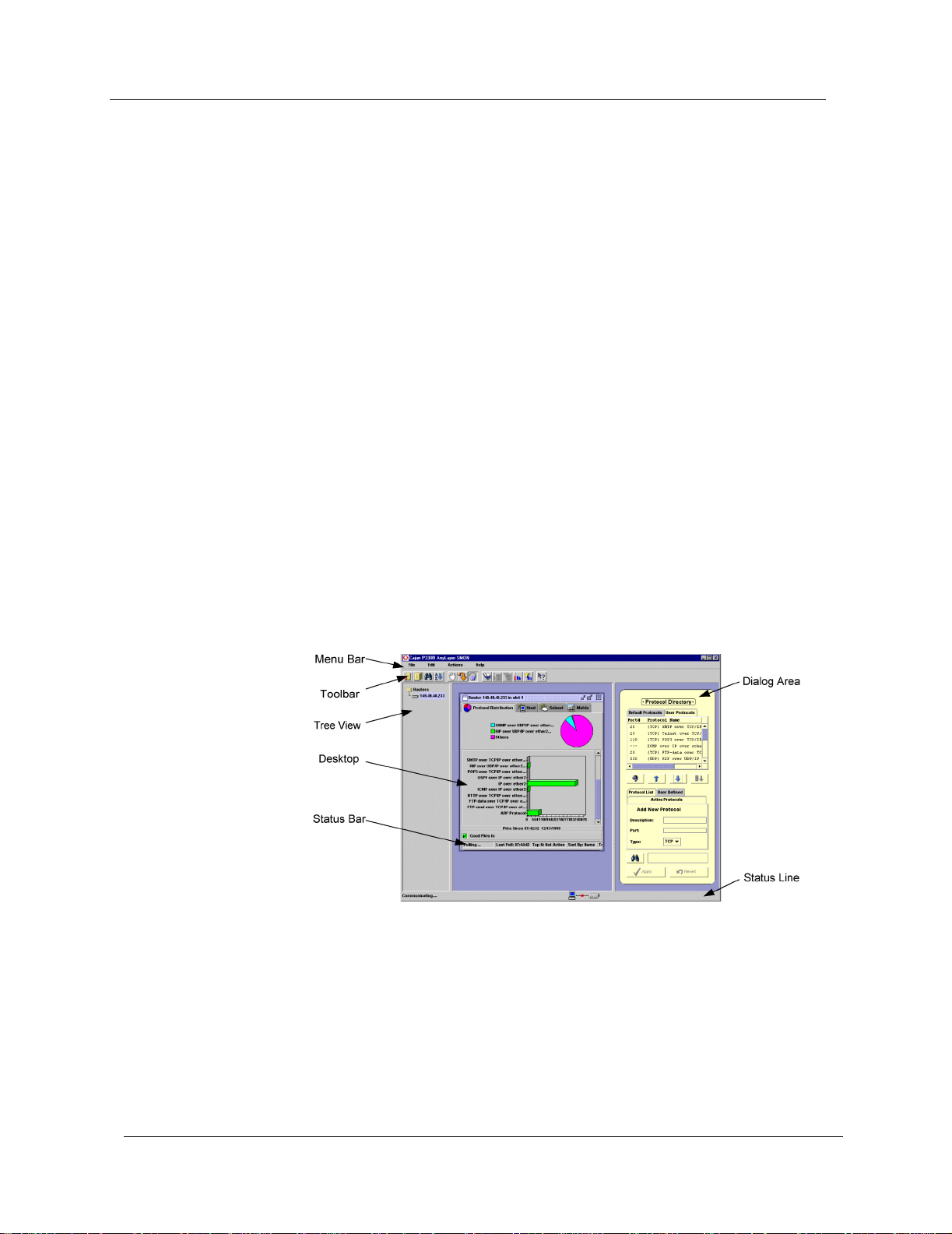
The Device SMON User Interface
The user interface consists of the following elements:
• Application Tabs - Tabs for switching between the different
views of the Avaya P120 Device.
• Menu Bar - Menus for accessing SMON functions.
• Device SMON Toolbar - Buttons providing shortcuts to
important functions in SMON tools.
• Dialog Area - A resizeable window where all dialog boxes appear.
• Desktop - A resizeable window where SMON windows are
displayed.
• Status Bar - An area at the bottom of each application window
where information about the current application is displayed.
• Status Line - An area at the bottom of the SMON window where
the communication status between Avaya P120 SMON
Avaya P120 Device is displayed.
and the
The figure below shows the user interface, with its various parts labeled.
Figure 2-1. Avaya P120 SMON User Interface
9 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Page 17
Application Tabs
The Application Tabs provide a method for selecting the view of the
device.
To switch to the device management view of the Avaya P120, click
Device Manager. The Avaya P120 Device Manager opens.
To switch to the Device SMON view of the Avaya P120, click
Device SMON. Avaya P120 SMON opens.
Device SMON Toolbar
The Toolbar provides shortcuts to the main Device SMON functions and
tools. The following table describes the buttons on the toolbar and lists the
equivalent menu options.
Device SMON
Table 2-1. Toolbar Buttons
Button Description Menu
Activates the Switch Statistics tool. View > Switch
Statistics
Activates the Port Statistics tool. View > Port
Statistics
Activates the VLAN Statistics tool. View > VLAN
Statistics
Opens the Alarms Table. Tools >
Table
Opens the General Options dialog box.
For more information, refer to Appendix
A, Using the General Options Dialog Box.
Produces a report file for importing to a
spreadsheet or word processor. For more
information, refer to Appendix A, Report
Setting.
Searches for a specific item. For more
information, refer to Appendix A, Using
the Find Dialog Box.
File > Options
File > Report Now
Edit > Find
Alarms
Temporarily stops and then restarts
collection of SMON data. When the
collection of SMON data is paused, the
background of the chart appears white.
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 10
Actions > Pause
Page 18
Chapter 2
Table 2-1. Toolbar Buttons (Continued)
Button Description Menu
Updates the data immediately rather than
at the next specified polling time. Resets
the polling interval timer.
Selects a specific list of ports for display
and analysis. For more information, refer
to Appendix A, Using the Define Port Filter
Dialog Box.
Activates or deactivates the filter specified
in Define Port Filter.
Selects a specific list of VLANs for display
and analysis. For more information, refer
to Appendix A, Using the Define VLAN
Filter Dialog Box.
Activates/Deactivates the filter specified
in Define VLAN Filter.
Selects the criterion and number of items
for TopN filtering. For more information,
refer to Appendix A, Using the Define TopN
Filter Dialog Box.
Activates/Deactivates the filter specified
in Define TopN Filter.
Actions > Poll Now
Actions > Define
Port Filter
Actions > Activate
Port Filter
Actions > Define
VLAN Filter
Actions > Activate
VLAN Filter
Actions > Define
TopN Filter
Actions > Activate
TopN Filter
Starts the Alarm Wizard. Edit > Add Alarm
Deletes the selected Alarm. Edit >
Saves all changes to the Alarms Table. Edit >
Undoes all unsaved changes to the Alarms
Table.
Opens the Device Event Log. View >
Opens the online-help. Help > Contents
Delete Alarm
Apply
Edit >
Undo
Event Log
If a tool is not active, clicking the corresponding Device SMON toolbar
button launches the tool. If a tool is already active, clicking the
corresponding Device SMON toolbar button brings the tool to the
foreground. For more information about the individual tools, refer to
Chapter 1, Device SMON Tools.
11 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Page 19

