Page 1

Avaya
TM
Computer-Telephony 1.2
G3PBX Driver and CVLAN
Administration and Maintenance Guide
Issue 1
December 2002
Page 2

Copyright © 2002, Avaya, Inc.
All Rights Reserved
Printed in U.S.A.
Notice
Every effort was made to ensure that the information in this
document was complete and accurate at the time of printing.
However, information is subject to change.
Preventing Toll Fraud
"Toll fraud" is the unauthorized use of your telecommunications
system by an unauthorized party (for example, a person who is not a
corporate employee, agent, subcontractor, or working on your
company's behalf). Be aware that there may be a risk of toll fraud
associated with your system and that, if toll fraud occurs, it can
result in substantial additional charges for your telecommunications
services.
Avaya Fraud Intervention
If you suspect that you are being victimized by toll fraud and you
need technical assistance or support, call Technical Service Center
Toll Fraud Intervention Hotline at +1 800 643 2353 for the United
States and Canada. For additional support telephone numbers, see
the Avaya Web site:
http://www.avaya.com
Select Support, then select Escalation Lists US and
International. This Web site includes telephone numbers for
escalation within the United States. For escalation telephone
numbers outside the United States, select Global Escalation List.
Providing Telecommunications Security
Telecommunicat ions secur ity (of voice, data, and/or video
communications) is the prevention of any type of intrusion to (that is,
either unauthorized or malicious access to or use of) your
company's telecommunications equipment by some party.Your
company's "telecommunications equipment" includes both this
Avaya product and any other voice/data/video equipment that could
be accessed via this Avaya product (that is, "networked
equipment"). An "outside party" is anyone who is not a corporate
employee, agent, subcontractor, or working on your company's
behalf. Whereas, a "malicious party" is anyone (including someone
who may be otherwise authorized) who accesses your
telecommunications equipment with either malicious or mischievous
intent.
Such intrusions may be either to/through synchronous
(time-multiplexed and/or circuit-based) or asynchronous (character-,
message-, or packet-based) equipment or interfaces for reasons of:
■ Utilization (of capabilities special to the accessed
equipment)
■ Theft (such as, of intellectual property, financial assets,or
toll-facility access)
■ Eavesdropping (privacy invasions to humans)
■ Mischief (troubling, but apparently innocuous, tampering)
■ Harm (such as harmful tampering, data loss or alteration,
regardless of motive or intent)
Be aware that there may be a risk of unauthorized intrusions
associated with your system and/or its networked equipment. Also
realize that, if such an intrusion should occur, it could result in a
variety of losses to your company (including but not limited to,
human/data privacy, intellectual property, material assets, financial
resources, labor costs, and/or legal costs).
Your Responsibility for Your Company's
T ele com mun icati ons Secu r ity
The final responsibility for securing both this system and its
networked equipment rests with you - an Avaya customer's system
administrator, your telecommunications peers, and your managers.
Base the fulfillment of your responsibility on acquired knowledge
and resources from a variety of sources including but not limited to:
■ Installation documents
■ System administration documents
■ Security documents
■ Hardware-/software-based security tools
■ Shared information between you and your peers
■ Telecommunications security experts
To prevent intrusions to your telecommunications equipment, you
and your peers should carefully program and configure:
q your Avaya-provided telecommunications systems and their
interfaces
■ your Avaya-provided software applications, as well as their
■ underlying hardware/software platforms and interfaces
■ any other equipment networked to your Avaya products.
Trademarks
Adobe, Adobe Acrobat, and the Adobe logo are registered
trademarks of Adobe Systems, Inc.
Avaya and MultiVantage are trademarks of Avaya, Inc.
CallVisor, DEFINITY, and the Avaya logotype are registered
trademarks of Avaya, Inc.
Internet Explorer is a trademark of SyNet, Inc.
Microsoft, DOS, Windows, Windows NT, Windows 2000, Windows
XP, Win32, and the Microsoft logo are registered trademarks and
Windows for WorkGroups, Windows 95, and Windows 98 are
trademarks of Microsoft.
Netscape Navigator is a registered trademark of Netscape
Communications.
Pentium is a registered trademark of Intel Corporation.
Sun, Sun Microsystems and the Sun logo are registered trademarks
and Java, Solaris, and Solaris SPARC are trademarks of Sun
Microsystems, Inc. in the USA and other countries.
UNIX is a registered trademark in the USA and other countries,
licensed exclusively through X/Open Company Limited.
UnixWare is a registered trademark of the Santa Cruz Operation,
Inc. in the USA and other countries.
All products and company names are trademarks or registered
trademarks of their respective holders.
Avaya Support
Avaya provides a telephone number for you to use to report
problems or to ask questions about your contact center.
The support telephone number is 1-800-242-2121 in the United
States. For additional support
telephone numbers, see the Avaya Web site:
http://www.avaya.com
Select Support, then select Escalation Lists US and
International. This Web site includes telephone numbers for
escalation within the United States. For escalation telephone
numbers outside the United States, select Global Escalation List
.
Page 3
Contents
1 Introduction 1-1
■ About this Guide 1-1
■ Reason for Reissue 1-1
■ Organization of This Document 1-2
■ Overview of DEFINITY G3 PBX Driver 1-2
■ Network Latency Requirements 1-4
Requirements for Vectors
with Adjunct Route Steps 1-4
■ Terms Used in This Guide 1-5
■ Related Documents 1-6
For More Information About
Avaya Products and Service 1-7
2 Security and Configuration 2-1
■ Overview 2-1
■ Security Issues 2-1
Restricting Administration Permissions 2-2
Configuring the Tserver for a Secure
LAN Gateway Connection 2-2
Requirements for Dual NIC Configurations 2-2
■ Using the G3 PBX Configuration Utilities 2-3
Changing the G3PD and CVLAN Configuration 2-3
Tunable G3PD Configuration Parameters 2-8
Additional Configuration Parameters 2-12
Changing IP Address or Hostname of Active Link 2-12
■ Configuring Avaya CT
In a Firewall Environment 2-14
Requirements for Configuring
Avaya CT in a Firewall Environment 2-14
Administering Multiple Avaya CT
Servers to Ensure Unique Links 2-17
Sample Scenario 2-17
Issue 1 — December 2002
iiiDEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 4
Contents
3 Maintenance 3-1
■ Overview 3-1
■ Starting the DEFINITY G3PD Administrator Utility 3-2
■ File Menu Options 3-4
■ Maint Menu Options 3-4
Block/Enable Command 3-5
Link Status Command 3-7
Offline/Online Command 3-9
Restart Command 3-10
Suspend/Resume Alarms Command 3-12
Test Command 3-14
Version Command 3-16
■ Help Menu Options 3-17
4 Troubleshooting 4-1
■ Overview 4-1
■ Problem Descriptions 4-2
G3PD Not Starting 4-2
Switch Connection Not Up 4-2
Clients Fail to Connect to Visible G3PD 4-3
Switch Link "Talking" But Not In Service
(Authentication Failed for ADJLK Connection) 4-4
Clients Cannot See Advertised PBX Driver
(G3PD Not Visible to DEFINITY G3PD
Administrator Utility) 4-4
Not All Events Received by Application 4-5
Slow Performance 4-5
G3PD Stops Responding 4-5
Users Receive CSTA Universal Failure Messages
with RESOURCE_OUT_OF_SERVICE (34) or
Notified Device Monitoring Ended 4-6
Users Receive ACS Universal Failure Messages
with TSERVER_DRIVER_CONGESTION (73) 4-6
iv
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 5
Contents
Users Receive ACS Universal Failure Messages
with TSERVER_NO_TDI_BUFFERS (74) 4-6
Users Receive Route End Report
with PEFORMANCE_LIMIT_EXCEEDED (52) 4-7
Users Receive CSTA Universal Failure Messages
with GENERIC_SUBSCRIBED_RESOURCE_
AVAILABILITY (41) 4-7
Questions about Switch Feature Operations? 4-7
■ LAN Link Problem Descriptions 4-8
LAN Link Will Not Initialize 4-8
DEFINITY G3PD Administrator Utility Reports
LAN Link Status Not Talking 4-9
How Dropped Link Affects T
elephony Services Reque sts 4-13
How Dropped Link Affects Open Streams 4-14
■ Tserver Error Log 4-14
IN Index IN-1
Issue 1 — December 2002
vDEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 6

Contents
vi
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 7
Introduction
About this Guide
This document describes configuration, maintenance, and troubleshooting of the
DEFINITY® G3 PBX Driver (G3PD) for Telephony Services. Information in this
document is provided for Telephony Services administrators and the Services
organization that assists administrators when they experience problems with the
G3PD.
Reason for Reissue
1
This document is reissued for Avaya Computer Telephony, Release 1.2 with the
following updates:
n To describe configuring Avaya CT in a firewall environment. This document
describes how to configure Avaya CT when a firewall is placed between
the Avaya CT server and the MultiV antage Switch. See ‘‘Configuring Avaya
CT In a Firewall Environment’’ on page 2-14.
For information about other supported firewall environments, see Avaya
Computer T elephony, Telephony Services Administration and Maintenance
(NETMANGD.PDF).
n To introduce the following new product terminology:
— Avaya Computer Telephony (the successor to CentreVu Computer
Telephony)
— Avaya MultiVantage (the successor to DEFINITY). The term
DEFINITY is still used in this document, and, from the viewpoint of
this document, the terms DEFINITY and MultiVantage are
synonymous.
Issue 1 — December 2002
1-1DEFNETM.PDF R1.2
Page 8
Introduction
Organization of This Document
This document is organized as follows:
Chapter 1, "Introduction" provides a list of chapters in this document, an overview
of the DEFINITY G3 PBX Driver, terminology important to the understanding of
Computer-Telephony Integration (CTI) and a list of related documents.
Chapter 2, "Security and Configuration" describes security measures and how to
reconfigure the G3PD using the G3 PBX Driver Configuration utility. Instructions
are also provided on how to use the PBX Link Change utility to change the IP
address or hostname of an active link.
Chapter 3, "Maintenance" describes the tools that can be used to observe and
test the G3PD. An Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OA&M) utility,
the DEFINITY G3PD Administrator utility, can be used from a Microsoft Windows
2000, Windows NT (4.0 or later), Windows XP, or Windows 95 machine to perform
OA&M tasks.
Chapter 4, "Troubleshooting " describes problems that can occur with the
DEFINITY G3 PBX Driver (G3PD), the switches, and the switch links, and
suggests possible solutions to these problems.
Overview of DEFINITY G3 PBX Driver
The DEFINITY G3 PBX Driver (G3PD) allows Telephony Services applications to
communicate with a DEFINITY G3 PBX.
n Telephony Services applications access the G3PD through Telephony
Services (the security database and advertised services).
n CVLAN applications bypass Telephony Services and access an ASAI link
directly using CallVisor Adjunct Switch Application Interface (ASAI)
messages.
The primary function of the G3PD is to interpret Computer Supported
Telecommunications Application (CSTA) requests made by Telephony Services
applications and to forward them to the PBX. To do this, the G3PD converts the
CSTA requests into CallVisor ASAI messages, and uses the CVLAN API to send
and receive these messages across an ASAI link connecting your Tserver to the
DEFINITY ECS system. Customer applications on the Tserver can use this API
directly. In addition, clients can access the API with CVLAN. See Figure 1-1.
1-2
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF R1.2
Page 9
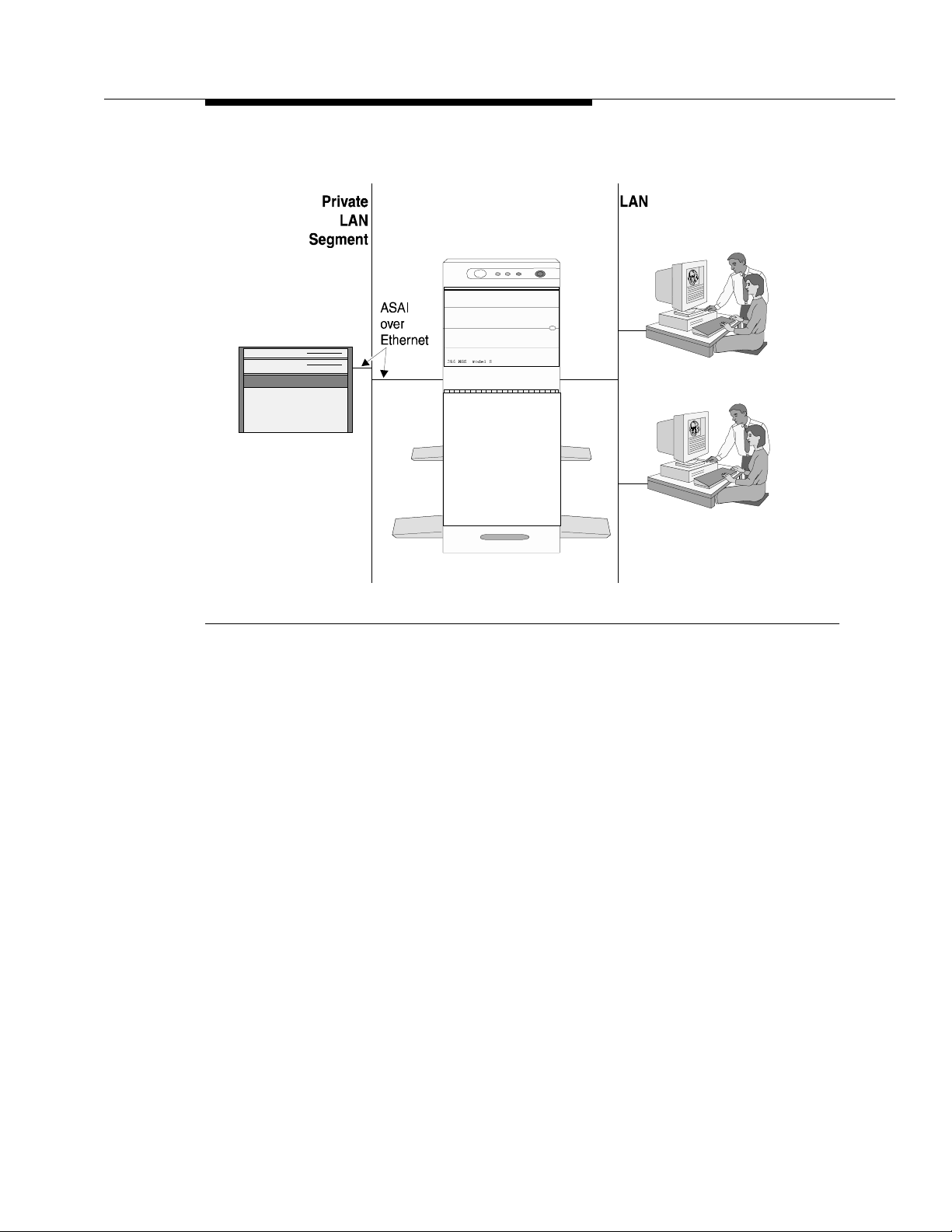
Introduction
Avaya
MultiVantage
Avaya CT Server
Tserver clients
Tserver
G3PD
CVLAN
CVLAN clients
Figure 1-1. DEFINITY CTI Client Server Diagram
Adjunct (ADJLK) links are provided over Ethernet. A Network Interface Card (NIC)
is installed in the Tserver to provide a link to a DEFINITY LAN Gateway.
DEFINITY LAN Gateway functionality is provided by the software running on the
Multi-function Board (MFB) or the Multi-Application Platform for DEFINITY
(MAPD) in the DEFINITY switch.
When installed with the ADJLK license (i.e., the station type parameter is
administered as ADJLK at the switch), G3PD supports both ASAI and ADJL K lin k
administration. When the ASAI license is used during G3PD installation (i.e., the
station type parameter is administered as ASAI at the switch), only switch ASAI
link administration is supported.
Issue 1 — December 2002
1-3DEFNETM.PDF R1.2
Page 10

