Page 1

ACPL-P346/W346
Isolated Power MOSFET Gate Driver Evaluation Board
User's Manual
Quick Start
Visual inspection is needed to ensure that the evaluation board is received in good condition.
All part references are designated with sux ‘a’ and ‘b’ to indicate the lower and the upper inverter arms, respectively. If
part references are made without suxes, then they are valid for both upper and lower inverter arms (except R6, which
is shared).
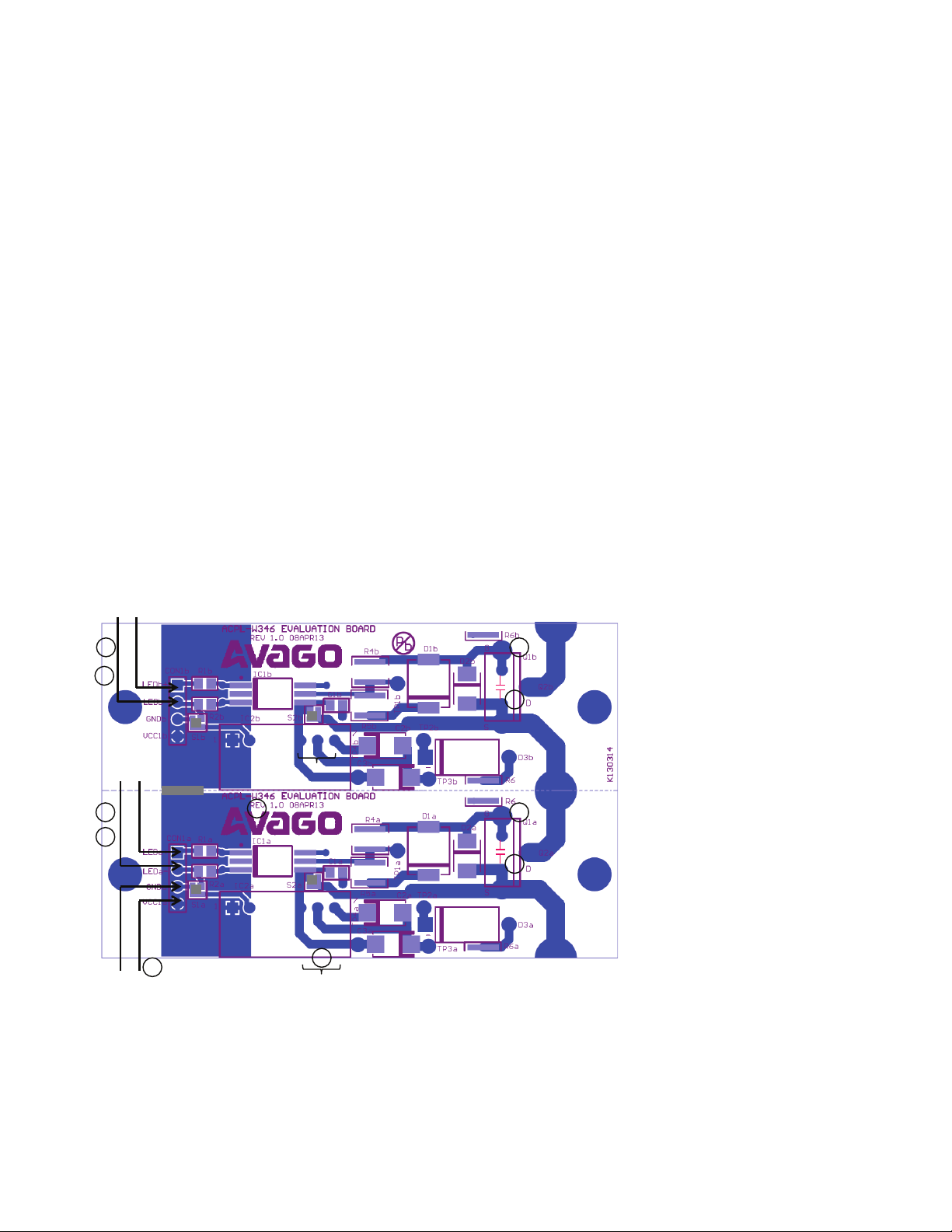
Figure 1 shows the default connections of the evaluation board:
1. Q1 and Q2 are not mounted. Actual Power MOSFET can be mounted at either Q1 (for TO-220 package) or Q2 (for TO247 package) or connected to the driver board through short wire connections from the holes provided at Q1 or Q2.