Dialog Area
Desktop
Status Bar
Device SMON
The area on the right side of the user interface is where all dialog boxes
appear. This area can be resized by dragging the vertical splitter bar with
the mouse. When a dialog box opens it replaces the current dialog box
open in the Dialog Area.
The left side of the application window is the Desktop. This area can be
resized by dragging the vertical splitter bar with the mouse. Device SMON
application windows can be resized and minimized. Minimized windows
are shown at the bottom of the Desktop.
The Status Bar provides important information about the current
window. The table below describes the items found in the status bar.
* Note: The table below describes all the items that can appear on
Avaya P120 SMON window status bars. Only some of the
items appear in the status bar for each individual window.
Table 2-2. Status Bar Items
Item Description
Graph Status Status of the display. Possible statuses are: frozen, alive.
Last Poll Time when the last poll was made.
Next Poll Time remaining before the next poll.
Session Start Date and time at which this session started.
Sort By The active sort options (port or VLAN).
T opN The active TopN variable, or TopN is not active.
Total Number of
Items
Total Number of
Samples
Total number of items in the collection.
Total number of samples in the collection.
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 12
Page 20
Chapter 2
Status Line
The Status Line provides important information about the
communication status between the application and the Avaya P120
Device. The following table shows the messages and icons that can appear
in the Status Line with a description of their meaning.
Table 2-3. Status Line Items
Message Icon Description
Ready The application is ready to
communicate with the device.
Communicating The application is currently
communicating with the device.
Error The last attempted
communication with the device
was not successful.
Working with Device SMON Tools
The following sections describe techniques that can help you use
Avaya P120 SMON tools more effectively. The topics include:
• Mouse Actions - Information on the application’s response to
various mouse actions.
• Using Dialog Box Options - Instructions on using the dialog box
options.
• Generating Reports - Instructions on how to generate reports.
13 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Page 21
Mouse Actions
The mouse actions that can be performed in Avaya P120 SMON windows
allow you added flexibility when using the applications. The table below
describes some of the mouse actions available in some of the SMON
applications.
Device SMON
Table 2-4. Mouse Actions
Action Description
Movement on a
graph, bar, or pie
Double-click in a
graph
Press SHIFT and
select a portion of the
graph using the
mouse
Left-click in a graph Unfreezes the graph.
Using Dialog Box Options
Information entered in a dialog box is not saved until you click the Apply
button. If you want to undo all changes made to the information in the
dialog box, click
it was when the dialog box was first opened. If you have already sent
information to the device from the dialog box and you click
information in the dialog box will revert to what it was when it was last
saved.
Revert. The information in the dialog box reverts to what
The Info Box is displayed.
The graph freezes and is compressed to show all of
the traffic on the device from the time the application
was opened until now.
The graph freezes, zooms in, and shows only the
portion of the graph that was selected.
Revert, the
* Note: When clicking
Revert, the application does not poll the device
for information. It is therefore possible that the dialog box
may not reflect the true state of the device.
To apply the changes made in the dialog box, click
To undo all changes made in the dialog box, click
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 14
Apply.
Revert.
Page 22

Chapter 2
Generating Reports
SMON allows you to produce two types of reports:
• Report Now
• Auto Report
Generated reports are text files that can be imported into spreadsheets
such as Excel and database programs such as Access. The reports can be
generated in a tab delimited format or a comma separated format. Whe n a
report is generated, it is saved to the directory specified in the
Directory
Data in a Report Now includes only the statistics collected during the last
polling interval.
For more information on selecting a format and a default directory for
reports, refer to Appendix A, Using the General Options Dialog Box.
field in the General Options dialog box.
Reports
For more information on generating a Report Now, refer to “Using the
Report Now Dialog Box” on page 46. For more information on generation
Auto Reports, refer to “Using the Auto Report Dialog Box” on page 46.
15 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Page 23

Switch Statistics
3
Switch Statistics provides you with detailed information about the traffic
passing through a switch. For a detailed overview of Switch Statistics,
refer to “Switch Statistics Overview” on page 4.
Using Switch Statistics
To access the Switch Statistics window:
Click .
Or
Select
opens.
Switch Statistics displays information using different types of graphs:
• Gauges that show error packets and capacity.
View > Switch Statistics. The Switch Statistics window
Figure 3-1. Switch Statistics Window
• A pie chart that shows the ratio of Unicast to Non-Unicast
packets.
• A traffic graph section that contains line graphs describing the
characteristics of the traffic traveling through the switch.
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 16
Page 24

Chapter 3
The title of the Switch Statistics window displays the Device IP Address.
The gauges, pie charts and bar graph show data for the time furthest to
the right currently visible on the traffic graph. For more information, refer
to “Traffic Graph in the Switch Statistics Window” on page 18.
You can use the gauges, pie charts, and the traffic graph to view data from
an earlier point in time by scrolling the traffic graph. For more
information about modifying the display, refer to Appendix A, Using the
General Options Dialog Box. For more information on the available toolbar,
status bar, and mouse movement options, ref er to Chapter 2, Working with
Device SMON Tools.
Gauges and Pie Charts in the Switch Statistics Window
For Avaya P120 Devices, the gauges at the top of the window display the
following information:
Table 3-1. Gauge Variables in Switch Statistics
Variable Description
Errors Displays the percentage of packets that contain errors going
through the device on a logarithmic scale. If this
percentage is high, this indicates that there may be a
problem.
Capacity Displays the proportion of traffic in relation to the device’s
configured capacity, as a percentage. If the capacity used
nears the device’s total capability, this indicates there may
be a problem.
For Avaya P120 Devices, the pie chart at the top of the window displays
the following information:
Table 3-2. Pie Chart Variables in Switch Statistics
Variable Description
Good Unicasts
Into Switch
Displays the percentage of unicast packets entering the
device. On most networks, the unicast packets should
constitute the vast majority of the pie gr aph. If non-unicast
packets begin to increase, this indicates there may be a
problem.
Good Bcasts/
Mcasts Into
Switch
17 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Displays the percentage of non-unicast packets entering
the device.
Page 25