Introduction
Network Latency Requirements
This section describes the network latency requirements, for the customer’s
network, that are needed to support CTI links over a LAN/WAN. These are links,
connected via a LAN/WAN, between the Avaya CT server and the MAPD based
DLG in an Avaya MultiVantage server that supports the MAPD, such as Avaya
MultiVantage S8700 Media Server.
Follow these requirements to maintain the CTI link over a LAN/WAN.
n Round Trip Time
A maximum 200 millisecond (ms) average round trip packet delivery time
as measured with "ping" over every one hour time period.
n Spiked Delays
Periodic spiked delays of no more than five seconds while maintaining the
200 ms average round trip delivery time as measured with "ping" over
every one hour time period.
Requirements for Vectors with Adjunct Route Steps
Vectors with "adjunct route" steps to the CTI server are connected over this
LAN/WAN link.
n If MultiVantage (Avaya call processing) is going to issue route requests,
then the associated "wait" step must always have a value greater than the
largest periodic spiked delay.
n With a maximum of five seconds allowed (see Spiked Delays), your “wait”
step should be greater than five seconds.
n If you can guarantee periodic spiked delays less than five seconds, you
can reduce the “wait” step time out accordingly.
n If no response to a route select is received by MultiVantage (Avaya call
processing), the call will follow the remaining vector steps in this specific
vector. In other words, you should program the vector to deal with the
possibility that the “adjunct route” step might time out.
1-4
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF R1.2
Page 11

Introduction
Terms Used in This Guide
In this guide, the following terms are used with the meanings shown below:
ADJLK Adjunct link(s). Label for the driver authorization disk or the
switch station type which is required to enable the
appropriate link connection and is provided with the G3PD.
ASAI Adjunct Switch Application Interface. An option on the
DEFINITY ECS switch that enables the ASAI Messaging
Interface between the switch and an Adjunct Processor
(such as a Tserver). This messaging interface allows the
Adjunct Processor to perform call monitoring and control
functions. Also known as CallVisor ASAI.
CVLAN CallVisor Local Area Network (CVLAN) software
implements the ASAI protocol on PCs on a LAN and
provides mapping to an application program interface (API)
for application software.
CSTA Computer Supported Telecommunications Applications. A
CTI standard established by the European Computer
Manufacturers Association (ECMA).
CTI Computer-Te le phon y Integ r atio n
DEFINITY
LAN Gateway
(DLG)
This gateway provides a virtual point-to-point connection
between a particular Telephony Server and an associated
port on the DEFINITY ECS switch. It translates Adjunct
Switch Application Interface ASAI) messages from
Q.931/Q.932 synchronous data frames to TCP/IP Ethernet
packets. DLG is:
n a software package that provides implementation of the
Ethernet-Switch Application Interface (ESAI).
n hardware used to run DLG software. Also known as the
ESAI tunnel protocol.
G3 PBX
Driver (G3PD)
The G3 PBX Driver is a Dynamic Link Library (DLL) on a
Windows NT machine. The G3PD software communicates
with both the DEFINITY G3 PBX and the Tserver to provide
switch services to Telephony Services applications.
Private Data
Support
Library
Private data is a mechanism that allows a switch to provide
value-added services that go beyond those defined in
CSTA. The G3PD provides a number of private data
services (for example, switch-collected call prompter digits
in events, or sending Dual Tone Multi-Frequency (DTMF)
tones that make up the support library).
LAN Local Area Network.
Issue 1 — December 2002
1-5DEFNETM.PDF R1.2
Page 12

Introduction
MAPD Multi-Application Platform for DEFINITY ECS. The MAPD
resides in a DEFINITY ECS carrier. It serves as an ISDN
brouter of ASAI messages through a TCP “tunnel” via
10Base-T Ethernet. A menu-based application allows
OA&M for the DEFINITY LAN Gateway. MAPD provides
DLG functionality; it can run in DLG mode, act as a CVLAN
server, or do both simultaneously.
NIC Network Interface Card. A circuit board residing in the
Tserve r that provide s an inte rface to the DEFINITY LAN
Gateway or to the local area network (LAN) with Tserver
clients.
NT machine A general name for any one of the following Windows NT
3.51 or 4.0 machines: NT Workstation, NT Server, NT
Backup Domain Controller, and NT Primary Domain
Controller.
PBX Driver A PBX-specific Dynamic Link Library (DLL) that receives
TSAPI messages from a Telephony Server, reformats them
into a set of messages understood by the PBX, and sends
the reformatted messages to the PBX over a CTI link.
Provided by the vendor supplying the PBX and CSTA
services for a switch. The G3PD is a PBX driver.
Telephony
Server
TSAPI Telephony Services Application Programming Interface. The
Tserver A program installed on a Windows NT, 4.0 (or higher) ;
Related Documents
For a list of related documents see the preface (“About This Document”) of Avaya
Computer Telephony Installation Guide (INSTALL.PDF).
A server that has Telephony Services software installed.
More than one Telephony Server can exist on a LAN. See
Tserver.
interface used by applications to make telephony requests,
such as call control requests (make a call, transfer a call),
monitor requests (trace a call), or routing requests.
Windows 2000 or Windows XP platform that provides
Telephony Services and receives TSAPI messages from
client and server applications. These messages are
checked for permissions and, if allowed, forwarded to the
PBX driver.
1-6
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF R1.2
Page 13

Introduction
For More Information About Avaya Products and Service
For information about Avaya products and service, go to www.avaya.com. For
product documentation for all Avaya products and related documentation, go to
www.avayadocs.com.
Issue 1 — December 2002
1-7DEFNETM.PDF R1.2
Page 14

Introduction
1-8
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF R1.2
Page 15
Security and Configuration
Overview
This chapter provides information on how to keep your network secure when
using Avaya Computer Telephony (Avaya CT). In addition, it provides
step-by-step instruc tion s on using the G3 PBX co nfi gurati on uti lit ies.
2
Security Issues
This chapter covers the following security-related topics.
■ ‘‘Restricting Administration Permissions’’ on page 2-2
■ ‘‘Configuring the Tserver for a Secure LAN Gateway Connection’’ on page
2-2
■ ‘‘Configuring Avaya CT In a Firewall Environment’’ on page 2-14
Issue 1 — December 2002
2-1DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 16

Security and Configuration
Restricting Administration Permissions
To ensure your environment’s security, it is recommended that you use
multiple-level administration permission to control which users are allowed to
grant administration permissions. For details, see “Controlling SDB Administration
Access” in Chapter 4 of Avaya Computer Telephony, Telephony Services
Administration and Mainte nan ce (NETMANGD.PDF).
Configuring the Tserver for a Secure LAN Gateway Connection
Although the Avaya CT server can be configured using a single NIC, it is
recommended that you configure the Avaya CT server with dual NICs, as follows.
■ Configure one NIC to communicate with the client LAN (or WAN). This NIC
can be Ethernet (10BaseT, 100BaseT, or 1000BaseT), T oken Ring, or Fiber
Distributed Data Interface (FDDI).
■ Configure the second NIC to communicate with the DLG (which could be
either Co-Resident on the MultiVantage server or on the MAPD). The
Co-Resident DLG can use Ethernet 10BaseT or 100BaseT and the MAPD
DLG uses Ethernet 10baseT. This NIC should be on a private isolated
segment.
There should be no IP forwarding on the Avaya CT server — that is, there should
be no IP forwarding between the Network Interface Card (NIC) used for the
DEFINITY LAN Gateway and the NIC used for client access.
Requirements for Dual NIC Configurations
Follow these requirements for the MAPD based DLG or the Co-Resident DLG.
When Connecting via the MAPD DLG
In a dual NIC configuration, the NIC used by the G3PD must be configured as
follows:
■ Ethernet 10BaseT
■ Half duplex
■ IP forwarding disabled
When Connecting via the Co-Resident DLG
In a dual NIC configuration, the NIC card used by the G3PD must be administered
as follows:
■ Ethernet 10BaseT or 100BaseT
■ Half duplex
2-2
■ IP forwarding disabled
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 17
Security and Configuration
Using the G3 PBX Configuration Utilities
During installation of the DEFINITY G3 PBX Driver (G3PD) and CVLAN,
administration of the driver is automatically performed. Following installation, you
can view and make changes to the G3PD configuration, if necessary, by running
the G3 PBX Driver Configuration utilities, that is, the G3 PBX Driver Configuration
utility or the G3 PBX Link Change utility. These utilities are run from the Avaya CT
sever.
The G3 PBX Configuration and G3 PBX Link Change utilities are discussed in the
following sections:
■ See ‘‘Changing the G3PD and CVLAN Configuration’’ to add or remove a
link, change an IP address or hostname, change an advanced
configuration parameter, or view the current configuration.
!
CAUTION:
The advanced configuration parameters listed in Table 2-2 are
established by default during the installation of the G3PD. In rare
instances, you may have to change them (most likely under the
direction of the TSO). Under normal circumstances, there is no
reason to change them.
■ See ‘‘Tunable G3PD Configuration Parameters’’ for descriptions of the
standard G3PD configuration parameters, as well as the advanced
configuration parameters, that are established by default during
installation.
■ See ‘‘Changing IP Address or Hostname of Active Link’’ to change an IP
address or hostname of an active link, without the need to stop the G3PD
and/or CVLAN services.
Changing the G3PD and CVLAN Configuration
Use the G3 PBX Driver Configuration Utility to change the G3PD configuration or
the CVLAN configuration. With this utility, you can:
■ add or remove a link
■ change an IP address or hostname of a link
■ change an advanced configuration parameter
■ view the configuration
NOTE:
To change an IP address or hostname of an active link (without unloading
the G3PD or CVLAN service) and have these changes take effect
Issue 1 — December 2002
2-3DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 18

Security and Configuration
immediately, use the G3 PBX Link Change Utility. Refer to ‘‘Changing IP
Address or Hostname of Active Link’’ later in this chapter.
To add or remove a link, change an IP address or hostname, change the
advanced configuration parameters, or view the G3PD configuration, take the
following steps:
1. Make sure that the G3PD is not loaded.
2. Make sure the CVLAN service is stopped. if you need to stop the CVLAN
service, follow these steps:
a. From the Control Panel double-click Administrative Tools, and
then double-click Services.
b. Select CVLAN Server from the list of services.
c. Click the Stop button.
3. Click Start, point to Programs, Avaya Computer Telephony,
DEFINITY G3 PBX Driver, and click G3 PBX Driver Configuration.
If the G3PD or CVLAN client is running, you will receive the following
warning message:
!
WARNING:
Either the DEFINITY G3 PBX Driver or a CVLAN Client is running.
Changes made to the configuration will not take effect until the next
time the DEFINITY G3 PBX Driver is loaded.
4. If you receive the warning message, click OK to proceed.
2-4
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 19
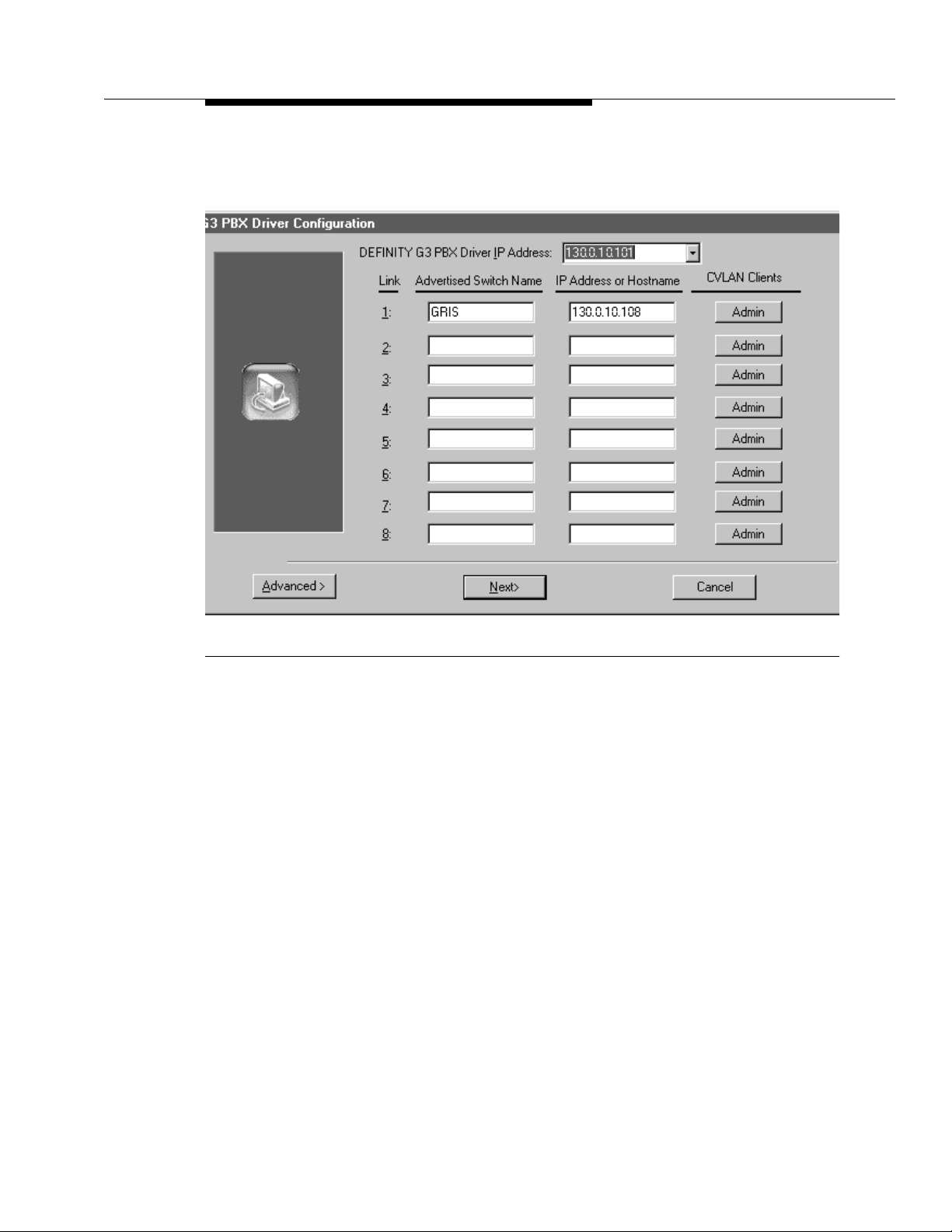
Security and Configuration
The system displays the G3 PBX Driver Configuration Dialog box.
Figure 2-1. G3 PBX Driver Configuration Dialog Box
5. Y ou can accomplish the following tasks in the G3 PBX Driver Configuration
dialog box. See Table 2-1 for descriptions of the standard configuration
parameters.
■ Change the link assignment by overwriting the fields under
Advertised Switch Name and IP Address or Hostname for any
link. Once you have completed your changes, click Next.
■ Add a link by entering a name and IP Address under Advertised
Switch Name and IP Address or Hostname. You can add up to
eight links per Avaya CT server. You can add links in any order that
suits your needs, and you can leave these fields blank. (In other
words, you can assign links in consecutive number order, odd
number order, even number order, or random order.) Once you have
completed your changes, click Next.
■ Remove a link by deleting the fields under Advertised Switch
Name and IP Address or Hostname. Once you have completed
your changes, click Next.
Issue 1 — December 2002
2-5DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 20

