Page 1

Deployment Guide
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
NN42030-301, 01.04
3.1
October 2010
Page 2

©
2010 Avaya Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
Notice
While reasonable efforts have been made to ensure that the
information in this document is complete and accurate at the time of
printing, Avaya assumes no liability for any errors. Avaya reserves the
right to make changes and corrections to the information in this
document without the obligation to notify any person or organization of
such changes.
Documentation disclaimer
Avaya shall not be responsible for any modifications, additions, or
deletions to the original published version of this documentation unless
such modifications, additions, or deletions were performed by Avaya.
End User agree to indemnify and hold harmless Avaya, Avaya's agents,
servants and employees against all claims, lawsuits, demands and
judgments arising out of, or in connection with, subsequent
modifications, additions or deletions to this documentation, to the
extent made by End User.
Link disclaimer
Avaya is not responsible for the contents or reliability of any linked Web
sites referenced within this site or documentation(s) provided by Avaya.
Avaya is not responsible for the accuracy of any information, statement
or content provided on these sites and does not necessarily endorse
the products, services, or information described or offered within them.
Avaya does not guarantee that these links will work all the time and has
no control over the availability of the linked pages.
Warranty
Avaya provides a limited warranty on this product. Refer to your sales
agreement to establish the terms of the limited warranty. In addition,
Avaya’s standard warranty language, as well as information regarding
support for this product, while under warranty, is available to Avaya
customers and other parties through the Avaya Support Web site:
http://www.avaya.com/support. Please note that if you acquired the
product from an authorized Avaya reseller outside of the United States
and Canada, the warranty is provided to you by said Avaya reseller and
not by Avaya.
Licenses
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE TERMS AVAILABLE ON THE AVAYA
WEBSITE,
APPLICABLE TO ANYONE WHO DOWNLOADS, USES AND/OR
INSTALLS AVAYA SOFTWARE, PURCHASED FROM AVAYA INC.,
ANY AVAYA AFFILIATE, OR AN AUTHORIZED AVAYA RESELLER
(AS APPLICABLE) UNDER A COMMERCIAL AGREEMENT WITH
AVAYA OR AN AUTHORIZED AVAYA RESELLER. UNLESS
OTHERWISE AGREED TO BY AVAYA IN WRITING, AVAYA DOES
NOT EXTEND THIS LICENSE IF THE SOFTWARE WAS OBTAINED
FROM ANYONE OTHER THAN AVAYA, AN AVAYA AFFILIATE OR AN
AVAYA AUTHORIZED RESELLER, AND AVAYA RESERVES THE
RIGHT TO TAKE LEGAL ACTION AGAINST YOU AND ANYONE
ELSE USING OR SELLING THE SOFTWARE WITHOUT A LICENSE.
BY INSTALLING, DOWNLOADING OR USING THE SOFTWARE, OR
AUTHORIZING OTHERS TO DO SO, YOU, ON BEHALF OF
YOURSELF AND THE ENTITY FOR WHOM YOU ARE INSTALLING,
DOWNLOADING OR USING THE SOFTWARE (HEREINAFTER
REFERRED TO INTERCHANGEABLY AS “YOU” AND “END USER”),
AGREE TO THESE TERMS AND CONDITIONS AND CREATE A
BINDING CONTRACT BETWEEN YOU AND AVAYA INC. OR THE
APPLICABLE AVAYA AFFILIATE (“AVAYA”).
Avaya grants End User a license within the scope of the license types
described below. The applicable number of licenses and units of
capacity for which the license is granted will be one (1), unless a
different number of licenses or units of capacity is specified in the
Documentation or other materials available to End User. “Designated
Processor” means a single stand-alone computing device. “Server”
means a Designated Processor that hosts a software application to be
HTTP://SUPPORT.AVAYA.COM/LICENSEINFO/ ARE
accessed
in object code, originally licensed by Avaya and ultimately utilized by
End User, whether as stand-alone products or pre-installed on
Hardware. “Hardware” means the standard hardware originally sold by
Avaya and ultimately utilized by End User.
Copyright
Except where expressly stated otherwise, no use should be made of
materials on this site, the Documentation(s) and Product(s) provided
by Avaya. All content on this site, the documentation(s) and the
product(s) provided by Avaya including the selection, arrangement and
design of the content is owned either by Avaya or its licensors and is
protected by copyright and other intellectual property laws including the
sui generis rights relating to the protection of databases. You may not
modify, copy, reproduce, republish, upload, post, transmit or distribute
in any way any content, in whole or in part, including any code and
software. Unauthorized reproduction, transmission, dissemination,
storage, and or use without the express written consent of Avaya can
be a criminal, as well as a civil, offense under the applicable law.
Third-party components
Certain software programs or portions thereof included in the Product
may contain software distributed under third party agreements (“Third
Party Components”), which may contain terms that expand or limit
rights to use certain portions of the Product (“Third Party Terms”).
Information regarding distributed Linux OS source code (for those
Products that have distributed the Linux OS source code), and
identifying the copyright holders of the Third Party Components and the
Third Party Terms that apply to them is available on the Avaya Support
Web site:
Trademarks
The trademarks, logos and service marks (“Marks”) displayed in this
site, the documentation(s) and product(s) provided by Avaya are the
registered or unregistered Marks of Avaya, its affiliates, or other third
parties. Users are not permitted to use such Marks without prior written
consent from Avaya or such third party which may own the Mark.
Nothing contained in this site, the documentation(s) and product(s)
should be construed as granting, by implication, estoppel, or otherwise,
any license or right in and to the Marks without the express written
permission of Avaya or the applicable third party.
Avaya is a registered trademark of Avaya Inc.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Downloading documents
For the most current versions of documentation, see the Avaya Support
Web site:
Contact Avaya Support
Avaya provides a telephone number for you to use to report problems
or to ask questions about your product. The support telephone number
is 1-800-242-2121 in the United States. For additional support
telephone numbers, see the Avaya Web site:
support
by multiple users. “Software” means the computer programs
http://www.avaya.com/support/Copyright/.
http://www.avaya.com/support
http://www.avaya.com/
2 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1: New in this release.................................................................................................7
Features............................................................................................................................................................7
Other changes...................................................................................................................................................7
Chapter 2: Introduction.............................................................................................................9
References........................................................................................................................................................9
Chapter 3: Planning and engineering....................................................................................11
Chapter 4: Planning.................................................................................................................13
Avaya 3100 MC - Client and Avaya 3100 MC - Web UI network deployment................................................13
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway network deployment.................................................................15
Communication server requirements..............................................................................................................16
Dialing plans and telephone numbers.............................................................................................................16
Security requirements.....................................................................................................................................18
High availability...............................................................................................................................................20
Capacity..........................................................................................................................................................22
Chapter 5: Engineering...........................................................................................................23
Client device specifications.............................................................................................................................23
Gateway specifications...................................................................................................................................23
Port tables.......................................................................................................................................................23
Chapter 6: Interworking requirements with CS 1000...........................................................29
Avaya CS 1000 deployment considerations....................................................................................................29
Avaya CS 1000 Source Based Routing..........................................................................................................29
Avaya CS 1000 package requirements...........................................................................................................30
Avaya CS 1000 engineering for Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator..............................................................30
SIP Trunk configuration...................................................................................................................................34
Device Handoff configuration..........................................................................................................................35
Avaya CS 1000 system redundancy...............................................................................................................36
Call Forward No Answer feature interactions..................................................................................................36
Avaya CS 1000 capacity requirements...........................................................................................................37
Trunk calculation: Method 1............................................................................................................................38
Trunk calculation: Method 2............................................................................................................................39
UEXT calculations...........................................................................................................................................42
Avaya CS 1000 and supported Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator features.................................................42
Call Detail Recording......................................................................................................................................44
Direct outbound call........................................................................................................................................44
Call-Me-First outbound call.............................................................................................................................44
Incoming call...................................................................................................................................................44
Chapter 7: Deployment planning...........................................................................................47
Navigation.......................................................................................................................................................47
Licensing requirements...................................................................................................................................48
Avaya 3100 MC - Client and Avaya 3100 MC - Web UI licenses....................................................................48
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway licenses....................................................................................49
Avaya CS 1000 SIP Gateway CLID Parameters configuration.......................................................................49
Parameter: Country Code.......................................................................................................................51
Deployment Guide October 2010 3
Page 4

Parameter: Area Code............................................................................................................................51
Parameter: Subscriber/Number of Digits to strip....................................................................................51
Parameter: Subscriber/Prefix to insert....................................................................................................51
Parameter: National/Number of Digits to strip........................................................................................51
Parameter: National / Prefix to insert......................................................................................................52
Mobility prefix..................................................................................................................................................52
Data access planning......................................................................................................................................53
Avaya CS 1000 data access considerations...................................................................................................53
Service DN......................................................................................................................................................53
Universal Extensions.......................................................................................................................................54
Caller ID table.................................................................................................................................................54
Chapter 8: Deployment work flow..........................................................................................57
Deploying the systems task flow.....................................................................................................................57
Chapter 9: Deployment prerequisites....................................................................................59
Establishing the Avaya CS 1000 and Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator system baseline...........................59
Checking the Avaya CS 1000 release from Element Manager.......................................................................61
Checking the Avaya CS 1000 release from the command line.......................................................................62
Chapter 10: Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway installation................................63
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway installation workflow.................................................................63
Preparation......................................................................................................................................................65
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway preparation workflow................................................................65
Installing the Linux base..................................................................................................................................67
Verifying the Enterprise network.....................................................................................................................71
Job aid: Supported LDAP servers...................................................................................................................71
Installation.......................................................................................................................................................72
Installation task flow........................................................................................................................................72
Job aid: Admin shell access............................................................................................................................73
Installing the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway software..............................................................73
Commissioning................................................................................................................................................74
Adding an Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway server......................................................................74
Configuring the Gateway settings...................................................................................................................75
Procedure job aid............................................................................................................................................76
Configuring the dial plan conversion parameters............................................................................................81
Variable definitions..........................................................................................................................................82
Rules that use the carat sign...........................................................................................................................82
Configuring the device settings.......................................................................................................................83
Procedure job aid............................................................................................................................................84
Configuring the emergency telephone numbers.............................................................................................87
Adding the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway license....................................................................88
Checking Gateway server status....................................................................................................................89
Procedure job aid............................................................................................................................................90
Solution commissioning..................................................................................................................................92
Chapter 11: Avaya CS 1000 configuration for client support..............................................95
Avaya CS 1000 configuration for client support task flow...............................................................................95
Configuring zones...........................................................................................................................................97
Configuring a D-channel for virtual trunks.......................................................................................................97
Configuring virtual routes................................................................................................................................98
Configuring virtual trunks..............................................................................................................................100
4 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 5

Configuring network control parameters data block......................................................................................101
Configuring ESN access codes.....................................................................................................................101
Configuring the Route List Block...................................................................................................................102
Coordinated Dialing Plan..............................................................................................................................103
Forwarding Service DN to Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway......................................................103
Configuring a Handoff key.............................................................................................................................105
Configuring a HOT P key..............................................................................................................................106
Configuring the SIP trunk gateway................................................................................................................107
Configuring the SIP Gateway settings..........................................................................................................109
Configuring the SIP URI to NPI/TON mapping..............................................................................................110
Restarting the Signaling Server.....................................................................................................................112
Warm restart..................................................................................................................................................112
Cold restart....................................................................................................................................................112
Configuring NRS............................................................................................................................................112
NRS Database...............................................................................................................................................113
Committing NRS Database...........................................................................................................................113
Configuring Domain names on the NRS.......................................................................................................114
Configuring gateway endpoints on the NRS.................................................................................................116
Adding a User Endpoint.................................................................................................................................119
Job Aid..........................................................................................................................................................122
Adding an NRS Routing rule for the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway.......................................122
Adding an NRS Routing rule for the Avaya CS 1000....................................................................................125
Chapter 12: CallPilot MWI configuration.............................................................................127
MWI for Avaya CS 1000................................................................................................................................127
Chapter 13: Validate deployment.........................................................................................129
Validating deployment task flow....................................................................................................................129
Validating Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway registration.............................................................130
Job aid...........................................................................................................................................................130
Validating Avaya 3100 MC - Client for BlackBerry communication...............................................................131
Validating Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator and Avaya CS 1000 ECS deployment..................................132
Chapter 14: Upgrade fundamentals.....................................................................................135
Navigation.....................................................................................................................................................135
Upgrade work flow........................................................................................................................................136
Upgrading from Release 2.x to Release 3.0.................................................................................................136
Release upgrade taskflow....................................................................................................................137
Capturing Release 2.x parameters.......................................................................................................138
Job Aid: Release 2.x parameter worksheet..........................................................................................139
Upgrading from Release 3.0 to Release 3.1.................................................................................................139
Prerequisites.........................................................................................................................................140
Upgrading from Release 3.0 to Release 3.1 taskflow..........................................................................140
Recording the Release 3.0 configuration parameters..........................................................................141
Release 3.0 system configuration job aid.............................................................................................142
Upgrading the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway software to a new software release................145
Upgrade commissioning.......................................................................................................................147
Upgrading for a Service Upissue..........................................................................................................147
Upgrading the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator system software from CD......................................147
Converting to a redundant configuration.......................................................................................................148
Deployment Guide October 2010 5
Page 6

Chapter 15: Maintenance......................................................................................................151
Navigation.....................................................................................................................................................151
Removing a Service Upissue........................................................................................................................151
Job Aid..........................................................................................................................................................152
Uninstalling the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator system software...........................................................152
Chapter 16: Common procedures........................................................................................155
Logging on to the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Web Administration Console as an administrator
......................................................................................................................................................................155
Changing the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Web Administration Console password..........................156
Managing the server processes from the Web Administration Console.......................................................157
Managing the server processes from the command line..............................................................................158
Accessing the server command line as nortel...............................................................................................159
Accessing the server command line as superuser........................................................................................159
Backing up the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway server databases...........................................160
Restoring the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway server databases.............................................161
Chapter 18: Appendix A: Installation worksheets and checklist......................................163
Linux base worksheet...................................................................................................................................163
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway worksheet...............................................................................164
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator solution checklist...................................................................................166
Chapter 18: Appendix B: Call flows from CS 1000.............................................................169
Index.......................................................................................................................................171
6 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 7
Chapter 1: New in this release
This section details what’s new in Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Deployment Guide, NN42030-301
for Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Release 3.1.
Features
This document is new for Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Release 3.1.
For more information about Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator, see Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Fundamentals, NN42030-109.
Other changes
This document is new for Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Release 3.1. It consolidates the
following documents:
• Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Planning and Engineering, NN42030-200
• Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Installation and Commissioning, NN42030-300
• Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator and Avaya Communication Server 1000 Solution
Integration Guide, NN49000-315
Revision History
October 2010 Standard 01.04. This document is issued to support Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Release 3.1. Removed obsolete external references.
July 2010 Standard 01.03. This document is issued to support Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Release 3.1. Updated Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
Gateway installation on page 63 and Upgrading the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway software to a new software release on
page 145. Added Converting to a redundant configuration on page
148.
April 2010 Standard 01.02. This document is up-issued to provide correction to
procedures.
January 2010 Standard 01.01. This document is issued to support Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Release 3.1.
Deployment Guide October 2010 7
Page 8

New in this release
8 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 9
Chapter 2: Introduction
This document guides you through the deployment steps for Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator (Avaya
3100 Mobile Communicator). These steps include planning, engineering, installation of the Avaya 3100
Mobile Communicator, and interworking the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator with the Avaya
Communication Server 1000 (Avaya CS 1000).
• Planning and engineering on page 11 takes you through the planning and engineering required.
At the end of this step, you will have completed a worksheet with parameters you need for
deployment.
•
Deployment work flow on page 57 takes you through the installation of Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator and interworking it with your ECS.
This document also includes the following related sections:
•
Upgrade fundamentals on page 135
• Maintenance on page 151
• Converting to a redundant configuration on page 148
• Appendix B: Call flows from CS 1000 on page 169
Important:
For Avaya CS 1000 platforms, Avaya personnel perform all installation and interworking activities.
References
For more information about Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator, see Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Fundamentals, NN42030-109.
For more information about administration tasks and tasks involving the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator clients, see Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Administration and Security,
NN42030-600.
For information about the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicatorclients, see
• Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator - Client for BlackBerry User Guide, NN42030-101
• Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator - Client for Nokia User Guide, NN42030-102
• Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator - Client for Windows Mobile User Guide,
NN42030-107
Deployment Guide October 2010 9
Page 10

Introduction
• Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator - Client for iPhone User Guide, NN42030-111
• Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator - Web UI User Guide, NN42030-110
10 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 11

Chapter 3: Planning and engineering
This chapter contains information that supports the activities that you must perform before installing an
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator (Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator) solution, including requirements,
network management, performance, and capacity requirements.
During the planning and engineering phase, use the worksheets in Appendix A: Installation worksheets
and checklist on page 163 to gather the information you need in order to install, configure, and interwork
your Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator with your Avaya Communication Server 1000 (Avaya CS 1000).
•
Planning on page 13
• Engineering on page 23
• Interworking requirements with CS 1000 on page 29
• Deployment planning on page 47
Deployment Guide October 2010 11
Page 12

Planning and engineering
12 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 13