SMON updates these gauges and pie charts in real-time according to the
specified sampling interval. By viewing the relationships among these two
variables, you can learn a lot about the general behavior of the switch.
* Note: If contact with the device is lost, then the graphs will display
the last data received until communications are restored.
Traffic Graph in the Switch Statistics Window
The lower portion of the Switch Statistics window is a traffic graph. The
traffic graph displays selected variables as a line graph, in real-time. To
select the color coded variables you want graphed, use the check boxes
under the traffic graph.
For more information about available traffic variables, refer to the table
below.
Table 3-3. Traffic Variables in Switch Statistics
Switch Statistics
Variable Description
Errors Filtered Out By
Switch
Good Bcasts/Mcasts
Into Switch
Good Pkts In Good packets traveling into the switch.
Good Unicasts Pkts In Good unicast packets traveling into the switch.
In Bandwidth (Kbits) Total number of Kilobits entering the device.
Total Pkts In Total packets traveling into the switch.
Error packets reaching the switch.
Good non-unicast packets traveling into the switch.
SMON continuously monitors statistics for all available Switch Statistics
traffic variables, even those that are not currently selected. For
information on finding the 5 highest peaks of traffic, refer to Appendix A,
Using the Find Top5 Peaks Dialog Box.
The X axis of the graph represents time. The scale on the X axis can be
changed using the
Samples Per Screen field in the Switch Options dialog
box. For more information, refer to Appendix A, Using the General Options
Dialog Box.
The units of the Y axis for all variables are packets. Th e scale on the Y axi s
depends on the maximum value among all of the variables. If the spread
of values is wide, the graphs of variables with small values may not be
visible. In this case, use the logarithmic traffic display to produce better
results (refer to Appendix A, Logarithmic Display).
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 18
Page 26

Chapter 3
Comparing the traffic graphs to the meters can often point you in the
right direction for locating a problem. For example, the pie chart may
show an abnormal amount of non-unicast packets, while the bandwidth
usage shown in the traffic graph has increased significantly. This may
suggest that one of the stations attached to the switch is generating the
non-unicast packets. By using VLAN Statistics you can locate the VLAN
where the problem originates. By using Port Statistics you can locate the
port to which the suspected station is attached.
* Note: All counters are in packets except counters that measure
bandwidth, which are in kilobits (Kbps), and utilization,
which is a percentage.
19 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Page 27

Port Statistics
4
Port Statistics allows you to see the data passing through each port and
LAG connected to the switch. For a detailed overview of Port Statistics,
refer to “Port Statistics Overview” on page 5.
Using Port Statistics
To access the Port Statistics window:
Click .
Or
Select
T o select a set of statistics to display, click one of the radio buttons on the
lower right-hand corner of the window. The statistics sets are:
• Packets - Counters for selected packet types for each port and
LAG.
• Bandwidth - The rate at which traffic is entering and exiting
each port and LAG.
• Utilization - The utilized capacity of each port and LAG.
The variables relevant to the selected set of statistics appear under the
graph. Check the variables you want displayed. Statistics for the checked
variables are displayed as bar graphs.
View > Port Statistics. The Port Statistics application opens.
Selecting Ports to Display
By default, information from all ports and LAGs is displayed in the Port
Statistics window. You can limit information being displayed to specific
ports using Port, VLAN, and TopN filters. For more information, refer to
Appendix A, Using the Define Port Filter Dialog Box, Appendix A, Using the
Define VLAN Filter Dialog Box, and Appendix A, Using the Define TopN Filter
Dialog Box.
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 20
Page 28

Chapter 4
Port Statistics Variables
The following graphics provide examples of Avaya P120 Port Statistics
windows. Each figure is followed by a list of variables available in each of
the windows.
Figure 4-1. Port Statistics Window - Packets
Table 4-1. Port Statistics Variables - Packets
Variable Description
Collisions The number of collisions occurring on the port or
LAG.
Errors Filtered Out By
Switch
Good Bcasts/Mcasts
Pkts In
Good Pkts Out The number of good packets leaving the switch.
Good Unicast Pkts In The number of good unicast packets entering the
The number of error packets filtered out by the
switch.
The number of good non-unicast packets entering
the switch.
switch.
21 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Page 29

Port Statistics
Figure 4-2. Port Statistics Window - BandWidth
Table 4-2. Port Statistics Variables - BandWidth
Variable Description
In Bandwidth (Kbits) The rate at which traffic is entering the port or LAG.
Out Bandwidth (Kbits) The rate at which traffic is exiting the port or LAG.
Figure 4-3. Port Statistics Window- Utilization
Table 4-3. Port Statistics Variables - Utilization
Variable Description
Utilization The percentage of the port or LAG’s capacity
currently being utilized.
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 22
Page 30

Chapter 4
The Port Statistics Window
The Port Statistics window is organized as follows:
• The title of the Port Statistics window shows the IP address of the
device.
• The X axis represents packets or percentage for Utilization.
• The Y axis represents ports and LAGs. Each row on the graph
corresponding to a port or LAG is labeled on the Y axis with a port
number, LAG number, or with the user defined name for a port.
• Link Aggregation Groups (LAGs) are displayed. These are a group
of ports serving as one logical link. When referencing the LAG’s
information box (place your cursor over the LAG bar), each port
within the LAG appears. In addition, the speed of the LAG is the
sum of the speed of all the ports within the LAG.
Figure 4-4. LAG Information Box
* Note: For high-speed ports with large polling intervals, bandwidth
and utilization counters may be inaccurate.
For more information about modifying the display, and the available
toolbar, status bar, and mouse movement options, refer to Chapter 2,
Working with Device SMON Tools.
23 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Page 31

VLAN Statistics
5
VLAN Statistics displays detailed statistics for each VLAN. These statistics
can help you maintain proper VLAN configuration. They can also help
you pinpoint problems you may discover using Switch Statistics. For a
detailed overview of VLAN Statistics, refer to “VLAN Statistics Overview”
on page 5.
* Note: The statistics collected for each VLAN only include the
packets that are sent to and from stations connected to the
switch of the device being analyzed. Therefore, any traffic
that does not pass through the switch fabric of the selected
device is not included in the statistics.
Using VLAN Statistics
To access the VLAN Statistics window:
Click .
Or
Select
opens.
T o select a set of statistics to display, click one of the radio buttons on the
lower right-hand corner of the window. The statistics sets are:
• Packets - Counters for selected packet types for each VLAN.
• Bandwidth - The rate at which traffic is entering and exiting
each VLAN.
The variables relevant to the selected set of statistics appear under the
graph. Check the variables you want displayed. Statistics for the checked
variables are displayed as bar graphs.
View > VLAN Statistics. The VLAN Statistics application
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 24
Page 32