Security and Configuration
■ Administer CVLAN clients. Click Admin to add, remove, or edit a
CVLAN client. (For more information see Chapter 5 of the Avaya CT
Installation Guide — INSTALL.PDF.
6. To change any of the advanced configuration parameters, click Advanced
to access the G3 PBX Driver Advanced Configuration dialog box. See
Figure 2-2. Refer to Table 2-2 for descriptions of the advanced
configuration parameters.
!
CAUTION:
The advanced configuration parameters listed in Table 2-2 are
established by default during the installation of the G3PD. In rare
instances, you may have to change them (most likely under the
direction of the TSO). Under normal circumstances, there is no
reason to change them.
2-6
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 21
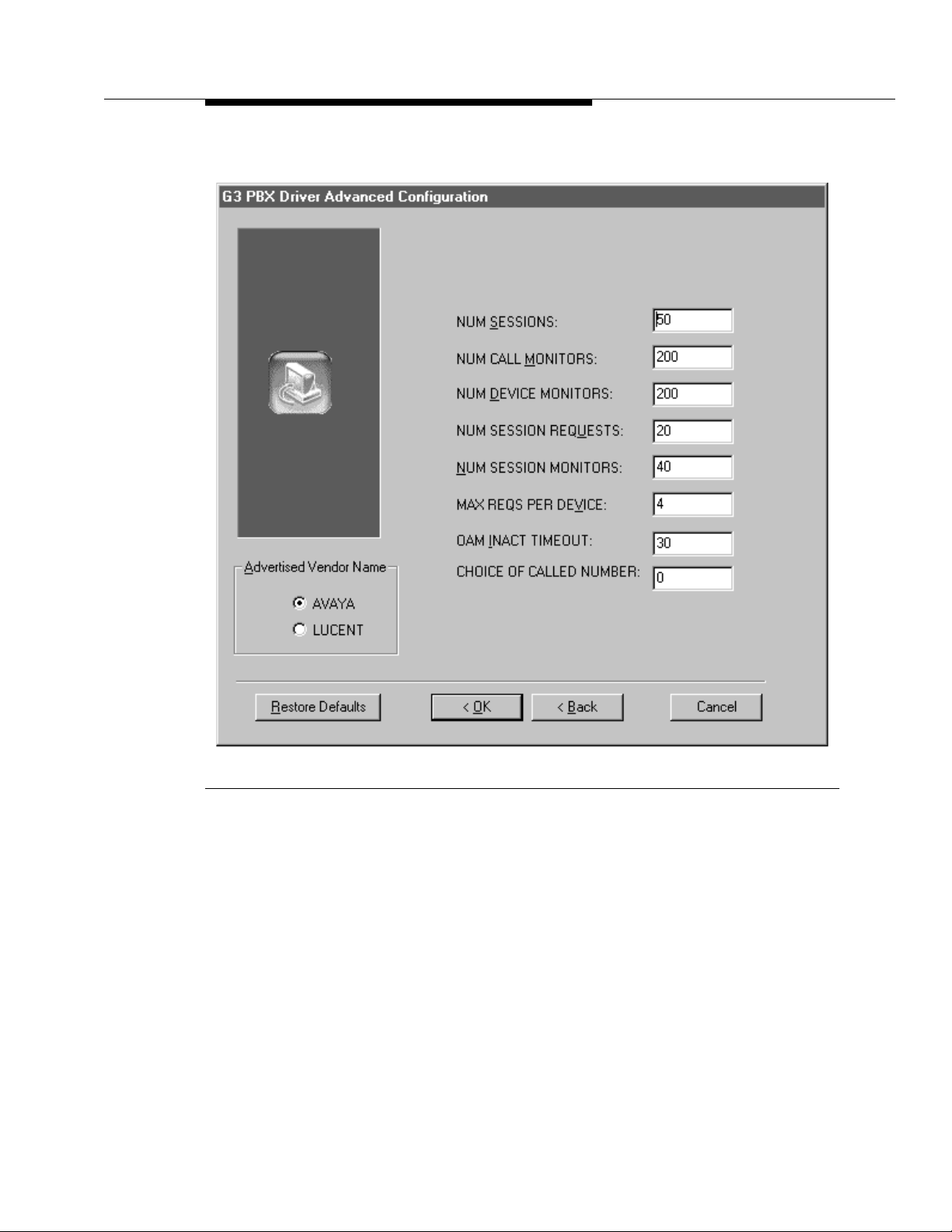
Security and Configuration
Figure 2-2. G3 PBX Driver Advanced Configuration Dialog Box
From the G3 PBX Driver Advanced Configuration dialog box, you can
make the following choices.
■ Enter changes and click OK. Your changes will take effect the next
time the G3PD, CVLAN client, or other applications are loaded.
■ Restore the defaults by clicking on Restore Defaults. Then click OK
to exit.
■ Leave the values undisturbed and click Back to return to the G3
PBX Driver Configuration dialog box.
Issue 1 — December 2002
2-7DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 22
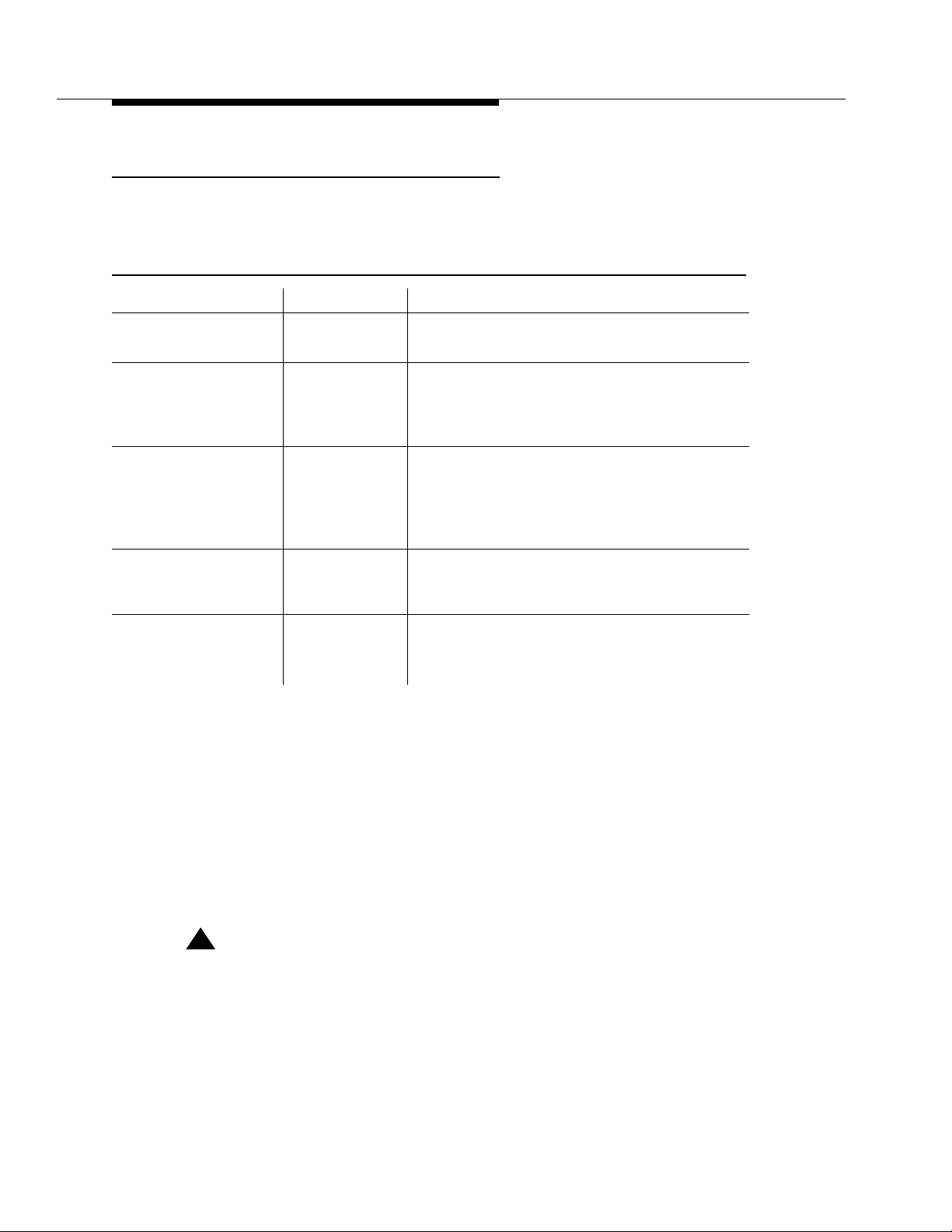
Security and Configuration
Tunable G3PD Configuration Parameters
Table 2-1 and Table 2-2 describe the G3PD configuration parameters that can be
viewed and administered using the G3 PBX Driver Configuration Utility.
Table 2-1. G3PD Configuration Parameters
PARAMETER DEFAULT COMMENTS
DEFINITY G3 PBX
Driver IP Address
Advertised Switch
Name (Link 1)
Advertised Switch
Name (Links 2 - 8)
IP Address or
Hostname (Link 1)
IP Address or
Hostname
(Links 2 - 8)
Advanced configuration parameters that are flagged with an
have the following meanings:
■ Default values for parameters flagged with an asterisk * are reserved for
the Technical Services Organization (TSO) (and you should not change
them). These parameters could affect overall system performance.
192.168.25.20 IP address of your DEFINITY G3PD driver
G3_SWITCH Advertised switch name (service name) for link
1. String up to 14 characters in length (will be
truncated if it is longer). The # sign is not a
valid character.
Advertised switch names (service names) for
Links 2 through 8. Each link may be given its
own advertised switch name. String can be up
to 14 characters in length (will be truncated if it
is longer). The # sign is not a valid character.
192.168.25.10 IP address or hostname for Link 1. This IP
address refers to the Ethernet interface for the
DLG.
IP address or hostname for Links 1 through 8.
There may be a separate IP address or
hostname for each link.
* or ** in Table 2-2
2-8
■ Default values for parameters flagged with a double asterisk ** are
guidelines. They should be properly sized for optimal performance, but are
not subject to strict limitations (for example, if they are sized too large,
memory may be wasted; if they are sized too small, performance
decreases slightly).
!
CAUTION:
The advanced configuration parameters listed in Table 2-2 are established
by default during the installation of the G3PD. In rare instances, you may
have to change them (most likely under the direction of the TSO). Under
normal circumstances, there is no reason to change them.
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 23
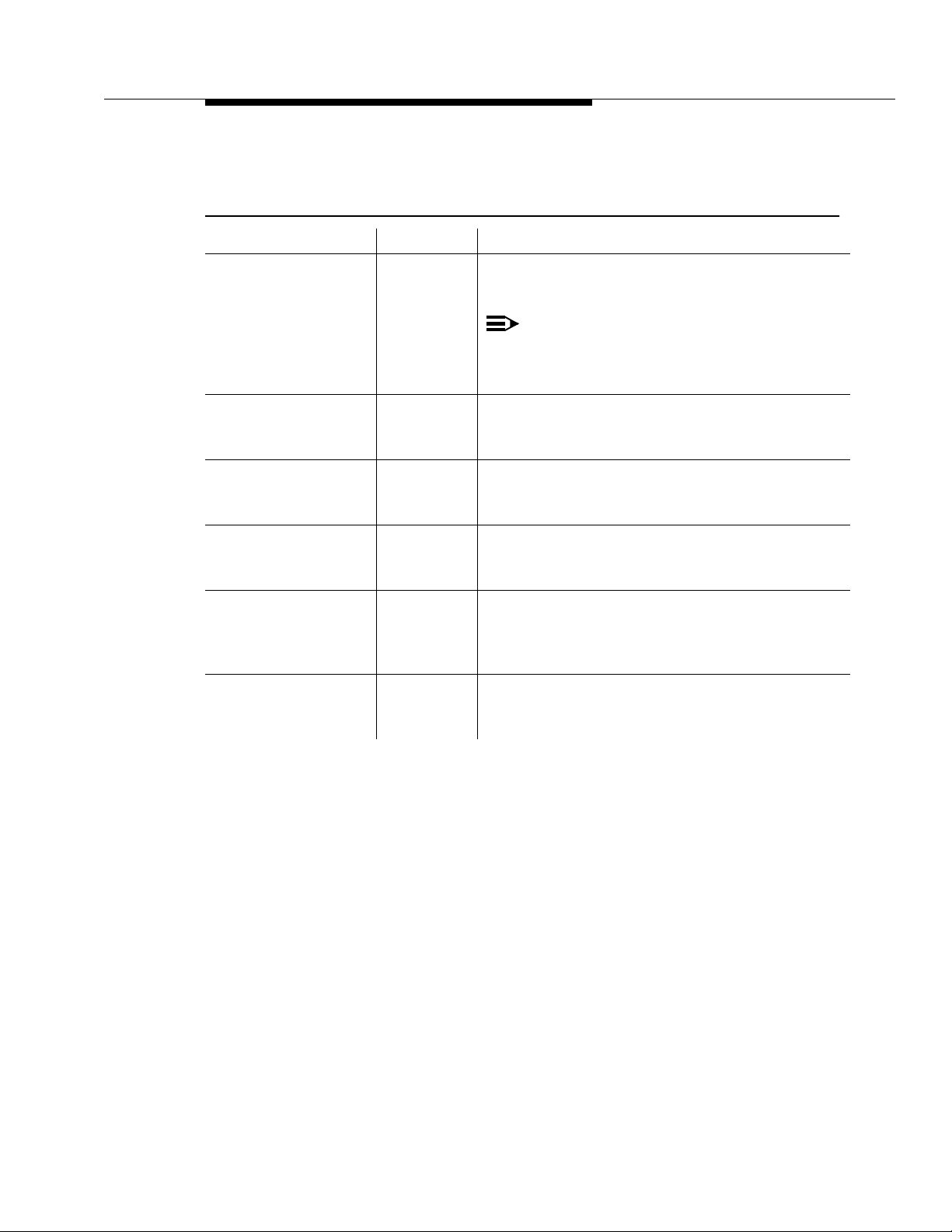
Security and Configuration
Table 2-2. G3PD Advanced Configuration Parameters
PARAMETER DEFAULT COMMENTS
Advertised V endor
Name
**NUM SESSIONS
**NUM CALL
MONITORS
**NUM DEVICE
MONITORS
**NUM SESSION
REQUESTS
**NUM SESSION
MONITORS
AVAYA Can be AVAYA or LUCENT. If this is a new
installation, choose AVAYA.
NOTE:
If you are upgrading Avaya CT and your
applications have LUCENT hardcoded in
Tlink names, select the LUCENT setting.
50 Guideline for number of simultaneous sessions
(active acsOpenStream requests). The minimum is
5 and the maximum is 5000.
200 Guideline for number of simultaneous
cstaMonitorCall requests. The minimum is 5 and
the maximum is 5000.
200 Guideline for number of simultaneous
cstaMonitorDevice requests. The minimum is 5 and
the maximum is 5000.
20 Guideline for number of simultaneous (not
confirmed) CSTA requests for a single session
(open stream). The minimum is 5 and the maximum
is 5000.
40 Guideline for number of active device or call
monitors for a single session (open stream). The
minimum is 5 and the maximum is 5000.
Issue 1 — December 2002
2-9DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 24