2. D4 and R7 are not mounted (on solder side). A 12 V Zener diode footprint at D4 is provided to allow for a single DC
power supply of 15 V ~25 V to be applied across V
Q2) can then be generated and it acts as the reference point at the source pin of each power MOSFET. V
stay at 12 V above the virtual ground VE. R7 is needed to generate the bias current across D4.
3. S2 and S3 jumpers are shorted by default to connect VE to VEE, assuming that a negative supply is not needed. Note:
If a negative supply is needed, then S2 and S3 jumpers must be removed.
4. Bootstrap diode D3b and resistor R6 are connected by default. These two components are provided to help generate
V
supply through bootstrapping assuming that V
CC2b
only when Q1 or Q2 are mounted in a half-bridge conguration and turned on and o through proper PWM driving
signals.
5. S1 is shorted by default to ground the IN- (or LED-, the cathode of LED) pin when V
removed if IN- cannot be grounded.
6. Upper and lower arms of the inverter will have common V
connected by solder between upper and lower inverter PCB portions (and GND1 on the solder side).
7. Provisions are also made to allow V
(and VEE) to be generated from V
CC2
this DC/DC converter is used, S2, S3 (and R6) should be disconnected.
and VEE if needed. A virtual ground VE (at Source pin of Q1 or
CC2
will then
CC2
supply is available. Note: Bootstrapping supply works
CC2a
is supplied. This short can be
CC1
(and GND1), a provision is made to allow V
CC1
through a DC/DC converter at IC2. When
CC1
CC1
to be
V
CC1b
V
CC1a
VCC1a and VCC1b (shorted)
GNDa and GNDb on solder side (also shorted)
S1 (shorted)
Figure 1. Actual ACPL-P346/W346 evaluation board showing default connections
S2 (shorted)
R6 mounted (shorted)
S3 on solder side (also shorted)
Page 2
Once inspection is done, the evaluation board can be powered up in ve simple steps. Figure 2 shows you how to test
the top or the bottom half-bridge inverter arms in simulation mode without the need for an actual power MOSFET.
Testing both arms of the half-bridge inverter driver (without a power MOSFET)
1. Solder a 10 nF capacitor across the gate and emitter terminals of Q1 or Q2. This is to simulate actual gate capacitance
of a power MOSFET.
2. Connect a +5 V DC supply (DC supply 1) across the +5V and GND terminals of CON1.
3. Connect another DC supply (DC Supply 2 with voltage range from 12 V ~ 20 V) across V
5 of IC2) terminals of IC2a, respectively. This can be non-isolated for testing purposes.
4. Connect drive signals:
a. A 10 kHz 5 V DC pulse (at slightly < 50% duty) from a dual-output signal generator across IN1+ and IN1- pins of
CON1a to simulate microcontroller output to drive the lower arm of the half-bridge Inverter.
b. Another 10 kHz 5V DC pulse (at 180° out of phase to the signal in 4a) from the dual-output signal generator across
IN2+ and IN2- pins of CON1b to simulate microcontroller output to drive the upper arm of the half-bridge inverter.
5. Use a multi-channel digital oscilloscope to capture the waveforms at the following points:
a. LED signal at the IN1+ pin with reference to (w.r.t.) GND.
b. LED signal at the IN2+ pin w.r.t. GND.