Chapter 5
Selecting VLANs to Display
By default, information from all VLANs is displayed in the VLAN Statistics
window. You can limit information being displayed to specific VLANs
using VLAN and TopN filters. For more information, refer to Appendix A,
Using the Define VLAN Filter Dialog Box, and Appendix A, Using the Define
TopN Filter Dialog Box.
VLAN Statistics Variables
The following graphics provide examples of VLAN Statistics windows.
Each figure is followed by a list of variables available in each of the
windows.
Figure 5-1. VLAN Statistics Window - Packets
Table 5-1. VLAN Statistics Variables - Packets
Variable Description
Good Broadcasts/
Multicasts Into Switch
Good Unicasts Into
Switch
25 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
The number of good non-unicast packets
entering the switch.
The number of good unicast packets entering
the switch.
Page 33

Figure 5-2. VLAN Statistics Window - Bandwidth
Table 5-2. VLAN Statistics Variables - Bandwidth
Variable Description
VLAN Statistics
In Bandwidth (Kbits) The rate at which traffic is entering the VLAN.
VLAN Statistics Window
The VLAN Statistics window is organized as follows:
• The title of the VLAN Statistics window displays the IP address of
the device.
• The X axis relates to packets over time or total packets, depending
on the display mode (refer to Appendix A, Display Mode).
• The Y axis relates to the VLAN name. Only VLANs with member
ports or LAGs defined VLANs appear in the window. If no VLANs
have been defined, the “Default” or “Generic” VLAN includes all
traffic.
For more information about modifying the display, and the available
toolbar, status bar and mouse movement options, refer to Chapter 2,
Working with Device SMON Tools.
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 26
Page 34

Alarms and Events
6
The Alarms and Events tool provides a method for defining thresholds
for packet types on a port. When a threshold is crossed, a trap is sent to
the device’ s manage r, or the Event is listed in SMON’ s Device Event Log.
The Alarms and Events tool consists of the following parts:
• Alarms Table - A table showing the alarms defined for the
device.
• Alarm Wizard - A wizard that enables you to add new Alarms.
• Device Event Log - A list of Events that occurred on the device.
Using Alarms and Events
To use Alarms and Events:
1. Add Alarms using the Alarm Wizard.
2. Review, edit, and delete Alarms defined for the device in the
Alarms Table.
3. View Events in SMON’s Device Event Log or in the Trap Log of
Avaya MultiService Console or HP-OV NNM.
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 27
Page 35

Alarms Table
To view a table of all the alarms defined for the device:
Alarms and Events
Click .
Or
Select
All the Alarms defined for the device are listed in the Alarms Table.
Tools > Alarms Table. The Alarms Table opens.
Figure 6-1. Alarms Table
Alarms Table Fields
The following table provides a list of the fields in the Alarms Table with
their description.
Table 6-1. Alarms Table Fields
Field Description
Index A number identifying the Alarm.
Port The port or LAG for which the Alarm was configured.
Counter The counter being monitored by the Alarm.
Interval The interval at which the counter is compared to the
defined thresholds.
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 28
Page 36

Chapter 6
Table 6-1. Alarms Table Fields (Continued)
Field Description
Method The method used for monitoring the variable. Possible
options are:
• Rate @ Interval - The Alarm uses the counter’ s rate
in the last interval.
• Total - The Alarm uses the absolute number of the
counter from the time the device was last reset.
* Note: The Alarms and Events tool can only
configure Alarms using the
Rate @ Interval method. To configure
Alarms based on the absolute number of
packets, use the CLI (Command Line
Interface) or a third-party application.
Startup Alarm The type of Event t hat can be generated as the first Event
for the Alarm. Possible types are:
• Rising - The first Event that can be generated must
be a Rising Event. If the rate falls below the Falling
Threshold before it rises above the Rising Threshold,
a Falling Event is not generated.
• Falling - The first Event that can be generated must
be a Falling Event. If the rate rises above the Rising
Threshold before it falls below the Falling Threshold,
a Rising Event is not generated.
• Rising and Falling - The first Event generated can
be a Rising or a Falling Event.
Rising Threshold The upper threshold for the counter.
Falling Threshold The lower threshold for the counter.
Owner The owner of the Alarm. This is usually the person who
created the Alarm.
29 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Page 37

Tooltips
Alarms and Events
Tooltips in the Alarms and Events tool provide information about an
Alarm. When the cursor is held over the
Index field of a row in the Alarms
Table a tooltip appears.
Figure 6-2. Alarm Tooltip
The tooltip provides information about the Alarm’ s definition. In addition,
it shows the ‘raw’ number of packets (or octets) which will generate a
Rising or Falling Event. The raw number is the actual number of packets
(or octets) that must enter the port in order to generate an Event. This
number is equal to the defined rate times the interval.
For example, if an Alarm is defined for Broadcast packets with an Interval
of 15 seconds, a Rising Threshold of 1,000 packets per second and a
Falling Threshold of 100 packets per second, the raw number for a Rising
Event is 15,000 and for a Falling Event 1,500. If 15,000 or more Broadcast
packets enter the port in a 15 second interval, a Rising Event is generated.
The following table provides a list of the fields in Tooltip with their
descriptions.
Table 6-2. Tooltip Fields
Field Description
Index A number identifying the Alarm.
Port The port or LAG for which the Alarm was configured.
Counter The counter being monitored by the Alarm.
Last Value The value of the counter calculated for the last interval.
Rising Threshold
[raw]
Last Rising Time The time of the last Rising Event.
The Rising Threshold expressed as the number of packets
or octets in an interval.
Falling Threshold
[raw]
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 30
The Falling Threshold expressed as the number of packets
or octets in an interval.
Page 38

Chapter 6
Editing Alarms
Alarms can be edited and deleted using the Alarms Table.
To edit an Alarm, change the Alarm’s parameters in the Alarms Table.
To delete an Alarm:
Table 6-2. Tooltip Fields (Continued)
Field Description
Last Falling Time The time of the last Falling Event.
1. Select an Alarm.
2. Click .
Or
Select
Edit > Delete Alarm. The Alarm is deleted from the Alarms
Table.
To save the changes to the Alarms Table:
Click .
Or
Select
Edit > Apply. All changes to the Alarm Table are saved.
To undo all unsaved changes to the Alarms Table:
Click .
Or
Select
Edit > Undo. All changes to the Alarm Table are undone.
31 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Page 39

Alarm Wizard
This section provides the information you need to use the Alarm Wizard.
It contains the following topics:
• Overview of the Alarm Wizard - An overview of the function of
the Alarm Wizard.
• Activating the Alarm Wizard - Instructions on how to run the
Alarm Wizard.
• Alarm Wizard Screens - Detailed explanations about each of the
steps in the Alarm Wizard.
Overview of the Alarm Wizard
The Alarm Wizard consists of several screens designed to enable you to
easily define Alarms for ports on the device. You can use the wizard to
define an alarm for a single port or for multiple ports. When defining an
alarm for more than one port, the wizard creates a separate Alarm for
each port.
Alarms and Events
* Note: A maximum of 150 Alarms can be defined on a single device.
Activating the Alarm Wizard
To activate the Alarm Wizard:
Click .
Or
Select
opens.
Edit > Add Alarm. The Welcome screen of the Alarm Wizard
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 32
Page 40