Security and Configuration
Table 2-2. G3PD Advanced Configuration Parameters
PARAMETER DEFAULT COMMENTS
*MAX REQS PER
DEVICE
OAM INACT
TIMEOUT
4 The maximum number of CSTA requests queued
on any single device (by all clients). The minimum is
1 and the maximum is 20. If the application
occasionally experiences Universal Failure with the
error code REQUESTS_ON_DEVICE_
EXCEEDED_REJECTION, this para meter should
be increased to a higher number, such as 10.
30 The number of minutes of inactivity before the
G3PD disconnects the DEFINITY G3PD
Administrator utility (formerly known as the
WG3OAM). Can be set from 10 to 720 minutes (12
hours).
2-10
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 25

Security and Configuration
Table 2-2. G3PD Advanced Configuration Parameters
PARAMETER DEFAULT COMMENTS
CHOICE OF
CALLED NUMBER
0 This parameter enables applications to determine
which called number the G3PD uses in a CSTA call
event. The value assigned to this parameter
determines which called number has the highest
priority (which number the G3PD uses first).
NOTE:
The CHOICE_OF_CALLED_NUMBER
parameter is global for the G3PD. It is not
configurable by application.
0 (default) — the Switch called number has the
highest priority, and G3PD will use the called
number from an event first. If the Switch called
number is not available for a specific event, the
called number saved from cstaMakeCall is used. If
the called number from cstaMakeCall is not
available, the called number from the Originated
event is used.
1 — the called number from cstaMakeCall has the
highest priority, and G3PD will use the called
number from cstaMakeCall first. If this number is
not available (e.g.,manual dial) for a specific event,
the called number saved from the Originated event
is used. If the called number from the Originated
event is not available, the called number from the
event is used.
2 — the called number saved from the Originated
event has the highest priority, and G3PD will use
the called number from the Originated event first. If
this number is not available, the called number from
cstaMakeCall is used. If the called number from
cstaMakeCall is not available, the called number
from an event is used.
!
CAUTION:
This parameter will affect the called number in
CSTA event messages.
Issue 1 — December 2002
2-11DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 26

Security and Configuration
Additional Configuration Parameters
There are additional parameters, such as Current Buffer Space Allocation, TSDI
Size, Max Flow Control (Flow Control), High Water Mark, etc. that may be set
through the Tlink Information Details dialog box in the TSA or the Tlink Status
Information dialog box in the TSM32. For information about these parameters,
refer to the “Tlink Status” section of Chapter 8 in Avaya Computer Telephony,
Telephony Services Administration and Maintenance (NETMANGD.PDF).
Changing IP Address or Hostname of Active Link
Use the G3 PBX Link Change utility to change an IP address or hostname of an
active link, (without the need to stop the G3PD and/or CVLAN services), and have
these changes take effect immediately.
NOTE:
To add or remove a link, change an IP address or hostname, change an
advanced configuration parameter, or view the configuration, see ‘‘Changing
the G3PD and CVLAN Configuration’’ earlier in this chapter.
To run the G3 PBX Link Change utility, follow these steps:
1. Click Start, point to Programs, Avaya Computer Telephony, DEFINITY
G3PBX Driver, and click G3PBX Driver Link Change.
The G3 PBX Link Change dialog box displays the number of each active
link with its associated IP address or hostname. See Figure 2-3.
!
CAUTION:
Changing a link is a very disruptive action. If you change a link, the
link will be torn down and all active associations will be lost!
NOTE:
You can not remove a link by deleting its IP address or hostname in
the G3PBX Link Change dialog box. To remove a link, see ‘‘Changing
the G3PD and CVLAN Configuration’’ earlier in this chapter.
2-12
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 27

Security and Configuration
Figure 2-3. G3 PBX Link Change Utility Dialog Box
2. To change the IP address or hostname of an active link, enter the new IP
address or hostname in the field that is associated with the link number and
click Change Link(s).
If the G3 PBX driver is not loaded, the following message will appear:
PROBLEM: Couldn’t communicate with the G3 PBX Driver.
Reload the driver for the changes to take effect.
Click OK and reload the G 3 PBX driver.
If the G3 PBX driver is loaded, the following confirmation message will
appear:
Changing a link will abort all open streams on that
link. Are you sure you want to continue?
3. Click Yes to continue.
If the change request was successful, the following message appears:
Your change request has been communicated to the G3 PBX
Driver.
4. Click OK to complete the action.
5. Click Quit to exit.
Issue 1 — December 2002
2-13DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 28

Security and Configuration
Configuring Avaya CT In a Firewall Environment
Avaya CT can be configured to function in different firewall environments. (Avaya
CT includes the Tserver and the CVLAN server). This section describes how to
configure Avaya CT when a firewall is placed between the Avaya CT server and
Avaya MultiVantage. See Avaya Computer Telephony, Telephony Services and
Administration and Maintenance Guide for information about other supported
firewall environments.
Requirements for Configuring Avaya CT in a Firewall Environment
Check with your firewall administrator to determine how your firewall is set up
before you configure Avaya CT.
Option 1: If your firewall manages ports only
If your firewall manages only ports (restricts the source IP address and the
destination IP address to use a specific port), the Avaya CT configuration
requirements are as follows. (See Figure 2-4 on page 2-15)
■ DLG Administration — use standard procedures for both the MAPD DLG
and the Co-Resident DLG, and administer the DLG to point to the IP
Address of the Avaya CT server.
■ G3PD Administration — use standard procedures.
■ Firewall Administration — port 5678 must be open to allow traffic between
the Avaya CT server and the DLG.
Option 2: If your firewall manages ports and IP addresses
If your firewall’s IP address acts as a proxy IP address, the Avaya CT
configuration requirements are as follows. (See Figure 2-5 on page 2-16)
■ DLG Administration — use standard procedures for both the MAPD DLG
and the Co-Resident DLG, and administer the DLG to point to the IP
Address of firewall.
■ G3PD Administration — use standard procedures.
■ Firewall Administration — port 5678 must be open to allow traffic between
the Avaya CT server and the DLG.
2-14
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 29

Security and Configuration
OPTION 1 -- with Single Avaya CT Server
Port 5678 must be
open to allow traffic
between the Avaya CT
servers and the DLG.
MultiVantage
DLG
192.168.25.10
AVAYA_ECS
CTI Link
or Port
Client Name or IP Address
*
DLG Administration
Port 5678
1 192.168.25.20 1
Firewall
AVAYACT1
NIC
Client Link
*
192.168.25.20
AVAYA_ECS
192.168.25.10
Avaya CT administration notes
- CTI links are administered to DLG
IP address (eithe r Co -re sid e n t
or MAPD based)
DLG administration notes
- CTI Link (or Port) number must be unique
and must correspond to client link number
For MAPD DLG, use port number instead of CTI Link
Figure 2-4. Option 1 - Firewall that Manages Port Only -- with Single Avaya CT Server
Issue 1 — December 2002
2-15DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 30

Security and Configuration
OPTION 2 -- with Single Avaya CT Server
IP address of
Firewall acts as a proxy
IP address for Avaya CT
server (AVAYACT1).
Port 5678 must be open.
MultiVantage
DLG
192.168.25.10
AVAYA_ECS
Port 5678
Firewall
135.8.12.199
AVAYACT1
NIC
192.168.25.2 0
AVAYA_ECS
192.168.25.10
Avaya CT administration notes
- CTI links are administered to DLG
IP address (either Co-resident
or MAPD based)
DLG Administration
CTI Link
or Port
Client Name or IP Addres s
*
1 135.8.12.199 1
Client Link
DLG administration notes
- CTI Link (or Port) number must be unique
and must correspond to client link number
*
For MAPD DLG, use port number instead of CTI Link
Figure 2-5. Option 2: Firewall that Manages Ports and IP Addresses - Single Avaya CT
Server
2-16
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 31

Security and Configuration
Administering Multiple Avaya CT Servers to Ensure Unique Links
The typical Avaya CT installation involves only one Avaya CT server. If your
configuration relies on more than one Avaya CT server, follow the steps described
in ‘‘Sample Scenario’’ to ensure that link assignments are unique. Figure 2-6 on
page 2-19 and Figure 2-7 on page 2-20 illustrate how to configure multiple Avaya
CT servers in a firewall environment.
Sample Scenario
This scenario depicts a configuration that uses two Avaya CT servers, AVAYACT1
and AVAYACT2. Both Avaya CT servers communicate with the same
MultiVantage system (indicated the Advertised Switch Name and IP Address or
Hostname). In this example, AVAYACT1 uses the default DEFINITY G3 PBX
Driver IP address (192.168.25.20) and AVAYACT2 uses an assigned DEFINITY
G3PBX Driver IP Address (192.168.25.30).
■ Administering A VAYACT1 — Assume that you will assign Link 1 to
AVAYACT1.
When you open the G3PBX Driver Configuration dialog box for AVAYACT1
complete the Advertised Switch Name and IP Address or Hostname
fields with the administered switch name (this example uses the default,
AVAYA_ECS) and the IP address of the DLG (this example uses the
default, 192.168.25.10)
IP Address of
AVAYA_ECS
192.168.25.20
192.168.25.10
AVAYACT1
IP Address of
DLG
■ Administering A VAYACT2 — Assume that you will assign Link 2 to
AVAYACT2 (you must use any link number other than 1 to ensure that the
identity of the link is unique).
When you open the G3PBX Driver Configuration dialog box for AV AYACT2,
skip to Link 2 (leave the fields for Link 1 blank). Complete the
Advertised Switch Name and IP Address or Hostname fields with the
Issue 1 — December 2002
2-17DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 32

Security and Configuration
administered switch name (for example, AVAYA_ECS) and the addre ss of
the DLG (for example, 192.168.25.10).
AVAYA_ECS
192.168.25.30
192.168.25.10
IP Address of
AVAYACT2
IP Address of
DLG
2-18
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 33

Security and Configuration
OPTION 1 - - with Multiple Avaya CT Servers
AVAYACT1
Port 5678 must be
open to allow traffic
between the Avaya CT
servers and the DLG.
MultiVantage
DLG
192.168.25.10
AVAYA_ECS
Port 5678
Firewall
NIC
AVAYACT2
NIC
AVAYACT3
AVAYA_ECS
AVAYA_ECS
192.168.25.20
192.168.25.10
192.168.25.30
192.168.25.10
192.168.25.40
NIC
AVAYA_ECS
192.168.25.10
Avaya CT administration notes
DLG Administration
CTI Link
or Port
Client Name or IP Address
*
1 192.168.25.20 1
2 192.168.25.30 2
3 192.168.25.40 3
Client Link
- CTI links are administered to DLG
IP address (either Co-resident
or MAPD based)
- Use blank addresses to maintain
unique link numbers when multiple
Avaya CT servers are used.
DLG administration notes
- CTI Link (or P ort ) nu m b e r m u st be un iqu e
and must correspond to client link number
*
For MAPD DLG, use port number instead of CTI Link
Figure 2-6. Option 1: Firewall that Manages Ports Only - Multiple Avaya CT Servers
Issue 1 — December 2002
2-19DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 34