Chapter 4: Planning
This chapter details the planning aspects of the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator (Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator).
Navigation
• Avaya 3100 MC - Client and Avaya 3100 MC - Web UI network deployment on page 13
• Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway network deployment on page 15
• Communication server requirements on page 16
•
Dialing plans and telephone numbers on page 16
• Security requirements on page 18
• High availability on page 20
• Capacity on page 22
Avaya 3100 MC - Client and Avaya 3100 MC - Web UI network deployment
The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator - Client (Avaya 3100 MC - Client) for BlackBerry, the
Avaya 3100 MC - Client for Nokia, the Avaya 3100 MC - Client for Windows Mobile, the Avaya
3100 MC - Client for iPhone, and the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator - Web UI (Avaya 3100
MC - Web UI) require access to the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway. In this
document, the terms Avaya 3100 MC - Client and clients refer to the supported clients and
Avaya 3100 MC - Web UI.
The Avaya 3100 MC - Client for BlackBerry supports two network deployment options:
• with the BlackBerry Enterprise Server (BES)
• without the BES
The Avaya 3100 MC - Client for BlackBerry with the BES uses the BES to route data and
provide security.
Avaya 3100 MC - Client for BlackBerry (without the BES), Avaya 3100 MC - Client for Nokia,
and Avaya 3100 MC - Client for Windows Mobile require a Wireless Access Point or an internet
connection through the Enterprise firewall. These clients can also use the cellular data network.
Figure 1: Typical Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator network architecture on page 14 shows
a typical network architecture.
Deployment Guide October 2010 13
Page 14
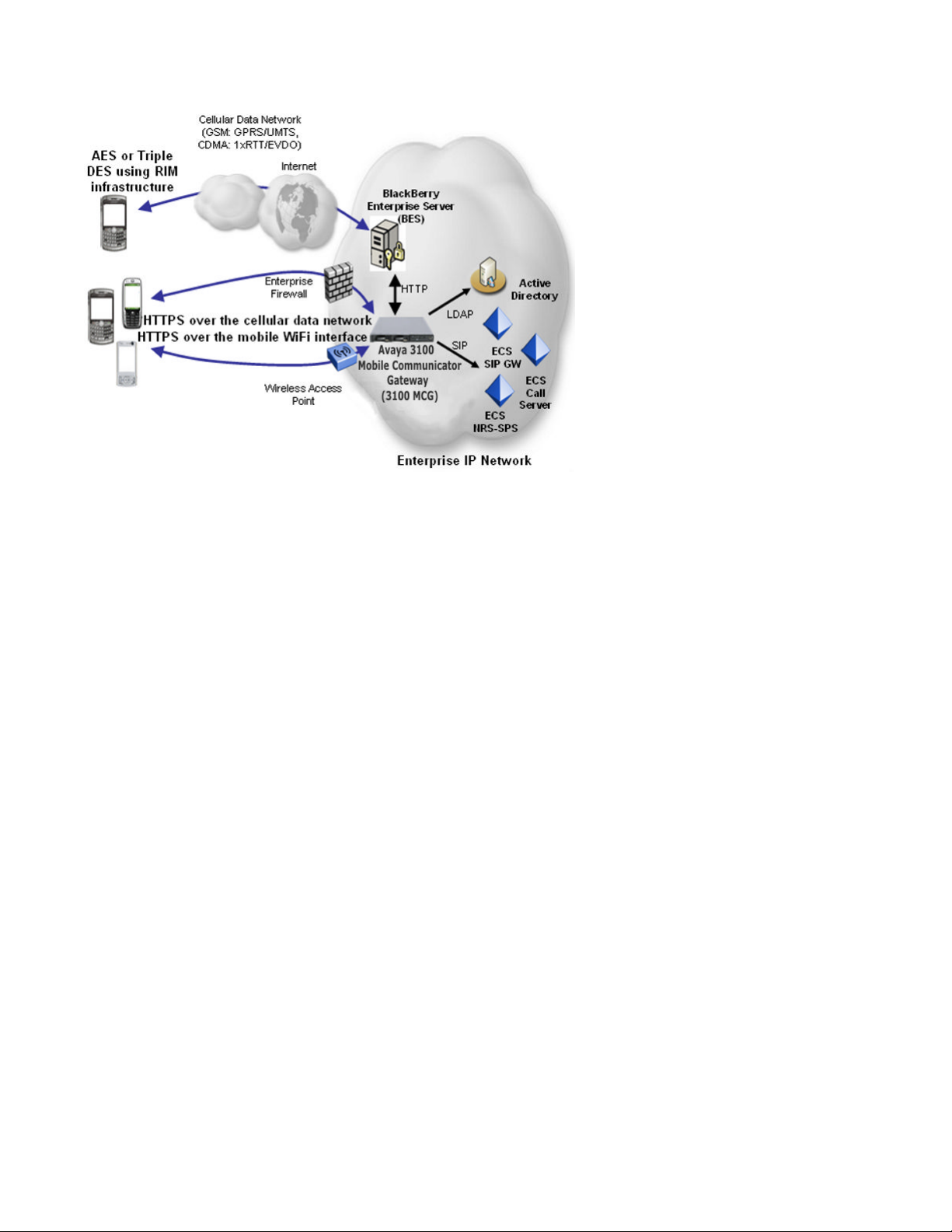
Planning
Figure 1: Typical Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator network architecture
The Avaya 3100 MC - Client for Nokia and Avaya 3100 MC - Client for Windows Mobile do not
contain integrated virtual private network (VPN) software. Any industry-standard VPN software
for the Nokia or Windows Mobile device can be used.
The Avaya 3100 MC - Client for Nokia and Avaya 3100 MC - Client for Windows Mobile
communicate directly to the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway. When deployed with
the BES, the Avaya 3100 MC - Client for BlackBerry communicates with the BES, which
communicates with the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway. When deployed without
the BES, the Avaya 3100 MC - Client for BlackBerry communicates directly with the Avaya
3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway.
The Avaya 3100 MC - Web UI does not require software installation on the device. When the
Avaya 3100 MC - Web UI runs on a BlackBerry that uses a BES, the BlackBerry Web browser
uses the Mobile Data Service (MDS) on the BES to access the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway. For the non-BES BlackBerry, and for Windows Mobile and Nokia
devices, the Avaya 3100 MC - Web UI (in the Web browser) uses HTTPS to connect to the
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway.
For examples of Avaya 3100 MC - Client and Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway call
flows, see Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Fundamentals, NN42030-109.
14 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 15
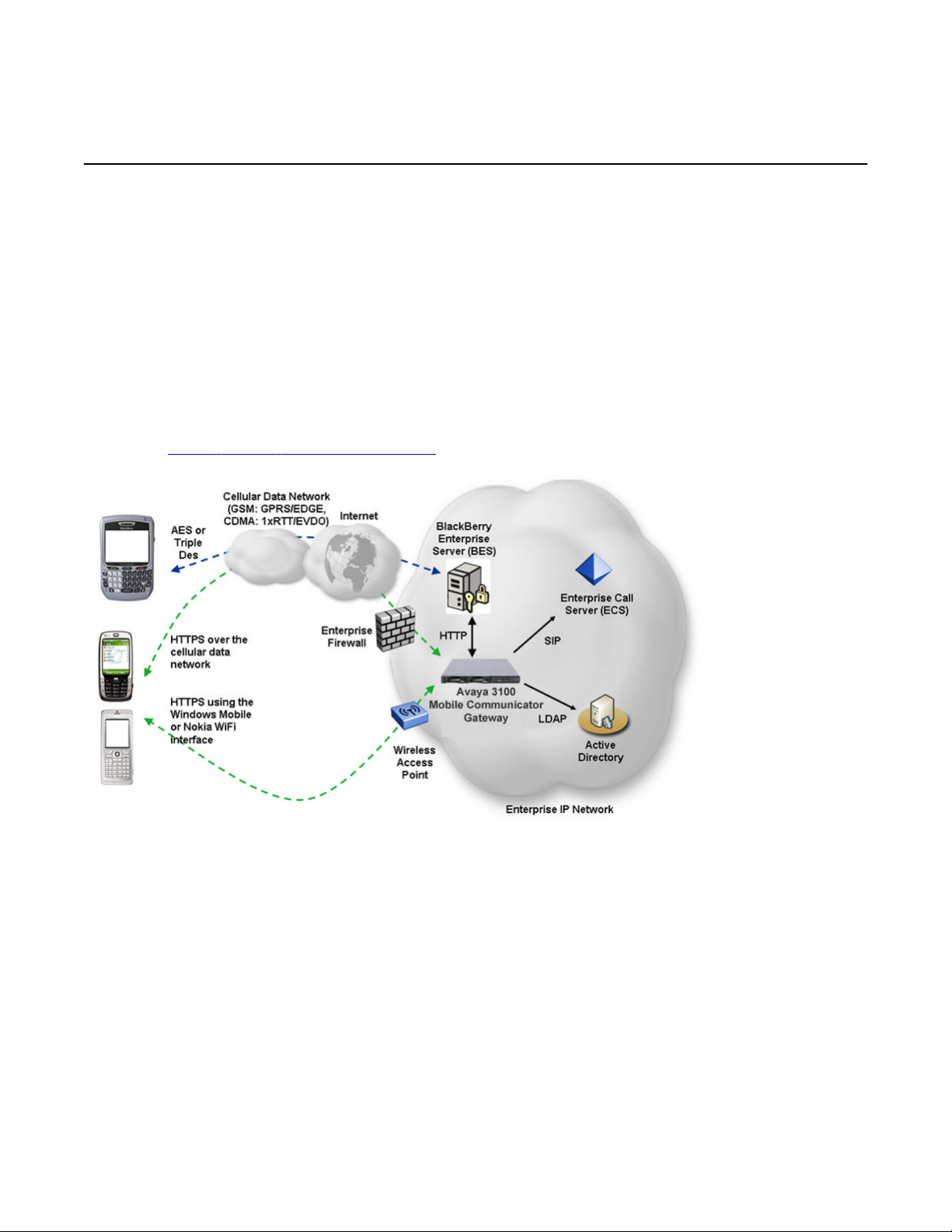
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway network deployment
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway network
deployment
The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway requires the following network infrastructure:
• access to an Enterprise Call Server (ECS) including a call server, Session Initiation
Protocol (SIP) gateway, and SIP Proxy Server (SPS)
• access to the ECS Telephony Local Area Network (TLAN), including all SIP infrastructure,
media gateways, and any IP endpoint that can originate or terminate real-time transport
• access to a BlackBerry Enterprise Server (BES) if the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
Gateway supports the Avaya 3100 MC - Client for BlackBerry with the BES
Figure 2: Data access from devices on page 15 shows data access from the devices.
Figure 2: Data access from devices
The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway requires the following network infrastructure
with the Avaya CS 1000:
For examples of Avaya 3100 MC - Client and Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway call
flows, see Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Fundamentals, NN42030-109.
Deployment Guide October 2010 15
Page 16
Planning
Communication server requirements
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Release 3.1 supports the following versions of Avaya
Communication Server 1000 (Avaya CS 1000):
• Avaya CS 1000 Release 5.5
- CS and SS: Deplist of February 3, 2009 or later
- SPS: SU 5.50.12.006 or later
• Avaya CS 1000 Release 6.0
latest deplist must be loaded
Avaya CS 1000 package requirements are discussed in
requirements on page 30.
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Release 3.1 supports the following versions of Avaya
Communication Server 2100 (Avaya CS 1000):
Avaya CS 1000 SE 11
Dialing plans and telephone numbers
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator supports telephone numbers in the following formats
• Dial strings, where the user enters all the digits to be dialed. Examples of dial strings
include 2356, 63432356, 93432356 and 3432356.
• E.164 Fully Qualified International Numbers, where telephone numbers start with the plus
(+) symbol. E.164 Fully Qualified International Numbers are also known as "plus
numbers". Examples of Fully Qualified International Numbers include +16131234567 and
+31123456789.
On all mobile phones, mobile carriers support the plus (+) sign in telephone numbers. The +
identifies that this is an E.164 fully qualified international number (for example, see http://
unifiedcommunicationsblog.globalknowledge.com/2009/07/02/e164-the-modern-dial-plan/).
Avaya CS 1000 package
If you use the +, you do not need to use an international dial prefix (for example,. 011). Avaya
3100 Mobile Communicator supports the same dial plan as the mobile carrier by supporting
the +. On devices with a keyboard, the + has its own key (for instance, the ‘O’ on a BlackBerry).
On devices without a QWERTY keyboard, inserting the + is specific to the device.
The dial plan available from Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator should be the same as the dial
plan for a desk telephone. That is, if the user has a desk telephone and an Avaya 3100 MC Client device, the dial plan should be the same.
16 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 17

Dialing plans and telephone numbers
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator users should use the E.164 Fully Qualified International
Numbers for all stored Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) numbers in address books
and mobile device applications. By using this format, the numbers can be dialed from any
region or country, within the wireless network or from the communication server.
The E.164 Fully Qualified International Numbers ensure that users do not need to be
concerned about dial prefixes or long distance codes. The network determines how to place
the call, based on the user's location and network connection.
When the user dials an E.164 Fully Qualified International Number, the communication server
puts the number in the request Uniform Resource Indicator (URI) of the SIP INVITE message in
the following format sip: +CCCXXXXXXXX@domain; user=phone.
When using the ECS, configure the CNTC, NATC, and INTC parameters in LD 15 to support
E.164 Fully Qualified International Numbers. These parameters ensure that fully qualified
numbers within the same country are dialed as national numbers, and international numbers
are prefixed correctly.
Example 1 (Switzerland)
ECS is Avaya Communication Server 1000 (Avaya CS 1000) AC1=0, CNTC=41, NATC=0,
INTC=00
Call to a number within Switzerland
A user initiates a call to a contact with the phone number +41123456789.
The URI incoming for the SIP INVITE for the call is sip:
+41123456789@domain.com;user=phone
Avaya CS 1000 digit processing strips the CNTC and adds <AC1 + NATC> to produce
00123456789
Call to a number outside Switzerland
A user initiates a call to a contact with the phone number +14161234567.
The URI incoming for the SIP INVITE for the call is sip:
+14161234567@domain.com;user=phone
Avaya CS 1000 digit processing adds <AC1 + INTC> to produce 00014161234567
Example 2 (North America)
ECS is Avaya CS 1000 AC1=6, CNTC=1, NATC=1, INTC=011
Call to a number within North America
A user initiates a call to a contact with the phone number +14161234567.
The URI incoming for the SIP INVITE for the call is sip:
+14161234567@domain.com;user=phone
Deployment Guide October 2010 17
Page 18