Chapter 6
Alarm Wizard Screens
This section provides detailed information on each of the Alarm Wizard’s
screens. T o accept the default options for any screen, click
to an earlier screen, click
any changes, click
Next. T o return
Back. To exit the Alarm Wizard without making
Cancel.
Welcome to
the Alarm
Wizard
Welcome to the Alarm Wizard. The Alarm Wizard provides a simple
method for defining Alarms for the device.
Figure 6-3. Alarm Wizard - Welcome Screen
To continue, click
screen.
Next. The Alarm Wizard continues with the Select Port
33 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Page 41

Alarms and Events
Select Port The Select Port screen of the Alarm Wizard allows you to select ports and
LAGs to be monitored by the Alarm.
Figure 6-4. Alarm Wizard - Select Port
The ports and LAGs on the device are listed in the
Device Ports list.
To select ports and LAGs to monitor, double-click a port or LAG in the
Device Ports list. The selected port or LAG appears in the Selected Ports list.
To remove ports or LAGs from the
LAG in the
Selected Ports list and appears in the Device Ports list.
Selected Ports list. The selected port or LAG is removed from the
To define an Alarm for the entire device, add
Selected Ports list, double-click a port or
Device to the Selected Ports
list.
When defining an Alarm for more than one port, a separate Alarm is
created for each port.
* Note: A maximum of 150 Alarms can be defined on a device.
When you finish selecting ports and LAGs to monitor, click
Next. The
Alarm Wizard continues with the Select Interval and Counter screen.
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 34
Page 42

Chapter 6
Select
Interval and
Counter
The Select Interval and Counter screen of the Alarm Wizard enables you
to select a variable to be monitored by the Alarm, and the interval at
which SMON gets the rate for the counter from the device.
Figure 6-5. Alarm Wizard - Select Interval and Counter Screen
Enter a number in the
SMON will get the rate of the counter from the device.
Select a counter from the
that will be monitored by the Alarm.
When you finish configuring the polling interval and selecting a counter
to monitor, click
Thresholds screen.
Alarm Interval field. This is the interval at which
Alarm Counters pull-down list. This is the counter
Next. The Alarm Wizard continues with the Set
35 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Page 43

Alarms and Events
Set
Thresholds
The Set Thresholds screen enables you to configure the behavior of the
Alarms and Events tool when SMON is started, and to configure
thresholds for the Alarm.
There are two thresholds, a Rising Threshold and a Falling Threshold. If
the rate of the selected counter rises above the selected Rising Threshold,
an Event is generated. If the rate of the selected counter falls below the
selected Falling Threshold, an Event is generated. For more information
about Thresholds, refer to “Alarms and Events Overview” on page 6.
Figure 6-6. Alarm Wizard - Set Thresholds
To configure the behavior of the Alarms and Events tool when SMON is
started, select a radio button in the
Alarm Startup field. The options are:
• Rising - The first Event that can be generated must be a Rising
Event. If the rate falls below the Falling Threshold before it rises
above the Rising Threshold, a Falling Event is not generated.
• Falling - The first Event that can be generated must be a Falling
Event. If the rate rises above the Rising Threshold before it falls
below the Falling Threshold, a Rising Event is not generated.
• Rising and Falling - The first Event generate d can be a Rising or a
Falling Event.
T o configure the thresholds, enter values in the
Rising and Falling fields. The
threshold levels are in packets or octets per second.
When you finish configuring the startup behavior and thresholds, click
Next. The Alarm Wizard continues with the Descriptions screen.
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 36
Page 44

Chapter 6
Descriptions The Descriptions screen enables you to give names to the Rising and
Falling Events of the Alarm.
Figure 6-7. Alarm Wizard - Descriptions
T o configure the names of Rising and Falling Events, enter a description in
the appropriate fields. These descriptions will appear in SMON’s Device
Event Log.
* Note: When configuring Alarms for multiple ports, the Event
descriptions will be identical for the Events of all the Alarms
being created.
When you finish configuring Event descriptions, click
Next. The Alarm
Wizard continues with the Set Event screen.
37 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Page 45

Alarms and Events
Set Event The Set Event screen of the Alarm Wizard allows you to determine the
action SMON takes when an Event occurs.
Figure 6-8. Alarm Wizard - Set Event
To configure the action SMON takes when a Rising Event occurs, select a
radio button in the
when a Falling Event occurs, select a radio button in the
Rising event fields. To configure the action SMON takes
Falling event fields.
The possible actions are:
• None - No action is taken when the Event occurs.
• Log - The Event is recorded in SMON’s Device Event Log.
• Trap - A trap is sent to the manager of the device. This trap can be
viewed in the T rap Log in Avaya MultiService Console or HP NNM.
• Log & Trap - The Event is recorded in SMON’s Device Event Log
and a trap is sent to the manager of the device.
When you finish configuring Event parameters, click
Next. If one or more
of the Event actions is Trap or Log & Trap, the Alarm Wizard continues
with the Set Trap Community screen. Otherwise, the Alarm Wizard
continues with the Summary screen.
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 38
Page 46

Chapter 6
Set Trap
Community
The Set Trap Community screen of the Alarm Wizard allows you to
configure community for Rising and Falling Events. The community is
needed to send traps to the station of the device’s manager.
Figure 6-9. Alarm Wizard - Set Trap Community
To configure the community for Events, enter the community of the
station of the device’s manager in the
When you finish configuring the trap community, click
Wizard continues with the Summary screen.
Rising and Falling fields.
Next. The Alarm
39 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Page 47

Alarms and Events
Summary The Summary screen of the Alarm Wizard provides a summary of the
options selected in the previous screens.
Figure 6-10. Summary
To make any changes to the summary information:
1. Click
2. Change the configuration parameters.
3. Click
To create the Alarm, click
Alarms Table.
Device Event Log
The Device Event Log provides a list of Events that triggered Alarms with
an action of Log. To view the Event Log:
Click .
Or
Select
Back until you reach the appropriate screen.
Next until you reach the Summary screen.
Finish. The Alarm is created and appears in the
View > Event Log. The Device Event Log opens.
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 40
Page 48

Chapter 6
Figure 6-11. Device Event Log
The Device Event Log has two tabs, one for Rising Events and one for
Falling Events. To view the Device Event Log for Rising or Falling Events:
1. Select an Alarm in the Alarms Table.
2. Click the appropriate tab. The Device Event Log opens to the
selected Event type for the Alarm.
The Device Event Log window has two parts. The upper part provides a
description of the Event. The following table provides a list of the fields
describing the Event and their descriptions.
Table 6-3. Event Description Fields
Field Description
Event A user defined description of the Event.
Type The action taken by SMON. Possible actions are:
• None - No action was taken when the event
occurred.
• Log - The Event was recorded in SMON’s Device
Event Log.
• Trap - A trap was sent to the manager of the device.
This trap can be viewed in the Trap Log in Avaya
MultiService Console or HP NNM.
• Log & Trap - The Event was recorded in SMON’s
Device Event Log and a trap was sent to the
manager of the device.
Time Last Sent The latest date and time this Event occurred.
Trap Community The Trap Community of the Event.
41 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Page 49