Security and Configuration
OPTION 2 - - with Multiple Avaya CT Servers
AVAYACT1
IP address of
Firewall acts as a proxy
IP address for Avaya CT
servers (AVAYACT1,
AVAYACT2, and
AVAYACT3).
Port 5678 must be open.
NIC
AVAYACT2
AVAYA_ECS
192.168.25.20
192.168.25.1 0
MultiVantage
DLG
192.168.25.1 0
AVAYA_ECS
CTI Link
or Port
*
Client Name or IP Address
Port 5678
Firewall
135.8.12.199
DLG Administration
1 135.8.12.199 1
2 135.8.12.199 2
3 135.8.12.199 3
NIC
AVAYACT3
NIC
Client Link
192.168.25.30
AVAYA_ECS
AVAYA_ECS
192.168.25.10
192.168.25.40
192.168.25.10
Avaya CT administration notes
- CTI links are administered to DLG
IP address (either Co-resident
or MAPD based)
- Use blank addresses to maintain
unique link numbers when multiple
Avaya CT servers a re used.
DLG administration notes
- CTI Link (or Port) number must be unique
and must correspond to client link numb er
*
For MAPD DLG, use port number instead of CTI Link
Figure 2-7. Option 2: Firewall that Manages Ports a nd IP Add resses - Multipl e Avaya CT
Servers
Issue 1 — December 2002
2-20
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 35

Maintenance
Overview
This chapter describes the DEFINITY G3PD Administrator utility.
The DEFINITY G3PD Administrator utility provides maintenance commands that
are particularly useful if there are communications problems between the server
and the DEFINITY LAN Gateway. This utility can be run from a Windows client
(Windows NT, Windows 2000, or Windows XP).
Communication with CVLAN is established from the DEFINITY G3PD
Administrator utility through the G3PD. Since all links between the G3PD and
CVLAN are shared, DEFINITY G3PD Administrator utility operation and
commands apply equally to both.
3
The sections that follow ‘‘Maint Menu Options’’ (i.e., ‘‘Block/Enable Command’’,
‘‘Link Status Command’’, ‘‘Offline/Online Command’’, ‘‘Restart Command’’,
‘‘Suspend/Resume Alarms Command’’, ‘‘Test Command’’, and ‘‘Version
Command’’) explain how to perform each task accessible through the DEFINITY
G3PD Administrator utility.
Most DEFINITY G3PD Administrator utility command execution is recorded in the
Tserver error log as AUDIT_TRAIL events.
Issue 1 — December 2002
3-1DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 36

Maintenance
Before you can log in to the DEFINITY G3PD Administrator utility, you must have
OA&M privileges administered on the Tserver. For more information, see
Chapters 4 and 5 of Avaya Computer Telephony, Telephony Services
Administration and Mainte nan ce (NETMANGD.PDF).
Starting the DEFINITY G3PD Administrator Utility
To start the DEFINITY G3PD Administrator utility click Start, point to Programs,
Avaya Computer Telephony, TS Win32 Client, and click Definity Driver
Admin. The Known DEFINITY G3PD Tlinks dialog box is displayed. See Figure
3-1.
When highlighting the name of the G3PD service you wish to access, the server
name has the following format:
AVAYAECS#G3_OAM#OAM#server_name
The first field of the server name is set by default to AVAYAECS,
the second is G3_OAM and the third is OAM.
The fourth field is the name assigned to the Windows NT machine where the
driver is loaded (you can only load one G3PD per server).
Figure 3-1. Known DEFINITY G3PD Tlinks Dialog Box
To select the service to which you want to attach, highlight the service name and
then double-click on it or select OK.
3-2
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 37

Maintenance
Once you have selected a service, the DEFINITY G3PD Administrator Login
dialog box is displayed. See Figure 3-2.
NOTE:
If no G3PD Tlinks are displayed, make sure that the G3PD is installed and
loaded and that the correct IP address or hostname of your server is in your
TSLIB.INI file. Use the Telephony Server Administrator for 32-bit client
platforms (TSM32) to display the Driver DLL Information dialog box, which
will report the status of the g3pd.dll as "Loaded"or "Unloaded".
Figure 3-2. DEFINITY G3PD Administrator Login Dialog Box
Complete the login to the G3PD service by entering a valid user name and
password, and selecting "OK".
NOTE:
The user must have login permission in the administration database. The
default user is "administrator".
Once the log in is processed, the DEFINITY G3PD Administrator utility main
window is displayed. There are three available menus: the File menu, the Maint
menu, and the Help menu.
Issue 1 — December 2002
3-3DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 38

Maintenance
File Menu Options
Use the File menu to log out or exit from the DEFINITY G3PD Administrator utility.
Logging out ends your current session and allows you to select a different G3PD
service to which you can log in.
If you select " Logout", you will end your current session and be presented with
the G3PD server selection screen.
If you select " Exit", the DEFINITY G3PD Administrator utility automatically logs
out from the G3PD server.
NOTE:
DEFINITY Driver Administration utility sessions are dropped if no activity is
detected for a specified interval of time. For more information, see the OAM
INACT TIMEOUT entry in Chapter 2.
Maint Menu Options
Use the Maint menu to view status and to perform various maintenance
operations. See Figure 3-3.
File HelpMaint
Block/Enable
L
ink Status
O
R
S
T
est
V
ersion
Figure 3-3. Maint Menu
DEFINITY G3PD Administrator
ff/On-line
estart
uspend/Resume Alarms
3-4
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 39

Maintenance
Block/Enable Command
The Block/Enable command is used to block or to enable a given switch link.
Blocking a link means that only previously established connections or sessions
(device and call monitors) will remain active on the link. Additionally, new
Telephony Services or CVLAN application requests using a call ID or monitor
previously established over the link will be serviced. No other new Telephony
Services or CVLAN application requests will be allowed over the link.
For example, if a device was already being monitored using Link 1 before it was
blocked, the monitor will remain active. If a Make Call request was issued over
Link 1 and the call ID is still active, any Hold Call and retrieve call requests using
that call ID will succeed. If the call ID (from a previous Make Call request) is still
active, it is possible to issue a device monitor on the calling deviceID. However a
Make Call request or a monitor of a completely different device will not be
serviced using a blocked link.
Figure 3-4 shows the Block/Enable screen. To change the state of a link, click on
the appropriate state, Enabled or Blocked, and select OK.
Figure 3-4. Block/Enable Dialog Box
Issue 1 — December 2002
3-5DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 40

Maintenance
After you select "OK", the Results screen is displayed. See Figure 3-5.
Figure 3-5. Block/Enable Results Screen
Select "Close" to complete the operation.
3-6
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 41

Maintenance
Link Status Command
The Link Status command displays the current status of each equipped G3PD
switch link. See Figure 3-6. To update the screen, select "Refresh". To exit, select
"Close". The screens are automatically refreshed every 30 seconds, but you can
refresh a screen immediately by selecting "Refresh".
Figure 3-6. Link Status Screen
Issue 1 — December 2002
3-7DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 42

Maintenance
The Link Status fields are described in Table 3-1.
Table 3-1. Link Status Screen Fields
Field Name Field Description
Link Type The link type is LAN or UNEQUIPPED.
Switch Name The advertised switch name is listed or unequipped.
Switch Version This is the DEFINITY Generic 3 version number (G3V2, G3V3,
G3V4, G3V5, or G3V6).
Blocked? Indicates whether new Telephony Service and CVLAN requests are
being accepted. This is controlled by the Block/Enable command.
No. of
Associations
ASAI Message
Rate
Link Status This field provides the status of a link with respect to the TCP/IP
Remote Host ID The host name or IP address of the DEFINITY LAN Gateway
The number of single association objects (SAO) currently in use.
The upper limit of SAO is 10,000.
The number of ASAI messages sent and received by the switch per
minute. Note that the G3PD "speaks" ASAI to the G3 switch and
CST A to the Telephony Server.
connection and the DEFINITY LAN Gateway Tunnel Protocol.
If the TCP/IP connection and the DEFINITY LAN Gateway
connection are established, this field has a value of "Talking";
otherwise, see Chapter 4.
If there is no TCP/IP connection and no DEFINITY LAN Gateway
connection, the link status field will indicate the reason.
If the TCP/IP and DEFINITY LAN Gateway connections are
established but the DEFINITY LAN Gateway link to the DEFINITY
switch is down, the link status field indicates the reason. For more
details, see Chapter 4, "Troubleshooting."
NOTE:
Changing the station type for link administration while the
DEFINITY G3 PBX Driver is running may affect the link status.
application to which the G3PD has the link.
Local Host ID The IP address associated with the Windows NT machine hosting
G3PD software.
Local Port The TCP port that is associated with the TCP/IP connection
established for this link.
Switch Gateway
Version
Switch Connection N/A
3-8
The version of the DEFINITY LAN Gateway Tunnel Protocol that is
running on the DEFINITY LAN Gateway application.
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 43

Maintenance
Table 3-1. Link Status Screen Fields
Field Name Field Description
Layer 1 Link
Status
Layer 2 Link
Status
Link Time Up Time elapsed since the link was in the talking state and the switch
N/A
N/A
version was known. Effectively, this is how long the link has been
able to deliver messages to/from the switch.
Offline/Online Command
The Offline/Online command is used to take a link off line or to put it on line.
The Online command allows G3PD to open a TCP/IP connection and establishes
the DEFINITY LAN Gateway connection on the specified link.
The Offline command closes both the TCP/IP connection and the DEFINITY LAN
Gateway connection on the specified link(s); for these reasons, this command is
disruptive and prevents future connections. Use the Online command if you want
to establish future connections.
The Offline command is destructive. While a link is offline, no CSTA or CVLAN
requests for that link can be processed. Furthermore, all existing device and call
monitors are dropped (aborted).
A confirmation screen must be acknowledged to complete an Offline request. See
Figure 3-7.
Issue 1 — December 2002
3-9DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 44

Maintenance
Figure 3-7. Offline/Online Dialo g Box
Restart Command
When a link is restarted with the Restart command (see Figure 3-8), the TCP/IP
connection is closed and a new connection is opened. Closing the TCP/IP
connection also causes the DEFINITY LAN Gateway connection to be closed.
When the new TCP/IP connection is opened, a new DEFINITY LAN Gateway
connection is established.
!
CAUTION:
This command is disruptive, and will cause all existing device and call
monitors to fail.
Issue 1 — December 2002
3-10
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 45

Maintenance
Figure 3-8. Restart Dialog Box
After you select a link to restart and click on OK, a confirmation dialog box will
open, and you must click on Yes to confirm the restart. A Results screen will be
displayed when the operation is completed.
NOTE:
The Restart command may take time to be completed. Use the Link Status
command to check the status of the link.
Issue 1 — December 2002
3-11DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 46

Maintenance
Suspend/Resume Alarms Command
The Suspend/Resume command is used to suspend or resume switch alarms for
a given link. See Figure 3-9. Suspend the switch alarms if you are working on the
switch link (or associated G3PD/server) and do not want to report an error if the
Tserver connection is lost.
Figure 3-9. Suspend/Resume Alarms Dialog Box
NOTE:
The G3PD will automatically activate alarms 4 minutes after being loaded.
If you were to suspend the alarms on switch Link 7 and select "OK", the Results
screen, as shown in Figure 3-10, would be displayed on the client.
Issue 1 — December 2002
3-12
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 47

Maintenance
Figure 3-10. Suspend/Resume Alarms Results Screen
Click on Close to proceed.
Issue 1 — December 2002
3-13DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 48

Maintenance
Test Command
To test a CTI link from the DEFINITY G3PD Administrator utility, first select the link
number in the Test dialog box and then click on the Test button. See Figure 3-11.
NOTE:
For CVLAN users, the Test command replaces the asai_test command.
Figure 3-11. Test Dialog Box
If the switch connection is active, a heartbeat request is sent to the switch. If a
test fails, other useful information is written to the Tserver error log. The Test
Results screen is displayed for the selected link, as shown in Figure 3-12.
3-14
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 49

Maintenance
Figure 3-12. Test Results Dialog Box
If you select "More Info", a Results screen providing more detailed information is
displayed. The example shown in Figure 3-13 indicates a successful test of the
heartbeat request.
Issue 1 — December 2002
3-15DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 50

Maintenance
Figure 3-13. "More Info" Test Results Screen
Click on Close to exit from the Test Results screen. Then, click on Close to exit
from the Test Results dialog box.
Version Command
The Version command displays the version strings for the G3PD driver, the ASAI
Protocol Stack, the CVLAN Build Date, the DEFINITY LAN Gateway/ ASAI
Protocol Stack, the DEFINITY LAN Gateway tunnel protocol on the G3PD, and
the IPCI pumpware. (IPCI pumpware is not applicable to the DEFINITY LAN
Gateway or MAPD.) The Version Information screen also contains the version of
the OA&M application you are currently using (i.e.,the G3PD Administrator utility).
See Figure 3-14.
NOTE:
The first line of the screen indicates whether the system is using ADJLK
authorization for the link.
3-16
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 51

Maintenance
Figure 3-14. Versi on Information Screen
Click on Close to exit from the Version Information screen.
Help Menu Options
The DEFINITY G3PD Administrator utility provides Help screens. Use them
when you need clarification or additional information on a specific command.
You can select "Help" from the bar of the DEFINITY Driver Administration Utility’s
main window; this window is titled DEFINITY G3PD Administrator On-Line
Help. See Figure 3-15.
To display information on the current version of the DEFINITY G3PD
Administrator uti lity, cl ick About on the main Help menu.
Issue 1 — December 2002
3-17DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 52

Maintenance
Figure 3-15. Administrator On-Line Help Menu
Select "Exit" from the File menu to return to the DEFINITY G3PD Administrator
utility main win dow. Then, select "Exit" from the File menu to have the DEFINITY
G3PD Administrator utility log out from the G3PD server.
Issue 1 — December 2002
3-18
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 53