Note: The V
components D3b and R6.
supply of voltage close to V
CC2b
should then be successfully generated through the built-in bootstrap
CC2a
c. VGa representing the output voltage of ACPL-P346/W346 (IC1a) at the gate pin of Q1a (or Q2a) w.r.t. VEa.
d. VGb (through an isolated probe) representing the output voltage of ACPL-P346/W346 (IC1b) at the gate pin of Q1b
(or Q2b) w.r.t. VEB.
(pin 7 of IC2) and VEE (pin
CC2
In2-
In2+
4b
5b
Signal Input
+-
V
CC2b
3
12~20 V
DC Supply 2
+-
4a
5a
In1-
In1+
Signal Input
DC Supply 1
2
+5V
Gnd
Figure 2. Simple Simulation Test Setup of Evaluation Board
10nF
10nF
5d
1
V
Eb
5c
1
V
Ea
2
Page 3
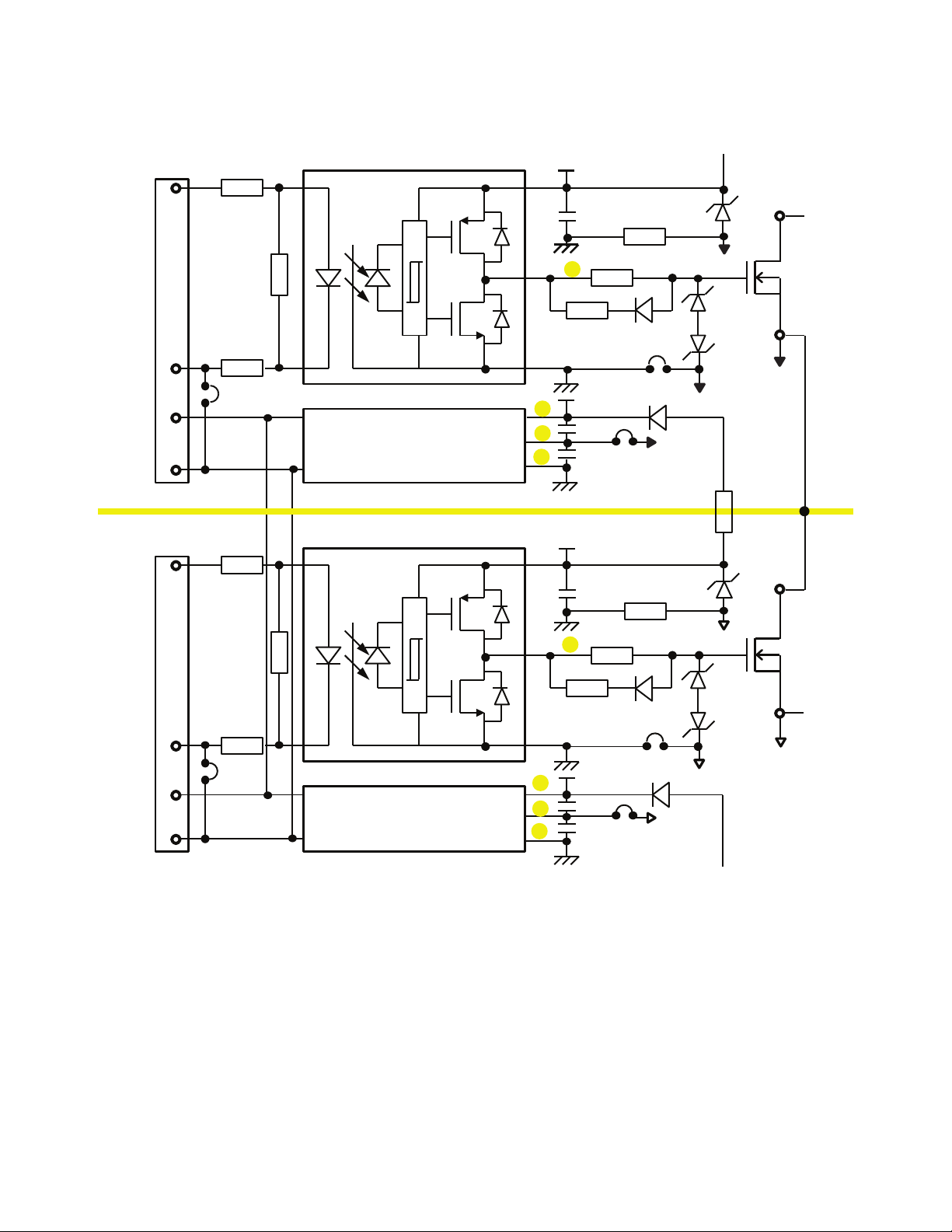
Schematics
Figure 3 shows the schematics of the evaluation board:
IC1b
ACPL-P346
IC2b
LEDb+
LEDb-
V
CC1b
CON1b
S1b
R1b
249R
R2b
130R
NM
R3b
1
3
1
NM
GNDb
LEDa+
LEDa-
V
CC1a
GNDa
CON1a
S1a
R1a
249R
R2a
130R
NM
R3a
2
IC1a
1
3
1
2
ACPL-P346
IC2a
R05P212D/R8
6
C1b
0.1µF
5
4
V
7
6
5
6
C1a
0.1 µF
5
4
V
TP2a
7
TP3a
6
TP4a
5
EEb
TP2b
TP3b
TP4b
EEa
V
CC2b
D4b
R7b
NM
R4b
TP1b
4R7 1W
R5b
NM
V
CC2b
C2b
10 µF T
C3b
10 µF T
V
EEb
V
CC2a
TP1a
R5a
NM
V
CC2a
C2a
10µF T
C3a
10µF T
V
EEa
SS32
D1b
BYM26F
S3b
a
a
R7a
NM
R4a
4R7 1W
SS32
D1a
S2a
BYM26F
S3a
a
a
S2b
SMBJ11CA
D3b
SMBJ11CA
D3a
NM
D4a
NM
D2b
D2a
G
R6
4R7 1W
G
D
S
V
Eb
D
S
V
Ea
NM
TO220/TO247
Q1b/Q2b
NM
TO220/TO247
Q1a/Q2a
Figure 3. Schematics of ACPL-P346/W346 evaluation board
3
Page 4