Alarms and Events
The lower part of the window is the Log List. This is a log of the selected
Alarm’s Events. Entri es will appear in the
Log List only if the T ype of Event
is Log or Log & Trap. The following table provides a list of the fields in
the
Log List and their descriptions.
Table 6-4. Event Log Fields
Field Description
Time The date and time of the Event.
Description A detailed description of the traffic that triggered the
Event.
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 42
Page 50

SMON Dialog Boxes
A
This appendix consists of dialog boxes that appear within the
Avaya P120 SMON tools.
Using the General Options Dialog Box
This dialog box enables you to change the general options for SMON for
the Avaya P120 Device.
To access the General Options dialog box:
1. Click .
Or
Select
2. Click the
Options dialog box opens.
File > Options. The Options dialog box opens.
General tab at the top of the dialog box. The General
Figure A-1. General Options Dialog Box
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 43
Page 51

The General Options dialog box enables you to change the following
options:
Polling Interval
The Polling Interval option allows you to configure the way in which
information is collected. If you make the polling interval smaller, you
receive more accurate data at the expense of using more network
resources. The objective is to use the ideal polling interval that provides
accurate data using minimum network resources.
To change the polling interval, enter the number of minutes and seconds
for the new polling interval in the
SMON Dialog Boxes
• Polling Interval
• Display Mode
• Report Setting
min and sec fields.
Display Mode
* Note: The polling interval must be between 15 seconds and
59 minutes and 59 seconds.
* Note: The new polling interval will take effect when the device is
next polled.
The Display Mode option allows you to select one of three display modes.
Select a display mode using the radio buttons.
The display mode options are:
•
Last Interval Rate - The statistics gathered since the last poll.
•
Cumulative - The accumulated statistics gathered since the start of
the session.
Session Average Rate - The average of the statistics per polling
•
interval since the start of the session.
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 44
Page 52

Appendix A
Report Setting
The Report Setting option enables you to select a default directory for
saving reports and configure the report format.
To select a default directory for saving reports:
1. Click
Browse. A directory browser window opens.
2. Navigate to the directory in which you want to save reports.
3. Click
Open. The path appears in the Reports Directory field.
Select a report format using the radio buttons.
The report format options are:
•
Tab-separated - The report is formatted as a tab-delimited file.
CSV - The report is formatted as a comma-delimited file.
•
45 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Page 53

Using the Report Now Dialog Box
This dialog box enables you to generate a report with the statistics from
the last time the device was polled.
To access the Report Now dialog box:
1. Click .
Or
SMON Dialog Boxes
Select
2. To change the filename and directory in which to save the report:
a. Click
File > Report Now. The Report Now dialog box opens.
Figure A-2. Report Now Dialog Box
Browse. A file browser window opens.
b. Select a directory and filename for the reports.
3. Click
Report. The report is generated.
Using the Auto Report Dialog Box
This dialog box enables you to start and stop generating reports
automatically.
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 46
Page 54

Appendix A
To access the Auto Report dialog box:
1. Select
File > Auto Report. The Auto Report dialog box opens.
Figure A-3. Auto Report Dialog Box
2. To change the filename and directory in which to save the reports:
a. Click
Browse. A file browser window opens.
CAUT
b. Select a directory and filename for the reports.
3. Click
Start. The first report is generated immediately. Subsequent
reports are generated according to the polling interval.
To stop generating Auto Reports:
1. Select
2. Click
File > Auto Report. The Auto Report dialog box opens.
Stop.
Or
1. Close the application for which you are running the Auto Report.
Auto Reports are no longer generated.
Auto Reports are automatically saved to the network
management station (NMS). If Auto Reports are generated on
many devices for a long period of time, and none of the files are
deleted, the NMS’s hard disk may become full.
If this occurs, stop the applications that are generating automatic
reports and delete the files that are not required.
47 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Page 55

Using the Switch Options Dialog Box
This dialog box enables you to change the display options for Switch
Statistics for the Avaya P120 Device.
To access the Switch Options dialog box:
1. Click .
Or
SMON Dialog Boxes
Select
2. Click the
Options dialog box opens.
File > Options. The Options dialog box opens.
Switch tab at the top of the dialog box. The Switch
Figure A-4. Switch Options Dialog Box
The Switch Options dialog box enables you to change the following
options:
• Samples Per Screen
• Samples To Store
• Logarithmic Display
• Level Indicators
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 48
Page 56

Appendix A
Samples Per Screen
The Samples Per Screen option enables you to configure the number of
samples visible in the Traffic Graph. To change the number of samples
visible on the screen, enter a number in the
* Note: The number of samples per screen must be between 3 and
Samples To Store
The Samples To Store option enables you to configure the number of
samples saved in the Traffic Graph. You can scroll the Traffic Graph to
view all of the saved samples. To change the number of stored samples,
enter a number in the
* Note: The number of samples to store must be between 100 and
Samples Per Screen field.
500.
Samples To Store field.
8000.
Logarithmic Display
The Logarithmic Display option enables you to specify whether or not you
want the Traffic Graph to be displayed on a logarithmic scale. This is
useful when the values in the graph are small.
To view the traffic graph with a logarithmic display, check the
Display
checkbox.
To view the traffic graph with a non-logarithmic display, uncheck the
Logarithmic Display checkbox.
Level Indicators
The Level Indicators option enables you to change the appearance of the
gauges at the top of the Switch Statistics window. This allows you to
determine the range corresponding to the colors of the gauge.
To configure the level indicators, slide the markers for each of the gauges
to the desired percentages.
Logarithmic
The leftmost marker sets the percentage at which the color on the gauge
changes from green to yellow. The rightmost marker sets the percentage
at which the color on the gauge changes from yellow to red.
49 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Page 57

SMON Dialog Boxes
Using the Port/VLAN Options Dialog Box
This dialog box enables you to change the display options for Port and
VLAN Statistics for the Avaya P120 Device.
To access the Port/VLAN Options dialog box:
1. Click .
Or
Select
2. Click the
Options dialog box opens.
File > Options. The Options dialog box opens.
Port/VLAN tab at the top of the dialog box. The Port/VLAN
Figure A-5. Port/VLAN Options Dialog Box
The Port/VLAN Options dialog box enables you to change the following
option:
• Items Per Screen
Items Per Screen
The Items Per Screen option enables you to configure the number of
ports, LAGs, and VLANs visible in the Port and VLAN Statistics windows.
To change the number of items visible on the screen, enter a number in
the
Items Per Screen field.
* Note: The number of items per screen must be between 1 and 15.
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 50
Page 58