Planning
Avaya CS 1000 digit processing strips the CNTC and adds <AC1 + NATC> to produce
614161234567
Call to a number outside North America
A user initiates a call to a contact with the phone number +41123456789.
The URI incoming for the SIP INVITE for the call is sip:
+41123456789@domain.com;user=phone
Avaya CS 1000 digit processing adds <AC1 + INTC> to produce 601141123456789.
Security requirements
The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway requires data access to the ECS TLAN and
uses the ECS SIP Proxy Server (SPS) as the SIP Signaling Proxy. The Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway can accept or transmit real time protocol (RTP) messages to any IP
endpoint in the Enterprise (for example, Media Cards, other SIP clients, or IP telephones).
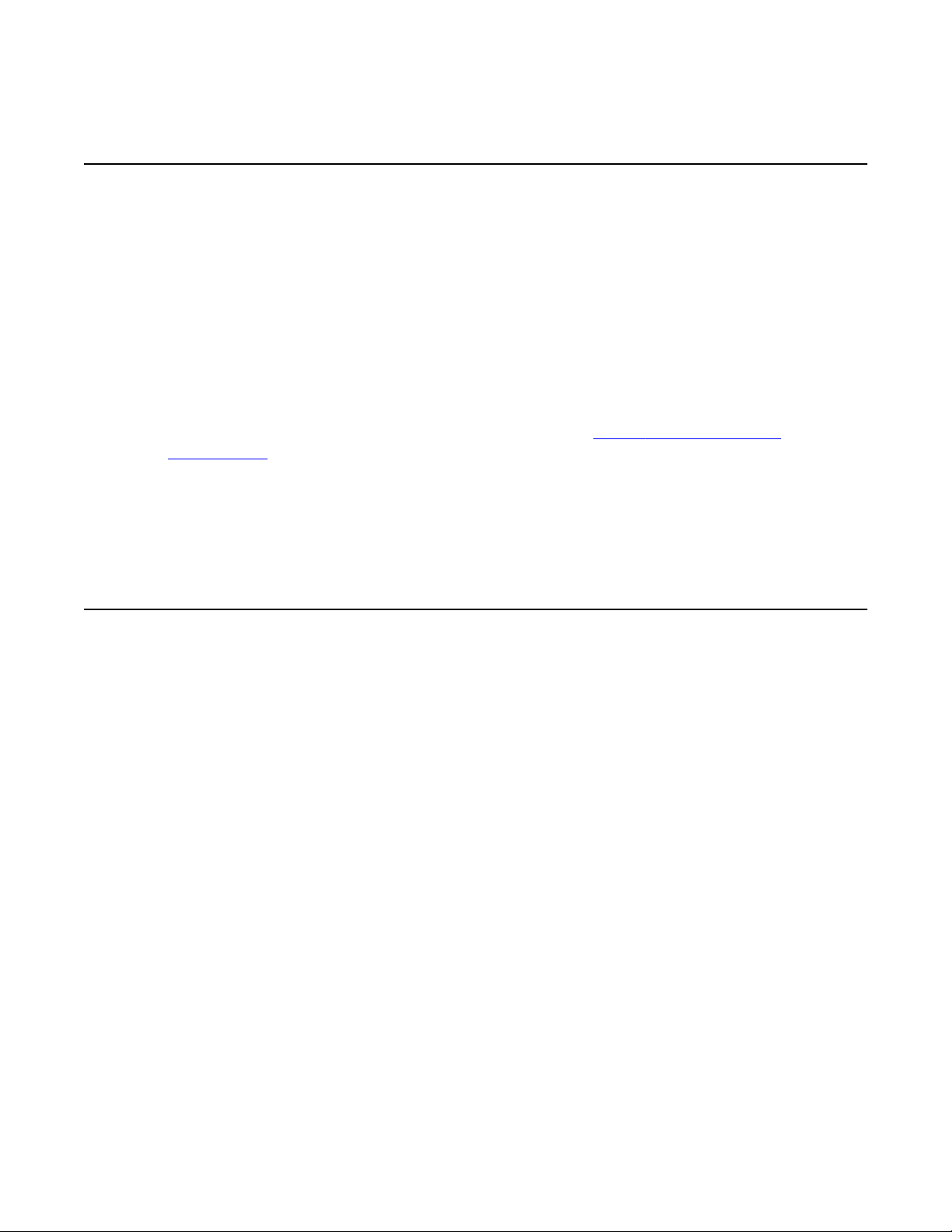
Figure 3: Sample Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway firewall configuration on
page 19 shows a firewall that separates the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway
from the remainder of the Enterprise voice infrastructure. The Avaya 3100 MC - Client for
BlackBerry (without the BES), Avaya 3100 MC - Client for Nokia, and Avaya 3100 MC - Client
for Windows Mobile require access on the internet to a public FQDN and a public IP address.
The figure also shows a sample firewall configuration and policy. For the purposes of this
example assume
• that the Avaya 3100 MC - Client (in the absence of a BES) requires a public FQDN and
IP for the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway to be accessible from the internet.
This in turn forces the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway to be placed in a
demilitarized zone (DMZ).
• Firewalls are used to filter traffic from the internet and from the DMZ to separate the Avaya
3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway and internet from the trusted Enterprise voice
infrastructure where other components on the ECS TLAN reside.
18 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 19
Figure 3: Sample Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway firewall configuration
Security requirements
If a user calls a client, the SIP signaling comes through the SPS. Real Time Protocol (RTP) for
announcements or Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Instant Conference calls takes place
between the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway and the IP telephone without using
the SPS.
To allow public internet traffic to reach the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway from
clients, while simultaneously providing Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway access to
the ECS TLAN for SIP and RTP, you must carefully consider the data network and security
requirements of the Enterprise.
Proprietary communication between the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway and the
Avaya 3100 MC - Client for BlackBerry (without the BES, using HTTP), the Avaya 3100 MC Client for Nokia (using HTTPS), and the Avaya 3100 MC - Client for Windows Mobile (using
HTTPS) enables clients to initiate and modify calls for the user on the ECS. In the BES
configuration, the Avaya 3100 MC - Client for BlackBerry communicates with the BES, which
communicates with the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway. The Avaya 3100 MC Client for Nokia and Avaya 3100 MC - Client for Windows Mobile communicates directly with
the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway, as well as the Avaya 3100 MC - Client for
BlackBerry when configured without the BES.
Access to user records in an active directory server configured against the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway uses a tunnel over HTTP or HTTPS. Configure the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway to specify the query search base, which limits the search to a subtree
of the base.
Deployment Guide October 2010 19
Page 20
Planning
The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway queries a corporate Lightweight Directory
Access Protocol (LDAP) server when the users use the Directory lookup feature on their clients.
The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway supports the following LDAP servers:
• Active Directory/Exchange Server 2000 or 2003
• Avaya Common Network Directory (CND)
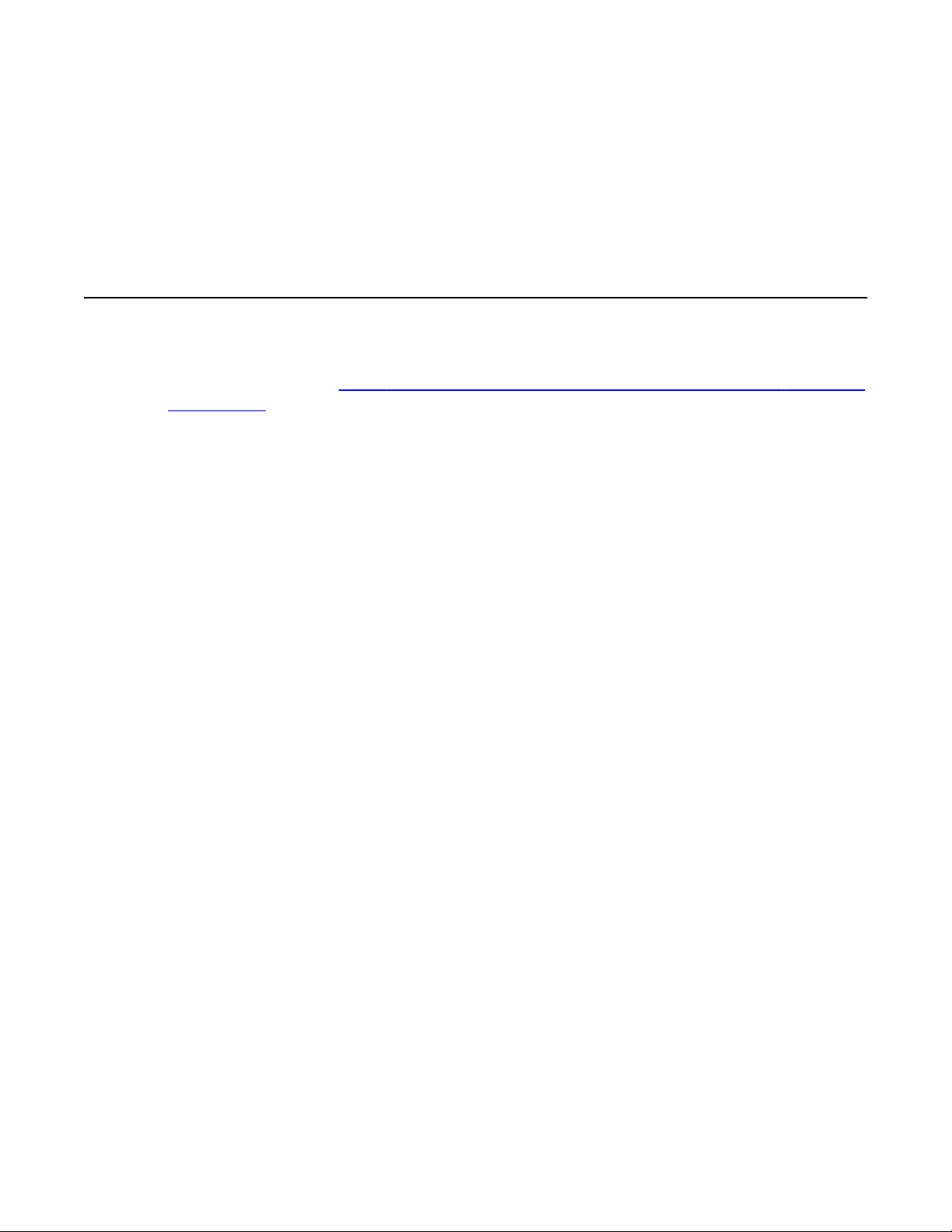
High availability
You can deploy the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway as a nonredundant server
or in a redundant pair. Figure 4: Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway high availability
configuration on page 21 shows the redundant pair configuration that enables the high
availability solution.
20 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 21
High availability
Figure 4: Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway high availability configuration
A redundant system includes an active server and a standby server. Mobile clients access the
active server, while the standby server functions as a backup. The two roles switch freely,
based on the following rules:
• If the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway does not have a configured backup IP
address, it starts in active mode.
• If the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway has a configured backup IP address,
it starts in inactive mode and attempts to locate the standby system.
- If the standby server is in standby mode, the system with the lower IP address
becomes active.
- If the standby server is in active mode, the standby server remains active.
- If the standby server is not located, the local system is declared active.
• If the active system stops, the standby system becomes active.
The pair of Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway servers must contain identical software
for redundancy to work. Each server acts as the backup for the other server.
The clients support Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway redundancy. The Primary
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway address and Secondary Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway address fields in the clients contain the active and standby Avaya
3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway IP addresses respectively. When the active Avaya 3100
Deployment Guide October 2010 21
Page 22

Planning
Mobile Communicator Gateway stops responding, the clients switch to the other Avaya 3100
Mobile Communicator Gateway.
The communication link between two Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway servers
in the redundant pair must be highly reliable and available. When the gateways cannot
communicate with each other, they both become active, start processing traffic, and try to
register with the NRS. The NRS has only one gateway endpoint associated with the Avaya
3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway, so the second gateway to register with the NRS
receives all the incoming SIP traffic.
Capacity
The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway supports 1500 users per gateway. Avaya
testing used a capacity of 8000 calls per hour. The 1500 users per gateway capacity
recommendation assumes each user makes on average four calls per hour (or approximately
6000 calls per hour). This results in a margin of safety for the capacity of the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway when servicing 1500 users per gateway.
Important:
22 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 23
Chapter 5: Engineering
This chapter details the engineering aspects of the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator (Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator).
Navigation
• Client device specifications on page 23
• Gateway specifications on page 23
• Port tables on page 23
Client device specifications
The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator - Client (Avaya 3100 MC - Client) application runs on
a number of devices. These devices have no special hardware or software requirements.
To view the list of supported devices, see the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Product
Bulletin at http://www.avaya.com.
Gateway specifications
The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway uses one of the following servers:
• HP DL320G4
• IBM x306m
The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway runs on the Avaya CS 1000 Linux Base
operating system. For more information, see Linux Platform Base and Applications Installation
and Commissioning, NN43001-315.
Port tables
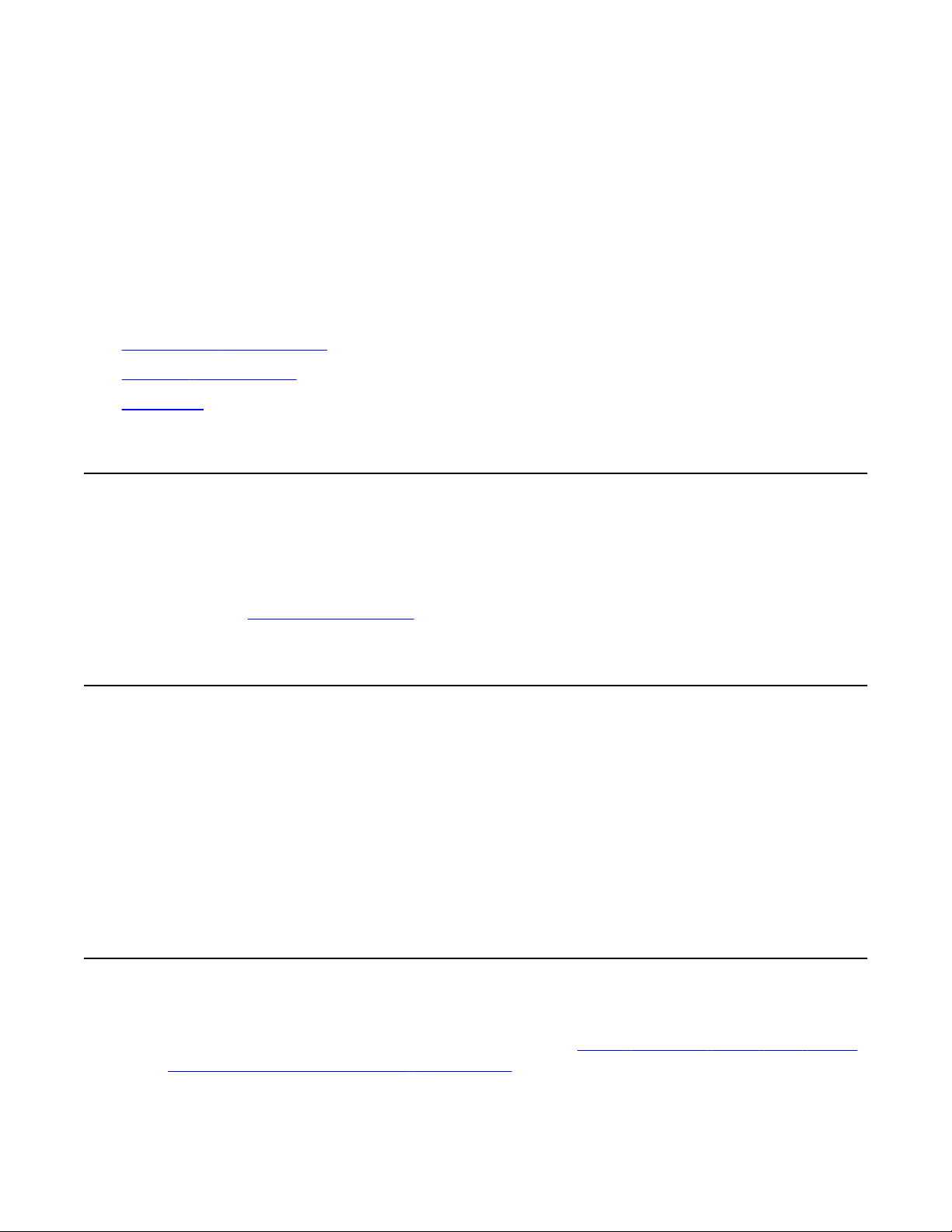
The following table details the ports used in the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway.
When using this section to configure firewalls, refer to Figure 3: Sample Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway firewall configuration on page 19.
Deployment Guide October 2010 23
Page 24
Engineering
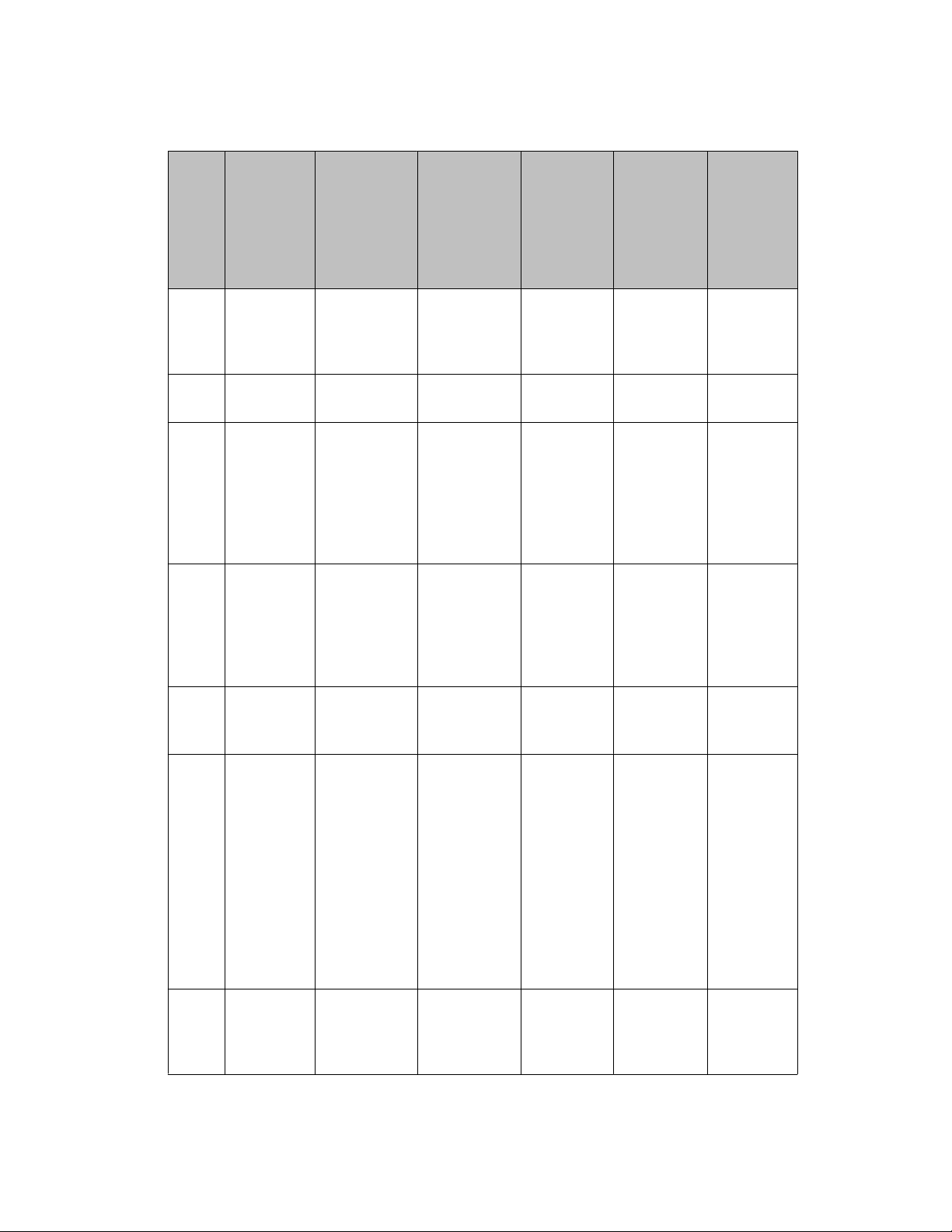
Table 1: Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway ports
Port Protocol Function Applica- tion Configur-
able?
21 Transmissi
on Control
Protocol
(TCP)
22 TCP Secure Shell
53
(Send
only)
123
(Send
only)
User
Datagram
Protocol
(UDP)
TCP Network
File Transfer
Protocol
(FTP)
(SSH)
Domain
Name
Server
(DNS)
queries to
external
DNS server
Time
Protocol
(NTP)
Base Linux No No No
Base Linux No No No
Base Linux No Yes,
Base Linux No Yes,
Configure
in Avaya
3100 MCG-
to-
Enterprise
Firewall
policy?
assuming
DNS is
within the
Enterprise
network
assuming
DNS is
within the
Enterprise
network
Configure
in Avaya
3100 MCG
Firewall
policy?
No
No
389
(Send
only)
1098 TCP Communicat
1099 TCP Communicat
LDAP
(TCP)
Directory
access
ion between
the Avaya
3100 MCG
Administrati
on server
and the
Avaya 3100
Mobile
Communicat
or Gateway
server
ion between
the Avaya
3100 MCG
Directory
access
Avaya 3100
MCG
Avaya 3100
MCG
Yes Yes No
No No No
No No No
24 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 25
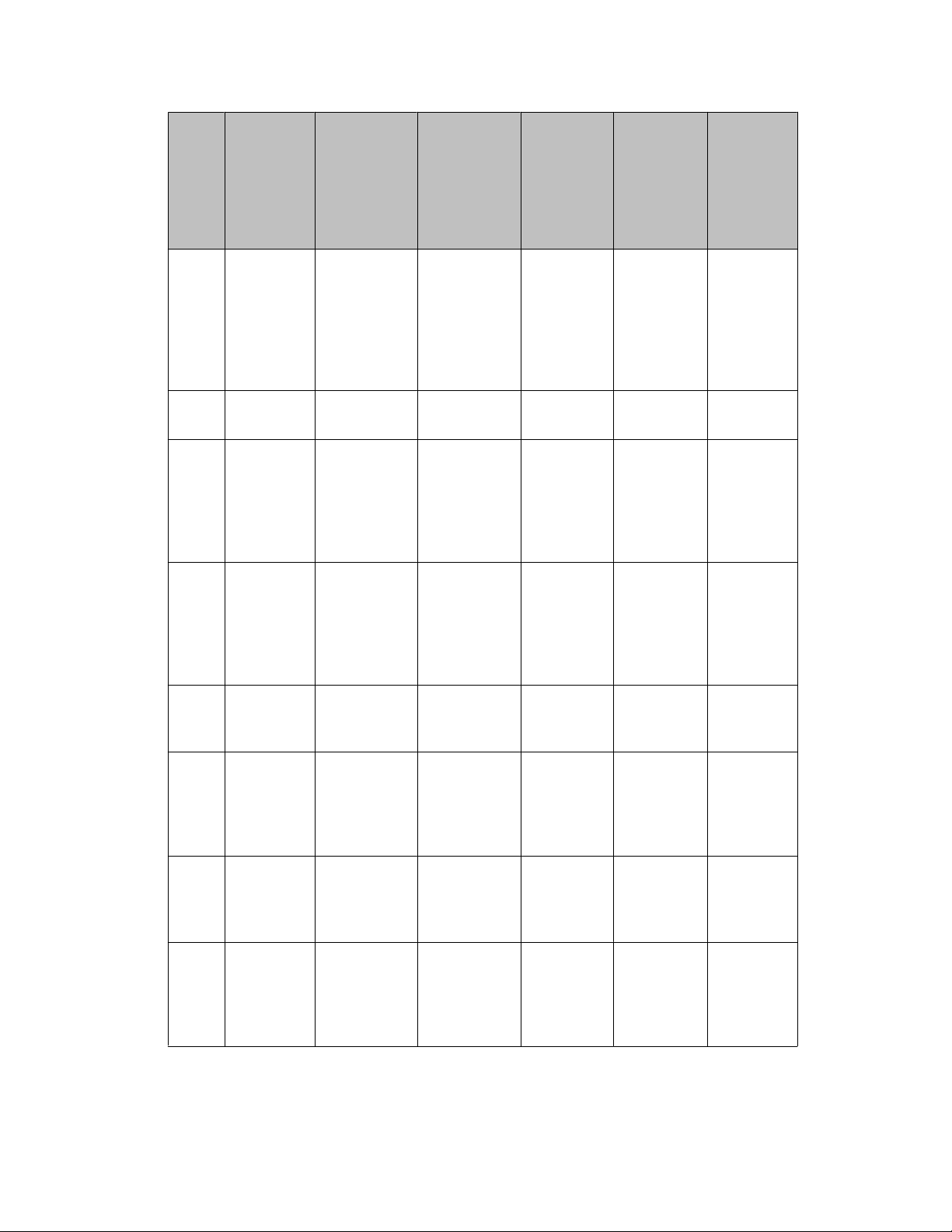
Port tables
Port Protocol Function Applica- tion Configur-
able?
server and
the Avaya
3100 Mobile
Communicat
or Gateway
Administrati
on server
3306 TCP SQL Client
Access
5060 Session
Initiation
Protocol
(SIP)
(UDP)
Avaya 3100
MCG listen
port for Voice
over IP
(VoIP)
Signalling
MySQL No No No
Avaya 3100
MCG
Yes Yes No
Configure
in Avaya
3100 MCG-
to-
Enterprise
Firewall
policy?
Configure
in Avaya
3100 MCG
Firewall
policy?
5072 SIP (UDP) Avaya 3100
MCG listen
port for VoIP
Signalling
(Instant Call
Server)
7800 TCP Avaya 3100
MCG Data
Replication
8008 HTTP
(TCP)
8080 TCP Avaya 3100
8282 HTTP
(TCP)
Licensing
validation
with
www199.nor
tel.com
MC - Client
open client
interface
Avaya 3100
MCG Open
Web Admin
Interface
(standalone
Avaya 3100
MCG
Avaya 3100
MCG
Avaya 3100
MCG
Avaya 3100
MC - Client
Avaya 3100
MCG Web
Administratio
n Console
Yes Yes No
No No No
No No No
Yes 8080 to
8089
No No No
No Yes
Deployment Guide October 2010 25
Page 26
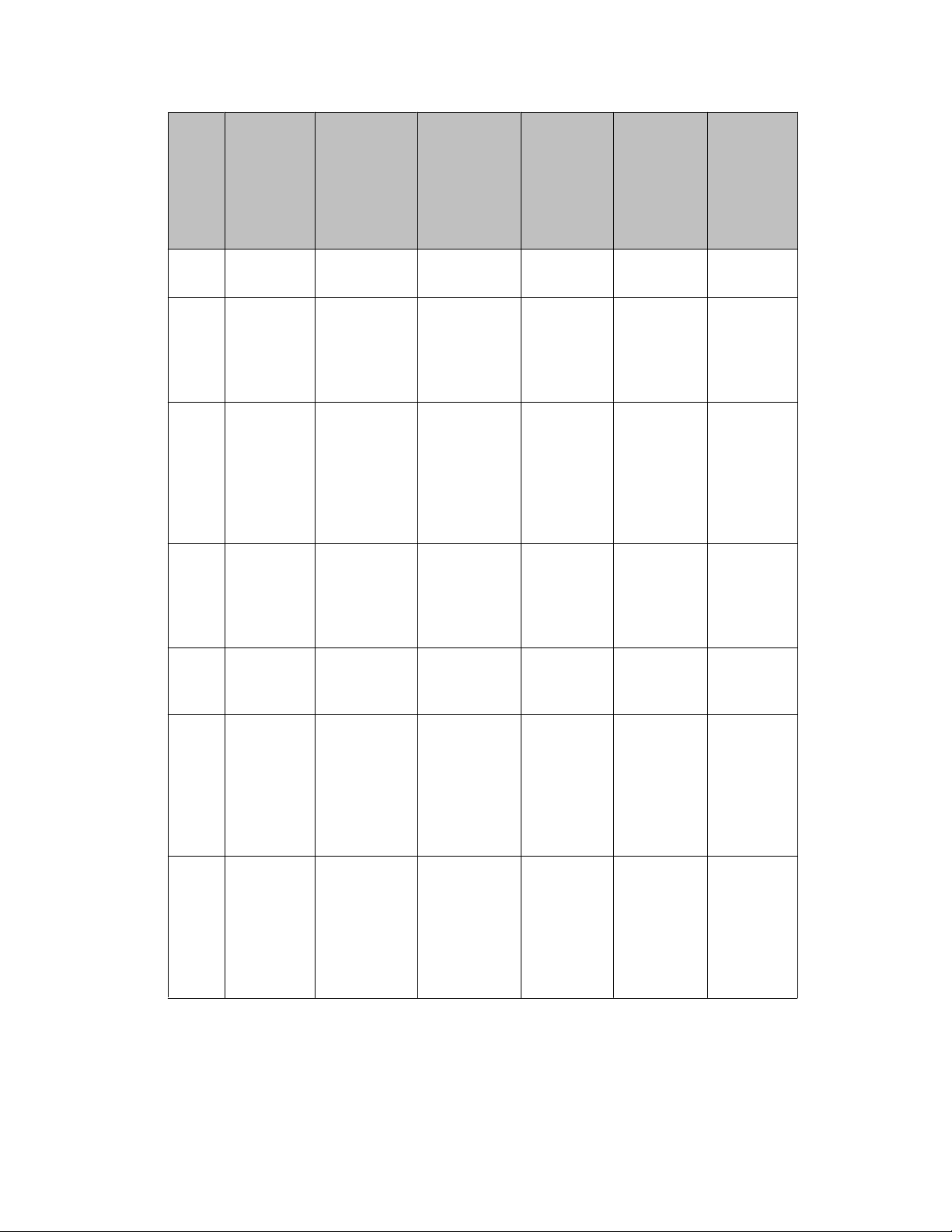
Engineering
Port Protocol Function Applica- tion Configur-
able?
managemen
t only)
8443 HTTPS
(TCP)
8553 TCP Avaya 3100
9800 TCP Avaya 3100
Avaya 3100
MC - Client
Secure
Client
Interface
MCG Secure
Admin
Interface
(standalone
managemen
t only)
MCG Server
Java Virtual
Machine
(JVM)
Avaya 3100
MCG
Avaya 3100
MCG Admin
Avaya 3100
MCG JVM
Yes 8440 to
8449
No No No
No No No
Configure
in Avaya
3100 MCG-
to-
Enterprise
Firewall
policy?
No Yes
Configure
in Avaya
3100 MCG
Firewall
policy?
9801 TCP Avaya 3100
MCGAdmini
stration JVM
26000
to
26099
(listen
only)
27000
to
27099
(listen
only)
UDP Media for all
Avaya 3100
MC - Client
calls
anchored on
the Avaya
3100 MCG
RTP (UDP) Media for all
Avaya 3100
MC - Client
calls
anchored on
the Avaya
3100 MCG
Avaya 3100
MCG Admin
JVM
Voice over IP
(VoIP)
Conference
Media
VoIP Media Yes Yes No
No No No
Yes Yes No
In the preceding table, the ranges 26000 to 26999 and 27000 to 27999 depend on the
configuration of the Maximum number of DTR ports parameter.
26 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 27
Port tables
The following table lists the ports that are defined by the Enterprise Call Server (ECS). You
configure these ports on the ECS.
Table 2: ECS ports
Protocol Function Application Configure in the
Avaya 3100
Mobile
Communicator
Gateway-to-
Enterprise
Firewall policy?
RTP
(UDP)
RTP
(UDP)
RTP
(UDP)
VoIP send port for the
Gateway server.
Configured on the
Avaya 3100 MCG.
VoIP send port for the
Instant Conference
Server. Configured on
the Avaya 3100 MCG.
VoIP send port for the
VoIP Conference
Media. RTP can be sent
to media gateways, IP
endpoints, or other SIP
User Agents. The range
of end point ports
defines the ports to
which the Avaya 3100
MCG sends media.
Avaya 3100
MCG
Avaya 3100
MCG
Avaya 3100
MCG
Yes No
Yes No
Yes No
Configure in the
Internet-to-Avaya
3100 Mobile
Communicator
Gateway Firewall
policy?
RTP
(UDP)
Deployment Guide October 2010 27
VoIP send port for
Media. RTP can be sent
to media gateways, IP
endpoints, or other SIP
User Agents. The range
of end point ports
defines the ports to
which the Avaya 3100
MCGsends media.
Avaya 3100
MCG
Yes No
Page 28