Troubleshooting
Overview
This chapter describes problems that can occur with the DEFINITY G3 PBX
Driver (G3PD), the switches, and the switch links, and suggests possible solutions
to these problems.
The section titled ‘‘Tserver Error Log’’ briefly describes errors related to the G3PD
and gives general recommendations for corrective actions. Other problems
related to the Tserver, the services it provides, and the applications running on it
are discussed in the "Troubleshooting ," Chapter 11 of Avaya Computer
Telephony , Telephony Services Administration and Maintenance Guide.
4
!
CAUTION:
Use caution before executing any tasks that may disrupt existing service. It
is safe to view the current status of the G3PD and associated switch link(s),
the error log, and the trace files, and to run nondisruptive tests while the
G3PD is providing Telephony Services. All other activities, such as taking
the link off-line, restarting the link, and uninstalling the G3PD, should be run
out-of-hours after providing a suitable warning to all affected users.
Issue 1 — December 2002
4-1DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 54

Troubleshooting
Problem Descriptions
The following list details possible G3PD problems and their solutions.
G3PD Not Starting
If you are experiencing problems when loading the G3 PBX Driver software from
the TSM32 Driver DLL Information dialog box, look for one of the error messages
listed below and take the suggested corrective action. If the driver status remains
at "loading" or goes back to "unloaded," view the Tserver error log.
If the driver is being loaded automatically when Telephony Services is started,
look in the error log for messages related to the errors below.
Load of driver library failed
The Tserver cannot find the driver software or one of its supporting DLLs.
Verify that the G3PD software is installed by looking in your system directory (for
example, \WINNT\system32) for G3PD.DLL, ASAI.DLL, and ATTPRV32.DLL. If
these libraries are not in the directory, you will need to install the G3PD. Follow
the installation procedures in Chapter 2 of Avaya Computer Telephony Installation
Guide and then attempt to load the G3PD.DLL.
If the driver software is installed and you receive this message, contact Services.
Switch Connection Not Up
This may be the problem if users are receiving ACS Universal Failure messages
with the error LINK UNAVAILABLE (1007) or CSTA Universal Failure messages
with the error RESOURCE_OUT_OF_SERVICE (34).
1. Use the DEFINITY G3PD Administrator utility’s Link Status command to
verify that the link status is "Talking". See ‘‘Link Status Command’’ in
Chapter 3. For information about this field, see Link Status in Chapter 3. If
the link status is "Not initialized" refer to ‘‘LAN Link Problem
Descriptions’’.
NOTE:
Changing the station type for link administration while the DEFINITY
G3 PBX Driver is running may affect the link status.
NOTE:
Unloading and reloading the DEFINITY G3 PBX Driver is required
after the station type parameter has been changed in the switch.
4-2
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 55

Troubleshooting
2. Compare the TCP/IP and brouter administration of the DEFINITY LAN
3. Check the configuration of the G3PD CTI link on the DEFINITY ECS G3.
4. Check the physical wiring between the Network Interface Card (NIC) for
Gateway connection with the configuration of the G3PD CTI link. Make
sure the IP addresses and link numbers match.
Go to the switch and type:
display station extension #
where extension # is the number that you assigned to the link.
To get a list of all stations, type:
list station type link type
where link type is asai or adjlk (for either ASAI or ADJLK links,
respectively).
Verify the settings and make sure they are consistent with the required
values specified in the table titled "CTI Link Settings" in Appendix B of Avay
Computer Telephony Installation Guide.
the G3PD and the DEFINITY LAN Gateway:
a. Verify that you are using a 10Base-T Ethernet connection only (not
100Base-T Ethernet).
b. Verify that you are connected through a hub.
5. Check the link integrity setting of the Ethernet cards and hubs; the
DEFINITY LAN Gateway requires link integrity.
6. Busy out and release the port for the CTI link on the DEFINITY LAN
Gateway; the DEFINITY LAN Gateway requires link integrity.
Clients Fail to Connect to Visible G3PD
If an acsOpenStream request fails, look up the error and follow the recommended
action. See "Troubleshooting," Chapter 11, of Avaya Computer Telephony,
Telephony Services Administration and Maintenance Guide.
1. Use the DEFINITY G3PD Administrator utility’s Link Status command to
make sure the link is not blocked. See the ‘‘Link Status Command’’ section
in Chapter 3. If the link is blocked, select "Block/Enable" from the Maint
menu to re-enable the link. See the ‘‘Block/Enable Command’’ section in
Chapter 3.
2. Use the DEFINITY G3PD Administrator utility’s Link Status command to
make sure the link is not off line. See the ‘‘Link Status Command’’ section
in Chapter 3. If the link status is "offline", select "Off/Online" from the
Maint menu to bring the link back on line. See the ‘‘Offline/Online
Command’’ section in Chapter 3.
Issue 1 — December 2002
4-3DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 56

Troubleshooting
Switch Link "Talking" But Not In Service
(Authentication Failed for ADJLK Connection)
The "Talking" state of the link connection does not necessarily mean that the
link is in service and can accept requests.
1. To verify that the link is in service, on the DEFINITY G3PD Administrator
utility’s Link Status screen, the "Switch Version" field should have the
correct version of the switch. See the ‘‘Link Status Command’’ section in
Chapter 3.
2. You can also use the DEFINITY G3PD Administrator utility’s Test
command; the "More Info" field should indicate if the heartbeat with the
switch was successful. See the ‘‘Test Command’’ section in Chapter 3.
3. You can also try recycling the station; busy out and release the BRI port
associated with the link.
4. If the problem persists, contact Services.
Clients Cannot See Advertised PBX Driver
(G3PD Not Visible to DEFINITY G3PD
Administrator Utility)
1. From the TSM32, choose the "Driver DLL Information" option to verify
that the driver is loaded. If it is not in the list or not loaded, try to load it. If
this fails, refer to the problem description ‘‘G3PD Not Starting’’.
2. Verify that TCP/IP is running on the client. To verify network connectivity
and ensure that you can communicate with the Tserver, use the ping
command to ping the Tserver from the client.
3. If you are migrating to T elephony Services for Windows NT from T elephony
Services for NetWare, check that you have the correct version of software
for the client libraries. Only the client libraries provided on the Telephony
Services for Windows CD-ROM will be able to connect to a Windows NT
Tserver.
4. Check that the TSLIB.INI includes the IP address of the Tserver; refer to
Avaya Computer Telephony Installation Guide.
If your TSLIB.INI file contains host names rather than IP addresses, verify
that host name resolution is operational from the client. (Use the command
ping <hostname> to verify.)
5. If the driver is loaded, run the TSM32 and choose the "Tlink Information"
option to verify that the driver is registered with the Tserver. If the Tlink
name is not in the list or it is not registered, view the Tserver error log for
more information. If the problem still exists, check a different client to see if
the problem is with the G3PD or Tserver, or with the client itself.
4-4
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 57

Troubleshooting
Not All Events Received by Application
For example, a user receives a call, but the application does not notify the user.
1. Start the tracing utility program for the client (TSspy) to see if the event is
being sent to the application. If it is, then there is a problem with the
application. If not, check the error log on the Tserver for possible problem
explanations.
2. Verify that the DEFINITY ECS G3 administration settings are correct for the
DEFINITY LAN Gateway connections; refer to Appendix B, "Administering
CTI LInks for DEFINITY G3PD" in Avaya Computer Telephony Installation
Guide.
3. On the switch, verify the ASAI station settings are correct:
TEI fixed? y
TEI 3
CRV Length 2
MIM n
NOTE:
Event Minimization should be set to "n" on the switch for the Basic
Rate Interface (BRI) link connected to the G3PD.
4. If the problem persists, report to Services.
Slow Performance
Check the T asking options on your Windows NT machine: from the Main program
group, select "C ontrol Panel" and then "System". In the System dialog box,
select "Tasking", and then select "Foreground and Background Applications
Equally Responsive."
Slow performance is usually caused by insufficient memory. You must reduce the
number of applications running on your server, reduce the load on the server,
reconfigure G3PD memory usage by ru nning the G3 PBX Driv er Configuration
Utility (refer to ‘‘Tunable G3PD Configuration Parameters’’ in Chapter 2), add
more memory, or consider moving to a faster processor.
G3PD Stops Responding
XID y
Event minimization n
Open the DEFINITY G3PD Administrator utility’s Maint menu and look at the Link
Status dialog box to verify the current state of the G3PD. See the ‘‘Link Status
Command’’ section in Chapter 3. If the link status is "Talking", use the Test
Issue 1 — December 2002
4-5DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 58

Troubleshooting
command to test the ASAI heartbeat with the switch. See the ‘‘Test Command’’
section in Chapter 3.
Also, check the Tserver error log and the Windows NT Event Viewer Log for
possible errors. (When viewing the Windows NT Event Log, be sure that
"Application" is selected from the Log menu.) If the G3PD is not responding, you
may have to unload and reload the G3PD; see the section "Loading and
Unloading PBX Drivers" in Chapter 8 of Avaya Computer-Telephony Telephony
Services Administration and Maintenance Guide.
Users Receive CSTA Universal Failure Messages
with RESOURCE_OUT_OF_SERVICE (34) or
Notified Device Monitoring Ended
Either or both of these problems may occur if the CTI link between the Telephony
Server and the DEFINITY G3PD goes down or is reset.
If the link is resetting, the RESOURCE_OUT_OF_SERVICE errors should clear
up when the link comes up, but if link failure persists, you should go to the switch
and check the port on the switch and on the DEFINITY LAN Gateway.
If either of these problems occurs frequently, for unexplained reasons, there is
most likely a problem with the CTI link and you should report to Services.
Users Receive ACS Universal Failure Messages with TSERVER_DRIVER_CONGESTION (73)
This error occurs when the number of requests for a particular Tlink exceeds the
size of the Tserver’s queue for requests to that Tlink.
If this is a transient problem, it may merely indicate a burst of activity across the
Tlink.
If the problem persists, use the Information tab on the Tlink Status dialog box in
the TSM32 to increase the value of the Max Flow Allowed field.
Users Receive ACS Universal Failure Messages
with TSERVER_NO _T DI_BU FFERS (74)
This error occurs when the Tserver cannot allocate any more memory for the
driver to which the application is connected.
If this is a transient problem, it may merely indicate a burst of activity across the
Tlink.
4-6
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 59

Troubleshooting
If the problem persists, use the Information tab on the Tlink Status dialog box in
the TSM32 to increase the value of the TSDI Size field.
Users Receive Route End Report
with PEFORMANCE_LIMIT_EXCEEDED (52)
A routing application will receive this error in a Route End Event when there is no
wait step after the adjunct routing vector step. When the adjunct routing vector
step is executed, a Route Request is sent to the G3PD. The switch expects a
Route Select within the time specified in the wait step that follows the adjunct
routing vector step. If there is no wait time, the switch does not wait and sends the
Route End event with CSTA error 52. When the Route Select is sent by the
application, it will be rejected with Cause Invalid Cross-Reference ID.
To avoid this problem, add a vector wait step after the adjunct routing step.
The amount of time to wait depends on how quickly the Route Select can be sent
back by the application.
Users Receive CSTA Universal Failure Messages
with GENERIC_SUBSCRIBED_RESOURCE_
AVAILABILITY (41)
This error might be generated if Switch ASAI capability groups (in
system-parameters customer-options) are not turned on. For example, if Domain
Control Grou p i s not set to " y" when a monitor is requested, or if Switch-Classified
Calls/Predi ctiv e Dialin g is no t set to "y" when predictive call is requested, then this
error might be generated.
Access the Customer Option Forms to display system parameters, press <Next
Page> until you reach the ASAI page. Verify that all fields in the ASAI capability
groups are set to "y".
NOTE:
Verify that the ASAI capability groups are available. If they are not available,
notify your Account Exec uti ve.
Questions about Switch Feature Operations?
Telephony Services Application Programming Interface (TSAPI),Version 2,
indicates the primitives to use to control calls. For actual feature behavior, you will
need to refer to a switch Feature Description document.
Issue 1 — December 2002
4-7DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 60

Troubleshooting
LAN Link Problem Descriptions
This section describes problems that can occur with the LAN link between the
DEFINITY G3PD and the DEFINITY LAN Gateway, and suggests possible
solutions to these problems.
NOTE:
In general, the ping and netstat commands are useful for
troubleshooting problems with a LAN link.
LAN Link Will Not Initialize
Use the DEFINITY G3PD Administrator utility’s Link St atus command to check the
status of the link. See ‘‘Link Status Command’’ section in Chapter 3. A link status
of "Not Initialized" indicates that link initialization has failed.
This means that the G3PD cannot complete its internal setup or cannot initially
complete the TCP/IP connection with the DEFINITY LAN Gateway.
Check the IP addresses on the G3PD Configuration screen and on the DEFINITY
LAN Gateway.
To verify that TCP/IP connectivity can be established between the T server and the
DEFINITY LAN Gateway, use the ping command and utility provided for
Windows NT and with the DEFINITY LAN Gateway. The ping command will
indicate whether it is possible to reach the DEFINITY LAN Gateway application
from the Tserver. If not, proceed with the following steps:
1. Check the configuration of the CTI link on the DEFINITY ECS G3.
Compare the parameter values from the display station command
and verify that they are consistent with the required values specified in the
table titled "CTI Link Settings" in Appendix B of Avaya Computer T elephony
Installation Guide.
2. Check the physical wiring between the Network Interface Card (NIC) for
the G3PD and the DEFINITY LAN Gateway.
3. Check the link integrity setting of the Ethernet cards and hubs.
Also, the Windows NT netstat command reports can be used to provide NT
active connections and their connection state. The Local Host ID and Local Port
fields pr ovided i n the DEFIN ITY G3PD Administ rator ut ility’ s Lin k S tatu s comman d
screen (see Figure 3-6) can be used to locate the corresponding table entry in the
NT netstat results report. For information on these fields, see Local Host ID and
Local Port in Chapter 3.
4-8
After resolving any networking problems, you will have to unload and reload the
G3PD.DLL to initialize the link.
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 61