Appendix A
Using the Find Dialog Box
Depending on the application you have initiated this option from, the
Find option allows you to locate a specific VLAN/port/LAG intersection in
the application window.
To search:
1. Click .
Or
Select
The information you are prompted for in the Find dialog box
differs depending on the application from which you have initiated
it.
Edit > Find. The Find dialog box opens.
Figure A-6. Find Dialog Box (for Ports)
For more detail, refer to “Finding a Port” on page 52, “Finding a
VLAN” on page 52, or “Finding a LAG” on page 52.
2. Enter the information in the dialog box and click
port/LAG intersection found is highlighted in the application for
easy identification.
To remove the highlight from the application window, click the graph.
The highlight disappears.
* Note: The
51 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Find button changes to Find Next until all instances of the
search information have been found.
Find. The VLAN/
Page 59

* Note: Since the number of VLANs/ports/LAG intersections may
Finding a VLAN
There are several ways to enter a value to find a VLAN. The following is a
list of the types of values to enter in the Find dialog box:
Finding a Port
SMON Dialog Boxes
change between sampling intervals, the one you search for
may move out of focus with the next refresh. In this case, you
may search again or scroll the display.
• The full VLAN Name, such as “Marketing”.
• The first part of the VLAN’s name, such as “Mark”. SMON will find
the first time the value appears.
• The VLAN Number.
Finding a LAG
There are several ways to enter a value to find a port.
To search for a port by name:
1. Click the
2. Enter the port name or part of the port name in the
3. Click
* Note: If you enter only part of the name, SMON will find the first
time the value appears.
To search for a port by number:
1. Enter the port number in the
2. Click
To find a LAG:
Port Name radio button.
Port Name field.
Find.
Port field.
Find.
1. Click the
2. Enter the LAG name in the
3. Click
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 52
Port Name radio button.
Port Name field.
Find.
Page 60

Appendix A
Using the Define Port Filter Dialog Box
To open the Define Port Filter dialog box:
1. Click .
Or
Select
Actions > Define Port Filter. The Define Port Filter dialog box
opens.
Figure A-7. Define Port Filter Dialog Box
* Note: Filtering changes are only applied after clicking
Apply.
To add ports to the
Select ports from the
List of Selected Ports:
List of Known Ports and click Add.
Or
Double-click ports in the
appear in the
To select all ports, click
Ports
.
53 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
List of Selected Ports.
Add All. All ports are added to the List of Selected
List of Known Ports. The selected ports
Page 61

To remove ports from the List of Selected Ports:
SMON Dialog Boxes
Select the ports in the
List of Selected Ports and click Remove.
Or
Double-click ports in the
removed from the
List of Selected Ports.
T o remove all items from the
are removed from the
List of Selected Ports.
To refresh the list of ports in the
To activate the port filter, click
List of Selected Ports. The selected ports are
List of Selected Ports, click Remove All. All ports
Known Ports list, click Refresh.
Apply.
To deactivate the port filter, click .
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 54
Page 62

Appendix A
Using the Define VLAN Filter Dialog Box
To open the Define VLAN Filter dialog box:
Click .
Or
Select
Actions > Define VLAN Filter. The Define VLAN Filter dialog
box opens.
Figure A-8. Define VLAN Filter Dialog Box
* Note: Filtering changes are only applied after clicking
Apply.
To add VLANs to the
Select VLANs from the
List of Selected VLANs:
List of Known VLANs and click Add.
Or
Double-click VLANs in the
appear in the
To select all VLANs, click
Selected VLANs
55 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
.
List of Selected VLANs.
Add All. All VLANs are added to the List of
List of Known VLANs. The selected VLANs
Page 63

To remove VLANs from the List of Selected VLANs:
SMON Dialog Boxes
Select the VLANs in the
List of Selected VLANs and click Remove.
Or
Double-click on a VLAN the
VLANs are removed from the
To remove all items from the
List of Selected VLANs, click Remove All. All
VLANs are removed from the
To refresh the list of VLANs in the
To activate the VLAN filter, click
List of Selected VLANs. The selected
List of Selected VLANs.
List of Selected VLANs.
Known VLANs list, click Refresh.
Apply.
To deactivate the VLAN filter, click .
2. Enter the subnet mask in the
Mask field.
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 56
Page 64

Appendix A
Using the Define TopN Filter Dialog Box
You can also filter using the TopN option. TopN filtering differs from item
filtering in that SMON chooses the items with the heaviest traffic. The
TopN filter produces a report for the 1-15 (N) most active items on the
network.
SMON chooses the TopN items by a rate base which you select from the
Define TopN Filter dialog box. SMON measures the rate base for all the
items to find the TopN items and then displays these items and their
statistics.
* Note: If you previously defined a filter, TopN will select the TopN
items from the specified subset.
To select the criterion for TopN Configuration:
1. Click .
Or
Select
box opens.
Actions > Define TopN Filter. The Define TopN Filter dialog
Figure A-9. Define TopN Filter Dialog Box
2. Select the number of items and the criterion for the TopN filter.
* Note: Filtering changes are only applied after clicking
57 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Apply.
Page 65

The dialog box contains the following fields:
•
TopN Number - Enter the number of items to be displayed when you
activate TopN.
Based On - Select the criterion for deciding which items fall in the
•
TopN. The rate base can be any one of the available counters.
Using the Find Top5 Peaks Dialog Box
In Switch Statistics, you can use the Find Top5 Peaks option to find the
largest value of any counter. This can help you find when a problem
occurred or when a problem was most severe.
To select the criterion for Find Top5 Peaks:
1. Click .
SMON Dialog Boxes
Or
Select
2. Select a counter.
Edit > Find. The Find Top5 Peaks dialog box opens.
Figure A-10. Find Top5 Peaks Dialog Box
3. Click
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 58
Find. The display scrolls the graph to the peak value and a
vertical line appears at the peak value. The pie values at the top are
correct for this time period. The graph is frozen.
Page 66

Appendix A
To find the next highest peak:
1. Click
You can find up to the fifth highest peak. The graph unfreezes the fifth
time you click
In Switch Statistics, all counters are listed in the Find Top5 Peaks dialog
box, including those counters not currently displayed in the Traffic Graph.
Find Next. The displays scrolls to the next highest peak value
in the graph.
Find Next.
Using the Sort Dialog Box
You may sort the display by one of the available categories in the list.
To perform a sort:
1. Select
Actions > Sort. The Sort dialog box opens.
Figure A-11. Sort Dialog Box
2. Select the appropriate sorting criterion from the
listbox.
3. Click
When sorting by Name, the bars appear in ascending order from bottom
to top. When sorting by packets, the bars appear in descending order
(most traffic at the bottom, least traffic at the top).
59 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Sort. Sorting begins immediately . New information is sorted at
each subsequent polling.
Sort By drop-down
Page 67