Engineering
28 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 29
Chapter 6: Interworking requirements with
CS 1000
This chapter details the interworking requirements for the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator (Avaya 3100
Mobile Communicator) and Avaya Communication Server 1000 (Avaya CS 1000), which is a supported
Enterprise Call Server (ECS).
Navigation
•
Avaya CS 1000 deployment considerations on page 29
•
Avaya CS 1000 Source Based Routing on page 29
• Avaya CS 1000 package requirements on page 30
• Avaya CS 1000 engineering for Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator on page 30
• Avaya CS 1000 capacity requirements on page 37
• Avaya CS 1000 and supported Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator features on page 42
•
Call Detail Recording on page 44
Avaya CS 1000 deployment considerations
The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway requires data access to the Avaya CS 1000
Telephony Local Area Network (TLAN). The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway uses
the Avaya CS 1000 Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) Proxy Server (SPS) as the SIP Signaling
Proxy. The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway accepts or transmits real time protocol
(RTP) messages to any IP endpoint within the Enterprise (for example, Media cards, other SIP
clients, or IP telephones).
To allow public internet traffic to reach the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway from
clients, while simultaneously providing Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway access to
the Avaya CS 1000 TLAN for SIP and RTP, you must carefully consider the data network and
security requirements of the Enterprise.
Avaya CS 1000 Source Based Routing
Avaya CS 1000 Source Based Routing (SBR) occurs when the request Uniform Resource
Indicator (URI) of the INVITE message sent from the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
Deployment Guide October 2010 29
Page 30

Interworking requirements with CS 1000
Gateway contains the tag x-nt-net-feature=x-nt-home. For example, the following request URI
triggers SBR:
INVITE sip:+16131234567@avaya.com;x-nt-sip-line-service;x-nt-net-feature=x-nt-home SIP/
2.0
SBR causes the Avaya CS 1000 Network Routing Service-SIP Proxy Service (NRS-SPS) to
route the call attempt (INVITE) to the P-Asserted-Id in the SIP INVITE instead of using the
Request URI.
Using SBR means that all calls from a SIP user route to the home call server for origination,
allowing the call server to apply features such as Calling Line ID (CLID) and Network Class of
Service (NCOS) to SIP calls.
In the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway, use the User Prefix/Phone-context for Call
origination field to configure SBR. For information, see Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
Administration and Security, NN42030-600.
Avaya CS 1000 package requirements
Avaya CS 1000 requires the following packages to support Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator:
• FMCL package (414)
• Mobile Extension (412)
• PCA (398)
• ISDN (145)
If the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator supports the CallPilot Message Waiting Indicator, the
following package must be licensed:
Premium Service and NMC (175, 219)
Avaya CS 1000 engineering for Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator - Web UI, Avaya 3100 MC - Client for BlackBerry, Avaya
3100 MC - Client for Nokia, Avaya 3100 MC - Client for Windows Mobile, and Avaya 3100
Mobile Communicator Gateway depend on the following Avaya CS 1000 components:
• Avaya CS 1000
30 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 31

Avaya CS 1000 engineering for Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
- Each user requires one Universal Extension (UEXT). Each UEXT supports the SIP
interface on the client. Configure the UEXT with the Fixed Mobile Convergence Line
(FMCL) subtype.
The FMCL subtype requires an Incremental Software Management (ISM)
independent of the Mobile Extension (MOBX) subtype.
- SIP Access Port license
• SIP Gateway
• SPS, using the Avaya CS 1000 NRS-SPS on the Linux-based NRS.
- Configure each Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway as a Dynamic Gateway
Endpoint with an endpoint name. Configure the Dynamic Gateway Endpoint with
authentication turned off.
- Each client requires the configuration of an NRS-SPS User Endpoint (UE). Clients
use the UE for user name and password information, not for SIP routing. Therefore,
the NRS-SPS must never match a destination number against the client UEs
(including the corresponding UEXT Target DN).
• SPS, using the Avaya CS 1000 Release 6.0 NRS
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway must be configured to use proxy mode
when registering to this server.
The Direct Inward Dial (DID) number for the Dial in Service DN terminates on the Avaya 3100
Mobile Communicator Gateway.
Configure the Avaya CS 1000 with a mobility prefix to support the client. The UEXT target DN
uses the mobility prefix as a prefix to identify mobile users. The Mobility Prefix is the Local
Exchange code (NXX) that directs the call to the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator within the
desired dialing plan. The Mobility Prefix is a unique digit sequence that does not conflict with
the existing Avaya CS 1000 Universal Dialing Plan (UDP), Coordinated Dialing Plan (CDP),
and routing configuration.
The Multiple Access Directory Number (MADN) is a DN that appears on multiple terminal
numbers (TN). The Multiple Appearance Directory Number Redirection Prime (MARP) is a
designation that is put on one of the TNs to identify that specific features apply to the DN that is
on multiple TNs should be configured for the group on the TN that is the MARP. For more
information, see Avaya Communication Server 1000 Features and Services Fundamentals,
NN43001-106.
The Avaya CS 1000 NRS-SPS supports the Source Based Routing (SBR) feature. SBR
ensures that, for all users of an Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway, the CLID NCOS
and dial plan they see on their mobile phone is consistent with their desk phone. The SPS
routes all Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator call attempts to the user's home call server so
that those features configured on the home call server can be applied to the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator call. For information about Source Based Routing (SBR), see
Avaya CS 1000
Source Based Routing on page 29.
Deployment Guide October 2010 31
Page 32

Interworking requirements with CS 1000
Figure 5: Client with Avaya CS 1000 and UDP on page 32 shows an example of clients using
Avaya CS 1000 and UDP.
Figure 5: Client with Avaya CS 1000 and UDP
Figure 6: Client with Avaya CS 1000 and CDP on page 32 shows an example of clients using
Avaya CS 1000 with CDP.
Figure 6: Client with Avaya CS 1000 and CDP
The UEXT configuration requirements are shown in the following table.
32 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 33

Avaya CS 1000 engineering for Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
Table 3: UEXT configuration parameters
Paramete
r
Subtype UEXT subtype; must be
primary
DN
target DN Extends the user's
Description UDP example CDP example
FMCL FMCL
FMCL
On key 0; this
determines the user's
published addresses for
both private electronic
switched network (ESN)
and public direct inward
dial (DID).
incoming calls to mobile
clients that are
accessible trough the
SIP domain
5335 contributes to an
ESN of 3435335 and a
DID of +16139615335
65553435335
where 555 is the Mobility
prefix
5335 contributes to a DN
of 3435335 and a DID of
+16139615335
888885335
where 88888 is the
Mobility prefix
On the NRS-SPS, configure the UE attributes as described in Table 4: User Endpoint
attributes on page 33.
For more information about UEXTs, see Avaya Communication Server 1000 Features and
Services Fundamentals – Book 6 of 6, NN43001-106-B6.
Table 4: User Endpoint attributes
Parameter Description Example
User name User’s Electronic Switched Network (ESN)
number
Tandem gateway
endpoint name
L0 DN Based on the user’s directory number (DN).
Endpoint name. Do not configure this
parameter
Cannot match anything in the Coordinated
Dialing Plan or unqualified dialing plan. This
cannot match because the only rule needed
on the NRS for routing Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator calls is the rule setup to route
any number with the mobility prefix to the
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
Gateway. All calls (service DN and UEXT
calls) destined for the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway must have the
mobility prefix and use that rule. If the user
endpoint had a DN that matched something
else in the dial plan it would conflict with the
mobility prefix routing rule or the basic
3435335
53435335
Deployment Guide October 2010 33
Page 34

Interworking requirements with CS 1000
Parameter Description Example
dialplan. Can be the last digit of the mobility
prefix with the User’s ESN DN.
L1 DN prefix not required
Authentication
enabled
Authentication
password
Determines if Authentication is required. Authentication on
The password for authentication xxxxxxxx
For information about SIP Gateway configuration, see IP Peer Networking Installation and
Commissioning, NN43001-313.
SIP Trunk configuration
You must configure the communication server SIP trunk that receives Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway calls, on behalf of mobile client users, to ESN5. You must configure
all associated Virtual trunks to WNK/WNK. The mobile client requires these settings so that
calls to the Public Network display the correct Calling Line ID (CLID) and have the same
Network Class of Service (NCOS) as a call from the associated communication server
telephone.
The output for the WNK/WNK Virtual Trunk, from Element Manager or a terminal window, looks
like this:
DES IPTIE
TN 081 0 00 02 VIRTUAL
TYPE IPTI
CDEN 8D
CUST 0
XTRK VTRK
ZONE 000
TRK ANLG
NCOS 0 RTMB 10 3
CHID 3
TGAR 0
STRI/STRO WNK WNK
SUPN YES
AST NO
IAPG 0 *
CLS UNR DIP WTA LPR APN THFD XREP
P10 NTC MID
TKID *
AACR NO
Important:
All of the SIP Virtual Trunks must be configured to WNK WNK.
The output for the ESN5 Route Data Block, from Element Manager or a terminal window, looks
like this:
34 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 35