Troubleshooting
DEFINITY G3PD Administrator Utility Reports
LAN Link Status Not Talking
When the DEFINITY G3PD Administrator utility’s Link Status command is run, the
Link Status field on the Link Status screen (see Figure 3-6) contains an entry that
is other than "talking." For more information on this field, see Link Status in
Chapter 3.
The following numbered items represent possible scenarios:
1. The LAN link to the DEFINITY switch is down.
When the link to the DEFINITY switch is down, the TCP/IP connection is
not closed. However, the G3PD cannot communicate over the link until it
receives a link status message that the link is up. To establish or
re-establish the link to the DEFINITY switch, you must first determine what
is wrong on the switch or on the DEFINITY LAN Gateway and correct it.
The G3PD should then receive a status update and the link to the
DEFINITY LAN Gateway should work properly.
■ Use the DEFINITY status bri-port command to verify that the
status of the ASAI port is "l3-established".
■ Choose "Port Status/Control" from the DEFINITY LAN Gateway
main menu. This command should indicate that the DEFINITY Port
State is "CONNECTED", the TCP/IP Connection State is
"Established", and the Brouter Service State is "in service".
The following bullet items list the values of the LAN link status that may be
reported:
■ BRI Down — There has been a problem in the communication
between the DLG and the switch. To clear this problem, do the
following:
1. On the DLG, verify that the port listed under "Brouter
Administration" agrees with the last two digits of the port on
the station form for the ASAI link on the switch. If it does not,
change the administration so that it does. Otherwise,
proceed to step 2.
2. On the switch, verify the ASAI station settings are correct:
TEI fixed? y
TEI 3
CRV Length 2
MIM n
XID y
Event minimization n
Issue 1 — December 2002
4-9DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 62

Troubleshooting
NOTE:
On some versions of the switch, the XID setting cannot
be changed. If an error was found, correct it with the
change station command. Otherwise proceed to
step 3.
3. On the switch, busy and release the ASAI station. Use the
status BRI command to check the connection status. It
should become "Layer 3 established" within a minute or so.
4. Restart with the DLG Maintenance option; select "Restart."
5. If the problem persists, reboot the DLG.
NOTE:
All connections will drop when the DLG is rebooted.
Schedule downtime if there are multiple users.
6. If the problem still persists, contact Services.
■ DEFINITY Down — The DEFINITY switch is being rebooted or the
interface between the DEFINITY LAN Gateway and the switch is
down.
The latter may occur if the carrier or cabinet in which the DEFINITY
LAN Gateway is located is not functioning properly .
■ L2 Down — ISDN layer 2 on the DEFINITY switch is not
established. This may occur if the BRI port has been busied out on
the DEFINITY LAN Gateway.
L2 Down can also occur if the DEFINITY LAN Gateway cannot
establish the link with the switch. This may also be a transient
status when the G3PD establishes a connection to the DEFINITY
LAN Gateway or the switch performs a maintenance activity. The
transient cases should not last longer than a few seconds; if they
persist, contact Services.
■ MFB Busy — Services has busied out the BRI port on the
DEFINITY LAN Gateway.
The BRI port may or may not be administered on the switch. If it is
administered on the switch and busied out at the LAN Gateway , this
prevents layer 2 from being established. (In this case, Services is
actively working on a problem; if not, the network manager should
contact Services to release the BRI port on the Gateway.)
■ Invalid Reason — The message received from the DEFINITY LAN
Gateway indicating that the link is down has an unknown reason.
This is an error. If it persists, report to Services.
4-10
NOTE:
If one of the following DEFINITY LAN Gateway error conditions is present,
the G3PD automatically tries to establish the link every ten seconds.
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 63

Troubleshooting
2. TCP Connection Problems
3. Other TCP/IP Problems
■ No Response — The G3PD expects, but did not receive, a
response to a connection request or a DEFINITY LAN Gateway
heartbeat message that it sent to the DEFINITY LAN Gateway
application. Check the physi c al co nnec tions .
■ Client T oo Slow — The DEFINITY LAN Gateway application closed
the TCP link because it did not receive the connection request from
the G3PD quickly enough.
■ No Reply to HB — The DEFINITY LAN Gateway application did not
get a response to a heartbeat message.
■ TCP Connect Fail — A remote failure (not a failure on the Windows
NT server) was detected.
■ TCP Internal — An internal software problem was encountered
when setting up the TCP connection with the Windows sockets.
The following steps may help solve other TCP/IP problems. If any problem
cannot be resolved, contact Services.
a. Check the Windows NT TCP/IP administration for the G3PD
Network Interface Card (NIC). Verify that the IP address and subnet
mask are correct.
b. Check that the IP address and remote host destination are correct
on the G3 PBX Driver Configuration dialog box (see Figure 2-1).
Refer to ‘‘Using the G3 PBX Configuration Utilities’’ in Chapter 2.
c. Check the TCP/IP administration and brouter administration for the
DEFINITY LAN Gateway.
d. Use the ping command provided with the DEFINITY LAN Gateway
and the netstat command on Windows NT to verify that TCP/IP
connectivity can be established between the Tserver and the
DEFINITY LAN Gateway.
The ping report can be used to see if it is possible to reach the
Tserver from the DEFINITY LAN Gateway.
4. Mismatched Version or Potential Software Problems
■ Unexpected Msg — The G3PD received a message that it did not
expect or a message with an invalid size.
■ Invalid Version — The G3PD and the DEFINITY LAN Gateway
application have different DEFINITY LAN Gateway Tunnel Protocol
versions. Check the version via the Maint menu of the DEFINITY
G3PD Administrator utility. See the ‘‘Version Command’’ section in
Chapter 3.
■ Invalid Context — The DEFINITY LAN Gateway received a valid
message type, but it was out of context and unexpected. Report to
Services.
Issue 1 — December 2002
4-11DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 64

Troubleshooting
■ Invalid Type — A message with an invalid type was received by the
DEFINITY LAN Gateway application.
■ Invalid Cause — A message with an invalid cause value was
received by the DEFINITY LAN Gateway application.
■ Too Much Data — The DEFINITY LAN Gateway application
received a message from the G3PD that was bigger in size than
expected.
A potential cause for these types of errors is that the G3PD and the
DEFINITY LAN Gateway application are using different DEFINITY LAN
Gateway Tunnel Protocol versions.
To determine the DEFINITY LAN Gateway Tunnel Protocol version with
which the G3PD is compliant:
a. Select " Version" on the DEFINITY G3PD Administrator utility Maint
menu. See the ‘‘Maint Menu Options’’and ‘‘Version Command’’
sections in Chapter 3.
b. Check the "DEFINITY LAN Gateway Tunnel Protocol".
■ If there is a version mismatch, the G3PD and DEFINITY LAN
Gateway application must be upgraded so that they are both
using the same version of the Tunnel Protocol.
■ If the versions match, contact Services for help with the
problem.
5. Other Problems:
■ Invalid Link — The link number sent to the DEFINITY LAN
Gateway is unknown by the DEFINITY LAN Gateway. This is a
configuration problem. Compare the link number from the brouter
administration screen of the DEFINITY LAN Gateway with the link
number configured for the G3PD. They must be the same.
■ Out of Servic e — A connected LAN link was taken out of service by
the DEFINITY LAN Gateway software. Contact Services.
■ Server Error — The DEFINITY LAN Gateway application
experienced a serious error. If the problem persists, contact
Services.
■ New Connection — The G3PD has a connection on this link and
another G3PD running on another server tries to connect with the
same host or IP address and link number. The original G3PD
connection will be taken down by the DEFINITY LAN Gateway
application. This error condition can happen if TCP/IP is not
configured properly for multiple G3PDs on multiple Tservers.
This may also occur if the G3PD disconnects its connection to the
DEFINITY LAN Gateway and attempts to connect again before the
gateway has processed the first disconnect. This is not an error
condition. Wait a few seconds for the link to be established. If the
link is not established, contact Services.
4-12
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 65

Troubleshooting
On the other hand, if there are multiple G3PDs on multiple Tservers
and this occurs, then two clients are using the same link. This is an
error condition. Change the configuration so that both clients are
not using the same link.
■ Invalid Client — The G3PD is not known to the DEFINITY LAN
Gateway application. Check the brouter administration on the
DEFINITY LAN Gateway. Verify that the brouter administration and
G3PD configuration are consistent.
■ Offline — A user has run an OA&M Offline command to take the link
off line. Use the DEFINITY G3PD Administrator utility’s Online
command to bring the link back on line. See ‘‘Offline/Online
Command’’ in Chapter 3.
If you need help with DEFINITY switch or DEFINITY LAN Gateway problems,
contact the Customer Care Center at:
How Dropped Link Affects T
elephony Services Requests
1-800-344-9670
If a particular link goes down, all existing requests associated with that link
(monitors, etc.) will be aborted by the switch. The client receives:
■ a CSTA Universal Failure Confirmation event for each outstanding request
(cstaMakeCall(), etc.). An outstanding CSTA request is one that has not
yet received a confirmation event. The error code in the CSTA Universal
Failure event is set to RESOURCE_OUT_OF_SERVICE (34).
The user should reissue the request. If other links are available, the new
request will succeed. If no other links are available, the client will continue
to receive RESOURCE_OUT_OF_SERVICE (34) and should assume
service is unavailable.
■ a Monitor Ended event for any previously established monitors. The cause
is EC_NETWORK_NOT_OBTAINABLE (21). The client should
re-establish the monitor request. This may require restarting the
application. If other links are available, the monitor request is honored. If
no other links are available, the client receives a CSTA Universal Failure
Confirmation with the error code returned RESOURCE_OUT_OF_
SERVICE (34) and should assume service to the switch is unavailable.
■ a Route Register Abort event is sent to the application when all of the CTI
links that support the routeRequestEvents for the registered routing device
are down. The application could make use of System and Link Status
Notification to determine when the link comes back up. If the application
wants to continue the routing service after the CTI link is up, it must issue a
cstaRouteRegisterReq() to re-establish a routing registration session for
the routing device.
Issue 1 — December 2002
4-13DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 66

Troubleshooting
■ a Route End event for any active Route Select dialogue. The client does
not need to do anything.
If all links to a switch go down or are blocked, service to the switch becomes
unavailable and the G3PD sends a CSTA Universal Failure event for any new
CST A requests. The error code is set to RESOURCE_OUT_OF_SERVICE (34).
In this situation, the client application could make use of System and Link Status
Notification to determine when service is restored.
If these problems persist, contact Services.
How Dropped Link Affects Open Streams
When a PBX has multiple links configured and one link goes out of service,
service to the affected switch can still be available if another link is available to
provide service. Service remains available to any previously opened streams,
and to any new acsOpenStream() requests.
If all links to a PBX become unavailable, any previously opened streams remain
open until either they are closed or the G3PD unloads. The client does not
receive a specific message stating that service is unavailable unless system
status event reporting has been requested via the API call, cstaSysStatStart().
If service becomes unavailable (because all links are down), any subsequent
Telephony Services requests over any open streams receive a CSTA Universal
Failure event (RESOURCE_OUT_OF_SERVICE (34)).
Any attempts to open a stream to a PBX that has no links available result in an
ACS Universal Failure message with the error code set to DRIVER_LINK_
UNAVAILABLE (1007).
Tserver Error Log
The Tserver Error Log provides a common log for viewing the errors generated by
the Tserver, the G3PD, and any other PBX driver that chooses to log to this file.
Following are the kinds of errors you may find during installation of the G3PD.
The Services Organization maintains a complete list of specific errors and
troubleshooting messages.
NOTE:
When viewing error files on the Tserver, do not use MS Word for Windows.
This editor can prevent the Tserver from accessing the file (this is the only
editor known to affect the Tserver).
4-14
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 67

Troubleshooting
You can use the G3 PBX Driver Configuration Utility to view the current
configuration and to reconfigure any items that are causing errors; refer to ‘‘Using
the G3 PBX Configuration Utilities’’, ‘‘Changing the G3PD and CVLAN
Configuration’’ and ‘‘Tunable G3PD Configuration Parameters’’ in Chapter 2.
■ Configuration errors — Check the G3PD configuration to make sure
■ Connection errors — The G3PD tried to connect with the DEFINITY LAN
■ TCP/IP bind errors — Check for an IP address mismatch between the
■ TCP/IP software function call errors — These should be reported with
there is an IP address or hostname assigned to LINK(1-8)_DEST. See the
section on ‘‘Changing the G3PD and CVLAN Configuration’’ in Chapter 2;
these instructions allow you to inspect the configuration for errors without
changing any configuration details unless necessary.
Gateway and did not receive a response. There may be a problem on the
DEFINITY LAN Gateway or with the G3PD configuration. Check that
LINK(1-8)_DEST is the hostname or IP address of the DEFINITY LAN
Gateway. After correcting any errors using G3install, use the ping
command to verify the connections in both directions.
LOCAL_IP address and the Bind error messages in the Tserver log.
any data recorded in the error log to the Services organization, if they
persist.
■ Can’t find or Missing destination/hostname error — Check that the
hostname is correct and that the IP address is in the correct dotted-decimal
notation form in the host file or on the domain name server. See the
section on ‘‘Changing the G3PD and CVLAN Configuration’’ in Chapter 2;
these instructions allow you to inspect the configuration for errors without
changing any configuration details unless necessary.
Issue 1 — December 2002
4-15DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 68

Troubleshooting
4-16
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 69

Index
Numerics
IN
Block/enable command ,3-5
Block/enable results scre en,3-6
Blocked? field, 3-8
Blocking requests, 3-5
Buffer space allocation,2-12
10Base-T Ethernet, 1-6
32-bit client platforms, 3-3
A
About this guide, 1-1
ACS Universal Failure messages. See Errors
acsOpenStream requests, number of simultaneous
sessions, 2-9
Activating alarms,3-12
Active acsOpenStream requests, 2-9
Active call monitors, number of, 2-9
Active device monitors, number of, 2-9
Active link
changing hostname, 2-12
changing IP address,2-12
Adding links, 2-3
ADJLK, 1-5
ADJLK authorization, 3-16
Adjunct, 1-5
Adjunct links. See ADJLK
Admission permissions, restricting, 2-2
Advanced configuration parameters. See Configuration
parameters, advanced
Advertised switch name. See Switch name
Advertised vendor name . See Vendor name
Alarms
resume, 3-12
suspend, 3-12
Application requests
blocking, 3-5
enabling, 3-5
ASAI
capability groups,4-7
description of, 1-5
message rate, 3-8
messages. See Message s
protocol stack,3-16
station settings,4-5
asai_test command,3-14
AUDIT_TRAIL events, 3-1
Avaya CT, configuring in firewall environment, 2-14
B
Backup domain controller,1-6
Bind errors. See Errors, TCP/IP bind
C
Call monitors, dropped, 3-9
CallVisor Local Area Network. See CVLAN
Changing advanced configuration parameters, 2-3
Changing CallVisor configuration, 2-3
Changing G3PD configuration, 2-3
Changing hostname, 2-3
Changing hostname of active link, 2-12
Changing IP address,2-3
Changing IP address of active link, 2-12
Chapters, overview of, 1-2
Commands
asai_test, 3-14
block/enable, 3-5
display station, 4-8
link status, 3-7
netstat, 4-8
offline/online, 3-9
ping, 4-8
restart, 3-10
status bri-port, 4-9
suspend/resume alarms, 3-12
test, 3-14
version, 3-16
Computer Supported Telecomm unications Applicatio ns. See
CSTA
Computer-Telephony Integration. See CTI
Configuration parameters, advanced
buffer space allocation, 2-12
changing, 2-3
current buffer space allocation, 2-12
flagged, 2-8
flow control, 2-12
high water mark, 2-12
list of, 2- 7
max flow control,2-12
MAX REQS PER DEVICE, 2-10
NUM CALL MONITORS, 2-9
NUM DEVICE MONITORS, 2-9
NUM SESSION MONITORS, 2-9
NUM SESSION REQUESTS, 2-9
NUM SESSIONS, 2-9
OAM INACT TIMEOUT, 2-10
reserved for Services, 2-8
TSDI size, 2-12
viewing, 2-3
Configuration parameters, standard
advertised switch name, 2-8
changing CallVisor,2-3
changing G3PD,2-3
Issue 1 — December 2002
IN-1DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 70