Setting Up the SMON
B
License
The Avaya MultiService SMON Manager (with Avaya MultiService
Network Manager) package contains a license which allows you to use
SMON on a permanent basis. The A vaya MultiService Network Manager
package does not include this license. Instead a trial version of SMON is
included. This trial version expires 60 days after its first use. In addition,
an embedded license is required for SMON for Avaya P120 Devices.
For information on entering the SMON license, refer to the
Avaya MultiService SMON Manager User Guide.
SMON Embedded License
To use SMON with Avaya P120 Devices, you must enter a valid
embedded license via the Avaya P120 CLI. A unique License is required
for each Avaya P120 Device. A group License is valid for the number of
devices for which it was purchased.
For information on entering the Avaya P120 embedded SMON License,
refer to the SMON for Avaya P120 Installation Guide.
Device SMON for Avaya P120 Devices does not require a license for the
first 60 days. After 60 days, this application will not run unless you enter
a valid embedded SMON license.
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 60
Page 68

Index
A
Accessing
Device SMON
port statistics
switch statistics
VLAN statistics
Activating
alarm wizard
port filter
port statistics
switch statistics
the LANE Wizard
TopN filter
VLAN filter
VLAN statistics
Alarm tooltip
Alarm wizard
activating
descriptions
overview
screens
select interval and counter
select port
set event
set thresholds
set trap community
summary
welcome screen
Alarms and events
overview
using
Alarms table
fields
Application, tabs
Auto report dialog box
Avaya Device SMON Guide, purpose
Avaya Device SMON User Guide
intended readers
organization of this guide
33
27
28
8
20
16
24
32
11
10
10
32
11
11
10
30
32
32
37
32
35
34
38
36
39
40
33
27
6
28
10
46
vii
vii
vi
C
Changing
display mode
general options
polling interval
Configuring
alarms
number of items per screen
samples per screen
Creating alarms
D
Deactivating
port filter
TopN filter
VLAN filter
Defining Top5 filter
Defining TopN filter
Desktop
Device event log
description
opening
Device SMON
accessing
toolbar
tools
user interface
working with the tools
Dialog area
Dialog boxes
auto report
find
general options
port options
report now
switch options
VLAN options
Display mode
E
Editing alarms
32
12
4
51
44
43
44
49
32
11
11
11
58
57
40
41
40
8
10
9
12
46
43
50
46
48
50
44
31
50
13
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 61
Page 69

Index
F
Filtering
specific
TopN
Filtering options
Find dialog box
Finding
host, subnet, or protocol
LAG
Port
source and/or destination host
VLAN
G
Gauges in switch statistics
General options
dialog box
display mode
opening dialog box
polling interval
Generating reports
H
Help, online
How to
activate the alarm wizard
configure number of samples to store
configure samples per screen
configure the polling interval
create alarms
define Top5 filter
define TopN filter
edit alarms
find a LAG
find a port
find a VLAN
generate reports
modify alarms
search for a graph
select directory to save reports
select view of device
switch to Device SMON view
use define host filter dialog box
use define matrix filter dialog box
use define port filter dialog box
use define subnet filter dialog box
use define VLAN filter dialog box
use Device SMON
use dialog box options
3
3
3
51
52
52
52
52
52
17
43
44
10
44
15
11
32
49
44
32
58
57
31
52
52
52
15
31
10
45
10
10
56
53
8
14
56
56
55
49
How to, continued
use display mode option
use port statistics
use switch statistics
use the find dialog box
use the polling interval option
use the sort dialog box
use VLAN statistics
view alarms
view the device event log
work with the Device SMON tools
I
Immediate polling
Intended users
Introduction
Items per screen
L
LAG, finding
Level indicators
License, purchasing
Logarithmic display
M
Modifying alarms
Mouse actions
O
Online help
Organization of this guide
Overview
alarm wizard
alarms and events
port statistics
RMON
SMON
switch statistics
VLAN statistics
Overview of SMON
P
Pie charts, switch statistics
Polling
immediately
interval
setting interval
Port options dialog box
1
11
1
2
44
20
28
11
vii
50
52
49
3
49
31
14
32
6
5
4
5
2
11
44
44
16
51
59
24
40
vii
17
50
44
13
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 62
Page 70

Index
Port statistics
accessing
activating
overview
tool
variables
window
Ports
finding
selecting to display
Producing a report file
Purchasing an SMON license
Purpose of this guide
R
Report now dialog box
Reports
format options
generating
producing a file
selecting a directory
Resetting polling interval timer
Resizing
Desktop
Dialog area
RMON standard
S
Samples
per screen
to store
Searching, in a graph
Selecting
criterion for TopN filtering
directory to save reports
ports for display
report formats
view of device
VLANs to display
Setting up the SMON license
SMON
devices
dialog boxes
license
overview
probes
standard
SMON overview
Sorting, the display
20
10
5
20
21
23
52
20
10
3
vi
46
45
15
10
45
12
12
1
49
49
10
11
45
11
45
10
25
60
3
43
60
1
3
2
2
59
11
Specific filtering
Starting collection of SMON data
Status
12
bar
13
line
Stopping collection of SMON data
Switch options dialog box
Switch statistics
accessing
activating
overview
16
tool
traffic graph
T
Toolbar buttons
Tools for Device SMON
tooltip fields
Tooltips
Top5 filter, defining
TopN filter
TopN filtering
Traffic graph
U
Updating data immediately
User interface
Using
30
defining
selecting criterion
logarithmic display
samples per screen
samples to store
switch statistics
desktop
dialog area
status bar
status line
alarms and events
auto report dialog box
define host filter dialog box
define matrix filter dialog box
define port filter dialog box
define subnet filter dialog box
define Top5 filter dialog box
define TopN filter dialog box
define VLAN filter dialog box
dialog box options
find dialog box
12
3
48
16
10
4
18
10
4
30
58
57
11
3
49
49
49
18
11
12
12
13
27
46
56
56
53
56
58
57
55
14
51
10
10
63 Avaya P120 SMON User Guide
Page 71

Index
Using, continued
general options dialog box
port options dialog box
port statistics
report now dialog box
sort dialog box
switch options dialog box
switch statistics
VLAN options dialog box
VLAN statistics
V
VLAN options dialog box
VLAN statistics
accessing
20
59
16
24
24
50
46
50
43
48
50
VLAN statistics, continued
activating
overview
tool
using
variables
window
VLANs
finding
selecting to display
W
Welcome to Avaya Device SMON
What is RMON?
What is SMON?
Who should use this guide
10
5
24
24
25
26
52
11, 25
1
2
vii
vi
Avaya P120 SMON User Guide 64
 Loading...
Loading...