Practical connections of the evaluation board using a power MOSFET for an actual inverter test
1. Solder actual power MOSFETs at Q1 (or Q2) for the top and bottom arms of the half-bridge inverter isolated drivers.
2. Connect a +5V DC isolated supply1 across +5V and GND terminals of CON1 for both arms of the isolated drivers.
3. Connect another isolated DC supply2 (voltage range from 12 V ~ 20 V) across V
respectively for the bottom arm.
4. Connect the signal output (meant to drive the bottom arm of the half-bridge inverter) from the microcontroller to
Signal Input 1 across pin IN1+ and IN1- of CON1a of the bottom inverter arm isolated driver.
5. Connect the signal output (meant to drive the top arm of the half-bridge inverter) from the microcontroller to Signal
Input 2 across pin IN2+ and IN2- of CON1b of the top inverter arm isolated driver. Note: Signal Input 2 should be
180° out of phase w.r.t. Signal Input 1. Check that V
(voltage close to V
CC2b
components D3b and R6.
6. Use a multi-channel digital oscilloscope to capture the waveforms at the following points:
a. LED signal at IN1+ pin w.r.t. GND for the bottom arm.
b. LED signal at IN2+ pin w.r.t. GND for the top arm.
c. Vga for the gate driving voltage of Q1a (or Q2a) w.r.t. VEa of the bottom inverter arm (dierential probe needed).
d. Vgb for the gate driving voltage of Q1b (or Q2b) w.r.t. VEb of the top inverter arm (dierential probe needed).