Device Handoff configuration
TYPE RDB
CUST 00
DMOD
ROUT 10
DES IPROUTE
TKTP TIE
...
VTRK YES
ZONE 100
PCID SIP
...
ANTK
SIGO ESN5
STYP SDAT
Important:
If the Route Data Block (RDB) already has associated Virtual Trunks and is configured to
SIGO STD, you must remove all Virtual Trunks before you can change the RDB to ESN5.
Device Handoff configuration
Device handoff permits the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator user to hand off an established
call between the mobile phone and the desk telephone. The desk telephone must be configured
with a handoff key. Device handoff can be used only when the desk telephone and the Universal
Extension (UEXT) share the same primary DN in a Single Call Ringing (SCR) configuration.
Device handoff is not supported when the desk telephone and Avaya 3100 MC - Client user
are in a Multiple Call Ringing (MCR) arrangement. In this situation, the user must transfer the
call between the appearances.
Device handoff requires the configuration of the handoff key on the desktop telephone. Device
handoff is supported on any Avaya CS 1000 telephone that supports the configuration of fixed
feature keys. These telephones include the Avaya IP Deskphones (with Unified Network IP
Stimulus Protocol [UNIStim] firmware), the IP Softphone 2050, and Time Division Multiplex
(TDM) telephones.
On the mobile phone, there is no privacy protection if the UEXT does not have Station Control
Password (SCPW) configured. For desk telephones (even with SCPW), there is no privacy
protection if the desk telephone has Privacy Override Allowed (CLS POA) or if the desk
telephone is an analog telephone (500- or 2500-type telephone).
For SCPW privacy protection on the mobile phone, the system administrator must configure
the SCPQ length under LD 15 CDB FFC_DATA SCPL, and the SPQ on the UEXT under LD
11 SCPW prompt.
In addition, the following configuration requirements must be met:
• FMCL and Mobile X (MOBX) cannot coexist with same DN.
• the DN can only have one of the following UEXT types: SIP3, SIPN, FMCL.
Deployment Guide October 2010 35
Page 36

Interworking requirements with CS 1000
For more information, see Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator and Avaya Communication
Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide, NN49000-315 and Avaya Communication Server
1000 Features and Services Fundamentals, NN43001-106.
Avaya CS 1000 system redundancy
The clients support a high availability configuration for improved redundancy and failover.
Configure the client with primary and secondary proxy addresses that refer to different NRSSPSs. The clients use an options heartbeat to determine proxy availability. You can configure
the heartbeat time.
The clients also support existing SIP redundancy mechanisms in both communication servers
within a SIP deployment.
Call Forward No Answer feature interactions
It can be necessary to increase the Call Forward No Answer (CFNA) timeout for mobile client
users. The UEXT extends all calls to the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway. The
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway then presents the incoming call to the Avaya 3100
MC - Client over the cellular data channel of the Avaya 3100 MC - Client (using HTTP/HTTPS).
It can take a few seconds for the data transmission to reach the client, depending on the current
state of the mobile client. If the CFNA timeout is too short, users do not have reasonable time to
(potentially) log on and answer the call before the call server invokes CFNA and sends the call
to the CFNA destination.
To increase the CFNA timeout, configure the CS 1000 using LD 15 and LD 11.
LD 15 configures the CFN0, CFN1, and CFN2 indexes:
LD 15
REQ: chg
TYPE: rdr
TYPE RDR_DATA
CUST 0
OPT
FNAD
FNAT
FNAL
CFTA
CCFWDN
CFN0
CFN1 6
CFN2
DFN0
DFN1
DFN2
MDID
NDID
36 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 37

MWFB
TRCL
CRTOD
CRDAY
CRHOL
LD 11 configures the number of ringing cycles for CFNA. Configure the CFN index that
corresponds to the RCO entry configured in LD 15 (for example, RCO 1 uses CFN 1).
LD 11
REQ: chg
TYPE: 1140
TN 100 0 8 23
ECHG yes
ITEM rco 1
ITEM
HNT FNA
HNT FNA
Avaya CS 1000 capacity requirements
An Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator implementation requires the CS 1000 system to include
the appropriate number of Public Service Telephone Network (PSTN) connections (for
example, Primary Rate Interface [PRI] or digital trunk interface [DTI] trunks), SIP Access Ports,
and UEXTs.
Avaya CS 1000 capacity requirements
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator licenses include one SIP Access Port per client license.
For deployments with unusual trunking requirements, the number of SIP Access Ports and
PSTN trunks must be calculated as described below.
The number of configured users and the required Centi-Call Seconds (CCS) per User
determine the required number of PSTN connections and trunks. The CCS per User represents
the amount of time a circuit is occupied by each user in 100 seconds (for example, 6 CCS per
user means each user is busy 600 seconds during an hour). Choose the CCS per User value
based on the typical call load requirements. A value of 6 CCS per User represents normal
users; heavier users have progressively higher values. For example, call center telephones
normally have CCS per User values of 33.
You can use one of the two following methods to calculate the PSTN trunks and SIP Access
Ports:
•
Trunk calculation: Method 1 on page 38
• Trunk calculation: Method 2 on page 39
To calculate the number of UEXTs required, see UEXT calculations on page 42.
For more information about Avaya CS 1000 capacity, see Avaya Communication Server 1000E
Planning and Engineering, NN43041-220.
Deployment Guide October 2010 37
Page 38

Interworking requirements with CS 1000
Trunk calculation: Method 1
Follow these steps:
1. Add the number of client users.
2. Locate the resulting number in the Number of Users column in Table 5: Poisson
trunk table on page 38.
3. Select the appropriate PSTN and SIP Access Port parameters based on the
required CCS per Users.
Table 5: Poisson trunk table on page 38 uses a Poisson value of P.01, which represents 1
percent blocking.
Table 5: Poisson trunk table
Number of
users
6
12
18
24
50
75
100
Parameter Up to 6
CCS per
User
PSTN 5 6 6 6
SIP Access Port 10 12 12 12
PSTN 7 10 12 12
SIP Access Port 14 20 24 24
PSTN 9 13 18 18
SIP Access Port 18 26 36 36
PSTN 10 16 22 24
SIP Access Port 20 32 44 48
PSTN 17 28 38 48
SIP Access Port 34 56 76 96
PSTN 22 38 53 68
SIP Access Port 44 76 106 136
PSTN 28 48 68 87
SIP Access Port 56 96 136 174
Up to 12
CCS per
User
Up to 18
CCS per
User
Up to 24
CCS per
User
PSTN 38 68 97 125
150
200
38 Deployment Guide October 2010
SIP Access Port 76 136 194 250
PSTN 48 87 125 162
SIP Access Port 96 174 250 324
Page 39

Trunk calculation: Method 2
Number of
users
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
Parameter Up to 6
CCS per
User
PSTN 68 125 180 238
SIP Access Port 136 250 360 476
PSTN 82 162 238 317
SIP Access Port 164 324 476 634
PSTN 106 198 297 396
SIP Access Port 212 396 594 792
PSTN 125 238 356 475
SIP Access Port 250 476 712 950
PSTN 144 277 416 554
SIP Access Port 288 554 832 1108
PSTN 162 317 475 633
SIP Access Port 324 634 950 1266
PSTN 180 356 534 712
SIP Access Port 360 712 1068 1424
Up to 12
CCS per
User
Up to 18
CCS per
User
Up to 24
CCS per
User
PSTN 198 396 594 792
1000
SIP Access Port 396 792 1188 1584
Example
In a system with 100 users and 6 CCS per User, use Table 5: Poisson trunk table on page 38 to
locate 100 in the Number of Users column. Use the Up to 6 CCS per User column to find the
following parameters:
• PSTN = 28
• SIP Access Port = 56
Trunk calculation: Method 2
Follow these steps:
1. To determine the number of PSTN trunks required, add the number of clients to
obtain the total number of users.
2. Multiply the total number of users by the desired CCS per User number to obtain a
CCS value.
Deployment Guide October 2010 39
Page 40

Interworking requirements with CS 1000
3. Use Table 6: Trunk traffic Poisson 1 percent blocking on page 40 to find the CCS
value and obtain the number of PSTN trunks (in the cell to the left of the CCS
number). If the CCS value is between two values in the trunks column, choose the
higher number of trunks. For trunk traffic greater than 6068 CCS, allow 30.34 CCS
per trunk.
4. Multiply the number of PSTN trunks by two to obtain the number of SIP Access
Ports required.
Table 6: Trunk traffic Poisson 1 percent blocking
Trunks CCS Trunks CCS Trunks CCS Trunks CCS
1 0.4 51 1291 101 2847 151 4460
2 5.4 52 1322 102 2879 152 4492
3 15.7 53 1352 103 2910 153 4525
4 29.6 54 1382 104 2942 154 4557
5 46.1 55 1412 105 2974 155 4590
6 64 56 1443 106 3006 156 4622
7 84 57 1473 107 3038 157 4655
8 105 58 1504 108 3070 158 4686
9 126 59 1534 109 3102 159 4721
10 149 60 1565 110 3135 160 4754
11 172 61 1595 111 3166 161 4786
12 195 62 1626 112 3198 162 4819
13 220 63 1657 113 3230 163 4851
14 244 64 1687 114 3262 164 4884
15 269 65 1718 115 3294 165 4917
16 294 66 1749 116 3326 166 4549
17 320 67 1780 117 3359 167 4982
18 346 68 1811 118 3391 168 5015
19 373 69 1842 119 3424 169 5048
20 399 70 1873 120 3456 170 5081
21 426 71 1904 121 3488 171 5114
22 453 72 1935 122 3520 172 5146
23 480 73 1966 123 3552 173 5179
24 507 74 1997 124 3594 174 5212
40 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 41

Trunk calculation: Method 2
Trunks CCS Trunks CCS Trunks CCS Trunks CCS
25 535 75 2028 125 3616 175 5245
26 562 76 2059 126 3648 176 5277
27 590 77 2091 127 3681 177 5310
28 618 78 2122 128 3713 178 5343
29 647 79 2153 129 3746 179 5376
30 675 80 2184 130 3778 180 5409
31 703 81 2215 131 3810 181 5442
32 732 82 2247 132 3843 182 5475
33 760 83 2278 133 3875 183 5508
34 789 84 2310 134 3907 184 5541
35 818 85 2341 135 3939 185 5574
36 847 86 2373 136 3972 186 5606
37 876 87 2404 137 4004 187 5639
38 905 88 2436 138 4037 188 5672
39 935 89 2467 139 4070 189 5705
40 964 90 2499 140 4102 19 5738
41 993 91 2530 141 4134 191 5771
42 1023 92 2563 142 4167 192 5804
43 1052 93 2594 143 4199 193 5837
44 1082 94 2625 144 4231 194 5871
45 1112 95 2657 145 4264 195 5904
46 1142 96 2689 146 4297 196 5937
47 1171 97 2721 147 4329 197 5969
48 1201 98 2752 148 4362 198 6002
49 1231 99 2784 149 4395 199 6035
50 1261 100 2816 150 4427 200 6068
Example
In a system with 100 users and 6 CCS per User, the number of CCS required is 600 (100 users
multiplied by 6 CCS per User). Locate 600 CCS in Table 6: Trunk traffic Poisson 1 percent
blocking on page 40.
The entry in the table shows the number of PSTN trunks is between 27 and 28 (between 590
and 618 CCS). Therefore, choose 28 as the number of PSTN trunks.
Deployment Guide October 2010 41
Page 42

Interworking requirements with CS 1000
The number of SIP Access Ports is the number of PSTN trunks multiplied by 2, which is
28 x 2 = 56.
UEXT calculations
You require one UEXT for each Avaya 3100 MC - Client user.
Avaya CS 1000 and supported Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator features
The following table describes the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator call features.
Table 7: Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator call features
Avaya
CS 1000
Mobile
Extension
Single Enterprise Number Identity (CDP, UDP, DID) √ √ √
Enterprise CLID for Outbound Calls from Mobile √ √ √
Access to Enterprise Dial Plan from Cellular Network √ √ √
Enterprise Calling Restrictions (NCOS) √ √ √
Call Forward Support on Call Server (CFB, CFIC,
hunting)
Ring Again (against mobile) √ √ √
Busy Lamp Indication on Attendant Console √ √ √
Call Detail Recording (CDR) √ √ √
Busy State (Active Call on Mobile appears on other
line appearances and OCS presence as "on the
phone" for mobile calls)
Device Handoff—Move active call from mobile to desk
phone - Move active call from desk phone to mobile
√ √ √
√ √ √
√ √ √
Avaya
3100 MC -
Web UI
Avaya
3100 MC -
Client
Single Enterprise Voicemail Mailbox √ √ √
Enterprise Voicemail Enforcement √ √ √
Music On Hold √ √ √
42 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 43

Avaya CS 1000 and supported Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator features
Avaya
CS 1000
Mobile
Extension
Support for any phone (mobile, home phone, other) √ √
Mid Call Features—Hold, Retrieve, Consultation Call,
Transfer, Conference
Client User Interface For Mobile Features X √ √
Enterprise Voicemail MWI
Advanced Call Control—Direct Outbound calls from
mobile via the enterprise voice network
Native Call Intercept—Send calls made from any
application on the mobile via the enterprise voice
network
Using
DTMF
Using
thirdparty
applica-
tion
Carrier
support
required
NA X √
Avaya
3100 MC -
Web UI
Using
DTMF
√ √
X √
Avaya
3100 MC -
Client
Requires
installed
client
√
Advanced Call Control—Call Me First calls via the
enterprise voice network
Advanced Call Control—Dynamically redirect
incoming calls to any phone number
Advanced Call Control—User configurable time of
day call routing for inbound calls
Support for Multiple SIM cards X √ √
Corporate Directory Search X √ √
Presence/IM Support X X √
Enterprise Call Logs X X √
Instant Conferencing (Invite a list of participants
defined using a user interface on the client)
Access to Local Directory on Mobile NA X √
Configurable Emergency Number Support via
Cellular network
Customizable voice prompts NA NA √
Integrated with Avaya CS 1000—No additional
hardware required
X √ √
X X √
X √ X
X X √
NA X √
COTS
√
platform
required
COTS
platform
required
Deployment Guide October 2010 43
Page 44

Interworking requirements with CS 1000
Call Detail Recording
The mobile clients support Call Detail Recording (CDR) for all calls initiated or accepted by the
mobile clients.
Interpret the CDR records according to the type of call made or received by the mobile clients.
Direct outbound call
When a user makes an outgoing call, the mobile client user's home Avaya CS 1000 generates
two CDR records.
• The first CDR record provides details of the call from the mobile phone to the service DN.
In this record, the originator is the mobile phone number and destination is the service DN.
• The second CDR record provides details of the outgoing call to the called party. In this
record, the originator is the username of the mobile client user and the destination is the
destination number dialed by the user.
Call-Me-First outbound call
When the user makes a Call-Me-First outbound call, the mobile client user's home Avaya CS
1000 generates two CDR records.
• The first CDR record provides details of the call from the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway to the mobile phone. In this record, the originator is the username
of the mobile client and the destination number is the mobile phone number.
• The second CDR record provides details of the outgoing call from the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway to the called party. In this record, the originator is the username of
the mobile client user and the destination is the destination number dialed by the user.
Incoming call
For incoming calls, the Universal Extension (UEXT) on the home CS 1000 extends incoming
calls to the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway (and eventually to the mobile client).
For each incoming call, the UEXT merges two calls: the incoming call to the DN on the Avaya
CS 1000 , and then the outgoing extended call to the mobile phone. Incoming calls to the
44 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 45

Incoming call
mobile client that the user answers on the mobile phone generate four CDR records on the
home Avaya CS 1000 .
• The first CDR record provides details of the incoming call to the Multiple Appearance DN
(MADN). In this record, the originator is the caller and destination is the multiple
appearance DN where the UEXT is configured.
• The second CDR record provides the details of the UEXT extended call to the Avaya 3100
Mobile Communicator Gateway (the target DN of the UEXT). In this record, the originator
is the MADN number of the UEXT, and the destination is the UEXT target DN that is
extending the call to the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway.
• The third CDR record (generated after the UEXT merges the calls) provides details of the
originating and terminating parties in the call.
• The fourth CDR record (generated after the user elects to answer the call on their mobile
phone) provides the details of the outgoing call from the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway to the mobile phone. In this record, the originator is the username
of the mobile client, and the destination is the mobile number of the mobile client user.
Deployment Guide October 2010 45
Page 46

Interworking requirements with CS 1000
46 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 47

Chapter 7: Deployment planning
This section describes the planning required to deploy the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator with the
Enterprise Call Server (ECS).
For information about the planning aspects related to the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator and ECS,
see Planning on page 13 and Engineering on page 23, which cover the following topics:
• Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator - Client (Avaya 3100 MC - Client) deployment considerations
• Dialing plans and telephone numbers
• Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator high availability support
• Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator port tables
• Avaya CS 1000 deployment considerations
Navigation
Licensing requirements on page 48
•
•
Avaya 3100 MC - Client and Avaya 3100 MC - Web UI licenses on page 48
• Avaya CS 1000 SIP Gateway CLID Parameters configuration on page 49
• Mobility prefix on page 52
• Data access planning on page 53
• Service DN on page 53
•
Universal Extensions on page 54
• Caller ID table on page 54
Deployment Guide October 2010 47
Page 48

Deployment planning
Licensing requirements
Avaya Communication Server 1000 licensing requirements:
• Requires the Avaya Communication Server 1000 Release and corresponding Linux
Baseed NRS
• Uses SIP Access Port Licenses for Avaya CS 1000 SIP infrastructure support
• Avaya CS 1000 requires 1 Universal Extension (UEXT) for each Avaya 3100 MC - Client
user. The UEXT is configured with the Fixed Mobile Convergence Line (FMCL) subtype.
Avaya Communication Server 2100 licensing requirements:
• Requires Avaya Communication Server 2100 Release SE 11
• Uses SIP Access Port Licenses for Avaya CS 1000 SIP infrastructure support
Avaya 3100 MC - Client licensing requirements
• Each Avaya 3100 MC - Client requires a license.
• Each license key can only be used once per user.
• The Avaya 3100 MC - Client licenses are installed on the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway.
The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway allocates the license on a first come, first
served basis as the Avaya 3100 MC - Client registers with the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway.
• There is no requirement to distribute licenses to each end user.
• The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway administrator can revoke licenses on a
per user basis, if necessary, to reclaim user licenses.
Avaya 3100 MC - Client and Avaya 3100 MC - Web UI licenses
The clients and Avaya 3100 MC - Web UI require the following licenses:
• On the Enterprise Call Server (ECS)
- a SIP Access Port License (on the Signaling Server) for SIP infrastructure support
- one Universal Extension (UEXT) for each client
• One client license key for each user
The clients require the following licenses with the Avaya CS 1000:
48 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 49

Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway licenses
The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway manages the client license keys using site
licenses. For more information about Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway licensing,
see Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway licenses on page 49.
A device which connects using the Avaya 3100 MC - Client or the Avaya 3100 MC - Web UI
only consumes one license. The user cannot be connected through the Avaya 3100 MC - Client
and the Avaya 3100 MC - Web UI at the same time. Logging in on one interface forces the
other interface to terminate.
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway licenses
The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway requires a site license that contains the
individual license keys for each client user. The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway
allocates the license keys, upon request, to the client.
On the Avaya CS 1000, the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway uses one SIP Access
Port license on the Signaling Server. Each client requires one UEXT.
The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway requires internet access to
www199.nortel.com (using port 8008) to validate the client licenses on the clients.
During installation, the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway stores the site license file.
The site license contains the licenses for the clients. The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
Gateway does not distribute the licenses to the clients.
When a user accesses the client application, the client software contacts the Avaya 3100
Mobile Communicator Gateway. The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway allocates
licenses on demand until the maximum number of licenses are allocated. The license returns to
the pool when the user logs off the client.
The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway administrator can revoke licenses from
individual users to reclaim the licenses.
Avaya CS 1000 SIP Gateway CLID Parameters configuration
The SIP Gateway CLID parameters are used to adjust the format of telephone numbers for
incoming call appearances. For Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator, these settings impact the
format of numbers that appear on the incoming call popup on the Avaya 3100 MC - Client 3100
client.
Deployment Guide October 2010 49
Page 50