Index
hostname, 2-8
IP address, 2-8
list of, 2-8
viewing, 2-3
Configuring Avaya CT in a firewall environment, 2-14
Connections
DLG, 3-8
TCP/IP, 3-8
CSTA
description of, 1-5
requests, for single sessions, 2-9
CSTA Universal Failure messages. See Errors
cstaMonitorCall requests, number of simultaneous, 2-9
cstaMonitorDevice requests, number of simultaneous, 2-9
cstaRouteRegisterReq(), 4-13
CTI, 1-5
CTI link
testing, 3-14
Current buffer space allocation, 2-12
Customer option forms, 4-7
CVLAN administrator commands. See G3PD administrator
commands
CVLAN commands
asai_test, 3-14
CVLAN service, stoppin g, 2-4
CVLAN, defined, 1-5
D
Default
user in G3PD administrator utility, 3-3
DEFINITY G3 PBX driver. See G3 PBX driver or G3PD
DEFINITY G3PD administrator utility. See G3PD administra-
tor utility
DEFINITY LAN Gateway. See DLG
Device monitors, droppe d,3-9
Dialog box
block/enable, 3-5
DEFINITY G3PD administrator login, 3-3
driver DLL information, 3-3
G3 PBX driver advanced configuration, 2-7
G3 PBX driver configuration, 2-5
known DEFINITY G3PD tlinks, 3-2
offline/online,3-10
restart, 3-11
suspend/resume alarms,3-12
test, 3-14
test results, 3-15
tlink information details,2-12
tlink status information,2-12
display station command, 4-8
Disruptive commands, 3-9, 3-10
DLG, 1-5, 3-8
closing connections ,3-10
different tunnel protocol versions, 4-12
invalid ca use value received, 4-12
LAN link problems. See LAN link problems
received bigger than expe cte d messa ge,4-12
tunnel protocol, 3-16
DLL, 1-5
Document
description of, 1-1
overview, 1-1
Domain controller. See NT
Driver administration,2-3
Driver DLL information, 3-3
DRIVER_LINK_UNAVAILABLE (1007), 4-14
Dropped link
affects open streams, 4-14
Dropped link, affect on TS requests, 4-13
DTMF, 1-5
Dual Tone Multi-Frequency. See DTMF
Dynamic Link Library. See DLL
E
EC_NETWORK_NOT_OBTAINABLE (21), 4-13
Enabling requests, 3-5
Error log, 3-1, 4-14
Errors
cannot find destination/hostname,4-15
DRIVER_LINK_UNAVAILABLE (1007), 4-14
EC_NETWORK_NOT_OBTAINABLE (21), 4 -13
G3PD configuration, 4-15
G3PD connection, 4-15
GENERIC_SUBSCRIBED_RESOURCE_AVAILABILITY
(41), 4-7
missing destination/hostname, 4-15
PERFORMANCE_LIMIT_EXCEEDED (52), 4-7
RESOURCE_OUT_OF_SERVICE (34), 4-6, 4-13
TCP/IP bind, 4-15
TCP/IP software function call, 4-15
TSERVER_DRIVER_CONGESTION (73)
TSERVER_NO_TDI_BUFFERS (74), 4-6
ESAI tunnel protocol, 1-5
Ethernet-Switch Application Interface. See ESAI
F
File menu, 3-4
Files
TSLIB.INI, 3-3
Firewall environment, 2-14
Flow control, 2-12
Forwarding. See IP forwarding
IN-2
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 71

Index
G
G3, 2-7
G3 PBX configuration parameters. See Configuration param-
eters, standard or Configuration parameters, advanced
G3 PBX configuration utilities
overview, 2-1
See also G3 PBX driver configuration utility or G3 PBX
link change utility
G3 PBX driver
advanced configuration dialog box, 2-7
alarms activated,3-12
IP address, 2-8
overview, 1-2
primary function, 1-2
See also G3PD
standard configuration dialog box, 2-5
G3 PBX driver configuration utility, 2-3
G3 PBX link change utility, 2-3, 2-12
G3PD
description of, 1-5
PBX driver, 1-6
primary function, 1-2
G3PD administrator commands
block/enable, 3-5
link status, 3-7
offline/online,3-9
restart, 3-10
suspend/resume alarms,3-12
test, 3-14
version, 3-16
G3PD adminis trator utility
default user, 3-3
exiting, 3-4
file menu, 3-4
format of server name, 3-2
help screens, 3-17
log out, 3-18
login permission, 3-3
maint menu, 3-4
no activity, 3-4
OA&M privileges, 3-2
overview, 3-1
sessions dropped, 3-4
timeout, 2-10
version number,3-16
G3PD administrator utility com mands . See G 3PD adm in istra-
tor commands
G3PD problems
admin utility reports LAN link not "talking", 4-9
cannot fi nd destination/hostname, 4 -15
clients cannot see advertised PBX driver, 4-4
clients fail to connect, 4-3
configuration errors,4-15
connection errors, 4-15
device monitoring ended, 4-6
DRIVER_LINK_UNAVAILABLE (1007), 4-14
EC_NETWORK_NOT_OBTAINABLE (21), 4 -13
G3PD not visible to admin utility, 4-4
G3PD stops responding, 4-5
G3PD won’t start, 4-2
GENERIC_SUBSCRIBED_RESOURCE_AVAILABILITY
(41), 4-7
missing destination/hostname, 4-15
not all events received by app, 4-5
PERFORMANCE_LIMIT_EXCEEDED (52), 4-7
RESOURCE_OUT_OF_SERVICE (34), 4-6, 4-13
See also LAN link problems
slow performance, 4-5
switch connection not up,4-2
switch link "talking" but not in service, 4-4
TCP/IP bind errors, 4-15
TCP/IP software function call errors, 4-15
Tserver cannot allocate more memory, 4 -6
TSERVER_DRIVER_CONGESTION (73), 4-6
TSERVER_NO_TDI_BUFFERS (74), 4-6
G3PD. See also G3 PBX driver
Gateway version. See Switch gateway version
Generic 3 version numbers, 3-8
GENERIC_SUBSCRIBED_RESOURCE_AVAILABILITY
(41), 4-7
Guidelines for advanced configuration parameters, 2-8
H
Heartbeat request,3-14
High water mark, 2-12
Host ID. See Local host ID or Remote host ID
Host machine. See IP address, associated with host m ac hin e
Hostname
changing for active link, 2-12
deleting, 2-12
for links, 2-8
in TSLIB.INI file, 3-3
I
Invalid character, in switch name, 2-8
IP address
associated with host machine,3-8
changing for active link, 2-12
default, 2-8
deleting, 2-12
description of, 2-8
for links, 2-8
in TSLIB.INI file, 3-3
IP forwarding, 2-2
IP routing, 2-2
IPCI pumpware, 3-16
ISDN brouter, 1-6
Issue 1 — December 2002
IN-3DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 72

Index
ISDN link type, 3-8
L
LAN link not "talking", 4-9
LAN link problems
admin utility reports LAN link not "talking", 4-9
different DLG tunnel protocol versions, 4-12
invalid ca use value received by DLG, 4-12
invalid client,4-13
invalid context,4-11
invalid link, 4-12
invalid size message, 4-11
invalid type received by DLG, 4-12
invalid versions, 4-11
link will not initialize
list of, 4-8
mismatched versions, 4-11
new connection, 4-12
offline, 4-13
out of service, 4-12
See also TCP connection problems or TCP/IP problems
server error, 4-12
software problems,4-11
too much data, 4-12
unexpected message ,4-11
LAN link status
BRI down, 4-9
DEFINITY down, 4-10
invalid reason,4-10
L2 down, 4-10
MFB busy, 4-10
LAN link ty pe, 3-8
Layer 1 link status, 3-9
Layer 2 link status, 3-9
Link change state,3-5
Link change utility, 2-12
Link hostname. See Hostname
Link IP address. See IP address
Link status, 3-8
affect of station type change, 4-2
Link status command, 3-7
Link status screen,3-7
Link status screen fields
ASAI message rate, 3-8
blocked?, 3-8
descriptions of,3-8
layer 1 link status,3-9
layer 2 link status,3-9
link status, 3-8
link time up, 3-9
link type, 3-8
local host ID, 3-8
local port, 3-8
no. of associations, 3-8
remote host ID, 3-8
switch connection,3-8
switch gateway versions ,3-8
switch name, 3-8
switch version, 3-8
Link time up, 3-9
Link type, 3-8
Link will not initialize
Links
adding, 2-3
blocked, ramifications, 3-5
changing hostname, 2-3
changing IP address,2-3
removing, 2-3, 2-12
shared, 3-1
testing, 3-14
viewing current status, 3-7
Local Area Network. See LAN
Local host ID, 3-8
Local port, 3-8
Login permissions in G3PD administrator utility, 3-3
M
Maint menu, 3-4
MAPD, 1-3, 1-6
Max flow allowed field, 4-6
Max flow cont rol, 2-12
MAX REQS PER DEVICE, 2-10
Menus
administrator on-line help, 3-18
file, 3-4
maint, 3-4
Message rate. See ASAI, message rate
Messages, number of, 3-8
MFB, 1-3
Migrating from NetWare, 2-9
MS Word for Windows, affect on Tserver error log, 4-14
Multi-Application Platform for DEFINITY ECS. See MAPD
Multi-function Board. See MFB
N
National Customer Care Center, 4-13
netstat command, 4-8
NetWare
ISDN link type, 3-8
migrating from, 2-9
Network Interface Card. See NIC
Network security, over v ie w,2-1
NIC, 1-3, 1-6
used for client access, 2-2
used for DLG, 2-2
No. of associations, 3-8
NT, 1-6
IN-4
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 73

Index
backup domain controller, 1-6
primary domain controller, 1-6
server, 1-6
workstation, 1-6
NUM CALL MONITORS, 2-9
NUM DEVICE MONITORS, 2-9
NUM SESSION MONITORS, 2-9
NUM SESSION REQUESTS, 2-9
NUM SESSIONS, 2-9
O
OA&M privileges, 3-2
OA&M utility. See G3PD administrator utility
OAM INACT TIMEOUT, 2-10, 3-4
Offline/online command, 3-9
On-line help, 3-17
Open streams, affect of dropped link, 4-14
Overview
G3 PBX driver, 1-2
of chapters, 1-2
P
PBX driver, 1-6
PERFORMANCE_LIMIT_EXCEEDED (52), 4-7
Permissions, restricting,2-2
ping command,4-8
Port. See Local port
Primary domain controller, 1-6
Private data, 1-5
Private Data Support Library, 1-5
Privileges, OA&M, 3-2
Problem descriptions,4-2
Protocol stack, 3-16
R
Remote host ID, 3-8
Removing links,2-3, 2-12
Reporting errors, disable, 3-12
RESOURCE_OUT_OF_SERVICE (34), 4-13
Restart command, 3-10
Restricting adminis trati on perm iss ion s,2-2
Route end report, 4-7
Routing. See IP routing
S
SAO, number of, 3-8
Screens
block/enable results, 3-6
link status, 3-7
more info test results, 3-16
suspend/resume alarms results, 3-13
version information, 3-17
Server name format,3-2
Shared links, 3-1
Single association objects. See SAO
Software function call errors. See Errors, TCP/IP software
function call
Standard configuration parameters. See Configuration
parameters, standard
Station settings. See ASAI, station settings
Station type
affect on link status,4-2
changing, 4-2
status bri- port command, 4-9
Stopping CVLAN service, 2-4
Stream, no links available, 4-14
Suspend/resume alarms command, 3-12
Switch ASAI capability groups. See ASAI, capability groups
Switch connection, 3-8
Switch gateway version, 3-8
Switch name, 3-8
description of, 2-8
invalid character specification, 2-8
Switch version,3-8
T
TCP connection problems
client too slow,4-11
no reply to heartbeat,4-11
no response, 4-11
TCP connect fail, 4-11
TCP internal, 4-11
TCP port. See Local port
TCP/IP
closing connections, 3-10
connection, 3-8
problems, 4-11
Telephony server. See Tserver
Telephony Services Application Programming Interface. See
TSAPI
Test command, 3-14
Tlink information details dialog box,2-12
Tlink status information dialog box, 2-12
TMS32, 3-3
TSAPI, description of, 1-6
TSDI size, 2-12, 4-7
Tserver
description of, 1-6
error log, 3-1, 3-14, 4-14
requests with dropped link, 4-13
viewing error log, 4-14
Issue 1 — December 2002
IN-5DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
Page 74

Index
TSERVER_DRIVER_CONNECTION (73), 4-6
TSERVER_NO_TDI_BUFFERS (74), 4-6
TSLIB.INI file, 3-3
U
Universal Failure me ss age s. See Errors
V
Vendor name, 2-9
Version command, 3-16
Version number, 3-8
W
Warnings
CVLAN client running,2-4
DEFINITY G3 PBX Driver running,2-4
Windows NT. See NT
IN-6
Issue 1 — December 2002
DEFNETM.PDF — Avaya CT 1.2
 Loading...
Loading...