7. Connect a power cable from the output pin (marked Load) to the inverter load.
8. Connect the high voltage cables from the top arm power MOSFET drain pin to HVDC+ and from the bottom arm
power MOSFET source pin to HVDC-, respectively, as shown. (Note: It is recommended that you enable the currentlimiting function of the HV power source supplying the high voltage DC bus voltage during this test to protect the
inverter and its driver circuitries).
and V
CC2a
) is generated through the bootstrap
CC2a
at pin 7 and pin 5 of IC2a
EEa
5
6b
IN2+
Signal Input 2
IN2-
Microcontroller
6a
IN1+
Signal Input 1
IN1-
4
DC Supply1
2
+5V
GND
Figure 4. Connection of evaluation board in actual applications
–
5
12~20V
3
–
12~20 V
DC Supply2
8
HVDC+
6d
1
Power MOSFET
mounted
+
7
Load
6c
1
Power MOSFET
mounted
+
HVDC–
8
4
Page 5

Application Circuit Description
The ACPL-P346/ACPL-W346 is an isolated gate driver that provides 2.5 A output current. The voltage and high peak
output current supplied by this optocoupler make it ideally suited for direct driving of MOSFET with ratings up to 1000
V/100 W. It is also designed to drive dierent sizes of buer stage that will make the class of power MOSFET scalable.
ACPL-P346 (and ACPL-W346) provides a single isolation solution suitable for both low and high power ratings of motor
control and inverter applications.
Each of the ACPL-P346/ACPL-W346 evaluation boards, as shown in Figure 5, accommodates two ACPL-P346/ACPL-W346
ICs. Therefore, each board is enough to drive the top and the bottom arms of the half-bridge inverter. It allows the designer to easily test the performance of a gate driver in an actual application under real-life operating conditions. Operation of the evaluation board requires merely the inclusion of a common 5 V DC isolated Supply1 on the input side and
an isolated DC Supply2 (range from 12 V ~ 20 V) for the bottom arm of the inverter power MOSFET, while the DC supply
needed for the top arm is easily generated through bootstrapping included in the evaluation board.
Note: As can be seen on the board, the isolation circuitry (at the far left) is easily contained within a small area while
maintaining adequate spacing for good voltage isolation and easy assembly.
Figure 5. Top and bottom views of ACPL-P346/W346 evaluation board
5
Page 6

Using the Board
It is easy to prepare the evaluation board for use. You just need to solder cables for DC supplies, have proper cables for
HVDC+/HVDC- high voltage bus, and load connections. The evaluation board has a default connection as shown in
Table 1 when it is shipped to the customer. We oer several power supply schemes from which you can choose.
Power Supply Schemes
The evaluation board is built with DC supply exibility in mind; choose a power supply scheme from the seven available.
Table 1 shows all the possible power supply schemes that work for the evaluation board. A description of each scheme
is given; you are encouraged to explore each scheme and decide which one works best for your needs:
1. Scheme 1 is the simplest and possibly the cheapest scheme. A +5 V isolated DC supply is supplied externally to
power the low voltage V
the power MOSFET at the bottom inverter arm. V
work, the bootstrap components D3b and R6 must be connected, all S2 jumpers must be shorted so that no negative
supply of Vee is allowed, and the Signal Input 2 is at 180° out of phase to Signal Input 1. All S2 jumpers are shorted to
connect V
to Ve so that there are no negative supplies. S3 jumpers are shorted by default but this has no eect on
ee
actual operation of the board. Contact Avago Technologies if bootstrapping operation works are required.