Deployment planning
Figure 7: SIP GW CLID Parameters
For all public calls (subscriber [for example, NXX in North America], national [for example, NPA
in North America], or international) E.164 fully qualified numbers are used to represent the
caller. This is made possible through the use of the following parameters:
• Country Code
• Area Code
50 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 51

Avaya CS 1000 SIP Gateway CLID Parameters configuration
• Subscriber/Number of Digits to strip
• Subscriber/Prefix to insert
• National/Number of Digits to strip
• National/Prefix to insert
The E.164 format of subscriber calls (for example, NXX in North America) is:
+<countrycode><area code><subscriber number>.
The parameters Subscriber/Number of digits to strip and prefix to insert are used to modify the
format of subscriber numbers presented from the PSTN due to region specific requirements.
The E.164 format of national calls (for example, NPA in North America) is:
+<countrycode><national number>.
The parameters National/Number of digits to strip and prefix to insert are used to modify the
format of national numbers presented from the PSTN due to region specific requirements.
Parameter: Country Code
This parameter defines the country code to be used in CLID generation.
Parameter: Area Code
This parameter defines the area code to be used in CLID generation.
Parameter: Subscriber/Number of Digits to strip
For incoming subscriber (NXX) calls this parameter defines the number of digits to strip from
the incoming phone number prior to conversion to E.164 format.
Parameter: Subscriber/Prefix to insert
For incoming subscriber (NXX) calls this parameter defines the prefix to insert after stripping
any digits necessary from the incoming phone number prior to conversion to E.164 format.
Parameter: National/Number of Digits to strip
For incoming national (NPA) calls this parameter defines the number of digits to strip from the
incoming phone number prior to conversion to E.164 format.
Deployment Guide October 2010 51
Page 52

Deployment planning
Parameter: National / Prefix to insert
For incoming national (NPA) calls this parameter defines the prefix to insert after stripping any
digits necessary from the incoming phone number prior to conversion to E.164 format.
Mobility prefix
Before configuring and deploying the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator solution, the
administrator determines the mobility prefixfor the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway.
The mobility prefix is a digit prefix used to prefix to all calls that will be sent to the Avaya 3100
Mobile Communicator Gateway. This includes the target DN number of all UEXTs for Avaya
3100 Mobile Communicator users as well as the service DN calls from Avaya 3100 MC - Client
clients. The mobility prefix provides a unique digit sequence within the SIP domain to route
calls to a specific Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway that does not conflict with the
existing dial plan and routing configuration for CDP and UDP numbers. If the UEXT target DN
did not have this prefix to distinguish Avaya 3100 MC - Client calls, the UEXT extended SIP
calls would loop back to the UEXT.
Mobility prefixes have the following requirements:
• One mobility prefix is required per gateway.
• On the call server you must configure
- The dial plan to send all calls with this prefix to the NRS.
- All UEXT’s for Avaya 3100 MC - Client users must have a target DN with the prefix
of the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway to which their Avaya 3100 MC Client is registered.
- The incoming service DN call must have its digits manipulated so that the PSTN
number dialed for the service DN is mapped to a number prefixed by the mobility
prefix. This mapping will trigger the NRS to send this call to the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway3100 and the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway
will strip this prefix as with any other mobility prefix prefixed call to reveal the service
DN configured on the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway.
• The NRS must have a routing rule to send all calls with this prefix to the Avaya 3100
Mobile Communicator Gateway.
• The mobility prefix is configured on the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway in
the User Prefix for Call Termination field.
52 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 53

Data access planning
This section describes things to consider when planning data access.
Avaya CS 1000 data access considerations on page 53
Avaya CS 1000 data access considerations
The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway requires data access to the TLAN of the
Avaya CS 1000. The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway uses the Avaya CS 1000
SPS as the SIP Signaling Proxy. The media for all calls to and from Avaya 3100 MC - Clients is
anchored on the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway. The Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway will accept or transmit RTP to any IP endpoint within the enterprise
(for example, Media Cards, Other SIP clients, IP sets).
Data access planning
Example
If an UNISTIM set calls a user answering through the Avaya 3100 MC - Client on the mobile
phone the RTP for the active call will be between the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
Gateway and IP set directly and then forwarded from the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
Gateway to the Avaya CS 1000 media gateway (for the trunk call to the mobile phone)
Careful consideration is required based on the data network and security requirements of the
Enterprise to allow the public internet traffic to reach the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
Gateway from the clients while at the same time giving the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
Gateway access to the TLAN of the Avaya CS 1000 for SIP and RTP.
Service DN
The Service DN is a PSTN DID DN that is downloaded to the Mobile Client from the Avaya
3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway when it registers to the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway for the first time. When the Mobile Client originates a direct outbound
call it dials the Service DN and is connected to the Avaya CS 1000. The Avaya CS 1000 is
configured to translate the Service DN to the format <mobility prefix><service DN>. The Avaya
CS 1000 then maps the call to the SPS/NRS for resolution. The SPS/NRS then maps the call to
the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway based on the routing rule built to resolve all
dialing strings preceded by the mobility prefix.
In the following example, 888 is the mobility prefix and 5066404681 is the service Directory
Number (DN).
Deployment Guide October 2010 53
Page 54

Deployment planning
Example: sip:8885066404681@avaya.com
Configure the mobility prefix on the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway configuration
tab as the incoming prefix for call termination. Configure the Service DN field on the Avaya
3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway configuration with the service DN.
Universal Extensions
An Avaya CS 1000 Universal Extension (UEXT) represents each mobile client instance.
The Primary DN of the UEXT determines the user’s published addresses: both private
electronic serial number (ESN) and public direct inward dialing DID (for example, Primary DN:
4680 contributes to the ESN address 8474680 and DID address +15066404680).
The mobility prefix is a prefix to all mobile user identities on the UEXT target DN. The mobility
prefix provides a digit sequence that is unique within the SIP domain to identify a mobile client
that does not conflict with the existing dial plan and routing configuration for their CDP and
UDP numbers.
The Target DN of the UEXT extends the user’s incoming calls to mobile clients that are
accessible through SIP domain. A typical setup would be AC1 + (mobility prefix) + the user’s
ESN number (for example, Target DN: 65553435335).
Important:
It can be necessary to increase the Forward No Answer (FNA) timeout for mobile client
users. The UEXT extends all calls to the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway. The
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway then presents the incoming call to the Avaya
3100 MC - Client clients over the cellular data channel of the Avaya 3100 MC - Client (using
HTTP or HTTPS).
It can take a few seconds for the data transmission to reach the client depending on the
current state of the mobile phone. If the FNA timeout is too short users do not have
reasonable time to (potentially log on) and answer the call before the call server invokes
FNA and sends the call to the FNA destination.
Caller ID table
All Avaya CS 1000 telephones use the Caller ID table. The Caller ID table is required for the
Avaya 3100 MC - Client to correctly build the Caller ID (CLID) for both Private network and
Public network calls from a number or extension.
Outgoing SIP calls from the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway on behalf of the
mobile client use the CLID table configured against the Multiple Appearance Directory Number
54 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 55

Caller ID table
Redirection Prime (MARP) TN in the Multiple Access Directory Number (MADN) group of the
Avaya 3100 MC - Client user.
Deployment Guide October 2010 55
Page 56

Deployment planning
56 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 57

Chapter 8: Deployment work flow
This section describes the order in which to install the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator system and then
to interwork the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator with the Avaya Communication Server 1000 (Avaya
CS 1000).
Deploying the systems task flow
Deploying the systems requires the following procedures.
Figure 8: Deploying the system task flow
Task flow navigation
• Deployment prerequisites on page 59
Deployment Guide October 2010 57
Page 58

Deployment work flow
• Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway installation on page 63
• Solution commissioning on page 92
• Validate deployment on page 129
58 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 59

Chapter 9: Deployment prerequisites
This section describes the prerequisites for Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator and Avaya Communication
Server 1000 (Avaya CS 1000) integration.
• Establishing the Avaya CS 1000 and Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator system baseline on
page 59
• Checking the Avaya CS 1000 release from Element Manager on page 61
• Checking the Avaya CS 1000 release from the command line on page 62
Establishing the Avaya CS 1000 and Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator system baseline
To successfully integrate voice services, you must first establish the system baseline for the
Avaya CS 1000 and Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator systems so that the systems are
configured and working in a stand-alone environment. Use the following table to complete
system baselines before integration.
Task Reference Comments
Avaya CS 1000
The Network Numbering
Plan is implemented.
Avaya CS 1000 software is
Release 5.5. or higher
Basic installation, setup, and
configuration of the Call
Server components are
complete.
Dialing Plans: Description,
NN43001-283
Avaya Communication
Server 1000M and Meridian
1: Large System Installation
and Commissioning,
NN43021-310 Avaya
Communication Server
1000S: Installation and
Are you using a Unified
Dialing Plan (UDP) or a
Coordinated Dialing Plan
(CDP), or both?
To check the release level,
see Checking the Avaya CS
1000 release from Element
Manager on page 61 or
Checking the Avaya CS 1000
release from the command
line on page 62.
Deployment Guide October 2010 59
Page 60

Deployment prerequisites
Task Reference Comments
Configuration, 553-3031-210
Avaya Communication
Server 1000E: Installation
and Commissioning,
NN43041-310
The CS 1000 must have the
latest DEP List loaded.
The following Avaya CS
1000 packages are required:
• FMCL (414) to allow the
FMCL UEXTs for Avaya
3100 Mobile
Communicator
• Mobile Extension (412) to
support the UEXT
• PCA to configure UEXT
sets for mobile users
• ISDN (145) to configure
ISDN routes when ISDN
trunks are used
ISMs are required for SIP
access ports and FMCL
UEXTs.
If Call Pilot Message Waiting
Indication is required, the
Premium Service and NMS
packages (175 and 219) are
required.
Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Release
Notes, NN42030-404
(Updates through Product
Bulletins)
NRS SIP Proxy Server (SPS)
NRS SPS software is Avaya
CS 1000 Release 5.5.12.006
or higher.
SPS must have the latest SU
loaded
Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator
60 Deployment Guide October 2010
Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Release
Notes, NN42030-404
(Updates through Product
Bulletins)
Page 61

Task Reference Comments
Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator is Release
3.1.
If using BlackBerry devices
and the BlackBerry
Enterprise Server (BES), the
devices and BES must have
the BlackBerry Mobile Data
Service (MDS) enabled and
the devices must be able to
access the Fully Qualified
Domain Name (FQDN) or IP
address of the Avaya 3100
Mobile Communicator
Gateway.
If using mobile devices from
the cellular data network (no
BES), the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway
requires an internetaccessible FQDN and IP
address.
Checking the Avaya CS 1000 release from Element Manager
Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway
must be able to access the
Avaya CS 1000 TLAN
through the firewall.
Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway
license file available
Checking the Avaya CS 1000 release from Element Manager
Use this procedure to check the version of the CS 1000 using Element Manager.
1. Log on to Element Manager.
2. On the left navigation pane, select Home.
The Home System View page appears.
3. In the Call Server section, the software release is referred to as Release.
Deployment Guide October 2010 61
Page 62

Deployment prerequisites
Checking the Avaya CS 1000 release from the command line
Use this procedure to check the version of the CS 1000 using the command line.
1. Log in to the Signaling server or the Enterprise Common Manager server using the
nortel account.
2. Enter the following command
swVersionShow
The installed software applications and version numbers are displayed. For an
example, see the following figure.
Figure 9: swVersionShow example
62 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 63

Chapter 10: Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway
installation
This chapter contains the instructions for installing a new Mobile Communications Gateway 3100. For
information about the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator - Client (Avaya 3100 MC - Client) installation,
see Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Administration and Security, NN42030-600.
Important:
Use the server system console for installations and upgrades. Do not use a remote terminal.
Prerequisites to Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway installation workflow
• Planning and engineering must be completed as discussed in Planning on page 13 and
Engineering on page 23.
• Obtain a copy of Linux Platform Base and Applications Installation and Commissioning,
NN43001-315.
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway installation workflow
Figure 10: Installation workflow on page 64 shows the steps required to install the Avaya
3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway. After completing the installation workflow, you configure
the system security, configure the client services, install the clients, and back up the Avaya
3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway database. For more information, see Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Administration and Security, NN42030-600. After configuring the Avaya 3100
Mobile Communicator Gateway, you configure the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator to
interwork with the appropriate communication server, using the appropriate Solution
Integration Guide.
Deployment Guide October 2010 63
Page 64

Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway installation
Figure 10: Installation workflow
Result
Workflow navigation
• Preparation on page 65
•
Installation on page 72
• Commissioning on page 74
• Solution commissioning on page 92
Table 8: Complete installation times on page 64 shows the times for completing each of the
above workflows.
Table 8: Complete installation times
Workflow Time to complete task
Preparation 25 minutes per server
Installation 15 minutes per server
Commissioning 20 minutes
64 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 65

Solution commissioning 4 hours, plus 20 minutes per user
Preparation
This section describes the tasks required to prepare for the installation of the Avaya 3100
Mobile Communicator Gateway.
Important:
Use the server system console for installations and upgrades. Do not use a remote terminal.
Before you begin, review Appendix A: Installation worksheets and checklist on page 163 for
useful worksheets and a checklist.
Prerequisites
Preparation
Workflow Time to complete task
Obtain a license file for the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway.
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway preparation workflow
Figure 11: Preparation taskflow on page 66 shows the required procedures.
Deployment Guide October 2010 65
Page 66

Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway installation
Figure 11: Preparation taskflow
Preparation workflow navigation
• Installing the Linux base on page 67
• Verifying the Enterprise network on page 71
Table 9: Preparation times on page 66 shows the estimated times for completing
each of the above procedures.
Table 9: Preparation times
Workflow Time to complete task
Installing the Linux Base 20 minutes per server
Verifying the enterprise network 5 minutes per server
66 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 67

Installing the Linux base
For installation instructions for the Avaya CS 1000 Linux base, see Linux Platform Base and
Applications Installation and Commissioning, NN43001-315.
Important:
Carefully observe the labels for the network interfaces of the specific platforms.
During the Linux base installation for Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway, you make
two platform-specific configuration changes.
• Physical connection—Use only the eth1 physical network interface.
- HP COTS platform—The network interfaces can be labelled (0,1) or (1, 2). The lower
number is eth0 and the higher number is eth1.
- IBM 306M platform—The network interfaces are labelled backwards. Interfaces (0,
1) are eth1 and eth0 respectively.
Installing the Linux base
• IP addresses—During the Linux base installation, the software prompts you to enter the
TLAN and ELAN network interface IP addresses.
- Configure the ELAN network interface IP with an unused private IP address. The IP
standard reserves specific address ranges within Class A, Class B, and Class C for
use by private networks (intranets).
page 67 lists the reserved ranges of the IP address space.
- Configure the TLAN network interface IP to the same IP address as the Avaya 3100
Mobile Communicator Gateway and corresponding physical eth1 network interface.
Table 10: Reserved IP address ranges
Class
A 10.0.0.0 10.255.255.255
B 172.16.0.0 172.31.255.255
C 192.168.0.0 192.168.255.255
Important:
This procedure documents the installation of Avaya Linux base on a commercial off-theshelf (COTS) server with no previous Avaya Linux base installation.
Connect to the COTS server using a serial console or keyboard, video monitor, and mouse
(kvm).
Private starting address Private ending address
Table 10: Reserved IP address ranges on
Important:
Before installing the Linux base, read all of the documentation provided by the manufacturer
of the COTS server.
Deployment Guide October 2010 67
Page 68

Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway installation
1. Insert the Linux base bootable CD-ROM in the CD-ROM tray.
2. Reboot the server.
3. Choose the method of installation:
• To install using a serial console on COM1, type com1 at the boot prompt and
press Enter.
• To install using an attached keyboard, video monitor, and mouse, type kvm at
the boot prompt and press Enter.
Note: It is not required to attach a keyboard, video monitor and mouse (KVM) to
view output. A console-based installation will also provide output.
4. Type Y and press Enter.
5. The Format all partitions screen appears. Press Enter to continue.
6. At the prompt, select the type of configuration data you wish to use. Type 1 for
Normal installation and press Enter, and then press Enter again when prompted,
as shown in
7. The System Configuration screen appears as shown in . Press Enter to continue.
Figure 12: System configuration window
8. When prompted, in the Network configuration screen, enter the customer
information for ELAN IP address, ELAN gateway, ELAN netmask, hostname,
domain name, Machine TLAN IP address, TLAN gateway, Default gateway, and
TLAN netmask .
9. The System Console Redirection screen appears. Select the redirection option and
press Enter to continue.
Note: This screen appears only if you chose to install using an attached keyboard,
video monitor, and mouse.
10. In the Time zone selection screen type the appropriate region number at the prompt
and then press Enter to continue.
68 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 69

The Time zone selection for region screen appears.
Figure 13: Time zone selection window
11. At the prompt, in the Timezone Selection for Region screen, type the appropriate
time zone number and then press Enter to continue.
Installing the Linux base
12. In the Configuration Validation 1 screen, type Y for yes or N for no, and then press
Enter to confirm the customer information for Machine ELAN IP address, ELAN
Gateway , ELAN Netmask, Hostname, FQDN, Machine TLAN IP address, Default
TLAN Gateway, TLAN Netmask, and Timezone, as shown in
If you select N, edit the information as required and repeat step 10.
13. In the Network Time Protocol (NTP) Configuration screen, type Y or N to choose the
NTP transfer mode for the system. Type 1, 2, or 3 and then press Enter to indicate
the clock source function of the Linux system.
Note: NTP uses Message Digest Algorithm 5 (MD5) signatures to authenticate the
exchange of timestamps when operating in secure mode.
14. In the NTP Clock Source Configuration screen type E for an external clock source, or
I for an internal clock source.
Press Enter to continue.
15. At the prompt, type the machine TLAN IP address of the clock source server.
Press Enter to continue.
16. At the prompt, configure the primary DNS server IP address.
17. Type Y and press Enter to configure the Primary DNS server IP address.
OR Type N and press Enter if you do not want to configure the Primary DNS server
IP address.
Note 1: In this example we do not configure the Primary DNS server IP address. If
you choose Y you receive a prompt to provide the Primary DNS server IP address.
Deployment Guide October 2010 69
Page 70

Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway installation
Note 2: You can use Base Manager to modify the static lookup table for host names.
18. In the Configuration Validation 2 screen, type Y if the information is correct and press
Enter, as shown in the
Note: The CLI command hostconfig can be used to modify the static lookup table
for host names.
The Configuration Validation 2 screen appears with the correct information. Press
Enter to continue.
19. In the Date and Time Configuration screen, configure the date and time, as shown
in
Type Y to keep the date and time, and then press Enter. To change the date and
time, press N, make the required changes, and press Enter. The Date and Time
Configuration screen appears with the new date and time. Press Enter to continue.
20. In the Password Configuration screen, at the prompt, enter the root password.
21. Enter the sysadmin password.
22. Enter the nortel password.
23. Press Enter to continue. The Configuration File Backup screen appears.
24. From the Configuration File Backup screen, select an option to back up the
configuration data.
The naming convention for the Linux base backup archive is hostname-installyyyy.mm.dd.hh.MM.ss.tar.gz The name for the backup archive is automatically
generated and includes the key word install to indicate that the archive is generated
as part of the installation or upgrade procedure. For example, hp3-einstall-2008.09.04.18.54.47.tar.gz is a backup archive name where hp3-e is the host
name. The archive name begins with the short host name (not the FQDN) and the
key word install, and contains the following fields:
• yyyy - year
• mm - month
• dd - day
• hh - hour
• MM - minutes
• ss - seconds
Note: Avaya Linux base uses the CLI command sysbackup to back up system
data to external storage. You can choose to back up the data to a USB device or to
an SFTP server.
25. After you back up the configuration data, the Package Installation screen appears.
The Post System Configuration screen appears. The system automatically reboots
as a Linux server.
70 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 71

Verifying the Enterprise network
Install and configure on the enterprise network:
• Domain Name Server (DNS) (required)
• Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) server (optional)
Important:
Avaya recommends that you program the DNS with the IP addresses of the License Server,
the primary Enterprise Call Server (ECS), and the alternate ECS.
You should ensure that the DNS and LDAP server can be accessed from the Avaya 3100
Mobile Communicator Gateway.
1. Access the Admin shell for your DNS server.
Verifying the Enterprise network
2. To verify that DNS is functional, use the ping command and enter the fully qualified
domain name (FQDN) of a server on the network.
3. To verify communication with the LDAP server, use the ping command.
After the installation and commissioning is complete, you can verify that LDAP is
working by performing a Corporate Directory (Corp Dir) search from a client.
Job aid: Supported LDAP servers
You can configure the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway server to query a corporate
directory so that the mobile clients can use the Directory lookup feature on their devices.
The Directory lookup feature uses LDAP to perform the query on one of the following supported
directory servers:
• Active Directory/Exchange Server 2000 or 2003
• Avaya Common Network Directory (CND)—Telephony Manager (TM) 3.1 in Avaya CS
1000 includes CND.
For information about configuring LDAP parameters on the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
Gateway, see Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Administration and Security, NN42030-600.
Deployment Guide October 2010 71
Page 72

Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway installation
Installation
This section describes the software installation.
Important:
Use the server system console for installations and upgrades. Do not use a remote terminal.
Installation task flow
Figure 14: Installation taskflow on page 72 shows the required procedures.
Figure 14: Installation taskflow
Result
Installation workflow navigation
Installing the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway software on page 73
Table 8: Complete installation times on page 64 shows the times for completing each of the
above procedures.
72 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 73

Job aid: Admin shell access
Job aid: Admin shell access
Many of the maintenance procedures require that you access the admin shell and log on using
the nortel user account. You have two options for admin shell access:
• serial port connection
• Secure Shell (SSH)
For more information about accessing the admin shell, see Linux Platform Base and
Applications Installation and Commissioning, NN43001-315.
Installing the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway software
During the software installation, a number of prompts appear. You can either accept the default
value or enter a new value at each prompt.
Prerequisites
• You must be logged into the server as nortel. For more information, see
server command line as nortel on page 159.
• You must know the root password to perform the following procedure.
• You require a compact disc (CD) containing the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
software.
1. Insert the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway software CD into the CDROM drive of the host server.
2. Enter the following command:
appinstall
The installation script prompts you for the root password.
3. Enter the root password.
4. Read the software license agreement.
5. To agree to the license agreement, enter YES
Accessing the
The software installation proceeds. Messages appear to show installation progress.
After the installation completes, the configuration script starts automatically.
6. At the prompt for the ethernet address, select the card that corresponds to the IP
address of this Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway server.
Deployment Guide October 2010 73
Page 74

Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway installation
7. At the prompt for the mode, do one of the following:
• If the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway configuration is not
redundant, select Standalone mode.
• If the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway configuration is redundant,
select Active-Standby mode, and go to
8. For Active-Standby mode, at the prompt, enter the following information:
• Server name: the domain name (if defined) or the internal IP address of the
primary Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway. This value is the same
for both the primary and secondary Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
Gateway servers.
• Cluster name: this value is not currently in use. Use the default value.
• Partner IP address: the IP address of the other Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway server.
9. Select Finish to save the configuration.
10. Remove the CD.
11. For a redundant configuration, repeat this procedure on the other server.
8 on page 74.
Commissioning
This section describes the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway commissioning.
After completing the commissioning, you configure the system security, configure the client
services, install the clients, and back up the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway
database. For more information, see Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Administration and
Security, NN42030-600
After you configure the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator solution, you configure the Avaya
3100 Mobile Communicator to interwork with the appropriate communication server, using the
appropriate Solution Integration Guide.
Adding an Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway server
Add the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway using the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Web Administration Console.
74 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 75

Configuring the Gateway settings
Prerequisites
• The Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway software must be installed on the server.
• You must be logged into the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Web Administration
Console as administrator. For more information, see Logging on to the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Web Administration Console as an administrator.
• You are familiar with the configuration settings for the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
Gateway. For more information, see Table 11: Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
Gateway configuration settings on page 76.
• You are familiar with the Device Configuration settings for the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway. For more information, see
settings on page 84.
1. Click the System Configuration tab.
2. On the System Configuration page, select Gateway Actions >
Configure Gateway.
3. On the Configure Gateway page, configure the parameters.
Table 12: Device configuration
4. Click Save.
5. Click Close.
You receive a prompt to restart the server.
6. At the prompt to restart the gateway, click Yes.
The primary and secondary gateway servers restart. Secondary gateway
configuration comes from the data you enter for the primary gateway. Secondary
gateway configuration is automatic; there is no need to configure it separately.
7. Click the Device Configuration tab.
8. On the Device Configuration page, configure the parameters for devices.
9. Click Save.
Configuring the Gateway settings
Configure the Gateway settings to enable the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway to
interact with the network elements. In redundant Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
deployments, most of the Gateway settings are shared between the two servers.
Deployment Guide October 2010 75
Page 76

Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway installation
Prerequisites
You must be logged into the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Web Administration Console
as administrator. For more information, see Logging on to the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Web Administration Console as an administrator.
1. Click the System Configuration tab.
2. Click Gateway Actions > Configure Gateway.
3. Click Edit.
4. Modify the Gateway settings.
Important:
Secondary gateway configuration comes from the data you enter for the primary
gateway. Secondary gateway configuration is automatic; there is no need to
configure it separately.
5. Click Save.
6. Click Close.
You receive a prompt to restart the server.
7. To restart the system, and apply the updated gateway configuration, click Yes.
OR
To restart the system at a later time, click No. The updated Gateway settings are
applied when the system is restarted later.
In a redundant configuration, both the primary and secondary gateway servers
restart.
Important:
Avaya recommends that you restart the gateway.
Procedure job aid
Use the following table to help you understand the Gateway settings. Use this job aid for Avaya
CS 1000 installations only.
Table 11: Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway configuration settings
Field Description
Mobility Server
SIP Port Enter the SIP server port. The default value is 5060.
76 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 77

Procedure job aid
Field Description
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
Domain Enter the SIP registration domain defined on the
Enterprise Call Server (ECS).
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
Gateway name Enter the gateway identity defined on the ECS for the
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway.
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
Media Server Default Locale Select the media server default locale. The Avaya 3100
Mobile Communicator Gateway plays prompts to the
Avaya 3100 MC - Client or Web UI user in the language
that the individual user has configured. If that language
is not installed on the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
Gateway, the prompts play in the language specified in
this field.
For more information about prompts, see Audio prompt
administration.
Media Server Enter the address and port of the Instant Conferencing
Server. Format: <IP address l FQDN> :<port>
This parameter is unique to the local server.
Incoming Call Reliable Timer Specify the amount of time, in seconds, that the Avaya
3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway waits after it plays
the cellular voice mail avoidance prompt, while waiting
for the pound (#) key to be pressed, before the call
forwards to the Enterprise voice mail system.
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
Enable Cellular Voicemail
Avoidance
Enable Music on Hold Select Yes to enable the Music on Hold feature. The
Select Yes to route unanswered cell phone calls to the
enterprise voice mail system. Select No to route
unanswered cell phone calls to the cellular voice mail
system.
When call screening mode is disabled, this parameter
controls whether an unanswered, incoming call diverts
to the enterprise voice mail system or to the cellular
voice mail system.
Default: No
system must have an audio file installed containing the
music to be played to the caller when on hold. Select No
to disable the Music on Hold feature. Default: Yes
Primary ECS Address Enter the address and port of the primary ECS. Format:
<IP address l FQDN> :<port>
Deployment Guide October 2010 77
Page 78

Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway installation
Field Description
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
Secondary ECS Address Enter the address and port of the secondary ECS.
Format: <IP address l FQDN> :<port>
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
Device Access
HTTP Port Select the hypertext transport protocol (HTTP) port used
by clients to access the system and to download
software over the air. The valid range is 8080 to 8089;
the default is 8080. Select 0 to disable the port.
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
HTTPS Port Select the HTTP Secure (HTTPS) port used by clients
to access the system and to download software over the
air. The valid range is 8440 to 8449; the default is 8443.
Select 0 to disable the port.
Use HTTPS when a certificate infrastructure exists on
the clients and Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
Gateway.
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
HTTPS certificate password Enter the password used for the HTTPS certificate
transmitted by clients to the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway server. The default is nortel.
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
Dial Plan
User Prefix/Phone-context for
Call Origination
Mobility Prefix Enter the user name mobility prefix for call termination.
Dial-In Service DN Enter the Service Directory Number (DN) for client calls
Enter the user name prefix or phone context for call
origination. This prefix applies to calls originated by the
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway server and
to the calling address.
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
This prefix applies to calls received by the Avaya 3100
Mobile Communicator Gateway server and to the called
address.
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
that will arrive at the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
Gateway on the SIP network. This field is mandatory.
The Service DN allows Avaya 3100 MC - Client for
78 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 79

Field Description
BlackBerry, Avaya 3100 MC - Client for Windows
Mobile, and Avaya 3100 MC - Client for Nokia users to
place calls directly from their wireless devices to other
parties using the client's Direct Outbound call mode. The
PSTN numbers that are dialed by the mobile on the
PSTN are defined on the device configuration page.
When the call arrives at the enterprise the PSTN number
must be converted to an internal format for use on the
SIP network, routed by the NRS, and which will
eventually arrive at the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway.
Mobility Prefix: 888
Username 343XXXX
Password XXXXXXX
Outgoing Call Service DN +15066404681
The mobile phone will dial +15066404681 for direct
outbound calls. This PSTN number will be routed to the
enterprise as a DID number. When the number arrives
at the Enterprise we must manipulate the PSTN number
(+15066404681 to be routed on the SIP network.
Procedure job aid
Important:
If you have a mapping on the incoming trunk route on
the call server to map a PSTN service DN number:
+15066404681 to 8885066404681, you would
configure the service DN on the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway as 5066404681. In the case
where an enterprise has multiple service DN’s all
incoming PSTN service DN calls must map to the
single service DN number configured in this field. For
example: +1613132 4567 to 8885066404681.
Dialplan Conversion List For information about configuring this field, see
Configuring the dial plan conversion parameters on
page 81.
DTR
Initial port for DTR (27000-27499) Enter the first port in the range of ports used by the
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway server
Digital Tone Receiver (DTR) engine. A DTR recognizes
Dual Tone Multi-Frequency (DTMF). 1500 ports are
allotted for DTR.
The port must be an even number (for example, 27000).
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
Mid-Call Cellular Prefix Enter the prefix used by clients to invoke mid-call
features using DTMF. Permitted values include the
characters star (*) and pound (#), and the numerals 0 to
Deployment Guide October 2010 79
Page 80

Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway installation
Field Description
9, entered in any combination. The default value is *,
which needs to be changed only if it conflicts with other
network resources.
For example, if clients use * to access conference
features, then you must change the Mid-Call Cellular
Prefix to a different value such as # or #99.
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
LDAP
URL Enter the address and port of the Lightweight Directory
Access Protocol (LDAP) server that hosts the corporate
directory. Obtain this value from the directory
administrator. Format: ldap://<IP address l FQDN> :<port>
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
Search Base Enter the distinguished name of the search base object
(node) that defines the location in the directory from
which the LDAP search begins. Obtain this value from
the directory administrator.
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
LDAP Username Enter the user name required to gain access to the
LDAP server that hosts the corporate directory. Obtain
this value from the directory administrator.
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
Authorization Enter the authorization mechanism required to connect
to the LDAP server. The default value is simple, which
causes user names and passwords to be sent as clear
text.
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
Password Enter the password required to gain access to the LDAP
server that hosts the corporate directory. Obtain this
value from the directory administrator.
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
LDAP attribute tag that contains
the user ID
LDAP attribute tag that contains
the user's first name
Enter the tag for the User ID attribute on the LDAP
server. The default is ipPhone.
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
Enter the tag for the User First Name attribute on the
LDAP server. The default is givenName.
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
80 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 81

Configuring the dial plan conversion parameters
Field Description
LDAP attribute tag that contains
the user's last name
LDAP attribute tag that contains
the user's display name
LDAP attribute tag that contains
the user's business phone #
LDAP attribute tag that contains
the user's mobile phone #
LDAP attribute tag that contains
the user's email address
LDAP attribute tag that contains
the user's extension
Enter the tag for the User Last Name attribute on the
LDAP server. The default is sn.
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
Enter the tag for the User Display Name attribute on the
LDAP server. The default is displayName.
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
Enter the tag for the User Business Phone Number
attribute on the LDAP server. The default is
telephoneNumber.
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
Enter the tag for the User Mobile Phone Number
attribute on the LDAP server. The default is ipPhone.
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
Enter the tag for the User E-mail Address attribute on
the LDAP server. The default is email.
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
Enter the tag for the User Extension attribute on the
LDAP server. The default is ipPhone.
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
LDAP attribute tag that contains
the user's home phone
Enter the tag for the User Home Phone Number attribute
on the LDAP server. The default is homePhone.
This parameter applies to both servers in the redundant
configuration.
Configuring the dial plan conversion parameters
Use this procedure to facilitate dial plan conversion.
Prerequisites
• You must be logged into the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Web Administration
Console as administrator. For more information, see
Communicator Web Administration Console as an administrator.
• Understand the dial plan of the Enterprise Call Server (ECS). For more information, see
Avaya Communication Server 1000 Dialing Plans Reference, NN43001-283.
• Understand the format of telephone numbers in the corporate directory server.
Logging on to the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Deployment Guide October 2010 81
Page 82

Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway installation
1. Click the System Configuration tab.
2. Select Gateway Actions > Configure Gateway.
3. Click Edit.
4. Click the corresponding link for Dialplan Conversion List .
Figure 15: Dialplan conversion list
5. In the Number box, type a number combination, and then click OK.
6. For each additional entry, click New Entry and in the Number box, type a new
number combination.
7. To save the changes, click OK.
8. Click Save.
Variable definitions
Variable Description
<number
combination>
Represents the elements of a dialable number and what these
elements translate to in order to be dialed. Format: <original
combination>=<converted number> Example: ESN=6 If the
corporate directory gives a telephone number as ESN1234567,
the ESN is changed to the digit 6 when the number is dialed,
resulting in the number 61234567 being dialed.
Rules that use the carat sign
When you write a rule without the carat (^) sign, the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
Gateway replaces all occurrences of what is on the left side of the equal (=) sign with what is
on the right. For example, if you have the following rule 0=00, the rule changes a phone number
dialed on the Avaya 3100 MC - Client as 0123456789 to 00123456789 but also changes a
phone number like 01230123 to 0012300123
82 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 83

When you write a rule with the ^ sign, the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway replaces
only the leading occurrence of the string of what is on the left side of the equal (=) sign with
what is on the right. For example, you have a rule ^0=00. If the phone number dialed on the
Avaya 3100 MC - Client is 0123456789, the number changes to 00123456789. However, if the
phone number dialed is 01230123, the number changes to 001230123.
You can use the ^ sign when writing rules in North America or Europe to dial national numbers
without adding the access code of 1 used within the enterprise. You can write a rule to look
for a leading 0 in Europe or 1 in North America and insert the proper access code to make the
number dialable in the enterprise. For example, in North America the rule would be ^1=61
assuming an access code of 6. This takes a number dialed as 16131234567 and substitutes
6161231234567 to make the number dialable in the enterprise. In Europe, this same rule would
be ^0=00. This adds an extra 0 to any number that a user dials on the Avaya 3100 MC - Client.
For example, 0123456789 becomes 00123456789 or 00411234567890 becomes
00041123456789.
Configuring the device settings
Configuring the device settings
The mobile device settings can automatically download to all the clients. A null value
downloads if a parameter is not configured.
The device configuration page is the list of configuration settings that are downloaded to the
device each time at login. You can change this behavior so that settings only download when
the user first logs in.
Prerequisites
• You must be logged into the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Web Administration
Console as administrator. For more information, see
Communicator Web Administration Console as an administrator.
• Add and configure the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateways before you begin
this procedure. For more information, see
Gateway server on page 74.
1. Click the Device Configuration tab.
Adding an Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
Logging on to the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Deployment Guide October 2010 83
Page 84

Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway installation
Figure 16: Device configuration tab
2. Click Edit.
3. Modify the Device settings.
4. Click Save.
The new device settings apply for the next successful logon by each user. On a
redundant system, the gateways automatically share the device settings.
Procedure job aid
Use the following table to help you understand the Devices settings.
Table 12: Device configuration settings
Field Description
Primary 3100 MCG (all configurations)
External: Address (IP/host:Port) Enter the address of the primary Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway public interface on the
Internet. Client application users connect to this
address. Format: <IP address l FQDN> :<port>
84 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 85