2. Scheme 2 is similar to Scheme 1: it has V
so does the driving power. Because a bootstrapped power supply can only handle a lower driving power, it is not
suitable for use when Qg of power MOSFET rises above 200 nanocoulombs (nC). A third external supply (+12 V~ 20
V for V
) will be needed.
cc2b
3. Scheme 3 is similar to Scheme 2 in that it uses three external supplies at V
the advantage of getting negative supplies for Vee (or V
of around 1 kΩ to provide proper biasing current at D4. For this scheme to work, both the S2 and S3 jumpers must be
open while the external supplies (+15 V ~ 24 V) on the high voltage driver side are to be connected across V
pins only, not the Ve pin. As the external supply changes from +15 V to +24 V, V
from -3 V to -12 V, all w.r.t. virtual ground at Ve.
4. Scheme 4 is another simple scheme; an alternative to Scheme 1. Here, only one external supply for V
V
is obtained by a lower power DC/DC converter at IC2a, with V
cc2a
supply is obtained from V
connected, all S2 jumpers must be shorted so that no negative supply of Vee is allowed, and the Signal Input 2 should
be 180° out of phase to Signal input 1. S2 is shorted to connect Vee to Ve so that there is no negative supply. S3
jumpers are shorted by default but this has no eect on actual operation of the board.
5. Scheme 5 is similar to Scheme 4: it has V
gets bigger, so does the driving power. Because a bootstrapped power supply can only handle a lower driving power,
it is not suitable for use when Qg of power MOSFET rises above 200 nanocoulombs (nC). A second DC/DC converter at
IC2b with V
as Vin and +12 V output at V
cc1
are no negative supplies. S3 jumpers are shorted by default but this has no eect on actual operation of the board.
6. Scheme 6 is similar to Scheme 5 with the use of V
dual outputs set at ±12 V to allow for the availability of negative Vee (at V
be open, while all S3 jumpers must be shorted.
7. Use Scheme 7 if dual-output ±12 V DC/DC converters are not available or dual-output ±9 V DC/DC converters are
preferred. 12 V V
can still be obtained using ±9 V DC/DC converters by introducing a 12V Zener diode at D4 and R7
cc2
of around 1kΩ to provide proper biasing current at D4. For this scheme to work, both the S2 and S3 jumpers must be
open. As the total voltage across V
D4 Zener diode, and -6V at Vee, all w.r.t. virtual ground at Ve.
circuit. Another external supply (+12 V~20 V for V
cc1
supply is obtained from V
cc2b
and V
cc1
by bootstrapping. For this to work, the bootstrap components D3b and R6 must be
cc2a
and a DC/DC converter for V
cc1
w.r.t .Veb. All S2 jumpers are shorted to connect Vee to Ve so that there
cc2b
w.r.t. Vee stays at 18V (=9V+9V), V
cc2
supplies. However, as the power MOSFET used gets bigger,
cc2a
and V
eea
and two DC/DC converters. Each DC/DC converter, however, has
cc1
) by introducing a 12 V Zener diode at D4 and R7
eeb
as Vin and +12 V output at V
cc1
eea
cc2
) is needed for the gate driver driving
cc2a
by bootstrapping. For this to
cc2a
, V
cc1
cc2a
and V
cc2a
will stay at +12V, but Vee changes
cc2
. However, as the power MOSFET used
and V
eeb
. Scheme 3, however, has
cc2b
cc1
w.r.t. Vea. V
cc2a
). Therefore, all S2 jumpers must
of 12 V will be obtained through the 12 V
and Vee
cc2
is needed.
cc2b
6
Page 7

Table 1. Power Supply Schemes
D4a/
V
cc1
1 +5 V
External
2 +5 V
External
3 +5 V
External
4 +5 V
External
5 +5 V
External
6 +5 V
External
7 +5 V
External
Note: As TVS D2 voltage is selected at a breakdown voltage of 12.2 V, it is not advised to set both V
To use a voltage higher than 12 V, please replace D2 with a bigger clamping voltage.