Procedure job aid
Field Description
External: Use Secure Connection Select Yes to enable HTTPS connections on the
primary Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway
public interface using security certificates on the clients
on Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway. Select
No to enable HTTP.
Use HTTPS when the clients use certificates to encrypt
communication with the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway.
The Nokia and Windows Mobile devices, along with
BlackBerry devices that do not employ the enterprisehosted BlackBerry Enterprise Server (BES), can use
HTTPS and certificates.
Default: Yes
Internal: Address (IP/host:Port) Enter the address of the primary Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway private interface on the
network.
Configure this parameter if your Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator system implementation uses
BlackBerry devices that use the BES.
Internal: Use Secure Connection Select Yes to enable HTTPS connections on the
primary Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway
private interface. Select No to enable HTTP.
Default: No
Secondary 3100 MCG (all configurations)
External: Address (IP/host:Port) Enter the address of the secondary Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway public interface on the
Internet. Client application users connect to this
address when the primary Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway fails. Format: <IP address l
FQDN> :<port>
External: Use Secure Connection Select Yes to enable HTTPS connections on the
secondary Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway
public interface using security certificates on the clients
on Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway. Select
No to enable HTTP.
Use HTTPS when the clients use certificates to encrypt
communication with the secondary Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway.
The Nokia and Windows Mobile devices, along with
BlackBerry devices that do not employ the enterprisehosted BlackBerry Enterprise Server (BES), can use
HTTPS and certificates.
Default: Yes
Internal: Address (IP/host:Port) Enter the address of the secondary Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway private interface on the
network.
Deployment Guide October 2010 85
Page 86

Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway installation
Field Description
Configure this parameter if your Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator system implementation uses
BlackBerry devices that use the BES.
Internal: Use Secure Connection Select Yes to enable HTTPS connections on the
secondary Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway
private interface. Select No to enable HTTP.
Default: No
Access Numbers
Voicemail Numbers Enter the list of valid regional or office based numbers
users of the system can use to call and access their
voice mail.
Service Numbers Enter the list of valid regional or office-based Direct
Outbound Mode numbers for client calls. These
numbers are PSTN/E.164 numbers. Avaya 3100
Mobile Communicator users use service numbers to
place calls directly from their wireless devices to other
parties using Direct Outbound call mode.
On the Avaya CS 1000, the PSTN number must map
to the gateway name assigned to the Avaya 3100
Mobile Communicator Gateway as a trunk steering
code.
On the Avaya CS 1000, the PSTN number must map
to the number populated in table DNROUTE of the
Avaya CS 1000.
Mobile Network Dialing
Emergency and Direct Dialed
Numbers
Auto-Download of Device Configuration
Allow Client Override Controls the automatic downloading of the device
Calling Features
Prefix Screen Setting Controls the use of prefixes by users.
Click to add new entries to the list of emergency or
direct dialed numbers. You can remove entries from the
list by clicking the corresponding x.
configuration (including blank values) to the clients.
Select No to download the configuration every time a
user logs in. The download overwrites local updates.
Select Yes to download the configuration the first time
each user logs in. After the initial download, users can
change their configuration.
Default: No
Select Disable to allow users to dial outgoing calls with
prefixes. For this setting and the Native Call Intercept
setting to work correctly, your dial plan must support
calls from the client in the same way that calls from the
native dialer are handled.
86 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 87

Configuring the emergency telephone numbers
Field Description
Select Enable to require users to enter a prefix every
time they make an outgoing call. This setting is useful
if your dial plan does not support E.164 numbers.
Default: Disable
Default for Native Call Intercept
Setting
Defines the default setting to control the ability for users
to make private calls that route through the Avaya 3100
Mobile Communicator Gateway. Private calls are calls
placed through the native dialer.
Select On to place private calls through the Avaya 3100
Mobile Communicator Gateway.
Select Off to place private calls through the native
dialer.
The user can override this setting on the client. If the
user overrides this setting, changes to this parameter
do not change the client configuration.
Default: On
Configuring the emergency telephone numbers
Add one or more entries to facilitate emergency number dialing from the device's native phone.
Prerequisites
• You must be logged into the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Web Administration
Console as administrator. For more information, see
Communicator Web Administration Console as an administrator.
Logging on to the Avaya 3100 Mobile
• You must know the emergency telephone numbers for your location.
1. Select the Device Configuration tab.
2. Click Edit.
3. Click the corresponding link for Emergency and Direct Dialed Numbers.
4. In the Number box, type an emergency number, and then click OK.
For example, to enable emergency number dialing in North America, add 911. When
a mobile client user dials that number, the Avaya 3100 MC - Client switches to the
native device phone and places the call over the cellular network.
5. For each additional entry, click New Entry and in the Number box, type a new
number combination.
Deployment Guide October 2010 87
Page 88

Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway installation
6. To save the changes, click OK.
7. Click Save.
Adding the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway license
This procedure installs the license file on the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway. This
license file controls the number of users that can log in to the system.
Prerequisites
• You must be logged into the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Web Administration
Console as administrator. For more information, see
Communicator Web Administration Console as an administrator.
• Obtain a license file from Avaya before beginning this procedure.
Logging on to the Avaya 3100 Mobile
• Add the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway server before beginning this
procedure.
1. Add the license file to a directory on your network that is accessible from the Avaya
3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway.
2. Click the System Configuration tab.
3. In the System Configuration page, click Gateway Actions, License beside the
Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway.
Figure 17: Gateway Actions
4. In the License Information window, click Browse.
5. In the Choose file dialog box, locate and select the license file.
88 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 89

6. Click Open.
7. Click Install.
8. Click Close.
Checking Gateway server status
9. On a redundant system, repeat step
second server.
Important:
For information about troubleshooting license file problems, see Avaya 3100
Mobile Communicator Troubleshooting, NN42030-700.
Checking Gateway server status
Check the Gateway server status to view the information such as the number of connections
and the system load.
The System Status page lists the server processes and autoupdates every five seconds.
Prerequisites
You must be logged into the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Web Administration Console
as administrator. For more information, see
Communicator Web Administration Console as an administrator.
3 on page 88 to step 8 on page 89 on the
Logging on to the Avaya 3100 Mobile
1. Click the System Status tab.
The System Status window appears.
Figure 18: System status tab
2. On the System Status page, monitor the status of the Gateway Server.
Deployment Guide October 2010 89
Page 90

Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway installation
Procedure job aid
Use the following table to help you understand the Gateway Server System status fields.
Field Description
IP Address Contains the IP Address of the Gateway Server.
Status information appears to the right of this field.
Click the IP Address to view statistical data related to
the associated server.
If the IP Address displays in red, the server is not
responding, which can indicate a server software
problem or system outage.
If the IP Address displays in grey, the server is
unavailable.
Domain Name Contains the Domain name for the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway server.
Status Indicates the status of the Gateway Servers.
• Running—The server is running and active.
• Network Error—Connectivity to the server has been
lost.
• Stopped—The server is stopped.
• Running-Standby—The server is in standby mode.
If users cannot log in for any reason, the gateway
status appears in red. If the server is running but needs
a restart (for example, to apply pending configuration
changes), the gateway status appears in orange and
an asterisk (*) appears beside the text.
Last Alarm Entry Click this field to open the alarm log file. The
timestamp (MM/DD/YYYY HH:MM:SS) indicates the
time of the most recent SEVERE or WARNING alarm
message. The total number of outstanding alarms
appears in brackets. For example, (5) indicates that
five alarms have been raised but not yet cleared.
Message examples:
• The “MandatoryGatewayConfig” alarm indicates
that you must enter configuration settings and
restart the server.
• The “GatewayStopped” information message
indicates that the server has been stopped from the
Web Administration Console or command line.
Notes:
90 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 91

Procedure job aid
Field Description
• You can access the alarm log file from the Tools
page under Server Logs.
• To clear an alarm, you must solve the original error
condition.
• Whenever the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator
Gateway server stops, all alarms and informational
messages clear. However, persistent error
conditions (such as missing or incorrect
configuration settings) immediately generate new
alarms. To permanently delete an alarm, you must
solve the original error condition.
• Recurrent events only generate one alarm.
Active Connections Indicates the current number of active connections
(clients) handled by the server. The license key
determines the maximum number of connections.
Queued Messages Indicates the current number of queued message
waiting to be sent from the server to the client.
The CPU and number of server processes determines
the maximum number of queued messages. A large
number of queued messages can be caused by
network congestion or by users having lost service. If
the queue reaches the maximum number, system
stability can be compromised.
You can check the message queue for individuals or
clear the message queue for individual users.
System Load Indicates the current load on the server CPU,
expressed as a percentage, averaged over the last
minute. The system load indicates the average
number of processes that are currently running on the
system.
A system load exceeding 100% adversely affects
system performance.
Tx(kbps) Indicates the current number of messages transmitted
by the server, expressed in kilobits per second (kbps),
averaged over the preceding minute.
Rx(kbps) Indicates the current number of messages received by
the server, expressed in kbps, averaged over the
preceding minute.
Licenses Used/Limit Displays the current number of licenses used against
the total number of licenses available.
Deployment Guide October 2010 91
Page 92

Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway installation
Solution commissioning
This section describes the final steps required to obtain a fully-working Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator (Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator) system. You perform these steps in order
to have the system working with your Enterprise infrastructure.
Before you perform these steps, the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway must be
installed, commissioned, and configured. For more information, see Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway installation workflow on page 63 and Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Administration and Security, NN42030-600.
In order to get a fully-working Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator system, you must do the
following commissioning steps:
1. On the firewall, configure the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway server
private addresses (on the Enterprise network) to the firewall public address (on the
internet).
For more information, see the firewall documentation.
2. On the Intranet Domain Name Server (DNS):
• Program a DNS entry to map to the internal IP address of the Avaya 3100
Mobile Communicator Gateway.
• Ensure that the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway can access the
DNS using port 53 through any firewalls that are in the network.
For more information, see the DNS documentation.
3. On the Enterprise Call Server (ECS):
• Assign a call service directory number for the Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator Gateway.
• Create a route that enables the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway
to reach the ECS.
• Create a user ID that enables the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway
to register with the ECS.
For more information, see
4. If using the BlackBerry Enterprise Server (BES), the RIM MDS service must be
enabled.
Deployment planning on page 47.
5. If required, implement a certificate infrastructure.
92 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 93

Solution commissioning
For more information, see Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Administration and
Security, NN42030-600.
6. After the interworking with the network is functioning correctly, send e-mail
messages to users that explain how to install and configure their clients.
For more information, see Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Administration and
Security, NN42030-600.
For more information about interworking with the Avaya CS 1000, see Avaya 3100 Mobile
Communicator and Avaya Communication Server 1000 Solution Integration Guide,
NN49000-315.
For more information about interworking with the Avaya CS 1000, see
Interworking
requirements with CS 1000 on page 29.
Important:
After you have a working Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator system, back up the Avaya
3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway. For the backup procedure, see Backing up the Avaya
3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway server databases on page 160.
Deployment Guide October 2010 93
Page 94

Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway installation
94 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 95

Chapter 11: Avaya CS 1000 configuration for
client support
Before implementing IP Peer Networking with the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway, some
prerequisite programming is required on the Call Server.
This section assumes that the system is already installed and fully operational, that the Customer data
Block (CDB) already exists, and the circuit-switched routes and trunks are already defined. Although you
can configure the system using the software overlays (LDs), the procedures here are described using
Element Manager.
Avaya CS 1000 configuration for client support task flow
Follow the procedures in the task flow to configure the Avaya CS 1000.
Deployment Guide October 2010 95
Page 96

Avaya CS 1000 configuration for client support
Task flow navigation
Complete the tasks in the order that they appear in the following list:
• Configuring zones on page 97
• Configuring a D-channel for virtual trunks on page 97
•
Configuring virtual routes on page 98
• Configuring virtual trunks on page 100
• Configuring network control parameters data block on page 101
• Configuring ESN access codes on page 101
• Configuring the Route List Block on page 102
• Coordinated Dialing Plan on page 103
96 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 97

• Forwarding Service DN to Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway on
page 103
• Configuring a Handoff key on page 105
Configuring a HOT P key on page 106
•
• Configuring the SIP trunk gateway on page 107
• Configuring NRS on page 112
Configuring zones
For information about configuring zones, see Converging the Data Network for VoIP
Fundamentals, NN43001-260.
Virtual Trunks must be configured with a different zone number than the endpoints.
Zone Number (ZONE):
Configuring zones
Intrazone Bandwidth (INTRA_BW):
Intrazone Strategy (INTRA_STGY):
Best Quality (BQ)Best Bandwidth (BB) Interzone Bandwidth (INTER_BW):
Interzone Strategy (INTER_STGY): Best Quality (BQ)Best Bandwidth (BB)
Resource Type (RES_TYPE): Shared (SHARED)Private (PRIVATE)
Zone Intent (ZBRN): MO (MO)BMG (BMG)VTRK (VTRK)
Description (ZDES):
Configuring a D-channel for virtual trunks
The NRS-SPS application requires Virtual Trunks (routes) to communicate with the Call Server.
Virtual Trunks require D-Channels for control and signaling information. Configure the Virtual
D-channels in Element Manager or LD 17 (ADAN gate opener).
The calls that use the virtual trunk on the Avaya CS 1000 are:
• calls from the UEXT to Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway (mobility prefixed)
• calls from the DID service DN to Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway (mobility
prefixed)
• calls from the Avaya 3100 Mobile Communicator Gateway outbound
Use this procedure to configure a Virtual D-channel using Element Manager.
Deployment Guide October 2010 97
Page 98

Avaya CS 1000 configuration for client support
1. Log on to Element Manager.
2. In the navigation pane, select Routes and Trunks, D-Channels.
If this is the first time that this Web page is accessed, a message indicates that no
D-channels are configured. Click OK.
3. Under the Configuration section, from the Choose a D-channel Number list, select
a D-Channel number.
4. From the type list, select the type of D-Channel.
5. Click to-Add.
6. Choose the D channel Card Type (CYTP) of D-Channel is over IP (DCIP).
7. Choose the Interface type for D-channel (IFC) of Meridian Meridian1 (SL1).
8. If you are defining the Network Name Display, from the Release ID of the switch
at the far end (RLS) list, select the release ID of the switch.
9. Click the Basic options (BSCOPT) link. The Basic options (BSCOPT) list expands.
10. Click Edit to configure Remote Capabilities (RCAP).
The Remote Capabilities Configuration page appears.
11. Select the Message waiting interworking with DMS-100 (MWI) check box.
12. Select the Network name display method 2 (ND2) check box.
13. At the bottom of the Remote Capabilities Configuration page, click Return - Remote
Capabilities.
The D-Channel xx Property Configuration page reappears.
14. Click Submit to save the changes.
The D-Channels page reappears with the changes.
Configuring virtual routes
To configure Virtual Trunk routes, you can use Element Manager or LD 16 of the Command
Line Interface.
Note: The zone parameter makes the codec selections and calculates the bandwidth usage
for calls to the trunk members of a given route.
Use this procedure to configure a Virtual Trunk Route using Element Manager.
1. Select Routes and Trunks , Routes and Trunksfrom the EM Navigator.
98 Deployment Guide October 2010
Page 99

Configuring virtual routes
The Routes and Trunks Web page opens.
2. Click Add route associated with the customer.
The Customer xx, New Route Configuration Web page opens (where xx is the
customer number).
3. Under Basic Configuration, fill in the required fields to create a new Virtual Trunk
Route:
• Select a Route Number (ROUT) from the drop-down list.
• Select the Trunk Type (TKTP) = TIE trunk data block (TIE). When Trunk Type
(TKTP) is selected, the following three options appear:
- The route is for a virtual trunk route (VTRK) (see step 4)
- Digital Trunk Route (DTRK)
- Integrated Services Digital Network option (ISDN) (see step 5)
• Enter the Access Code for the trunk route (ACOD).
4. Select The route is for a virtual trunk route (VTRK) check box. The following
three fields display:
• Enter a ZONE number.
• Enter the NODE ID (the node served by this Signaling Server).
• Select the Protocol lD for the route (PCID). Select SIP from the two available
options.
Note:When SIP is selected as the Protocol ID for the route (PCID), then the Print
Correlation ID in CDR for the route (CRID) check box is displayed. CRID only
appears if VTRK is YES and PCID is SIP and CDR is turned on for the route.
5. Select the Integrated Services Digital Networks option (ISDN) check box.
The ISDN section expands with:
• Choose Mode of operations (MODE) = Route uses ISDN Signaling Link (ISLD).
• Choose Interface type for route (IFC) = Meridian M1 (SL1)
• Select the Network Calling Name Allowed (NCNA) check box
6. Select the Network Call Redirection (NCRD) check box.
7. Click Network Options.
8. Select Signaling arrangement (SIGO) = DTI data calls plus all other types (ESN5).
9. Click General Options.
The General Options list expands.
10. Enter the Trunk Access Restriction Group (TARG) value if you are configuring a
single customer.
Deployment Guide October 2010 99
Page 100

Avaya CS 1000 configuration for client support
11. Enter the appropriate information in the text boxes and in Basic Route Options,
Network Options, General Options, and Advanced Configurations.
12. Click Submit.
The Trunks and Routes Web page opens and the newly configured route is
displayed for the customer.
Configuring virtual trunks
To configure Virtual Trunk, you can use Element Manager or LD 14 of the Command Line
Interface.
Use this procedure to configure a Virtual Trunk using Element Manager.
1. Select Routes and Trunks, Routes and Trunksfrom the EM Navigator.
The Routes and Trunks Web page opens.
2. Select the Customer.
3. Click Add trunk associated with the VTRK route the trunks are being added to.
The New Trunk Configuration Web page opens.
4. Under Basic Configuration, fill in the required fields to create the new Virtual Trunk.
• Choose Multiple trunk input number (MTINPUT) = 32
• Choose Trunk data block (TYPE) = IP Trunk (IPTI)
• Enter the Terminal Number (TN)
• Enter the Route number, Member number (RTMB)
• Choose a Card Density (CDEN) of Octal Density (8D)
• Choose a Start arrangement Incoming (STRI) = Wink OR Fast Flash (WNK)
• Choose a Start arrangement Outgoing (STRO) = Wink OR Fast Flash (WNK.
• Enter the Trunk Group Access Restriction (TGAR)
• Enter the Channel ID for this trunk (CHID)
Note: When creating multiple virtual trunks, select a CHID of 1. The software auto
fills the CHID for the additional trunks.
100 Deployment Guide October 2010
 Loading...
Loading...