V
cc2a
+12V~20V
External
V
eea
S2a S3a
R7a V
cc2b
0 V s/c s/c NM Bootstrapped
from V
cc2a
(+12V~20V)
+12V~20V
External
+15V~24V External
0 V s/c s/c NM +12V~20V
External
open open 12V/
+15V~24V External
1k
12V -3V~-12V 12V -3V~-12V
DC/DC
(=V
/+12V)
cc1
DC/DC
(=V
/+12V)
cc1
DC/±DC (=V
0 V s/c s/c NM Bootstrapped
0V s/c s/c NM DC/DC
(=V
cc1
/±12V)
open s/c NM
DC/±DC (=V
from V
(+12V)
cc1
cc2a
/+12V)
cc1
+12V -12V +12V -12V
DC/±DC (=V
cc1
open open 12V/
/±9V)
1k
DC/±DC (=V
cc1
+12V -6V +12V -6V
V
S2b S3b
eeb
0 V s/c s/c NM Default (simplest)
0 V s/c s/c NM Higher Power
open open 12V/1k Vee available
0 V s/c s/c NM Cheap
0 V s/c s/c NM Higher Power
/±12V)
/±9V)
open s/c NM Vee available
open open 12V/1k Vee available
D4b/
R7b Remarks
- Two external supplies needed
for V
and V
cc1
- Three external supplies needed
for V
, V
cc1
- Three external supplies needed
for V
, V
cc1
- Virtual gnds Vea and Veb
generated through D4 and R7
- One single output DC/DC
converter for V
- Only one external supply is
needed (V
- Two single output DC/DC
converters for V
- Only one external supply is
needed (V
- Two dual output DC/DC
converters for V
and V
eeb
- Only one external supply is
needed (V
- Dual output DC/DC converters
for V
cc2a
- only 1 external supply is
needed (V
- Virtual gnds Vea and Veb
generated through D4 and R7
and Vee voltage at a voltage beyond ±12 V.
cc2
cc2a
cc2a
cc1
cc1
cc1
and V
cc1
cc2a
and V
and V
cc2a
)
cc2a
)
cc2a,Vcc2b
)
cc2b
)
cc2b
cc2b
and V
, V
cc2b
eea
7
Page 8

Output Measurement
A sample of input LED and various output waveforms are captured and shown in Figure 6. The default setup connection
is adopted, except with Q1a and Q1b power MOSFETs are mounted. The power MOSFETs used have a gate capacitance
equivalent to 10 nF.
Figure 6. Input LED signal and Power MOSFET Gate Voltage Waveforms
Figure 6 also shows that, once a bootstrap supply is adopted, the amplitude of the output voltage at the top inverter arm
will be slightly smaller than that of the bottom inverter arm, at 180° out of phase. (IN1+ is set at 49% duty ratio, while
IN2+ (not shown) is also set with 49% duty ratio, plus a turn-on delay of 100 ns with respect to IN1+).
Figure 7 shows the turn-o signal of IN1+, the turn-o signal at gate of Q1a, and the turn-on signal at gate of Q1b.
Figure 7. Turn-o and Turn-on Gate waveforms of Q1a and Q1b
8
Page 9

Figure 8 shows the turn-on signal of IN1+, the turn-on signal at gate of Q1a and the turn-o signal at gate of Q1b.
Figure 8. Turn-on and Turn-o Gate waveforms of Q1a and Q1b
As can be seen from Figure 7 and Figure 8, the turn-o speed of the power MOSFET will be slow, due to the capacitive
eects of D2 and the gate capacitance of Q1. To improve the turn-o speed, the board is provided with a diode resistor pair footprints at D1 and R5 (not mounted NM) to increase the gate current during turn-o. Another way to further
improve the turn-on and turn-o speed is by reducing the gate resistance of R4, but make sure the gate drive current is
not more than 2.5 A.
For product information and a complete list of distributors, please go to our web site: www.avagotech.com
Avago, Avago Technologies, and the A logo are trademarks of Avago Technologies in the United States and other countries.
Data subject to change. Copyright © 2005-2013 Avago Technologies. All rights reserved.
AV02-4051EN - May 2, 2013
 Loading...
Loading...